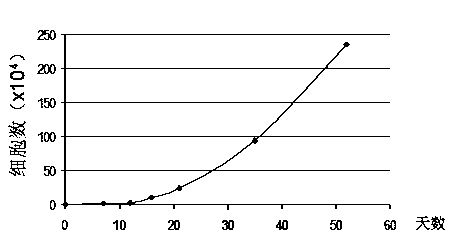
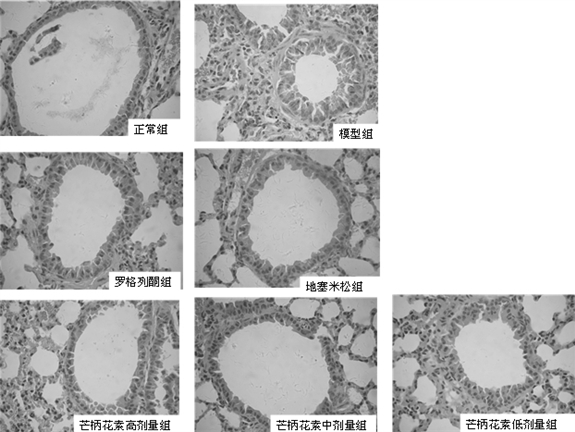
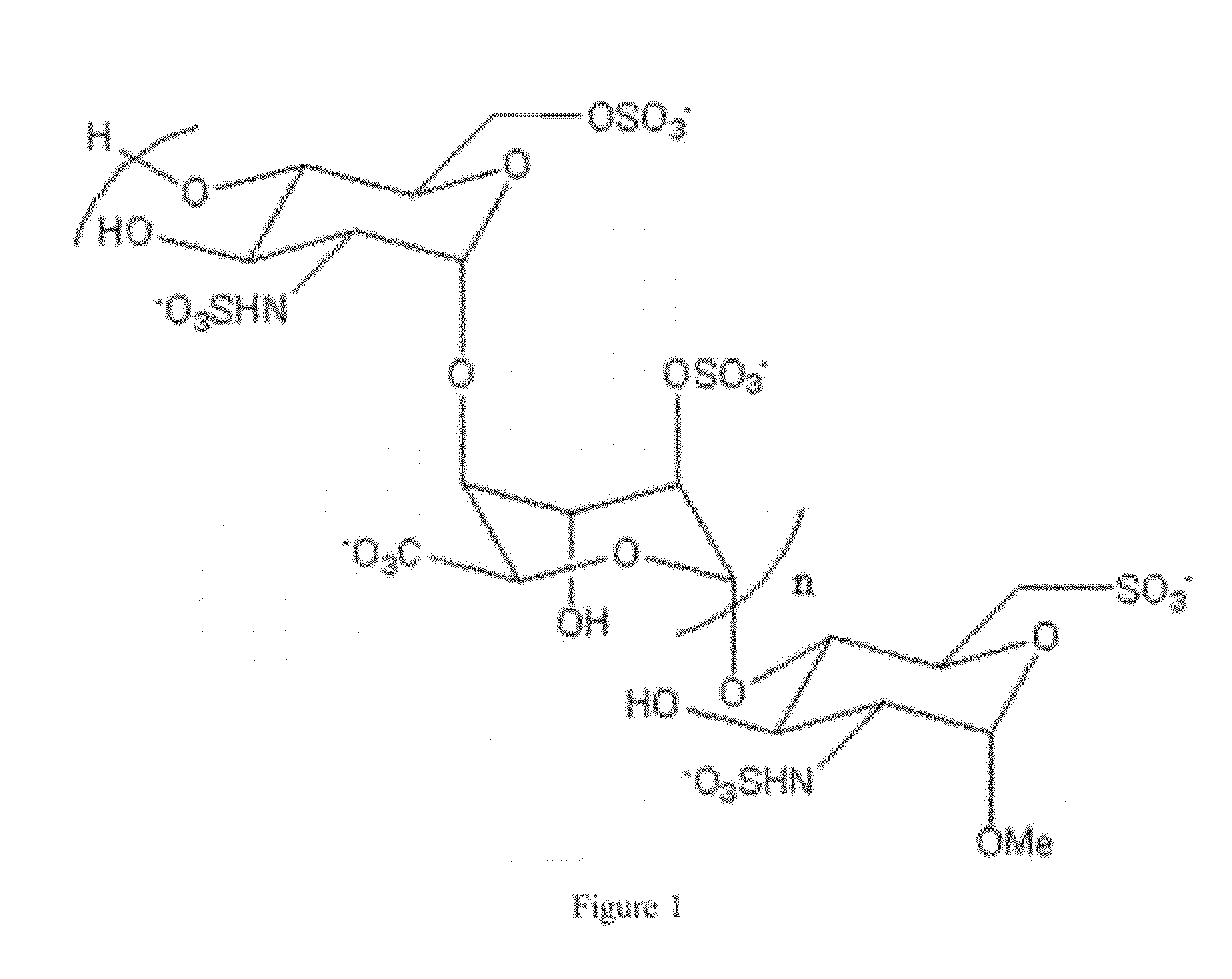
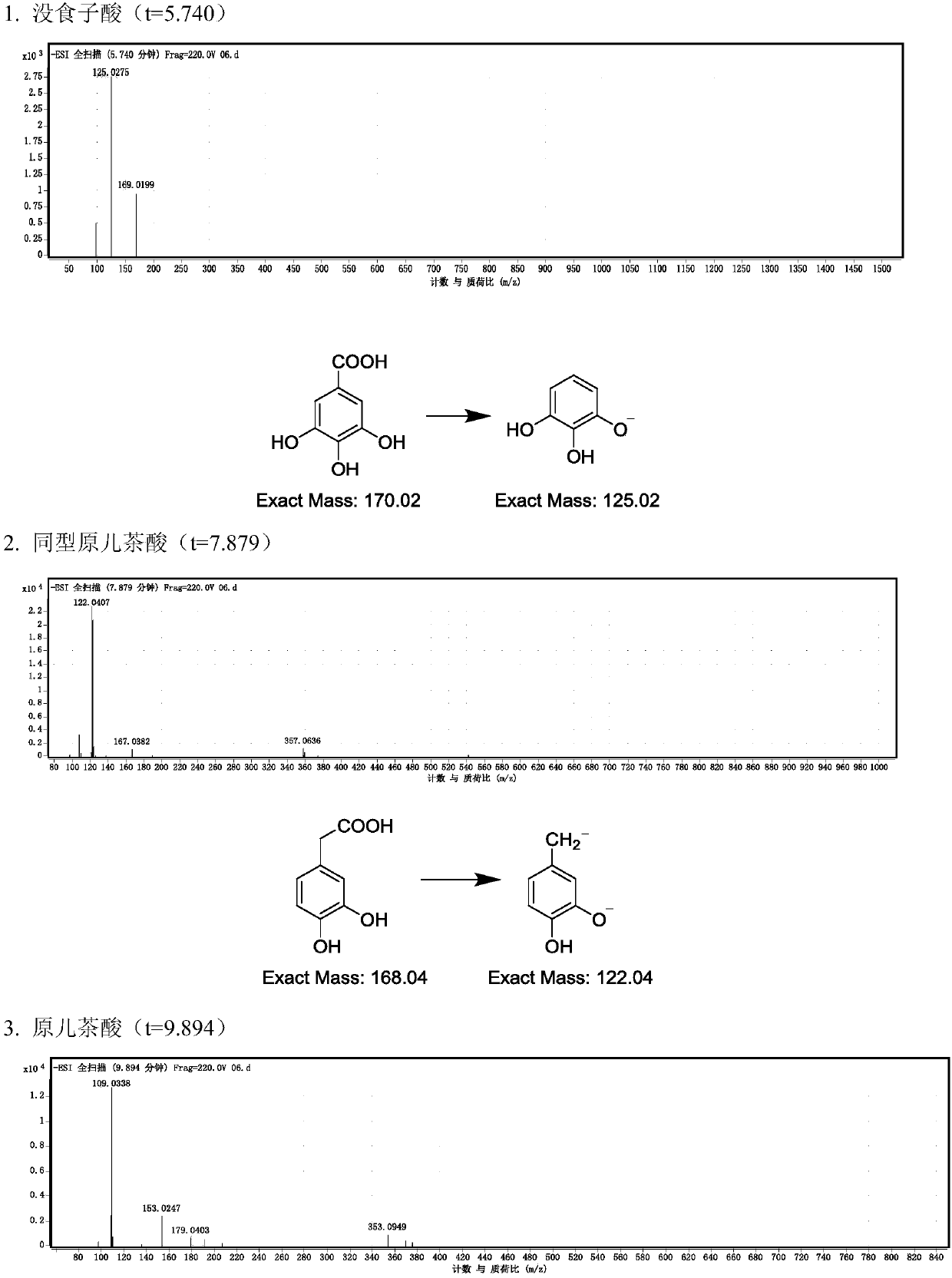
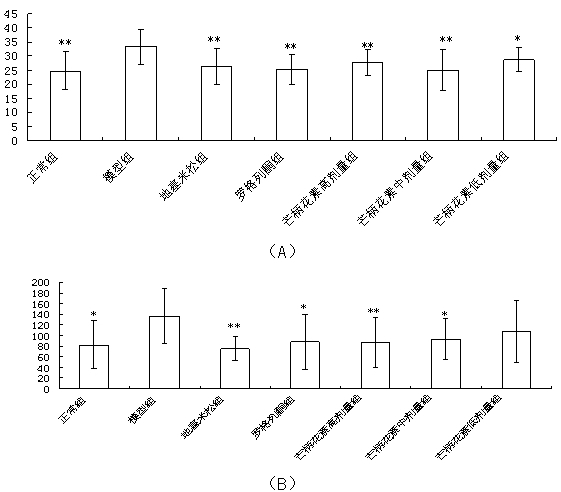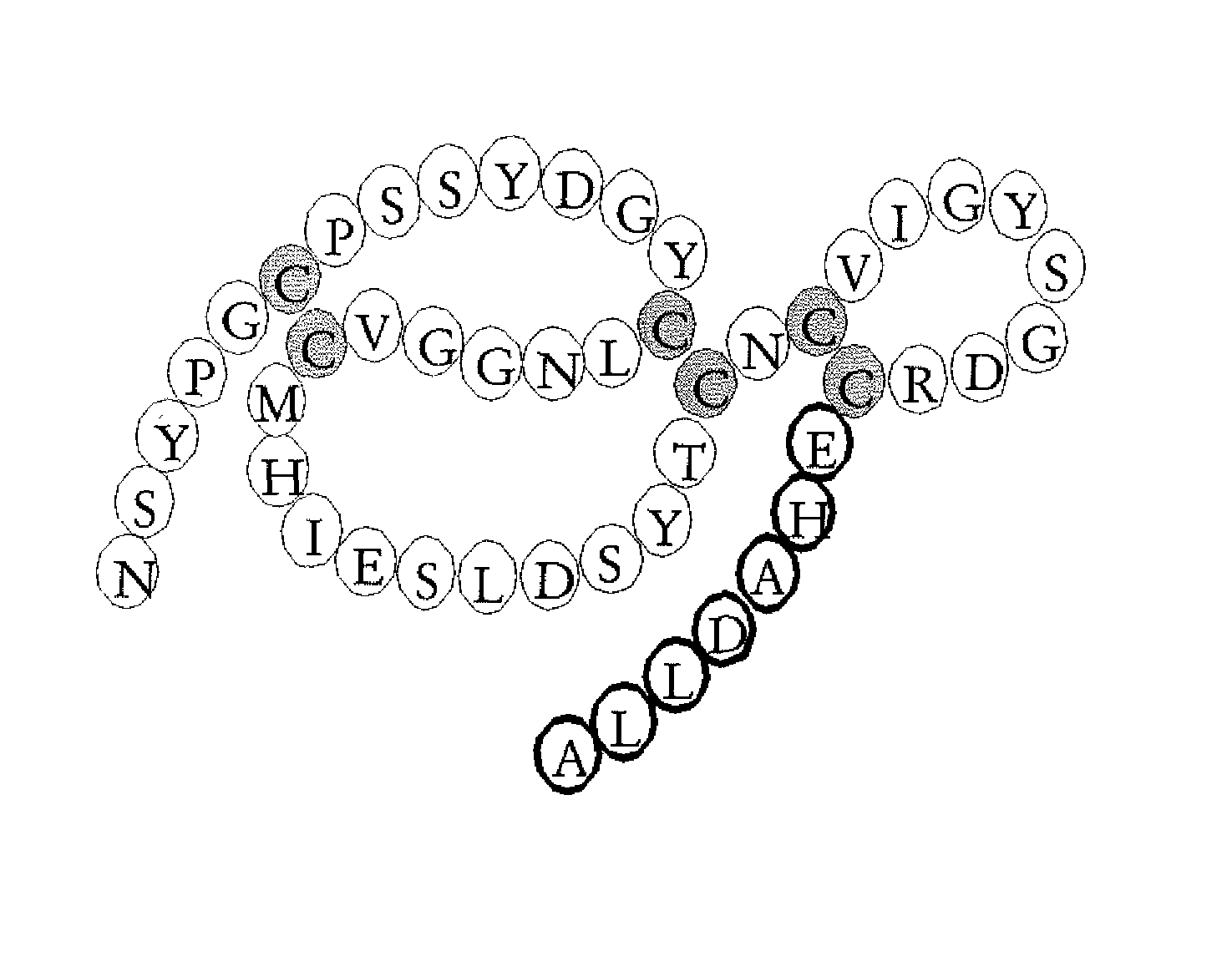Patents
Literature
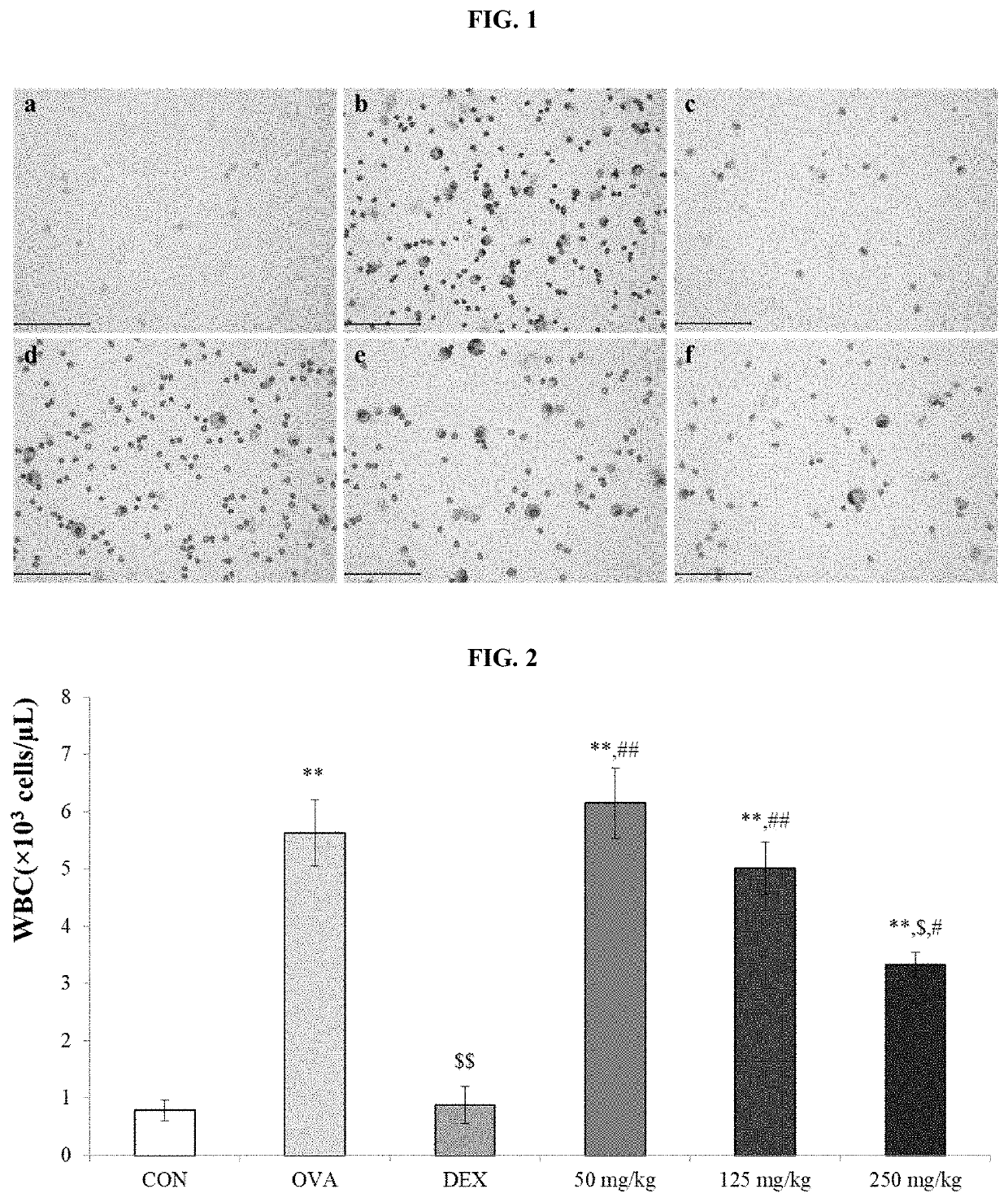
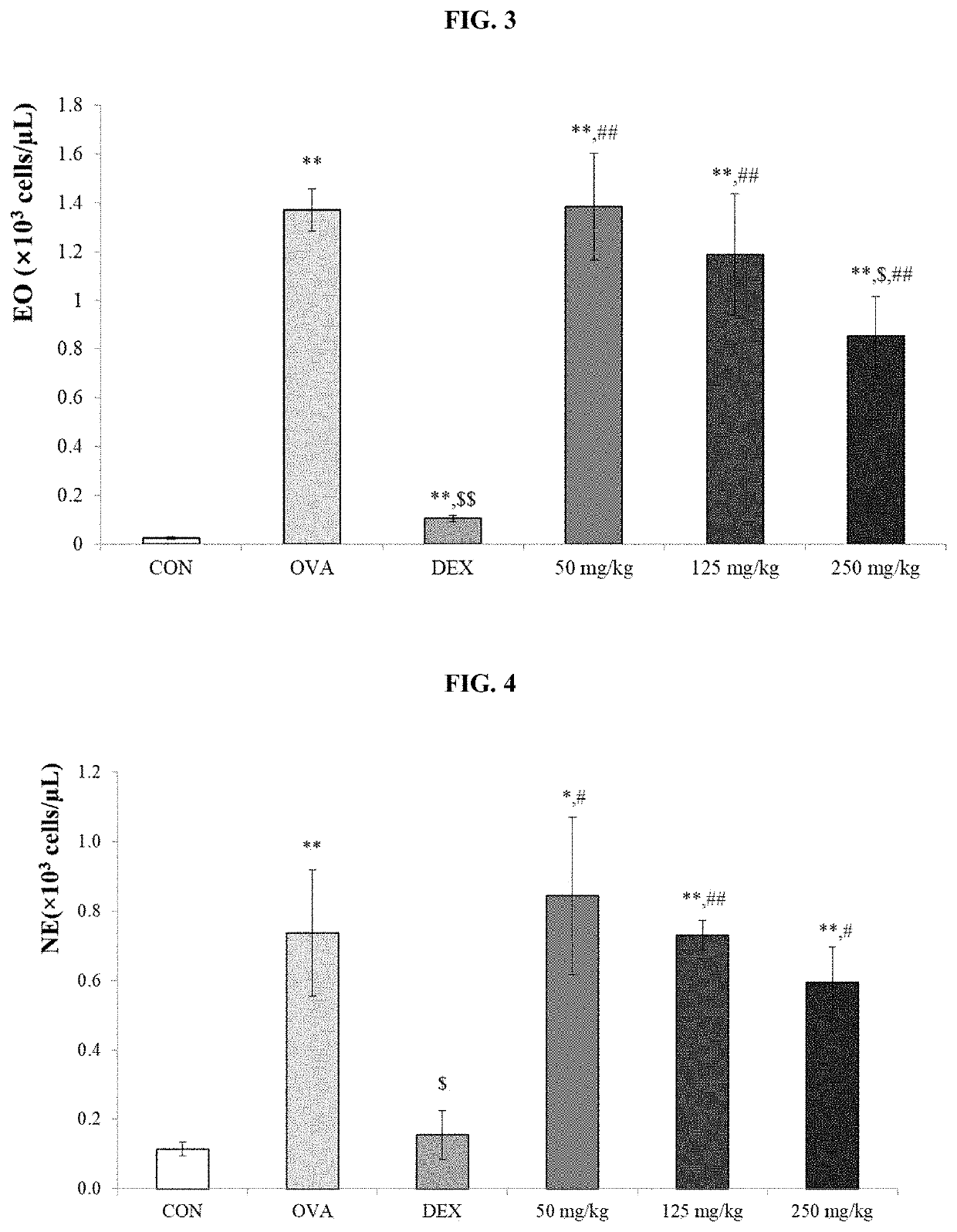
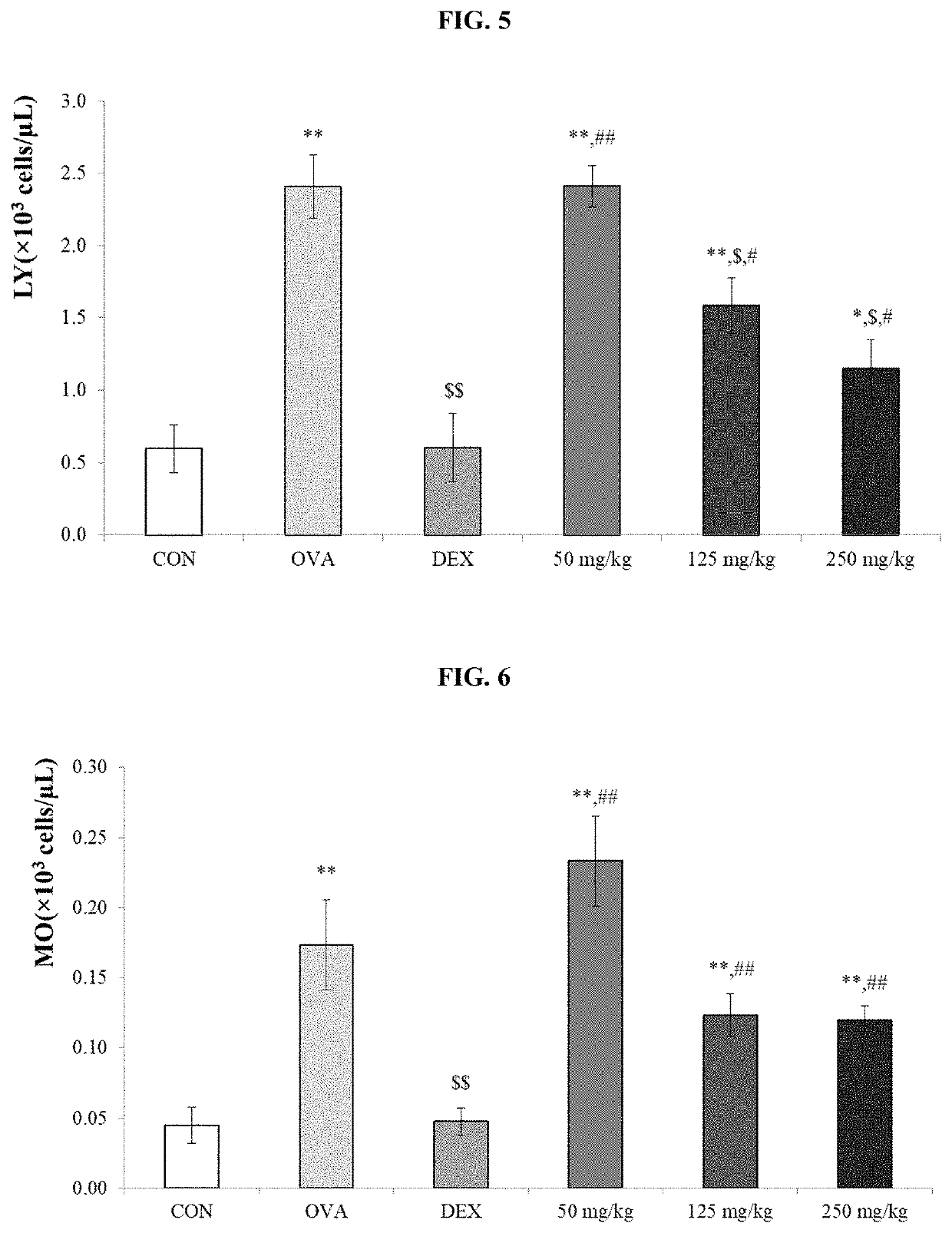
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
71 results about "Bronchial Epithelial Cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. MatTek’s Normal Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells (NHBE) provide an ideal serum-free culture system to study cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, drug effects, gene regulation, cell differentiation, tissue development, wound healing, inflammation and toxic effects to the bronchial epithelium.
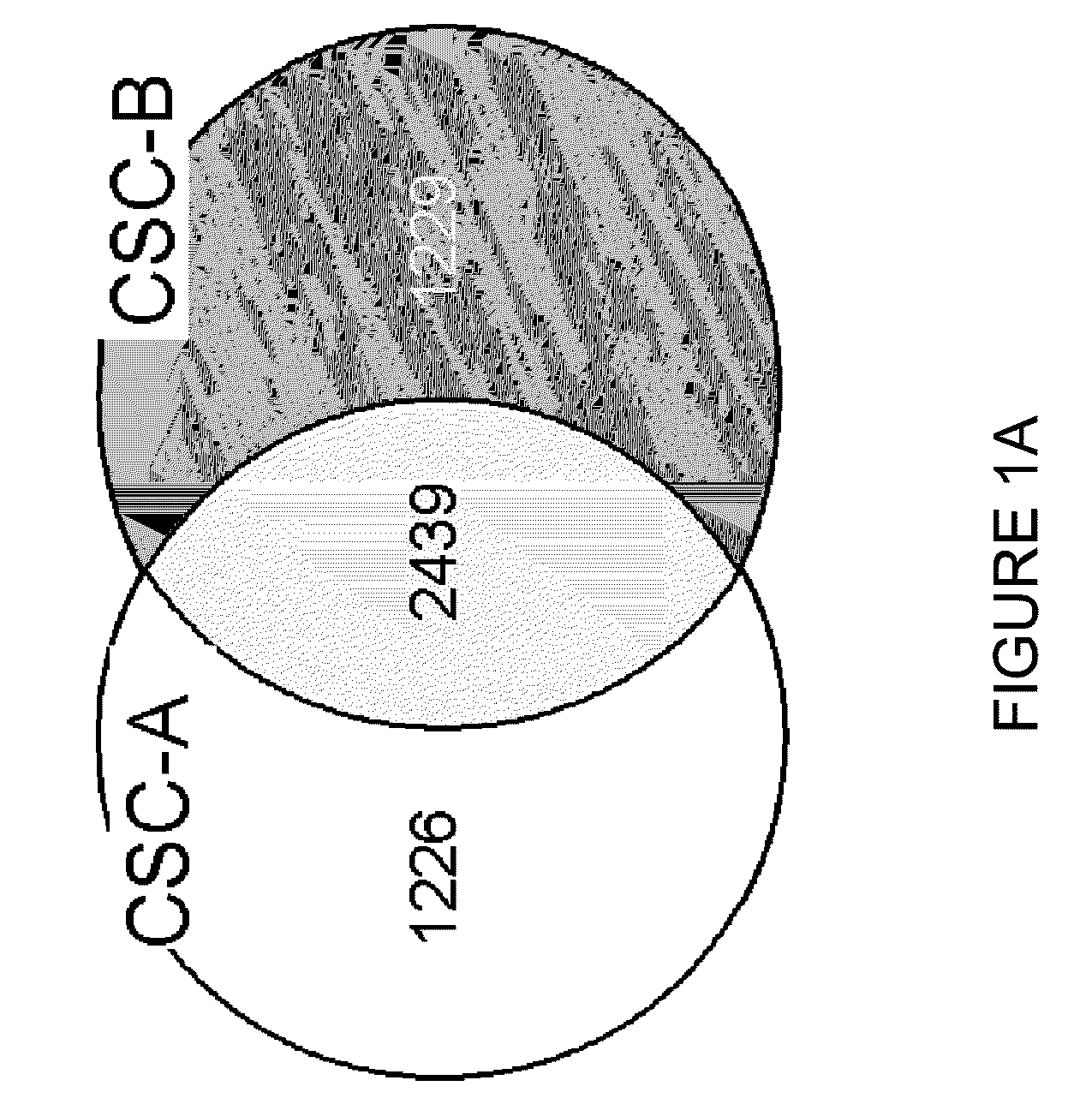
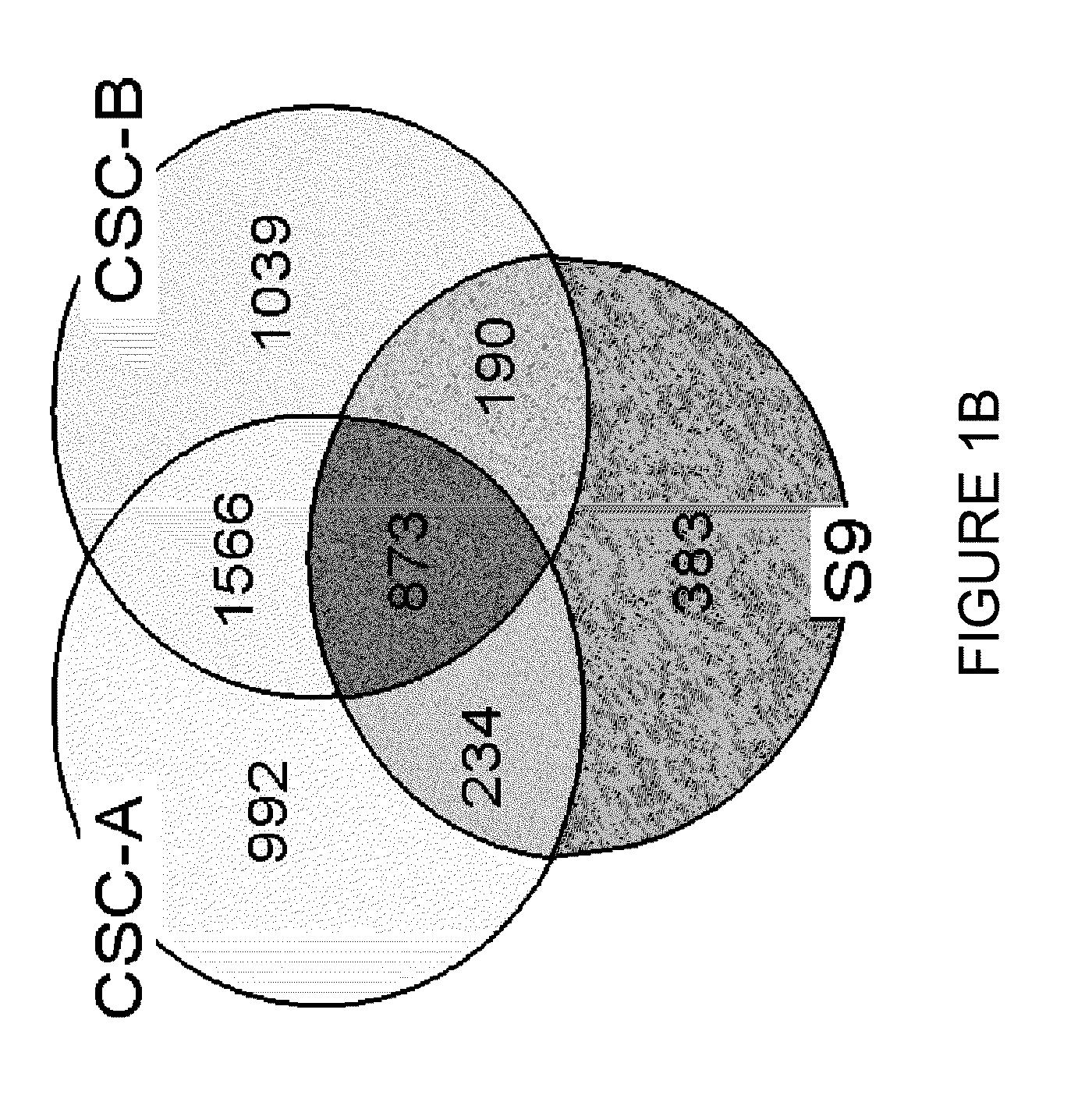
Global Gene Expression Analysis of Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Exposed to Cigarette Smoke, Smoke Condensates, or Components Thereof
InactiveUS20080052789A1Reduced potential to contributeReduced expression levelSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNicotiana tabacumBiomarker (petroleum)
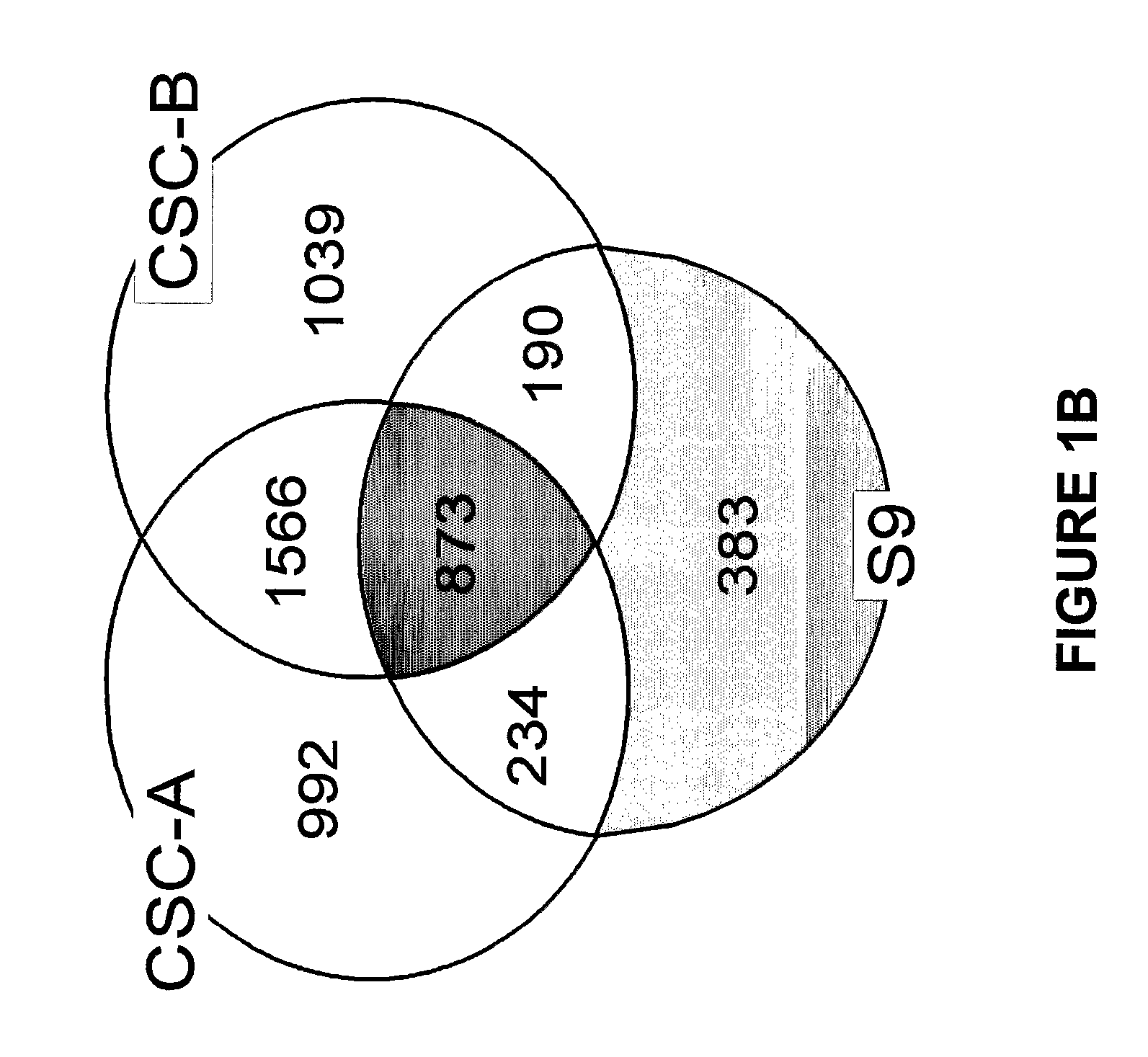
Aspects of the present invention concern the identification of several methods to analyze the genes that are modulated in normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells after exposure to cigarette smoke condensates (CSC) or cigarette smoke (CS). Embodiments described herein include methods to identify a gene that is modulated in response to exposure to CSC or CS, methods to identify tobacco products that have a reduced potential to contribute to tobacco-related disease, methods to make tobacco products that have a reduced potential to contribute to a tobacco-related disease, methods to identify a subject's predilection to acquire a tobacco related disease, the use of particular genes as biomarkers for tobacco-related disease, and patterns of gene expression or genetic signatures that are unique to each particular tobacco product.
Owner:VECTOR TOBACCO LLC
MTT (thiazolyl blue) cell toxicity test method of biological assessment of total particle matter in cigarette smoke
InactiveCN103088105AReduce the number of steps to wash cellsStrong targetingMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsBronchial epitheliumCell system
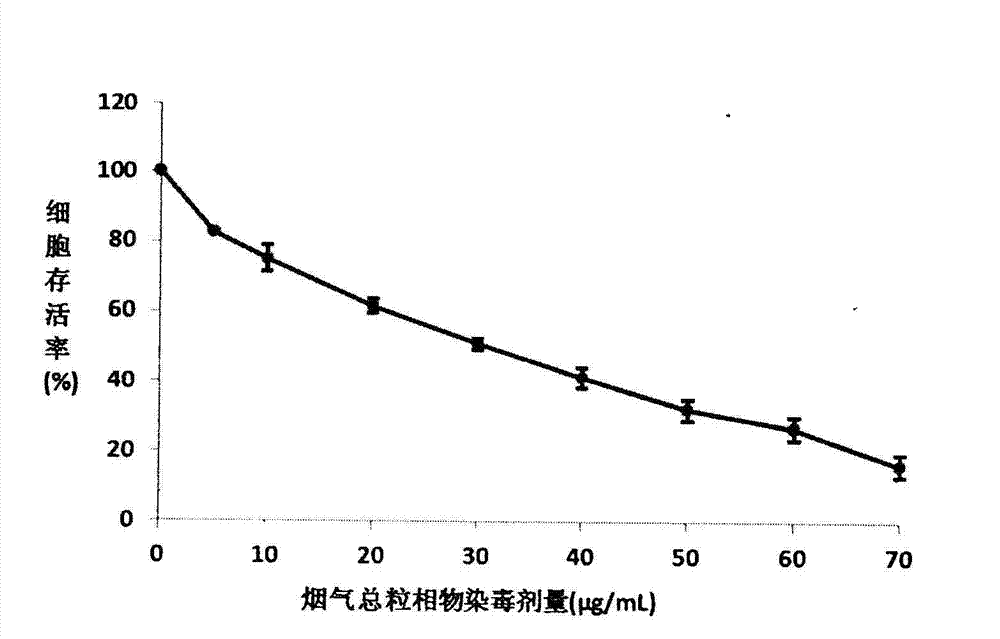
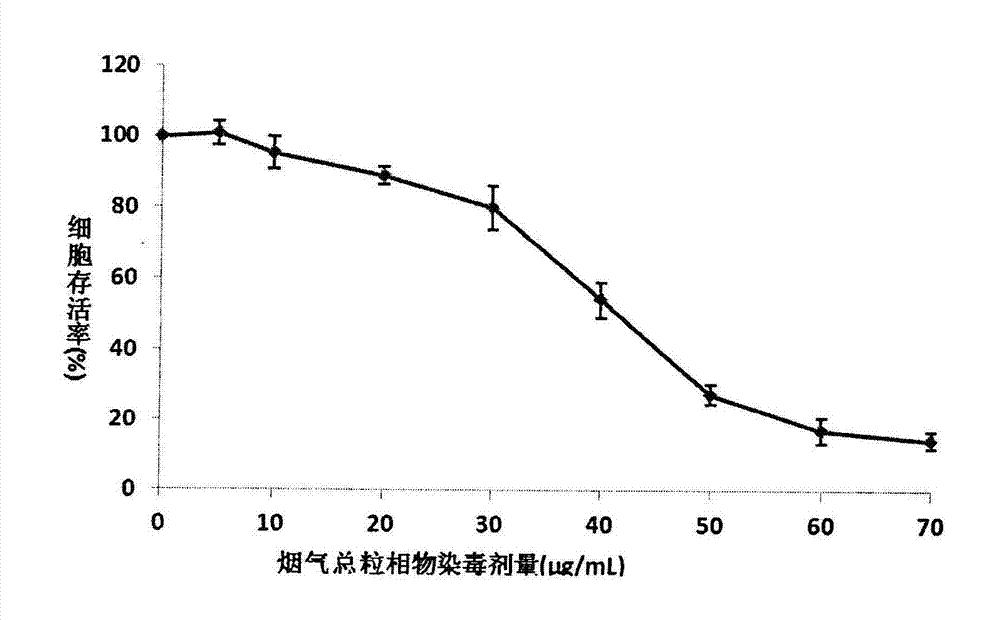
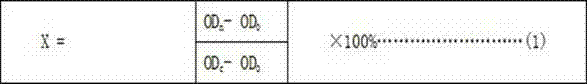
The invention relates to an MTT (thiazolyl blue) cell toxicity test method of biological assessment of a total particle matter in cigarette smoke and belongs to the technical field of safety assessment of tobacco and cigarette smoke. The MTT cell toxicity test method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: inoculating and culturing immortalized human bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B cells) and contaminating the total particle matter in the cigarette smoke; detecting the cell survival rate by adopting an MTT method; and analyzing and evaluating the cell toxicity of the total particle matter in the cigarette smoke according to a test result. Compared with the prior art, the MTT cell toxicity test method has the following characteristics that BEAS-2B cells are human cells and are target organ source cells acting on a human body by the smoke; a BEAS-2B cell system is used for carrying out cell toxicity assessment on the cigarette smoke and has the strong pertinence; in a testing process, steps of washing the cells for a plurality of times are reduced; and a formaldehyde fixing step does not need to be carried out so that a testing period is shortened, the operation is rapid and convenient, the sensitivity is high and the result is stable and reliable. Moreover, the MTT test method disclosed by the invention is further applicable to a smoke cell toxicity test of various cell systems and the commonality is strong.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Method for rapidly separating and culturing human bronchial epithelial cells, and optimized medium
ActiveCN107974429AEasy to separateEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsCuticleFeeder Layer
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
Method for preparing three-dimensional cell scaffold for in-vitro toxicological evaluation of tobacco products and method for cell culture by use of three-dimensional cell scaffold
ActiveCN107674141AEvaluation results are objectiveThe evaluation result is trueEpidermal cells/skin cellsArtificial cell constructsIn vitro toxicology3D cell culture
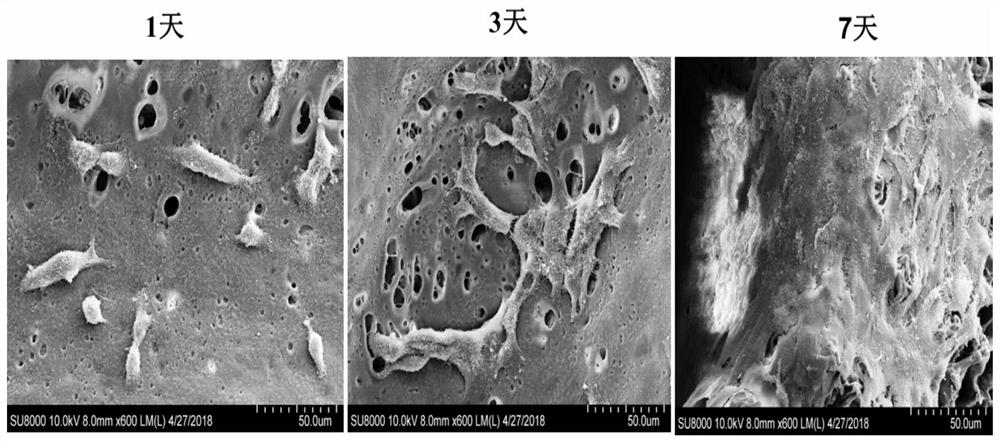
A method for preparing a three-dimensional cell scaffold for in-vitro toxicological evaluation of tobacco products is characterized in that an interconnected and porous material provided with a polymer is obtained through high-internal-phase emulsion polymerization in a cell culture dish, the material has large holes of the size of cells for in-vitro toxicological evaluation of tobacco products, the holes are communicated with one another, thereby facilitating input of oxygen and nutrients required for cell growth and output of cell metabolism waste, and the material surface is modified, so that the material has good cell affinity. Compared with existing panel type monolayer cell culture methods commonly adopted for toxicological evaluation, the method has the advantages that cells can realize three-dimensional growth on the scaffold and have more closer three-dimensional shape and biochemical and functional properties as compared with that originally in vivo. Therefore, when the cellscultured by use of the three-dimensional cell scaffold are used for in-vitro toxicological evaluation of the tobacco products, the evaluation result is more objective and real. The cell scaffold is prepared in the culture dish and is more convenient for following experiments.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Human normal bronchial epithelial cell and preliminary isolated culture and subculture methods and purposes thereof
The invention discloses a human normal bronchial epithelial cell and preliminary isolated culture and subculture methods and purposes of the human normal bronchial epithelial cell. The cell is named as the human normal bronchial epithelial cell HNBEC / HL-001, the preservation number of the cell is CCTCCNO: C201311. The preliminary isolated culture method includes the steps that fat in a para-carcinoma tissue sample excised from a patient with lung cancer through an operation is removed, dispase and DNasel are added to the fat for action after the fat is digested, the cell is collected through filtering and centrifugal operations, and the cell is suspended again with an HL culture medium for inoculated culture. The subculture method includes the steps that when the cell proliferates to 70-90% abundance, pancreatin-EDTA is used for digestion, and then DMEM is used for neutralization; the cell is collected through a centrifugal operation, and the cell is suspended again with an HL culture medium for inoculated culture. The human normal bronchial epithelial cell can be used for physiological research of human normal cells, drug toxicity research and detection of external normal cells, and research on pathogenesis of bronchia and lung diseases including bronchogenic carcinoma.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Application of formononetin in preparing medicine for preventing and treating airway inflammation and asthma
InactiveCN102552241AReduce cytokine levelsProtects against inflammatory damageOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseInflammatory factors
The invention relates to a novel application of formononetin in the medical science, in particular to the application of formononetin in preparing medicine for preventing and treating airway inflammation and asthma. Pharmacological test result shows that the formononetin participates in reducing the allergic airway inflammation of model animals / occurring and developing of asthma lesion; reducing the of damage inflammatory factor to the human bronchial epithelial cell in vitro and the formononetin can be used for preparing the medicine for treating airway inflammation diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis, capillary bronchitis and air or non-air idiotoxin or inflammatory or non-inflammatory of irritant; and specifically, the formononetin has the application in preparing medicine for treating allergic airway inflammation and asthma disease.
Owner:NANJING UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
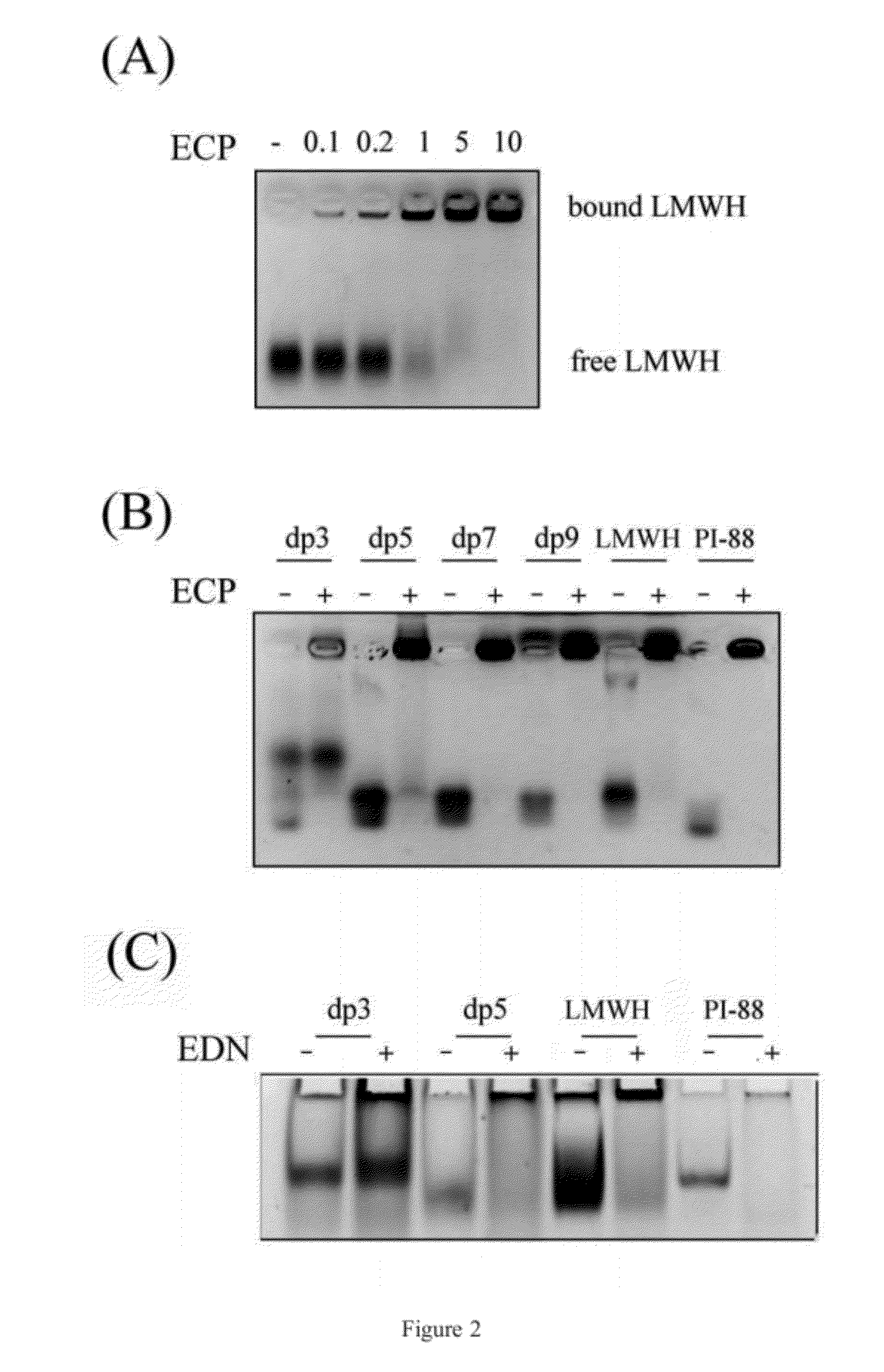
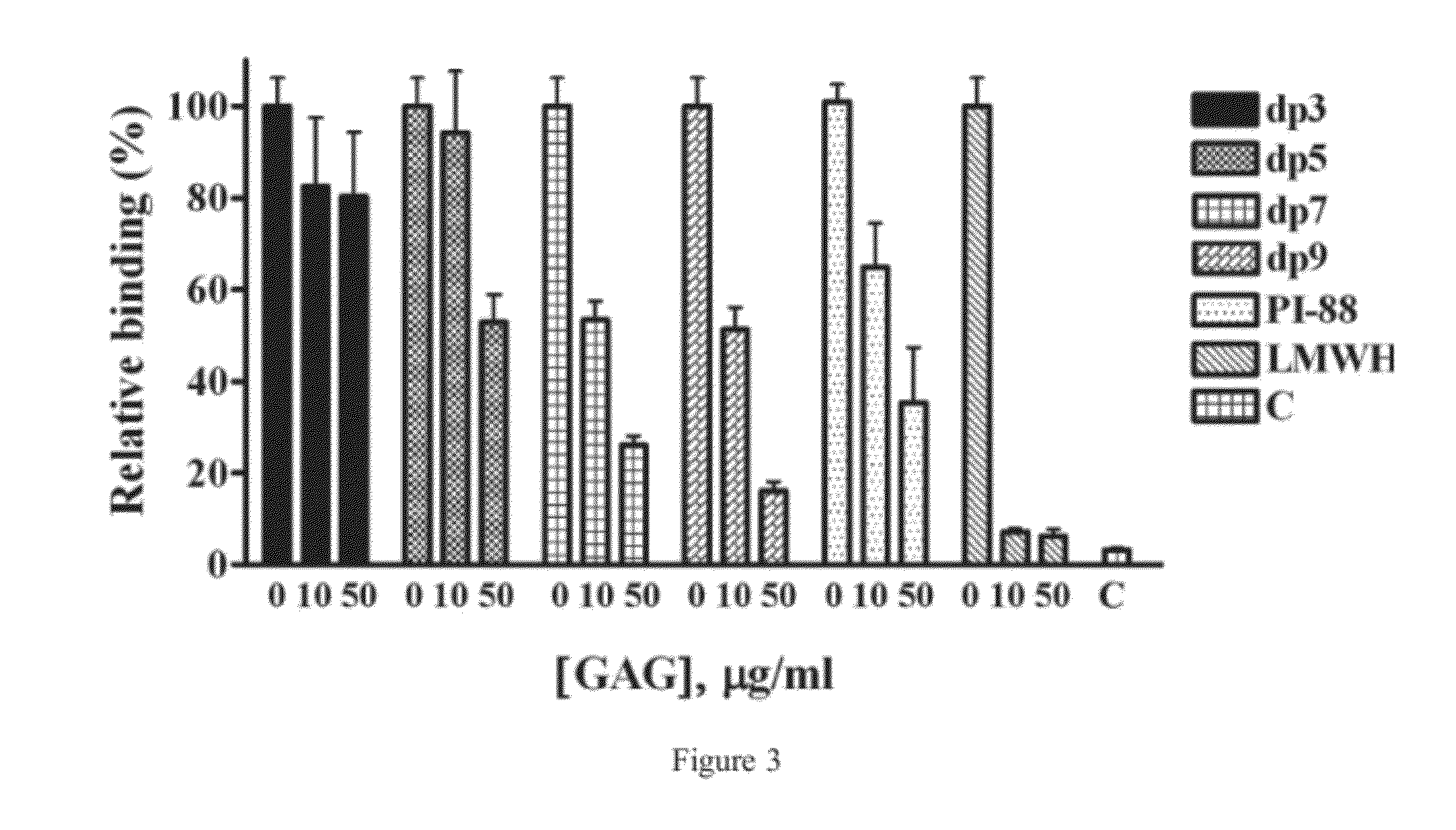
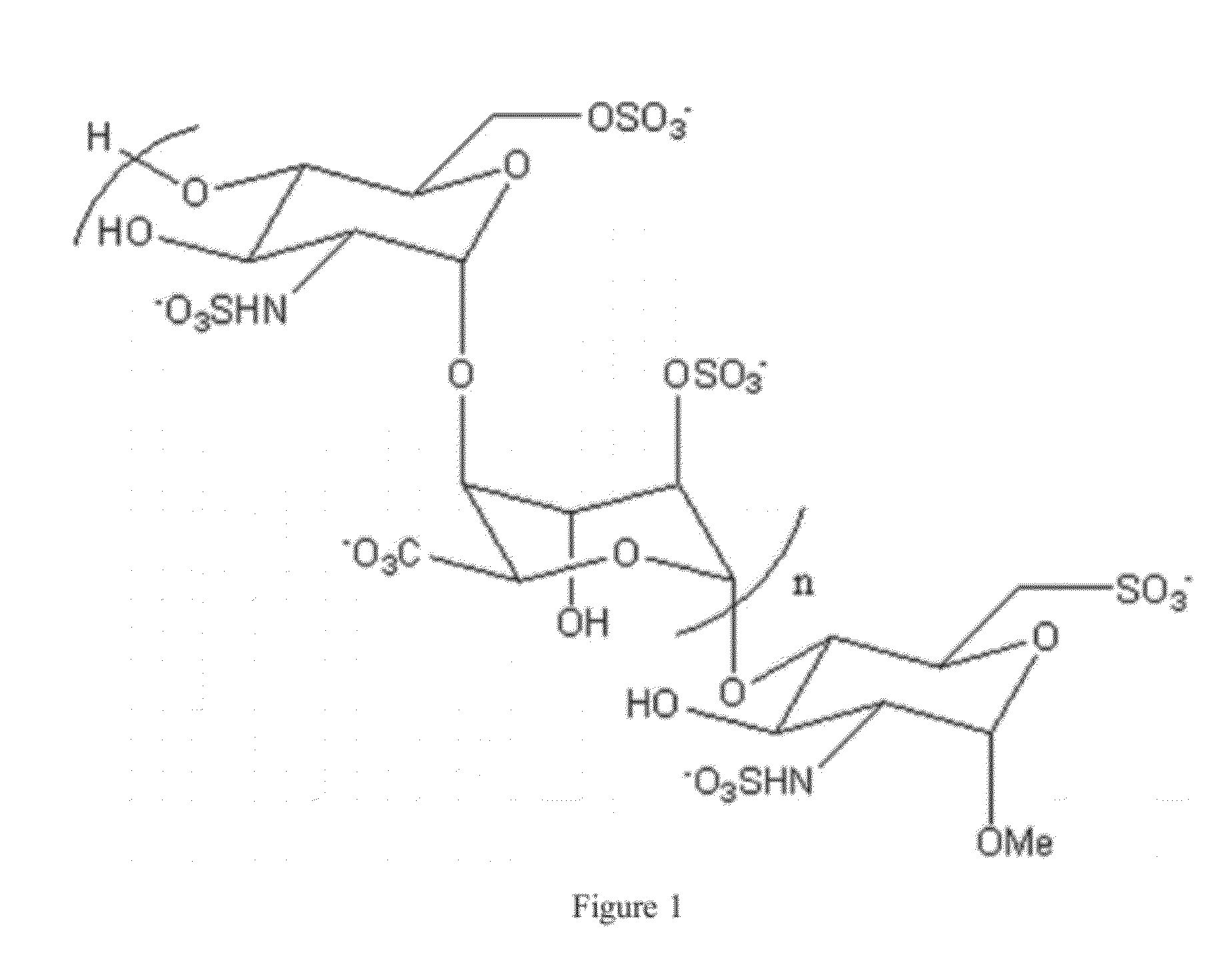
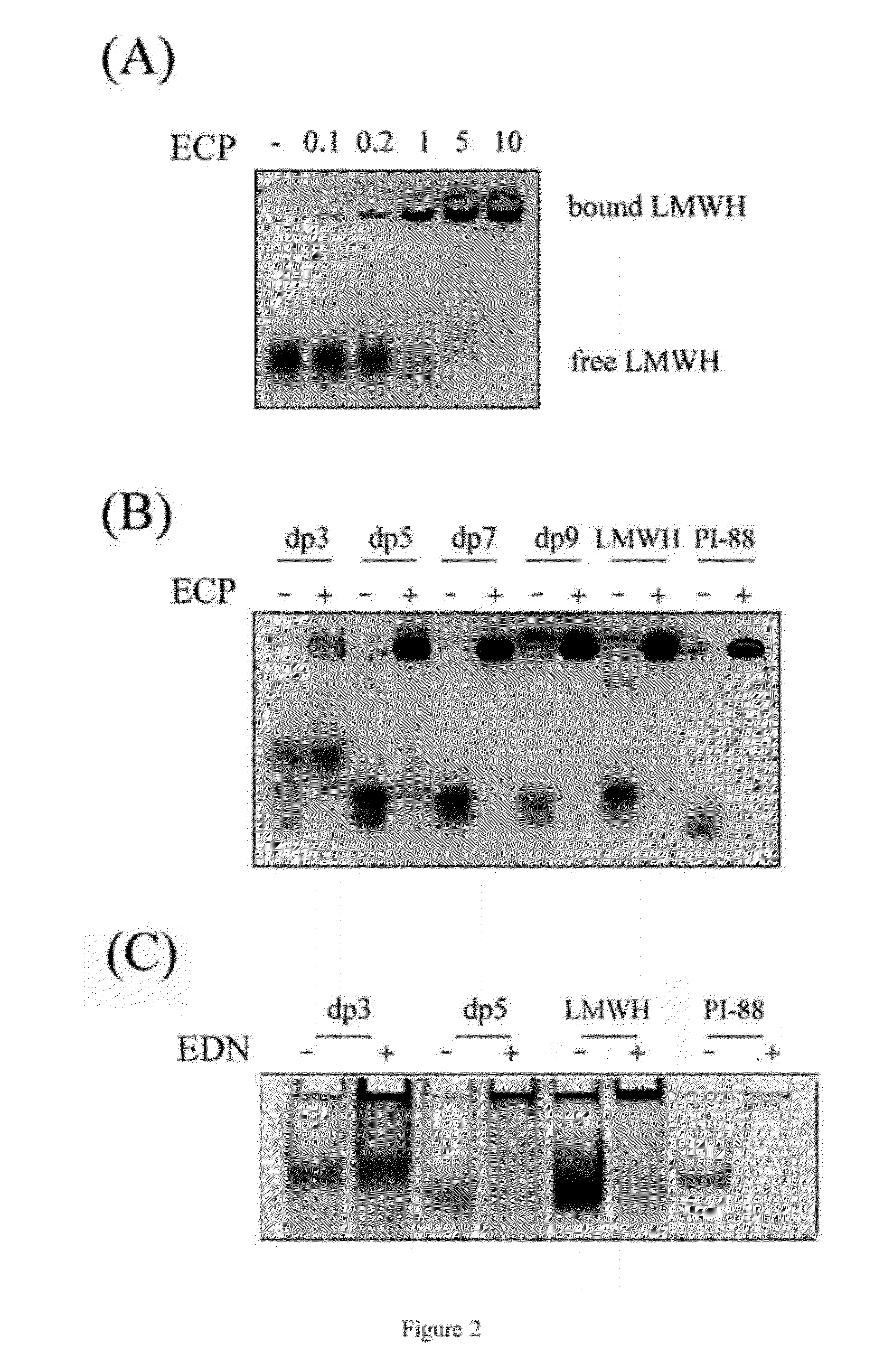
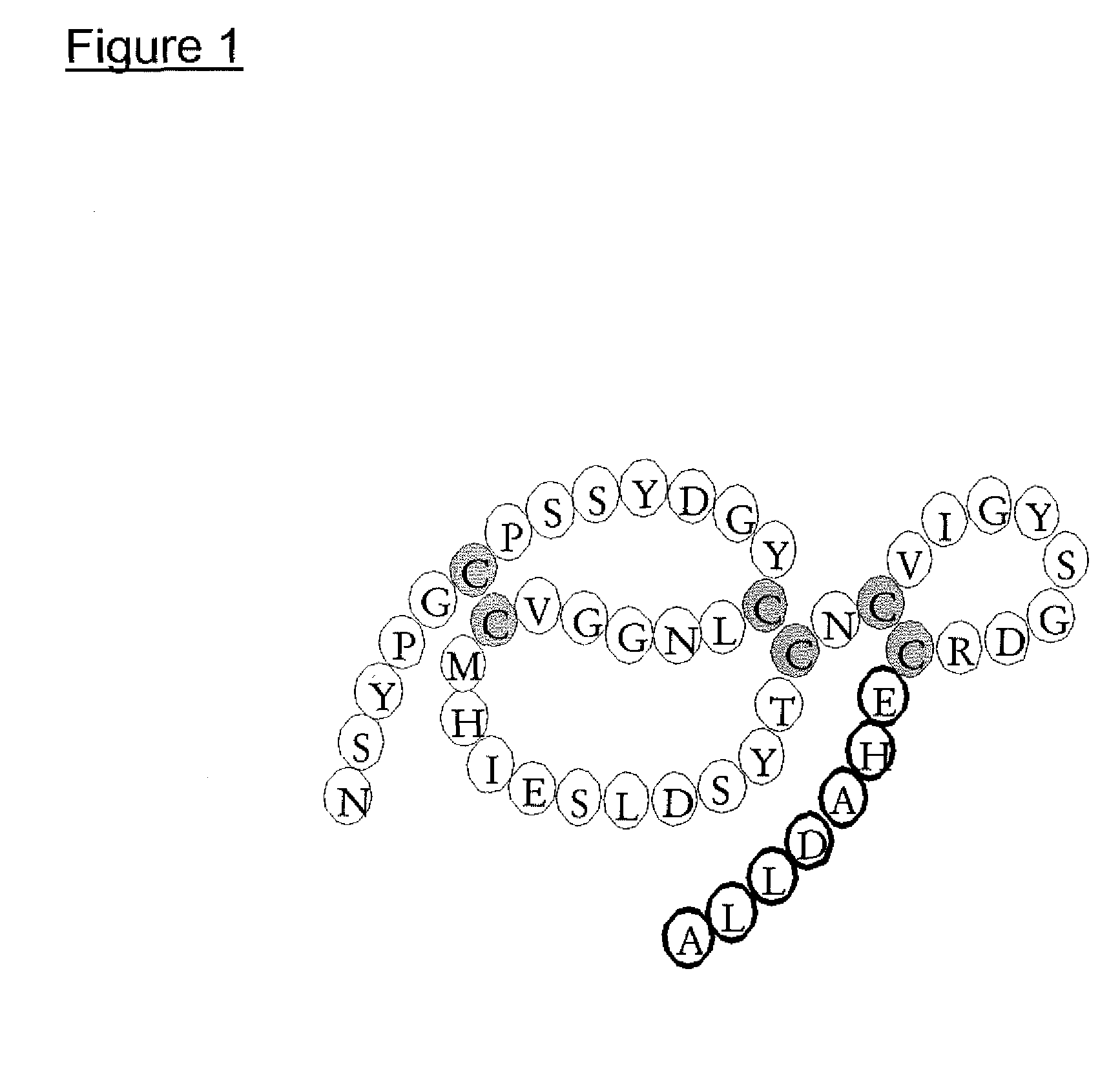
Method of using heparin binding motif for treating asthma
The present invention is for an isolated peptide consisting of the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 9 and using the peptide for treating asthma by reducing cytotoxicity of eosinophil derived toxins in bronchial epithelial cells of the subject suffers from asthma. The method comprises preparing a pharmaceutical composition having the peptide of SEQ ID NO: 9 and administering an effective amount of the composition to the subject.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method of using heparin binding motif for treating asthma
ActiveUS20120214730A1Increased IC5 valueLess cytotoxicHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsCytotoxicityEosinophil
The present invention is for an isolated peptide consisting of the amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO: 9 and using the peptide for treating asthma by reducing cytotoxicity of eosinophil derived toxins in bronchial epithelial cells of the subject suffers from asthma. The method comprises preparing a pharmaceutical composition having the peptide of SEQ ID NO: 9 and administering an effective amount of the composition to the subject.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Compounds, compositions, and methods for increasing cftr activity
ActiveUS20190308960A1High activityGroup 4/14 element organic compoundsSilicon compound active ingredientsMedicineCystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator
The present disclosure features disclosed compounds which can increase cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) activity as measured in human bronchial epithelial (hBE) cells. The present disclosure also features methods of treating a condition associated with decreased CFTR activity or a condition associated with a dysfunction of proteostasis comprising administering to a subject an effective amount of a disclosed compound.
Owner:PROTEOSTASIS THERAPEUTICS
Extraction method of glycyrrhiza polysaccharide and application
InactiveCN103073655ASmoking quality has no effectImprove survival rateTobacco preparationOrganic acidEthanol precipitation
The invention discloses an extraction method of glycyrrhiza polysaccharide and application. The glycyrrhiza polysaccharide is prepared by combining a high temperature organic acid method and ultrafiltration membrane treatment. The method comprises the steps of: smashing liquorice, and extracting with high temperature organic acid, ultrafiltration intercepting, concentrating and precipitating and separating by ethanol to obtain glycyrrhiza polysaccharide. The glycyrrhiza polysaccharide prepared by the invention is added to cigarettes by 0.05-0.2% of weight of cut tobacco, and the human bronchus epithelium BEAS-2B cell viability of a tobacco agglutinator of cigarettes obtained is remarkably higher than that of a blank sample, so that the glycyrrhiza polysaccharide has a positive effect.
Owner:乌鲁木齐天格尔农业科技开发有限公司
IncRNA application, kit and medicine
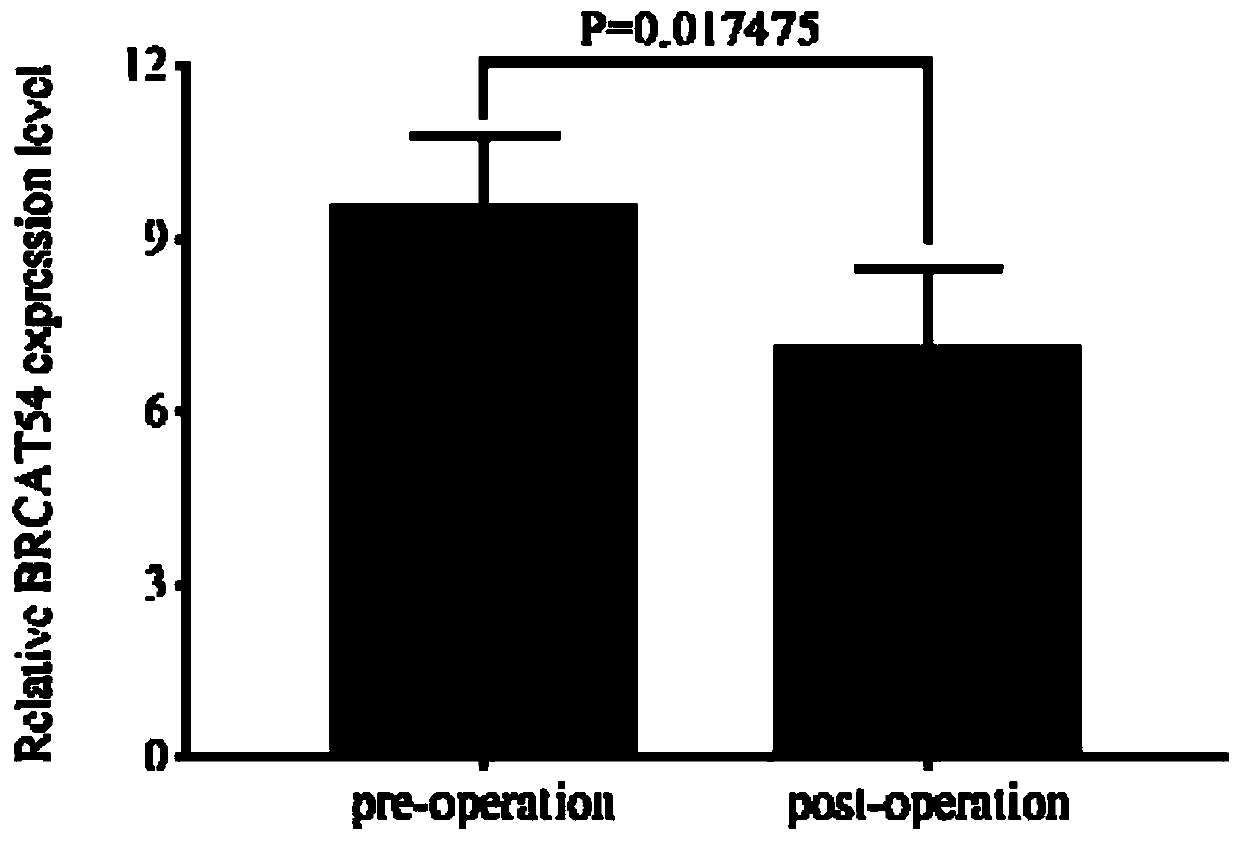
ActiveCN110358834ATumor suppressor activityOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular diagnostic techniquesBlood plasma
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular diagnosis, and particularly relates to IncRNA application, a kit and medicine. According to the application of IncRNA for preparing the kit for diagnosis and / or prognosis evaluation of NSCLC. The nucleotide sequence of the IncRNA is shown in SEQ ID No.1. The IncRNA is highly expressed in plasma before the NSCLC patient surgery, after the surgery, the expression level in the plasma is remarkably lowered, the expression levels in the NSCLC cancer tissue, the NSCLC patient plasma and the NSCLC cells are all remarkably higher than those ofpara-carcinoma tissue, healthy human plasma and normal bronchus epithelial cells. The study result suggests that the IncRNA has the remarkable capability for inhibiting the NSCLC cell tumor activity,and the IncRNA is newly found for tumor inhibition.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
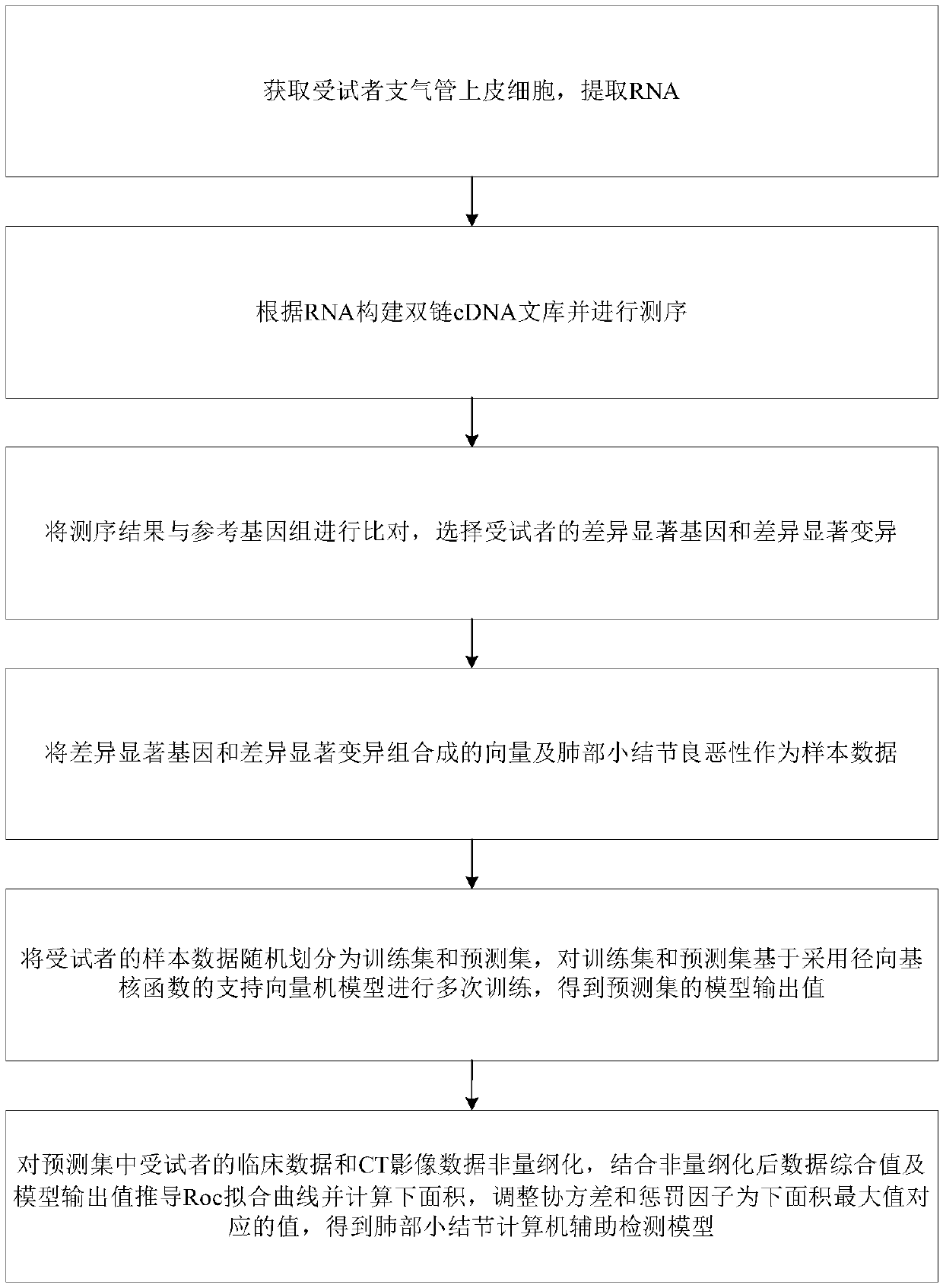
Method for constructing pulmonary nodule computer-aided detection model
PendingCN110819700ASave computing resourcesHigh-precision detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementPulmonary noduleCDNA library
The present invention discloses a method for constructing a pulmonary nodule computer-aided detection model. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining bronchial epithelial cells of a subjectand extracting RNA; constructing a double-stranded cDNA library according to the RNA and conducting sequencing; comparing a sequencing result with a reference genome and selecting a differential significant gene and a differential significant variation of the subject; using a vector formed by combining the differential significant gene and the differential significant variation, and benign and malignant pulmonary nodules as sample data; randomly dividing the sample data of the subject into a training set and a prediction set and carrying out multiple times of training on the training set andthe prediction set on the basis of a support vector machine model adopting a radial basis kernel function to obtain a model output value of the prediction set; and carrying out non-dimensionalizationon clinical data and CT image data of the subject in the prediction set, deducing a Roc fitting curve by combining a non-dimensionalized data comprehensive value and the model output value, calculating a lower area, and adjusting covariance and penalty factors to be the value corresponding to the maximum value of the lower area to obtain the pulmonary nodule computer-aided detection model.
Owner:上海朗曳医疗科技有限公司
Hempleaf groundsel herb phenolic acid ingredient as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108635391ALow impurity contentHigh purityAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticTherapeutic effectPhenolic acid
The invention provides a hempleaf groundsel herb phenolic acid ingredient as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The hempleaf groundsel herb phenolic acid ingredient is the ethanol washing part obtained by separating a hempleaf groundsel herb aqueous extract through D101 macroporous resin, and the total phenolic acid purity is 70.42-76.43%. The antioxidant, anti-inflammation andanti-bacterial capabilities of the hempleaf groundsel herb phenolic acid ingredient are evaluated through a chemical and biological method, and the result shows that the hempleaf groundsel herb phenolic acid ingredient has the outstanding treatment effect in a oxidative damage model of human bronchial epithelial cells. The hempleaf groundsel herb phenolic acid ingredient can be applied to treatment or auxiliary treatment of diversified human or animal bacteriosis, lung infection, cancers and various kinds of diseases such as systemic inflammation and oxidative stress caused by different reasons, and has the wide application prospects.
Owner:吉林益民堂制药有限公司 +1
Canine primary bronchial epithelial cell and application thereof in preparation of immortalized cells
ActiveCN104531607AHigh purityOvercome the disadvantage of very limited proliferative abilityArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsTelomeraseBeagle
The invention provides a canine primary bronchial epithelial cell and an application thereof in preparation of immortalized cells, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The canine primary bronchial epithelial cell is prepared by taking 45-day-old clean male beagles; separating canine tracheal tissues, cutting into pieces, adding collagenase and trypsin to digest, so as to obtain intact bronchiole tissues; cultivating the obtained cells, and further carrying out indirect immunofluorescence assay to detect keratin 18 expression, wherein an experiment proves that the canine primary bronchial epithelial cell is successfully obtained. A eukaryotic expression vector pEGFP-hTERT containing telomerase genes (hTERT) is built; after the canine primary bronchial epithelial cell is transfected, the hTERT gene is highly expressed; the bronchial epithelial cell can be stably subcultured for at least 20 generations. According to the canine primary bronchial epithelial cell provided by the invention, important biological materials are provided for research of infection mechanism of canine pathogens such as canine influenza viruses.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
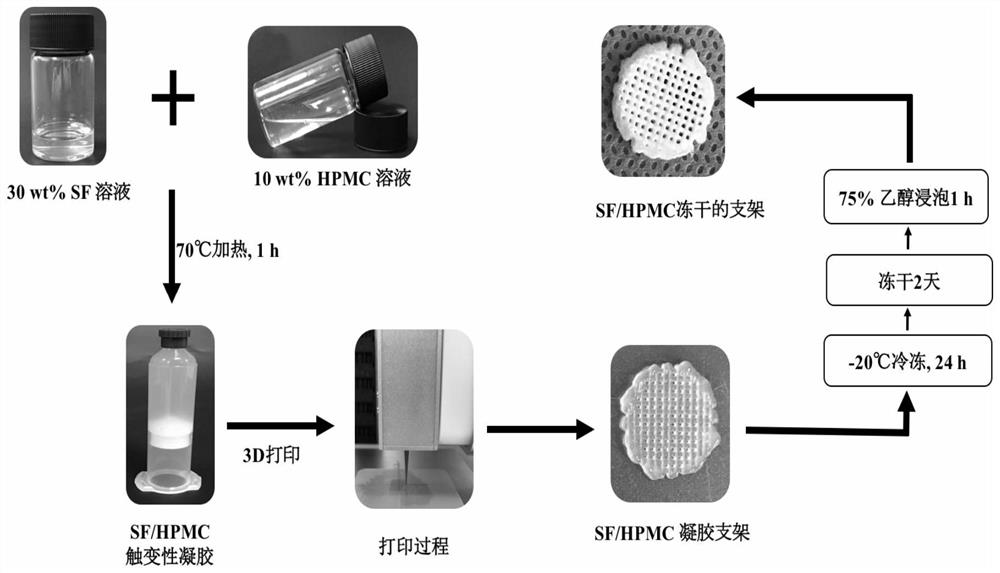
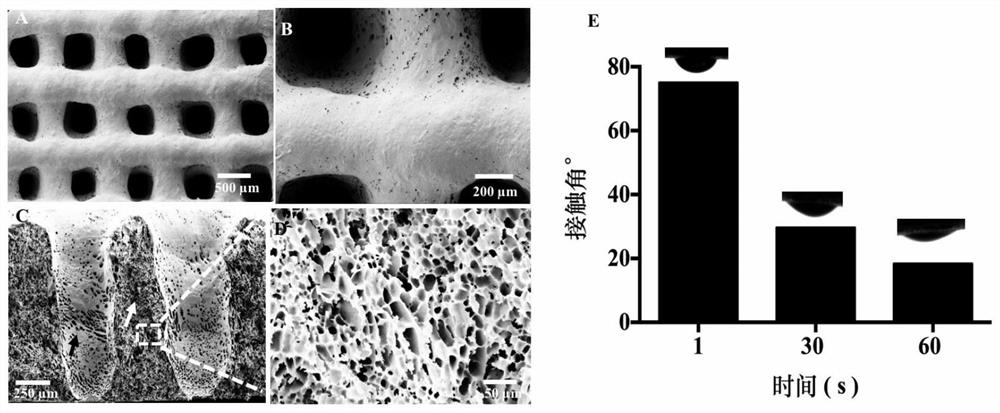
Silk fibroin 3D printing based biological scaffold and preparation method and application thereof
The invention belongs to the field of tissue engineering and medical materials, and relates to a silk fibroin 3D printing based biological scaffold suitable for bronchial mucosa epithelial growth anda preparation method thereof. The biological scaffold is characterized in that silk fibroin / hydroxypropyl carboxymethyl cellulose is adopted as a scaffold material, a 3D printing and freeze drying combined technology is adopted, a bronchial epithelial cell line (BEAS-2B cells) is used as seed cells, the BEAS-2B cells grow on a porous 3D printed silk fibroin / hydroxypropyl carboxymethyl cellulose scaffold, and then the 3D printed silk fibroin / hydroxypropyl carboxymethyl cellulose scaffold is obtained. The silk fibroin 3D printing based scaffold can be used for tracheal defect repair and can provide meaningful reference for development of tissue engineering artificial trachea.
Owner:AFFILIATED HUSN HOSPITAL OF FUDAN UNIV
Global gene expression analysis of human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke, smoke condensates, or components thereof
InactiveUS7727715B2Reduced potential to contributeReduced expression levelSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNicotiana tabacumBiomarker (petroleum)
Aspects of the present invention concern the identification of several methods to analyze the genes that are modulated in normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells after exposure to cigarette smoke condensates (CSC) or cigarette smoke (CS). Embodiments described herein include methods to identify a gene that is modulated in response to exposure to CSC or CS, methods to identify tobacco products that have a reduced potential to contribute to tobacco-related disease, methods to make tobacco products that have a reduced potential to contribute to a tobacco-related disease, methods to identify a subject's predilection to acquire a tobacco related disease, the use of particular genes as biomarkers for tobacco-related disease, and patterns of gene expression or genetic signatures that are unique to each particular tobacco product.
Owner:VECTOR TOBACCO LLC
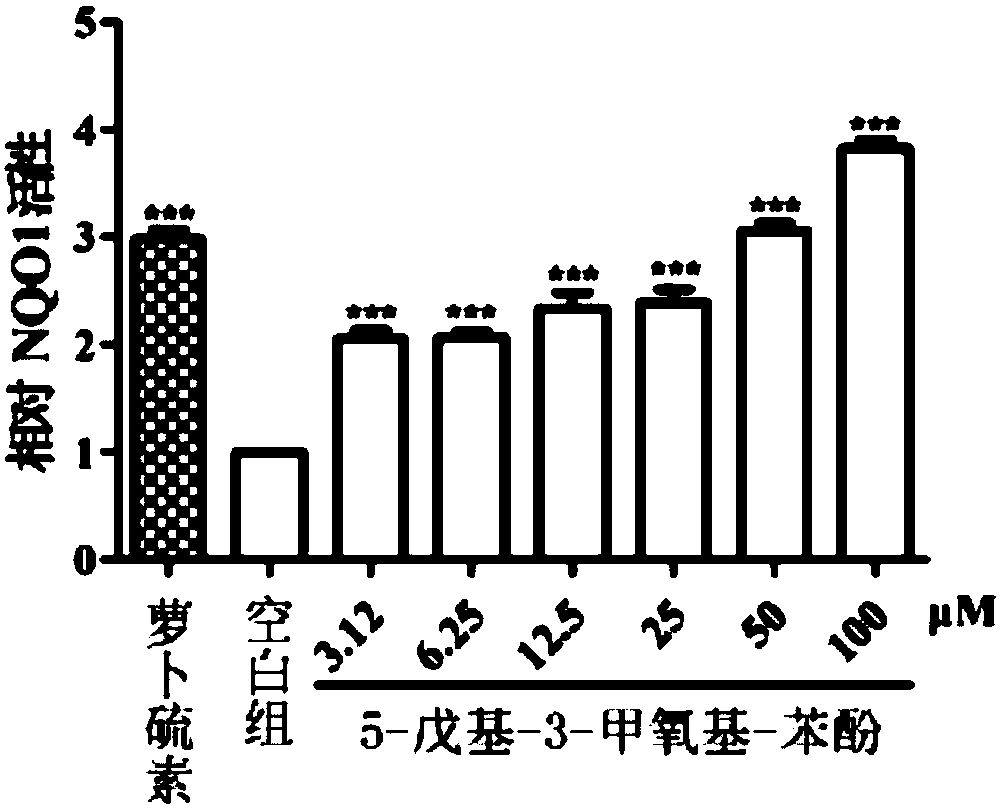
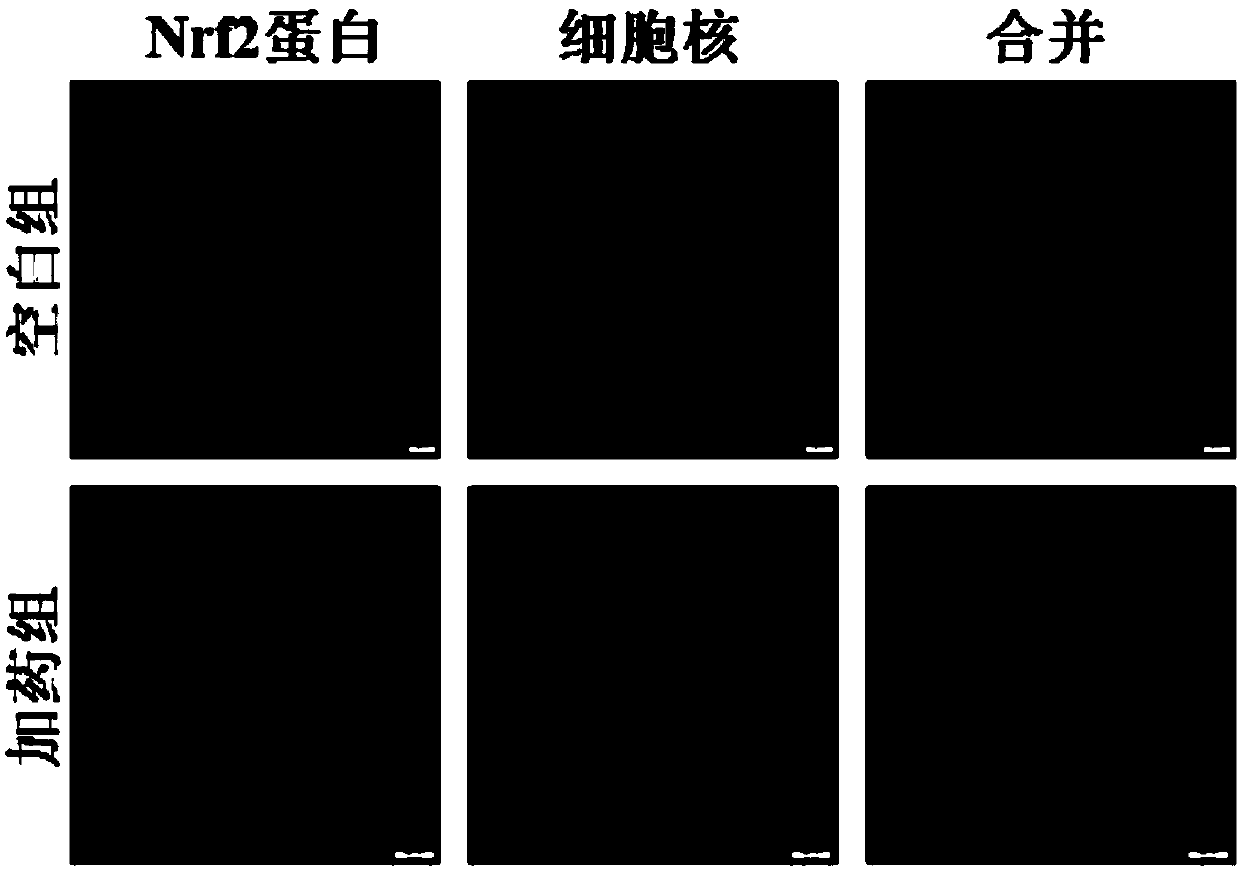
Application of 5-pentyl-3-methoxy-phenol to preparation of products for preventing and treating oxidative stress or inflammatory response induced diseases
The invention discloses an application of 5-pentyl-3-methoxy-phenol to preparation of products for preventing and treating oxidative stress or inflammatory response induced diseases. The chemical formula of 5-pentyl-3-methoxy-phenol is shown in the description. 5-pentyl-3-methoxy-phenol is an Nrf2 (nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2) signaling pathway agonist and an NF (nuclear factor)-kappa B signaling pathway inhibitor. 5-pentyl-3-methoxy-phenol can up-regulate the protein levels of Nrf2 as well as phase II detoxification enzyme NQO1 and antioxidant enzyme GCLM which are regulated by Nrf2, increase the level of glutathione as an endogenous antioxidant and inhibit generation of exogenous toxicant induced reactive oxygen species, and has a protective effect on exogenous toxicant induced oxidative damage to pulmonary bronchial epithelial cells, glomerular mesangial cells, human nerve cells and human breast cancer cells. 5-pentyl-3-methoxy-phenol can inhibit activation of an NF-kappa B signaling pathway, down-regulate inflammatory gene expression and inhibit LPS induced inflammatory response of macrophage RAW 264.7 of a mouse.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
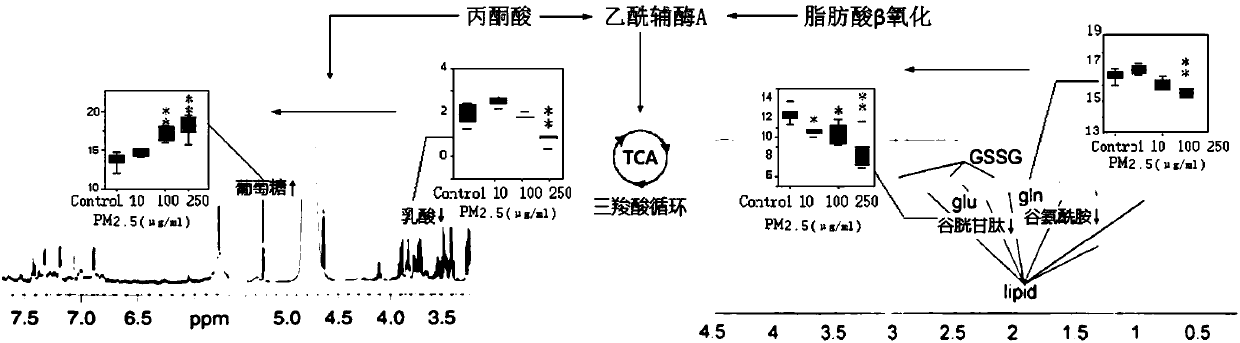
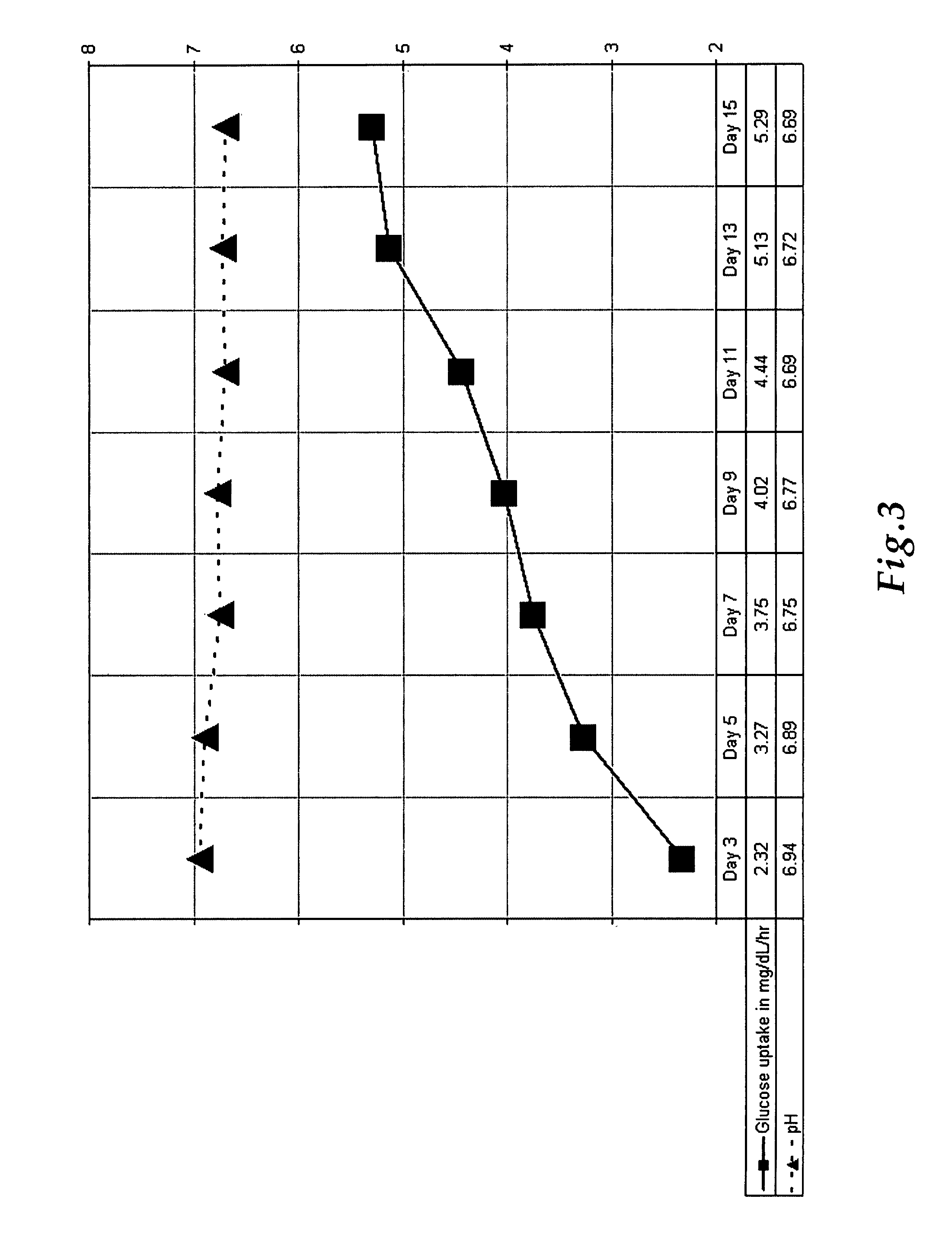
Method for evaluating effect of PM2.5 particles on free radical metabolic pathways in human lung cells
InactiveCN109839498AReflect the real situationIntuitive informationBiological testingMetaboliteOxygen
The invention discloses a method for evaluating an effect of PM2.5 full chemical component particles on free radical metabolic pathways in human lung cells. The method is characterized in that human lung-bronchial epithelial cells are exposed by means of the PM2.5 full chemical component particles, a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC- MS) can be used for effectively analyzing micromolecular metabolites in cells, enzymatic activity is quickly analyzed by combining with a biological detection method, and changes of the micromolecular metabolites related associated with intracellular free radical metabolism and activity changes of a rate-limiting enzyme that plays a key role in energy metabolism are integrated, in summary, a set of new methods for evaluating the interference on intracellular oxygen free radical metabolism after cells are exposed to toxic effect of exogenous pollution are constructed based on molecular biology. The method can analyze the influence of contaminantson the free radical metabolic pathways in the cells intuitively, and has the advantages of simple preprocessing method, rapid detection, good repeatability, comprehensive information acquisition andthe like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
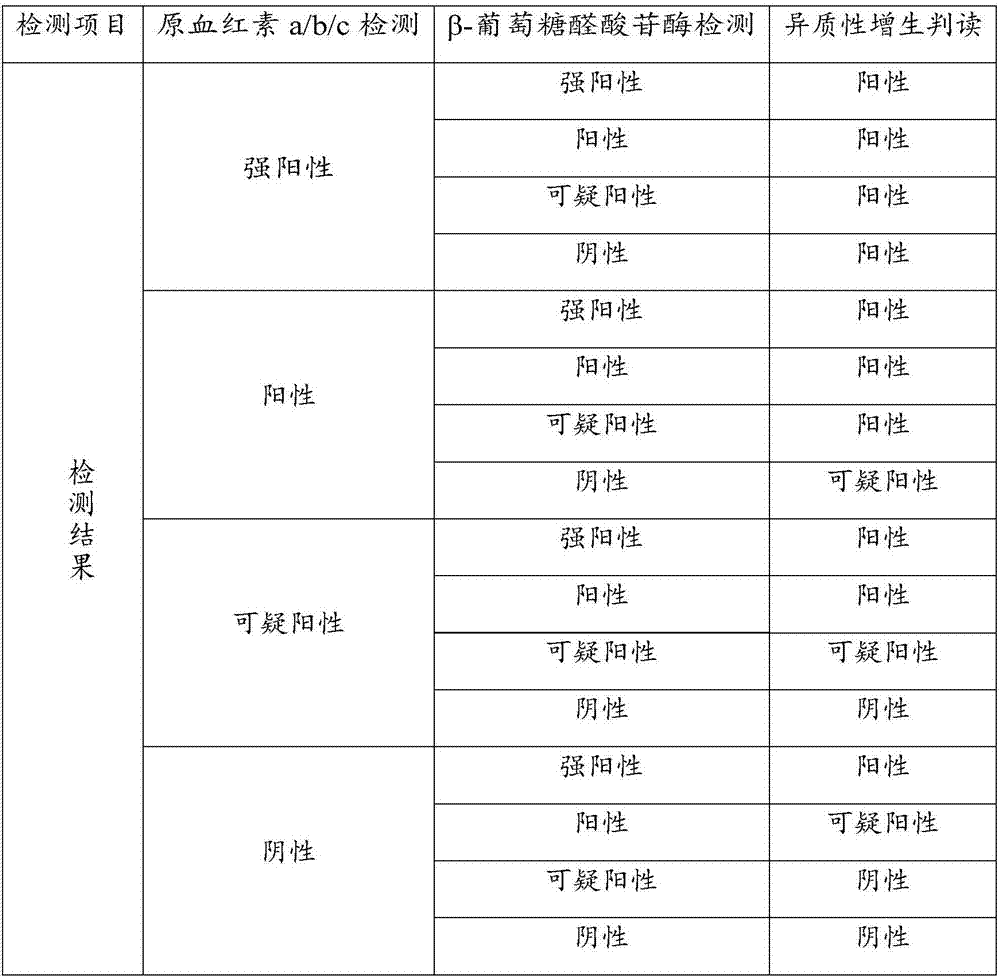
Application of protoheme and beta-glucuronidase in bronchial epithelial cell heterogeneity hyperplasia detection and kit
InactiveCN107044979AImprove accuracyIncreased sensitivityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorHemeBeta-glucuronidase
The invention discloses an application of protoheme and beta-glucuronidase in bronchial epithelial cell heterogeneity hyperplasia detection and a kit and belongs to the technical field of liquid biopsy pathology detection. The protoheme and the beta-glucuronidase are applied to the field of bronchial epithelial cell heterogeneity hyperplasia detection as associated markers for the first time, and people are surprised to find that the sensitivity, the specificity and the Youden index of detection employing the protoheme and the beta-glucuronidase as the associated markers are obviously improved in comparison with those of detection employing the protoheme or the beta-glucuronidase as the marker separately, so that the protoheme and the beta-glucuronidase are conducive to improvement of the accuracy of the diagnosis result on a lung cancer caused by bronchial epithelial cell heterogeneity hyperplasia as the associated markers.
Owner:山东瓦博格生物技术有限公司
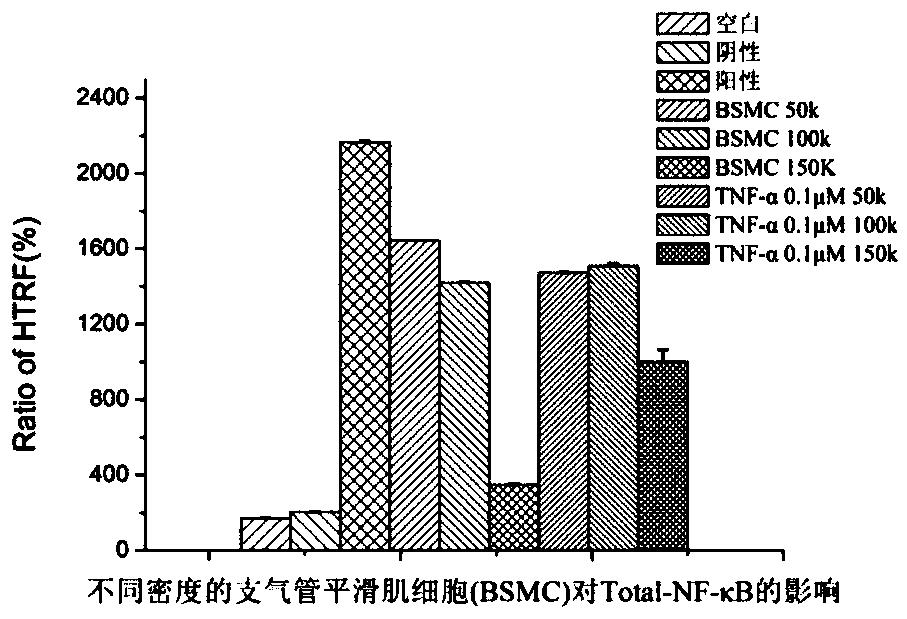
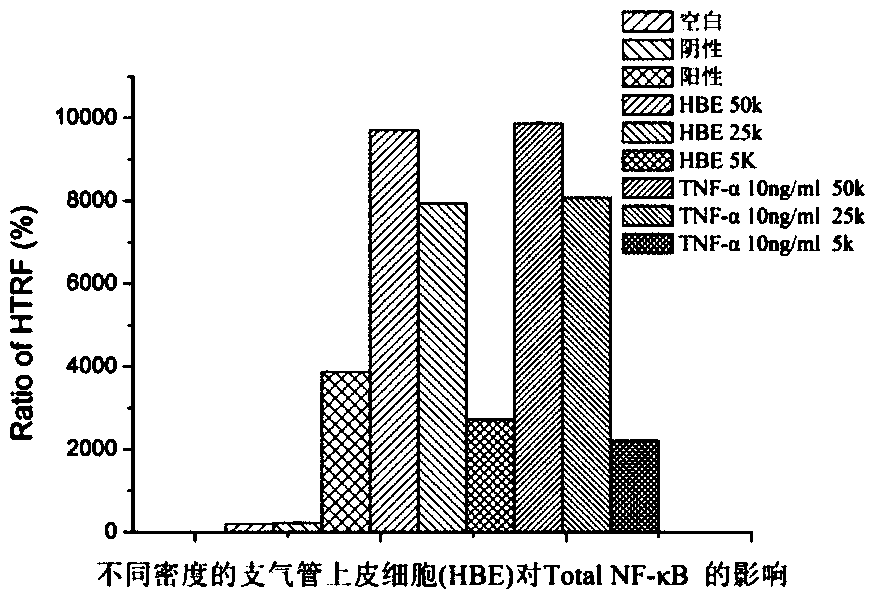
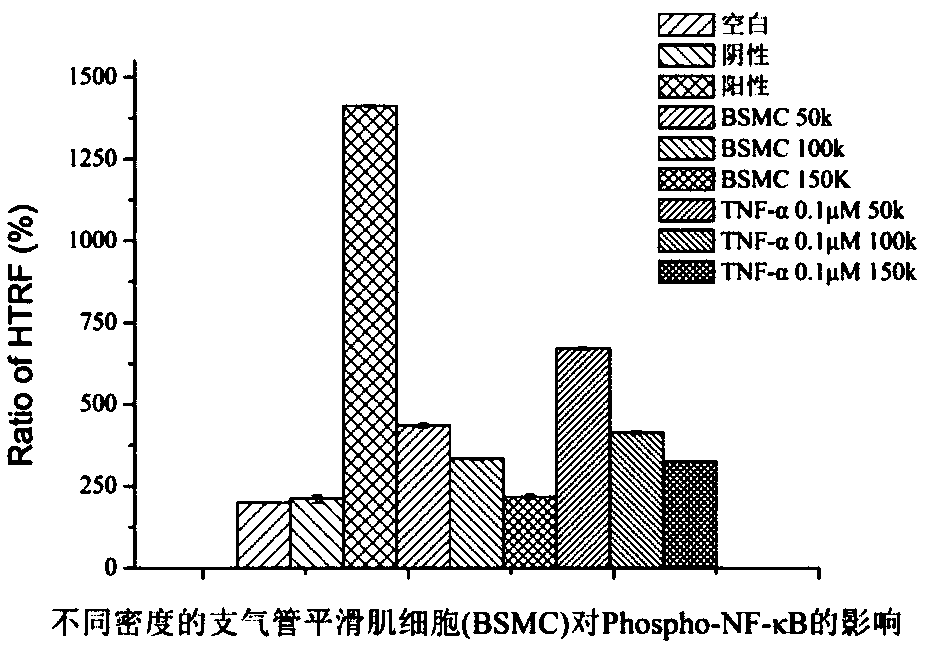
Preparation method of high-throughput airway inflammatory drug screening cell model based on NF-kappaB signaling pathway, and application of cell model
ActiveCN108998408AMicrobiological testing/measurementEpidermal cells/skin cellsSmooth muscleFluorescence
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-throughput airway inflammatory drug screening cell model based on an NF-kappaB signaling pathway, and an application of the cell model. The preparation method uses a bronchial smooth muscle cell or a bronchial epithelial cell as a source cell, NF-kappaB in the cell is activated by a stimulating factor, and the total NF-kappaB ratio and the phosphorylated NF-kappaB ratio in the cell are detected by a homogeneous time-resolved fluorescence technique to obtain the phosphorylation level of NF-kappaB; and parameters are adjusted to make a ratioof the phosphorylation level of NF-kappaB in a model group cell to the phosphorylation level of NF-kappaB in a normal group cell be equal to or more than 1.2 in order to obtain the cell model. The inflammatory cell model is constructed by screening the influences of the type and the density of the cell and the type, the concentration and the stimulation time of the stimulating factor on the phosphorylation of NF-kappaB and detecting the phosphorylation level of NF-kappaB in the cell through an HTRF technology, so a basis is provided for screening and studying of airway inflammation drugs.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACAD OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Global gene expression analysis of human bronchial epithelial cells exposed to cigarette smoke, smoke condensates, or components thereof
InactiveUS20100273171A1Reduced potential to contributeReduced expression levelMicrobiological testing/measurementNicotiana tabacumTobacco product
Aspects of the present invention concern the identification of several methods to analyze the genes that are modulated in normal human bronchial epithelial (NHBE) cells after exposure to cigarette smoke condensates (CSC) or cigarette smoke (CS). Embodiments described herein include methods to identify a gene that is modulated in response to exposure to CSC or CS, methods to identify tobacco products that have a reduced potential to contribute to tobacco-related disease, methods to make tobacco products that have a reduced potential to contribute to a tobacco-related disease, methods to identify a subject's predilection to acquire a tobacco related disease, the use of particular genes as biomarkers for tobacco-related disease, and patterns of gene expression or genetic signatures that are unique to each particular tobacco product.
Owner:VECTOR TOBACCO LLC
Composition for the prevention and treatment of allergic inflammatory disease
Disclosed herein is a composition for the treatment and prevention of allergic inflammatory diseases comprising N-hydroxy-4-{5- [4- (5-isopropyl-2-methyl-l, 3-thiazol-4- yl)phenoxy]pentoxy}-benzamidine, 4-{5- [4- (5-isopropyl-2- methyl-1, 3-thiazol-4-yl)phenoxy]pentoxy}-benzamidine or pharmaceutically acceptable salts. The composition exhibits excellent medicinal effects on allergic inflammatory diseases, with a great reduction in typical chronic inflammation symptoms, such as an increase of eosinophil level in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, total leukocyte level and eosinophil level in blood, the hypertrophy or hyperplasia of bronchial epithelium due to an increase in the number of mucus cells, a reduction in alveolar surface area resulting from the hypertrophy of alveolar walls, and the infiltration of inflammatory cells.
Owner:DONG WHA PHARM CO LTD
Method for preparing pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20160215258A1Reduce riskLarge scaleSkeletal/connective tissue cellsUnknown materialsInduced pluripotent stem cellHuman hepatocyte
An object of the present invention is to provide a method capable of inexpensively and conveniently preparing cells having pluripotency and a very low risk of tumorigenic transformation. The cells having pluripotency and a very low risk of tumorigenic transformation can be prepared by suspension-culturing mammalian mesenchymal stem cells such as human mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow (hMSC-BM) and human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells (hAT-MSC) (also referred to as “human adipose-derived stem cells [hADSC]”), 7 types of human adherent mature cells (human hepatocyte cells [hHEP cells], human umbilical vein endothelial cells [HUVEC cells], human dermal lymphatic microvascular endothelial cells [HMVEC cells], human epidermal keratinocyte cells [NHEK cells], human bronchial epithelial cells [NHBE cells], human melanocyte cells [NHEM cells], and human smooth muscle cells [UASMC cells]), and 3 types of human adherent precursor cells (human dermal fibroblast cells [NHDF cells], human skeletal muscle myoblast cells [HSMM cells], and human osteoblast cells [NHOst cells]) to form cell masses (spheroids).
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM FAB INC
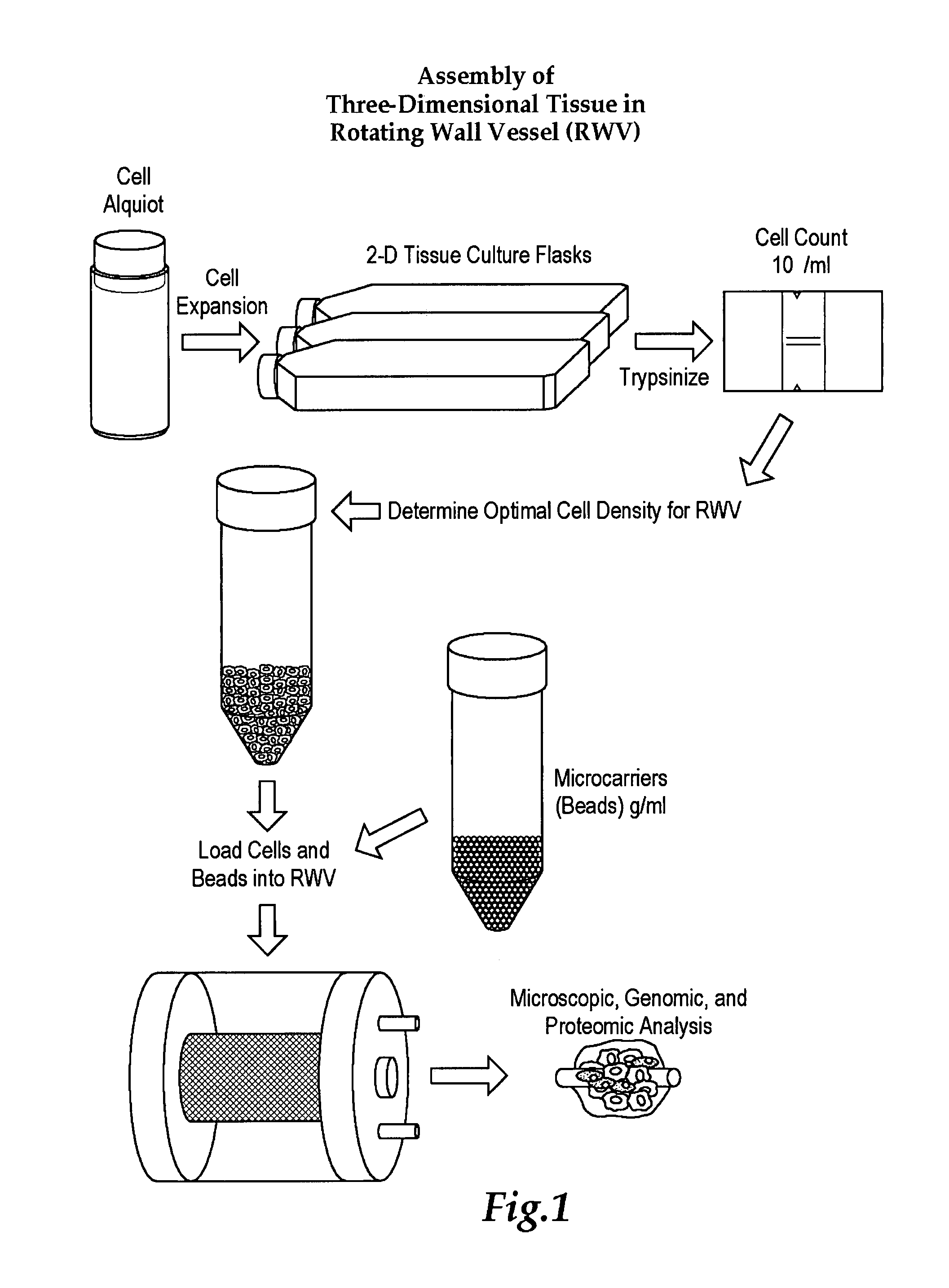
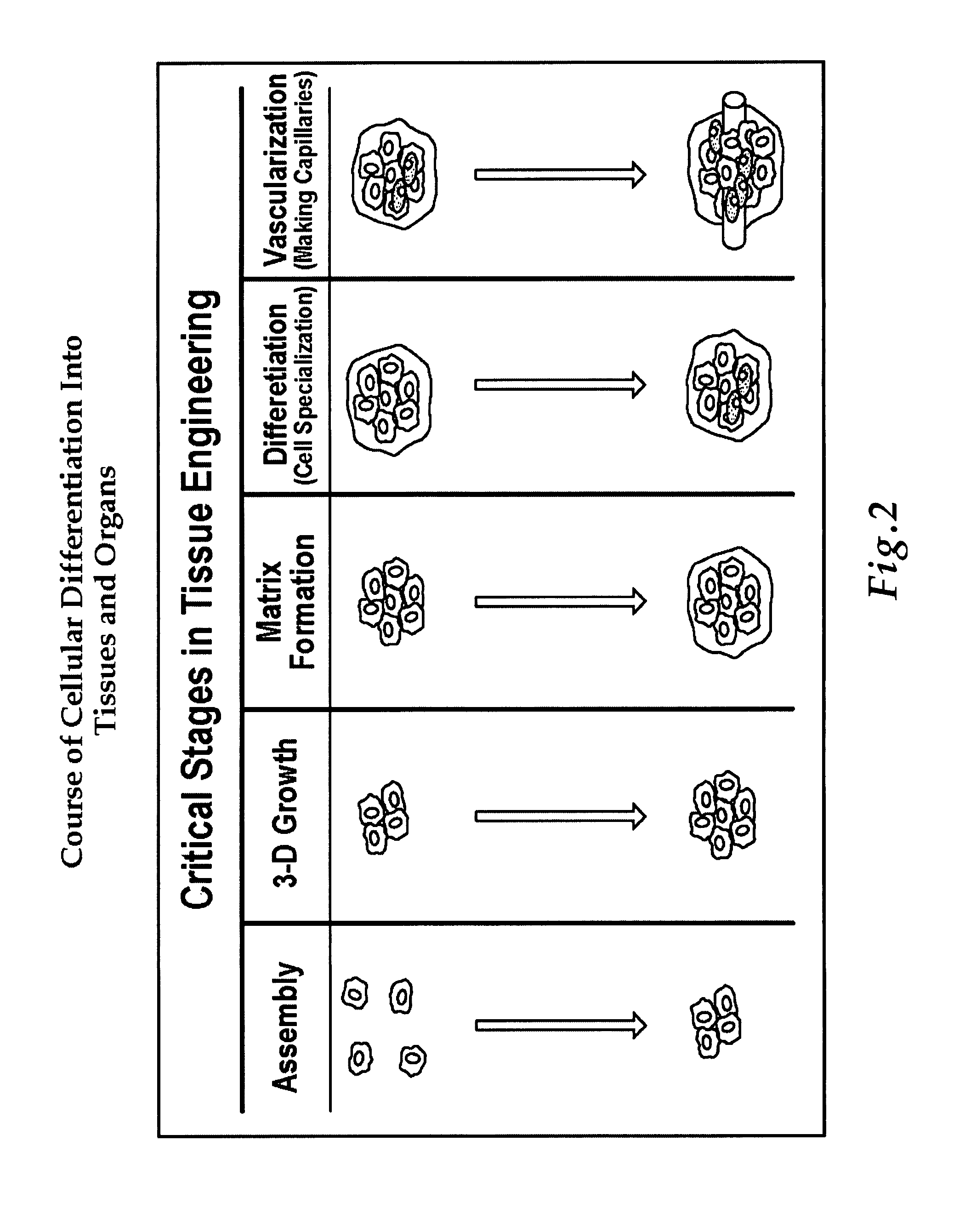
Engineered human broncho-epithelial tissue-like assemblies
ActiveUS8338114B1Promote rapid developmentEfficient responseMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture processCytotoxicityBronchial epithelium
Three-dimensional human broncho-epithelial tissue-like assemblies (TLAs) are produced in a rotating wall vessel (RWV) with microcarriers by coculturing mesenchymal bronchial-tracheal cells (BTC) and bronchial epithelium cells (BEC). These TLAs display structural characteristics and express markers of in vivo respiratory epithelia. TLAs are useful for screening compounds active in lung tissues such as antiviral compounds, cystic fibrosis treatments, allergens, and cytotoxic compounds.
Owner:NASA
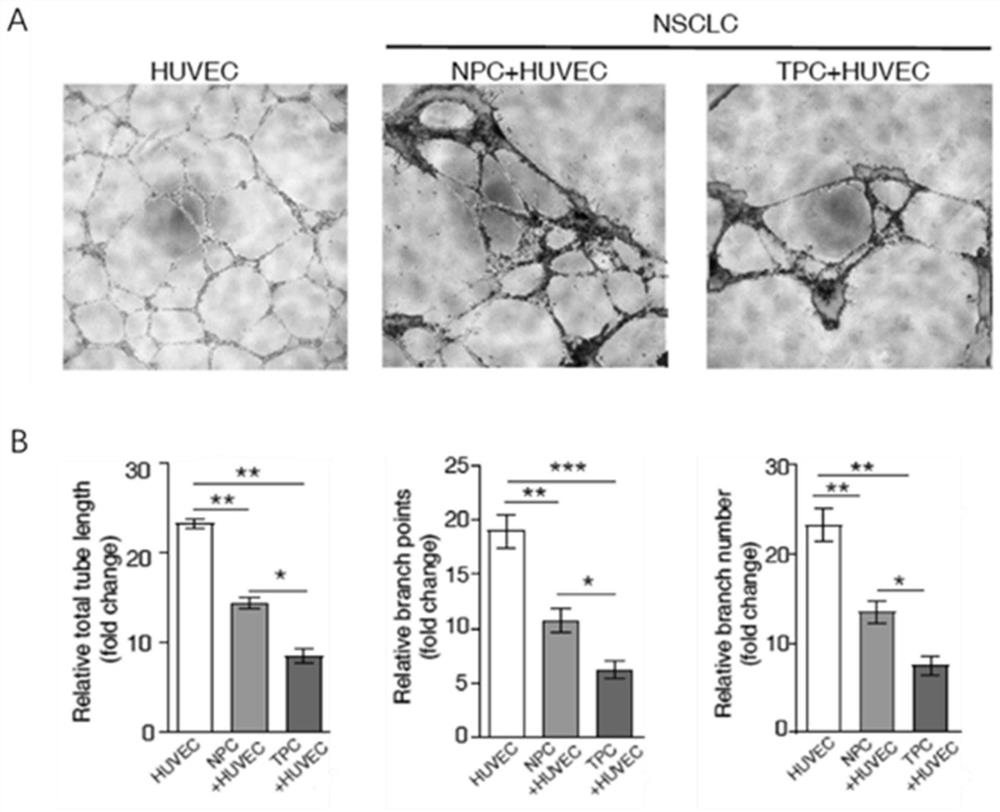
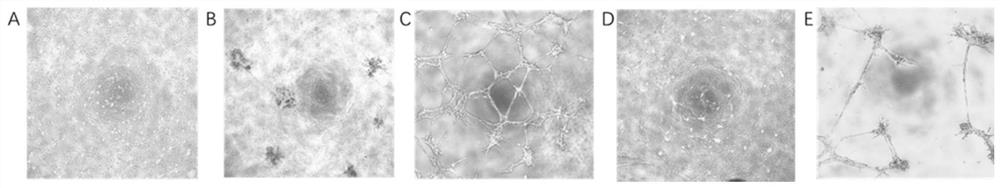
Construction method of endothelial cell and pericyte co-culture model for researching tubulation
ActiveCN113308434AFunction increaseAccurately Test Preclinical EffectivenessCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsHuman tumorStaining
The invention discloses a construction method of an endothelial cell and pericyte co-culture model for researching tubulation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) digesting umbilical vein endothelial cells with trypsin to obtain umbilical vein endothelial single cells; (2) digesting pericytes into single cells of the pericytes by using trypsin, and then adding CFSE dye with the final concentration of 2-10 [mu]mol / L for staining to obtain stained pericytes; and (3) uniformly mixing the umbilical vein endothelial single cells and the stained pericytes according to the cell number ratio of (5-20):1, conducting culturing by using a bronchial epithelial cell culture medium, and observing the formation condition of the tube on a fluorescence microscope. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the influence of pericytes on the formation of endothelial cell tubes can be dynamically observed through a fluorescence microscope, the effect of human tumor pericytes on tumor blood vessels can be reflected through in-vitro experiments, and the method has good social and economic values.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Composition for Preventing or Treating Asthma Comprising Fatty Acid as Active Ingredient
InactiveUS20200246298A1Reasonable benefit/risk ratioAlleviating and preventing asthmaRespiratory disorderAnhydride/acid/halide active ingredientsWhite blood cellTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to a composition for preventing or treating asthma, having, an active ingredient, a saturated or unsaturated fatty acid having 12 to 22 carbon atoms. The saturated or unsaturated fatty acid functions to inhibit or eliminate various asthma symptoms induced by ovalbumin. Specifically, the fatty acid inhibits the proliferation of leukocytes, neutrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes in BALF and serum, inhibits the proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells, reduces mucus in bronchioles, and reduces infiltration of inflammatory cells around bronchioles and blood vessels in a dose-dependent manner. Also, the fatty acid induces a decrease in the expression of IFN-γ, IL-12p40, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13 and TNF-α, which are Th2 cell-related cytokines. Therefore, the fatty acid overcomes the side effects of current asthma therapeutic agents, has an excellent therapeutic effect without having toxicity, and may advantageously be used as a composition for preventing, treating or alleviating asthma.
Owner:DONGSHIN UNIV IND ACAD COOPERATION
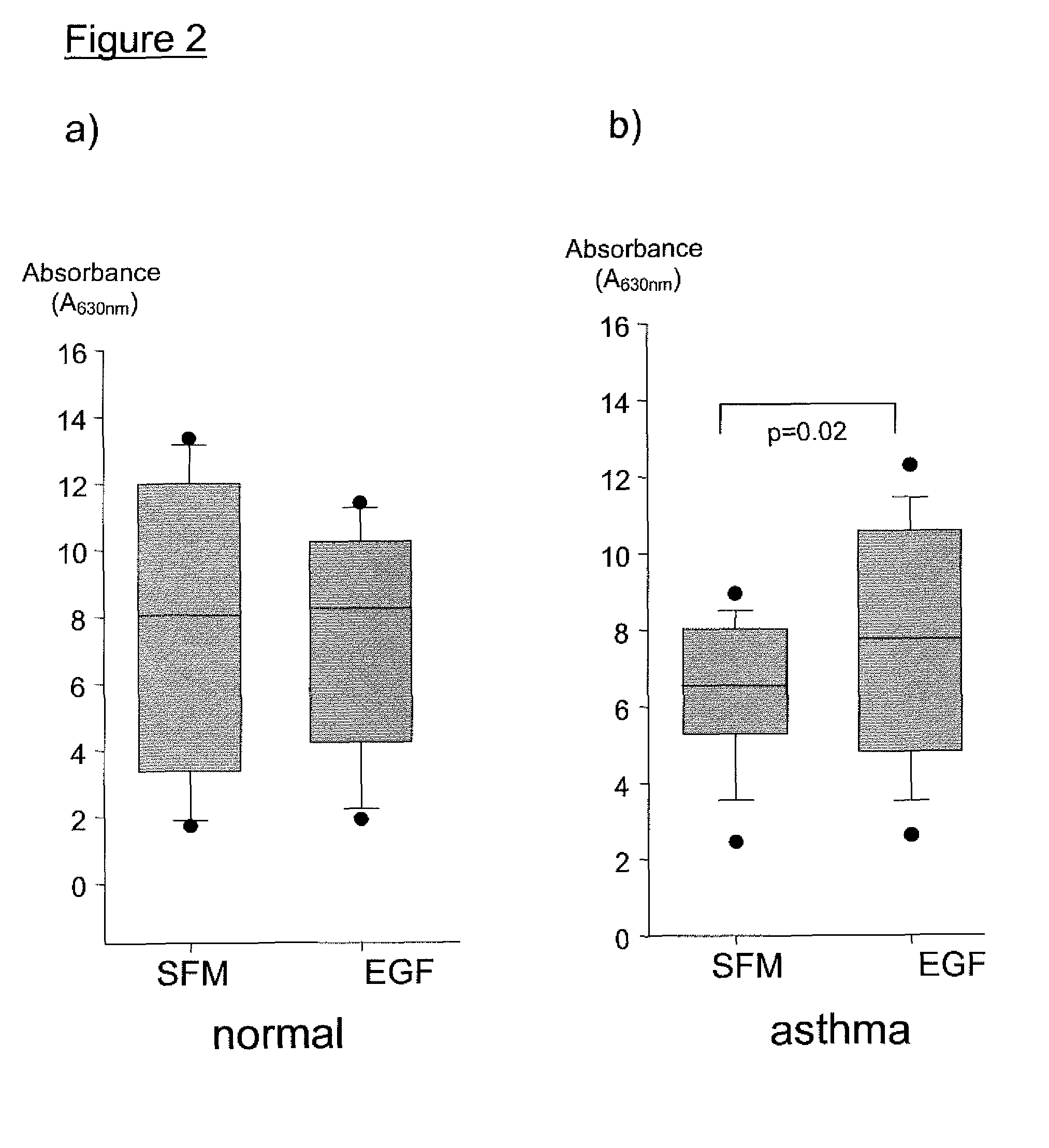
Growth Factor Treatment for Asthma
InactiveUS20080070838A1Extended half-lifePromote repairPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementFibroblastBronchial epithelium
The present invention relates to use of epidermal growth factor (EGF) analogues to treat, or protect from, bronchial epithelium damage in asthma patients. Suitable such analogues target the EGF receptor and exhibit ability to promote in asthma patients preferential proliferation of bronchial epithelial cells compared to airway fibroblasts.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
tRNA-derived fragment (tRF) related to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and application of tRF
ActiveCN110468134APromote tumor activityHas anti-cancer application valueOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementMolecular diagnostic techniquesNucleotide
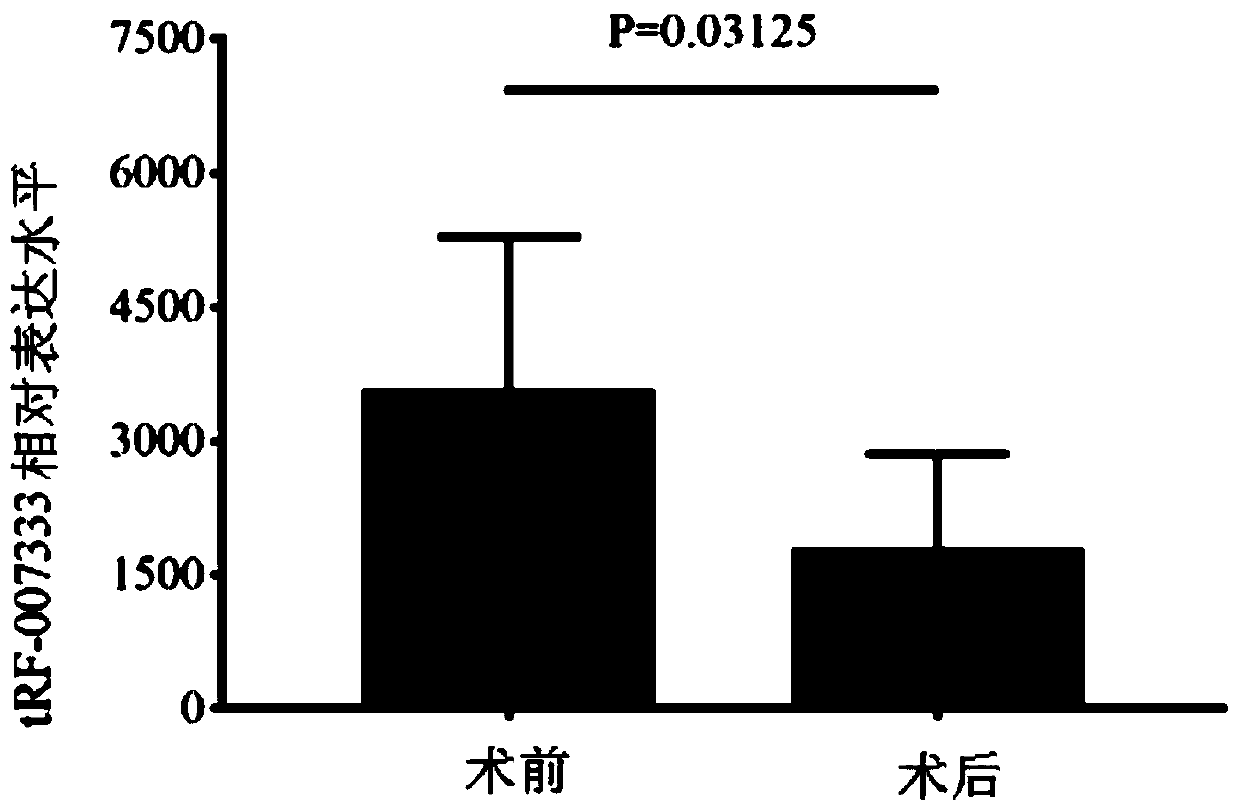
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular diagnosis, and particularly relates to a tRNA-derived fragment (tRF) related to non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and application of the tRF.Through experimental analysis, the tRF (AS-tDR-007333, the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID No.1) is significant in cancer-promoting activity, and the expression of the tRF in NSLC tissue, in plasma of NSCLC patients and in NSLC cells is significantly higher than that of the tRF in para-carcinoma tissue, healthy human plasma and normal bronchial epithelial cells. The results show that the tRF has the ability to significantly promote the tumor activity of NSCLC cells; and the expression of the tRF is inhibited to significantly inhibit the proliferation of the NSCLC cells.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Application of human GRK5 genes
ActiveCN108245686APrevent proliferationInhibit migrationAntineoplastic agentsGene therapyCancer cellTreatment targets
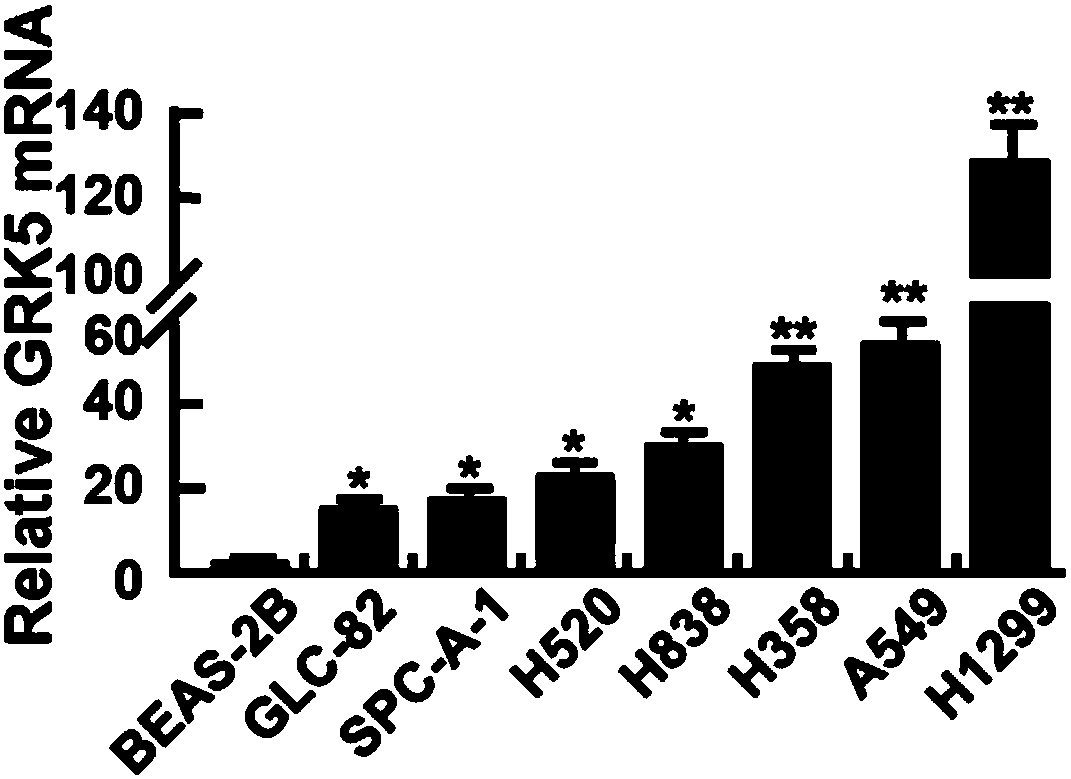
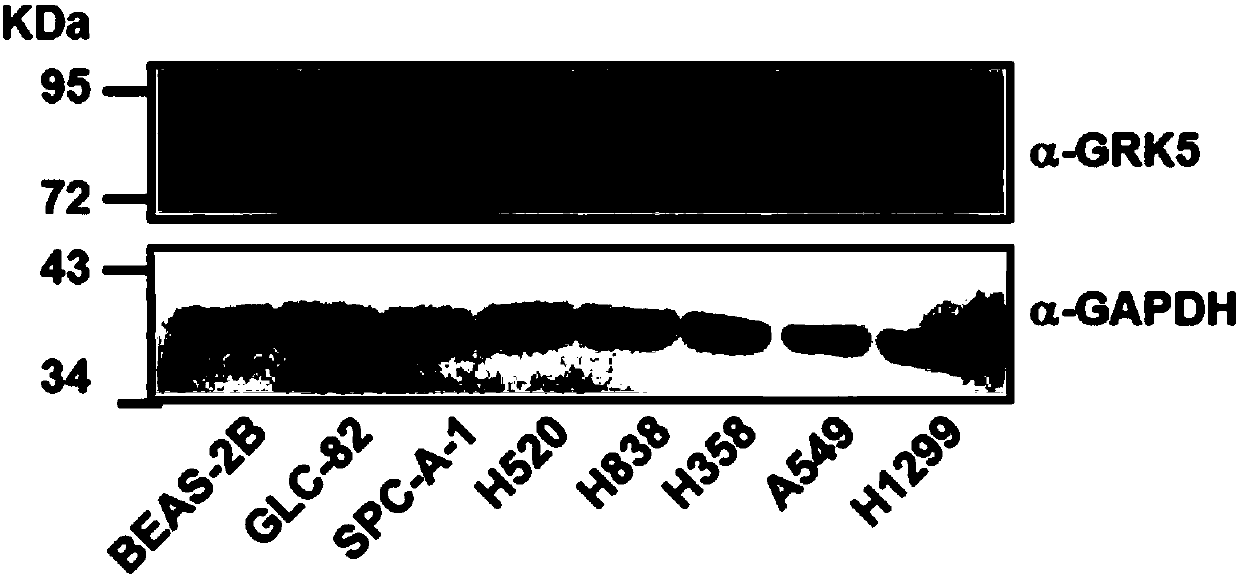
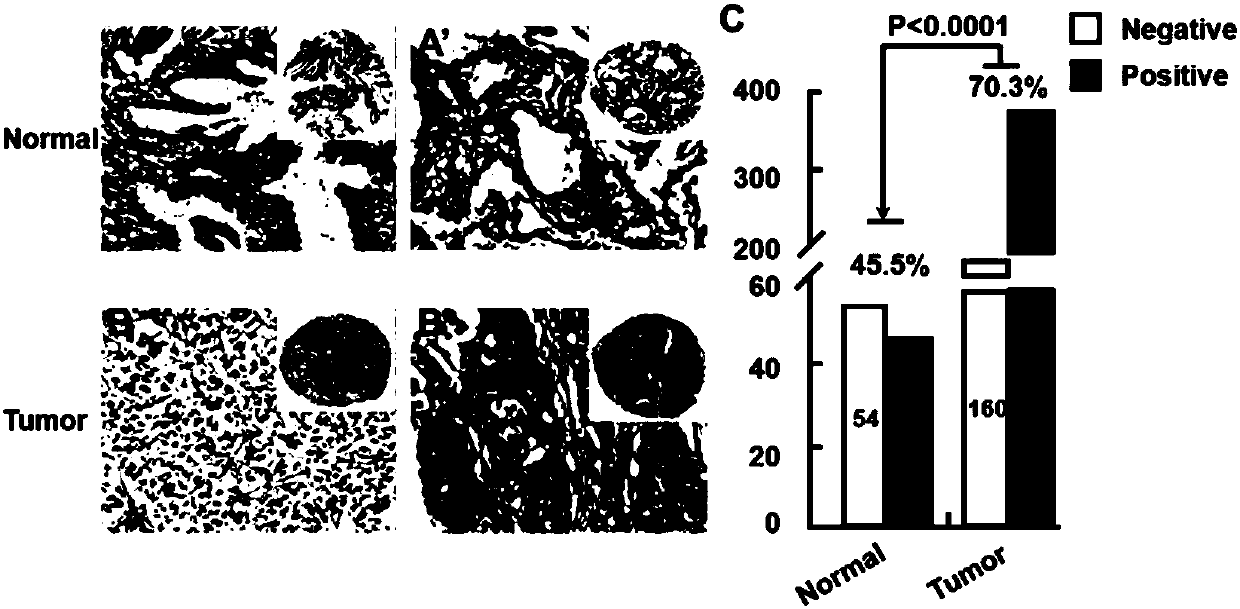
The invention discloses application of human GRK5 genes, namely application of human GRK5 genes serving as cancer cell specified action targets in preparation of drugs for treating non-small cell lungcancer. The cancer cell specified action targets are RNA interference effect targets. Compared with normal pulmonary bronchial epithelial cells, the GRK5 genes have high expressions in the non-smallcell lung cancer cells; RNA interfering lentivirus designed aiming at the GRK5 genes can inhibit GRK5 expression and is capable of obviously inhibiting proliferation of the non-small cell lung cancercells, blocking tumor cell division at a G2 / M phase, promoting cells apoptosis, inhibiting cell migration and inhibiting formation of xenograft tumor in nude mice, and the aim of treating the non-small cell lung cancer can be further achieved. The human GRK5 genes can serve as treatment targets of the non-small cell lung cancer, and provide wide prospects for developing medicines in treatment of the non-small cell lung cancer based on the GRK5 genes in future.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
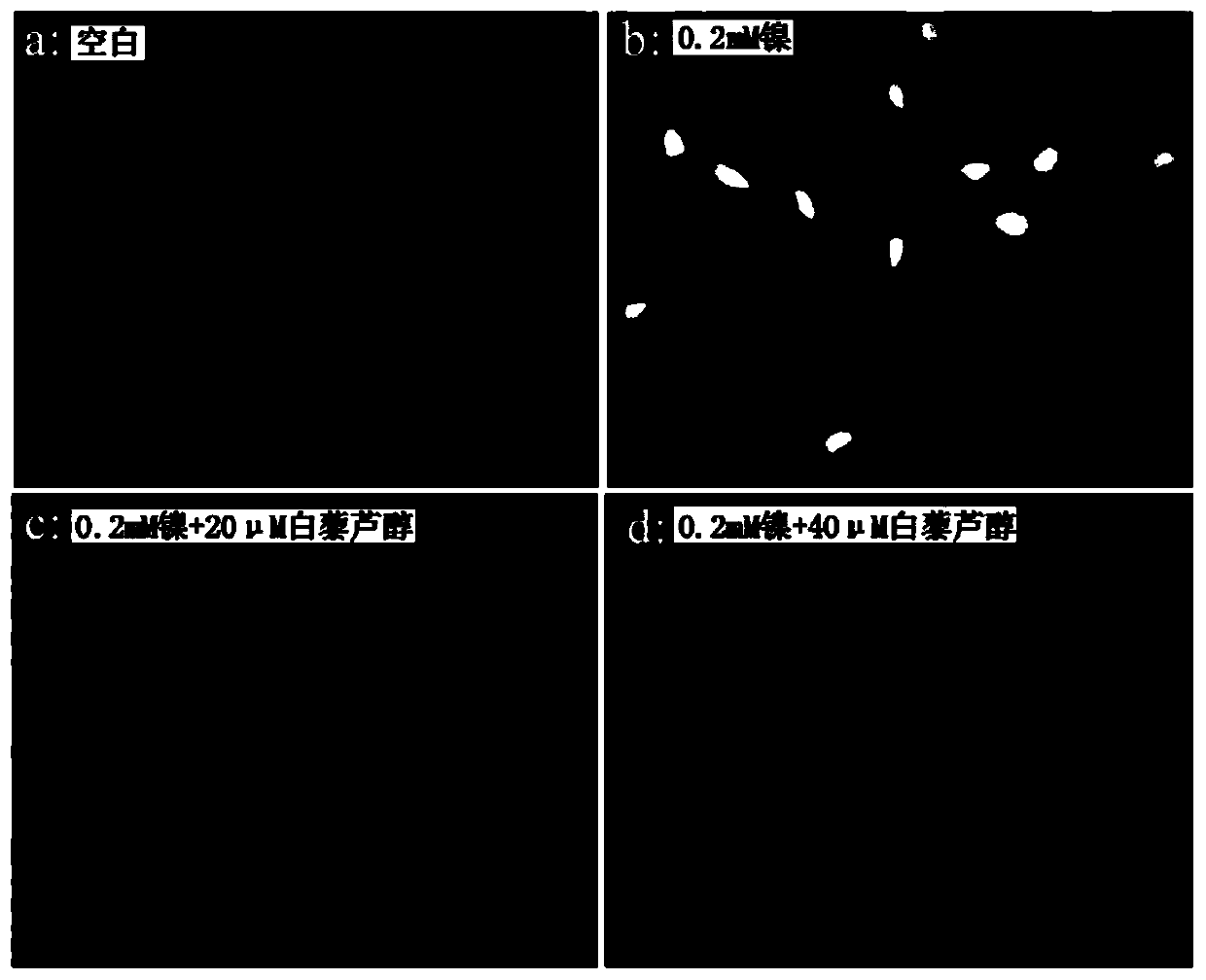
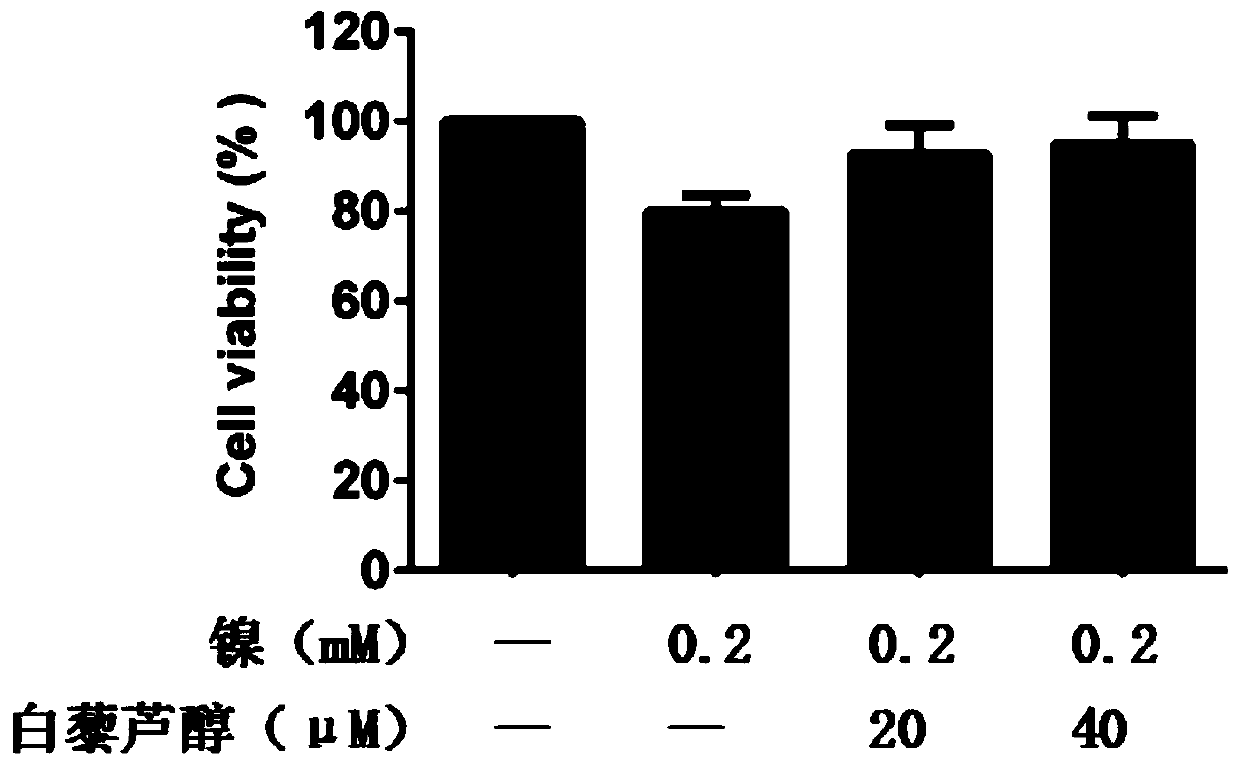
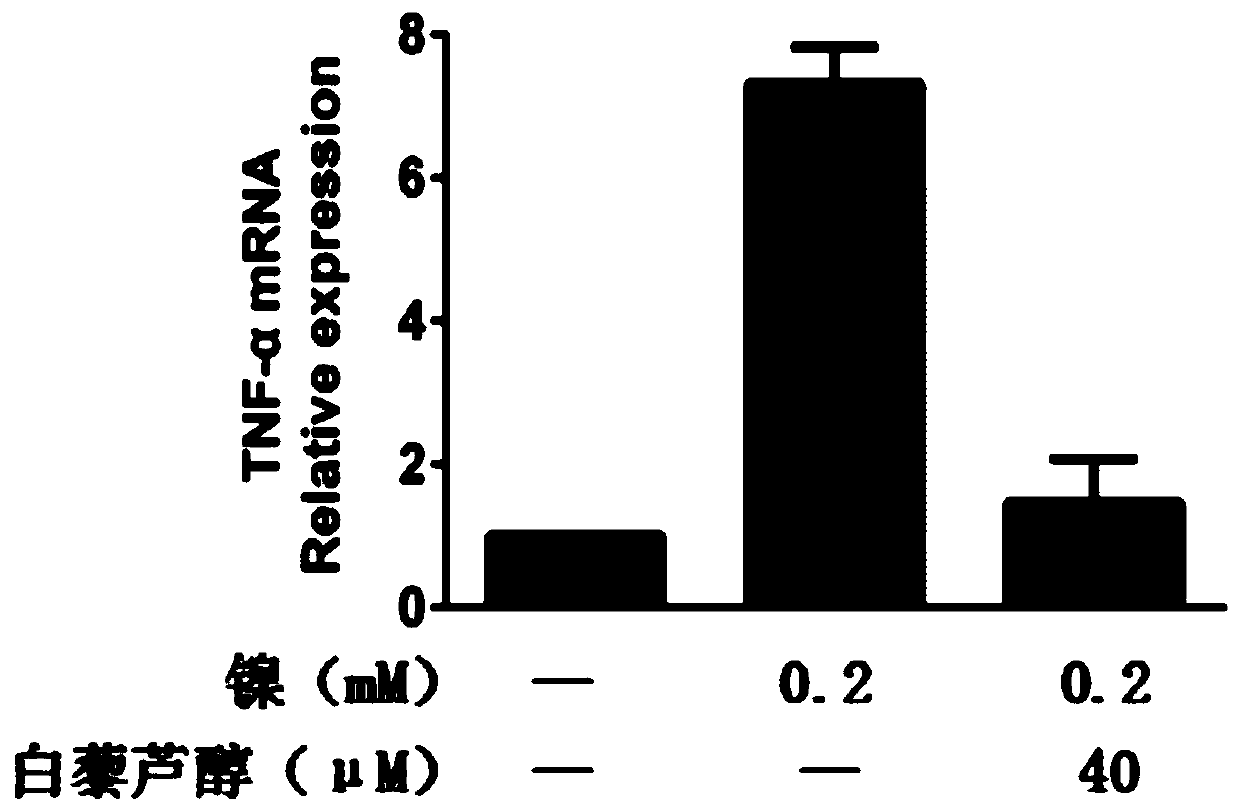
Application of resveratrol in preparation of drugs for treatment of human bronchial epithelial cell injury
InactiveCN109820841AAvoid damageHydroxy compound active ingredientsRespiratory disorderObserved SurvivalRectal epithelium
The invention discloses the application of resveratrol in preparation of drugs for treatment of human bronchial epithelial cell injury. The resveratrol has a significant effect on ensuring the survival rate of human bronchial epithelial cells induced by divalent nickel ions, and can inhibit the cell damage induced by the divalent nickel ions by regulating the formation of reactive oxygen species clusters. The invention provides a new idea for the application of resveratrol in the prevention and treatment of the human bronchial epithelial cell injury induced by heavy metals.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com