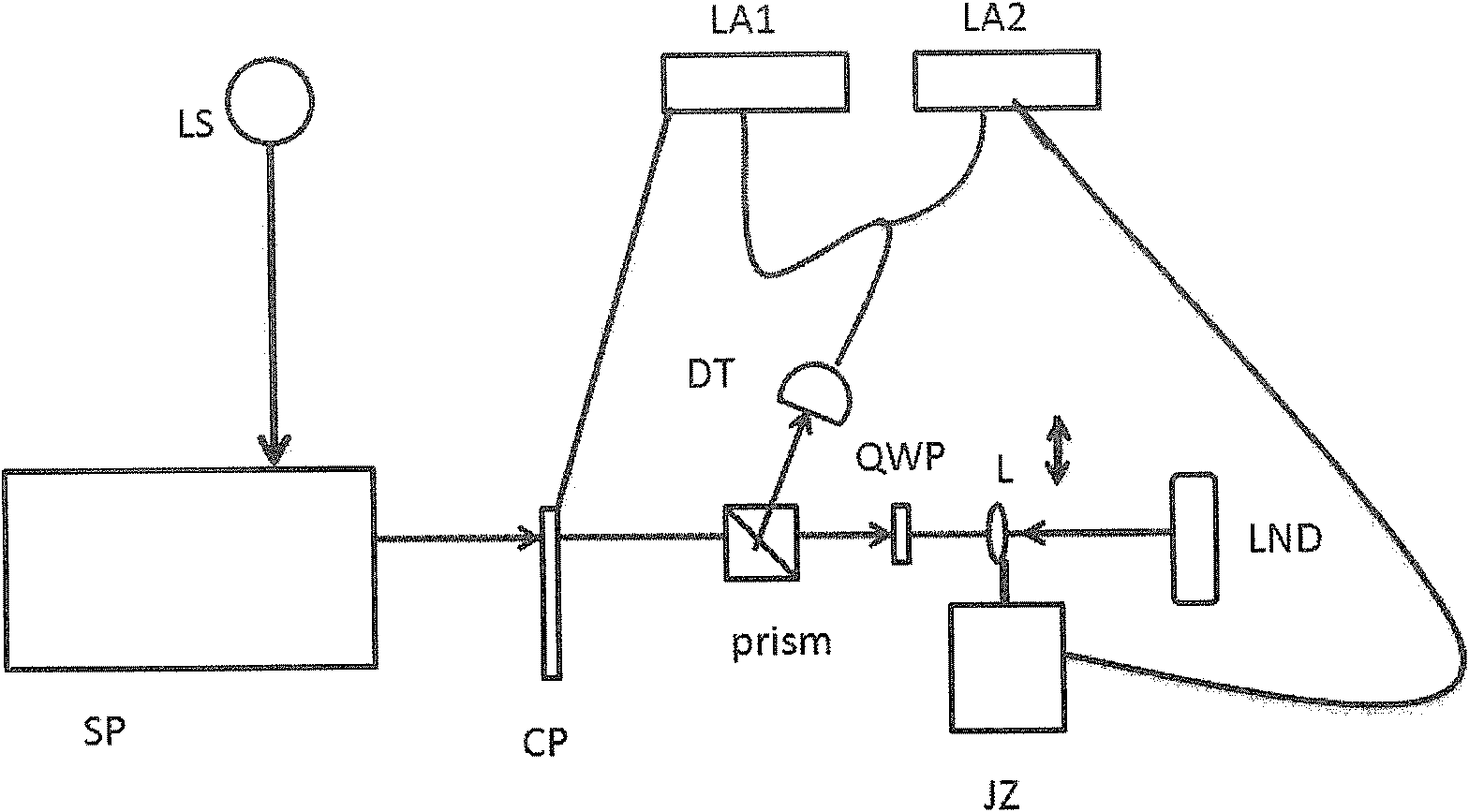
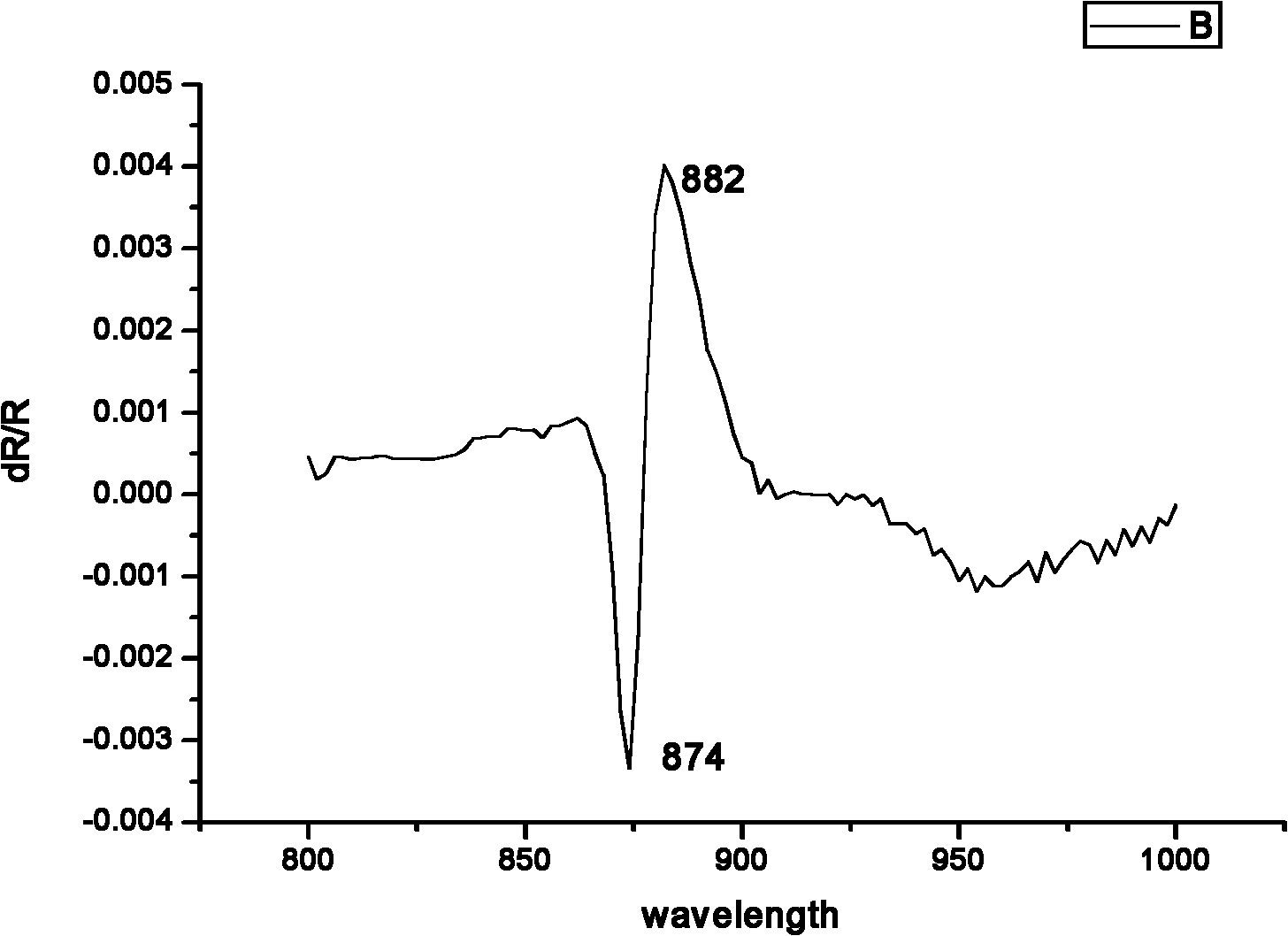
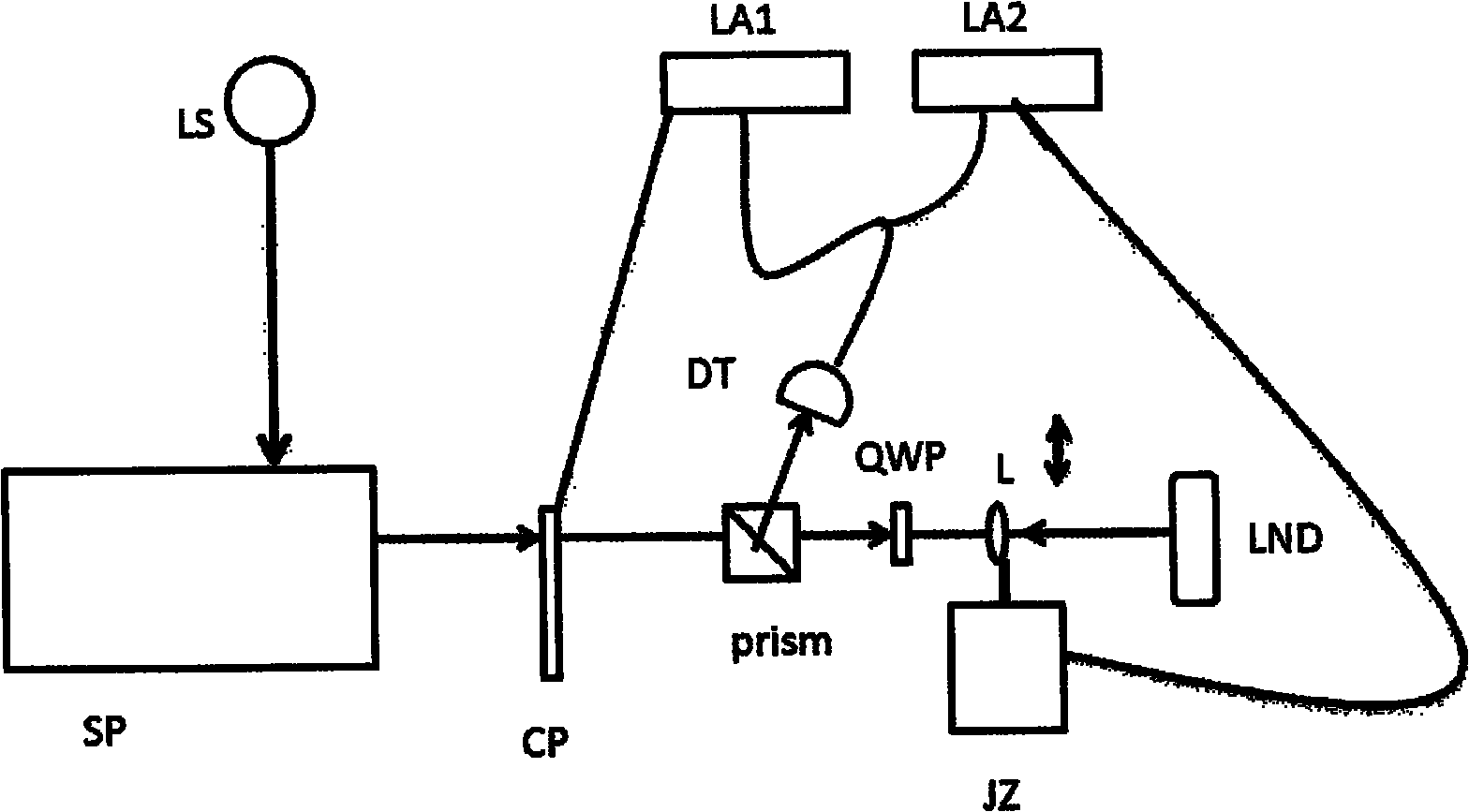
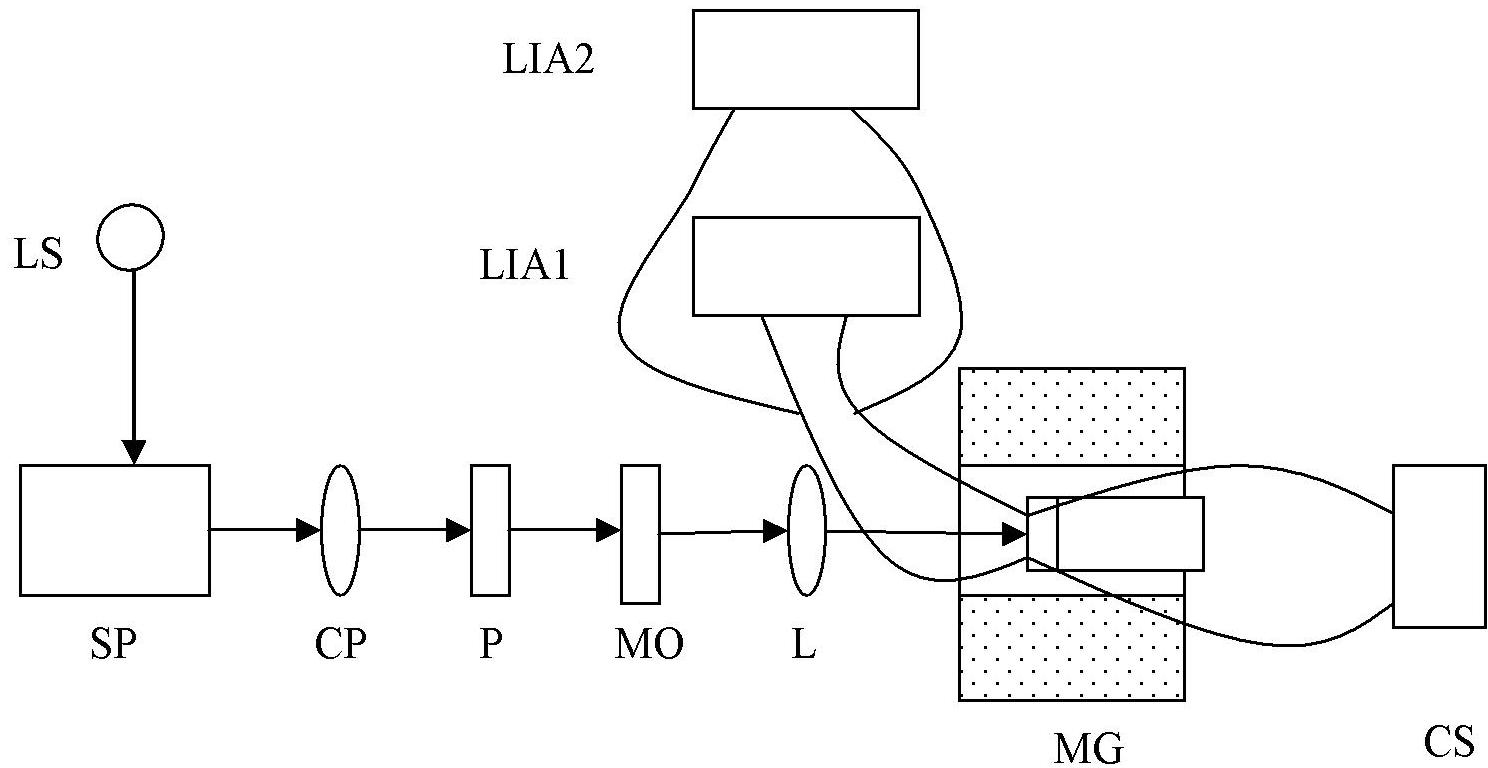
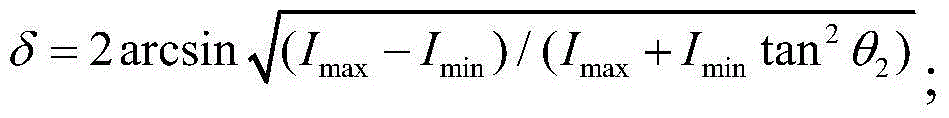Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
49 results about "Glan–Taylor prism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A Glan–Taylor prism is a type of prism which is used as a polarizer or polarizing beam splitter. It is one of the most common types of modern polarizing prism. It was first described by Archard and Taylor in 1948.
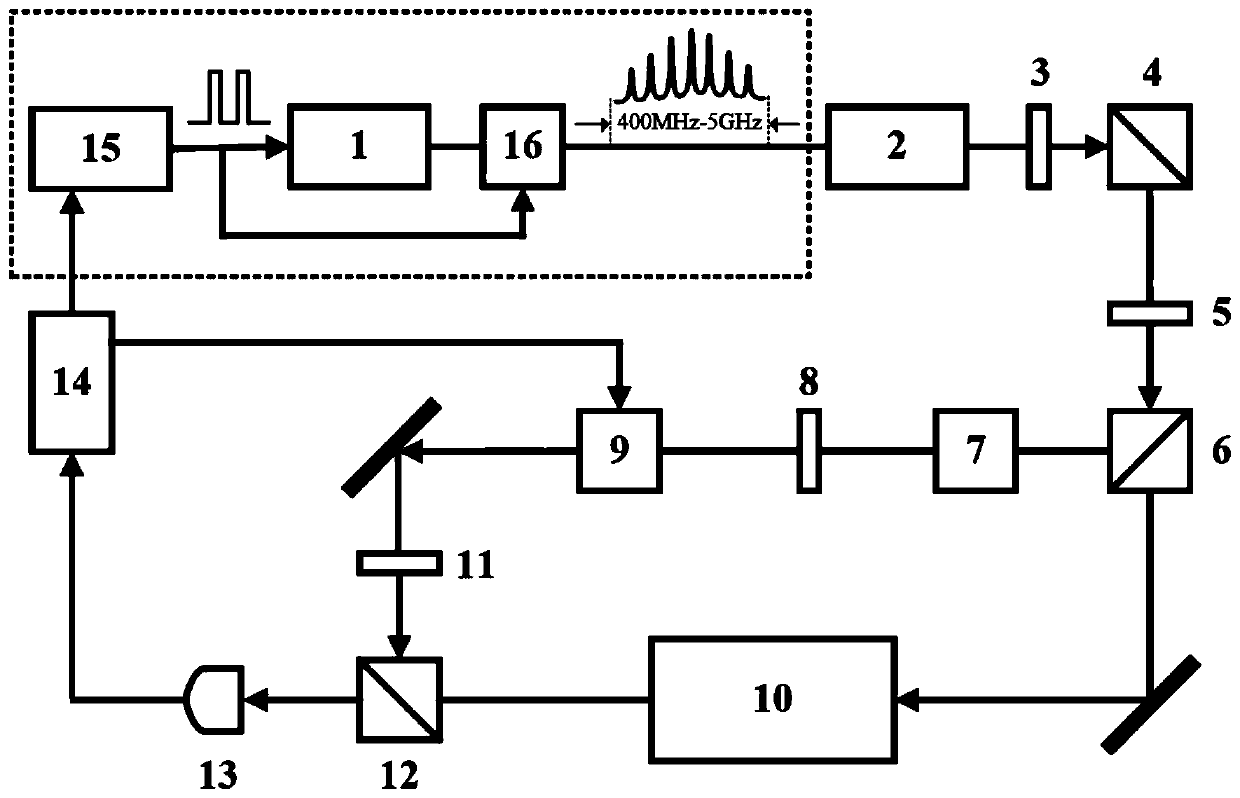
Rubidium atomic clock with high contrast ratio frequency discrimination signal
ActiveCN102799103AImprove performanceImprove stabilityApparatus using atomic clocksPolarizerParticle physics
The invention discloses a rubidium atomic clock with a high contrast ratio frequency discrimination signal. The rubidium atomic clock comprises a controlled crystal oscillator, a frequency multiplication synthesizer, a modulation oscillator, a direct current amplifier, a quantum system and a phase detector, wherein a first Glan-Taylor polarizer is placed on a light path between a beam expander and a physical device; a second Glan-Taylor polarizer is placed between the physical device and the photoelectric detector; and the first Glan-Taylor polarizer and the Glan-Taylor polarizer are orthogonally placed. The transmission backlight intensity is filtered, the first order light frequency shift is eliminated, and the contrast ratio of the frequency discrimination and the rubidium atomic clock property are improved. The high performance atomic clock is provided for satellite navigation, communication and precision measurement.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
All-optical switch based on rubidium-atom optical filter and method thereof
InactiveCN103996966AClear design principlesSimple structureLaser detailsOptical elementsEngineeringPrism
The invention discloses an all-optical switch based on a rubidium-atom optical filter and a method thereof. The all-optical switch based on the rubidium-atom optical filter comprises an alkali-metal rubidium-atom glass air chamber with a V-type energy level structure, two Glan-Taylor polarizers with the polarization directions perpendicular to each other and a stable magnetic field source used for generating a magnetic field with uniform intensity for the alkali-metal rubidium-atom glass air chamber, wherein the alkali-metal rubidium-atom glass air chamber, the two polarizers with the polarization directions perpendicular to each other and the stable magnetic field source form a standard atomic optical filter. The all-optical switch based on the rubidium-atom optical filter further comprises a 420 nm laser device serving as a control part of the all-optical switch of the atomic optical filter and a 780 nm laser device serving as a performance testing and application wavelength testing part of the all-optical switch of the rubidium-atom optical filter. The all-optical switch based on the rubidium-atom optical filter has the advantages of being clear in design principle, simple in structure, easy to manufacture, good in switching performance, stable in operation and long in service life.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
Near-field polarized light scanning probe microscope
ActiveCN105588954AImprove signal-to-noise ratioScanning probe microscopyBeam splitterScanning Hall probe microscope
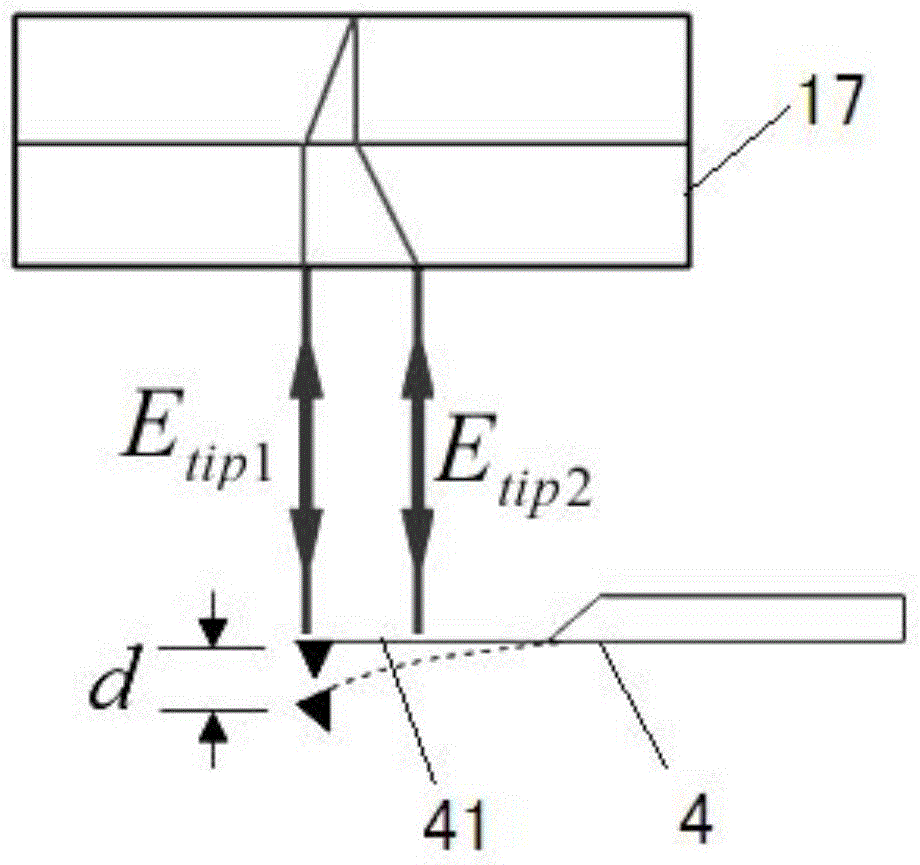
The invention relates to a near-field polarized light scanning probe microscope having a near-field optics detecting optical path in which a bundle of linearly polarized lights emitted from an He-Ne laser successively pass a quarter-wave plate A, a beam splitter, an objective lens A, and a probe to an objective table to form a near-field optics generation optical path. The reflected lights reflected from the probe successively pass the objective lens A, the beam splitter, a quarter-wave plate B, a Glan-Taylor prism, and the objective lens and are received by a photoelectric receiver to an image display system. The near-field polarized light scanning probe microscope can effectively inhibit a far-field background light and improves the signal to noise ratio of a near-field light, and the spatial resolution is less than 10 nanometers.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Magneto-optic circular polarization dichroism measuring system capable of adjusting measuring geometry
InactiveCN101196559AGood collimationNo lossMagnetic property measurementsTesting optical propertiesFrequency spectrumLantern
A measuring system for measuring the dichroism of the magneto-optical circular polarization with adjustable measuring geometry is provided, whose structure is that: a femtosecond laser excites the white light of the ultra-continuous spectrum, and divides the light by a monochrometer, which forms a monochromatic light whose wavelength can be adjustable. The monochromatic light can polarize through a purified Glan-Taylor prism with the extinction coefficient of 10 <5>; a lantern fly modulator, whose optical axis is 45degree angled with the optical axis of the Glan-Taylor prism to make the light become the circularly polarized light with the alternative variation of the sinistrality and the dextrorotation; a sample, which is put on the center of the cryogenic magnet; The circularly polarized light focuses on the sample, and the reflex reflected from the sample is focuses on the first LED detector; a phase-locking amplifier, whose reference signal is provided by the lantern fly modulator used for testing the difference of light intensity between the sinistrality and the dextrorotation of the circularly polarized light. The invention can not only test the frequency spectrum of the dichroism of the magneto-optical circular polarization of the materials, magnetic density and temperature dependence, but also can test the magnetocrystalline anisotropy of the magnetic semiconductor.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
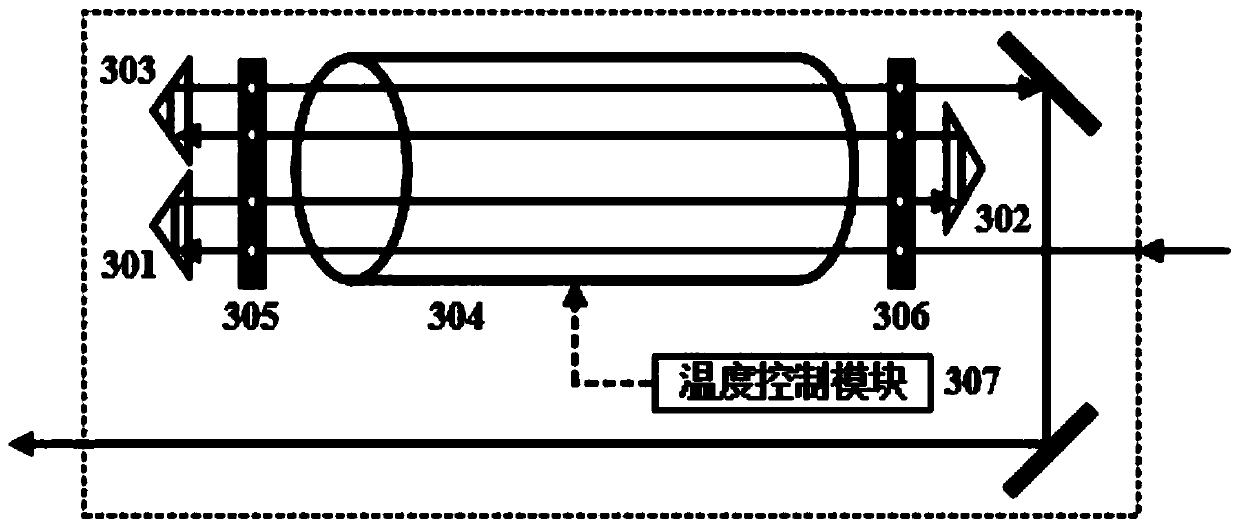
Mixed gas multi-waveband atomic optical filter and method thereof
ActiveCN104297950ASolution to short lifeSimple structureNon-linear opticsOptical elementsRubidiumPrism
The invention discloses a mixed gas multi-waveband atomic optical filter and a method thereof. The mixed gas multi-waveband atomic optical filter comprises a glass gas chamber with mixed alkali metal rubidium and cesium atoms, a first Glan Taylor prism and a second Glan Taylor prism which are orthometric in the direction of polarization of light, and a stable magnetic field source. The prisms are arranged at two sides of the glass gas chamber with the mixed alkali metal rubidium and cesium atoms and right face to the alkali metal atom glass gas chamber, and complete Faraday rotation effect can be achieved through the mixed rubidium and cesium atoms of the glass gas chamber with the mixed alkali metal rubidium and cesium atoms and laser; the stable magnetic field source is used for producing a gradient magnetic field with changing strength onto the glass gas chamber with the mixed alkali metal rubidium and cesium atoms, and the direction of the magnetic field of the gradient magnetic field is parallel to the direction of light propagation. The filter has the advantages that the filter is simple in structure, easy to manufacture, fine in performance, stable in operation and long in service life.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
Parameter calibration system of acousto-optic tunable filter
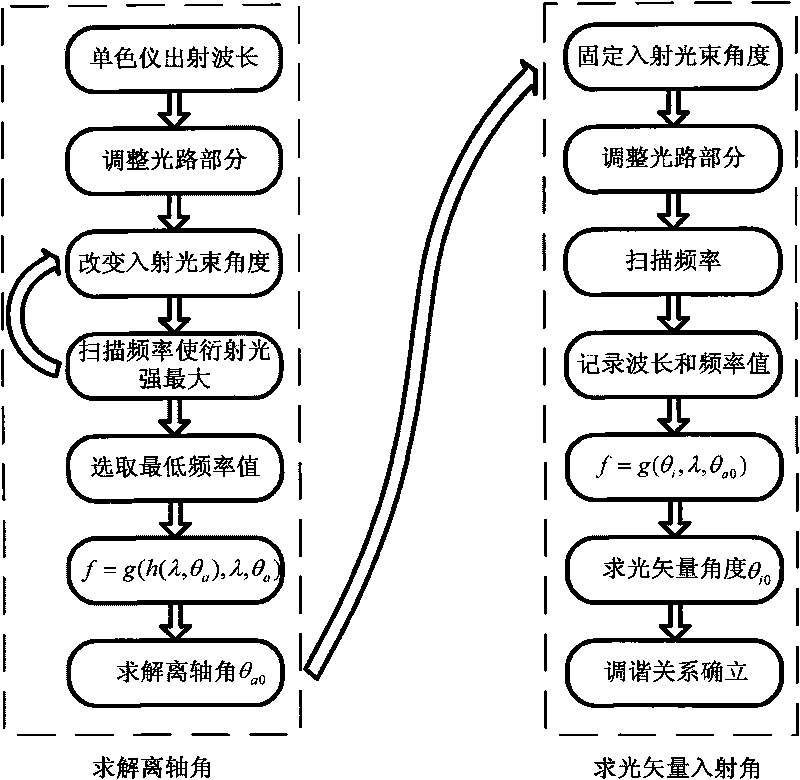
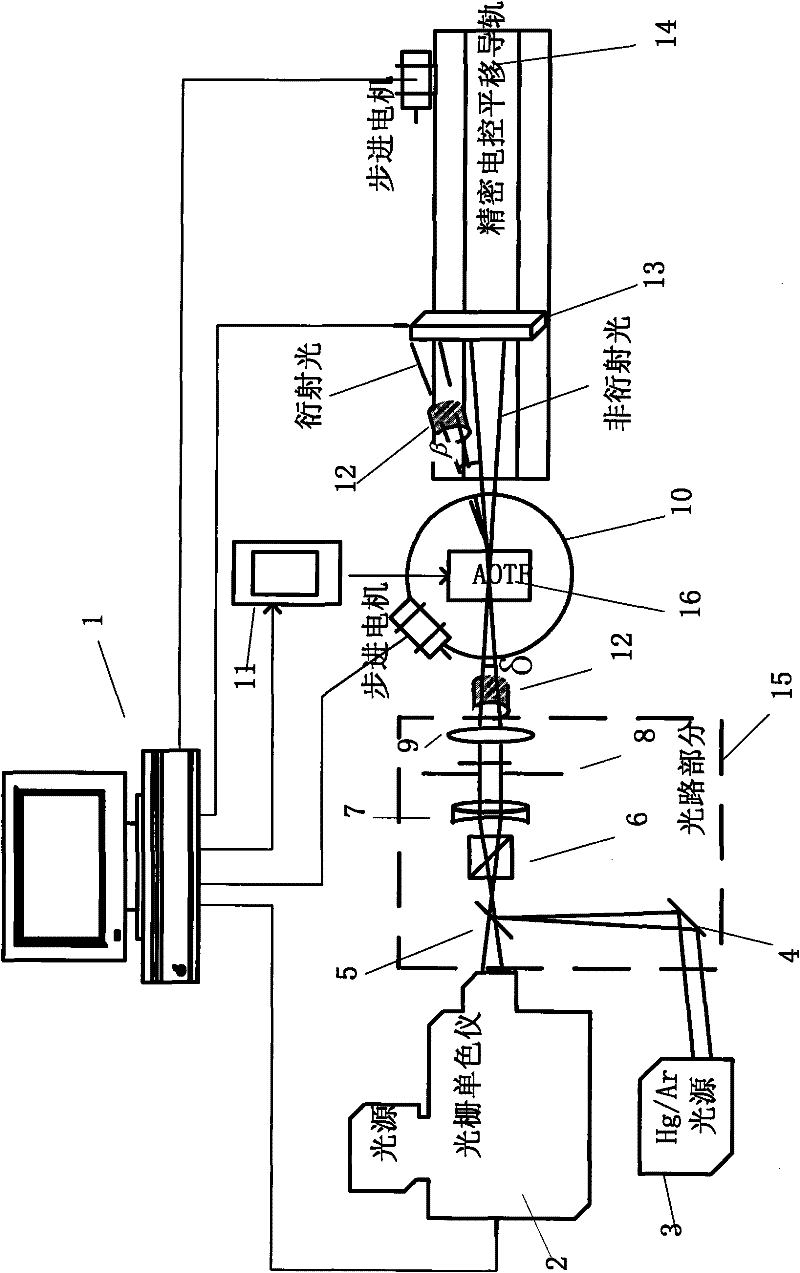
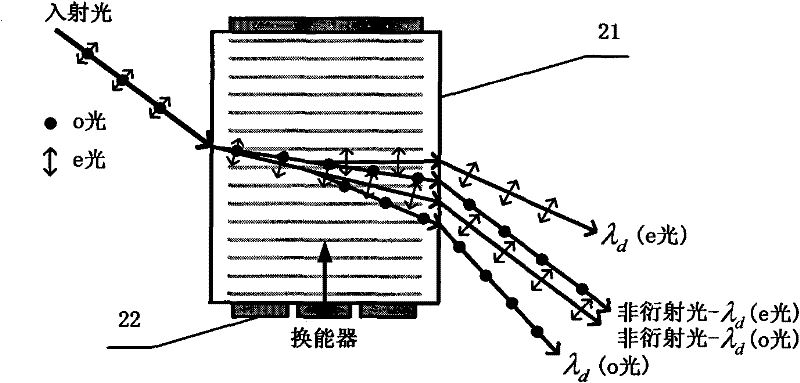
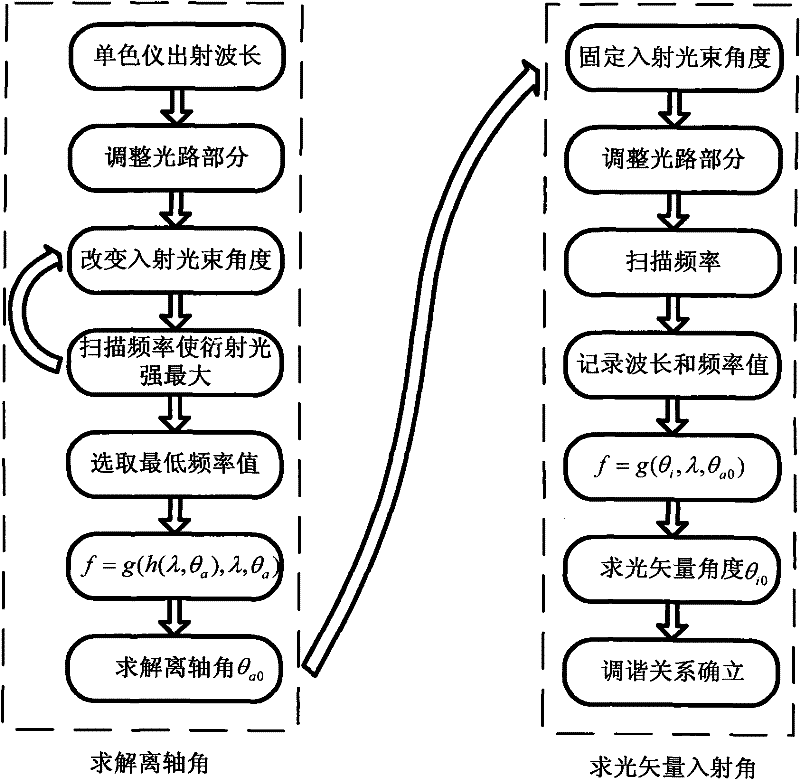
InactiveCN101718621AOvercome the disadvantages of complexity, low calibration accuracy and low degree of automationHigh precisionTesting optical propertiesAxis–angle representationGrating
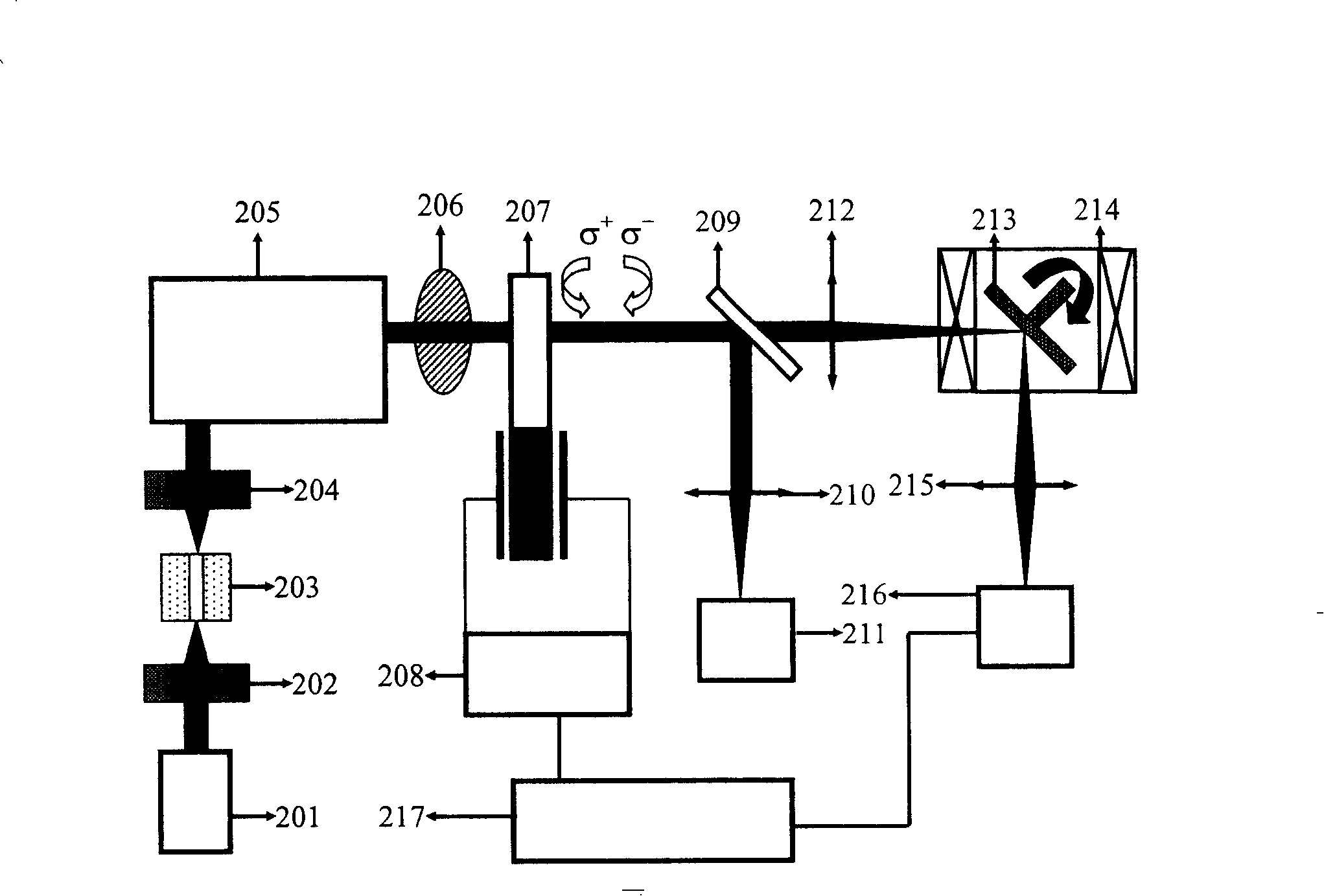
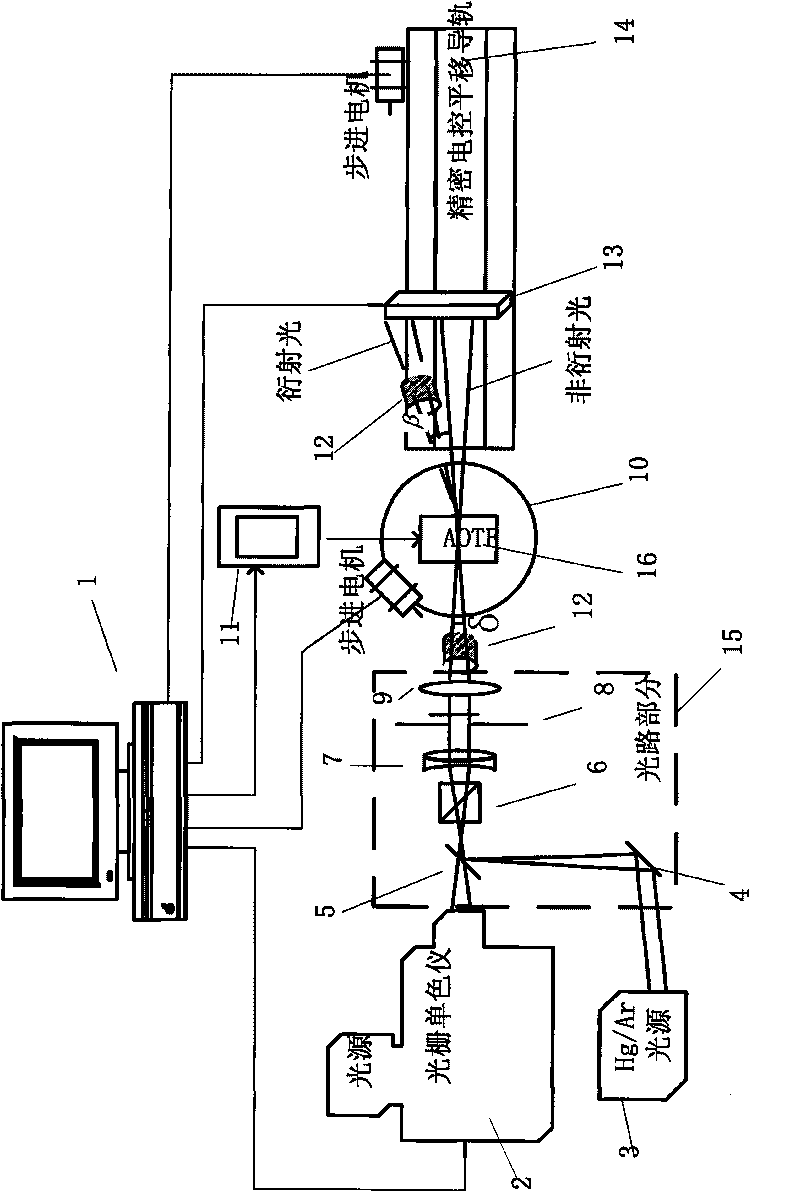
The invention provides a parameter calibration system of an acousto-optic tunable filter, comprising a controlling and processing computer, an optical grating monochrometer, a mercury argon gas light source, an optical path section, a precision electronic control rotary table, a high-precision radio frequency driver, a photomultiplier, a CCD light distribution detector and a precision electronic control translation guide rail; and the optical path section is mainly composed of a reflecting mirror, a semi-transparent semi-reflective lens, a Glan-Taylor prism, a collimating lens, an aperture and a focusing lens. The invention has complete calibrating system and high calibrating precision, can carry out automatic calibration on parameters like AOTF light beam incident angle, the off-axis angle theta alpha, the angular aperture delta, wavelength response function, wavelength frequency tuning relation, deflection angle beta and the like, is applicable to the index inspection of the AOTF product, the research of AOTF light spectrum and imaging characteristics, and provides technical parameters for the integration of AOTF spectrometer.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
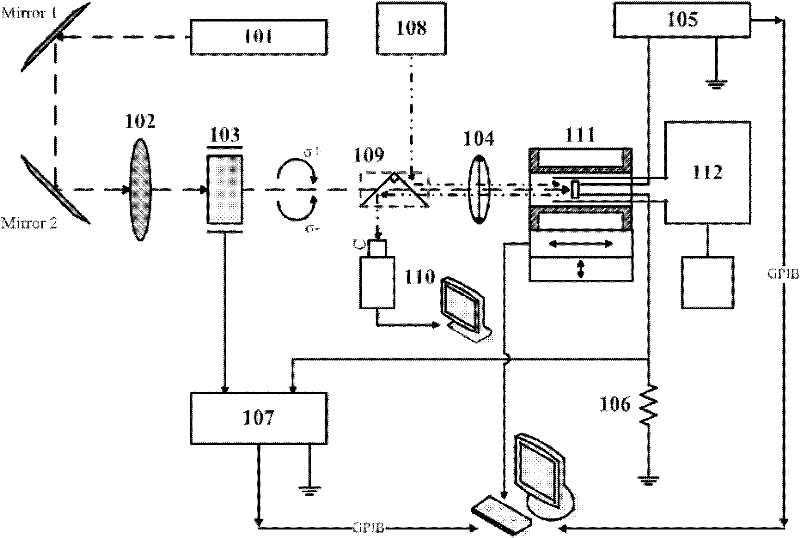
Variable temperature microscopic measurement system for measuring related electron-spin transportation
InactiveCN102253323AAccurate measurementAccurate Spin InjectionRate of change measurementMagnetic property measurementsDisplay devicePrism
The invention discloses a variable temperature microscopic measurement system for measuring related electron-spin transportation, which comprises an HeNe laser, a Grand taylor prism, a photoelastic modulator, a micro objective, a variable temperature liquid nitrogen Dewar sample holder, a digital voltage current source meter, a sampling resistance, a phase locked amplifier, a half-reflecting and half-transmitting lens group, a white light source, a camera, a display and a neodymium iron boron ring-shaped permanent magnet, wherein, the laser sent out by the HeNe laser is converted into linearly polarized light by the Grand taylor prism; the micro objective is used for focusing the incident lasers onto the platform surface of a sample; the variable temperature liquid nitrogen Dewar sample holder comprises a temperature control meter and a red copper cold finger which is used for fixing the sample to be detected on the top of the red copper cold finger; the control end of the digital voltage current source is connected with a computer through a general purpose interface bus (GPIB); the sampling resistance is used for extracting an alternating current voltage signal of the sample to be detected; the control end of the phase locked amplifier is connected with the computer through the GPIB; the half-reflecting and half-transmitting lens group is positioned on a main optical path; the white light source is used for observing the position on the platform surface of the sample to be detected; the camera and the display are used for displaying and outputting a platform surface image of the sample to be detected and the laser light spot position; and the neodymium iron boron ring-shaped permanent magnet is coaxially sheathed outside the red copper cold finger of the variable temperature liquid nitrogen Dewar sample holder.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Polarization resolution differential reflection spectrum measuring system
InactiveCN102095689AAchieving Polarization-Resolved Differential Reflectance SpectroscopyPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsPrismPolarizer
The invention discloses a polarization resolution differential reflection spectrum measuring system, comprising a liquid nitrogen Dewar, a manual three-dimensional translation stage, an achromatic lens, an exciter used for vibrating a lens periodically, a wide band quarter wave plate, a dual-output Gran-Taylor prism, a wide band linear polarizer and a wide band half wave plate, a monochromator, an ultra continuous white light source, a detector, two phase-locked amplifiers and a chopper. By utilizing the system disclosed by the invention, the polarization resolution differential reflection spectrum of a sample at 77-300K can be measured by adopting a low temperature Dewar, thus the energy band structure and characteristics of substances related to spin can be researched and analyzed.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic circular dichroism photoconduction spectrum measurement system
InactiveCN102680408AFlexible wavelength changeThe magnetic field can be changed flexiblyMaterial analysis by optical meansElectronic band structureCircular dichroism
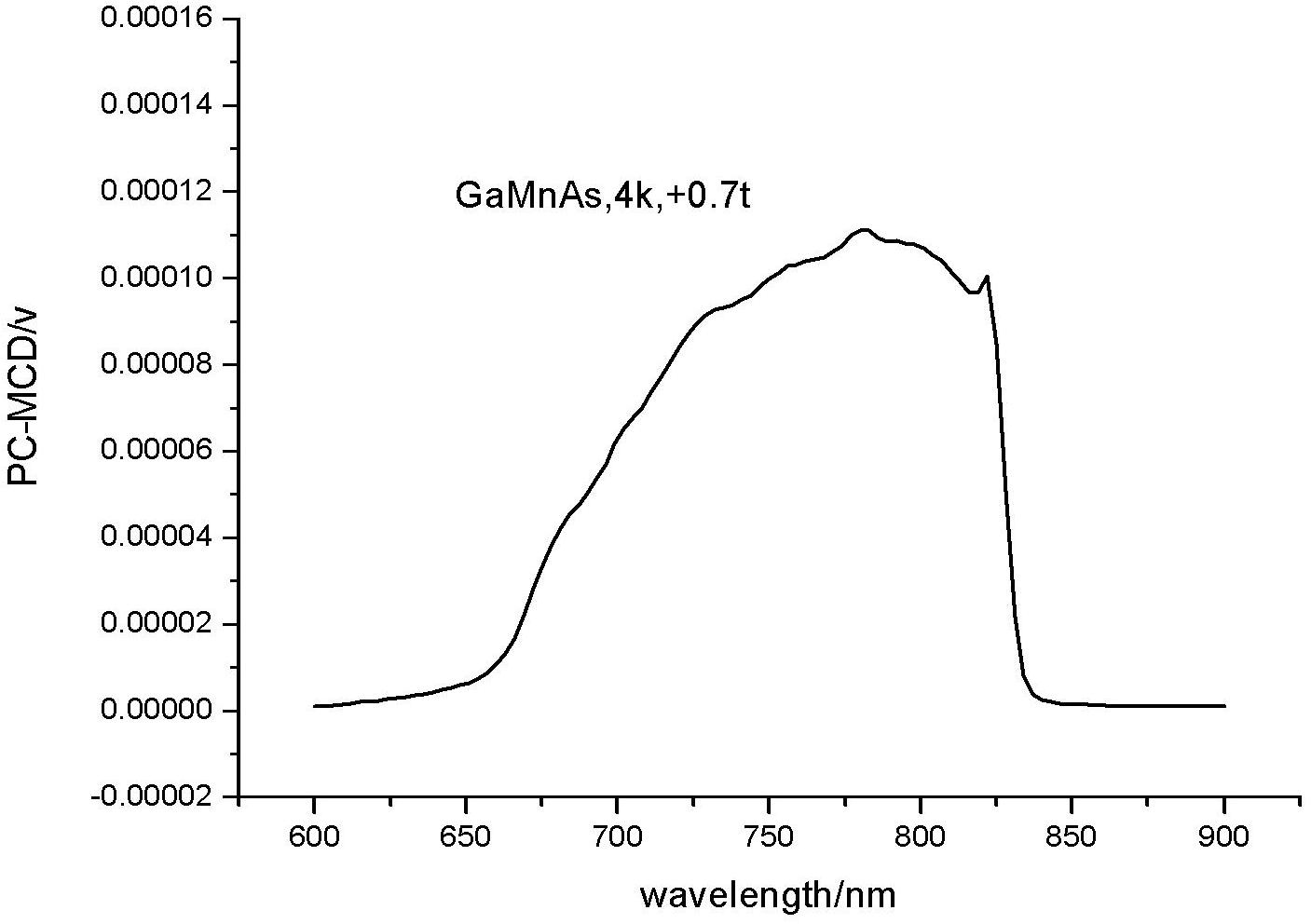
The invention discloses a magnetic circular dichroism photoconduction spectrum measurement system which comprises a liquid helium refrigerating machine, a low-temperature superconducting magnet system, an ultra-continuous white light source, a monochromator, a chopper, a Glan-Taylor polarizer, a photoelastic modulator, an achromatic lens, a current source, two phase-locking amplifiers and a computer. By using the magnetic circular dichroism photoconduction spectrum measurement system, the magnetic circular dichroism (PC-MCD) can be measured, therefore, the magnetic properties of a material and the spin-dependent energy band structure and characteristics can be further researched.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Microimaging integrated measuring device and measuring method for optical limiting property of multi-wavelength sample
InactiveCN106872415AEasy to measureEasy to operateTransmissivity measurementsBeam splitterMeasurement device
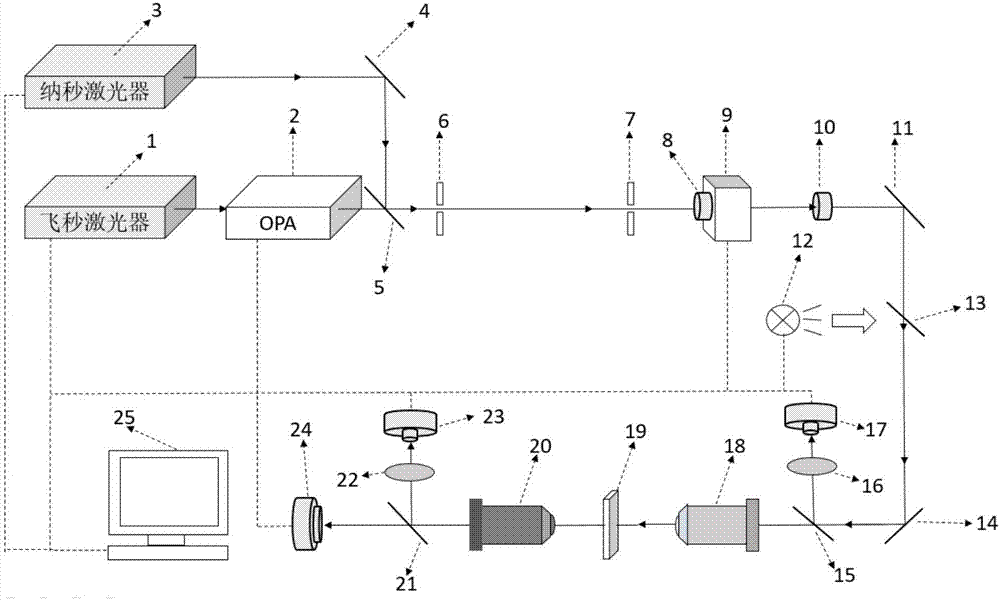
The invention discloses a microimaging integrated measuring device for an optical limiting property of a multi-wavelength sample. The microimaging integrated measuring device comprises a femtosecond laser unit, an OPA device, a coating total reflective mirror II, a diaphragm I, a diaphragm II, a Glan-Taylor prism I mounted on an electric rotary table, a Glan-Taylor prism II, a coating total reflection mirror, an illuminating light source, a beam splitter I, a coating total reflective mirror IV, a beam splitter II, a focusing lens I, an energy meter I, a focusing objective lens, a collecting objective lens, a beam splitter III, a focusing lens II, an energy meter II, a CCD and a computer. The microimaging integrated measuring device realizes measuring for the wide-spectrum optical limiting property of the sample, can observe the surface topography of the optical limiting sample, the spot size of incident laser as well as sample damage condition after laser irradiation, and has the characteristics of being automatic in measuring, flexible and convenient to regulate, wide in dynamic test range, and efficient and sensitive in response speed.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Light-scattering device and method for measuring diameter and length of short carbon nano-tube
InactiveCN102506720AMeasurement applicableFast measurementUsing optical meansPlane mirrorCarbon nanotube
The invention relates to light-scattering device and method for measuring the diameter and length of a short carbon nano-tube, wherein the method for measuring the diameter and length of a short carbon nano-tube comprises the following steps: the light emitted by a helium-neon laser becomes a linearly-polarized laser in a vertical direction via Glan-Taylor prism; an incident linearly-polarized laser irradiates on particle samples in a sample cell after being reflected by a plane mirror and focused by a lens, the scattered light in a 90-degree direction generated by the sample particles irradiated by the laser beam orderly enters in two faced pores; the scattered light is decomposed into a polarized scattered light in the vertical direction and a polarized scattered light in a horizontal direction via Wollaston prism; and the polarized scattered lights in the two directions are detected by two photomultipliers respectively, and the measured light signal is converted to a TTL (transistor-transistor logic) pulse voltage signal and conveyed in a mathematic correlator to obtain the measured diameter and length. Relative to the most general microscope measuring method at present, the method for measuring the diameter and length of a short carbon nano-tube is a non-contact measuring method, as well as is fast in measuring speed, low in cost and low in operational requirements. Relative to Raman spectrometry, the method for measuring the diameter and length of a short carbon nano-tube can measure diameter and length simultaneously, and is suitable for measurement for multi-wall carbon nano-tube.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
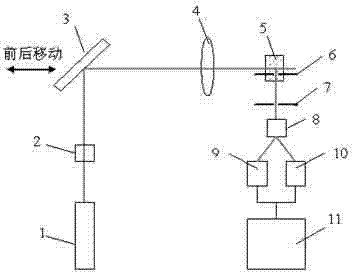
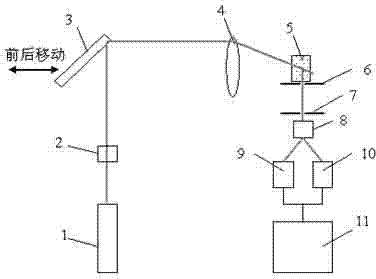
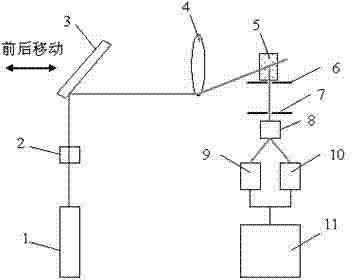
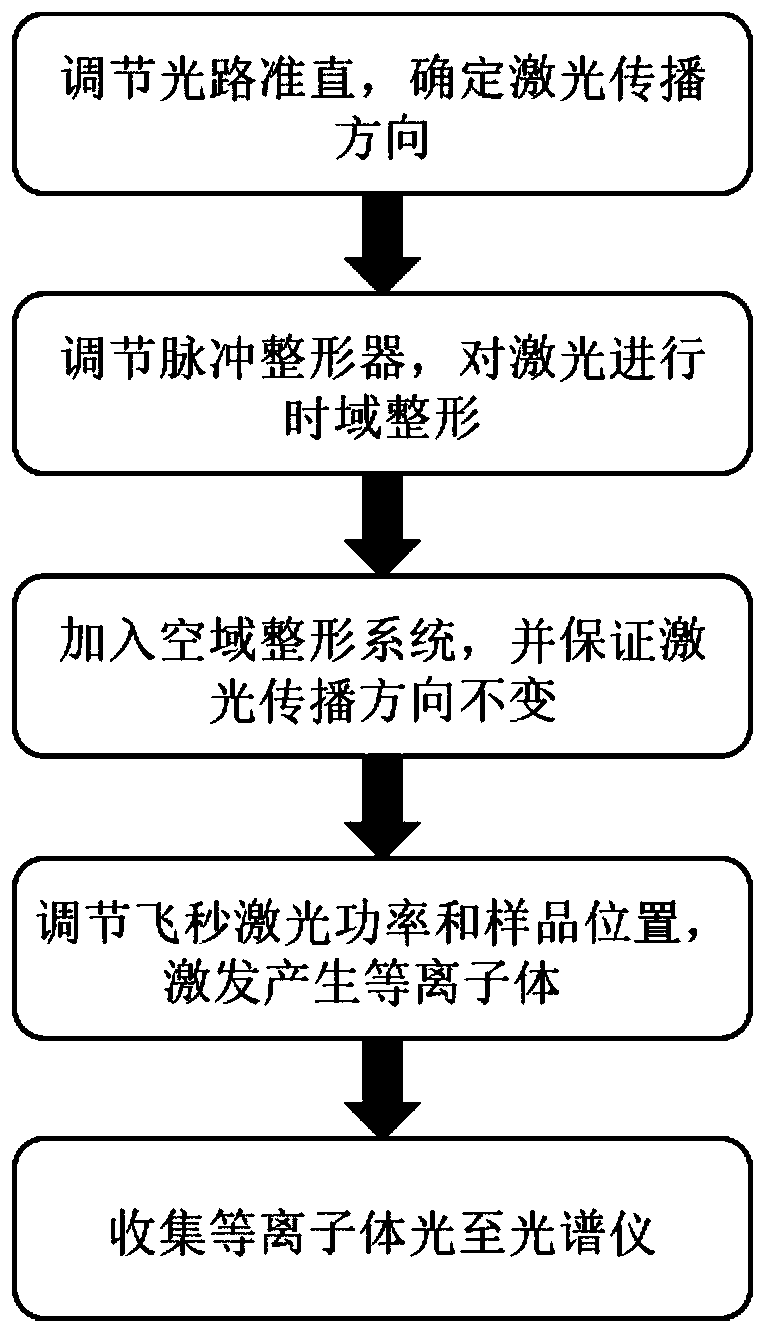
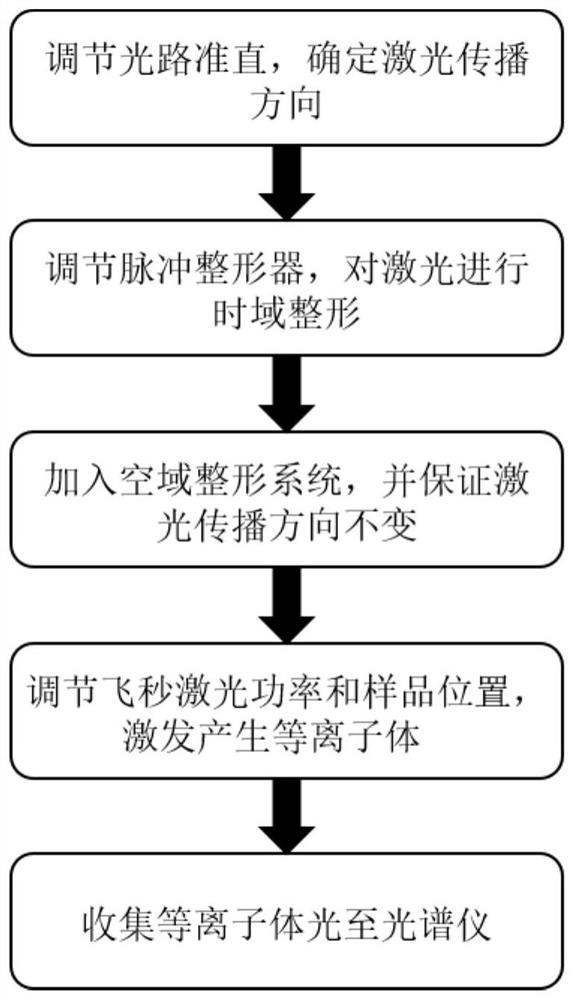
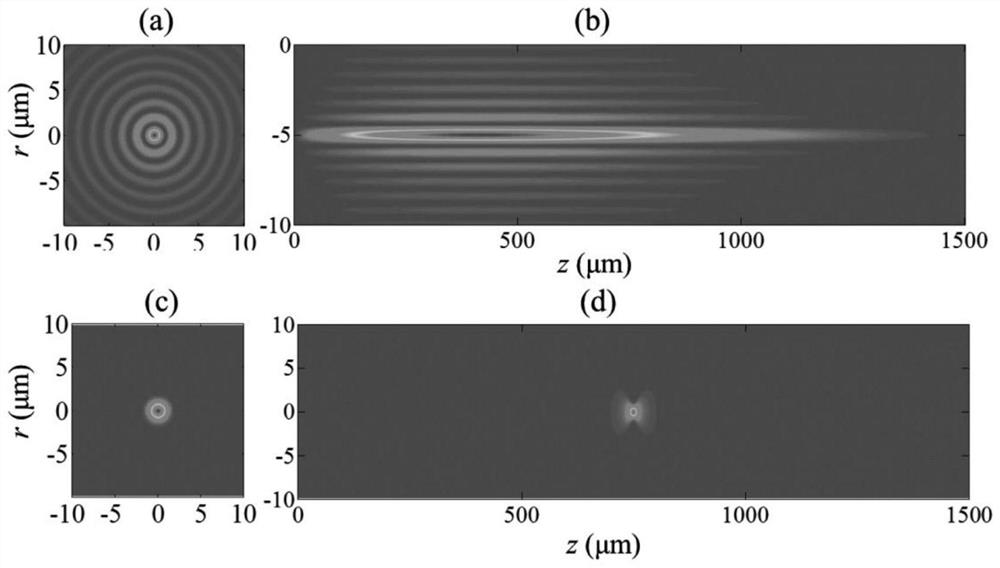
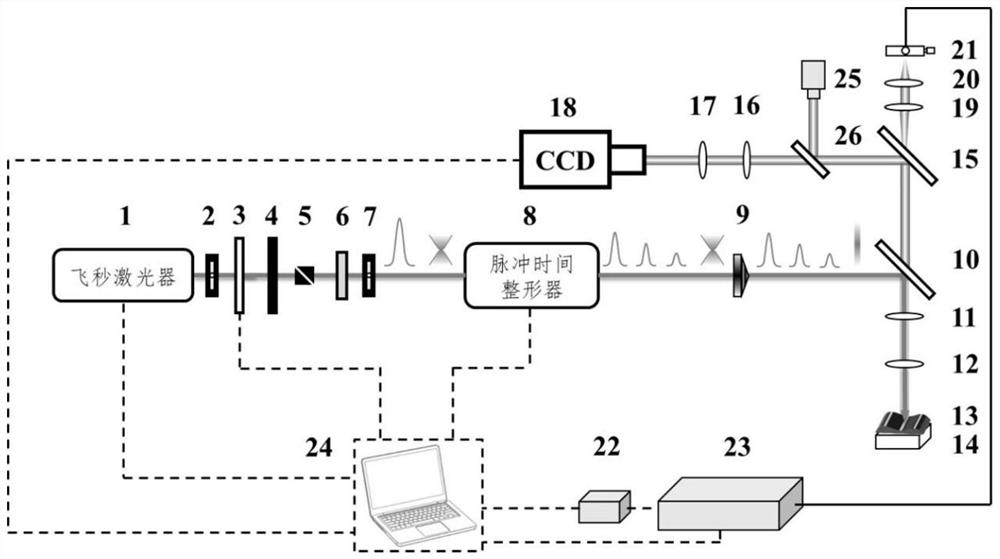
Femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectrum generation and acquisition system based on space-time shaping
ActiveCN110940659AImprove experimental operation efficiencyEnables continuous linear regulationAnalysis by thermal excitationFemto second laserLight beam
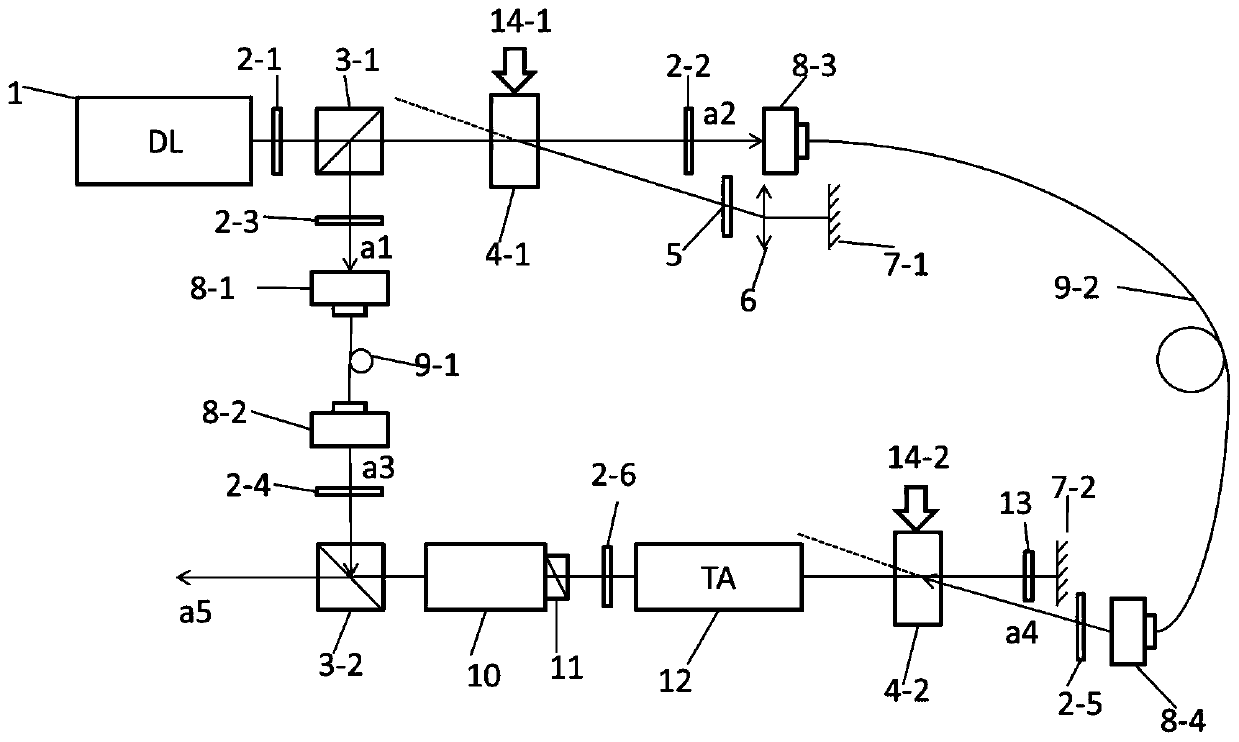
The invention discloses a femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectrum generation and acquisition system based on space-time shaping, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. A Bessel light beam with a long focal depth is used for exciting material plasmas after being shrunk; under the condition that focusing is not carried out, plasma excitation with the same energy density is achieved at different height positions of a sample, the process of single-point independent focusing is omitted, possible human and machine errors in each time of focusing operation are avoided, and the stability, repeatability and collection efficiency of spectrum collection are guaranteed. The system can adjust parameters of the conical lens and the beam shrinking lens group to obtain Bessel regions with different focusing lengths, and a device suitable for samples with different height change ranges is designed according to individual requirements. When a femtosecond laser Bessel beam is adopted to excite plasmas on the surface of a rough sample, the combination of a half-wave plate and a Glan-Taylor prism in the system realizes the continuous linear adjustment of pulse energy,and realizes the sample detection and analysis under the nearly lossless condition.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Rapid pulse laser polarization degree measurement device
InactiveCN103234909AQuick measurementAchieve separationPolarisation-affecting propertiesBeam splitterMeasurement device
The invention relates to a rapid pulse laser polarization degree measurement device and belongs to the technical field of laser. The device comprises a laser (1), a beam shaping lens (2), a Glan-Taylor polarizer (3), a depolarizing beam splitter prism (4), a polarizing beam splitter prism (5), a photoelectric detector A (6) and a photoelectric detector B (7). According to the device, by adoption of the polarizing beam splitter prism, horizontal polarization P light and vertical polarization S light in back scattering light beams of a tested sample can be separated, a horizontal polarization P light voltage value VP and a vertical polarization S light voltage value VS in the light beams are measured, and the back scattering polarization degree of the tested sample is calculated by utilizing (VP-VS) / (VP+VS), so that the polarization degree of the tested sample is rapidly measured. In a measurement process, the error brought by the operation of respectively acquiring the horizontal polarization P light and the vertical polarization S light by regulating an analyzer is avoided, so that the measurement precision is high.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Preparation method of self-organizing periodic micro-nano structure with alternately arranged glass and crystals
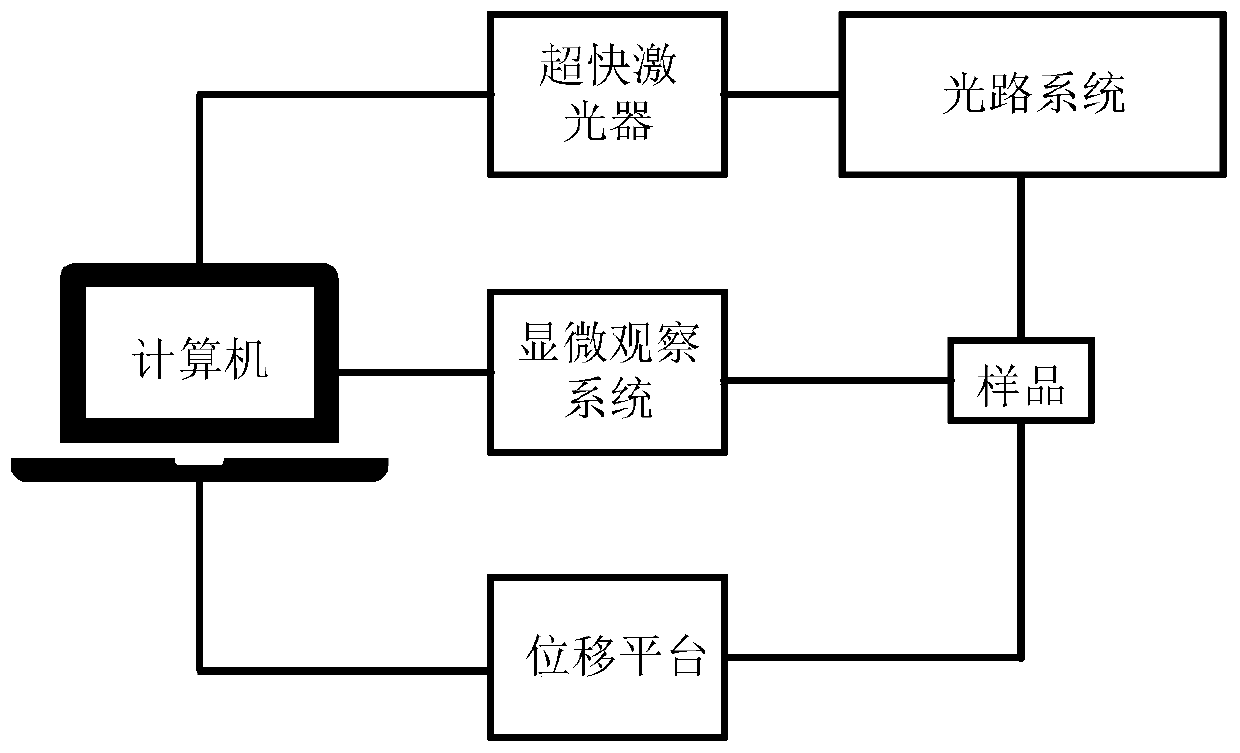
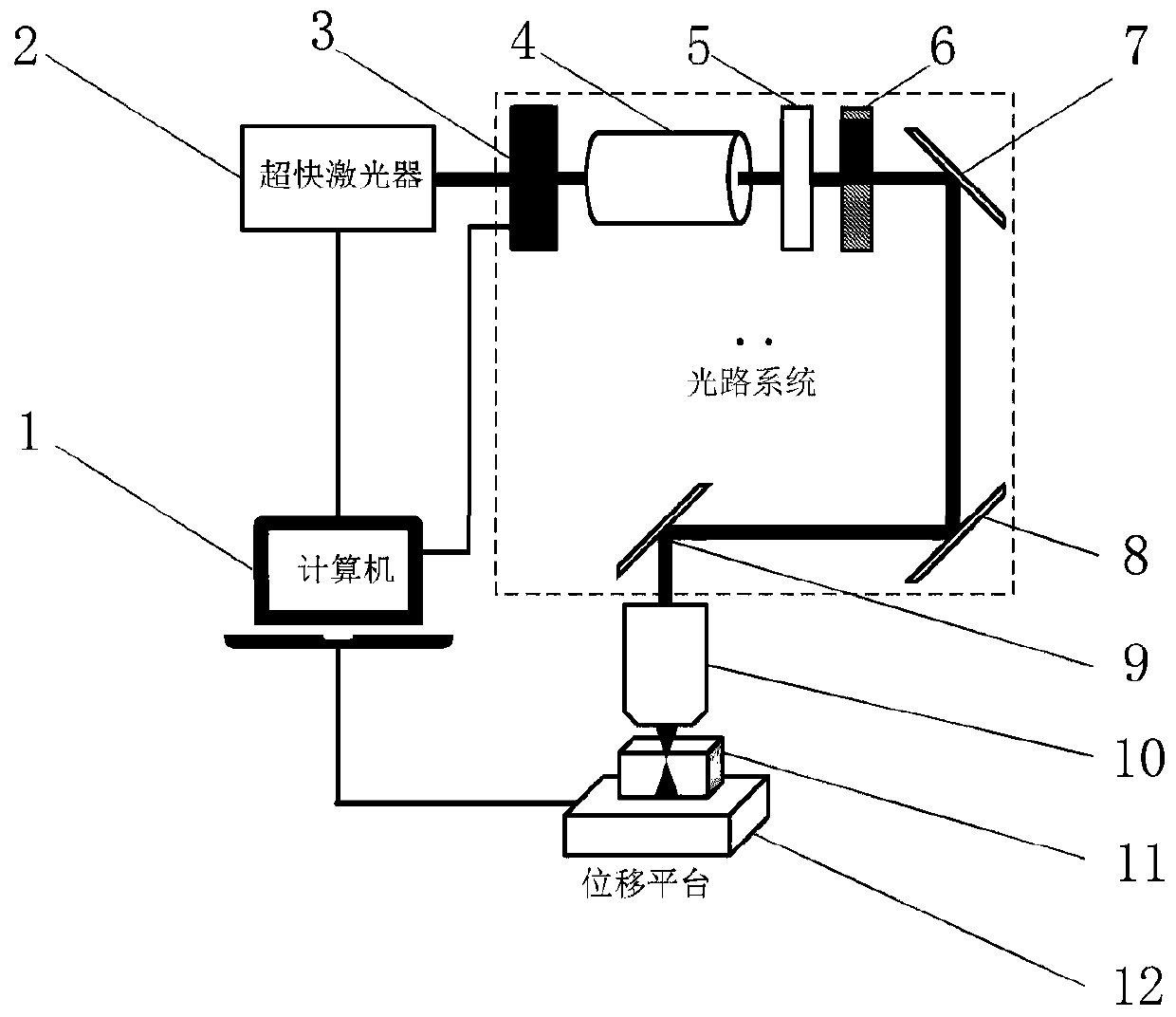
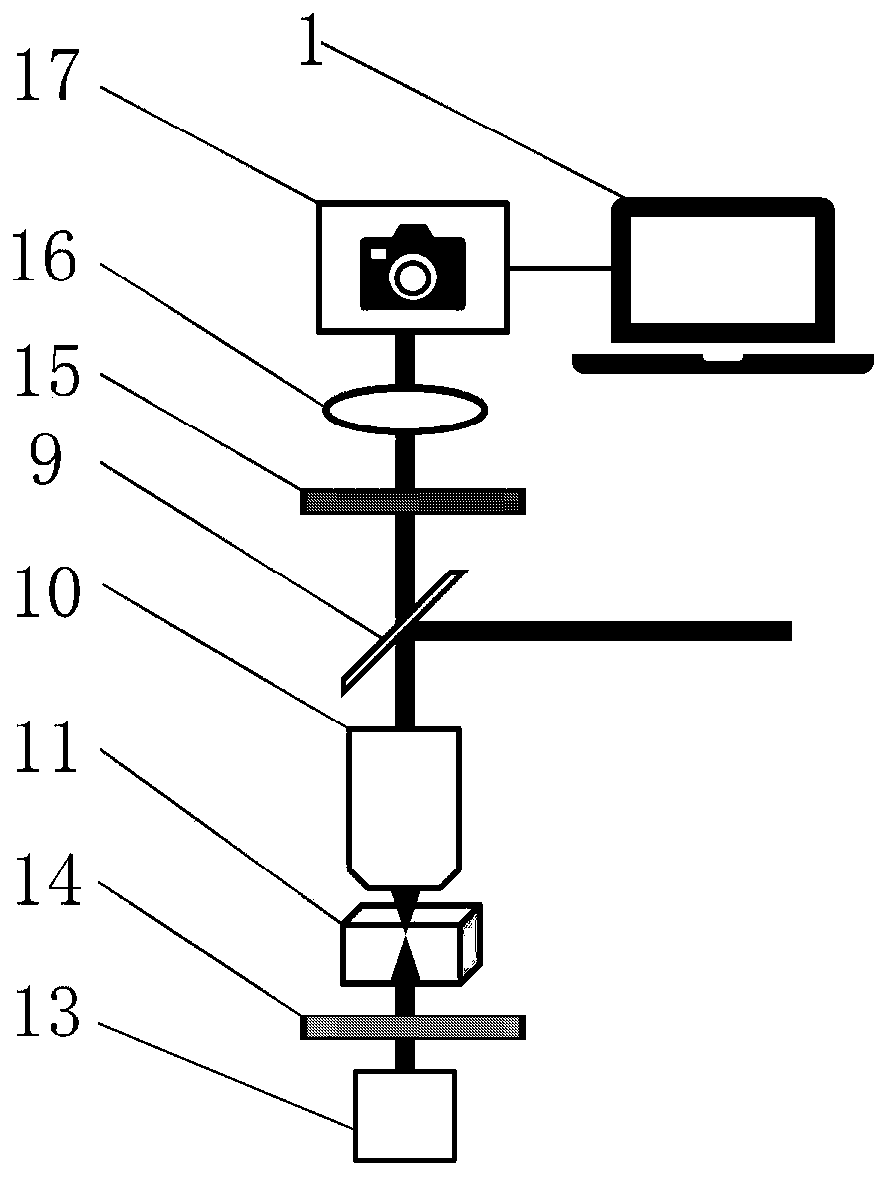
ActiveCN110171801AHigh forming precisionAchieve nanoscale processingDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMicro nanoMotion parameter
The invention discloses a preparation method of a self-organizing periodic micro-nano structure with alternately arranged glass and crystals. A sample is prepared by utilizing a suspension method, andthe sample is ternary glass 35La2O3-xTa2O5-(65-x)Nb2O5 (5<x<45) or 35La2O3-xTiO2-(65-x)Nb2O5 (30<x<60), wherein x represents a molar percentage (mol.%); the sample is fixed on a displacement platform, an ultrafast laser emits an ultrafast laser beam, the ultrafast laser beam irradiates the sample through a shutter, a Glassy prism and a half-wave plate, and focuses into the sample; when the sampleat the focused position is excited by the ultrafast laser beam to generate visible light, the displacement platform is started, so that the sample moves relative to the laser beam according to a setpath and motion parameters, and a polarization-dependent periodic micro-nano structure is generated at the focused position of the laser beam through induction. According to the preparation method, high-efficiency preparation of the polarization-dependent periodic micro-nano structure is realized, and a functional material which can be used for forming the periodic micro-nano structure is expanded.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
System for synchronously measuring polar magneto-optic Kerr spectrum and magnetic circular dichroism spectrum
InactiveCN102654450AFlexible temperature changeFlexibility to change the magnetic fieldMaterial analysis by optical meansMagnetic property measurementsBeam splitterPrism
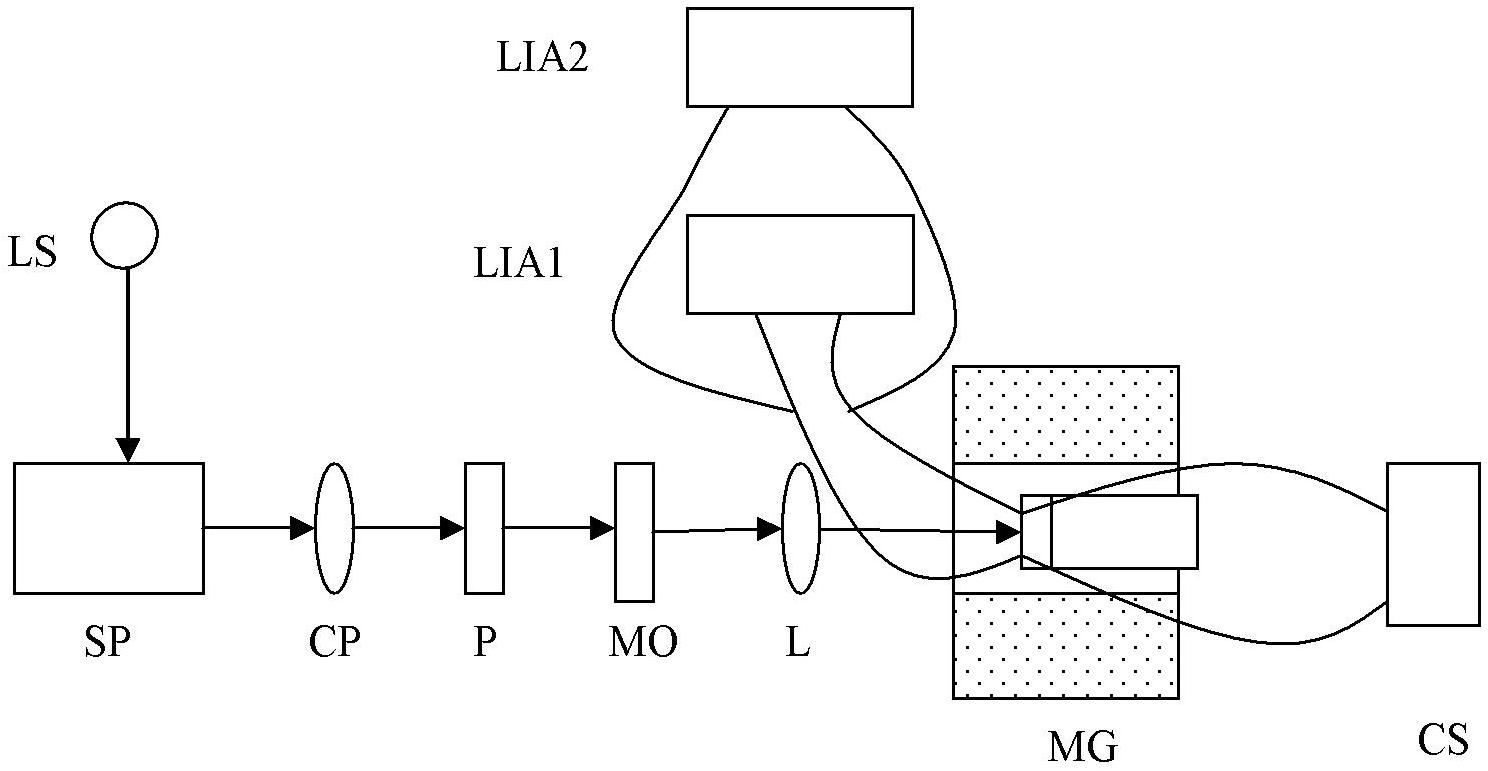
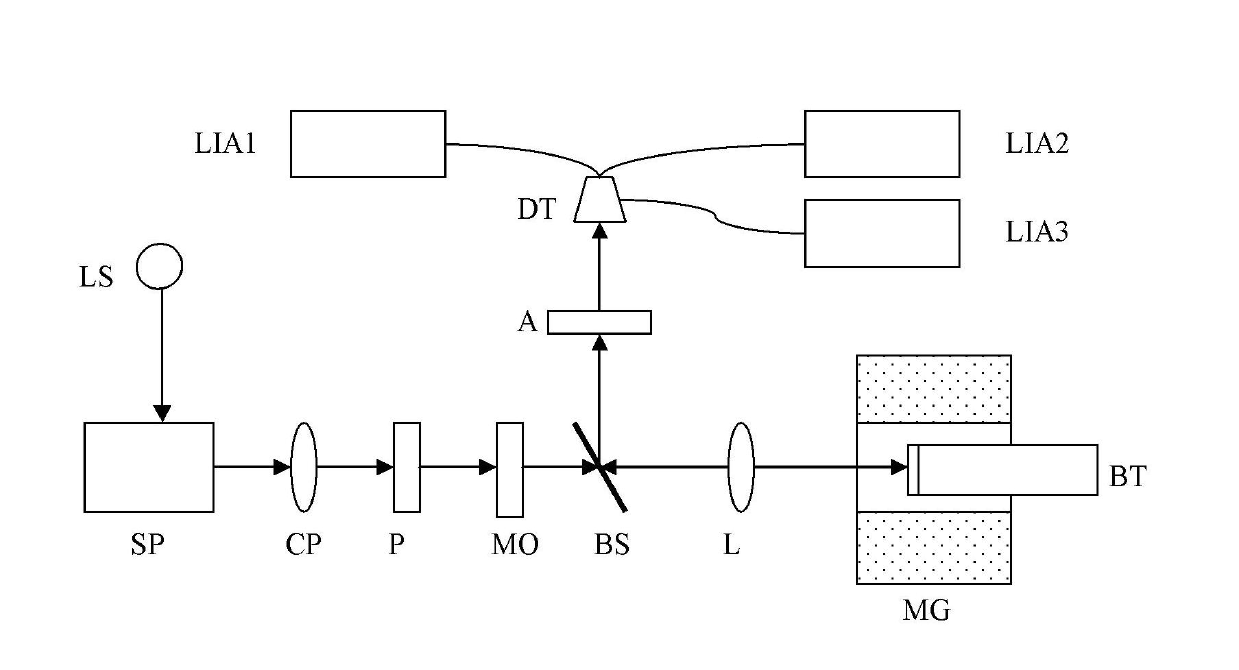
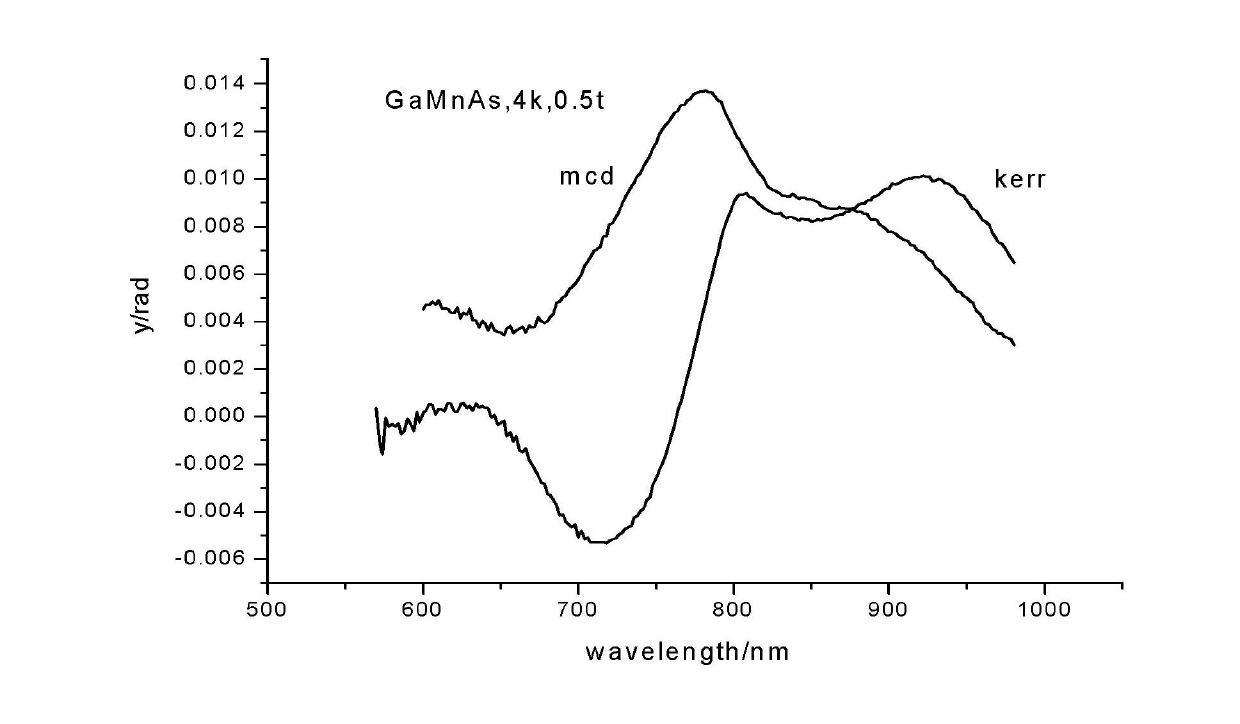
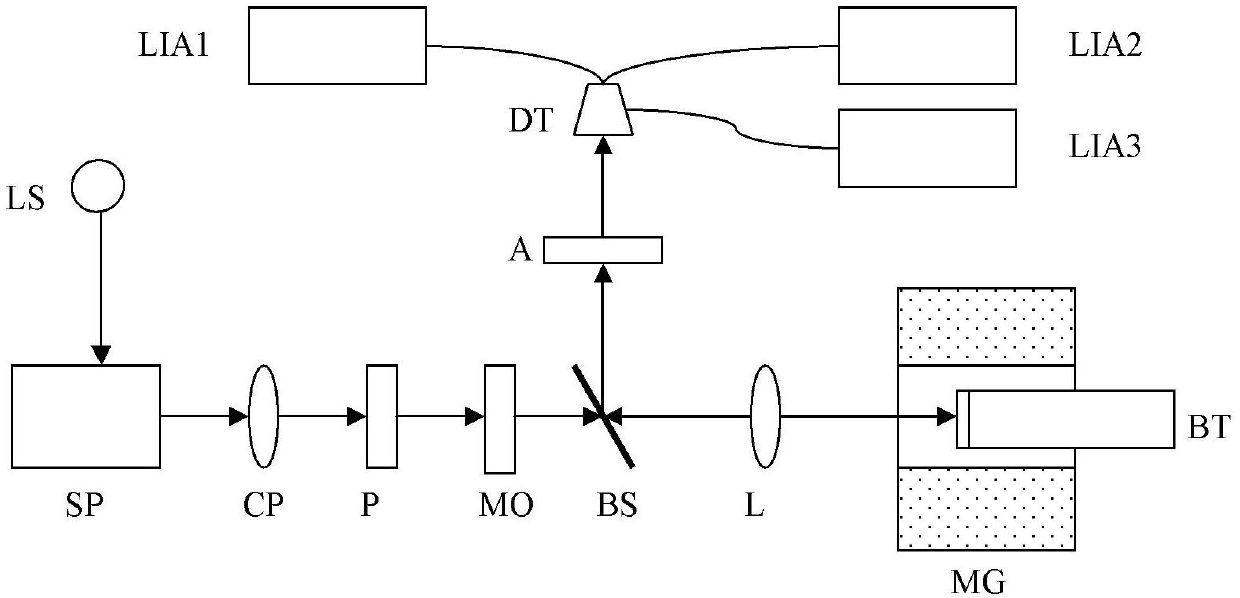
The invention discloses a system for synchronously measuring a polar magneto-optic Kerr spectrum and a magnetic circular dichroism spectrum, comprising a liquid helium refrigerator, a low-temperature superconducting magnet system, a super-continuous white light source, a monochromator, a chopper, two Glan-Taylor prisms, a photoelastic modulator, a broadband depolarizing beam splitter prism, an achromatic lens, a silicon detector, three lock-in amplifiers and a computer. With the system provided by the invention, the polarized magneto-optic Kerr (KERR) spectrum and the magnetic circular dichroism (MCD) spectrum of a sample can be simultaneously measured, so that the magnetism, as well as energy band structure and properties related to spinning of substances can be further studied.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Semiconductor cone laser amplifying system in single-way and two-way composite mode
ActiveCN110112648ALow costReduced laser power requirementsLaser output parameters controlICT adaptationBeam splittingPolarization-maintaining optical fiber
The invention discloses a semiconductor cone laser amplifying system in a single-way and two-way composite mode and relates to a laser amplifier. The system includes a semiconductor laser, first, second, third, fourth, fifth and sixth half-wave plate, first and second polarization beam splitting prisms, first and second acousto-optic modulators, a quarter-wave plate, a flat convex lens, first andsecond mirrors, first, second, third and fourth fiber coupling mirrors, first and second single-mode polarization-maintaining fibers, a Faraday rotator, a Glan-Taylor prism, a semiconductor cone laseramplifier, a filter and first and second RF sources. The system can work in different modes in a time-sharing manner, only one semiconductor laser and one semiconductor cone laser amplifier are used,the high-performance laser can be outputted, the high-efficiency amplification of the laser power can be achieved, and a cold-atomic interference instrument experiment laser light path is greatly simplified and integrated.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Low noise micro-cantilever beam thermal vibration signal measuring device
InactiveCN104819767ASolve the noise problemSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansLow noisePhase difference
The invention provides a micro-cantilever thermal shock signal measuring apparatus. The apparatus comprises an incident optical path assembly and two detection optical path assemblies. The incident optical path assembly comprises a line polarizer, a first spectroscope, a Wollaston prism, a first convergent lens and a second spectroscope. Polarization laser forms two beams of incident ray polarized light with mutually vertical polarization directions through the line polarizer, the first spectroscope and the Wollaston prism, after convergence, is respectively vertically incident to the tip end and the substrate of a cantilever arm, after reflection respectively, forms two beams of reflection polarized light with mutually vertical polarization directions, converges through the Wollaston prism and is incident to the second spectroscope to form two beams of detection polarized light. Each detection optical path assembly comprises a photoelectric detection circuit, the two beams of detection polarized light are respectively incident to the two photoelectric detection circuits, and the photoelectric detection circuits, after converting optical signals into electric signals, obtain a phase difference of the two beams of reflection line polarized light through calculating the two electric signals.
Owner:SHAOXING UNIVERSITY
Method and device for detecting ratio of components of buffer gas-containing atomic gas
InactiveCN103472000ASolve the key problem that the component characteristics are difficult to carry out non-destructive testingMaterial analysis by optical meansPolarizerIntegrating sphere
The invention discloses a method for detecting a ratio of components of buffer gas-containing atomic gas. The method comprises the following steps that a collimation laser as a detection light source outputs a collimated light beam; the collimated light beam goes through a Glan-Taylor polarizer to form a linearly-polarized collimated light beam; the total light intensity of the linearly-polarized collimated light beam is measured by a light intensity power meter and the measuring result is transmitted to a computer; the linearly-polarized collimated light beam enters into a sample table and then forms transmission light diffusing around after going through the sample table; the light intensity of the transmission light diffusing around is measured by an integrating sphere and an oscilloscope and the measured data is transmitted to the computer; and the computer carries out data analysis computation on the intensity of the transmission light diffusing around and the total light intensity of the linearly-polarized collimated light beam so that transmissivity of the transmission light diffusing around is obtained, and further carries out computation so that the ratio F of nonbuffered gas to buffer gas in the buffer gas-containing atomic gas is obtained. The method realizes a nondestructive test on components of the buffer gas-containing atomic gas in a closed gas chamber. The invention also discloses a device for detecting the ratio of the components of the buffer gas-containing atomic gas.
Owner:周超
Faraday laser with locked resonant cavity membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112542757AOvercome the shortcomings of large power fluctuationsReduce power fluctuationsOptical resonator shape and constructionNon-linear opticsFrequency stabilizationBeam splitter
The invention discloses a Faraday laser with a locked resonant cavity membrane and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the steps of carrying out detection on the outgoing power of the laser, and obtaining the corresponding relation between the resonant cavity membrane and the center of a gain spectral line through judgment; locking the cavity membrane and the center of the gain spectral line by adopting a modulation and demodulation technology so as to achieve accurate correspondence of the laser frequency and an atomic spectral line, thereby further improving the power and frequency stability of the Faraday laser. The Faraday laser comprises a laser diode, a collimating lens, a first Glan-Taylor prism, an atomic gas chamber, a second Glan-Taylor prism, piezoelectric ceramic, an endoscope, a beam splitter prism, a photoelectric detector, a signal generator, a frequency mixer and a servo feedback circuit, wherein the second Glan-Taylor prism is completely orthogonal to the first Glan-Taylor prism; the reflected light beam is used for locking the resonant cavity membrane; and the Faraday laser with the locked resonant cavity membrane is obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
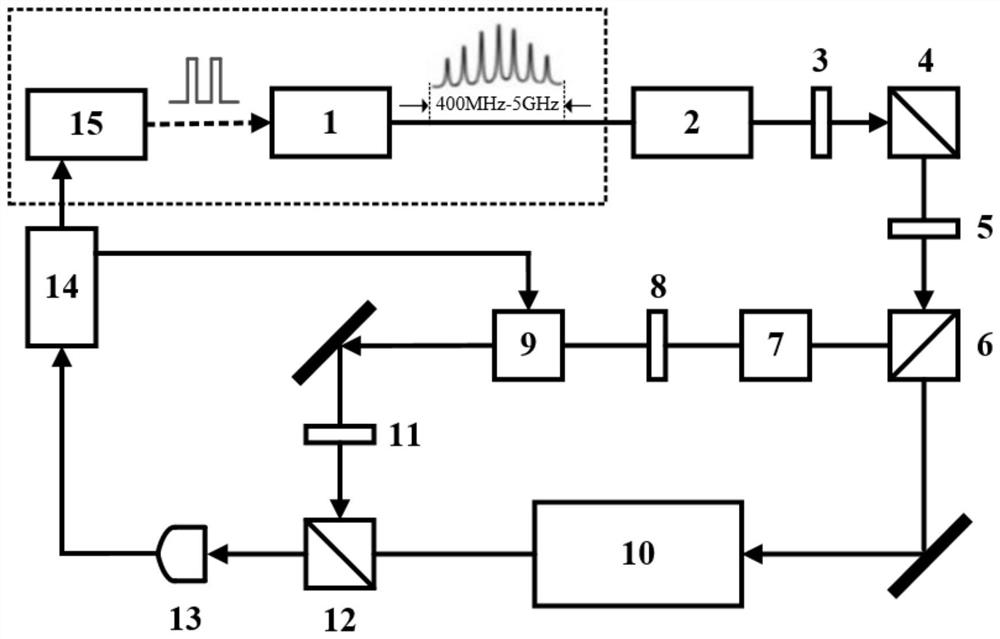
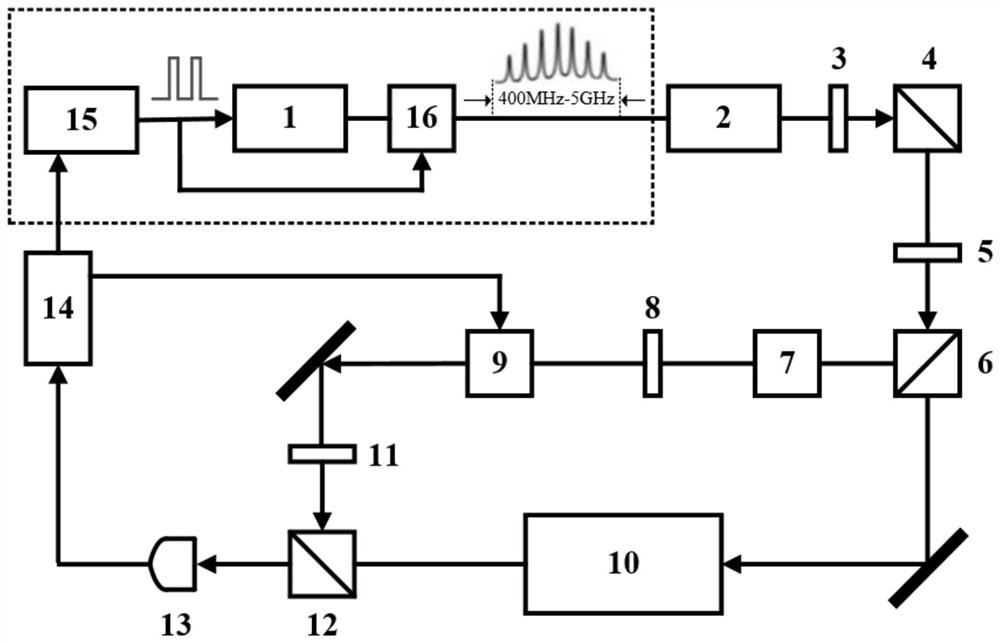
Iodine molecular optical clock based on pulse modulation wide-spectrum comb-tooth-type laser and control method of iodine molecular optical clock
ActiveCN111413859AImprove effective utilizationImprove signal-to-noise ratioApparatus using atomic clocksPower control systemControl system
The invention relates to an iodine molecular optical clock based on pulse modulation wide-spectrum comb-tooth-type laser and a control method. A power supply control system of the iodine molecule optical clock generates a pulse modulation signal and transmits the pulse modulation signal to a laser system to generate a pulse signal, optical feedback isolation is performed on a rear optical path through an isolator, and a first half-wave plate and a first polarization splitting prism are sequentially connected behind the isolator; a laser frequency stabilization light path comprises a second half-wave plate and a second polarization splitting prism which are connected in sequence and divide the laser for the laser frequency stabilization light path into two beams; one beam with stronger light intensity is used as a pump laser, passes through a Glan-Taylor prism, a third half-wave plate and an electro-optic phase modulator in sequence, and is reflected to a light path multiplication system by a third polarization splitting prism; and the beam with weaker light intensity is used as a detection laser to pass through the light path multiplication system and the third polarization splitting prism, is received by a high-speed photoelectric detector and then is input into a laser phase discrimination and high-speed servo feedback control circuit to generate a servo signal of the power supply control system.
Owner:PKU HKUST SHENZHEN HONGKONG INSTITUTION
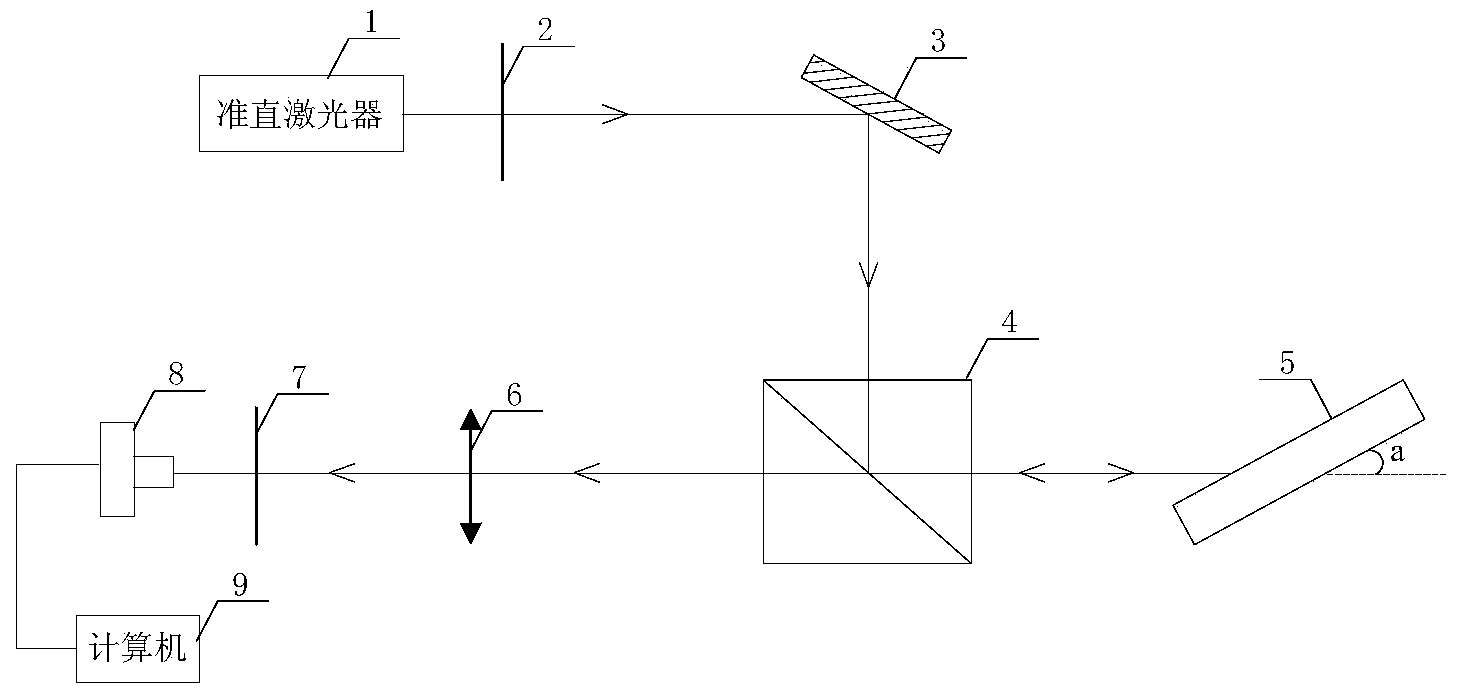
Atom gas concentration detecting apparatus and method based on optical coherent backscattering effect
InactiveCN103528994ARealize non-destructive testingPhase-affecting property measurementsElectricityCoherent backscattering
The invention discloses an atom gas concentration detecting apparatus and a method based on optical coherent backscattering effect. The atom gas concentration detecting apparatus comprises a laser aligner (1), a Glan-Taylor prism (2), a reflector (3), a depolarizing splitting prism (4), a sample beach (5), a Fourier lens (6), a polarization analyzer (7), a detector (8) and a computer (9); the laser aligner (1), the Glan-Taylor prism (2) and the reflector (3) are successively arranged on one same straight line along the transverse direction; the reflector (3) and depolarizing splitting prism (4) are arranged on one same straight line along the vertical direction; the sample beach (5) is arranged at one side of the depolarizing splitting prism (4), and the other side of the depolarizing splitting prism (4) is provided with the Fourier lens (6), the polarization analyzer (7) and the detector (8); the detector (8) is electrically connected with the computer (9) via data lines; and the detector (8) is arranged on the focal plane of the Fourier lens (6). The atom gas concentration detecting apparatus and the method help to realize nondestructive test on atom concentration of the atom gas in an enclosed gas room.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
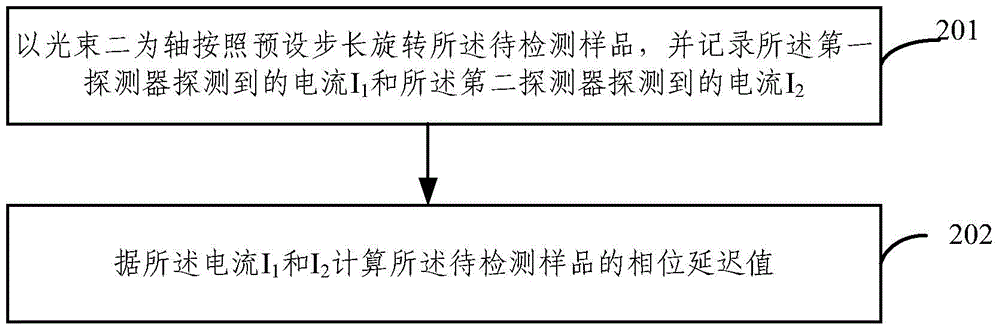
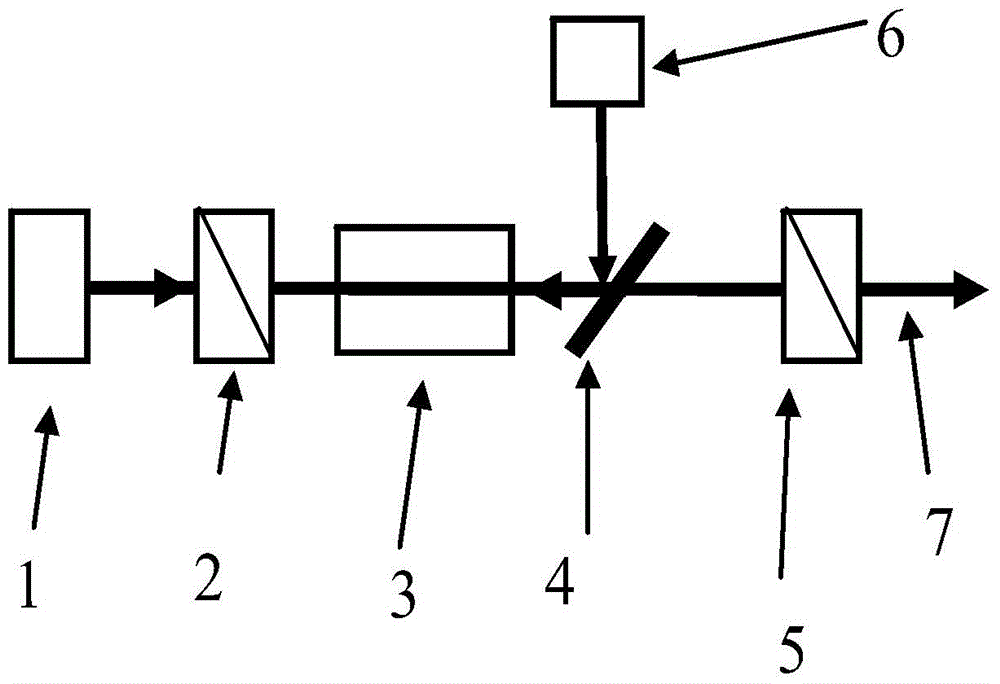
Phase delay measuring apparatus and method
InactiveCN103604776AHigh precisionPhase-affecting property measurementsPhase retardationBeam splitting
The invention provides a phase delay measuring apparatus and a phase delay measuring method. The apparatus comprises a beam splitting meter, a first detector, a second detector, a first rotary table and a Glan-Taylor prism. The first rotary table is used for bearing a to-be-measured sample and enabling the sample to rotate along a horizontal axis; monochromatic polarized light undergoes beam splitting by the beam splitting meter, then one light beam I irradiates onto the first detector, and the other light beam II irradiates onto the Glan-Taylor prism and then irradiates onto the second detector after passing through the Glan-Taylor prism. The phase delay measuring apparatus and the phase delay measuring method provided by the invention have measurement accuracy independent on the characteristics of a material and can greatly improve measurement precision.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
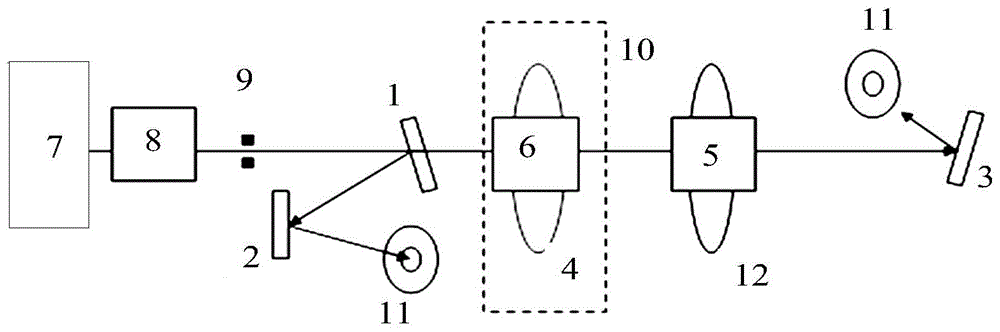
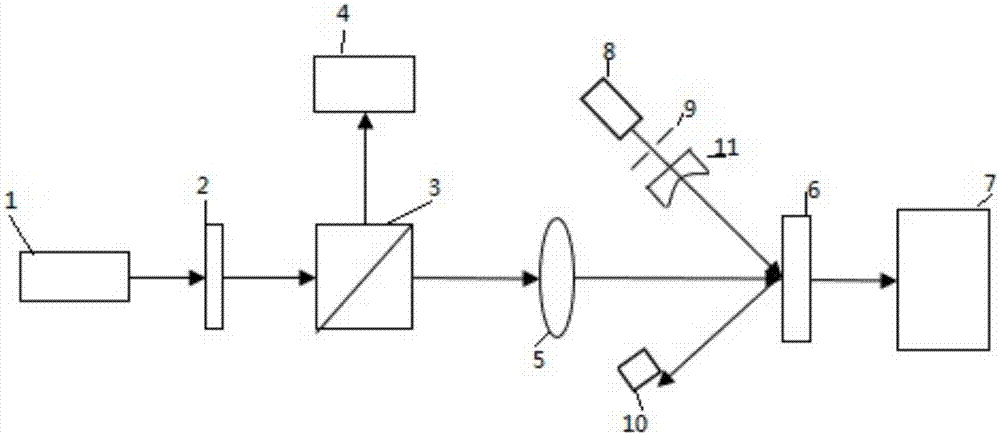
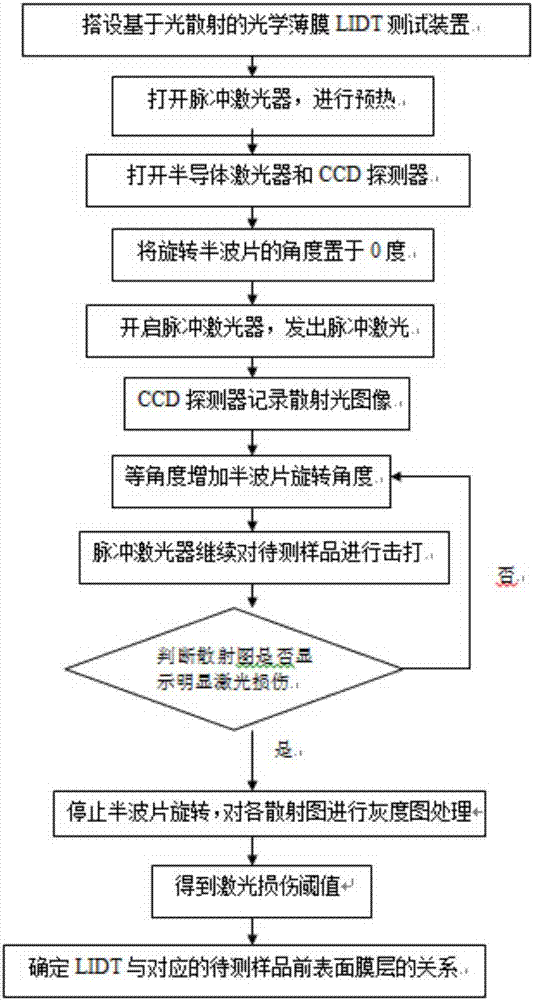
Optical thin film LIDT (laser induced damage threshold) testing device and method based on light scattering
InactiveCN107271403AAccurate measurement accuracyImprove stabilityScattering properties measurementsTesting optical propertiesOptical thin filmPrism
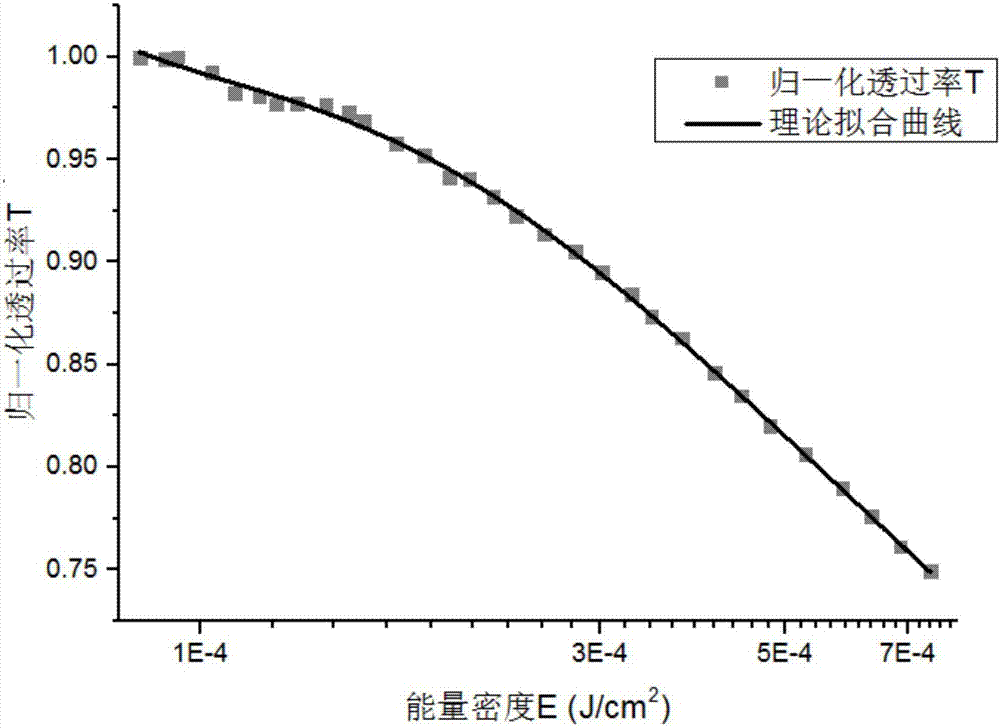
The invention discloses an optical thin film LIDT (laser induced damage threshold) testing device based on light scattering. The device comprises a pulsed laser, a half wave plate, a Glan-Taylor prism, a convergent lens and a to-be-tested sample which are sequentially arranged along the co-optical axis, and the optical axis is a pulse beating optical axis; the device further comprises a semiconductor laser, a beam expander and an aperture diaphragm which constitute a co-optical axis testing light path, the optical axis is a testing optical axis, the included angle alpha is formed between the testing optical axis and the pulse beating optical axis, and testing light emitted by the semiconductor laser irradiates the front surface of the to-be-tested sample after passing through the beam expander and the aperture diaphragm, is scattered by the front surface of the to-be-tested sample and is received by a CCD detector; pulse laser emitted by the pulsed laser passes through the half wave plate to reach the Glan-Taylor prism and is reflected and transmitted by the Glan-Taylor prism, and transmission light is converged to the to-be-tested sample by the convergent lens. The device is more stable and efficient, suitable to be used and set up in an optical plant, low in cost and convenient to operate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Acousto-optic tunable filter parameter calibration system
InactiveCN101718621BEasy to operateReduce human errorTesting optical propertiesAxis–angle representationGrating
Acousto-optic Tunable Filter (AOTF) parameter calibration system, which consists of control and processing computer, grating monochromator, mercury-argon gas light source, optical path part, precision electronically controlled turntable, high-precision RF driver, photoelectric It consists of multiplier tube, CCD light intensity distribution detector, and precise electronically controlled translation guide rail. The optical path part is mainly composed of reflector, half mirror, Glan Taylor prism, collimating lens, diaphragm and focusing lens. The calibration system of the invention is complete and has high calibration accuracy, and can automatically calibrate parameters such as AOTF beam incident angle, off-axis angle θa, angular aperture δ, wavelength response function, wavelength-frequency tuning relationship, deflection angle β, etc. Index inspection of AOTF products, research on AOTF spectra and imaging characteristics, and also provide technical parameters for the integration of AOTF spectrometers.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
All-optical switch based on rubidium atomic filter and its method
InactiveCN103996966BClear design principlesSimple structureLaser detailsOptical elementsPolarizerPrism
The invention discloses an all-optical switch based on a rubidium-atom optical filter and a method thereof. The all-optical switch based on the rubidium-atom optical filter comprises an alkali-metal rubidium-atom glass air chamber with a V-type energy level structure, two Glan-Taylor polarizers with the polarization directions perpendicular to each other and a stable magnetic field source used for generating a magnetic field with uniform intensity for the alkali-metal rubidium-atom glass air chamber, wherein the alkali-metal rubidium-atom glass air chamber, the two polarizers with the polarization directions perpendicular to each other and the stable magnetic field source form a standard atomic optical filter. The all-optical switch based on the rubidium-atom optical filter further comprises a 420 nm laser device serving as a control part of the all-optical switch of the atomic optical filter and a 780 nm laser device serving as a performance testing and application wavelength testing part of the all-optical switch of the rubidium-atom optical filter. The all-optical switch based on the rubidium-atom optical filter has the advantages of being clear in design principle, simple in structure, easy to manufacture, good in switching performance, stable in operation and long in service life.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
Light beam displacement amplification technology
PendingCN112710387AUsing optical meansPhotometry using electric radiation detectorsLight spotEngineering
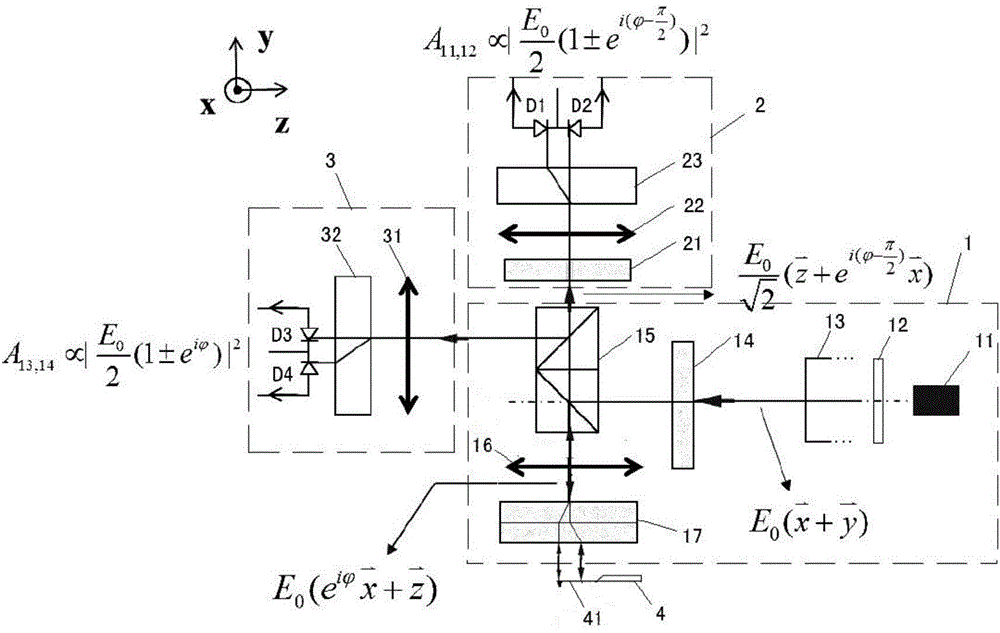
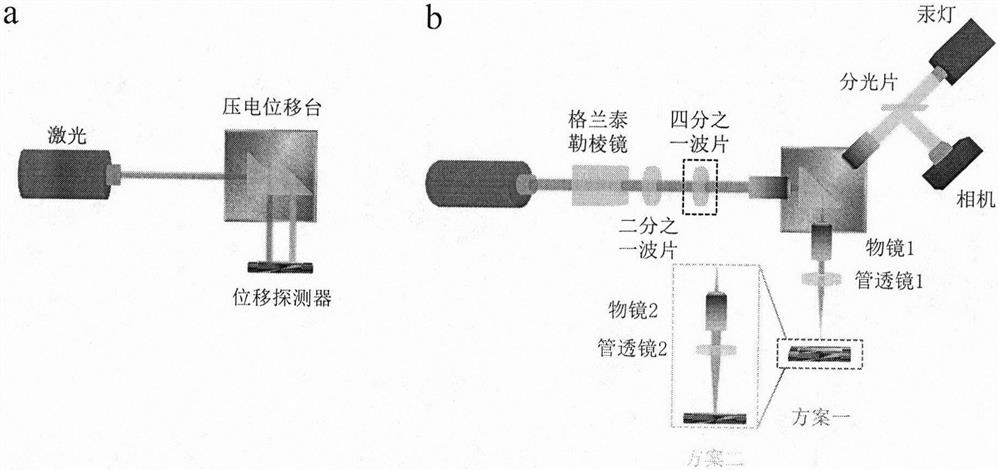
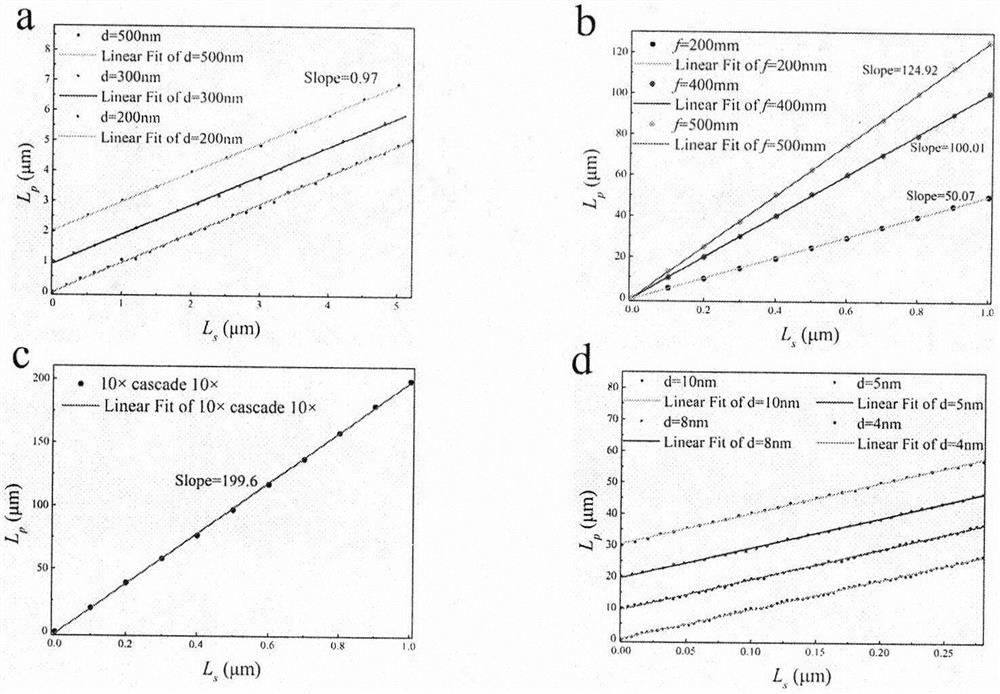
A light beam displacement amplification technology is based on an optical objective lens imaging principle and a high-sensitivity position sensor, displacement can be amplified by 200 times at most, the theoretical displacement resolution reaches 1 nm, incident light spots are converged by an objective lens, the light spots are smaller than 5 microns, and micro-area materials such as mechanical stripping two-dimensional materials can be measured. Incident light spots are polarized by the Glan-Taylor prism, the half-wave plate and the quarter-wave plate, then irradiate a sample and interact with the sample to generate transverse photon spin Hall effect displacement and longitudinal Goos Hansen displacement, the displacement is amplified by the collection objective lens, and the amplified displacement is measured by the position sensor. The amplification factor is only related to the multiple of the objective lens and the focal length of the corresponding tube lens, the real displacement of the light spot in the sample can be obtained by calculating the amplification factor, multiple collection objective lenses can be cascaded for multiple amplification; wherein the amplification factor is the product of the amplification factors of each objective lens and is constant once determined. Therefore, the light beam displacement measurement technology is a direct measurement technology.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
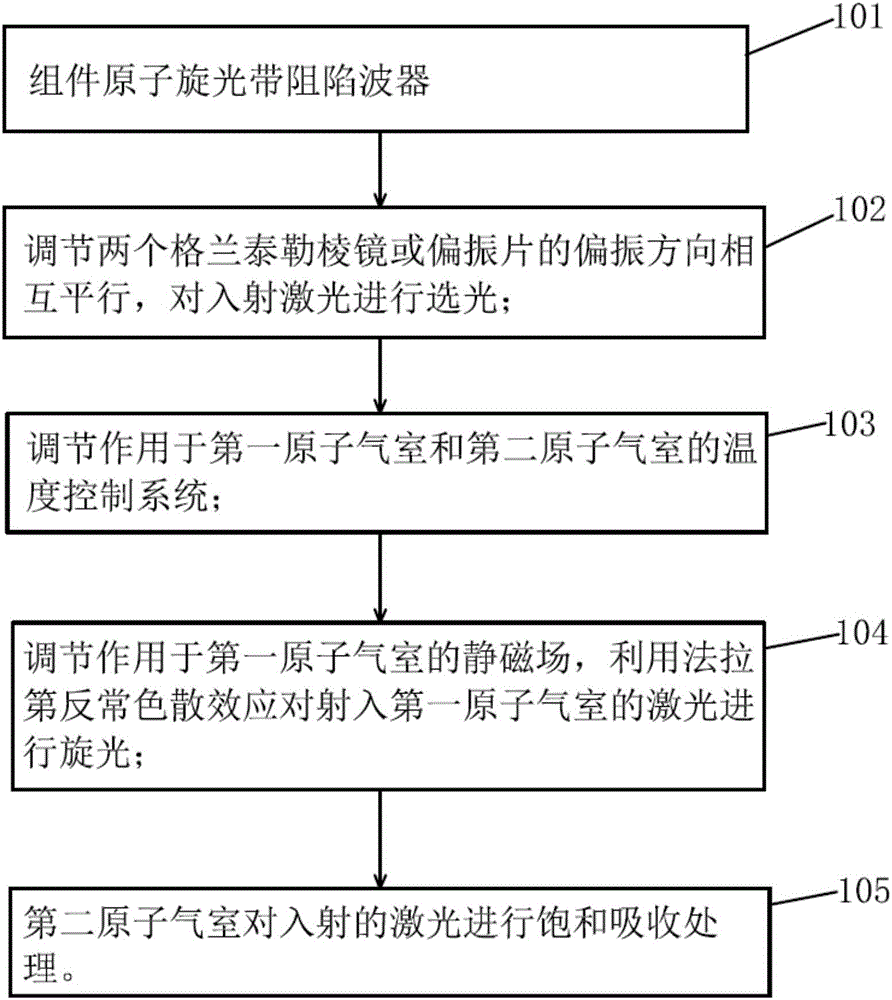
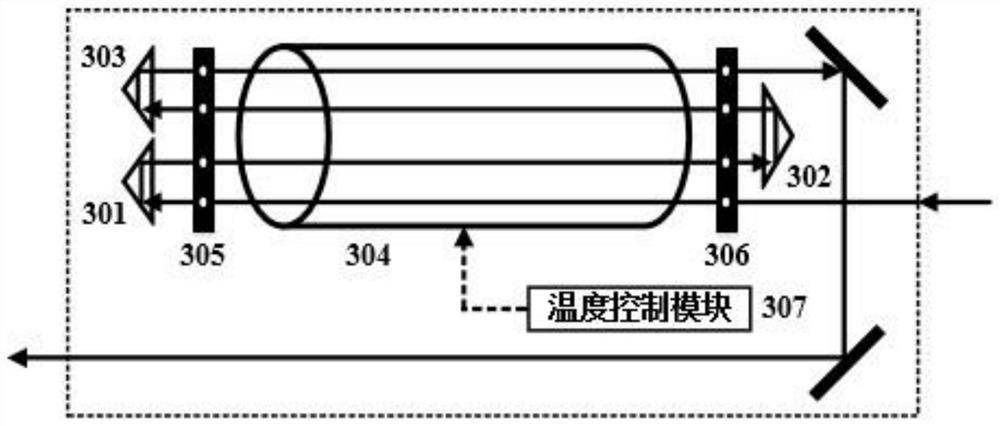
Atomic optical rotation type band-rejection trap and application method thereof
PendingCN106444098AHigh rejection ratioImprove performanceNon-linear opticsTwo temperatureWavelength
The invention relates to an atomic optical rotation type band-rejection trap. The atomic optical rotation type band-rejection trap comprises a first atomic gas chamber filled with atomic gas, two Glan-Taylor prisms, a stable static magnetic field source, a second atomic gas chamber filled with atomic gas and two temperature control circuit systems, wherein the two Glan-Taylor prisms are parallel to each other in the polarization directions of two beams of light and are disposed on two sides of the first atomic gas chamber, and gas atoms in the first atomic gas chamber and laser can have sufficient Faraday optical rotation effect under the condition of an external magnetic field; the stable static magnetic field source generates an even static magnetic field for the first atomic gas chamber, and the magnetic field direction is parallel to the laser propagation direction; the second atomic gas chamber and the laser can have saturated absorption effect; the two temperature control circuit systems act on the first atomic gas chamber and the second atomic gas chamber respectively. The invention further discloses an application method of the atomic optical rotation type band-rejection trap. The atomic optical rotation type band-rejection trap and the application thereof have the advantages that narrow-band band-rejection characteristics on specific wavelengths, high transmittance beyond a rejection band and a high rejection ratio in the rejection band are obtained through controllable Faraday anomalous dispersion effect and saturated absorption effect at the atomic transition wavelength position.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV CITY COLLEGE
Iodine molecular optical clock based on pulse-modulated broad-spectrum comb laser and its control method
ActiveCN111413859BImprove effective utilizationImprove signal-to-noise ratioApparatus using atomic clocksPhotodetectorPower control system
The invention relates to an iodine molecular optical clock based on a pulse-modulated broad-spectrum comb-shaped laser and a control method. The power control system of the iodine molecular optical clock generates a pulse modulation signal and transmits it to the laser system to generate a pulse signal, which is isolated from the optical feedback of the rear optical path by the isolator, and the isolator is connected to the first half-wave plate and the first polarization beam splitter in turn; The frequency-stabilizing optical path is the second half-wave plate and the second polarization beam-splitting prism connected in sequence; after the second polarization beam-splitting prism, it is divided into two beams: the beam with stronger light intensity is used as the pump laser in turn through the Glan-Taylor prism, the third half-wave beam The light beam and the electro-optical phase modulator are reflected by the third polarization beam splitter to the optical path multiplication system; the beam with weaker light intensity is used as the detection laser optical path multiplication system and the third polarization beam splitter, and is input to the laser phase detector after being received by the high-speed photodetector And high-speed servo feedback control circuit to generate the servo signal of the power control system.
Owner:PKU HKUST SHENZHEN HONGKONG INSTITUTION
Femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectrum generation and acquisition system based on spatiotemporal shaping
ActiveCN110940659BImprove experimental operation efficiencyEnables continuous linear regulationAnalysis by thermal excitationFemto second laserSpectroscopy
The invention discloses a femtosecond laser-induced breakdown spectrum generation and acquisition system based on space-time shaping, and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. A Bessel light beam with a long focal depth is used for exciting material plasmas after being shrunk; under the condition that focusing is not carried out, plasma excitation with the same energy density is achieved at different height positions of a sample, the process of single-point independent focusing is omitted, possible human and machine errors in each time of focusing operation are avoided, and the stability, repeatability and collection efficiency of spectrum collection are guaranteed. The system can adjust parameters of the conical lens and the beam shrinking lens group to obtain Bessel regions with different focusing lengths, and a device suitable for samples with different height change ranges is designed according to individual requirements. When a femtosecond laser Bessel beam is adopted to excite plasmas on the surface of a rough sample, the combination of a half-wave plate and a Glan-Taylor prism in the system realizes the continuous linear adjustment of pulse energy,and realizes the sample detection and analysis under the nearly lossless condition.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
High precision linear polarization radiometer
InactiveCN105043551AReduce system errorReduce random errorLight polarisation measurementRadiometerOptoelectronics
The invention discloses a high precision linear polarization radiometer and a use method thereof. The high precision linear polarization radiometer comprises a filter wheel. The filter wheel is connected with a motor. A position sensor is arranged on one side of the filter wheel. A window film, an aperture diaphragm and a Glan-Taylor prism are successively arranged from top to bottom along the incident light direction just above the filter wheel. A photoreceptor system is arranged just below the filter wheel. The photoreceptor system comprises a parabolic reflector. A field diaphragm, a focusing lens and a dual-color detector are successively arranged on the reflection light path of the parabolic reflector. The dual-color detector and the signal output end of the position sensor are connected with a control acquisition system. Compared with a traditional polarization radiometer, the high precision linear polarization radiometer provided by the invention does not require the advantage of polarization degree calibration, and can be theoretically used as the carrier of a standard linear polarization source in the form of an instrument.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com