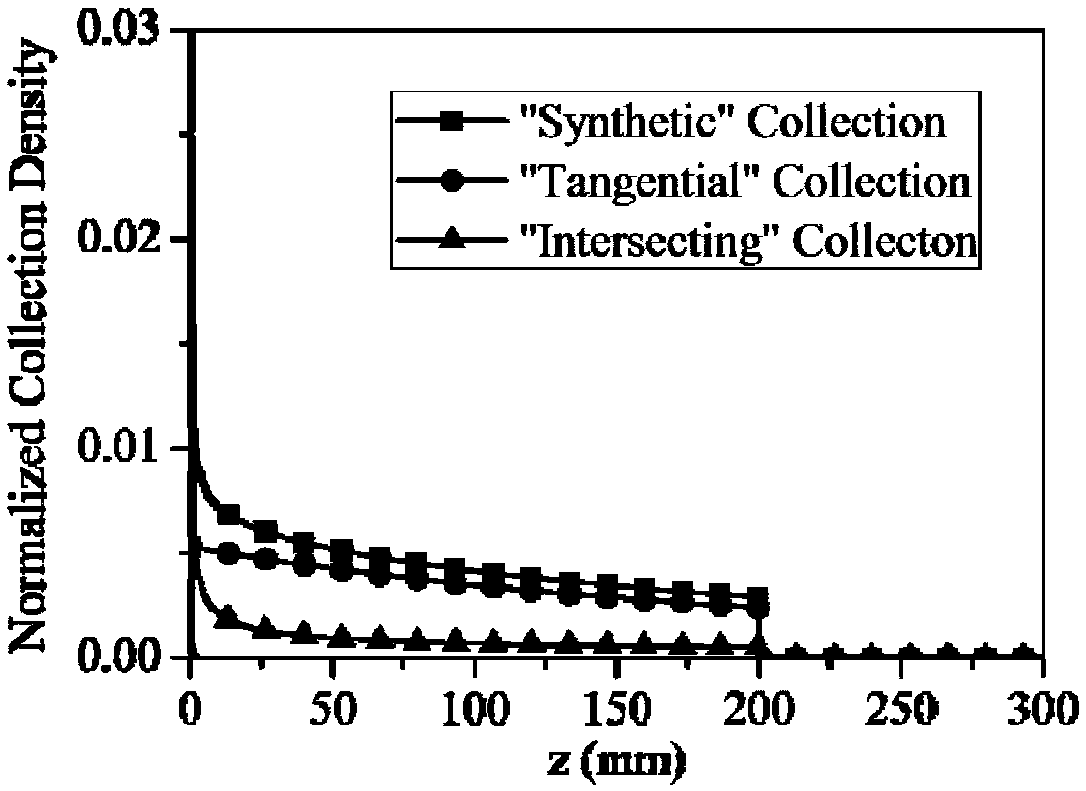
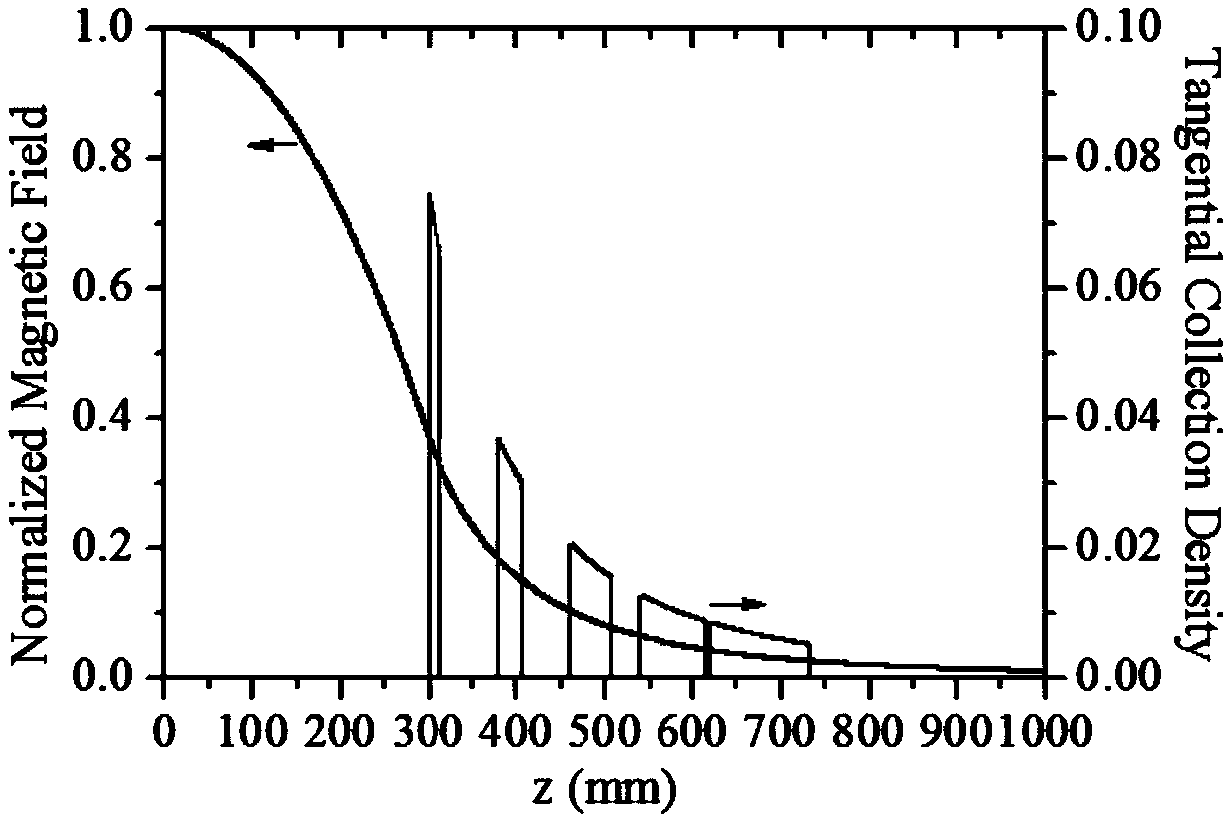
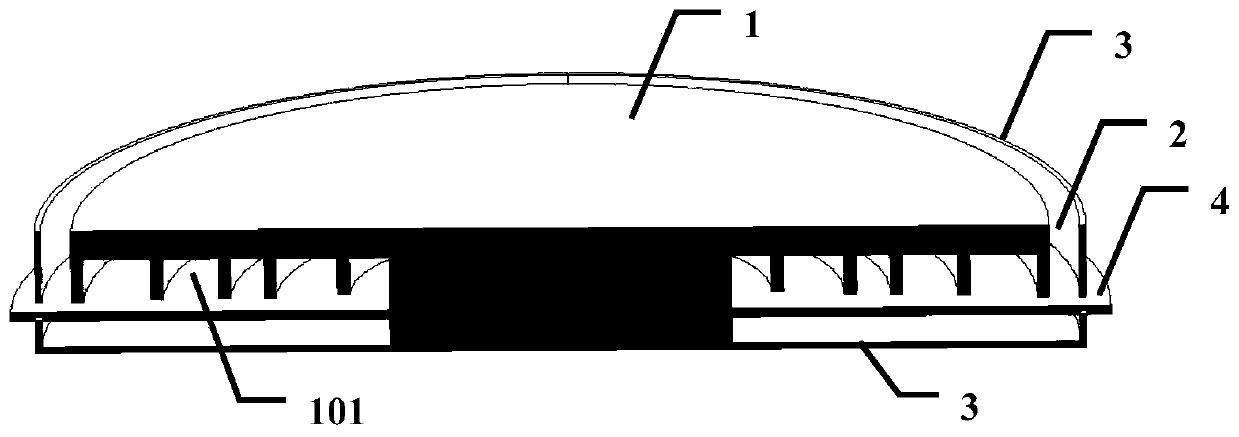
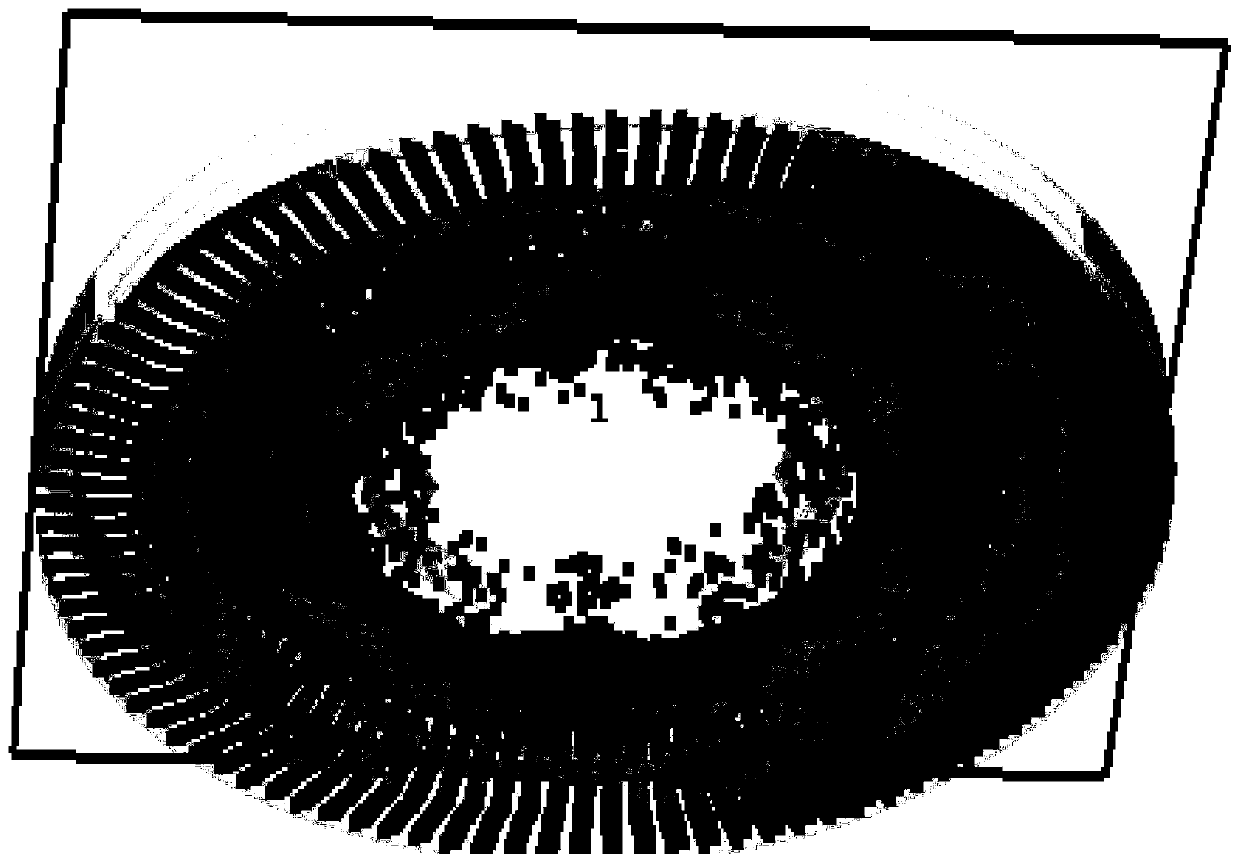
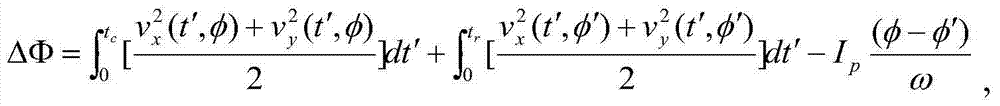Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Electron motion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Programmable motion-sensitive sound effects device
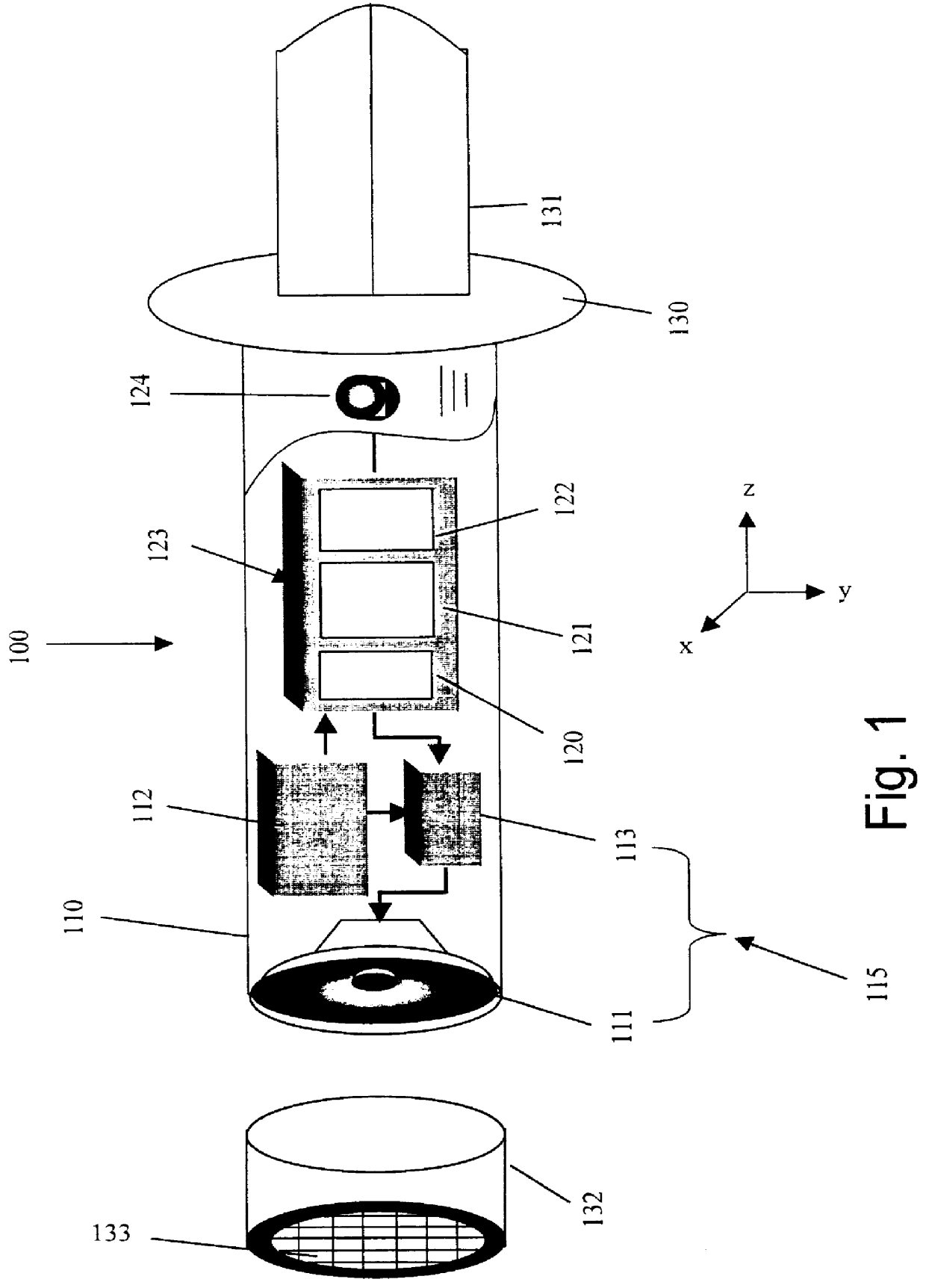
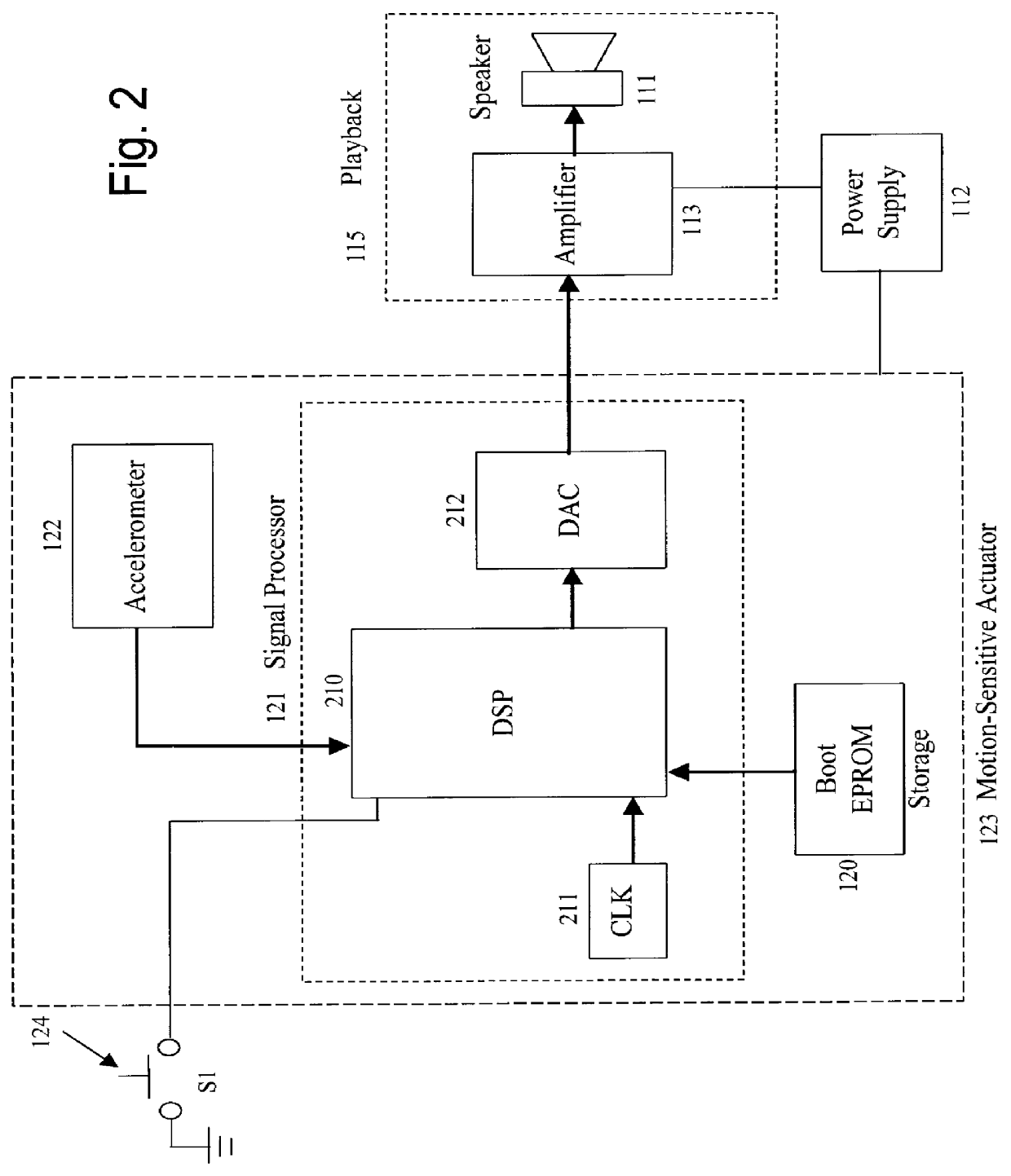
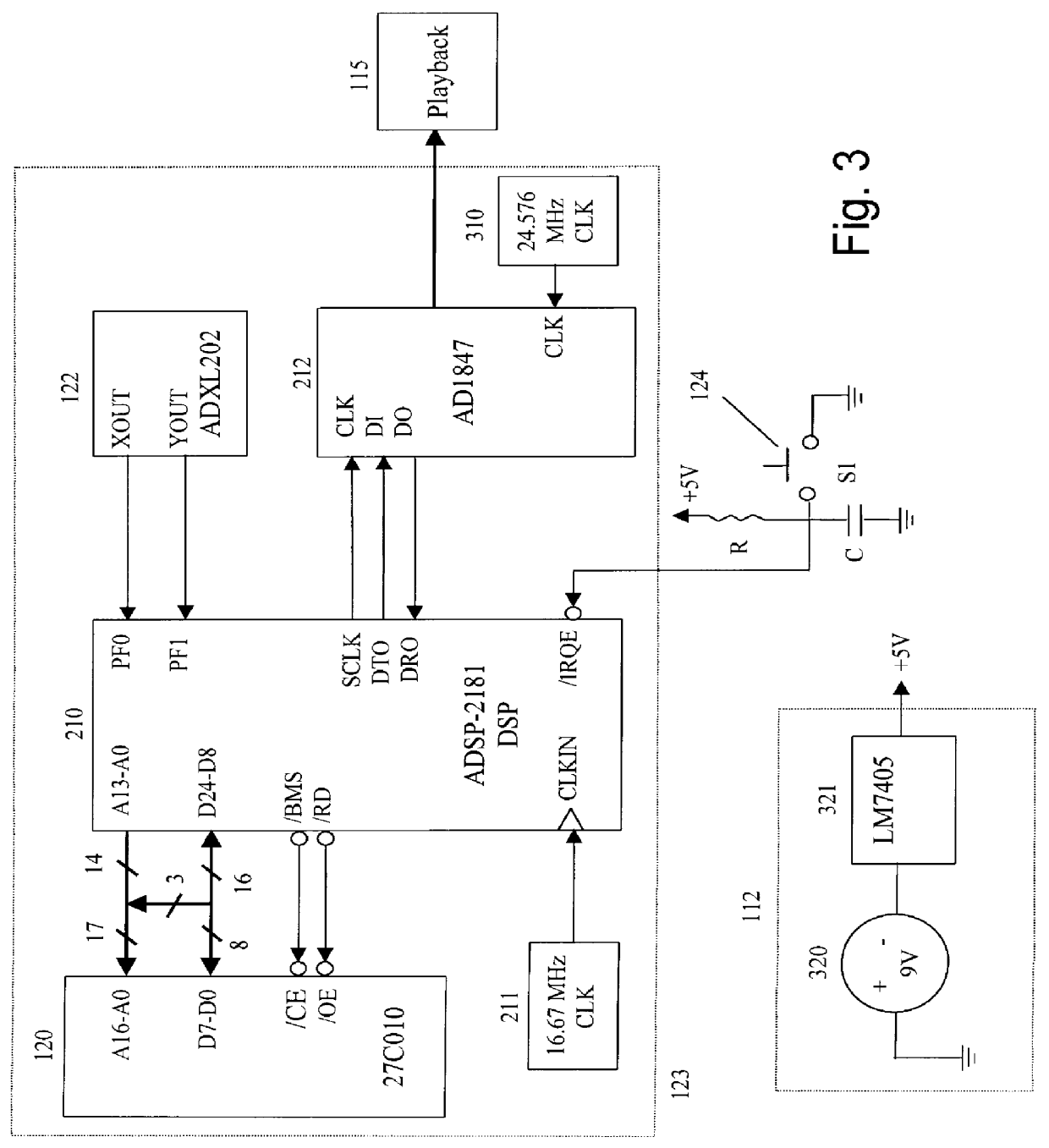
A programmable sound effects device which utilizes a motion-sensitive mechanism for selecting unique sound effects. The device is comprised of an electronic motion-sensitive actuator, a sound effect storage media for storing a plurality of predetermined sound effects, and a playback mechanism for audibly emitting the motion-activated sound effects. This device is designed to be used with amusement and entertainment type products such as toys, games, dolls, and props, with exemplary uses in toy swords, drumsticks, magic wands, and the like. A preferred embodiment is comprised of a unit which is physically incorporated into the handle of a toy sword. As the user moves the toy sword in a predefined manner, the motion-sensitive actuator senses the motion and plays out a plurality of unique sound effects as a function of the user's movements. The motion-detection algorithm which triggers the different sound effects is programmable. In another embodiment, the device is contained within a single housing unit that is worn on the user's body. This embodiment is well suited for many toys, props, games, and the like that do not have any sound effects capability but would benefit from such capability.
Owner:RPX CORP
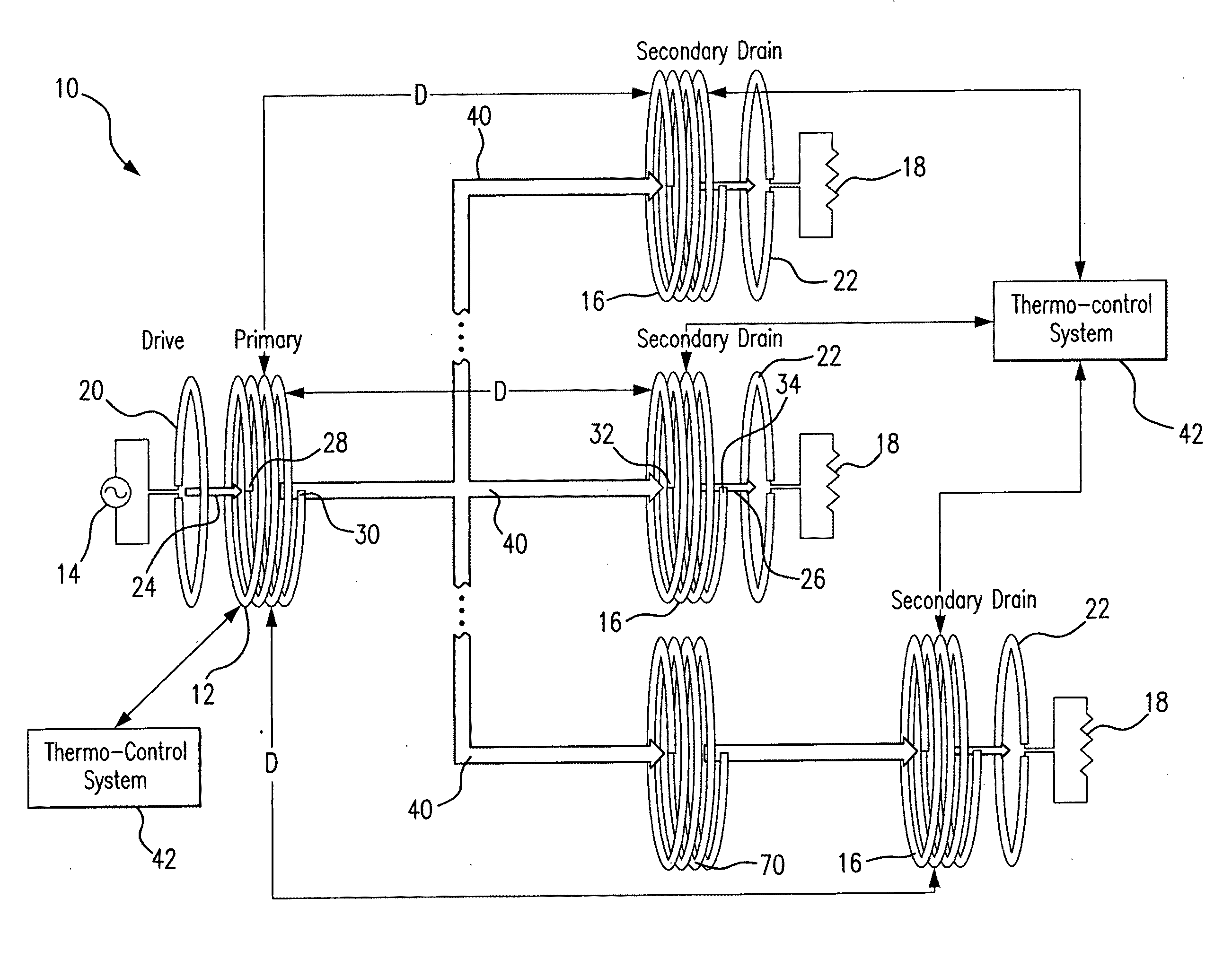
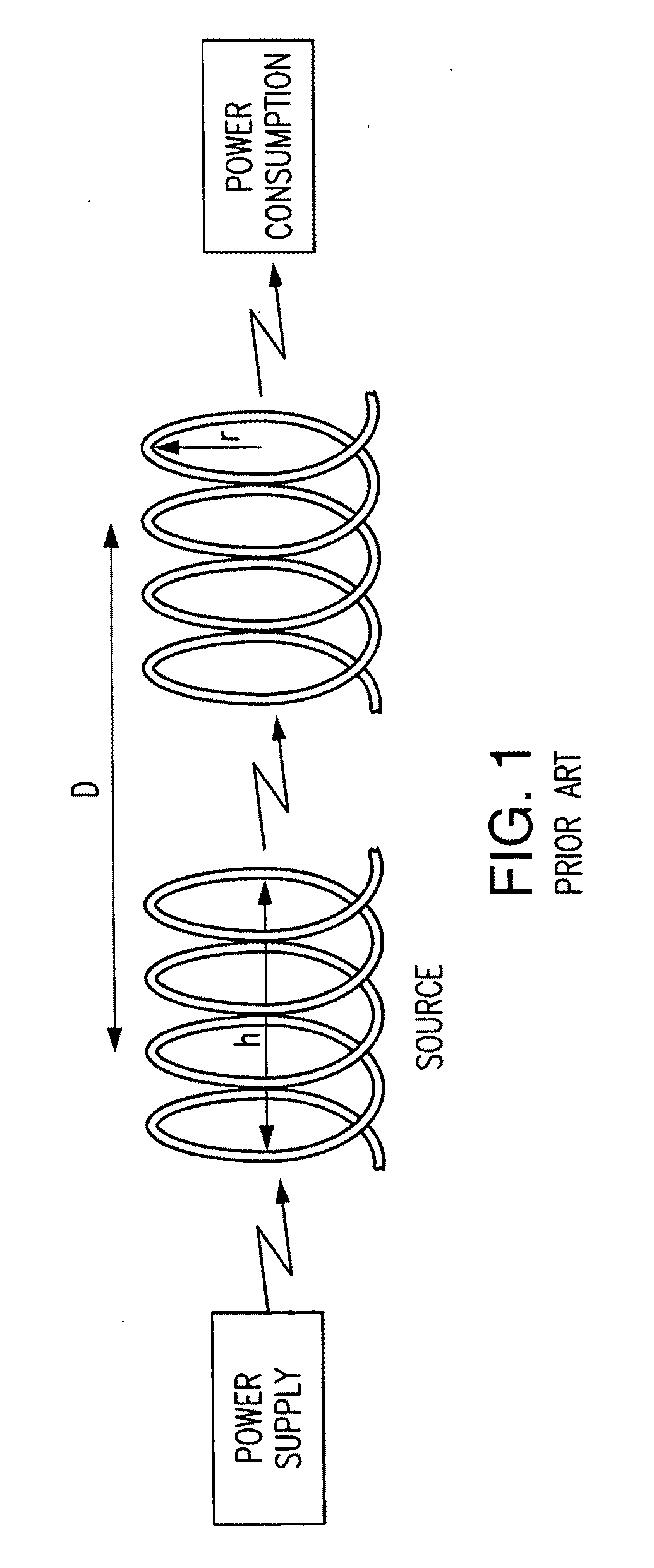
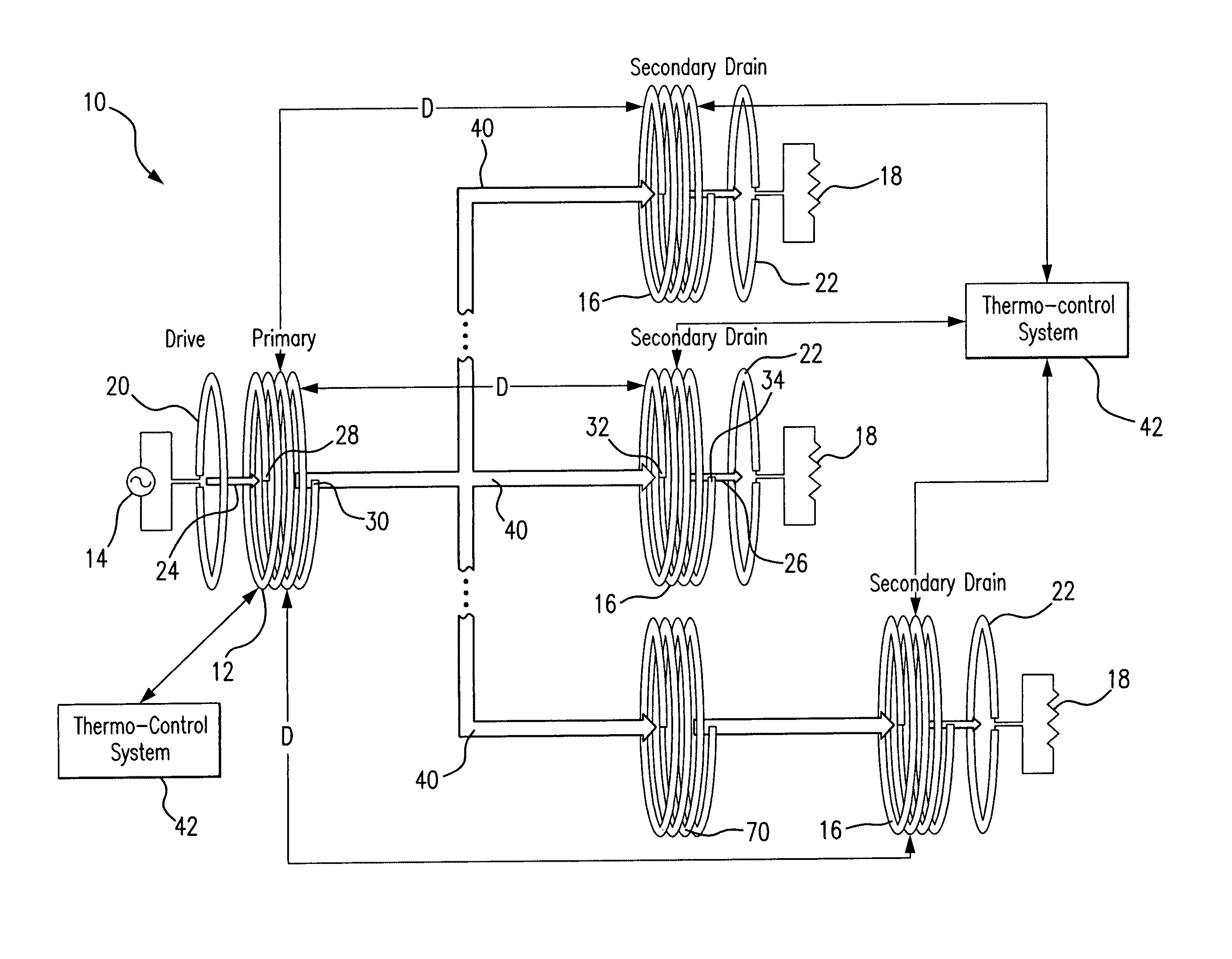
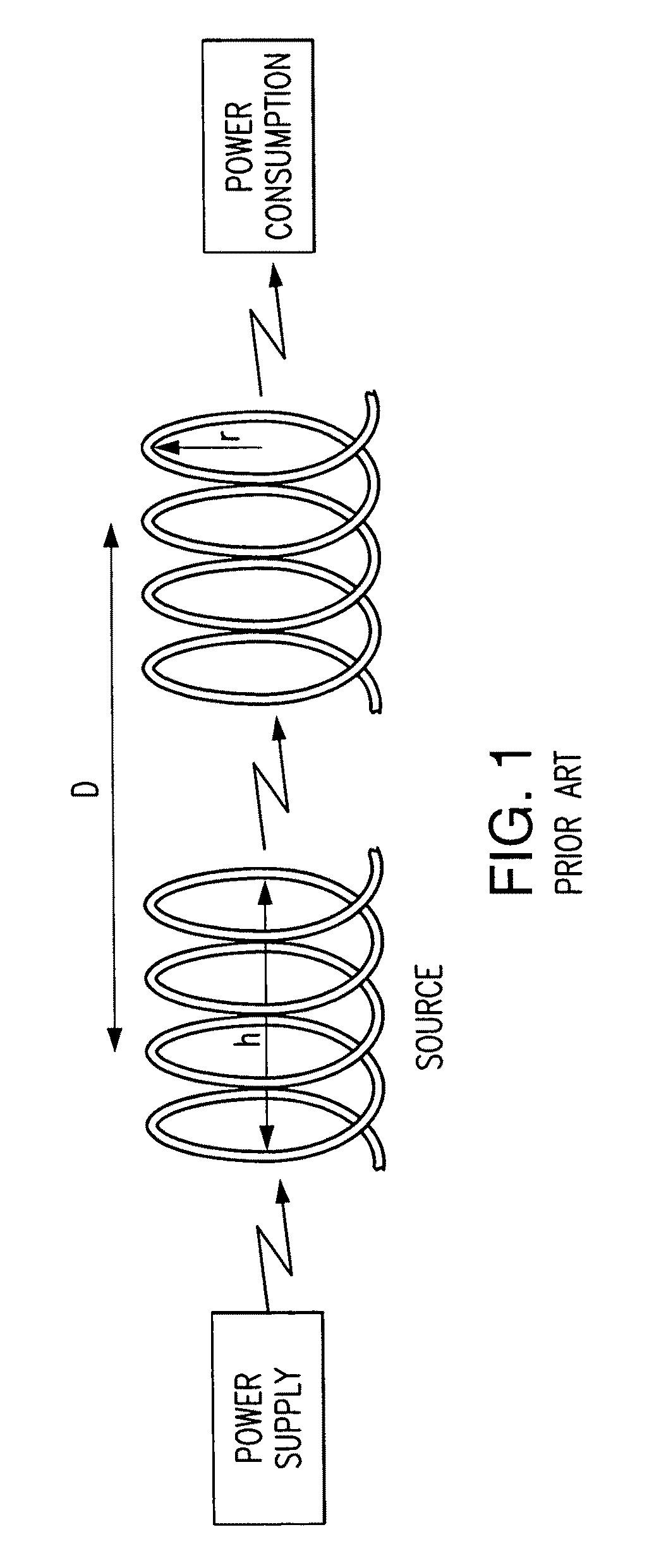
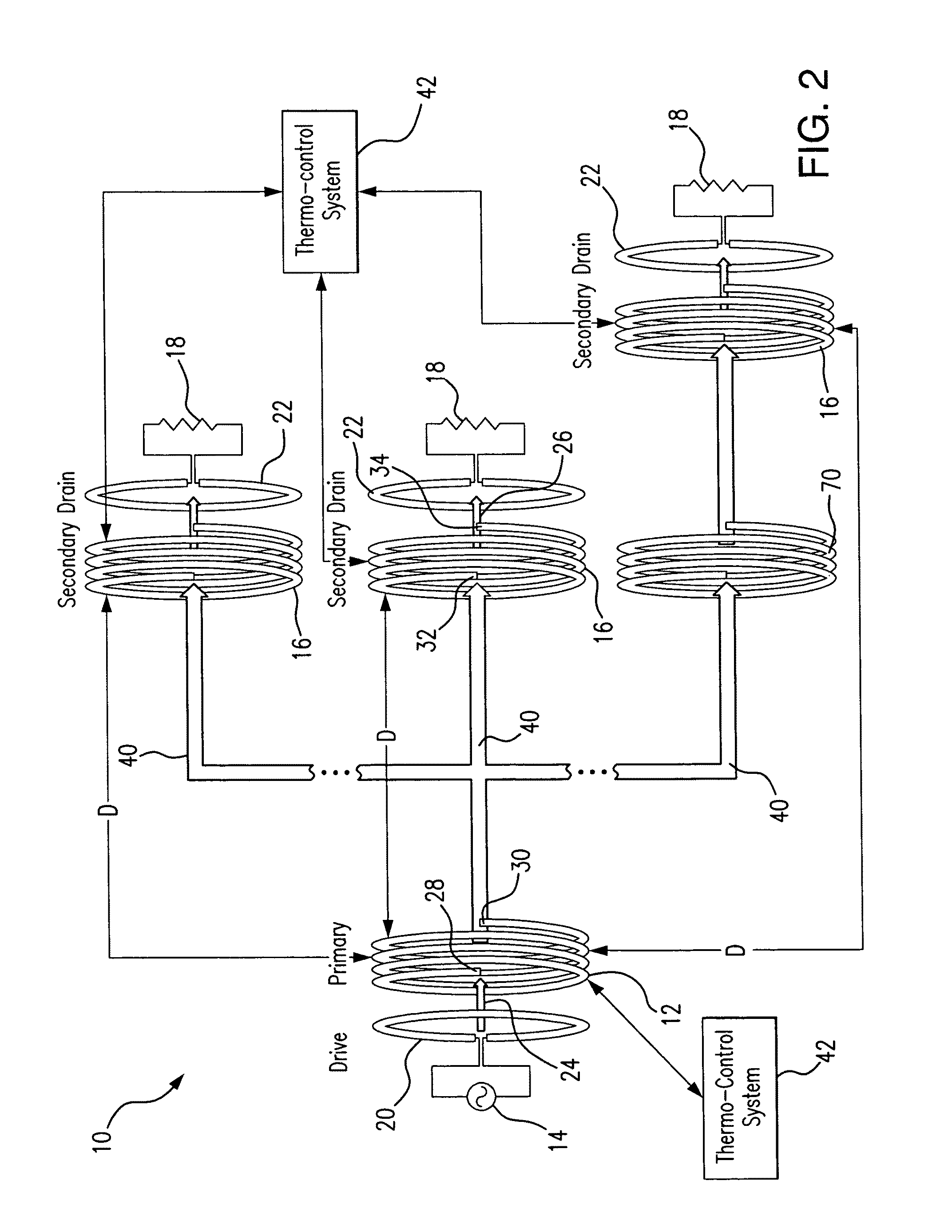
Method and system for long range wireless power transfer
ActiveUS20120010079A1Improve power transfer efficiencyReduce eliminateDc network circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemLow dissipationCapacitance
A wireless energy transfer system includes a primary and one (or more) secondary oscillators for transferring energy therebetween when resonating at the same frequency. The long range (up to and beyond 100 m) efficient (as high as and above 50%) energy transfer is achieved due to minimizing (or eliminating) losses in the system. Superconducting materials are used for all current carrying elements, dielectrics are either avoided altogether, or those are used with a low dissipation factor, and the system is operated at reduced frequencies (below 1 MHz). The oscillators are contoured as a compact flat coil formed from a superconducting wire material. The energy wavelengths exceed the coils diameter by several orders of magnitude. The reduction in radiative losses is enhanced by adding external dielectric-less electrical capacitance to each oscillator coil to reduce the operating frequency. The dielectric strength of the capacitor is increased by applying a magnetic cross-field to the capacitor to impede the electrons motion across an air gap defined between coaxial cylindrical electrodes.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
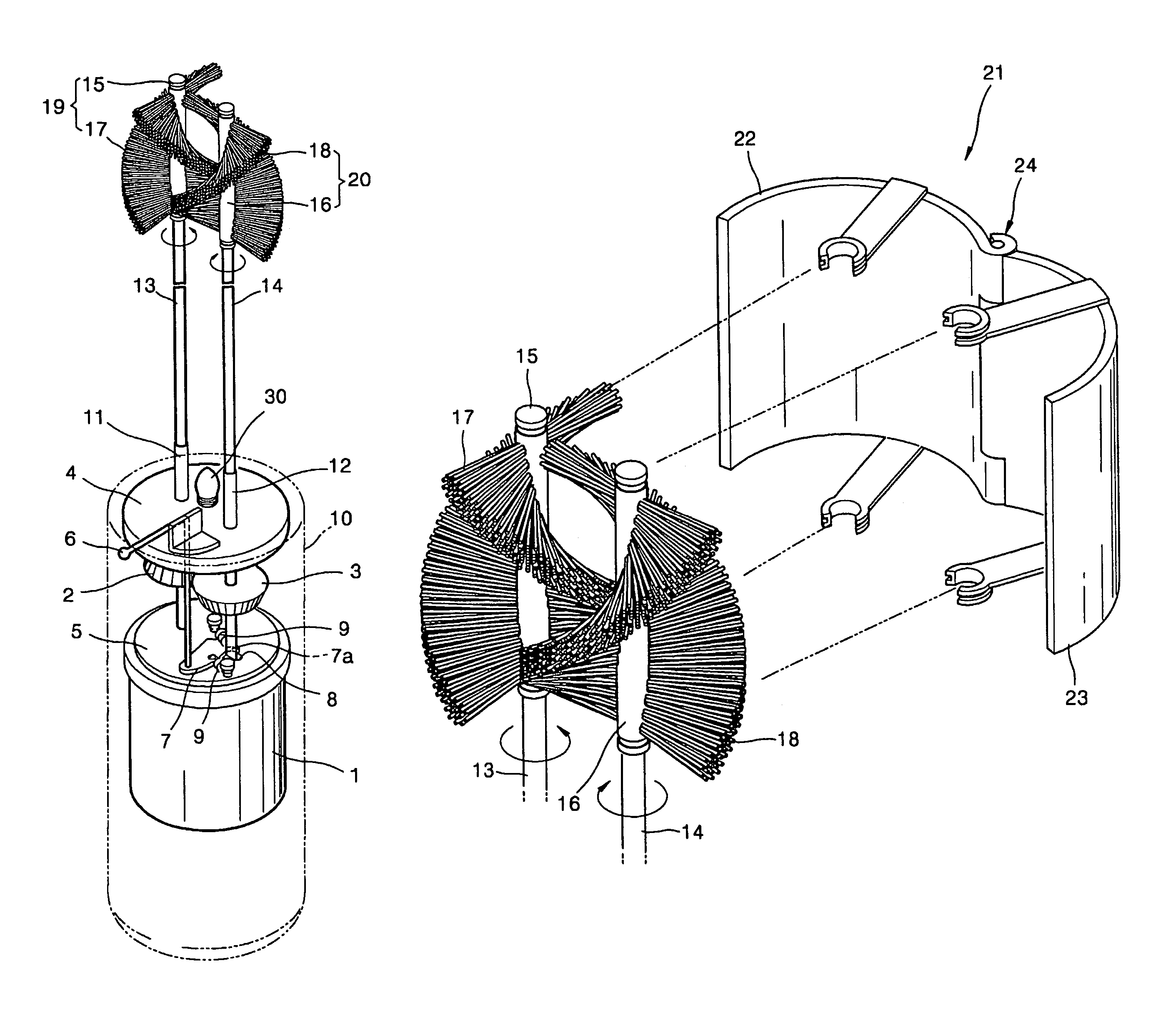
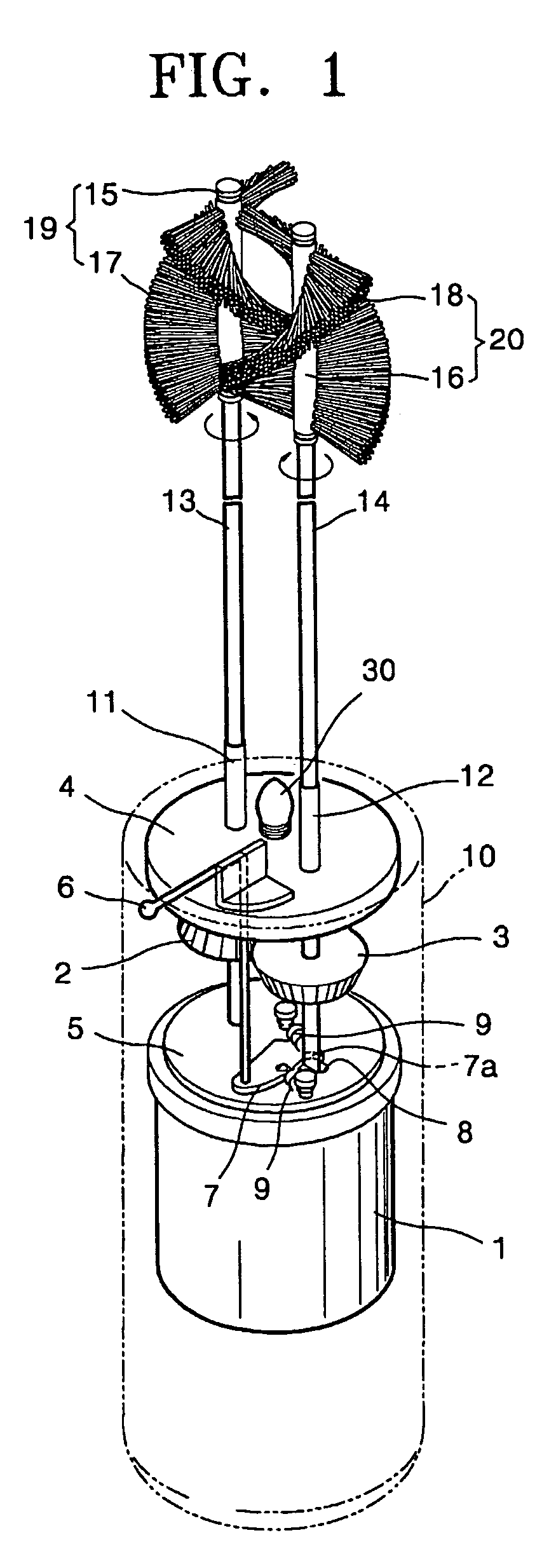
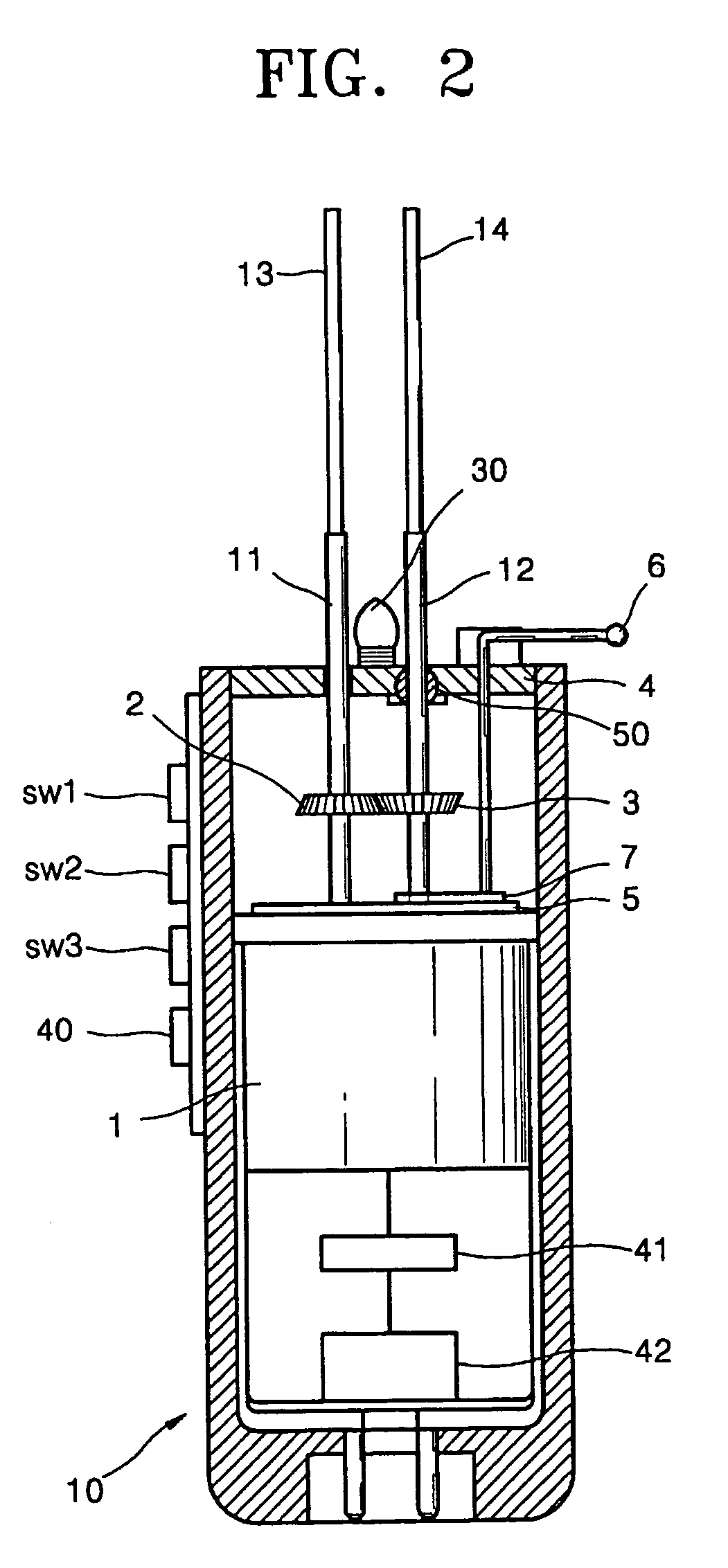
Electron-motion toothbrush
An electro-motion toothbrush includes a case containing a driving unit. First and second toothbrush support rods are flexible and rotated by the driving unit in directions opposite to each other. First and second toothbrush heads are connected to upper ends of the first and second toothbrush support rods, respectively. First and second toothbrush bristles are implanted along a lengthwise direction of the first and second toothbrush heads, interweave with each other, and not to cross each other during operation.
Owner:CHOI JOO A +1
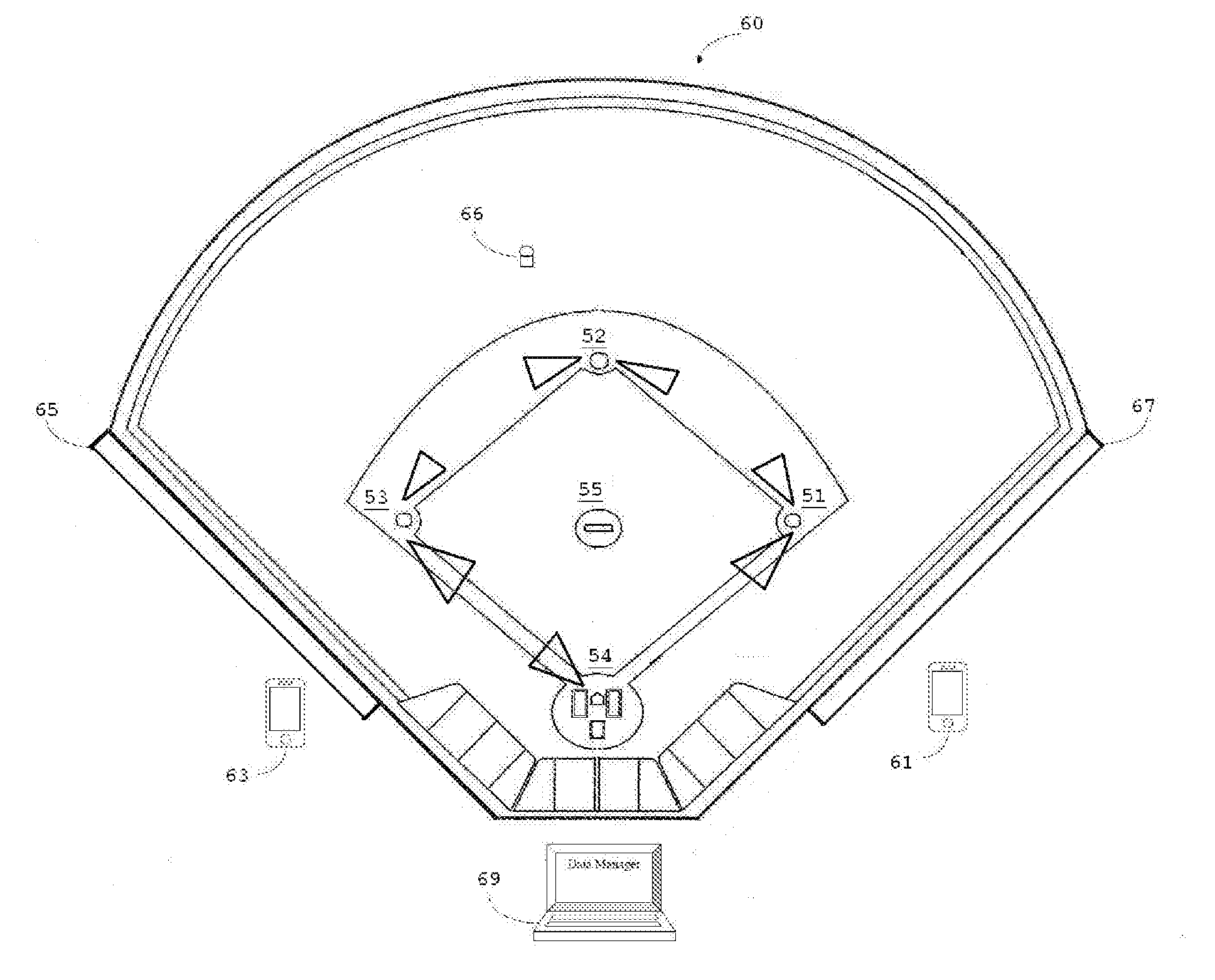
Arena baseball game system
Arena Baseball Game system method of play includes base excessive force, no collision contact slide zones and describes a protective helmet apparatus for use by baseball fielders. The protective sport television or radio audio device means of communication equipped with display, GPS, infrared scan and sensors to monitor performance and physiological parameters. In operation one or more infrared sensor sits against skin of a user to measure his or her heart rate. In response to oscillation translation and / or rotation of the electronic sport device, portions of forces induced by the mass are transferred to the piezoelectric elements. Electrical energy output by these piezoelectric elements is received in a power controller and can be applied to the battery as self charging.
Owner:JENNINGS JAMES EDWARD
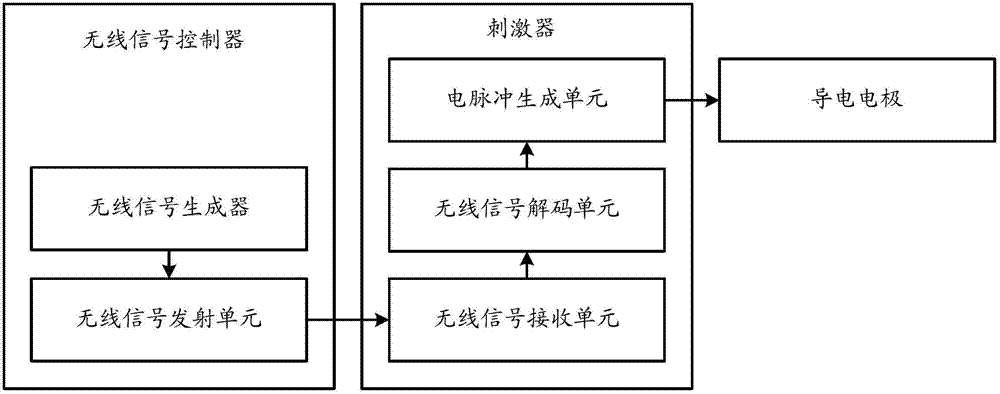
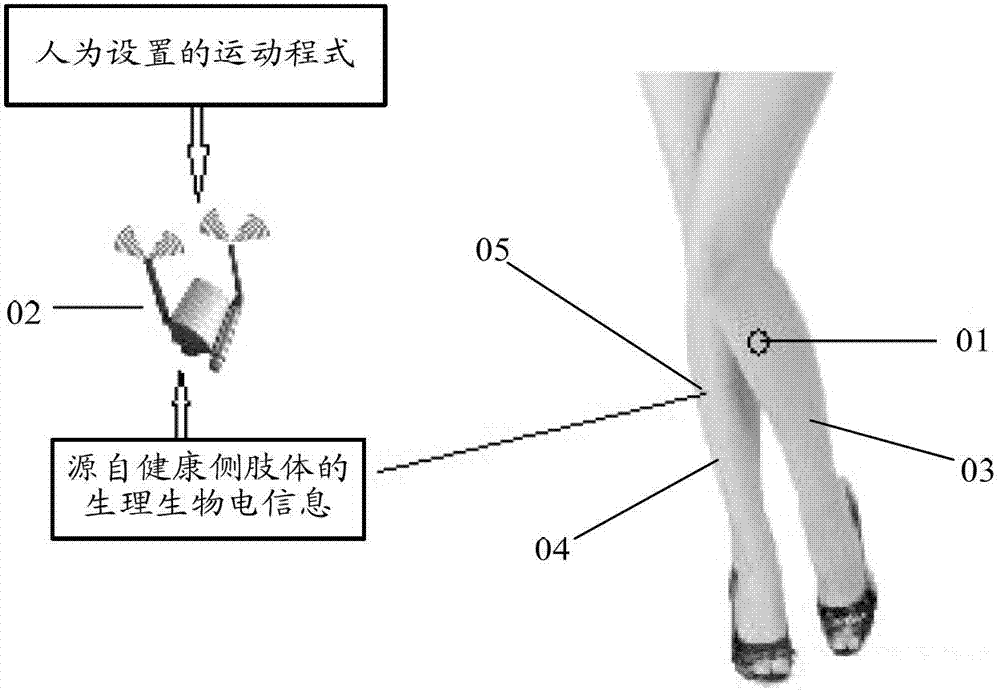
Muscle restoration system for paralyzed limbs
ActiveCN102872533AReduce waste degradationTake advantage ofArtificial respirationNODALMedical equipment
The invention relates to the field of medical equipment, and discloses a muscle restoration system for paralyzed limbs. The limbs of a patient with upper motor neuron paralysis are paralyzed due to denervation, but a lower motor neuron, a muscle and a motor end plate of the patient with upper motor neuron paralysis are not directly damaged in spite of tissue or cells and can completely receive stimulation, conduct information and do contraction motion; a nerve can conduct bioelectricity, receive electric stimulation and conduct an electric signal; and manual electron motion control is performed at the terminal of a nerve motion conduction path, namely a muscle door node of which the nerve enters the muscle, an external wireless signal controller remotely controls a stimulator in a body through wireless signal transmission, the muscle is directly stimulated by stimulation sent by the stimulator and starts doing contraction motion after receiving stimulation information, and the limbs are driven to act, so that the paralyzed limbs move, and the requirements of training rehabilitation and self-care are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI EAST HOSPITAL
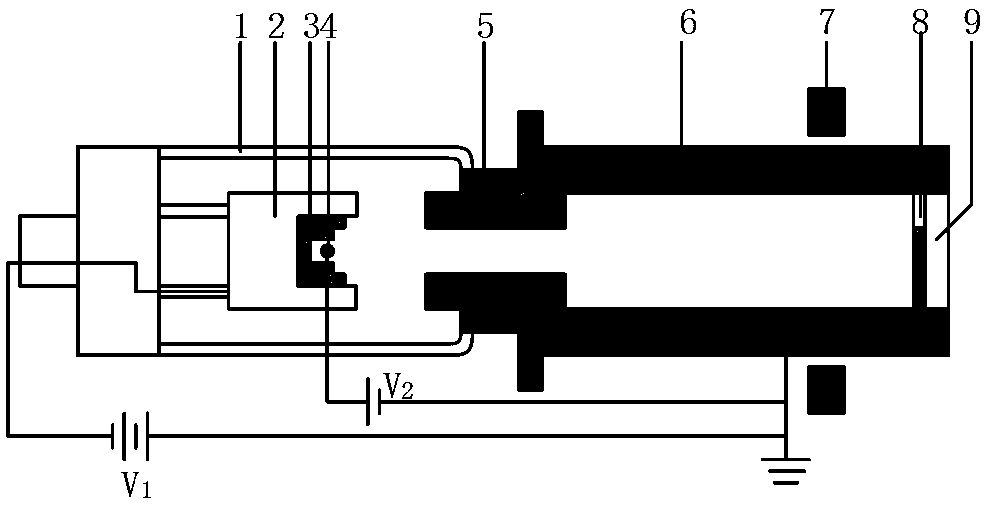
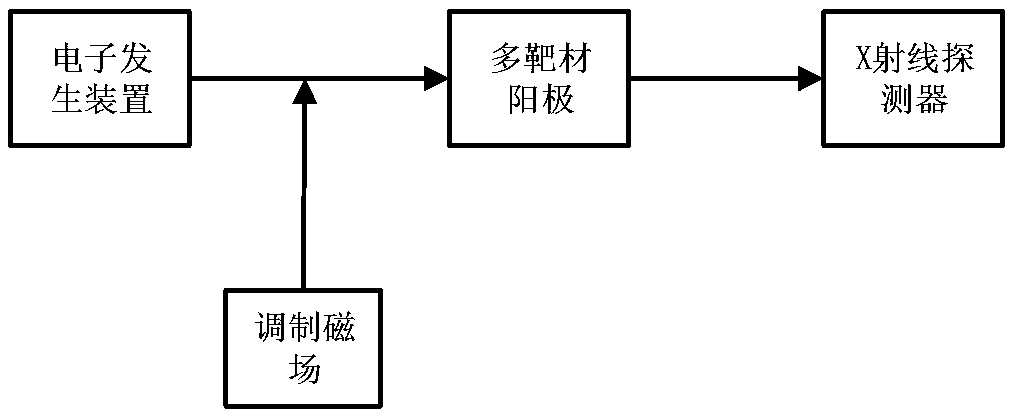
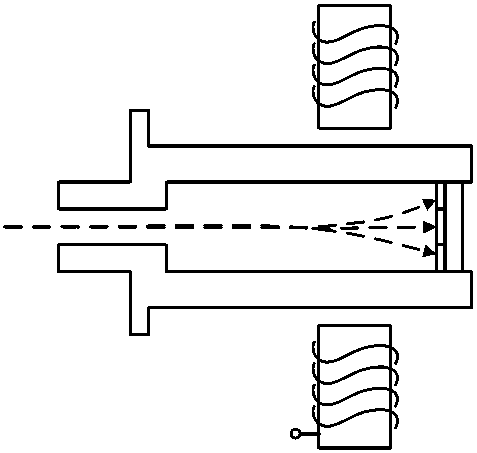
Magnetic field modulated multi-target X-ray source for spatial X-ray communication
ActiveCN108470668AA large amount of communication informationThe amount of communication information increasesX-ray tube structural circuit elementsX-ray tube electrodesX-rayHigh pressure
A magnetic field modulated multi-target X-ray source for spatial X-ray communication comprises a cathode structure, a focusing groove, an electron emission source, a glass shell, a Kovar alloy ring, afocusing electrode, a modulation electromagnetic device, a multi-target metal anode, and a transmission window. The cathode is connected with a negative high voltage, the electron emission source isdisposed in the focusing groove, the glass shell and the focusing electrode are in tight coupling by the Kovar alloy ring, the modulation electromagnetic device is disposed near the multi-target metalanode, the multi-target metal anode is grounded, and one side is facing a focus channel and the other side is plated on the transmission window layer. The magnetic field modulated multi-target X-raysource utilizes a fast-responding high-frequency modulation magnetic field, changes the electron motion trajectory to bombard the multi-target metal anode, excites characteristic X-rays of different energies, and uses characteristic X-rays of different energies as signal transmission carriers to solve the problem that the existing intensity modulation X-ray source technology is less in loading symbol signal and low in communication rate. The magnetic field modulated multi-target X-ray source has the advantages of multiple types of loading symbol signals and large communication rate.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
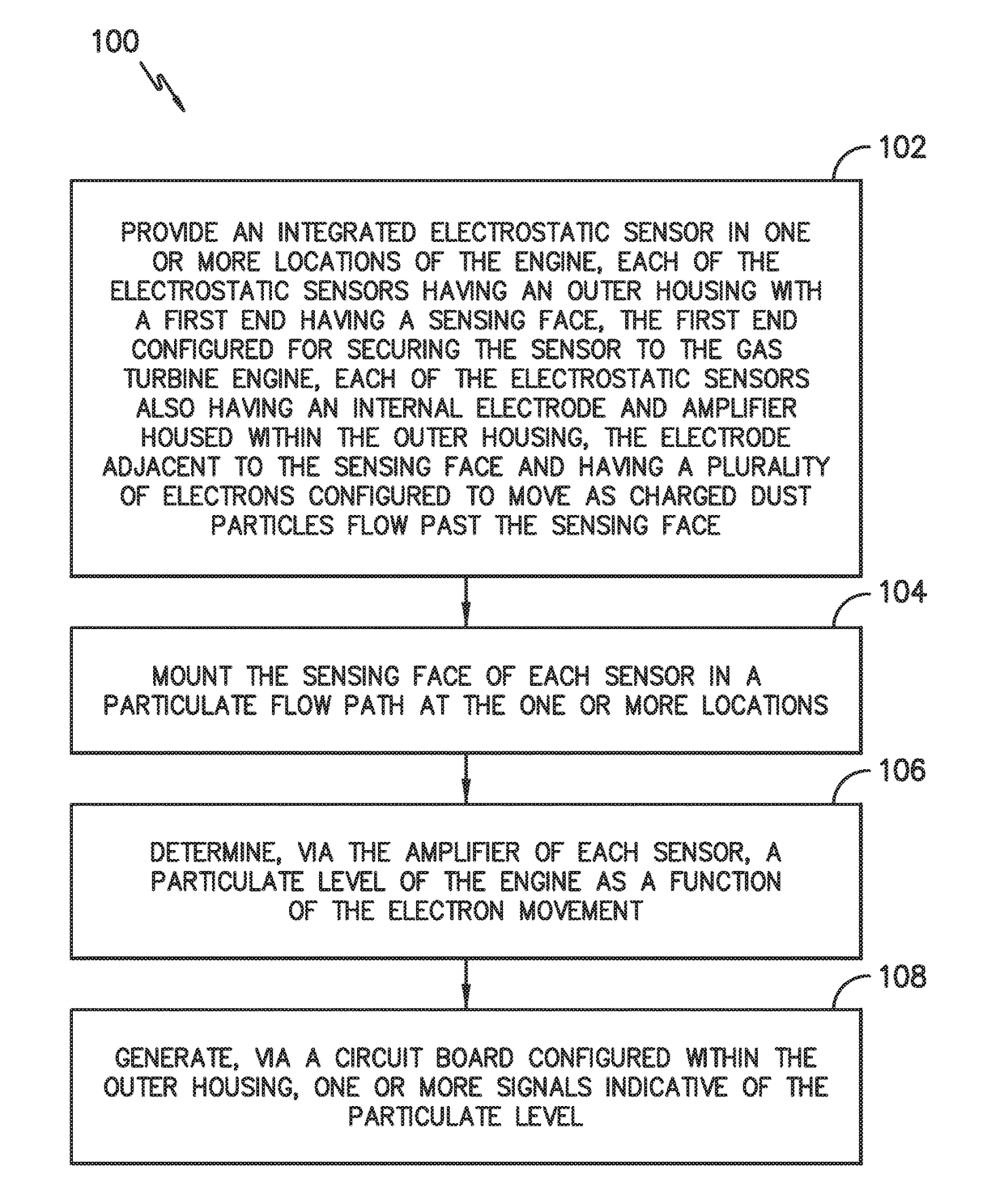
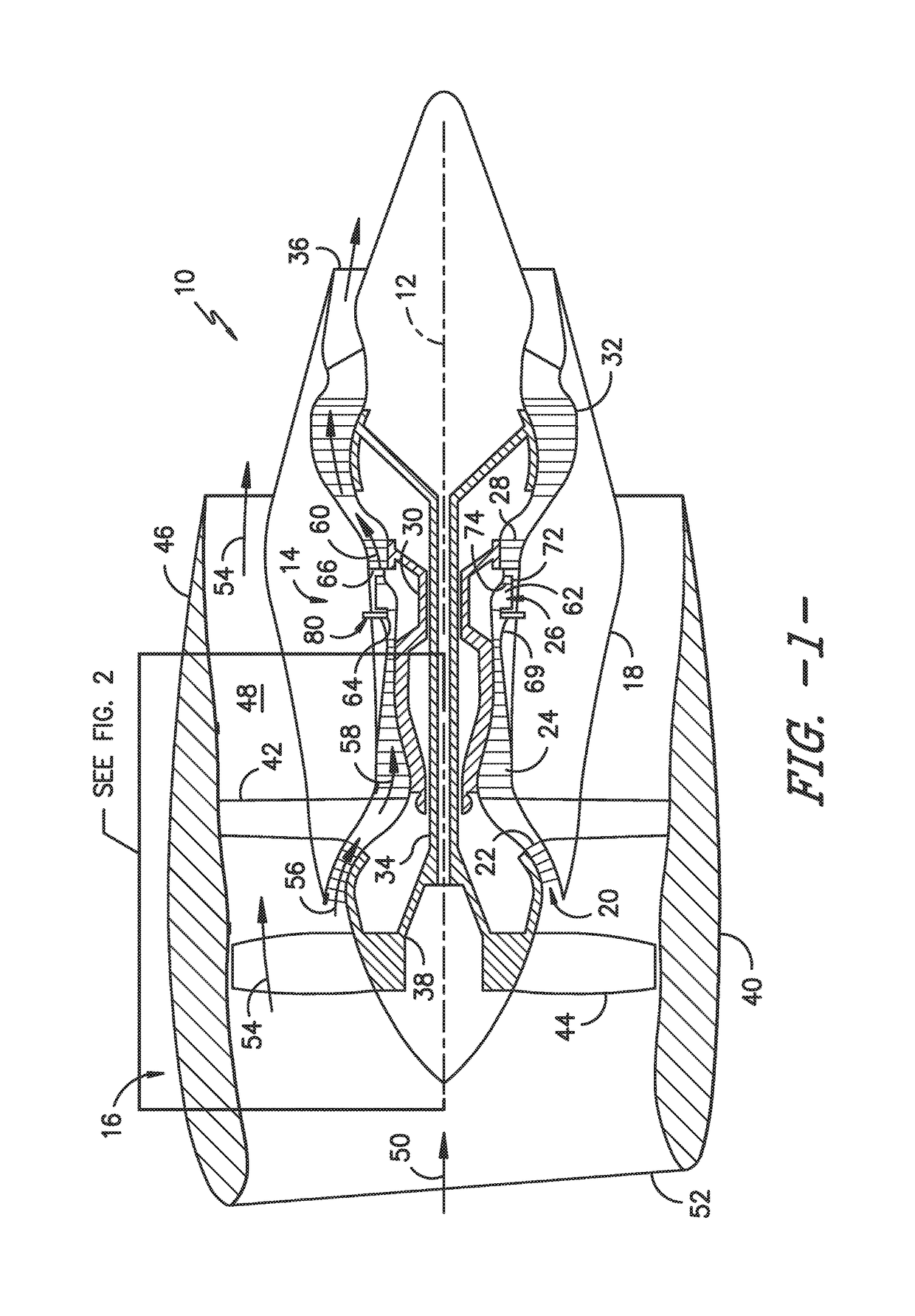
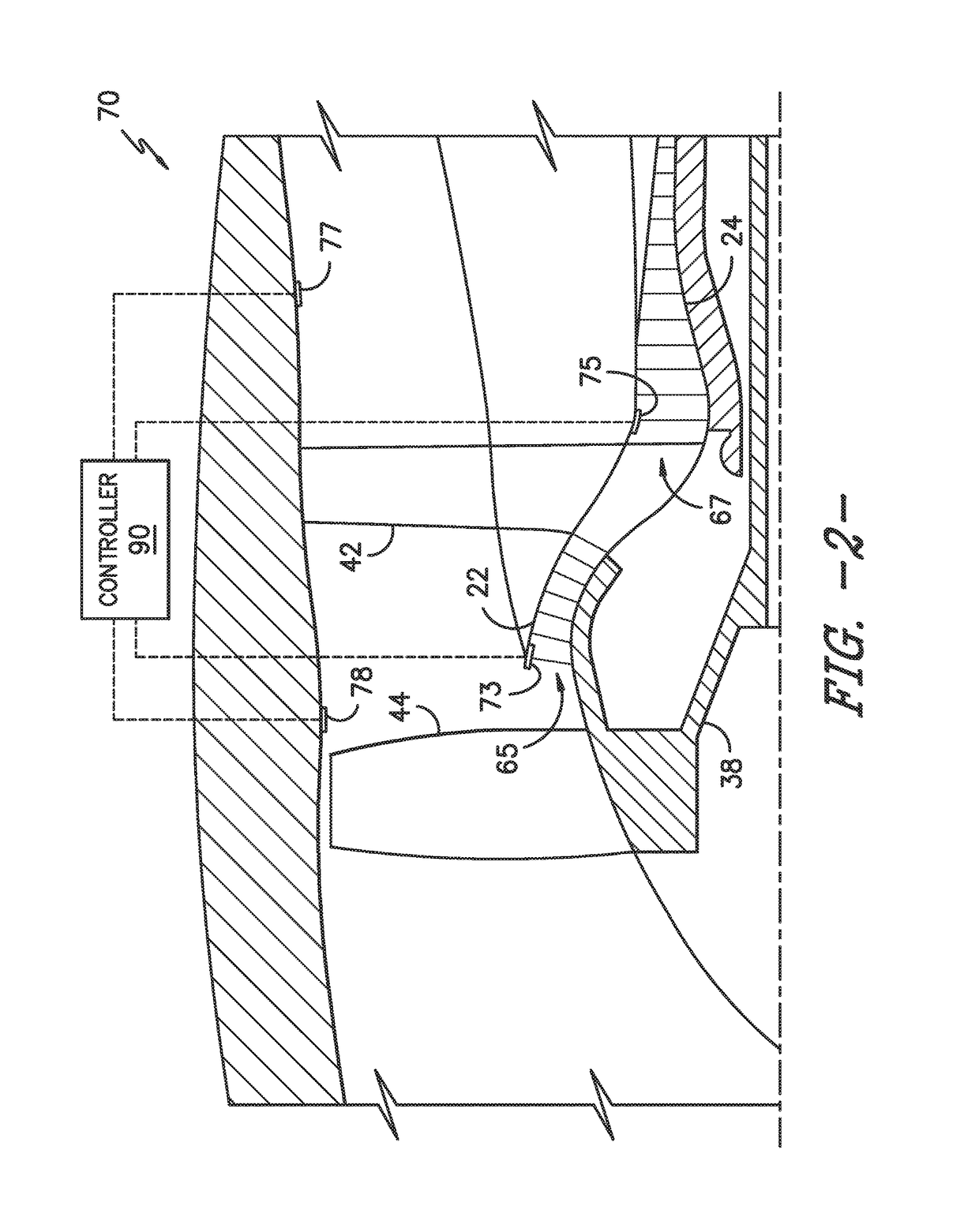
Electrostatic dust and debris sensor for an engine
ActiveUS9714967B1Gas-turbine engine testingMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansParticulatesElectricity
The present disclosure is directed to an integrated electrostatic sensor for an engine. The sensor includes an outer housing having a body with a first end and a second end. The first end is configured for securing the sensor to the engine and includes a sensing face. The sensor also includes an electrode configured within the housing adjacent to the sensing face and an amplifier configured with the electrode. The electrode contains a plurality of electrons configured to move as charged particles flow past the sensing face. Thus, the amplifier is configured to detect a particulate level as a function of the electron movement. The electrostatic sensor also includes a circuit board configured within the housing and electrically coupled to the amplifier. As such, the circuit board is configured to send one or more signals to a controller of the engine indicative of the particulate level.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Planar radio-frequency ion source drive-in target neutron tube
InactiveCN104363693ARaise the ratioIncrease profitDirect voltage acceleratorsNeutron sourcesEngineeringRadio frequency
The invention belongs to a neutron source, and particularly relates to a turn-off planar radio-frequency ion source drive-in target neutron tube. The neutron tube is mainly composed of a planar radio-frequency ion source, a gas storage element, accelerating electrodes, a target and a vacuum system. The planar radio-frequency ion source substitutes for a penning source and is composed of a small-recombination-coefficient quartz discharge cup, a planar helical antenna clinging to the cup bottom and a Kovar material leading-out pole sealing the cup rim, a cusped magnetic field is formed by a plurality of magnets along the tube diameter of the discharge cup, plasma density is increased, and electron motion is limited while recombination losses of the tube wall are reduced. Radio-frequency power is transmitted to plasma from the antenna by means of inductive coupling. A shielding case is added to the outside of the ion source, influence of the radio-frequency electric field on other equipment is reduced, saturation adsorption of deuterium-tritium gas is realized by the internal gas storage device, and heating release is performed. The proportion of monatomic ions is increased greatly, utilization rate of reaction gas is increased, sputtering of a leading-out hole is reduced, and accordingly yield of the neutron tube is increased while service life of the same is prolonged.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving performance of AlTiSiN coating through low-negative bias high-energy Ar <+> etching cleaning
ActiveCN108165925AImprove cutting performanceHigh bonding strengthVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingIon bombardmentHigh energy
The invention discloses a method for improving performance of an AlTiSiN coating through low-negative bias high-energy Ar <+> etching cleaning. The method comprises the steps that a multi-arc ion plated vacuum furnace is vacuumized, then, Ar gas is introduced and is heated to 450 DEG C, a cleaning Ti target is started, then, an anode target material is started, the cleaning Ti target and the anodetarget material perform positive-negative traction electron motion, Ar <+> is generated through collision of electrons and the Ar gas, negative bias is controlled to be minus 180 V, and Ar <+> is attracted to perform ion bombardment on the surface of a substrate for 30 min; and the AlTiSiN composite coating is deposited on the treated substrate. According to the method, the substrate is subjectedto etching cleaning through only high-energy Ar ions in the low-negative bias condition, the film-substrate binding force of the AlTiSiN coating can be remarkably improved through the etching cleaning technology, wear and friction resistance and cutting performance of the coating are improved, and the coating is applicable to a harsh high-hardness material high-speed cutting environment, and hasgreat application prospects in the field of cutter and surface protection.
Owner:安徽工业大学科技园有限公司
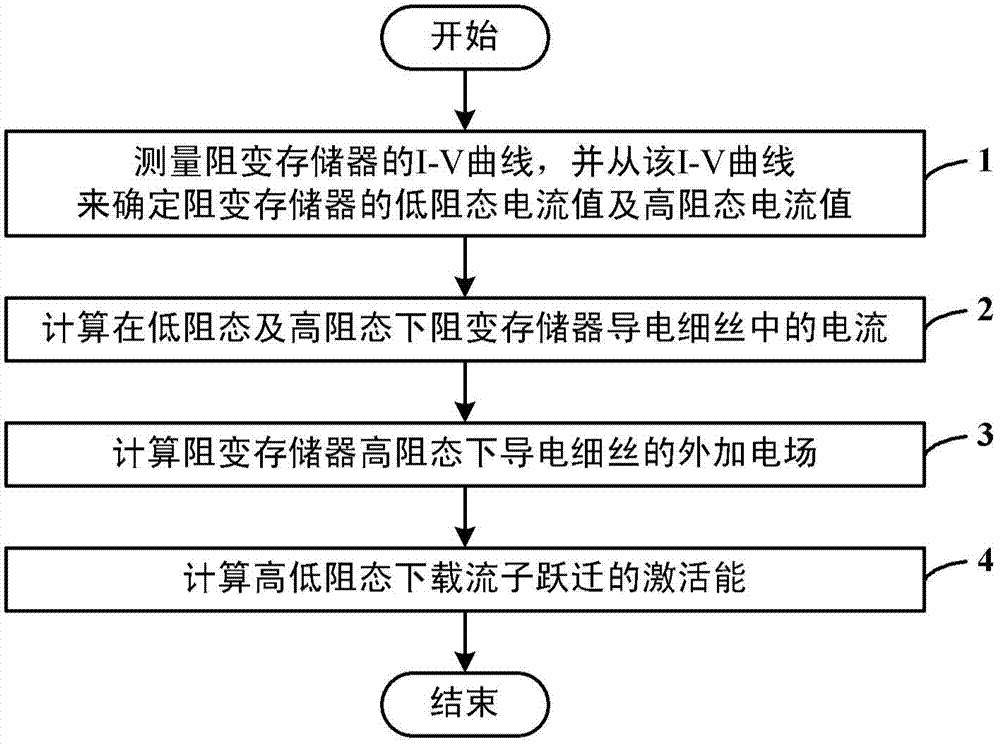
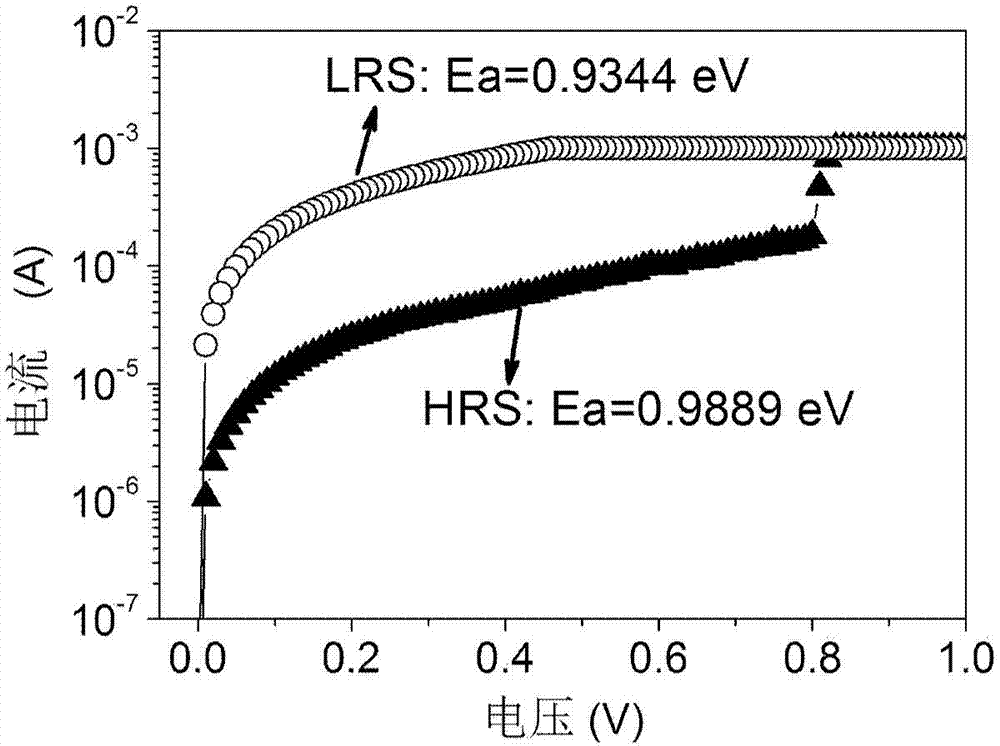
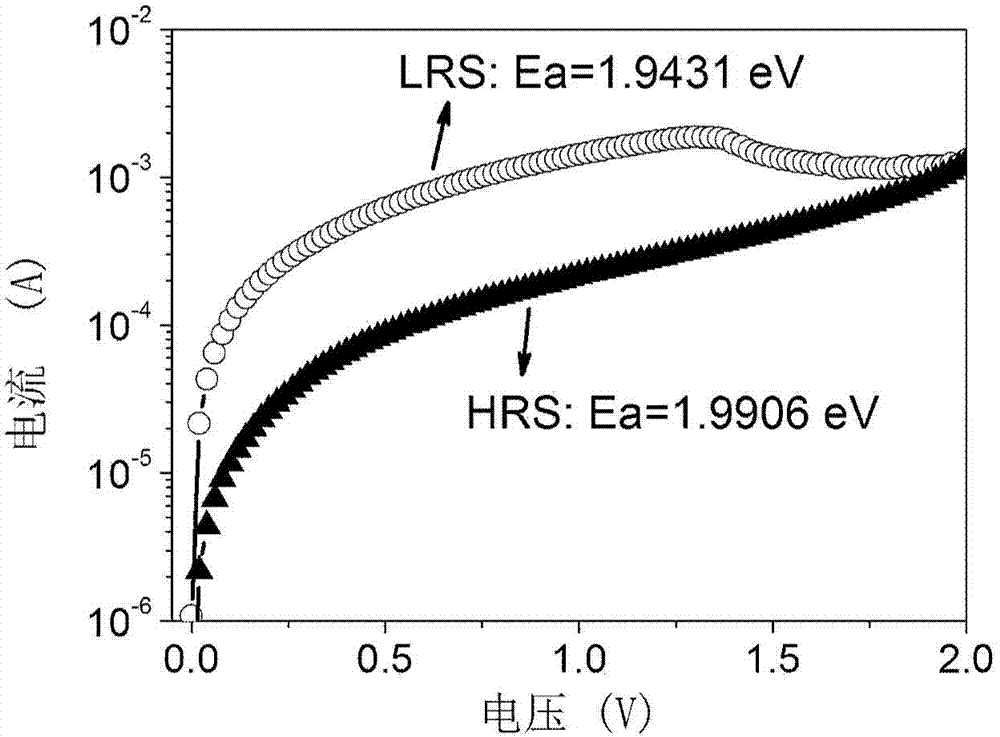
Method for measuring activation energy of resistive random access memory
ActiveCN103928057AReduce measurement errorActivation can distinguishStatic storageHigh resistanceObservational error
The invention discloses a method for measuring the activation energy of a resistive random access memory. The method comprises the following steps of measuring an I-V curve of the resistive random access memory, and determining a low resistance state current value and a high resistance state current value of the resistive random access memory according to the I-V curve; calculating the current in a conductive filament of the resistive random access memory in a low resistance state and a high resistance state; calculating an external electric field of the conductive filament of the resistive random access memory in the high resistance state; calculating the activation energy of carrier transition in the low resistance state and the high resistance state. After the method is adopted, the activation energy of the resistive random access memory can be measured by a simple method, so that the measurement error is greatly reduced, the activation energy during carrier movement such as electron motion, and ion diffusion can be distinguished, and the theoretical direction is provided for the research of microscopic physical mechanism of the resistive random access memory.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Positron-electron magnetic spectrometer with angular resolution capability
ActiveCN105425277AReasonable structureIngenious designX-ray spectral distribution measurementElectron magnetic dipole momentPositron
The invention discloses a positron-electron magnetic spectrometer with the angular resolution capability. The positron-electron magnetic spectrometer comprises an alignment hole array, a cylindrical magnet device and a positron-electron recording medium, wherein the alignment hole array is used for leading positrons and electrons into the cylindrical magnet device; the cylindrical magnet device comprises an outer shell, an inner shell and permanent magnets, the permanent magnets are fixed between the outer shell and the inner shell and are radially distributed; a magnetic field loop in which the movement directions of the positrons and the electrons are deflected is formed by space enclosed by all of the permanent magnets; the positron-electron recording medium is used for recording the intensity distribution of the positrons and the electrons on an imaging plane, so as to obtain the angular distribution of the positrons and the electrons and the information of an energy spectrum of the angular distribution. The positron-electron magnetic spectrometer has the advantages of reasonable structure and skillful design, the technical defects of low measurement precision and long time for adjusting a measurement range of an existing magnetic spectrometer are preferably overcome, and the diagnosis precision of an energy spectrum of the angular distribution of the positrons and the electrons is greatly increased, and therefore, the positron-electron magnetic spectrometer is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Terrestrial lightning-powered magnetic organized single crystal diamond blocks: The forces of nature to form the beautiful gem
InactiveUS20090016950A1Less effortLow costUltra-high pressure processesDiamondMagnetizationSingle crystal
The new century thrives for the synthesis of larger single crystal diamond blocks for various engineering applications and esthetic marvel. This invention makes use of triggered lightning bolts for instantaneously driving large cross-sections of high electric current density through compresses heated carbonaceous precursor (possibly seeded seed diamond and / or group VIII transition metal catalysts). The said conditions provide huge spin polarized electron motion over large volume for organized magnetization and spin interactions of the lightning bolt with many carbon atoms for the spin induced orbital rehybridization of sp and sp2 carbon to sp3 carbon and the voluminous condensation of single diamond crystals.
Owner:LITTLE REGINALD BERNARD
System and Method of Computing and Rendering the Nature of Dipole Moments, Condensed Matter, and Reaction Kinetics
ActiveUS20100121619A1Analogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationGraphicsDisplay device
A method and system of physically solving the charge, mass, and current density functions of organic molecules using Maxwell's equations and computing and rendering the physical nature of the chemical bond using the solutions. The solutions can be used to solve the dipole moments in molecules or induced dipole moments between species that in turn can be used to solve condensed matter parameters and reaction kinetics. The results can be displayed on visual or graphical media. The display can be static or dynamic such that electron motion and specie's vibrational, rotational, and translational motion can be displayed in an embodiment. The displayed information is useful to anticipate reactivity and physical properties. The insight into the nature of the chemical bond of at least one species can permit the solution and display of those of other species to provide utility to anticipate their reactivity and physical properties.
Owner:BRILLIANT LIGHT POWER
Method of generating molecular photoelectric hologram under elliptic polarization laser action
InactiveCN103697809AAccurately make holographic imagesSimple methodUsing optical meansPhase differenceDegree of polarization
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method of generating a molecular photoelectric hologram under an elliptic polarization laser action. The method comprises the following steps of a) computing movement conditions of an ionized electron in a laser field so as to obtain speed and a movement locus of the ionized electron; b) obtaining the movement conditions, which include an initial phase, a return moment and a drift time, of a required signal electron on the basis of the movement speed and the movement locus of the ionized electron; c) computing to obtain an ionization phase and the drift time of a reference electron on the basis of the computation of the movement conditions of the ionized electron in the laser field and the movement conditions of the signal electron thereof; d) respectively computing to obtain phase accumulations of movements of the signal electron and the reference electron in the laser field; e) computing to obtain a phase difference so as to make a photoelectric hologram. By adopting the method, through changing a degree of polarization of elliptic laser, a dynamic process of an ionized electron wave packet is influenced, so that generation of the molecular photoelectric hologram is further controlled, thus the molecular photoelectric hologram is precisely made. The method is simple and easy to apply, and has important significance to understanding dynamic behaviors of the electron wave packet in strong field physics and characteristics of the molecular photoelectric hologram.
Owner:SHANTOU UNIV
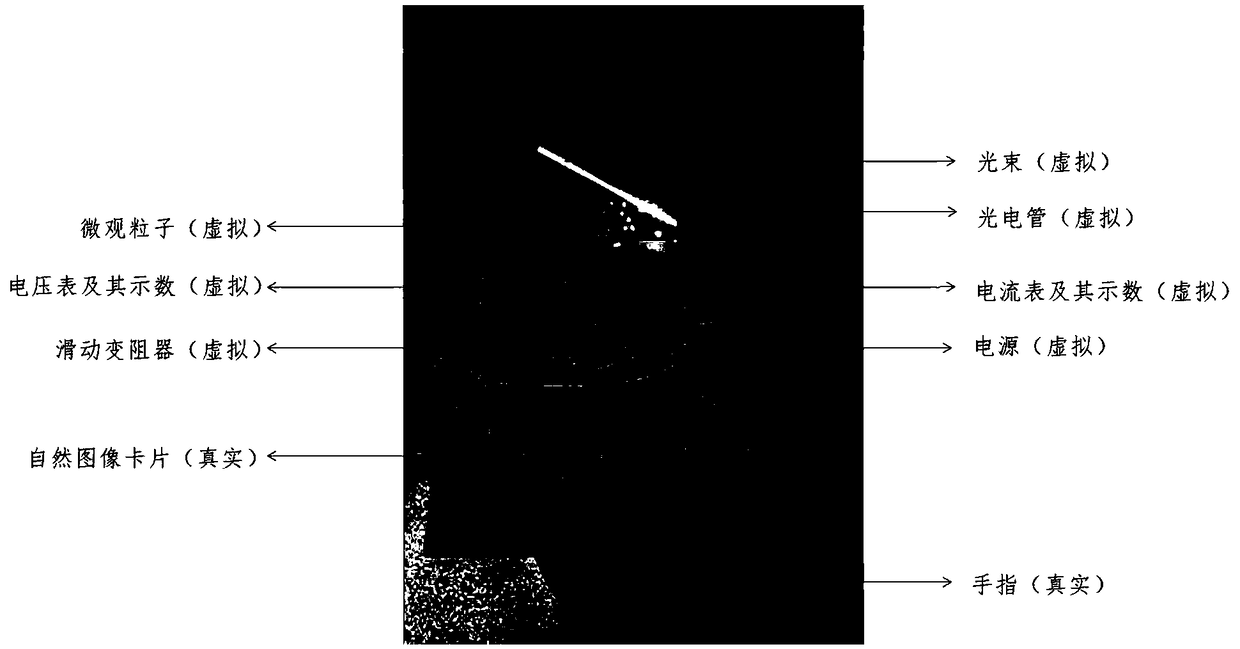
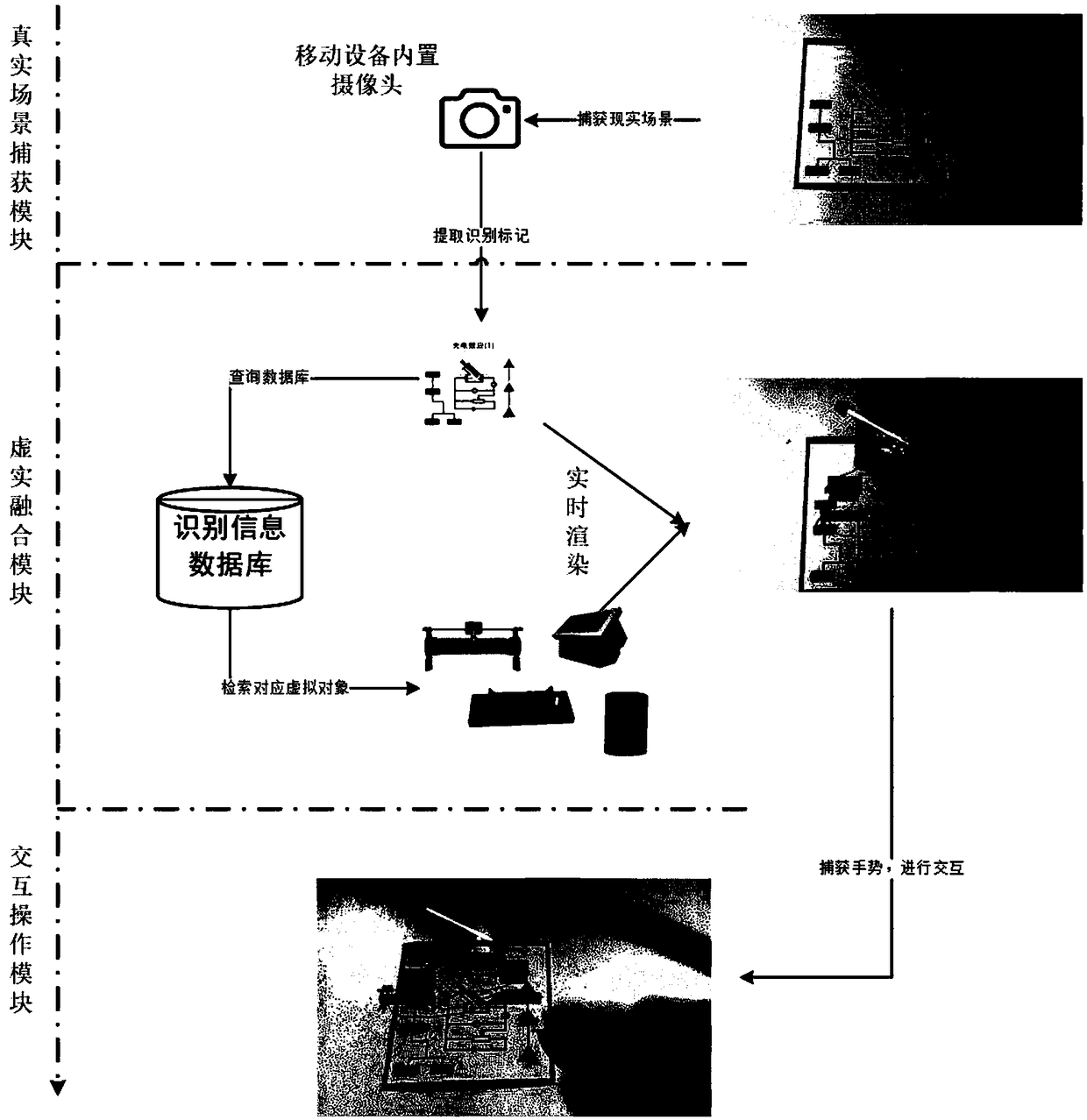
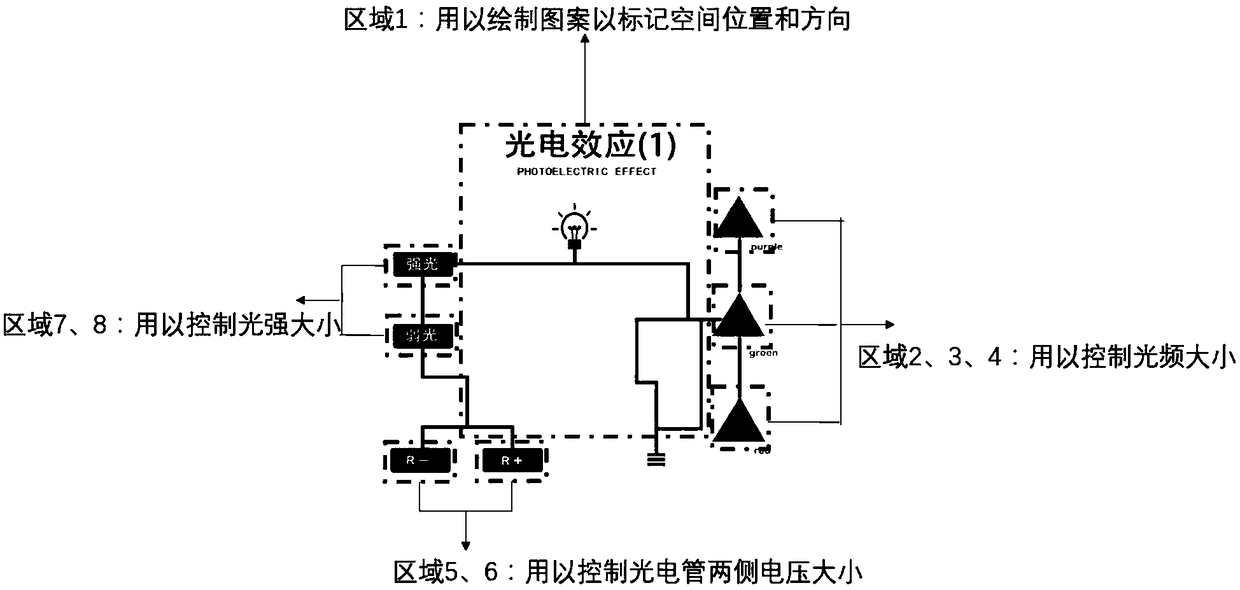
Virtual and real combination display system and method for photoelectric effect experiment
InactiveCN108847057AEnhance sensory experienceLow priceImage data processingElectrical appliancesSimulationComputer module
The invention relates to a virtual and real combination display system and method for a photoelectric effect experiment. The system is composed of a real scene capture module, a virtual reality fusionmodule and an interaction operation module. A pre-processed natural image card in a real scene is captured through a mobile device or a regular self-contained camera of a computer, the spatial position and the direction of the card are calculated and mapped to a three-dimensional model generated in real time of a virtual photocell or a virtual electrical component, the spatial position and the direction of the card are synthesized with a captured real scene to obtain a virtual reality fusion scene, an experimenter can directly click a virtual button preset on the natural image card through ahand, interaction with the virtual reality fusion scene is carried out to observe the photoelectric effect electron motion state that is invisible in real life, and experimental rules are explored. The system and the method are advantaged in that the system and the method are applied to physics experiment teaching, the equipment is simple, cost is low, interaction behaviors are natural, learners can adjust parameters of optical frequency, light intensity and the voltage on both sides of the photocell at any time, the photoelectric effect phenomenon is observed, and the good teaching effect isachieved.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Symmetrical type carbon nanotube cathode ionization gauge
ActiveCN105070628AExtend the motion pathAvoid interferenceGas pressure measurement discharge tubesCarbon nanotubeHeat sensitive
The invention discloses a symmetrical type carbon nanotube cathode ionization gauge. A carbon nanotube array capable of achieving electron field emission at room temperature is taken as a cathode, interferences of the high-temperature thermionic cathode to a heat sensitive, light sensitive and strong magnetic field system are overcome, and a power consumption demand is reduced based on a field emission mechanism. The carbon nanotube array cathode grows on two faces of a substrate, and symmetrical double-electrode arrangement is adopted; and, on the premise that the complexity of a circuit is not changed, the lengths of electron trajectories are effectively prolonged, and improvement of the sensitivity of an ionization gauge in the kind is facilitated. Furthermore, higher-voltage anodes 5 are added between gate electrodes 4 and collecting electrodes 6, so electrons oscillates between the gate electrodes 4 and the collecting electrodes 6, the electron trajectories are also prolonged, and the sensitivity of the ionization gauge is further improved.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
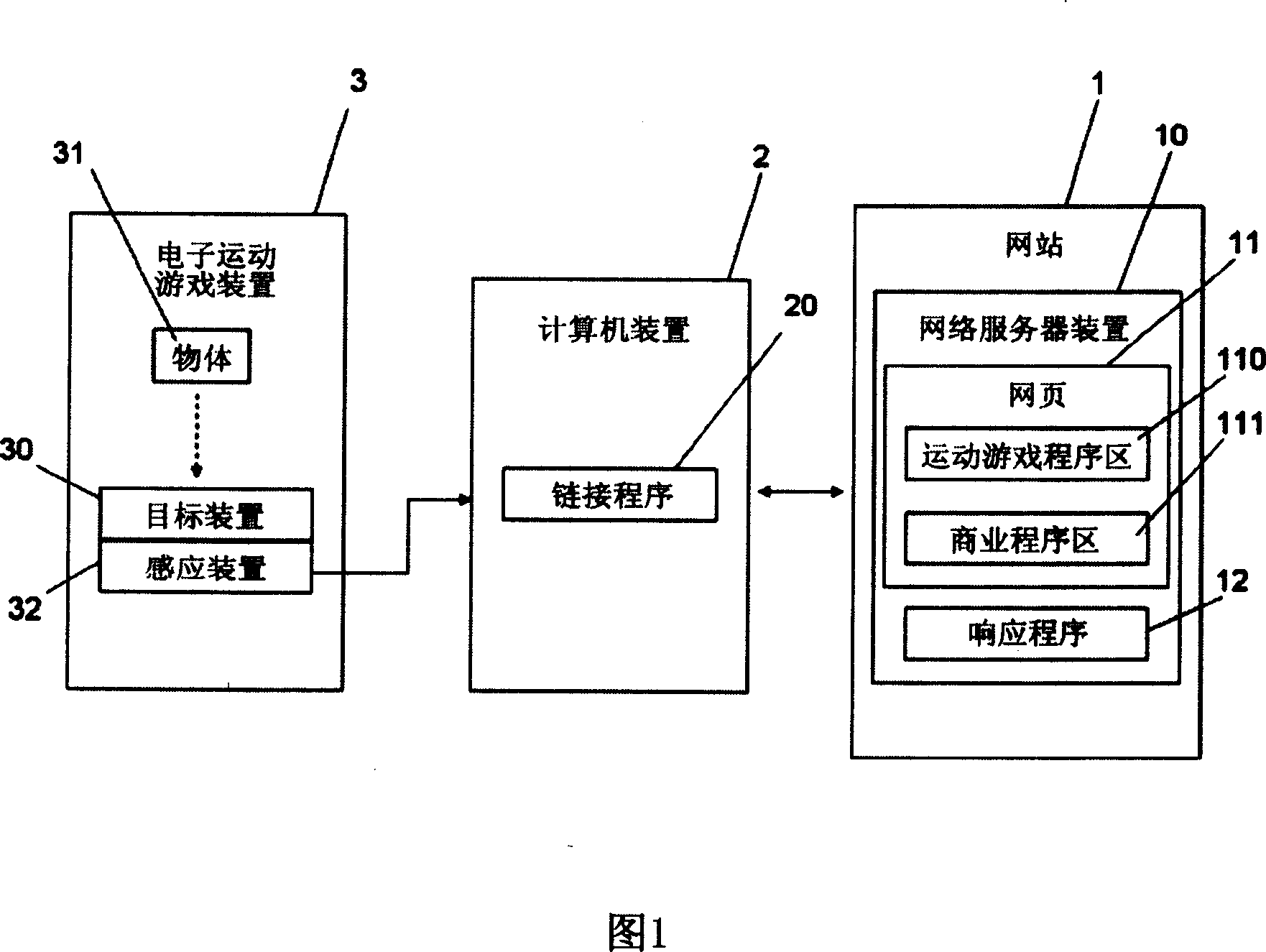
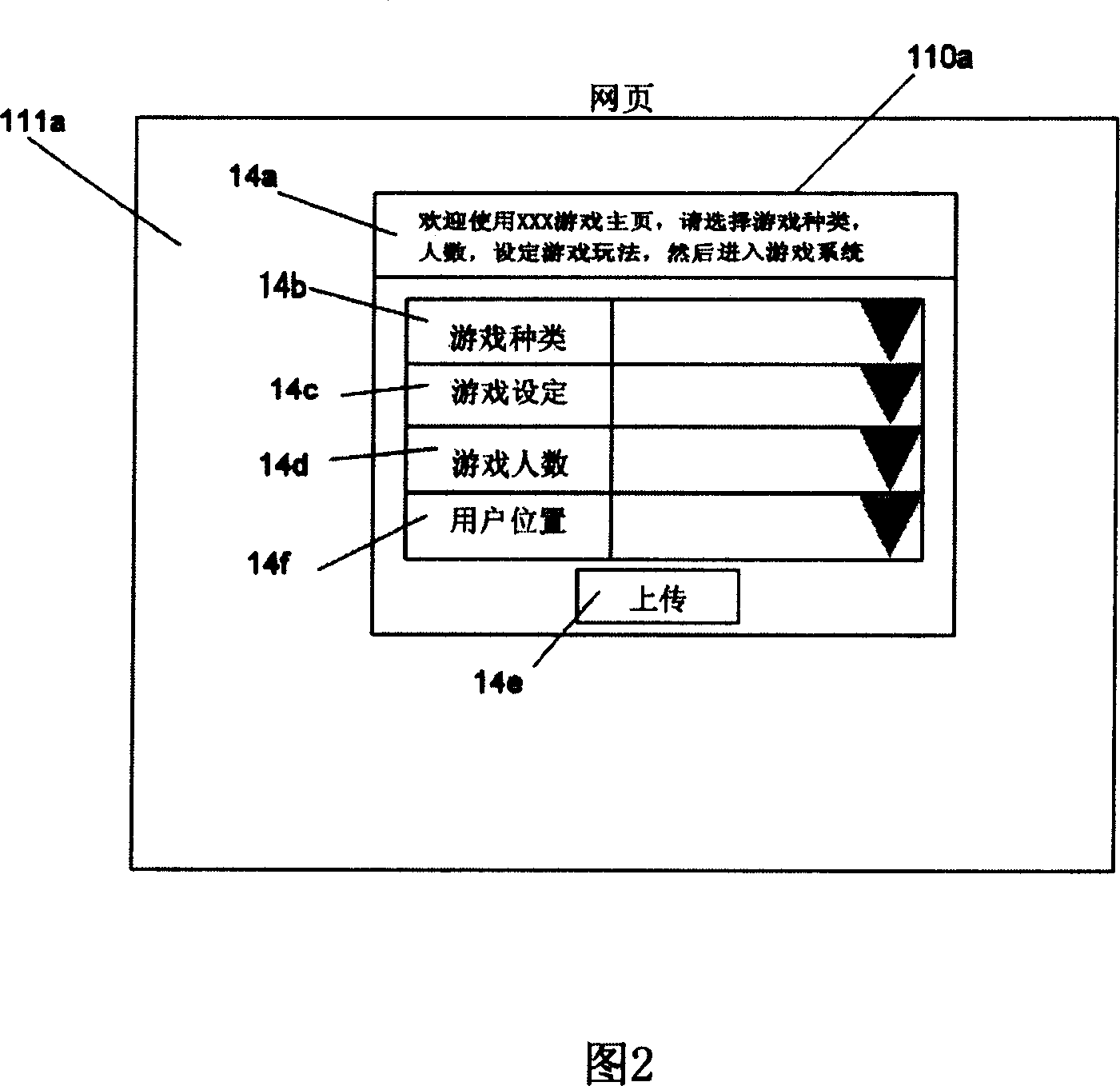
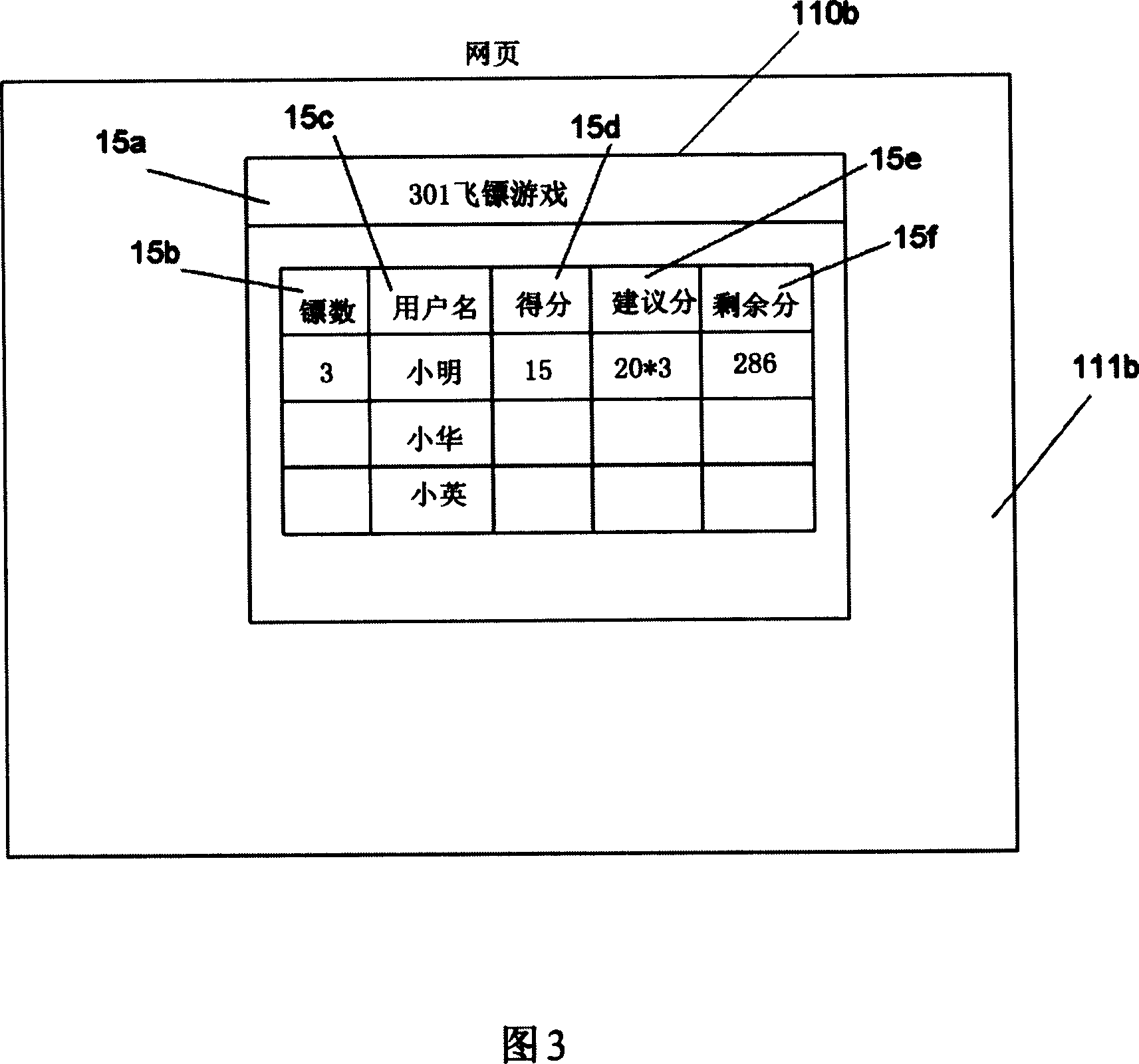
Electron motion game system based on network and method thereof
The invention discloses an internet electronic sports game system and a method of the system, which includes a website, a computer device and an electronic sports game device; the computer device can upload a piece of set data from a webpage of a server device on the website to the server device; a response program in the server device receives the set data, and respond the corresponding webpage to the computer device according to the set data; the corresponding web page is provided with a sports game program area and a commercial program area; the sports game program area provides corresponding sports games according to the set data, controls the sports games to run according to the signal, and displays the progress of the sports games; the commercial program area publishes at least a piece of advertisement. The system the and method can not only provide entertainment and sports for the users, but also increase the browse rate of the website, so as to initiatively promote commodities or services.
Owner:邵学悌 +1
Superlattice device structure regulated by THz (terahertz) wave
ActiveCN104485368ASimple structure and processSimple preparation processSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesPotential wellElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention provides a superlattice device structure regulated by a THz (terahertz) wave. The superlattice device structure at least comprises a semiconductor superlattice device, a heavy doping contact layer located on a periodic structure, an upper electrode on the heavy doping contact layer, a resistor forming a closed circuit with the semiconductor superlattice device, a THz wave applied to a superlattice growth direction, and a magnetic field applied perpendicular to the superlattice growth direction, wherein the semiconductor superlattice device is provided with a substrate and the periodic structure that is formed by alternately stacking potential barriers and potential wells and located on the substrate. The THz wave is coupled into the superlattice to achieve regulation of an electron motion state. The motion state of a superlattice micro-strip electron is obtained by measuring current of a superlattice external circuit or voltage across the resistor by the action of a THz field and the magnetic field. The device structure is simple in technology, and can very conveniently modulate the electron motion state in a superlattice system.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
System and Method of Computing and Rendering the Nature of Molecules,Molecular Ions, Compounds and Materials
InactiveUS20110066414A1Data visualisationAnalogue computers for chemical processesDisplay deviceMaxwell's equations
A method and system of physically solving the charge, mass, and current density functions of pharmaceuticals, allotropes of carbon, metals, silicon molecules, semiconductors, boron molecules, aluminum molecules, coordinate compounds, and organometallic molecules, and tin molecules, or any portion of these species using Maxwell's equations and computing and rendering the physical nature of the chemical bond using the solutions. The results can be displayed on visual or graphical media. The display can be static or dynamic such that electron motion and specie's vibrational, rotational, and translational motion can be displayed in an embodiment. The displayed information is useful to anticipate reactivity and physical properties. The insight into the nature of the chemical bond of at least one species can permit the solution and display of those of other species to provide utility to anticipate their reactivity and physical properties.
Owner:MILLS RANDELL L
High-frequency transform type power supply and audio power amplification processing circuit with same
InactiveCN101710791ANot easy to generate inflowRemove thermal noiseAc-dc conversion without reversalDc-dc conversionFiltrationEngineering
The invention discloses a high-frequency transform type power supply which comprises a rectification and filtration circuit, wherein the rectification and filtration circuit can directly rectify and filter AC commercial power to obtain stable direct current. And the high-frequency transform type power supply particularly comprises a starting protection oscillation circuit, a commutation circuit and a transform self excited oscillation circuit which are electrically connected with the rectification and filtration circuit, wherein the transform self excited oscillation circuit comprises a half-bridge AC transform circuit. During processing power supplies, the high-frequency transform type power supply does not neglect any noise on the power grid, can get rid of thermal noise generated by electron motion on circuits ideally, and enable current to move in the form of a complete sinusoidal wave at the same time so that the current self can not generate a harmful wave to flow into output circuits. Since the transform self excited oscillation circuit comprises a half-bridge AC transform circuit, the structure of the whole high-frequency transform type power supply becomes simpler and the cost is lower. An audio power amplification processing circuit equipped with the high-frequency transform type power supply has the same advantages.
Owner:张仁增
Water magnetizer
InactiveUS6706179B2Dissolve more oxygenAvoid it happening againElectrostatic separatorsSludge treatmentMagnetic heatingPower flow
The present invention relates to a water magnetizer including a permeance member and a cooking recipient. The permeance member consists of two parallel disks spaced apart each other by a plurality of partitions located along the periphery of the disks, such that there is clearance between the two parallel disks. The permeance member is placed into the cooking recipient that is charged with water. Then, the cooling recipient is placed onto an electromagnetic heater. When the electromagnetic heater powers on, inner coils of the electromagnetic heater regularly vibrate at high frequency to change the direction of electric current and then induce a swirled magnetic field in the clearance. The water would be boiled by a lot of heat generated from electron movement in the induced magnetic field.
Owner:AQUATECH LIFESCI
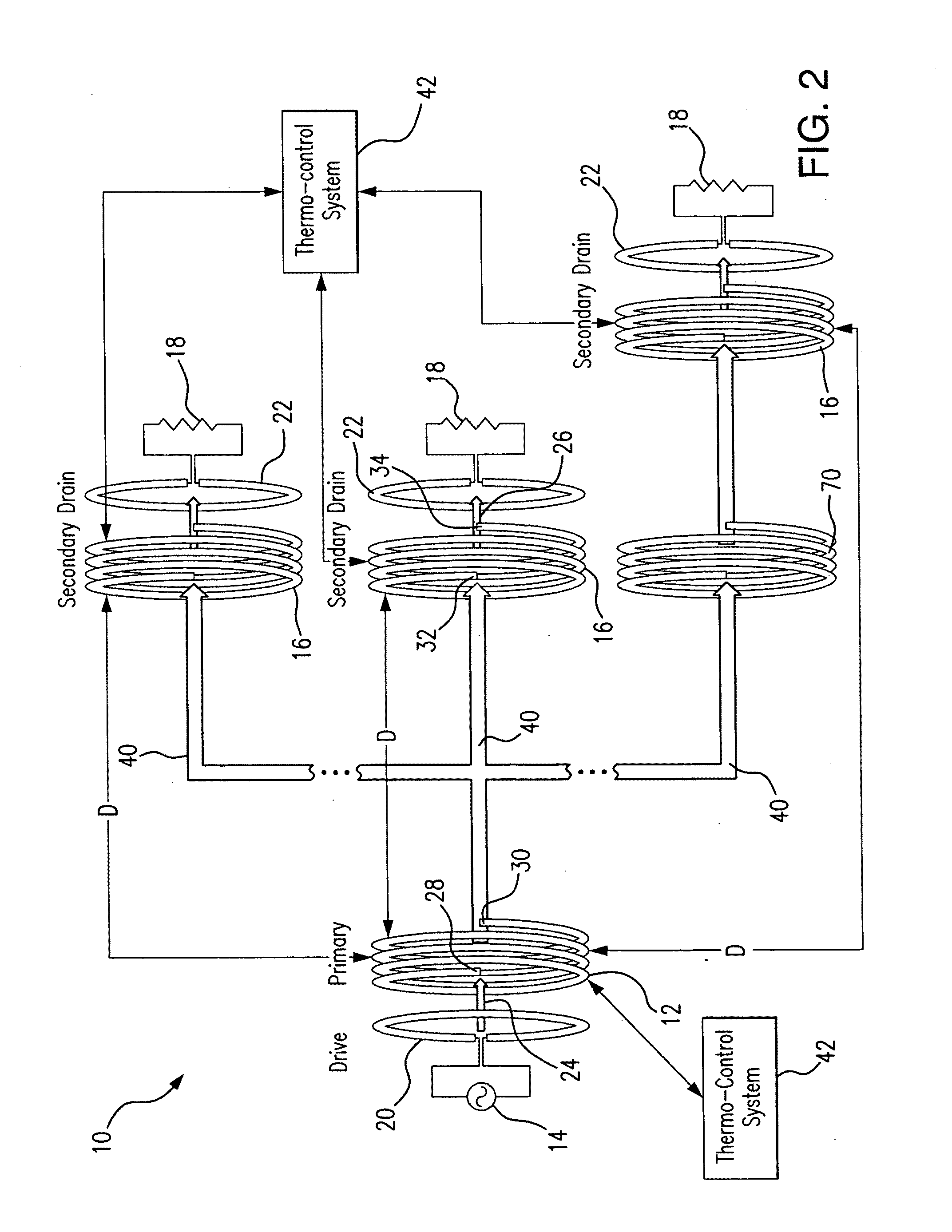
Method and system for long range wireless power transfer
ActiveUS8994221B2Improve power transfer efficiencyReduce eliminateDc network circuit arrangementsElectromagnetic wave systemCapacitanceEngineering
A wireless energy transfer system includes a primary and one (or more) secondary oscillators for transferring energy therebetween when resonating at the same frequency. The long range (up to and beyond 100 m) efficient (as high as and above 50%) energy transfer is achieved due to minimizing (or eliminating) losses in the system. Superconducting materials are used for all current carrying elements, dielectrics are either avoided altogether, or those are used with a low dissipation factor, and the system is operated at reduced frequencies (below 1 MHz). The oscillators are contoured as a compact flat coil formed from a superconducting wire material. The energy wavelengths exceed the coils diameter by several orders of magnitude. The reduction in radiative losses is enhanced by adding external dielectric-less electrical capacitance to each oscillator coil to reduce the operating frequency. The dielectric strength of the capacitor is increased by applying a magnetic cross-field to the capacitor to impede the electrons motion across an air gap defined between coaxial cylindrical electrodes.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF
Gyrotron collector collection profile design method and gyrotron collector and gyrotron
ActiveCN109241638AIncrease the areaImprove uniformityGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsCondensed matter physicsDesign methods
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
An electromagnetic wave oscillator
ActiveCN109148242BReduce emission densityReduce lossTransit-tube cathodesTransit-tube cooling methodsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
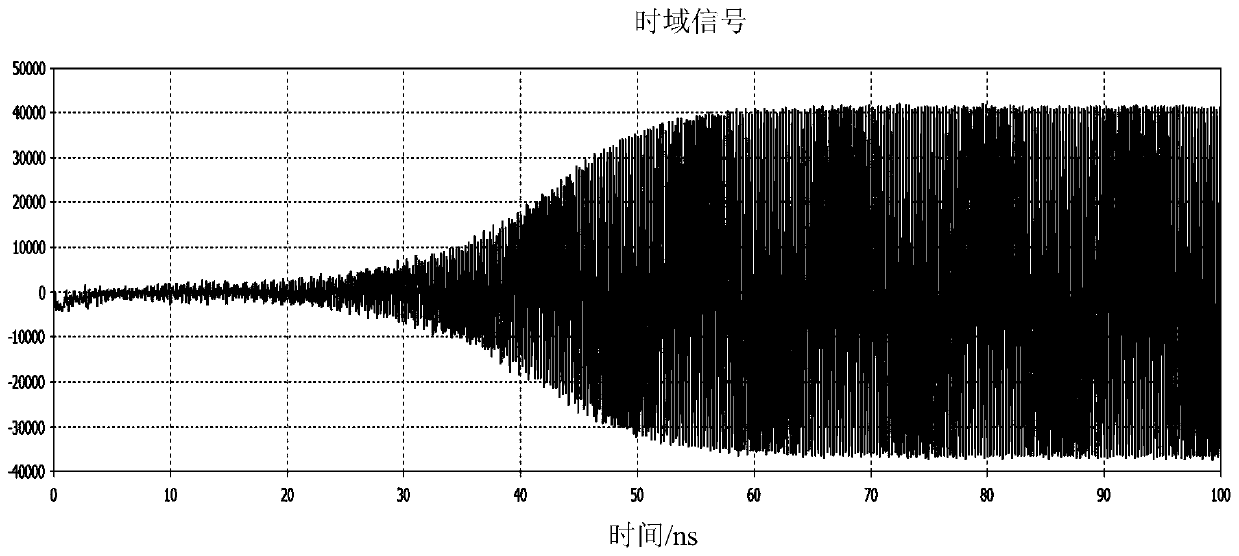
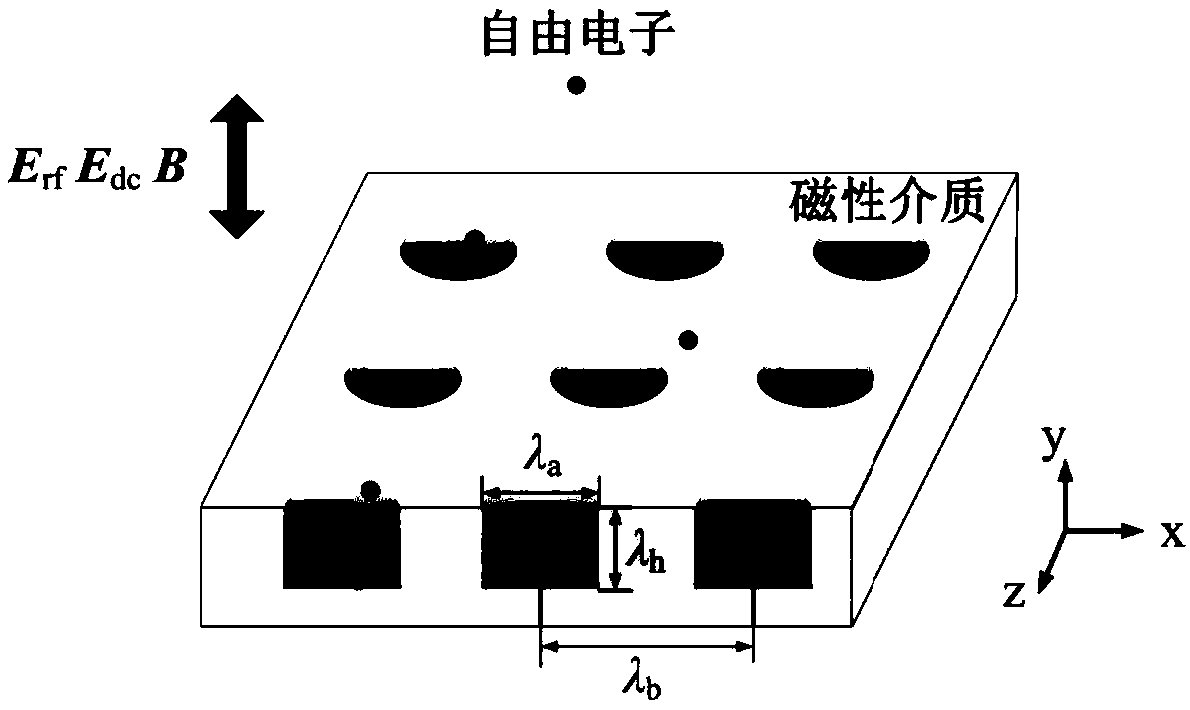
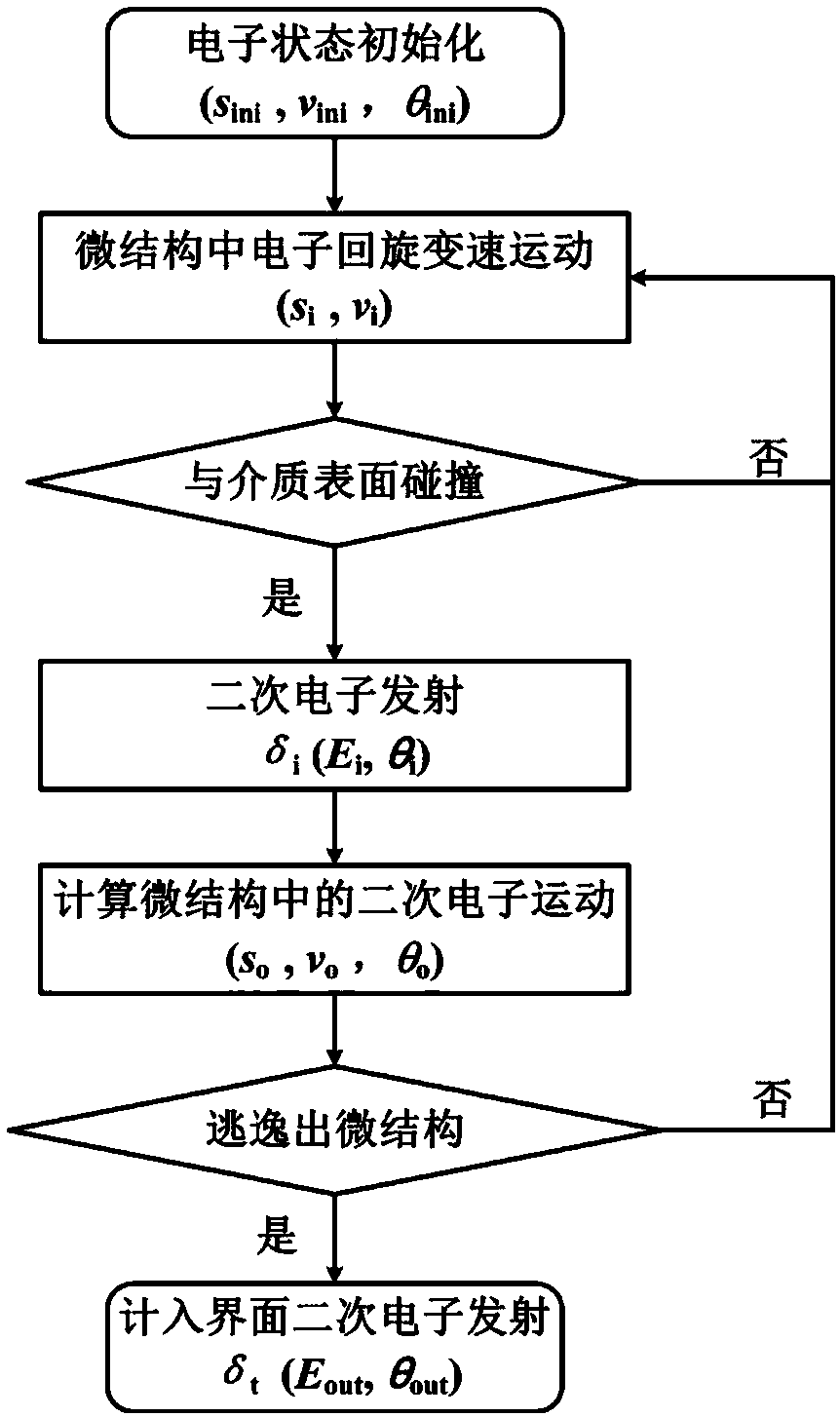
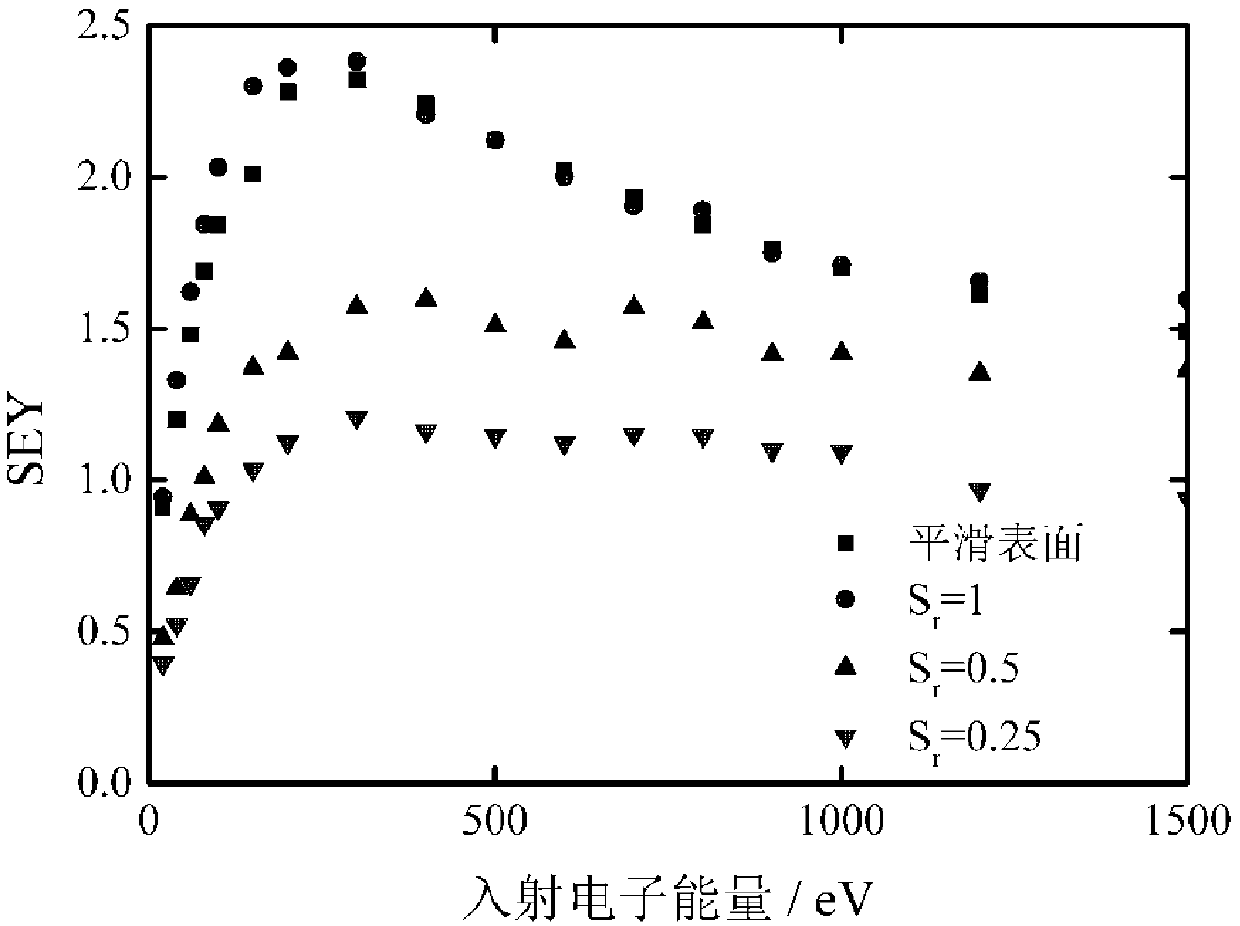
Method for determining secondary electron emission characteristics of periodic porous medium surface
ActiveCN109060854AEmission reduction and effective suppressionRaise the microdischarge thresholdMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionPorous mediumSecondary electrons
The invention relates to a method for det`ermining secondary electron emission characteristics of a periodic porous medium surface. Firstly, the material properties, surface periodic pore characteristics, radio frequency electromagnetic field, static charge accumulation field, static magnetic field and initial electronic information of a dielectric material are determined; then, each electron motion rail in the surface pore of the dielectric material and the motion time before the electron collides with the pore boundary are determined, and further, the collision angle and the collision energyof the electron and the pore boundary are obtained by calculation; finally, it is judged whether the electron is emitted from the por in combination with an electron motion rail equation and pore boundary condition according to secondary electron emission information of each electron being collided with the pore boundary, so as to obtain the secondary electron emission characteristics of the periodic porous dielectric material surface.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
Water magnetizer
The present invention relates to a water magnetizer including a permeance member and a cooking recipient. The permeance member consists of two parallel disks spaced apart each other by a plurality of partitions located along the periphery of the disks, such that there is clearance between the two parallel disks. The permeance member is placed into the cooking recipient that is charged with water. Then, the cooling recipient is placed onto an electromagnetic heater. When the electromagnetic heater powers on, inner coils of the electromagnetic heater regularly vibrate at high frequency to change the direction of electric current and then induce a swirled magnetic field in the clearance. The water would be boiled by a lot of heat generated from electron movement in the induced magnetic field.
Owner:AQUATECH LIFESCI
Electronic Motion Sensing Devices and Method of Operating Same
The invention relate to a set of methods that can be used in portable electronic or wearable motion sensing devices or game controller assemblies, to calculate a plurality of motion parameters. Simplified binary values for motion information is also provided as well as a method to determine the orientation of the device relative to a body part that it is attached to. Embodiments of the invention can be wearable, e.g., worn on the human body, handheld in a game assembly, handheld in a toy or more generally attached to any movable body. The invention also provides a method for observers of a player of a video game or user of a computer application to combine camera data from the observer's smart device with the game play or application screen of the player or user's smart device on the observer's smart device.
Owner:DIGIBIT LLC
Electronic protection device and IOB (internet of bodies) system
ActiveCN108926831AReduce harmDisplay changes in exercise statusSport apparatusWireless transmissionAdhesive
The invention provides an electronic protection device. The electronic protection device comprises an air bag, a force measuring system, a position measuring system and a protection device body, wherein the force measuring system comprises an air pressure sensor arranged in the air bag and used for measuring the air pressure change value of the air bag under the effect of external force, the position measuring system comprises a first circuit layer configured to be connected with the air bag and is used for measuring an electric signal change value of the first circuit layer under the effect of external force, the IOB (internet of bodies) system comprises the electronic protection device, an electron motion adhesive tape, analysis systems, a wireless transmission system and a mobile terminal, the first analysis system is configured to analyze the striking force of the external force according to the air pressure change value of the air pressure sensor, the second analysis system is used for analyzing the position and area of the effect of the external force according to the electric signal change values of the first circuit layer and the electron motion adhesive tape, the wirelesstransmission system is configured to transmit the information of the analysis systems to the mobile terminal, and the mobile terminal displays the force value of the external force, the position and area of the effect of the external force, and the stress value in the unit area.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
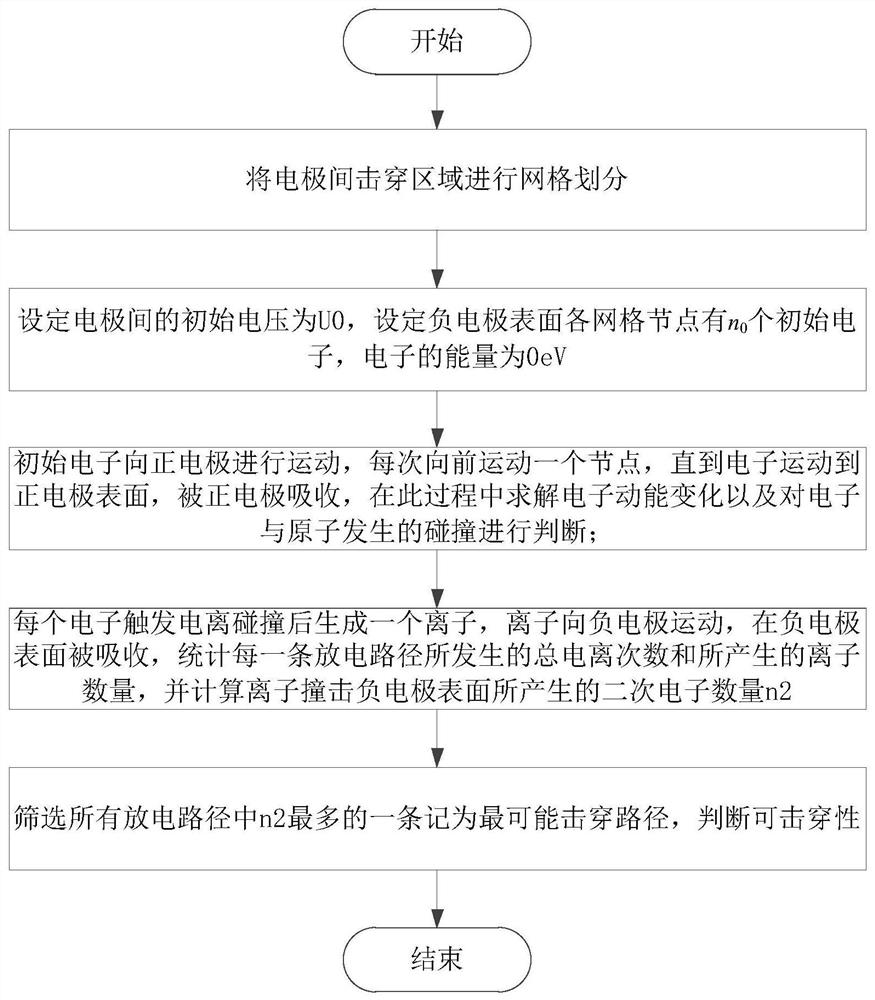
Numerical simulation method and system for breakdown voltage and position of low-pressure gas
PendingCN113987881AImprove computing efficiencyShort calculation timeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsSecondary electronsParticle physics
The invention provides a numerical simulation method and system for breakdown voltage and position of low-voltage gas. The method and the system are suitable for simulation of a gas discharge process between electrodes with complex structures in a vacuum environment. According to the method, on the basis that a discharge path is set as a gap electric field line, calculation domain grids are divided according to the discharge path and a potential equipotential line; after the initial number of electrons on the surface of a negative electrode is set, calculation is carried out according to electron movement, electron and atom collision, ion generation and secondary electron generation on the discharge path; then, the total secondary electron generation amount of each discharge path is compared, and the most probable breakdown path is screened out; and the secondary electron quantity of the path is compared with the initial electron quantity to judge whether critical breakdown can be triggered or not. According to the method, the breakdown voltage and the breakdown position between the electrodes with the complex structures can be estimated, and calculation efficiency is high.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE PROPULSION
Electron bombardment ionization source device, ionization bombardment method and substance analysis method
ActiveCN111551628AAccurate qualitative analysisIncrease the actual running pathMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansIon sources/gunsIonization chamberElectron bombardment
The embodiment of the invention provides an electron bombardment ionization source device, an ionization bombardment method and a substance analysis method, and the device comprises the steps: placinga pair of radial acceleration electrodes at the inner side, close to an ionization chamber, of a first electron repulsion electrode and at the upper and lower parts or the front and rear parts of a first filament, and forming an electric field perpendicular to a magnetic field direction between the radial acceleration electrodes; enabling electrons overflowing from the electrified and heated first lamp filament to move in a spiral line under the acting force in the magnetic field direction, wherein the radius of the spiral line where the electrons move is increased under the action of an electric field perpendicular to the magnetic field direction, and then the actual movement path of the electrons is increased. According to the device, the electric field perpendicular to the electron motion reference axis is added, under the action of the electric field, the radius of spiral line operation of electrons is increased, then the actual operation path of the electrons in the ionization chamber is increased, the collision sectional area of the electrons and measured object molecules is increased, and then the ionization efficiency of the ion source is improved.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com