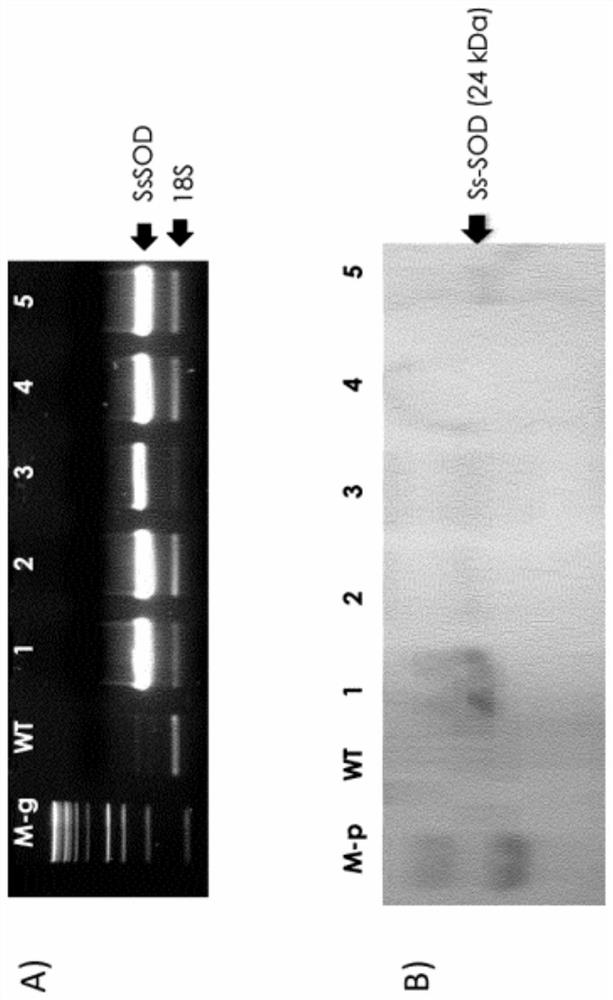
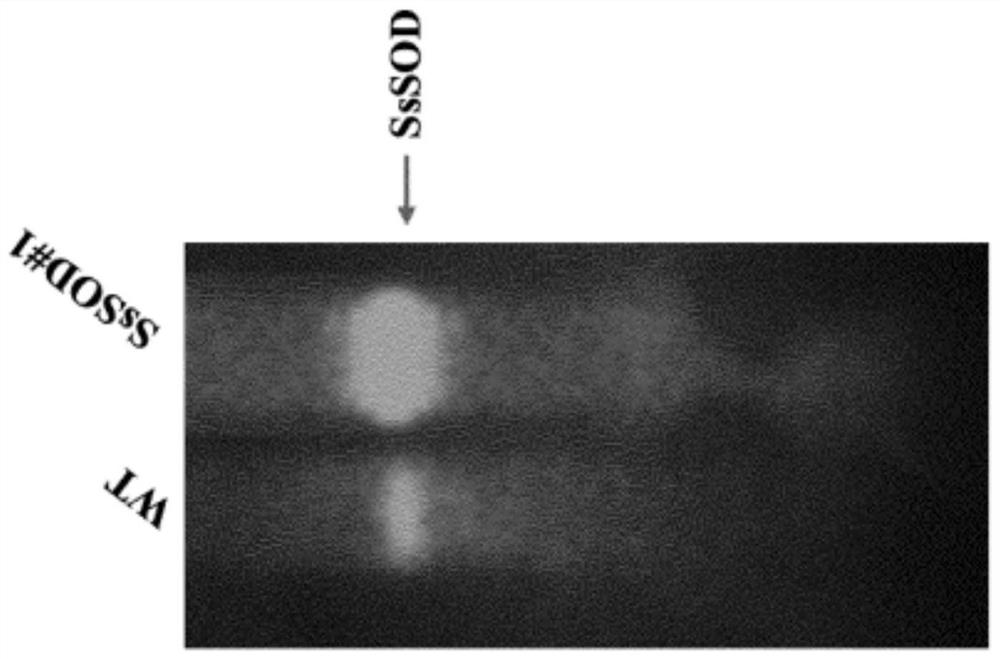
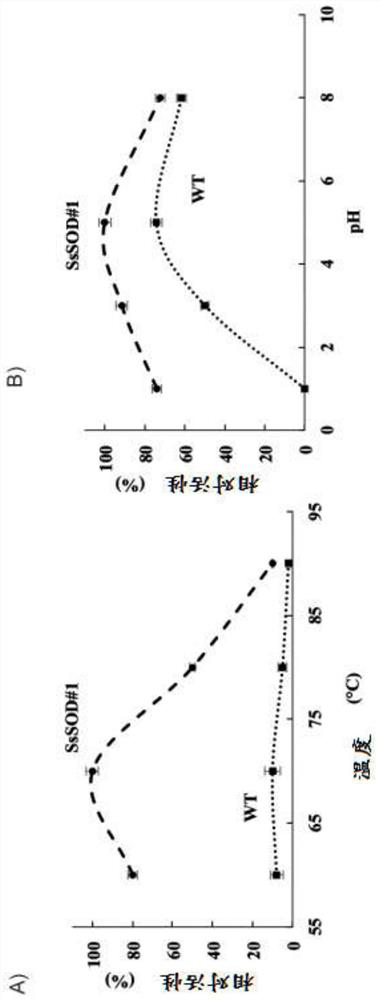
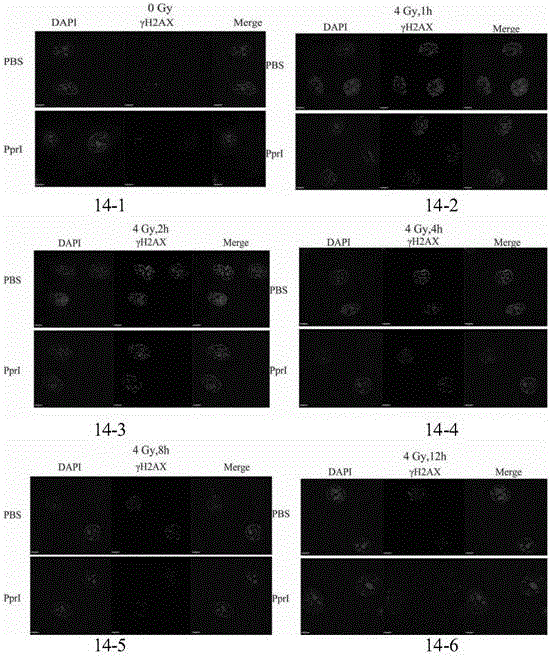
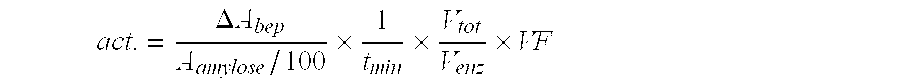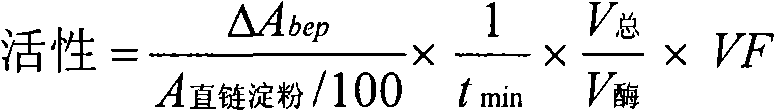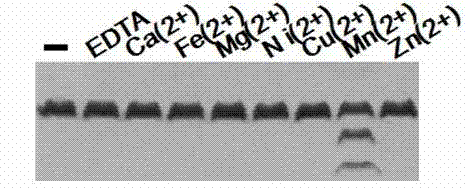Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42 results about "Deinococcus radiodurans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Deinococcus radiodurans is an extremophilic bacterium, one of the most radiation-resistant organisms known. It can survive cold, dehydration, vacuum, and acid, and is therefore known as a polyextremophile and has been listed as the world's toughest bacterium in The Guinness Book Of World Records.
Process for Chromosomal Engineering Using a Novel Dna Repair System
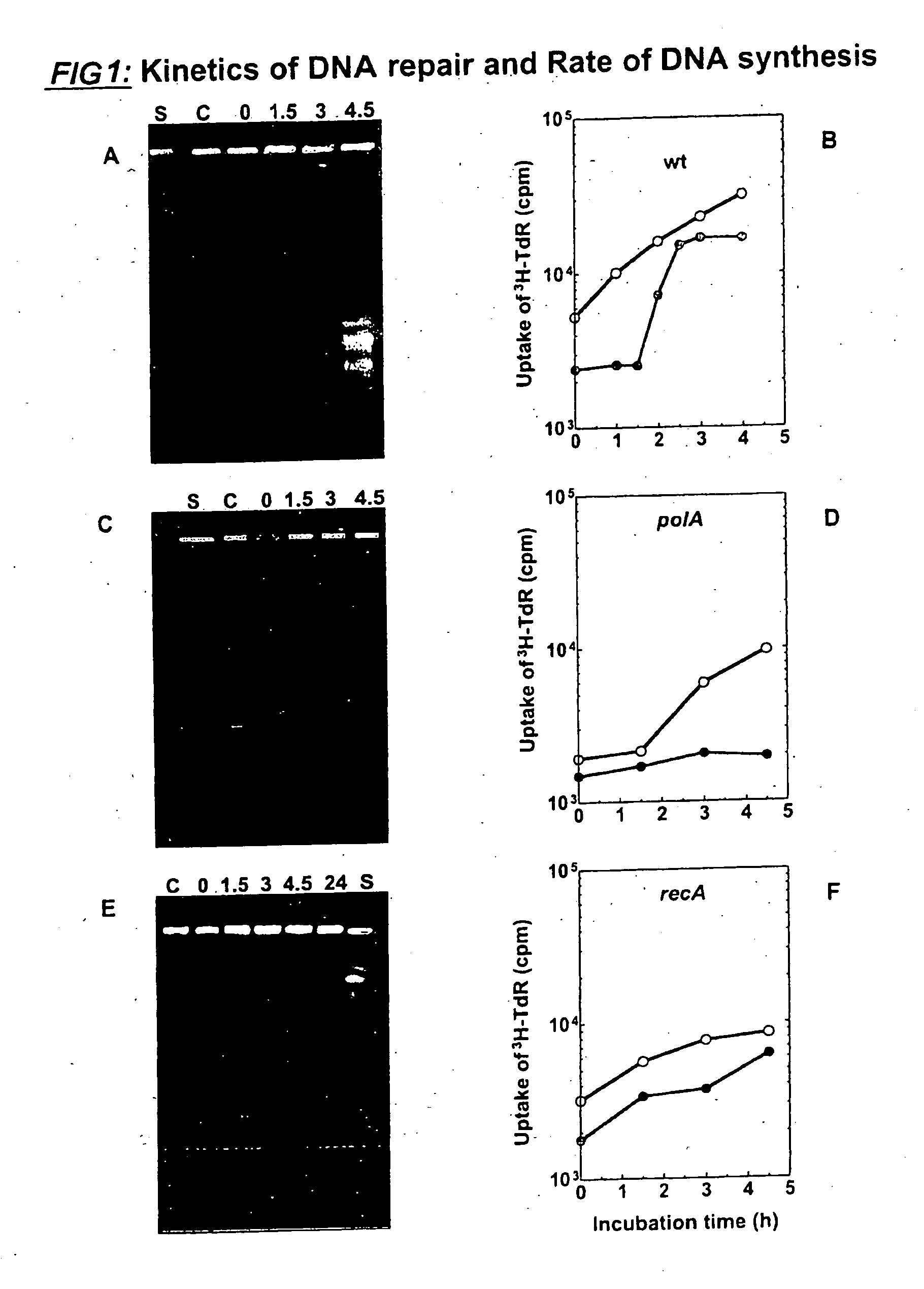
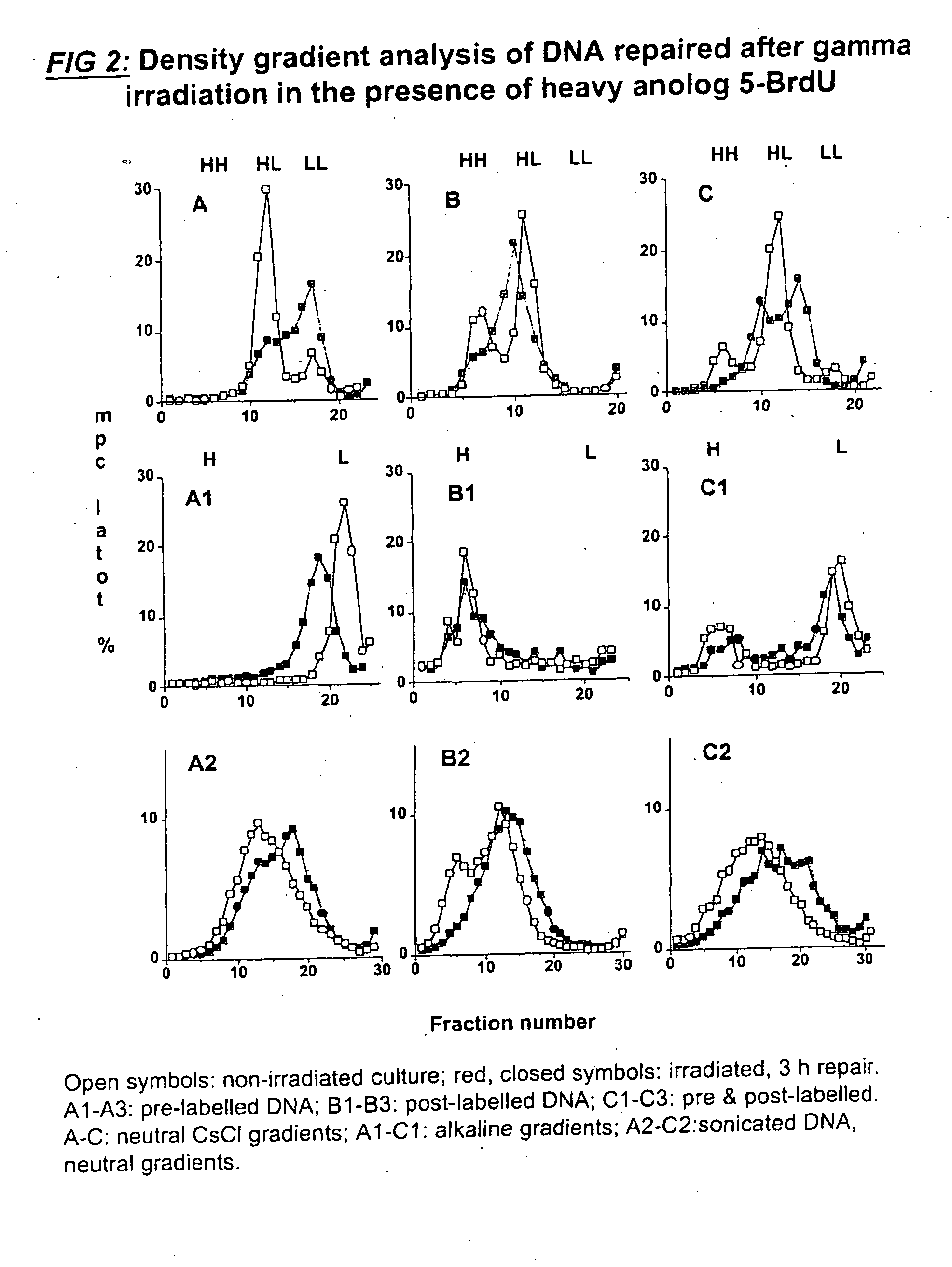
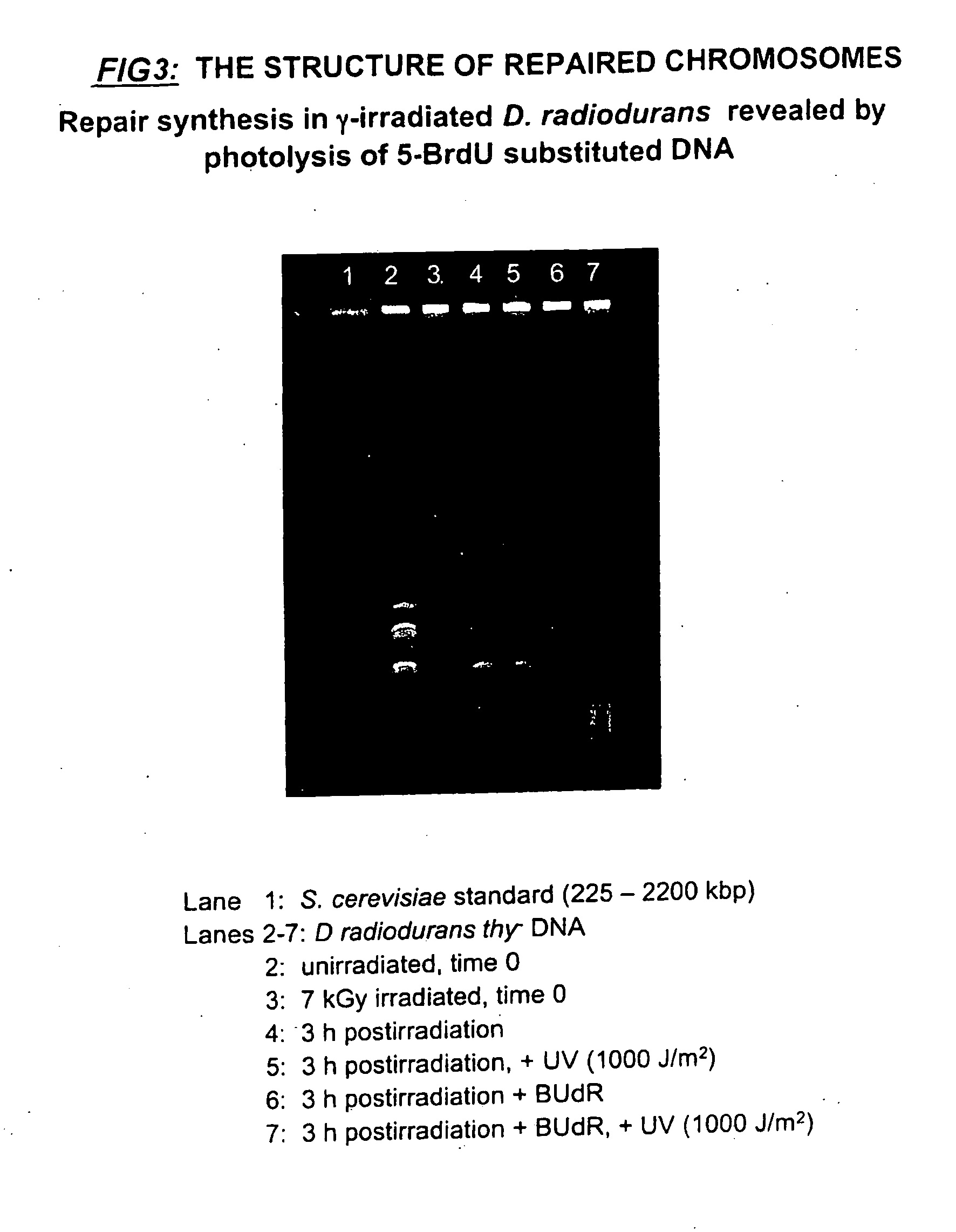
This invention relates to chromosomal engineering via DNA repair process. The process of the invention comprises the steps of: 1) submitting at least one source of biological activity, e.g. Deinococcus radiodurans, to radiation, desiccation and / or chemical treatment liable to damage the DNA, so as to substantially shatter its chromosomes into short fragments; 2) annealing complementary single strand tails extended by the synthesis templated on partially overlapping DNA fragments of said shattered chromosomes; 4) converting the resulting long linear DNA intermediates into intact circular chromosomes, by means of a RecA dependent homologous recombination; whereas at least one foreign source of genetic material, e.g. DNA, can be introduced during steps 2 and / or 3; and 4) optionally separating and collecting the recombined chromosomes thus obtained.
Owner:DEINOVE SA
Novel slowly digestible storage carbohydrate
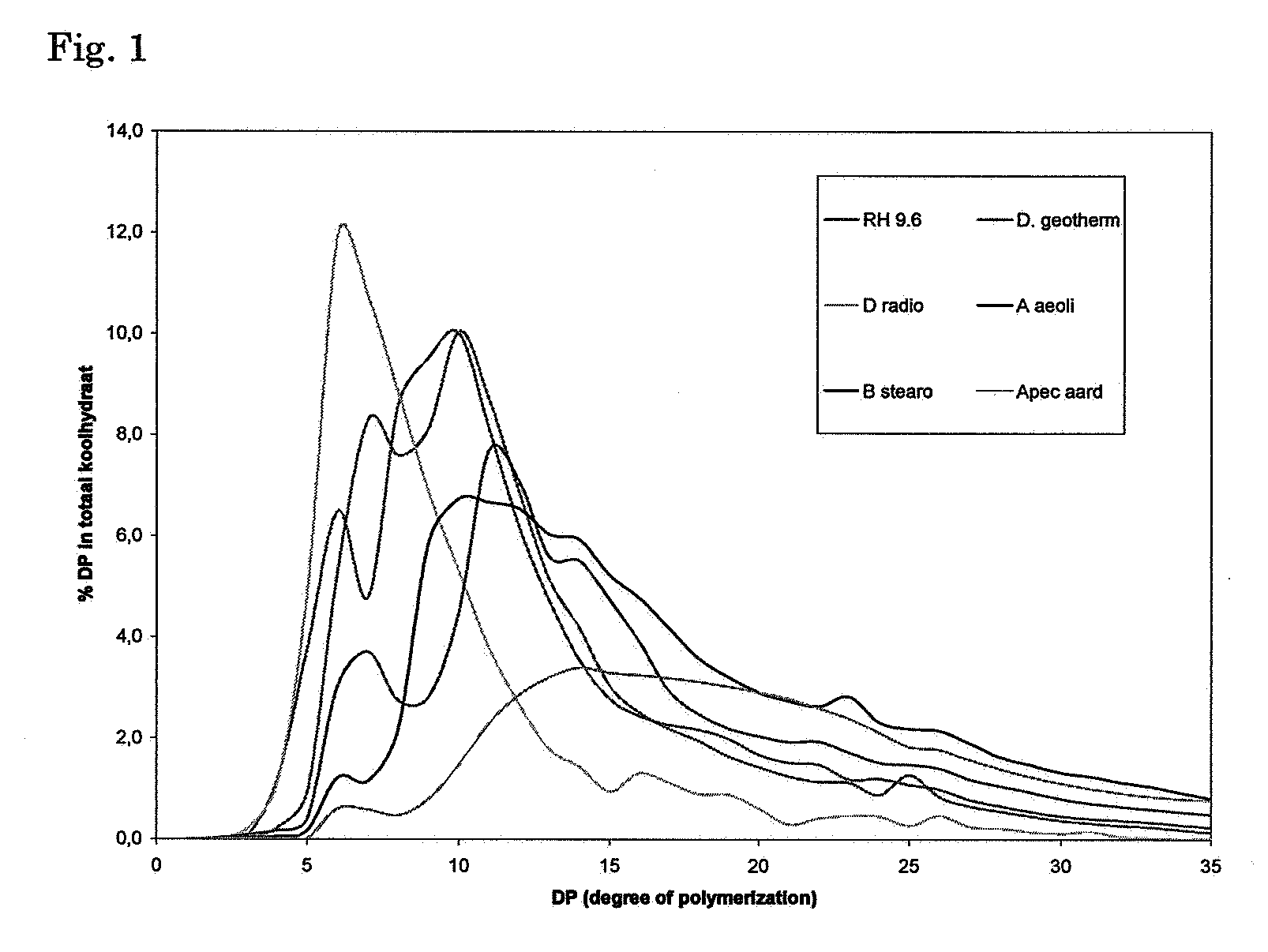
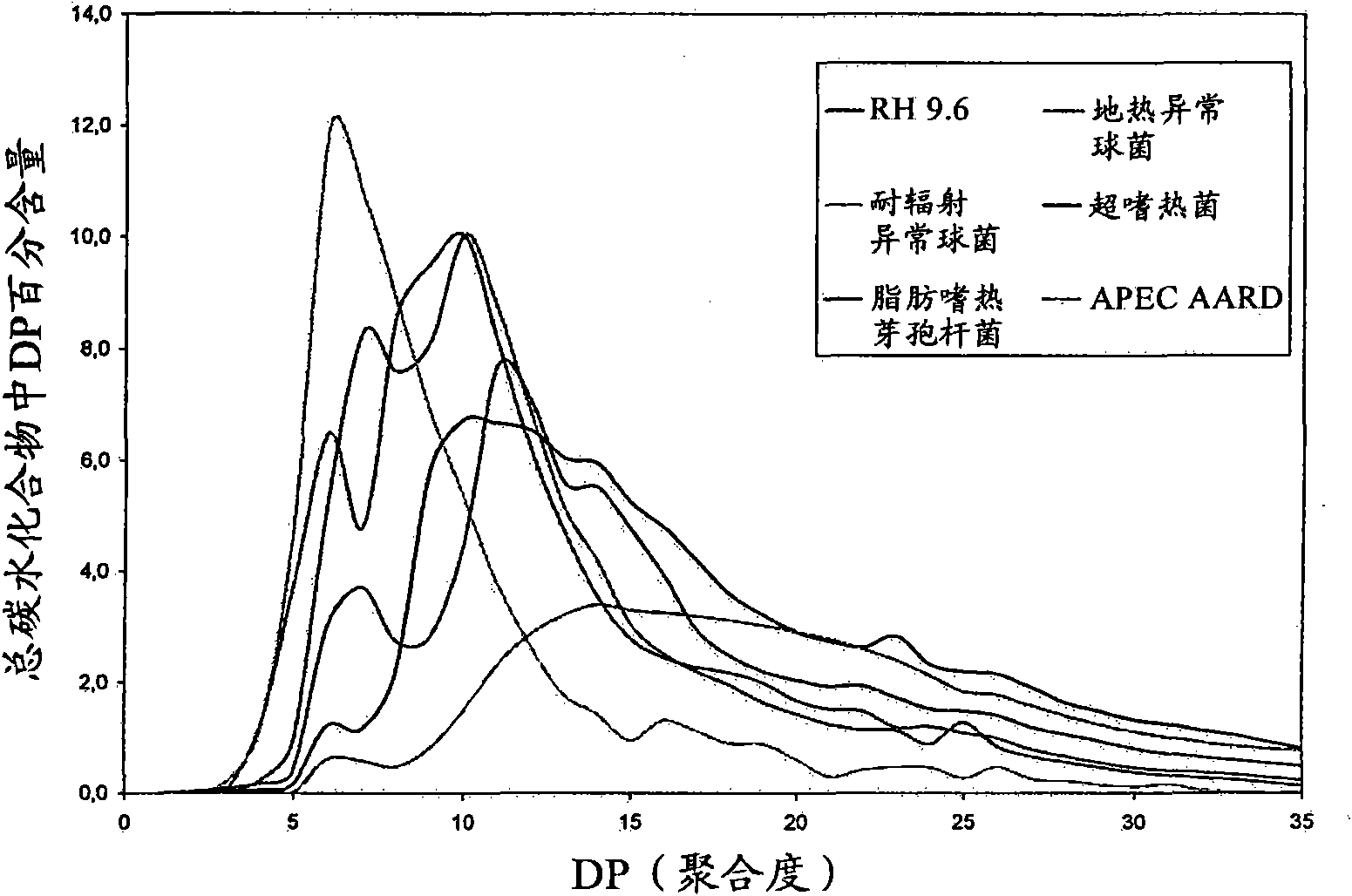
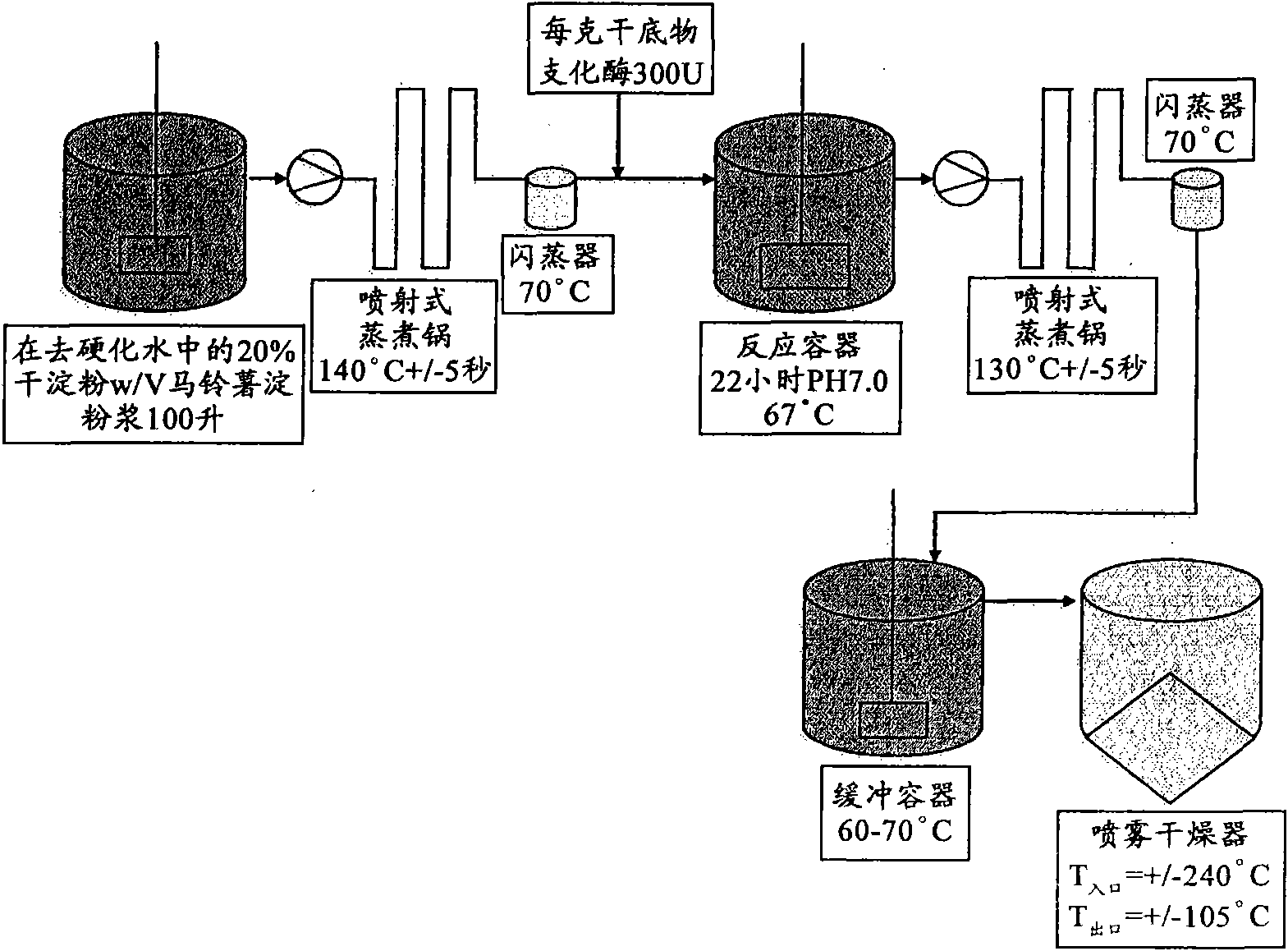
The present invention relates to slowly digestible storage carbohydrates (starch, glycogen) having a branching degree of at least 8.5% and a side chain composition comprising at least 10% of DP 5-7. Said slowly digestible carbohydrates can be produced by treating the substrate (glycogen, starch) from a native source with a glycogen branching enzyme derived from Rhodothermus obamensis, Rhodothermus marinus, Deinococcus radiodurans or Deinococcus geothermalis.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Novel slowly digestible storage carbohydrate
The present invention relates to slowly digestible storage carbohydrates (starch, glycogen) having a branching degree of at least 8.5% and a side chain composition comprising at least 10 % of DP 5-7. Said slowly digestible carbohydrates can be produced by treating the substrate (glycogen, starch) from a native source with a glycogen branching enzyme derived from Rhodothermus obamensis, Rhodothermus marinus, Deinococcus radiodurans or Deinococcus geothermalis.
Owner:NEDERLANDSE ORG VOOR TOEGEPAST-NATUURWETENSCHAPPELIJK ONDERZOEK (TNO)
Enzyme activity starting and improving method of Deinococcus radiodurans protease PprI
ActiveCN104212782AIncrease enzyme activityShort reaction timeHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEnzyme digestionPromoter
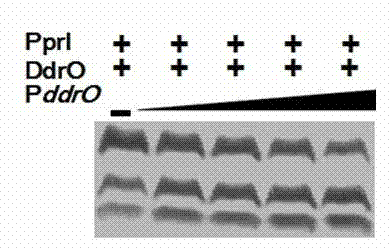
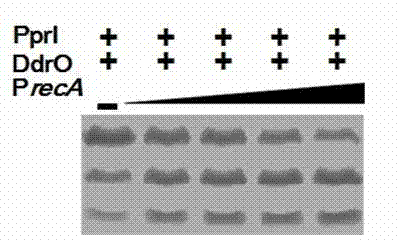
The invention discloses an enzyme activity starting and improving method of protease PprI. The enzyme activity starting of the protease PprI needs 2.0-5.0mM of Mn<2+> ions. An enzyme digestion reaction buffer solution contains 150-250mM OF NaCl, 10-50Mm of Tris-HcL 8.0, 0.1mM of DTT and 2.0-5.0mM of MnCl2. The combination of gene dr2574 and dr2340 promoter fragments with a substrate DdrO improves the enzyme digestion activity of the protease PprI, shortens the reaction time, and has positive contribution to future utilization of the enzyme.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
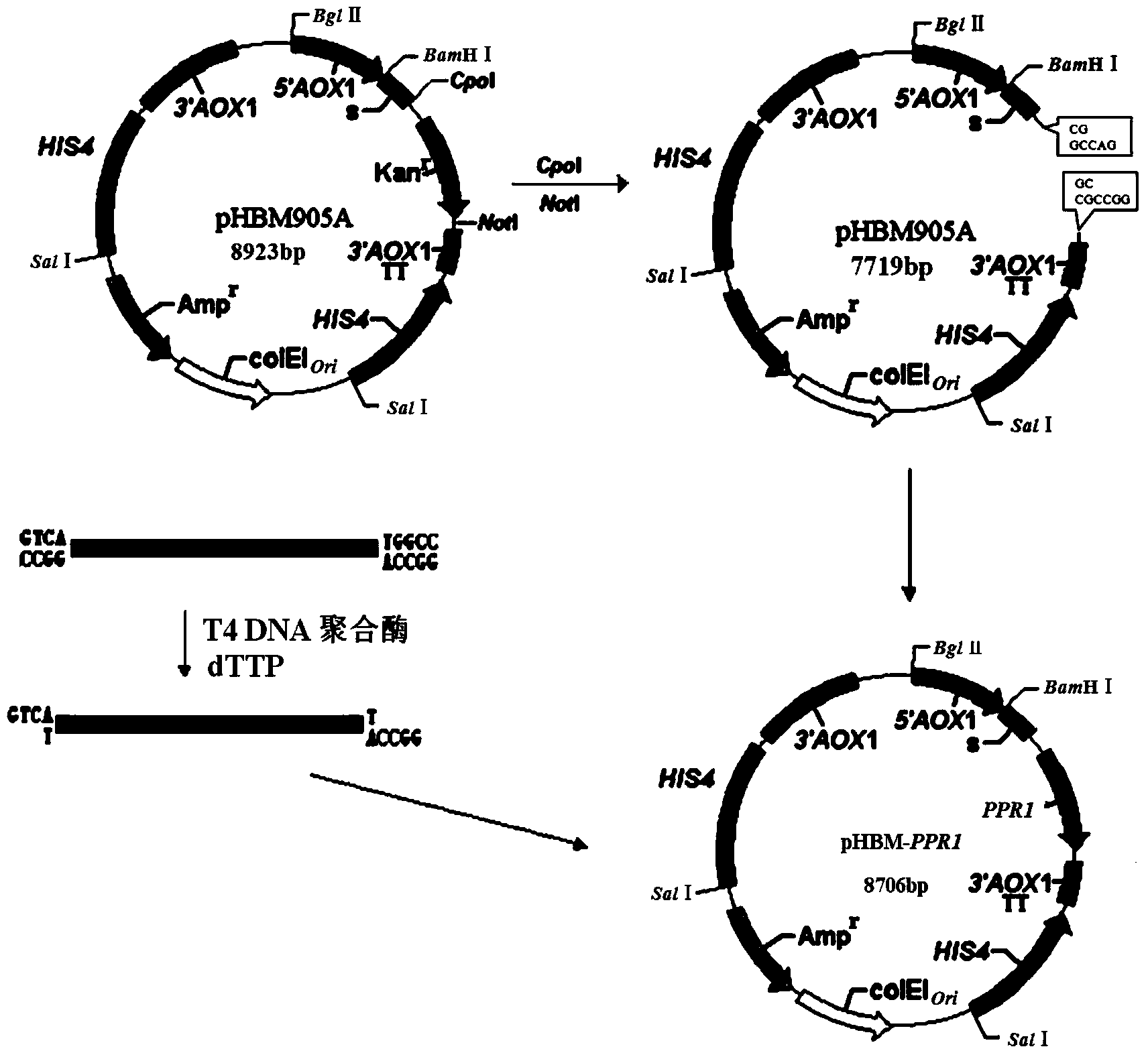
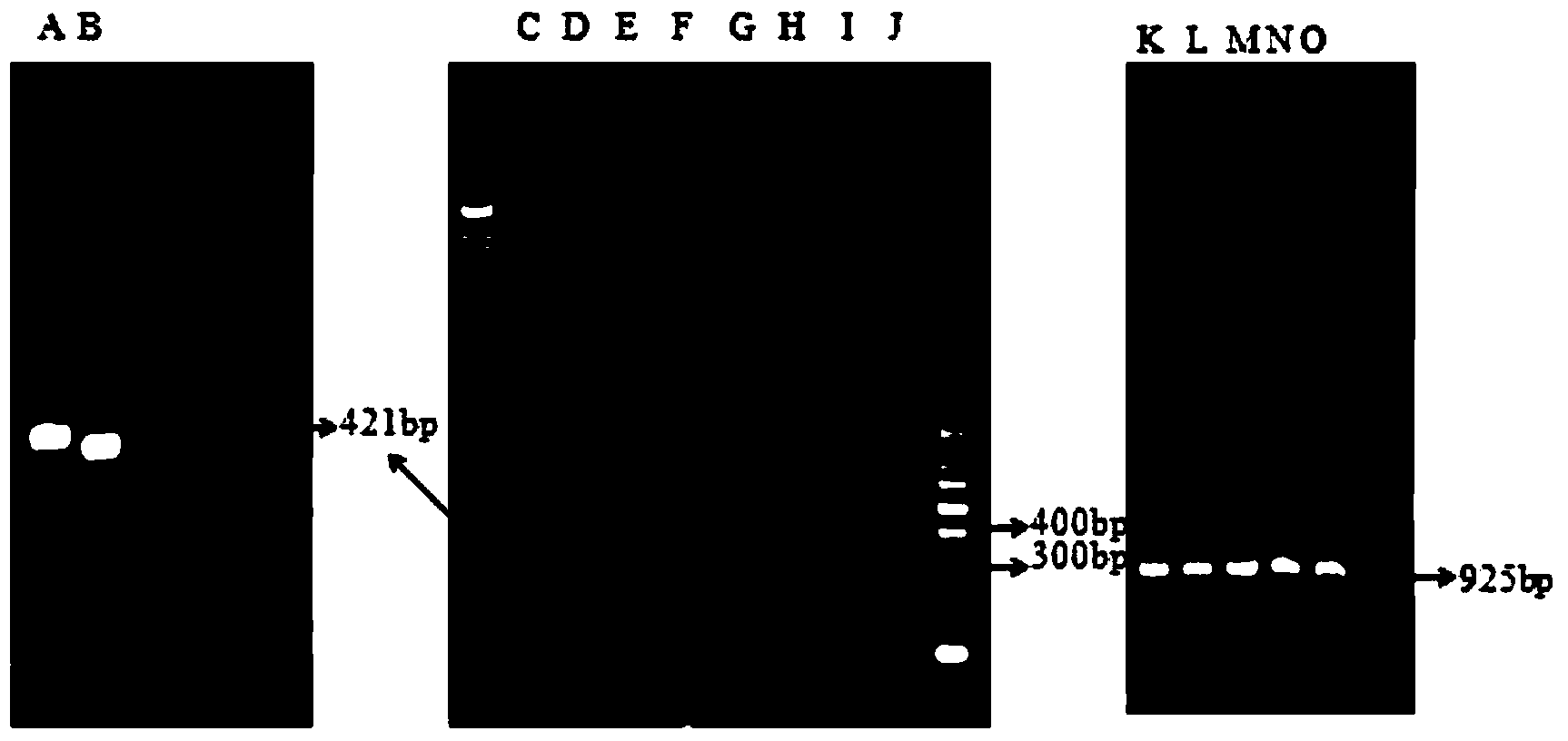
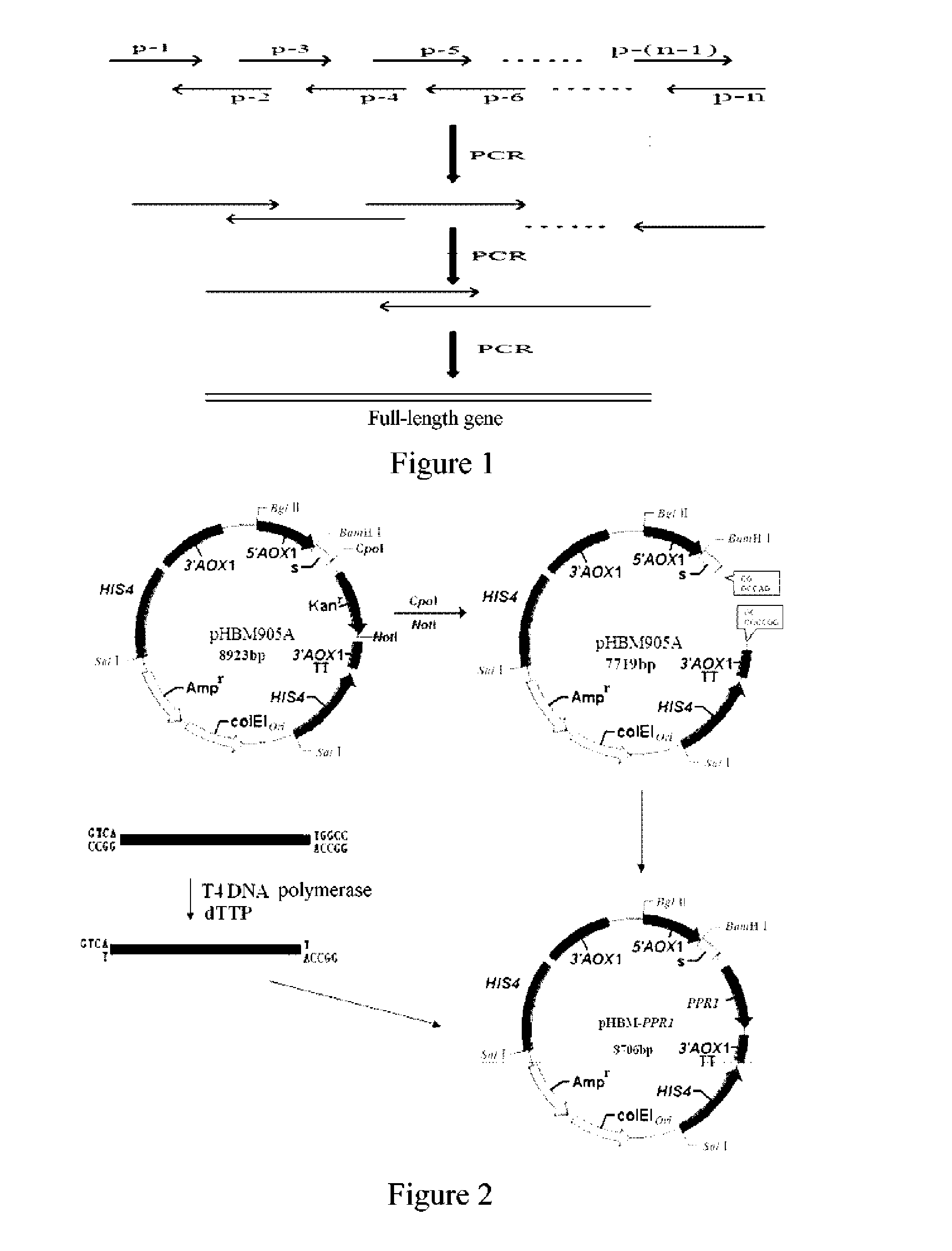
DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecule, pichia pastoris recombinant plasmid and pichia pastoris recombinant bacterium for efficiently expressing PprI protein of deinococcus radiodurans
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and discloses a DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) molecule containing a sequence shown as SEQ ID NO:1, a pichia pastoris recombinant plasmid inserted into the DNA molecule and a pichia pastoris recombinant bacterium which is used for converting the pichia pastoris recombinant plasmid into a pichia pastoris competent cell and efficiently expressing the PprI protein of deinococcus radiodurans. The pprI gene sequence of the deinococcus radiodurans is optimized and modified on the premise that an amino acid sequence of the PprI protein is not changed, so that a new Pi-pprI gene is synthesized in a coding manner; and a recombinant plasmid pHBM-905A-Pi-pprI of the pichia pastoris Pi-pprI gene and a pichia pastoris recombinant engineering bacterium GS115-Pi-pprI for the secretory expression of the PprI protein are successfully constructed for the first time, so that the efficiently expressed and purified PprI protein is obtained, thereby laying a solid foundation for the development and the application of protein radiation resisting medicines independently developed in China in the field of radiation injury prevention and treatment.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
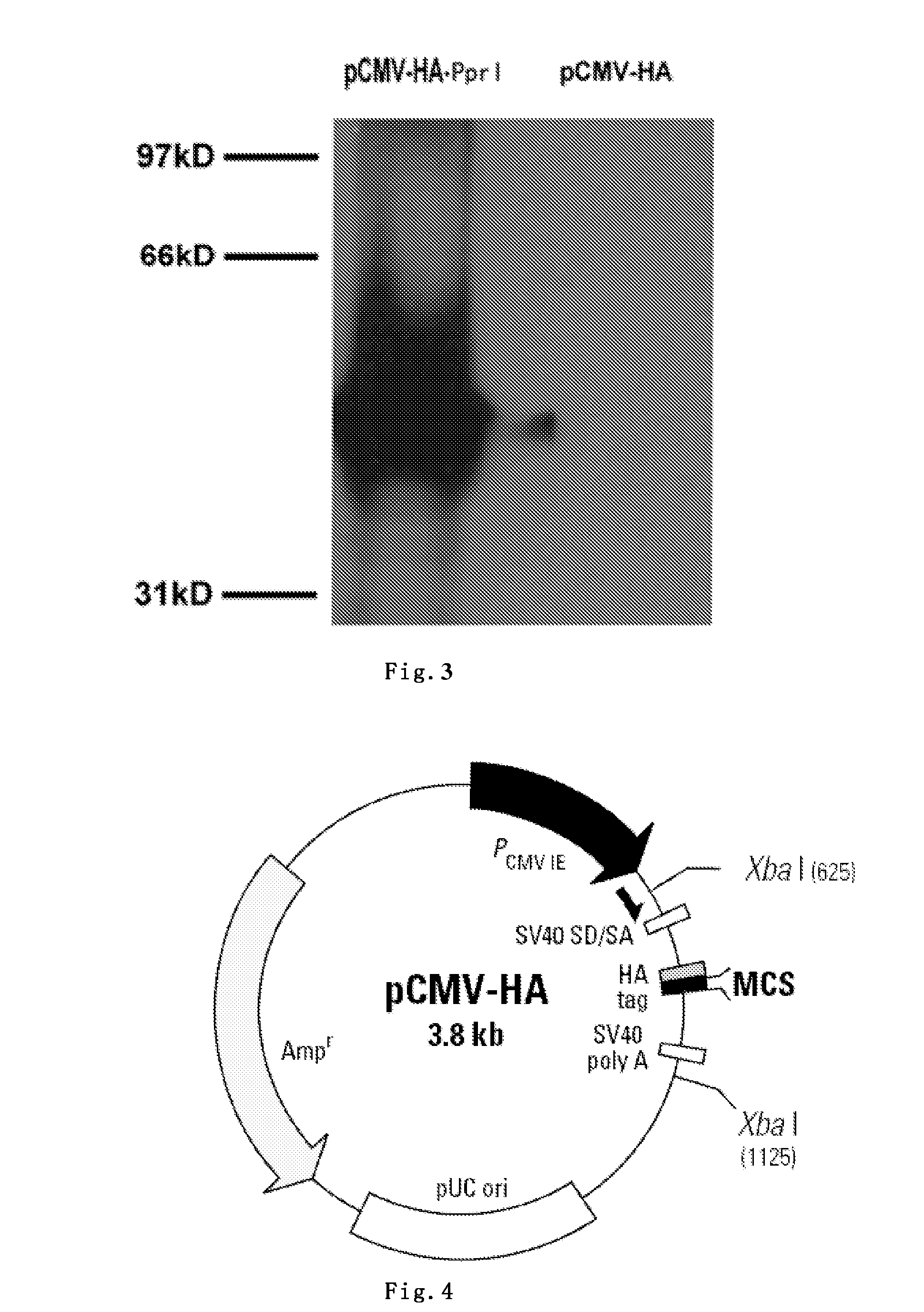
RECOMBINANT EUKARYOTIC EXPRESSION PLASMID ENCODING pprI GENE OF DEINOCOCCUS RADIODURANS R1 AND ITS FUNCTIONS
InactiveUS20110236933A1Maximum efficacySignificant preventionBacteriaGenetic material ingredientsTherapeutic effectElectroporation
The present invention concerns a novel recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmid pCMV-HA-pprI encoding the pprI gene isolated from Deinococcus radiodurans R1, the method for preparing pCMV-HA-pprI, and its expression in human 293T cells. The present invention also discloses the optimal method and process of pprI gene transfection by in vivo electroporation, and the radioprotective and therapeutic effects of the recombinant pCMV-HA-pprI on lethally irradiated mice.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
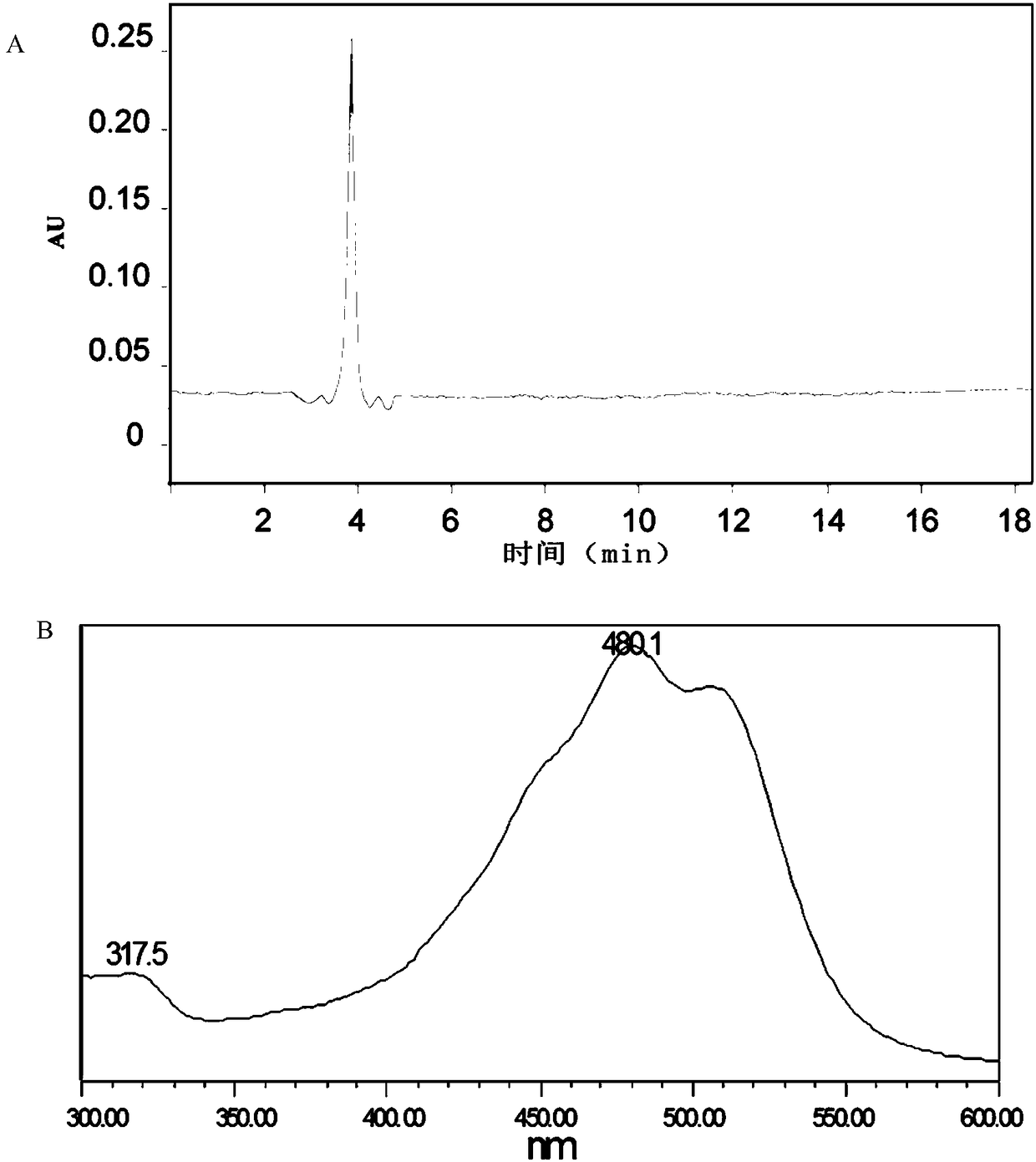
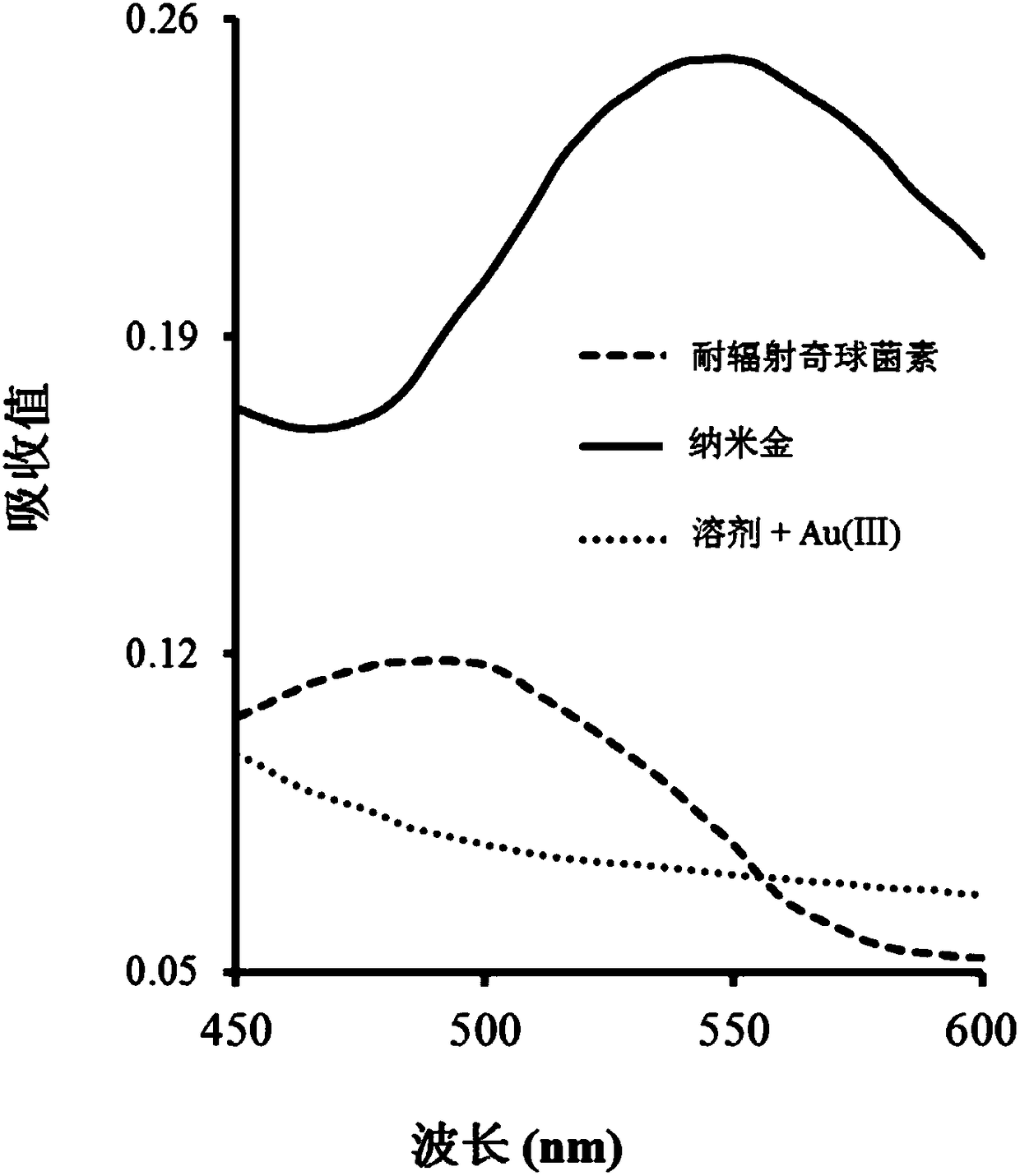
Preparation method of gold nanoparticles, gold nanoparticles and application
ActiveCN108372307AIncrease profitReduce usageMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingAntioxidant capacitySolubility
The invention discloses a preparation method of gold nanoparticles, the gold nanoparticles and application. The preparation method comprises the following steps that (1) a deinococcus radiodurans rhzomorph solution is provided; (2) an Au3+-containing solution is provided; (3) the solutions in the step (1) and the step (2) are mixed to react; and (4) after reaction is completed, products are collected and purified, and the gold nanoparticles are obtained. The method for preparing the gold nanoparticles has the advantages of simpleness, convenience, controllability, high efficiency, energy conservation and environmental friendliness, and the synthesized gold nanoparticles are good in water solubility, high in purity degree, good in uniformity, moderate in size (29.83+ / -4.18 nm), high in stability and high in antioxidant capacity, have the anticancer effect, and can be applied to the aspect of oxidation resistance or cancer inhibition.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Proteins that fluoresce at infrared wavelengths or generate singlet oxygen upon illumination
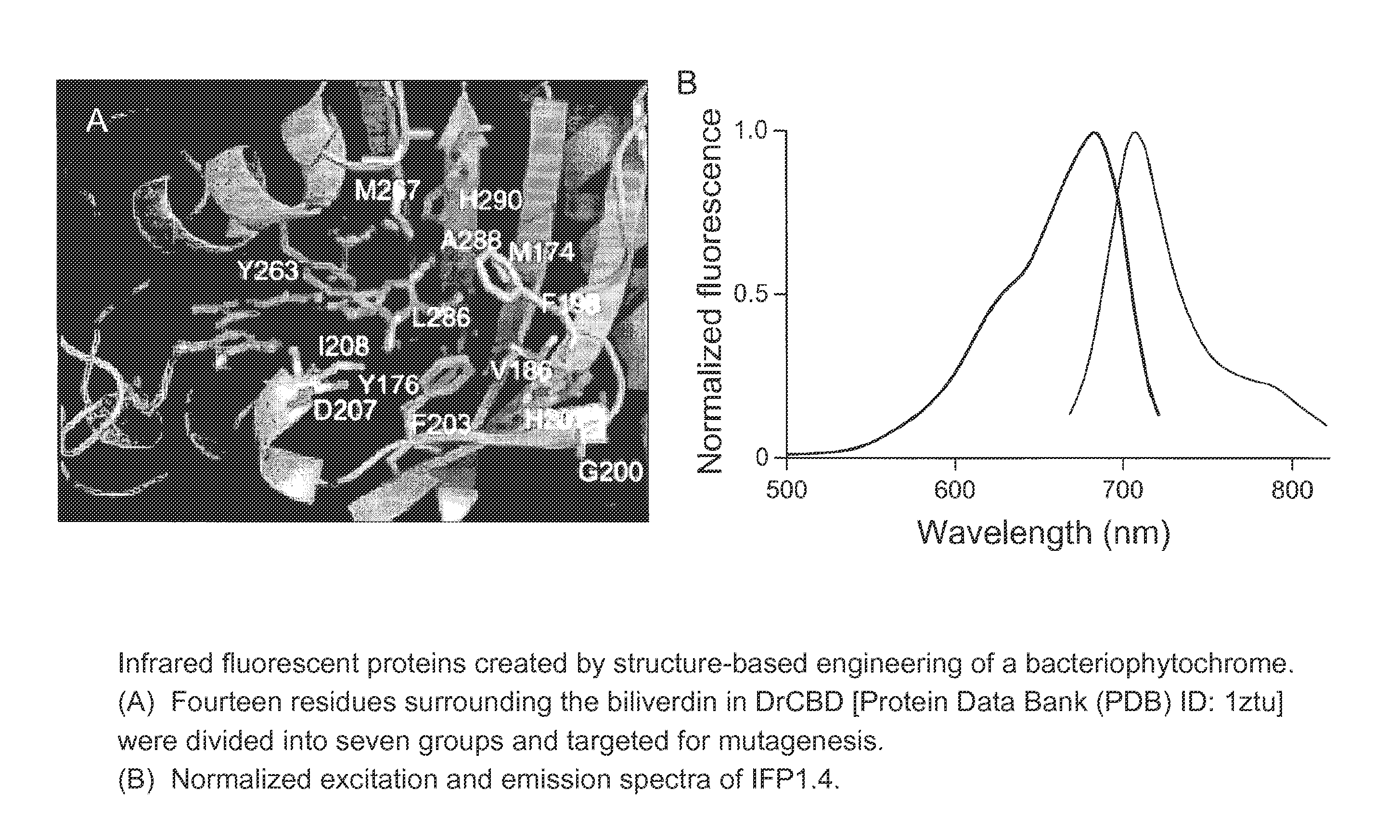
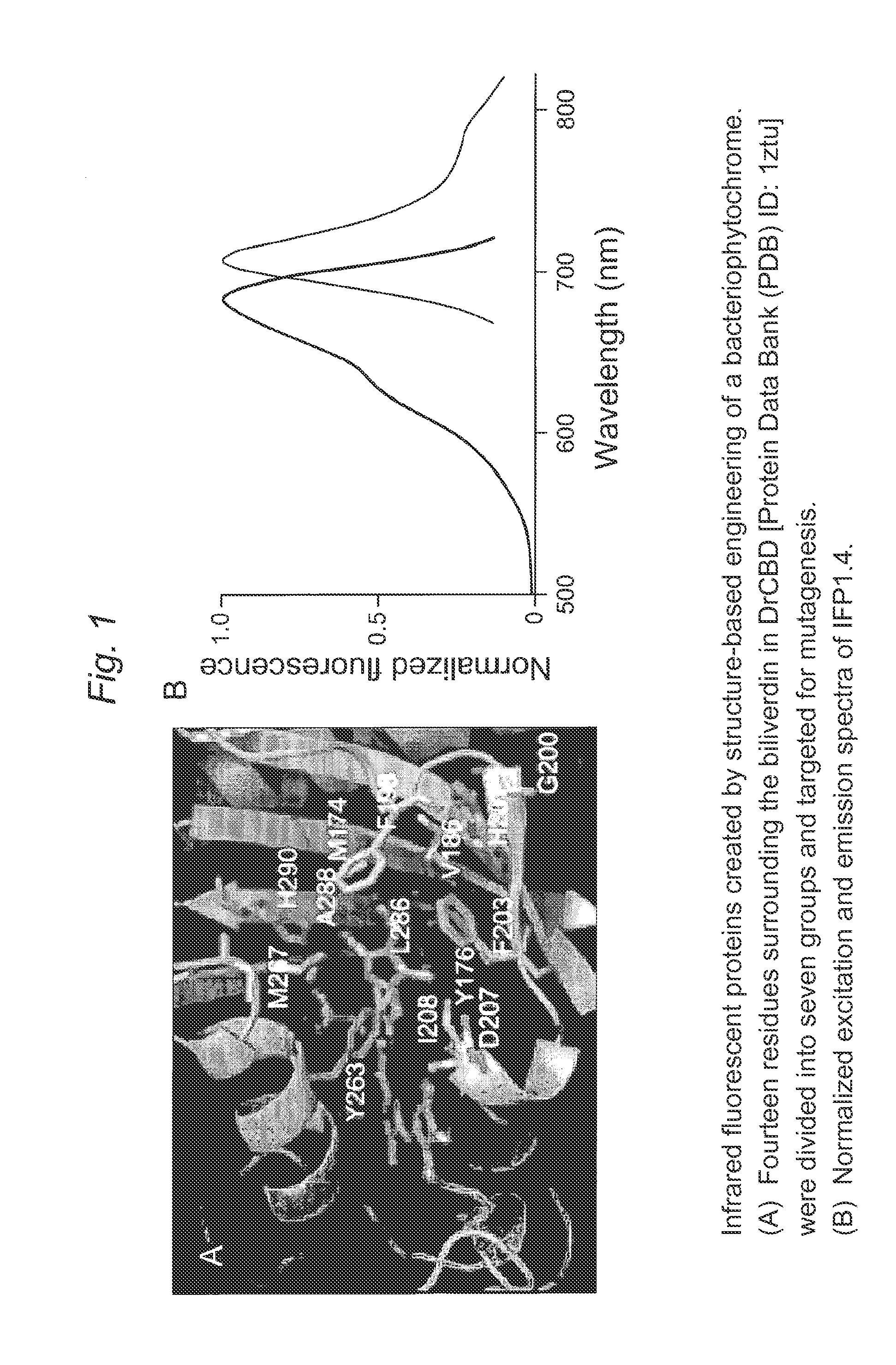
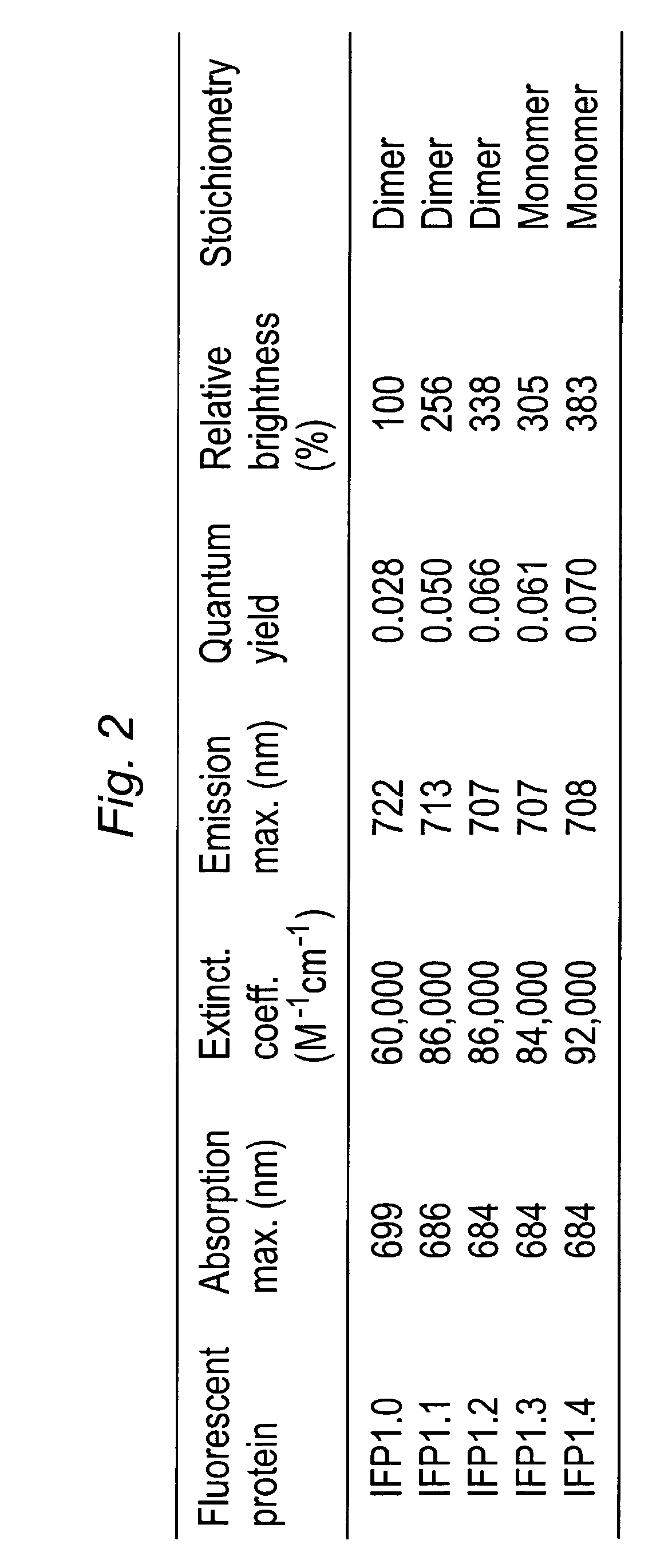
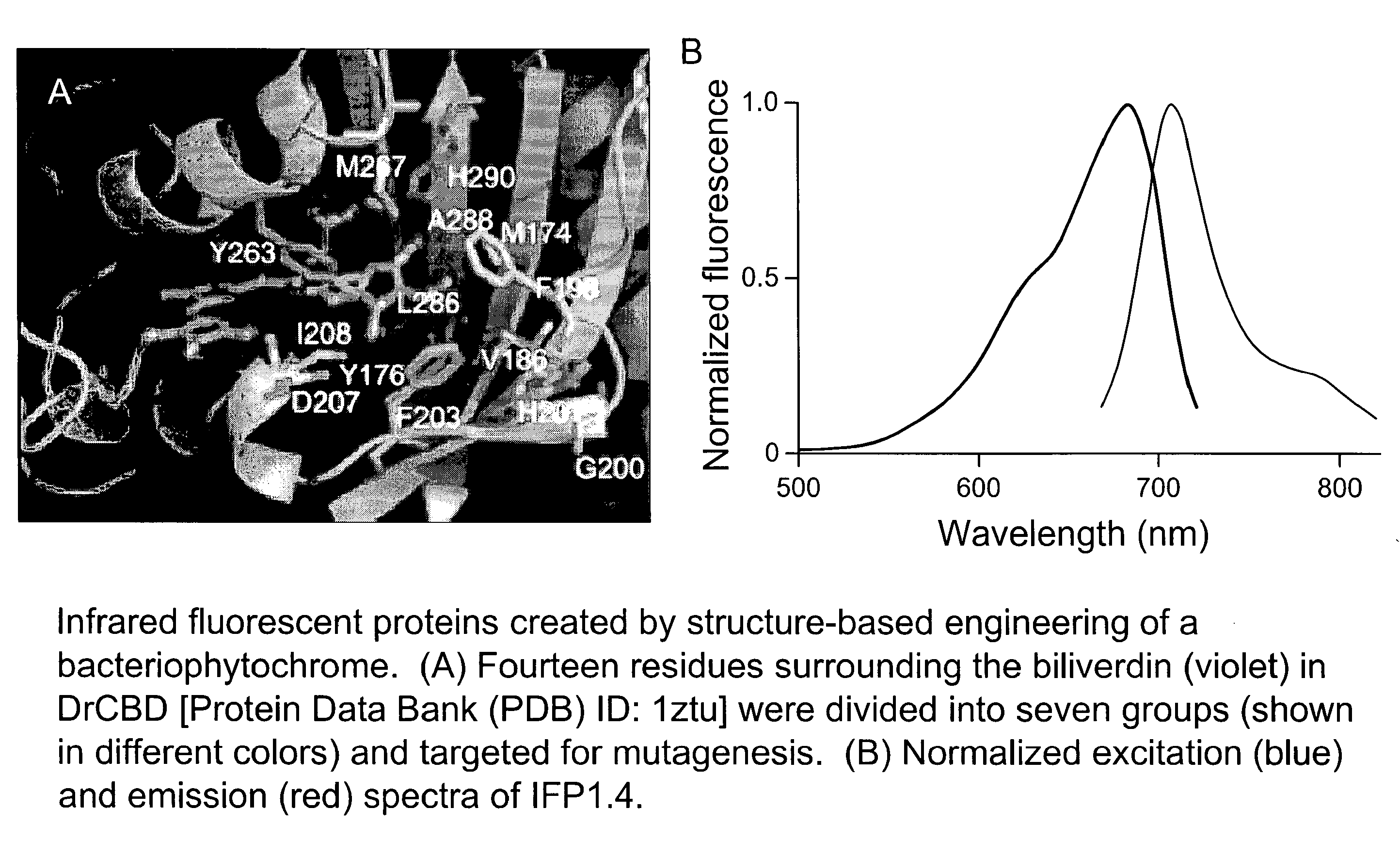
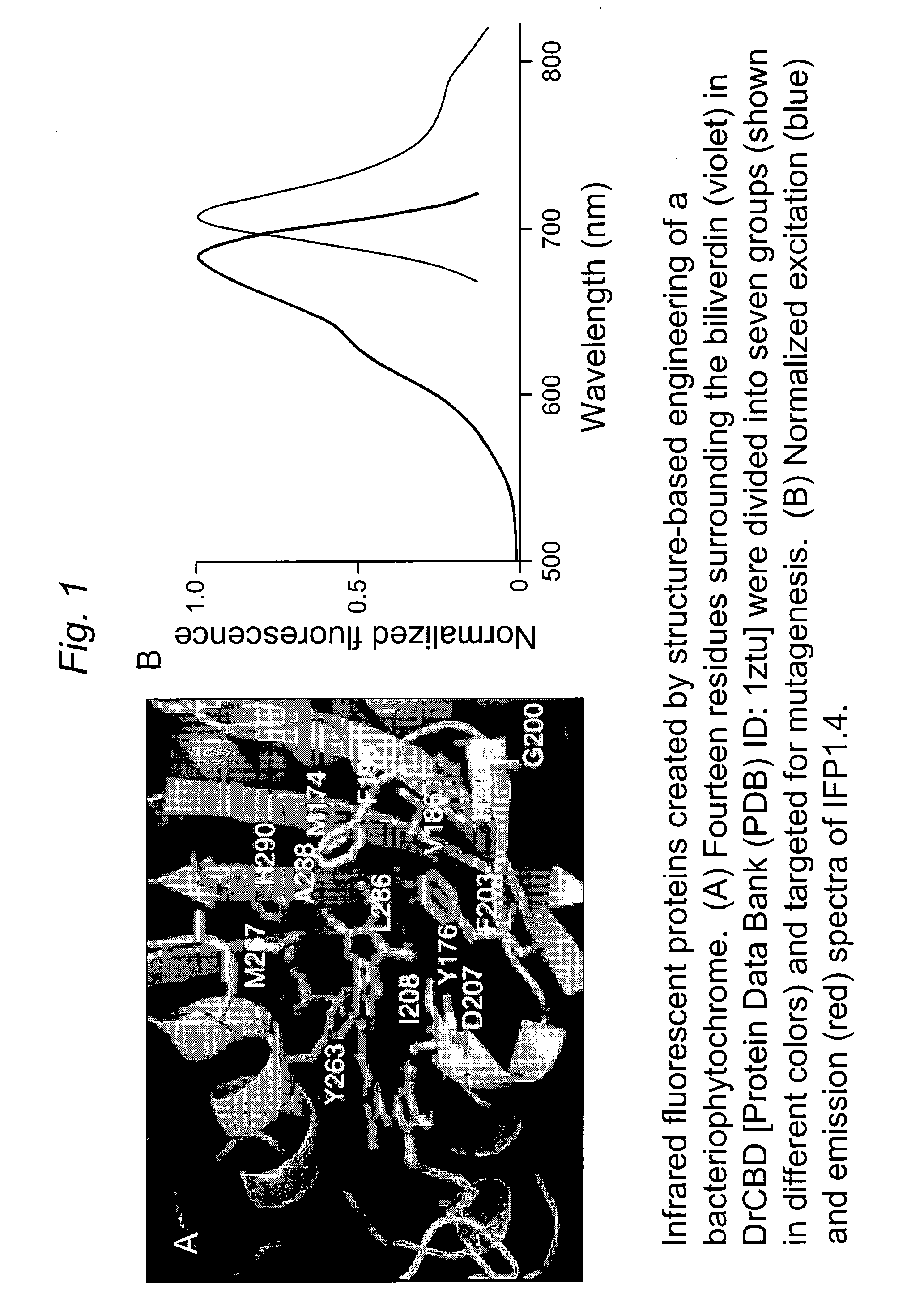
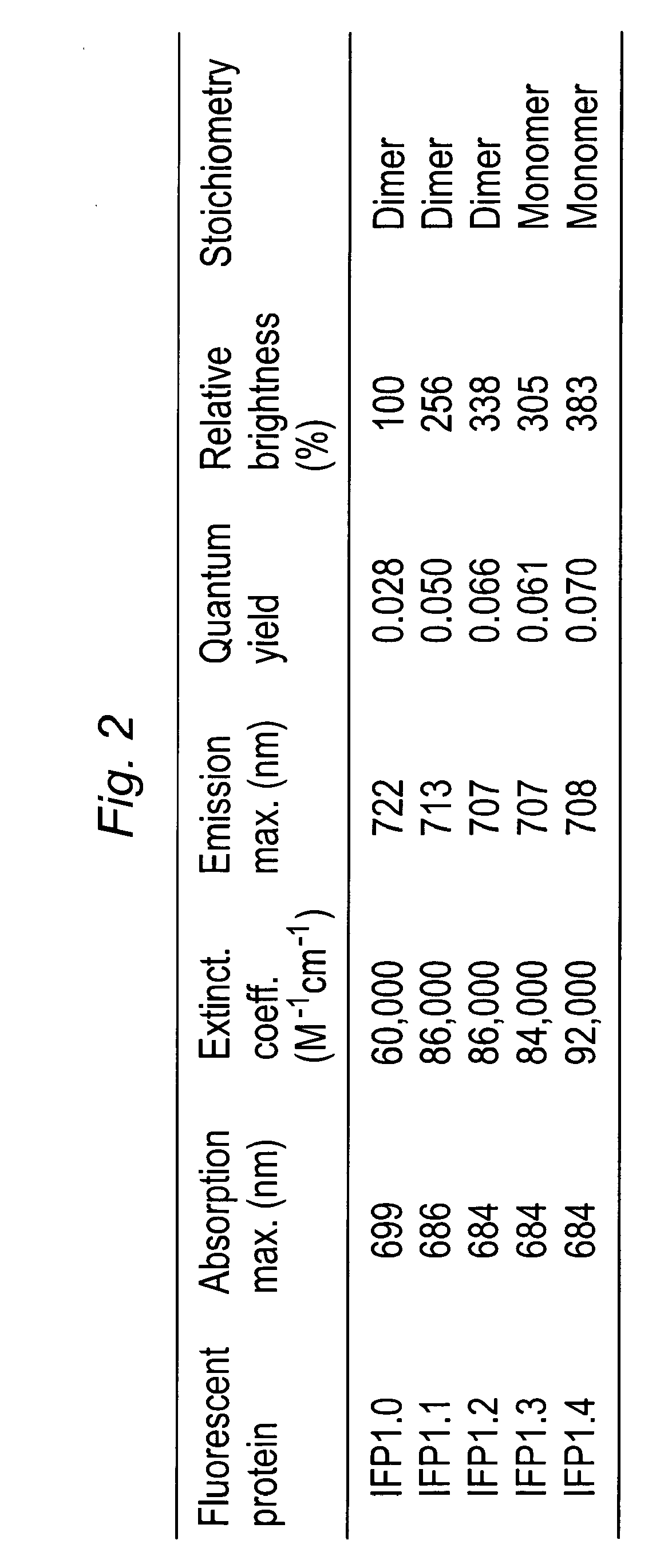
This invention provides novel truncation mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. When expressed either in bacteria or mammalian cells, these mutant phytochromes spontaneously incorporate biliverdin, a ubiquitous intermediate in heme catabolism, and become fluorescent in the infrared (IR) region. These phytochromes are the first genetically encoded labels that can be excited by far-red light and fluorescent in the true IR (>700 nm). If these mutants instead incorporate protoporphyrin IX, an intermediate in heme biosynthesis, illumination now generates significant amounts of singlet oxygen. Singlet oxygen is useful because it can be used to kill individual proteins or cells, detect long-range protein-protein interactions, or generate electron-microscopic contrast. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such proteins and protein variants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Genetically engineered bacterium with high-yield electroactivity and environmental stress tolerance
ActiveCN106520653AImprove electricity production activityHigh electroactivityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySynechococcus
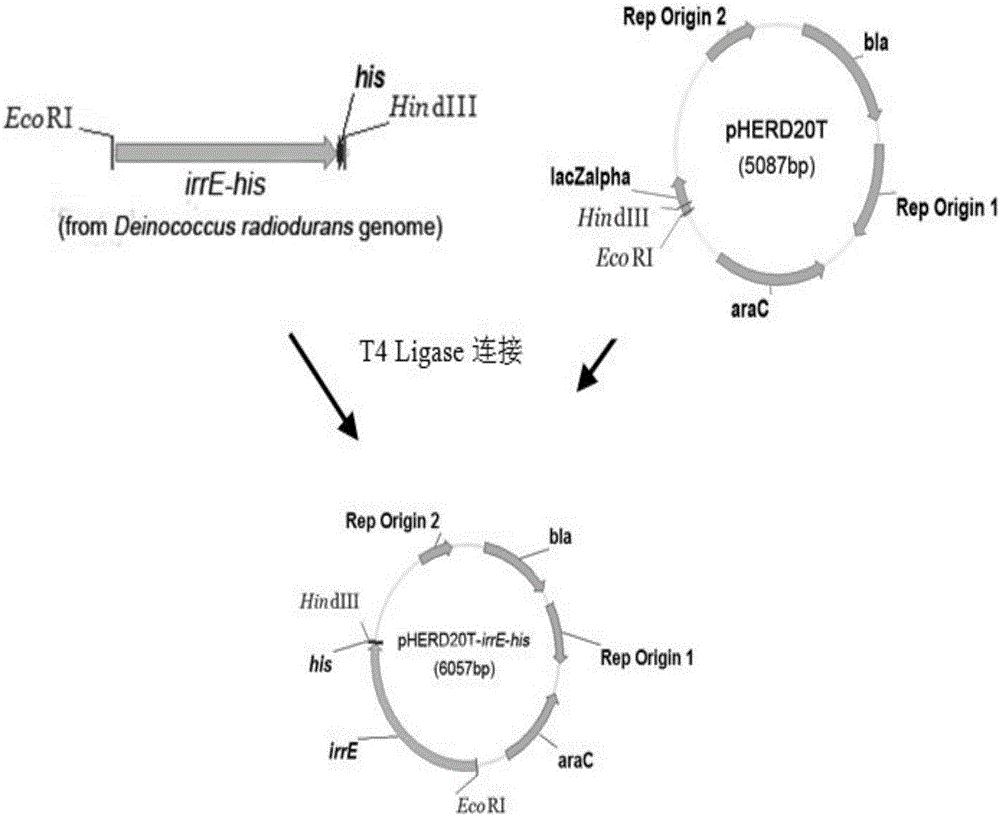
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium with high-yield electroactivity and environmental stress tolerance. The lactic dehydrogenase gene ldhA in a pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 genome is knocked out, and the PAOl knockout strain is obtained; then a global regulatory factor IrrE of the deinococcus radiodurans is guided into the ldhA-, and the genetic engineering strain ldhA--irrE is obtained. After the thallus treated through a chemical agent is inoculated to a microbial fuel cell, the generated voltage and power density are improved by 46.76%-53.33% than those of the wild type strain, the time for stabilizing a system is shortened by 28.57%, the internal resistance of the system is reduced by 12.66%, the voltage under polyethylene glycol treatment is 543, the power density is 207, the stabilizing time is 130 h, the internal resistance reaches 420.32, and the survival rate of the engineered strain under the hunger condition, the high-acid-base condition and high-salt condition are improved by one time than those of the wild type strain.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for efficiently determining a DNA strand break
InactiveUS7361462B2Potent and specific binding activitySpecifically and sensitively detect DNA strand break(s)Microbiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationA-DNAIn vivo
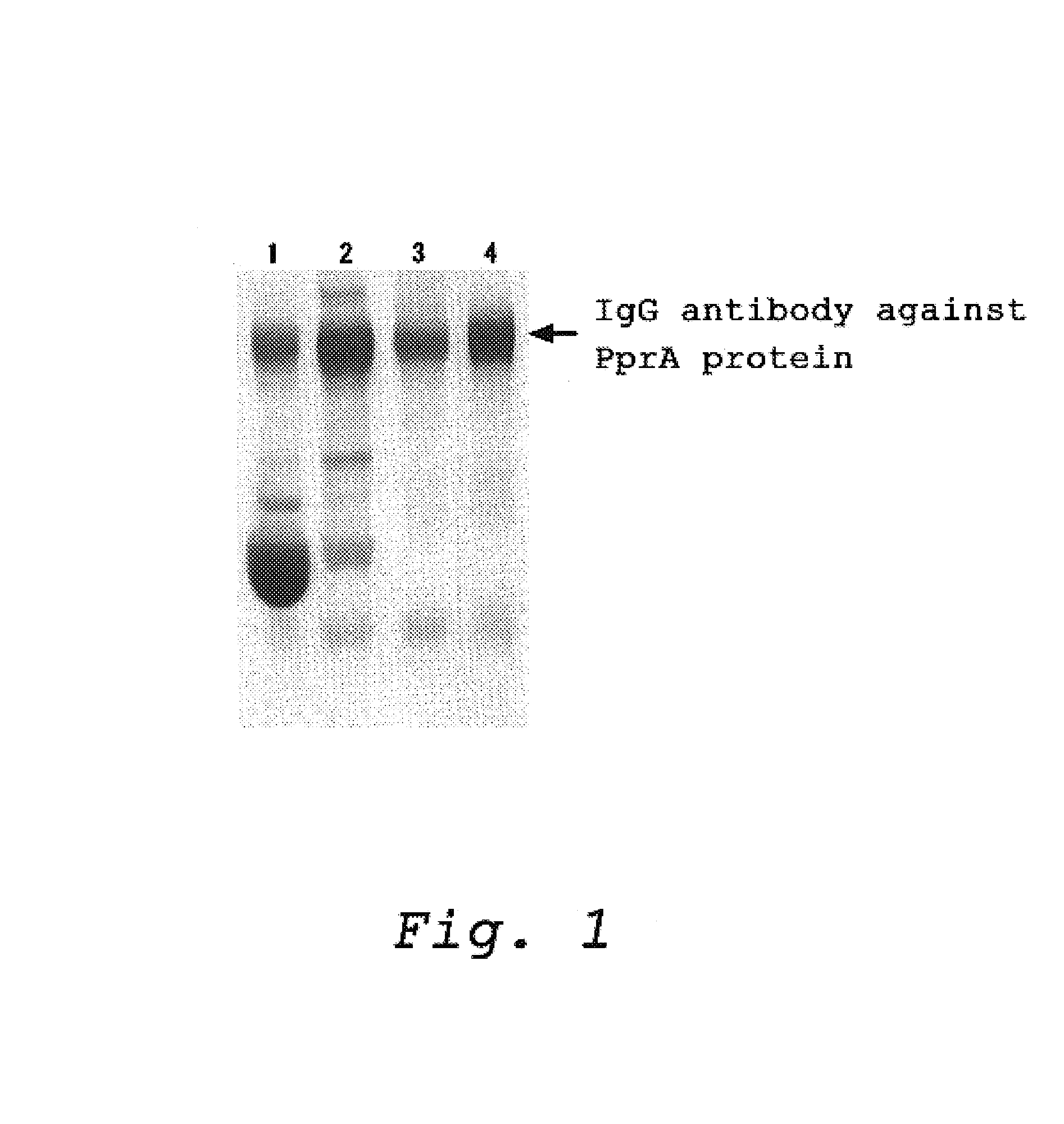
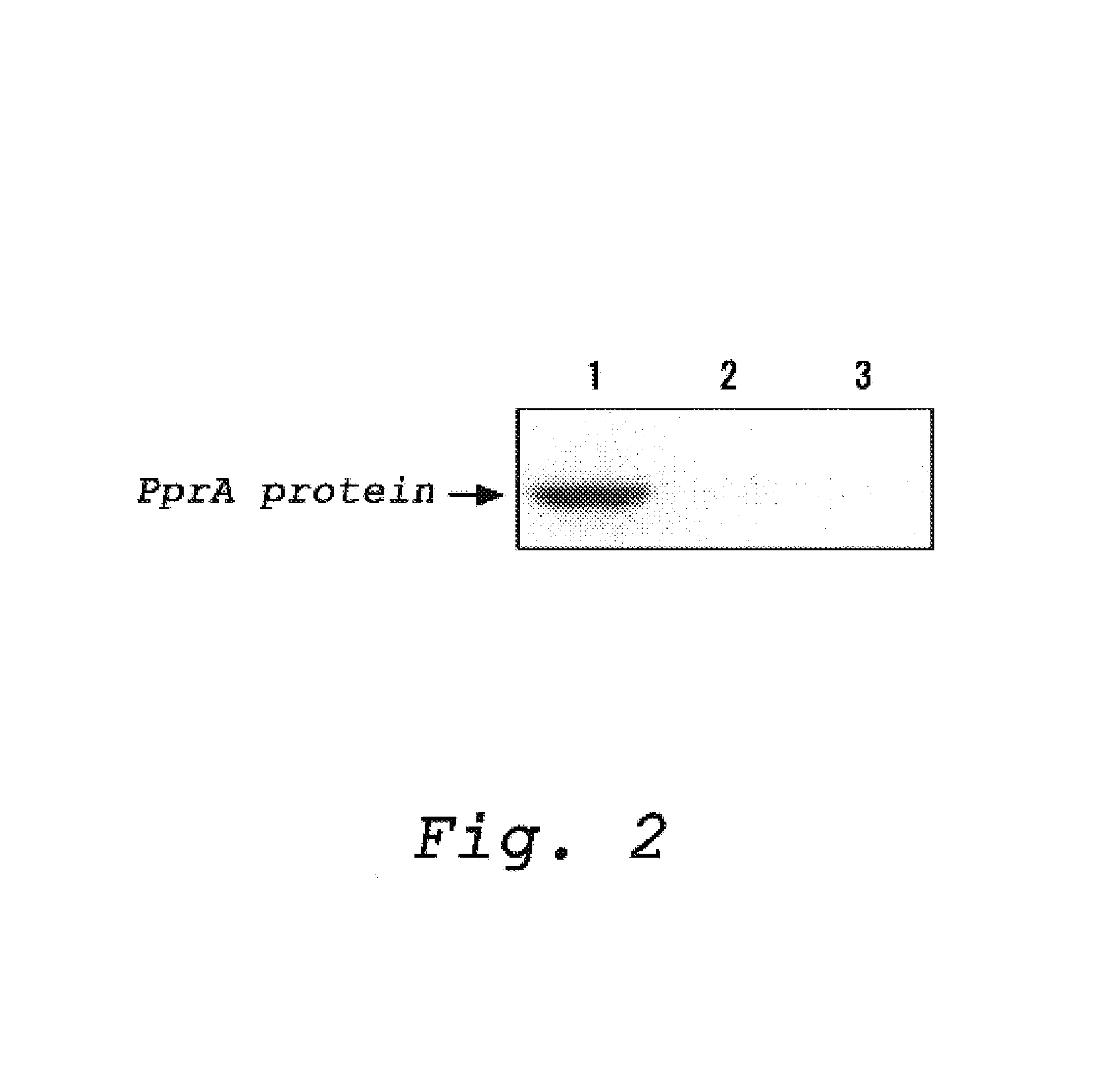
The present invention is directed to directly measure distribution in vivo and the frequency of generation in vivo of DNA strand breaks which induce cell death and mutations. The present inventors accomplished the present invention by providing a method for detecting a DNA strand break in a sample, which comprises a step of binding a PprA protein derived from Deinococcus radiodurans to a DNA strand break and a step of detecting the PprA protein which is bound to the DNA strand break; as well as by providing a kit for detecting a DNA strand break in a sample which comprises PprA proteins derived from Deinococcus radiodurans and a means for detecting a PprA protein which is bound to a DNA strand break.
Owner:JAPAN ATOMIC ENERGY AGENCY INDEPENDANT ADMINISTRATIVE CORP
Novel peptide tag and uses thereof
InactiveCN105636976AEliminate non-specific reactionsEfficient detectionAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against bacteriaEpitopePlant photoreceptors
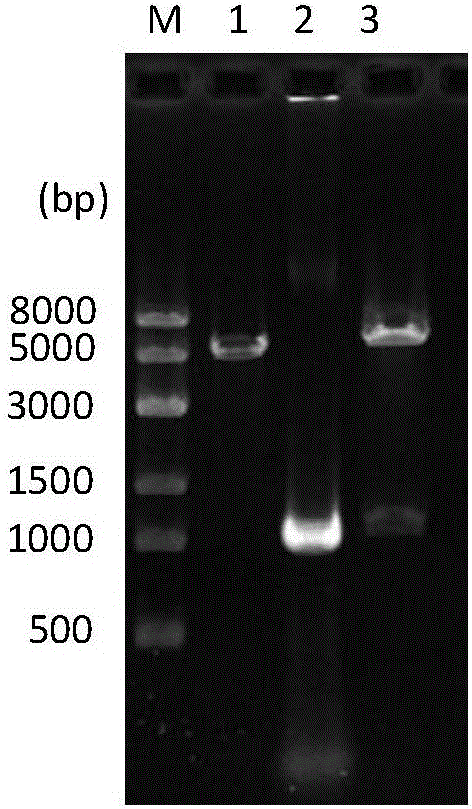
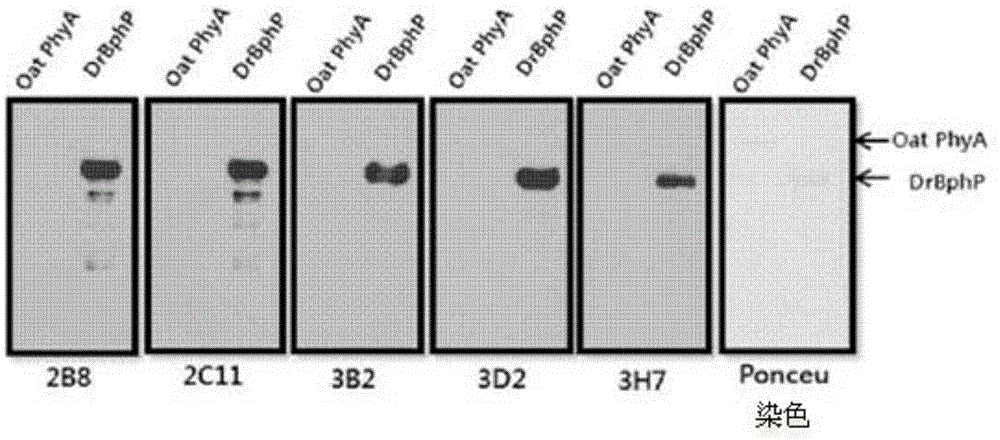
There are provided peptide tags derived from bacteriophytochrome (BphP) that is photoreceptor protein of Deinococcus radiodurans, an antibody capable of specifically recognizing the peptide tags, hybridoma cell lines capable of producing the antibody, and uses thereof. The novel peptide tag has advantages in that it has a short length and can remove a non-specific reaction of the conventional c-myc tag and FLAG tag. Therefore, in the case of using the novel peptide tag and antibody thereto, the fusion protein expressed in a recombinant cell can be very effectively detected or purified. In addition, an epitope tagging system including the novel peptide tag and antibody thereto can be applied in various fields such as a determination of an intracellular site, a confirmation of functionality, detection and purification of specific protein, and researches on interaction between proteins.
Owner:UNIV IND COOP GRP OF KYUNG HEE UNIV +1
Biological surfactant functional modification method for deinococcus radiodurans (DR) and application thereof
ActiveCN105498718AAvoid dischargeOvercoming Radiation Resistance IssuesOther chemical processesRadioactive contaminantsSorbentBacterial strain
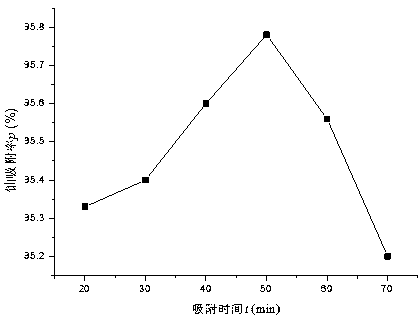
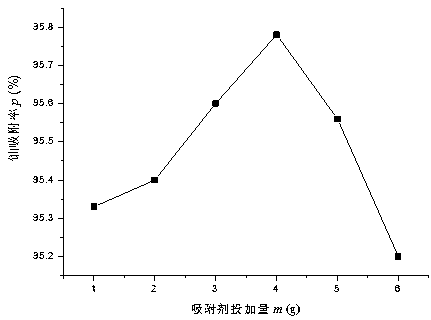
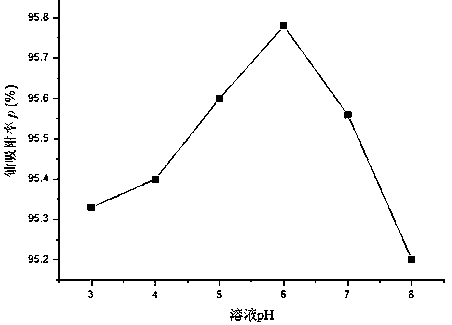
The invention relates to a biological surfactant functional modification method for deinococcus radiodurans (DR). The biological surfactant functional modification method comprises the following steps: firstly embedding rice straws and rice husks in farmland soil for composting, carrying out enrichment cultivation, ferment cultivation and flat chemical cultivation primary screening to obtain a biological surfactant bacterial strain liquid, carrying out functional modification on the deinococcus radiodurans (DR) to obtain a biological surfactant functional modification deinococcus radiodurans (DR) adsorbent, and applying the adsorbent to uranium-polluted water body repair. The method disclosed by the invention uses natural resource biomasses as raw materials, and is free of toxicity or pollution to the environment, so that recycling and resource recovery of natural resources are realized. Meanwhile, the method is simple and mild in reaction conditions, the obtained adsorbent can enable the content of uranium in a uranium-polluted water body with the concentration of 0.45-0.50 mg / L to be decreased by 95.2% to 95.78%, and the method has excellent social and economic benefits.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Application of ytxH gene in deinococcus radiodurans R1 to cultivating salt-tolerant plants
The invention finds that a ytxH gene (DR0105) in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 has the function of improving the adversity resistance of prokaryotes and plants. The invention constructs recombinant vectors containing the gene and the recombinant vectors are respectively transferred into prokaryotic and eukaryotic host cells. Experiments prove that the ytxH gene (DR0105) can improve the salt tolerance of prokaryotes and the transgenic plants obtained after transplanting the gene into the plants also have salt tolerance.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
DNA molecule used for recombinant pichia plasmid and recombinant pichia strain expressing ppri protein of deinococcus radiodurans
ActiveUS20170016009A1Successfully and efficiently expressSuccessfully and efficiently express and purify PprIHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsPlasmidVirology
A DNA molecule comprising the sequence set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1, a recombinant Pichia plasmid into which the DNA molecule is inserted, and a recombinant Pichia strain obtained by the transformation of the recombinant Pichia plasmid into a competent Pichia cell and efficiently expressing the PprI protein of Deinococcus radiodurans.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Application of dap gene in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 in breeding of salt tolerant plants
The invention discovers that dap gene (DRB0118) in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 improves the resistance of prokaryotes and plants. The invention constructs a recombinant vector comprising the gene; and the recombinant vector is transferred into prokaryotic and eukaryotic host cells. Experiments prove that: after the dap gene (DRB0118) is expressed in prokaryotic host cells and tobacco, the salt resistance of the prokaryotic host cells and the tobacco can be improved.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Proteins that fluoresce at infrared wavelengths or generate singlet oxygen upon illumination
ActiveUS20110177003A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBacteriaHaem biosynthesisProtoporphyrin IX
This invention provides novel truncation mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. When expressed either in bacteria or mammalian cells, these mutant phytochromes spontaneously incorporate biliverdin, a ubiquitous intermediate in heme catabolism, and become fluorescent in the infrared (IR) region. These phytochromes are the first genetically encoded labels that can be excited by far-red light and fluoresce in the true IR (>700 nm). If these mutants instead incorporate protoporphyrin IX, an intermediate in heme biosynthesis, illumination now generates significant amounts of singlet oxygen. Singlet oxygen is useful because it can be used to kill individual proteins or cells, detect long-range protein-protein interactions, or generate electron-microscopic contrast. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such proteins and protein variants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Broad specificity DNA damage endonuclease
InactiveUS7060455B1Simple structurePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesInsertion deletionSchizosaccharomyces pombe
The present disclosure describes DNA damage endonucleases which exhibit broad specificity with respect to the types of structural aberrations in double stranded DNA. These enzymes recognize double stranded DNA with distortions in structure, wherein the distortions result from photoproducts, alkylation, intercalation, abasic sites, mismatched base pairs, insertion deletion loops, cisplatin adducts and other types of base damage (for example, uracil resulting from cytosine deamination). The UVDE (Uve1p) of Schizosaccharomyces pombe, certain truncated forms of that UVDE (lacking from about 100 to about 250 amino acids of N-terminal sequence) and certain endonucleases from Homo sapiens, Neurospora crassa, Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus anthracis, Methanococcus jannaschii, and Deinococcus radiodurans. The present disclosure further provides methods for cleaving double stranded DNA having structural distortions as set forth herein using the exemplified endonucleases or their stable, functional truncated derivatives.
Owner:EMORY UNIVERSITY
Industrial applications of plant cell extracts comprising sod enzymes of extremophilic micro-organisms
InactiveCN112912059AImprove catalytic performanceStable and long-lasting antioxidant effectCosmetic preparationsMilk preparationBiotechnologyDismutase
The present invention relates to a composition with an antioxidant activity, comprising a first dry extract derived from plant cell cultures comprising superoxide dismutase of Sulfolobus solfataricus, a second dry extract derived from plant cell cultures comprising superoxide dismutase of Aeropyrum pernix and a third dry extract derived from plant cell cultures comprising superoxide dismutase from Deinococcus radiodurans, wherein said plant cell cultures are cultures of cells belonging to Solanum lycopersicum species.
Owner:ARTERRA BIOSCI
Application of deinococcus radiodurans R1 trkB genes to cultivation of salt-tolerant plants
The invention discovers that trkB genes (DR1667) in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 are capable of enhancing resistance capability of prokaryotes and plants. Recombinant vectors comprising the trkB genes (DR1667) are constructed and are respectively transferred into prokaryotic and eukaryotic host cells. Experiments prove that salt tolerance of the prokaryotic host cells and rape can be enhanced after the trkB genes (DR1667) are expressed in the prokaryotic host cells and rape.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Novel application of Deinococcus radiodurans PprI protein and its pharmaceuticals
InactiveCN105267947AReduce apoptosis rateReduce mortalityPeptide/protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsRadiation injuryHuman cell
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to an application of PprI protein and its pharmaceuticals. The application of the PprI protein in the preparation of pharmaceuticals for controlling radiation injury in higher eukaryotes is provided. Researches discover that the PprI protein is significant to controlling acute radiation injury in human cells and mice and enhances the antioxidant ability and DNA damage repairing ability.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Application of hydroxylase gene Dr2473 to catalytic synthesis of microorganisms
The invention discovers a gene with a hydroxylase function discovered from deinococcus radiodurans. The invention constructs a recombinant vector containing the gene, and the recombinant vector is expressed in prokaryotic host cell Escherichia coli. An experiment proves that after the gene is expressed in the prokaryotic host cell, carotenoid can be catalyzed to perform hydroxylation reaction. The gene can be used in the catalytic synthesis of the microorganisms.
Owner:THE INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
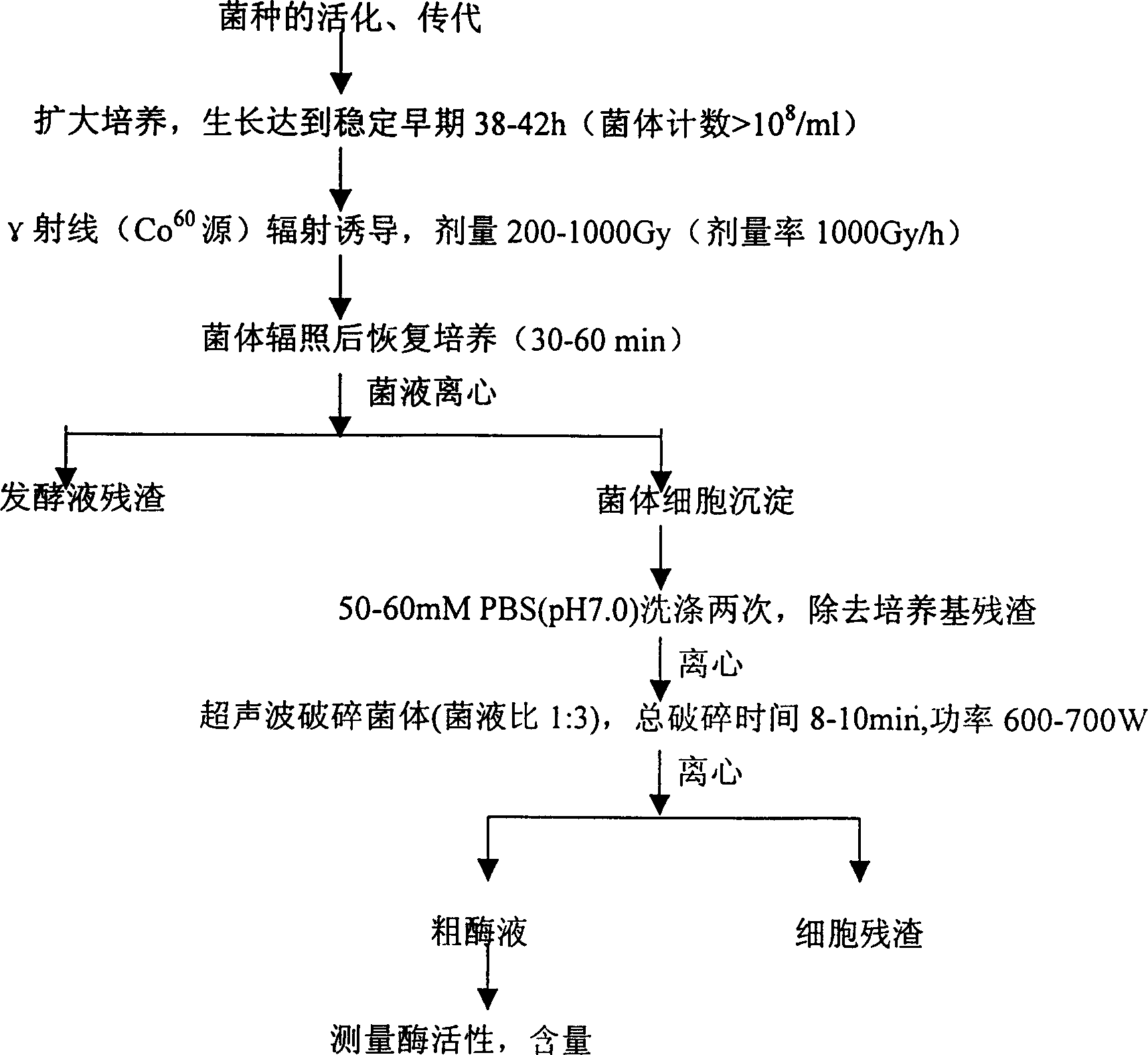
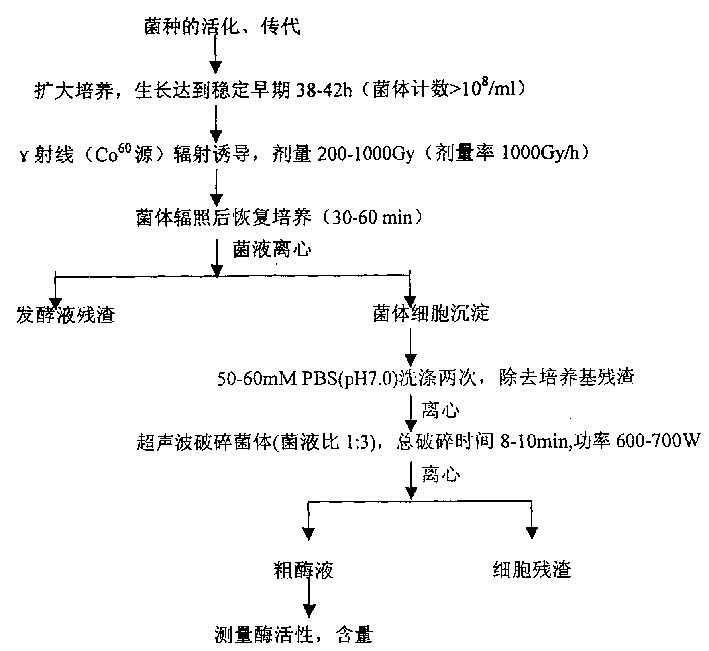
Method for increasing yield of superoxide dismutase of radioresistant coccus by radiation induction
InactiveCN1200099CIncrease SOD enzyme activitySimple processBacteriaOxidoreductasesYeastMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for increasing the superoxide dismutase production of Radiation Coccus radiodurans induced by radiation, inducing the bacterial superoxide dismutase SOD by irradiating and post-culturing the radioresistant coccus radiodurans cultured to the stable early stage through gamma ray irradiation Synthesis, increase the production of bacterial enzymes. The bacterial cells of the present invention are separated, ultrasonically treated and extracted, and the obtained SOD enzyme activity is increased by more than 75% compared with that before irradiation treatment, which is 3 times that of the SOD-producing yeast enzyme activity. At the same time, the process flow is simple and the cost is low. The advantages.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
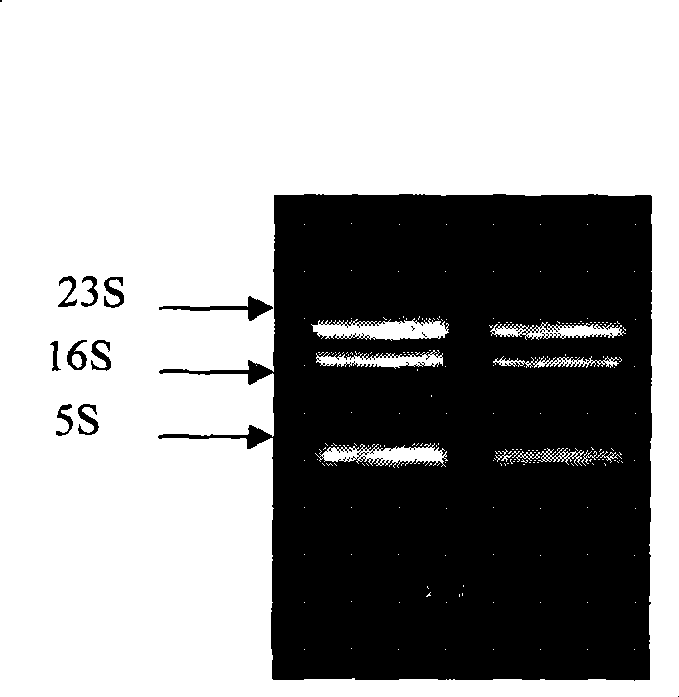
Method for quick extraction of total RNA from radioresistant bacterium
The invention relates to a method for rapidly extracting total RNA from radio resistant bacteria, which comprised the following steps: 1) material: exponential phase of radio resistant bacteria (Deinococcus radiodurans) is taken as the material; 2) the total RNA is extracted and schizolysis is carried out: 500mu L of cell lysis solution is added and is whirled evenly; 120-200mu L 50mg / mL of muramidase is added and is heated up to 50 DEG C for heat preservation for 15min; extraction: 1mL of Ezol is added to be degraded for 15min at the room temperature; 200mu L of chloroform is added to be centrifugated, and supernatant fluid is taken out and is added with 1.5-2.5 times of isopropanol precipitation; washing and storage of samples: RNA samples are washed to be added with DEPC water for solution and stored at 80 DEG C below zero; 3) quality test on the RNA: according to the obtained data and electrophoresis result, the obtained total RNA has high purity quotient, high production rate and good integrity. The method has the advantages that the experiment process is rapid, simple and has good repeatability, which is also applicable to the extract of total RNA of the bacteria with complicated cytoderm structure.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
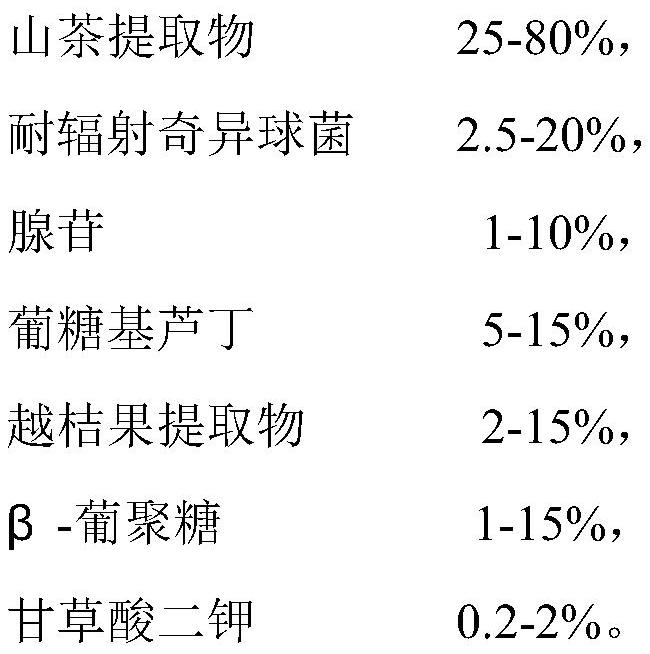
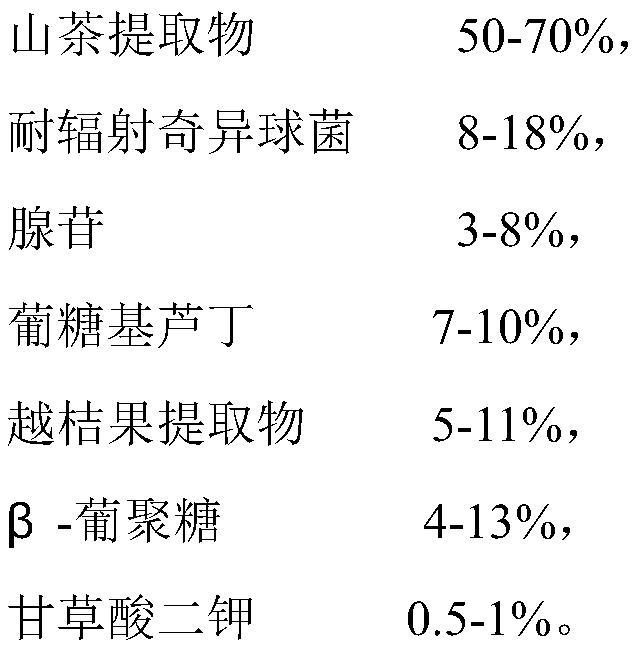
Anti-blue-ray repairing composition containing camellia extract and application of anti-blue-ray repairing composition
ActiveCN111686069AInhibitory activityReduce degradationCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdenosineCamellia cuspidata
The invention relates to an anti-blue-ray repairing composition containing camellia extract and application of the anti-blue-ray repairing composition. The composition contains the following components in percentage by weight: 25%-80% of the camellia extract, 2.5%-20%of Deinococcus radiodurans, 1%-10% of adenosine, 5%-15% of glycosylrutin, 2%-15% of a bilberry fruit extract, 1%-15% of beta-glucanand 0.2%-2% of dipotassium glycyrrhizinate. The composition is capable of weakening pigment induction of blue rays to skin in multiple ways, effectively defending subsequent chromatosis, relieving injury caused by the blue rays to the skin and keeping the skin elastic and glossy and is safe and efficient. The prepared anti-blue-ray repairing composition can be widely applied to products such as cosmetics including smoothing toners, emulsions and creams for repairing photoaging skin problems such as dryness, darkness and slackness.
Owner:SHANGHAI FOREST CABIN BIOLOGICAL TECH
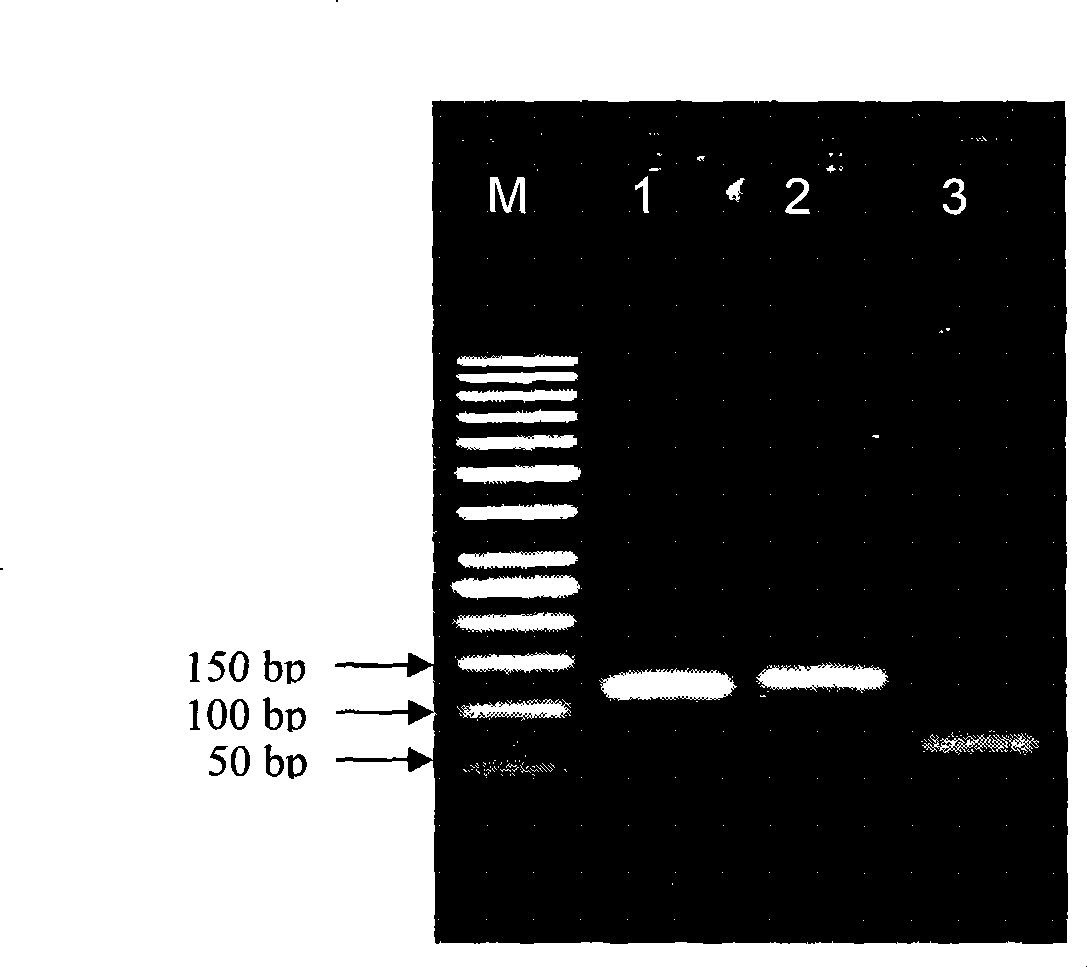
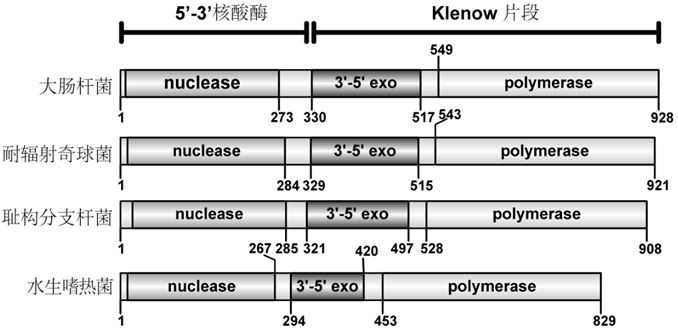
A high-fidelity polymerase with gap DNA preference and its application
ActiveCN111849939BAvoid degradationMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesDNA polymerase INucleotide
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
A kind of method that utilizes Deinococcus radiodurans r1 to synthesize 5-hydroxymethyl furoic acid
ActiveCN109988792BOvercome the disadvantage of unfriendlinessImprove toleranceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh concentration
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing 5-hydroxymethylfuroic acid by using Deinococcus radiodurans R1, inoculating Deinococcus radiodurans R1 on a TGY solid medium by streaking, picking a single colony and inoculating it on a TGY liquid medium after cultivation, After culturing to the logarithmic growth phase, insert it into fresh TGY liquid medium according to the inoculation amount of 1%, cultivate for 48 hours, collect the bacterial cells, add them to the buffer solution containing 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, and heat them at a temperature of 20-60 Reaction at ℃ for 3-48 hours to obtain 5-hydroxymethylfuroic acid. Deinococcus radiodurans R1 used in the present invention is used as a biocatalyst, which has high tolerance to 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, can catalyze the selective oxidation of high-concentration substrates to synthesize the target product, and the yield is more than 86%. The method of the present invention It has the characteristics of higher substrate concentration, better reaction efficiency and good selectivity.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Application of deinococcus radiodurans R1 trkB genes to cultivation of salt-tolerant plants
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Application of ytxH gene in deinococcus radiodurans R1 to cultivating salt-tolerant plants
The invention finds that a ytxH gene (DR0105) in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 has the function of improving the adversity resistance of prokaryotes and plants. The invention constructs recombinant vectors containing the gene and the recombinant vectors are respectively transferred into prokaryotic and eukaryotic host cells. Experiments prove that the ytxH gene (DR0105) can improve the salt tolerance of prokaryotes and the transgenic plants obtained after transplanting the gene into the plants also have salt tolerance.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Deinococcus radiodurans having gold nanoparticle synthesis ability, and method for removing radioactive iodine by using same
A method for removing iodine by using Deinococcus radiodurans having a gold nanoparticle synthesis ability is disclosed. More particularly, a method for removing radioactive iodine by adsorbing radioactive iodine onto gold nanoparticles synthesized in cells of Deinococcus radiodurans is disclosed. A recombinant microorganism having an enhanced radioactive iodine removal ability according to the present invention may selectively remove radioactive iodine present in various types of solutions at a high efficiency of 99% or higher, and thus may be very effective in removing radioactive iodine generated in large-scale hospitals, industries, nuclear facility accidents, and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF SEOUL IND COOP FOUND
Application of dap gene in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 in breeding of salt tolerant plants
ActiveCN102559728BMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionSalt resistanceBiotechnology
The invention discovers that dap gene (DRB0118) in Deinococcus radiodurans R1 improves the resistance of prokaryotes and plants. The invention constructs a recombinant vector comprising the gene; and the recombinant vector is transferred into prokaryotic and eukaryotic host cells. Experiments prove that: after the dap gene (DRB0118) is expressed in prokaryotic host cells and tobacco, the salt resistance of the prokaryotic host cells and the tobacco can be improved.
Owner:LONGPING BIOTECHNOLOGY (HAINAN) CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com