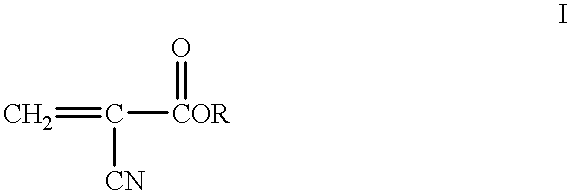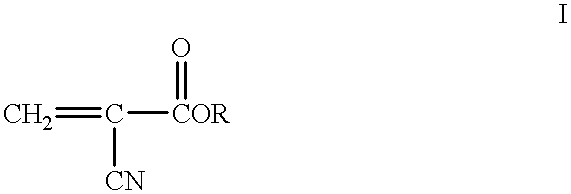Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
480 results about "Electron beam radiation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method of making electron beam polymerized emulsion-based acrylate pressure sensitive adhesives
InactiveUS6103316AImprove adhesionHigh polymerizable contentFilm/foil adhesivesVacuum evaporation coatingEmulsionElectron
A one-step process using electron beam radiation to polymerize pressure sensitive adhesives on web from acrylate emulsions is disclosed. The radiation may be supplied in a single or multiple dose. Products using such pressure sensitive adhesives are also disclosed.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
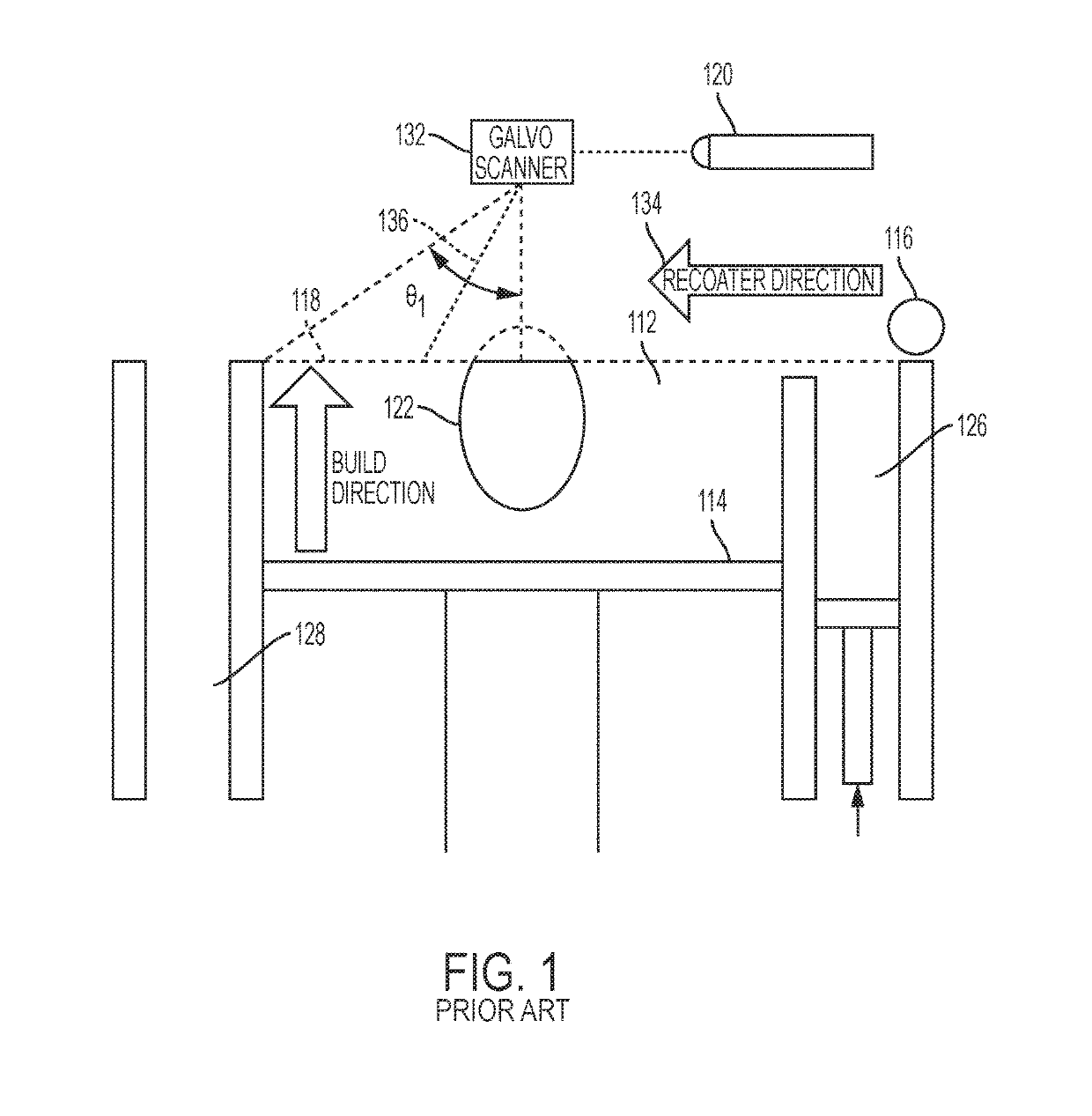
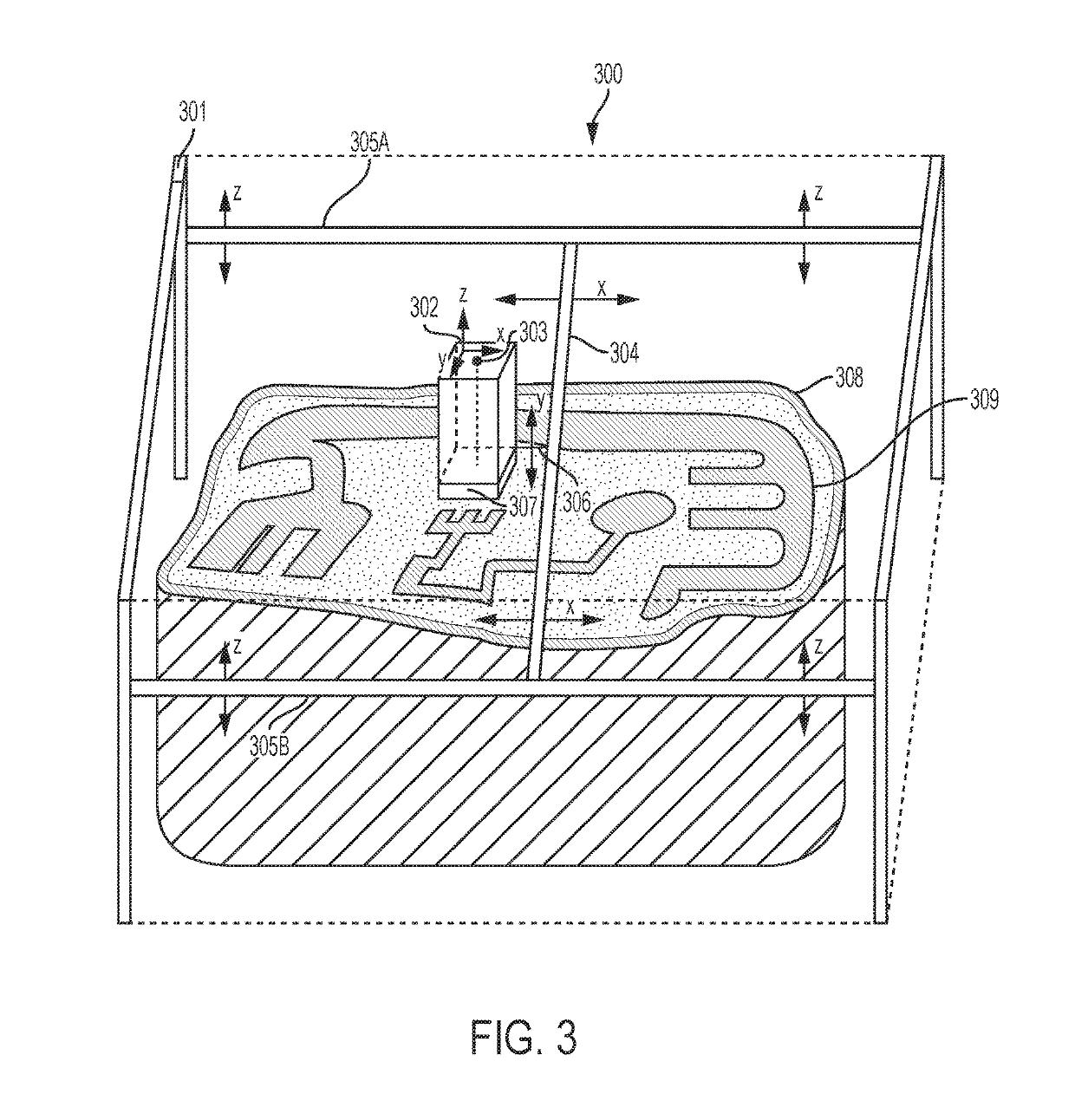
Additive manufacturing using a selective recoater
ActiveUS10478893B1Welding/cutting auxillary devicesIncreasing energy efficiencyEngineeringDirect device
The present disclosure generally relates to additive manufacturing systems and methods on a large-scale format. One aspect involves a build unit that can be moved around in three dimensions by a positioning system, building separate portions of a large object. The build unit has an energy directing device that directs, e.g., laser or e-beam irradiation onto a powder layer. In the case of laser irradiation, the build volume may have a gasflow device that provides laminar gas flow to a laminar flow zone above the layer of powder. This allows for efficient removal of the smoke, condensates, and other impurities produced by irradiating the powder (the “gas plume”) without excessively disturbing the powder layer. The build unit may also have a recoater that allows it to selectively deposit particular quantities of powder in specific locations over a work surface to build large, high quality, high precision objects.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Collagen/glycosaminoglycan matrix stable to sterilizing by electron beam radiation
InactiveUS6969523B1Facilitate cross-linkingImprove performanceBiocideMechanical working/deformationCross-linkGlycosaminoglycan
Compositions of cross-linked collagen and a glycosaminoglycan are provided which retain characteristics rendering them useful as tissue engineering matrices or scaffolds following terminal sterilization. Also provided are methods for producing these compositions and terminally sterilized matrices or scaffolds from these compositions as well as methods of using these matrices or scaffolds as tissue engineering devices.
Owner:INTEGRA LIFESCI
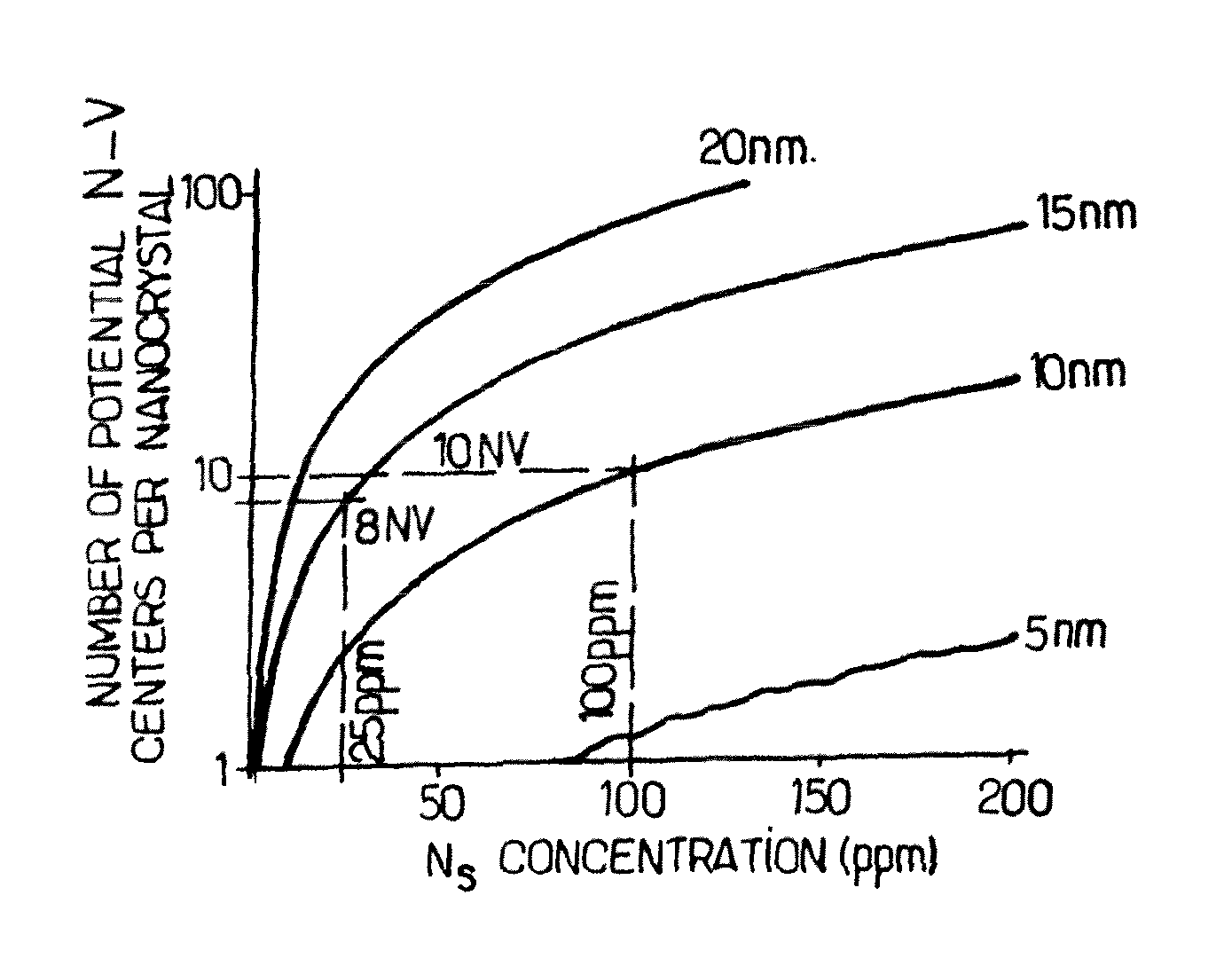
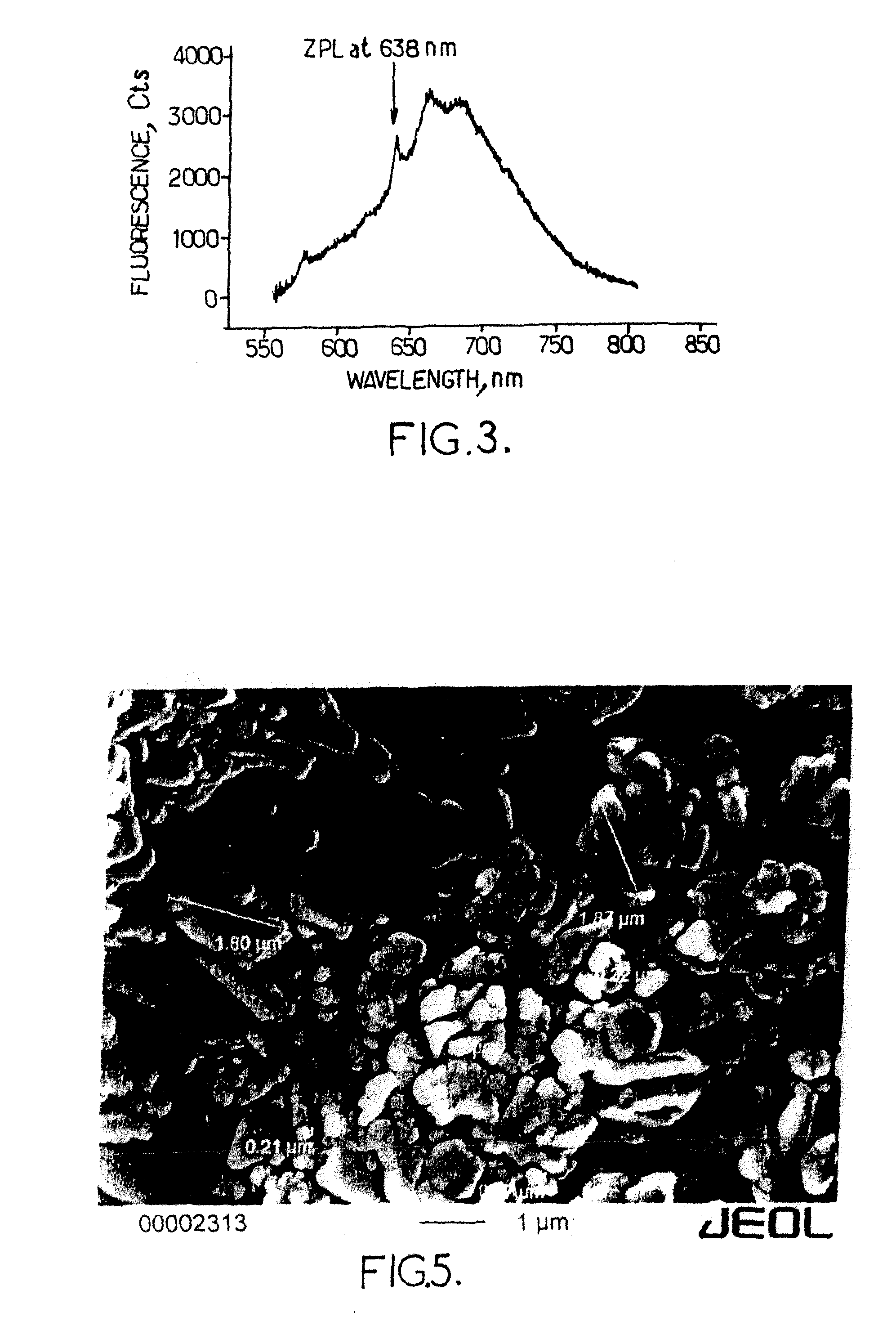
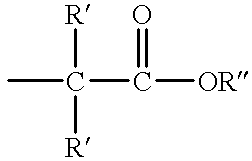
Method to produce light-emitting nano-particles of diamond
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Methods for sterilizing cyanoacrylate compositions
Disclosed are methods for sterilizing cyanoacrylate prepolymer compositions under E-beam irradiation conditions wherein the prepolymer remains in polymerizable form after sterilization.
Owner:ADVANCED MEDICAL SOLUTIONS PLYMOUTH
Multi-stage curing of low K nano-porous films
InactiveUS20050230834A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesThermal energyGas phase
Embodiments in accordance with the present invention relate to multi-stage curing processes for chemical vapor deposited low K materials. In certain embodiments, a combination of electron beam irradiation and thermal exposure steps may be employed to control selective outgassing of porogens incorporated into the film, resulting in the formation of nanopores. In accordance with one specific embodiment, a low K layer resulting from reaction between a silicon-containing component and a non-silicon containing component featuring labile groups, may be cured by the initial application of thermal energy, followed by the application of radiation in the form of an electron beam.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
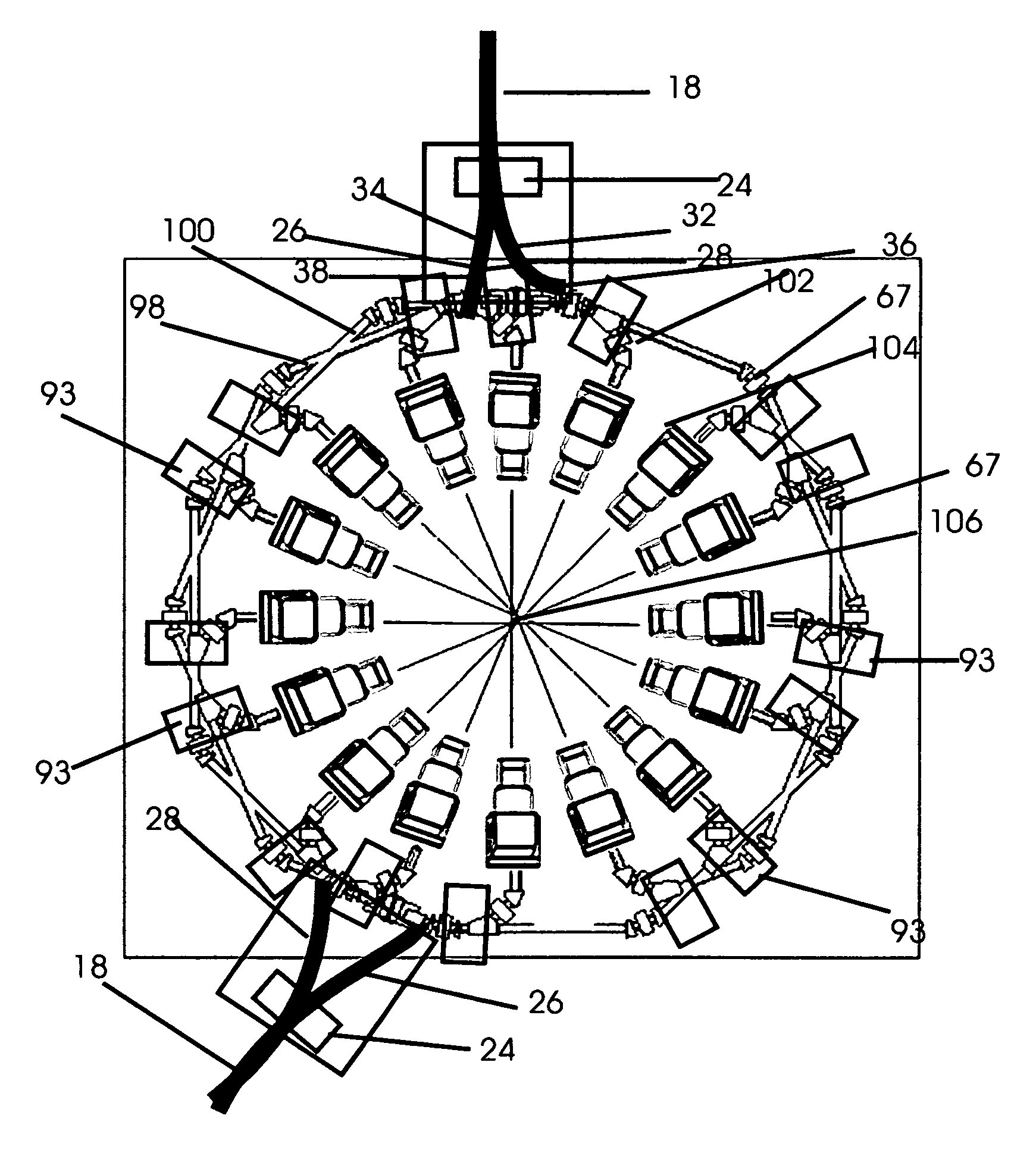
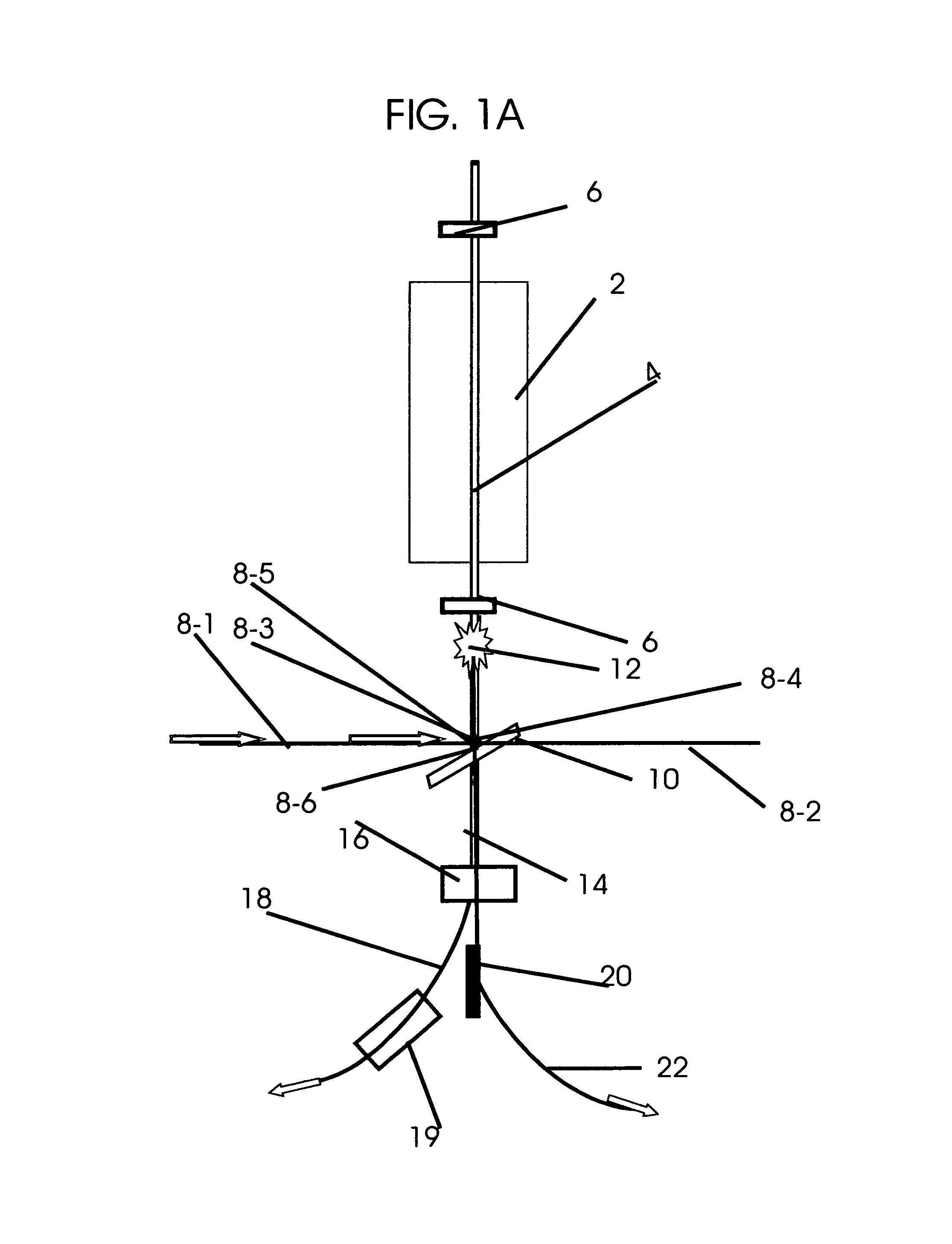
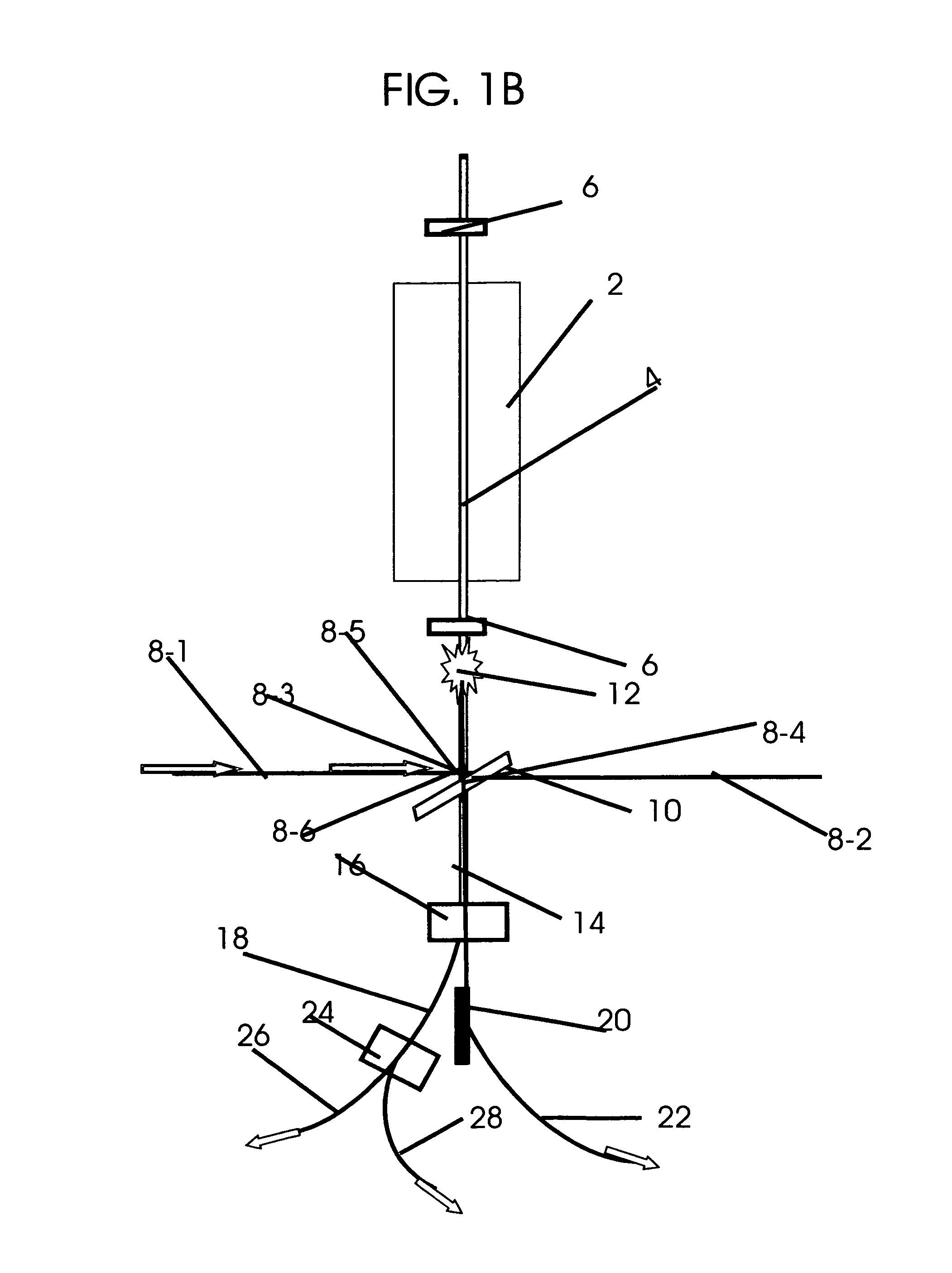
All field simultaneous radiation therapy
InactiveUS8173983B1Increase dose rateOvercome disadvantagesRadiation pyrometryElectrotherapyProstate cancerEstrogen receptor
This invention describes a system for generating multiple simultaneous tunable electron and photon beams and monochromatic x-rays for all field simultaneous radiation therapy (AFSRT), tumor specific AFSRT and screening for concealed elements worn on to the body or contained in a container. Inverse Compton scattering renders variable energy spent electron and tunable monochromatic x-rays. It's spent electron beam is reused for radiation with electron beam or to generate photon beam. Tumor specific radiation with Auger transformation radiation is facilitated by exposing high affinity tumor bound heavy elements with external monochromatic x-rays. Heavy elements like directly iodinated steroid molecule that has high affinity binding to estrogen receptor in breast cancer and to iodinated testosterone in prostate cancer or with directly implanted nanoparticles into the tumor are exposed with tuned external monochromatic x-rays for tumor specific radiation therapy. Likewise, screening element's atom's k, l, m, n shell specific Auger transformation radiation generated by its exposure to external monochromatic x-rays is used to screen for concealed objects. Multiple beam segments from a beam storage ring or from octagonal beam lines are simultaneously switched on for simultaneous radiation with multiple beams. The beam on time to expose a tumor or an object is only a few seconds. It also facilitates breathing synchronized radiation therapy. The intensity modulated radiation therapy (IMRT) and intensity modulated screening for concealed objects (IMSFCO) is rendered by varying beam intensities of multiple simultaneous beams. The isocentric additive high dose rate from simultaneously converging multiple beams, the concomitant hyperthermia and chemotherapy and tumor specific radiation therapy and the AFSRT's very low radiation to the normal tissue all are used to treat a tumor with lower radiation dose and to treat a radioresistant and multiple times recurrent tumors that heave no other alternative treatments.
Owner:SAHADEVAN VELAYUDHAN
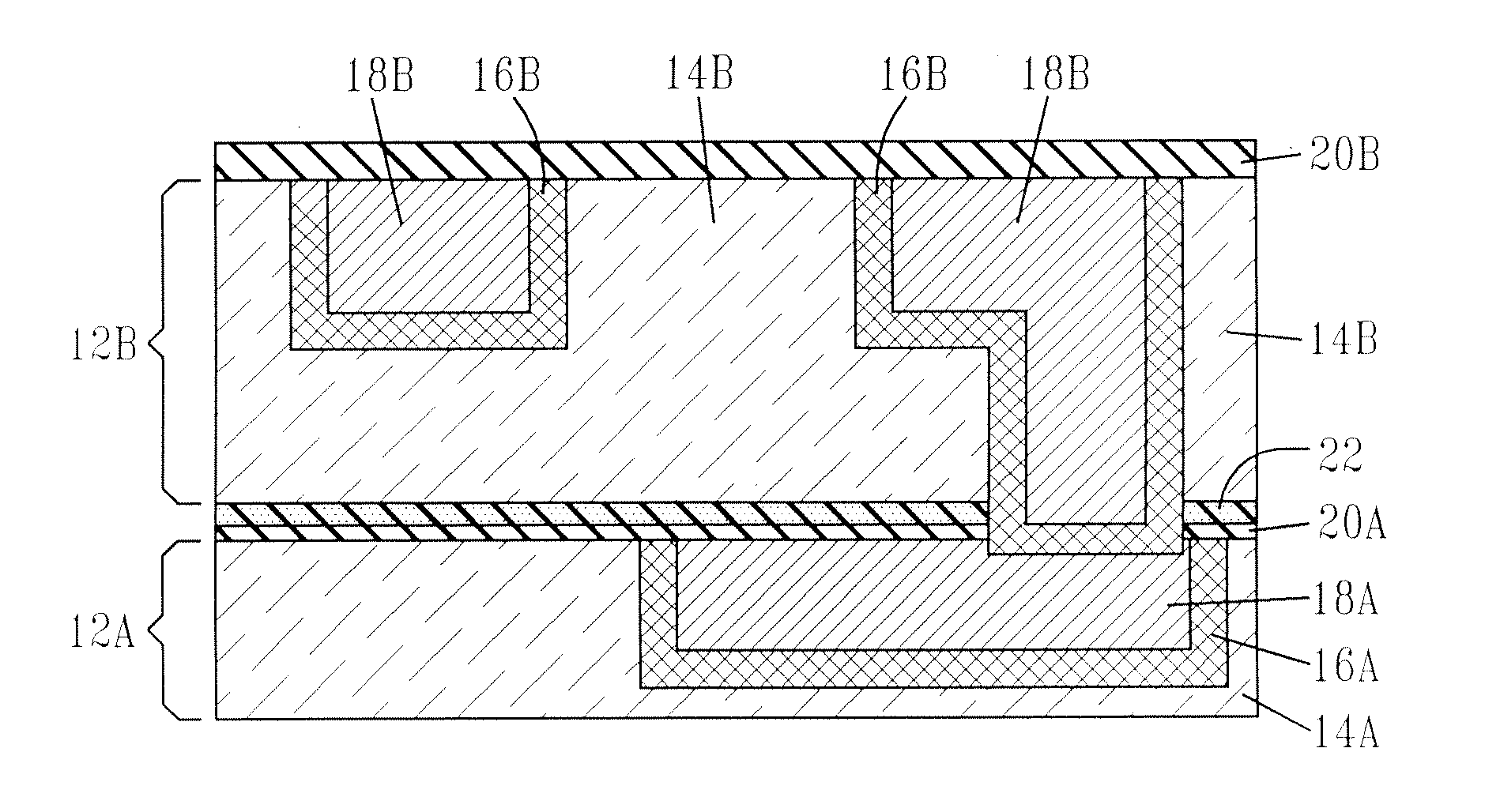
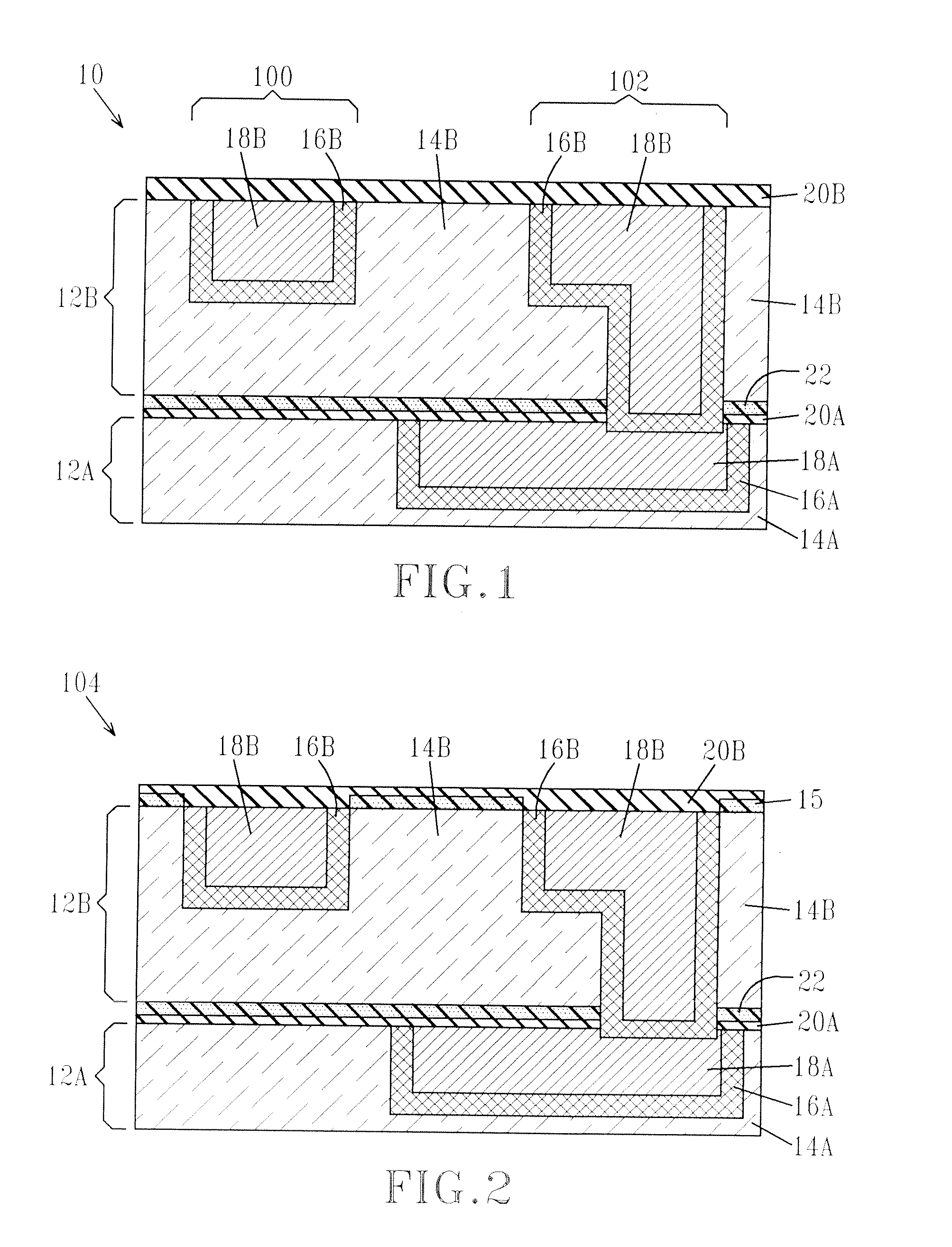
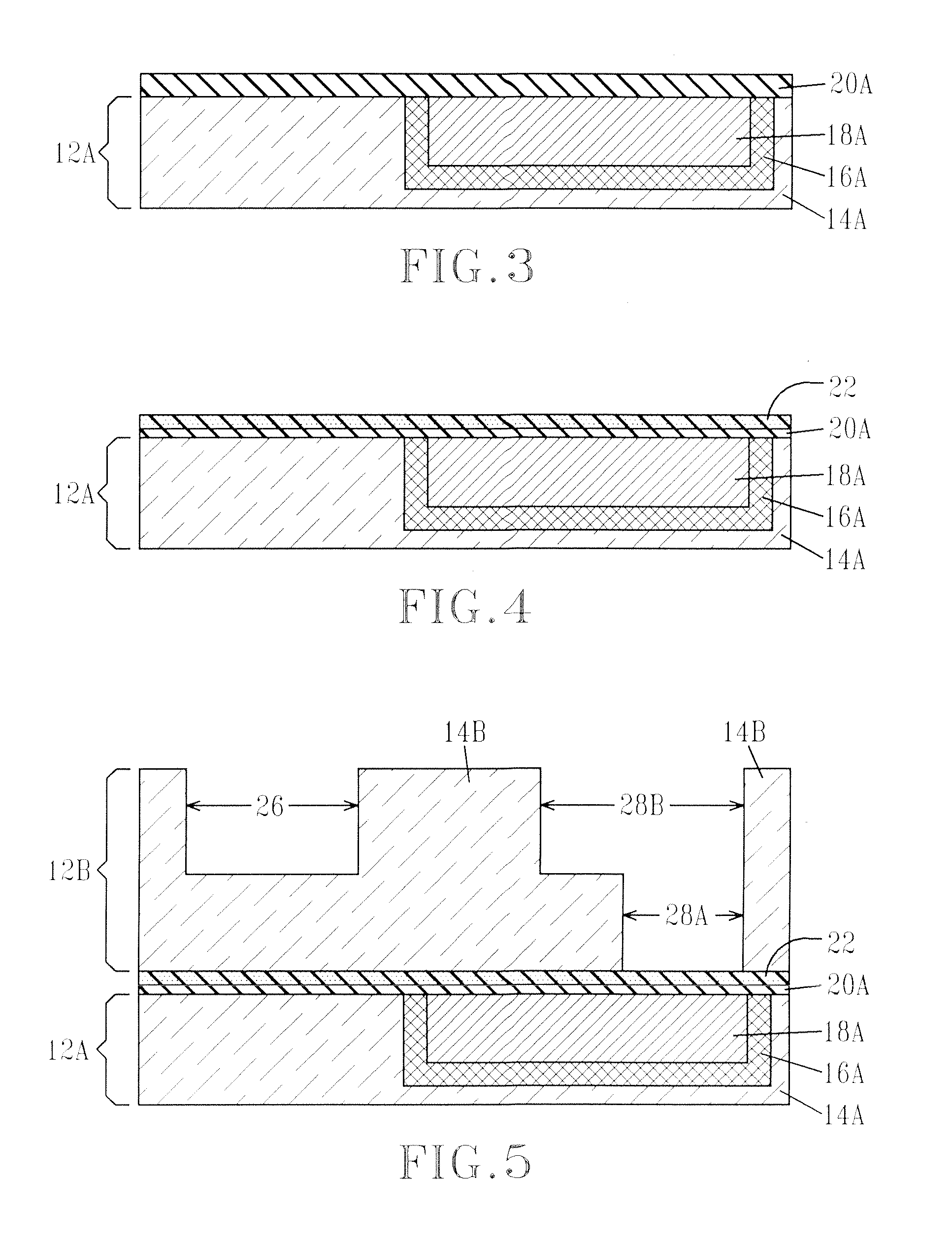
MECHANICALLY ROBUST METAL/LOW-k INTERCONNECTS
InactiveUS20080173984A1Improve adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface layerSemiconductor structure
A mechanically robust semiconductor structure with improved adhesion strength between a low-k dielectric layer and a dielectric-containing substrate is provided. In particular, the present invention provides a structure that includes a dielectric-containing substrate having an upper region including a treated surface layer which is chemically and physically different from the substrate; and a low-k dielectric material located on a the treated surface layer of the substrate. The treated surface layer and the low-k dielectric material form an interface that has an adhesion strength that is greater than 60% of the cohesive strength of the weaker material on either side of the interface. The treated surface is formed by treating the surface of the substrate with at least one of actinic radiation, a plasma and e-beam radiation prior to forming of the substrate the low-k dielectric material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Ultra low k (ULK) SiCOH film and method
InactiveUS7288292B2Improve mechanical propertiesHigh elastic modulusPigmenting treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsNano sizeGas phase
The present invention provides a multiphase, ultra low k film which exhibits improved elastic modulus and hardness as well as various methods for forming the same. The multiphase, ultra low k dielectric film includes atoms of Si, C, O and H, has a dielectric constant of about 2.4 or less, nanosized pores or voids, an elastic modulus of about 5 or greater and a hardness of about 0.7 or greater. A preferred multiphase, ultra low k dielectric film includes atoms of Si, C, O and H, has a dielectric constant of about 2.2 or less, nanosized pores or voids, an elastic modulus of about 3 or greater and a hardness of about 0.3 or greater. The multiphase, ultra low k film is prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition in which one of the following alternatives is utilized: at least one precursor gas comprising siloxane molecules containing at least three Si—O bonds; or at least one precursor gas comprising molecules containing reactive groups that are sensitive to e-beam radiation. Electronic structures including the multiphase, ultra low k film are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Polyolefin-Based Crosslinked Articles
ActiveUS20090298964A1Excellent set propertyHigh tensile strengthImpression capsElectric discharge tubesElastomerFiber
Methods for making a crosslinked elastomeric composition and articles made of the same are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, an elastomeric composition comprising at least one propylene-based polymer is blended with at least one component selected from the group consisting of multifunctional acrylates, multifunctional methacrylates, functionalized polybutadiene resins, functionalized cyanurate, and allyl isocyanurate; and blended with at least one component selected from the group consisting of hindered phenols, phosphites, and hindered amines. The propylene-based polymer can include propylene derived units and one or more dienes, and have a triad tacticity of from 50% to 99% and a heat of fusion of less than 80 J / g. The blended composition can then be extruded and crosslinked. The extruded polymer can be crosslinked using electron beam radiation having an e-beam dose of about 100 KGy or less. The crosslinked polymers are particularly useful for making fibers and films.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Bimodal compounds having an elastomeric moiety
A bi-modal compound is provided having an elastomeric moiety and a second moiety derived from any of a metal, a ceramic, and thermoplastic. At least one free radical site is generated (preferably with electron beam radiation) on an elastomer molecule to provide the elastomeric moiety; and a metal, ceramic, or thermoplastic are then bonded to the free radical site.
Owner:FREUDENBERG NOK GEN PARTNERSHIP
Method and apparatus for validation of sterilization process
InactiveUS20050135965A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationDosimeterEngineering
An apparatus, system and method for verifying the achievement of a desired sterility assurance level (SAL) for components manipulated within a low-energy electron beam sterilization chamber. The components are preferably pre-sterilized and connected together in an assembly fashion which creates and maintains the sterility of the connection by subjecting the components to low-energy (less than 300 KeV) electron beam radiation. The verification is completed by measuring the sterilization dose delivered to a sensor, also known as a dosimeter, positioned within the sterilization process to simulate the components.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Layer transfer of films utilizing controlled shear region
ActiveUS20090277314A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMetal working apparatusEngineeringThermal treatment
A film of material may be formed by providing a semiconductor substrate having a surface region and a cleave region located at a predetermined depth beneath the surface region. During a process of cleaving the film from the substrate, shear in the cleave region is carefully controlled. According to certain embodiments, an in-plane shear component (KII) is maintained near zero, sandwiched between a tensile region and a compressive region. In one embodiment, cleaving can be accomplished using a plate positioned over the substrate surface. The plate serves to constrain movement of the film during cleaving, and together with a localized thermal treatment reduces shear developed during the cleaving process. According to other embodiments, the KII component is purposefully maintained at a high level and serves to guide and drive fracture propagation through the cleave sequence. In one embodiment, the high KII component is achieved by adiabatic heating of silicon through exposure to E-beam radiation, which imparts a highly abrupt thermal gradient and resulting stress at a precisely defined depth in the silicon.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
MECHANICALLY ROBUST METAL/LOW-k INTERCONNECTS
InactiveUS20090294925A1Improve adhesionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSurface layerSemiconductor structure
A mechanically robust semiconductor structure with improved adhesion strength between a low-k dielectric layer and a dielectric-containing substrate is provided. In particular, the present invention provides a structure that includes a dielectric-containing substrate having an upper region including a treated surface layer which is chemically and physically different from the substrate; and a low-k dielectric material located on a the treated surface layer of the substrate. The treated surface layer and the low-k dielectric material form an interface that has an adhesion strength that is greater than 60% of the cohesive strength of the weaker material on either side of the interface. The treated surface is formed by treating the surface of the substrate with at least one of actinic radiation, a plasma and e-beam radiation prior to forming of the substrate the low-k dielectric material.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Electron beam inter-curing of plastic and elastomer blends
Two-phase or single-phase admixtures of a plastic and an elastomer, two or more thermoplastics, or two or more elastomers are irradiated (preferably with electron beam radiation) to cross-link the thermoplastic and, in the case of elastomer and thermoplastic admixtures, generate bi-modal molecules having moieties derived from both the elastomer and the thermoplastic.
Owner:FREUDENBERG NOK GEN PARTNERSHIP
UV/EB cured integrated magnets-composition and method of fabrication
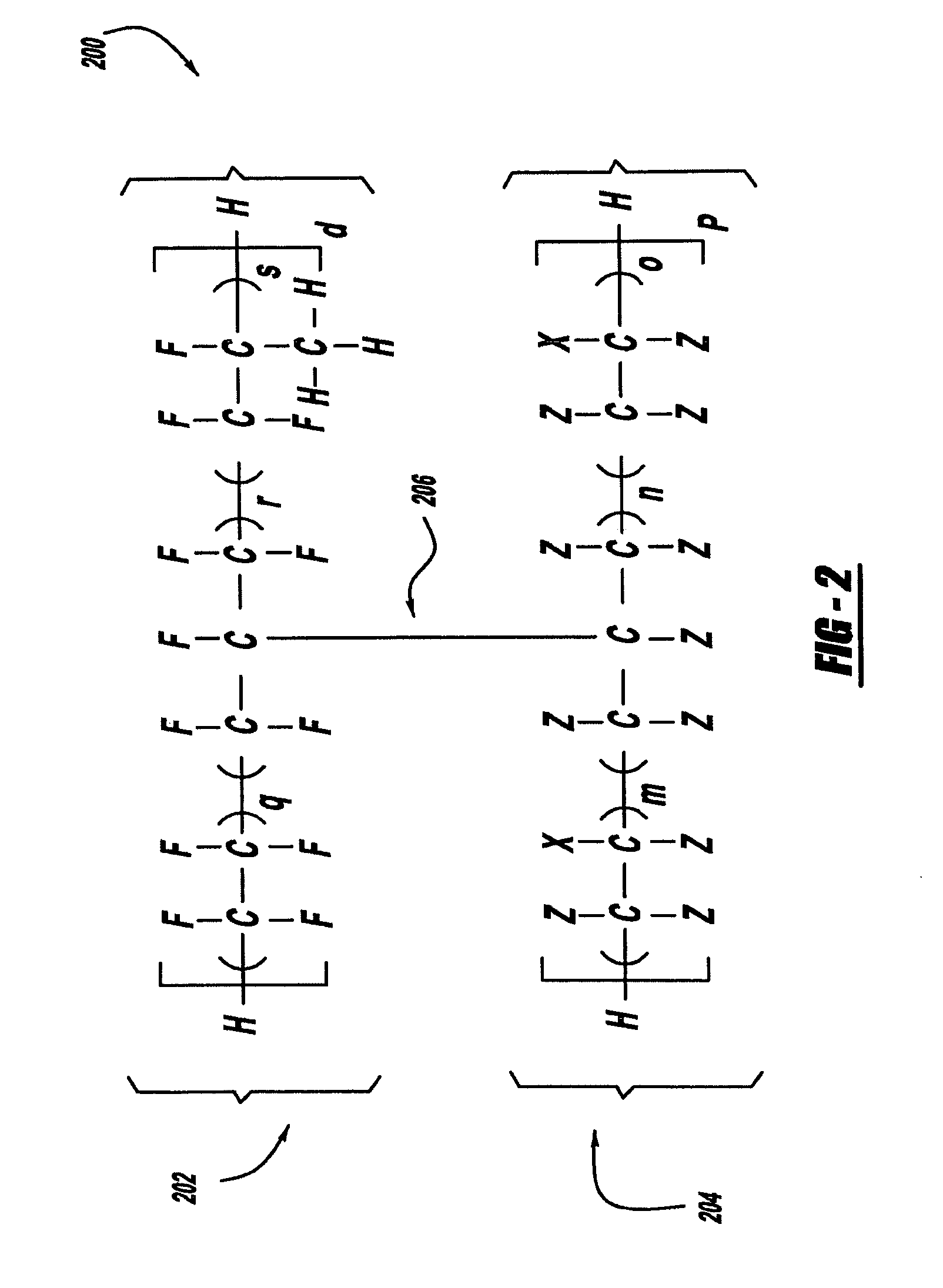
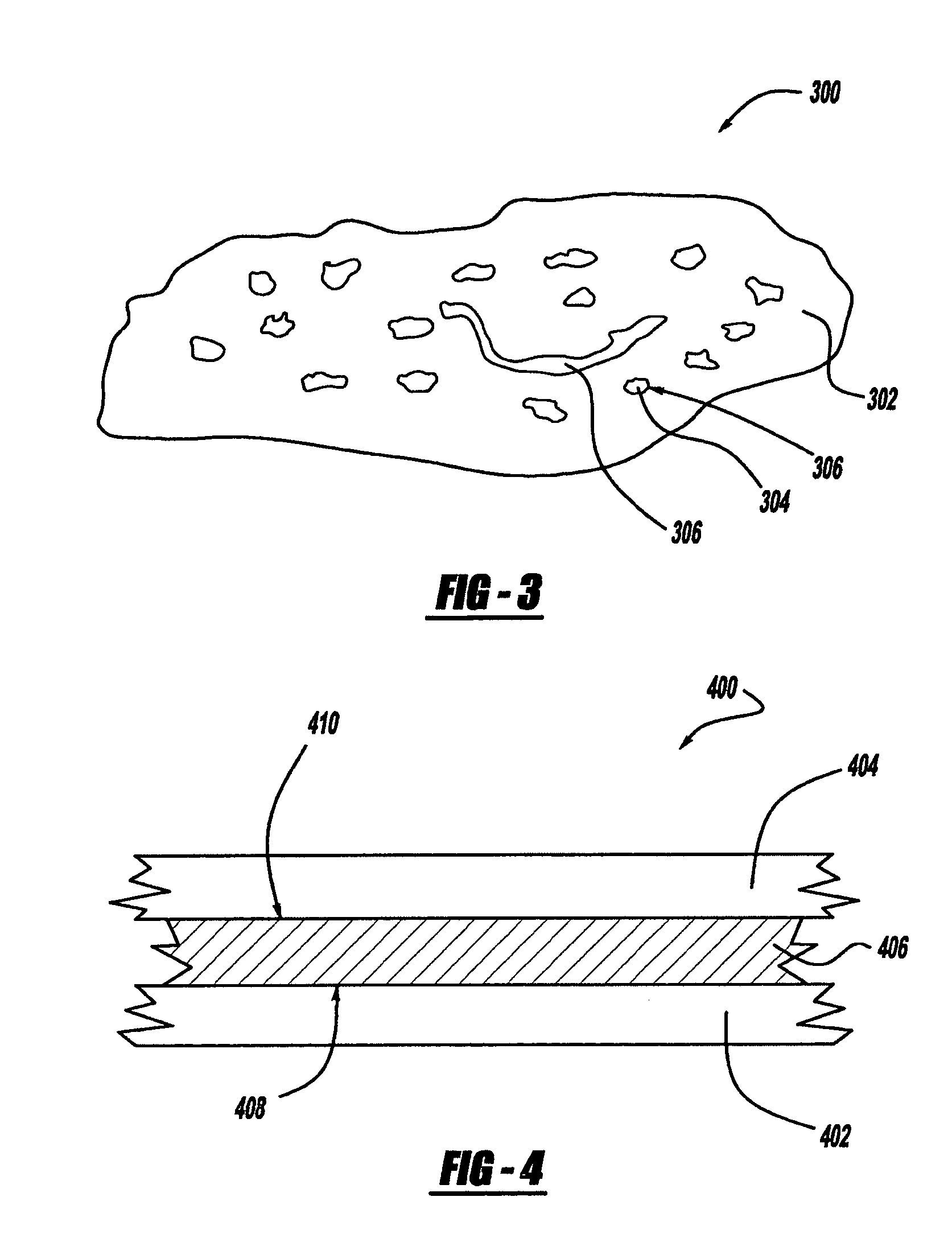
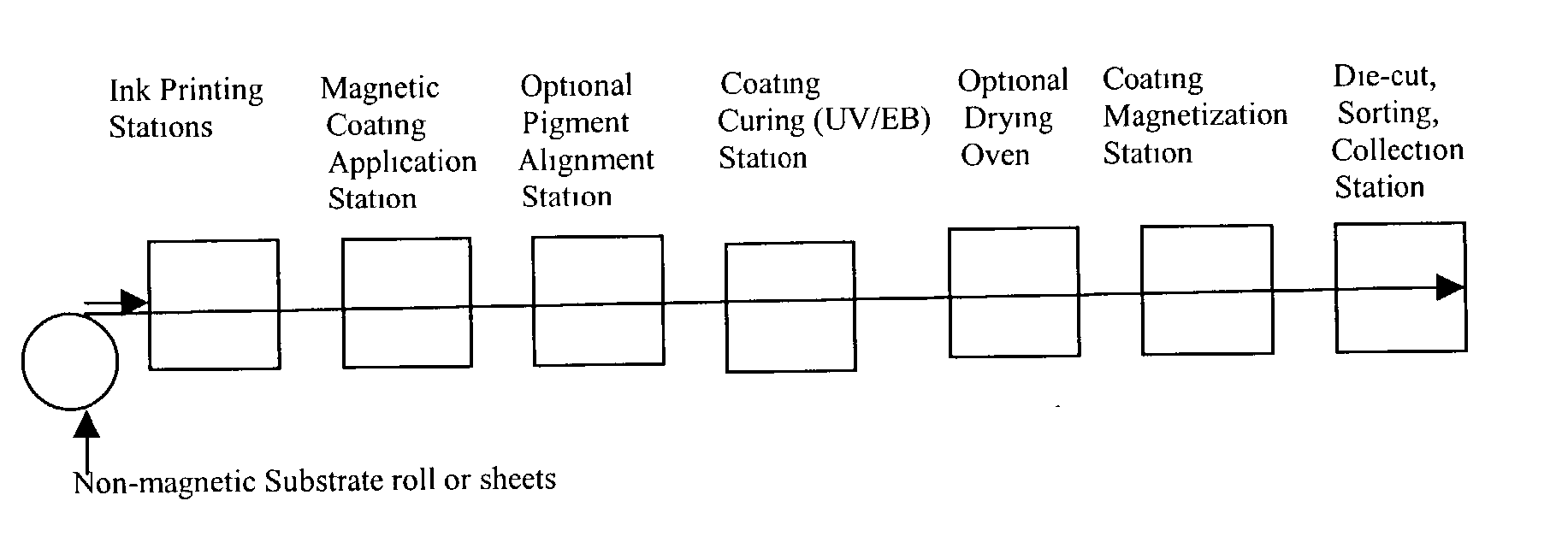
The present invention comprises a radiation curable composition for in-line printing containing magnetic pigments capable of being magnetized to possess permanent magnetic properties after the composition is cured. The composition is cured by an ionizing radiation source, preferably by UV light or electron beam radiation (UV / EB). The present invention is also directed to an in-line process for printing magnetic images on non-magnetic substrate, comprising: pattern applying the above mentioned radiation curable composition on the substrate opposite to a print side, pre-aligning the magnetic pigment particles (if necessary) of the applied composition, curing the composition by ionizing radiation source (UV / EB), magnetizing the cured composition, then finishing the final piece. The finishing step could involve delivering the final piece in a simple sheet with die cut magnets or creating an "integrated magnet" format involving plow folding over the magnet panel, pattern coating or flood coating an adhesive that will only adhere the non-magnet matrix areas between die cut magnets, thus, allowing for the individual magnets to be "popped" out of the carrier by the final end user. The resulting magnetized pieces will possess holding power like magnets (refrigerator and office magnets) and are capable of carrying personalized, Scitex imaged and direct marketing information (including redemption value for coupons, local public service access numbers, etc.)
Owner:SOVEREIGN SPECIALTY CHEM +1
Electron beam curing in a composite having a flow resistant adhesive layer
ActiveUS20060003127A1Improve performanceLamination ancillary operationsOther chemical processesBi modalAdhesive
A composite having two structural layers of (independently) metal, polymer, or ceramic is connected with a polymeric adhesive layer positioned in solid form between the two layers. The adhesive layer is inter-bonded after positioning with at least one structural layer by a bi-modal molecule derived from treating the solid adhesive and other layers with radiation (preferably, electron beam radiation). Items such as a dynamic and static seals, gaskets, pump diaphragms, hoses, and o-rings all benefit from the technique.
Owner:FREUDENBERG NOK GEN PARTNERSHIP
Ultra low K (ULK) SiCOH film and method
InactiveUS20050276930A1Improve mechanical propertiesHigh elastic modulusPigmenting treatmentSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsGas phaseElectron
The present invention provides a multiphase, ultra low k film which exhibits improved elastic modulus and hardness as well as various methods for forming the same. The multiphase, ultra low k dielectric film includes atoms of Si, C, O and H, has a dielectric constant of about 2.4 or less, nanosized pores or voids, an elastic modulus of about 5 or greater and a hardness of about 0.7 or greater. A preferred multiphase, ultra low k dielectric film includes atoms of Si, C, O and H, has a dielectric constant of about 2.2 or less, nanosized pores or voids, an elastic modulus of about 3 or greater and a hardness of about 0.3 or greater. The multiphase, ultra low k film is prepared by plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition in which one of the following alternatives is utilized: at least one precursor gas comprising siloxane molecules containing at least three Si—O bonds; or at least one precursor gas comprising molecules containing reactive groups that are sensitive to e-beam radiation. Electronic structures including the multiphase, ultra low k film are also disclosed.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Electron beam curable toners and processes thereof
A process having a step of radiating toner with electron beam radiation, wherein the radiation results in curing the toner is disclosed. A toner curing process is disclosed wherein toner is radiated, wherein the toner comprises at least one resin and at least one colorant, and wherein the toner is generated by an emulsion aggregation coalescence method. A method for crosslinking toner particles is disclosed wherein toner particles formed by an emulsion aggregation process are radiated with electron beam radiation, and wherein the toner particles contain at least one resin with crosslinkable functional groups.
Owner:XEROX CORP
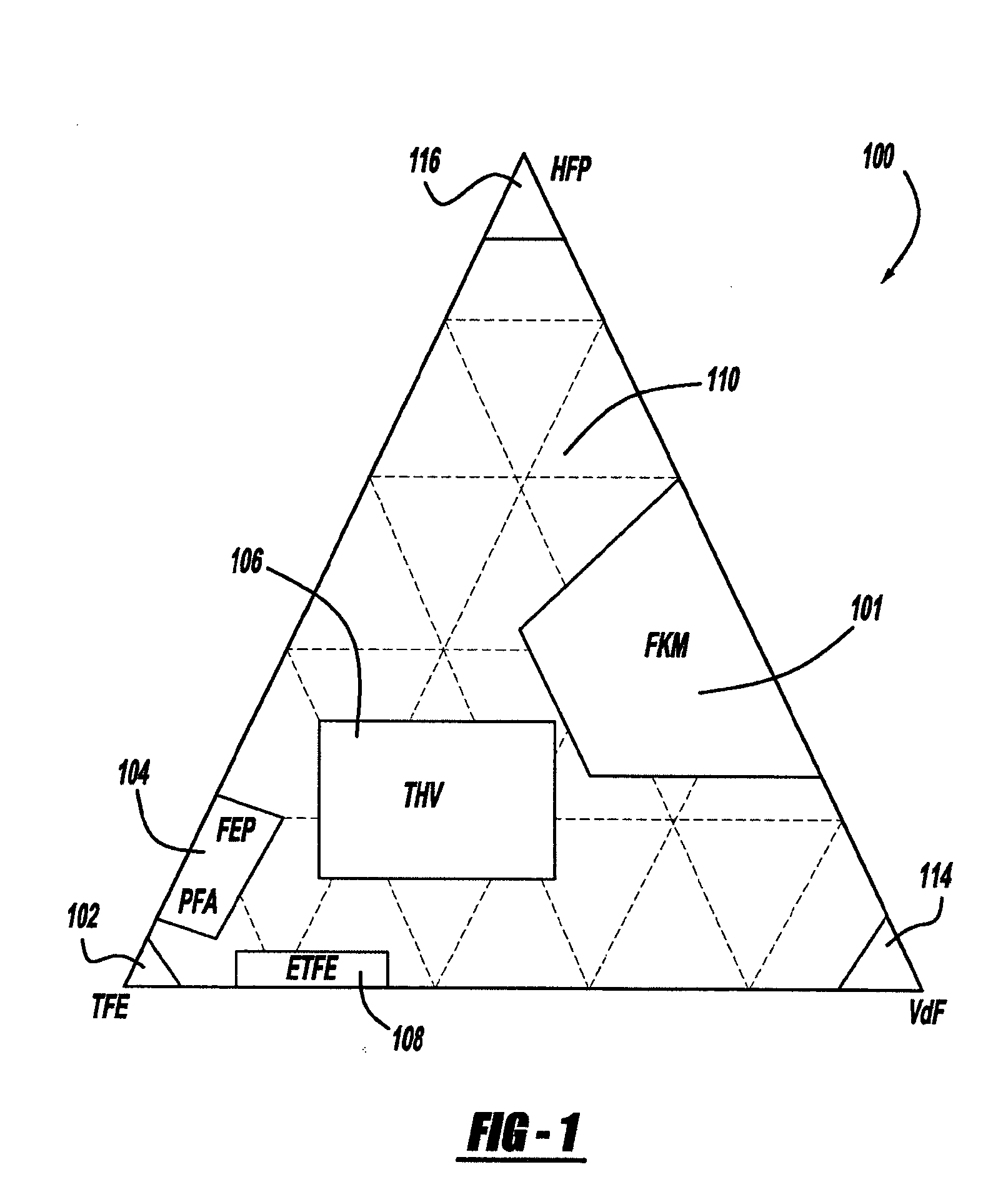
Block copolymers and lithographic patterning using same
ActiveUS20140370442A1Electric discharge tubesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusLithographic artistFiltration
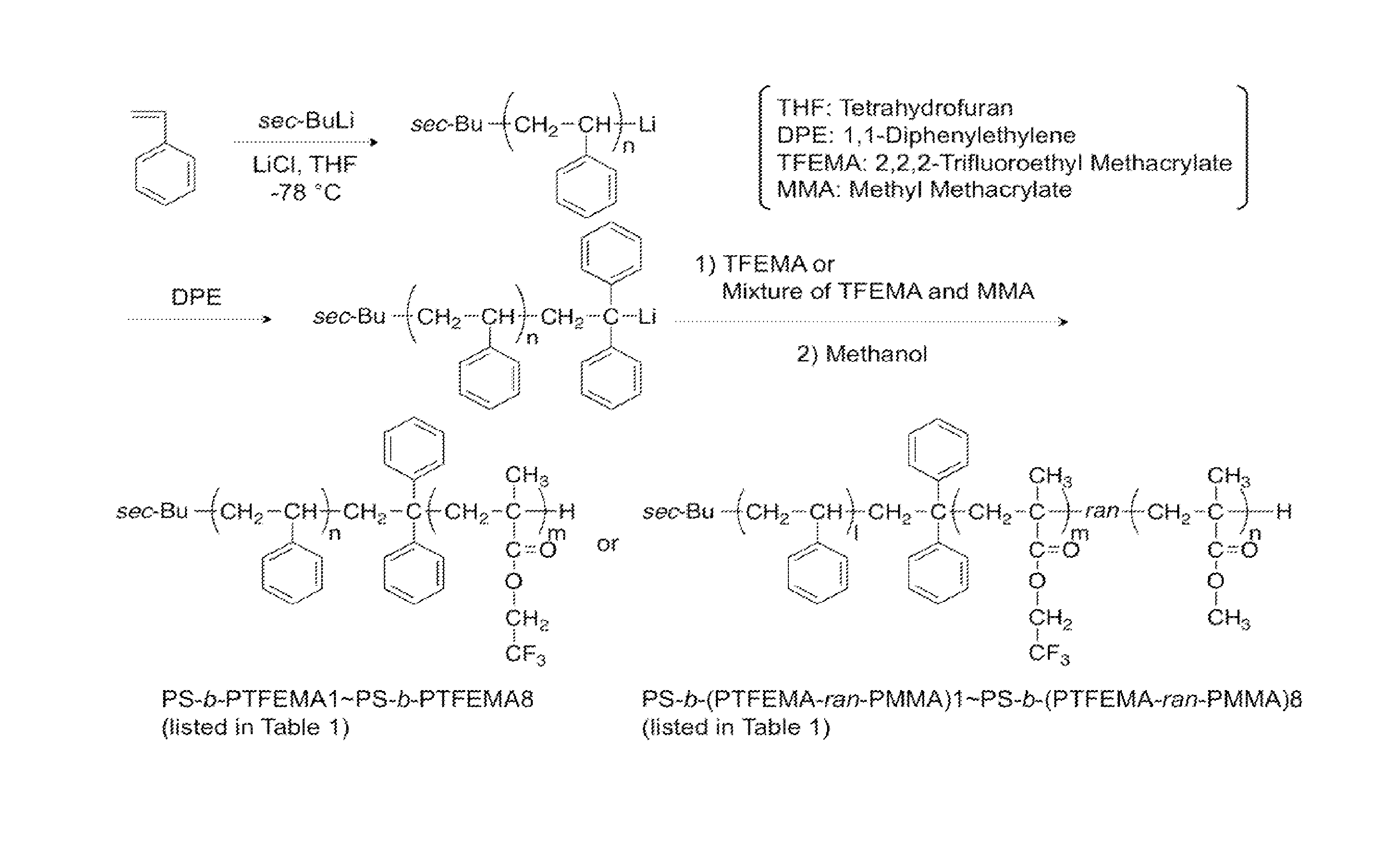
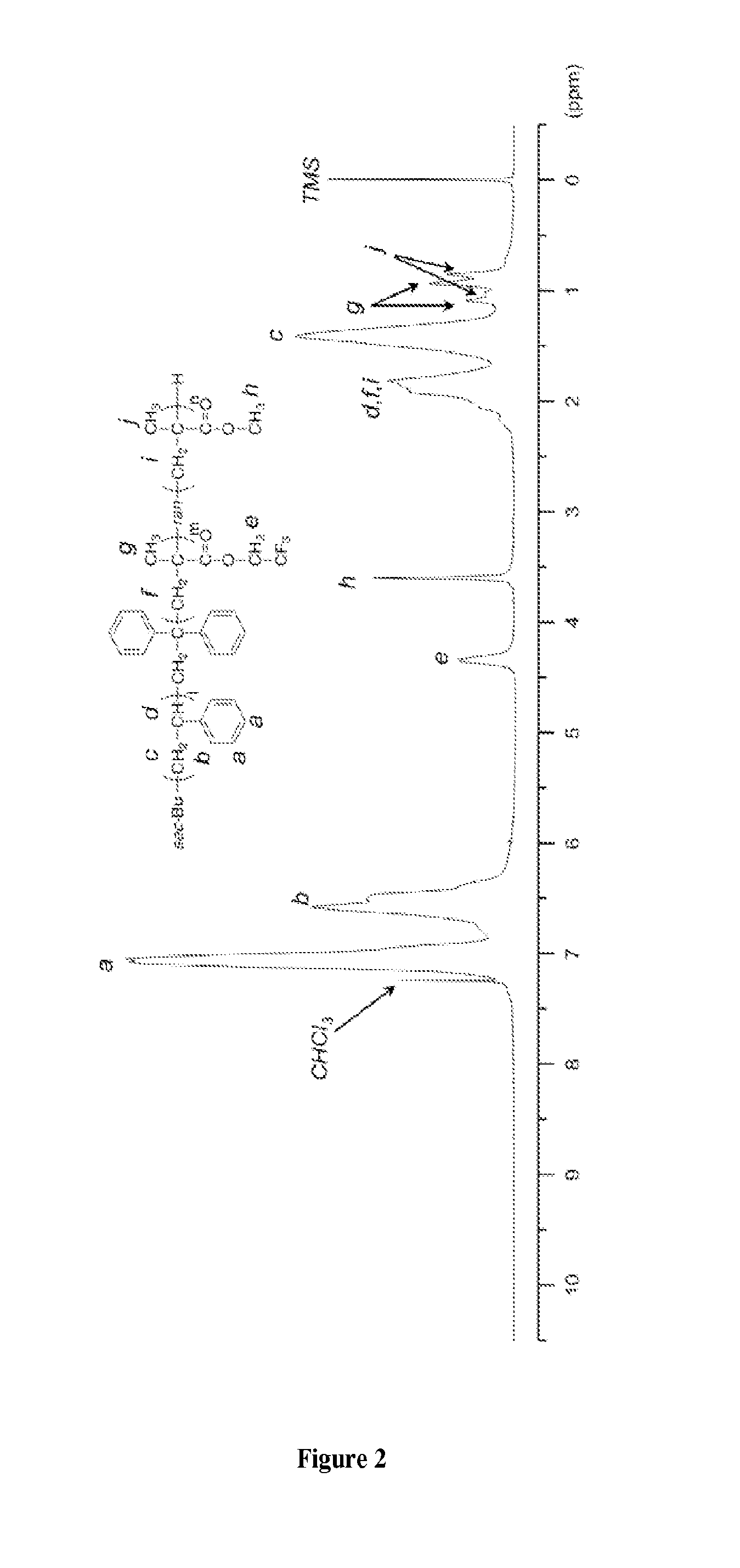
Block copolymers and methods of making patterns of organic thin films using the block copolymers. The block copolymers comprise a fluorinated block. Thin films of the block copolymers have microdomains that can be aligned. As a result the patterns of organic thin films having smaller dimensions than the pattern of incident deep-UV or e-beam radiation can be formed. For example, the block copolymers can be used in lithography, filtration, and templating applications.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
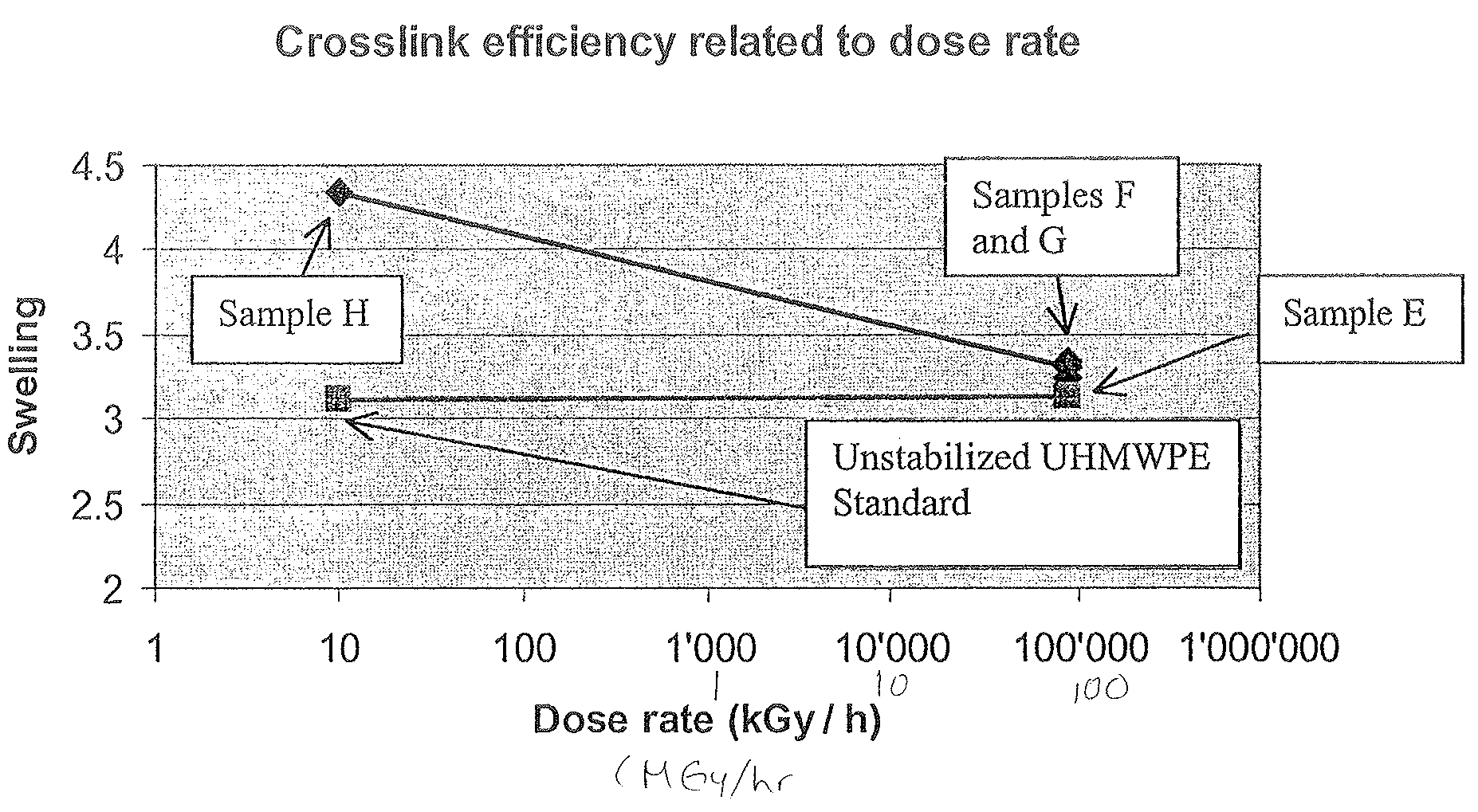
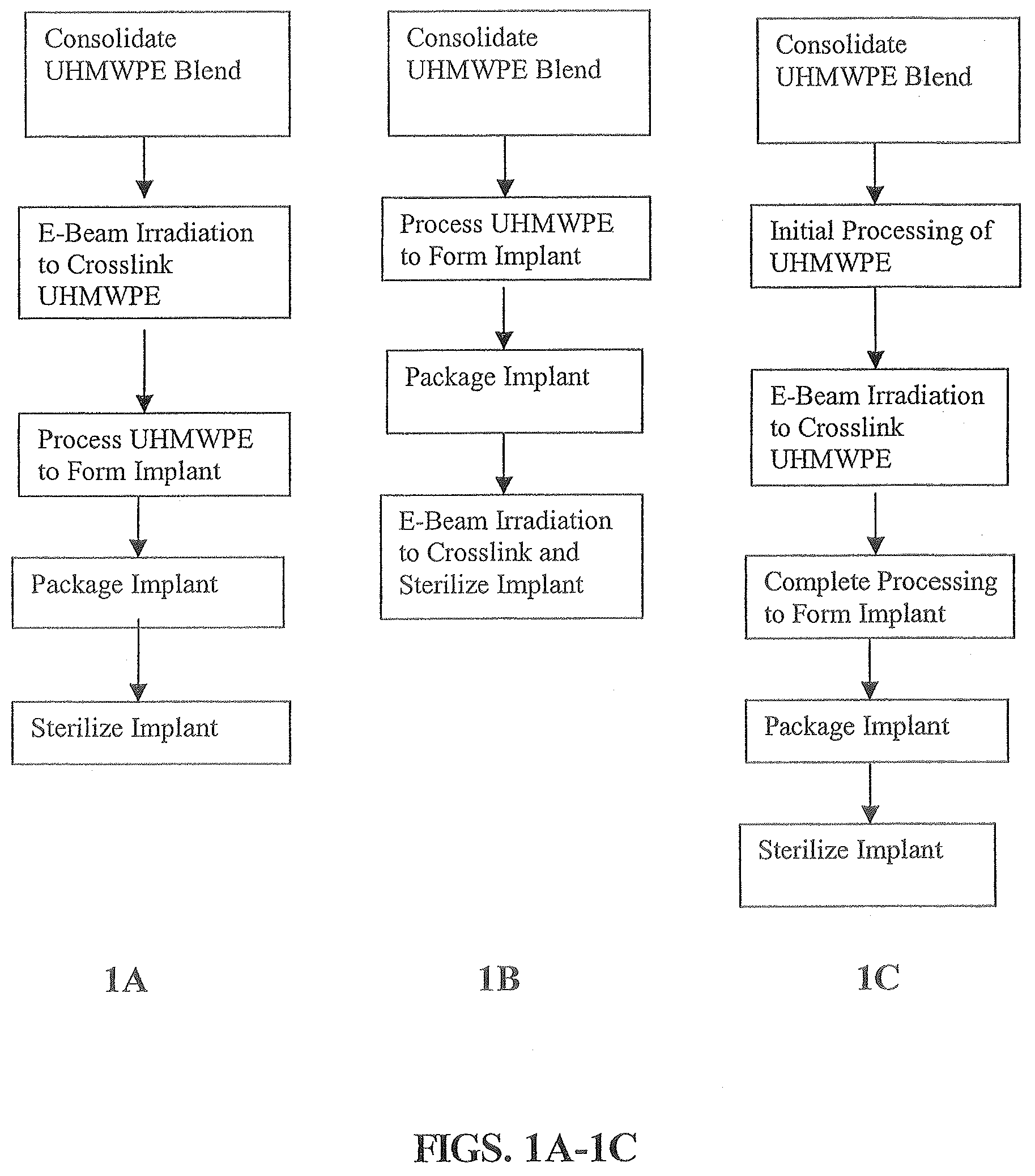
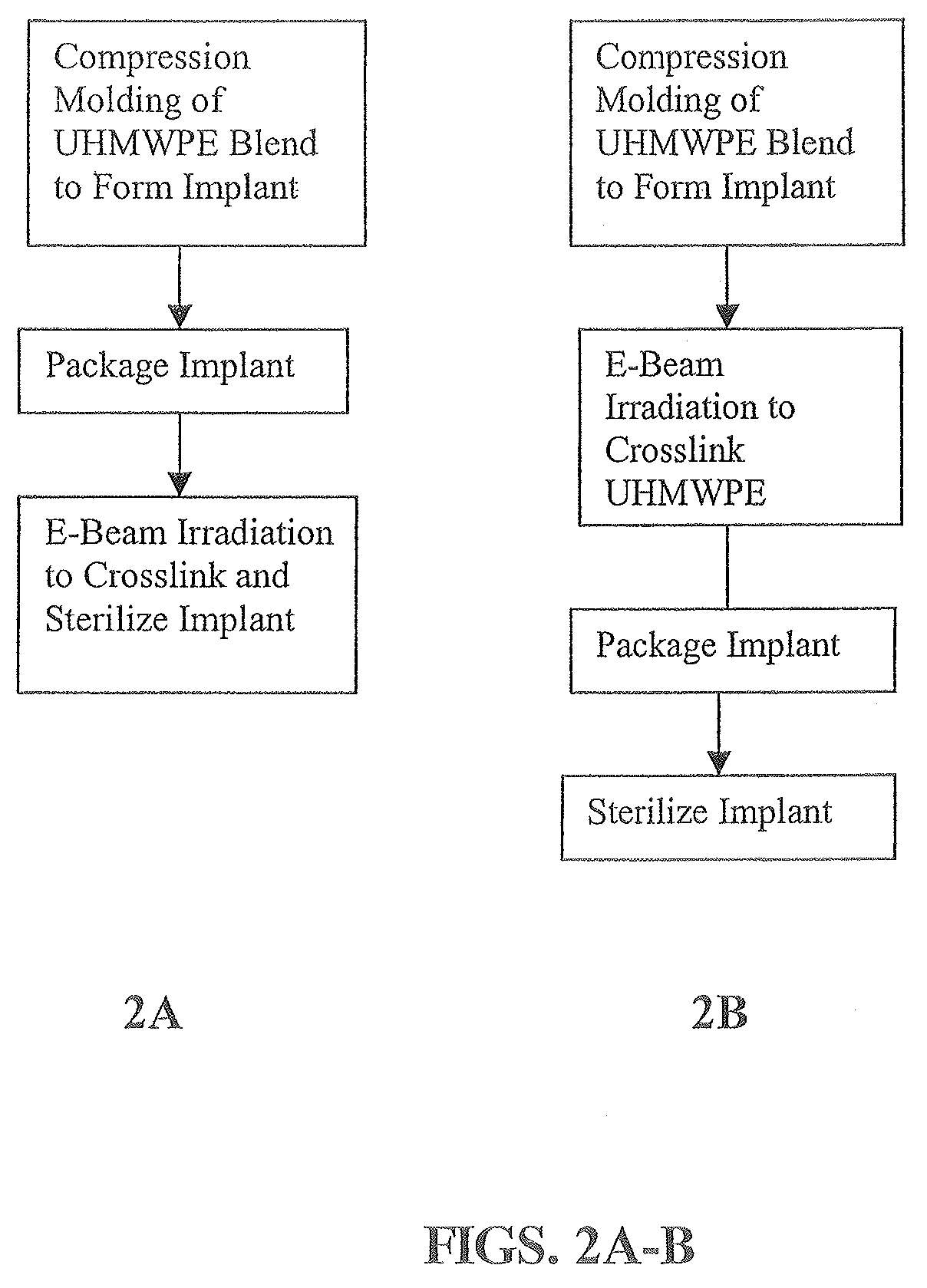
Ultra high molecular weight polyethylene articles and methods of forming ultra high molecular weight polyethylene articles
ActiveUS7863348B2Evenly distributedOrganic active ingredientsImpression capsMedicineUltra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene
The present invention generally provides implantable articles and methods of forming implantable articles from a crosslinked ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene (“UHMWPE”) blend stabilized with Vitamin E. The crosslinked UHMWPE blend may be prepared by combining the UHMWPE material and vitamin E prior to irradiating the UHMWPE blend with electron beam radiation at a sufficient radiation dose rate to induce crosslinking. The crosslinked UHMWPE blend may be incorporated into a variety of implants, and in particular, into endoprosthetic joint replacements
Owner:ZIMMER GMBH
Method and apparatus for forming silicon-containing insulation film having low dielectric constant
ActiveUS20050034667A1Low dielectric constantHigh mechanical strengthElectric discharge tubesPretreated surfacesPhysical chemistryDielectric permittivity
A silicon-containing insulation film is formed on a substrate by plasma reaction using a reaction gas including (i) a source gas comprising a silicon-containing hydrocarbon compound containing multiple cross-linkable groups, (ii) a cross-linking gas, and (iii) an inert gas, into a reaction chamber where a substrate is placed. The insulation film is then exposed to electron beam radiation, thereby increasing mechanical strength of the film without substantial alternation of its dielectric constant.
Owner:ASM JAPAN
Preparation process of ethylene propylene diene rubber foaming materials
InactiveCN101824189AUniform Radiation VulcanizationIncreased Radiation Processing EnergyCross-linkVulcanization
The invention discloses a preparation process of ethylene propylene diene rubber foaming materials. A rubber compounding recipe of the invention consists of ingredients of rubber base materials, an anti-aging system, a filling system, a plasticizing agent, a vulcanizing system, a foaming system and a radiation cross linking sensitizing agent. The ethylene propylene diene rubber foaming materials are prepared through vulcanization foaming and demolding after the pretreatment of compounding, sheet cutting and electronic beam radiation pretreatment. The rubber sheets of the invention after radiation pretreatment have a certain pre-cross-linking degree before the heating vulcanization foaming, the fit of the vulcanization speed and the foaming velocity can be realized, the integral performance of products can be improved, the pre-vulcanization time can be shortened, energy sources can be saved, and the production efficiency can be improved.
Owner:BEIJING RADIATION APPL RES CENT
Layer transfer of films utilizing controlled propagation
ActiveUS20100055874A1Quality improvementImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductorSilicon
A film of material may be formed by providing a semiconductor substrate having a surface region and a cleave region located at a predetermined depth beneath the surface region. During a process of cleaving the film from the substrate, shear in the cleave region is carefully controlled to achieve controlled propagation by either KII or energy propagation control. According to certain embodiments, an in-plane shear component (KII) is maintained near zero by adiabatic heating of silicon through exposure to E-beam radiation. According to other embodiments, a surface heating source in combination with an implanted layer serves to guide fracture propagation through the cleave sequence.
Owner:SILICON GENERAL CORPORATION
Dual-network hydrogel electrolyte and preparation and application thereof
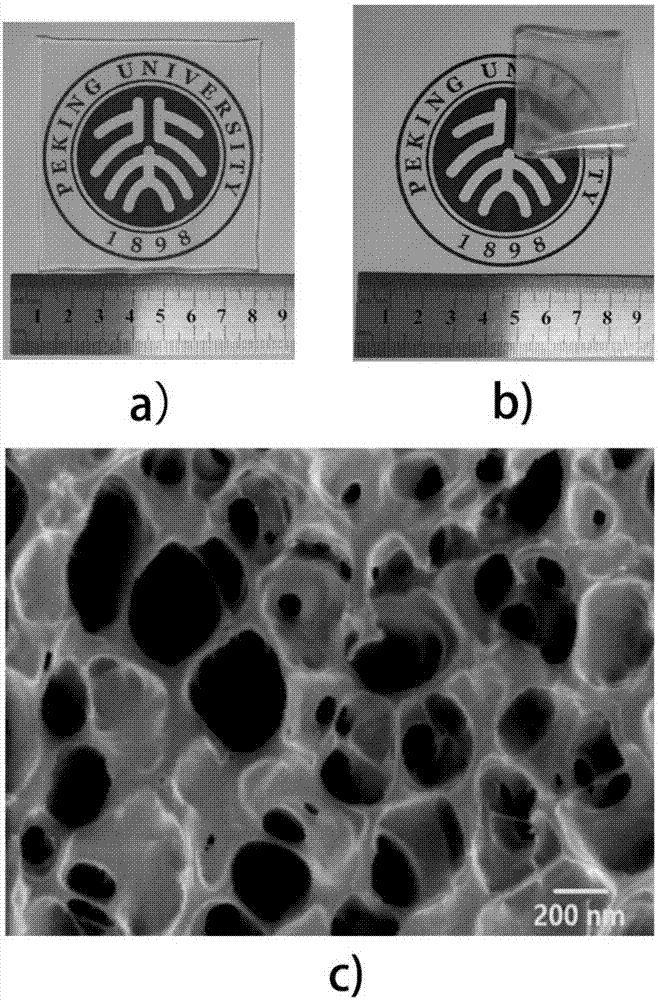
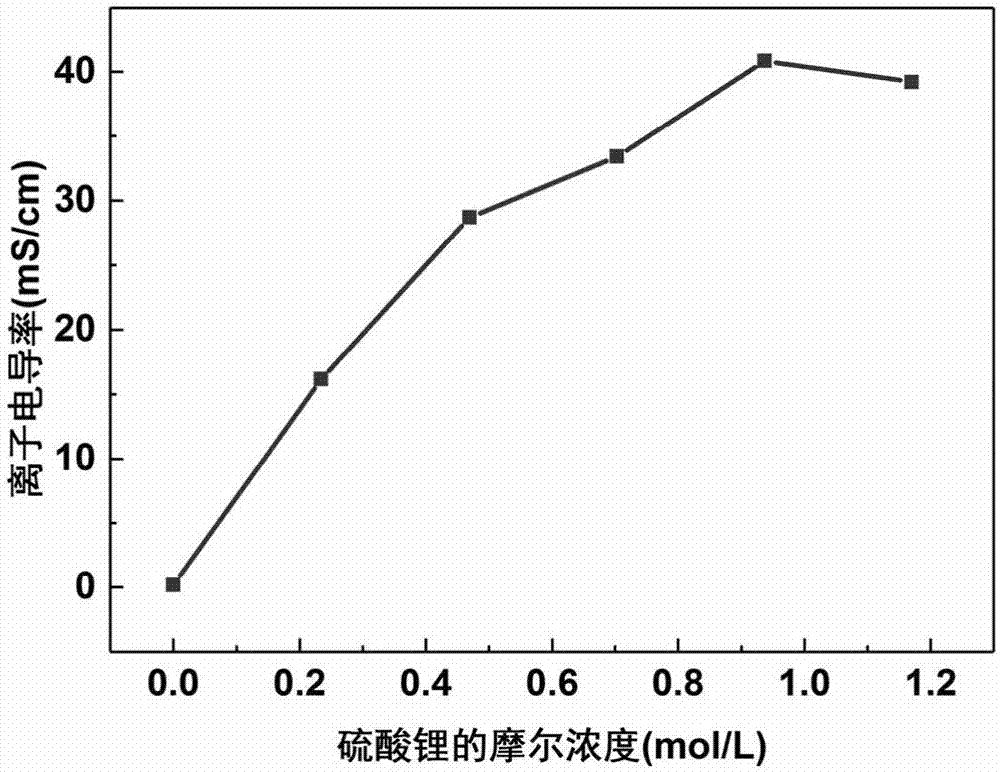
ActiveCN107481869AImprove conductivityCompliance with flexibilityHybrid capacitor electrolytesCapacitancePolymer network
The invention discloses a high-strength and high-conductivity neutral dual-network hydrogel electrolyte and a preparation method and an application thereof. The rigid and water-soluble natural high-molecular material is used as a first polymer network, the flexible and water-soluble synthetic high-molecular material acts as a second polymer network, the sulfate acts as neutral conductive inorganic salt, and the natural high-molecular / synthetic high-molecular neutral dual-network hydrogel electrolyte containing the sulfate is obtained by using the preparation method of gamma-ray or electron beam radiation polymerization crosslinking. The hydrogel electrolyte and activated carbon electrode are assembled into a flexible supercapacitor which has the same specific capacitance and better rate performance and charge and discharge cycling stability in comparison with the supercapacitor assembled by using the same sulfate aqueous solution as the electrolyte and also has excellent anti-compression and compression-resistant performance and anti-bending and bend-resistant performance.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Polyolefin-based crosslinked articles
ActiveUS7867433B2Little to no loss in tensile strengthMaintain good propertiesImpression capsElectric discharge tubesElastomerFiber
Methods for making a crosslinked elastomeric composition and articles made of the same are provided. In at least one specific embodiment, an elastomeric composition comprising at least one propylene-based polymer is blended with at least one component selected from the group consisting of multifunctional acrylates, multifunctional methacrylates, functionalized polybutadiene resins, functionalized cyanurate, and allyl isocyanurate; and blended with at least one component selected from the group consisting of hindered phenols, phosphites, and hindered amines. The propylene-based polymer can include propylene derived units and one or more dienes, and have a triad tacticity of from 50% to 99% and a heat of fusion of less than 80 J / g. The blended composition can then be extruded and crosslinked. The extruded polymer can be crosslinked using electron beam radiation having an e-beam dose of about 100 KGy or less. The crosslinked polymers are particularly useful for making fibers and films.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
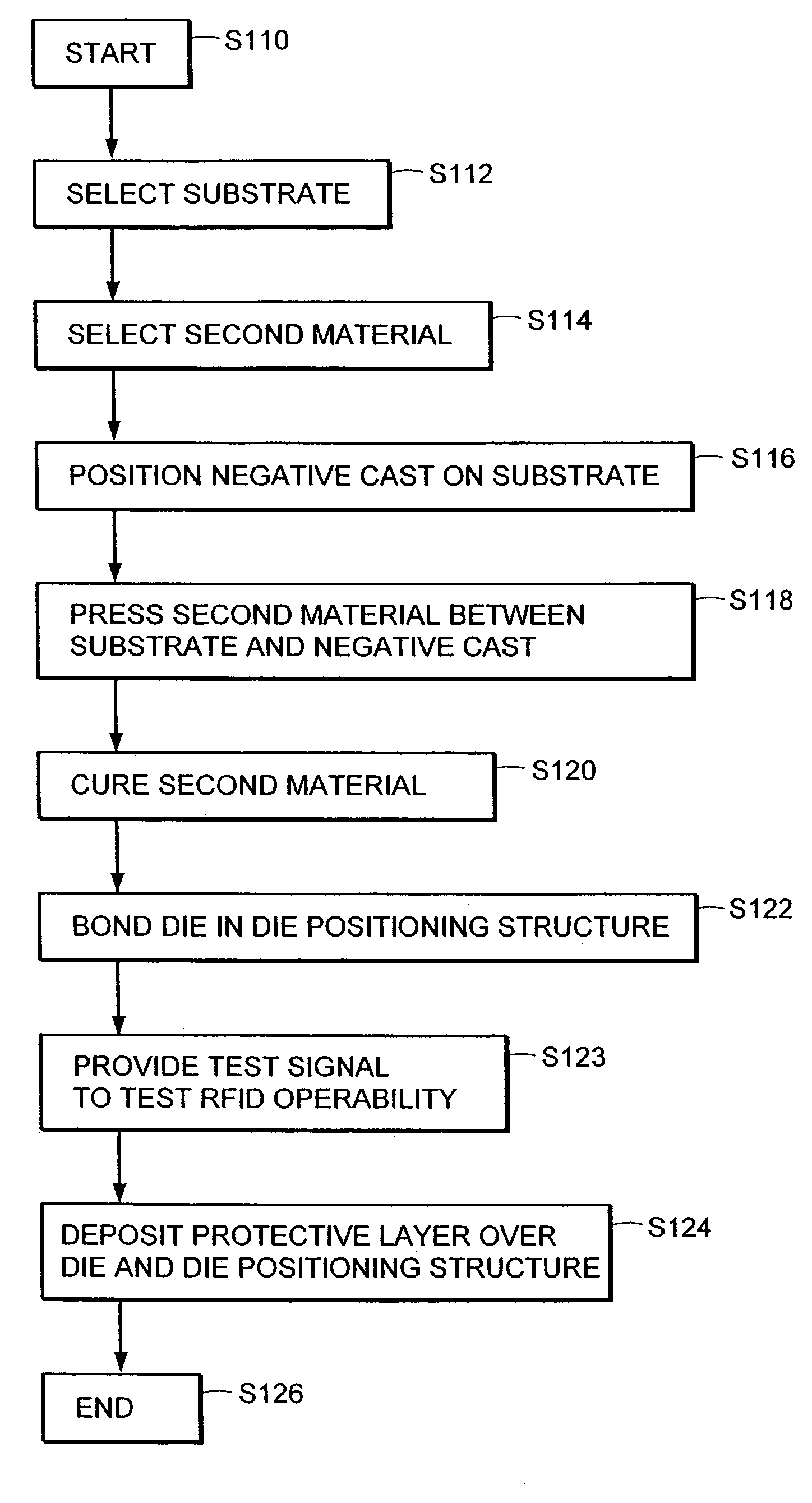
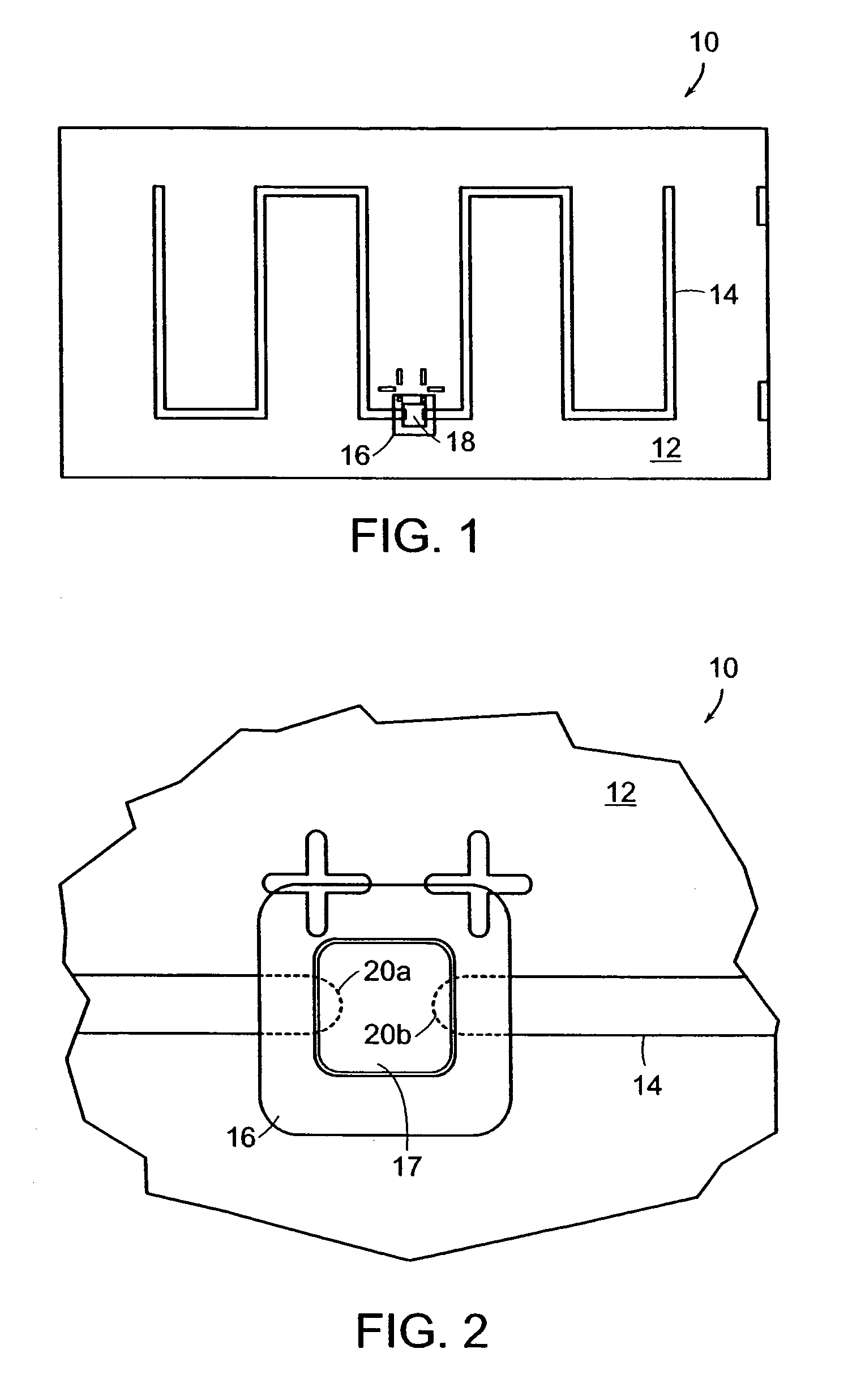
Radio frequency identification tag and method of making the same
ActiveUS7221277B2Efficient and reliable and high fidelityEasy to operateRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalOptoelectronicsRadio frequency
The present invention describes a process for manufacture of RFID tags. The RFID tag of the present invention includes a substrate, an antenna, and a die positioning structure disposed on the substrate that is cast and cured specifically for receiving a silicon die of the type typically used in RFID applications. The substrate is selected from a number of materials, the properties of which render it penetrable by electron beam radiation. The die positioning structure is a second material which is electron beam curable, and which is deposited and cured at high speed on the substrate in a novel fashion in accordance with the present invention in a highly efficient, reproducible and economical manner.
Owner:TRACKING TECH
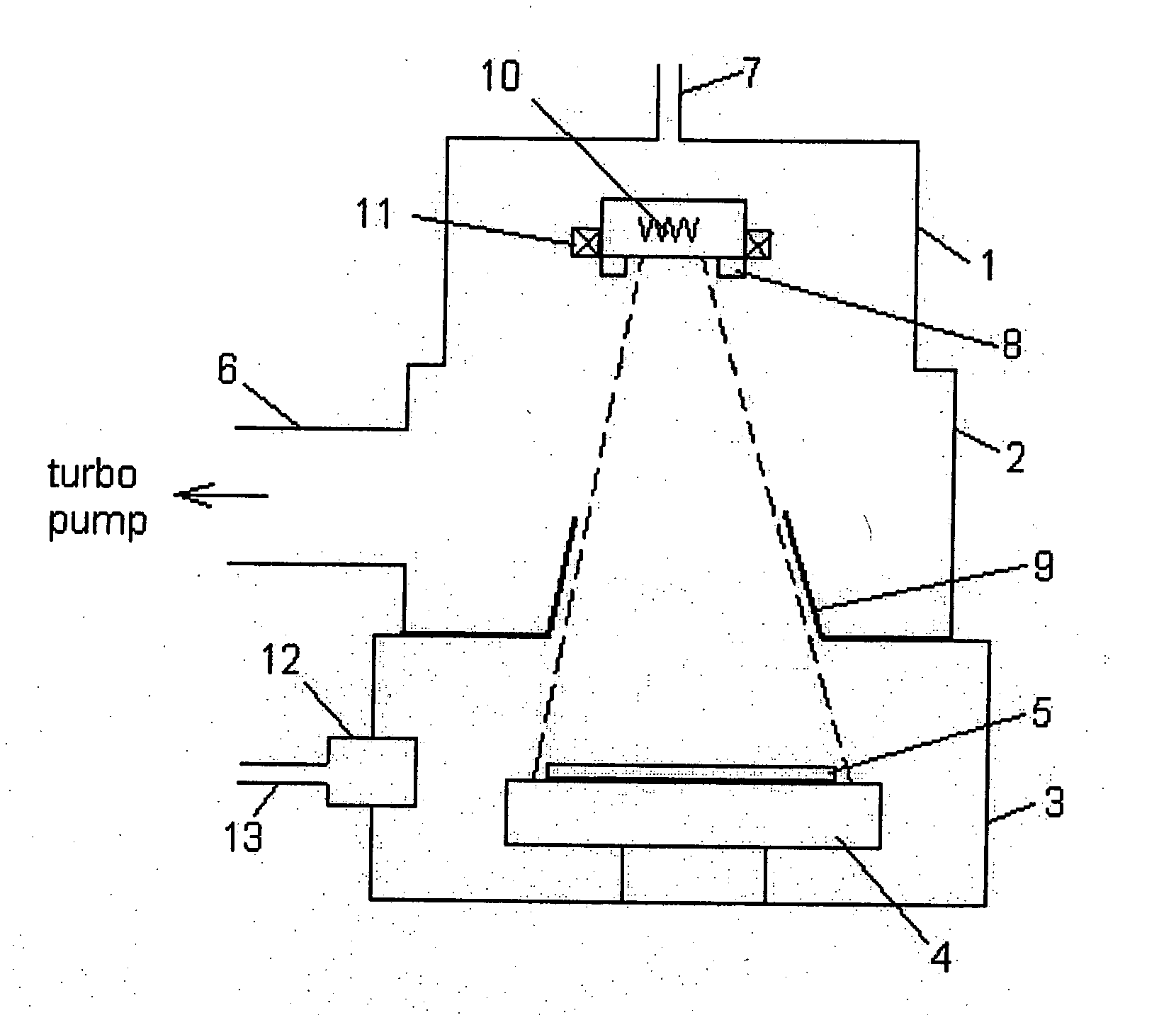
Method and system for electron beam applications
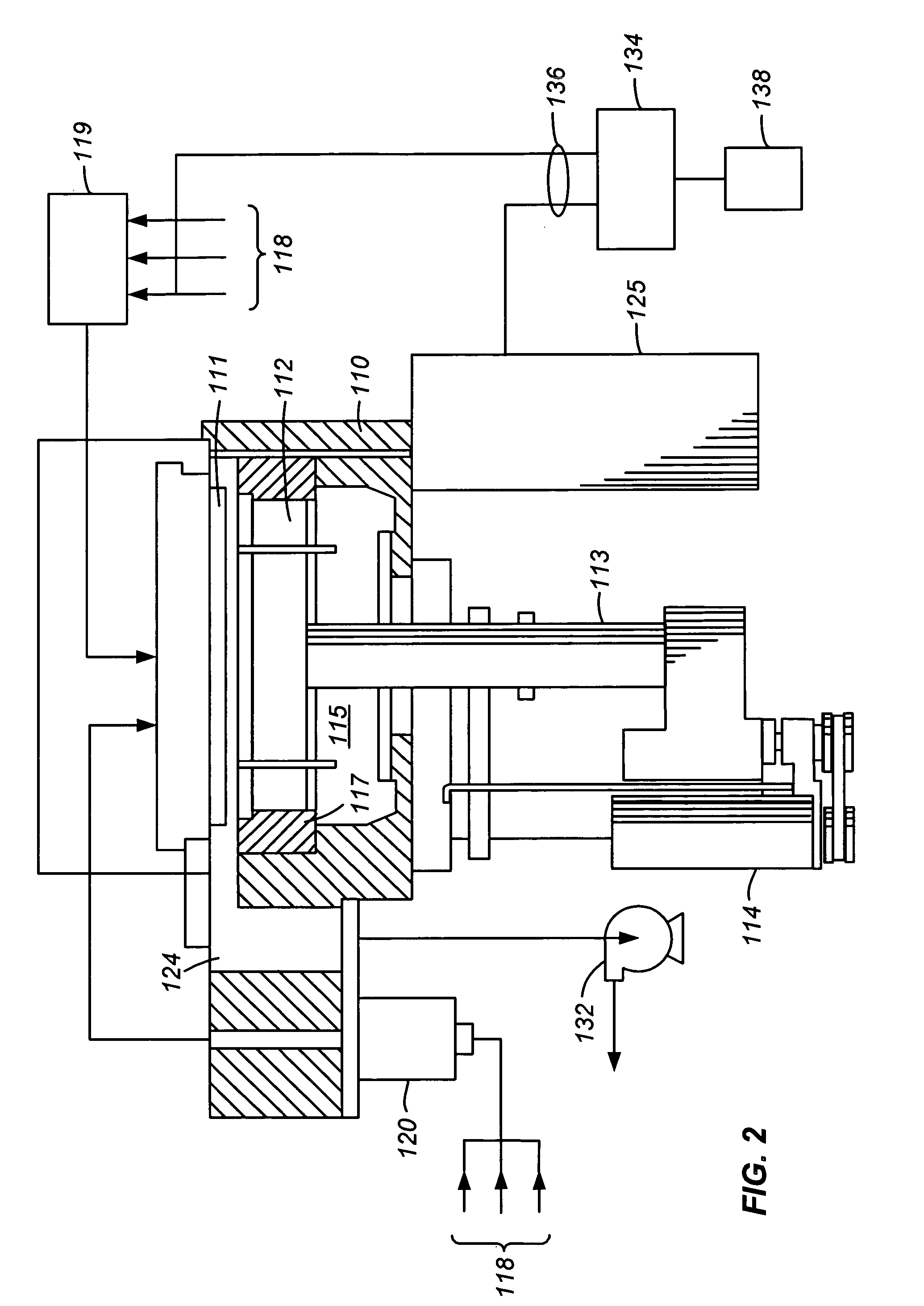
ActiveUS20110017920A1Eliminate needIncrease exposureStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEnergy controlControl system
The present invention relates to methods and systems for use of an electron beam system. The electron beam system may be used within a treatment center with very little radiation shielding. The electron beam system may be used in conjunction with low-z moderators that reduce the energy level of the electron beam without the need for complex or expensive energy control systems. The electron beam system may be used to treat skin cancer and dermatological patients in non-traditional treatment facilities, as well as invasive cancers, either in an unshielded operating room to deliver intraoperative radiation therapy (“IORT”) or in an unshielded room in the oncology department to deliver electron beam radiation treatment (“EB-RT”).
Owner:INTRAOP MEDICAL
Low-energy electron beam radiation curing coating and use method thereof
The invention discloses a low-energy electron beam radiation curing coating, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 40-90 percent of reactivity oligomer, 10-60 percent of reactivity monomer, 0.3-5 percent of additive, 0-30 percent of thermoplastic resin, 0-15 percent of photoinitiator and 0-30 percent of pigment and filler. The coating is particularly suitable for coating processing on substrate made of plastic or paper. A use method of the low-energy electron beam radiation curing coating comprises the following steps of: (a) printing at least one layer of the electron beam radiation curing coating on the plastic or paper substrate; (b) radiating the coating by adopting an electron beam of no more than 200+ / -10kV; or repeating the use steps. The coating has low cost and good environment protection property. The coating obtained by using the low-energy electron beam radiation curing coating has good abrasive resistance, scratching resistance and solvent resistance.
Owner:恒昌涂料(惠阳)有限公司
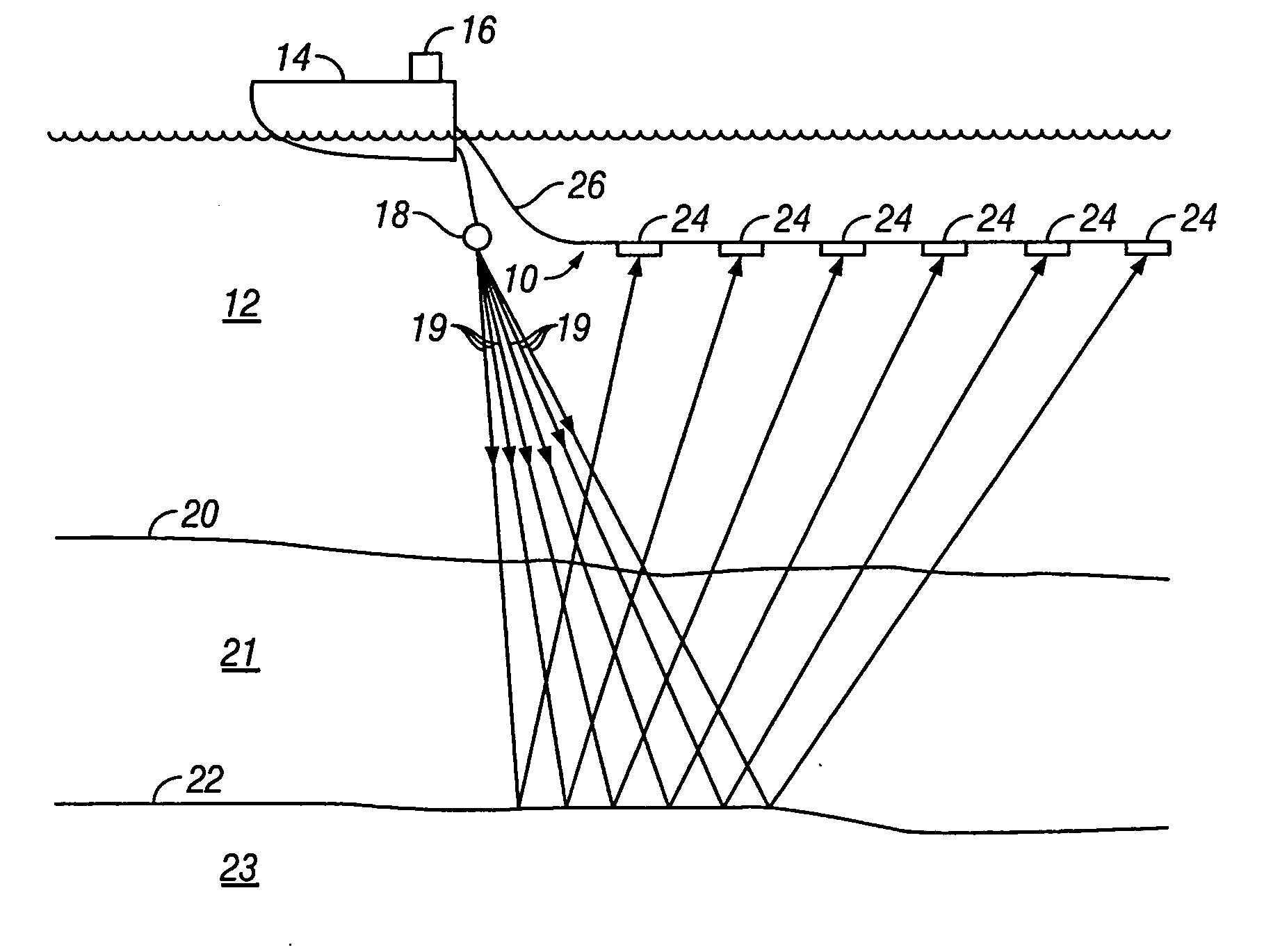
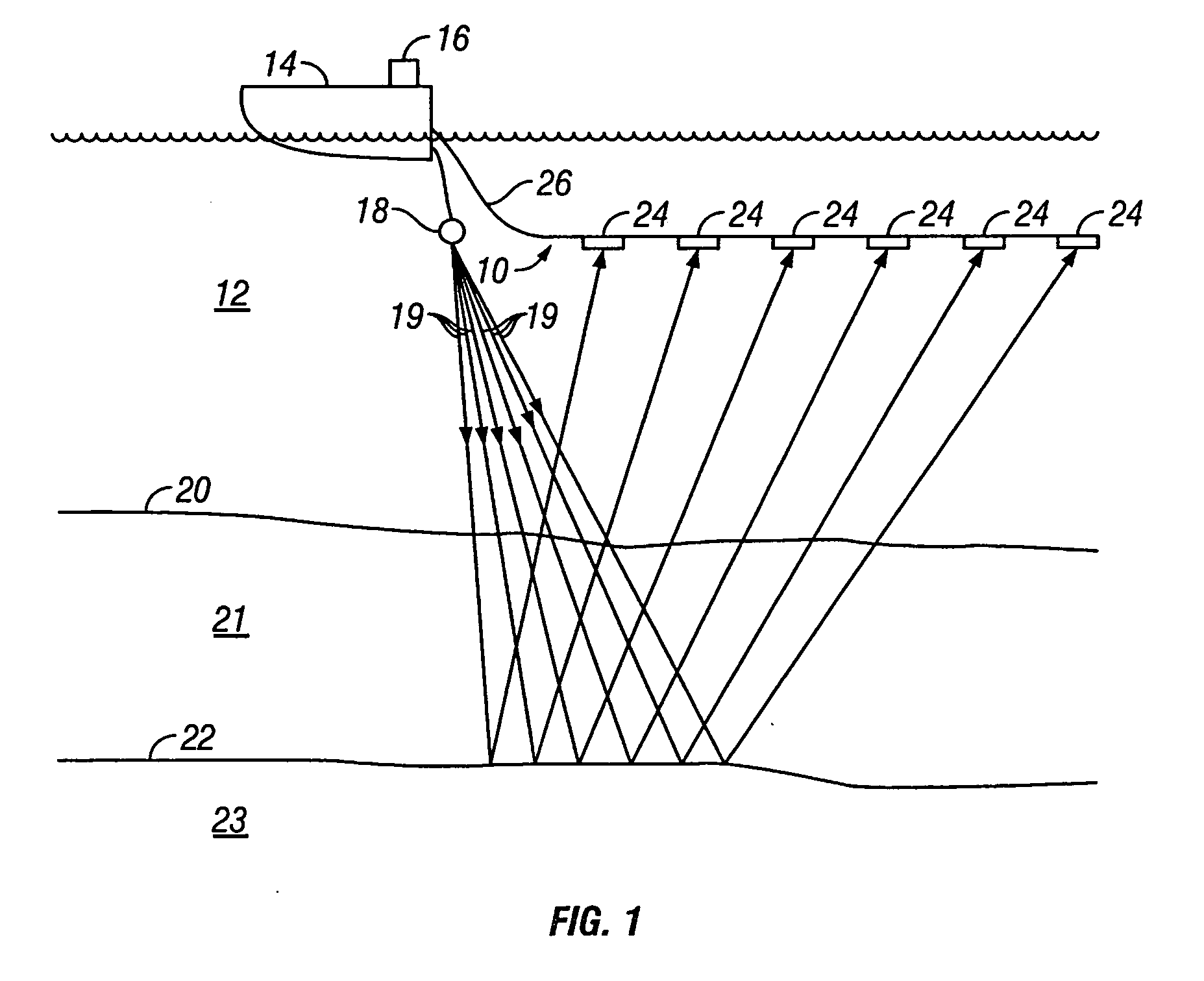
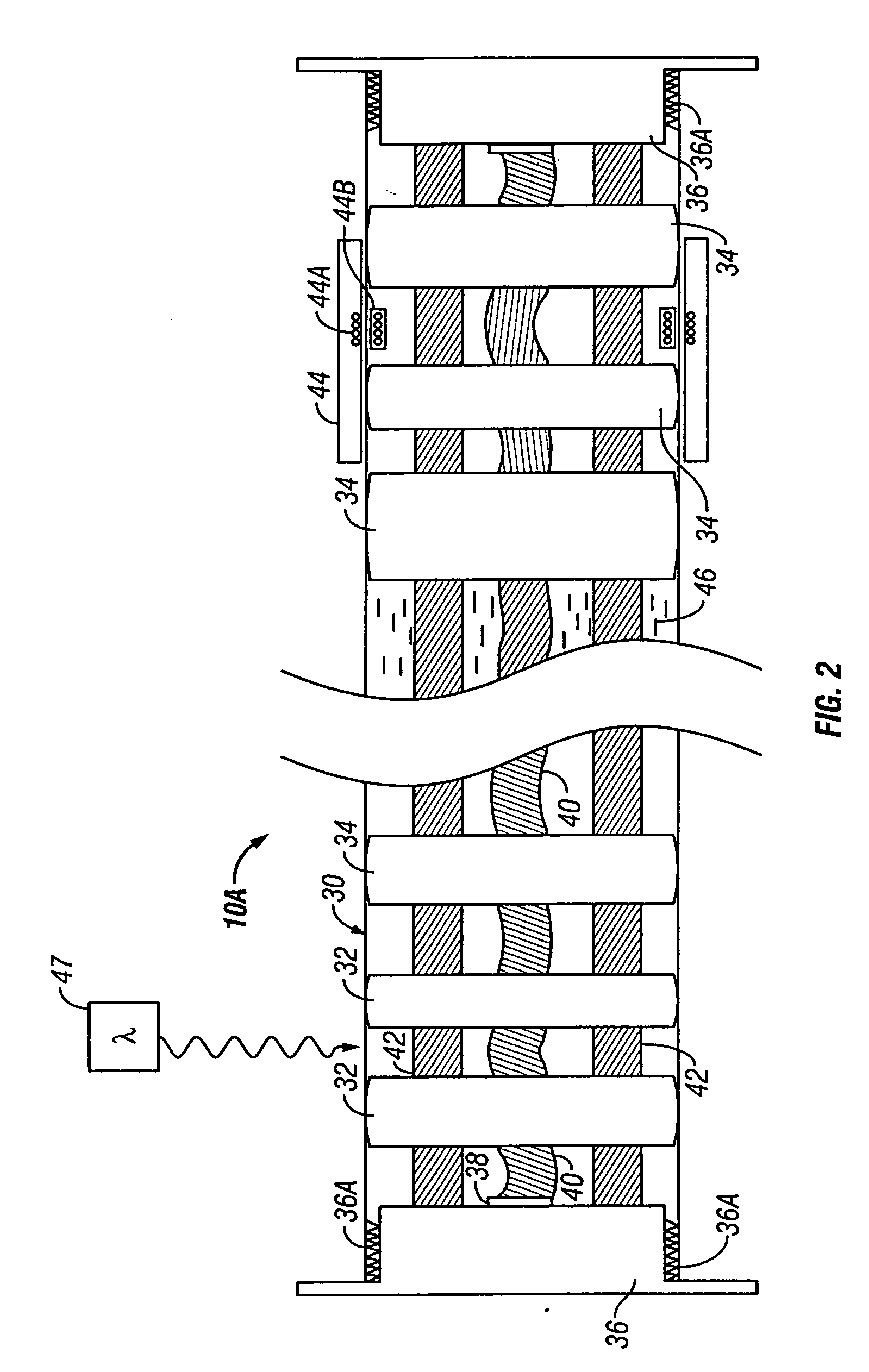
Marine seismic streamer and method for manufacture thereof
A seismic streamer includes a jacket covering an exterior of the streamer. At least one strength member extends along the length of the jacket. The strength member is disposed inside the jacket. Seismic sensors are disposed at spaced apart locations along the interior of the jacket. An acoustically transparent material fills the space inside the jacket. The material is introduced into the inside of the jacket in liquid form and undergoes a state change upon exposure to radiation. The radiation in one embodiment is ultraviolet radiation. The radiation in one embodiment is electron beam radiation.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com