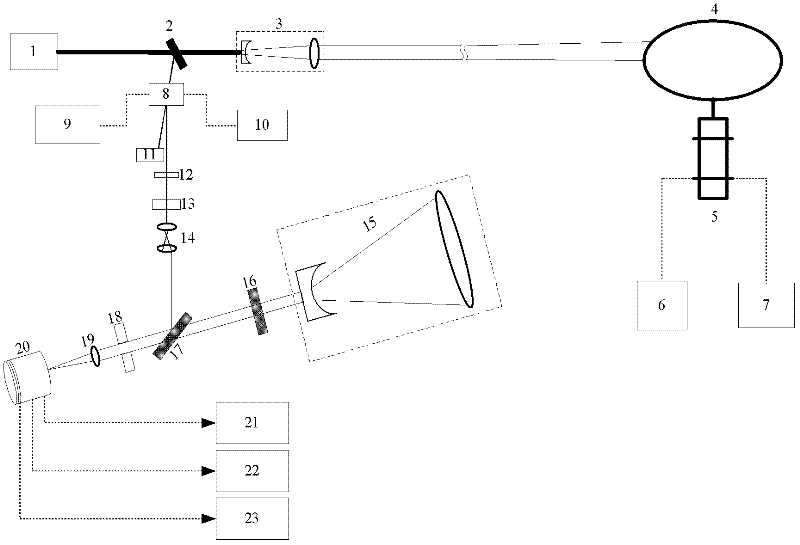
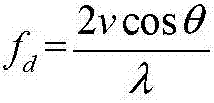Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
181 results about "Heterodyne detection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
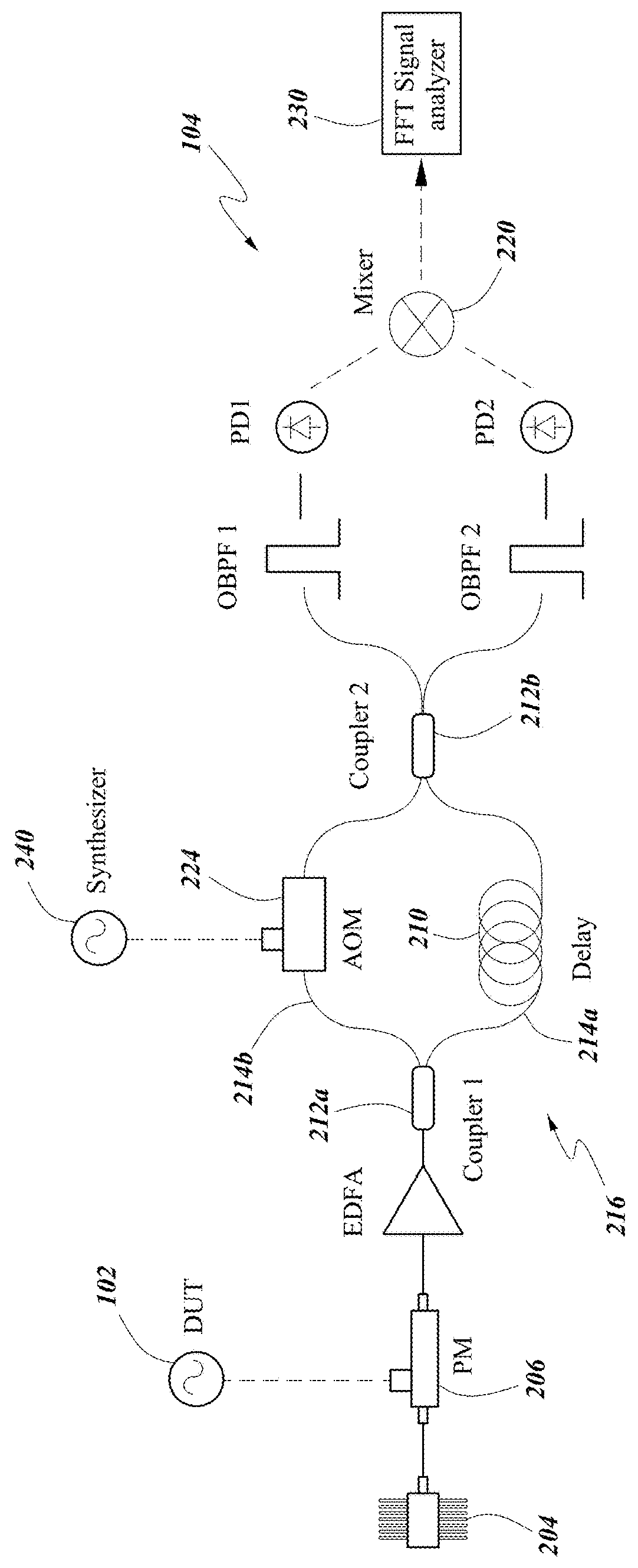
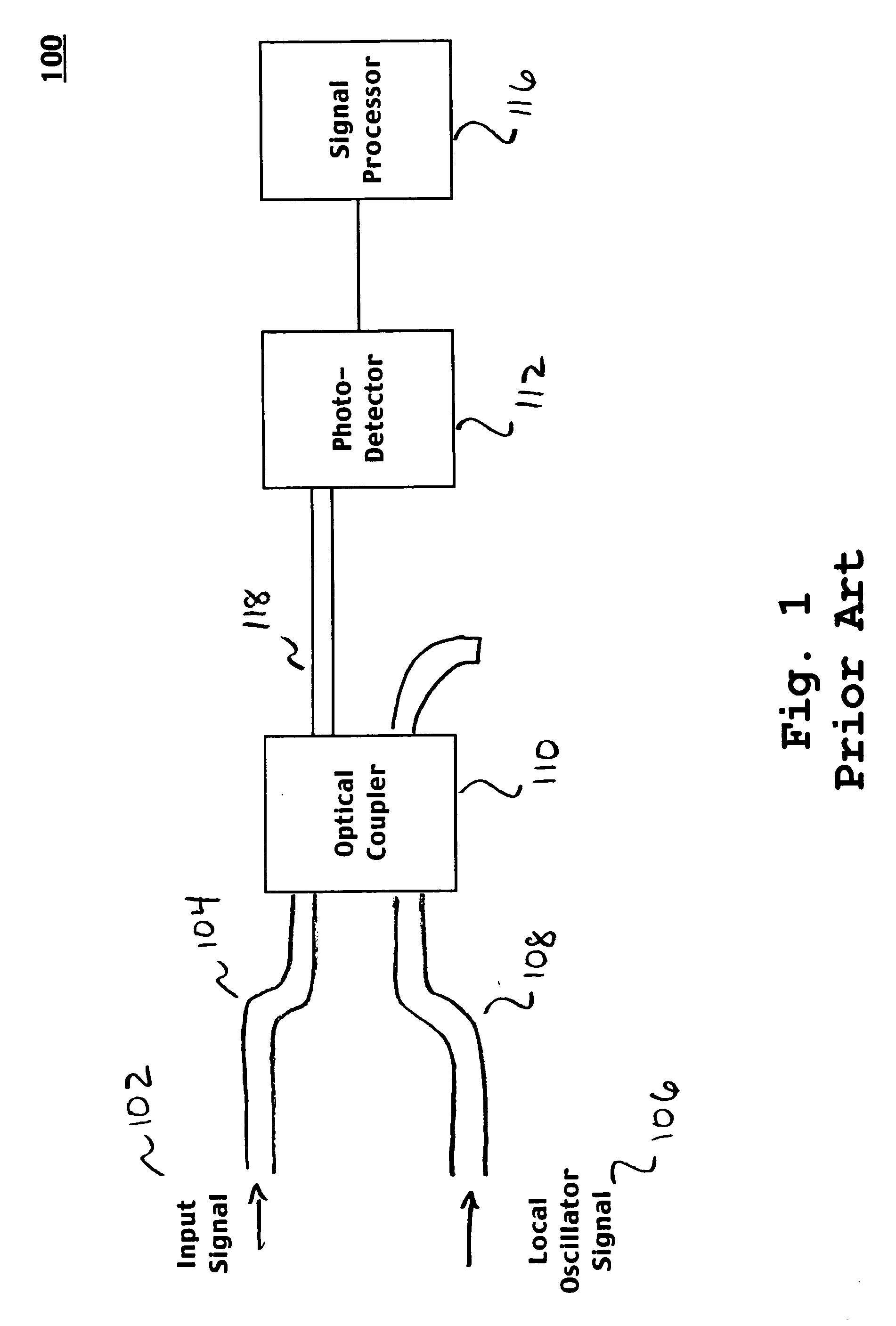
Heterodyne detection is a method of detecting radiation by non-linear mixing with radiation of a reference frequency. It is commonly used in telecommunications and astronomy for detecting and analysing signals. The radiation in question is most commonly either radio waves or light. The reference radiation is known as the local oscillator. The signal and the local oscillator are superimposed at a mixer. The mixer, which is commonly a diode, has a non-linear response to the amplitude, that is, at least part of the output is proportional to the square of the input. The received signal can be represented as and that of the local oscillator can be represented as For simplicity, assume that the output I of the detector is proportional to the square of the amplitude: The output has high frequency and constant components. In heterodyne detection, the high frequency components and usually the constant components are filtered out, leaving the intermediate frequency at . The amplitude of this last component is proportional to the amplitude of the signal radiation. With appropriate signal analysis the phase of the signal can be recovered as well.
Confocal microscopy
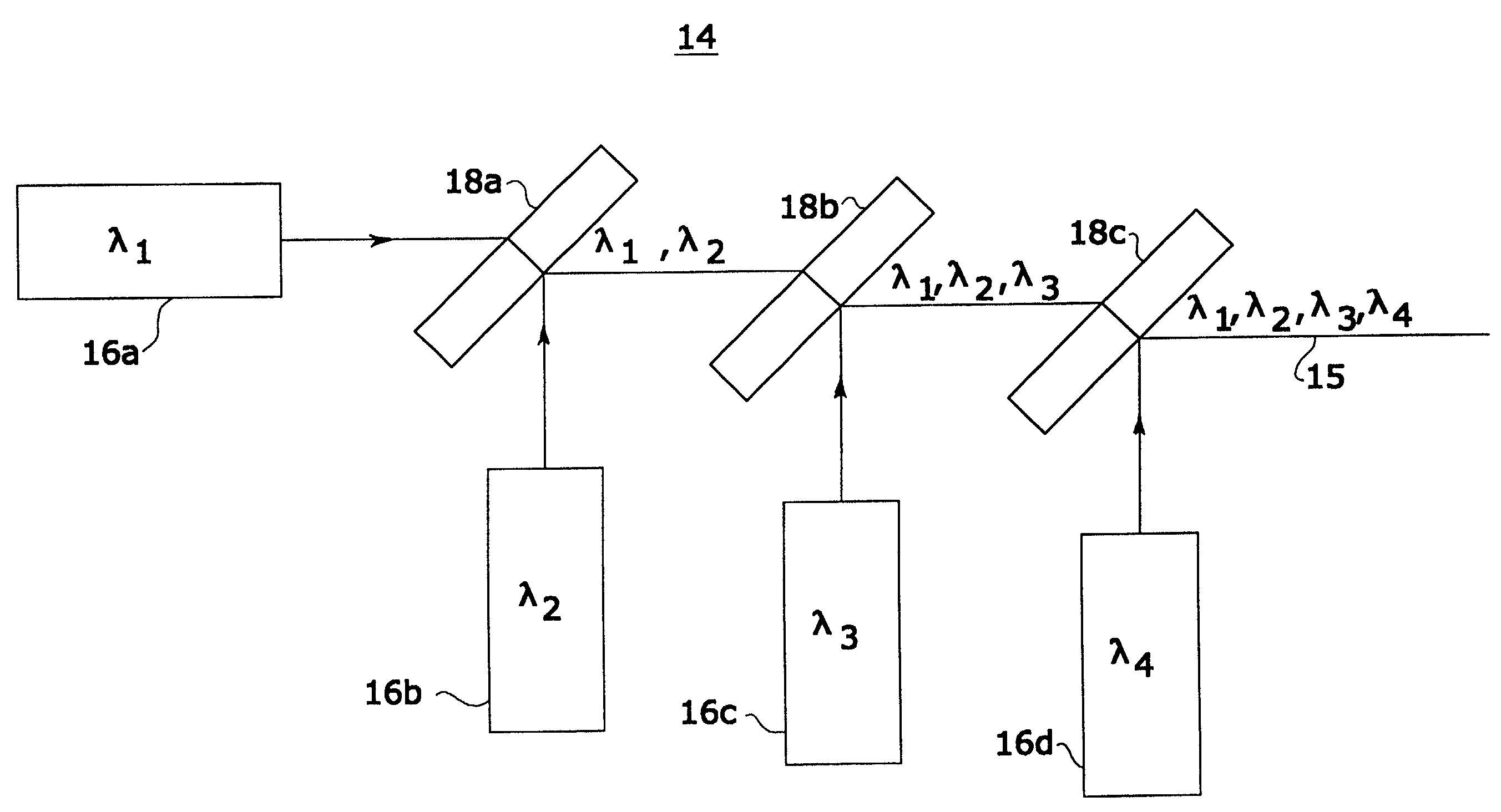
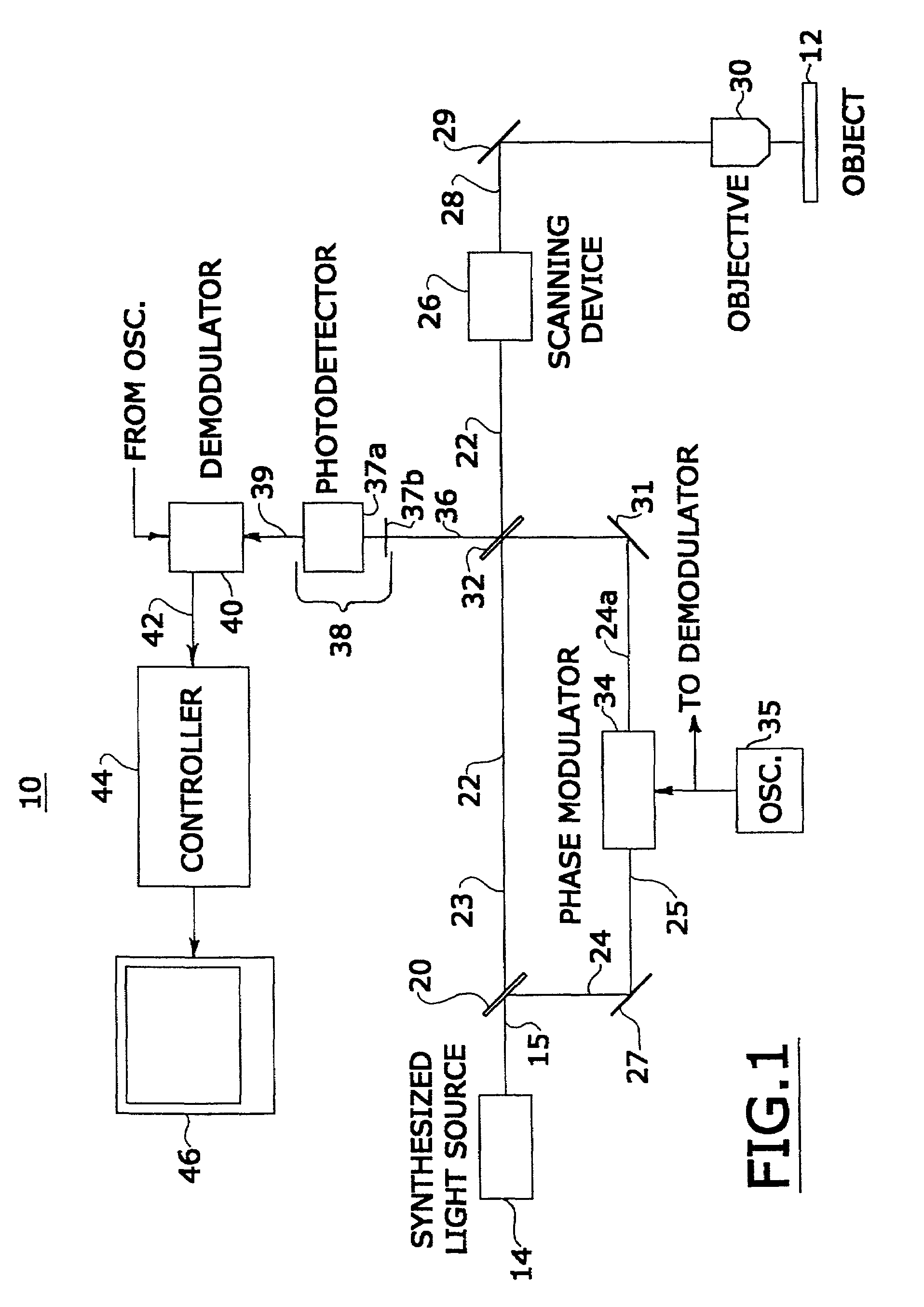
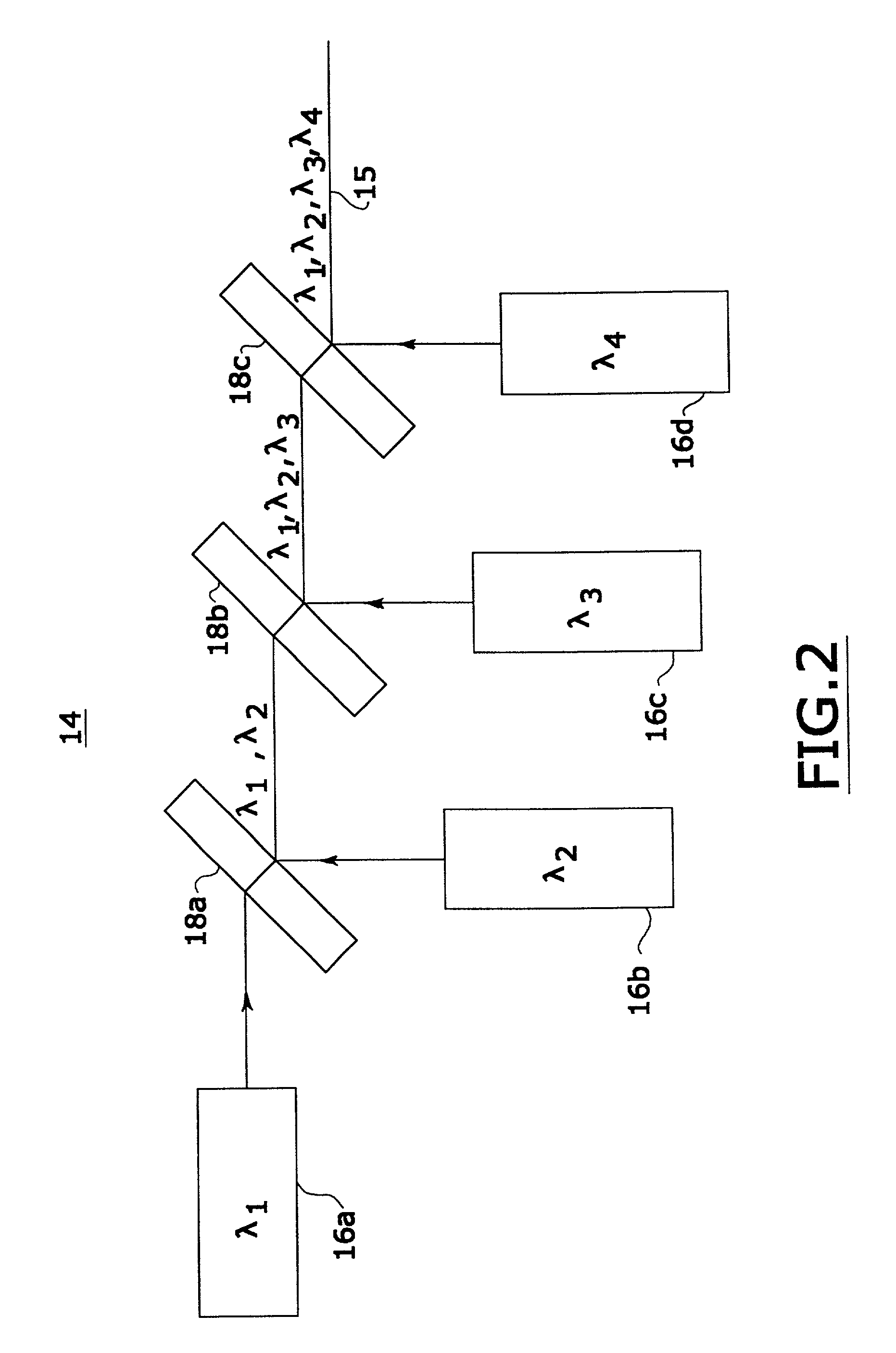
InactiveUS7333213B2Improves confocal microscopyMicroscopesUsing optical meansPhotodetectorDisplay device
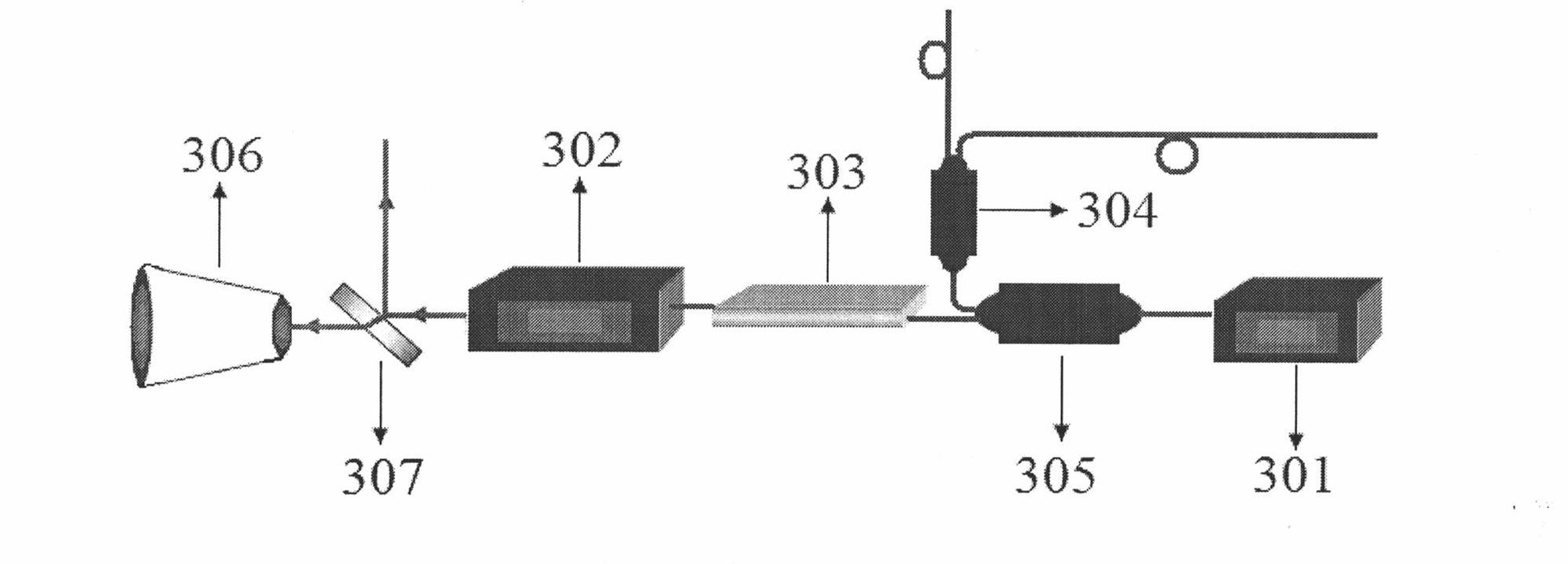
An improved confocal microscope system is provided which images sections of tissue utilizing heterodyne detection. The system has a synthesized light source for producing a single beam of light of multiple, different wavelengths using multiple laser sources. The beam from the synthesized light source is split into an imaging beam and a reference beam. The phase of the reference beam is then modulated, while confocal optics scan and focus the imaging beam below the surface of the tissue and collect from the tissue returned light of the imaging beam. The returned light of the imaging beam and the modulated reference beam are combined into a return beam, such that they spatially overlap and interact to produce heterodyne components. The return beam is detected by a photodetector which converts the amplitude of the return beam into electrical signals in accordance with the heterodyne components. The signals are demodulated and processed to produce an image of the tissue section on a display. The system enables the numerical aperture of the confocal optics to be reduced without degrading the performance of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
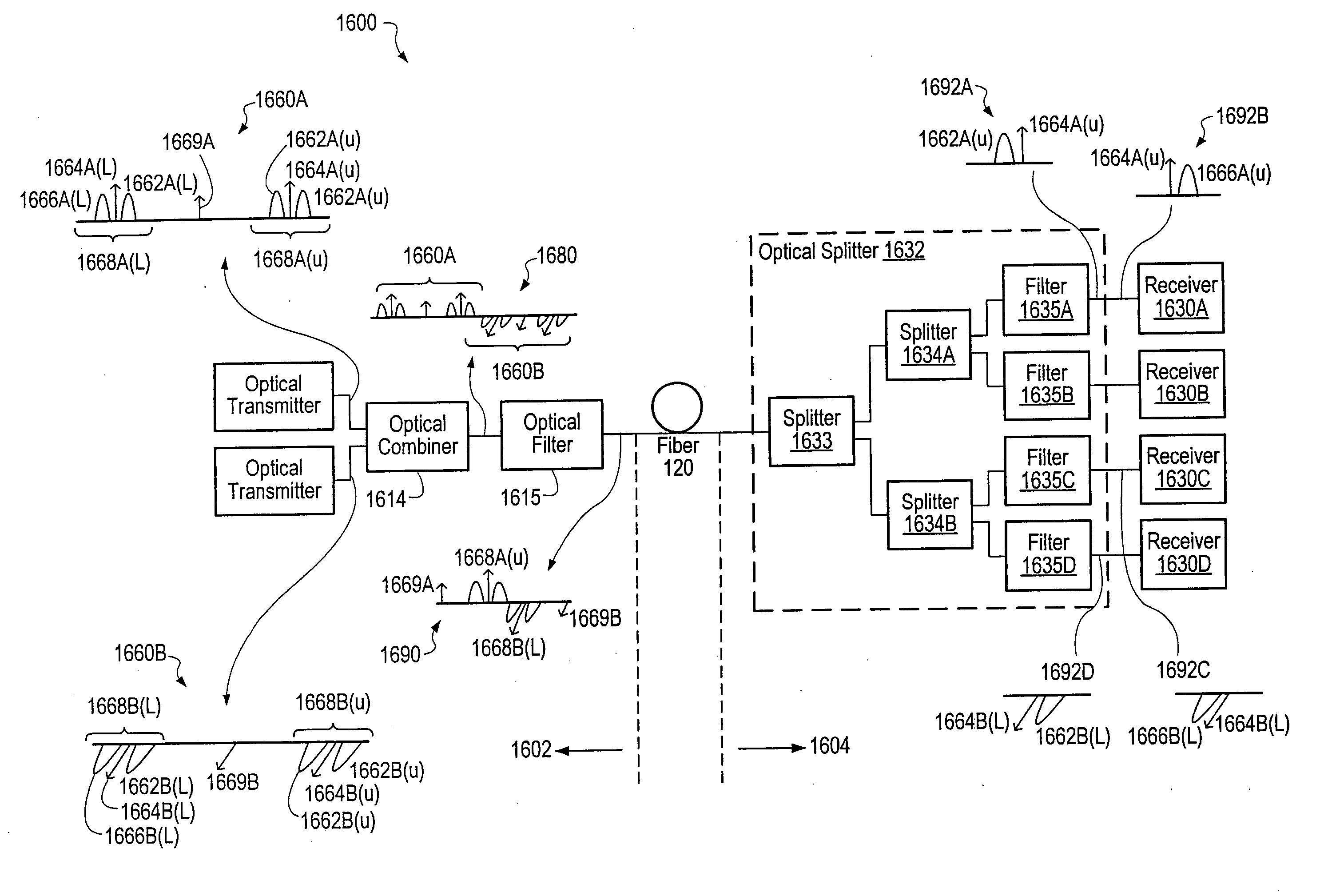
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
InactiveUS7447436B2Less interactionImprove bandwidth utilizationFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingEngineering
Owner:XYLON LLC
Full-distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor based on coherent heterodyne detection
InactiveCN102168953AImprove signal-to-noise ratioReduce false negative rateSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansContinuous lightPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
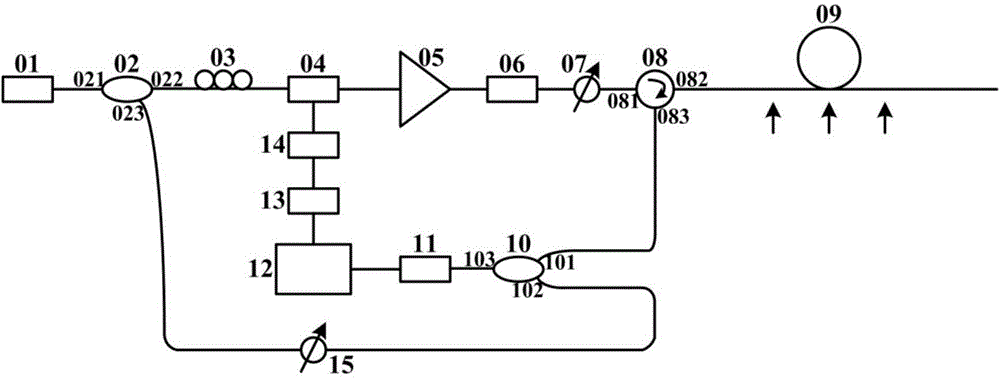
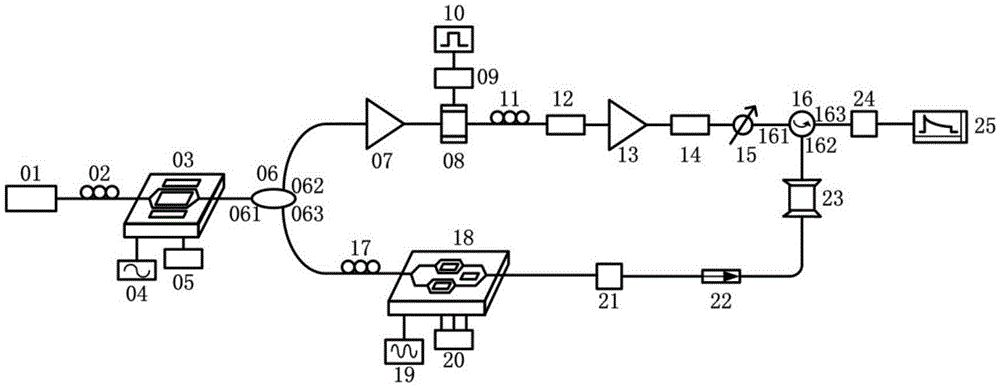
The invention relates to a full-distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor based on coherent heterodyne detection, which comprises a laser (1), a coupler, a pulse modulation module, a programming gain amplifier (4), an optical amplifier, a circulator (6), a sensing fiber (7), a polarization-preserving fiber (8), the coupler, a balancing photoelectric detector (10), a reversal switch, a mixer, a microwave source, a band-pass filter, and a signal processing unit, wherein the continuous light output by the laser (1) is divided into two paths after passing through the coupler (2); an output end of the balancing photoelectric detector is connected to the reversal switch; the reversal switch is switched to a channel 1 and a channel 2; when the channel 1 is switched on, the system utilizes the Brillouin optical fiber time domain reflection to measure; and when the programming gain amplifier (4) is closed and the channel 2 is switched on, the system utilizes the polarization optical time-domain reflection to measure. By using the full-distributed optical fiber strain and vibration sensor provided by the invention, the full-distributed measurement for strain as well as the weak vibration and the full-distributed measurement for vibration can be performed on a single optical fiber.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
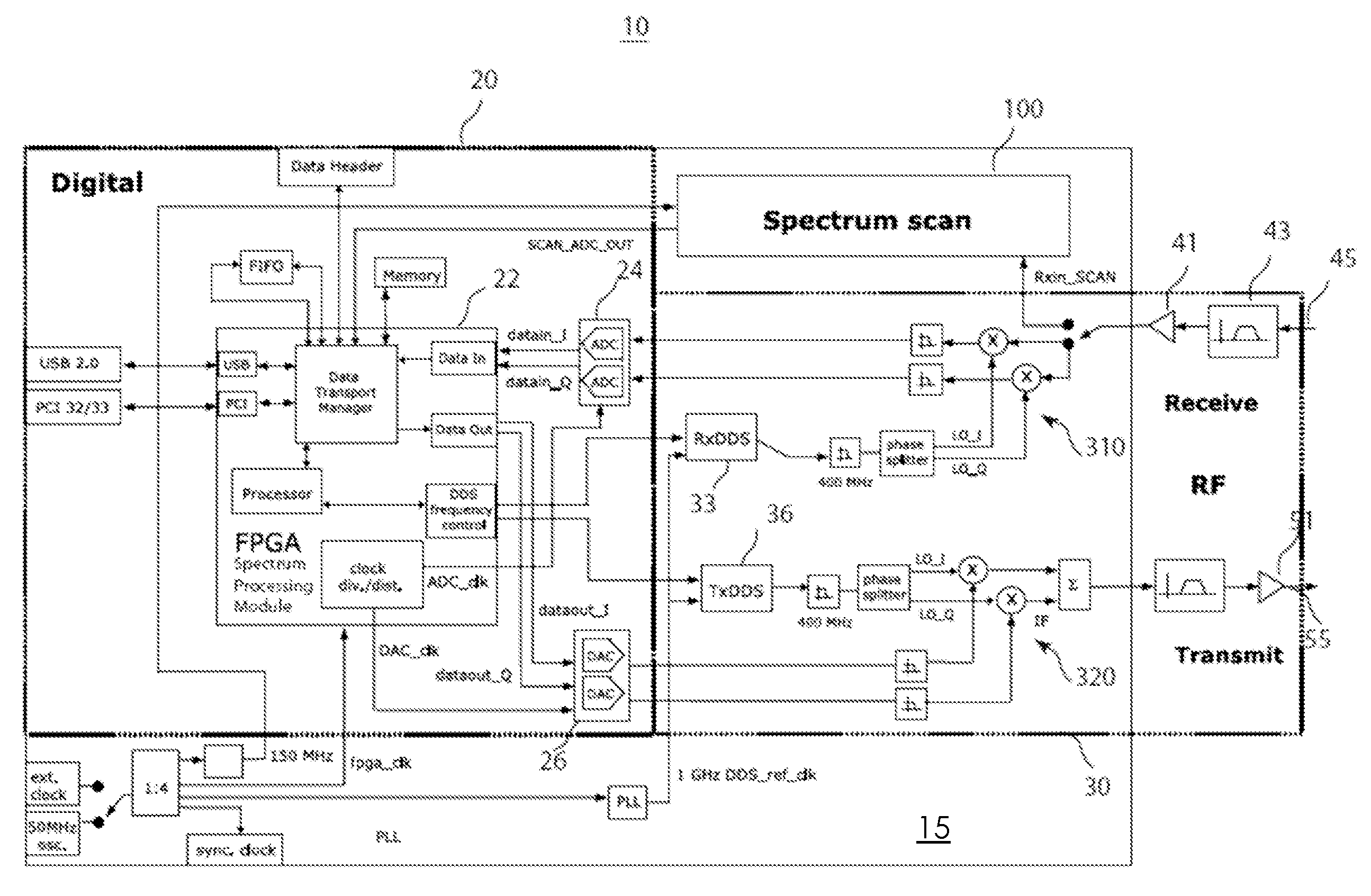
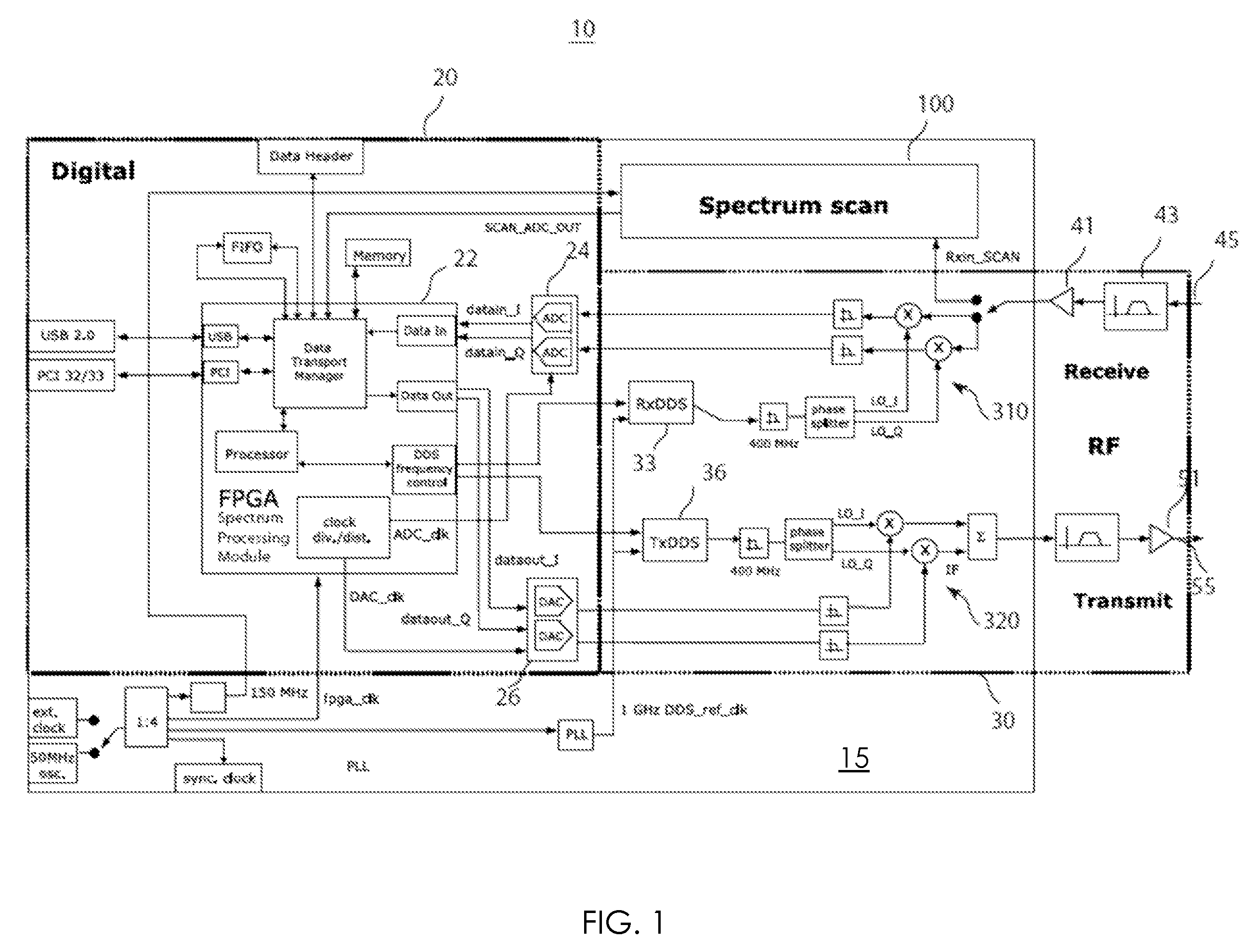
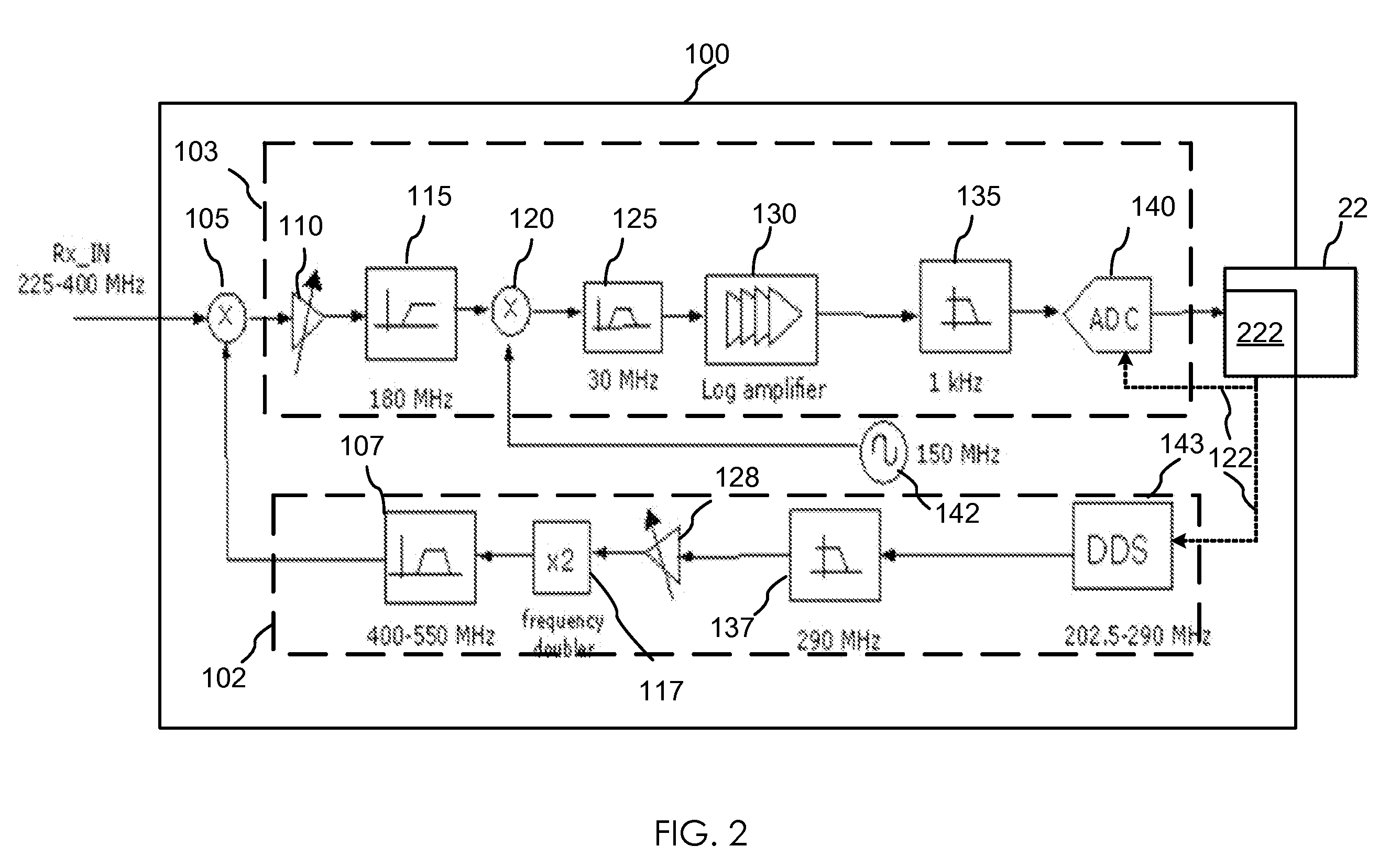
Agile spectrum monitoring in a radio transceiver
InactiveUS20080291985A1Duplex signal operationAngle demodulation by oscillations samplingFrequency spectrumAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a method and an apparatus for agile RF spectrum monitoring in a radio system with dynamic frequency access. It provides a spectrum monitor based on non-coherent heterodyne detection that utilizes a DDS signal generator to digitally generate a reference signal at a variable reference frequency for mixing with an input RF signal received from an RF antenna, a pass-band filter and a log amplifier for obtaining energy estimates at a monitored transmission frequency corresponding to the reference frequency. A processor is provided for adaptively selecting sets of monitored transmission frequencies, for controlling the DDS signal generator, and for processing obtained spectral energy estimates to assess spectral usage data.
Owner:HER MAJESTY THE QUEEN & RIGHT OF CANADA REPRESENTED BY THE MIN OF IND THROUGH THE COMM RES CENT
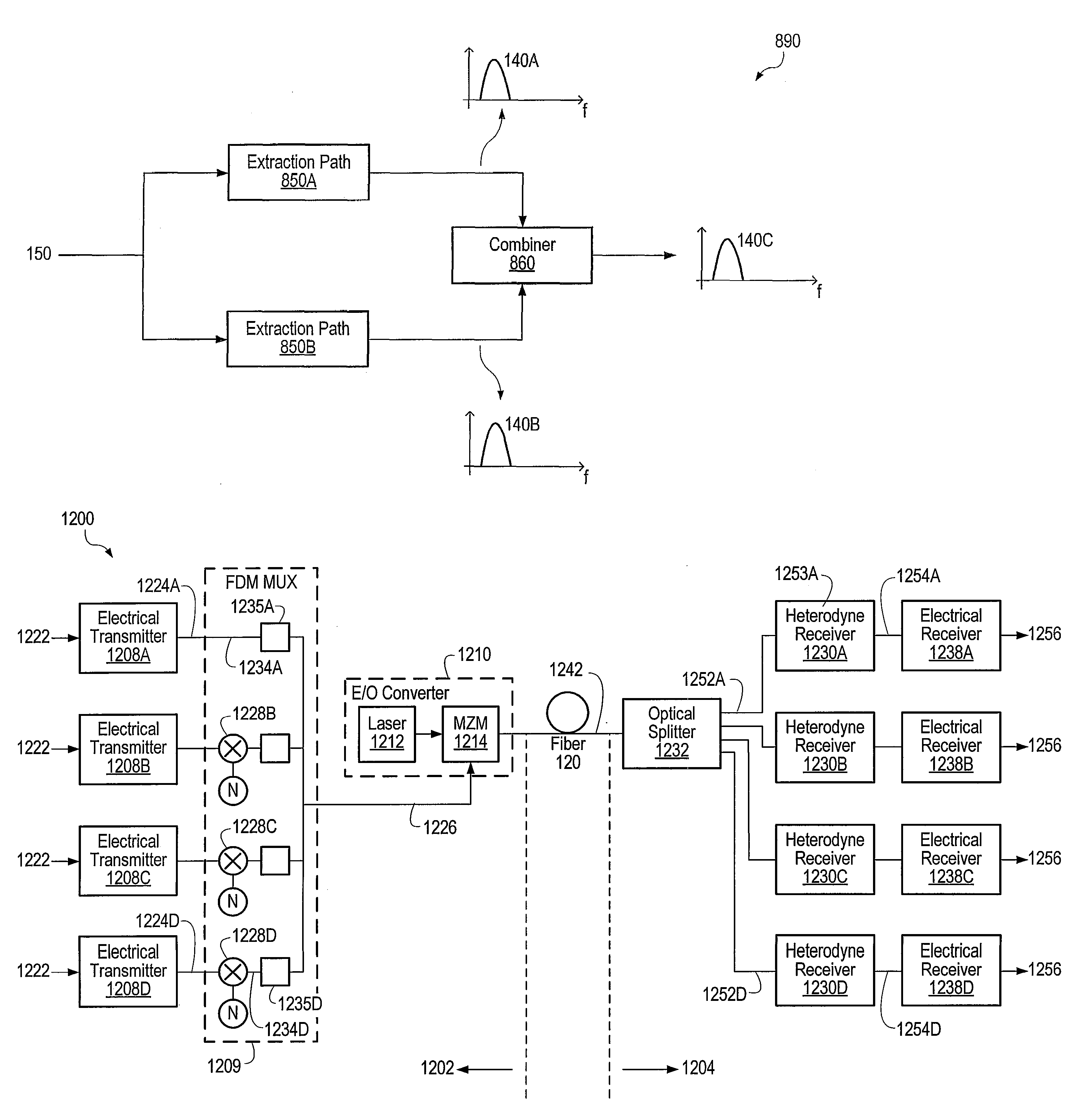
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
InactiveUS7146103B2Less interactionImprove bandwidth utilizationFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingOptical communication
A transmitter subsystem generates an optical signal which contains multiple subbands of information. The subbands have different polarization. For example, in one approach, two or more optical transmitters generate optical signals which have different polarization. An optical combiner optically combines the optical signals into a composite optical signal for transmission across an optical fiber. In another aspect, each optical transmitter generates an optical signal containing both a lower optical sideband and an upper optical sideband (i.e., a double sideband optical signal). An optical filter selects the upper optical sideband of one optical signal and the lower optical sideband of another optical signal to produce a composite optical signal.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
InactiveUS20060291868A1Less interactionUnwanted effectElectromagnetic transmittersElectromagnetic receiversMultiplexingBirefringent crystal
A transmitter subsystem generates an optical signal which contains multiple subbands of information. The subbands have different polarizations. For example, in one approach, two or more optical transmitters generate optical signals which have different polarizations. An optical combiner optically combines the optical signals into a composite optical signal for transmission across an optical fiber. In another approach, a single optical transmitter generates an optical signal with multiple subbands. The polarization of the subbands is varied, for example by using a birefringent crystal. In another aspect of the invention, each optical transmitter generates an optical signal containing both a lower optical sideband and an upper optical sideband (i.e., a double sideband optical signal). An optical filter selects the upper optical sideband of one optical signal and the lower optical sideband of another optical signal to produce a composite optical signal.
Owner:FORSTER ENERGY
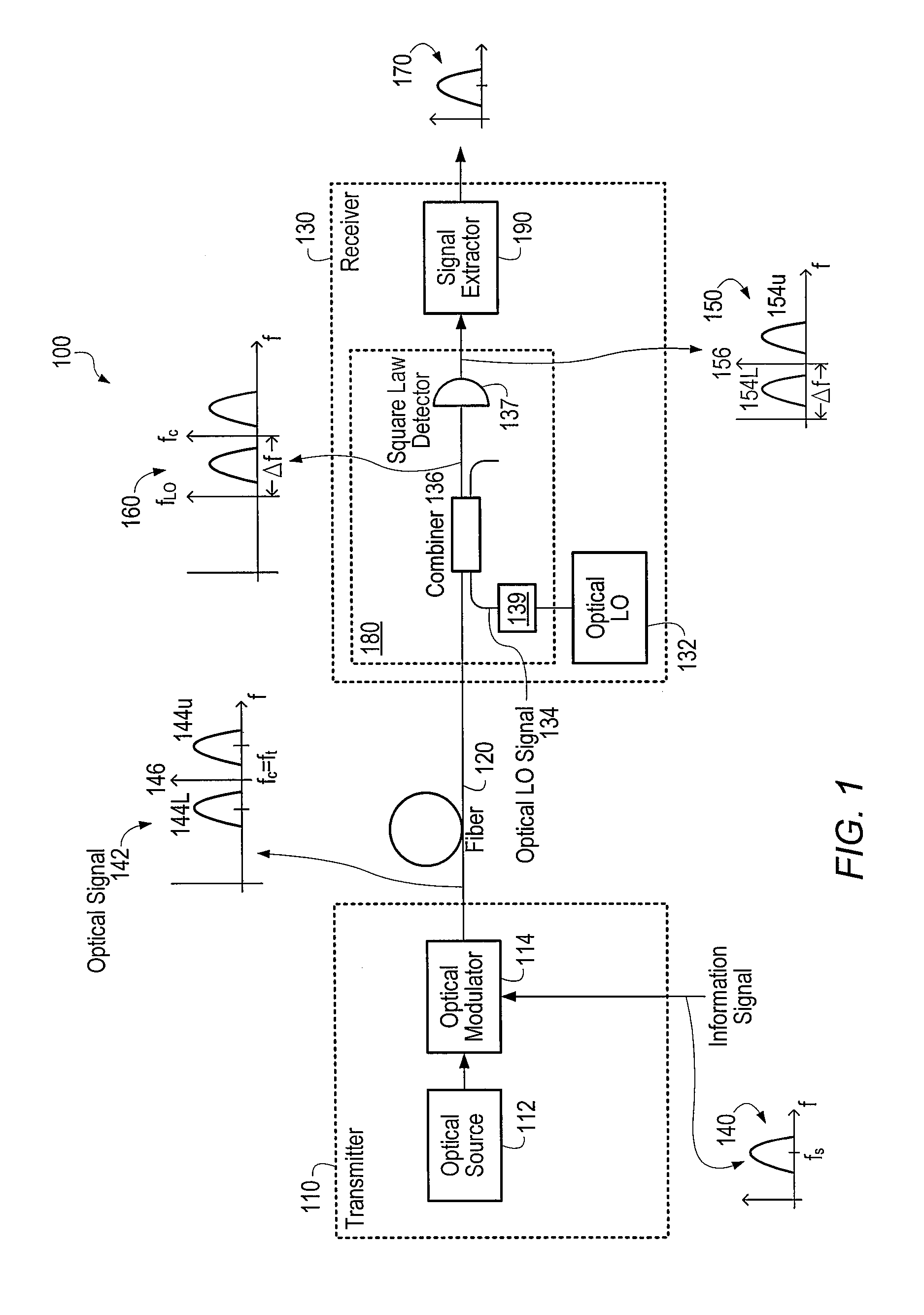
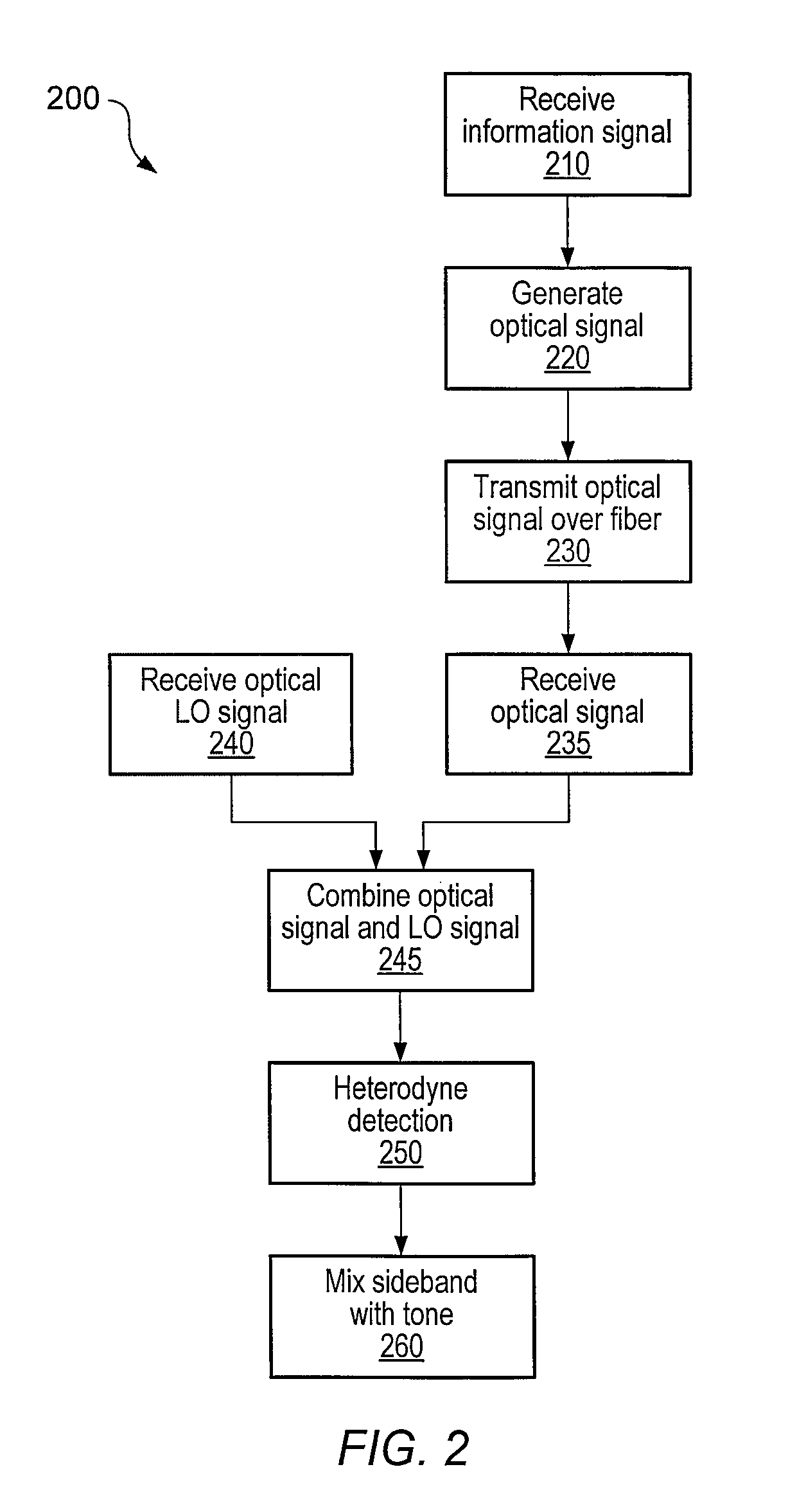
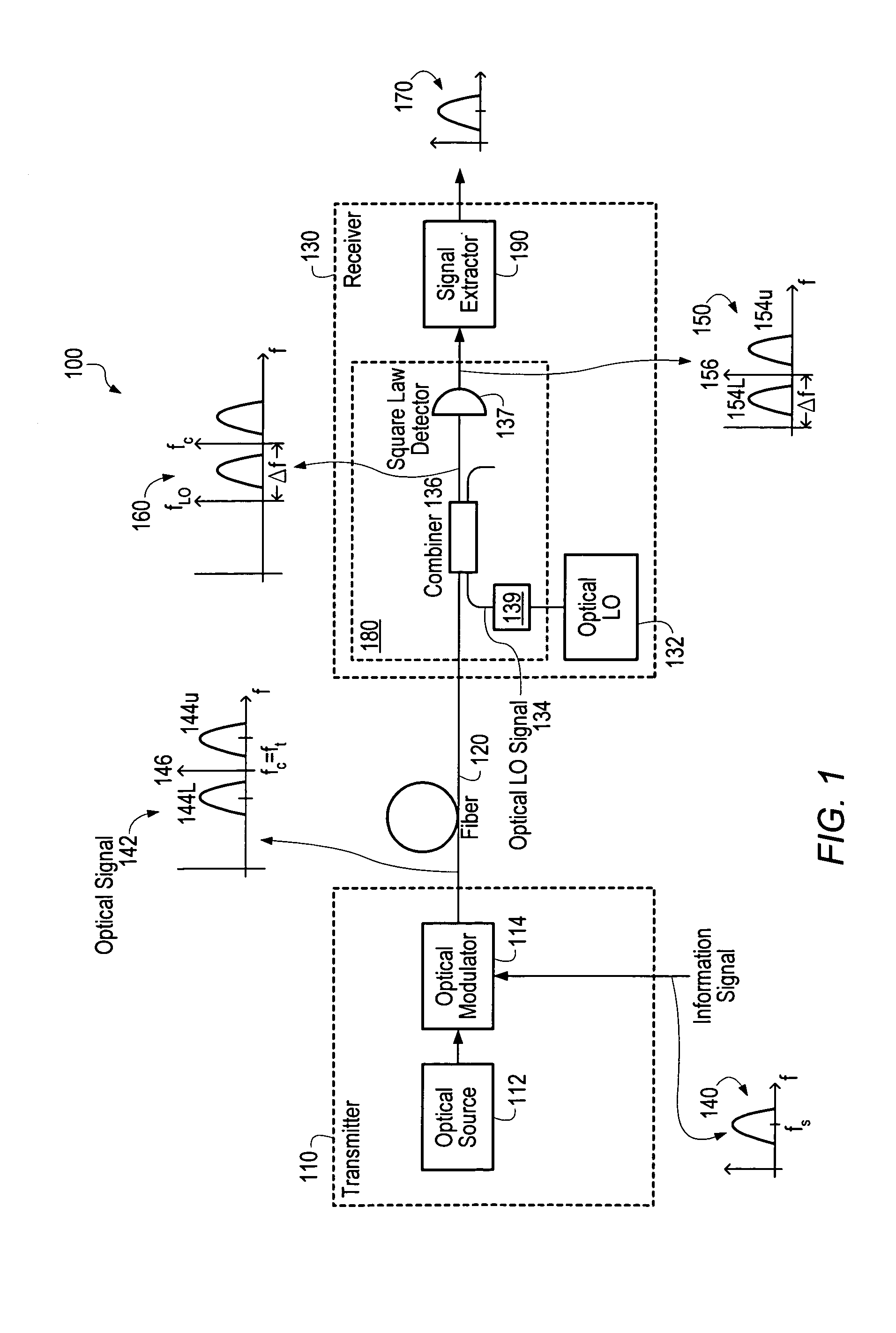
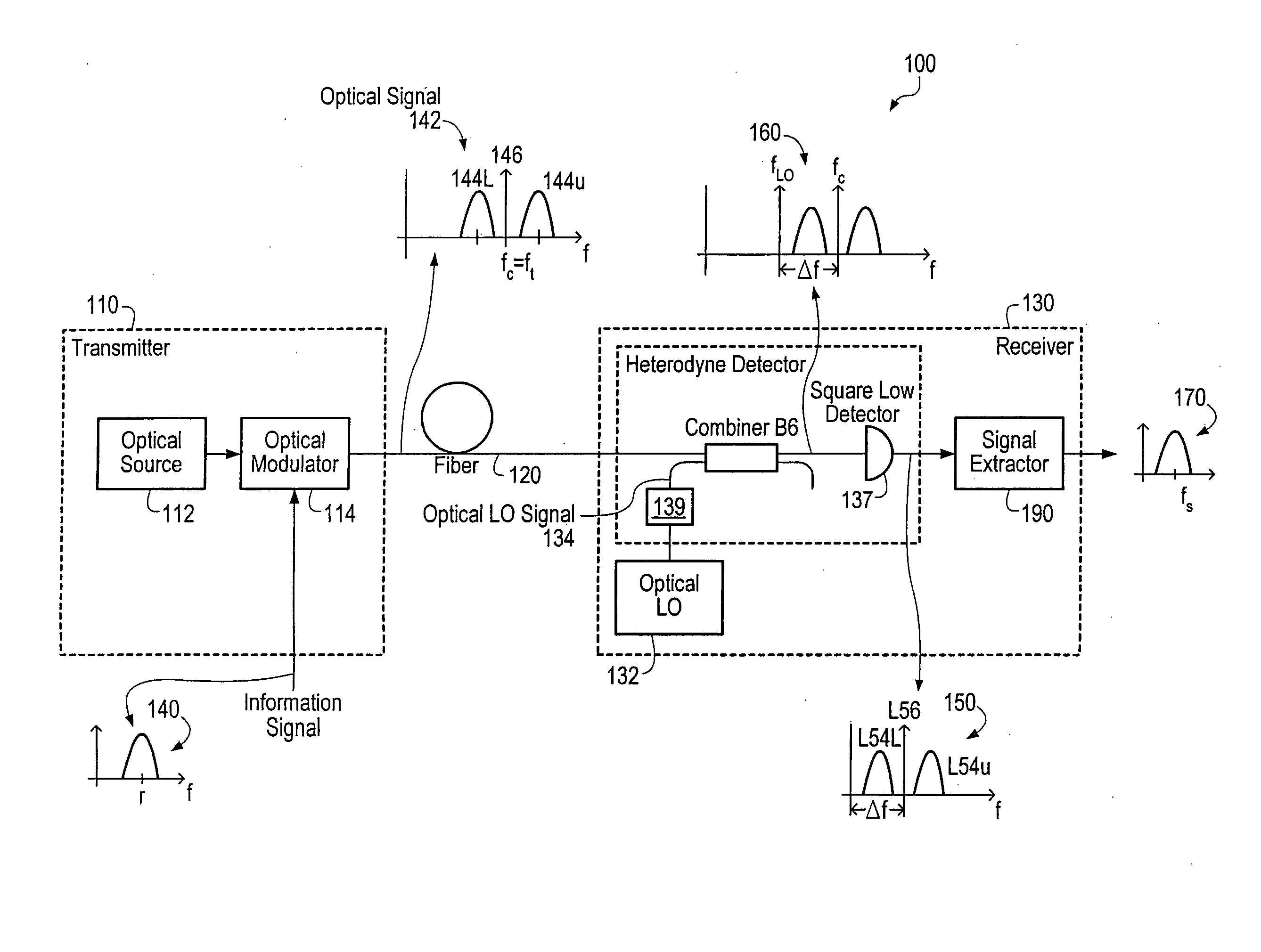
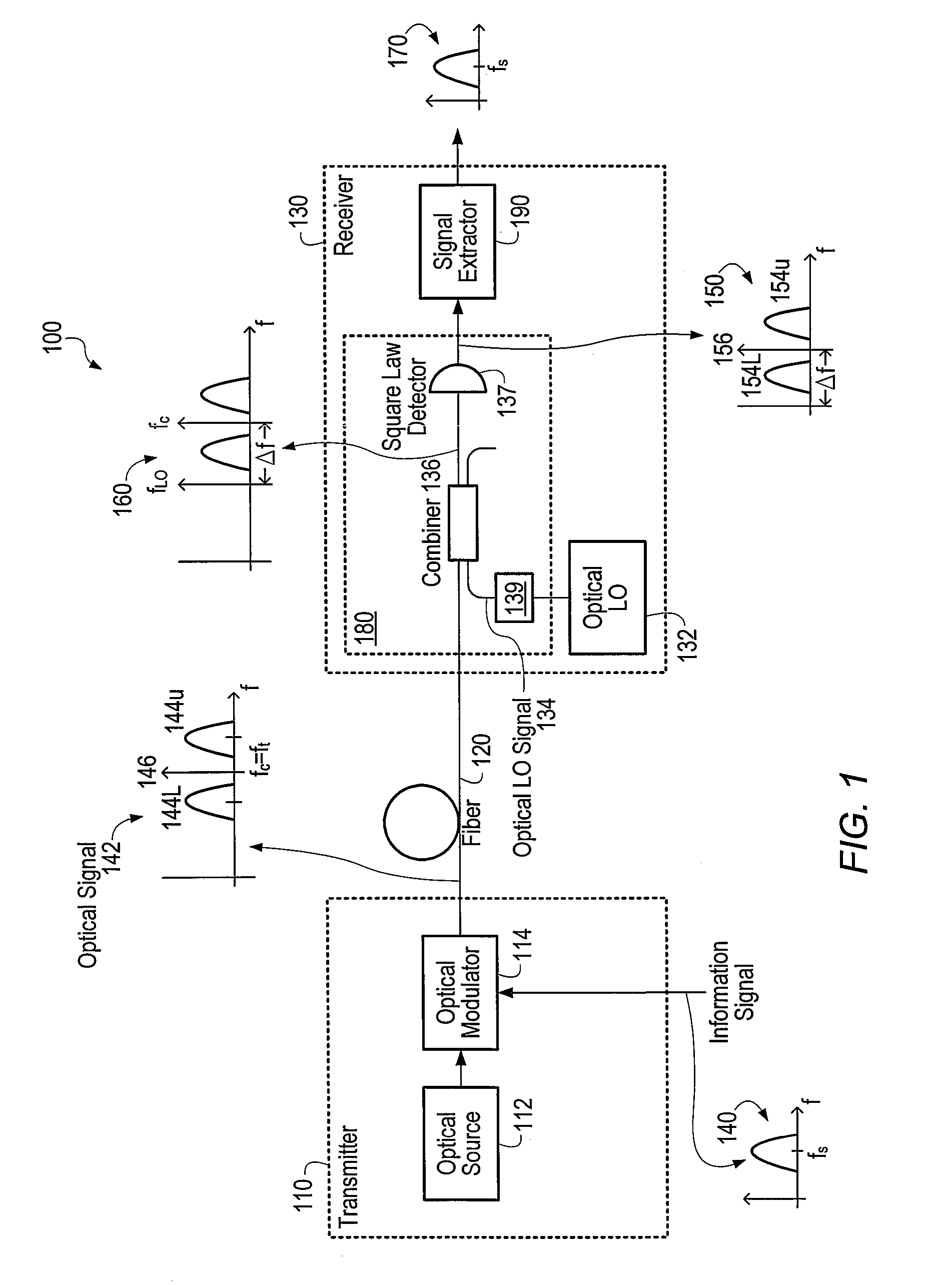
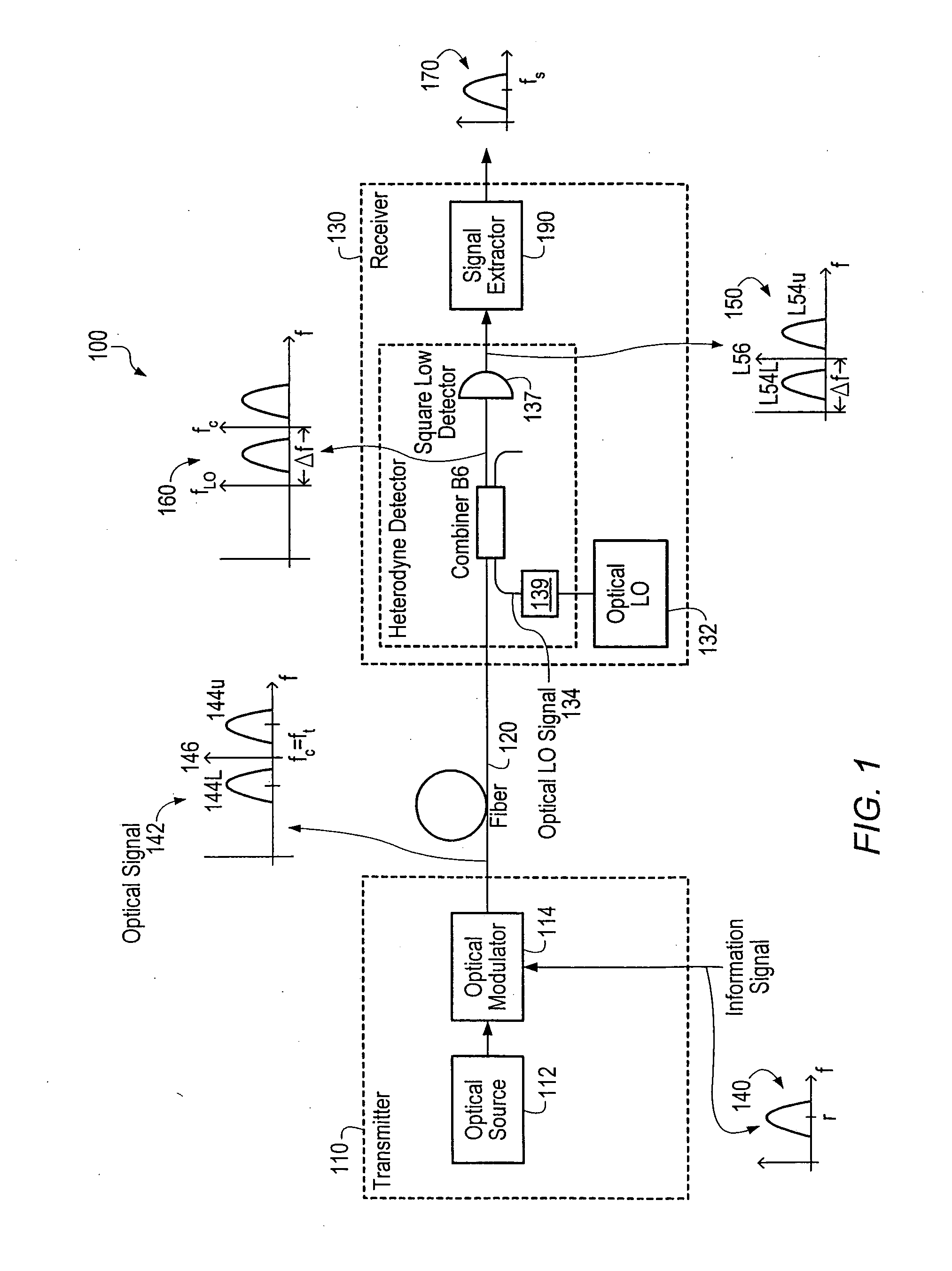
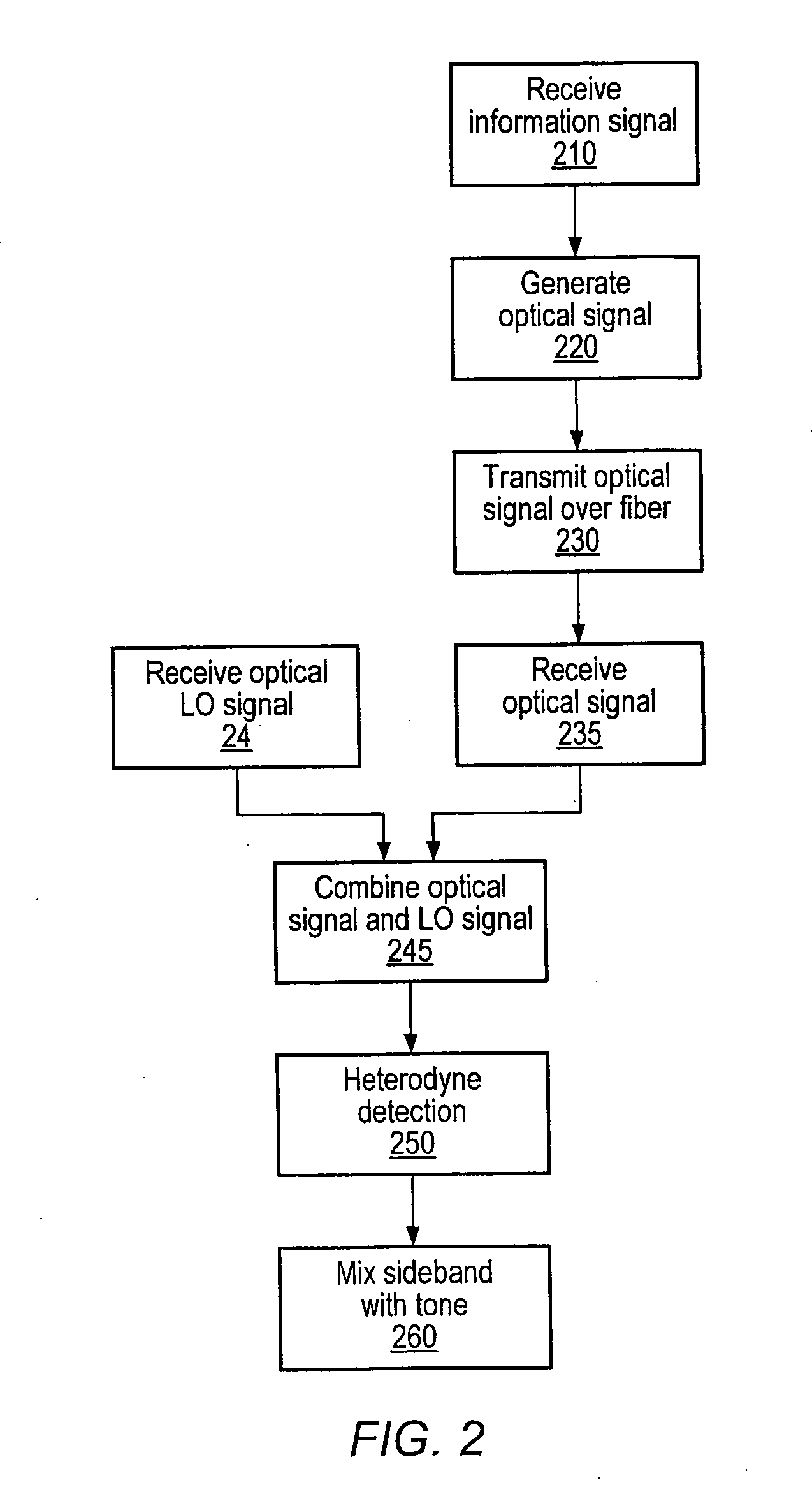
Optical communications using heterodyne detection
InactiveUS7209660B1High sensitivityGood wavelength selectivityFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemLocal oscillator
An optical communications system includes a receiver subsystem with at least two heterodyne receivers. The receiver subsystem receives a composite optical signal having two or more subbands of information and corresponding tones. An optical splitter splits the composite optical signal into optical signals. Each optical signal includes a subband(s) and corresponding tone. Each heterodyne receiver receives an optical signal. The receiver includes a heterodyne detector coupled to a signal extractor. The heterodyne detector mixes the optical signal with an optical local oscillator to produce an electrical signal which includes a frequency down-shifted version of the subband and the tone of the optical signal. The signal extractor mixes the frequency down-shifted subband with the frequency down-shifted tone to produce a frequency component containing the information.
Owner:XYLON LLC
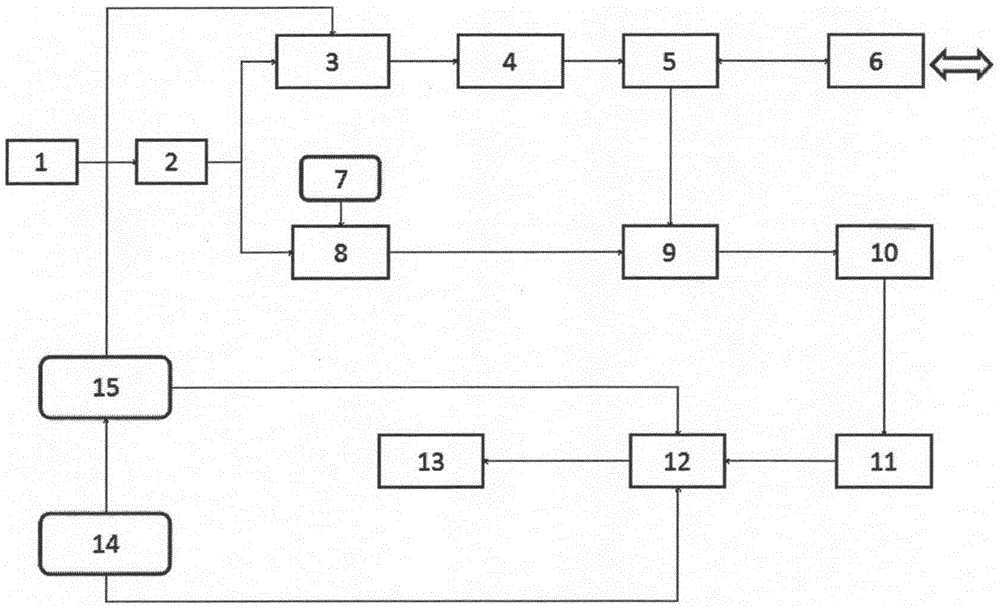
Speed measurement and distance measurement system and speed measurement and distance measurement method based on pseudo-random code phase modulation and heterodyne detection
InactiveCN105629258AImprove electro-optic efficiencyEasy to operateElectromagnetic wave reradiationLocal oscillator signalAcousto-optics
The invention provides a speed measurement and distance measurement system and a speed measurement and distance measurement method based on pseudo-random code phase modulation and heterodyne detection. The basic principle is that laser is divided into two parts via a coupler. The majority part is subjected to phase modulation through an electro-optic phase modulator according to a pseudo-random code signal and is transmitted by a telescope as emergent laser; the other part is subjected to frequency shift through an acousto-optic frequency shifter and is used for coherent detection as a local oscillator signal; a laser echo signal and the local oscillator signal are subjected to a coherent action in the coupler, an electric signal is converted through a photoelectric balance detector, and a digital signal is converted through a dual-channel AD acquisition card; the other channel of the dual-channel AD acquisition card acquires a driving signal of the electro-optic phase modulator; and the acquired two ways of signals are subjected to signal processing in a computer. The invention provides a new method of simultaneously acquiring the target speed and the distance information in a high-precision mode.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system
InactiveCN101825710AMake up for the defect of environmental interferenceSolve the problem of all-fiber miniaturizationElectromagnetic wave reradiationNon-linear opticsRadar systemsOperability
The invention discloses a 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, which consists of a 2 mu m off-axis Cassegrain optical antenna system, a 2 mu m laser beam splitting system, a 2 mu m seed implantation laser amplifier, a 2 mu m monitoring detector system, and a 2 mu m balanced heterodyne detection system. The system overcomes the defect of ambient interference existing in a free space optical path, overcomes the influence of shot noise on heterodyne reception signal-to-noise ratio, and solves the problems of all fiber and miniaturization of the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, so that the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system has a more compact structure. In addition, the system has the characteristics of safe laser for human eye, optical path connection by adopting flexible optical fiber devices, high operability and stability, low cost, good real time, long effectively measured distance, high measurement accuracy (speed measurement and distance measurement) and the like, and has high practical value in the field of coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
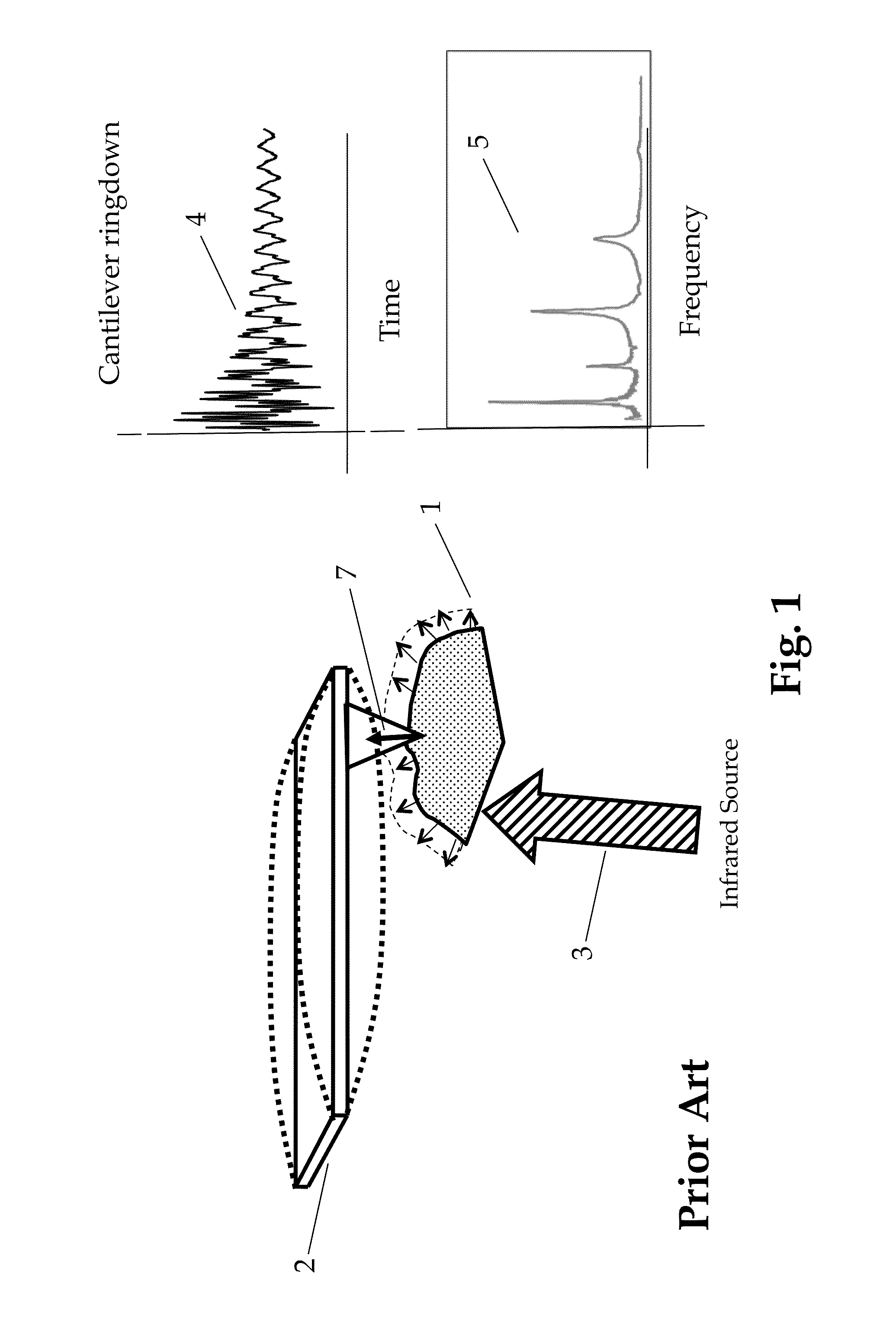
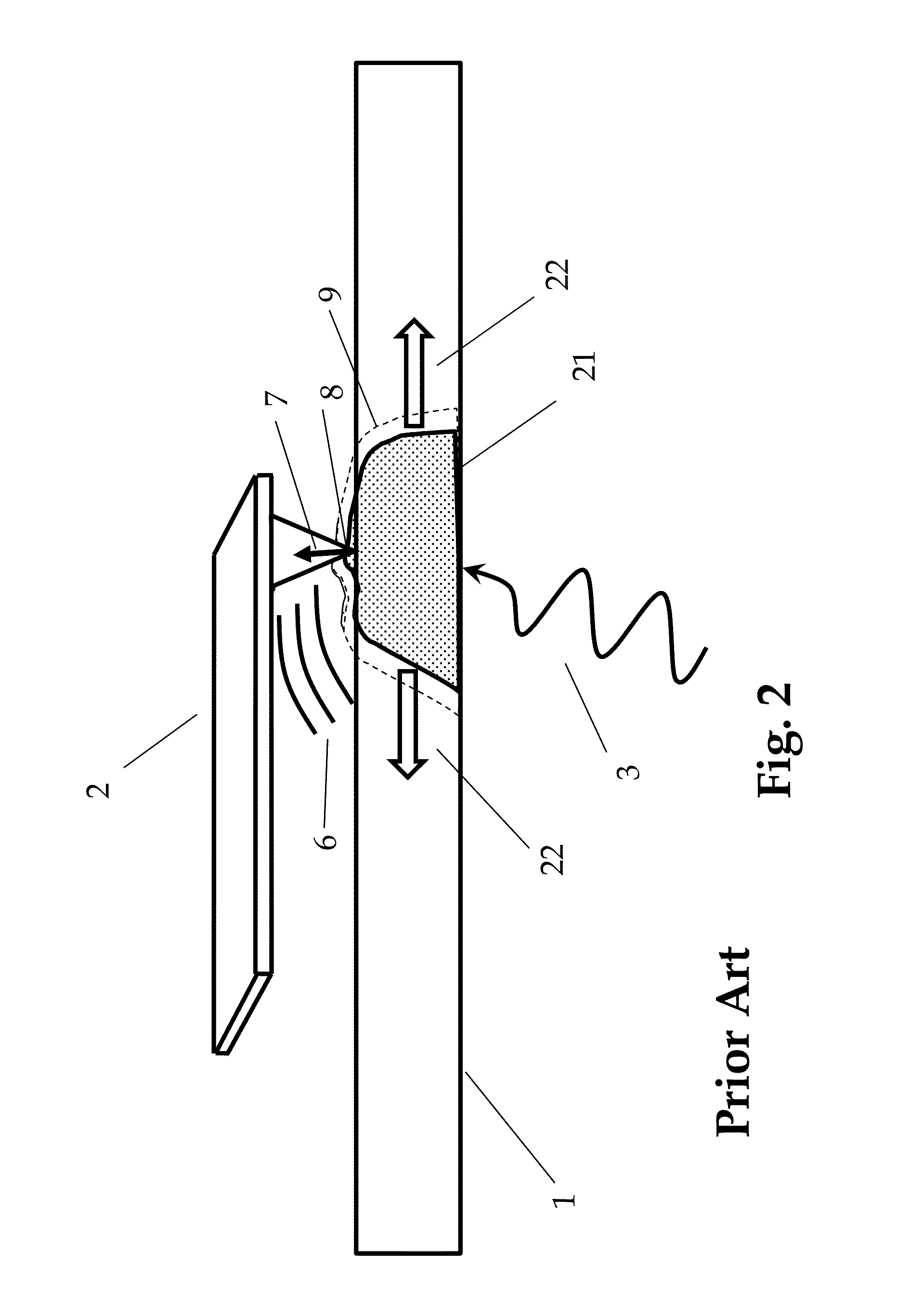
Multiple modulation heterodyne infrared spectroscopy
ActiveUS20120204296A1Large responseSufficient powerMaterial analysis by optical meansNanotechnologyImage resolutionResonance
A heterodyne detection technique for highly localized IR spectroscopy based on an AFM. A pulsed IR source illuminates a sample and causes contact resonance of an AFM probe, which is a function of localized absorption. The probe is operated in intermittent contact mode and is therefore oscillated at a resonance frequency. A secondary oscillation is mixed in to the probe oscillation such that the sum of the secondary oscillation and the IR source pulse frequency is near another harmonic of the probe. A mixing effect causes measurable probe response at the other harmonic allowing data to be taken away from the pulse frequency, resulting in background effect rejection and improved spatial resolution.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
Digital-analog hybrid heterodyne detection receiving device and data processing method adopted by same
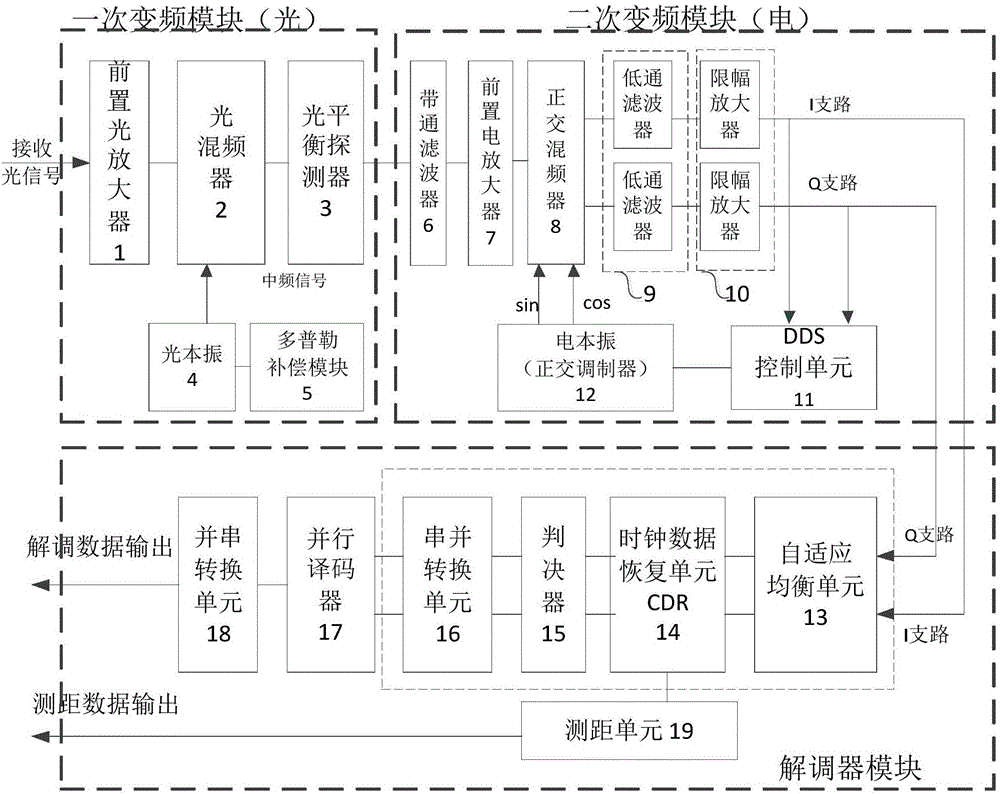
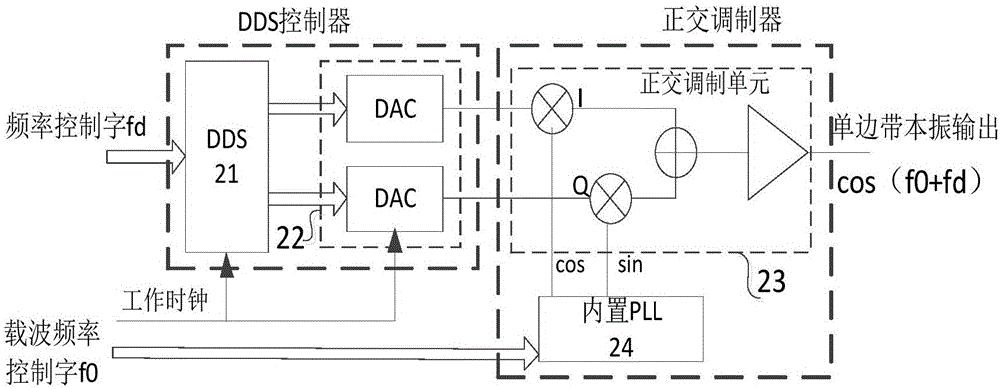
ActiveCN107181532ACompensation for Carrier Doppler VariationsLarge frequency dynamic rangeCarrier regulationSatellite communication transmissionIntermediate frequencyFrequency conversion
The invention discloses a digital-analog hybrid heterodyne detection receiving device applicable to space laser communication and a data method. The digital-analog hybrid heterodyne detection receiving device applicable to space laser communication comprises a primary frequency conversion module, a secondary frequency conversion module and a demodulator module, and is characterized in that the primary frequency modulation module comprises a preposed optical amplifier, an optical mixer, a optical balance detector, an optical local oscillator and a Doppler compensation module, Doppler compensation forms voltage signals used for compensating the Doppler frequency shift, and the voltage signals are outputted to the optical local oscillator; the optical local oscillator forms optical local oscillation signals; the optical mixer receives optical signals and the optical local oscillation signals and acquires low-intermediate frequency IF optical signals through mixing; the optical balance detector is connected with an output end of the optical mixer, converts the low-intermediate frequency IF optical signals into electric intermediate-frequency signals and outputs the electric intermediate-frequency signals to the secondary frequency conversion module; and the secondary frequency conversion module performs amplitude-limiting sampling on the electric intermediate-frequency signals and outputs the sampled signals to the demodulator module, and the demodulator module demodulates the sampled signals and outputs demodulated data.
Owner:SHANGHAI ENG CENT FOR MICROSATELLITES
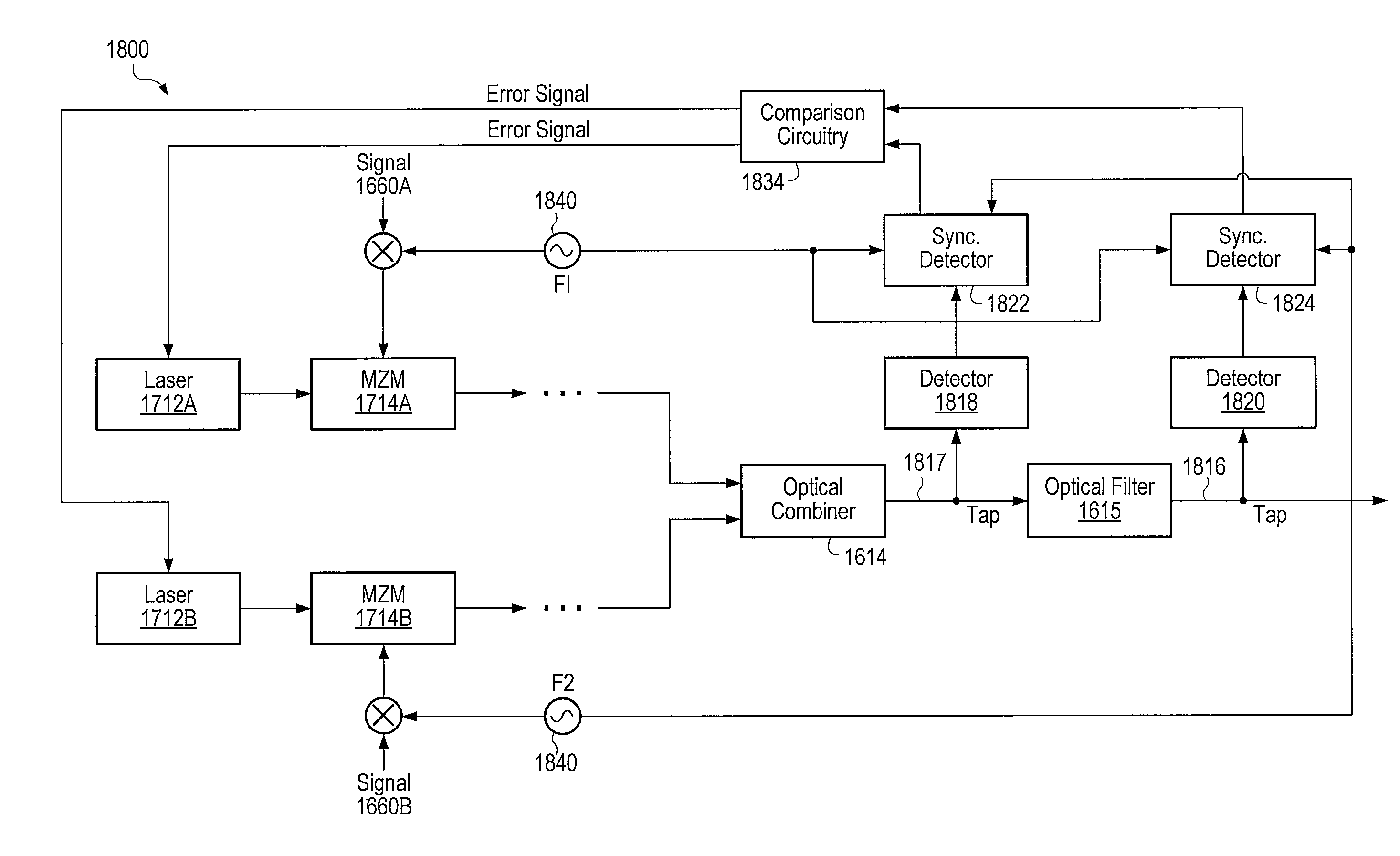
Ultra-low noise photonic phase noise measurement system for microwave signals
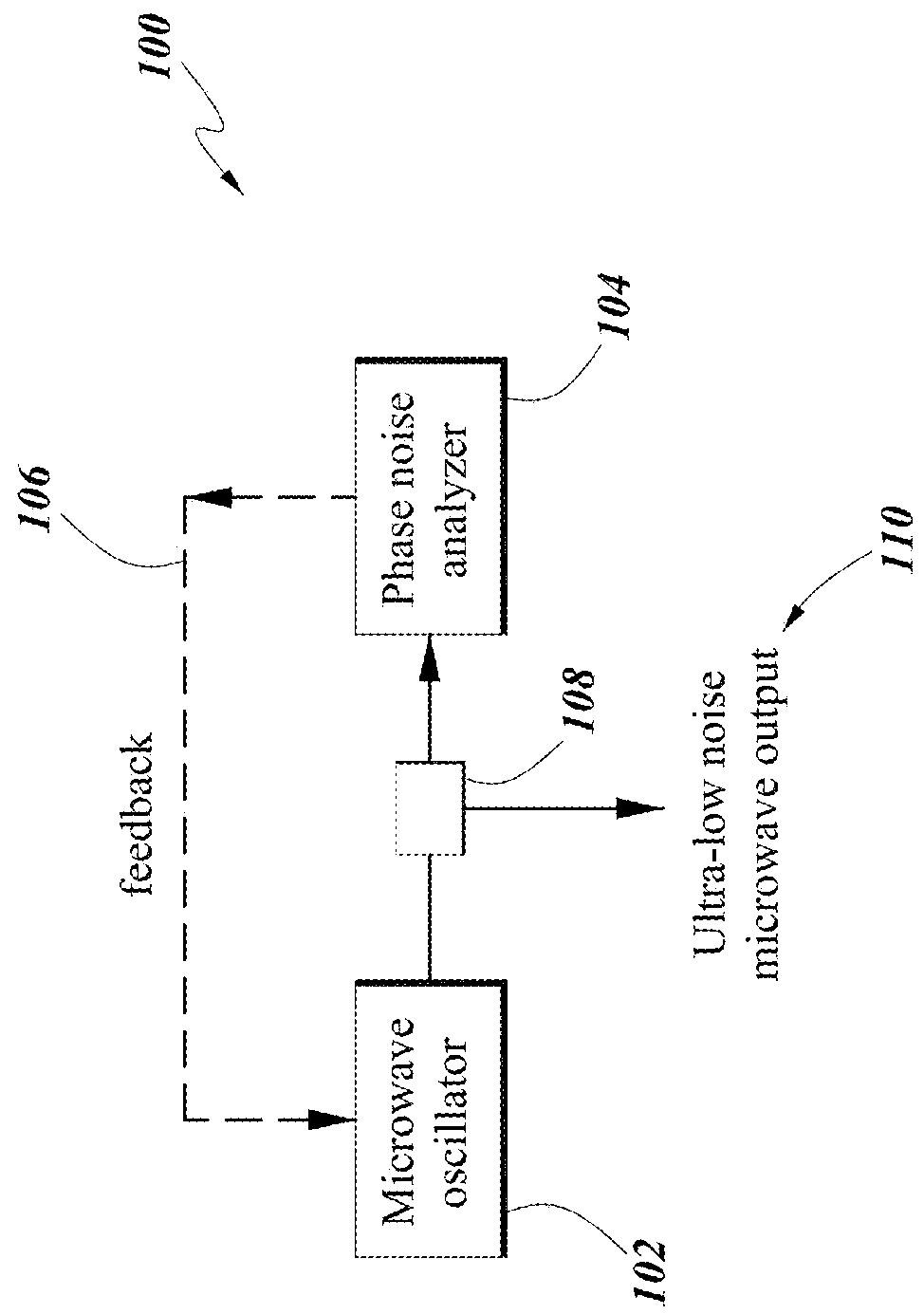
InactiveUS20180180655A1Reduce the noise floorHigh sensitivitySpectral/fourier analysisNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementLow noisePhase noise
Systems and methods for precision phase noise measurements of radio frequency (RF) oscillators are provided. An RF signal under test can be modulated on a continuous wave (cw) laser carrier frequency via generation of modulation sidebands using an appropriate modulator. A photonic delay line can be implemented as a self-heterodyne detection system for the phase noise, allowing for photonic down-conversion of the phase noise measurement to direct current (DC). The self-heterodyne detection system allows detection outside of any 1 / f noise issues. Ultra-low phase noise detection for RF frequencies in a range from below 1 GHz to beyond 100 GHz is enabled with a low noise floor in the whole frequency range. Higher-order modulation sidebands can further reduce the noise floor of the system. Ultra-low noise RF (microwave) output can be generated. The RF signal under test can be generated by a dielectric resonance oscillator or opto-electronic oscillator.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Phase-light time domain reflection device and method based on heterodyne detection phase demodulation
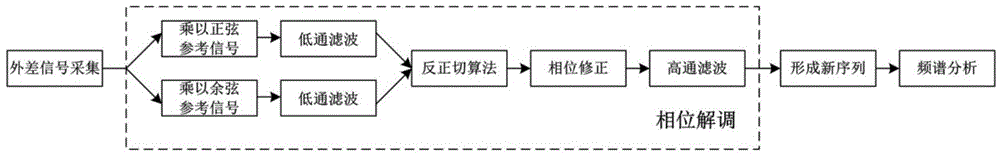
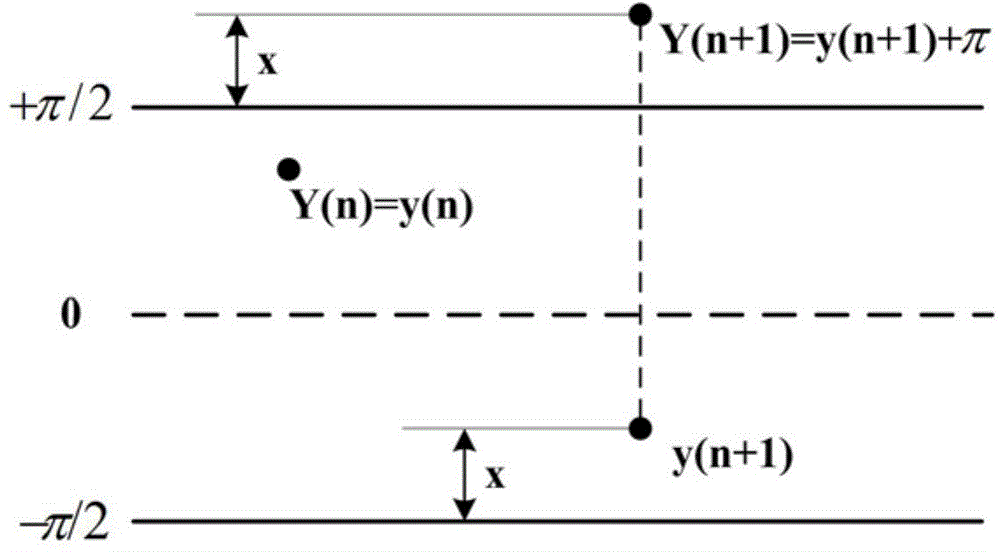
ActiveCN104819770AHigh sensitivityAccurate identificationSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansErbium dopingOptical fiber coupler
The invention relates to the field of optical fiber sensing, specifically a phase-light time domain reflection device and method based on heterodyne detection phase demodulation. The device consists of a narrow linewidth laser, an optical fiber coupler with a coupling model of 1*2, a polarization controller, a sound-light modulator, an erbium-doped optical fiber amplifier, a narrow-band optical fiber filter, a first variable optical attenuator, a three-port circulator, a sensing optical fiber, an optical fiber coupler with a coupling model of 2*1, a photoelectric detector, a signal collection and processing module, an arbitrary waveform generator, a power amplifier, and a second variable optical attenuator. The device and method enable the heterodyne detection phase demodulation to be combined together, achieve external vibration sensing through direct phase demodulation, and are higher in sensitivity. In addition, the device and method employ a brand new direct phase modulation method to sense the external vibration, so the positioning method, compared with a conventional method, of each vibrating point is different.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
Multiple modulation heterodyne infrared spectroscopy
A heterodyne detection technique for highly localized IR spectroscopy based on an AFM. A pulsed IR source illuminates a sample and causes contact resonance of an AFM probe, which is a function of localized absorption. The probe is operated in intermittent contact mode and is therefore oscillated at a resonance frequency. A secondary oscillation is mixed in to the probe oscillation such that the sum of the secondary oscillation and the IR source pulse frequency is near another harmonic of the probe. A mixing effect causes measurable probe response at the other harmonic allowing data to be taken away from the pulse frequency.
Owner:BRUKER NANO INC
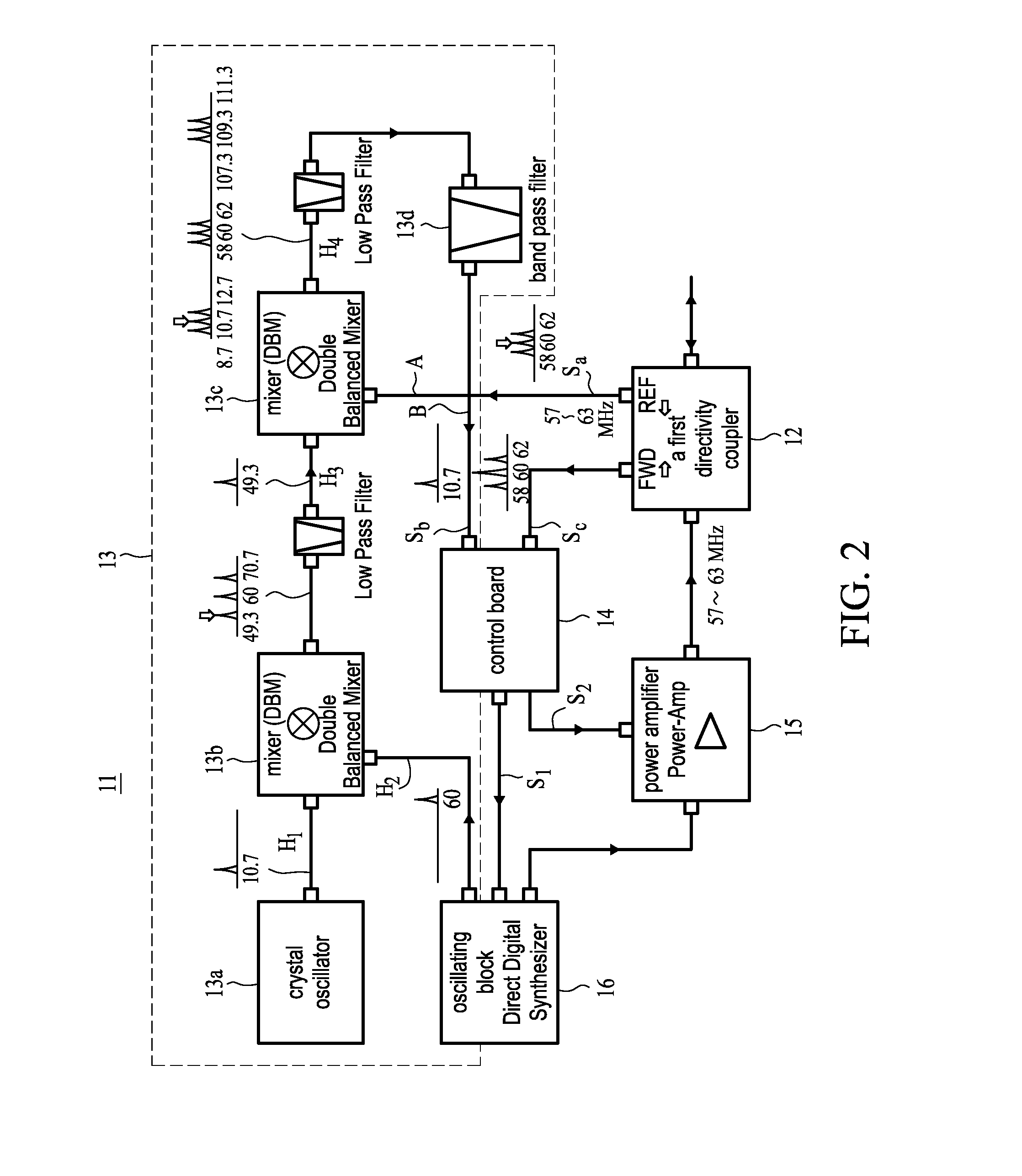
High frequency power supply device and high frequency power supplying method
InactiveUS20080128087A1Improve efficiencyImprove accuracyLiquid surface applicatorsElectric discharge heatingHigh frequency powerControl power
A high frequency power supply device and power supplying method are disclosed, which can rapidly and accurately control power used for generation of plasmas. The device includes a first high frequency power supply, providing power at frequency f1, and a second high frequency power supply providing power at frequency f2 (f1>f2). The first power supply includes: a first high frequency oscillator, which excites the high frequency power at the first frequency and has a variable frequency; a first power amplification block, which amplifies the power of the high frequency oscillator; a heterodyne detection block, which performs heterodyne detection of a reflected wave; and a first control block, which receives a signal after detection of the heterodyne detection block and a traveling wave signal, and controls an oscillating frequency of the first high frequency oscillating block and an output of the first power amplification block.
Owner:PEARL IND +1
Laser radar system for tracking and identifying low, small and slow object based on laser micro-Doppler effect
InactiveCN107045129AHigh sensitivityEffective filteringElectromagnetic wave reradiationObject basedRadar systems
The invention provides a laser radar system for tracking and identifying a low, small and slow object based on the laser micro-Doppler effect, belongs to the field of laser radar detection, and aims at solving the problem that a present micro-Doppler microwave radar is interfered by ground clutters seriously. A laser source module outputs relatively strong signal light and relatively weak local oscillation light, a frequency shift modulation module carries out frequency shift on the signal light, and the signal light after frequency shift is input to a heterodyne detection module; the heterodyne detection module uses the signal light after frequency shift to scan a target area and obtains a target echo; beam combination is carried out on the target echo and the local oscillation light, the light after beam combination is detected, an intermediate-frequency signal is collected and processed, signal spectral distribution including target motion and micro-motion information is obtained, whether an object is the low, small and slow object is determined, and if YES, the speed and distance of the object are obtained; and the object is tracked according to the obtained speed and distance of the object.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Optical communications using multiplexed single sideband transmission and heterodyne detection
InactiveUS20070133993A1Less interactionImprove bandwidth utilizationWavelength-division multiplex systemsElectromagnetic transmittersMultiplexingBirefringent crystal
A transmitter subsystem generates an optical signal which contains multiple subbands of information. The subbands have different polarizations. For example, in one approach, two or more optical transmitters generate optical signals which have different polarizations. An optical combiner optically combines the optical signals into a composite optical signal for transmission across an optical fiber. In another approach, a single optical transmitter generates an optical signal with multiple subbands. The polarization of the subbands is varied, for example by using a birefringent crystal. In another aspect of the invention, each optical transmitter generates an optical signal containing both a lower optical sideband and an upper optical sideband (i.e., a double sideband optical signal). An optical filter selects the upper optical sideband of one optical signal and the lower optical sideband of another optical signal to produce a composite optical signal.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Sensor for Measuring a Vibrating Surface Obscured from View
InactiveUS20080074674A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansElectricityLight beam
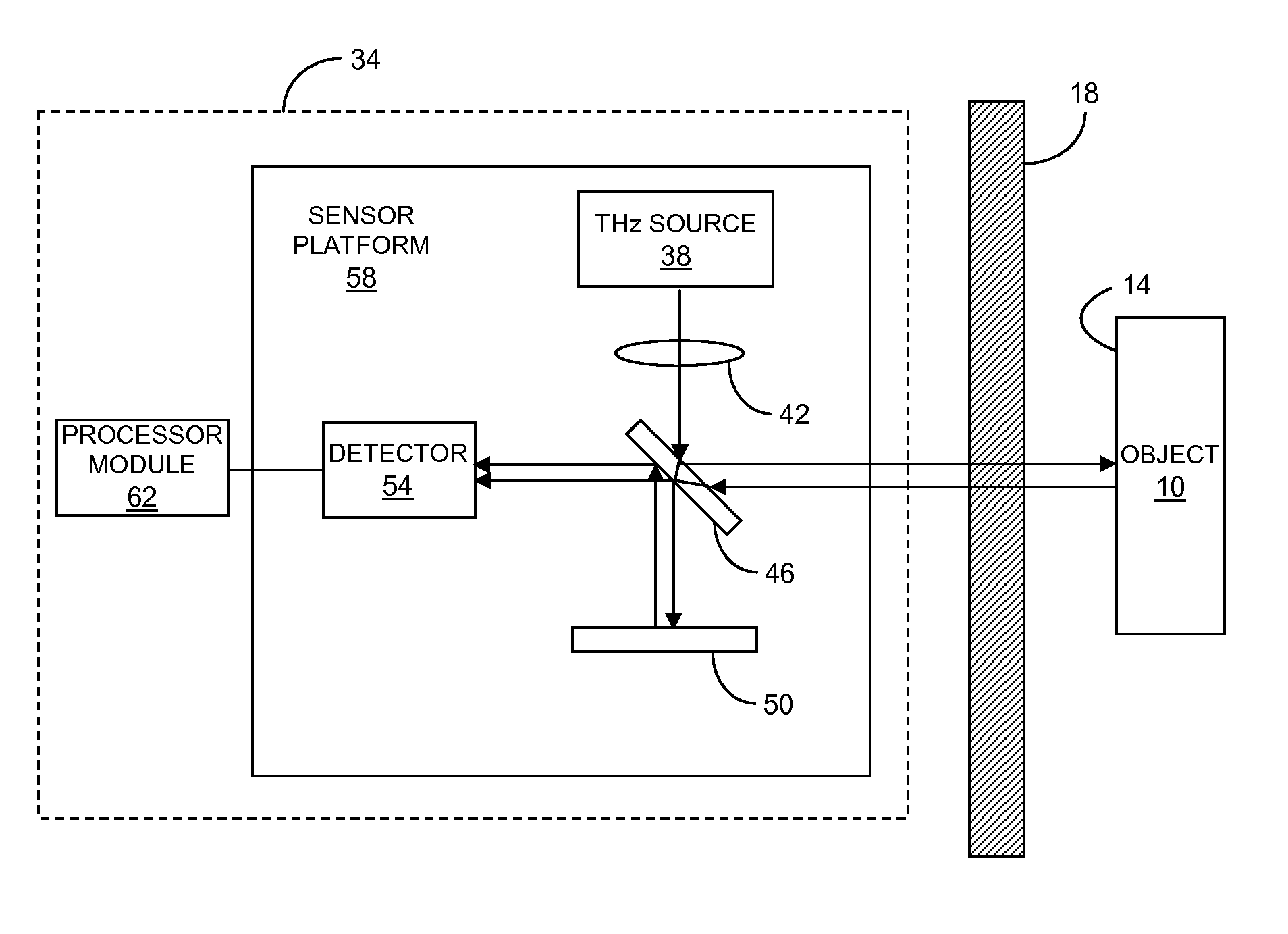
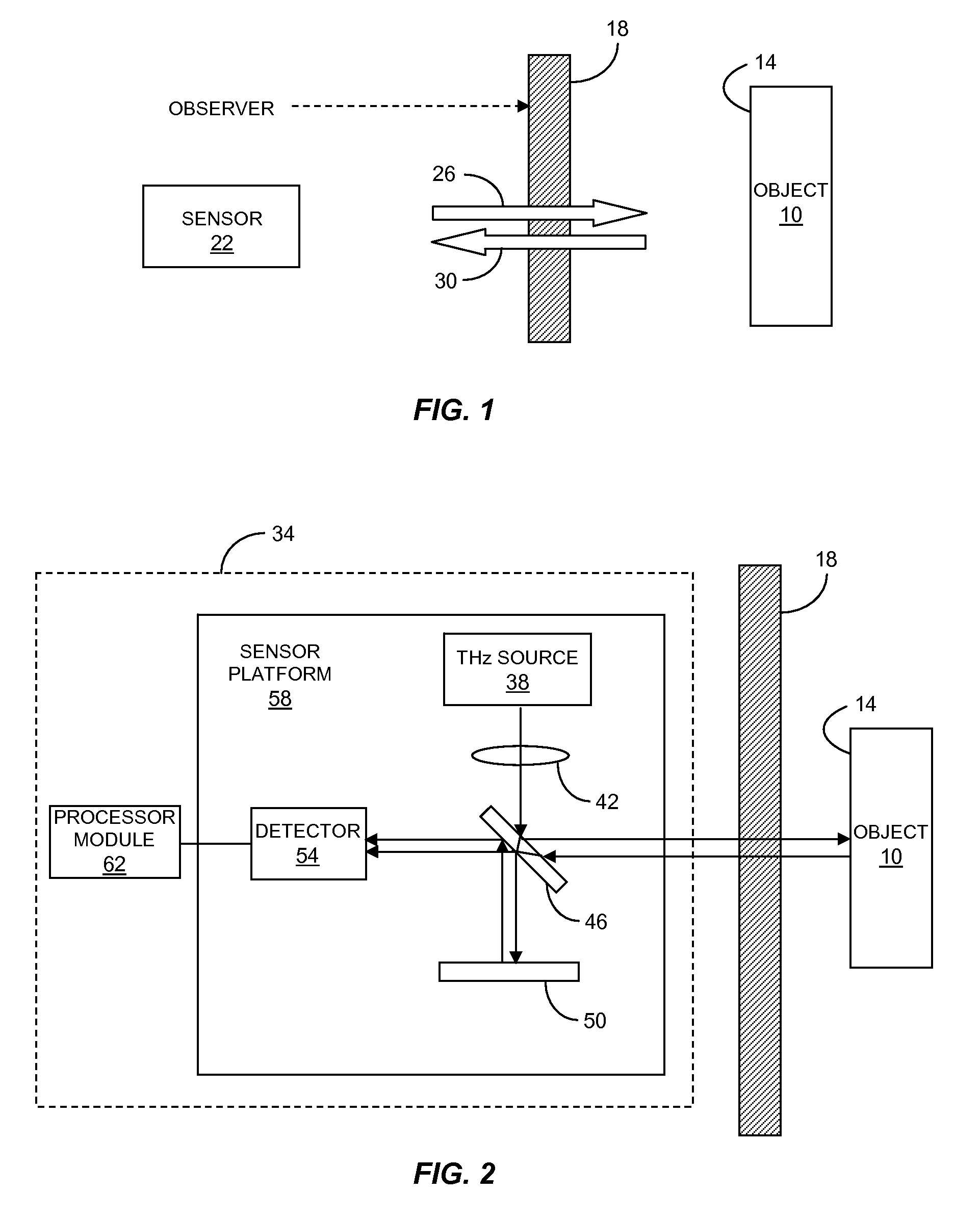
Described are a sensor and a method for measuring a vibration of a surface obscured from view. The sensor includes a narrowband source of a terahertz beam, a beamsplitter, a beam combiner and a terahertz detector. The beamsplitter splits the terahertz beam into a sample beam for irradiating the surface and a reference beam. The beam combiner combines the sample beam scattered from the surface and the reference beam. The terahertz detector generates an electrical signal based on a modulation of the power of the combined beams due to the vibrating surface. The electrical signal indicates a characteristic of the surface vibration. Homodyne or heterodyne detection can be utilized. Advantageously, the sensor can see surfaces that are covered, concealed or otherwise obscured behind optically opaque materials, including plastic, cloth, foam, paper and other materials. Thus the sensor has a wide variety of applications where conventional vibrometers are not practical.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
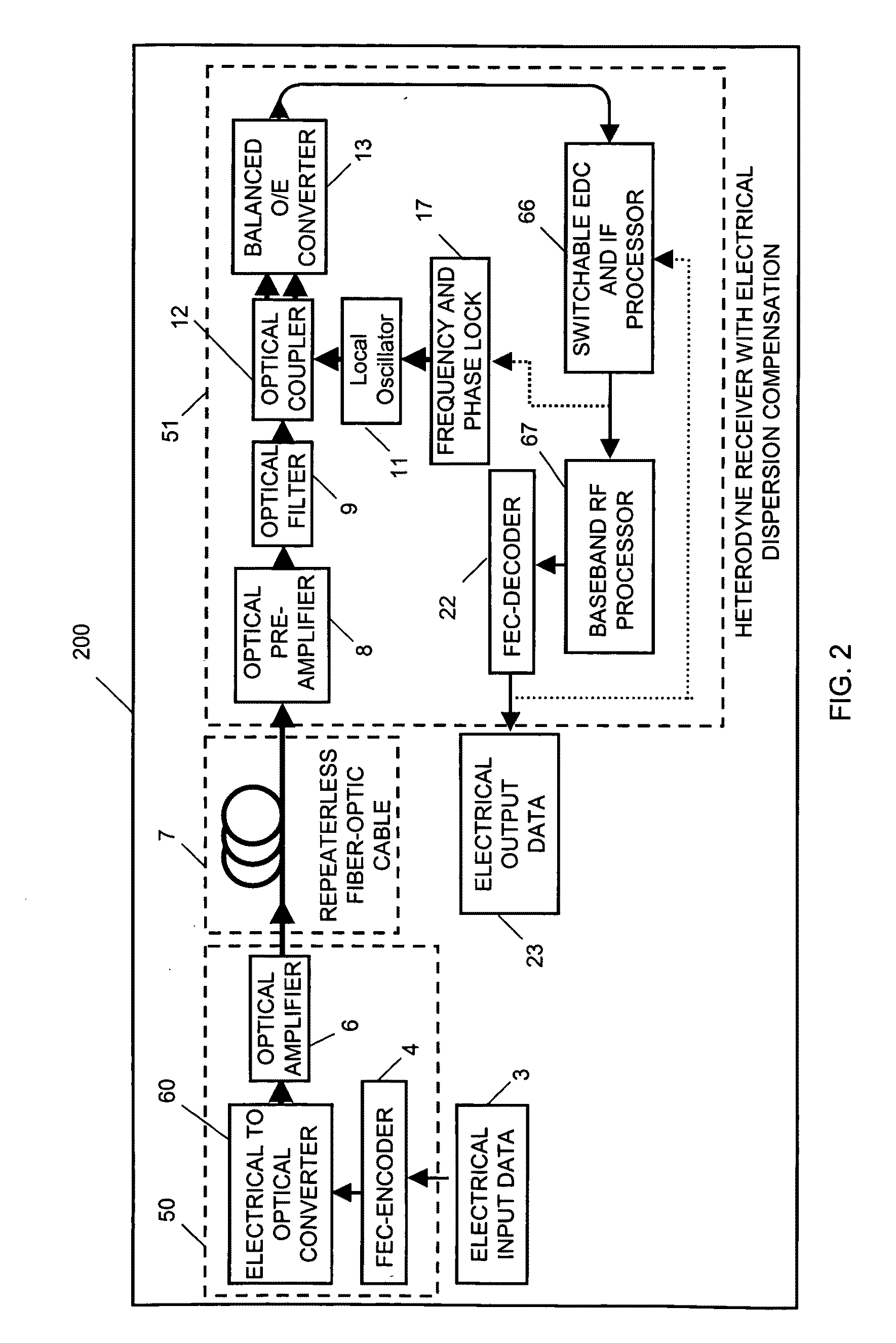
Method and apparatus for repeaterless high-speed optical transmission over single-mode fiber using coherent receiver and electronic dispersion compensation
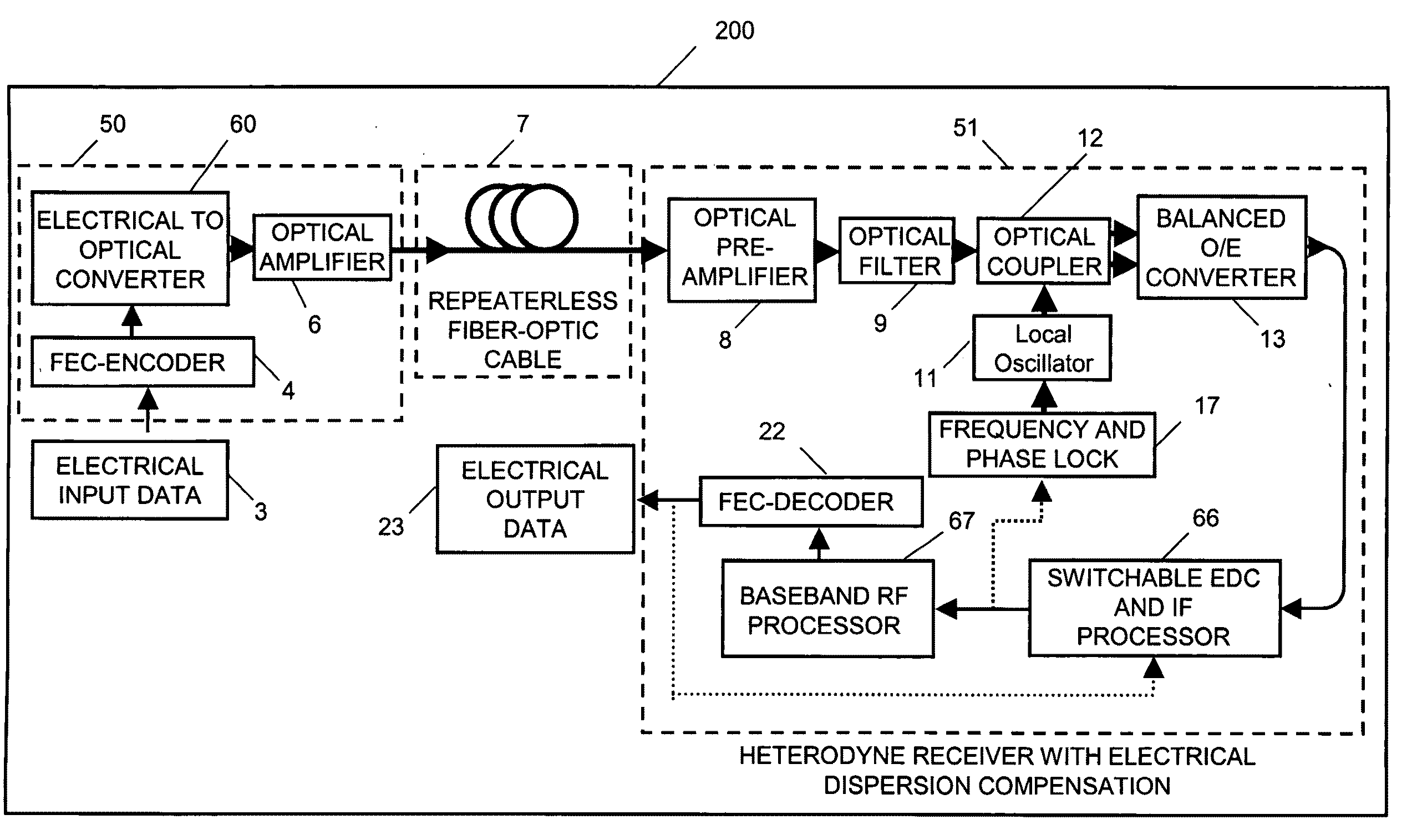
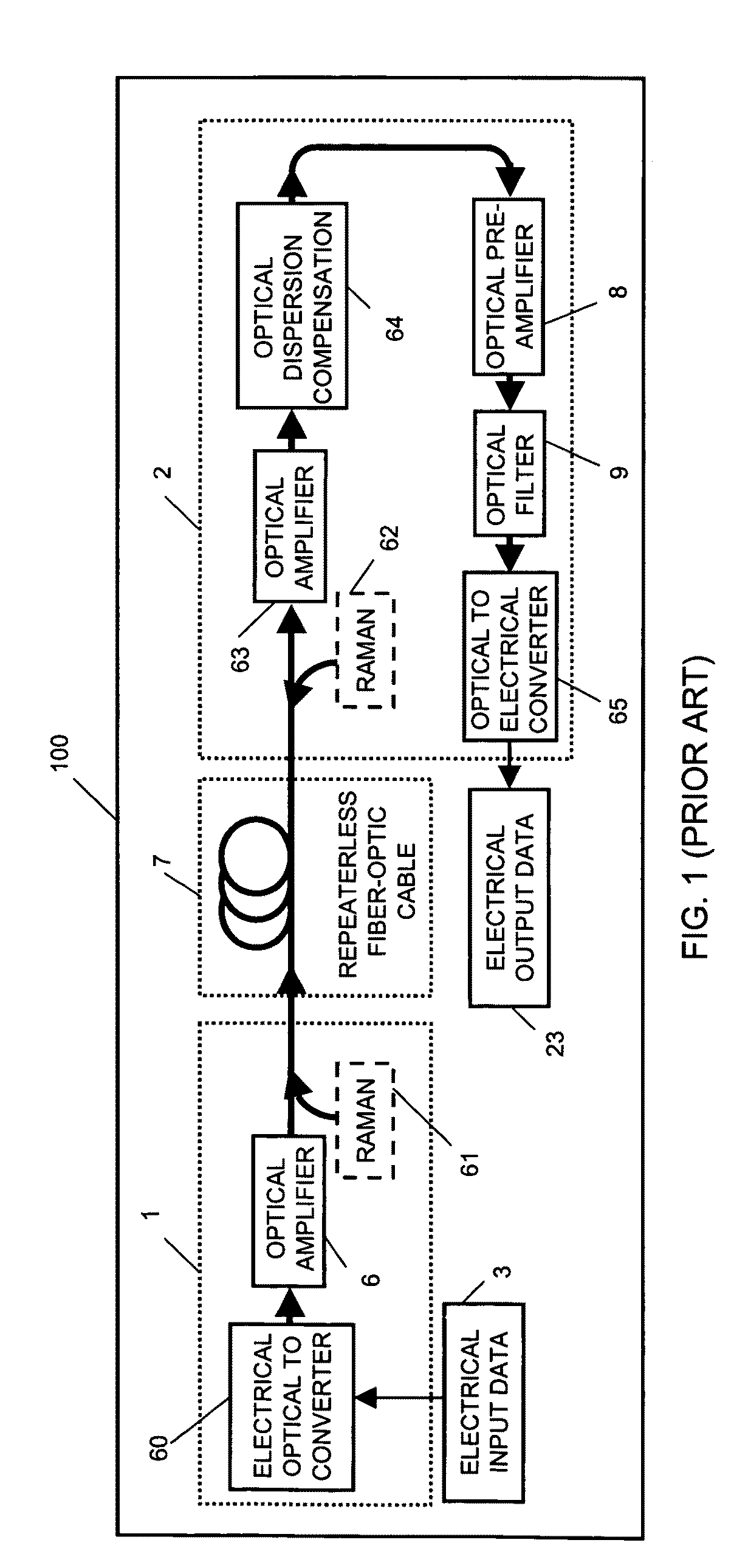
ActiveUS20090142069A1High sensitivityCompensation for dispersionElectromagnetic receiversPhase distortionDifferential phase
Repeaterless transmission of differential phase-shift keying (DPSK) at 10.7 Gb / s over at least 304 km of standard single-mode fiber is obtained through use of a coherent optical receiver including electronic dispersion compensation. High receiver sensitivity and high tolerance to nonlinearities of DPSK, allow overcoming a total link loss of 58 dB with a 3 dB system margin, through use in the receiver of heterodyne detection to preserve phase distortions resulting from chromatic dispersion, to permit electronic dispersion compensation to be used.
Owner:DISCOVERY SEMICON
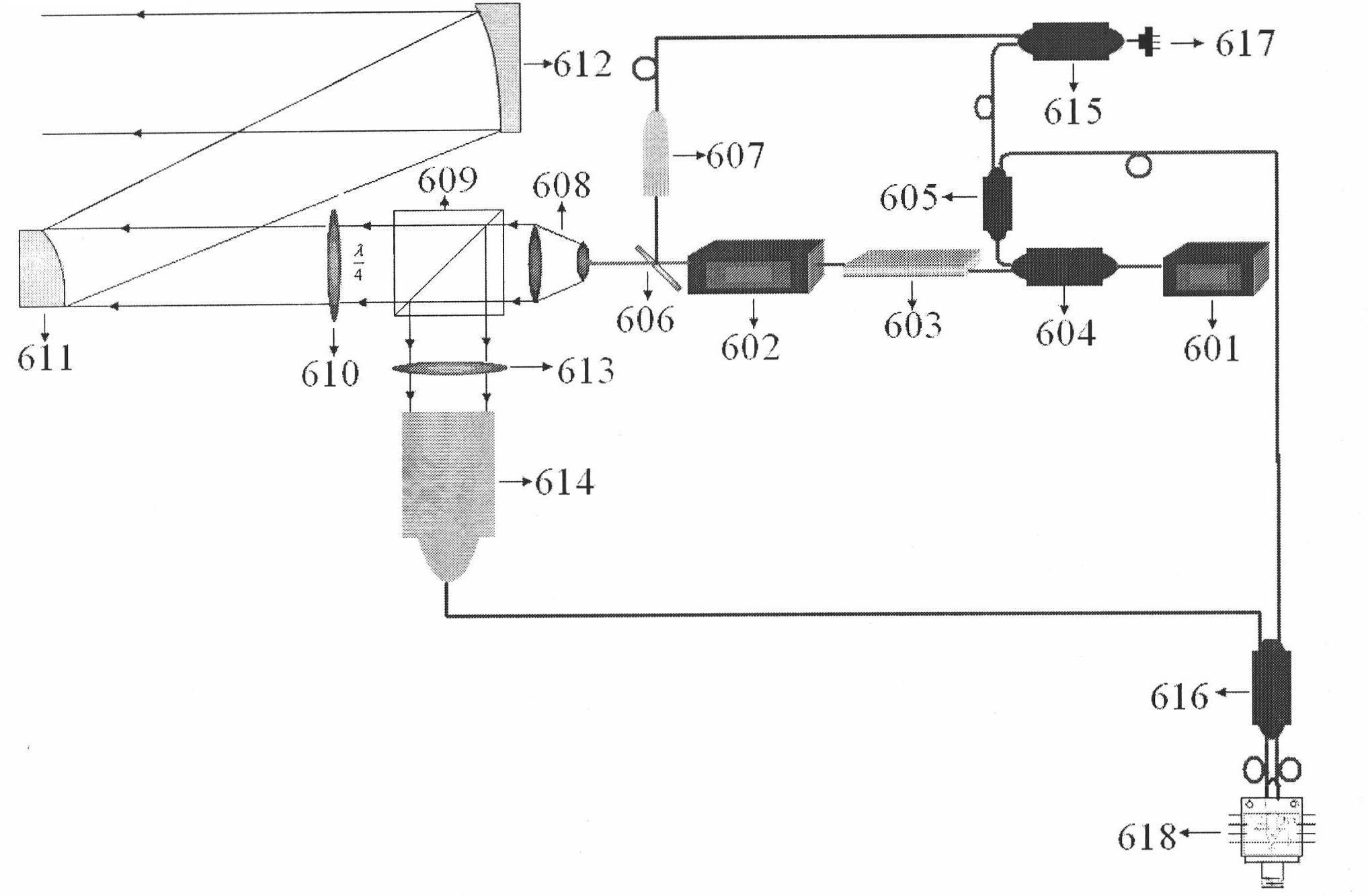
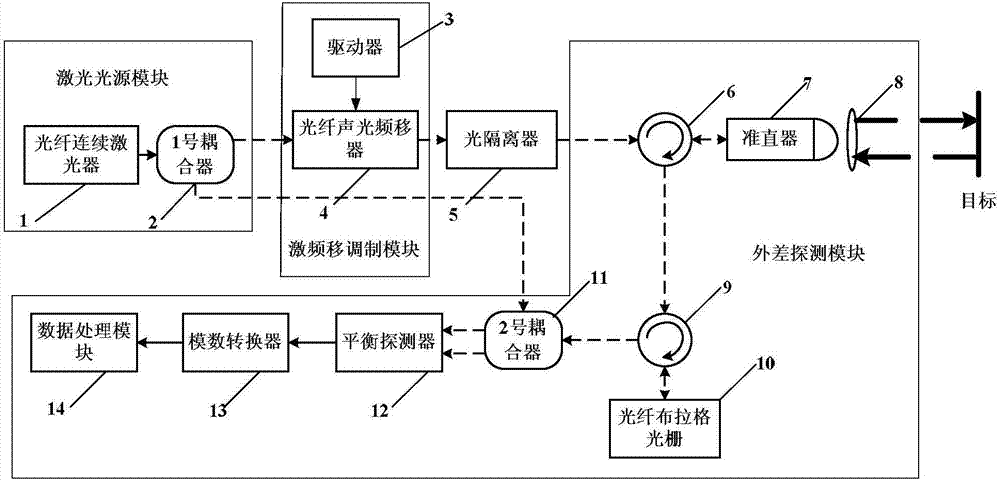
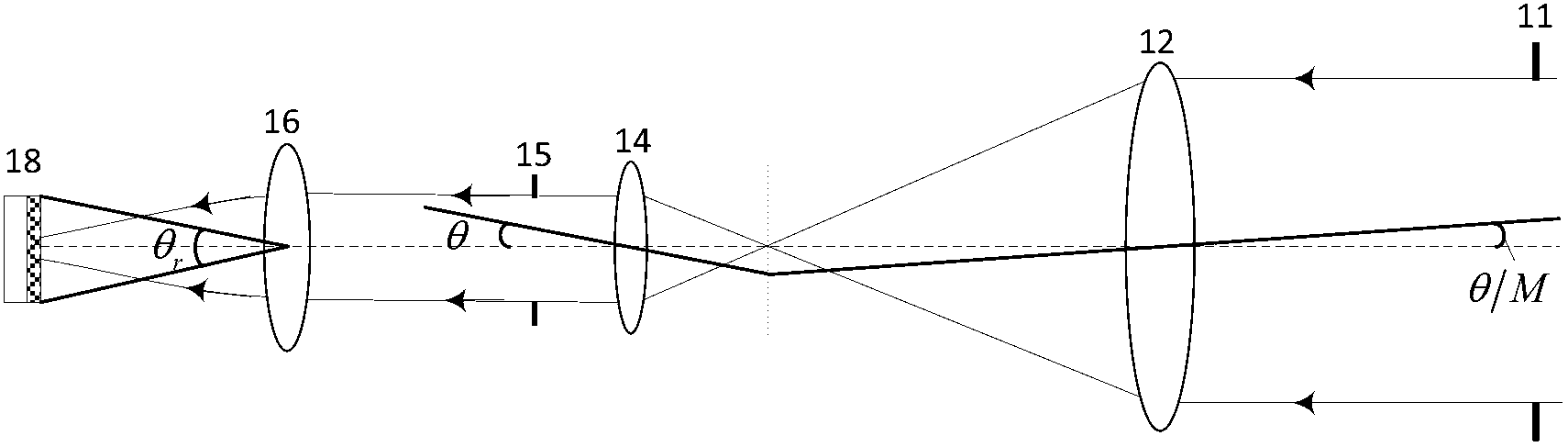
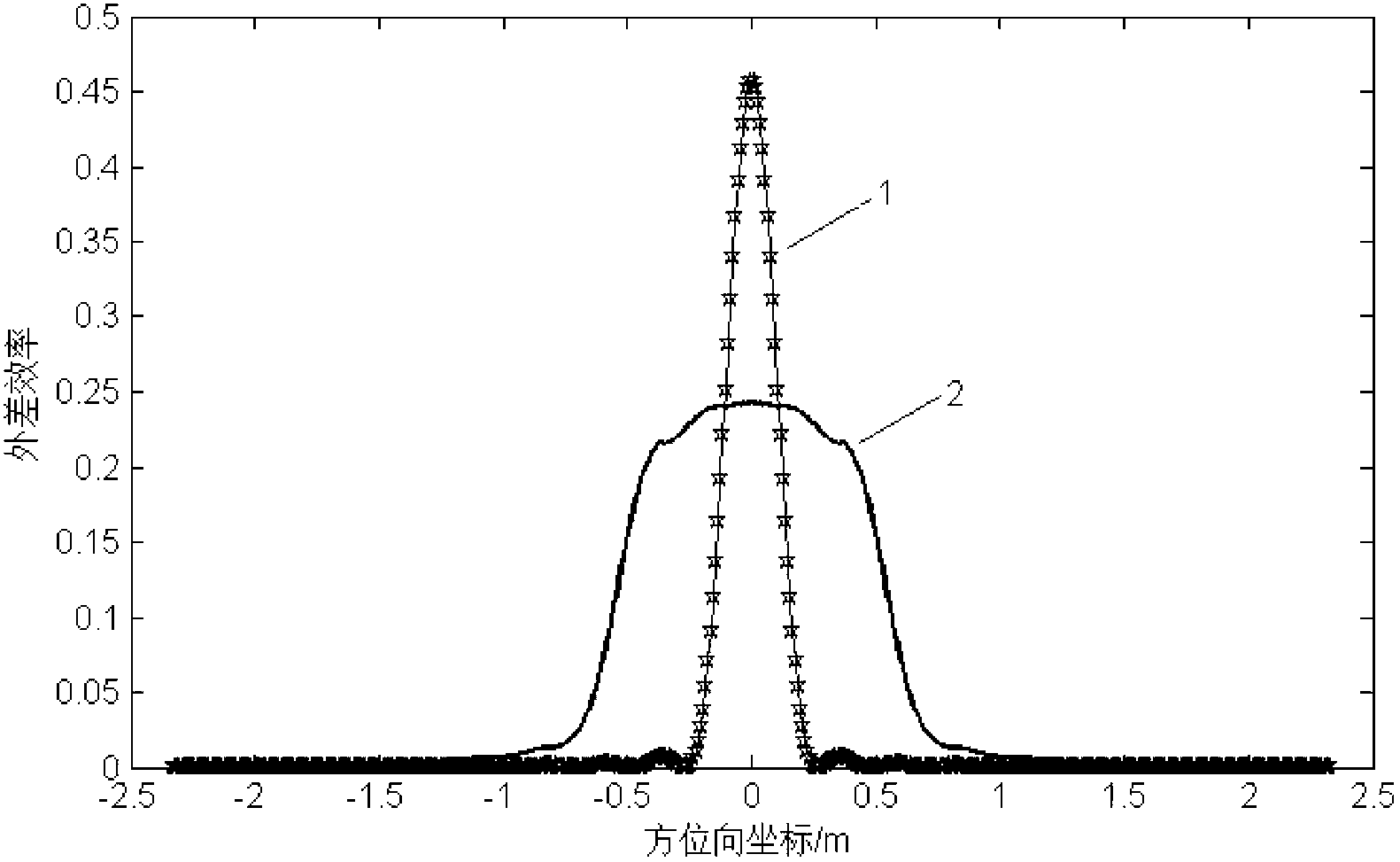
Synthetic aperture laser imaging radar large-visual-field heterodyne detection device
ActiveCN103018735AEliminate the influence of wavefront phase difference of the received signalIncrease signal powerElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splitterLight energy
A synthetic aperture laser imaging radar large-visual-field heterodyne detection device uses a synthetic aperture and a heterodyne reception technique as a base and comprises a collimating lens, a beam splitter, a transmitting telescope, an defocusing receiving telescope, an adjustable convergent lens diaphragm, a focusing lens, a heterodyne receiving beam combiner and a detector, wherein the transmitting telescope and defocusing receiving telescope are separated. The synthetic aperture laser imaging radar large-visual-field heterodyne detection device utilizes a receiving telescope defocusing structure, and can eliminate influence of received signal wave-surface aberration. The aperture of the receiving telescope is much larger than that of the transmitting telescope, and received signal power is increased. A convergent lens is used so as to achieve a receiving visual field much larger than a visual field received by a telescope directly and determined by optical antenna aperture diffraction, heterodyne efficiency in the whole visual field is relatively constant, and stable heterodyne current signals can be received. The adjustable convergent lens diaphragm can control matching of signal flare and the area of the detector, increases local oscillator light energy utilization rate, and improves heterodyne signal strength.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
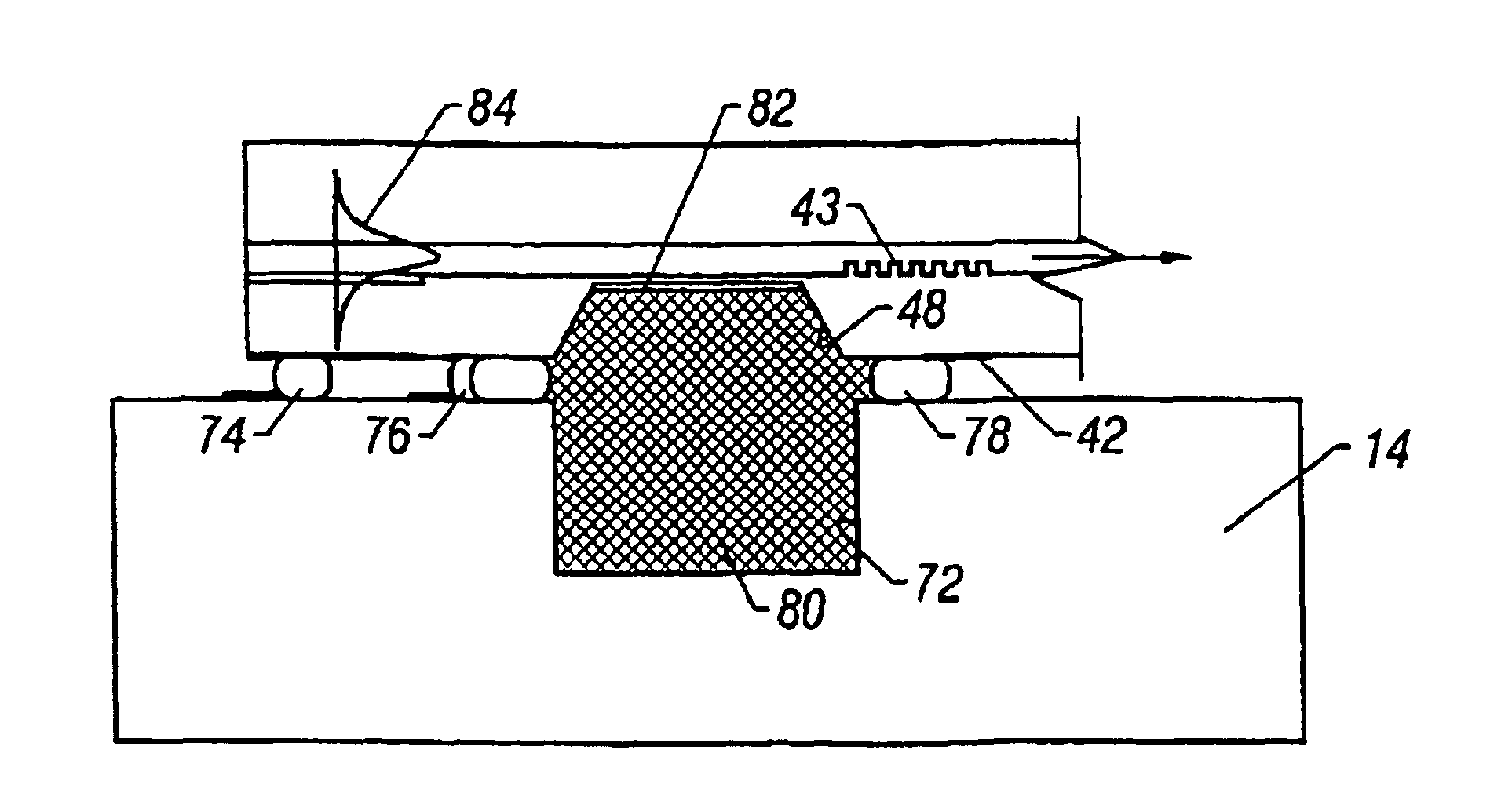
Integrated sensor
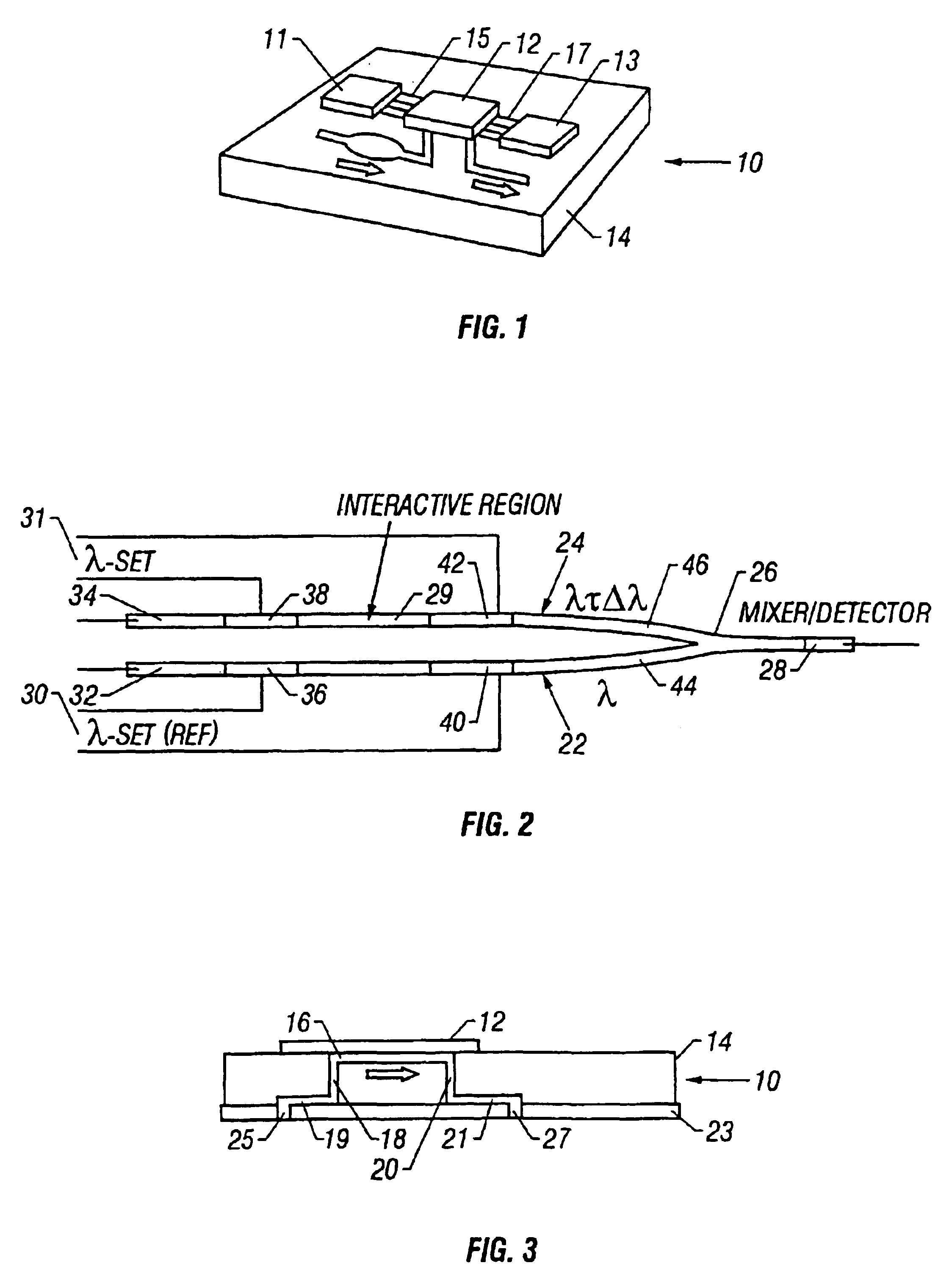
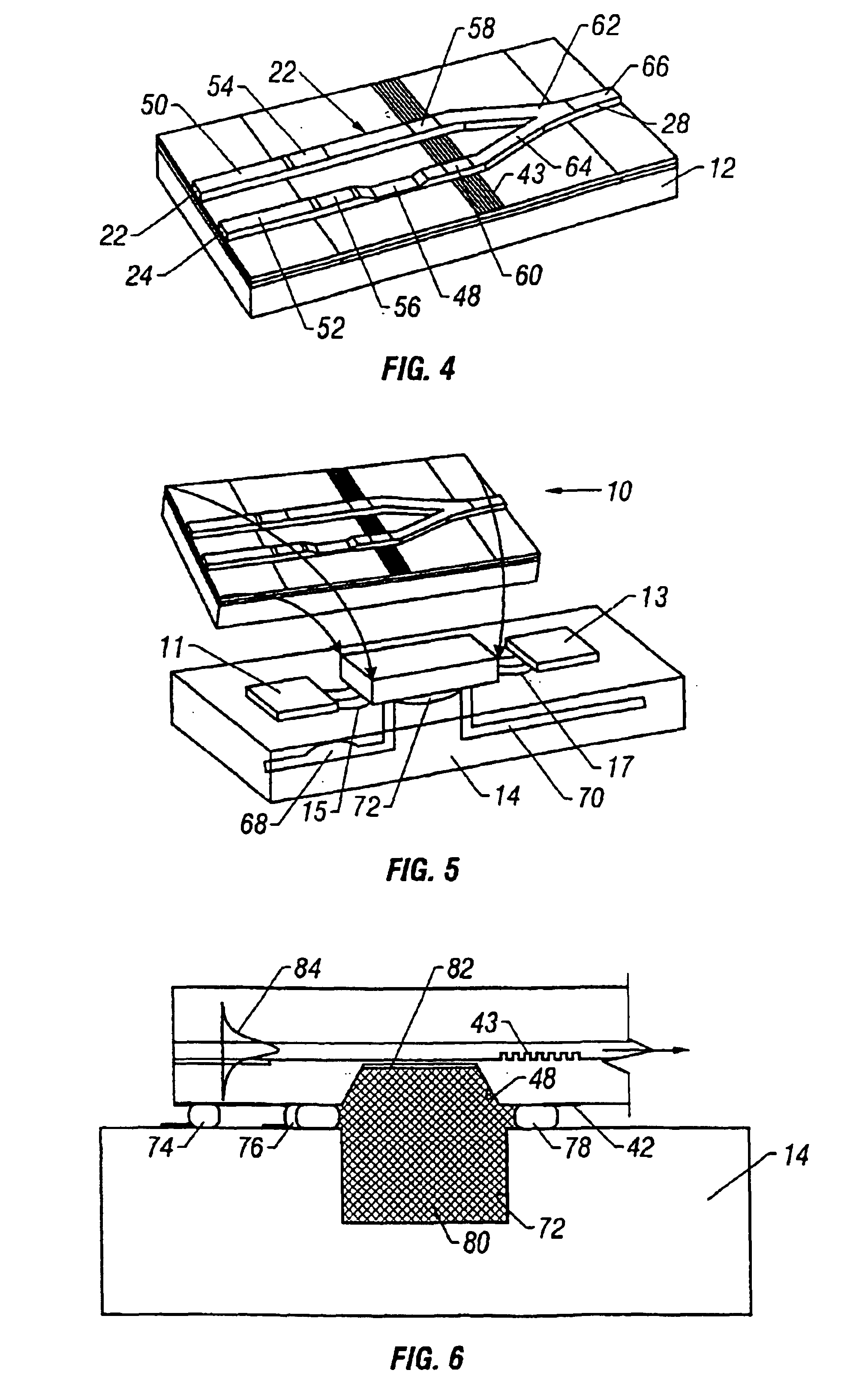
InactiveUS6899849B2Avoid preparationPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHeterodyne detectionSample chamber
An integrated optical chip device for molecular diagnostics comprising a tunable laser cavity sensor chip using heterodyned detection at the juncture of a sensor laser and a reference laser, and including a microfluid chip to which the sensor chip is flip-chip bonded to form a sample chamber that includes exposed evanescent field material of the tunable laser cavity to which fluid to be diagnosed is directed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
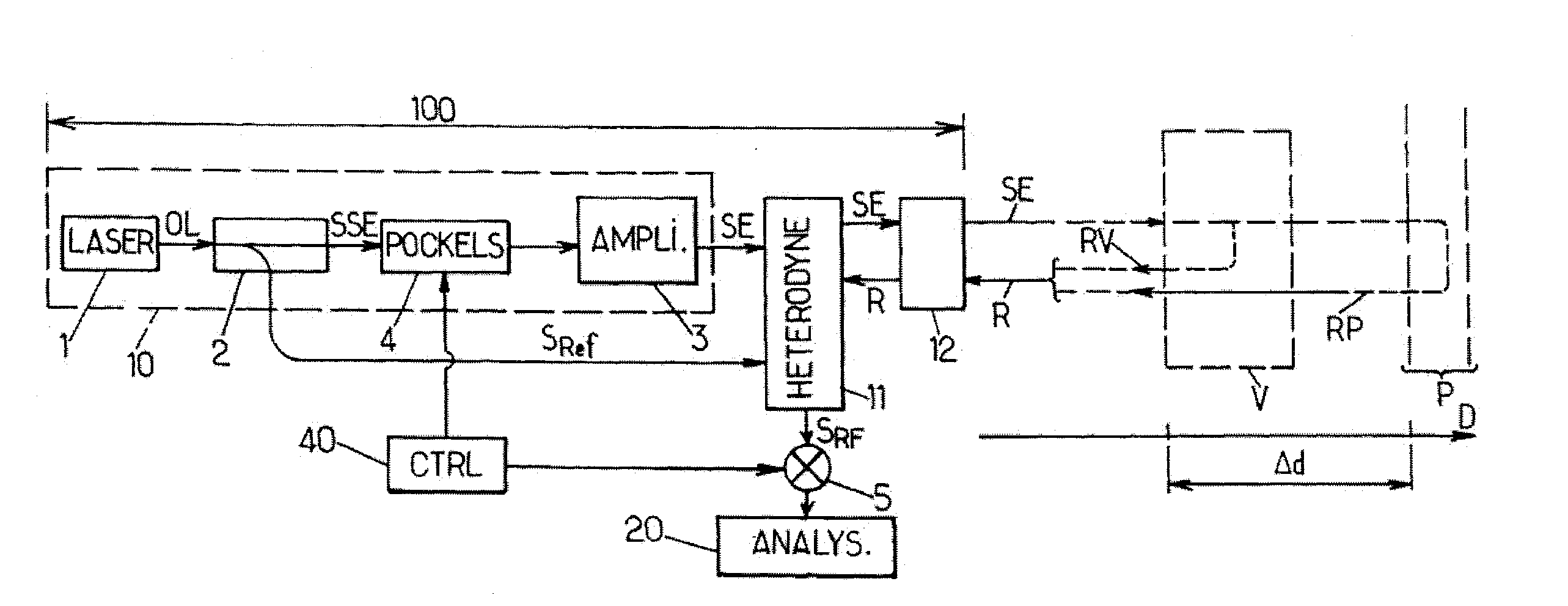
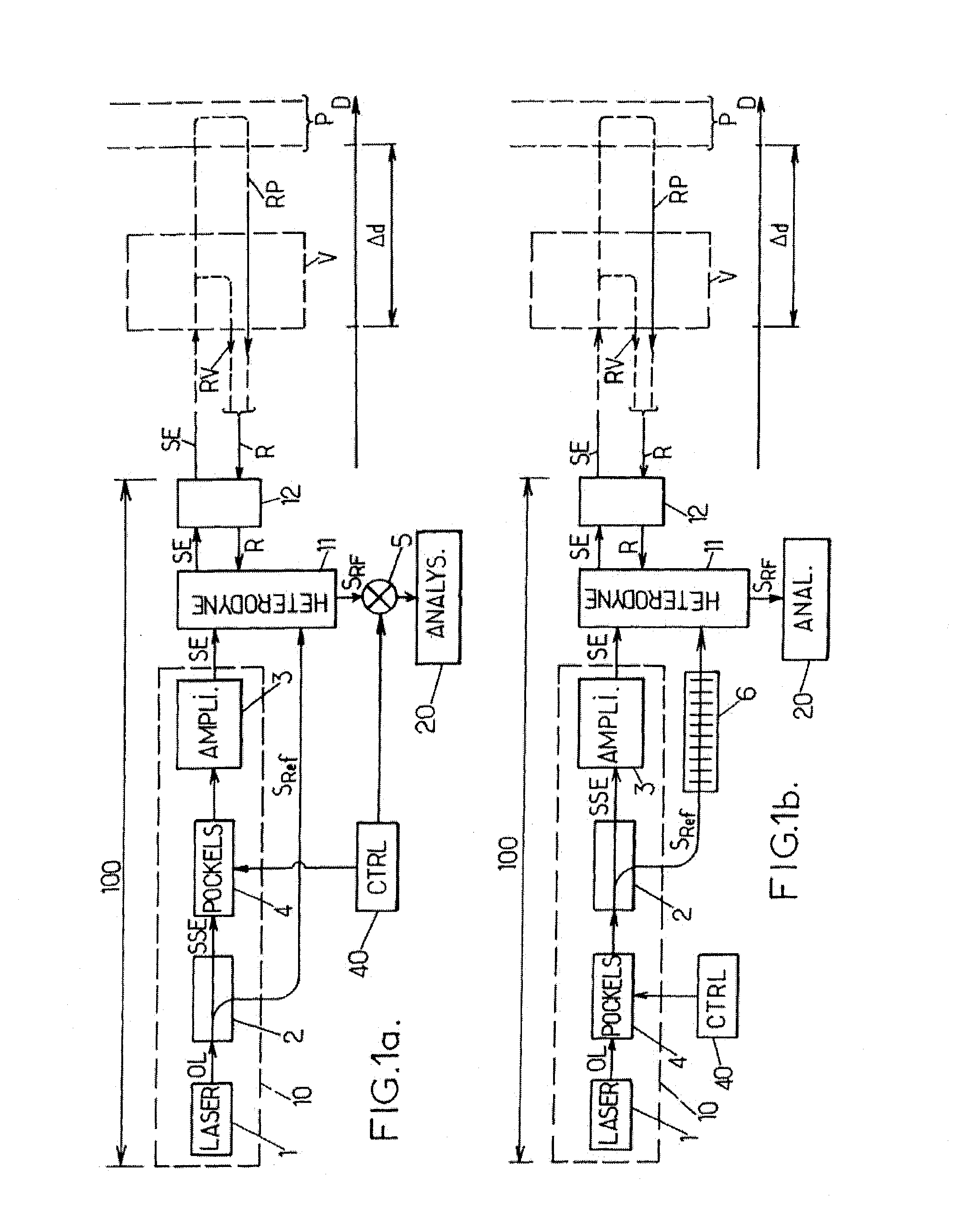
Measurement of Speed or Vibration Characteristics Using a Lidar Device with Heterodyne Detection
ActiveUS20110116074A1Easily only slightly modifyingImprove spatial resolutionOptical rangefindersVolume/mass flow measurementVibration measurementRadar
A process for measuring speed or vibration characteristics using a LIDAR device allows the separation of a useful contribution and an interfering contribution in a backscattered signal. To this purpose, a phase characteristic of an optical wave emitted in the direction of a target volume is modulated. The interfering contribution, which originates from a source at a distance from the target volume, appears with variable shifts of said phase characteristic in a heterodyne detection signal. An accumulation then isolates the useful contribution, from which a result is obtained for the speed or vibration measurement. The process can be implemented with a frequency modulation or phase modulation of the optical wave.
Owner:OFFICE NAT DETUD & DE RECH AEROSPATIALES
Method and system for superheterodyne detection of an optical input signal
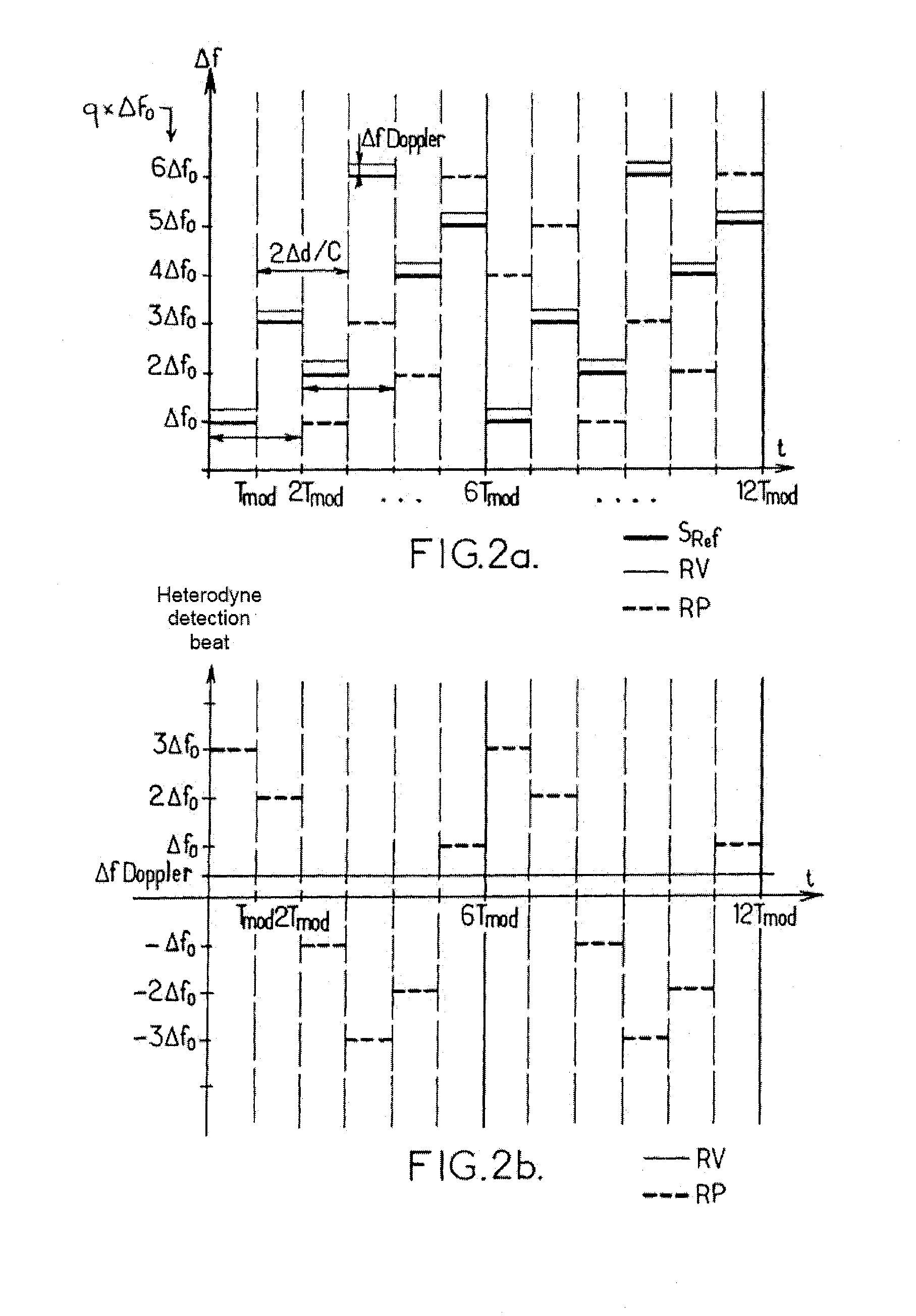
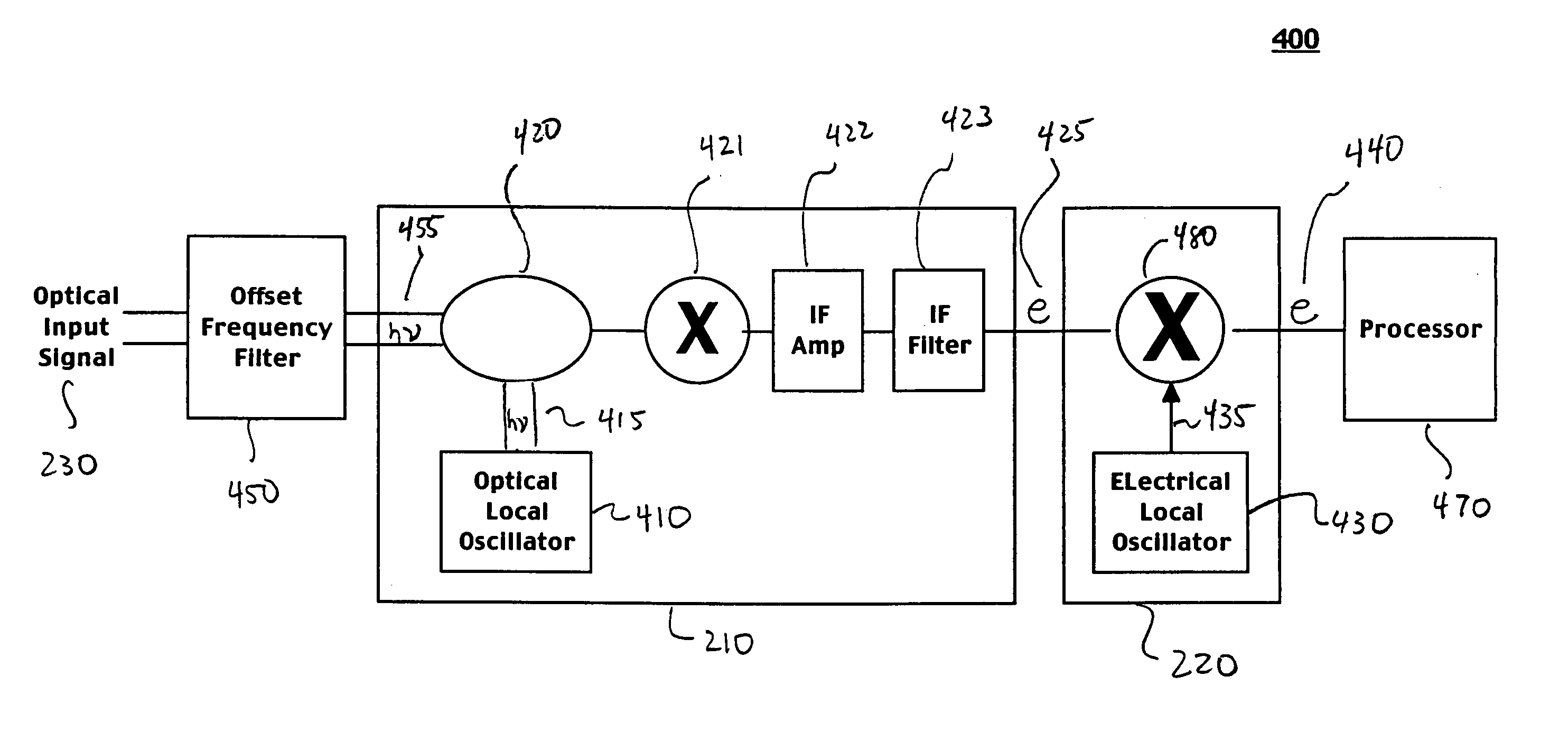
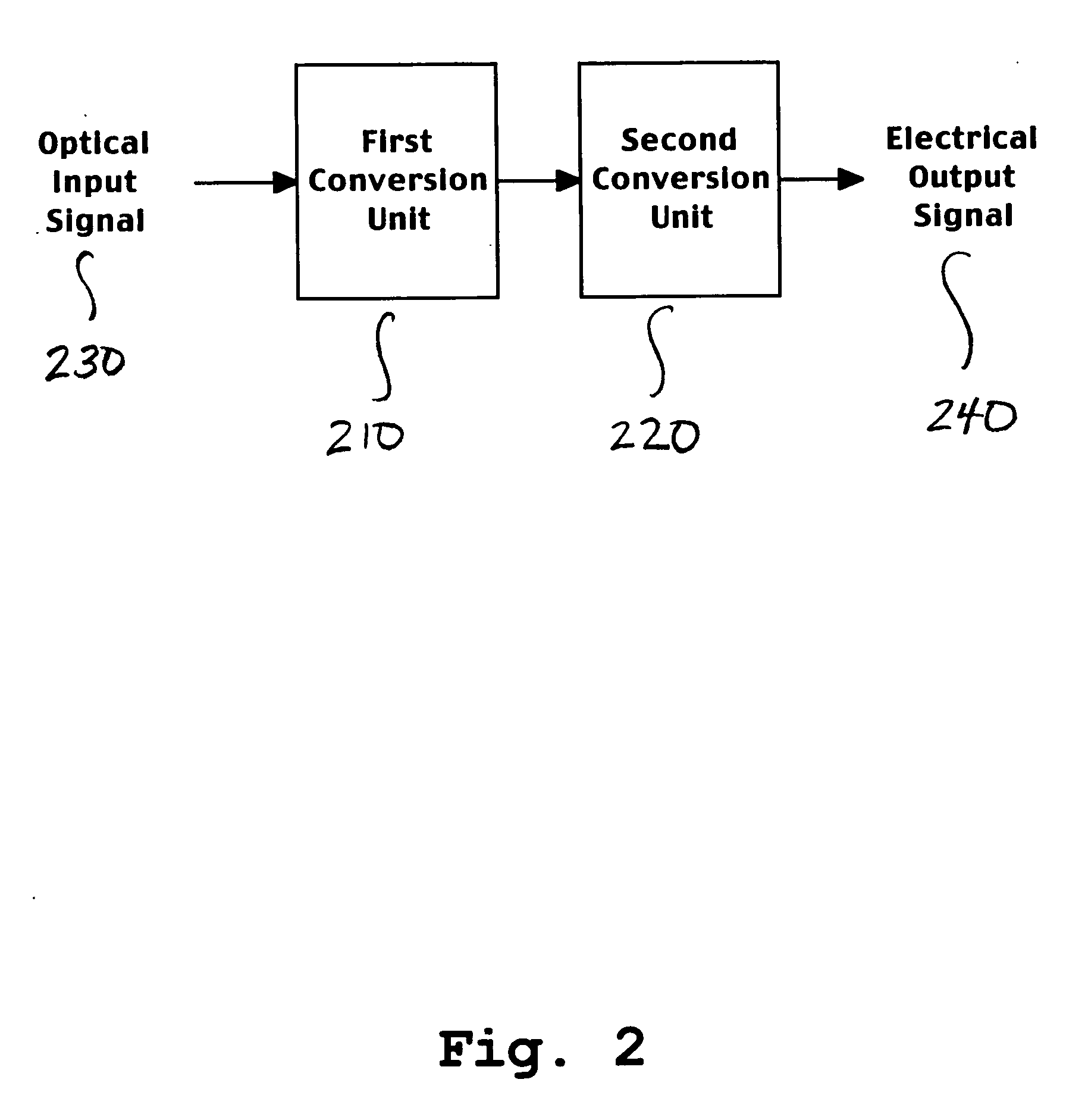
InactiveUS20050202793A1Reduce impactIncreases separation in frequencyRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryEngineeringTransformation unit
A system and method for superheterodyne detection in accordance with the invention. The system comprises a first conversion unit for performing a first heterodyne operation on an optical input signal to generate an electrical IF signal. A second conversion unit is electrically or optically coupled to the first conversion unit. The second conversion unit performs a second heterodyne operation to generate an electrical output signal suitable for signal processing.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
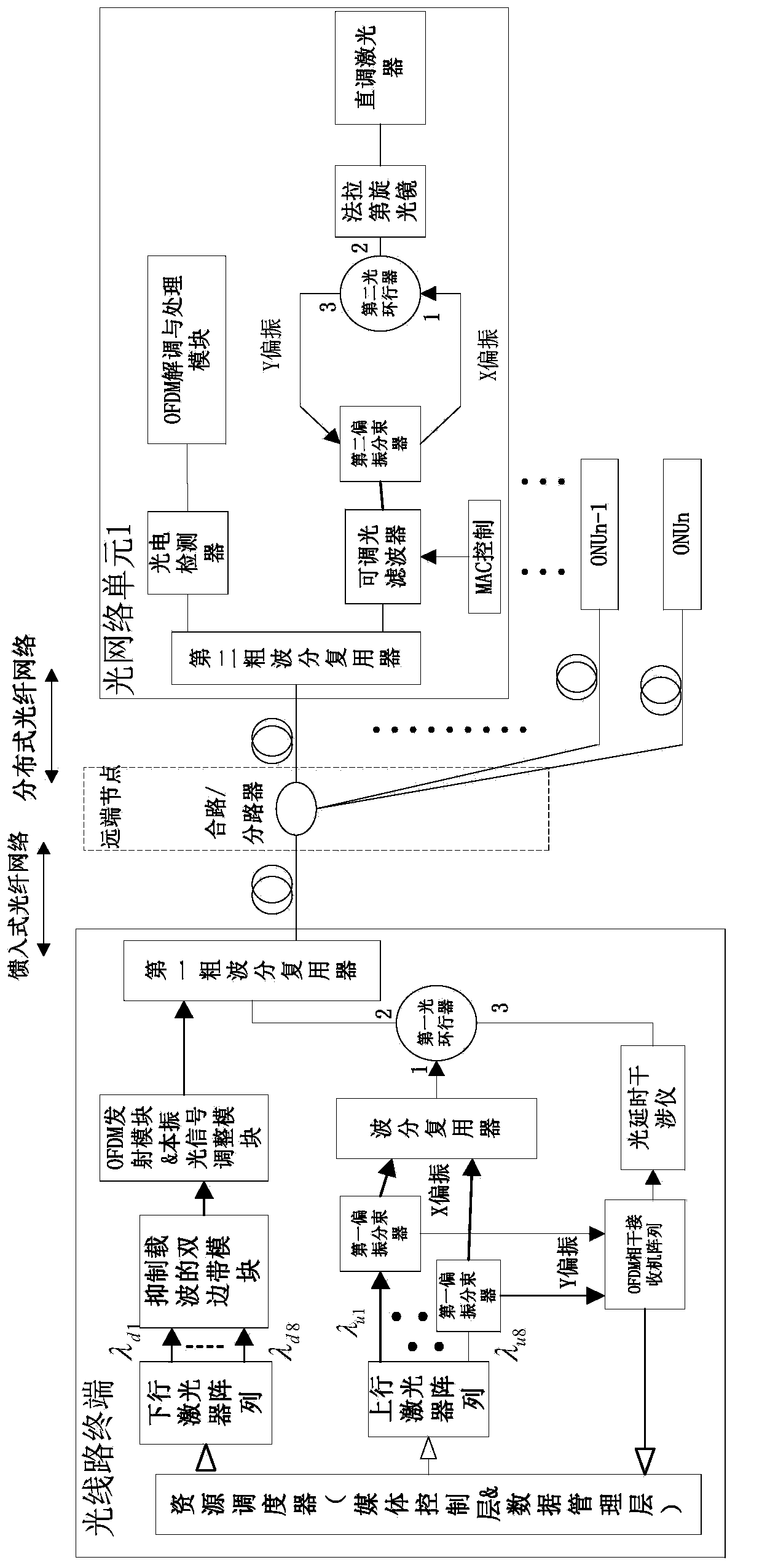
Wavelength division multiplexing OFDM-PON transmission system based on remote difference frequency detection
InactiveCN103686474AIncrease uplink access bandwidthImprove access bandwidthMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsTransmission channelLocal oscillator
The invention provides a wavelength division multiplexing OFDM-PON transmission system based on remote difference frequency detection. The system comprises an optical line terminal, a feed-in type optical fiber network, a far-end node, multiple distribution type optical fiber networks and multiple optical network units which are connected in turn. The optical network units are used for processing a downlink OFDM signal and extracting a specific X-polarized optical carrier used for modulating an uplink OFDM signal. Heterodyne detection of the downlink OFDM signal and a downlink local oscillator optical signal is realized by the optical network units, and the uplink OFDM signal is outputted to the far-end node and the optical line terminal via the distribution type optical fiber networks simultaneously. The optical line terminal receives the uplink OFDM signal and performs self-homodyne detection on the uplink OFDM signal. With adoption of an OFDM and WDM reuse mode, effective transmission channels and data transmission rate are increased so that larger transmission capacity is realized. Meanwhile, receiving sensitivity is enhanced by adopting the difference frequency detection technology so that transmission in longer distance is realized.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
An underwater communication system based on continuous variable quantum key distribution and method realization method thereof
InactiveCN109039610ANot easy to be stolenEasy to detectKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBeam splitterHomodyne detection
The invention discloses an underwater communication system based on continuous variable quantum key distribution and a realization method thereof, belonging to the technical field of free space quantum communication. The optical signal is outputted to the receiving end through the cooperation of a first laser, a first electro-optic intensity modulator, a signal source, a first beam splitter, a second electro-optic intensity modulator, a first electro-optic phase modulator and a tunable laser attenuator at the transmitting end; The second laser generates local oscillation light, which is modulated by the second electro-optical phase modulator, the local oscillation light and the optical signal outputted from the transmitting end enter the homodyne detector for detection, and finally the security key is established within the effective distance. The invention applies the continuous variable quantum key distribution technology to the underwater optical communication system, the optical signal is not easy to be stolen by a third party, and the safe underwater communication system is realized. Heterodyne detection is used to filter the ambient stray light, which also achieves good detection effect in the daytime and the environment with background light.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Self-heterodyne single-ended vector BOTDA-based dynamic strain measurement method and apparatus
ActiveCN105783758AHigh sensitivityImprove signal-to-noise ratioUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyContinuous lightFiber
The invention relates to a self-heterodyne single-ended vector BOTDA-based dynamic strain measurement method and apparatus. A laser outputs three paths of light; lower frequency-shift continuous light is generated at the first path; the light at the second path is used as pulse substrate light; and double-sideband-structure-based coding pulse light is generated at the third path. The synthesized light from the three paths enters from one end of a sensing fiber. Back Rayleigh scattering light generated by the light from the first path and the second path in the sensing fiber is used as local oscillator light and detection light respectively; the two kinds of light are led into a photoelectric detector to carry out self-heterodyne detection and quadrature and in-phase components in an obtained electric signal are extracted; according to a function relationship between the quotient of the two kinds of components and a stimulated Brillouin scattering phase shift, a stimulated Brillouin scattering phase shift value is obtained. And then a corresponding dynamic strain value is demodulated based on a corresponding relation curve of the stimulated Brillouin scattering phase shift and the dynamic strain. According to the invention, the structure is simple; the application becomes convenient; the reliability and stability are high; non-destructive high-sensitivity and high-signal-to-noise-ratio dynamic strain measurement can be realized.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Brillouin light time domain analysis device and method based on dual-wavelength polarization orthogonal light
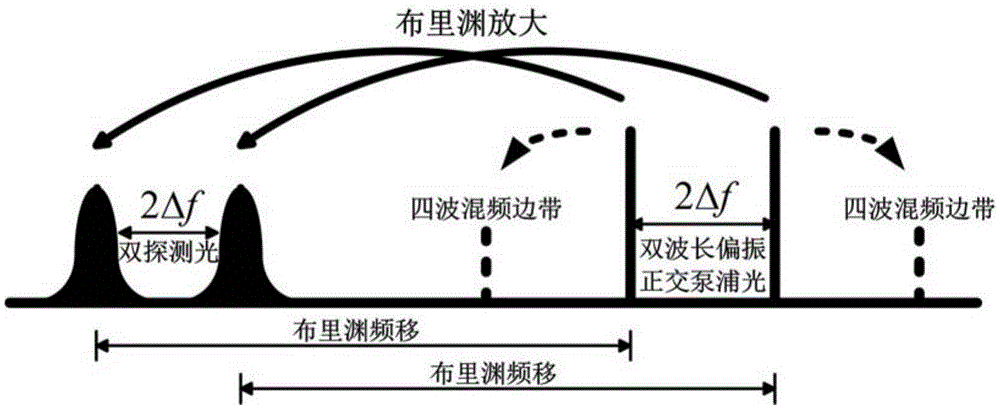
ActiveCN105628063ALong sensing distanceReduce signal to noise ratioConverting sensor output opticallySignal-to-quantization-noise ratioHeterodyne detection
The invention relates to the field of optical fiber sensing technology, in particular to a Brillouin light time domain analysis device and a method based on dual-wavelength polarization orthogonal light. Two beams of polarization orthogonal light with different wavelengths are used as pump light, so a four-wave mixing phenomenon between the two beams of the pump light is completely restrained and the signal to noise ratio of the tail end of a sensing optical fiber can be truly increased by 3dB. In addition, according to the invention, a direct detection mode is adopted on a detection end, so compared with a Brillouin light time domain analysis device and a method in which a heterodyning detection mode is adopted, quite expensive detection devices and time-consuming demodulation processes are omitted; and development of a Brillouin light time domain analysis system towards a dynamic measuring direction is facilitated.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system
InactiveCN101825712AMake up for the defect of environmental interferenceSolve the problem of all-fiber miniaturizationCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic wave reradiationRadar systemsOperability
The invention discloses a 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, which consists of a 2 mu m off-axis Cassegrain optical antenna system, a 2 mu m laser beam splitting system, a 2 mu m seed implantation laser amplifier, a 2 mu m monitoring detector system, and a 2 mu m balanced heterodyne detection system. The system overcomes the defect of ambient interference existing in a free space optical path, overcomes the influence of shot noise on heterodyne reception signal-to-noise ratio, and solves the problems of all fiber and miniaturization of the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system, so that the 2 mu m all-fiber coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar system has a more compact structure. In addition, the system has the characteristics of safe laser for human eye, optical path connection by adopting flexible optical fiber devices, high operability and stability, low cost, good real time, long effectively measured distance, high measurement accuracy (speed measurement and distance measurement) and the like, and has high practical value in the field of coherent laser Doppler wind finding radar.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
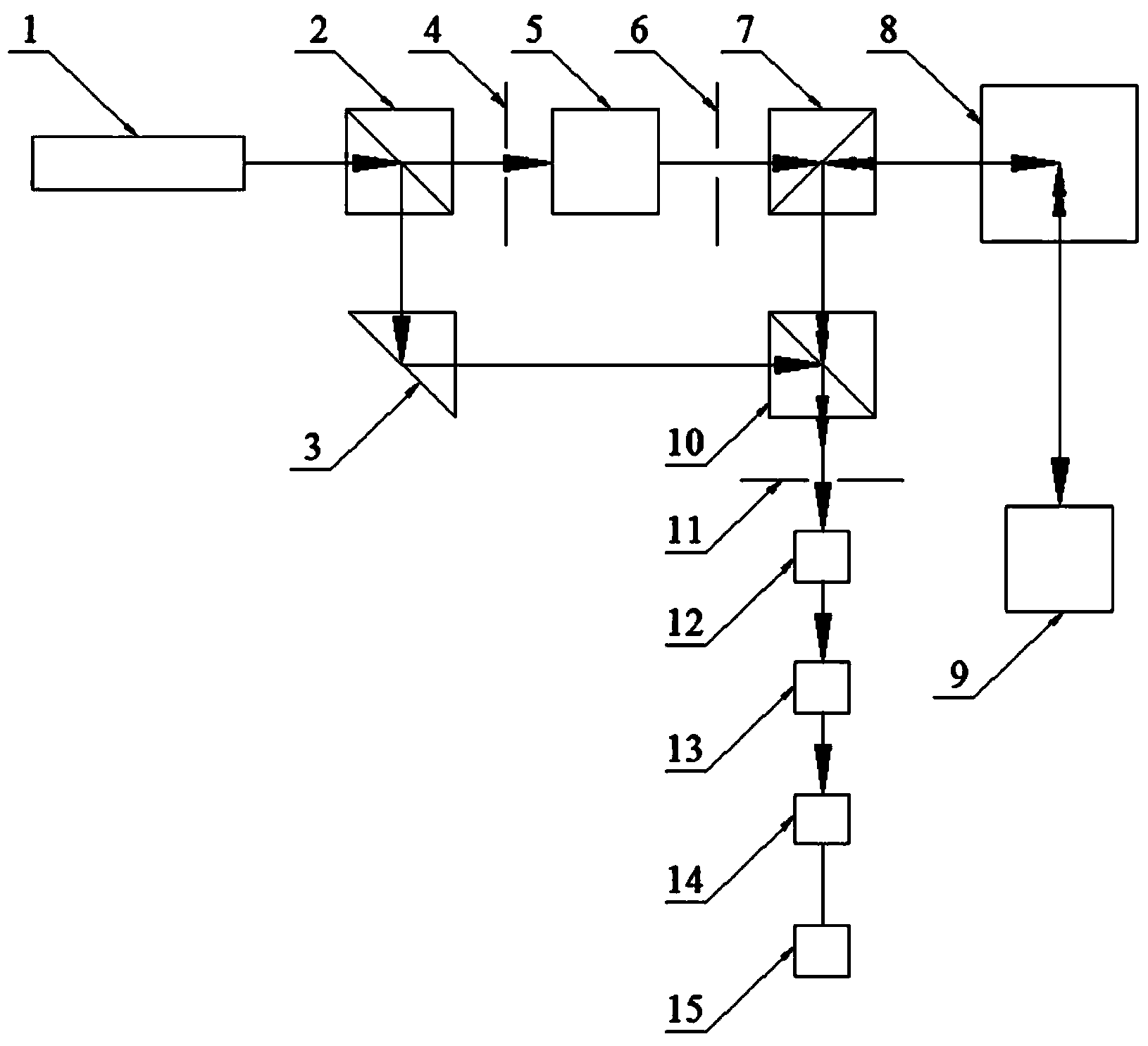
Scanning laser vibration measurement system
InactiveCN103900681AEasy change detectionRealize non-contact measurementSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing optical meansBeam splitterIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a scanning laser vibration measurement system. A laser beam emitted by a laser passes through a first beam splitter prism to be split, where one path of the laser beam serves as local oscillator light for heterodyning detection to be reflected to a beam combiner through a reflection prism to be combined; the other path of the laser beam reaches a two-dimensional scanning control system through a first aperture, an AO modulator, a second aperture and a second beam splitter prism and then is emitted to a target, and scattered beams reach the beam combiner through the two-dimensional scanning control system and the second beam splitter prism to be combined with the local oscillator light; after the laser beams are combined, the combined laser beam reaches a signal processor through a third aperture, a polarization analyzer, a photoelectric detector and an intermediate frequency amplifier. The scanning laser vibration measurement system has the advantages that on the principle of heterodyning laser interference measurement, characteristics of vibration, speed and displacement of the target can be measured in a non-contact mode, and thus the scanning laser vibration measurement system is high in measurement precision and anti-interference capacity and the like; in the heterodyning detection, the design of receiving and transmitting integration and two-dimensional scanning measurement is adopted, and thus the scanning laser vibration measurement system is firm and compact in structure, convenient to measure and adjust and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Laser heterodyne device based on photon counting statistics of MPPC (multi-pixel photon counter)
InactiveCN102565807AExpand the receiving areaHigh detection sensitivityElectromagnetic wave reradiationBeam splittingAcousto-optics
The invention discloses a laser heterodyne device based on photon counting statistics of MPPC (multi-pixel photon counter), relates to the field of laser active detection research and aims at solving the problem of contradiction between the power of a light source and a coherent phase in the existing laser heterodyne detection. According to the device disclosed by the invention, a light beam emitted by a laser passes through a laser beam splitter mirror and then is reflected and transmitted, a reflected light beam passes through an acousto-optic modulator for acousto-optic diffraction and then is incident to a polarization beam-splitting flat plate, and the light beam after passing through the polarization beam-splitting flat plate is reflected to a laser coupling lens; the transmitted light beam passes through a laser beam expanding lens and then is incident to the surface of a rotating diffused reflection target, echo photons which are collected by a laser echo receiving telescope is subject to filtering processing through an optical narrow-band filter, and the light beam after passing through the polarization beam-splitting flat plate is transmitted to the laser coupling lens; and electric signals are received by a signal receiving device after the light beam is focused to the surface of the MPPC and optical interference occurs. The MPPC is larger in the receiving surface, and a detector can work in a non-high-voltage state so as to facilitate the implementation of signal receiving.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com