Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94 results about "Pericyte" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
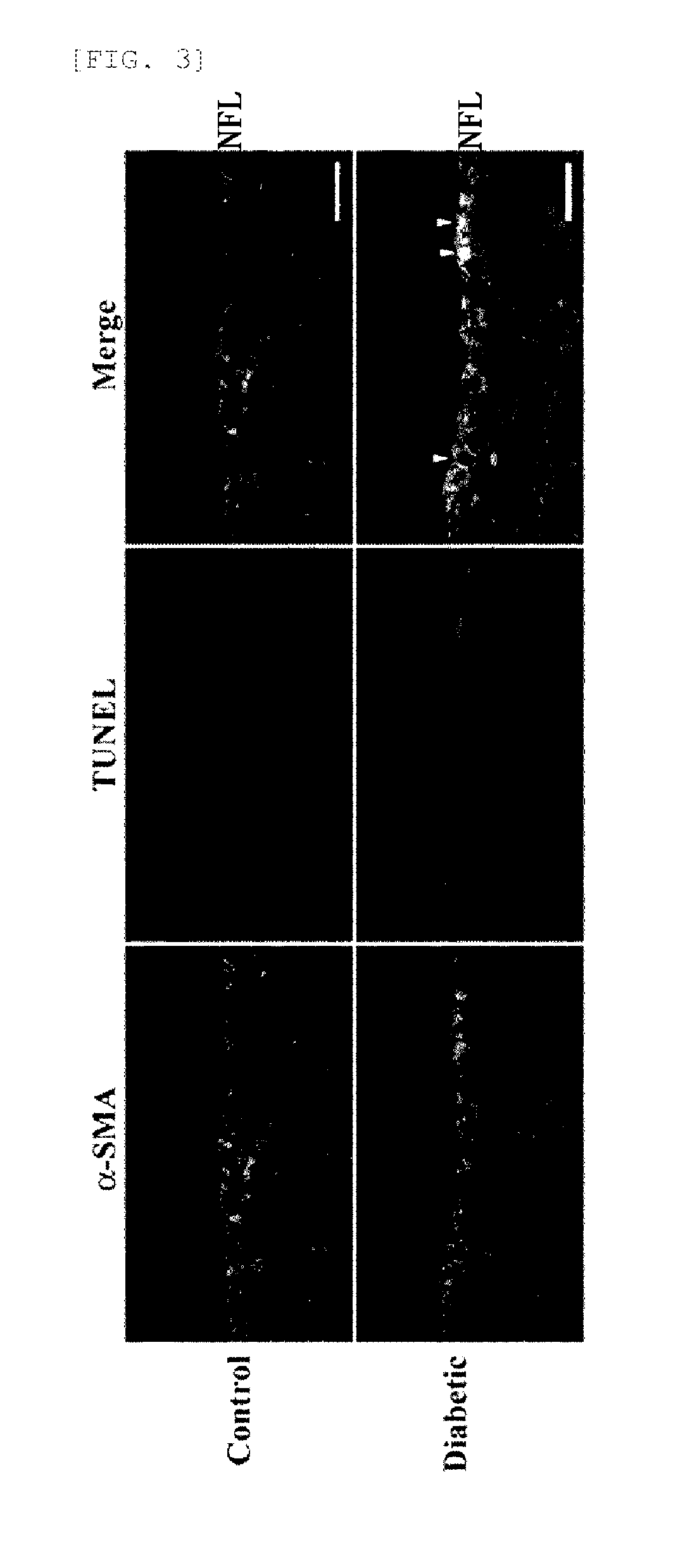
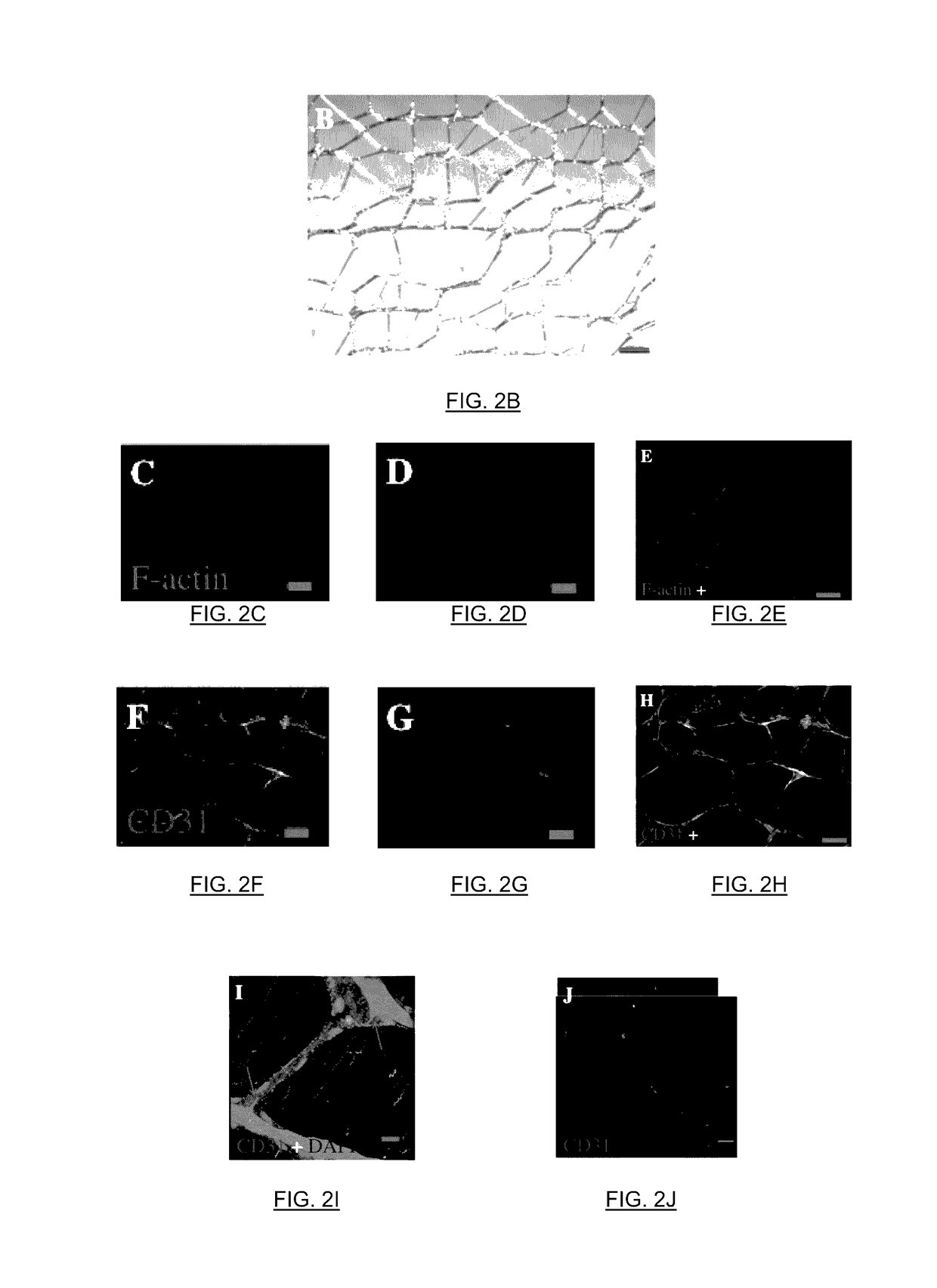
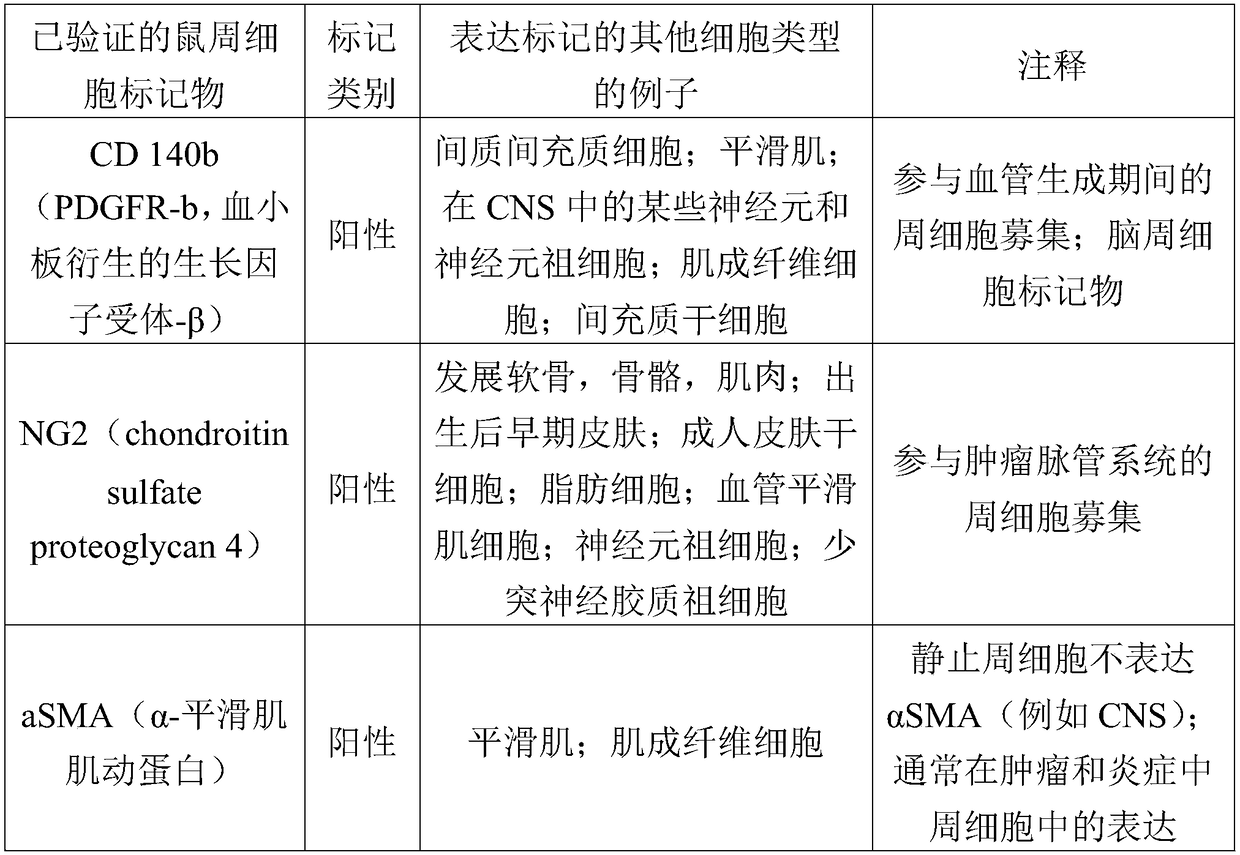
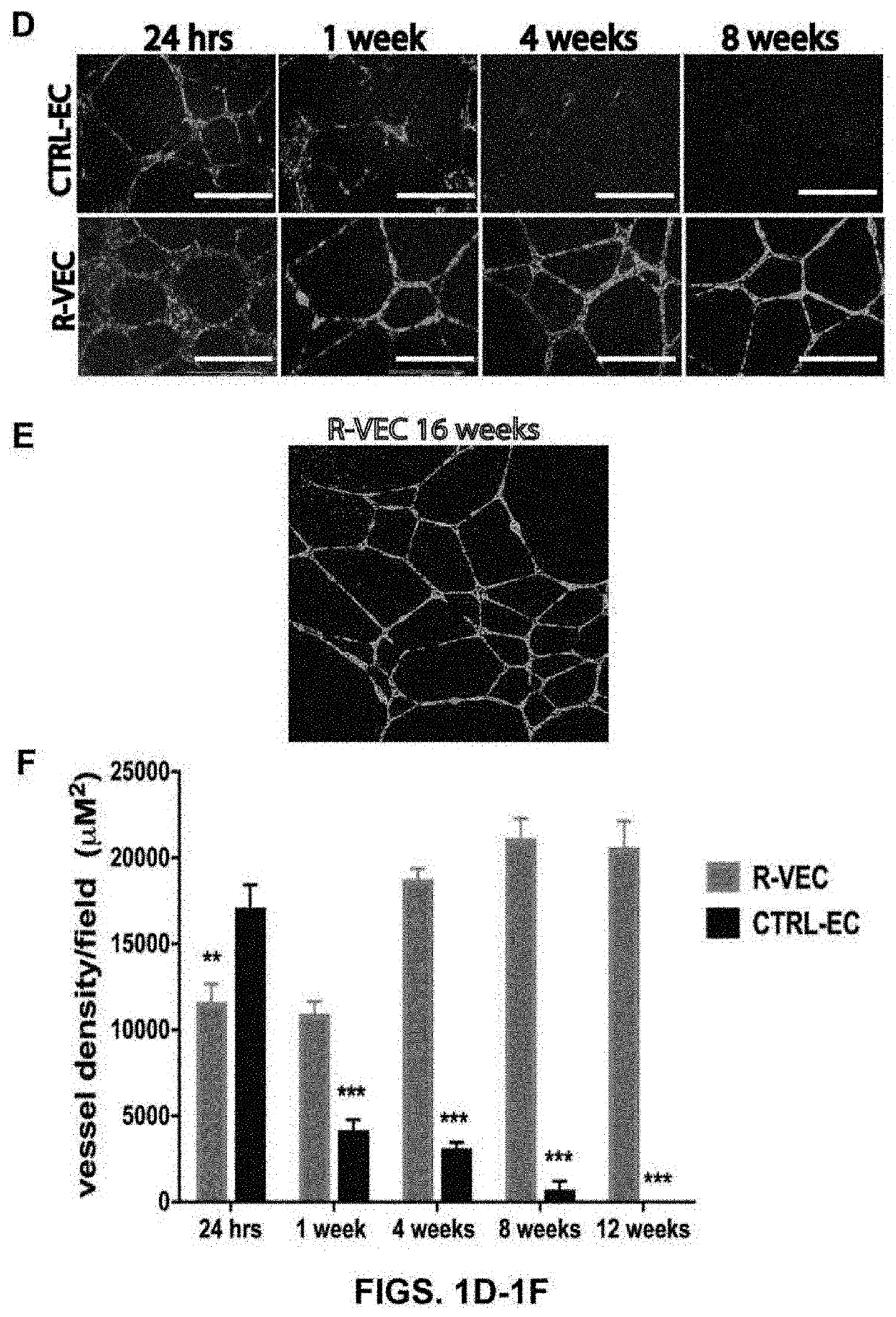
Pericytes (previously known as Rouget cells) are multi-functional mural cells of the microcirculation that wrap around the endothelial cells that line the capillaries and venules throughout the body. Pericytes are embedded in basement membrane, where they communicate with endothelial cells of the body's smallest blood vessels by means of both direct physical contact and paracrine signaling. Pericytes help to maintain homeostatic and hemostatic functions in the brain and also sustain the blood–brain barrier. These cells are also a key component of the neurovascular unit, which includes endothelial cells, astrocytes, and neurons. Pericytes regulate capillary blood flow, the clearance and phagocytosis of cellular debris, and the permeability of the blood–brain barrier. Pericytes stabilize and monitor the maturation of endothelial cells by means of direct communication between the cell membrane as well as through paracrine signaling. A deficiency of pericytes in the central nervous system can cause the blood–brain barrier to break down.
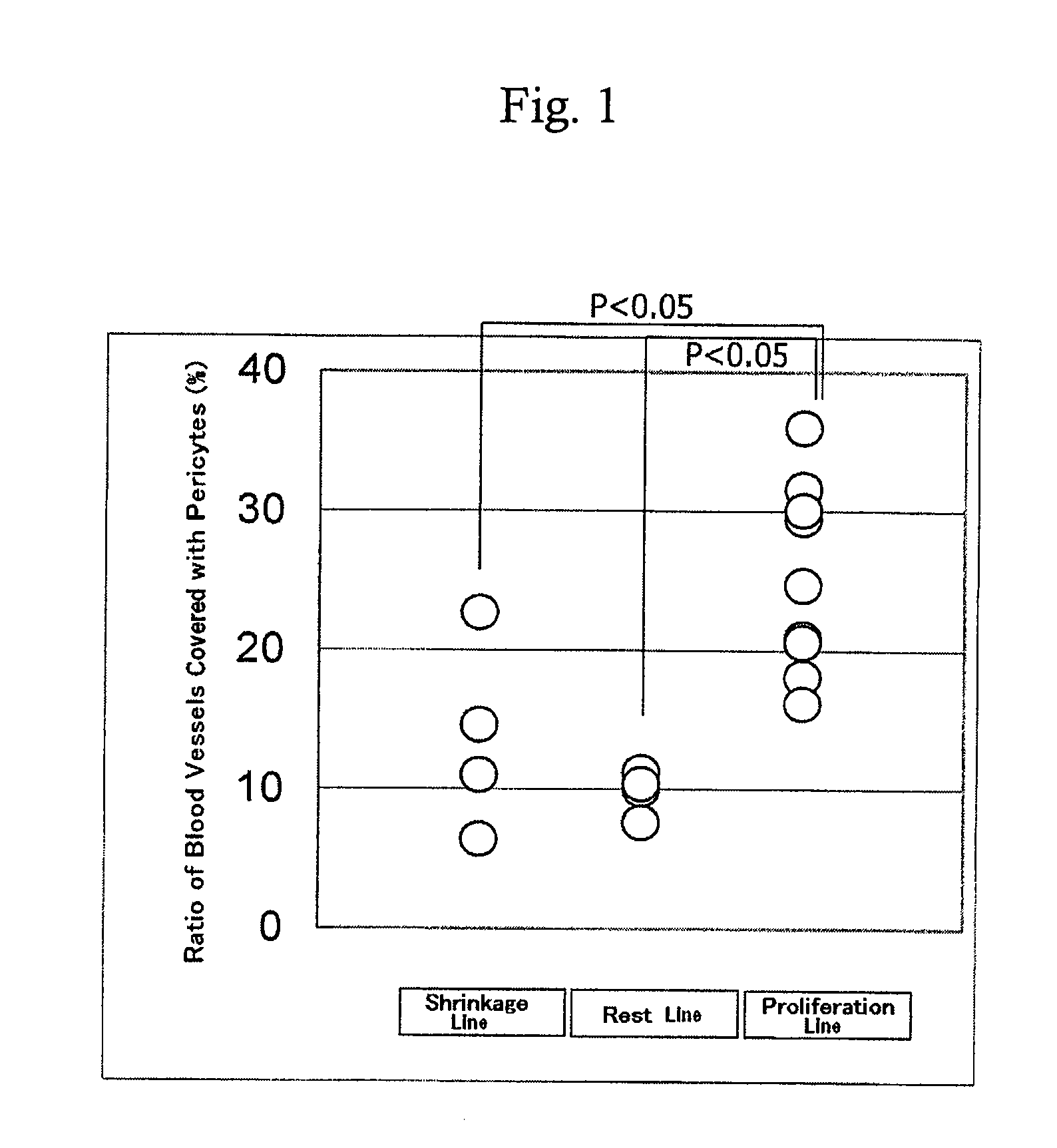
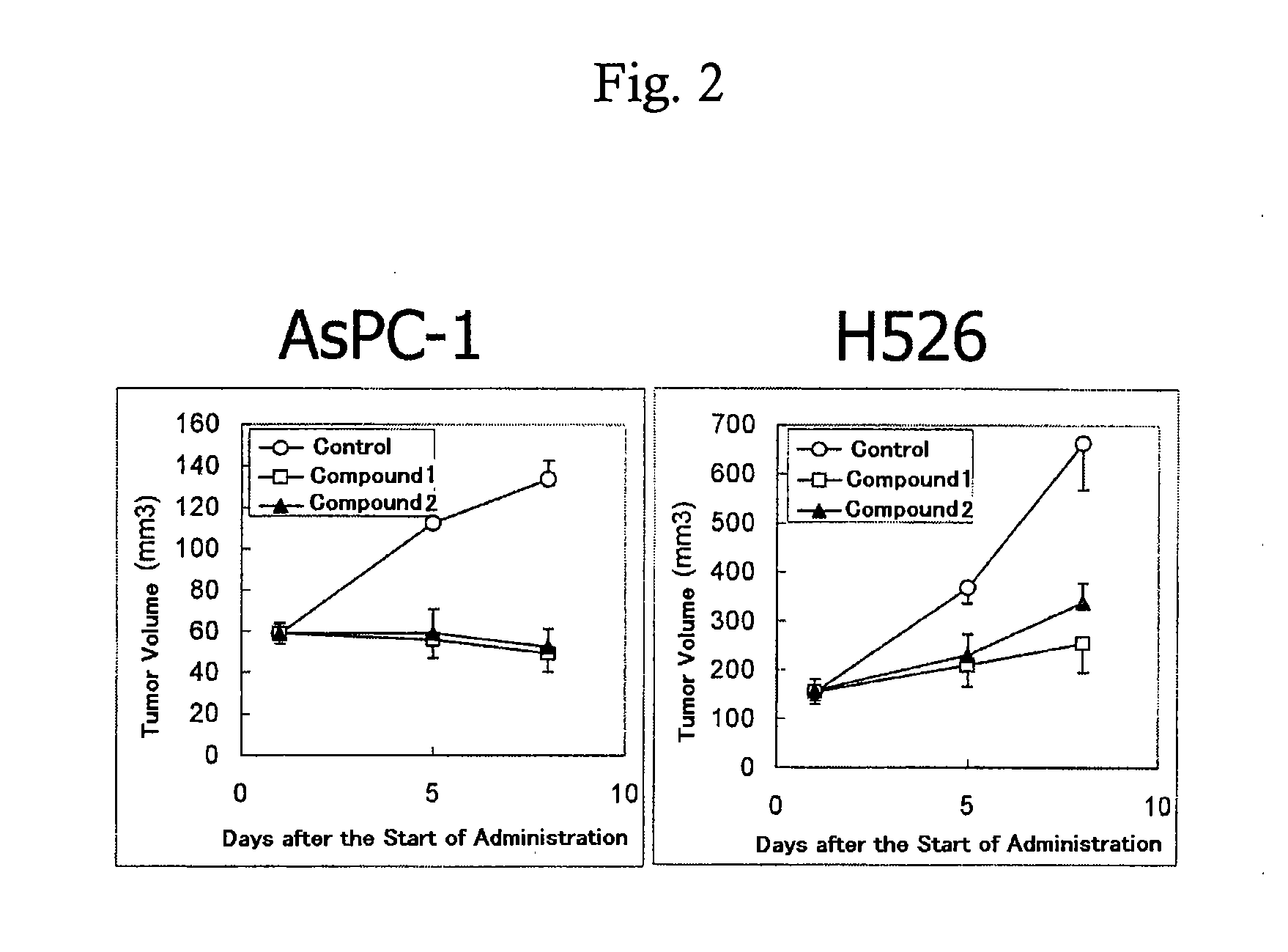
Method for prediction of the efficacy of vascularization inhibitor
InactiveUS20100105031A1Predict antitumor effectImprove anti-tumor effectMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisAbnormal tissue growthCancer research
Disclosed is a method for the prediction of the efficacy of a vascularization inhibitor. In the method, the anti-tumor effect of a vascularization inhibitor can be predicted by measuring the number of blood vessels surrounded by pericytes in a tumor and using the measurement value as a measure for the anti-tumor effect.
Owner:EISIA R&D MANAGEMENT CO LTD
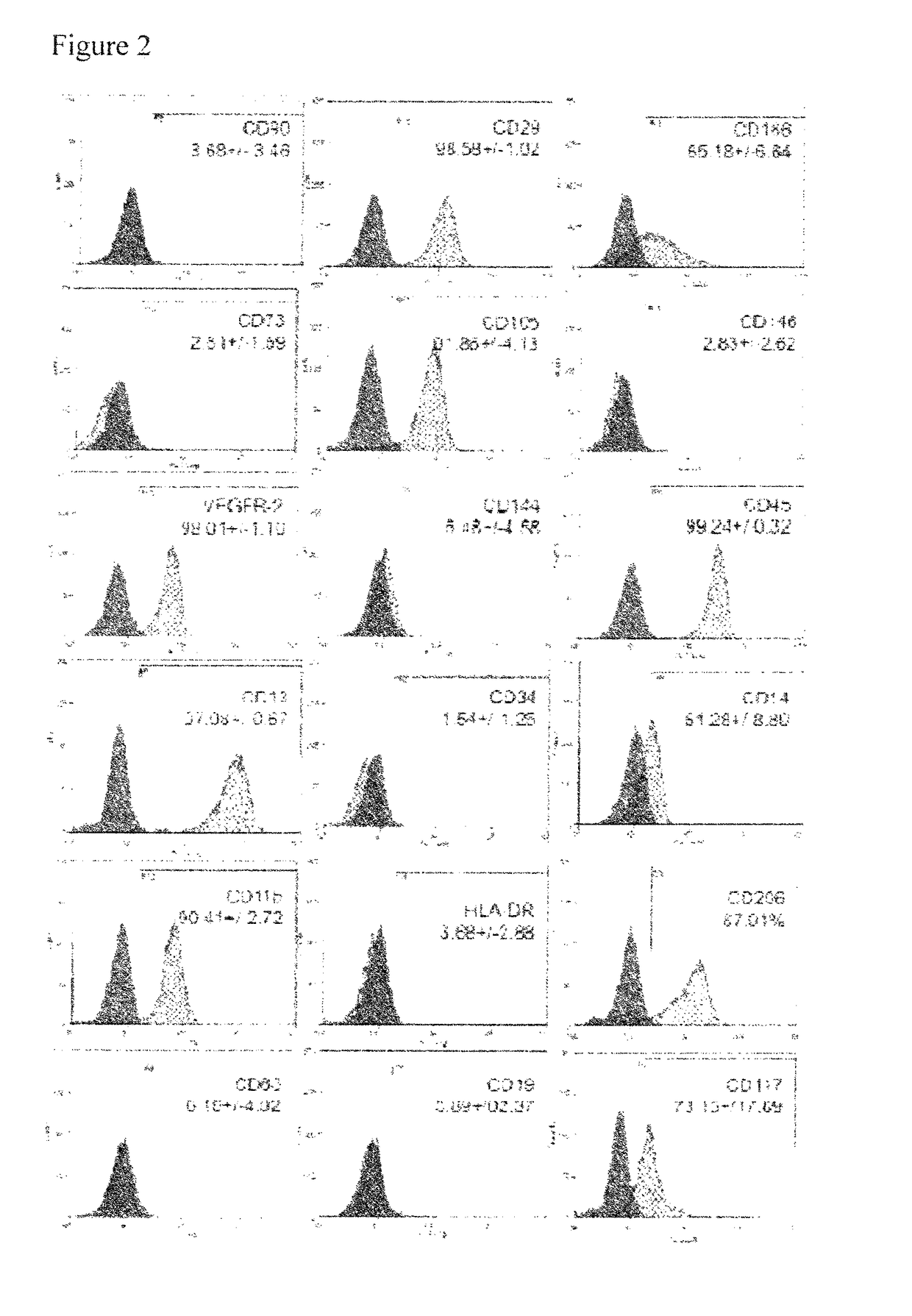
Isolation of pericytes
In one embodiment, the invention provides a pericyte having a marker pattern comprising CD146+, CD34−, and CD45−, wherein said pericyte is substantially isolated from cells that are CD146− or CD31+ or CD34+ or CD45+ or CD56+ or NG2− or CD133−. The invention also provides populations of such pericytes. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method for isolating a pericyte. In another embodiment, the invention provides a method for modeling tissue in vivo.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Bioartificial filtration device for filtering blood to mimic kidney function
InactiveUS6942879B2Long life-timeImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBioartificial liver deviceUltrafiltration
A novel cell seeded hollow fiber bioreactor is described as a potential bioartificial kidney. Endothelial cells along with pericyte, vascular smooth muscle, and / or mesangial cells or any mesenchymally derived support cells are seeded along a hollow fiber in a perfused bioreactor to reproduce the ultrafiltration function and transport function of the kidney. Maintenance of tissue specific function and ultrastructure suggest that this bioreactor provides an economical device for treating renal failure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Methods and compositions of bioartificial kidney suitable for use in vivo or ex vivo
A novel cell seeded hollow fiber bioreactor is described as a potential bioartificial kidney. Endothelial cells along with pericyte, vascular smooth muscle, and / or mesangial cells or any mesenchymally derived support cells are seeded along a hollow fiber in a perfused bioreactor to reproduce the ultrafiltration function and transport function of the kidney. Maintenance of tissue specific function and ultrastructure suggest that this bioreactor provides an economical device for treating renal failure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Method For Treating Cancer
InactiveUS20090311174A1Radioactive preparation carriersAntineoplastic agentsCancer cellAngiogenesis growth factor
The present invention relates to methods, kits, compositions and uses thereof for treating cancer. In particular, the present invention relates to methods, kits, compositions and uses thereof for the treatment of metastatic cancer, the treatment of angiogenesis associated with metastatic cancer, inhibiting formation of vasculature associated with metastatic cancer, killing pericytes associated with metastatic cancer and killing cancer cells contiguous with tumour capillaries associated with metastatic cancer, comprising a killing agent conjugated to a protein, and wherein said killing agent conjugated to said protein binds to at least one cell associated with the metastatic cancer.
Owner:ALLEN BARRY JOHN
Adipose Tissue Stem Cells, Perivascular Cells and Pericytes
InactiveUS20080213235A1Improve angiogenesisIncreased vascularityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDiseaseAdipose tissue
The present invention provides methods for growing and inducing perivascular cell differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. The invention further provides methods for administering such adipose tissue-derived cells to a subject. The cells of the invention are useful for treating diseases, disorders, conditions, and injuries requiring new or enhanced angiogenesis, vascular remodeling, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Retinoic Acid Enhanced Human Stem Cell Derived Blood Brain Barrier Model
ActiveUS20140127800A1Increase valueCulture processNervous system cellsProgenitorInduced pluripotent stem cell
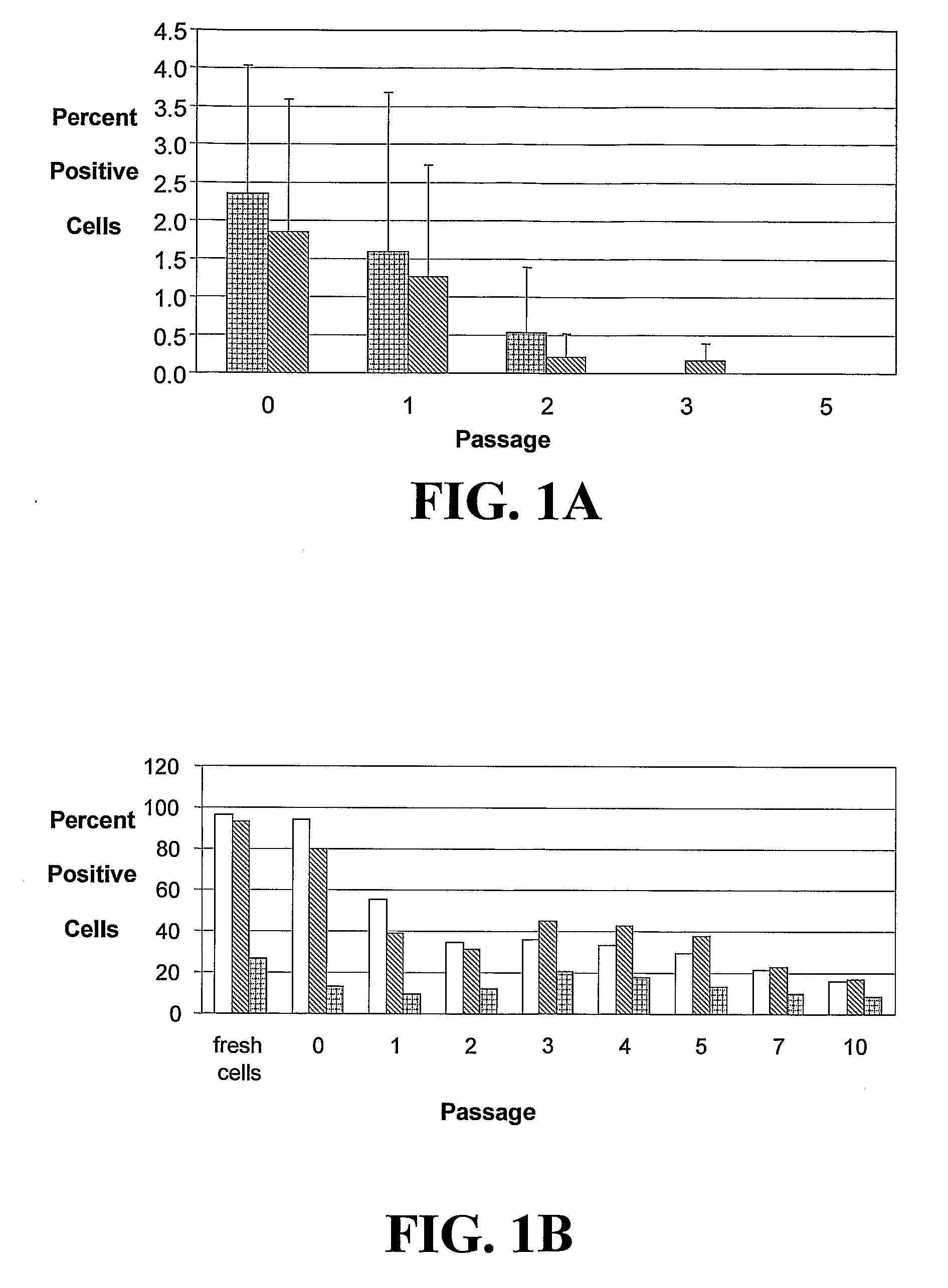
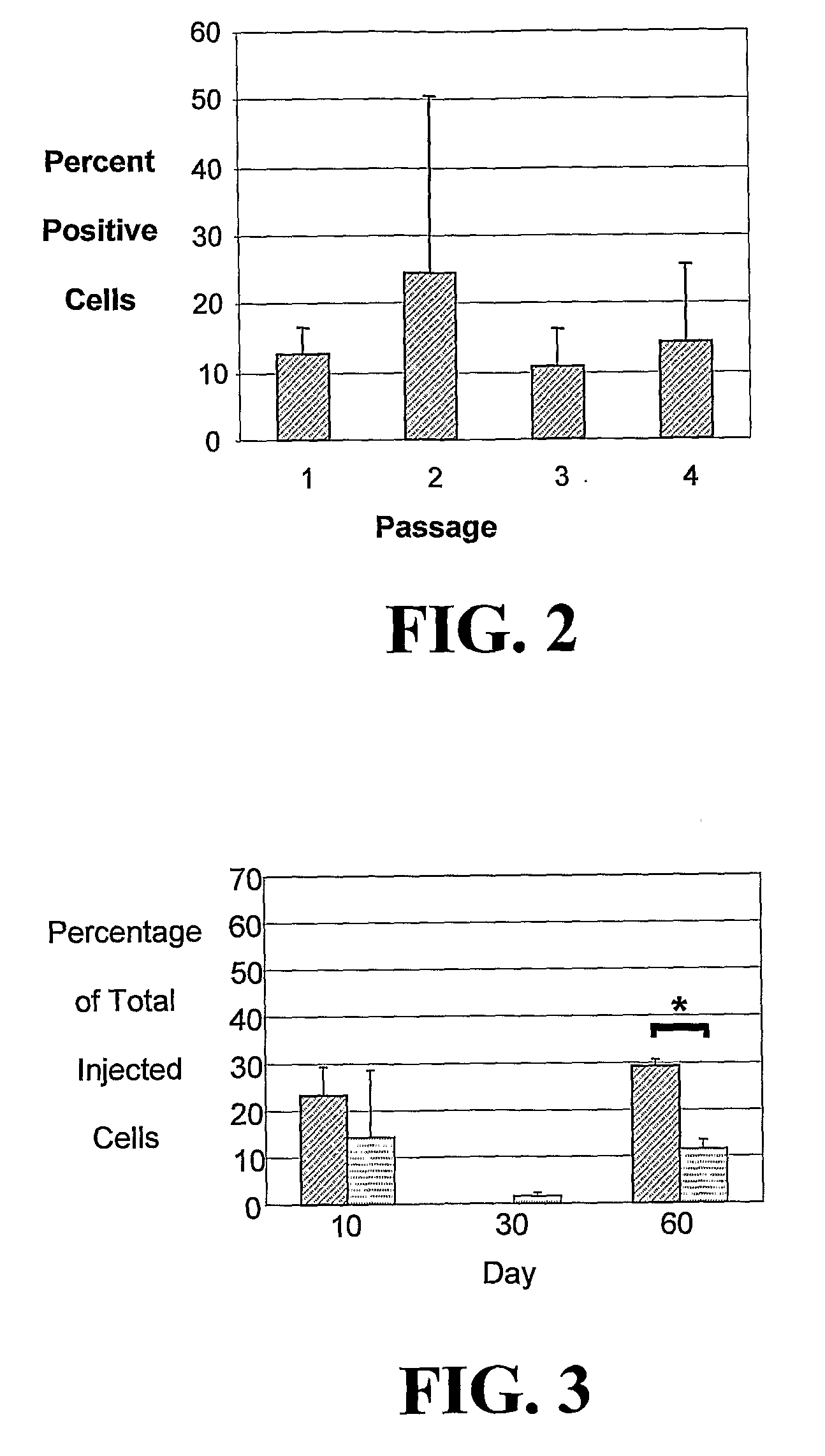
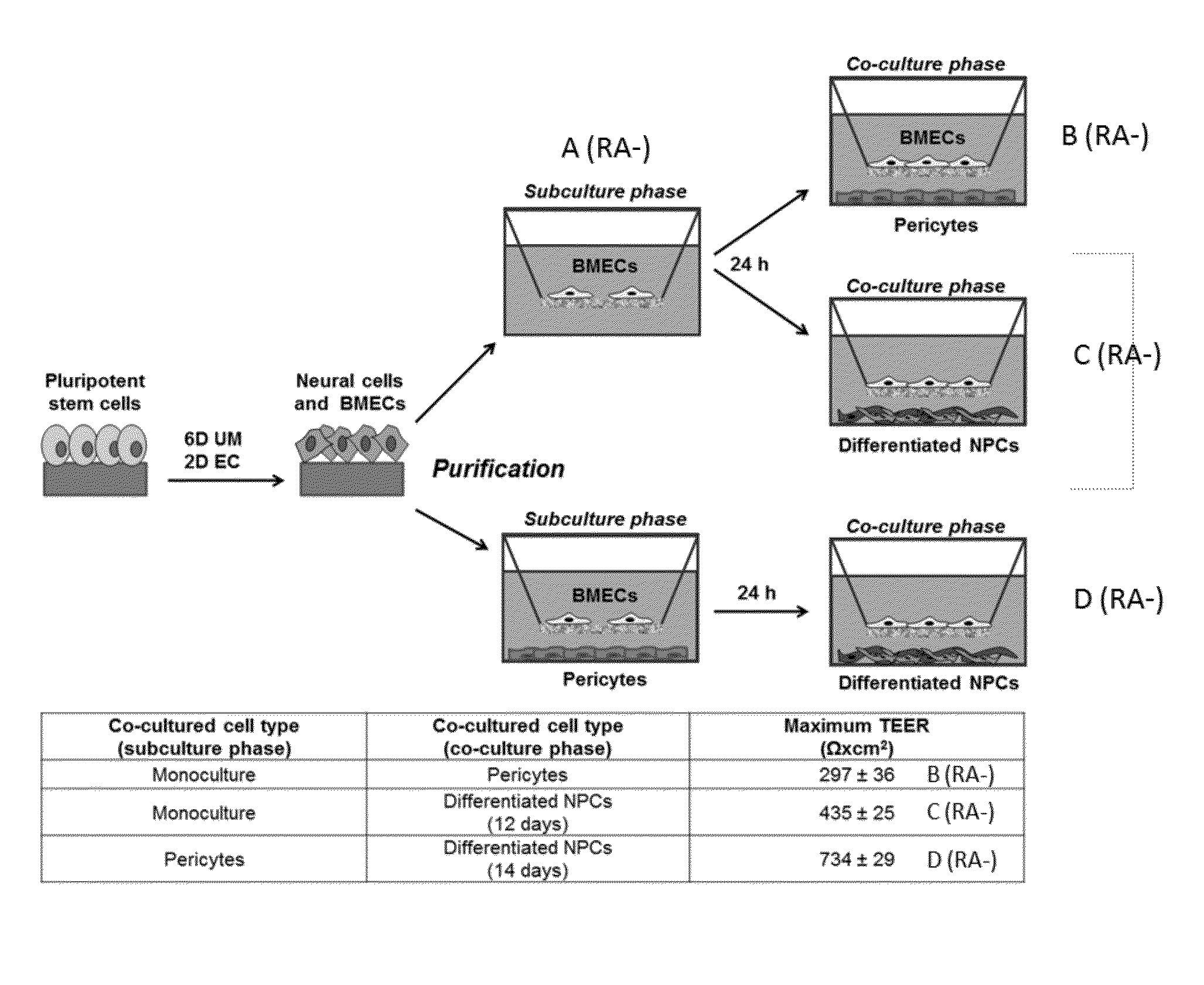
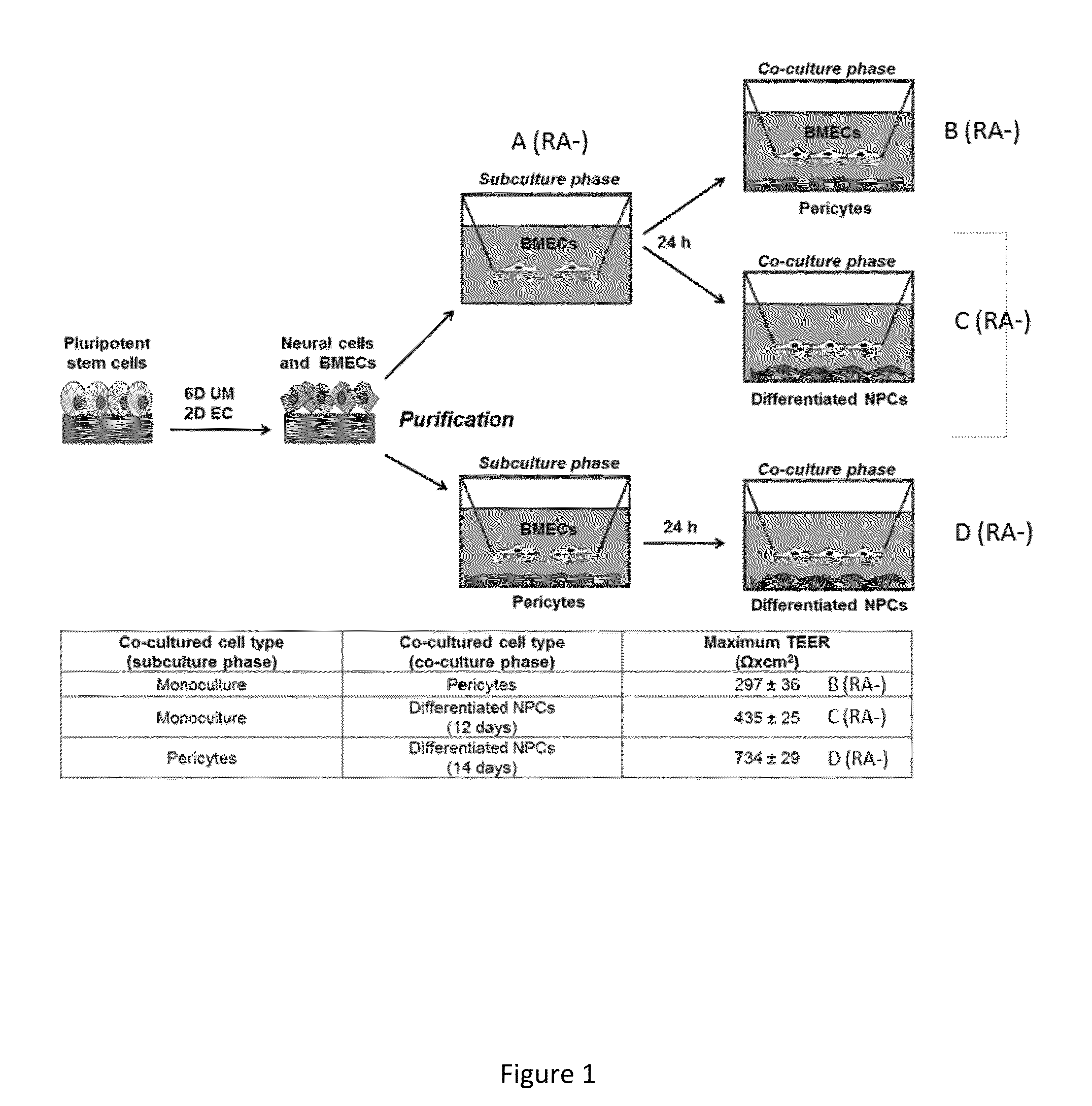
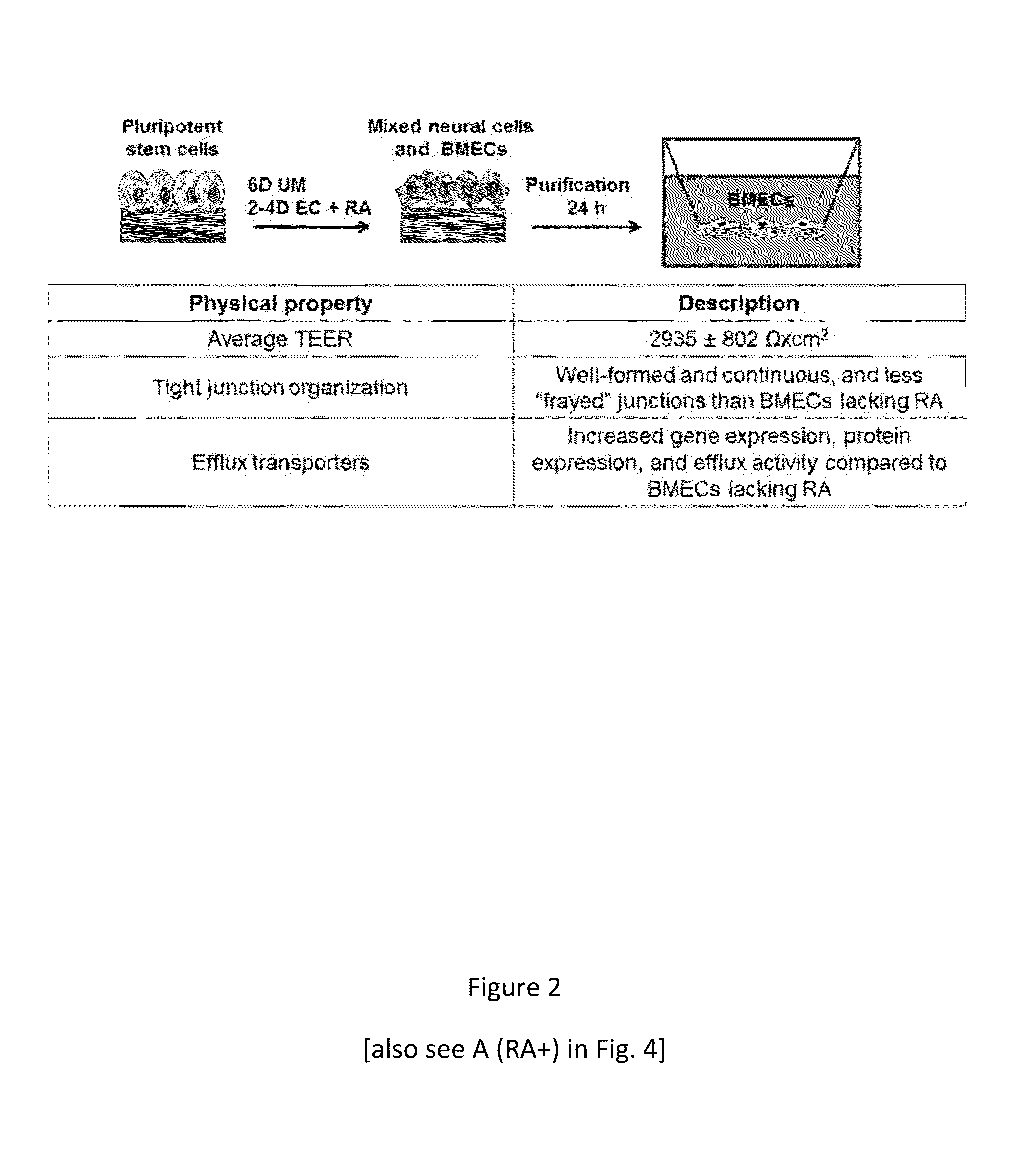
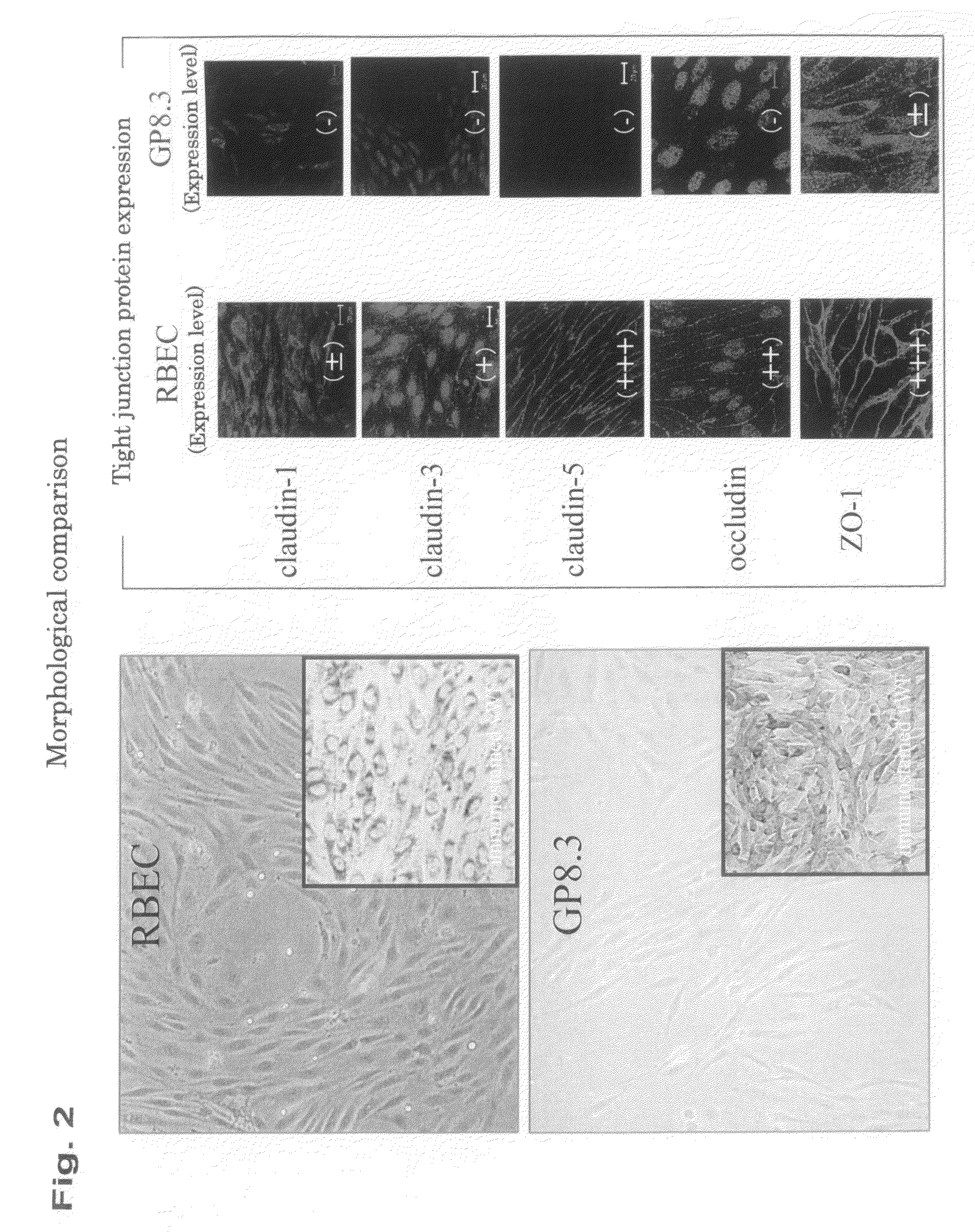
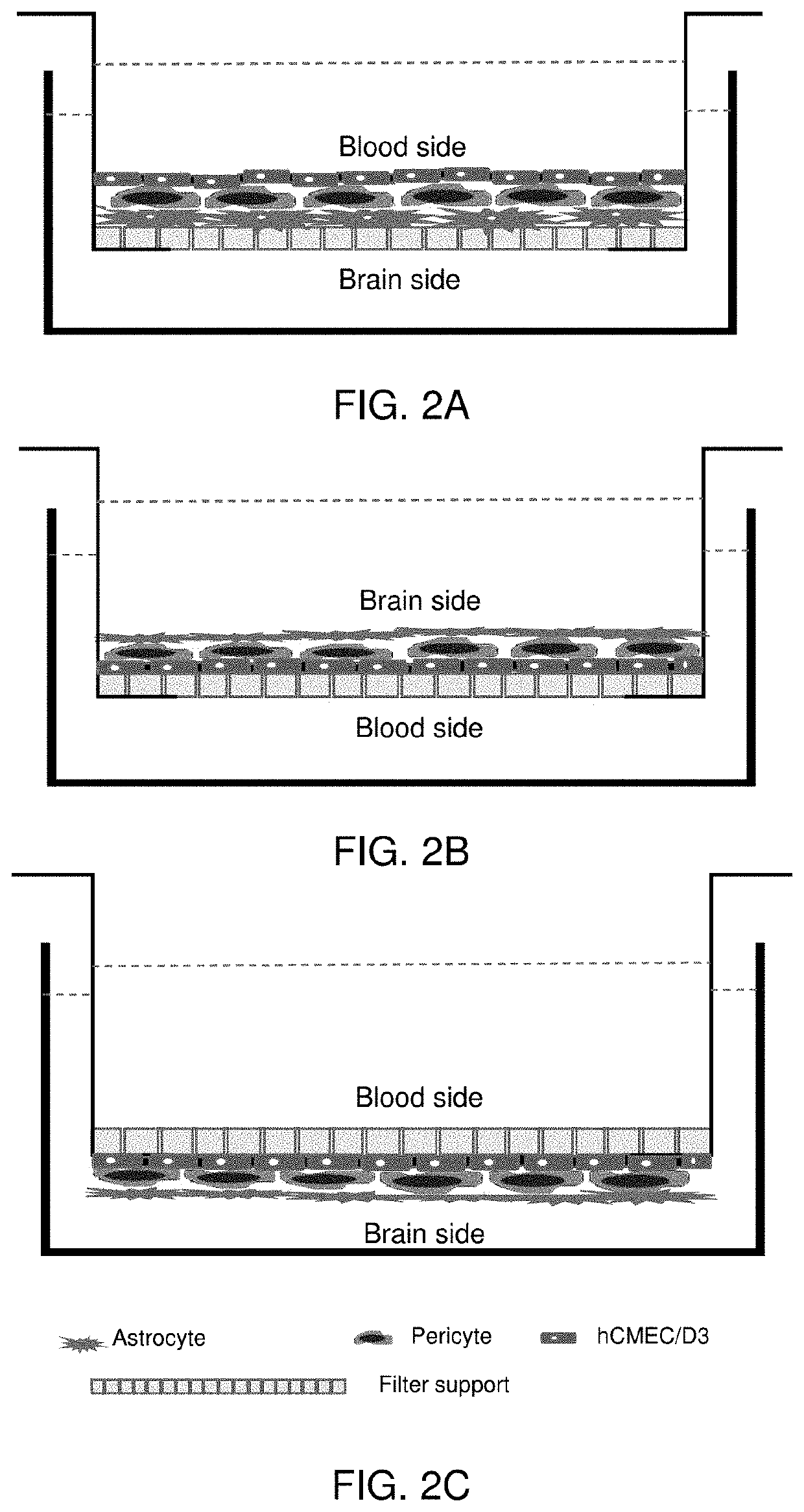
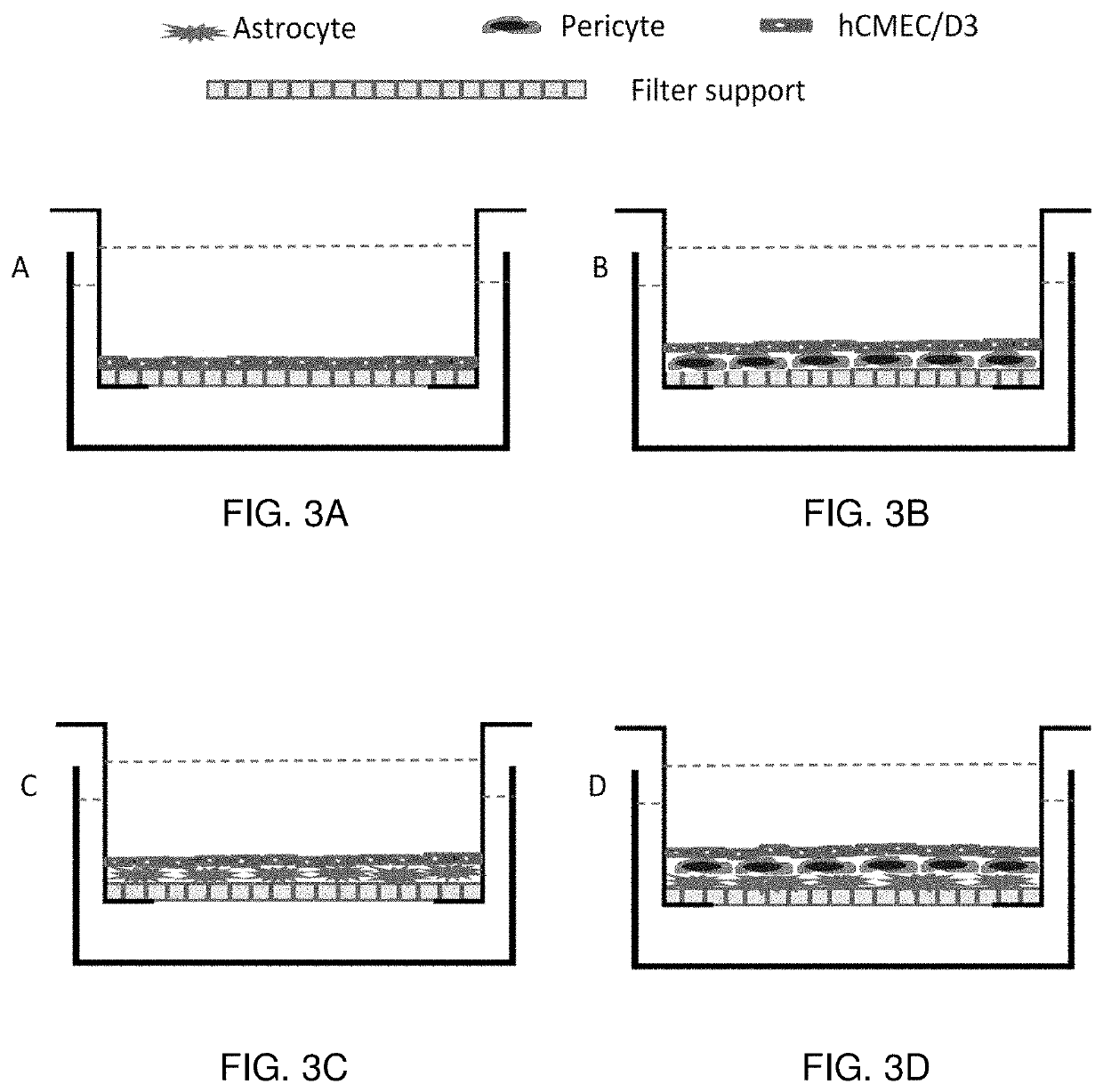
In one embodiment, the present invention is a method of creating a fully-human blood-brain barrier (BBB) model, comprising the steps of (a) obtaining a mixture of neural cells and brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMECs), wherein the neural cells and BMECs that comprise the mixture were produced from the differentiation of human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs); (b) purifying BMECs from the mixture of neural cells and BMECs of step (a); and (c) co-culturing the purified BMECs with a cell type selected from the group consisting of pericytes, astrocytes and differentiated neural progenitor cells (NPCs), wherein a blood brain barrier model is created.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Self-Organized Vascular Networks from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in a Synthetic Matrix
ActiveUS20140273220A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsMorphogenesisBiological activation
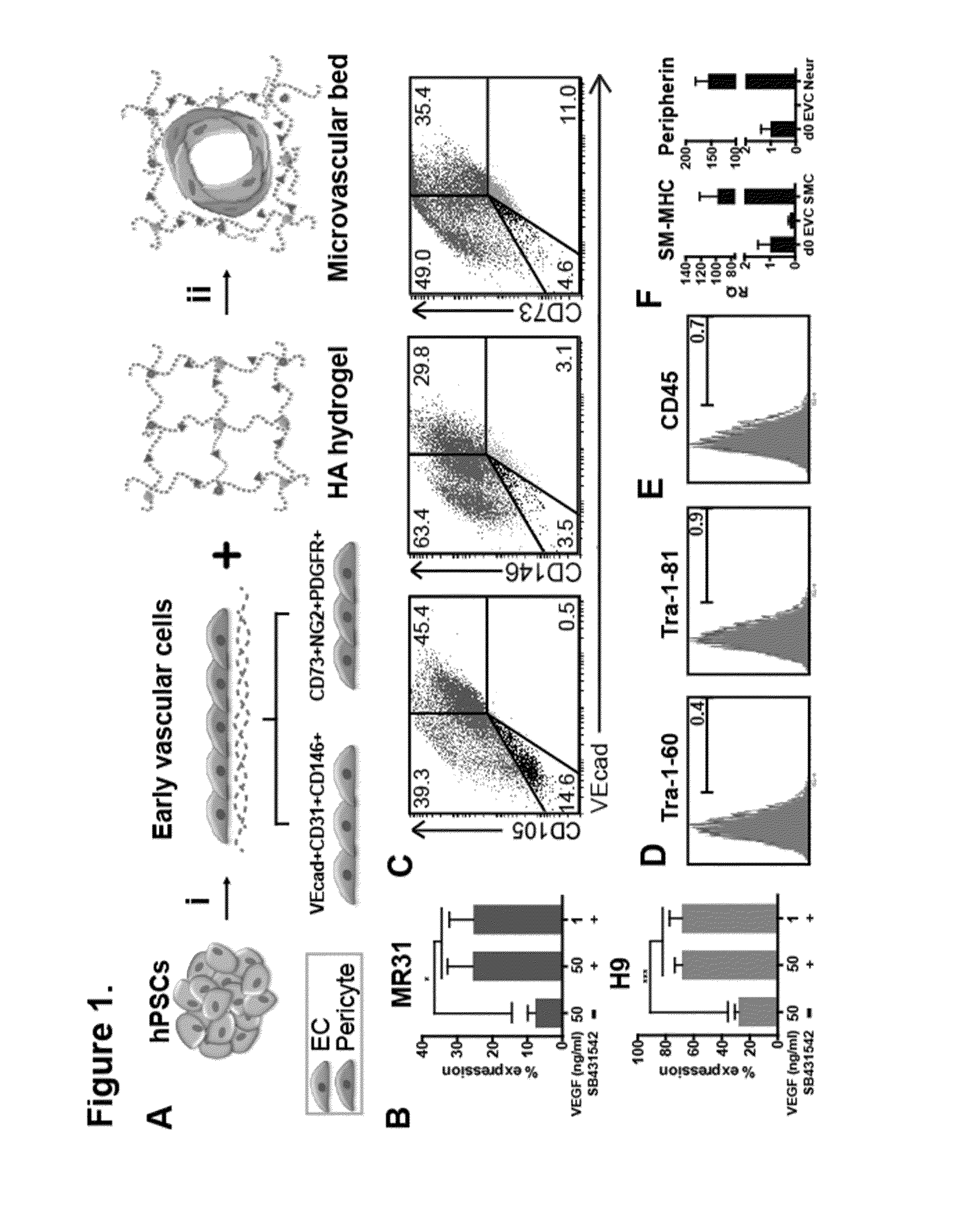
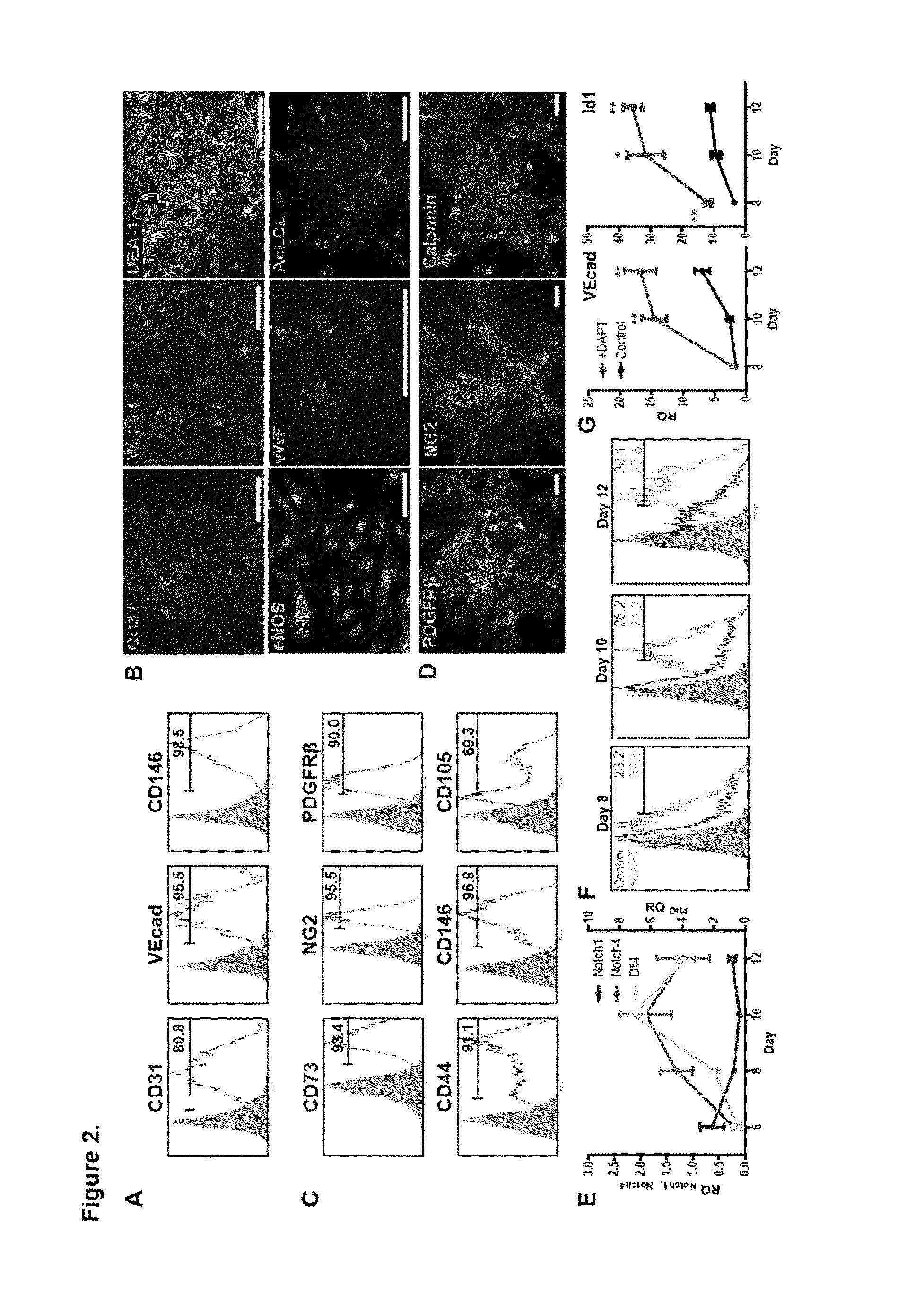
A bicellular vascular population derived from human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) undergoes morphogenesis and assembly in a synthetic hydrogel. It is shown that hPSCs can be induced to co-differentiate into early vascular cells (EVCs) in a clinically-relevant strategy dependent upon Notch activation. These EVCs mature into ECs and pericytes, and self-organize to form vascular networks in an engineered matrix. Upon in vivo implantation, multicellular human vascular networks are functionally perfused. Thus, a derived bicellular population is exploited for its intrinsic self-assembly capability to create functional microvasculature in a deliverable matrix.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
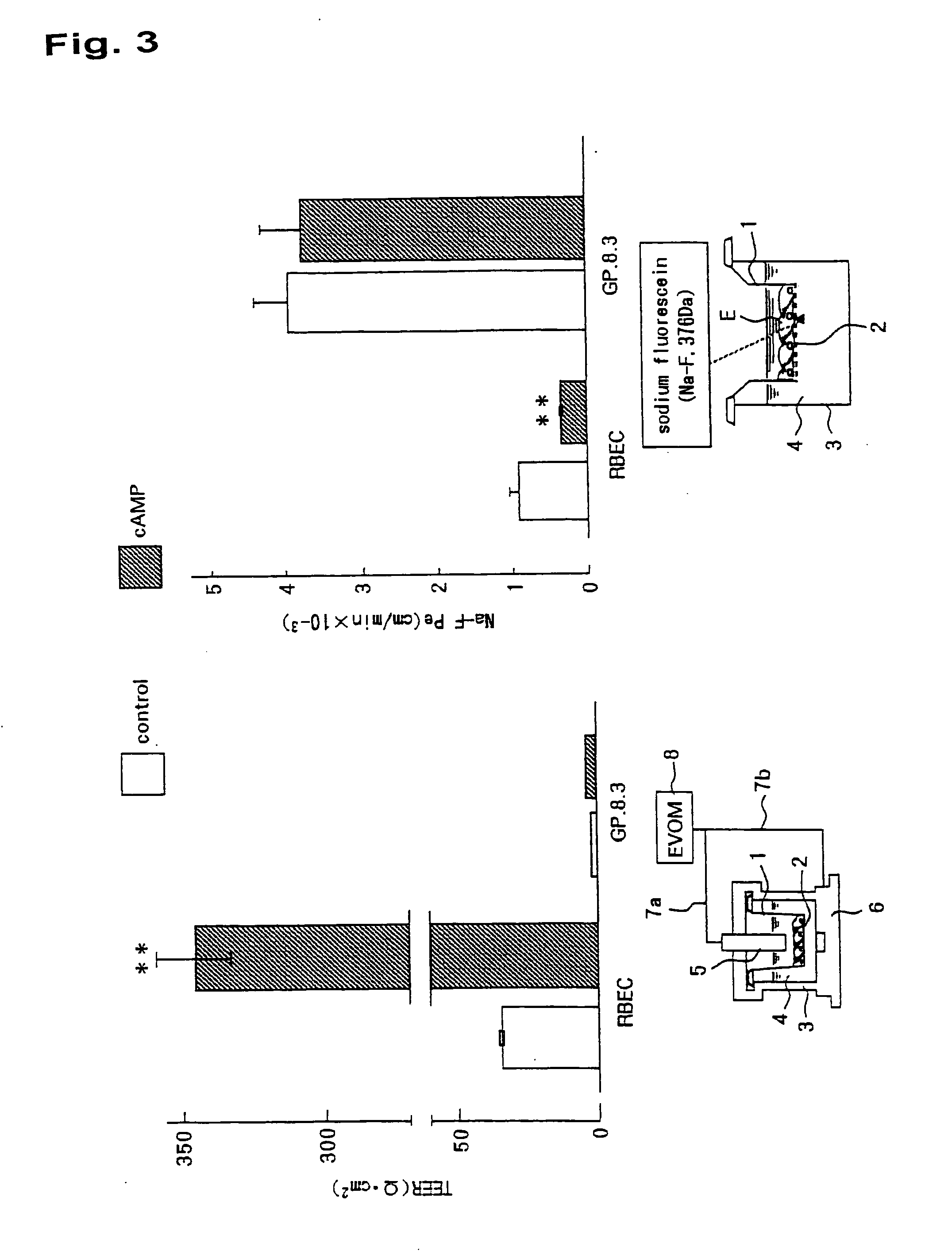
In-Vitro Model of Blood-Brain Barrier, In-Vitro Model of Diseased Blood-Brain Barrier, and Drug Screening Method, Analysis Method for Functions of Diseased Blood-Brain Barrier, and Analysis Method for Pathogenesis Using the Same
InactiveUS20100273200A1Efficient developmentMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsDiseaseScreening method
It is intended to provide a screening system for a centrally acting drug transported across the blood-brain barrier, a drug acting on the blood-brain barrier itself, or a drug transferred into the brain without being expected to centrally act. Moreover, another object of the present invention is to achieve pathogenesis analysis study or the screening in a diseased state by applying various diseased environments to this screening system. The present invention provides an in-vitro model of blood-brain barrier obtained by using a three-dimensional culture apparatus comprising: a culture solution; a plate holding the culture solution; and a filter immersed in the culture solution and placed in no contact with the inside bottom of the plate, the filter having plural pores of 0.35 to 0.45 μm in diameter, and by comprising: seeding primary cultured brain capillary endothelial cells onto the upper surface of the filter; seeding primary cultured brain pericytes onto the under surface of the filter; seeding primary cultured astrocytes onto the inside surface of the plate; and coculturing these cells in a normal culture solution.
Owner:PHARMACO CELL
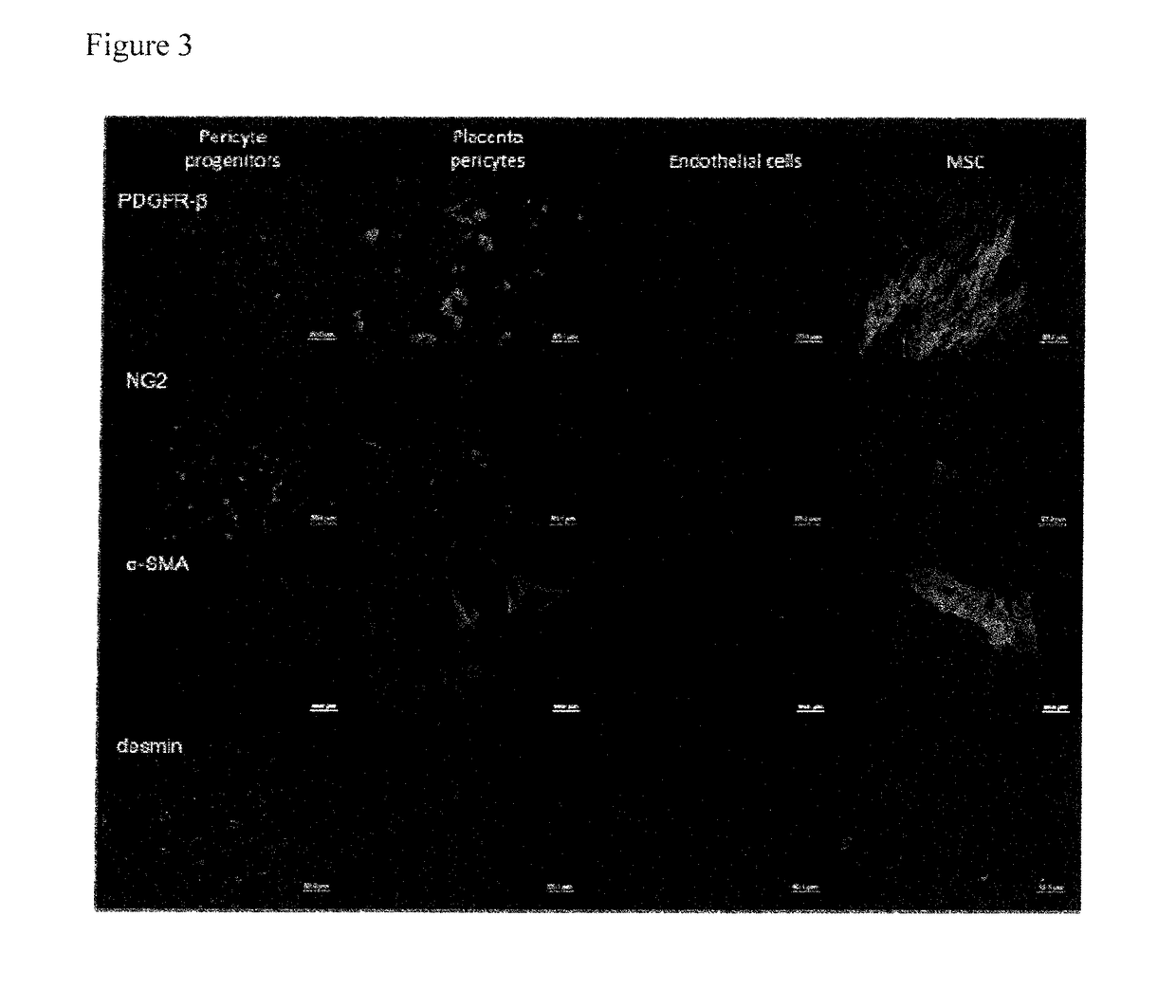
Pericyte Progenitors From Peripheral Blood
ActiveUS20140004046A1Increase depositionAmplifies differentiation responseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsProgenitorPericyte
Thus, provided herein are pericyte progenitor cells (e.g., isolated pericyte progenitor cells), methods for generating pericyte progenitors in clinically relevant numbers for various applications applying macromolecular crowding during cell culture, and methods of using the pericyte progenitor cells.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Recombinant adenovirus expressing alpha-a-crystallin gene and gene therapy for retinalvascular disease using the same
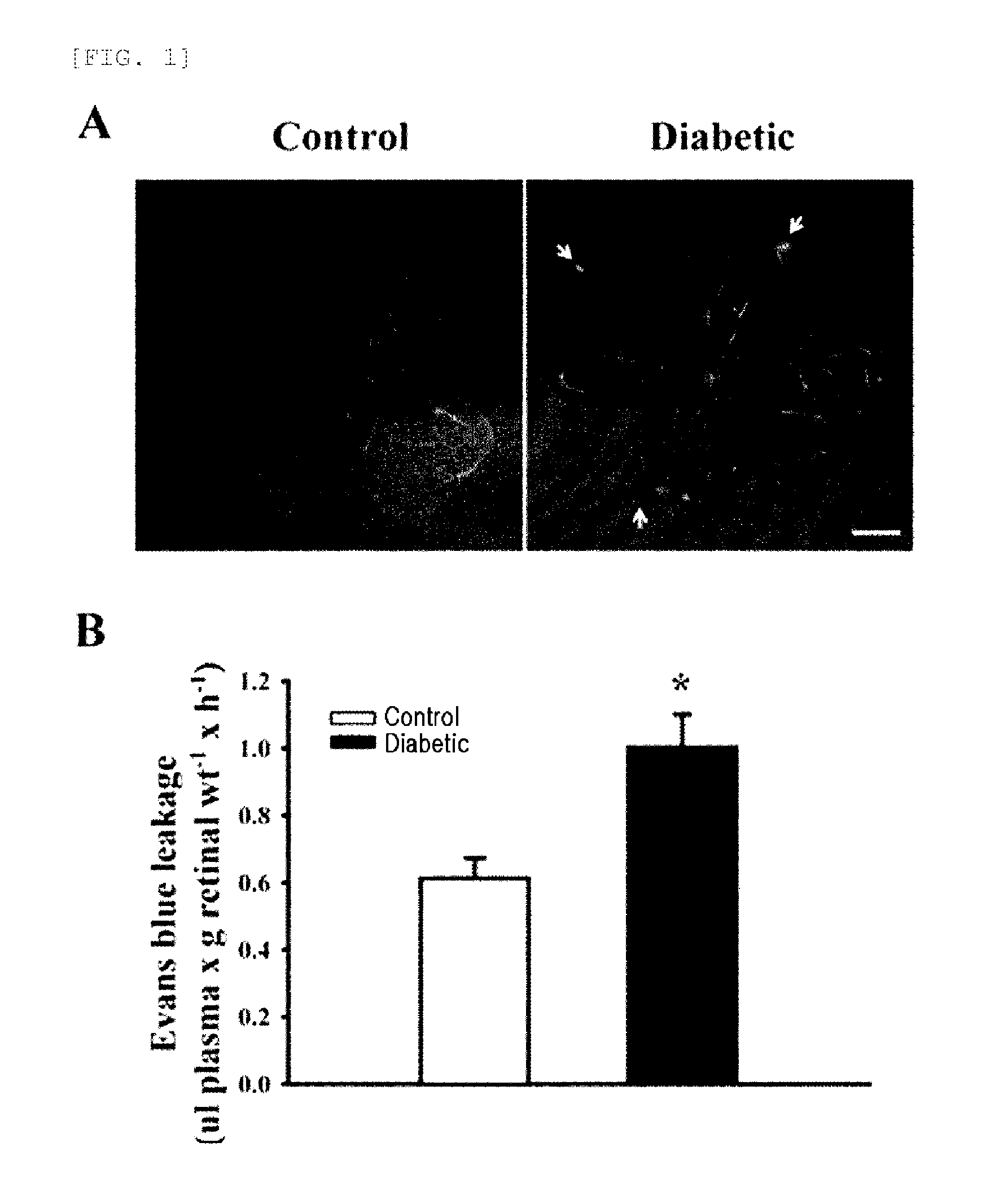
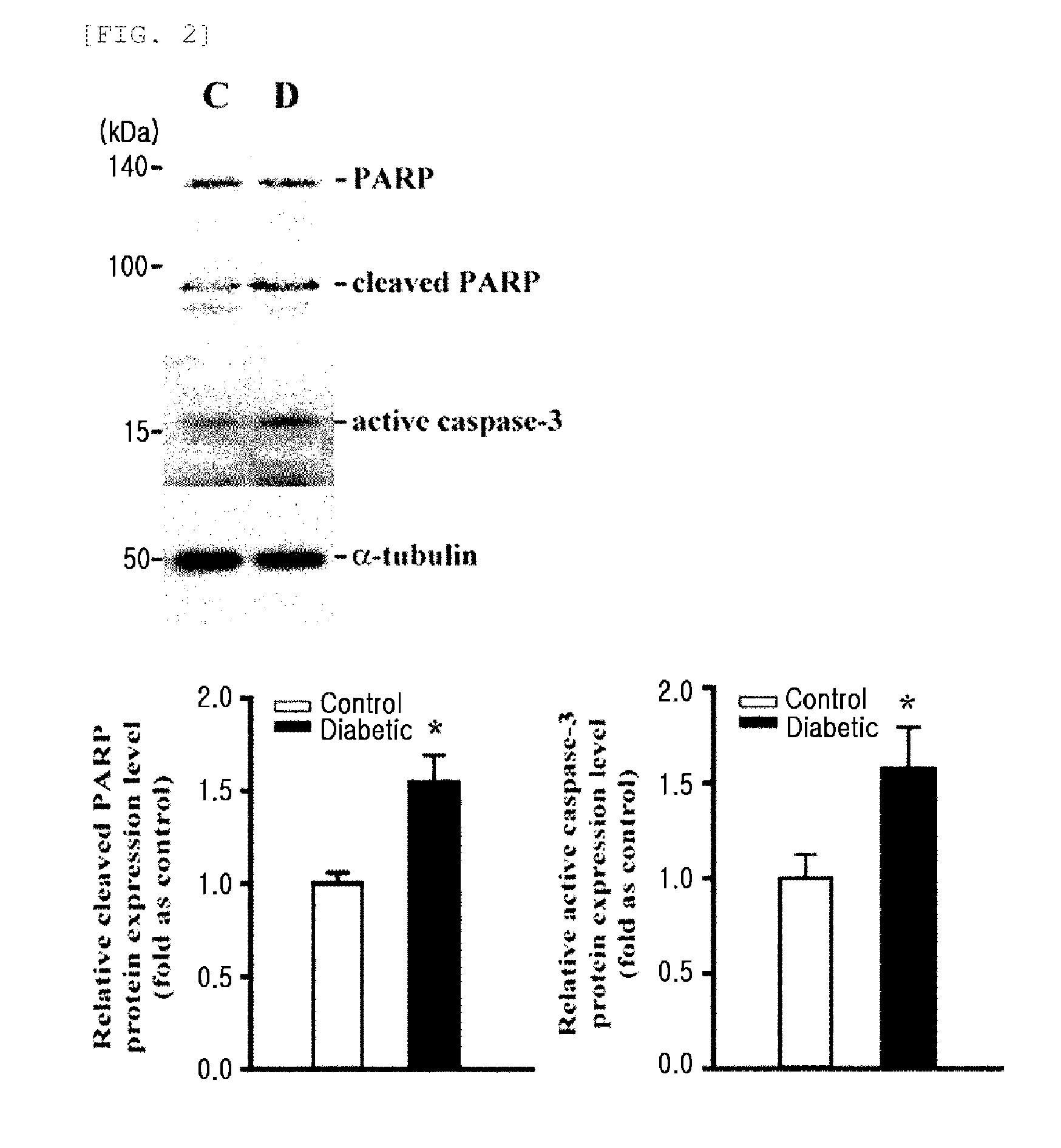
The present invention relates to a recombinant adenovirus expressing an αA-crystallin gene, and gene therapy for retinal vascular disease using the recombinant adenovirus. Gene therapy using the recombinant adenovirus comprising an αA-crystallin gene of the present invention increases the expression level of the αA-crystallin gene in the damaged retinal pericytes to suppress pericyte loss and death, retinal vascular leakage, and leukocyte adhesion surrounding retinal vessels, thereby protecting the pericytes. Therefore, it can be used for the prevention and treatment of various retinal vascular diseases including diabetic retinopathy.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND GYEONGSANG NAT UNIV
Controllable formation of microvascular networks using sacrificial microfiber templates
InactiveUS20170088815A1Easily integrated into tissue-engineered tissue constructRaise the potentialCell culture supports/coatingCell culture active agentsProgenitorMicrovascular Network
The present disclosure relates to fabricating sacrificial microfiber templates from any biocompatible and resorbable materials depending on the time needed for dissolving the microfiber template to free the endothelial tube with open lumen. Microfiber networks with distinct patterns and defined diameters initially serve as a template to support the growth of vascular cells (endothelial cells or their progenitor cells, or combined with mural cells such as pericytes) and then dissolve to form an empty endothelium lumen. The incorporation of sacrificial microfiber networks encapsulated with vascular cells into 3D cell-rich constructs allows for the creation of various vascularized tissues.
Owner:STEVENS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
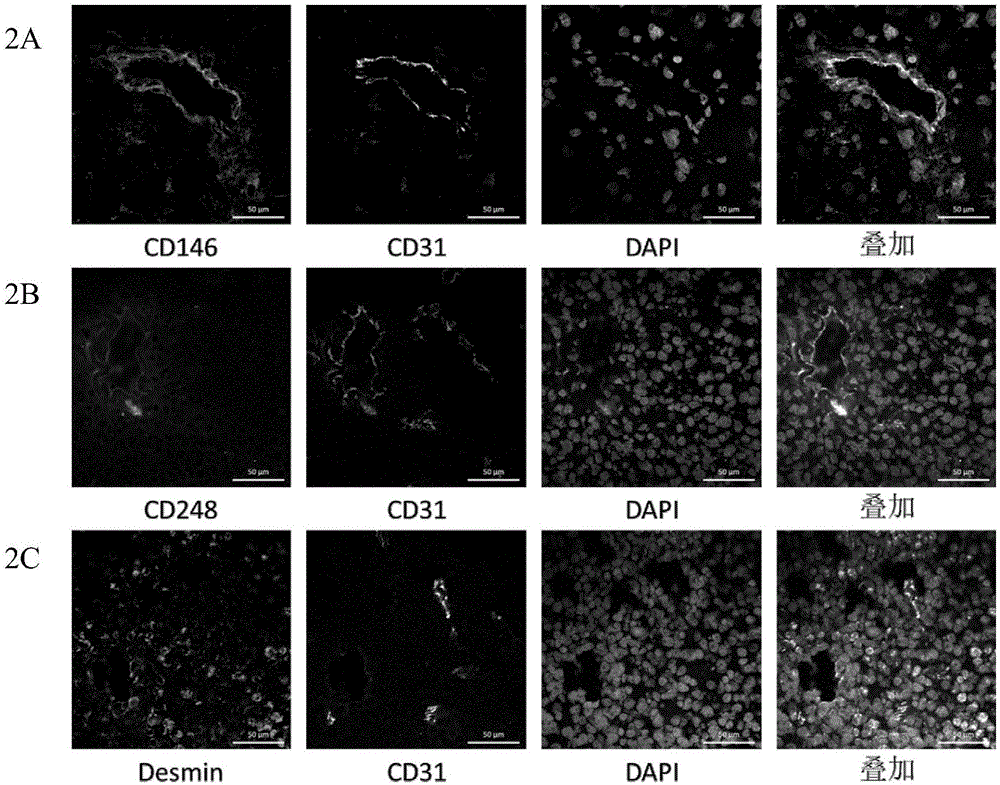
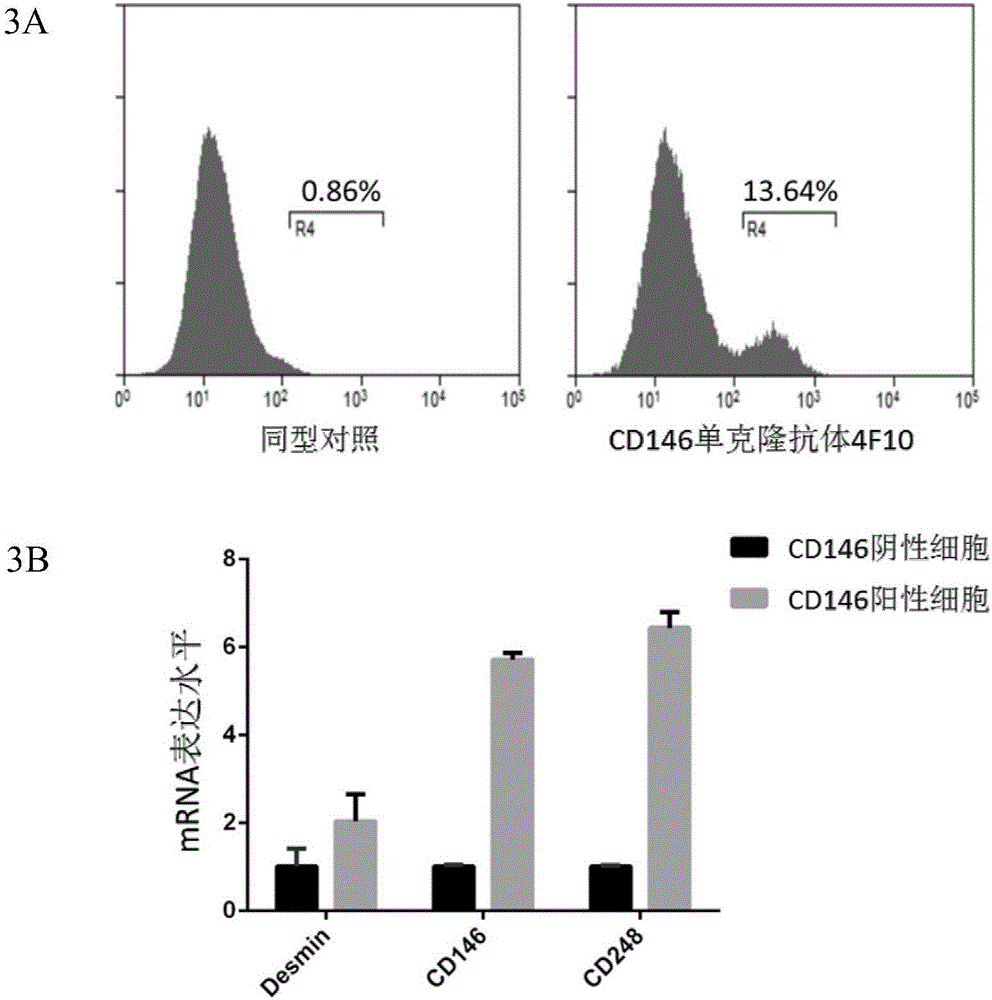
Application of CD146 monoclonal antibody in detection and separation and identification of glioma perivascular cells
ActiveCN106589124AConforms to the characteristics of the structural hierarchyAccurate identificationCell dissociation methodsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsTumor vesselCell strain
An application of a CD146 monoclonal antibody in detection and separation and identification of glioma perivascular cells. The CD146 monoclonal antibody is prepared from a hybridoma cell strain which is assigned the accession number of CCTCC No: C2016183. The CD146 monoclonal antibody 4F10 has excellent specificity and can accurately recognize tumor perivascular cells. In addition, the CD146 monoclonal antibody 4F10 can be used for flow cytometry sorting and detection of glioma-derived pericytes.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
Method for separating and bionic culturing pericytes of tumor cells
ActiveCN108715836AConform to the morphological characteristicsCell dissociation methodsCell culture active agentsAbnormal tissue growthTumour tissue
The invention discloses a method for separating and bionic culturing pericytes of tumor cells and relates to the field of metastasis of tumor. The method for separating and bionic culturing pericytesof tumor cells provides a departure from the traditional method of using two non-specific antibodies to label pericytes; 10 antibody labels including 5 positive labels and 5 negative labels are firstly used to separate, purify and identify pericytes. And through the morphological identification under a mircoscope, the pericytes can form microtubules in bionic culturing base, which can be seen obviously and which meet the morphological characteristics of pericytes, furthermore, the growth of pericytes in body is reproduced, and further explore of the function of the pericytes is based.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Differentiation and expansion of endothelial cells from pluripotent stem cells and the in vitro formation of vasculature like structures
ActiveUS20160115453A1Equal efficiencyPromote regenerationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSmooth musclePluripotential stem cell
The disclosure is concerned among others with means and methods for obtaining endothelial cells and to means and methods for in vitro cell culture comprising endothelial cells and pericytes and / or smooth muscle cells derived from the pericytes. The endothelial cells or the pericytes and / or smooth muscle cells, or both, are preferably derived from in vitro differentiated pluripotent stem cells.
Owner:ACADEMISCH ZIEKENHUIS BIJ DE UNIV VAN AMSTERDAM ACADEMISCH MEDISCH CENT
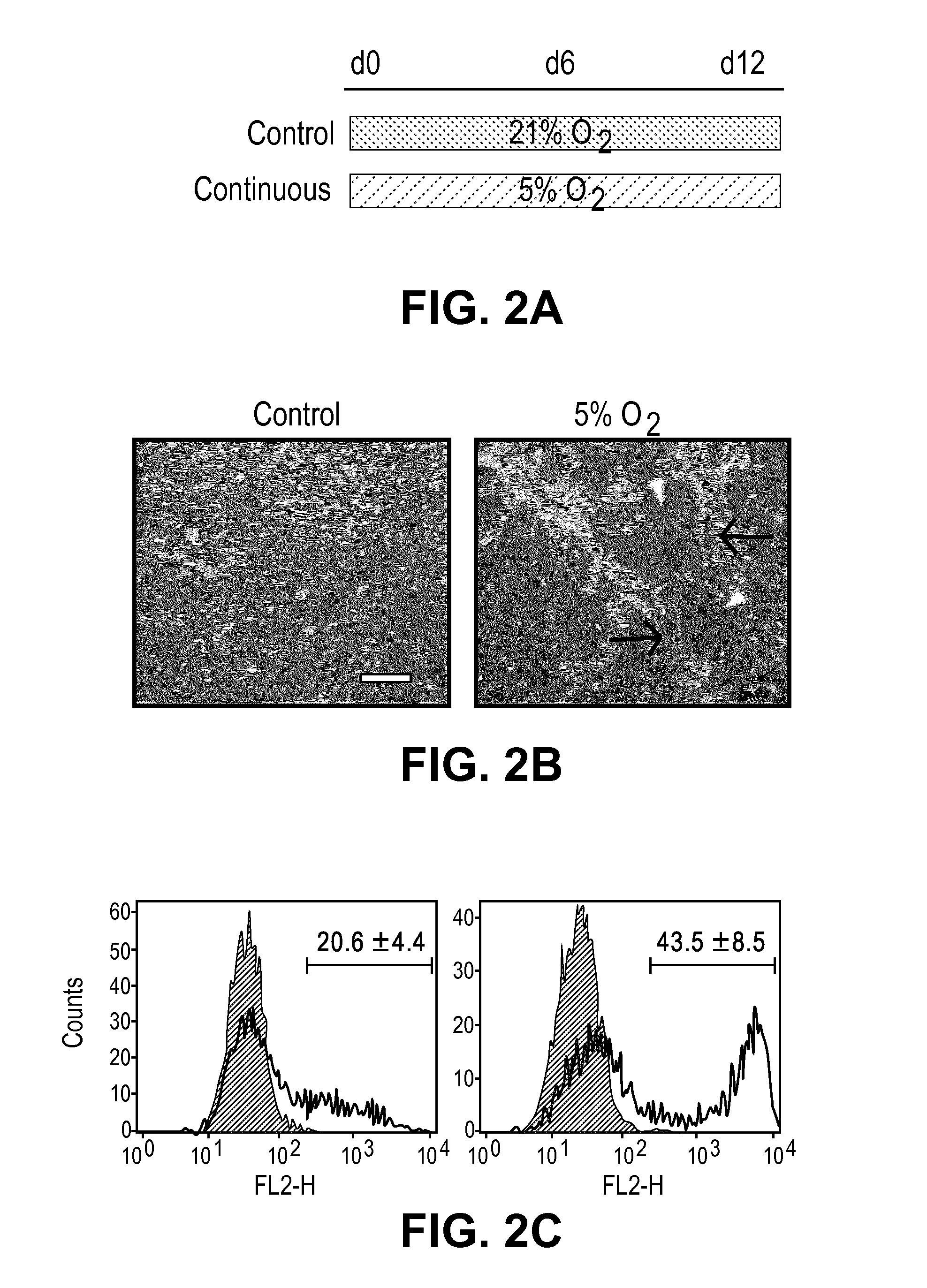
Low oxygen tension enhances endothelial fate of human pluripotent stem cells
ActiveUS20170009204A1Lower oxygen partial pressureInduces endothelial commitmentCulture processArtificial cell constructsInduced pluripotent stem cellEndothelial NOS
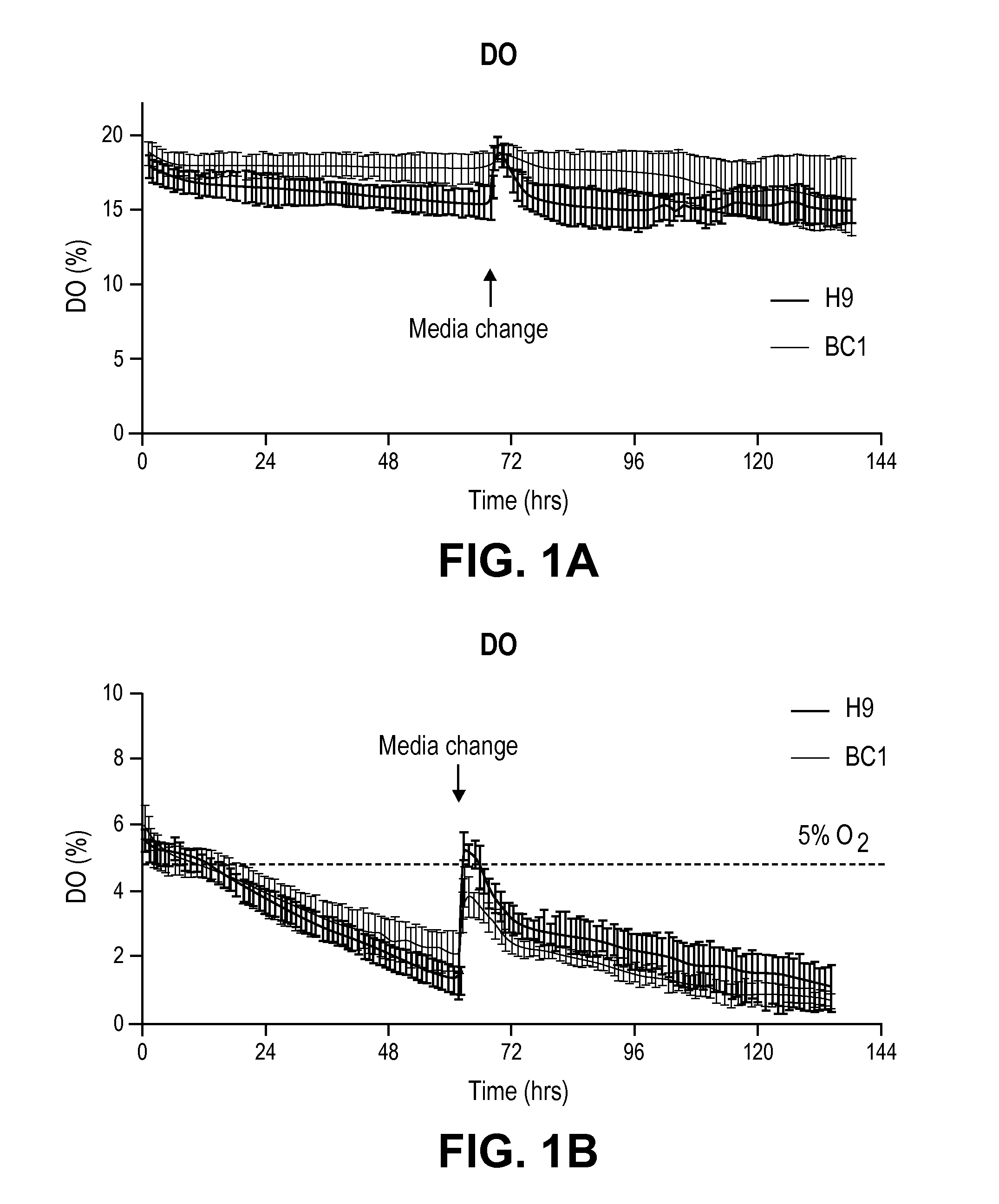
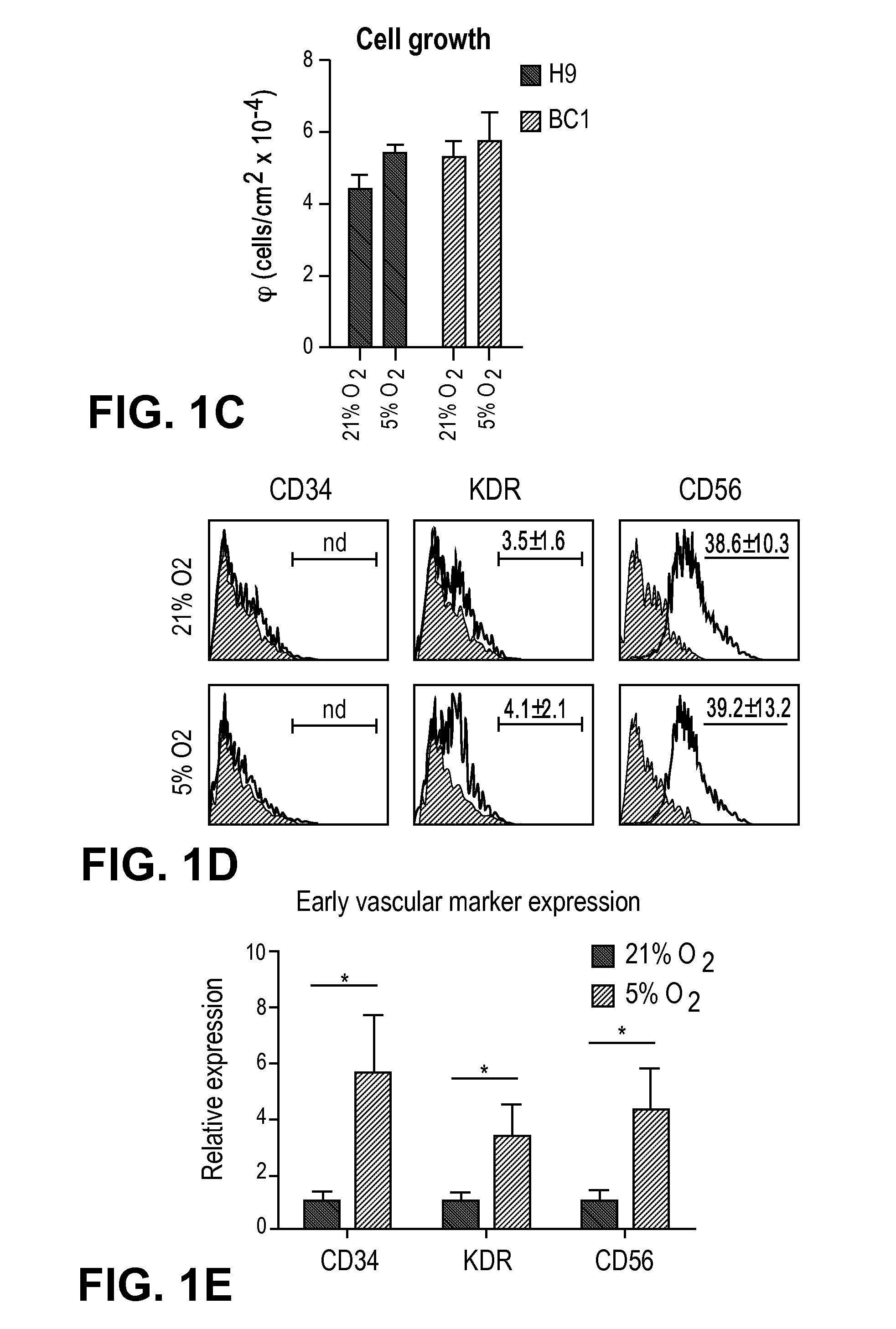
Low oxygen tension is a critical regulator of the developing or regenerating vasculature. The present invention is based on the determination that low oxygen tension during early stages of early vascular cell (EVC) derivation induces endothelial commitment and maturation of pluripotent stem cells. Inhibition of reactive oxygen species generation during the early stages of differentiation abrogates the endothelial inductive effects of the low oxygen environments. Methods of generating various types of cells from pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) are described, as well as compositions and methods of use thereof. In particular, generation of EVCs, bicellular vascular populations, early endothelial cells (ECs) and pericytes via culture in a low oxygen environment is described.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Pericyte progenitors from peripheral blood
ActiveUS9809798B2Increase depositionAmplifies differentiation responsePeptide/protein ingredientsCulture processProgenitorPericyte
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Pericytes for use as stem cells
A method of promoting perictye differentiation by selectively culturing pericytes in an enriched environment containing a promoter specific to a type of differentiation. Isolated and purified multipotent pericytes or pericyte precursors are provided. A stem cell therapy replacement comprising isolated and purified multipotent pericytes. A treatment of disease comprising an effective amount of isolated and purified multipotent pericytes or pericyte precursors is provided.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV
Method to construct in-vitro human blood brain barrier model
InactiveUS20140295547A1High medical research availabilityEffective simulationNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsBrain vesselsVascular endothelium
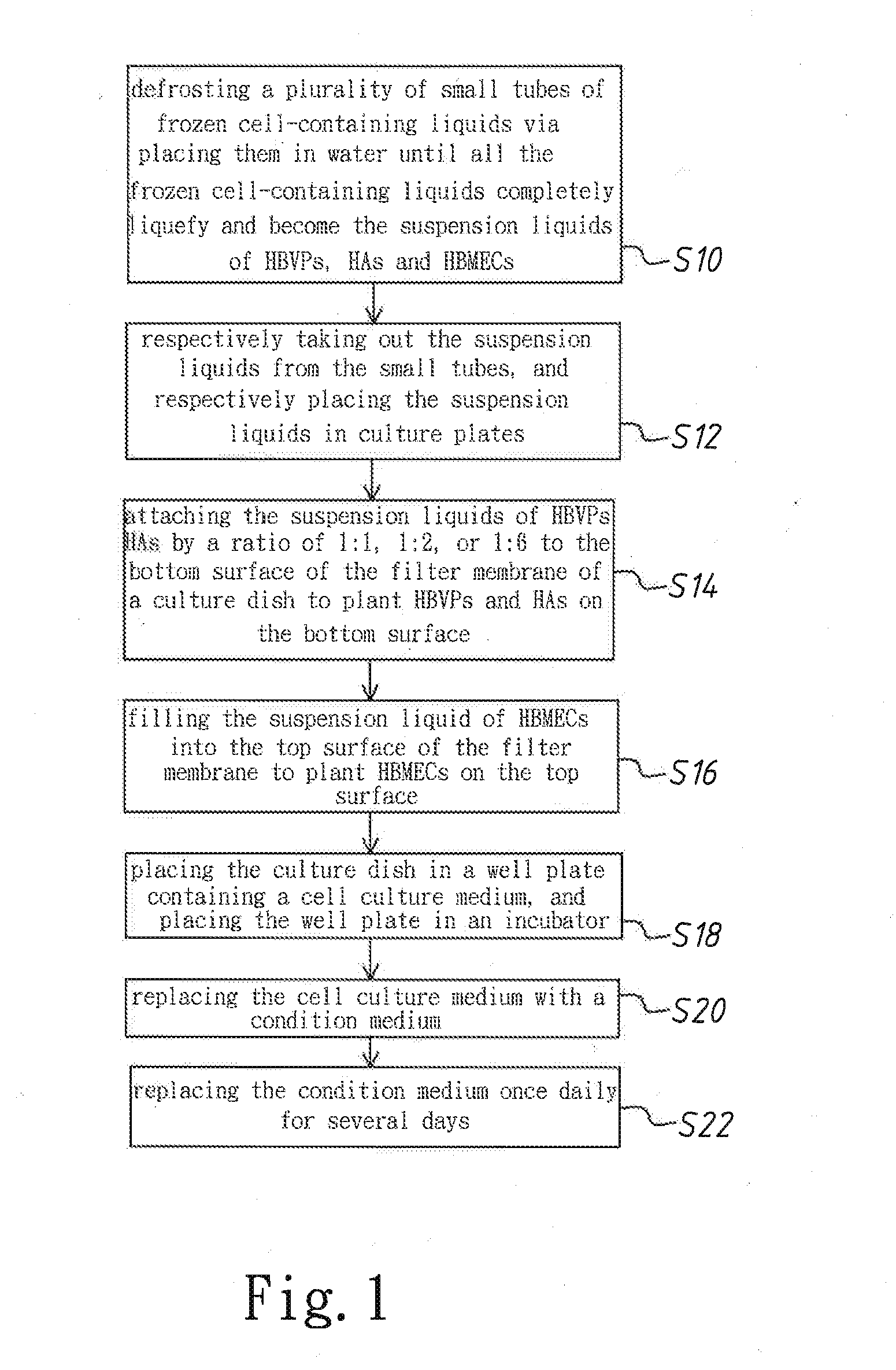
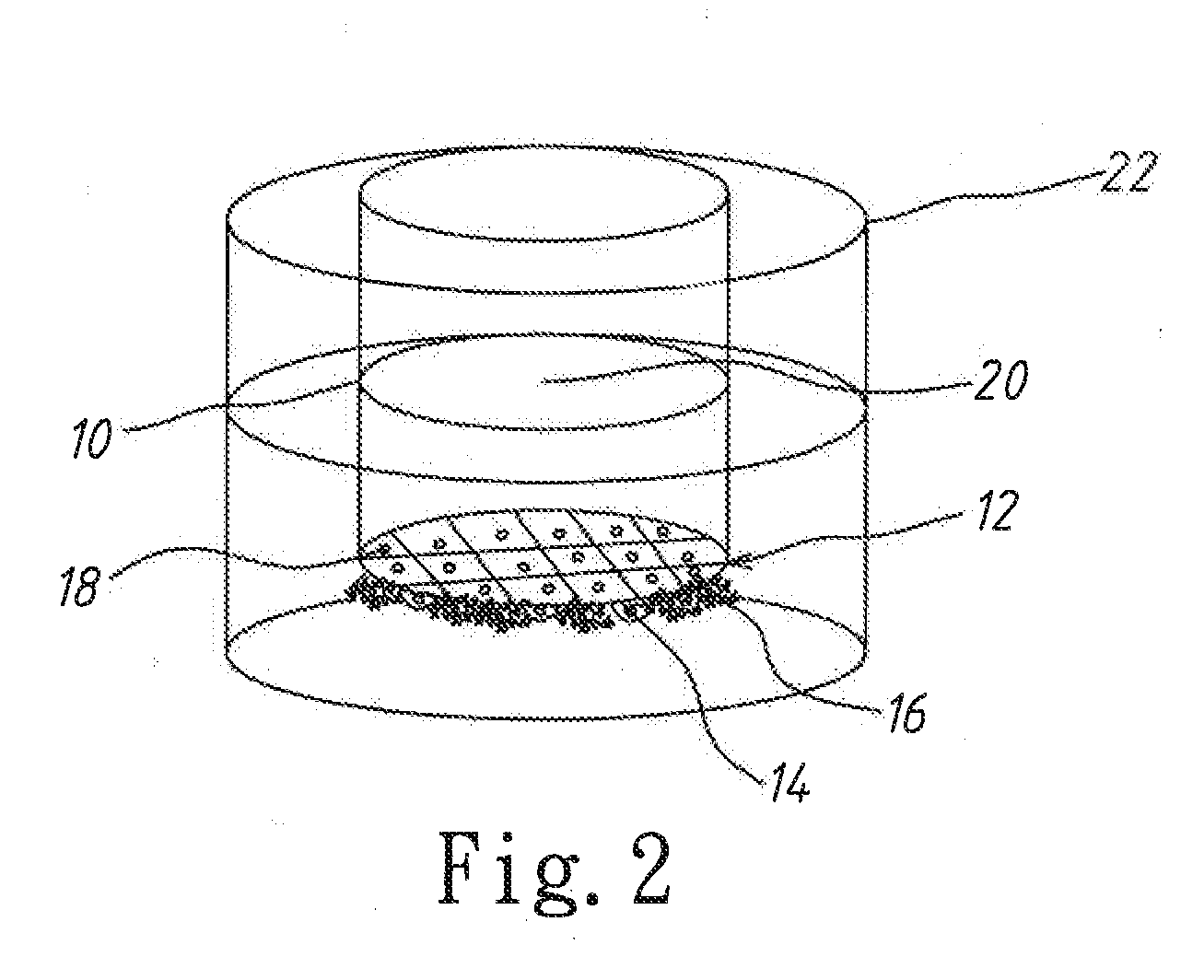
A method to construct an in-vitro human blood brain barrier (BBB) model is disclosed, which comprises steps: attaching suspension liquids of human brain vascular pericytes (HBVPs) and human astrocytes (HAs) by a ratio of 1:1, 1:2, or 1:6 to a bottom surface of a filter membrane of a culture dish to plant HBVPs and HAs on the bottom surface; filling a suspension liquid of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) into a top surface of the filter membrane to plant HBMECs on the top surface; placing the culture dish in a well plate containing a culture medium, and placing the well plate in a carbon-dioxide incubator; replacing the culture medium with a condition medium; and replacing the condition medium once daily for a plurality of days. Thereby is constructed an in-vitro human BBB model of high medical research availability.
Owner:NATIONAL CHUNG CHENG UNIV
Electrostretched polymer microfibers for microvasculature development
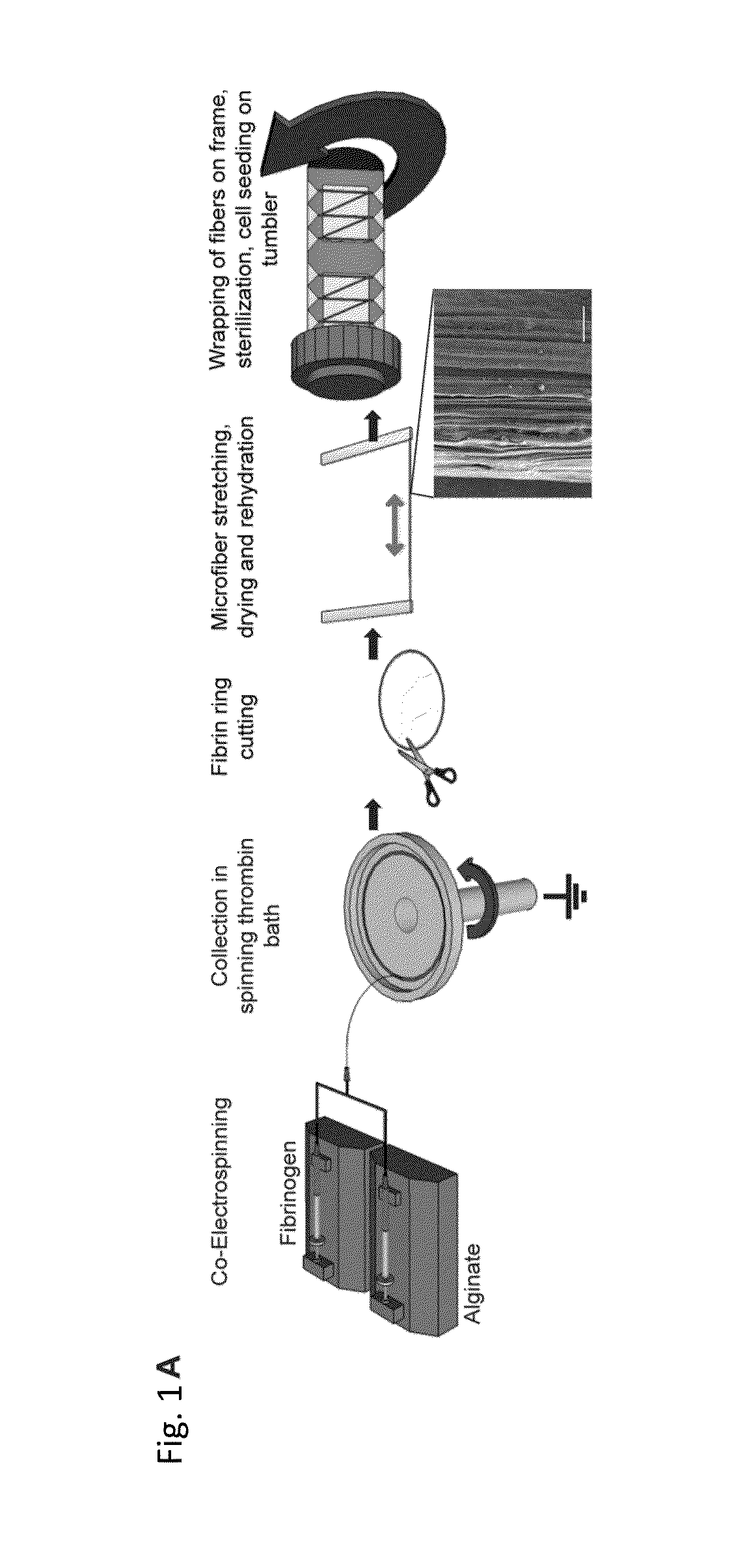
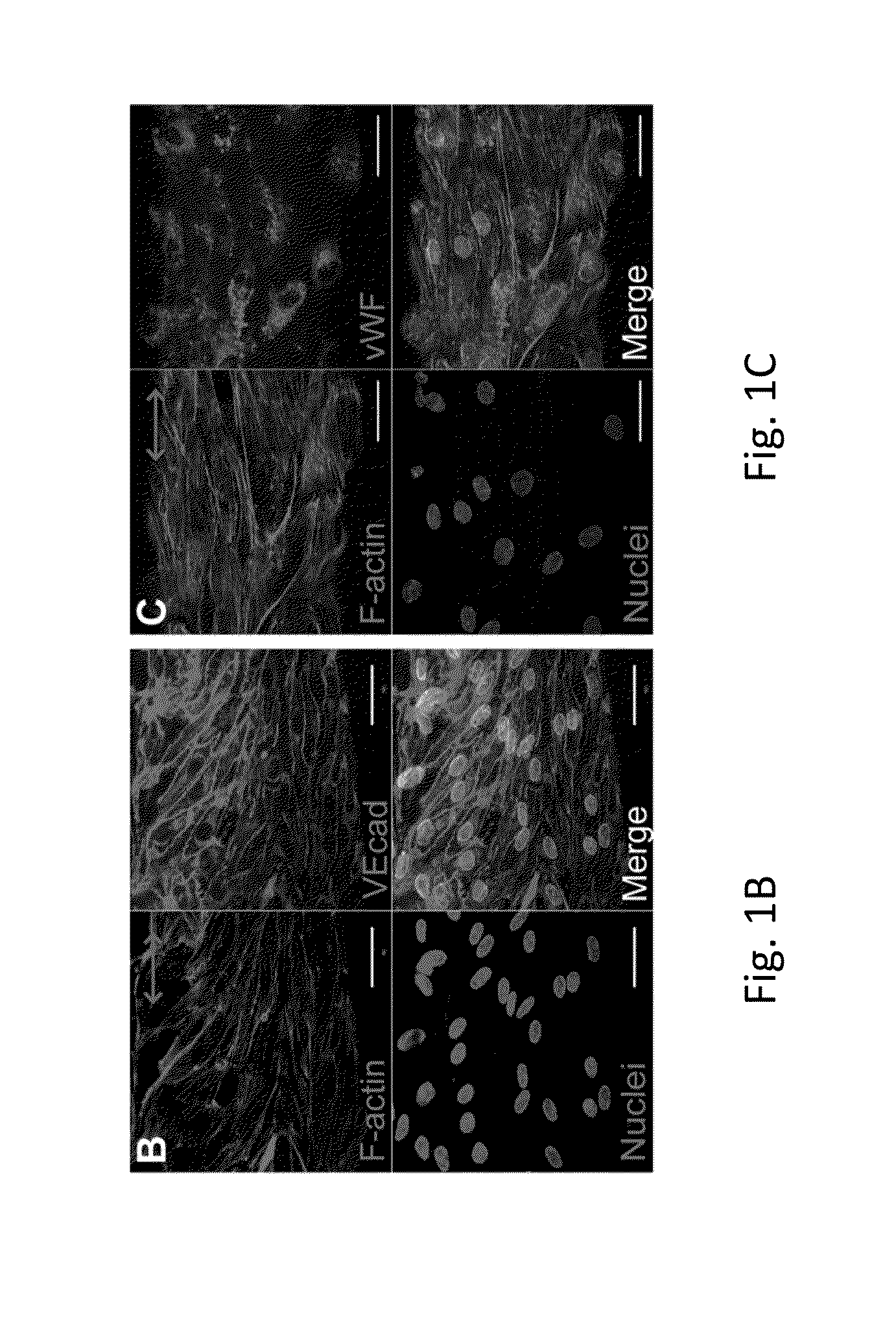
An in vitro model system that guides the development of microvasculature, recapitulating the detailed organization of both its cellular and a-cellular components is established. Use of electrostretched fibrin microfibers enables both endothelial layer organization and co-culture of supporting perivascular (mural) cells such as vascular smooth muscle cells and pericytes. The fiber curvature affects the circumferential deposition of endothelial-produced ECM independently of cellular organization and induces deposition of higher quantities of vascular ECM proteins. Further, a luminal multicellular microvascular structure is disclosed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Novel screens to identify agents that modulate retinal blood vessel function and pericyte function and diagnostic and therapeutic application therefor
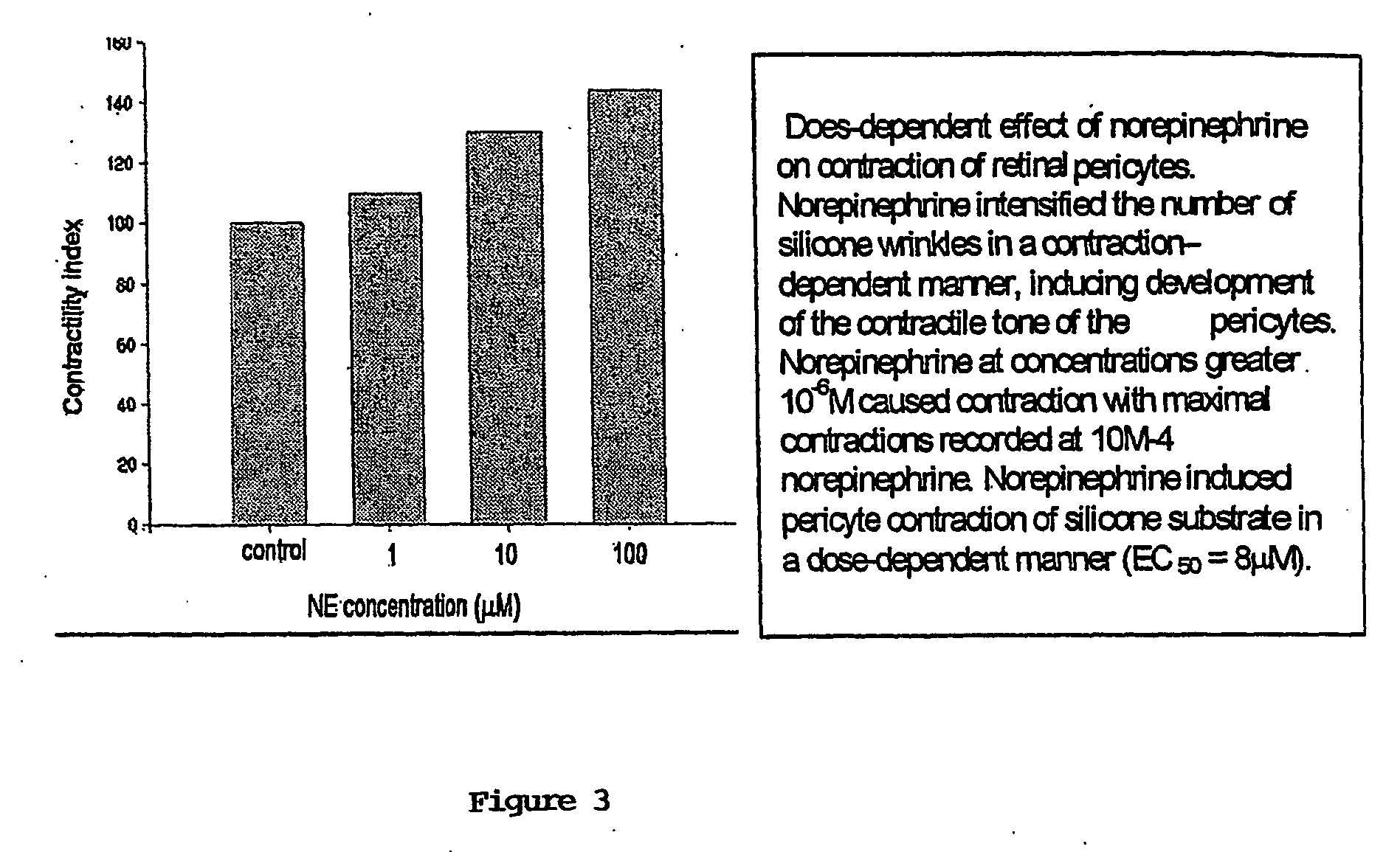
InactiveUS20050232916A1Reduced stateRapid contractionCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsMedicineRetina
The present invention provides methods for determining or identifying compounds that modulate the function of an isolated retinal pericyte or blood vessel, wherein a change in the contractile state of said pericyte or blood vessel is determined in the presence of a test compound, said change indicating that the test compound modulates the function of pericytes and / or blood vessels.
Owner:MARTIN DONALD KEITH +1
Composition and method for treating peripheral t-cell lymphoma and cutaneous t-cell lymphoma
InactiveUS20200289520A1High activityPharmaceutical delivery mechanismAntineoplastic agentsPTK InhibitorsPharmaceutical drug
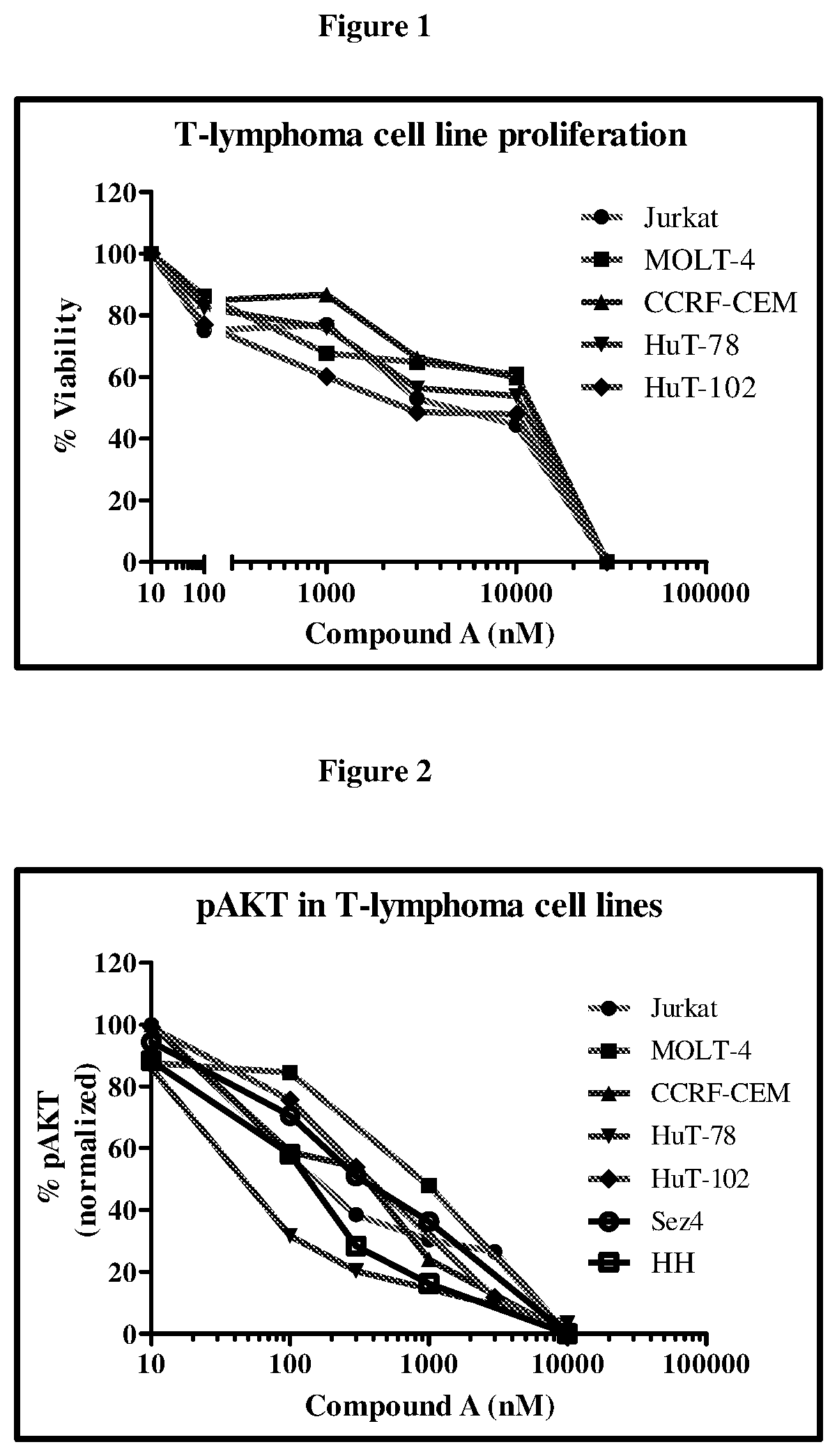
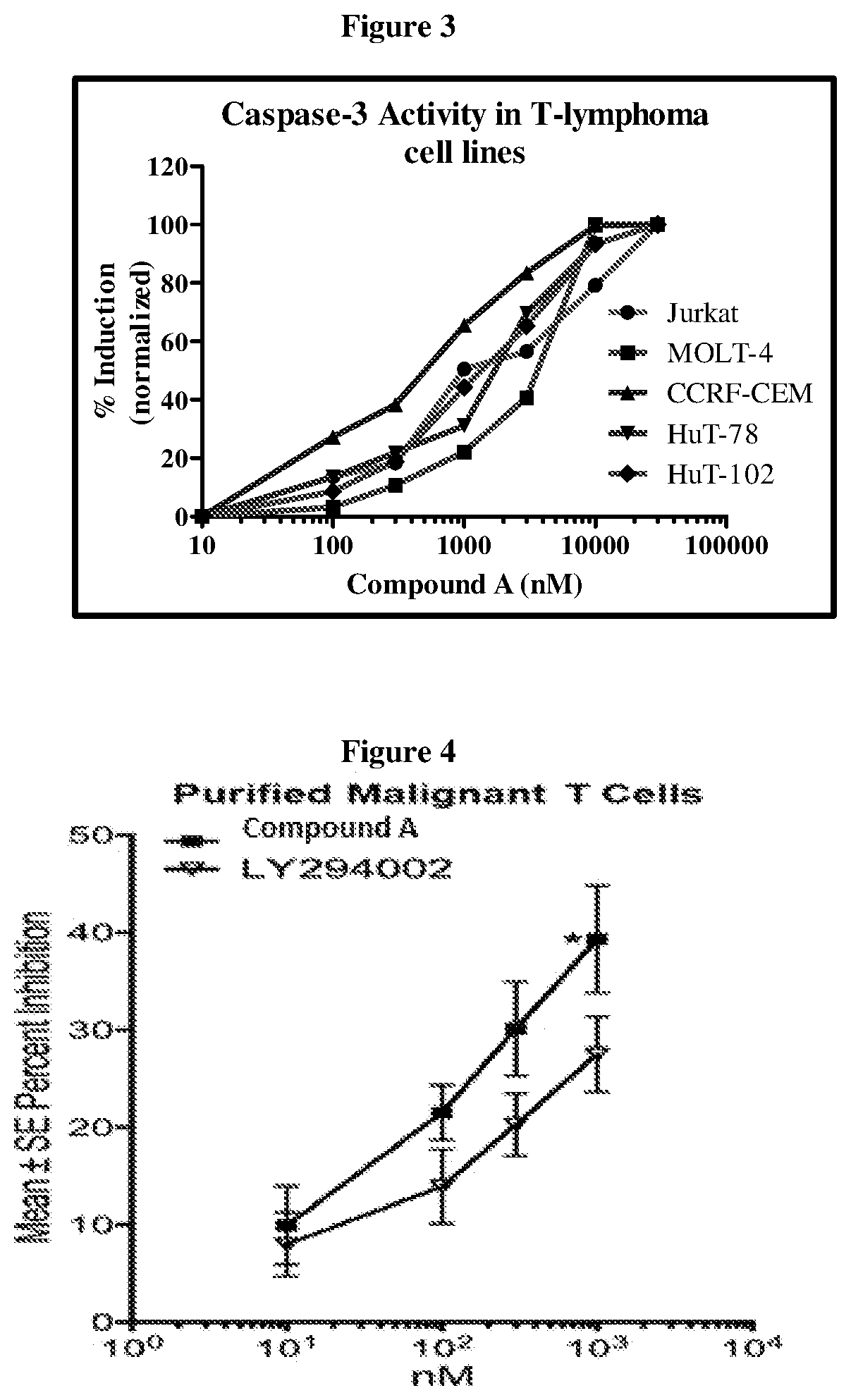
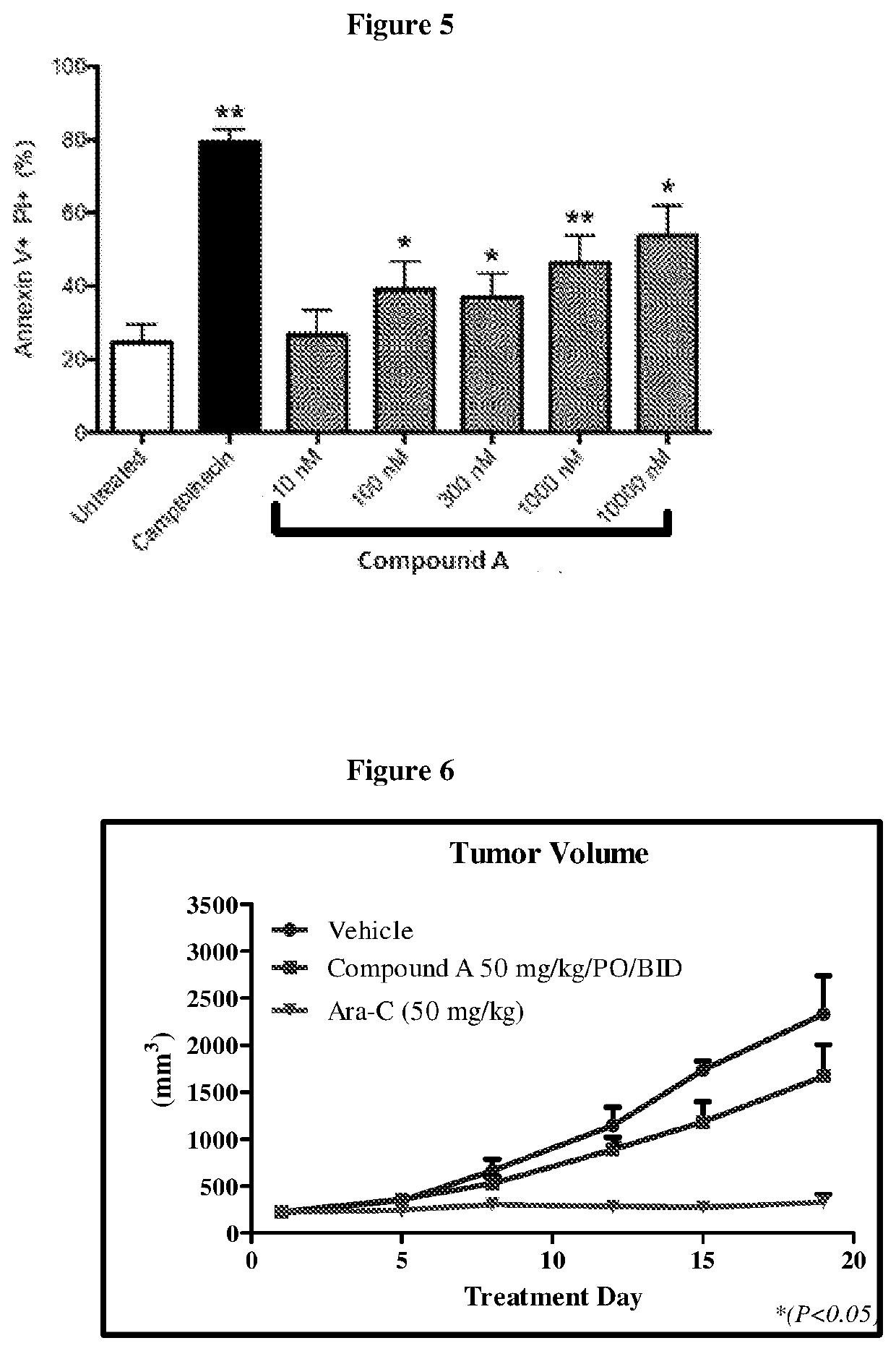
The present invention relates to the use of a dual selective PI3K delta and gamma protein kinase inhibitor, such as (S)-2-(1-((9H-purin-6-yl)amino)propyl)-3-(3-fluorophenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (Compound (A), also known as tenalisib) or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof or a pharmaceutical composition containing such an inhibitor for the treatment of peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) and cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL). 34 139095.00100 / 115268675v.1
Owner:RHIZEN PHARMACEUTICALS AG
Compositions and methods for treating retinopathy
PendingUS20170080030A1Encourages regenerationStabilizes retinal microvasculaturePeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismDiabetic retinopathyMedicine
The present invention encompasses the use of adipose tissue derived cells, or conditioned medium of such cells, to treat and prevent vascular related injuries, diseases, disorders, and conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, where, in one aspect, pericytes such as retinal pericytes have been lost or damaged. The present application further discloses compositions and methods useful for enhancing the function and activity of the adipose tissue derived cells in the treatment and prevention of injuries, diseases, disorders, and conditions including the use of TGFβ to condition the cells to enhance their activity.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Blood brain barrier models and methods to generate and use the same
ActiveUS10877026B2High expressionImprove tightnessNervous system cellsArtificial cell constructsMedicinePharmaceutical drug
The present disclosure generally relates to a process to prepare a cell culture system that mimics the structure of blood brain barrier (BBB) and are useful to study the functions thereof. In particular, the present invention relates to a direct-contact coculture and triculture systems prepared by plating BMECs on a pre-formed lawn of coculture of astrocytes and pericytes on the apical surface of a culture-chamber to achieve a truly direct contact triculture model for BBB. The cell culture systems disclosed herein are also useful for studying the functions of the blood brain barrier and predicting the efficacy and potential toxicity of a drug candidate.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
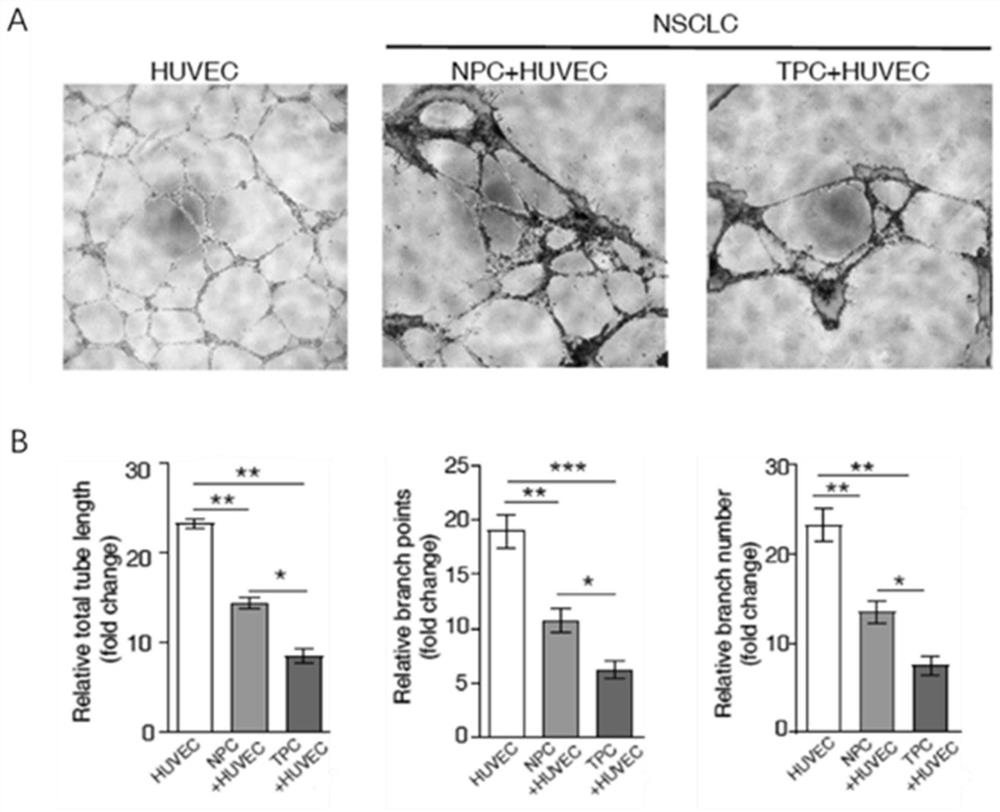
Construction method of endothelial cell and pericyte co-culture model for researching tubulation
ActiveCN113308434AFunction increaseAccurately Test Preclinical EffectivenessCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsHuman tumorStaining
The invention discloses a construction method of an endothelial cell and pericyte co-culture model for researching tubulation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) digesting umbilical vein endothelial cells with trypsin to obtain umbilical vein endothelial single cells; (2) digesting pericytes into single cells of the pericytes by using trypsin, and then adding CFSE dye with the final concentration of 2-10 [mu]mol / L for staining to obtain stained pericytes; and (3) uniformly mixing the umbilical vein endothelial single cells and the stained pericytes according to the cell number ratio of (5-20):1, conducting culturing by using a bronchial epithelial cell culture medium, and observing the formation condition of the tube on a fluorescence microscope. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the influence of pericytes on the formation of endothelial cell tubes can be dynamically observed through a fluorescence microscope, the effect of human tumor pericytes on tumor blood vessels can be reflected through in-vitro experiments, and the method has good social and economic values.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN MEMORIAL HOSPITAL SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Genetically modified human umbilical cord perivascular cells for prophylaxis against or treatment of biological or chemical agents
ActiveUS20110177023A1Extend your lifeReduce riskAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseBiological agent
The invention provides methods of preventing or treating diseases or disorders caused by biological agents or chemical agents in a subject (e.g., a mammal, such as a human) by administering genetically modified human umbilical cord perivascular cells.
Owner:TISSUE REGENERATION THERAPEUTICS
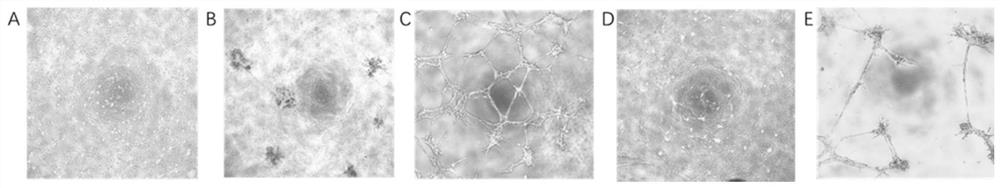
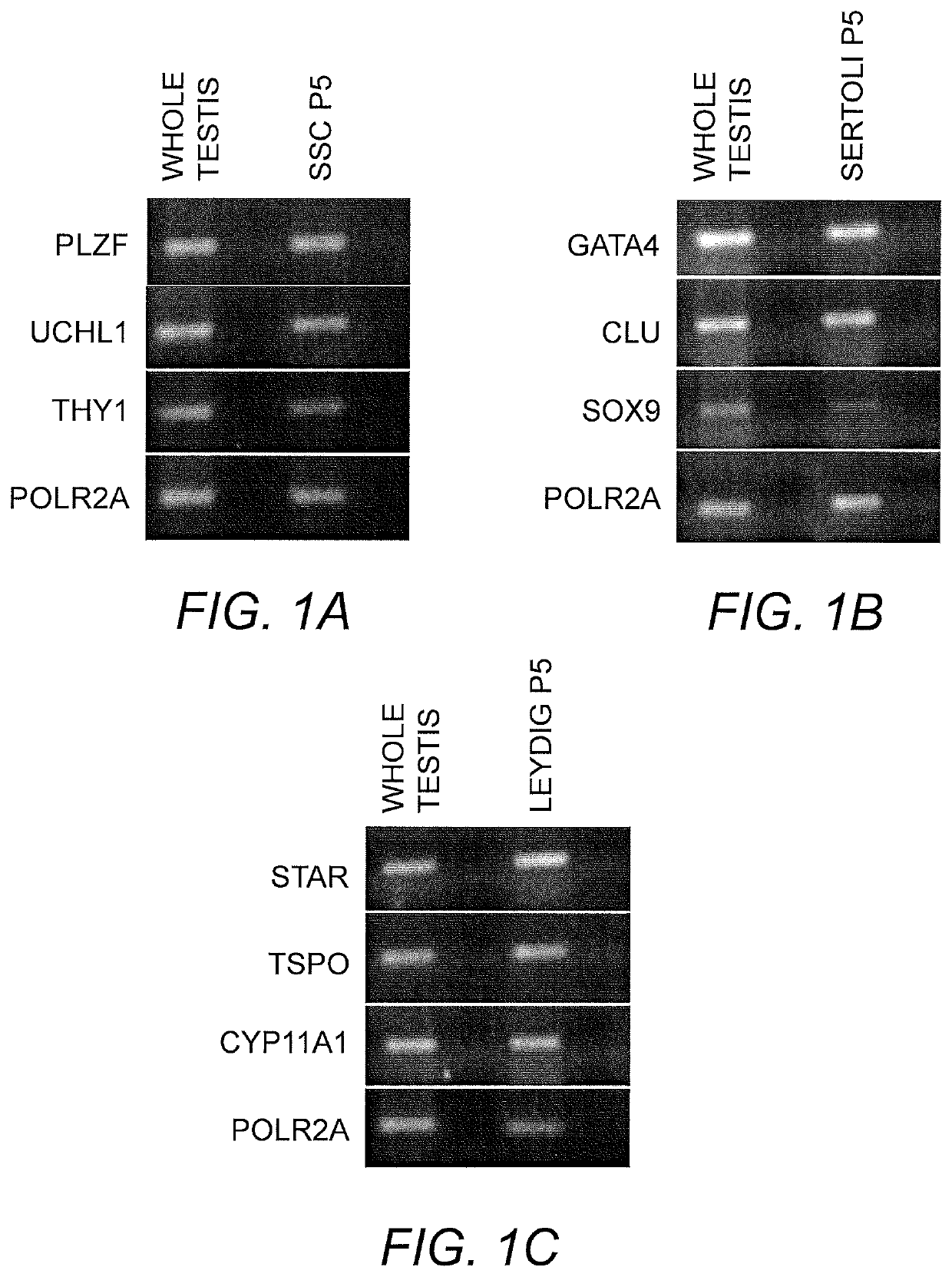
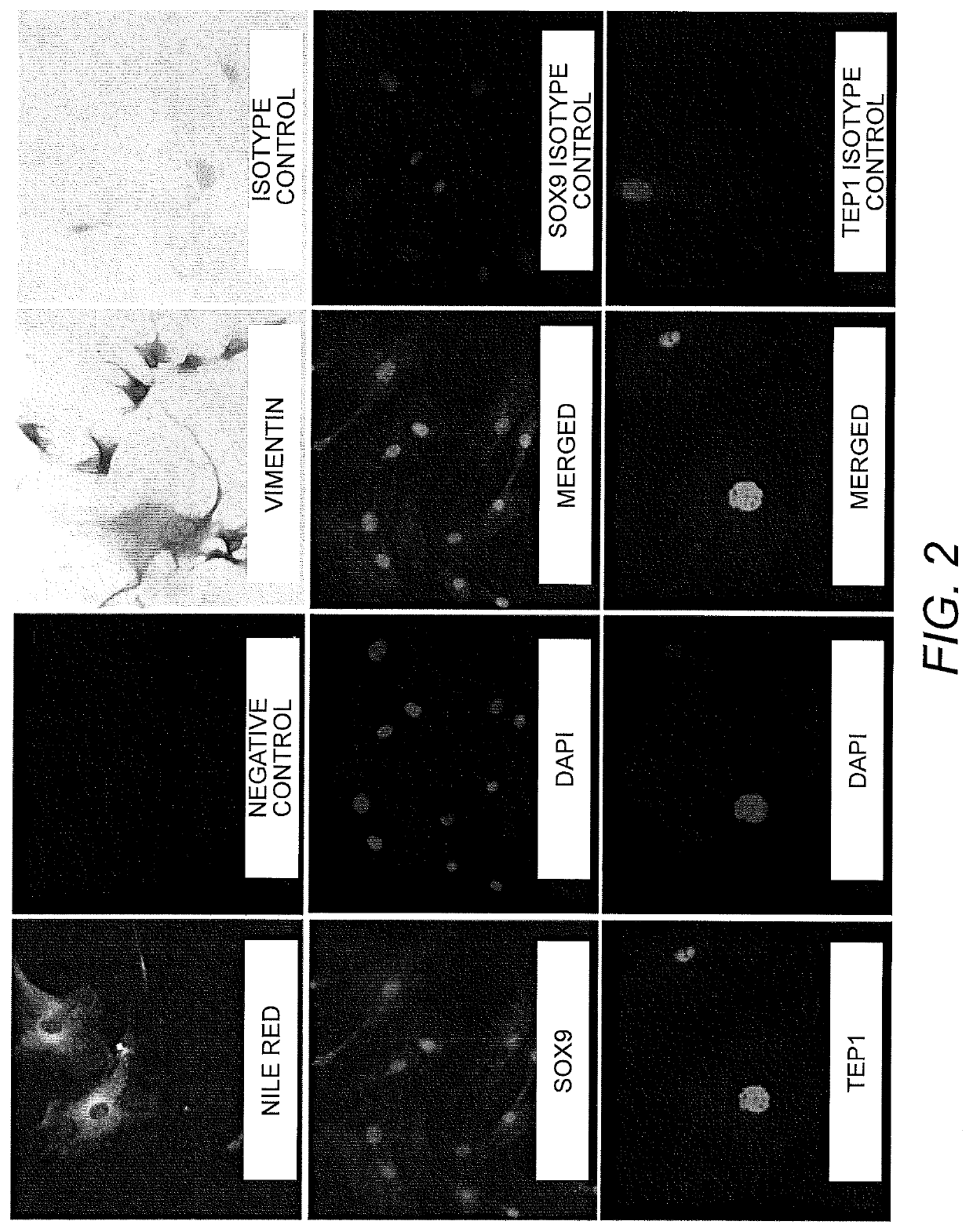
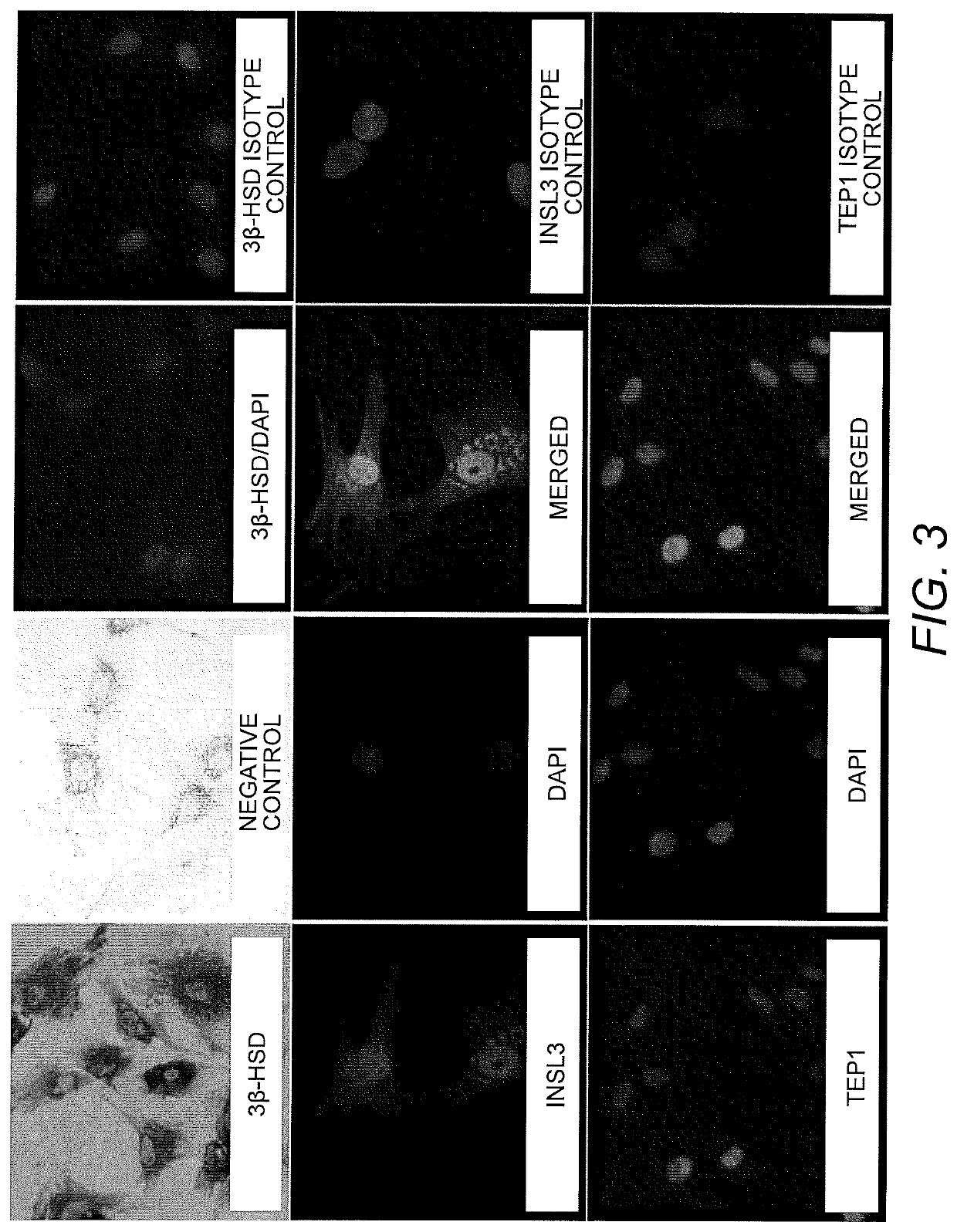
Method of producing in vitro testicular constructs and uses thereof
A cell composition composed of spermatogonial stem cells, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells and optionally peritubular cells, is provided, as is a culture composition, artificial testicular construct, hydrogel composition, and device containing the same. A method for using the device as a physiologically relevant in vitro model of human testicular function to screen compounds for pharmacological or toxicological activity is also provided.
Owner:WAKE FOREST UNIV HEALTH SCI INC
Mixed stem cell injection containing three vascular regeneration attributes and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111544453AAvoid the defects that are difficult to apply clinicallyRealize the function of regenerating blood vesselsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMammal material medical ingredientsCell-Extracellular MatrixUmbilical cord artery
Owner:高连如
Stable three-dimensional blood vessels and methods for forming the same
PendingUS20190376044A1Costly and time-consumeGenetically modified cellsCulture processEndothelial cell cultureVascular structure
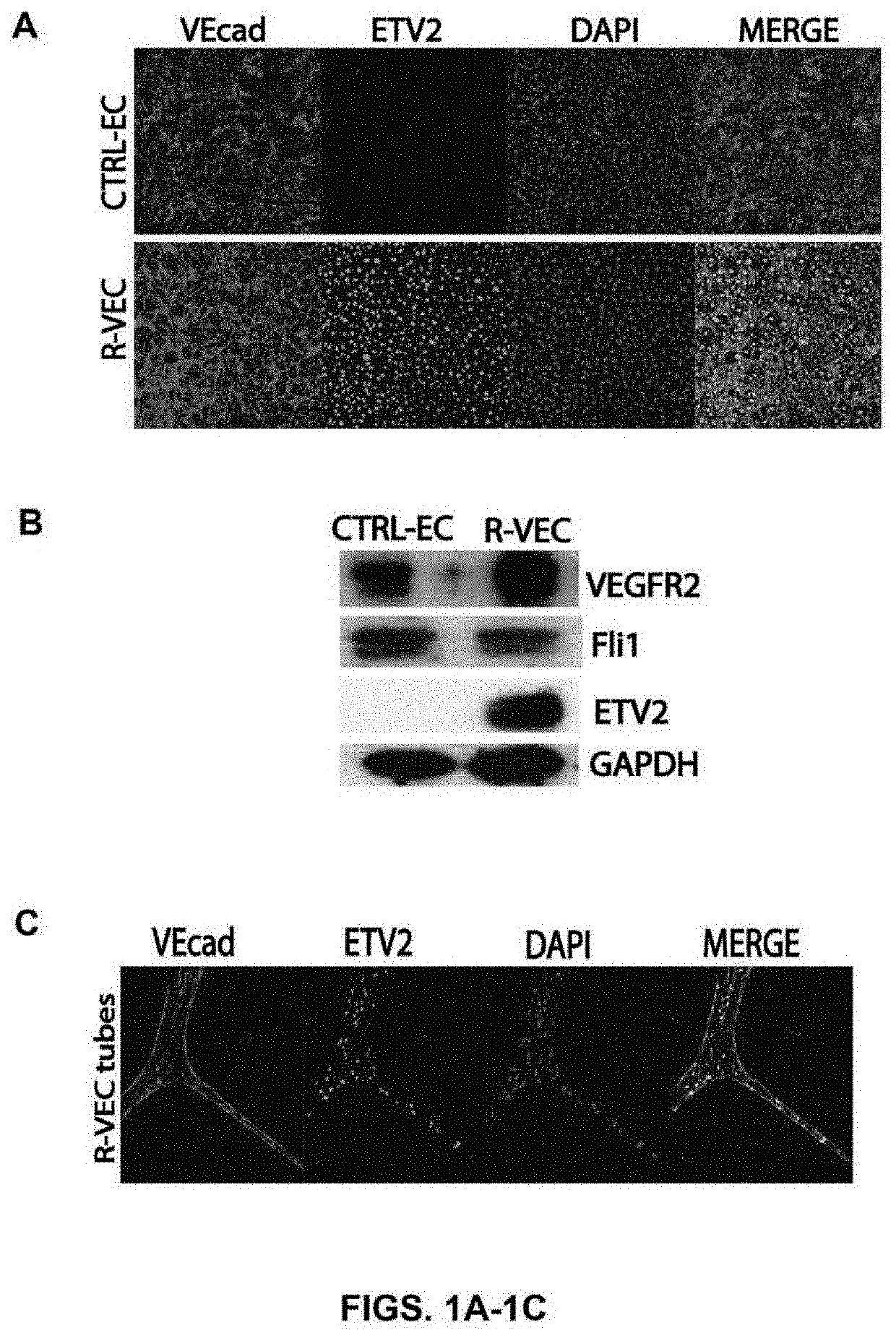
The present disclosure provides methods for forming stable three-dimensional vascular structures, such as blood vessels and uses thereof. More specifically, the present disclosure provides methods for culturing differentiated endothelial cells that include an exogenous nucleic acid encoding ETV2 transcription factor on a matrix under conditions that express exogenous ETV2 protein in the endothelial cell to form stable three-dimensional artificial blood vessels without the use of a scaffold, pericytes or perfusion. The present disclosure also provides stable three-dimensional blood vessels that are capable of autonomously forming a functional three-dimensional vascular network, and uses thereof. In addition, the present disclosure includes methods for vascularizing an organoid and a decellularized organ by culturing the organoid or decellularized organ with endothelial cells that include an exogenous nucleic acid encoding ETV2 transcription factor under conditions that express exogenous ETV2 protein in the endothelial cell to vascularize the organoid or decellularized organ.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Neural crest-lineage pericyte derived from multi-potential stem cells and induced differentiation method of neural crest-lineage pericyte
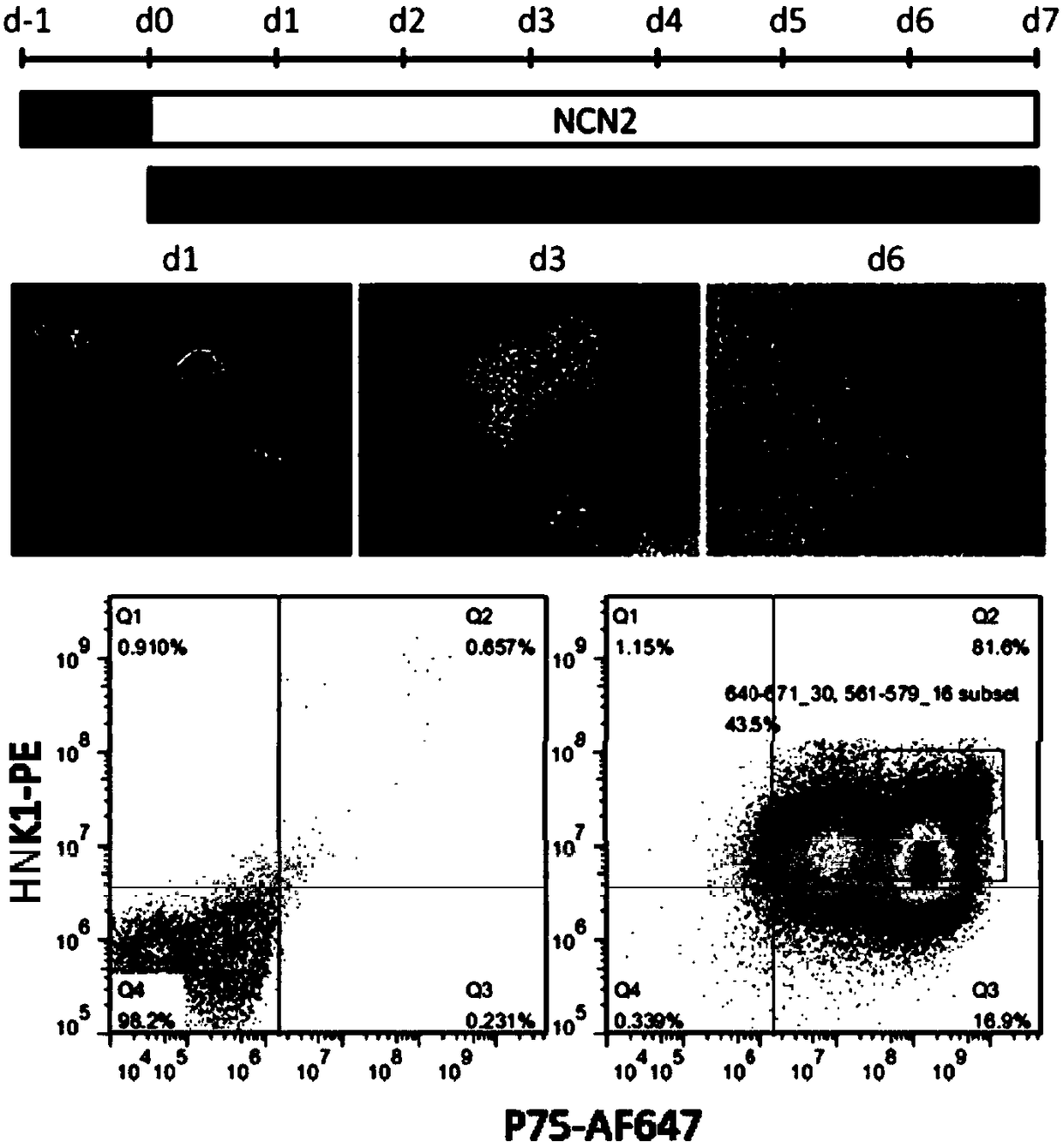
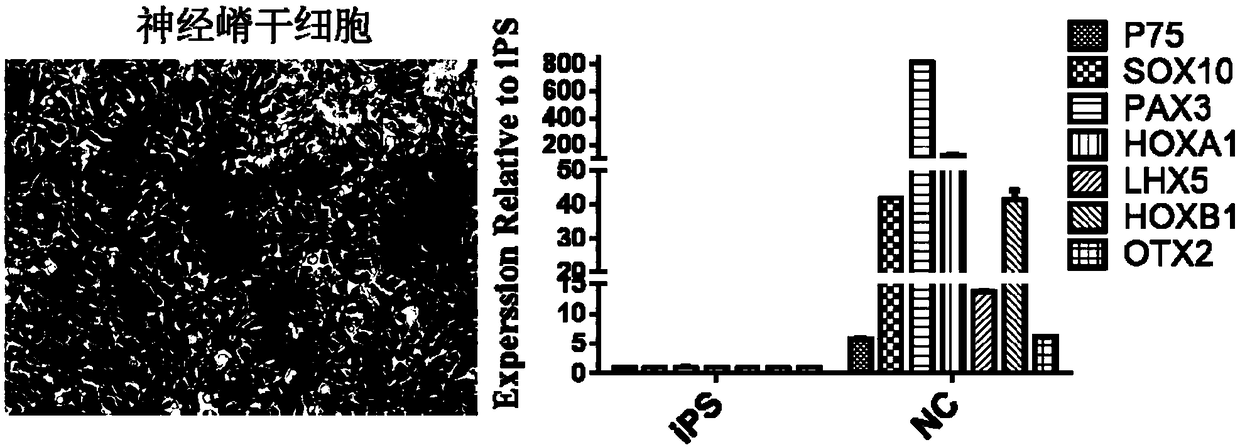
ActiveCN108949688AEnhanced CytologyIncreased therapeutic functionNervous system cellsCell culture active agentsCell phenotypePluripotential stem cell
The invention discloses a neural crest-lineage pericyte derived from multi-potential stem cells and an induced differentiation method of the neural crest-lineage pericyte. The induced differentiationmethod comprises the following steps: dissociating the multi-potential stem cells to obtain single-cell suspension, inoculating the single-cell suspension into a matrigel-coated pore plate, and changing the suspension through an NCN2 culture medium each day; carrying out culturing for a certain period of time, carrying out digestion, and collecting cells; carrying out adherent culture on the collected cells, changing culture liquid into pericyte induced culture liquid, carrying out subculture, and detecting the cell phenotype of the pericyte. According to the induced differentiation method, the disadvantages of limited source of human cerebral vessel pericytes, and the heterogeneity and linkage heterogeniety of the pericytes derived from multi-potential stem cells obtained in other non-finite induction ways are solved, and the obtained neural crest-lineage pericyte has very strong blood vessel stabilizing capacity and contractility; and by virtue of a standardized induced differentiation procedure, cell populations obtained in different batches have good coherence.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com