Phase noise compensation for interferometric absolute distance measuring
A technology of absolute distance and distance, applied in the field of computer program products, capable of solving complex problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
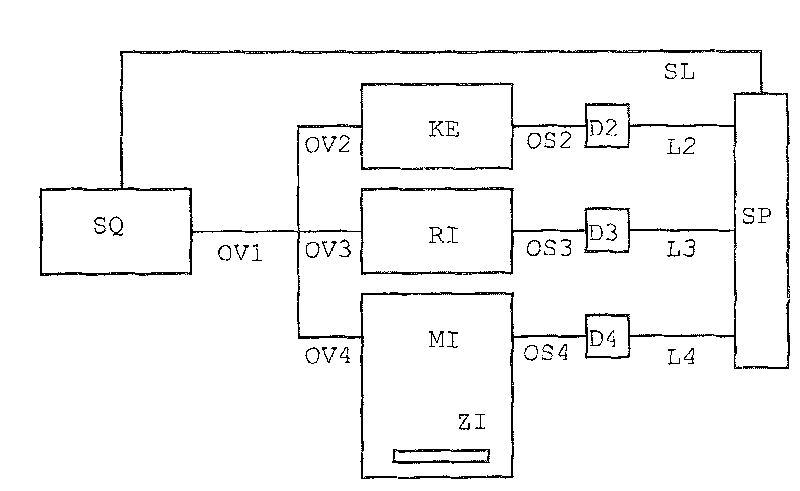
[0072] figure 1 Represents the underlying measurement construct. Signal source SQ is coupled in via optical connectors OV1-OV4 to measuring interferometer MI, reference interferometer RI and optional component calibration unit KE. The target ZI to be measured is an integral part of the measurement interferometer in the measurement. Via optical paths OS2, OS3 and OS4, the signals are transmitted to detector units D2, D3 and D4. The detector signals are sent to the signal processor SP via cables L2, L3 and L4. The signal processor SP is responsible for processing and analyzing the signal and also controls the signal source SQ via the control line SL.
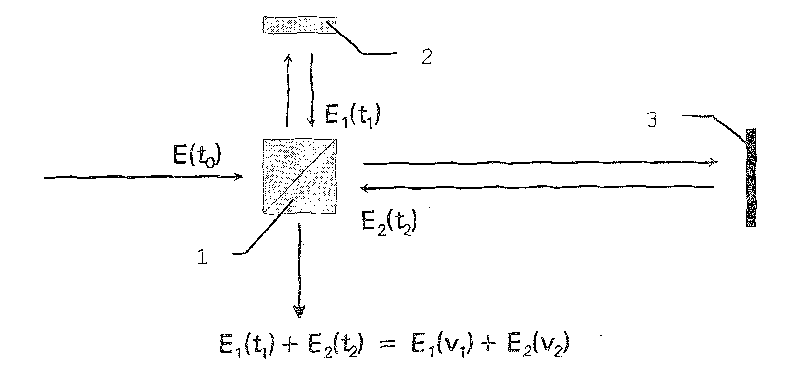
[0073] figure 2 A schematic diagram of the interferometer used to form the heterodyne mixing product is shown. Part of the emitted light is coupled out by the beam splitter 1 , reflected on the reflector 2 and passed through the beam splitter, and superimposed with the light signal scattered back from the reflector 3 . For ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com