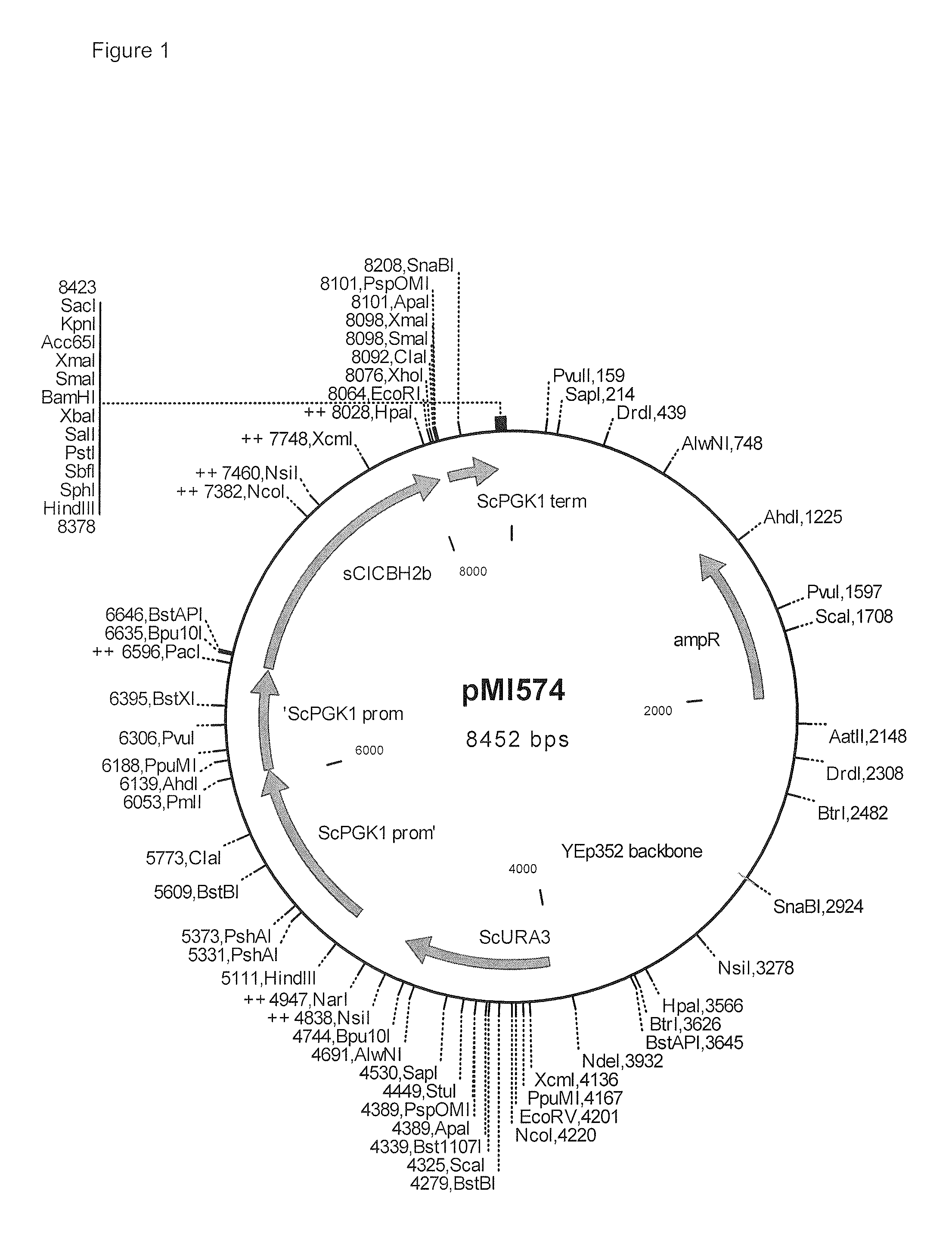
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
40 results about "Irpex lacteus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Irpex lacteus is a common crust fungus distributed throughout temperate areas of the world. It is the type of the genus Irpex. Irpex lacteus is considered a polypore, but depending on growth conditions it can also produce a hydnoid hymenophore. Due to this variability and abundance of the species it has been described as a new species to science numerous times and subsequently has an extensive synonymy. The complete genome sequence of Irpex lacteus was reported in 2017.
Methods of culturing fungi and producing cellulases and chitin
The fungus Irpex lacteus is efficiently cultured on a solid substrate with a high content of crystalline cellulose. The fungal culture can be used to produce cellulases that are useful in conversion of cellulose to sugars. The fungal culture can also be used to produce chitin, which is itself valuable and can also be converted to chitosan. Use of the fungal culture for co-production of cellulases and chitin is also described.
Owner:ECLIPSE BIOPROD +1
Irpex lacteus capable of efficiently degrading lignin and application of irpex lacteus
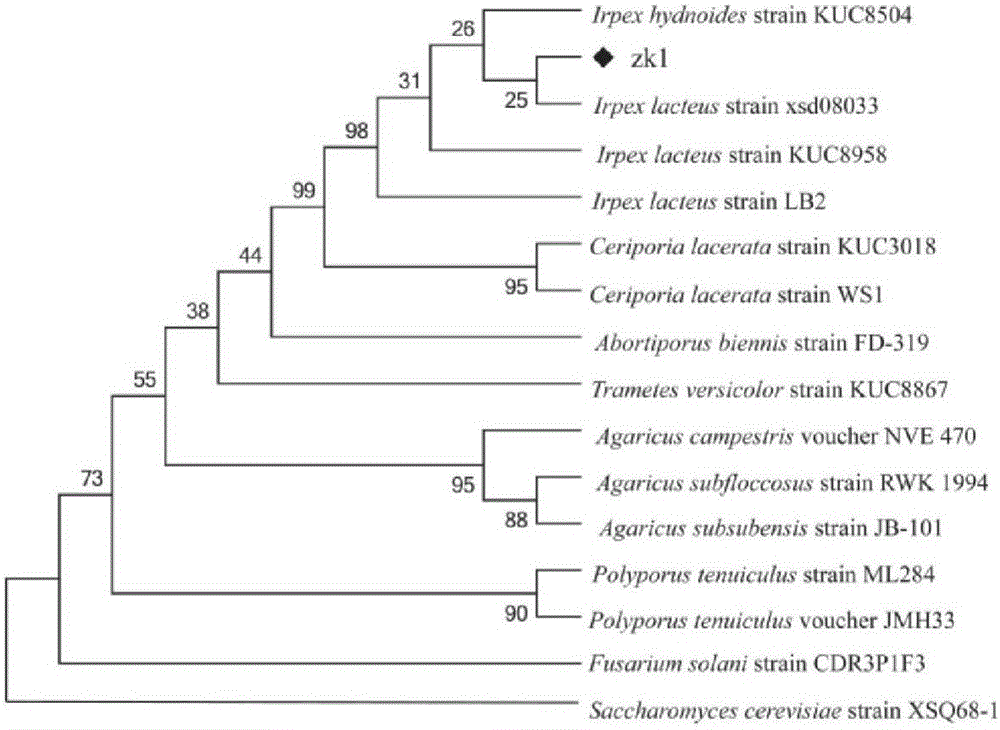
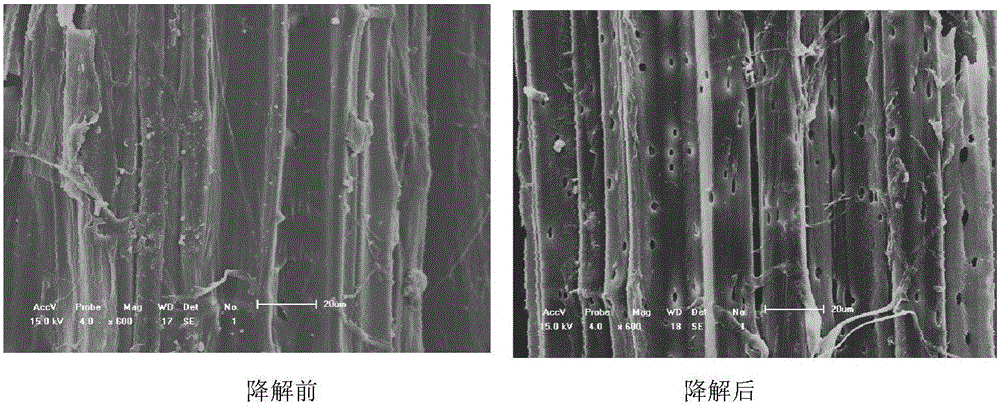
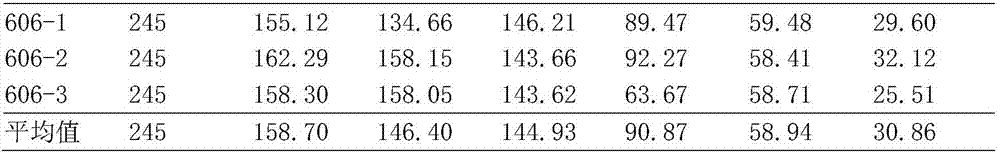
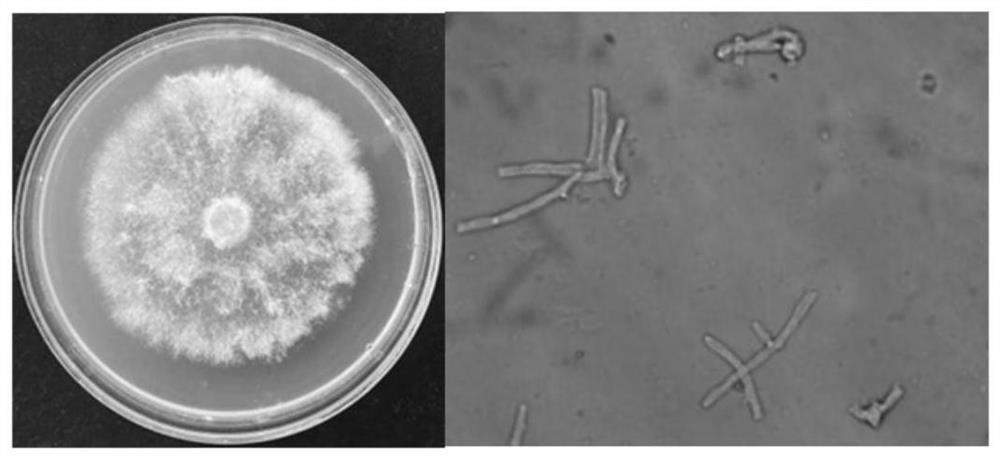
The invention relates to irpex lacteus capable of efficiently degrading lignin and application of irpex lacteus. The irpex lacteus is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation No. is CGMCC No.11920. The ZK1 irpex lacteus can be adopted to ferment straw composite feed prepared from a mixed material of straw powder, feather powder and oyster shell powder, the content of polysaccharide of the straw composite feed is as high as 203.2 [mu]g / g, the content of real protein of the straw composite feed is as high as 72.68%, the pH value of the straw composite feed is kept within 7.5-8.5, the lignin degradation rate of the straw composite feed is as high as 62.45%, and the degradation rate of cellulose of the straw composite feed is as high as 45.48%, so that the digestion rate of the straw composite feed is increased, and the healthcare function of the straw composite feed is improved.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Nutritive feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102860413ASimple design processLess capital to buildFood processingAnimal feeding stuffRoom temperatureSterile water
The invention relates to a nutritive feed prepared by mixing bagasse and brewer's grain and a preparation method of the nutritive feed. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: taking sawdust, sterilizing, adding sterile water, inoculating irpex lacteus according to the weight part proportion of the sawdust to the irpex lacteus of 1:1*10<-5>-3*10<-5>, culturing for 15h-18h under room temperature to obtain a strain; mixing the bagasse with the brewer's grain according to the weight part proportion of 1:(1.5-1.8), adding the strain, fermenting for 15h-18h at room temperature, then adding a bacterium liquid containing nitrobacteria, continuously fermenting for 9h-10h; and after the fermenting is ended, freezing and drying to obtain the nutritive feed. The preparation method is simple in designed process, is little in construction cost, is easy to operate, and is suitable for small farms and retail farmers; meanwhile, the waste of the sugar industry and the brewing industry is recycled without polluting the environment; and the prepared feed is rich in nutrition and can better improve the intestinal tract digestive system of livestocks.
Owner:GUANGZHOU YOURUI BIOSCI
Irpex lacteus and application thereof
ActiveCN107384811AReduce poisonIncrease vitalityFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismEcological environment
The invention belongs to the field of environmental microorganism, and relates to irpex lacteus and application thereof. The irpex lacteus is a strain IFP00606 and preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation date is July 13, 2017, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.14352. A degrading bacterium produced by the technical scheme can effectively repair tetracycline antibiotic residue polluted water, reduce the harm on a human body by the antibiotic residue and protect the ecological environment.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Irpex lacteus LL210, application thereof and biocontrol microbial agent
The invention relates to irpex lacteus LL210, application thereof and a biocontrol microbial agent. The irpex lacteus provided by the invention is classified and named as Irpex lacteus, and the preservation number of the Irpex lacteus is CGMCC No.21057. A strain is separated from tomato leaves, and is non-toxic and free of pathogenicity. A plate confrontation test shows that the strain can effectively inhibit mycelial growth and spore germination of tomato botrytis cinerea and tomato late blight, and can be used for antagonizing plant pathogenic fungi tomato botrytis cinerea and / or phytophthora. The biocontrol microbial agent prepared from the irpex lacteus LL210 is used for preventing and treating tomato diseases, the prevention and treatment effects on tomato botrytis cinerea and late blight reach 81.35% and 87.68%, the biocontrol microbial agent has a good disease prevention effect and good compatibility with the environment, and a new microbial resource is provided for biological prevention and treatment of diseases of plants such as tomatoes.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Irpex lacteus capable of efficiently degrading lignin
ActiveCN111961596APromote degradationHigh decolorization rateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
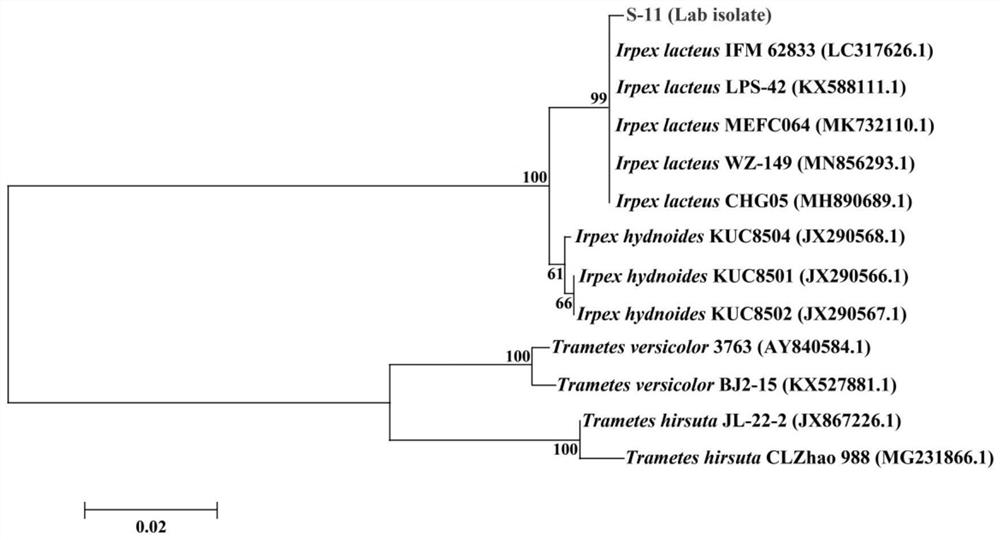
The invention discloses an irpex lacteus S-11 capable of efficiently degrading lignin, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. A liquid medium containing 4 g / L lignin is inoculated with the strain, the strain is cultured at 28 DEG C at 180 rpm for 11 days, and the degradation rate and decolorization rate of the strain for lignin reach 33.81% and 41.79% respectively. The methodfor degrading the lignin by using the strain is convenient to operate, low in cost and suitable for biological pretreatment of lignin in biorefinery industry. The strain has the degradation rate of apure lignin substrate higher than that of same-species strains reported at home and abroad, is shorter in degradation time and is suitable for biological pretreatment application in the biorefinery industry.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Preparation method of recombinant manganese peroxidase and application of recombinant manganese peroxidase in degradation of Chinese herbal medicine lignin
ActiveCN111808831AEasy accessRealize industrial productionFood processingMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCellulose
The invention belongs to the field of biological feed, and relates to a preparation method of recombinant manganese peroxidase and application of the recombinant manganese peroxidase in degradation ofChinese herbal medicine lignin. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out preference optimization on a gene sequence of manganese peroxidase coming from Irpex lacteus, carryingout PCR amplification by taking the optimized gene as a template, connecting the optimized gene with pREP, then converting the connected gene into escherichia coli competent cells to obtain recombinant shuttle plasmids, and introducing the recombinant shuttle plasmids into defective schizosaccharomyces pombe competent cells to obtain recombinant manganese peroxidase engineering bacteria; and performing culture to obtain a crude enzyme liquid, mixing the crude enzyme liquid with Chinese herbal medicines, and then adding calcium chloride, manganese sulfate, laccase, glucose oxidase and a small molecular substance activator for a multi-enzyme synergistic enzymolysis reaction. According to the method provided by the invention, a large amount of manganese peroxidase can be rapidly obtained, industrial production of the manganese peroxidase is realized, a good and stable peroxidase product is prepared, and effective degradation of Chinese herbal medicine lignin is realized.
Owner:浙江康星生物科技有限公司
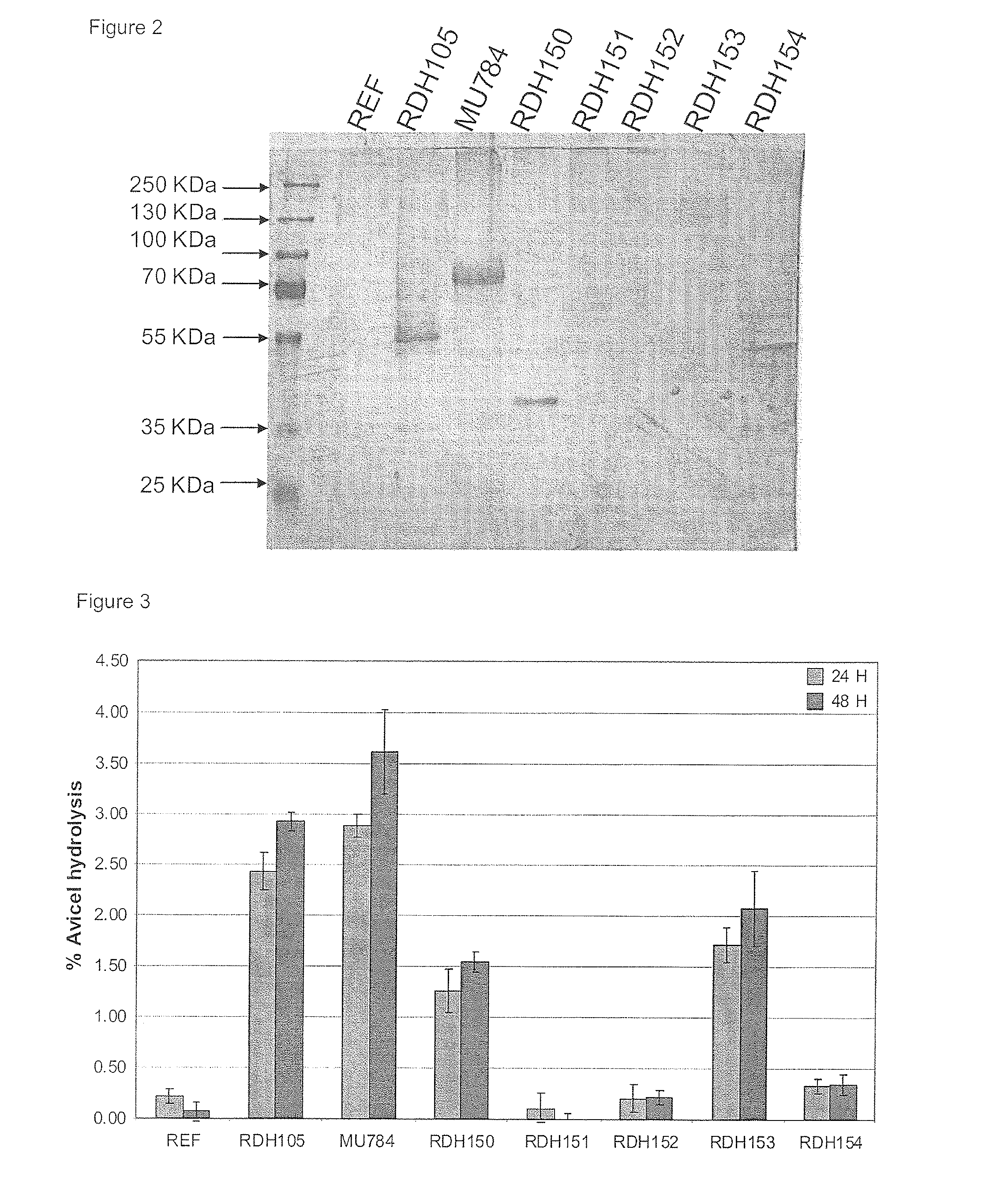
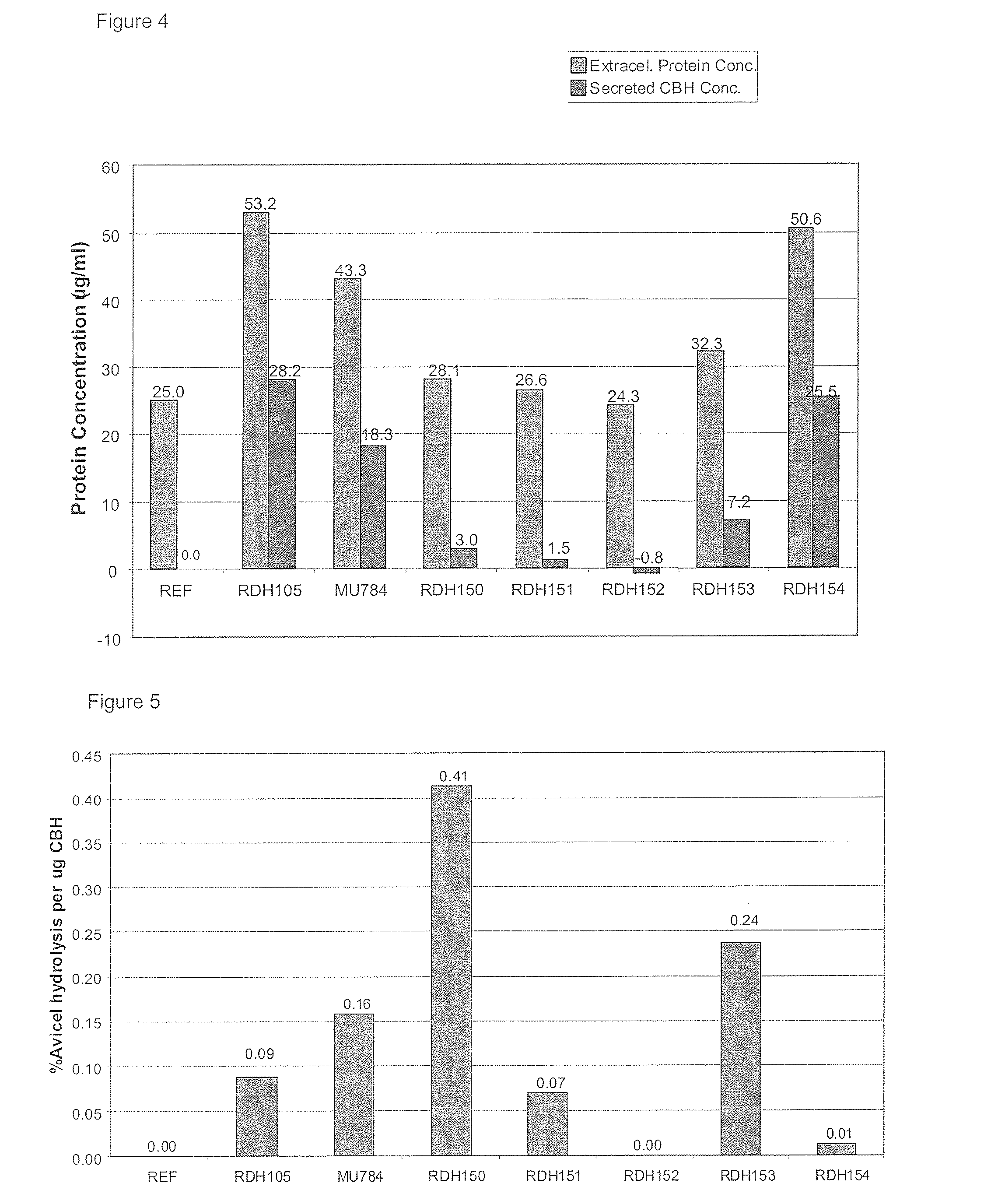
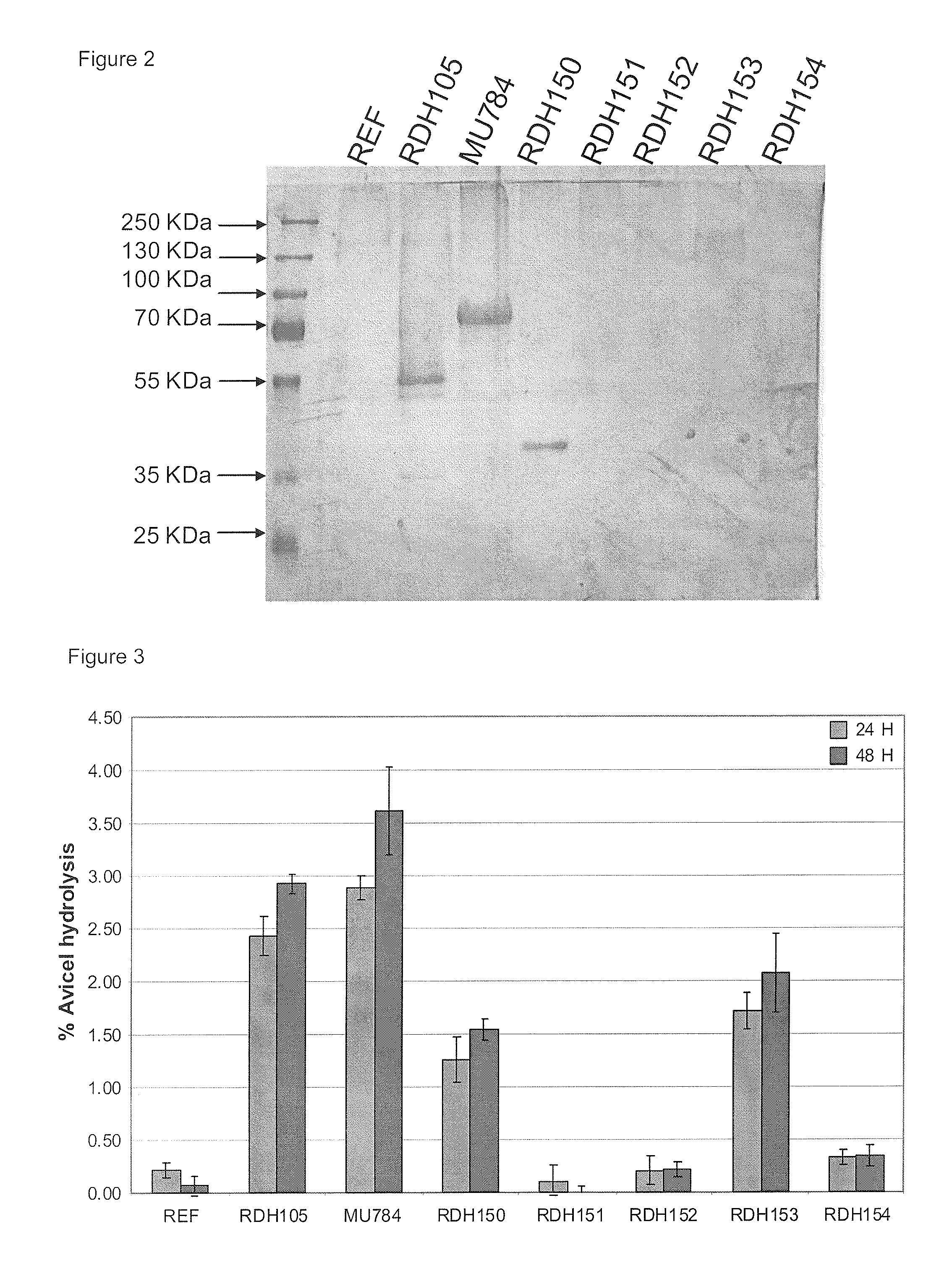
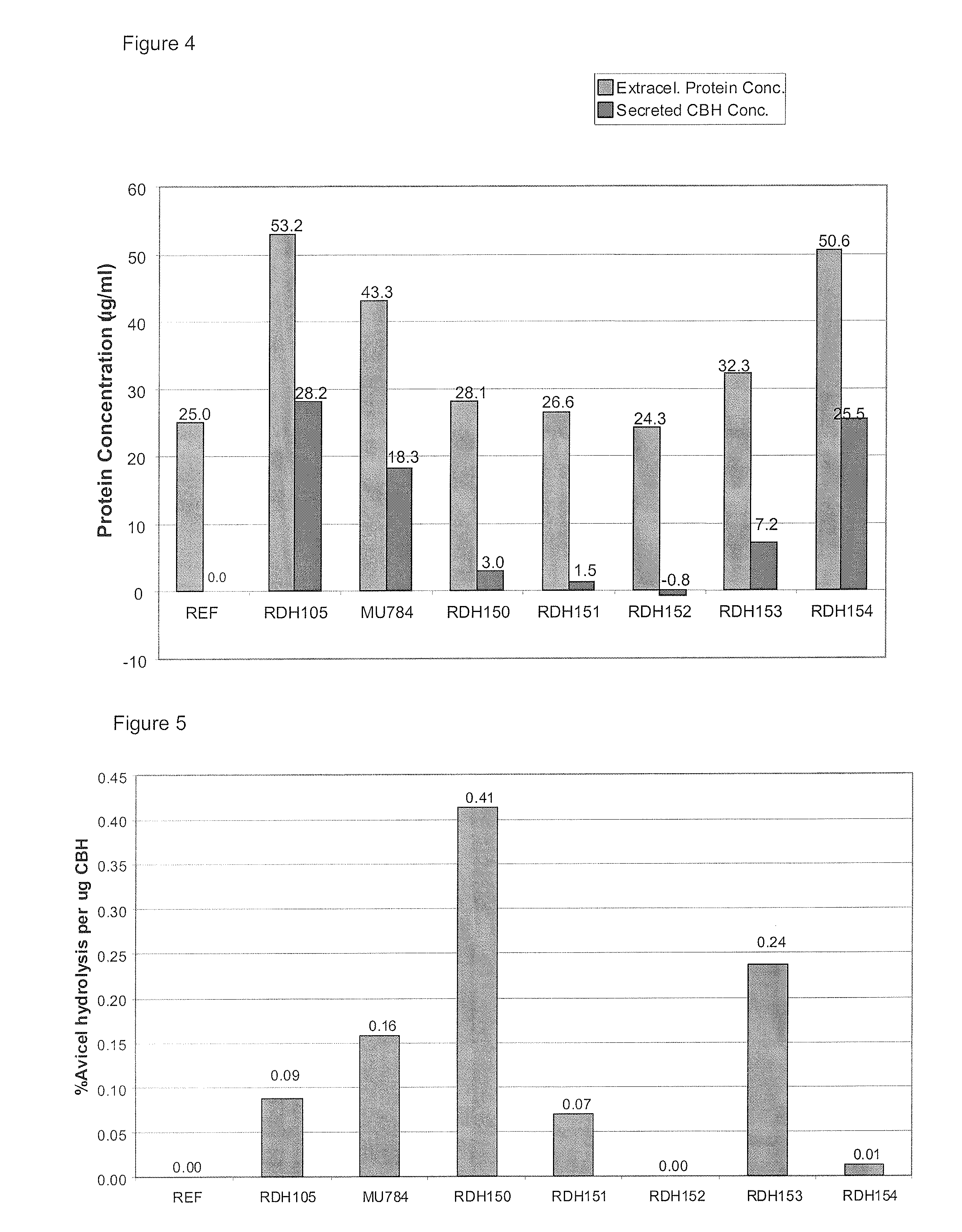
Heterologous Expression of Fungal Cellobiohydrolase 2 Genes in Yeast
ActiveUS20130217072A1Augment cellulose hydrolysisFacilitate ethanol productionAnimal cellsBacteriaHeterologousEnzyme Gene
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of polypeptides encoded by wild-type and codon-optimized cbh2 genes from the organisms Cochliobolus heterostrophus, Gibberella zeae, Irpex lacteus, Volvariella volvacea, and Piromyces sp. in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed cellobiohydrolases. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
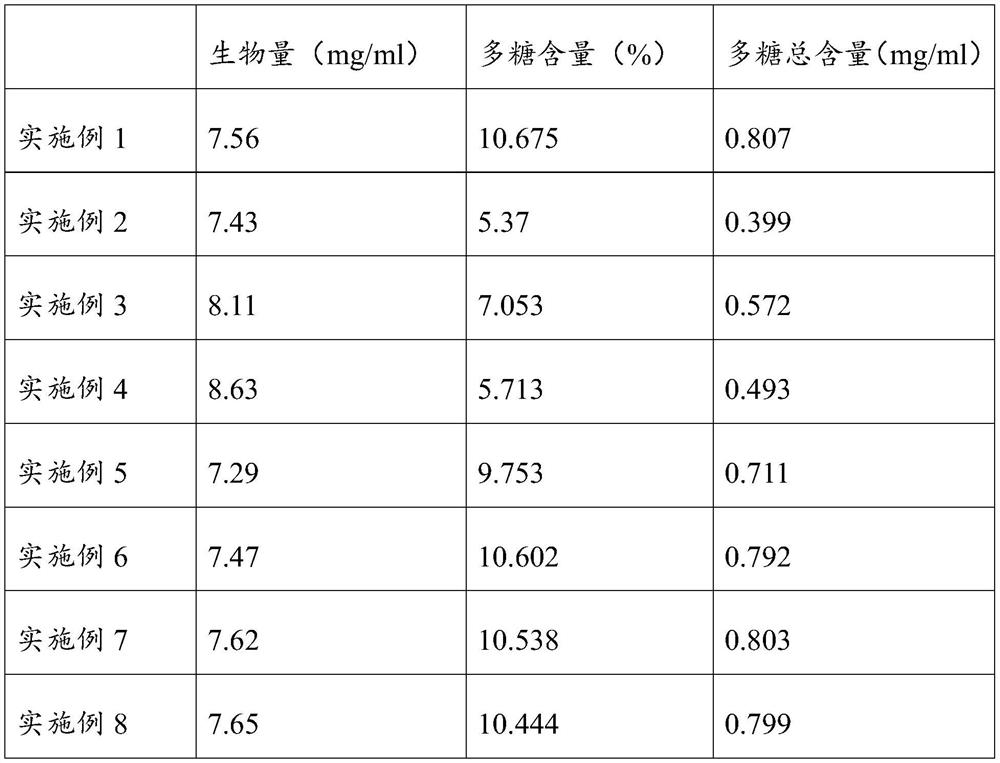
Method of increasing content of polysaccharide in mycelia of lucid ganoderma by means of fungal polysaccharides, and lucid ganoderma product prepared therefrom
ActiveCN108588142AHigh in polysaccharidesBreak the technical bottleneck of low polysaccharide contentFungiMicroorganism based processesFusarium oxysporumGanoderma pseudoferreum
The invention relates to a method of increasing content of polysaccharides in mycelia of lucid ganoderma by means of fungal polysaccharides, and a lucid ganoderma product prepared therefrom. In the method, lucid ganoderma is inoculated on a liquid culture medium for fermenting cultivation, wherein the liquid culture medium contains 30-110 [mu]g / ml of fungal polysaccharides; the fungal polysaccharides are extracted from one or more of monascus, aspergillus niger, fusarium oxysporum and irpex lacteus. The method can increase the content of polysaccharides in culture of the lucid ganoderma by increasing biomass of mycelia and / or content of intercellular polysaccharides in the mycelia during liquid fermentation of the lucid ganoderma. The method breaks a technical bottleneck of low polysaccharide content in a liquid fermentation process of the lucid ganoderma. The lucid ganoderma product is high in polysaccharide content and has great nutritional value.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Complex microbial inoculant for degrading corn straws at low temperature
PendingCN114262672AImprove degradation efficiencyEfficient degradationFungiBio-organic fraction processingBacillus licheniformisBacillus cereus
The invention relates to a complex microbial inoculant for degrading corn straws at low temperature. The complex microbial inoculant is prepared from bacillus cereus TK-2 (Bacillus cereus), bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis), bacillus licheniformis (Bacillus licheniformis), bacillus megatherium (Bacillus megatherium), Pseudomonas fragi (Pseudomonas fragi), Trichoderma viride (Trichoderma viride), Aspergillus niger (Aspergillus niger), Phanerochaete and Irpex lacteus (Irpex lacteus), and the complex microbial inoculant can be used for degrading corn straws at low temperature. The complex microbial inoculant formed by nine strains including bacillus cereus has the degradation efficiency of 38.71% at the indoor constant temperature of 15 DEG C, can efficiently degrade the corn straw and accelerate the decomposition time in the natural environment of 1-10 DEG C, has a high degradation rate, has the degradation rate of 35.93% after 30 days, and has excellent stability.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Preparation method and application of microbial straw degradation microbial agent
InactiveCN110922975AEfficient degradationSolve technical problemsAgriculture tools and machinesFungiMicroorganismContinuous fermentation
The invention discloses a preparation method and an application of a microbial straw degradation microbial agent. The method comprises the steps: firstly, preparing strains of Irpex lacteus, Aspergillus sydowii, Penicillium citrinum and Schizophyllum comune; taking the prepared strains, respectively activating, culturing and fermenting; and finally, obtaining a fermentation liquids of each strain,and treating and compounding the fermentation liquids to obtain a soil conditioner. The method is scientific and reasonable, safe and convenient in use; different tool microorganisms are respectivelyand independently cultured and then mixed and compounded according to a concentration ratio of 1:1:1:1, and an optimal microbial straw degradation microbial agent is obtained; the microbial agent isinoculated to treated plant straw for continuous fermentation; and the fermentation product is subjected to solid-liquid separation and innocent treatment and is dried at the temperature of 60 DEG C to form the soil conditioner. Through optimized tool microorganism proportioning, the technical problems of straw returning to the field and soil improvement are solved while high-efficiency degradation of the plant straw is realized.
Owner:南京朴厚生态科技有限公司
Application of irpex lacteus in preparing anti-hypoxia medicaments
ActiveCN104138395AConducive to cultivationEasy to prepareAntinoxious agentsFungi medical ingredientsBiotechnologyDrugs preparations
The invention provides application of irpex lacteus in preparing anti-hypoxia healthy products. The irpex lacteus is prepared by fermentation, water extraction, alcohol sedimentation and lyophilizing methods. Animal experiments prove that the irpex lacteus has a remarkable anti-hypoxia effect. The irpex lacteus has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost, small toxic and side effect and remarkable anti-hypoxia effect, and is suitable for preparation of anti-hypoxia healthy foods or medicinal preparations.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Heterologous Expression of Fungal Cellobiohydrolase 2 Genes in Yeast
InactiveUS20130230888A1Augment cellulose hydrolysisFacilitate ethanol productionBacteriaSugar derivativesHeterologousBiotechnology
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of polypeptides encoded by wild-type and codon-optimized cbh2 genes from the organisms Cochliobolus heterostrophus, Gibberella zeae, Irpex lacteus, Volvariella volvacea, and Piromyces sp. in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed cellobiohydrolases. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
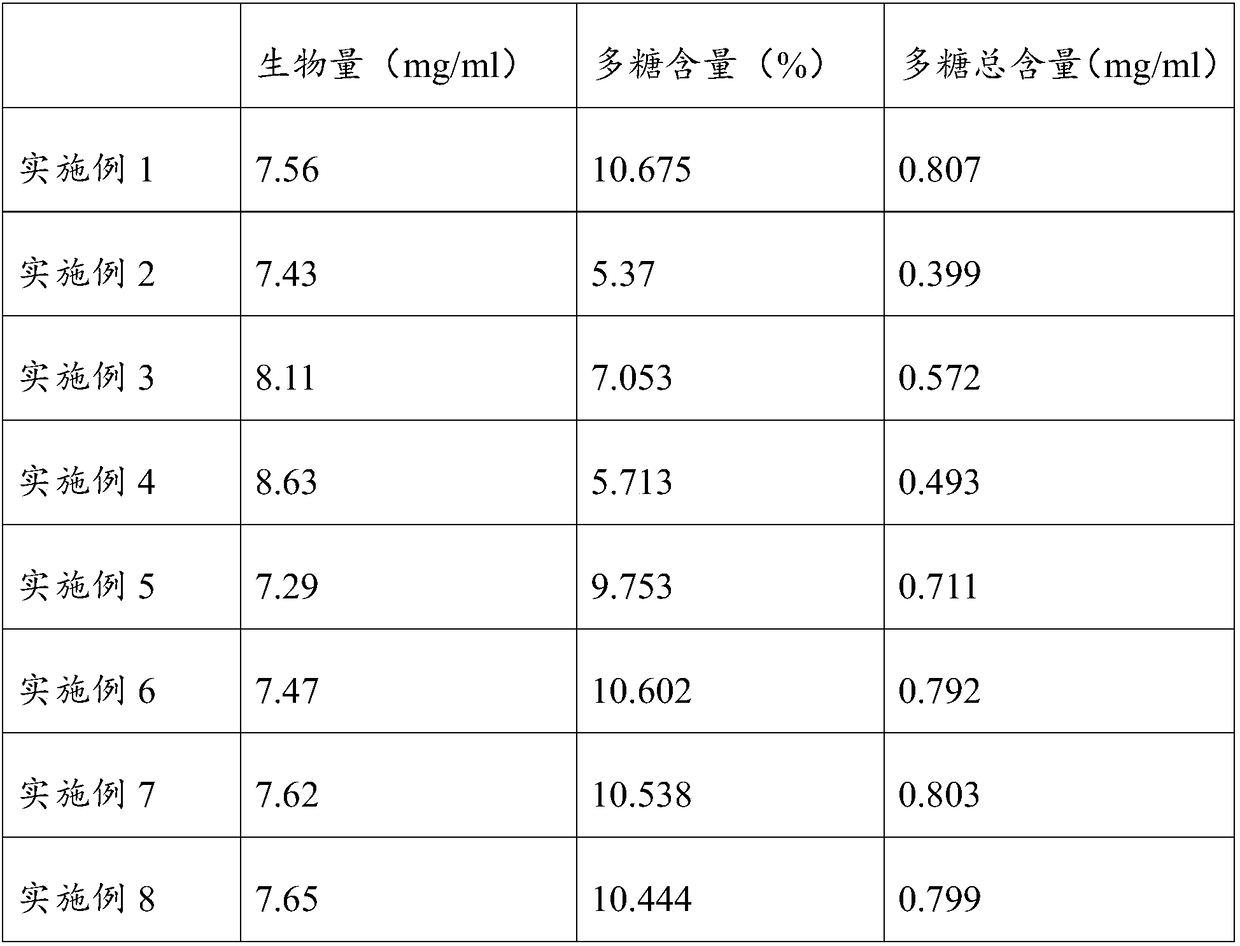
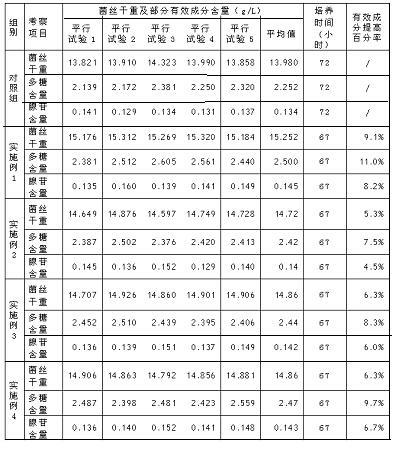
Additive for liquid nutrient medium for Irpex lacteus fermentation
InactiveCN102690147ADry weight increaseHigh in polysaccharidesFertilizer mixturesBiotechnologyIndustrial fermentation
The invention provides an additive for a liquid nutrient medium for Irpex lacteus fermentation, relating to formula optimization of a liquid nutrient medium for Irpex lacteus fermentation. Calcium lignosulphonate and natural borneol are added into the broad liquid nutrient medium to enhance the transport efficiency of Irpex lacteus cells, and promote the absorption and utilization of the Irpex lacteus for nutrient substances, thereby enhancing the yield of the cellular metabolism products adenosin and polysaccharide and the dry weight of hypha. The total adenosin content is up to 0.135-0.149 g / L, which is enhanced by 8.2% on average as compared with the liquid nutrient medium without the additive; the total polysaccharide content is up to 2...381-2.605 g / L, which is enhanced by 11.0% on average as compared with the liquid nutrient medium without the additive; and the dry weight of hypha is up to 15.176-15.320 g / L, which is enhanced by 9.1% on average as compared with the liquid nutrient medium without the additive. The additive can be used as a liquid nutrient medium additive for industrially fermenting Irpex lacteus.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Application of irpex lacteus in preparing anti-fatigue healthy products
ActiveCN104138396AConducive to cultivationEasy to prepareAntinoxious agentsFungi medical ingredientsBiotechnologyFermentation
The invention provides an application of irpex lacteus in preparing anti-fatigue healthy products. The irpex lacteus extract is prepared by fermentation, water extraction, alcohol sedimentation and lyophilizing methods. Animal experiments prove that the irpex lacteus has a remarkable anti-fatigue effect. The irpex lacteus has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost, small toxic and side effect and remarkable anti-fatigue effect, and is suitable for preparation of anti-fatigue healthy products.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cooking agent used for pulping in papermaking
ActiveCN109024034AExtended usable lifeGood cooking effectPulping with acid salts/anhydridesCellulose treatment using microorganisms/enzymesPapermakingGraphene
The invention relates to a cooking agent used for pulping in papermaking and belongs to the field of papermaking. The cooking agent is composed of graphene aerogel powder and an enzyme supported thereby; wherein the enzyme consists of an enzyme liquid I and an enzyme liquid II according to mass ratio of 1-3:1. The enzyme liquid I is prepared by performing fermentation with Irpex lacteus Fr. and separating the bacteria; the enzyme liquid II is prepared by performing fermentation with Coriolopsis gallica and separating the bacteria. The cooking agent is mainly used in a pulping process with a grass type raw material, wherein by combining the bio-enzymes and the supporter, the cooking agent can prevent loss of the enzyme during use. The cooking agent can be repeatedly utilized and is long inservice life, and has great cooking effect.
Owner:淮安市井沅科技有限公司
Irpex lacteus and application of Irpex lacteus in degradation of waste branches in orchard
ActiveCN114196555AImprove degradation efficiencyImprove the activity of degrading enzymesFungiBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses Irpex lacteus and application thereof in degradation of waste branches in orchards, and relates to the technical field of microorganisms. The Irpex lacteus SDAU-B disclosed by the invention is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC), the preservation number is CGMCC No.23855, the preservation date is November 17, 2021, and the preservation address is No.3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The Irpex lacteus provided by the invention has the capability of degrading lignin and cellulose, can improve the activity of degrading enzyme in waste piles, can play a degrading role to promote the increase of the content of ammonium nitrogen in the piles, and can improve the degradation efficiency of waste branches in orchards.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing active dietary fibers through fermentation of irpex lacteus and schizophyllum commune
ActiveCN107574124AOvercoming refractoryImprove efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBranCulture mediums
The invention relates to novel strains, namely, irpex lacteus (Irpex lacteus PCV1) and schizophyllum commune (schizophyllum commune SCF1) for preparing active dietary fibers by fermenting potato dregs, and a method for converting the potato dregs to synthesize the active dietary fibers through degradation of irpex lacteus PCV1 and schizophyllum commune SCF1. The Irpex lacteus PCV1 is the strain belonging to the polyporales, polyporaceae and the irpex lacteus genus; the Irpex lacteus PCV1 strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 6, 2016,and is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC NO.12529. The schizophyllum commune SCF1 is the strain belonging to the agaricales, schizophyllaceae and the schizophyllum; the schizophyllum commune SCF1 strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on July 6, 2016, and is assigned with the accession number of CGMCC NO.12530. The method comprises thefollowing steps: inoculating Irpex lacteus PCV1 into a liquid fermentation culture medium containing the potato dregs, brain and inorganic salt for fermentation culture, after culture is finished, inactivating the fermentation liquor, after inactivating, inoculating the schizophyllum commune SCF1 for fermentation culture, carrying out homogenization treatment on the fermentation final product, and thus the active dietary fiber product is obtained.
Owner:孙敏
A strain of albicans and its application
ActiveCN106399132BPromote growthIncrease productionPlant growth regulatorsBiocideSolventCulture fungus
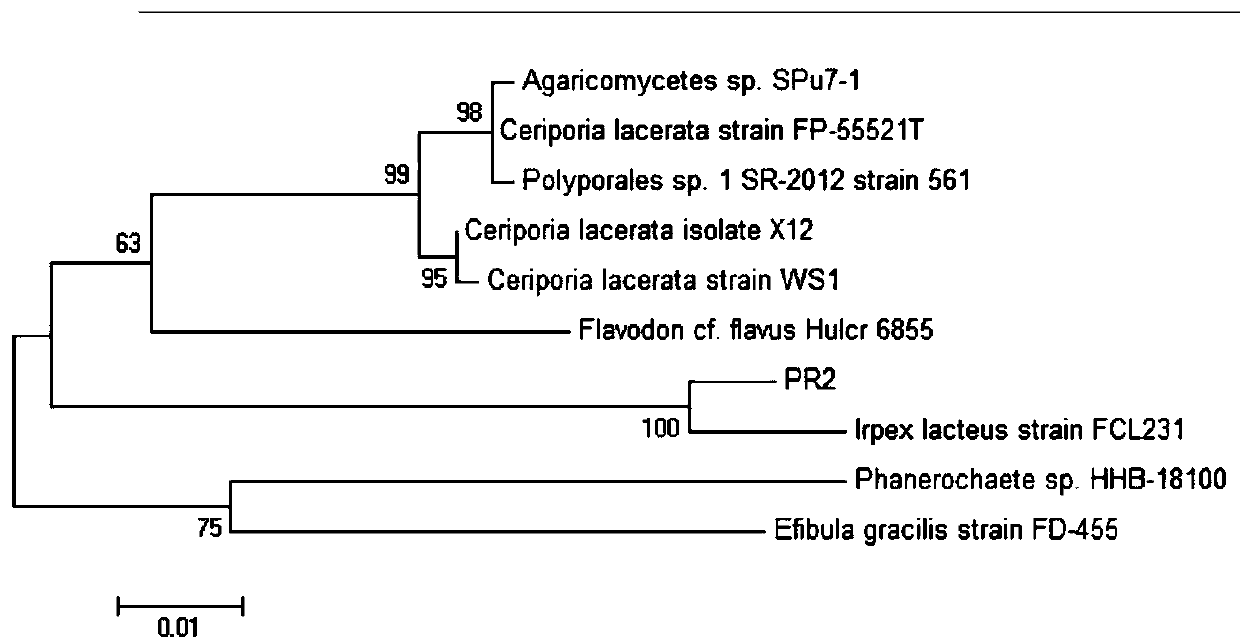
The invention discloses a strain of Irpex lacteus, named Irpex lacteus (Irpex lacteus) PR2, which has been preserved in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, referred to as CGMCC, and the address is: Beichen, Chaoyang District, Beijing No. 3, No. 1 Yard, West Road, Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, strain preservation number is CGMCC NO.13190. The present invention is the first time to isolate and purify a kind of R. albicans from the root of wild blueberry in Daxing'an Mountains. It uses liquid aerobic fermentation to obtain a large number of hyphae of R. albicans, uses ethanol as the extraction solvent, and obtains it through ultrasonic extraction. Natural substances that grow crop roots, improve stress resistance, promote flowering, increase yield and crop quality, are conducive to the further development of natural compounds with ultra-high life-promoting activities; and no three wastes are generated during the entire production process, which is cost-effective and meets the requirements of Social needs for environmental protection and food safety production.
Owner:SHANDONG PENGBO BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method beneficial to extraction of gutta-percha
The invention discloses a eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method beneficial to extraction of gutta-percha. The eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method comprises the steps: (1), preparing an irpex lacteus seed solution; (2), inoculating and culturing a eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull; and (3), treating after fermenting. The dry weight of the treated eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull is reduced by 35-42 percent due to effective degradation of the irpex lacteus, the gutta-percha in the fruit hull can reach 50-60 percent, the efficiency and rate of extracting the gutta-percha by using organic solvents such as petroleum ether are greatly increased, and the glue quality is remarkably improved. The treatment effect of the eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method is superior to an existing enzymic method and a distiller's yeast and yeast fermentation method; the eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method has no damage to environment; the environment benefit of the eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method is superior to that of an alkali treatment method; the eucommia ulmoides key fruit hull treating method is stronger in actual application value.
Owner:JISHOU UNIVERSITY
Heterologous expression of fungal cellobiohydrolase 2 genes in yeast
ActiveUS9447398B2Promote productionAugment cellulose hydrolysisBiofuelsFermentationHeterologousBiotechnology
The present invention provides for heterologous expression of polypeptides encoded by wild-type and codon-optimized cbh2 genes from the organisms Cochliobolus heterostrophus, Gibberella zeae, Irpex lacteus, Volvariella volvacea, and Piromyces sp. in host cells, such as the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The expression in such host cells of the corresponding genes, and variants and combinations thereof, result in improved specific activity of the expressed cellobiohydrolases. Thus, such genes and expression systems are useful for efficient and cost-effective consolidated bioprocessing systems.
Owner:STELLENBOSCH UNIVERSITY
A kind of huperzine A derivative and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107574193BEasy to trainNovel structureMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobial transformationChemical compound
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Use of albicans albicans in the preparation of hypoxia-resistant medicine
ActiveCN104138395BConducive to cultivationEasy to prepareAntinoxious agentsFungi medical ingredientsAlcoholPharmaceutical formulation
The present invention provides the use of A. albicans in the preparation of hypoxia-resistant health care products. The extract of A. albicans is prepared by fermentation, water extraction, alcohol precipitation and freeze-drying. Animal experiments have proved to have significant Resistant to hypoxia. The preparation method of the invention is simple, the cost is low, the toxic and side effects are small, the hypoxia-resistant effect is remarkable, and it is suitable for the preparation of hypoxia-resistant health food or pharmaceutical preparation.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
The use of albicans albicans in the preparation of anti-fatigue health products
The invention provides an application of irpex lacteus in preparing anti-fatigue healthy products. The irpex lacteus extract is prepared by fermentation, water extraction, alcohol sedimentation and lyophilizing methods. Animal experiments prove that the irpex lacteus has a remarkable anti-fatigue effect. The irpex lacteus has the advantages of simple preparation method, low cost, small toxic and side effect and remarkable anti-fatigue effect, and is suitable for preparation of anti-fatigue healthy products.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Method for extracting polypeptides from Irpex lacteus
ActiveCN105368907AKeep aliveLess investment in production equipmentPeptide preparation methodsFermentationUltrafiltrationImpurity
The invention discloses a method for extracting polypeptides from Irpex lacteus. The method comprises steps as follows: the Irpex lacteus is subjected to impurity removal, freezing and crushing, degreasing is performed with a supercritical CO2 fluid extraction method, then protein and peptide substances are extracted with a NaOH solution, and the polypeptides are extracted from the Irpex lacteus after further enzymolysis and ultrafiltration. The method is simple in technology, safe and free of pollution, the obtained product is high in purity and extraction rate, side reactions and addition products are few, and the method is easy to operate and popularize and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:TONGHUA JITONG PHARMA
Method for preparing active dietary fiber by fermenting Racula albicans and Schizophyllum
ActiveCN107574124BOvercoming refractoryEnhance immune functionFungiMicroorganism based processesSaccharumBran
The invention relates to new bacterial strains capable of fermenting potato dregs to prepare active dietary fiber——Irpex lacteus PCV1 and Schizophyllum commune SCF1, and a method for synthesizing active dietary fiber by using them to degrade and transform potato dregs. A kind of bacterium PCV1, belonging to Polyporaceae, Polyporaceae, and genus Racula, which was preserved in China Common Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center on July 6, 2016. The deposit number is CGMCC NO.12529. A Schizophyllum SCF1, belonging to the order Agaricaceae, the family Schizophyllum, and the genus Schizophyllum, the strain was preserved in the China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center, and the preservation time was July 06, 2016. The number is CGMCC NO.12530. The method is to first insert the above-mentioned Raketooth albicans PCV1 into a liquid fermentation medium containing potato dregs, bran and inorganic salts for fermentation and culture, inactivate the fermentation liquid after the cultivation, and then insert The schizophyllum SCF1 is fermented and cultured, and the final fermentation product is homogenized to obtain an active dietary fiber product.
Owner:孙敏
A method for synergistically fermenting wheat straw to prepare high-quality biological feed
ActiveCN113416663BAchieve mass productionEnsure biosecurityFungiFood processingBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention belongs to the field of biological feed, in particular to a method for synergistically degrading and fermenting wheat straw into high-quality biological feed. First, the lignin peroxidase gene from R. albicans was optimized and introduced into the defective Schizosaccharomyces pombe to obtain the lignin peroxidase-Schizophrenia pombe recombinant engineered strain; The strains were combined with Neurospora crassa, Lactobacillus fermentum, Candida rugugenens, and S.pombe‑pREP‑mnp fermentation strains producing manganese peroxidase, and added glucose, nitrogen source, laccase and glucose oxidase, and small Molecular substances are used to synergize bacteria and enzymes to ferment straw to obtain high-quality biological feed. The method rationally utilizes agricultural waste, promotes the conversion of lignocellulose in straw, increases the true protein content in the straw feed, degrades the lignocellulose content therein, significantly improves the quality and nutritional value of the fermented feed in a short time, and obtains high-quality straw fermented feed.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for increasing polysaccharide content of ganoderma mycelia by using fungal polysaccharides and ganoderma products obtained
ActiveCN108588142BHigh in polysaccharidesBreak the technical bottleneck of low polysaccharide contentFungiMicroorganism based processesFusarium oxysporumMycelium
The invention relates to a method of increasing content of polysaccharides in mycelia of lucid ganoderma by means of fungal polysaccharides, and a lucid ganoderma product prepared therefrom. In the method, lucid ganoderma is inoculated on a liquid culture medium for fermenting cultivation, wherein the liquid culture medium contains 30-110 [mu]g / ml of fungal polysaccharides; the fungal polysaccharides are extracted from one or more of monascus, aspergillus niger, fusarium oxysporum and irpex lacteus. The method can increase the content of polysaccharides in culture of the lucid ganoderma by increasing biomass of mycelia and / or content of intercellular polysaccharides in the mycelia during liquid fermentation of the lucid ganoderma. The method breaks a technical bottleneck of low polysaccharide content in a liquid fermentation process of the lucid ganoderma. The lucid ganoderma product is high in polysaccharide content and has great nutritional value.
Owner:INST OF BAST FIBER CROPS CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Albicans ll210 and its application, biocontrol agent
The present invention relates to albicans LL210, its application and biocontrol agent. The Irpex lacteus LL210 provided by the present invention is classified as Irpex lacteus and has a preservation number of CGMCC No. 21057. The strain is isolated from tomato leaves and is non-toxic and non-pathogenic. The plate confrontation test shows that the strain can effectively inhibit the mycelium growth and spore germination of Botrytis cinerea and Phytophthora infestans, and can be used to antagonize plant pathogenic fungi Botrytis cinerea and / or Phytophthora. The present invention utilizes the biocontrol fungus agent prepared by the albicans LL210 to prevent and control tomato diseases, and the control effects on tomato gray mold and late blight respectively reach 81.35% and 87.68%, and have good disease control effects and are compatible with the environment Well, it provides a new microbial resource for the biological control of plant diseases such as tomato.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Irpex lacteus fermented tea and preparation method thereof
PendingCN114097906AGood hypolipidemic effectReduce contentPre-extraction tea treatmentBiotechnologySecondary metabolite
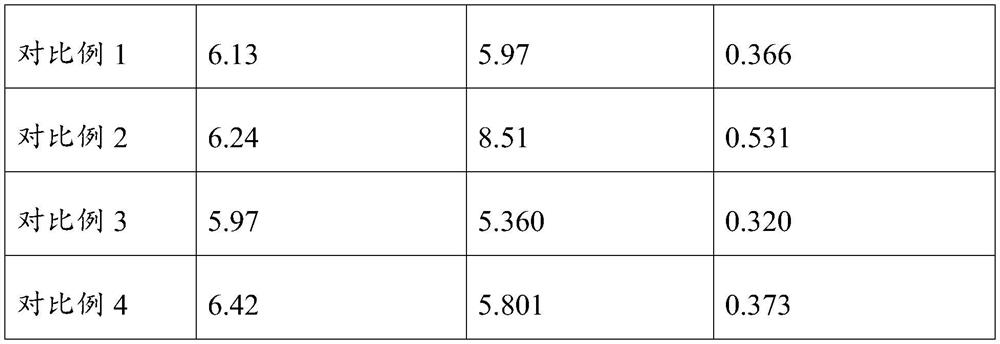
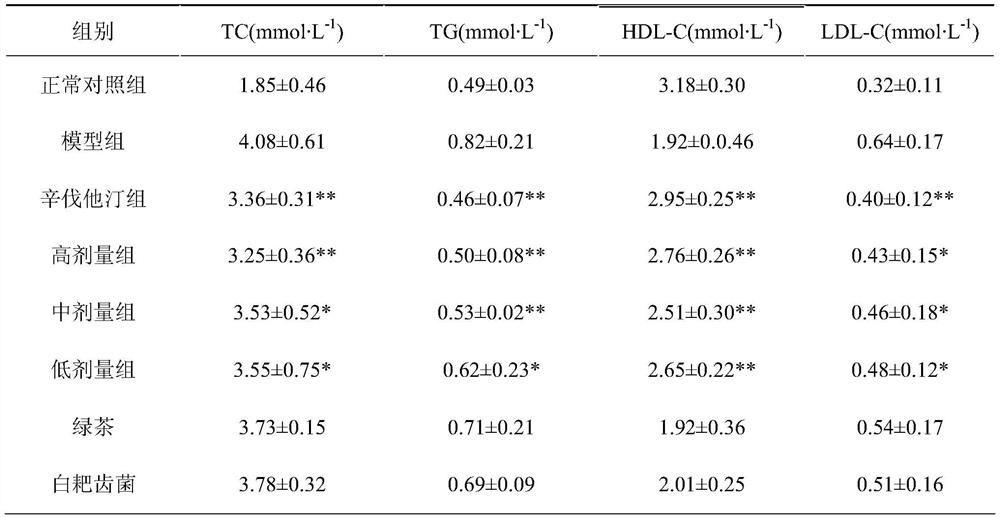
The invention discloses irpex lacteus fermented tea. The irpex lacteus fermented tea is obtained by co-fermentation culture of irpex lacteus and tea leaves. Accordingly, the inventor also establishes a corresponding preparation method, and Irpex lacteus hyphae obtained through tea water culture are selected to be domesticated, cultured, overgrown and dried in the sun to obtain the Irpex lacteus fermented tea. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating Irpex lacteus into a culture medium containing tea leaves for fermentation culture, co-fermenting the domesticated Irpex lacteus and the tea leaves to form Irpex lacteus fermented tea, and generating a new secondary metabolite of the Irpex lacteus fermented tea in the process. A further research shows that the irpex lacteus fermented tea can significantly reduce the content of blood fat indexes TG, TC and LDL-C of hyperlipidemia model mice, significantly improve the HDL-C level, and has a good blood fat reducing effect on hyperlipidemia. Therefore, the irpex lacteus fermented tea has the blood fat reducing effect superior to that of the irpex lacteus and the tea leaves, and a theoretical basis is provided for deep research and development of the irpex lacteus and the irpex lacteus fermented tea.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com