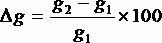Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
57 results about "Biorefinery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A biorefinery is a refinery that converts biomass to energy and other beneficial byproducts (such as chemicals). The International Energy Agency Bioenergy Task 42 defined biorefining as "the sustainable processing of biomass into a spectrum of bio-based products (food, feed, chemicals, materials) and bioenergy (biofuels, power and/or heat)" . As refineries, biorefineries can provide multiple chemicals by fractioning an initial raw material (biomass) into multiple intermediates (carbohydrates, proteins, triglycerides) that can be further converted into value-added products.. Each refining phase is also referred to as a "cascading phase". The use of biomass as feedstock can provide a benefit by reducing the impacts on the environment, as lower pollutants emissions and reduction in the emissions of hazard products. In addition, biorefineries are intended to achieve the following goals...
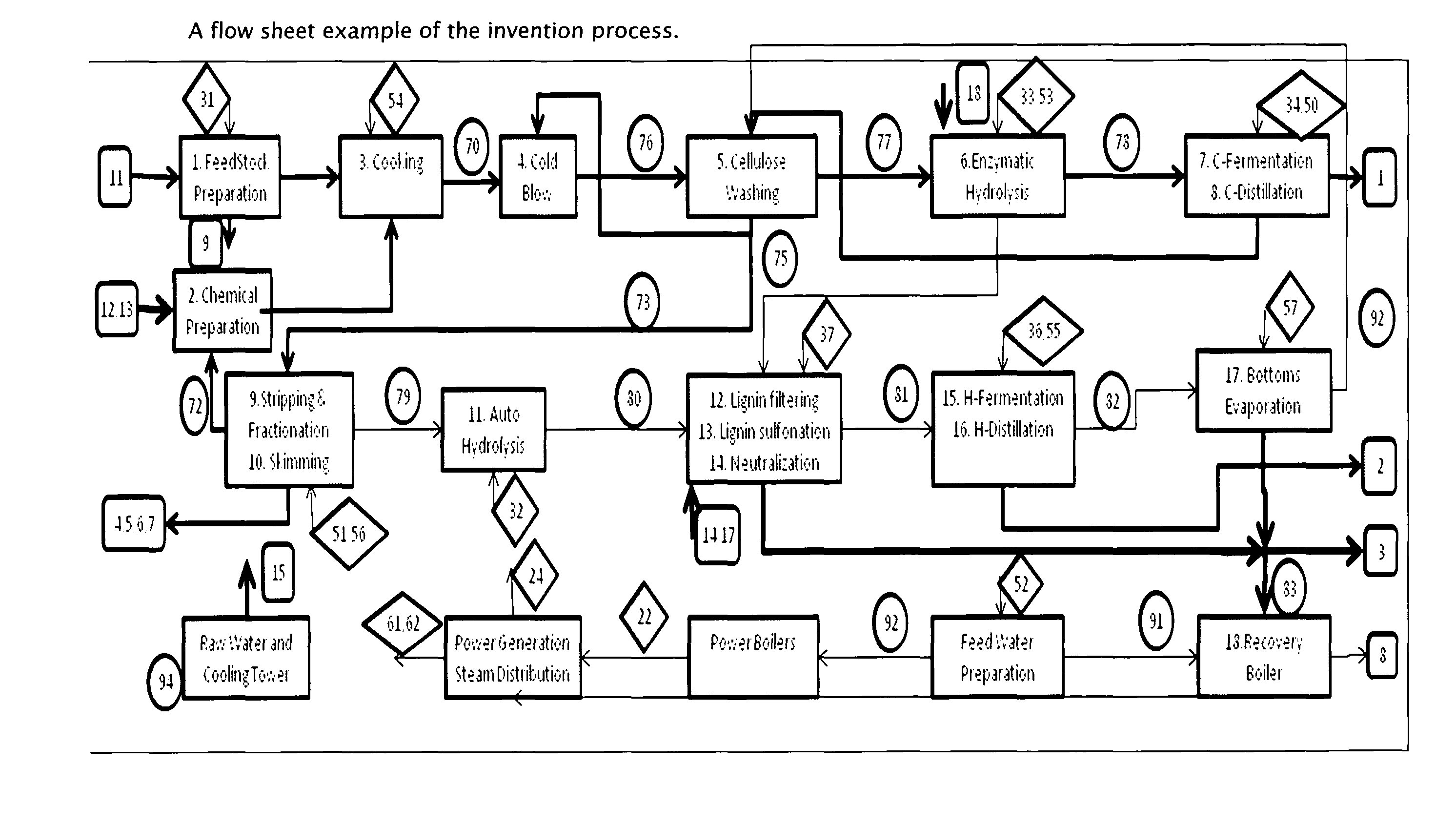
Nano-catalytic-solvo-thermal technology platform bio-refineries
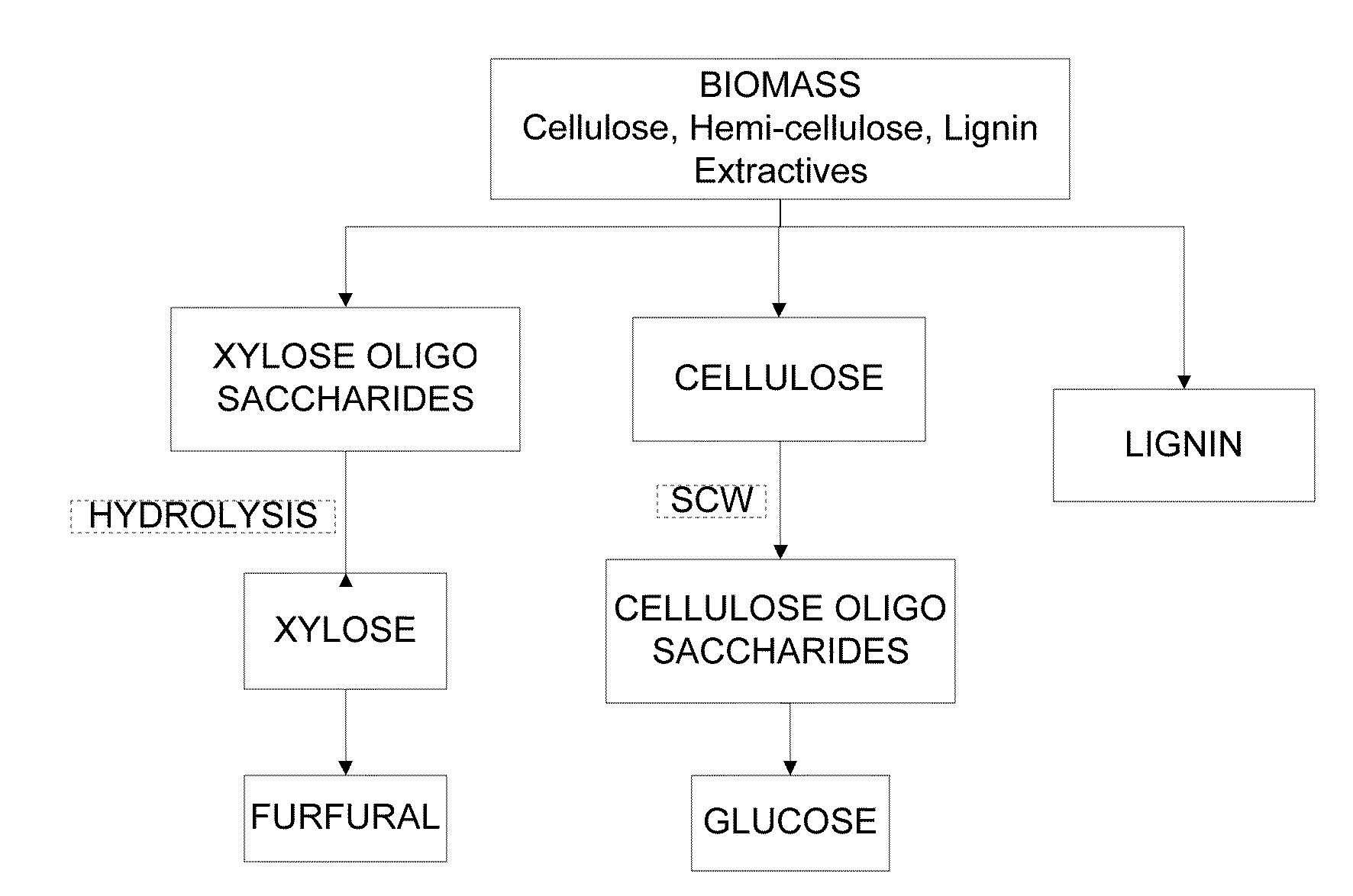
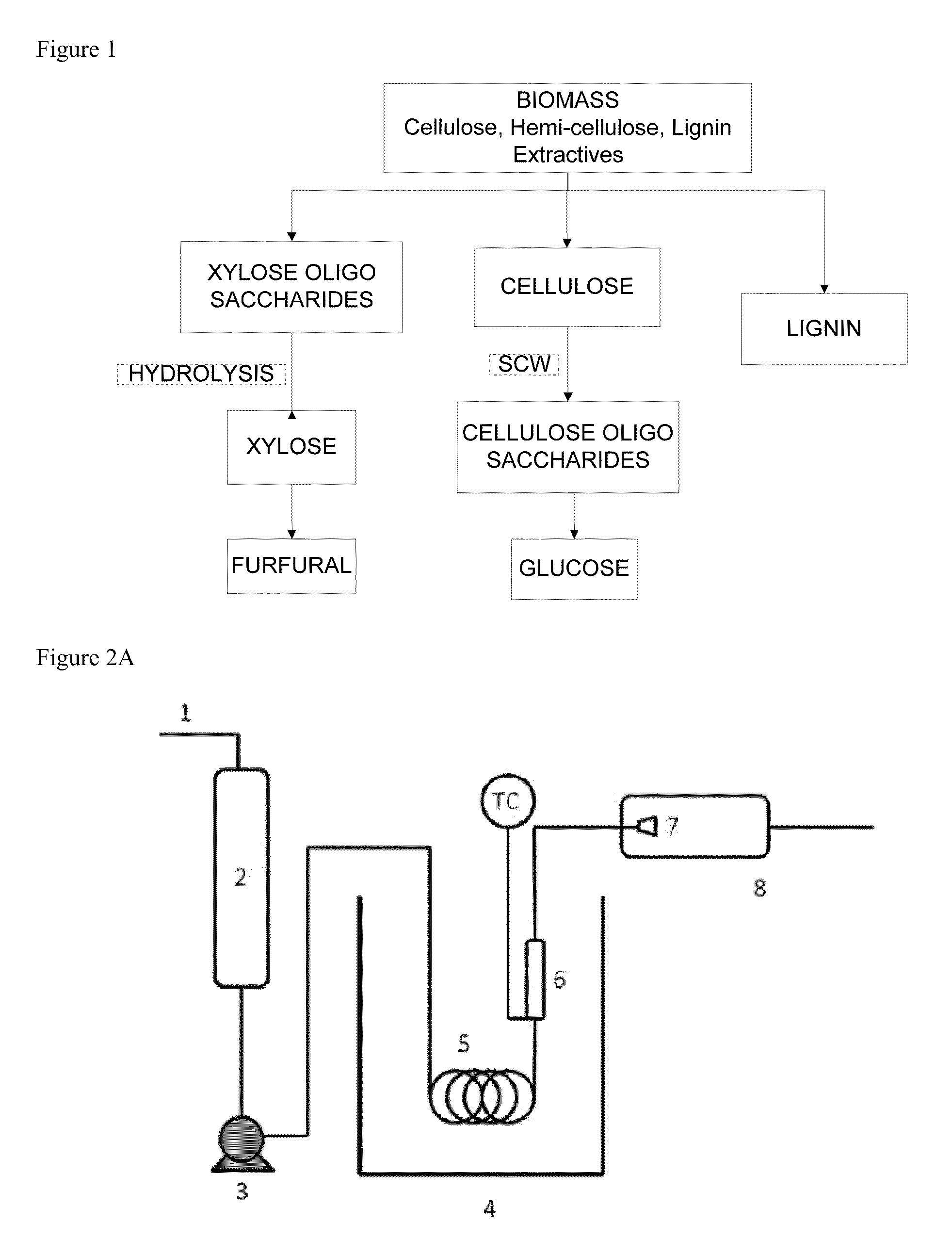
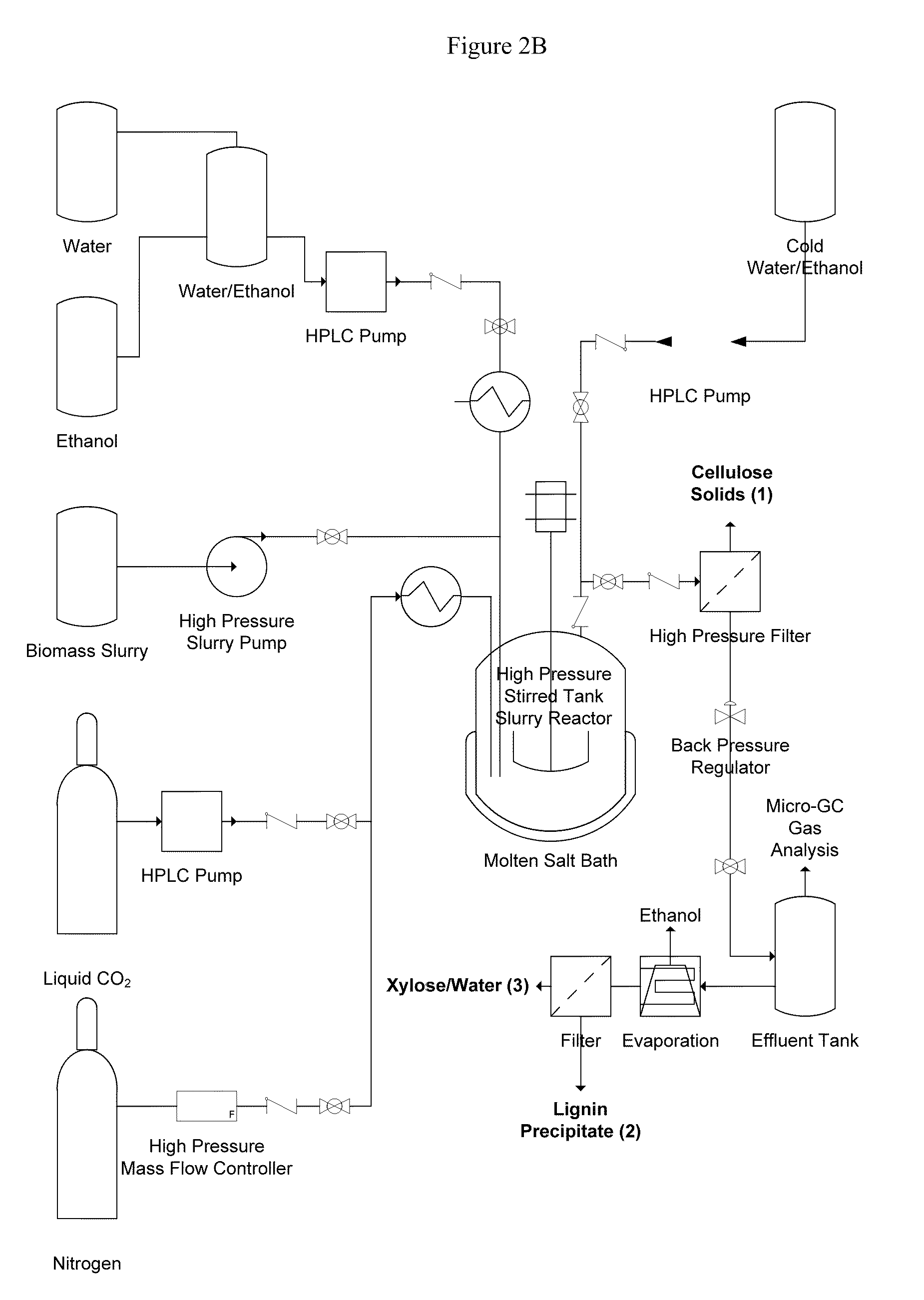
Methods of making glucose and / or furfural from biomass require one or more supercritical fluids that may be used to process biomass, cellulose from the biomass, and / or xylose from the biomass. Examples of supercritical fluids for use in processing biomass include ethanol, water, and carbon dioxide at a temperature and pressure above the critical points for ethanol and carbon dioxide but at a temperature and / or pressure below that of the critical point for water. A supercritical fluid containing carbon dioxide and water may be used to convert cellulose to glucose or convert xylose to furfural. The fluid has a temperature and pressure above the critical point of carbon dioxide, but at least one of the temperature and pressure is below the critical point for water.
Owner:RENMATIX INC
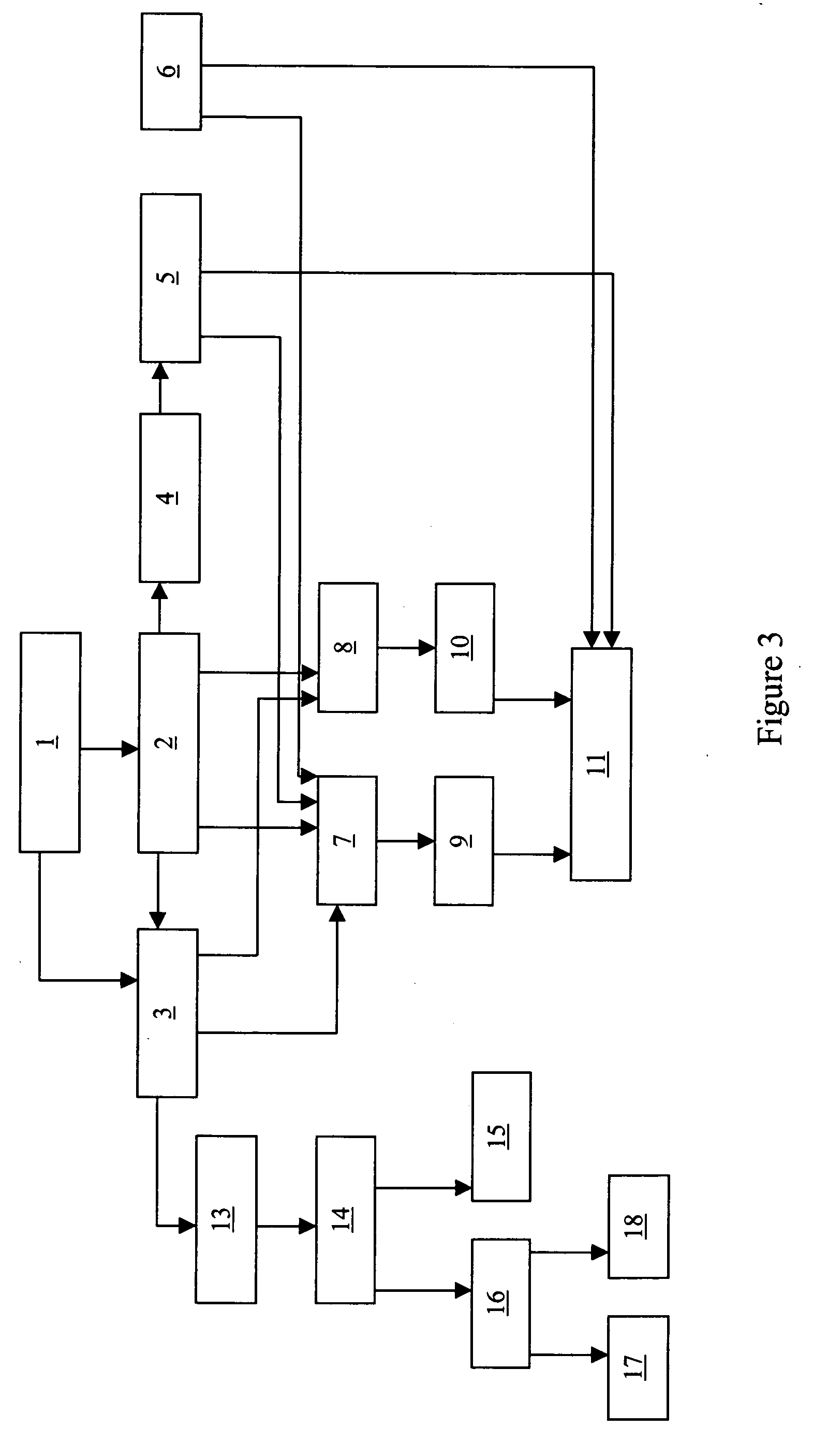
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
ActiveUS20070079944A1Easy to optimizePretreatment with water/steamPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp and paper industrySugar
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
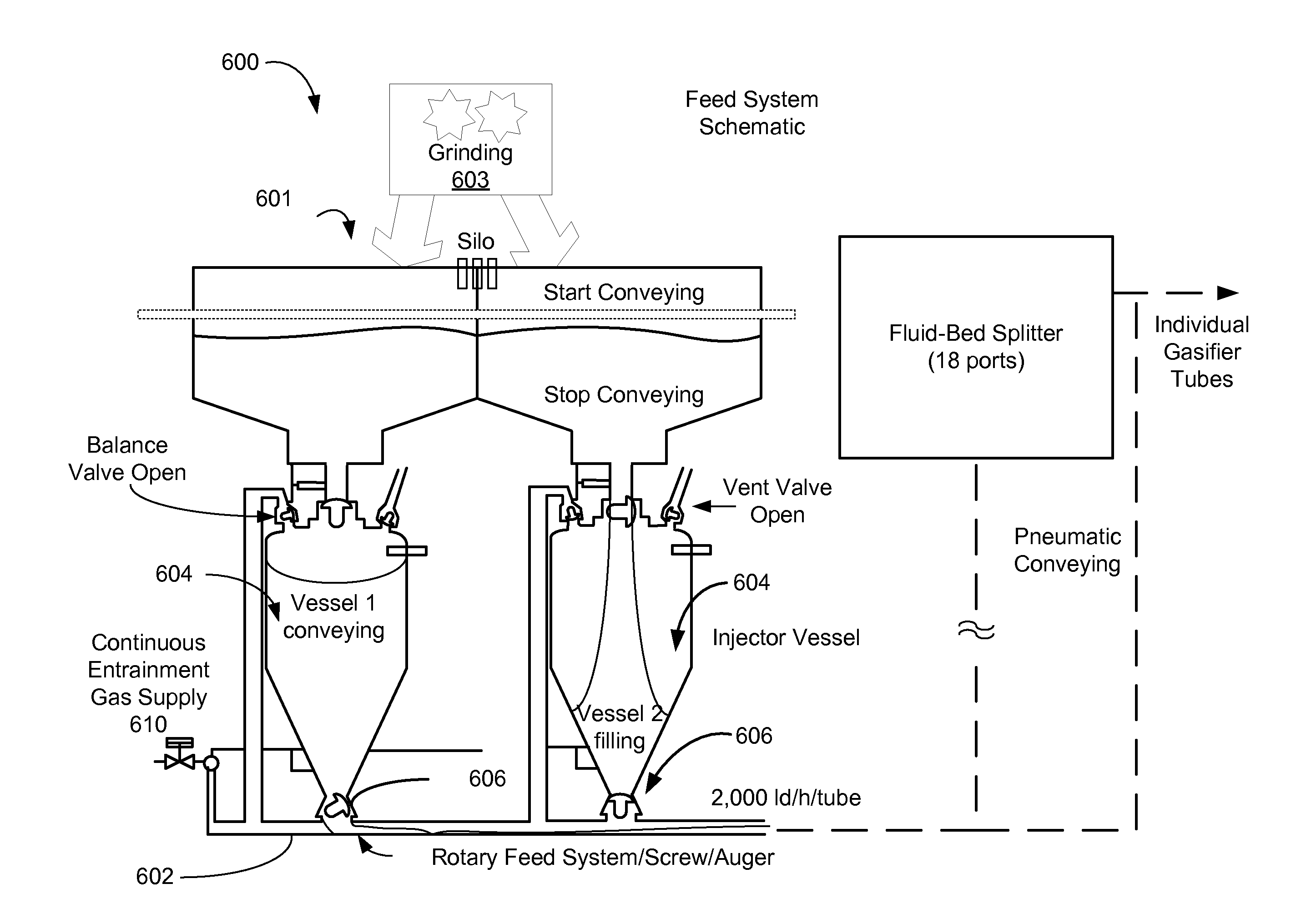
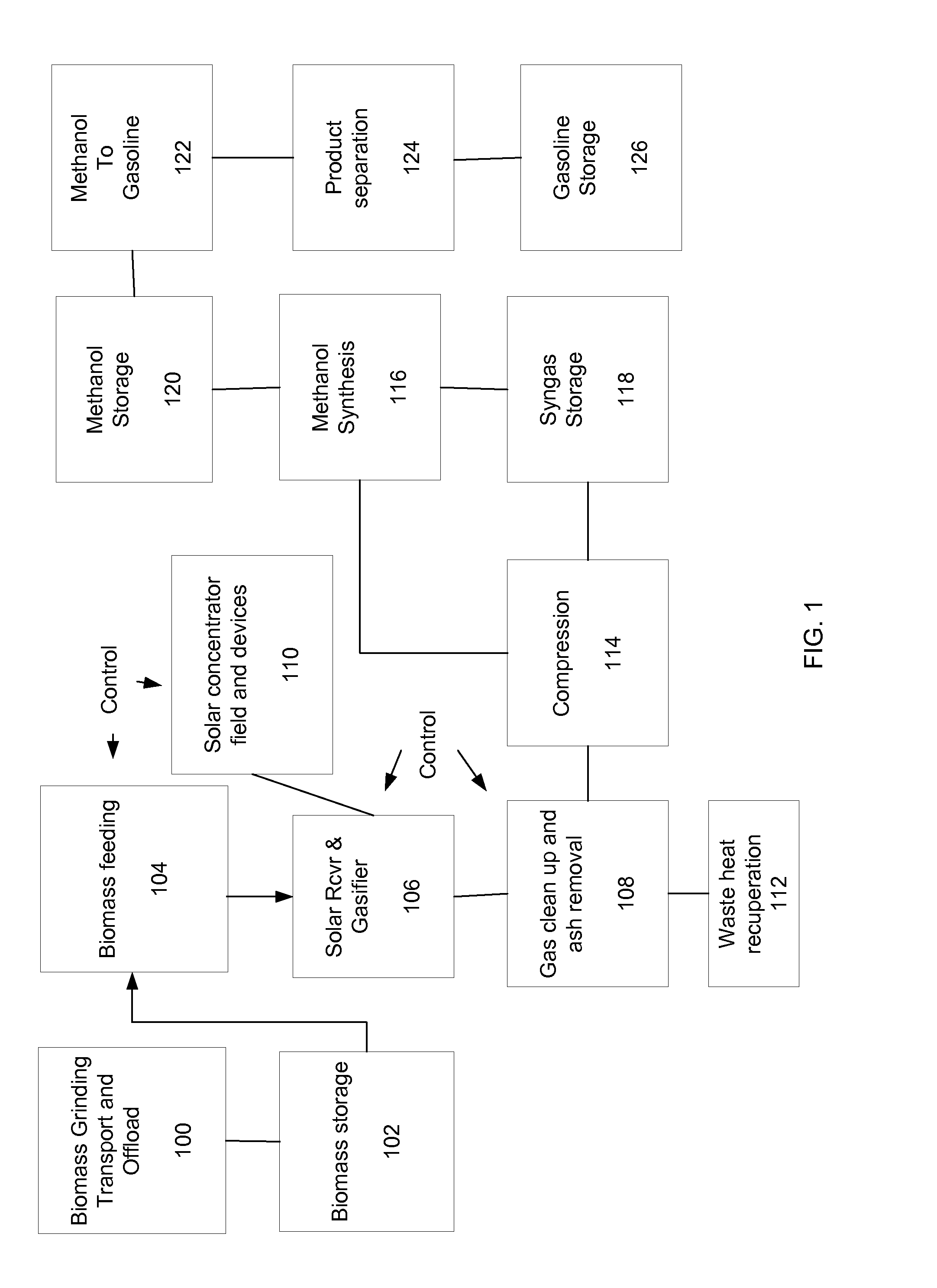
Systems and methods for biomass grinding and feeding
InactiveUS20100242353A1Process control/regulationSolar heating energyChemical reactorLiquid hydrocarbons
A method, apparatus, and system for a solar-driven bio-refinery that may include a entrained-flow biomass feed system that is feedstock flexible via particle size control of the biomass. Some embodiments include a chemical reactor that receives concentrated solar thermal energy from an array of heliostats. The entrained-flow biomass feed system can use an entrainment carrier gas and supplies a variety of biomass sources fed as particles into the solar-driven chemical reactor. Biomass sources in a raw state or partially torrified state may be used, as long as parameters such as particle size of the biomass are controlled. Additionally, concentrated solar thermal energy can drive gasification of the particles. An on-site fuel synthesis reactor may receive the hydrogen and carbon monoxide products from the gasification reaction use the hydrogen and carbon monoxide products in a hydrocarbon fuel synthesis process to create a liquid hydrocarbon fuel.
Owner:SUNDROP IP HLDG LLC
Method for preparing bagasse dissolving pulp and pre-extracting hemicellulose and product thereof
InactiveCN101613970AHigh extraction rateReduce the content of non-sugar organic debrisSugar derivativesPretreatment with acid reacting compoundsLiquid ratioDissolving pulp
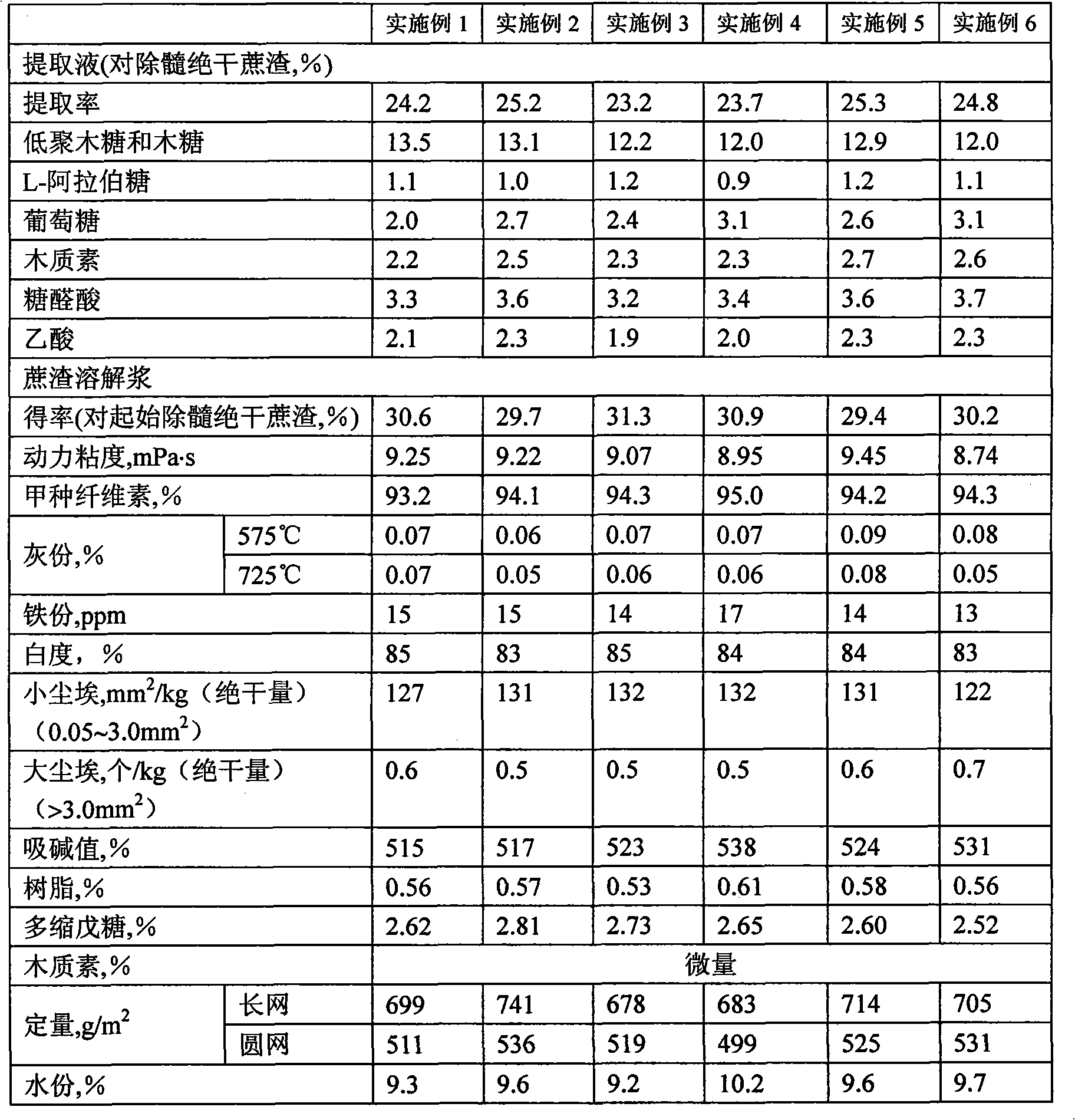
The invention relates to a method for preparing bagasse dissolving pulp and pre-extracting hemicellulose and products thereof; the method comprises the following steps: bagasse preparation which comprises the steps of depithing and washing; prehydrolysis which is carried out in a globe digester or a hydrolysis boiler; wherein, the process conditions are as follows: in the process for depithing and oven-drying bagasse, the solid-to-liquid ratio is 1:0.4-8.0, the hydrolysis temperature is 100-200 DEG C, the hydrolysis time is 15-240min, the pH value of the end point of hydrolysis is 2-5; in the process of the solid-to-liquid separation and washing, the filtrate is collected to prepare extracting solution; dissolving pulp is prepared by residue alkali method. By adopting the method, bagasse dissolving pulp and bagasse extracting solution which is used to prepare oligosaccharides are obtained. Most of pentosan in bagasse can be extracted by controlling the process conditions of the prehydrolysis, the technical route and the process conditions have strong pertinence so that the reactivity and the uniformity of bagasse dissolving pulp can be improved; by improving the traditional dissolving pulp alkali method for pulping, bagasse biorefinery based on dissolving pulp pulping can be realized in engineering so that the production costs for preparing bagasse dissolving pulp and pre-extracting hemicellulose are reduced.
Owner:上海士林纤维材料有限公司
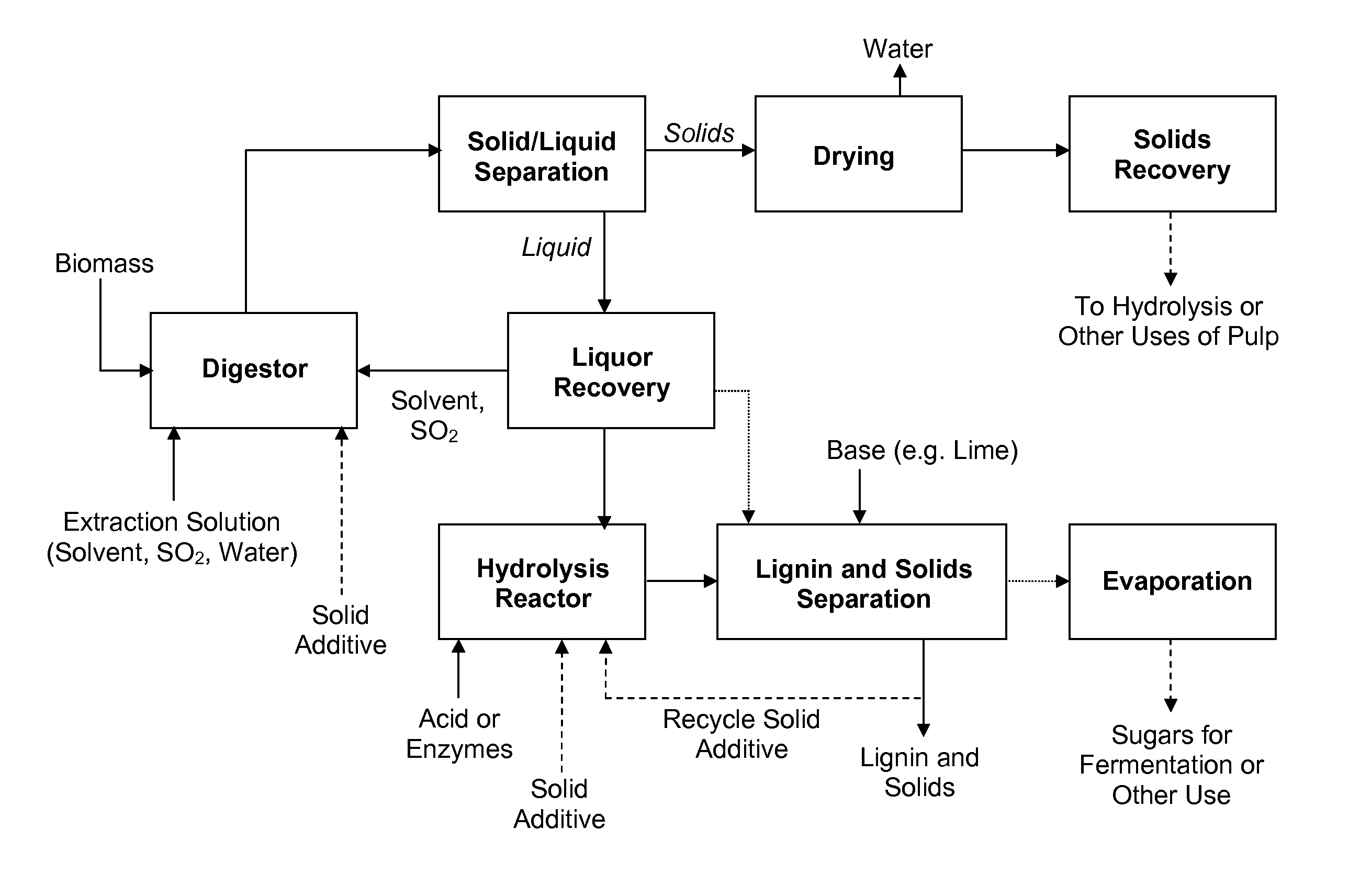
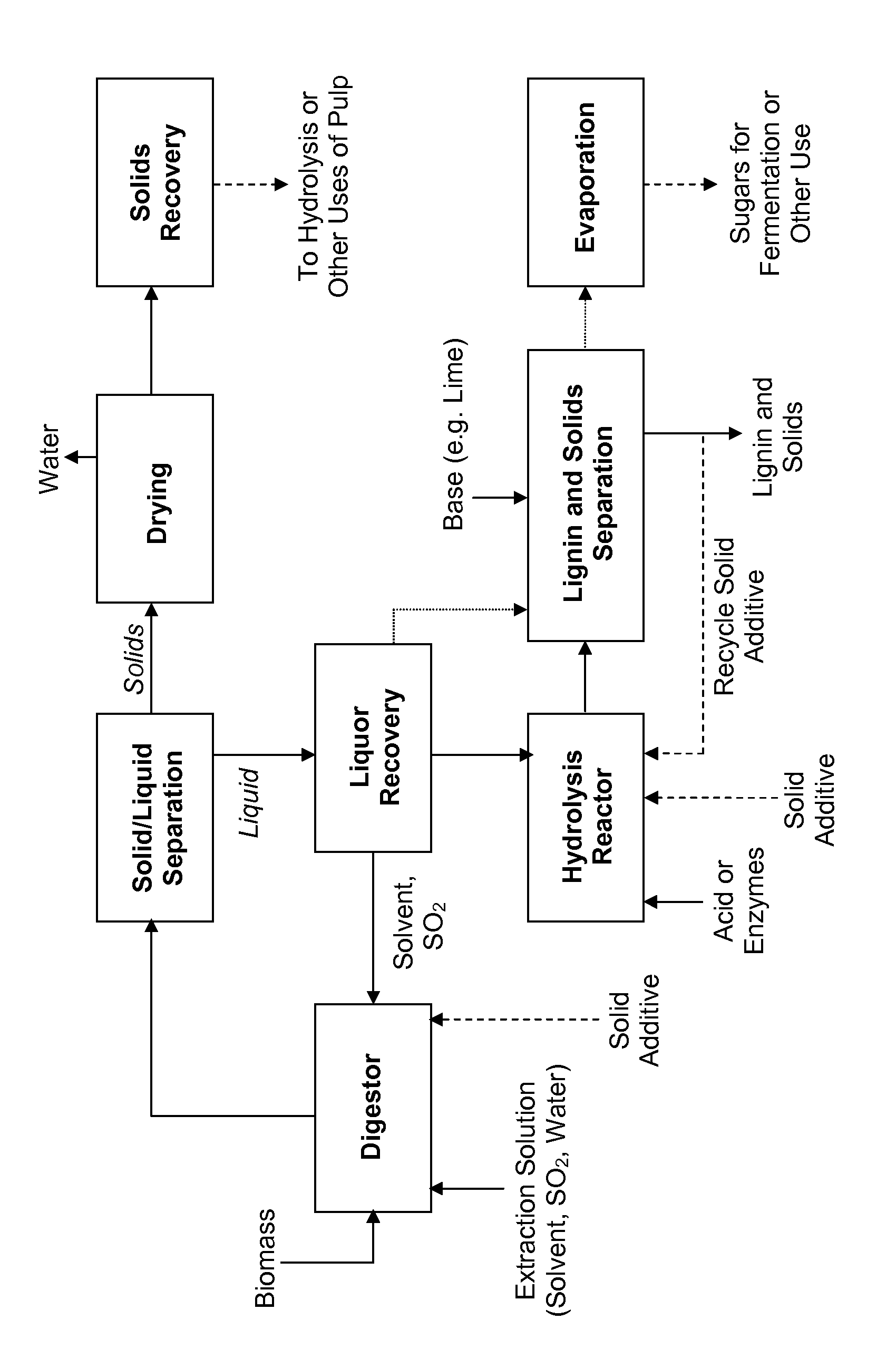
Processes and apparatus for lignin separation in biorefineries
ActiveUS20140163210A1Reduce viscosityIncrease settlement rateWaste based fuelLignin derivativesOligomerFractionation
The present invention generally provides methods of improving lignin separation during biomass fractionation with an acid to release sugars and a solvent for lignin (such as ethanol). In some embodiments, a digestor is employed to fractionating a feedstock in the presence of a solvent for lignin, sulfur dioxide, and water, to produce a liquor containing hemicellulose, cellulose-rich solids, and lignin. A solid additive is added to the digestor, wherein the solid additive combines with at least a portion of the lignin. Then a mixture of lignin and the solid additive is separated from the liquor, prior to hemicellulose recovery. Optionally, a solid additive may also be introduced to a hydrolysis reactor for converting hemicellulose oligomers to monomers, to improve separation of acid-catalyzed lignin. In some embodiments, the solid additive is gypsum or a gypsum / lignin mixture.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Production of xylitol from a mixture of hemicellulosic sugars
ActiveUS20130217070A1Reduce D-xyloseMinimal productionBacteriaFermentationEnvironmental engineeringSugar
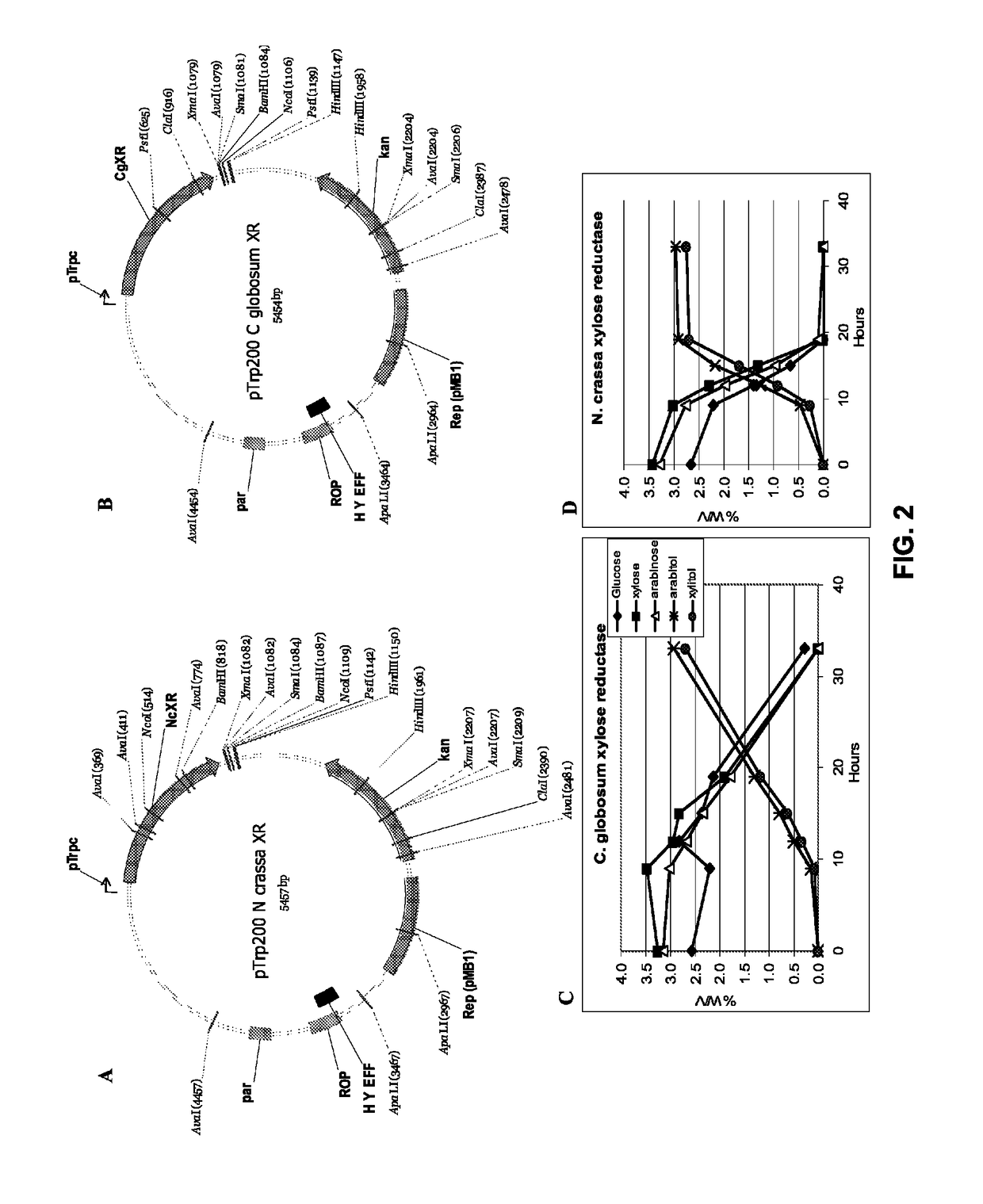
Materials and methods are described to produce xylitol from a mixture of hemicellulosic sugars by several routes. Examples include either as a direct co-product of a biorefinery or ethanol facility, or as a stand-alone product produced from an agricultural or forestry biomass feedstock including using, e.g. ethanol waste streams.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
An omnibus process of pulping and bleaching lignocellulosic materials in which a charge of a lignocellulosic material is biopulped and / or water extracted prior to pulping and bleaching. The lignocellulosic material may be mechanically pulped and bleached in the presence of an enzyme that breaks lignin-carbohydrate complexes. The aqueous extract in embodiments including a water extract step is separated into acetic acid and hemicellulose sugar aqueous solutions.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
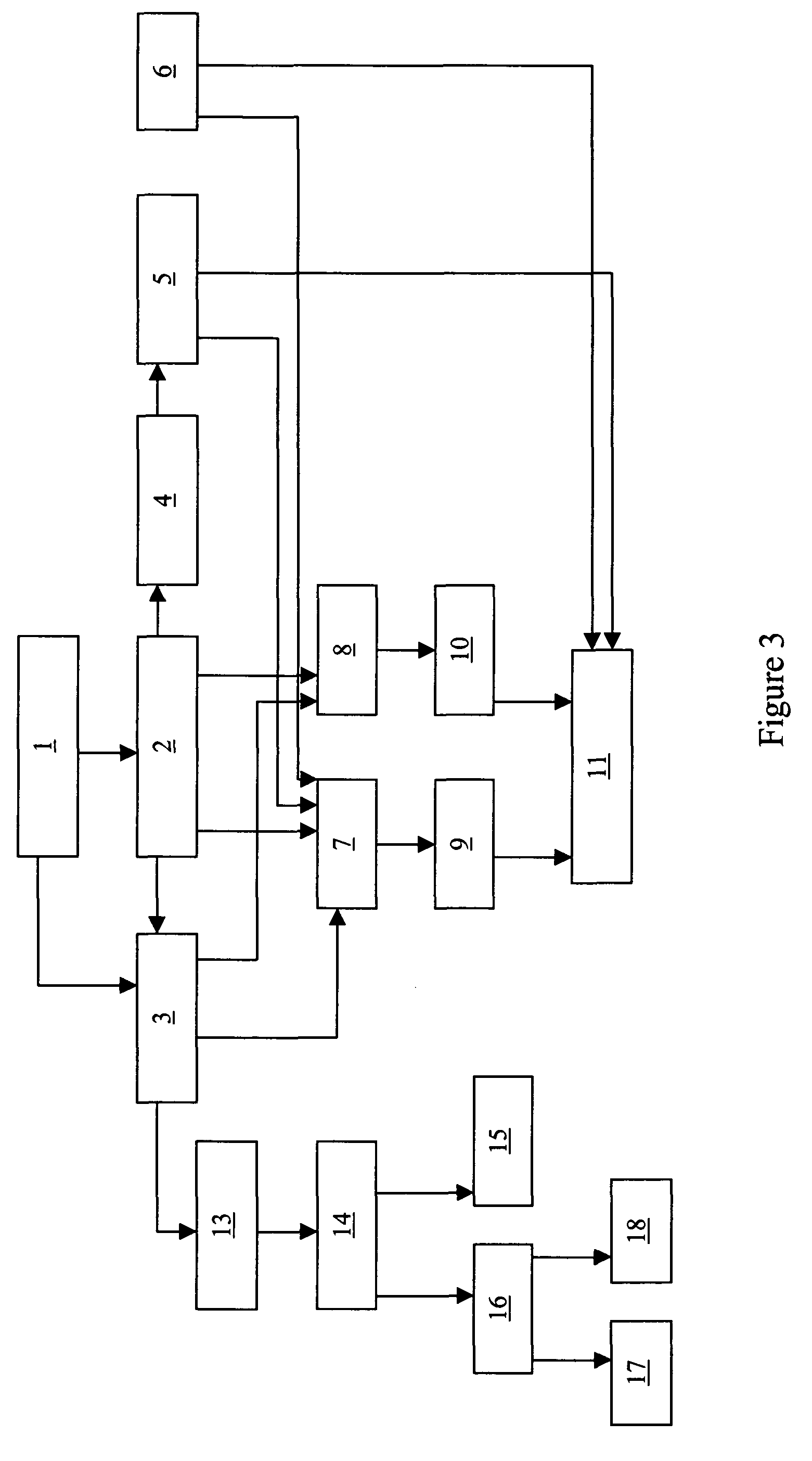
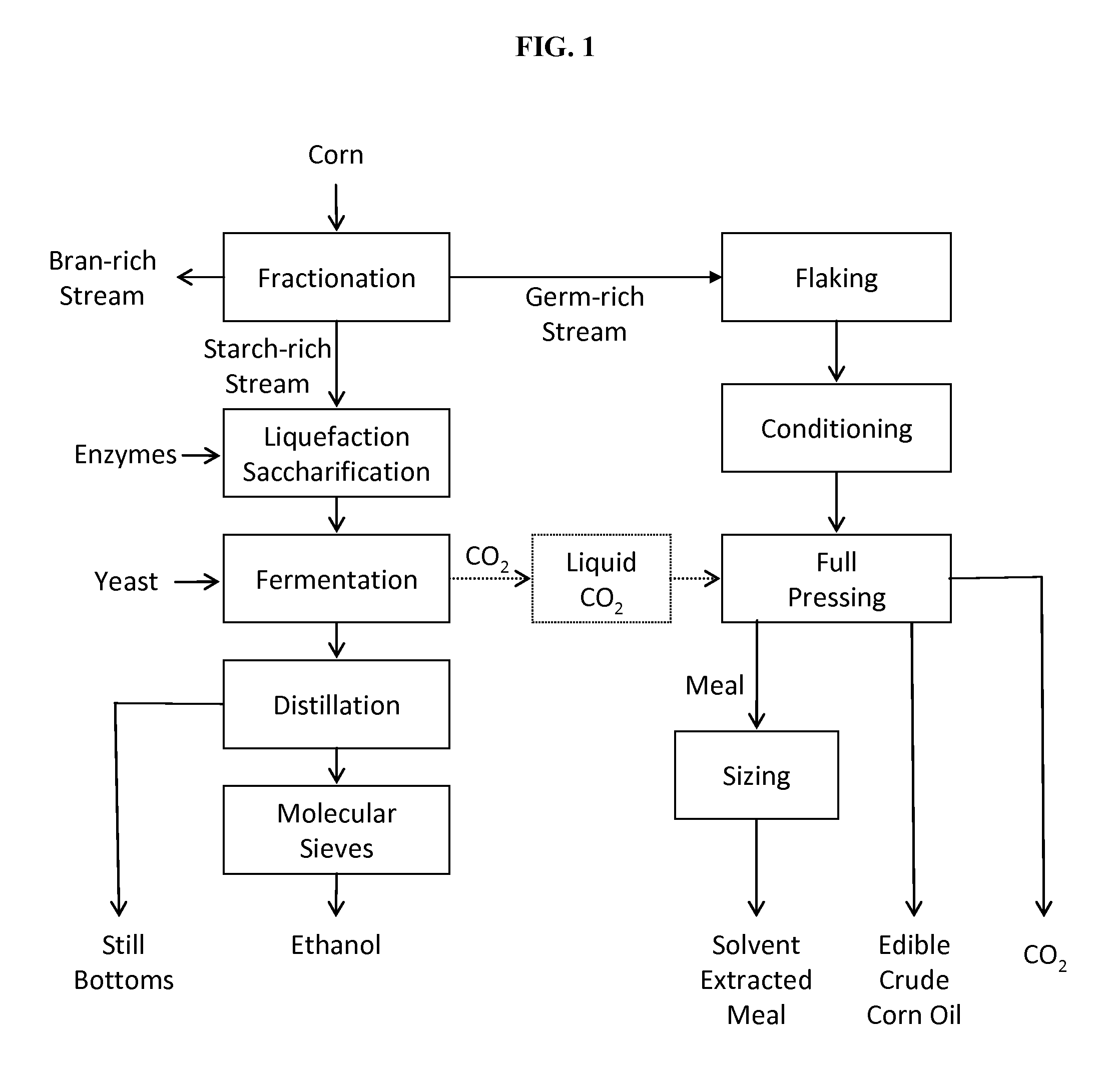
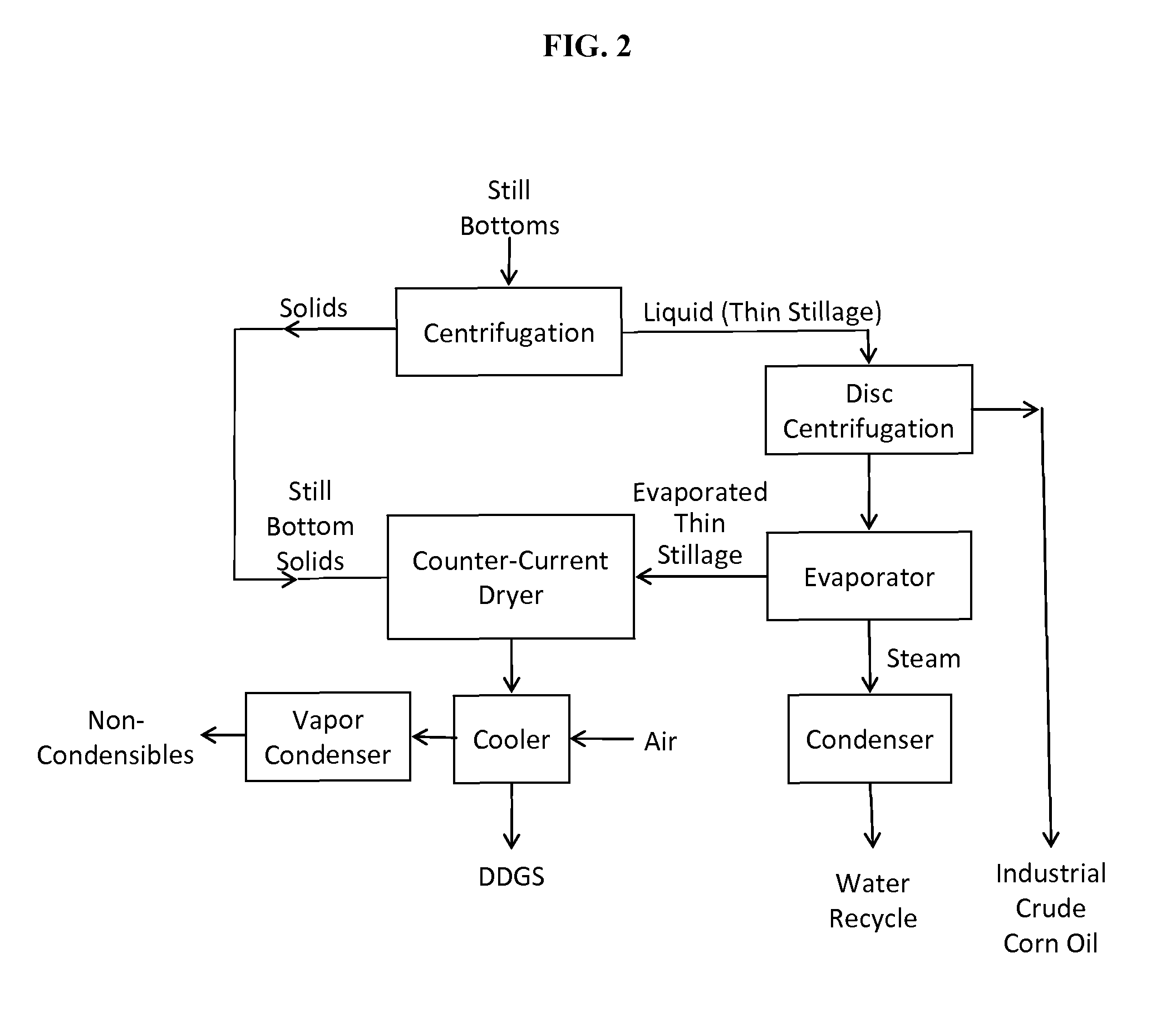
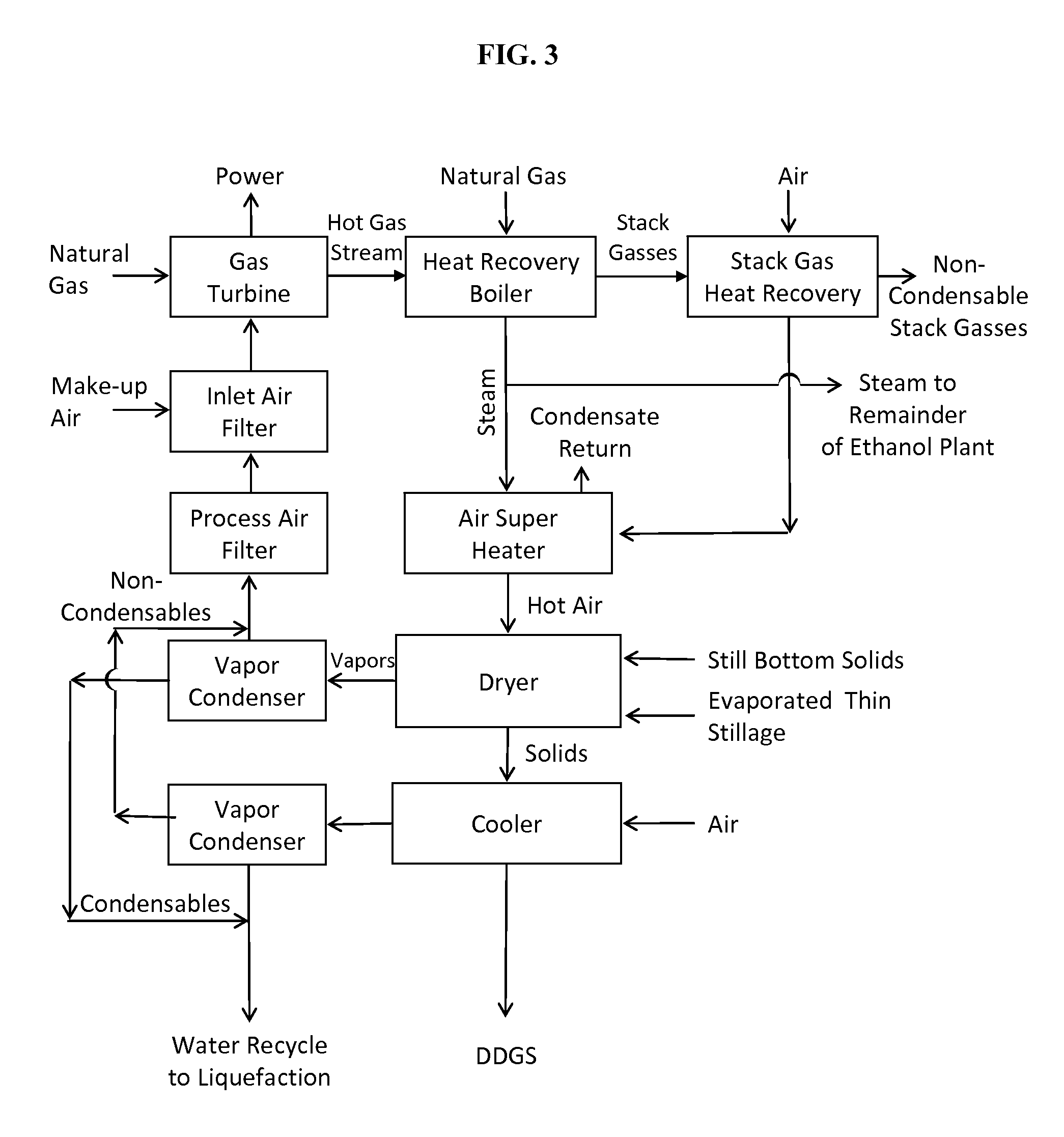
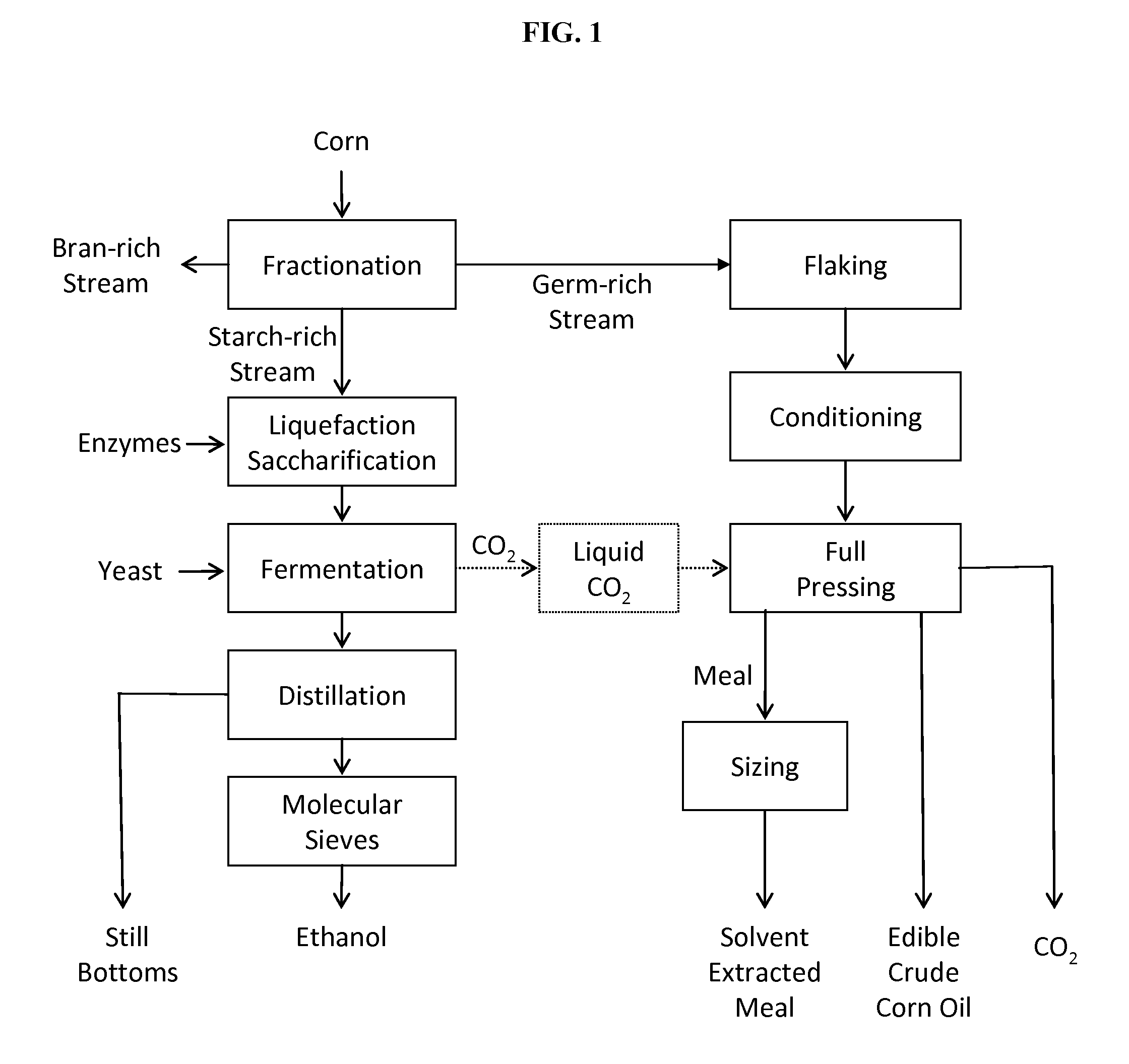
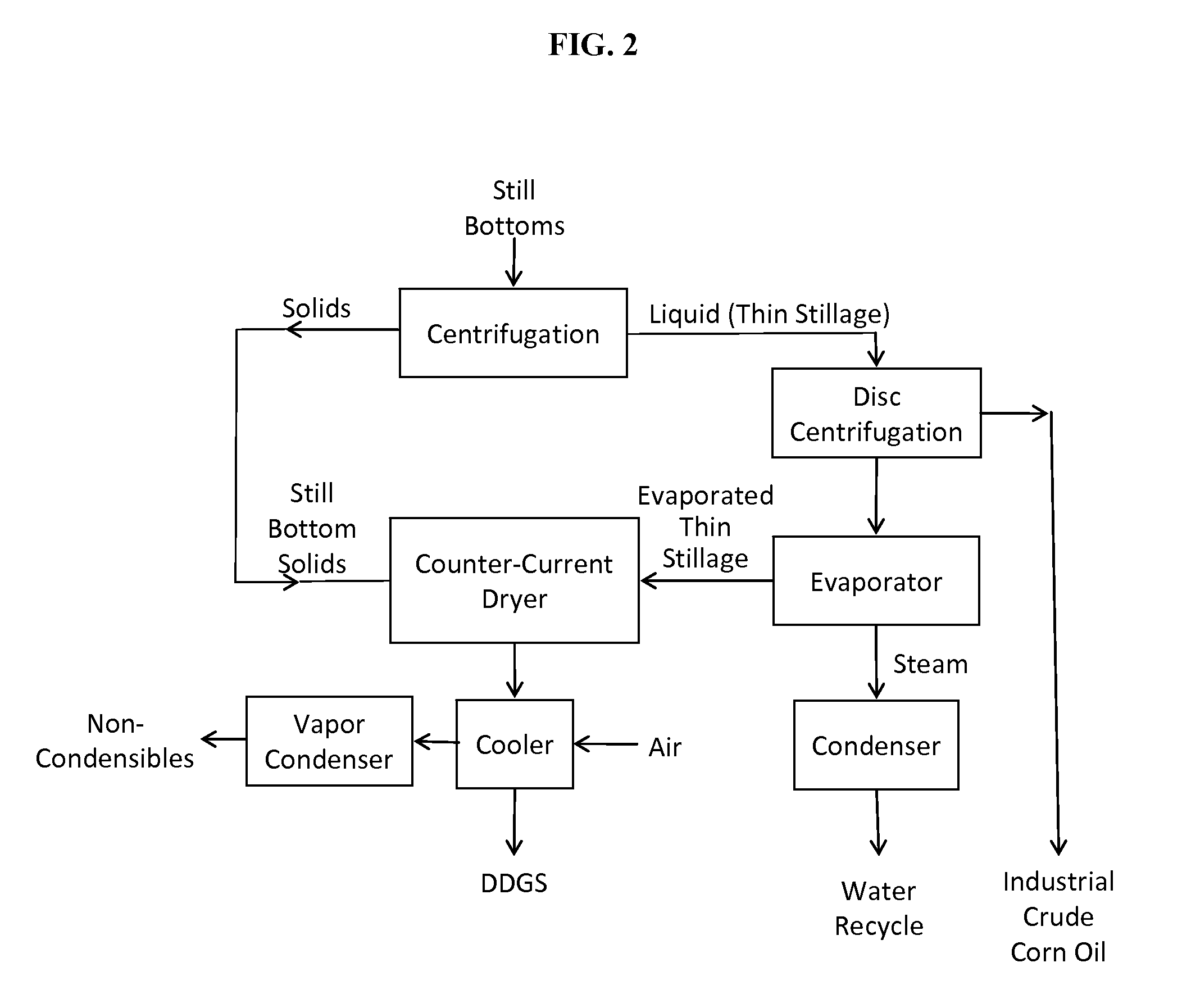
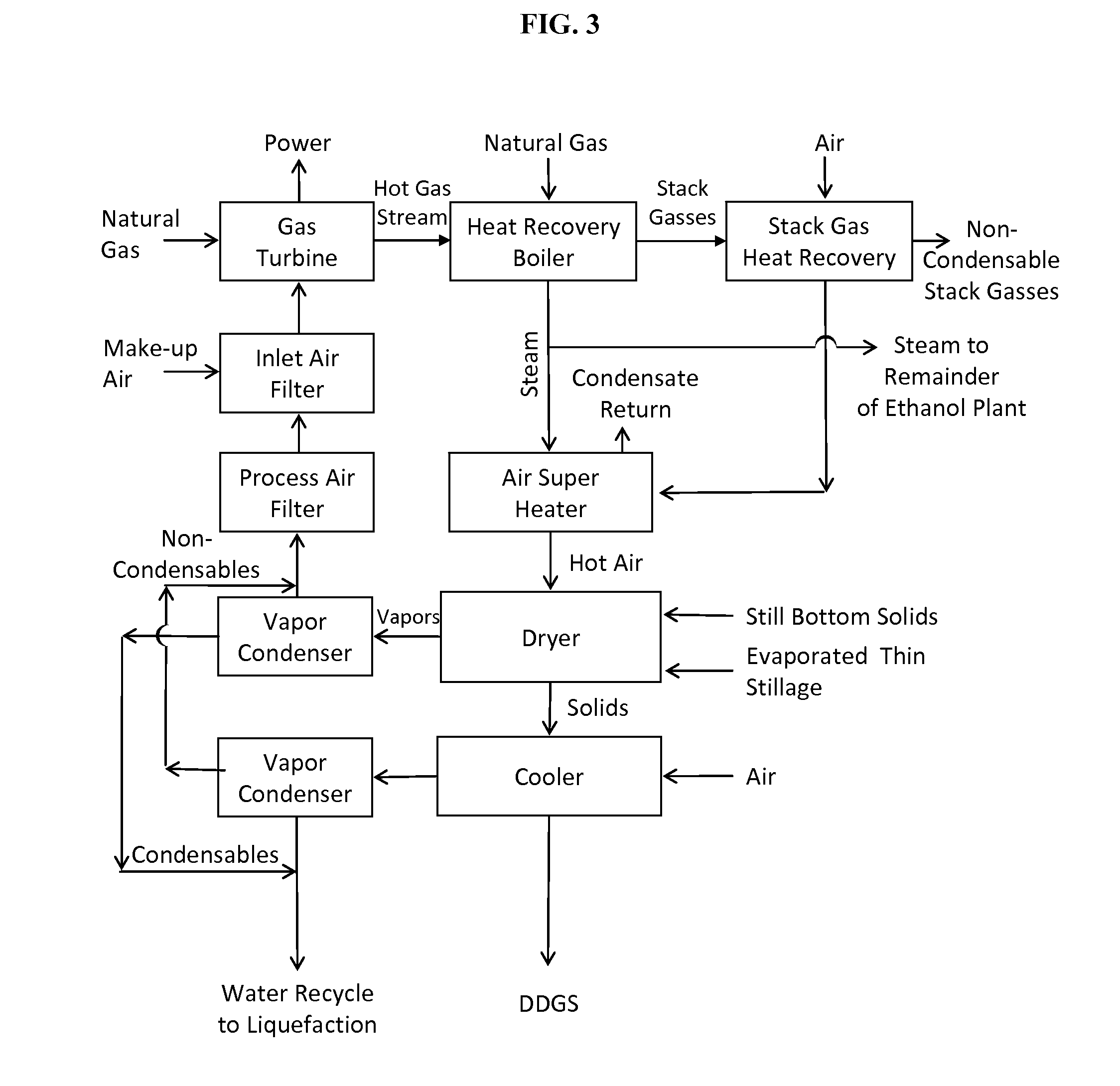
Processes and systems for dry-milled corn ethanol and corn oil production with improved carbon footprint
InactiveUS20130130343A1Increased ethanol productionDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatCarbon footprintMycotoxin
The present invention improves corn dry milling in several ways. Integrated corn biorefinery processes are disclosed which can produce ethanol, edible corn oil, DDGS, solvent-extracted meal, power, and optionally crude corn oil, starting from corn. Some variations employ corn fractionation and edible corn oil recovery using liquid carbon dioxide, avoiding hazardous hydrocarbon-based solvents to produce edible corn oil. Some variations employ integration of gas-fired co-generation into the dry-milled corn ethanol plant to significantly reduce energy usage and carbon footprint associated with the overall process. Counter-current drying is preferably employed to produce a high-quality DDGS product with high protein content, low mycotoxin content, and low residual ethanol content.
Owner:GLENMORE CONSULTING
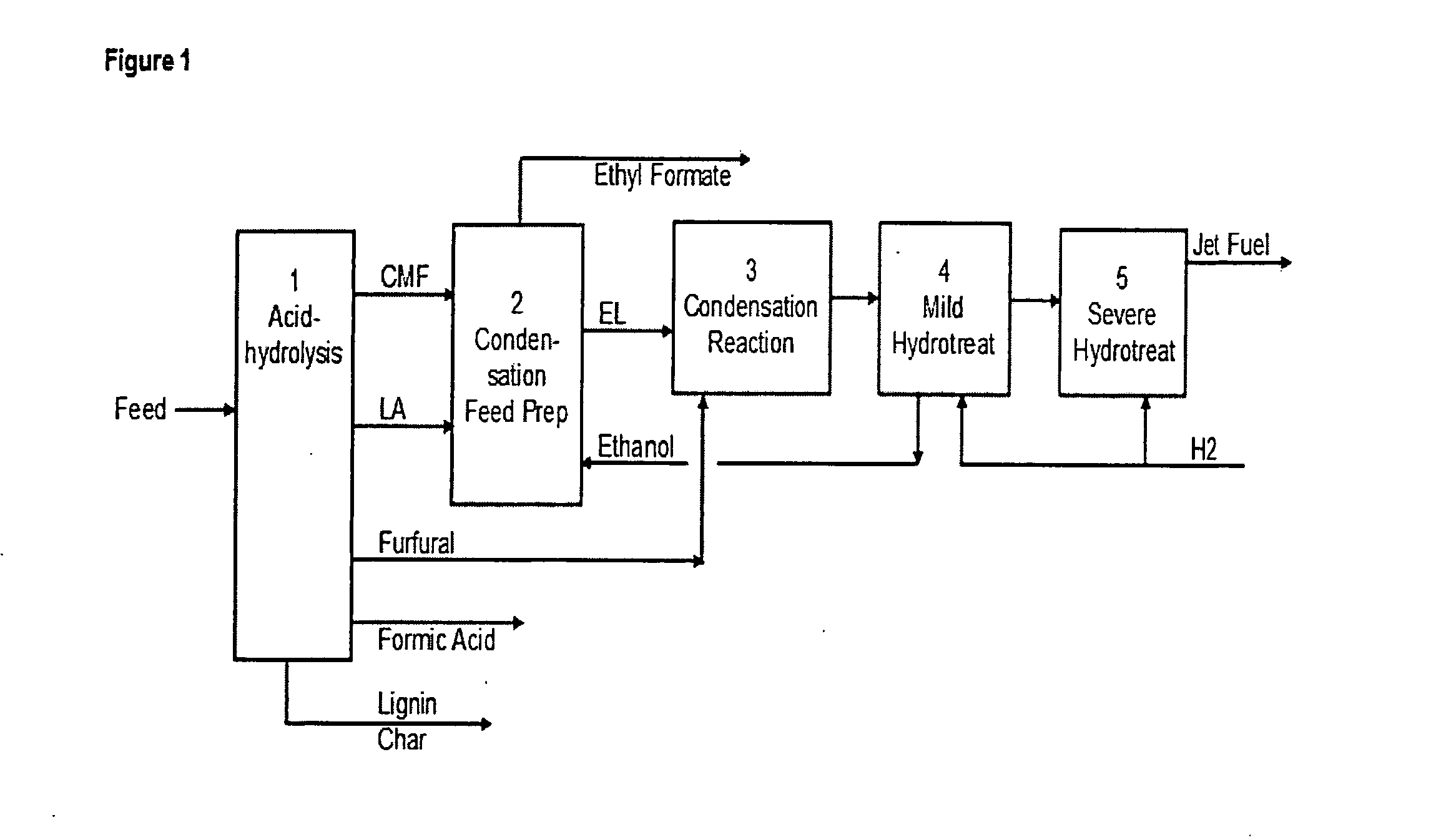
Biorefinery for conversion of carbothdrates and lignocellulosics via primary hydrolysate cmf to liquid fuels
InactiveUS20130217932A1Increase fuel capacityReduction tendencyHydrocarbon from oxygen organic compoundsLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionCelluloseAlkane
A method of making alkanes from lignocellulosic sources of C5 and C6 sugars. Suitable biomass feedstocks are converted into alkane-based fuels such as diesel and jet fuel blendstocks. Sugar monomers from the feedstocks are converted to chlormethylfurfural (CMF) with a levulinic acid (LA) byproduct. The CMF and LA are converted to ethyl levulinate (EL) and hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF), which are then combined into longer chain molecules via aldol condensation reactions. The condensation products are partially or fully saturated by mild hydrotreating, followed by deoxygenation to form alkanes with boiling ranges suitable for use as liquid fuels.
Owner:MERCURIUS BIOREFINING INC
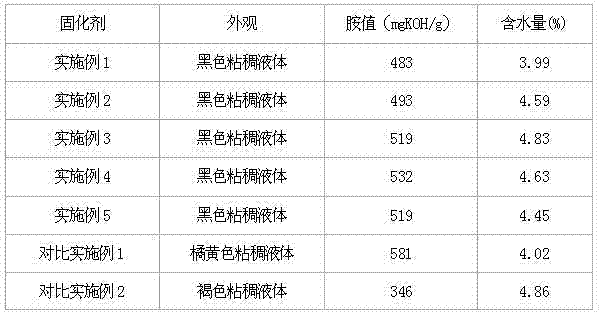
Solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102134305ARetain chemical activityHigh purityEpoxy resin coatingsPtru catalystMannich reaction
The invention provides a solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and a preparation method thereof. The epoxy resin curing agent is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 10 to 30 parts of solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin, 30 to 60 parts of phenol, 15 to 35 part of aldehyde, 20 to 45 part of ammine and 0.05 to 0.2 part of sulfuric acid catalyst. The phenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent is prepared by the Mannickreaction of the solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin and the phenol, aldehyde and ammine. When the solvent lignin-modified phenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent provided by the invention is used, petrochemical and coal chemical products can be replaced, the consumption of the petrochemical and coal chemical products is reduced, the cost of the epoxy resin is reduced, the lignin renewable resource in the waste from biorefinery is fully utilized, and the development of low-carbon economy is promoted.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Method for obtaining transformable substrate by using fungi leftovers
InactiveCN101591688APromote digestionIncrease resource valueFermentationBiotechnologyEconomic benefits
The invention provides a method for obtaining a transformable substrate by using fungi leftovers, which comprises two steps of diluted alkaline pretreatment and cellulase saccharification. The method uses the fungi leftovers after fruiting as raw materials, changes waste materials generated by edible fungi and medicinal fungi into valuable, and not only improves the economic benefit of the productions of the edible fungi and the medicinal fungi, but also finds a new raw material for biorefinery. The method has the advantages of simple flow, simple reagent, low cost, and suitability for popularization and application.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Processes and systems for dry-milled corn ethanol and corn oil production with improved carbon footprint
InactiveUS9068205B2Increased ethanol productionDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials with heatCarbon footprintMycotoxin
The present invention improves corn dry milling in several ways. Integrated corn biorefinery processes are disclosed which can produce ethanol, edible corn oil, DDGS, solvent-extracted meal, power, and optionally crude corn oil, starting from corn. Some variations employ corn fractionation and edible corn oil recovery using liquid carbon dioxide, avoiding hazardous hydrocarbon-based solvents to produce edible corn oil. Some variations employ integration of gas-fired co-generation into the dry-milled corn ethanol plant to significantly reduce energy usage and carbon footprint associated with the overall process. Counter-current drying is preferably employed to produce a high-quality DDGS product with high protein content, low mycotoxin content, and low residual ethanol content.
Owner:GLENMORE CONSULTING
Efficient method for separating solid residue and product in lignocellulose fermented mash
InactiveCN103100260AReduce energy consumptionIncrease the production processFiltration separationCarboxylic compound separation/purificationCelluloseFiltration
The invention relates to an efficient method for separating solid residue and products in lignocellulose fermented mash. The method comprises the specific steps of: (1) preparing a flocculant solution; (2) evenly mixing the lignocellulose fermented mash with a flocculant solution, and stirring for 5 min to fully contact the flocculant with the lignocellulose solid; and (3) conducting a solid-liquid separation on the mixed fermented mash by using a mill or a vacuum filtration device, so as to obtain a clear liquid containing fermentation products and lignocellulose solid residue. The invention has wide raw material resources, greatly reduces energy consumption of the solid-liquid separation in the condition of ensuring yield of effective products in the lignocellulose fermented mash, further improves the production process of fuel ethanol and bulk chemicals from biotransformation lignocellulose, and provides technical reserve for industrialization of lignocellulose biorefinery.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preprocessing lignocellulose raw materials for biorefinery
InactiveCN103451986APulping with inorganic basesNon-woody plant/crop pulpAcetic acidPretreatment method
The invention provides a method for preprocessing lignocellulose raw materials for biorefinery and discloses a method for preprocessing raw materials for biorefinery. The method comprises the following steps of promoting stripping of acetyl on hemicellulose in a preprocessing process by use of a small amount of alkali, and neutralizing formed acetic acid; carrying out precorrection on an acid environment formed in a hydrothermal preprocessing process, destroying chemical bonds between the hemicellulose and lignin by utilizing a high-temperature liquid water environment, so as to change the existence state of cellulose. The preprocessing method can be used for effectively avoiding generation of degradation products sourced from the hemicellulose and the lignin in the preprocessing process, greatly improving the hemicellulose recovery rate, and meanwhile ensuring that enzymolysis of the cellulose and the hemicellulose is easy. The preprocessed biomass raw materials can be used for production of cellulosic ethanol, oligosaccharide, xylitol and high-quality lignin.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pretreatment method for biorefinery of lignocellulose
InactiveCN101736630AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyEffective prolapsePaper material treatmentPretreatment methodStrong acids
The invention relates to a pretreatment method for biorefinery of lignocellulose, comprising the following steps: preparing five carbon sugar and a small amount of six carbon sugar which are used for fermenting in the steps of enabling the raw material of lignocellulose to be subjected to the autocatalytic hydrolysis reaction at medium temperature for one time, filtering, washing and concentrating, and preparing lignose and cellulose in the steps of enabling the five carbon sugar and the six carbon sugar to be subjected to the basic carbonate catalytic degradation reaction, filtering, washing, reducing pressure and steaming. Because the carbonate is used as the catalyst, the lignose can be effectively removed from the biomass of the lignocellulose, the cellulose enzymolysis efficiency can be improved and the cellulosic ethanol production cost can be reduced. The method for preprocessing and biologically refining the lignocellulose can ensure that 90 percent of the five carbon sugar, more than 91 percent of lignose and more than 93 percent of cellulose can be recovered, and in addition, the method for preprocessing and biologically refining the lignocellulose has low cost, needs no strong base or strong acid and is simple and environmental friendly.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
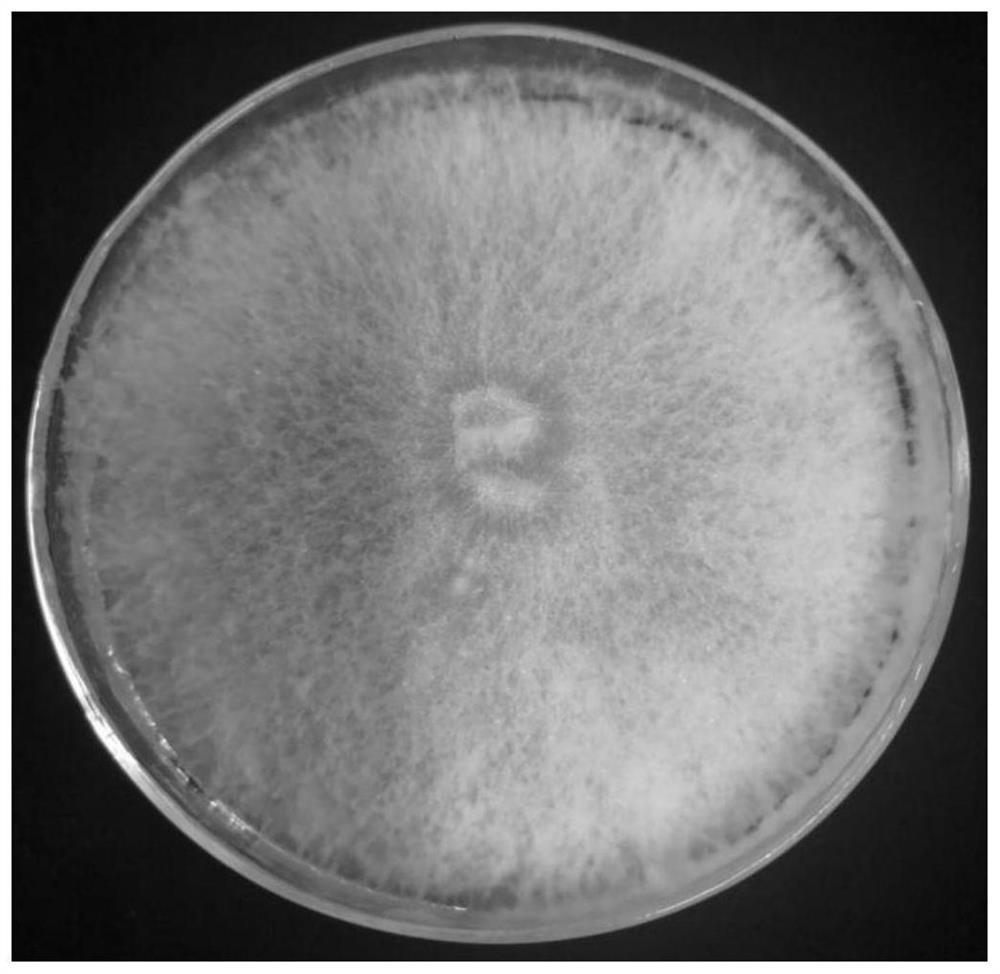
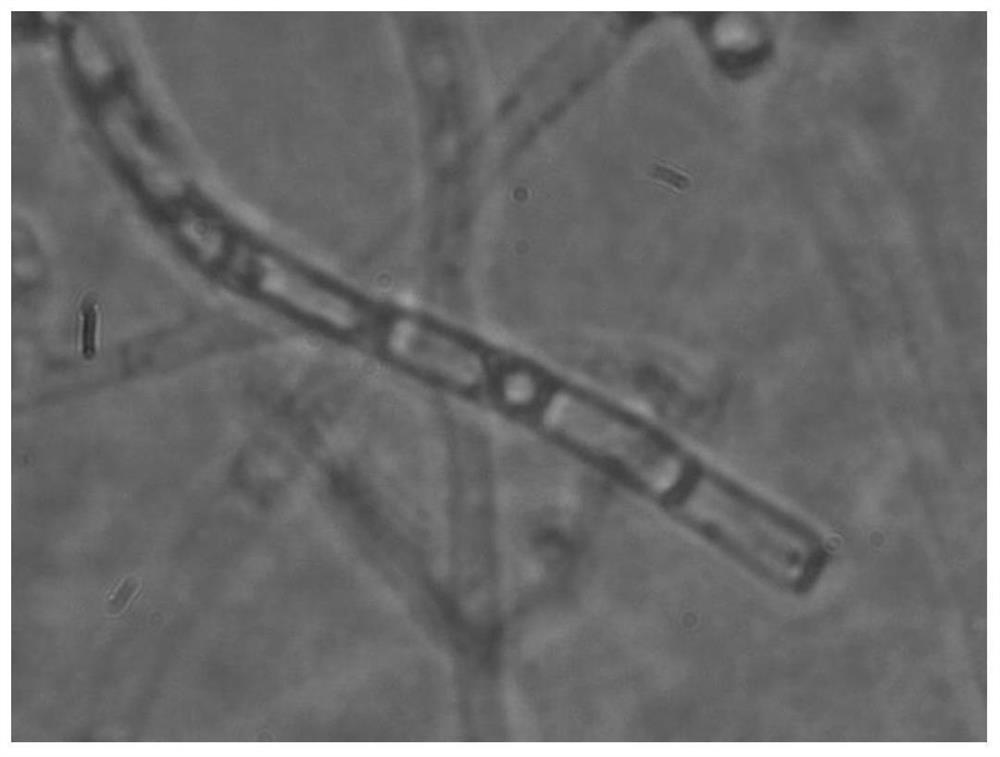
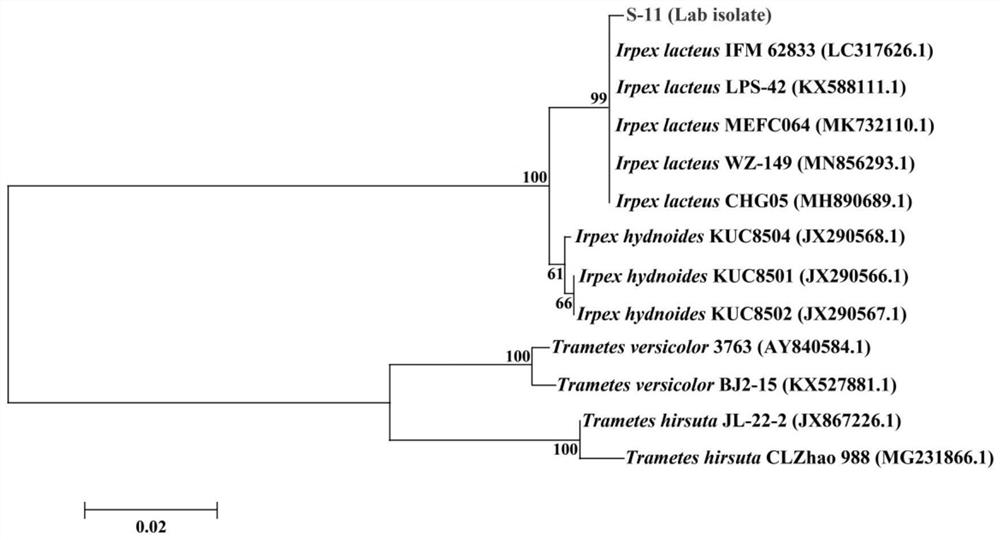
Irpex lacteus capable of efficiently degrading lignin
ActiveCN111961596APromote degradationHigh decolorization rateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses an irpex lacteus S-11 capable of efficiently degrading lignin, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. A liquid medium containing 4 g / L lignin is inoculated with the strain, the strain is cultured at 28 DEG C at 180 rpm for 11 days, and the degradation rate and decolorization rate of the strain for lignin reach 33.81% and 41.79% respectively. The methodfor degrading the lignin by using the strain is convenient to operate, low in cost and suitable for biological pretreatment of lignin in biorefinery industry. The strain has the degradation rate of apure lignin substrate higher than that of same-species strains reported at home and abroad, is shorter in degradation time and is suitable for biological pretreatment application in the biorefinery industry.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Processes and apparatus for lignin separation in biorefineries
ActiveUS9322072B2High densityIncrease settlement rateWaste based fuelLignin derivativesOligomerFractionation
The present invention generally provides methods of improving lignin separation during biomass fractionation with an acid to release sugars and a solvent for lignin (such as ethanol). In some embodiments, a digestor is employed to fractionating a feedstock in the presence of a solvent for lignin, sulfur dioxide, and water, to produce a liquor containing hemicellulose, cellulose-rich solids, and lignin. A solid additive is added to the digestor, wherein the solid additive combines with at least a portion of the lignin. Then a mixture of lignin and the solid additive is separated from the liquor, prior to hemicellulose recovery. Optionally, a solid additive may also be introduced to a hydrolysis reactor for converting hemicellulose oligomers to monomers, to improve separation of acid-catalyzed lignin. In some embodiments, the solid additive is gypsum or a gypsum / lignin mixture.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Product and processes from an integrated forest biorefinery
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Alcohol sulfite biorefinery process
A biorefinery process to fractionate lignocellulosic materials into cellulose, hemicelluloses and lignin using a pretreatment with mixture of alcohol, sulfur dioxide and water. Further treatment with enzymes, micro-organisms, and optionally bisulfite ion, are used to convert intermediate products to alcohol and lignin derivatives.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Biochemical crude oil
InactiveCN102154040APromote leapfrog developmentLow costBiofuelsLiquid carbonaceous fuelsChemical industryPetroleum
The invention discloses biochemical crude oil which mainly consists of biological oil and petroleum and / or alcohol ether fuel. In the invention, fossil petroleum is subversively replaced with a biomass from the raw material phase, so that an economic structure which does not depend on the fossil petroleum is established, and by ecological restoration of saline alkali and mineral waste lands, the greening of the heavy chemical industry is promoted simultaneously when biorefinery is developed; the biochemical crude oil is prepared by the existing petroleum production, refining and sale system or equipment of oil refining enterprises, chemical plants, clean fuel enterprises and the like; and the biochemical crude oil can be pumped and stored by a pump and is conveyed by a pipeline, a road, a railway and an oil tanker. Therefore, the original eliminated unenlightened or polluted productivity is converted into the productivity of a green oil field, a low sulphur oil refinery and a greening industry; the biochemical crude oil not only has little investment and low cost and is rapid to start; in the developing process, the environment is protected, the original huge productivity is prevented from changing into waste properties so as to promote the forward development of the emerging industry and the low-carbon economy.
Owner:窦观一
Integrated biorefinery
InactiveUS20150329887A1Reduce operating costsImprove penetration efficiencyBiofuelsWaste based fuelCelluloseFermentable sugar
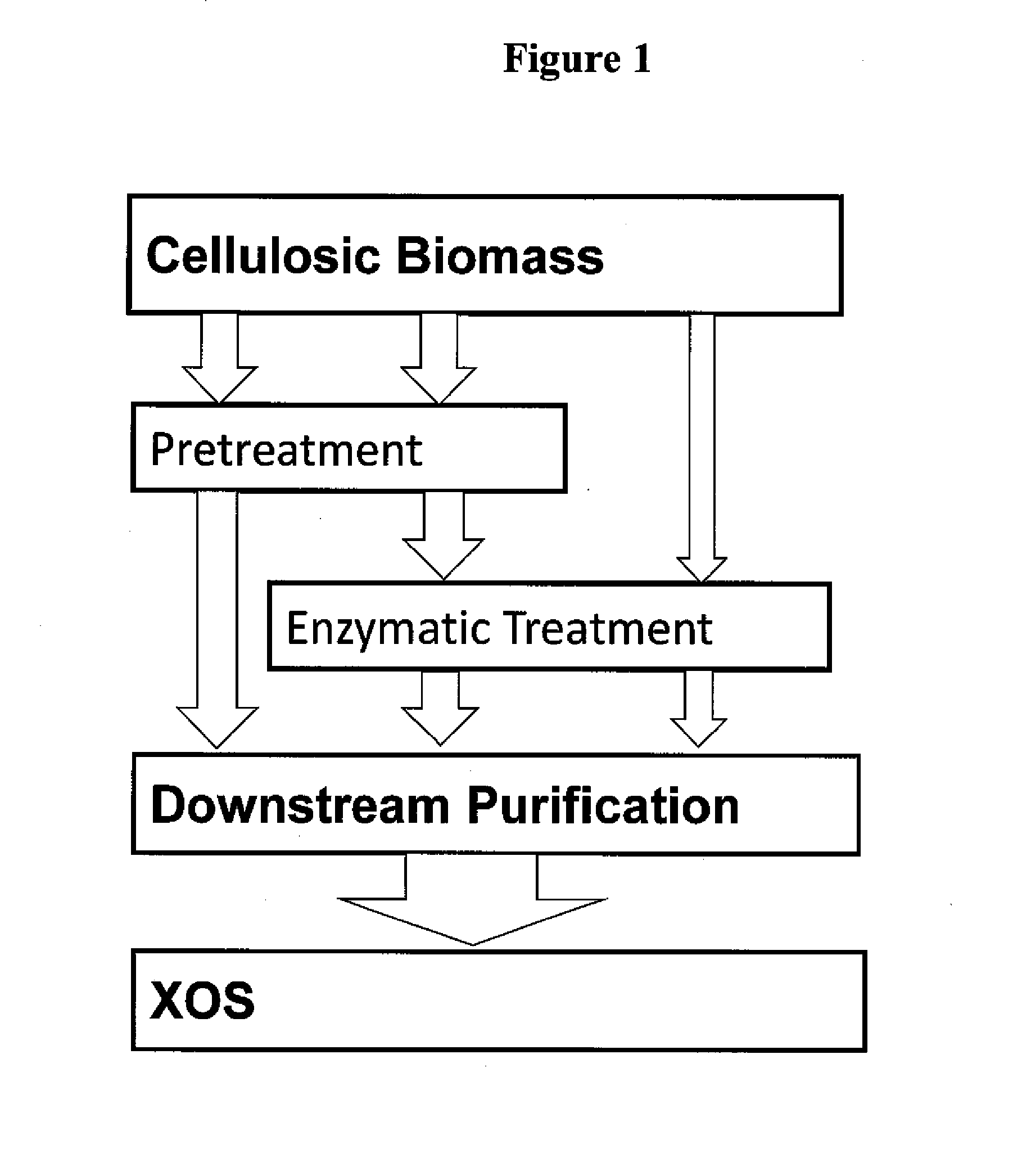
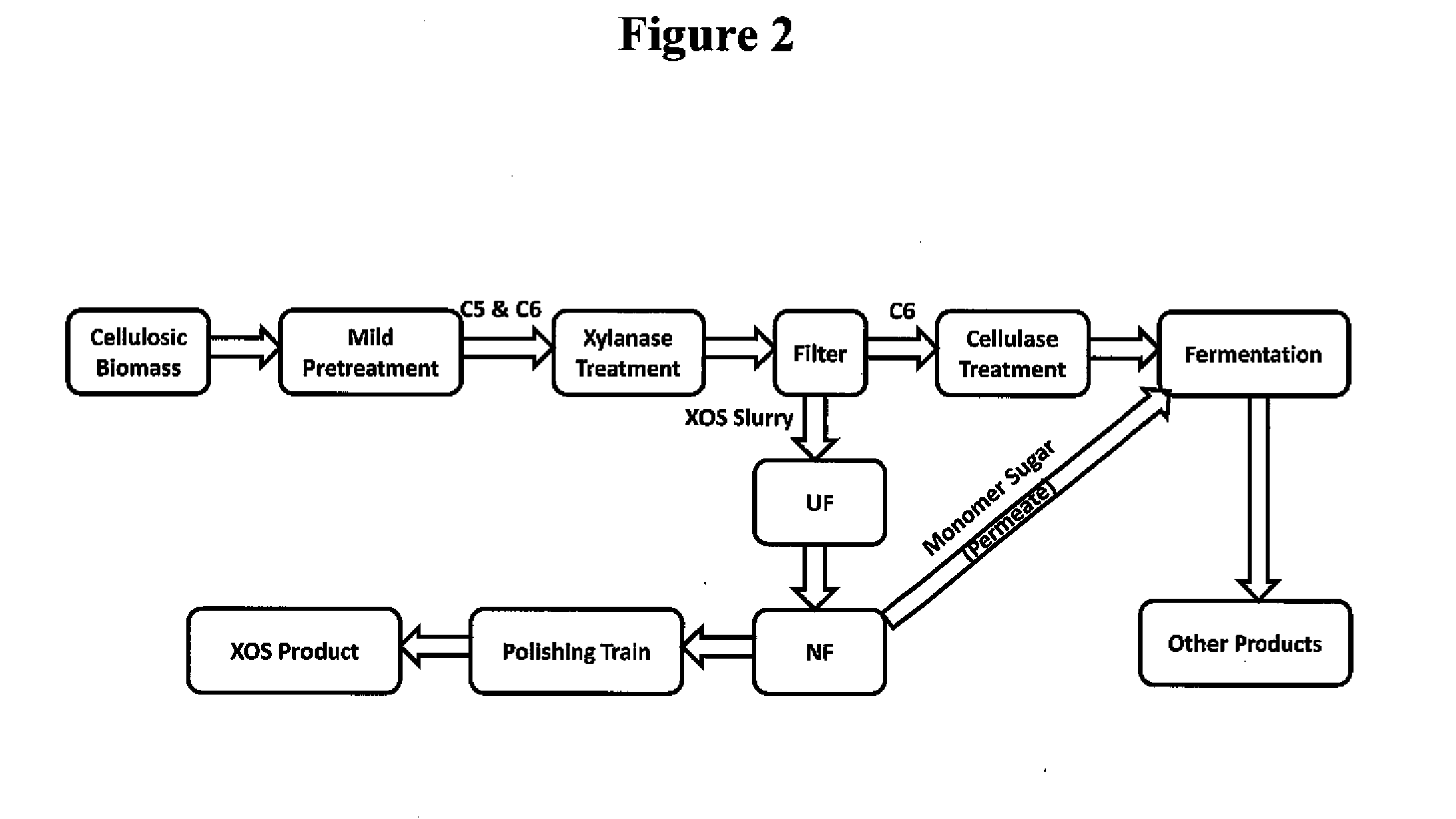
This invention relates to the operation of a biorefinery for manufacturing either biofuels or renewable chemical feedstock using lignocellulosic biomass as a source of carbon. The present invention provides a cost-effective process for pretreating lignocellulosic biomass in the recovery of fermentable sugars. More specifically, the present invention describes an integrated approach for efficiently recovering and using six-carbon and five-carbon sugars along with value-added oligosaccharides such as xylooligosaccahrides from lignocellulosic biomass so that the cost of manufacturing biofuels and renewable chemical feedstock is substantially lowered.
Owner:MYRIANT CORP
Production of xylitol from a mixture of hemicellulosic sugars
ActiveUS9624517B2Reduce D-xyloseMinimal productionSugar derivativesBacteriaEnvironmental engineeringSugar
Materials and methods are described to produce xylitol from a mixture of hemicellulosic sugars by several routes. Examples include either as a direct co-product of a biorefinery or ethanol facility, or as a stand-alone product produced from an agricultural or forestry biomass feedstock including using, e.g. ethanol waste streams.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS +1
Preparing method for furfural
The invention discloses a preparing method for furfural, and belongs to the technical field of biorefinery. The preparing method is characterized by including the steps that 1) corncobs are micro-smashed, methyl alcohol is added, and the mixture is stirred and soaked to be subjected to solid-liquid separation; 2) methylbenzene and dilute sulphuric acid with the mass concentration of 3% to 10% aredirectly added into a solid-liquid-separation liquid phase, and an acidolysis reaction is conducted under the stirring condition, wherein the mass ratio of the dilute sulphuric acid to methylbenzene to the corncobs in the step 1) is (20-50):(15-45):10; 3) acidolysis is completed, standing is conducted, then separation of the water phases and oil phases is conducted, and oil phases distill to recover methylbenzene, and the biorefinery is obtained. Solid in the preparing method is not subjected to acid treatment, residual methyl alcohol is easy to volatilize and treat, and follow-up using is notinfluenced. In the hydrolytic process, the generated furfural is continuously separated through methylbenzene, it is also promoted that hydrolysis normally runs, and the yield is greatly increased; the used methylbenzene can be distilled, recycled and reused.
Owner:王国锋
Systems and methods for integrated CO2 reuse using vapor compression
ActiveUS10947486B1By-product recoveryFermented solutions distillation/rectificationThermodynamicsDistillation
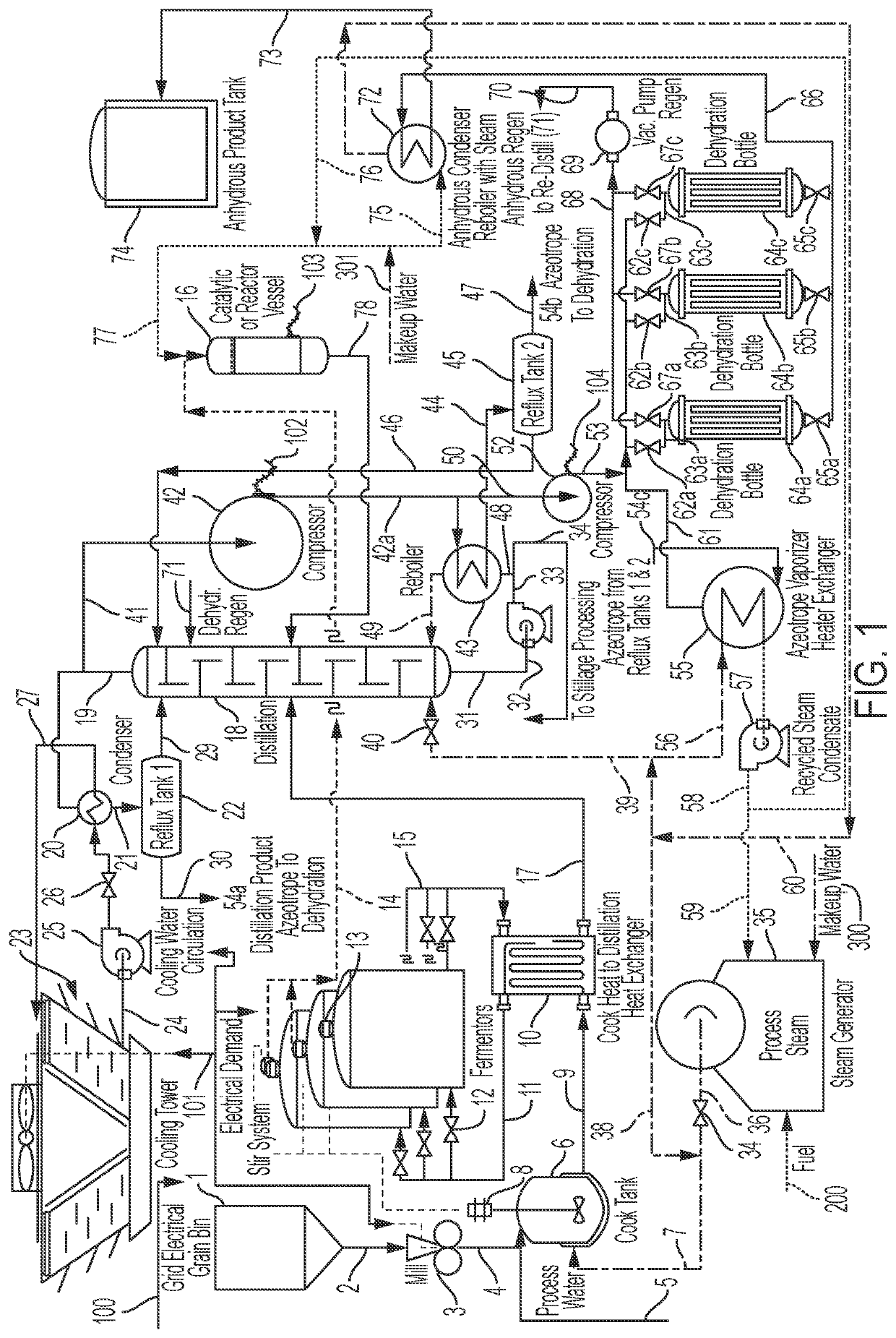
Systems and methods are disclosed for optimizing the process energy required for the conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) to biochemicals through vapor compression. Mechanical or thermal vapor compression are used to minimize both the process energy and the cooling in condensers, integrating the heat required by those processes and reusing heat that is typically lost. Some variations provide a process for producing biochemicals from biomass, comprising: cooking biomass to release saccharides; fermenting the saccharides to generate a biochemical in aqueous solution, and carbon dioxide; hydrogenating the carbon dioxide with a hydrogen source to generate an additional quantity of biochemical; feeding the fermentation-derived biochemical, as well as the CO2-derived biochemical, to a distillation column for purification; and compressing vapors from the distillation column, using mechanical vapor recompression and / or thermal vapor recompression, to recover heat of distillation that is utilized elsewhere in the biorefinery to reduce overall process energy usage.
Owner:ENERGY INTEGRATION INC
Solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102134305BRetain chemical activityHigh purityEpoxy resin coatingsPtru catalystMannich reaction
The invention provides a solvent lignin-modified epoxy resin curing agent and a preparation method thereof. The epoxy resin curing agent is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 10 to 30 parts of solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin, 30 to 60 parts of phenol, 15 to 35 part of aldehyde, 20 to 45 part of ammine and 0.05 to 0.2 part of sulfuric acid catalyst. Thephenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent is prepared by the Mannickreaction of the solvent lignin or derivative of the solvent lignin and the phenol, aldehyde and ammine. When the solvent lignin-modified phenol-aldehyde-ammine epoxy resin curing agent provided by the invention is used, petrochemical and coal chemical products can be replaced, the consumption of the petrochemical and coal chemical products is reduced, the cost of the epoxy resin is reduced, the lignin renewable resource in the waste from biorefinery is fully utilized, and the development of low-carbon economy is promoted.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Lignin valorization in ionic liquids and deep eutectic solvent via catalysis and biocatalysis
This invention relates to a method for extracting valorized compounds from lignin by contacting lignins with an ionic liquid and / or a deep eutectic solvent and adding a catalyst and / or a biocatalyst to assist in breaking down the source material. Converting lignin into high value chemicals adds revenues for a bio-refinery and helps to improve the economic viability of biofuel production.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
Processes and systems for dry-milled corn ethanol and corn oil production with improved carbon footprint
InactiveUS20150299735A1Increased ethanol productionDrying using combination processesFood processingMycotoxinCarbon footprint
Owner:GLENMORE CONSULTING
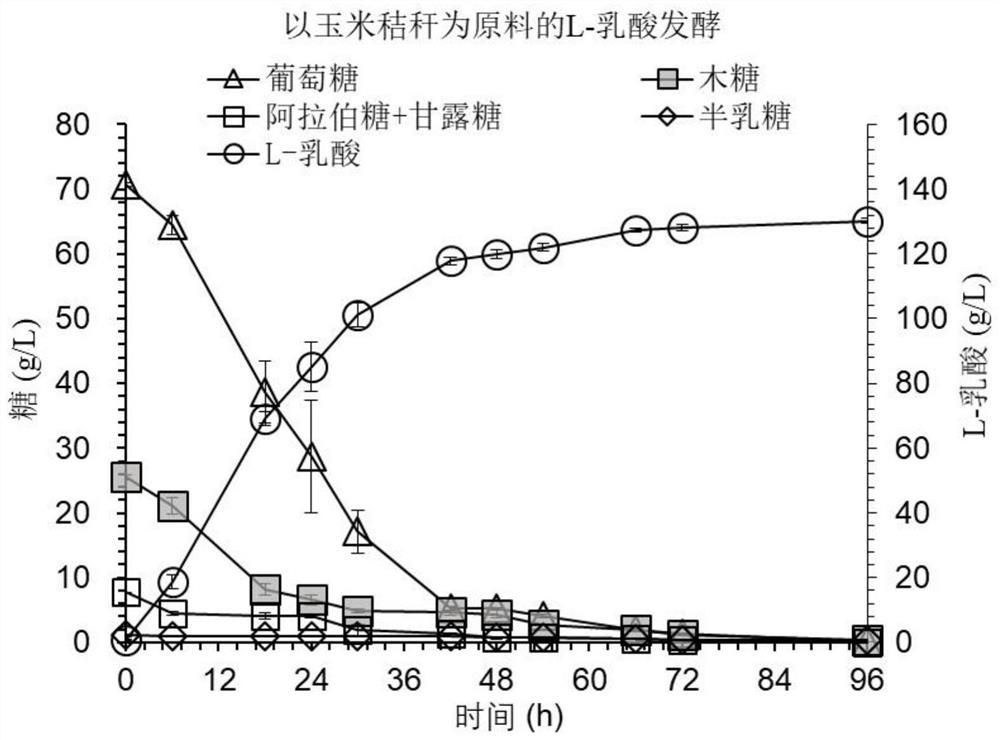
Method for synthesizing L-lactide from chiral L-lactic acid produced by using lignocellulose biomass as raw material
PendingCN112941117AAchieve synthesisDefermentationMicroorganism based processesFermentationCellulosePolymer science
The invention belongs to the field of biorefinery, and relates to a method for synthesizing L-lactide by producing chiral L-lactic acid from a lignocellulose raw material. The method comprises the following steps: (1) removing an inhibitor from a pretreated lignocellulose raw material in an ultimate biodegradation manner; (2) performing high-solid-content synchronous saccharification and co-fermentation on the lignocellulose raw material to obtain cellulose L-lactic acid with high concentration, high chirality and extremely low residual sugar; (3) preparing polymer grade L-lactic acid; and (4) carrying out dehydration, polycondensation, depolymerization and purification on the purified cellulose chiral L-lactic acid to obtain L-lactide. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the influence of an inhibitor on L-lactic acid fermentation and L-lactic acid purity is relieved by adopting a biodegradation method, high-concentration and extremely low-residual-sugar cellulose chiral L-lactic acid is obtained by adopting a high-solid-content total-sugar co-fermentation method, and the cellulose chiral L-lactic acid is subjected to the steps of purification, polycondensation, depolymerization and the like; the synthesis of the L-lactide from the lignocellulose raw material is realized.
Owner:SHANXI SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY INST CO LTD
Preparation method of broadleaf wood dissolving pulp
PendingCN113293636AHigh whitenessHigh degree of polymerizationPretreatment with water/steamPretreatment with alkaline reacting compoundsSodium chloratePulp and paper industry
The invention belongs to the technical field of dissolving pulp preparation, and particularly relates to a preparation method of broadleaf wood dissolving pulp. The preparation method of the broadleaf wood dissolving pulp is characterized by comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out steaming treatment on broadleaf wood chips and then carrying out extrusion treatment; (2) pretreating the extruded wood chips by using a mixed solution of p-toluenesulfonic acid, sodium hypochlorite and sodium chlorite to obtain crude pulp, performing ultrasonic dispersion treatment on the crude pulp, and then washing and filtering the pulp until the crude pulp is neutral; (3) carrying out two-stage oxygen delignification treatment on the slurry; (4) carrying out chlorine dioxide bleaching treatment on the pulp subjected to oxygen delignification; (5) carrying out secondary bleaching treatment on the pulp by using enhanced alkali to obtain the dissolving pulp. The method has the beneficial effects that the reaction condition is mild, the reaction time is short, the pulping process flow is simple, the environmental pollution and machine corrosion are small, and the green concept of modern biorefinery is met.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method of increasing the gas-liquid interface in a fermentation process
ActiveUS8647862B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProduct gasEngineering
Owner:HAKALEHTO EINO ELIAS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com