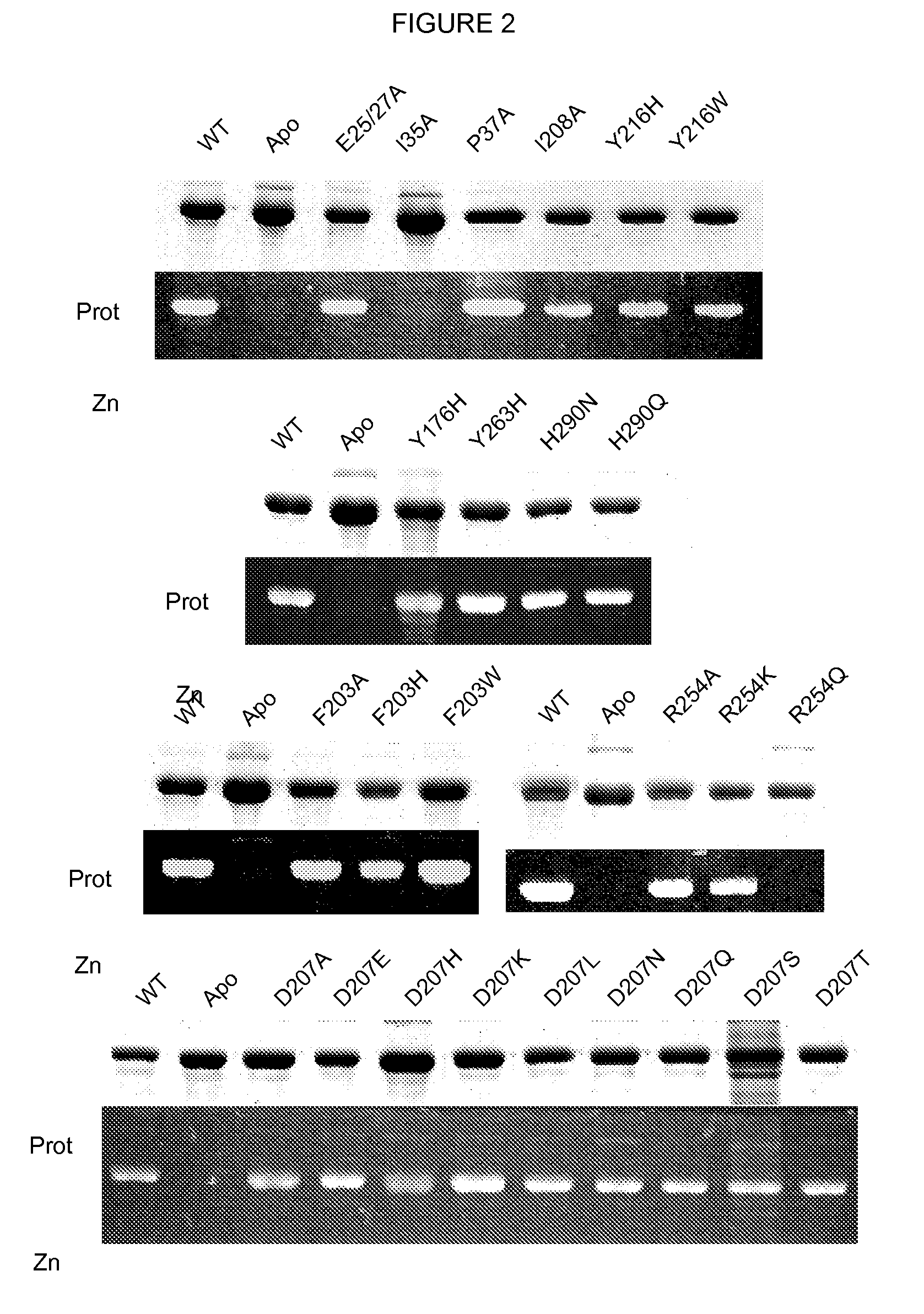
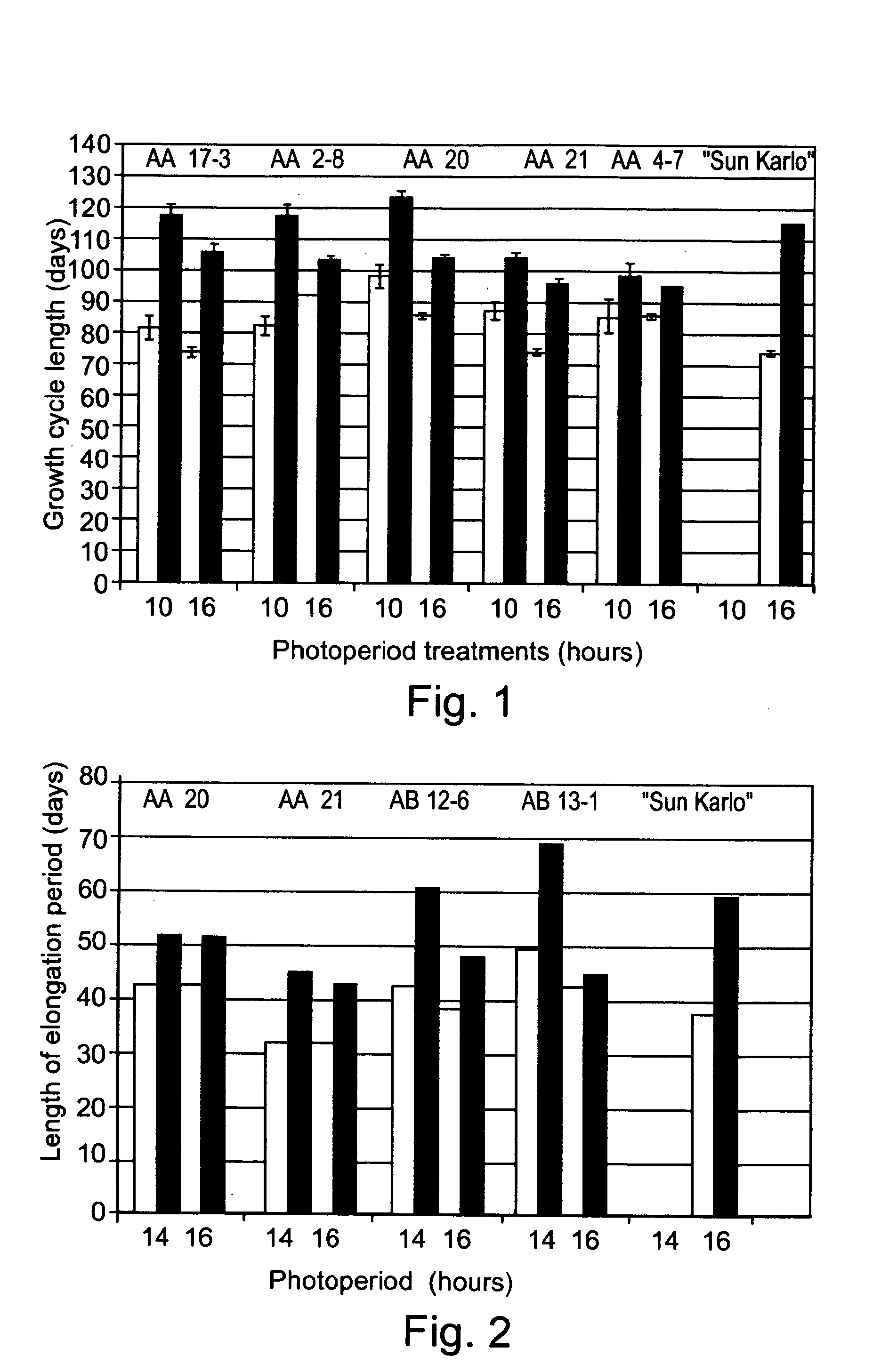
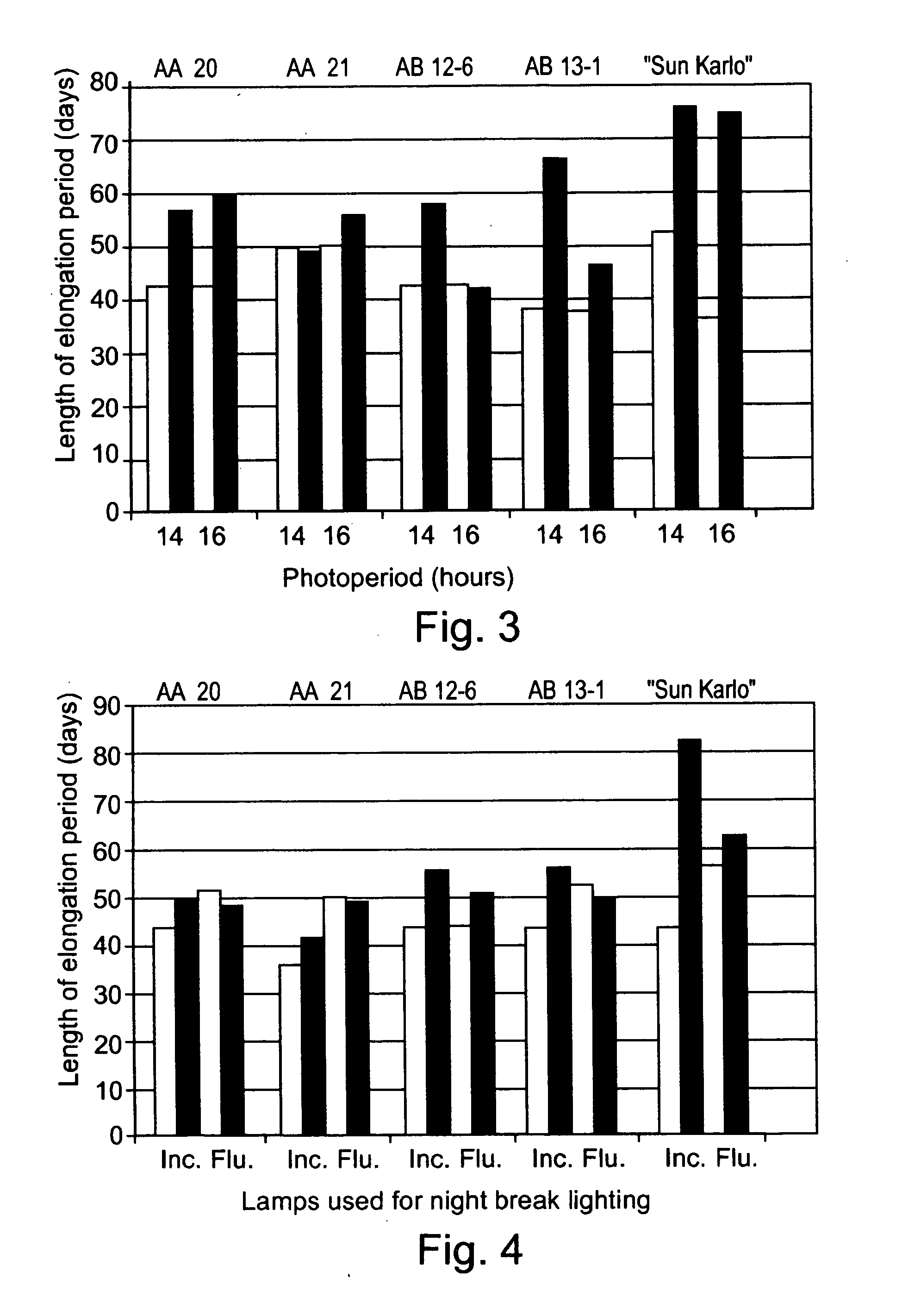
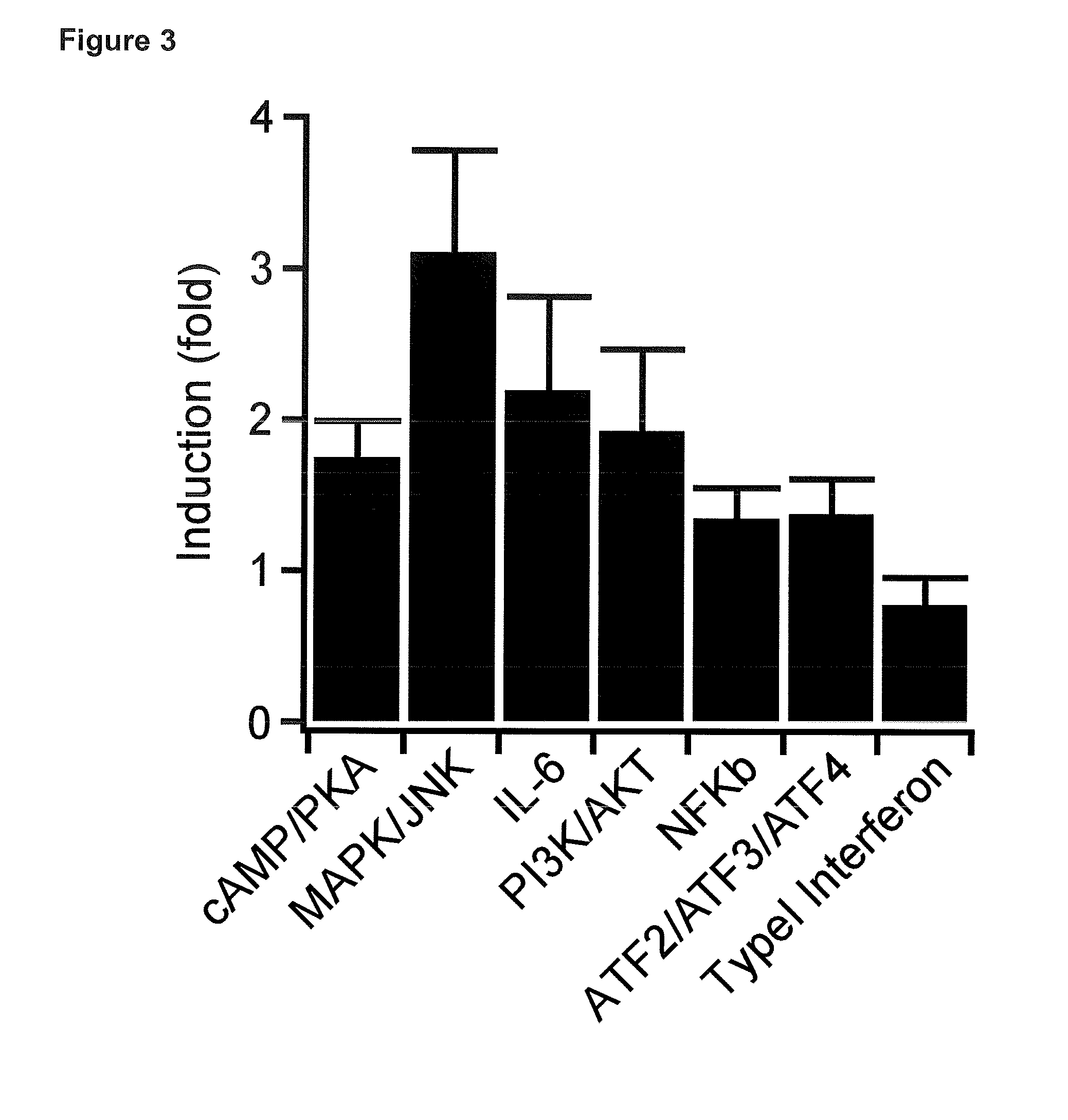
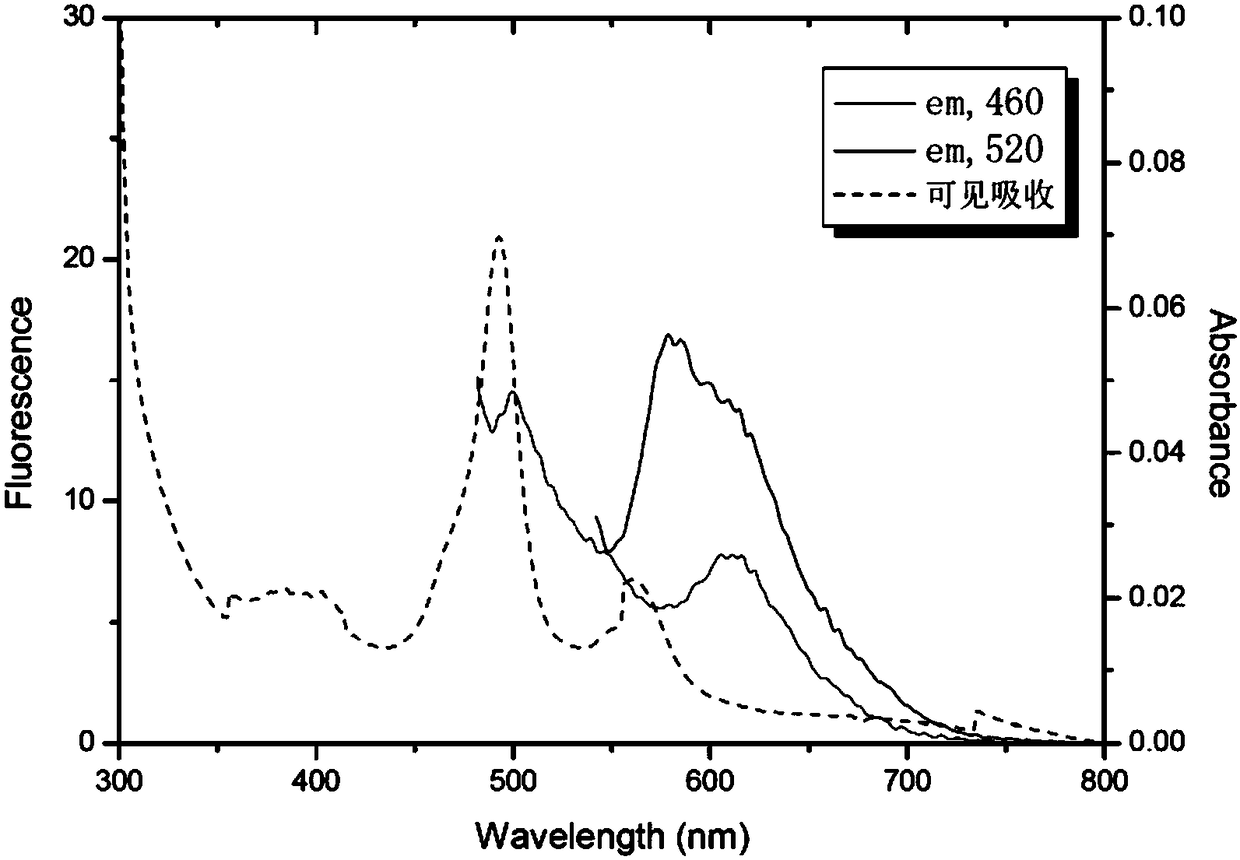
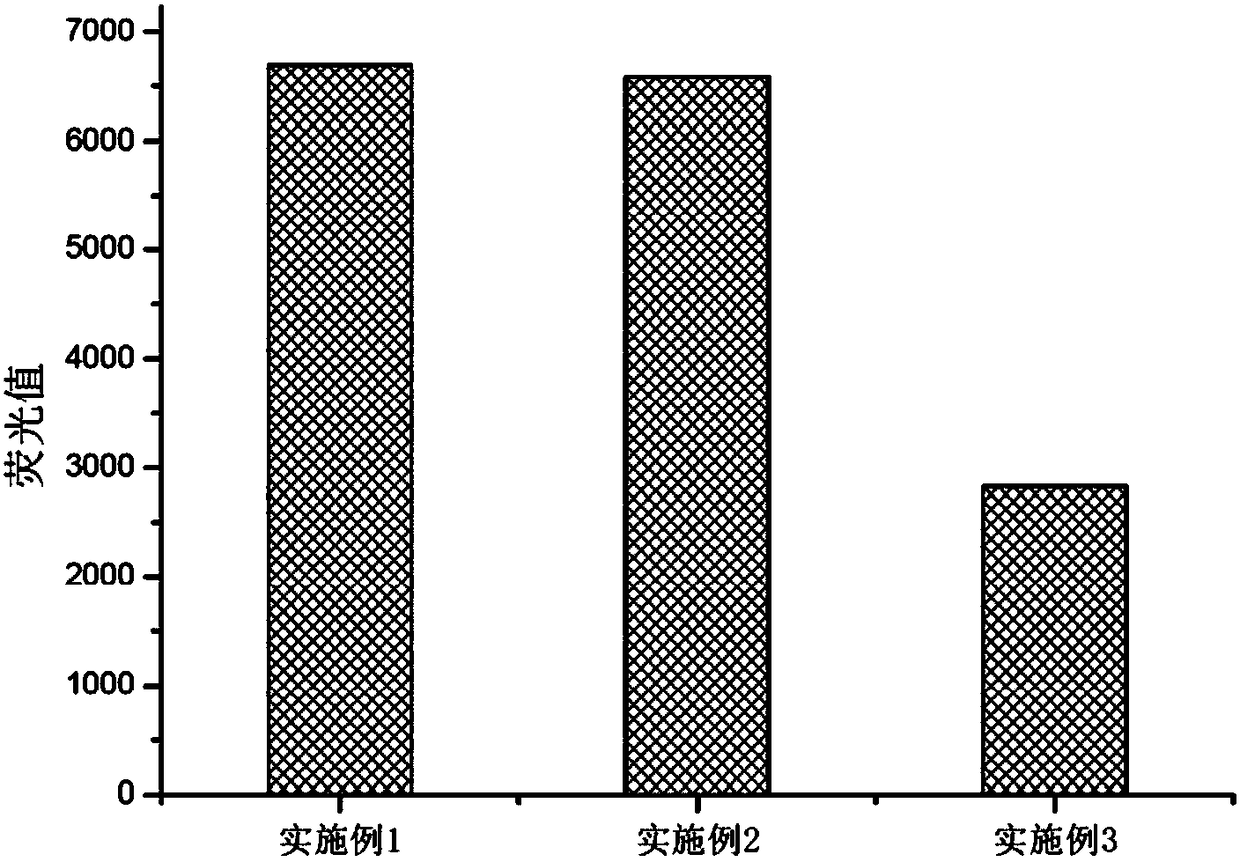
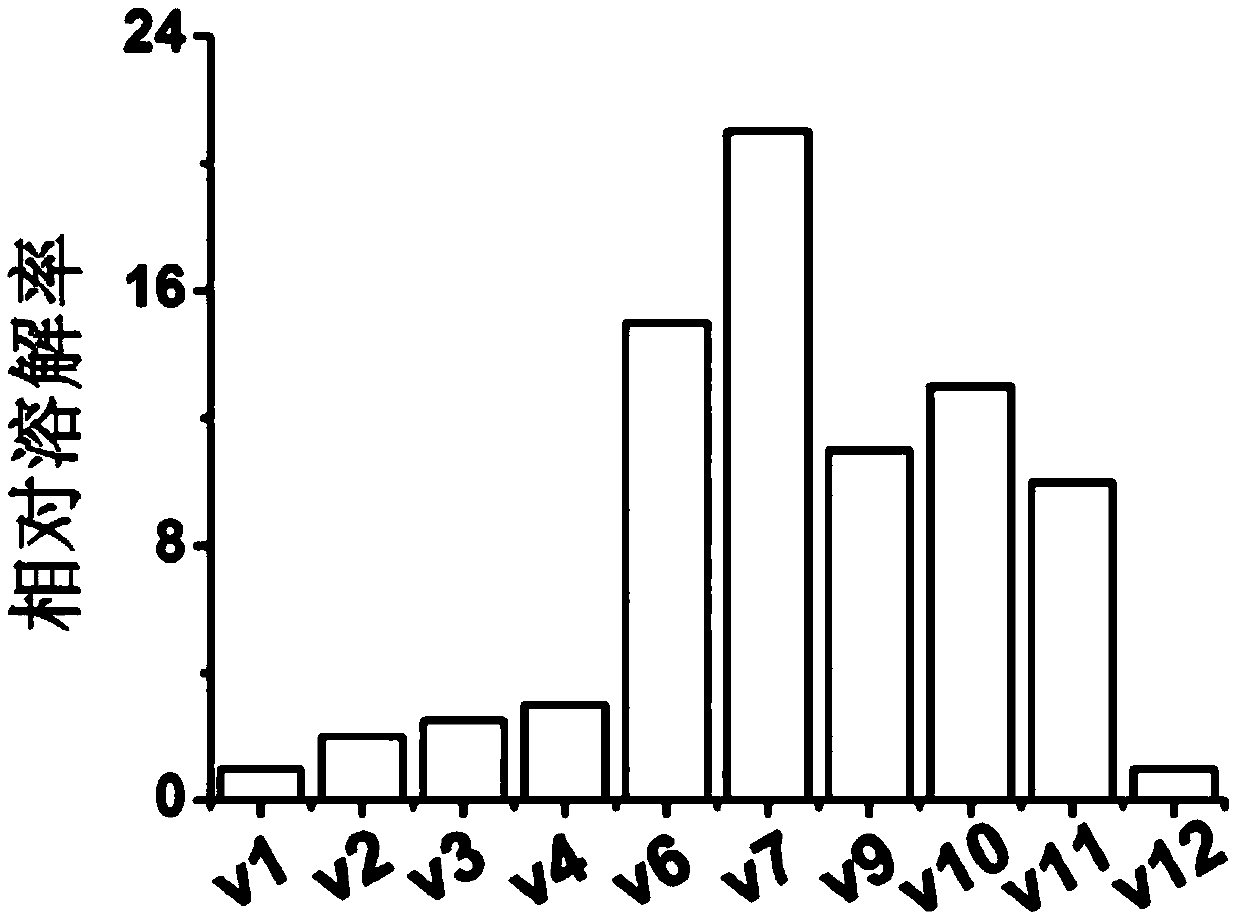
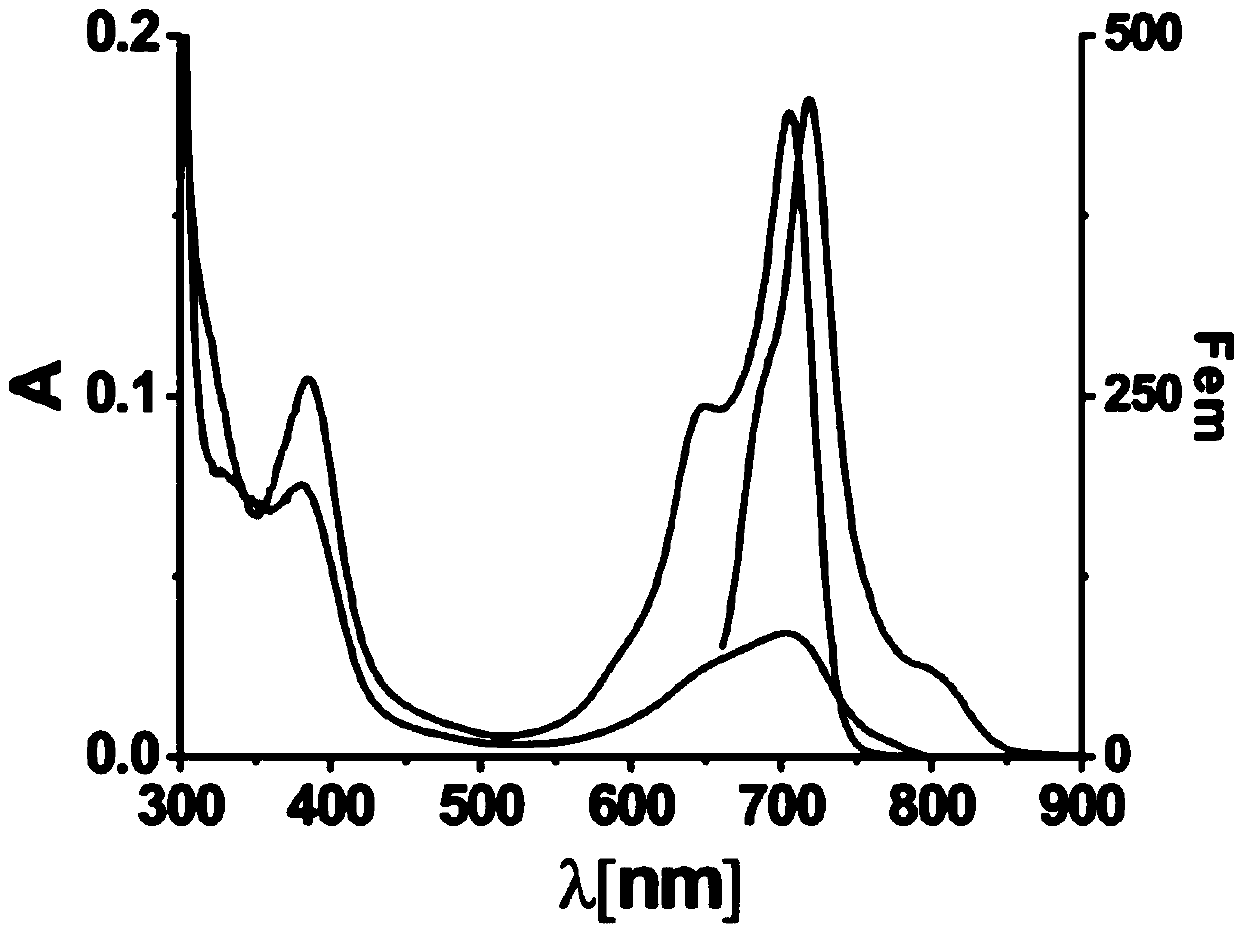
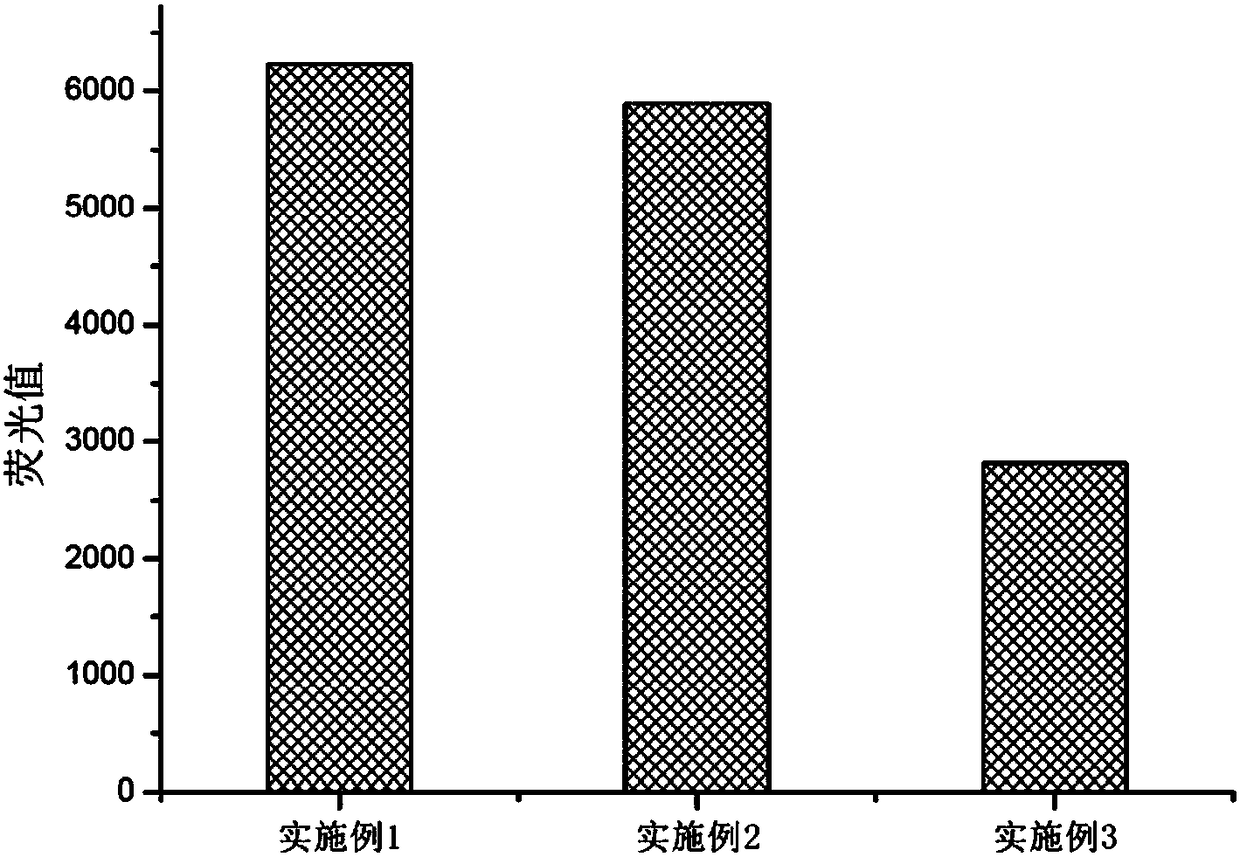
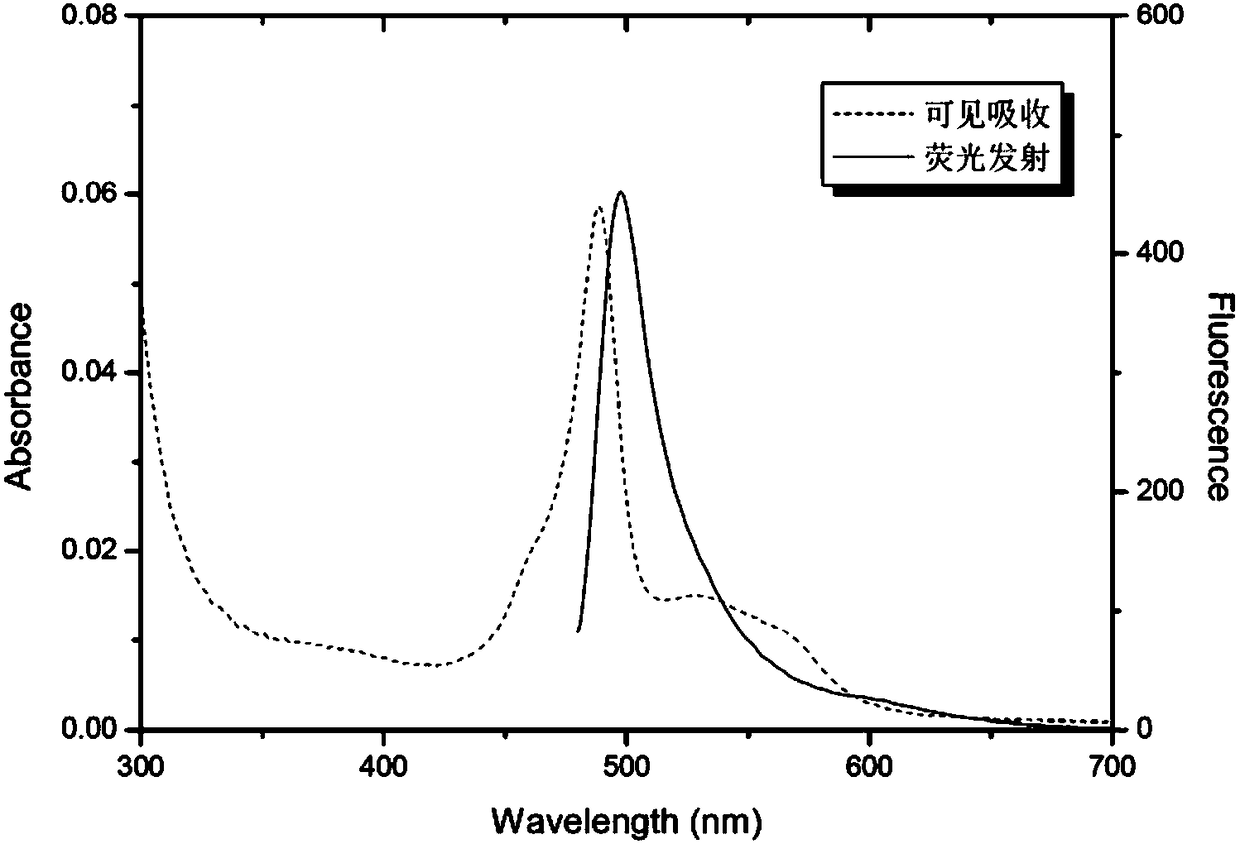
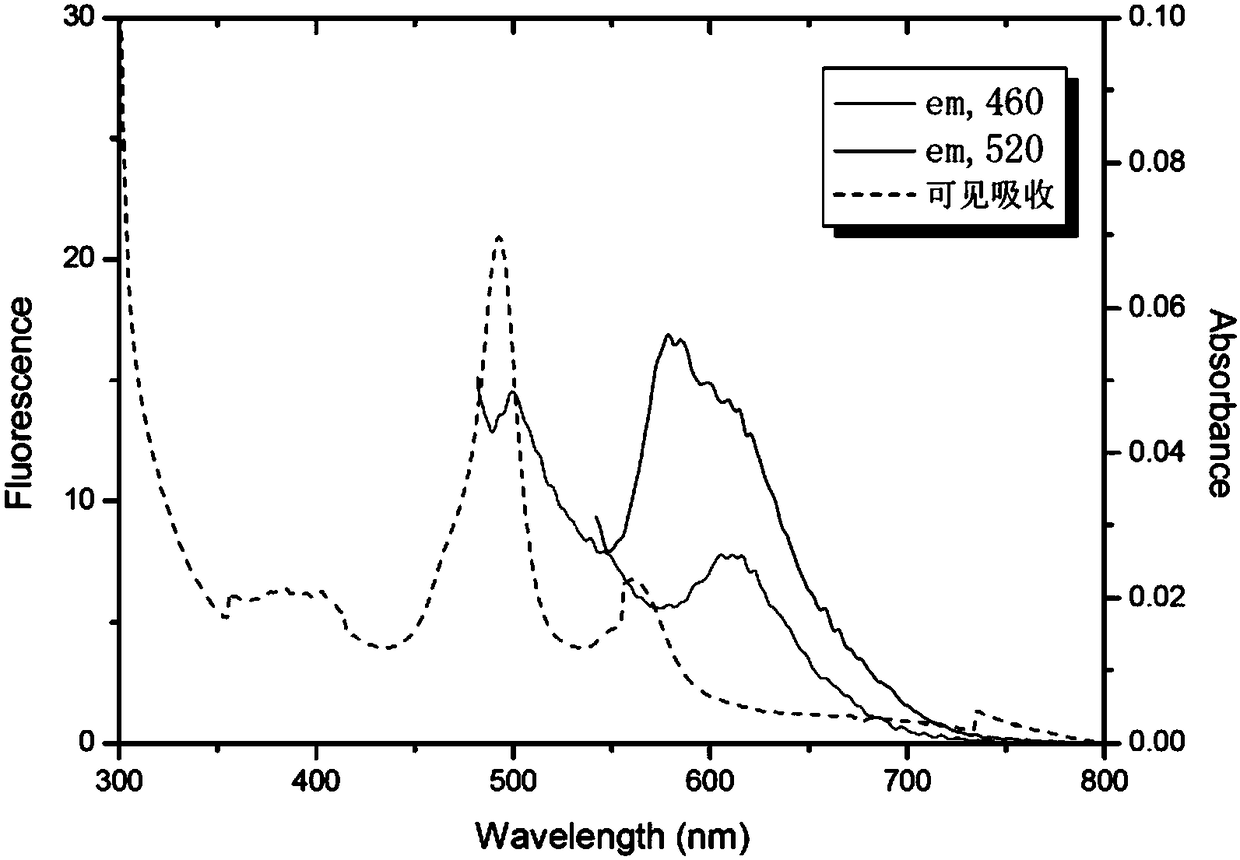
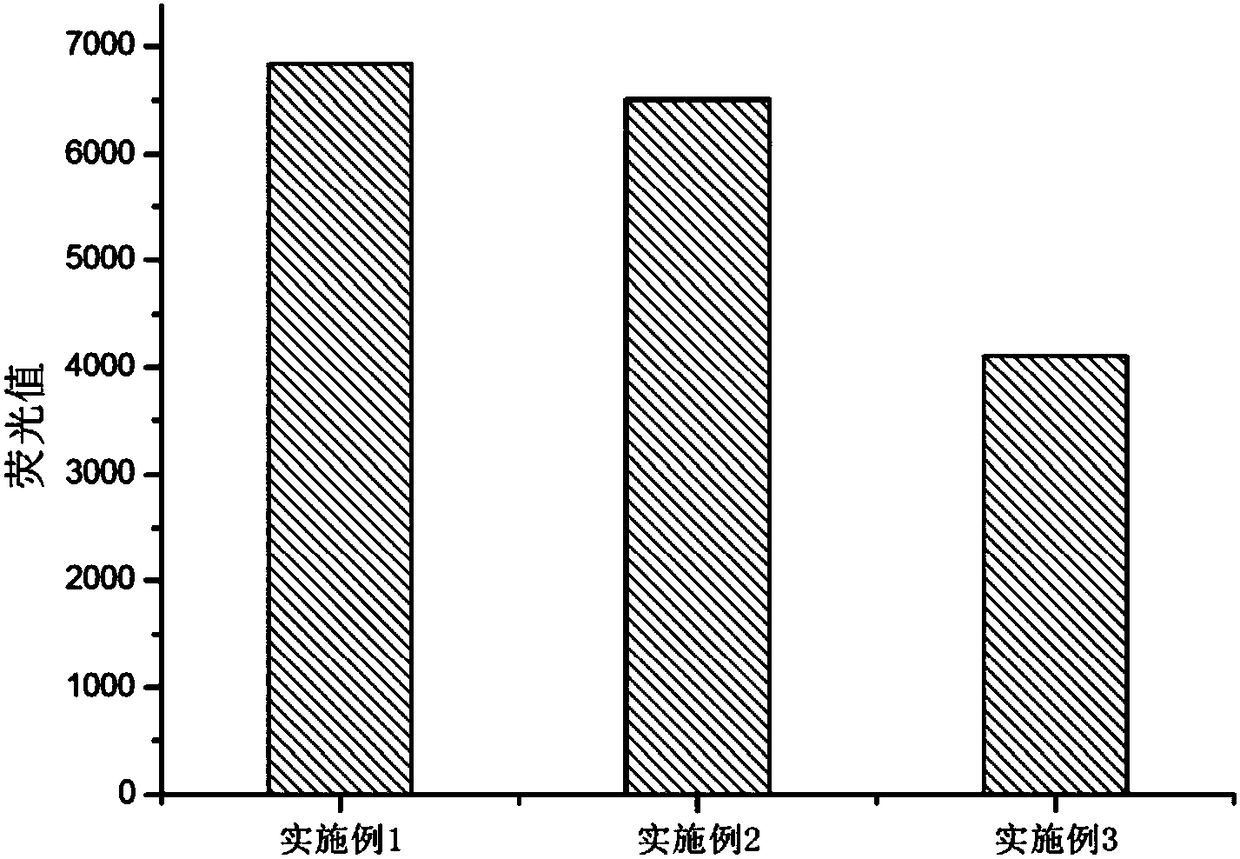
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
68 results about "Phytochrome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Phytochromes are a class of photoreceptor in plants, bacteria and fungi use to detect light. They are sensitive to light in the red and far-red region of the visible spectrum and can be classed as either Type I, which are activated by far-red light, or Type II that are activated by red light. Recent advances have suggested that phytochromes also act as temperature sensors, as warmer temperatures enhance their de-activation. All of these factors contribute to the plants ability to germinate.
Natural hair dye prepared by using phytochrome curcumin and hair dyeing method of natural hair dye
InactiveCN102423286AImprove dyeing effectEasy to floatCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsPolyolHair dyes
The invention relates to a hair dye, in particular to a natural hair dye prepared by using phytochrome curcumin and a hair dyeing method of the natural hair dye. The hair dye comprises an agent A and an agent B, and is characterized in that: the agent A contains 0.1 to 10 weight percent of curcumin, 20 to 50 weight percent of polyol, 1 to 5 weight percent of thickening agent, 1 to 10 weight percent of surfactant and the balance of water, and the pH value is regulated to be 3 to 7; and the agent B contains 1 to 10 weight percent of metal ion mordant, 1 to 5 weight percent of thickening agent, 1 to 10 weight percent of surfactant, 0.1 to 0.3 weight percent of natural essence and the balance of water, and the pH value is regulated to be 3 to 7. The hair dyeing method comprises the following steps of: uniformly spreading the agent A on the hair when the hair is dyed, and dyeing the hair for 10 to 40min at the temperature of between normal temperature and 60 DEG C; and uniformly spreading the agent B on the hair, mordanting for 10 to 20min, cleaning the hair and blow-drying. The curcumin has a good dyeing effect and also has the effects of resisting bacteria and protecting skin. Reagents which are toxic to human bodies are not used in the hair dye, and substances which are toxic to the human bodies are also not generated in the hair dyeing process, so the hair dye is high in safety. The adopted curcumin is insoluble in water and cannot fall off easily in the washing process, so the hair dye has a good dyeing effect, and the color of the dyed hair can be kept for a long time.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Universal light-switchable gene promoter system
InactiveUS6858429B2Low background activityImprove induction abilityFungiBacteriaProtein kinase domainLight activation
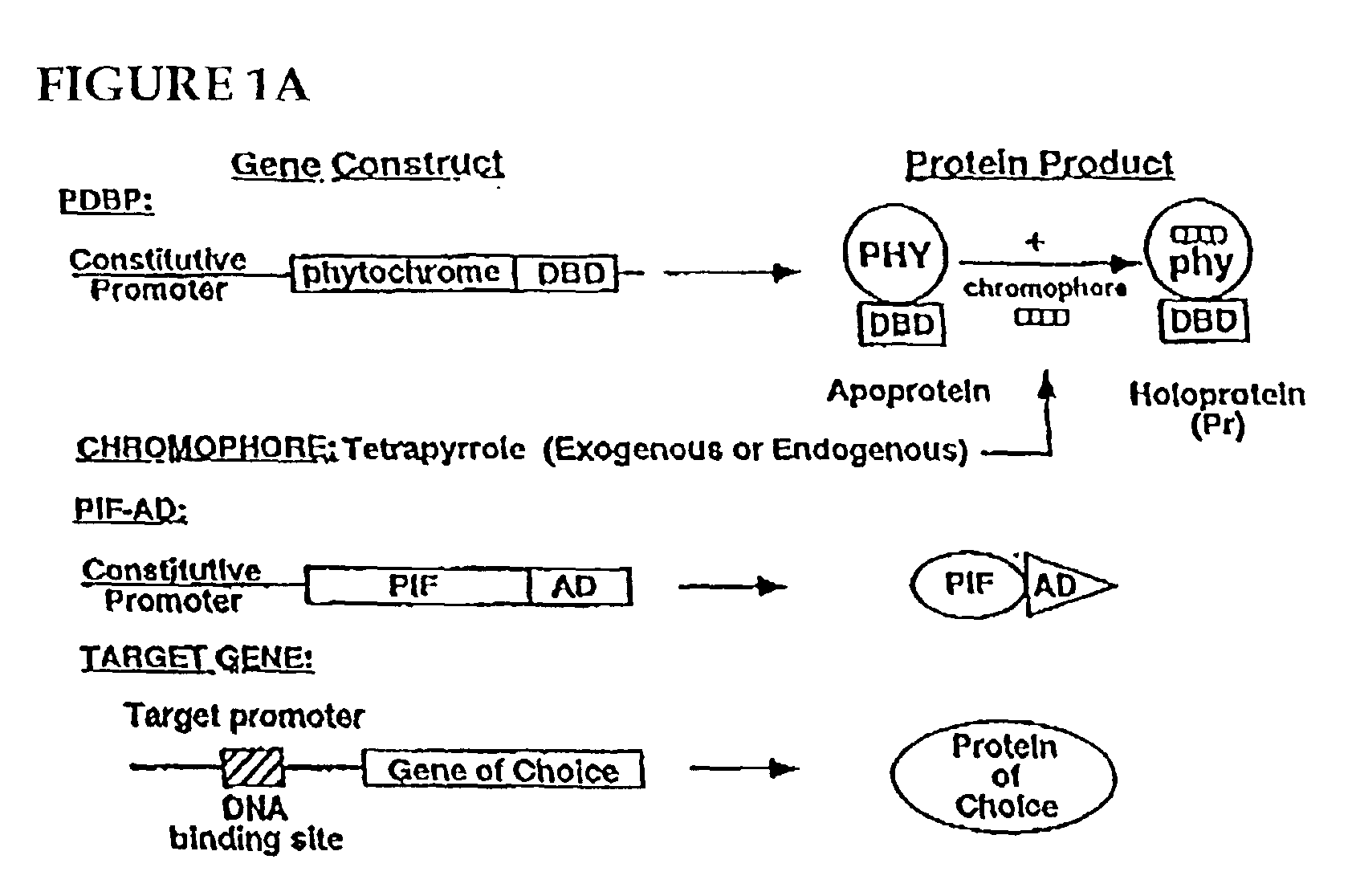
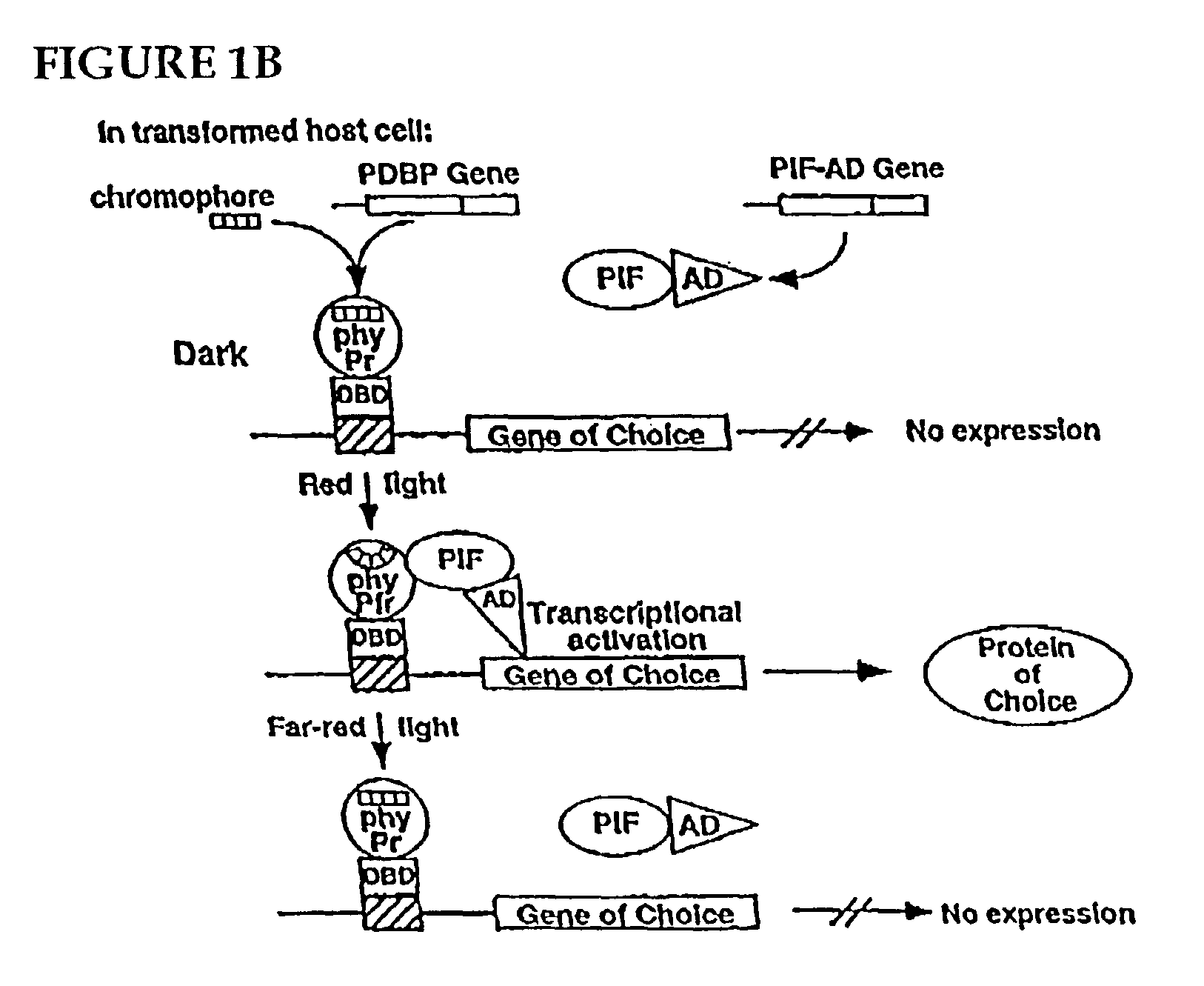
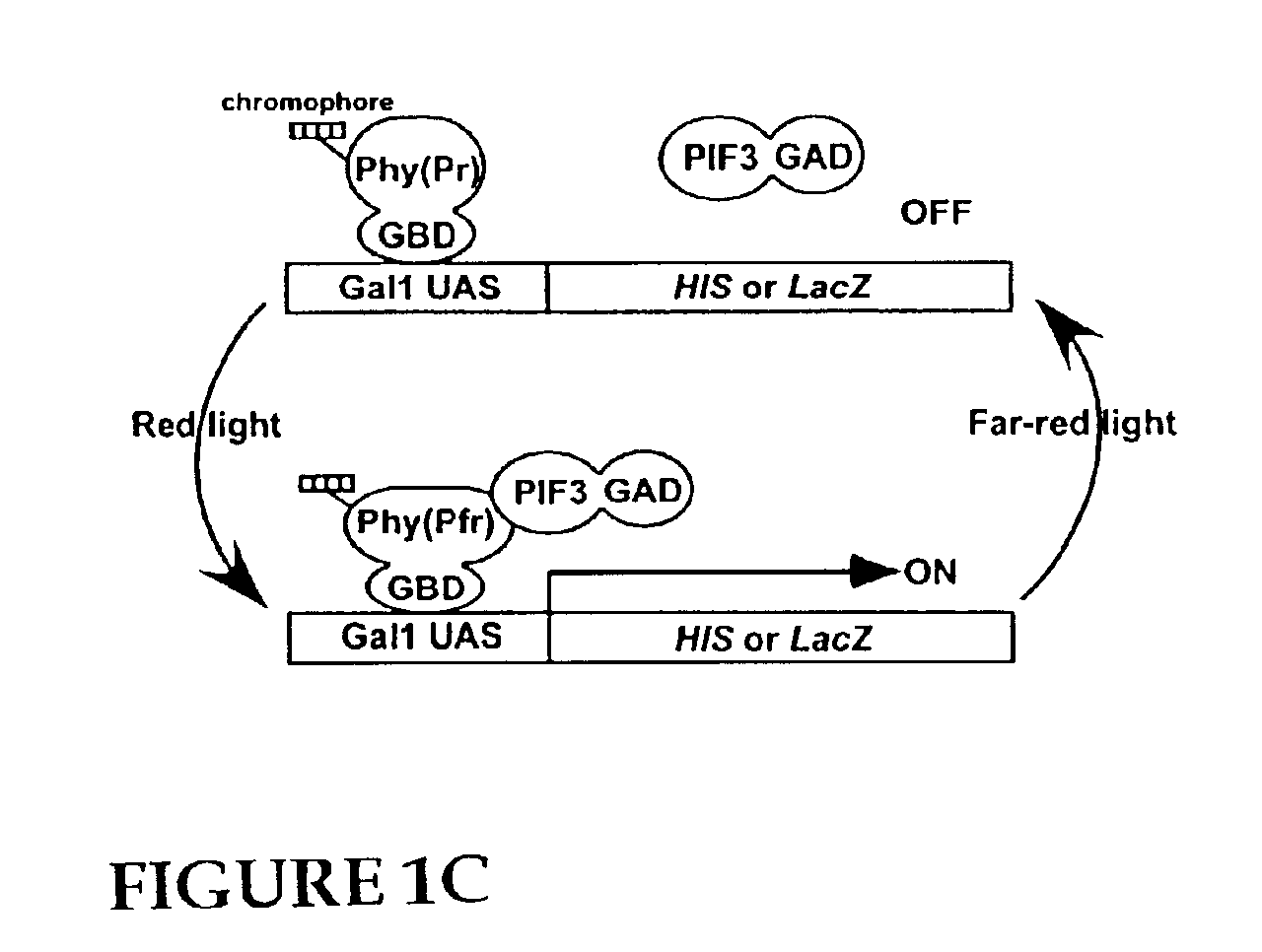
An artificial promoter system that can be fused upstream of any desired gene enabling reversible induction or repression of the expression of the gene at will in any suitable host cell or organisms by light is described. The design of the system is such that a molecule of the plant photoreceptor phytochrome is targeted to the specific DNA binding site in the promoter by a protein domain that is fused to the phytochrome and that specifically recognizes this binding site. This bound phytochrome, upon activation by light, recruits a second fusion protein consisting of a protein that binds to phytochrome only upon light activation and a transcriptional activation domain that activates expression of the gene downstream of the promoter.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
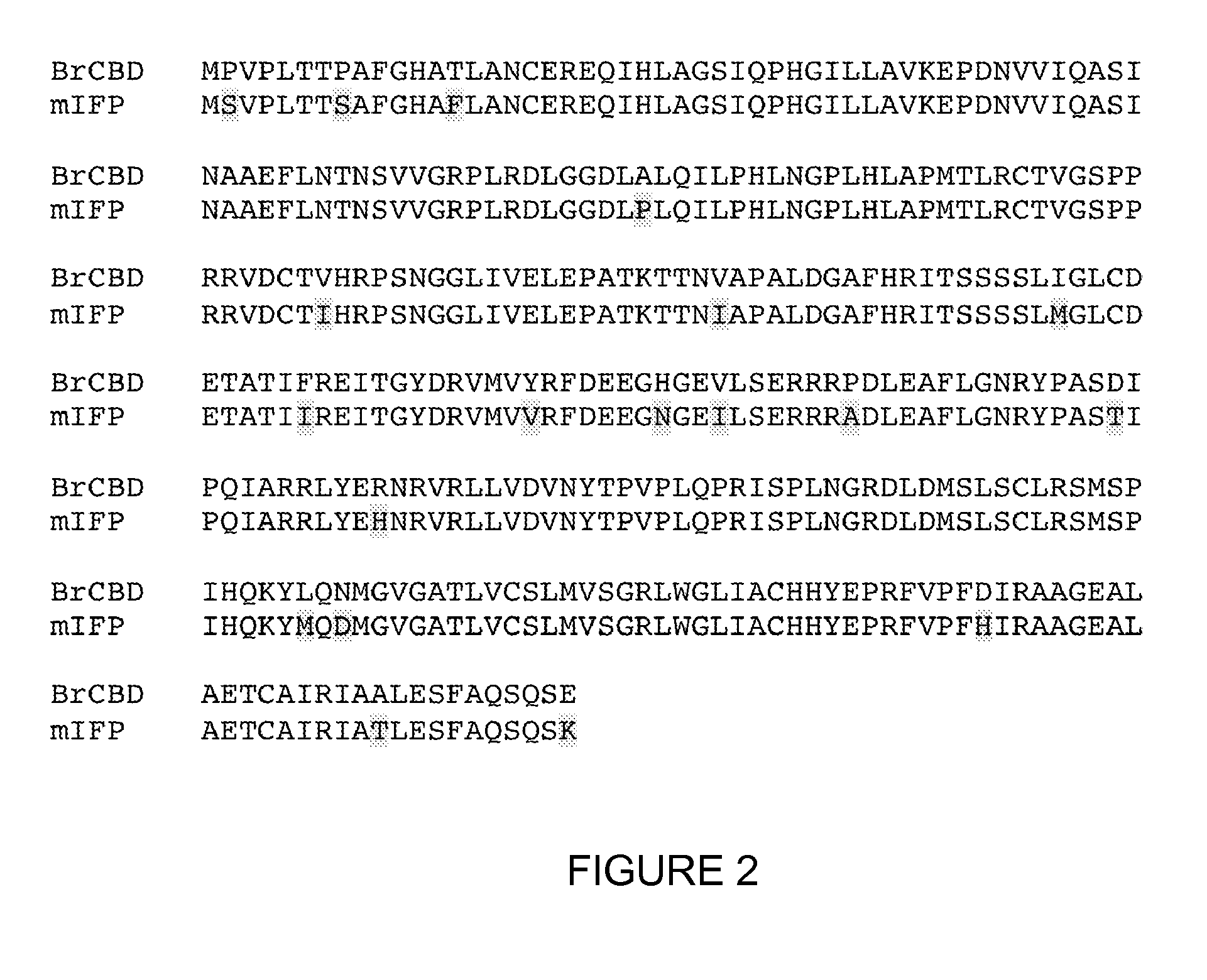
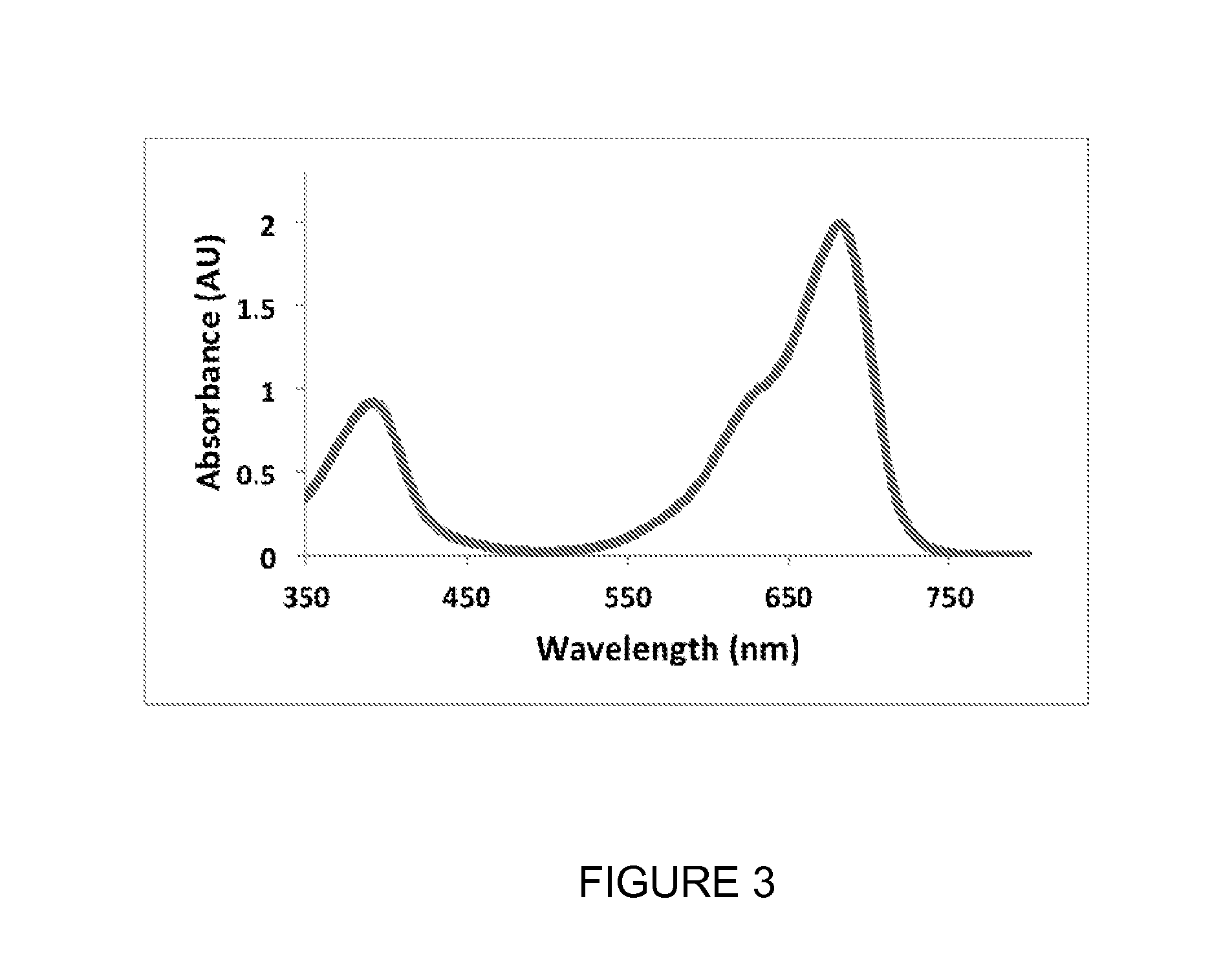
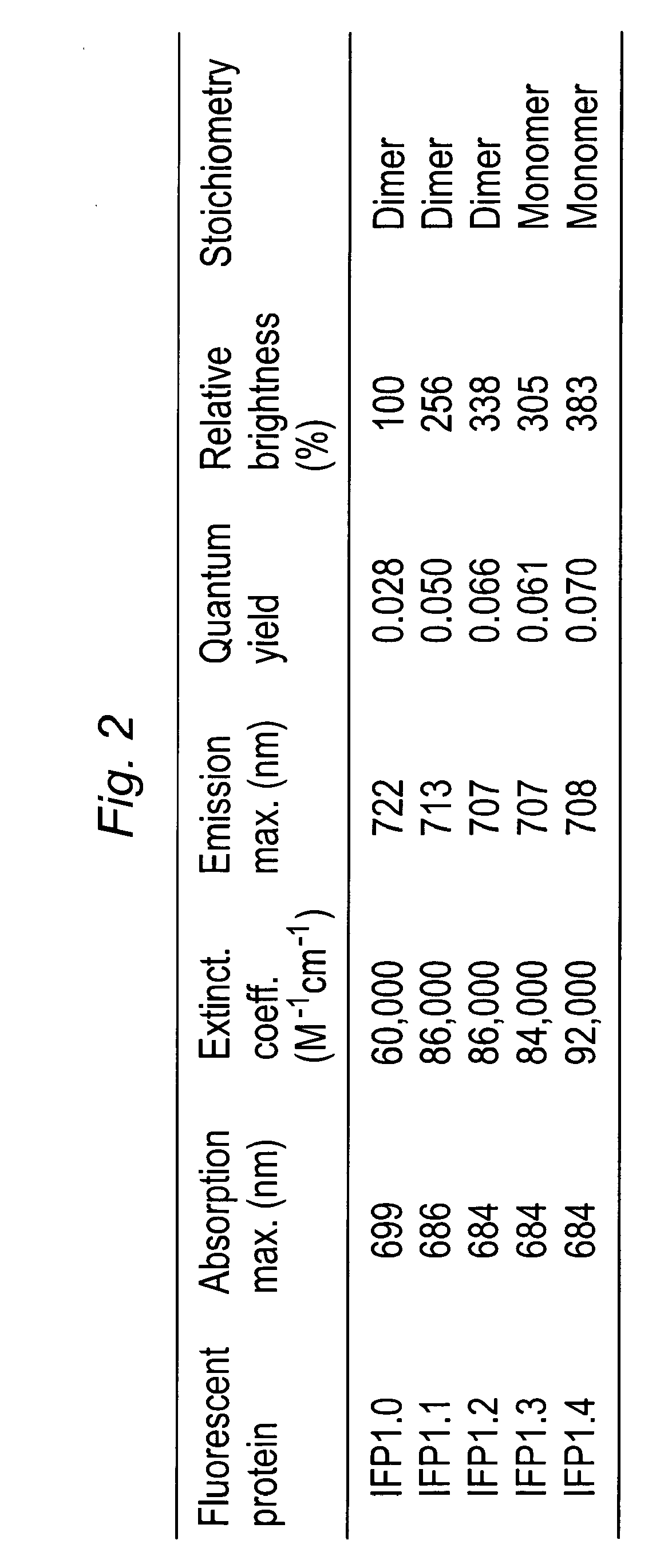
Phytochrome-based fluorophores
Genetically-engineered fluorophore molecules with increased fluorescence are provided. These fluorophores are derived from the domains of phytochromes, and in particular bacterial phytochromes. Methods for generating these fluorophores and various applications of these fluorophores are also provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Long day plants transformed with phytochrome characterized by altered flowering response to day length
InactiveUS20050120412A1Alter responsivenessImprove featuresOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationShootPhytochrome
A long day plant cultivated for commercial production of flowering-shoots, flowering pots, flowers, seeds or fruits is provided. The long day plant overexpresses a phytochrome protein such that the flowering-shoots, flowering pots, flowers, seeds or fruits thereof develop under substantially shorter natural days and lower sun irradiance than those required for development of the flowering-shoots, flowering pots, flowers, seeds or fruits in a similar long day plant not over expressing the phytochrome protein.
Owner:AGRI RES ORG
Rice flowering related protein and coding gene LHD3 thereof and application thereof
The present invention discloses a rice flowering related protein and a coding gene LHD3 thereof and an application thereof in rice breeding. The provided rice flowering related protein has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The present invention also provides the gene LHD3 encoding the above-mentioned protein and a nucleotide sequence of the gene LHD3 is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The gene LHD3 is applied in improving rice heading stage and rice photomorphogenesis. The rice flowering gene LHD3 is isolated, cloned and identified, and besides, gene functions are verified according to a complementation experiment. Results of map-based cloning indicate that the gene encodes rice phytochrome C. The rice flowering related protein and the coding gene LHD3 thereof provide germplasm resourcesand theoretical support for breeding new rice varieties with early heading and good photomorphogenesis, and have broad application prospects.
Owner:JIANGXI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
Fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementary system, and applications
ActiveCN105624178AEnhanced inhibitory effectEase of evaluationFluorescence/phosphorescenceVector-based foreign material introductionProtein pairPhytochrome
The invention discloses a fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementary system, and applications. According to the fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementary system, phytochrome fluorescent protein iRFP is taken as a template, and is divided into a non-fluorescent nitrogen terminal fragment iRN97 and a non-fluorescent carbon terminal fragment iRC98 at the amino acid 97-98 sites; when fusion expression of the two fragments with protein pairs with interactions is realized, the two non-fluorescent fragments are drawn to be close to generate iRFP fluorescence; fusion expression of iRN97 with human immunodeficiency virus integrase IN, and fusion expression of iRC98 with cell protein P75 are realized respectively, the interaction between IN and p75 is studied in living cells via fluorescent complementation of iRN97 with iRC98; when a drug is capable of inhibiting the protein-protein interaction, it is impossible for iRN97 and iRC98 to be drawn to be close, so that fluorescence recovery is inhibited. The fluorescent protein iRFP-based dimolecular fluorescent fragment complementation system is a simple, effective, and convenient evaluation system of drugs used for inhibiting protein interactions.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Proteins that fluoresce at infrared wavelengths or generate singlet oxygen upon illumination
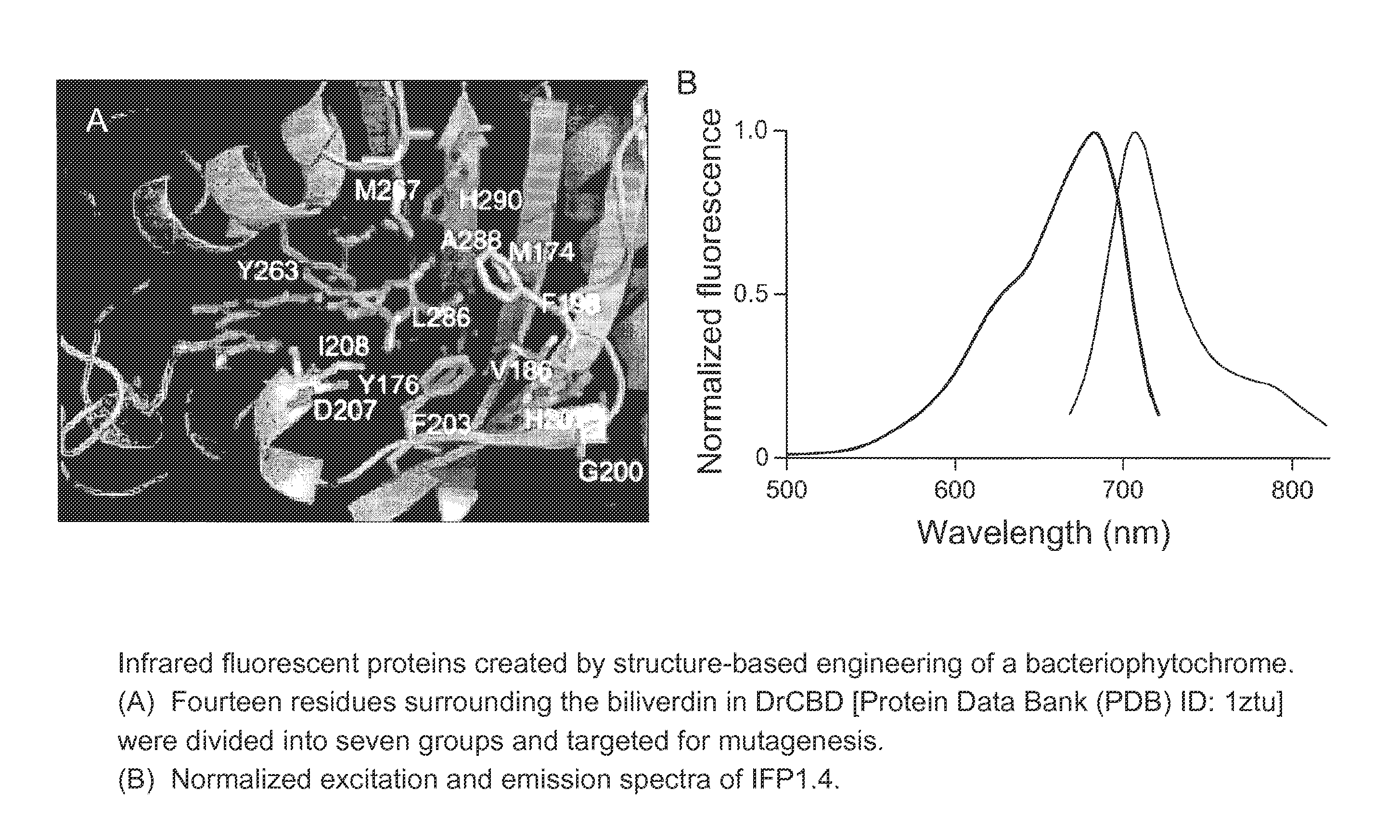
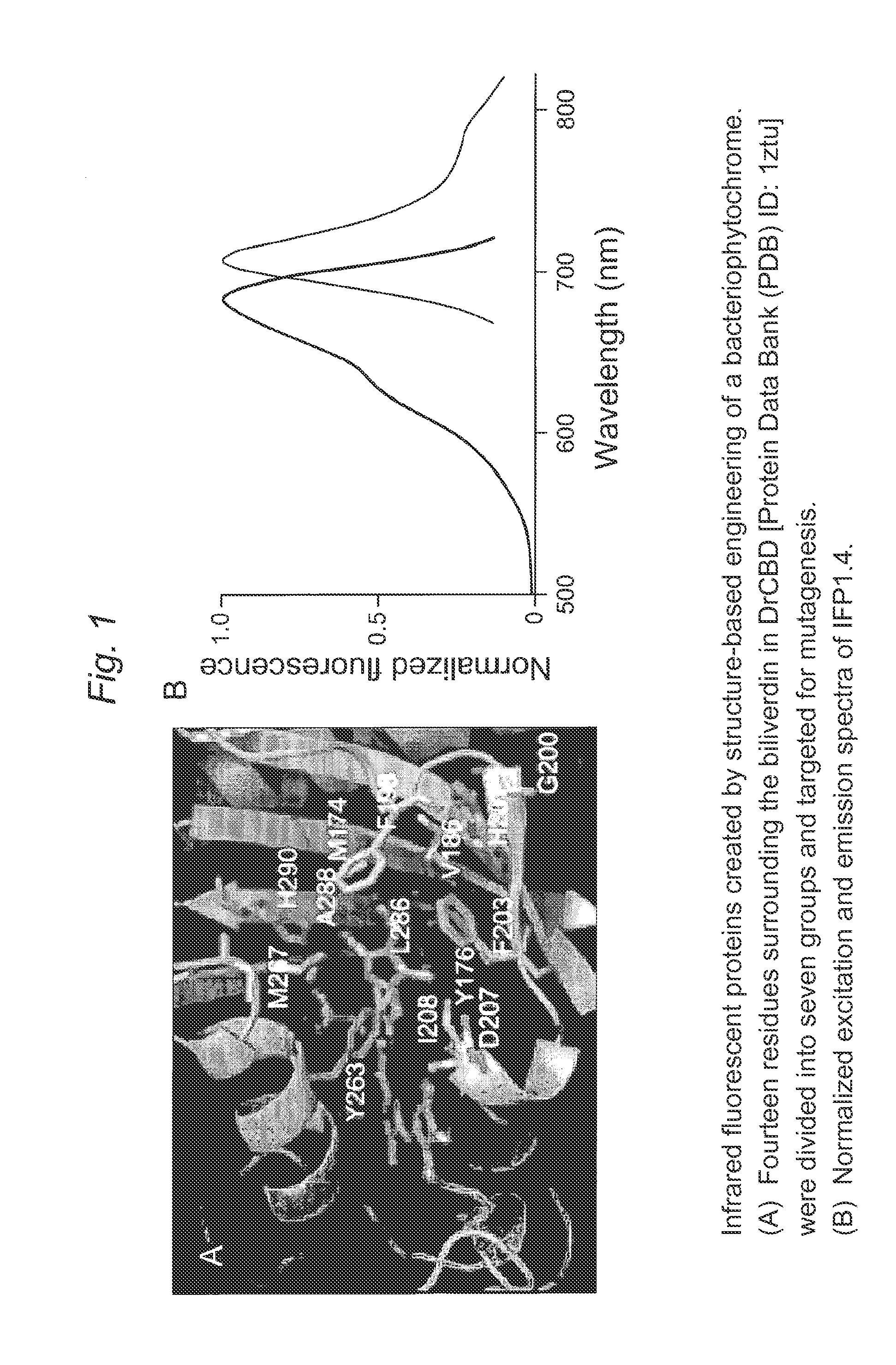
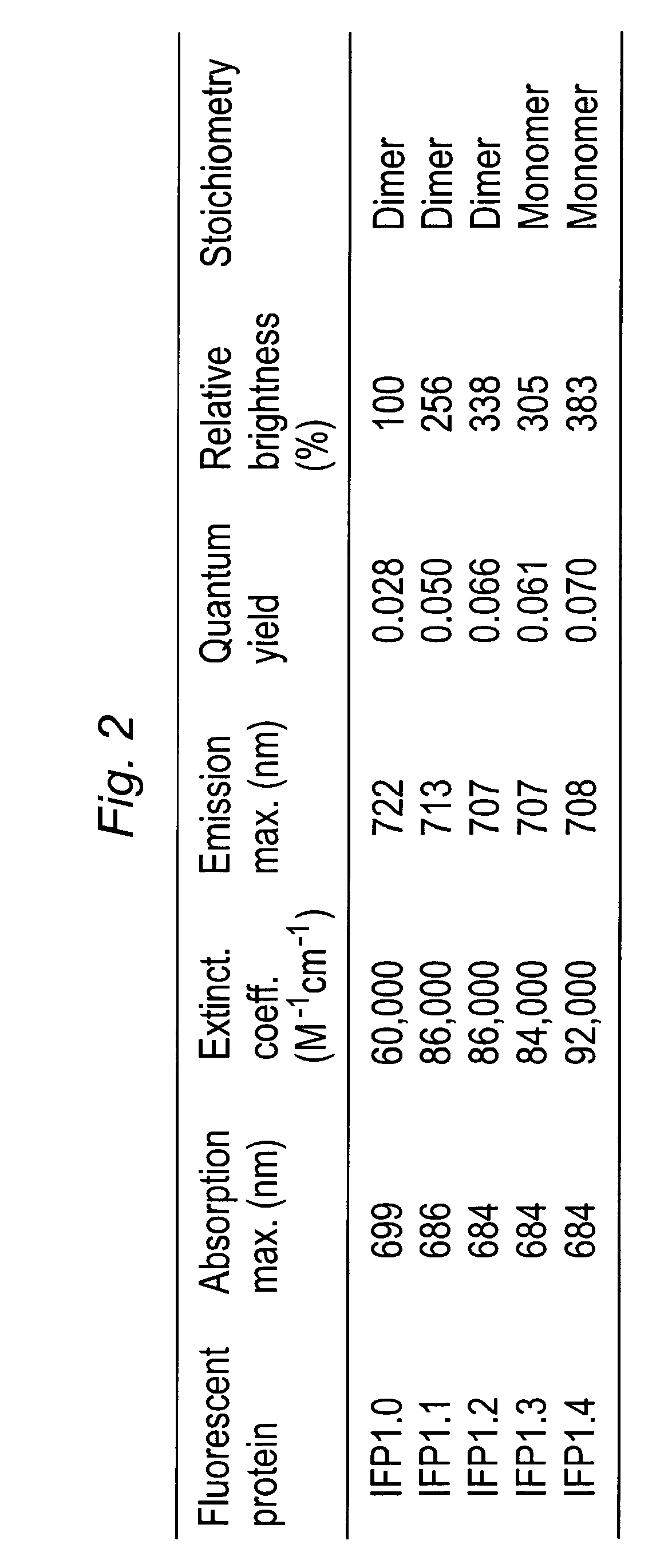
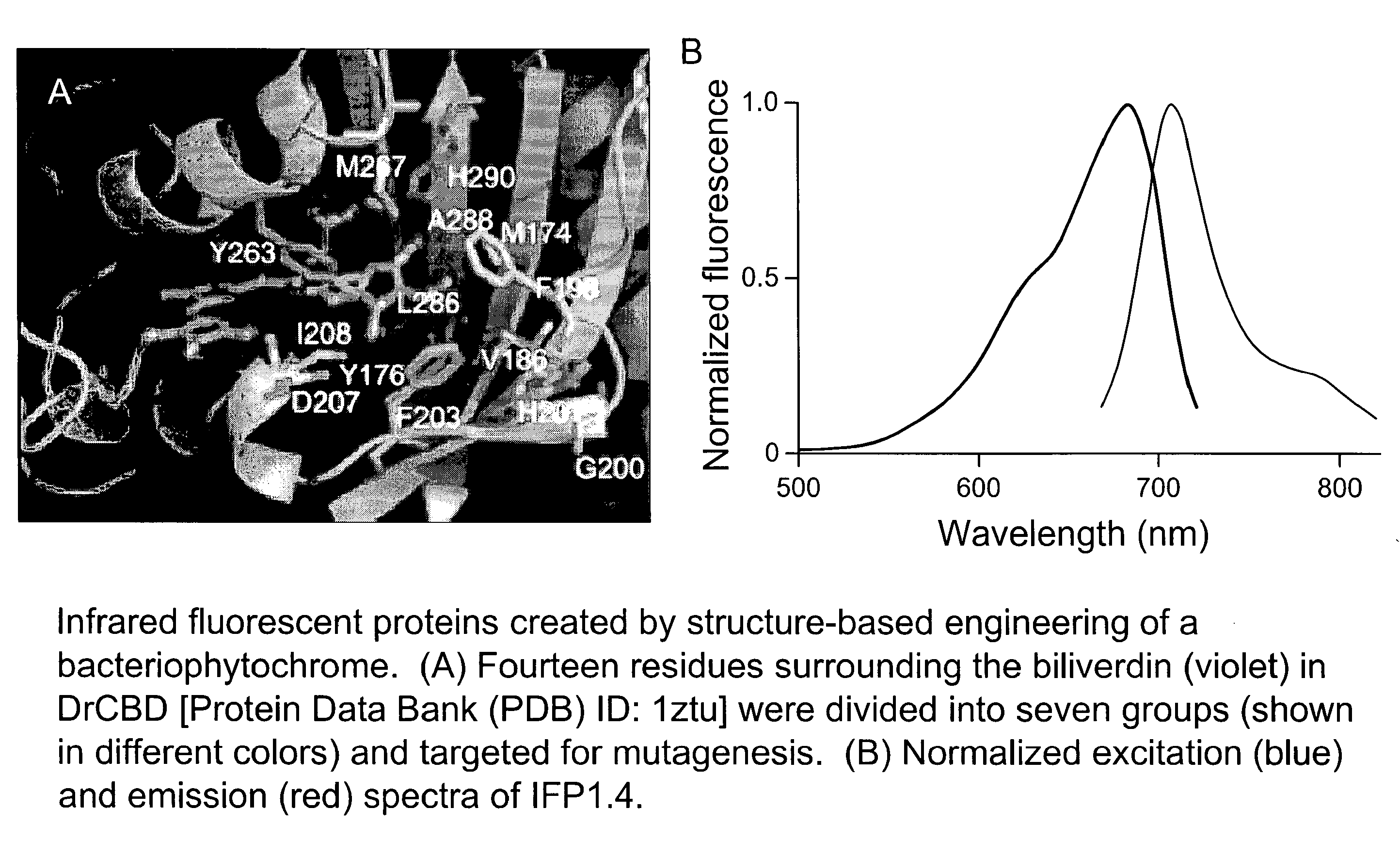
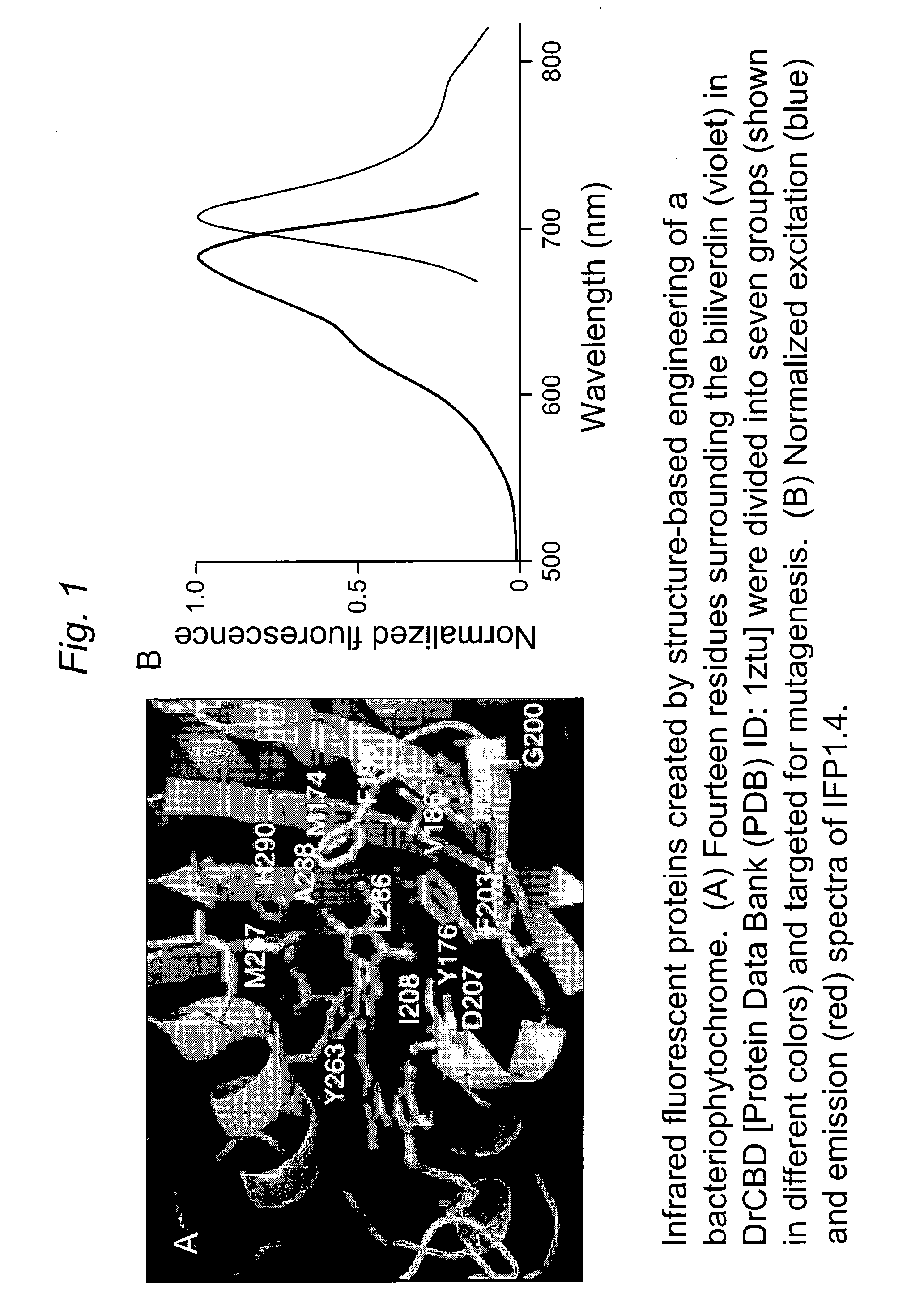
This invention provides novel truncation mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. When expressed either in bacteria or mammalian cells, these mutant phytochromes spontaneously incorporate biliverdin, a ubiquitous intermediate in heme catabolism, and become fluorescent in the infrared (IR) region. These phytochromes are the first genetically encoded labels that can be excited by far-red light and fluorescent in the true IR (>700 nm). If these mutants instead incorporate protoporphyrin IX, an intermediate in heme biosynthesis, illumination now generates significant amounts of singlet oxygen. Singlet oxygen is useful because it can be used to kill individual proteins or cells, detect long-range protein-protein interactions, or generate electron-microscopic contrast. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such proteins and protein variants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Nucleic acid molecules encoding hyperactive nucleoside di-phosphate kinase 2 and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070136897A1Efficient developmentImprove lighting efficiencySugar derivativesClimate change adaptationPhosphatePhytochrome
The present invention includes modified Arabidopsis Nucleoside Di-Phosphate Kinase 2 (NDPK2) nucleic acid molecules whose enzymatic activity have been increased (i.e. hyperactive). NDPKs are ubiquitous housekeeping enzymes that catalyze the transfer of γ-phosphoryl group from a nucleoside triphosphate (NTP) to a nucleoside diphosphate (NDP), and also multifunctional proteins that regulate a variety of eukaryotic cellular activities, including cell proliferation, development, and differentiation. In plants, NDPKs are reported to play a key role in the signaling of both stress and light. Among three NDPKs (NDPK1, NDPK2, NDPK3) in a model plant, Arabidopsis thaliana, NDPK2 was reported as a positive signal transducer of phytochrome-mediated plant light signaling and to regulate cellular redox state, which enhances multiple stress tolerance in transgenic plants. Thus, the plants with the hyperactive NDPK2 are expected to possess higher efficiency of light utilization and enhanced tolerance to various environmental stresses such as cold, salt, and oxidative stresses. Since abiotic stress is one of the most important factors to limit the productivity of many crops, the hyperactive NDPK2 can be used for the development of high-yielding multiple stress tolerant plants with higher efficiency of light utilization. In this invention, several hyperactive NDPK2 were generated by C-terminal deletion and site-directed mutagenesis. Therefore, the present invention can be utilized to develop multiple stress tolerant and efficiently light-utilizing plants, which can eventually increase crop yields. The invention also includes plants having at least one cell expressing the modified NDPK2, vectors comprising at least one portion of the modified NDPK2 nucleic acids, and methods using such vectors for producing plants with enhanced light sensitivity and stress tolerance.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Nucleic acid molecules encoding hyperactive mutant phytochromes and uses thereof
The present invention includes modified phytochrome A (PHYA) nucleic acid molecules in which DNA sequences coding for “active site” amino acid residues have been mutated to generate hyperactive phytochromes. In particular; a serine / threonine residue at the hinge between the N- and C-terminal domains as well as at the N-terminal serine / threonine cluster of phytochromes (e.g., serine-598 and serine-7 in oat phytochrome A) for (a) Pr / Pfr-dependent phosphorylation and (b) dephosphorylation by a phytochrome phosphatase (PP2A) was substituted with alanine. (c) In addition, amino acid residues within the phytochrome chromophore pocket are mutated to generate the bathchromic shift of the Pr-absorption band of both wild type and above-mentioned mutant phytochromes. The plants with the bathchromically shifted absorption spectrum are expected to respond to the canopy and shade conditions for growth and greening responses to far-red light with greater efficiency than are the wild type plants with normal absorption band maxima. These mutative modifications confer hyperactivity to the far-red light responsive phytochromes A. Thus, the biological activity of the modified oat PHYA was shown to be hyperactive compared to wild type PHYA, characterized by its ability to reduce internode elongation of adult plants. Overexpression of the phytochrome phosphatase exhibits a suppressed growth with shorter internodes and belated flowering, qualitatively consistent with the phenotype of a ser598ala mutant oat phytochrome. The invention also includes plants having at least one cell expressing the modified PHYA, vectors comprising at least one portion of the modified PHYA nucleic acids, and methods using such vectors for producing plants with reduced stature.
Owner:KOREA KUMHO PETROCHEMICAL CO LTD
Fusion protein containing ApcE2 mutant and application of fusion protein containing ApcE2 mutant
ActiveCN109553689ARaising the issue of weaker fluorescent markersImprove weak fluorescence problemsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesFluorescencePhytochrome
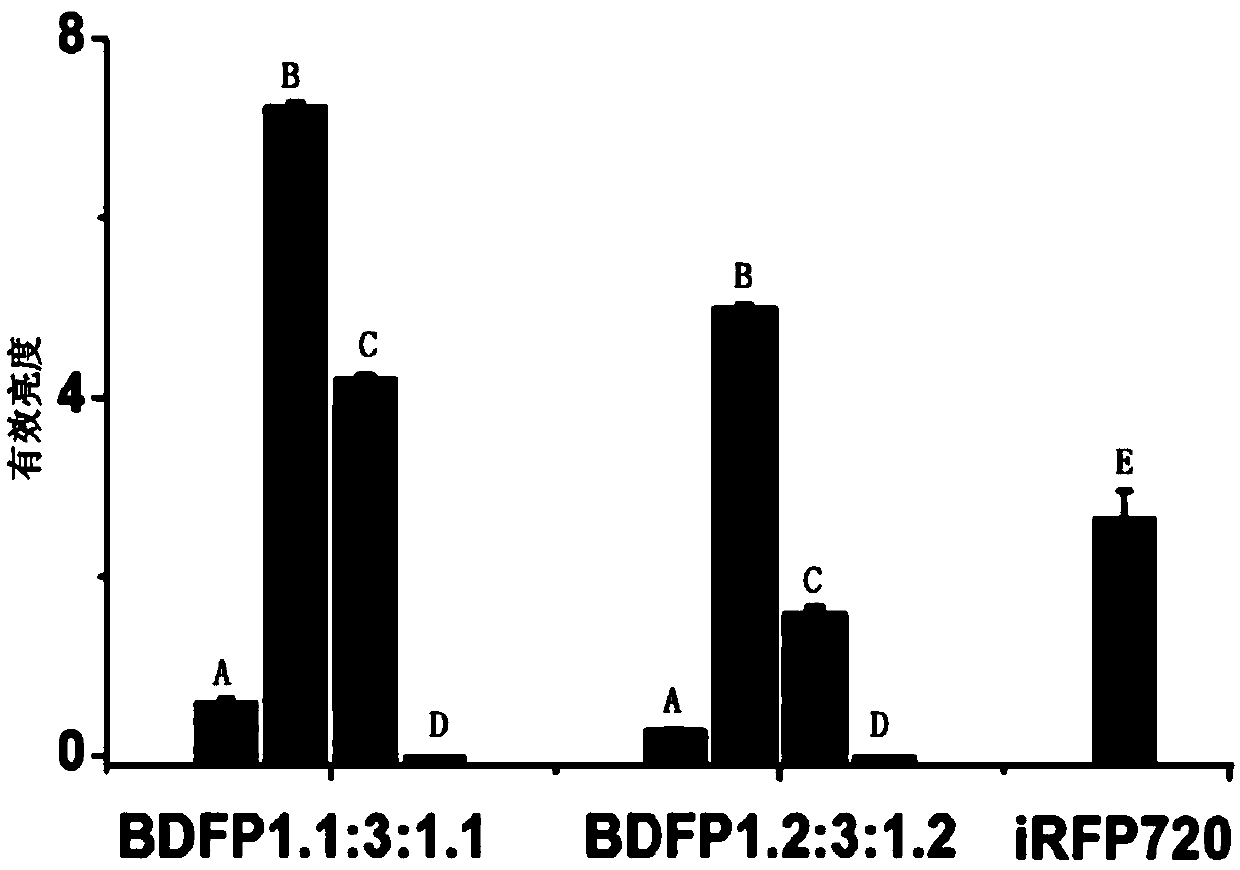
The invention discloses fusion protein. The fusion protein is characterized in that the amino acid sequence of the fusion protein is F1 polypeptide, connected protective peptide 1, F2 polypeptide, connected protective peptide 2 and F1 polypeptide, wherein the sequence of the F1 polypeptide is any of SEQID No.1 and SEQID No.2; and the sequence of the F2 polypeptide is any of SEQID No.3 to SEQ ID No.14. An ApcE2 mutant and allophycocyanin subunits BDFP1.1 or BDFP1.2 which are subjected to genetic engineering are merged to obtain the fusion protein, and the problem that the ApcE2 mutant marked fluorescence in lactation animal cells is weak, is solved. In the fluorescence marking process, phytochrome P phi B is added in vitro, so that the brightness of the fusion protein for cell labelling canbe effectively improved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV +1
Monomeric and bright infrared fluorescent proteins
The invention described herein features variants related to infrared fluorescent proteins, in particular to mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Bradyrhizobium sp. ORS278. The variants show approximately a ten-fold increase in brightness compared to other known infrared fluorescent proteins. The variants are monomeric, allowing them to be used as a protein tag without disrupting the function of the tagged protein of interest.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
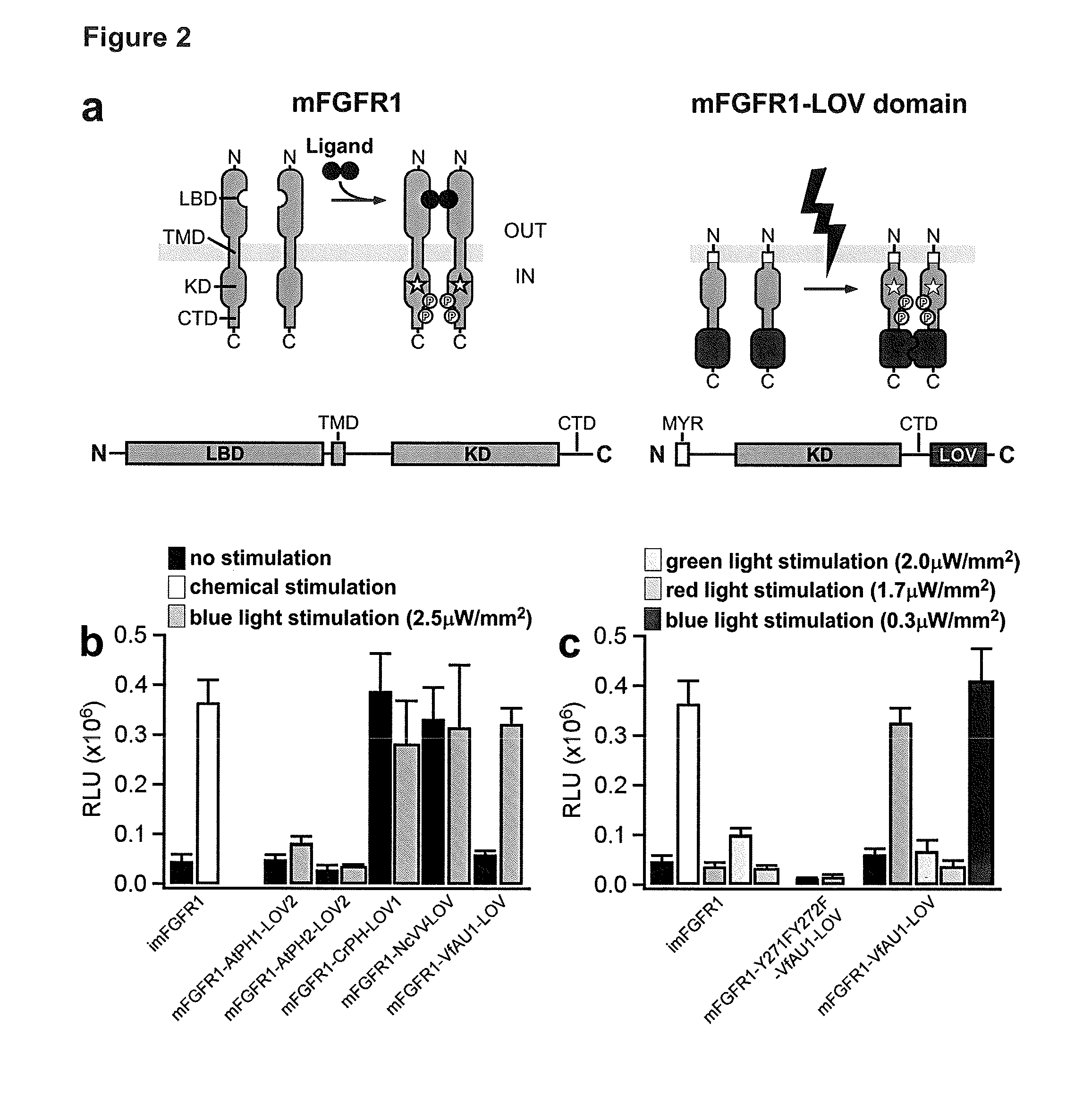
Optically activated receptors
InactiveUS20160326219A1Sure easyCompound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein kinase domainScreening method
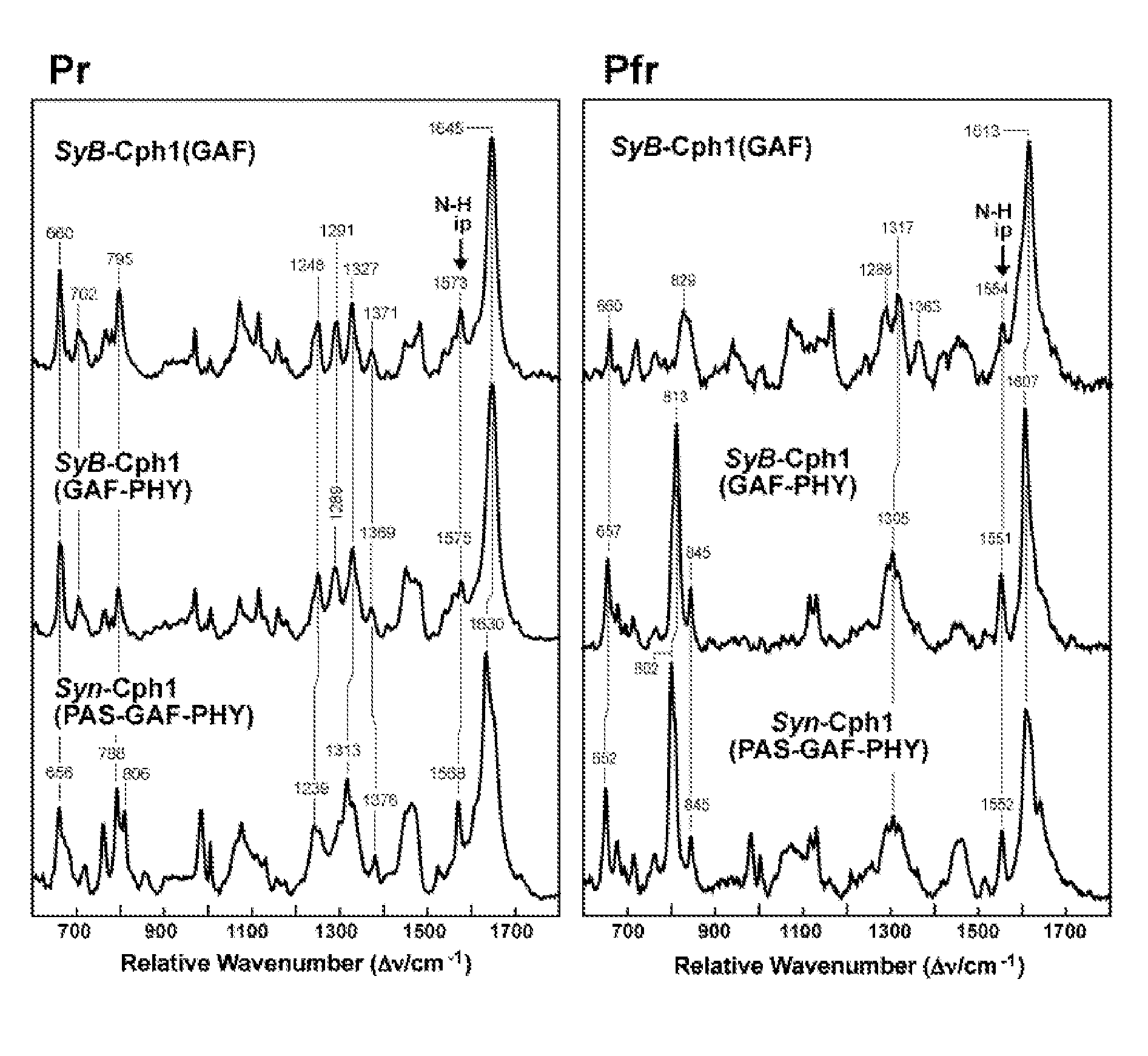
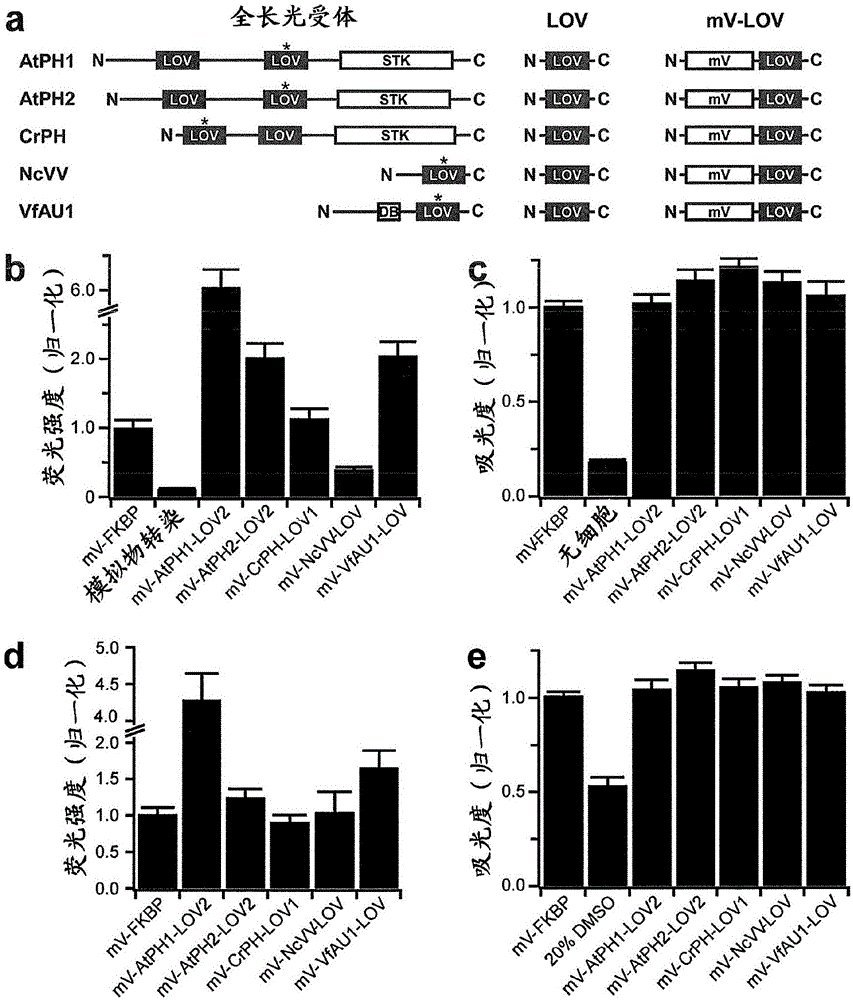
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology. More specifically, the invention relates to chimeric fusion proteins comprising a light activated protein domain, e.g., a newly characterized light-oxygen-voltage-sensing (LOV) domain or a light sensing domain of the cyanobacterial phytochrome (PHY) CPH1, wherein the chimeric fusion protein is capable of dimerizing upon excitation with light of a suitable wavelength. Said fusion proteins further comprise the intracellular part of a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). The invention further relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding said chimeric fusion proteins; non-human transgenic animals expressing the chimeric fusion protein encoded by said nucleic acid molecules; as well as uses of said chimeric fusion proteins, e.g. in a screening method.
Owner:INST OF SCI & TECH AUSTRIA +1
Optically activated receptors
The present invention belongs to the field of biotechnology. More specifically, the invention relates to chimeric fusion proteins comprising a light activated protein domain, e.g., a newly characterized light-oxygen-voltage-sensing (LOV) domain or a light sensing domain of the cyanobacterial phytochrome (PHY) CPH1, wherein the chimeric fusion protein is capable of dimerizing upon excitation with light of a suitable wavelength. Said fusion proteins further comprise the intracellular part of a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK). The invention further relates to nucleic acid molecules encoding said chimeric fusion proteins; non-human transgenic animals expressing the chimeric fusion protein encoded by said nucleic acid molecules; as well as uses of said chimeric fusion proteins, e.g. in a screening method.
Owner:奥地利科技学院 +1
Far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic, preparation method thereof and lamp for plants
ActiveCN108314332AEasy to meet lighting application requirementsImprove thermal stabilitySaving energy measuresGlass shaping apparatusMass ratioLight energy
The invention belongs to the field of inorganic luminescent materials, and particularly relates to a far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic, a preparation method thereof and a lamp for plants. The far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic is prepared from red fluorescent powder and silicate glass powder, and the mass ratio of the red fluorescent powder to the silicate glass powder is (5 to30) to (70 to 95); the structural formula of the red fluorescent powder is ZnGa[2-x]O[4]:xCr<3+>, wherein x is greater than 0.002 and less than 0.0016. The preparation method is as follows: the red fluorescent powder and the glass powder are weighed according to a mass ratio and uniformly mixed in an agate mortar, the mixture is then pressed into a sheet in a die, afterwards, the sheet is heated to react, and is cooled after reaction is completed, and after cutting, grinding and polishing, the far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic is obtained. The far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic disclosed by the invention has higher heat conductivity and appropriate excitation wavelength, the red light wavelength emitted by the far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic is between 650nmand 780nm, the far-infrared type fluorescent glass ceramic and blue light LED (light-emitting diode) chips can be assembled to form the lamp for plants, luminous energy absorbed by far-infrared type phytochrome which is more than luminous energy provided by conventional lamps for plants is provided, and the plant illumination effect is better and closer to the demand of plant growth.
Owner:成都本农农业咨询合伙企业(有限合伙)
Monomeric near-infrared fluorescent proteins engineered from bacterial phytochromes and methods for making same
ActiveUS20180044383A1Reduction tendencyReduce and eliminate abilityAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesPhytochromeMutant
Nucleic acid molecules encoding monomeric near-infrared fluorescent proteins, variants and derivatives thereof are provided, as well as proteins and peptides encoded by these nucleic acids. Also provided are proteins that are substantially similar to, or derivatives, homologues, or mutants of, the above-referenced specific proteins. Also provided are fragments of the nucleic acids and the peptides encoded thereby, specifically split fluorescent proteins. In addition, host-cells, stable cell lines and transgenic organisms comprising above-referenced nucleic acid molecules are provided. The invention also refers to methods of making and using monomeric fluorescent proteins derived from bacterial phytochromes. The subject protein and nucleic acid compositions find use in a variety of different applications and methods, particularly for labeling of biomolecules, cells or cell organelles, and for detecting protein-protein interactions. Finally, kits for use in such methods and applications are provided.
Owner:ALBERT EINSTEIN COLLEGE OF MEDICINE OF YESHIVA UNIV
Light-emitting material for plant light-controlled development, preparation method of light-emitting material, and light-emitting device
ActiveCN108929680ASatisfy the requirement of physiologically active Pfr stateSimple processLuminescent compositionsSemiconductor devices for light sourcesFar-redFluorescence
The invention discloses a light-emitting material for plant light-controlled development, a preparation method of the light-emitting material, and a light-emitting device, and relates to the fields ofsolid-state semiconductor illumination and photosynthetic agriculture. The invention is provided on the basis of the problems that the cost of a plant growth lamp containing 730-nm far-red light is high, and a light-emitting material capable of converting blue light into a light which meets the requirement of a plant in a physiological activity Pfr state does not exist. The chemical general formula of the light-emitting material is A<3>BF<6>:Cr, wherein A is one or more selected from monovalent metal ions comprising Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs, and B is one or more selected from trivalent metal ionscomprising Al, Ga, Sc, Y and La. According to the invention, the beneficial effects are as follows: the emission wavelength of the far-red light-emitting material for plant light-controlled development provided by the invention is matched with the absorption wavelength of the plant phytochrome of a physiological activity Pfr state, the production cost of using a far-red light fluorescent materialpackaged LED device is lower than the production cost of using a far-red light LED chip, the service life of the existing LED blue-light chip growing process and equipment can be prolonged, the preparation method is simple, and the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:INTELLIGENT MFG INST OF HFUT +1
Molecular markers for identifying PHYB wild type and mutant of rice phytochrome gene
ActiveCN106282345AValid identificationRapid identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
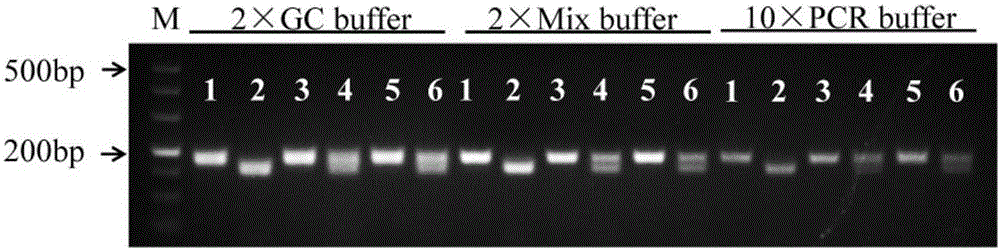
The invention discloses molecular markers for identifying the PHYB wild type and mutant of a rice phytochrome gene. The nucleotide sequences of the markers related to phyB wild type site detection and phyB mutant site detection are shown as Seq No.1-2 respectively. A primer PHYBF4 / PHYBR1 is used for carrying out PCR amplification, and an amplification product is subjected to BamH I digestion and electrophoretic analysis, wherein if the PCR product can not be digested by BamH I and is a 175bp DNA fragment, the PCR product is the wild type phyB, and if the PCR product can be digested by BamH I, and the digestion products are a 25bp DNA fragment and a 151bp DNA fragment, the PCR product is the mutant phyB1. The molecular markers have the advantages that amplification is easy and fast, and cost is low. The molecular markers can be used for effectively, rapidly and reliably identifying the phyB allelotype, and a powerful tool is provided for subsequent application of the phyB mutant in breeding population screening.
Owner:SHANDONG RICE RES INST
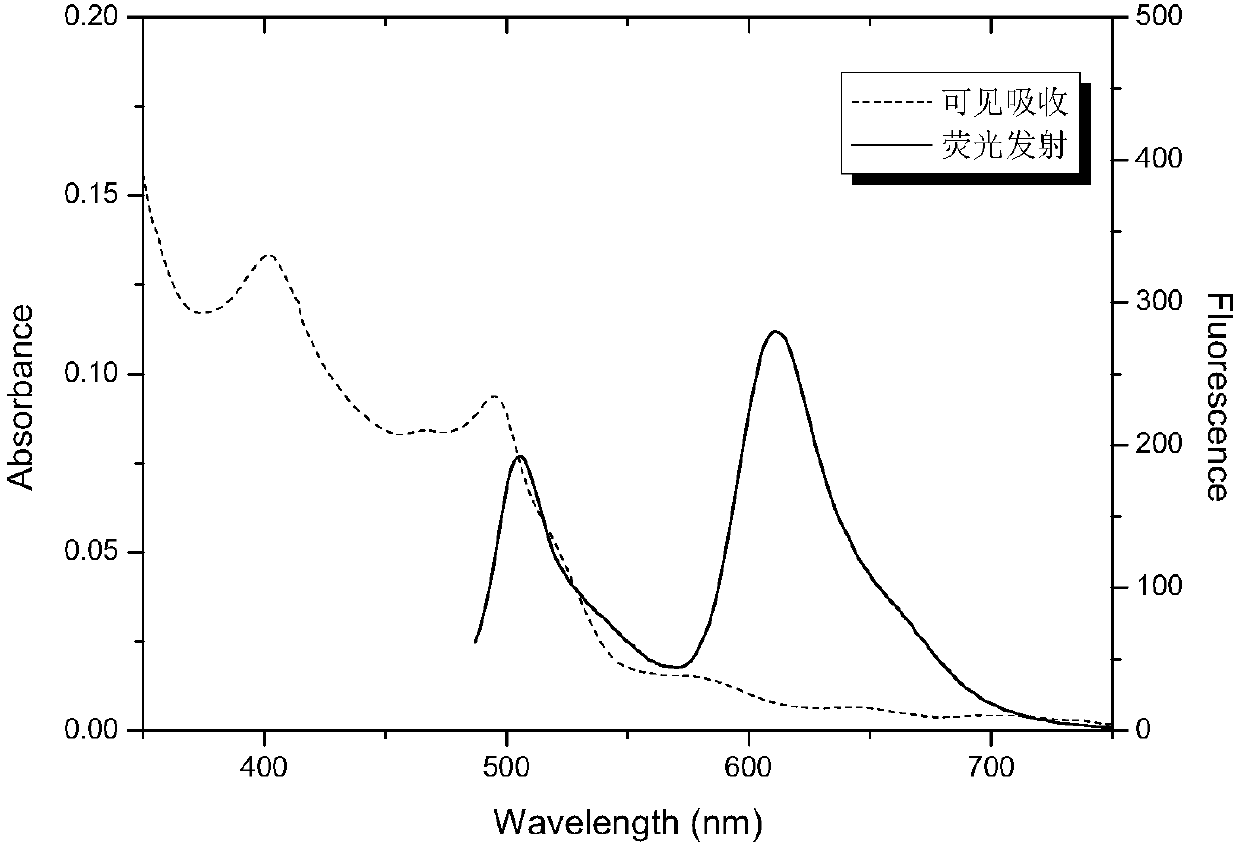
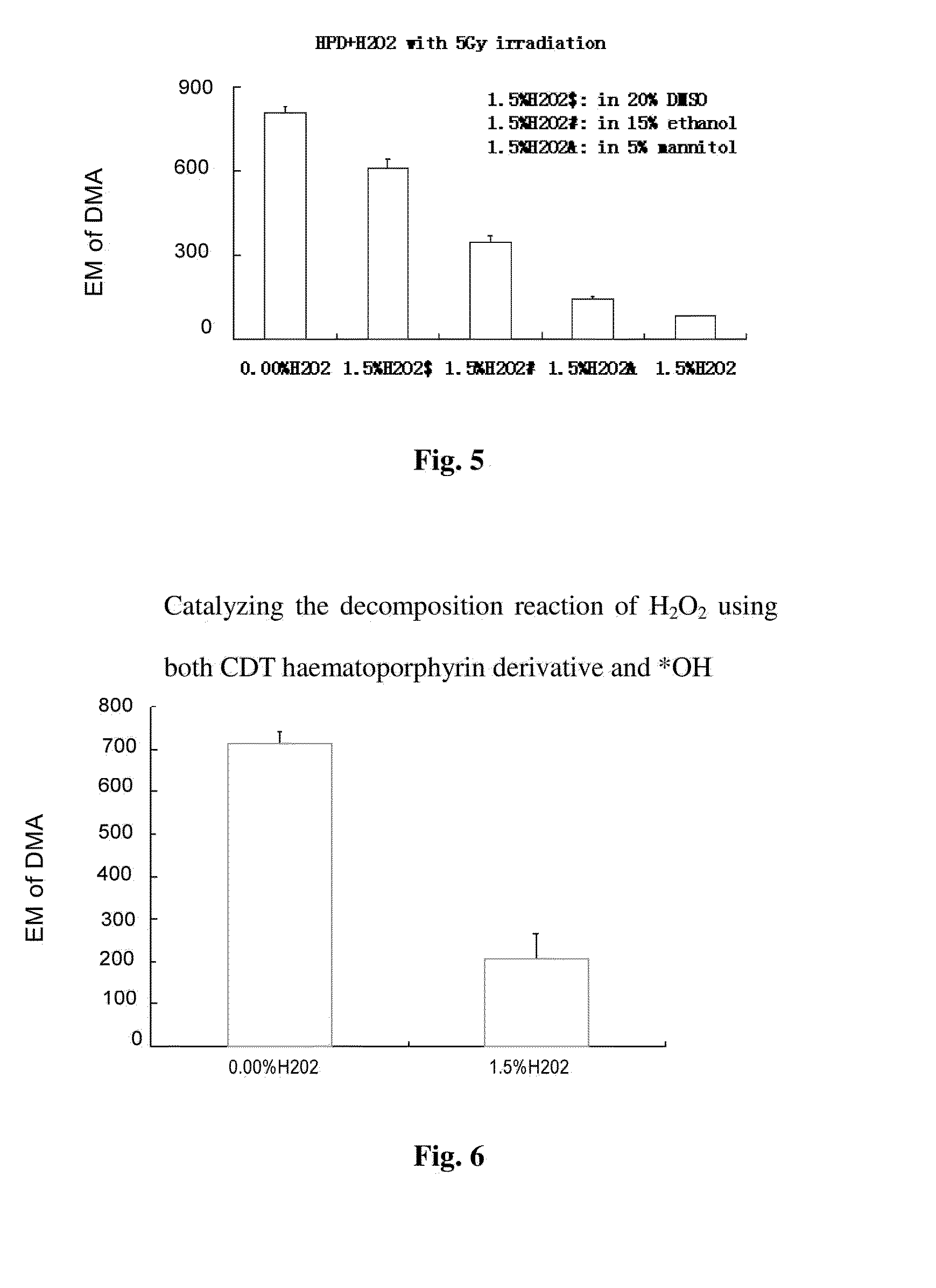
Series of drugs using photofrin to catalyze decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
InactiveUS20140107332A1Easy to operateOrganic active ingredientsSenses disorderDiseaseSinglet oxygen
The present invention relates to a series of new drugs which refer to chemical series capable of catalyzing the decomposition of H2O2 to generate singlet oxygen (1O2). The drugs relate to therapeutic mechanisms, different from traditional photodynamic therapy, in which the specific affinity of photofrin to focus, such as tumors, vascular plaques and skin diseases is utilized. The activation of photofrin is carried out by specific protein binding or by electron beam, x-ray, r-ray, or other means, to focus, catalyze the decomposition reaction of H2O2 to generate 1O2 in the focus, 1O2 further induces apoptosis and necrosis of cells with pathological changes. The drugs are useful in tumors, vascular plaques and skin diseases, and cosmetic effects on skin are prompted. The drugs obtained via the screening and studying of the present invention are used for chemodynamic therapy (CDT), or for radiochemodynamic therapy (RCDT) carried out via radioactive rays.
Owner:WUXI ZHAOZHEN RADIATION TECH
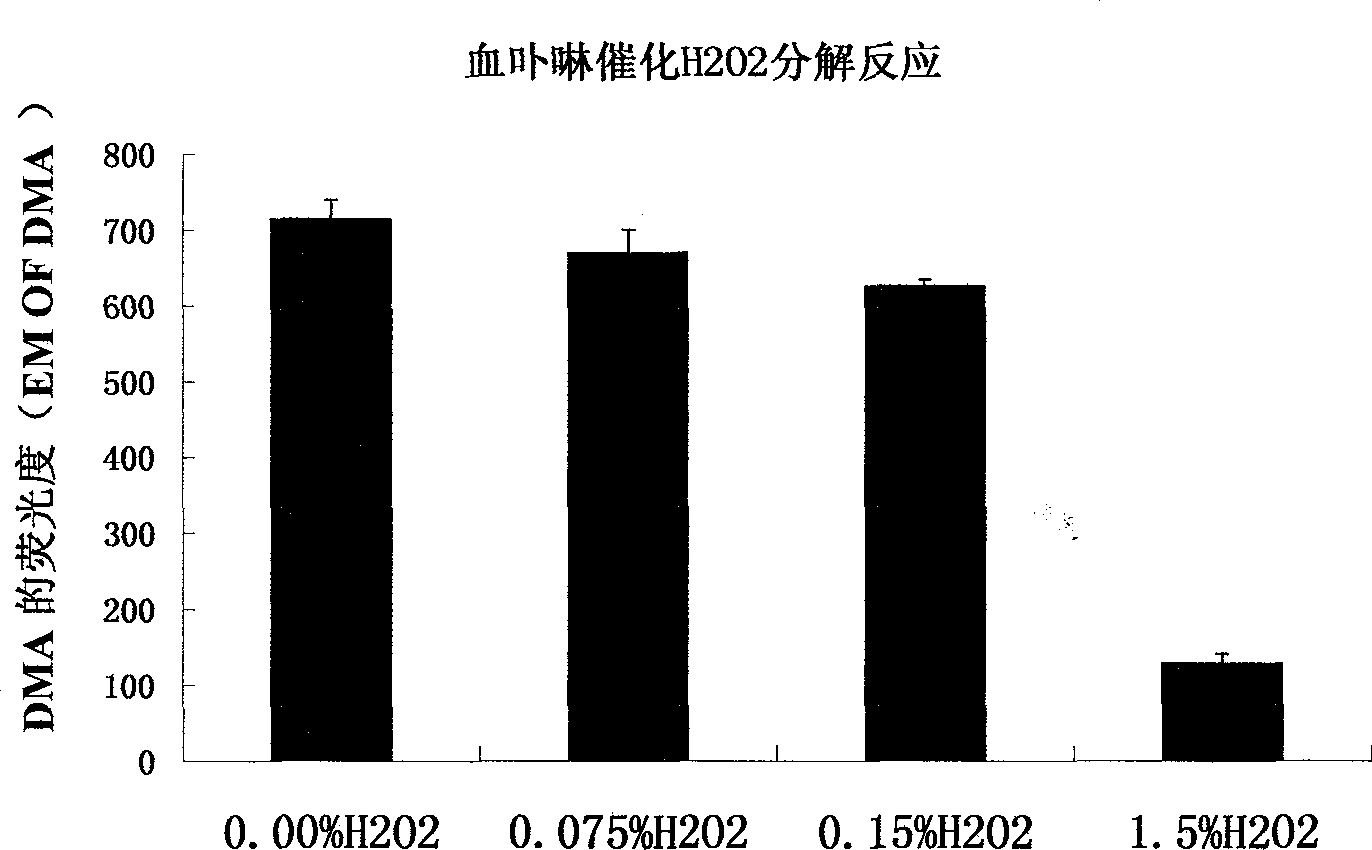
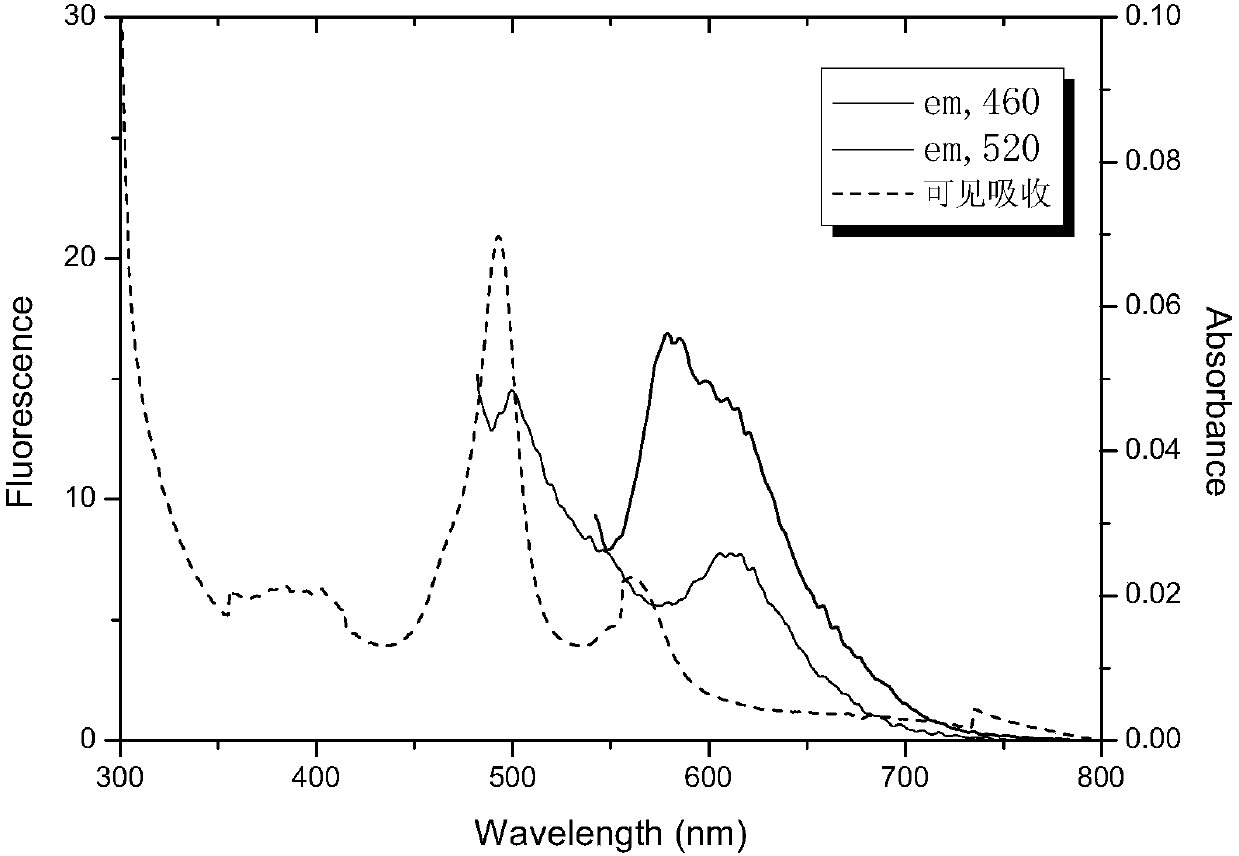
Serial drug capable of catalyzing decomposition of hydrogen dioxide by phytochromes
In the invention, phytochromes are activated in focuses such as tumors, vascular patches and skin diseases, in a fixed-point and fixed-quantity way by a specific means through the utilization of the specific affinity action of the phytochromes on the focuses, the decomposition reaction of H2O2 is catalyzed by the phytochromes to generate <1>O2, and the apoptosis or the necrosis of pathological cells is caused, thereby achieving the purpose of treating the diseases. A corresponding serial novel drug is screened, developed and used for CDT (Chemodynamic Therapy) or RCDT (Radiochemodynamic Therapy). The invention relates to the serial novel drug which is used for CDT and RCDT. The serial novel drug can catalyze the chemical reaction of decomposing the H2O2 to generate the <1>O2, does not have obvious side effect on the normal tissues and organs of a human body, and meanwhile, has the capability of affiliating the focuses. The phytochromes are used as a catalyst, and the acting mechanism, the usage, the therapeutic effect and the like of the phytochromes are completely different from those of traditional photo-dynamic therapy. Oxygen and visual light are not needed, and a completely independent novel drug series can be formed.
Owner:WUXI ZHAOZHEN RADIATION TECH
Modulation of flowering time by the pft1 locus
InactiveUS20060242737A1Prolong flowering timeShorten flowering timeControl devices for washing apparatusFermentationPhytochromeShade avoidance
The PFT1 (Phytochrome and Flowering Time 1) locus is described and identified. PFT1 acts in a light-quality pathway downstream of phyB that acts through modulation of FT transcription. Plants containing a truncated pft1 gene display an altered shade avoidance syndrome including an increase in time to flowering. The corresponding PFT1 gene has been isolated and characterized. Recombinant vectors, recombinant plants containing the PFT1 gene and methods of using the PFT1 gene to modulate a photosensitive trait, especially time to flowering, are described.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Proteins that fluoresce at infrared wavelengths or generate singlet oxygen upon illumination
ActiveUS20110177003A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsBacteriaHaem biosynthesisProtoporphyrin IX
This invention provides novel truncation mutants of a phytochrome from the bacterium Deinococcus radiodurans. When expressed either in bacteria or mammalian cells, these mutant phytochromes spontaneously incorporate biliverdin, a ubiquitous intermediate in heme catabolism, and become fluorescent in the infrared (IR) region. These phytochromes are the first genetically encoded labels that can be excited by far-red light and fluoresce in the true IR (>700 nm). If these mutants instead incorporate protoporphyrin IX, an intermediate in heme biosynthesis, illumination now generates significant amounts of singlet oxygen. Singlet oxygen is useful because it can be used to kill individual proteins or cells, detect long-range protein-protein interactions, or generate electron-microscopic contrast. The invention also relates to methods of making and using such proteins and protein variants.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Preparation method of orange-fluorescence cyanobacteria phytochrome fluorescence indicator
InactiveCN108250304AStable expressionSolve access difficultiesBacteria peptidesHybrid peptidesBiotin-streptavidin complexPhylum Cyanobacteria
The invention discloses a preparation method of an orange-fluorescence cyanobacteria phytochrome fluorescence indicator. A fusion protein comprises a first structural protein and streptavidin of a GAFstructural domain of a cyanobacteria phytochrome protein all2699. The sequence of the fusion protein of the invention is easily stably expressed in a microorganism, so that shortcomings of the difficulty in obtaining a high-purity natural phycobiliprotein and cyanobacteria phytochrome, relatively high preparation cost, use of a chemical modifier, an instable polymerization shape of the natural phycobiliprotein and the like are avoided. According to an expression method disclosed by the invention, no participation of phycobiliprotein lactase is needed, the number of transformed genes is reduced, and the strain stability and the screening efficiency are improved. Meanwhile, by optimizing a fermentation culture medium and a fermentation condition, the yield of the fusion protein is greatly increased.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TEBSUN BIO TECH DEV
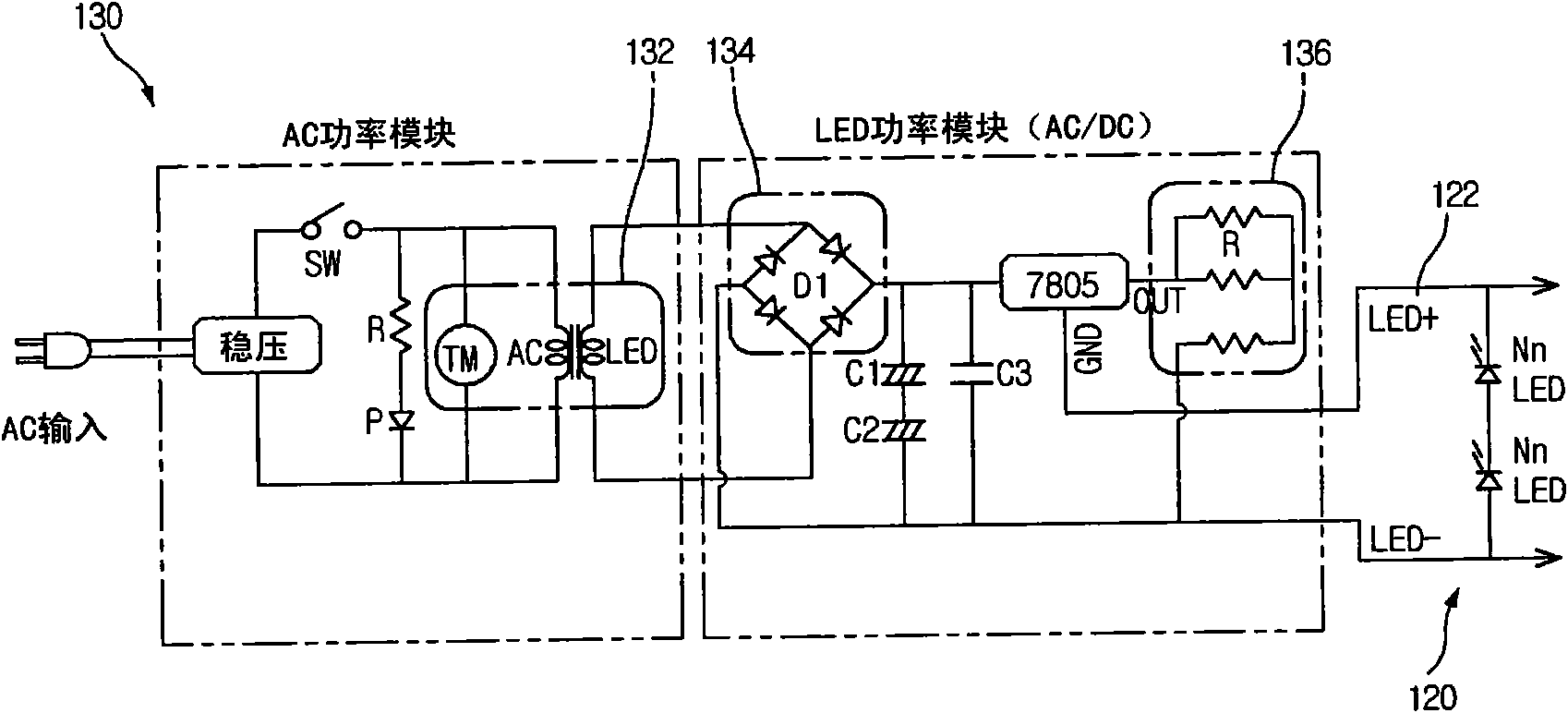
Farm size light quality control apparatus
InactiveCN101676604AQuality growthReduce scatterPoint-like light sourceGreenhouse cultivationEngineeringRadiation angle
Disclosed is a light quality control apparatus for crops, capable of ensuring installation, expand and maintenance of a light source, and improving crops growth and seeds collection. According to a demonstration embodiment of the invention, the light quality control apparatus for crops includes a plurality of LEDs arranged in a module mode to control light radiation angles appropriately, and mounted on a support so as to connect a plurality of light quality control apparatus units by a connector easily. The support is in a shape with at least 16 faces so as to improve manufacturing convenienceand irradiate crops equably without shade areas. Furthermore, according to another demonstration embodiment of the invention, the light quality control apparatus for crops is capable of transmittingred light of 660 nm wavelengh to activate phytochrome as photoreceptor protein, so as to control the crops growth, compared with other apparatus, the light quality control apparatus saves 60%-86% electric charge and reduces production costs. For example, if the crops is irradiated by light having at least 0.2 [Mu]mol m<-2>.s<-1> strength, the crops photosynthesis may be improved, such that the crops growth is accelerated. For purple perilla, the light having at least 0.177 [Mu]mol m<-2>.s<-1> strength and 660 [Mu]m wavelengh may restrain the flowering of the crops to ensure the dependable upgrowth of the crops.
Owner:大韩民国:农村振兴厅 +1
Method for preparing cyanobacterial phytochrome fluorescent marker with orange-red fluorescence
InactiveCN108047334AStable expressionSolve access difficultiesPolypeptide with affinity tagBacteria peptidesLyaseBacterial strain
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cyanobacterial phytochrome fluorescent marker with orange-red fluorescence. Fusion protein comprises a first GAF structural domain of cyanobacterial phytochrome protein alr5272 and streptavidin. A fusion protein sequence of the fluorescent marker is easily and stably expressed in microorganisms, and the defects that acquirement of high-purity natural phycobiliprotein and cyanobacterial phytochrome is difficult, the preparation cost is high, chemical modifiers are used and the polymerization form of natural phycobiliprotein is unstable are avoided. According to an expression method of the fluorescent marker, participation of phycobiliprotein lyase is not required, the number of transformed genes is reduced, and the stability and screening efficiency of bacterial strains are improved. At the same time, the yield of fusion proteins is greatly increased by optimizing a fermentation culture medium and fermentation conditions.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TEBSUN BIO TECH DEV
Series of drugs using photofrin to catalyze decomposition of hydrogen peroxide
The present invention relates to a series of new drugs which refer to chemical series capable of catalyzing the decomposition of H2O2 to generate singlet oxygen (1O2). The drugs relate to therapeutic mechanisms, different from traditional photodynamic therapy, in which the specific affinity of photofrin to focus, such as tumors, vascular plaques and skin diseases is utilized. The activation of photofrin is carried out by specific protein binding or by electron beam, x-ray, r-ray, or other means, to focus, catalyze the decomposition reaction of H2O2 to generate 1O2 in the focus, 1O2 further induces apoptosis and necrosis of cells with pathological changes. The drugs are useful in tumors, vascular plaques and skin diseases, and cosmetic effects on skin are prompted. The drugs obtained via the screening and studying of the present invention are used for chemodynamic therapy (CDT), or for radiochemodynamic therapy (RCDT) carried out via radioactive rays.
Owner:WUXI ZHAOZHEN RADIATION TECH
Preparation method of phytochrome-derived yellow fluorescent label
InactiveCN108164604AStable expressionSolve access difficultiesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesPhylum CyanobacteriaLyase
The invention discloses a preparation method of a phytochrome-derived yellow fluorescent label. According to the preparation method, a fusion protein comprises the 3th GAG domain of cyanobacteria phytochrome protein slr1393 and streptavidin. Stable expression of the fusion protein sequence can be realized in microorganisms; defects such as acquisition difficulty of high purity natural phycobiliprotein and cyanobacteria phytochrome, high preparation cost, applications of chemical modifying agents, and unstable natural phycobiliprotein polymeric species are avoided. In the expression method, nophycobiliprotein lyase is needed, the number of converted genes is reduced, bacterial strain stability and screening efficiency are increased; and optimization of fermentation culture medium and fermentation conditions is capable of increasing fusion protein yield greatly.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TEBSUN BIO TECH DEV
ApcE2 protein mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN109553661AImprove solubilityIncrease unit outputBacteria peptidesGenetic engineeringSolubilityEscherichia coli
The present invention discloses a wild type ApcE2 protein mutant. The mutant is characterized by being obtained by mutation of at least one amino acid in an amino acid sequence shown in a SEQ ID No.1,and wherein the amino acid mutation is selected from at least one of mutation of a amino acid site outside a loop, mutation of an amino acid site inside a loop, and a loop structure sequence with partial deletion mutation. The ApcE2 protein mutant of the present invention has a higher solubility than that before the mutation, and the unit yield expressed in Escherichia coli is remarkably improved. The ApcE2 protein mutant of the invention can be used for fluorescence labeling tissue localization, preparation and extraction of phytochrome P[phi]B, preparation of other phycobiliproteins, such as phycoerythrin PEB and phycocyanobilin PCB, and in vitro recombination of fluorescent phycobiliprotein. The preparation method of the present invention realizes higher unit yield and better solubility of the pigment protein.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TEBSUN BIO TECH DEV
Streptavidin and phytochrome fused yellowish-green fluorescent indicator preparation method
InactiveCN108148140AStable expressionSolve access difficultiesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesBiotin-streptavidin complexFluorescence
The invention discloses a streptavidin and phytochrome fused yellowish-green fluorescent indicator preparation method. A fusion protein comprises a second GAF structural domain of cyanobacterium phytochrome protein all1280 and streptavidin. A sequence of the fusion protein can be easily and stably expressed in microorganisms, and defects of difficulty in acquisition of high-purity natural phycobiliprotein and cyanobacterium phytochrome, high preparation cost, chemical modifier consumption, polymerization morphological instability of natural phycobiliprotein and the like are avoided. The expression method is free of phycobiliprotein lyase participation, transformational gene amount is decreased, and strain stability and screening efficiency are improved. In addition, by optimization of fermentation media and fermentation conditions, fusion protein yield is greatly increased.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TEBSUN BIO TECH DEV
Cyanochrome fluorophores
Genetically-engineered cyanochrome fluorophore molecules (fluorophores) with increased fluorescence and with absorbing fluorescence in the blue and green (blue / green) portion of the light spectrum are provided. These fluorophores are derived from the domains of phytochromes, and in particular cyanobacterial phytochromes. Methods for generating these fluorophores and various applications of these fluorophores are also provided.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Green fluorescent cyanobacterium phytochrome fluorescence indicator preparation method
InactiveCN108148141AStable expressionSolve access difficultiesAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsBacteria peptidesBiotin-streptavidin complexFluorescence
The invention discloses a green fluorescent cyanobacterium phytochrome fluorescence indicator preparation method. A fusion protein comprises a second GAF structural domain of cyanobacterium phytochrome protein all3691 and streptavidin. A sequence of the fusion protein can be easily and stably expressed in microorganisms, and defects of difficulty in acquisition of high-purity natural phycobiliprotein and cyanobacterium phytochrome, high preparation cost, chemical modifier consumption, polymerization morphological instability of natural phycobiliprotein and the like are avoided. The expressionmethod is free of phycobiliprotein lyase participation, transformational gene amount is decreased, and strain stability and screening efficiency are improved. In addition, by optimization of fermentation media and fermentation conditions, fusion protein yield is greatly increased.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TEBSUN BIO TECH DEV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com