Optically activated receptors
A technology of photoactivation and receptors, applied in the fields of biology and optogenetics, which can solve the problem of not mentioning the photosensitive domain, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
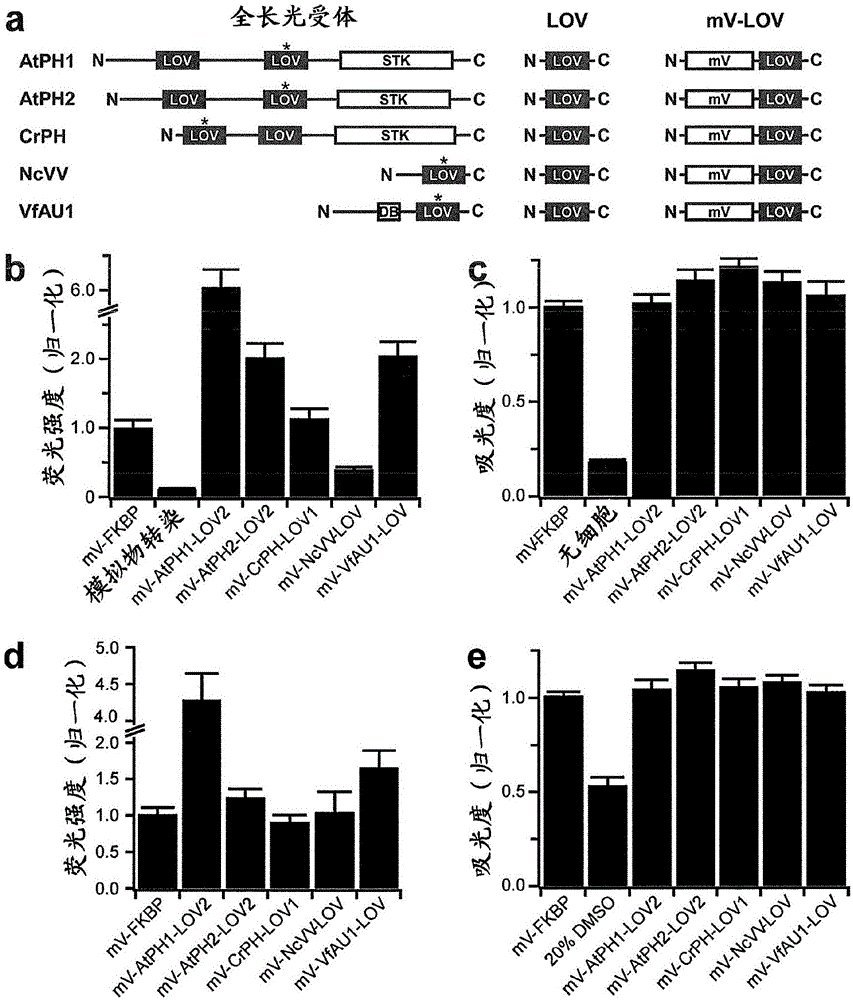
[0509] Since it was initially unclear which LOV domain would be suitable for activation as a mammalian RTK, the inventors compiled an unbiased panel of diverse candidate LOV domains (one from fungi; two from algae, and two from plants) ( figure 1 a and SEQ ID NO: 1-14).
[0510] Table 1. Photophysical and Equilibrium Binding Parameters of LOV Domains
[0511]
[0512] 1 Three exponential decays with lifetimes ranging from 20 to 800 s were observed.
[0513] 2 Compared to the VfAU1-LOV of this study, the LOV domain includes C-terminal and N-terminal extensions.
[0514] 3 When necessary, the published half-life values (t1 / 2) were converted to lifetimes (τ = t1 / 2 / ln(2)) assuming first order reactions.
[0515] For these domains, light-dependent changes in the oligomeric state were previously reported (Katsura, 2009; Kaiserli, 2009; Kutta, 2008; Zoltowski, 2008; Toyooka, 2011). Since most of these domains have never been studied in mammalian cells, the inventors first ex...
Embodiment 2
[0526] Cancer development and progression are often associated with mutations in RTKs or RTK overexpression, and many cancer cells respond to growth factors with increased proliferation, migration, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) (Metzner et al. 2011, Sakuma et al. 2012) . To establish a cellular model of human cancer associated with FGF / FGFR signaling, the inventors tested the effect of FGF2, a prominent FGFR ligand, on cells from different tumor entities. The inventors found that M38K cells derived from malignant pleural mesothelioma (Kahlos et al. 1998) responded to FGF with characteristic changes in cell behavior. To investigate whether Opto-FGFR1 allowed light to control the behavior of these human tumor cells, the inventors virally delivered Opto-mFGFR1 into these cells and propagated the cells with stable Opto-mFGFR1 expression. Stimulation with blue light resulted in rapid phosphorylation of Opto-mFGFR1 and ERK1 / 2, which returned to pre-stimulation levels ...
Embodiment 3
[0533] The inventors first identified a protein domain that undergoes homodimerization in response to red light (the photosensitive domain of the cyanobacterial phytochrome (PHY) CPH1 (SyCP1-PHY) of Synechocystis sp. PCC6803). The inventors then prepared fusion proteins in which SyCP1-PHY was linked to the intracellular catalytic domain of murine FGFR1 (mFGFR1) or rat trkB (rtrkB) ( Figure 10 and 11 ). The extracellular ligand-binding module of mFGFR1 / rtrkB was omitted to obtain a fusion protein that does not respond to the native ligand. Cells expressing the fusion protein should respond to red light with activation of the signaling pathway characteristic of mFGFR1 / rtrkB. The inventors performed cell signaling experiments (Materials and Methods) in a custom-made incubator that allowed cells and tissues to be illuminated with light of defined intensity and colour. As in Example 1, the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway was first examined.
[0534] The fusion ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com