Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
309 results about "Petroleum production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
3-D prestack/poststack multiple prediction
InactiveUS6735527B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNormal moveoutCommon depth point
System and method for analyzing seismic data from a formation. Stacked seismic data are provided, including a plurality of stack traces, e.g., by collecting seismic data from source and receiver locations and stacking the collected seismic data to produce the stacked seismic data. 3-dimensional (3-D) prestack traces are generated from the plurality of stack traces, e.g., by performing inverse moveout of stack traces, e.g., in a specified neighborhood, at common-depth-points, e.g., by inverse normal moveout, ray tracing, spike synthesis, etc. The inverse moveout corrected traces are convolved to compute predicted multiples which are useable in analyzing the formation. The multiples may be adaptively subtracted from the stacked seismic data, or optionally, from prestack data, to generate processed seismic data useable in analyzing the formation, e.g., for petroleum production potential. Dip moveout (DMO) corrected seismic data may be used, where DMO velocities are adjusted by dividing by cosine of the dip angle.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
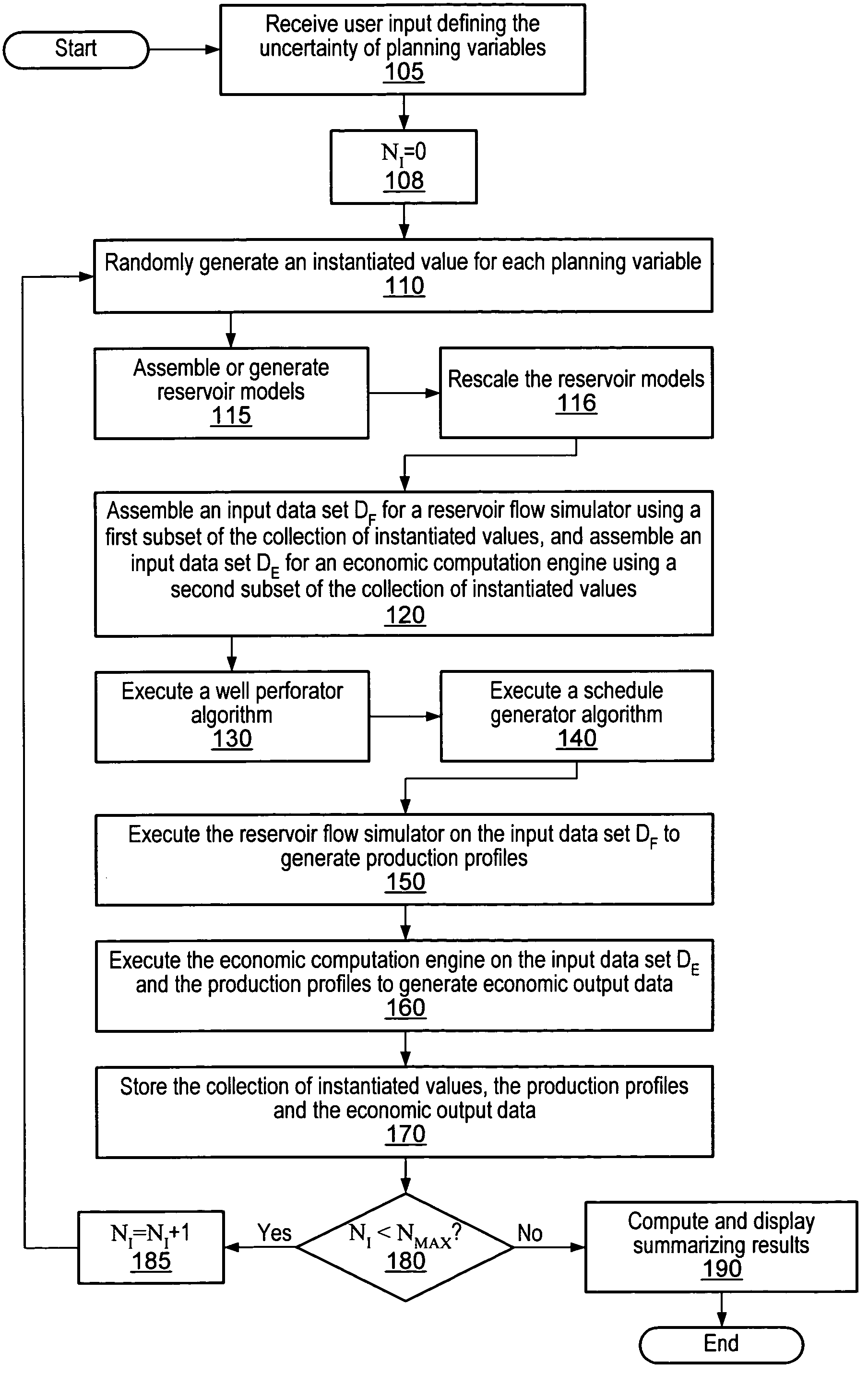
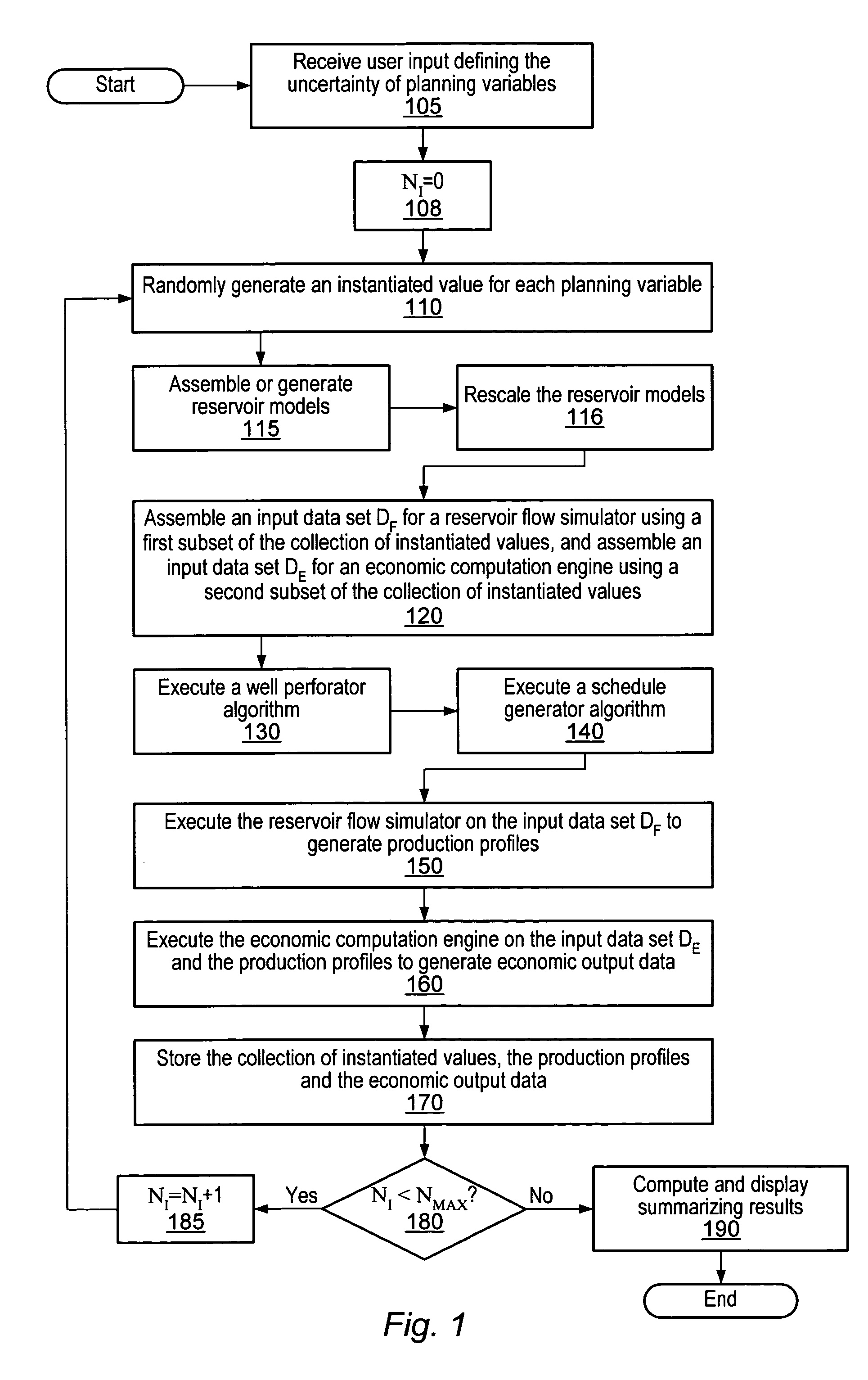
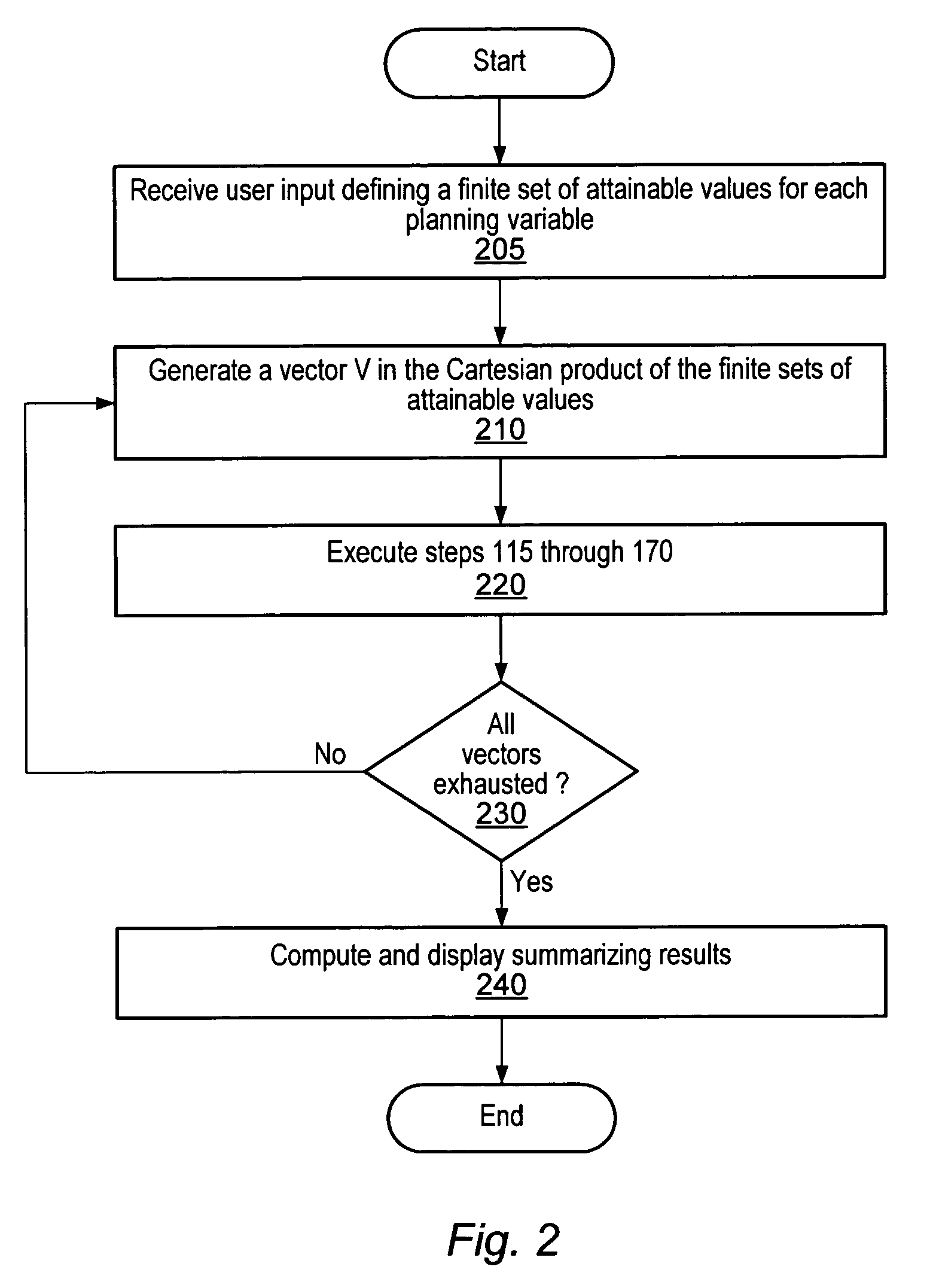
Decision support method for oil reservoir management in the presence of uncertain technical and economic parameters
The method of the invention is applicable to oil production to obtain the impact of technical and economic uncertainties on the economic profitability of a reservoir and / or to optimize the position of a new well in order to meet a development strategy. The invention includes in stage 1, uncertain technical parameters having an influence on the reservoir production are selected; in stage 2, an analytic model expressing the reservoir production in the course of time is determined as a function of the parameters selected in stage 1, from production values obtained by means of a flow simulator; and in stage 3, a model expressing the economic profitability of the reservoir is determined as a function of the technical and economic parameters, from the analytic model determined in stage 2.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
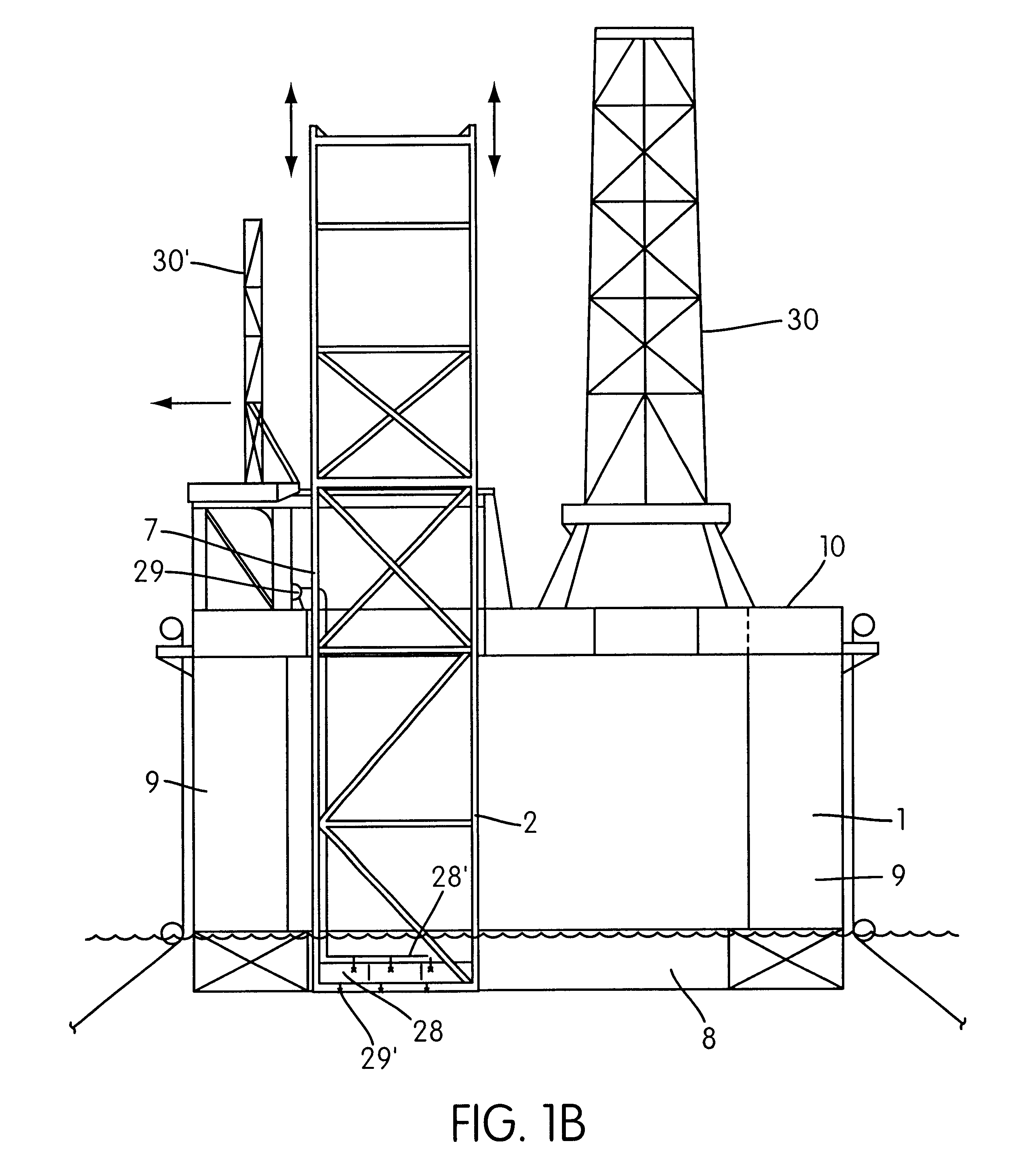
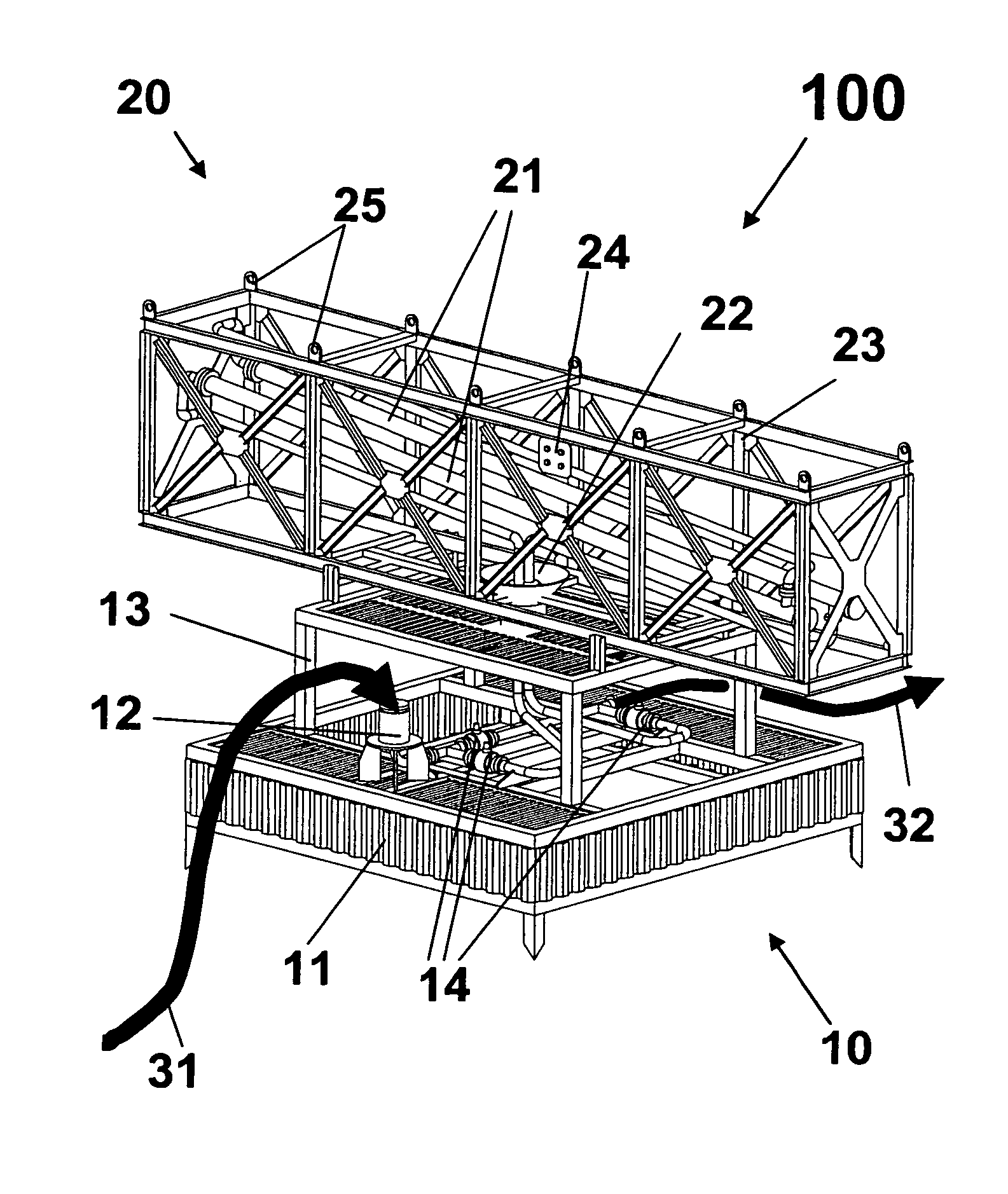
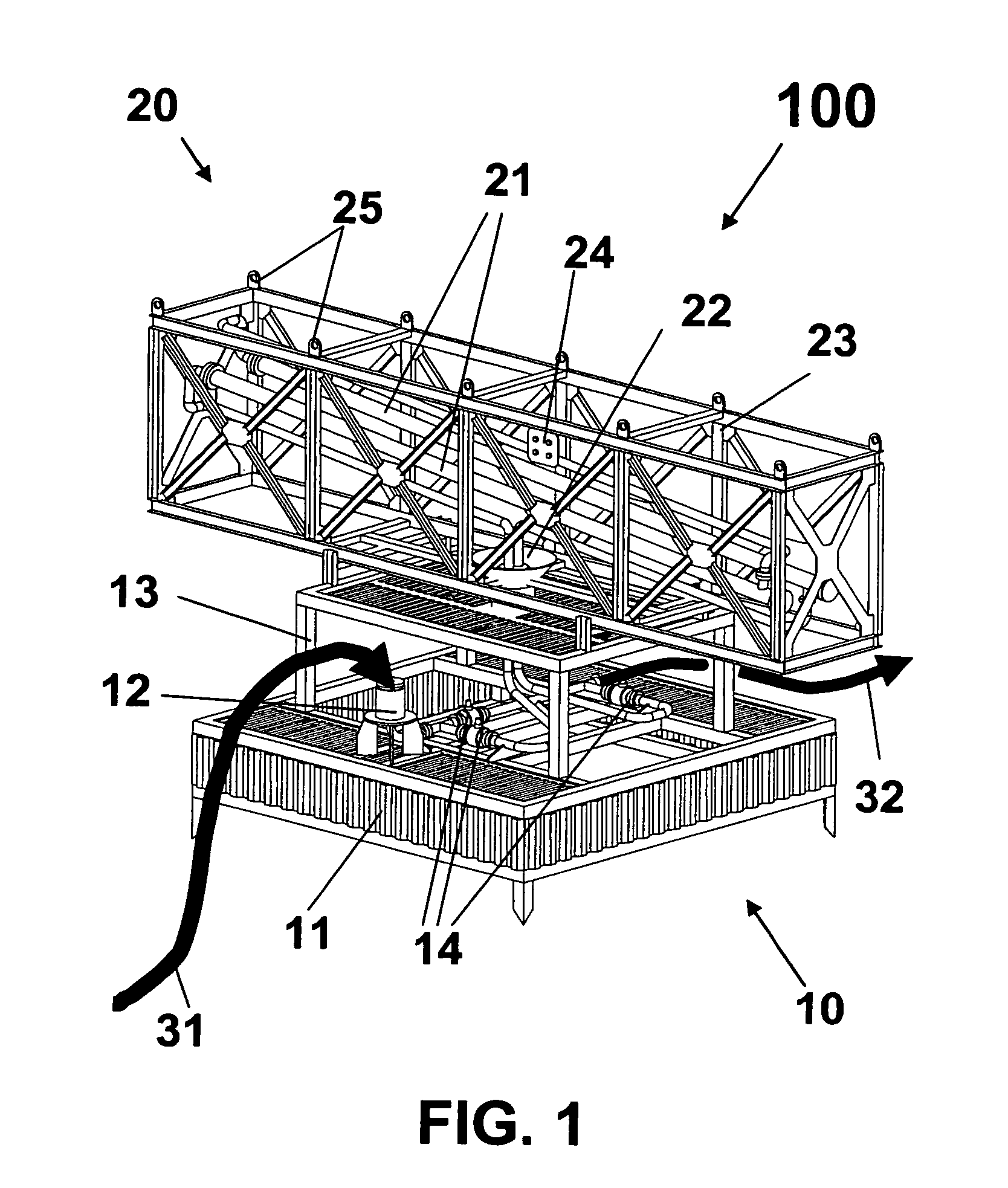
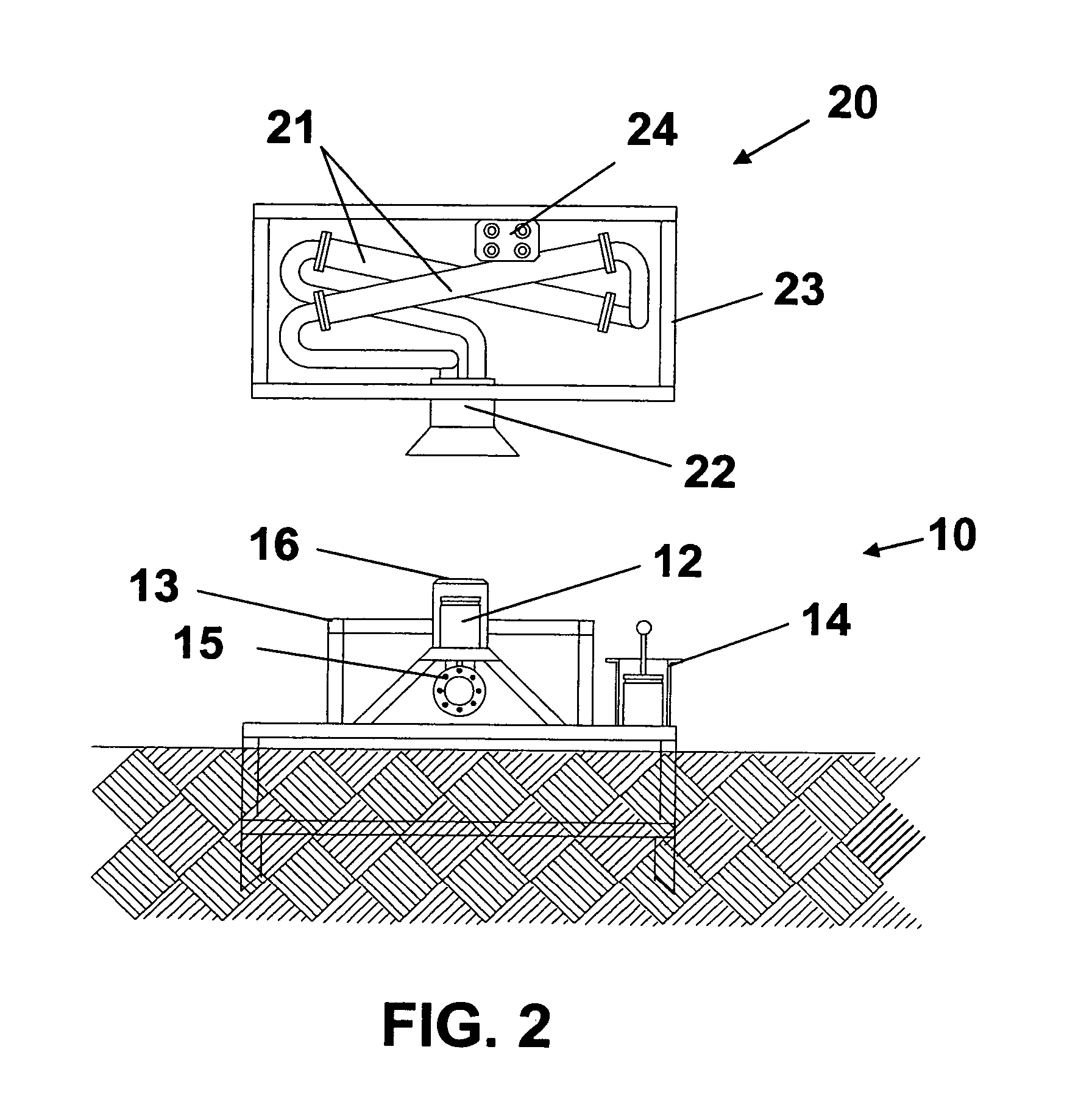
Self-supported riser system and method of installing same
InactiveUS20070044972A1Save rig timeReducing maneuvering stepCargo handling apparatusDrilling rodsBuoyPetroleum oil
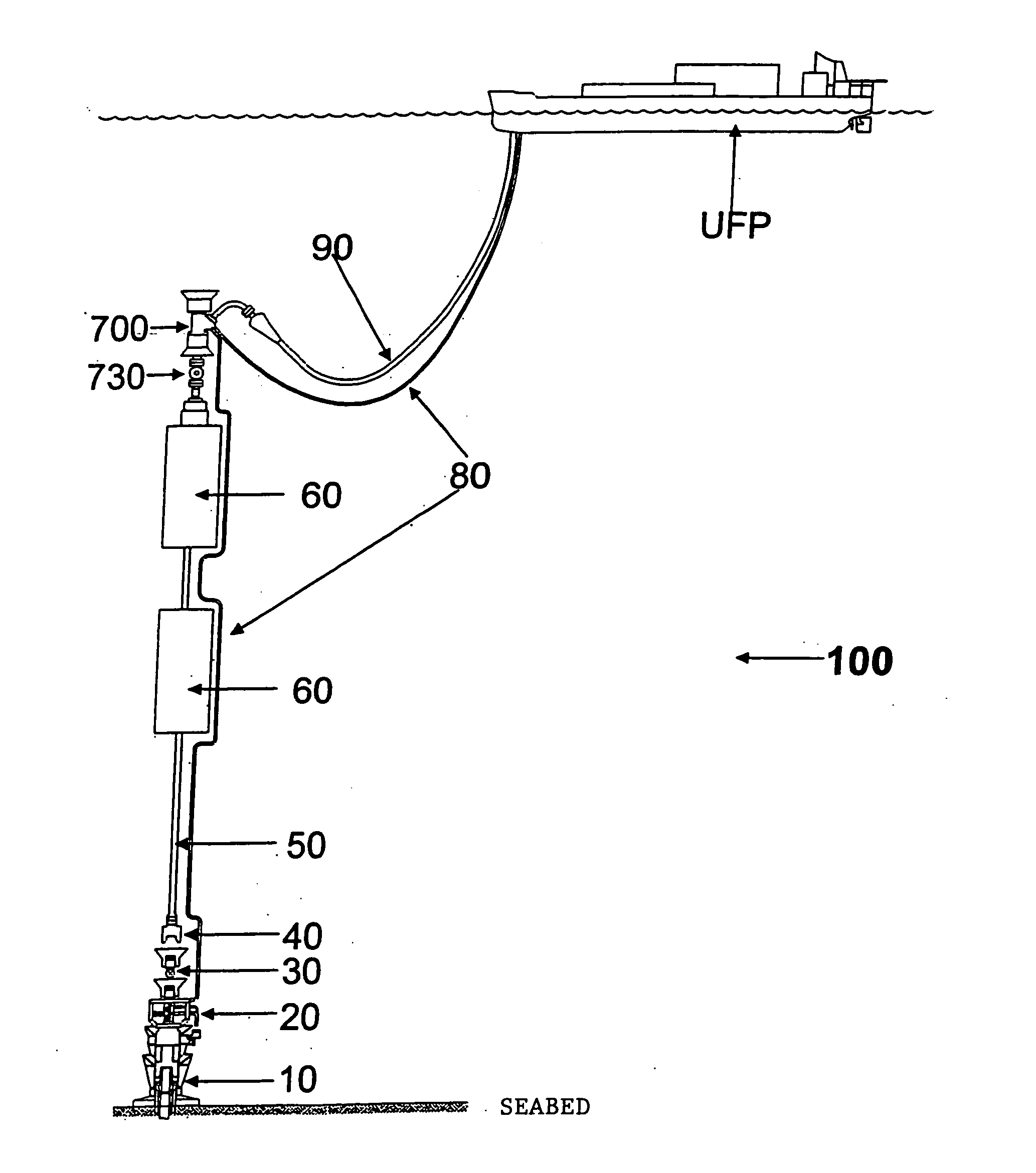
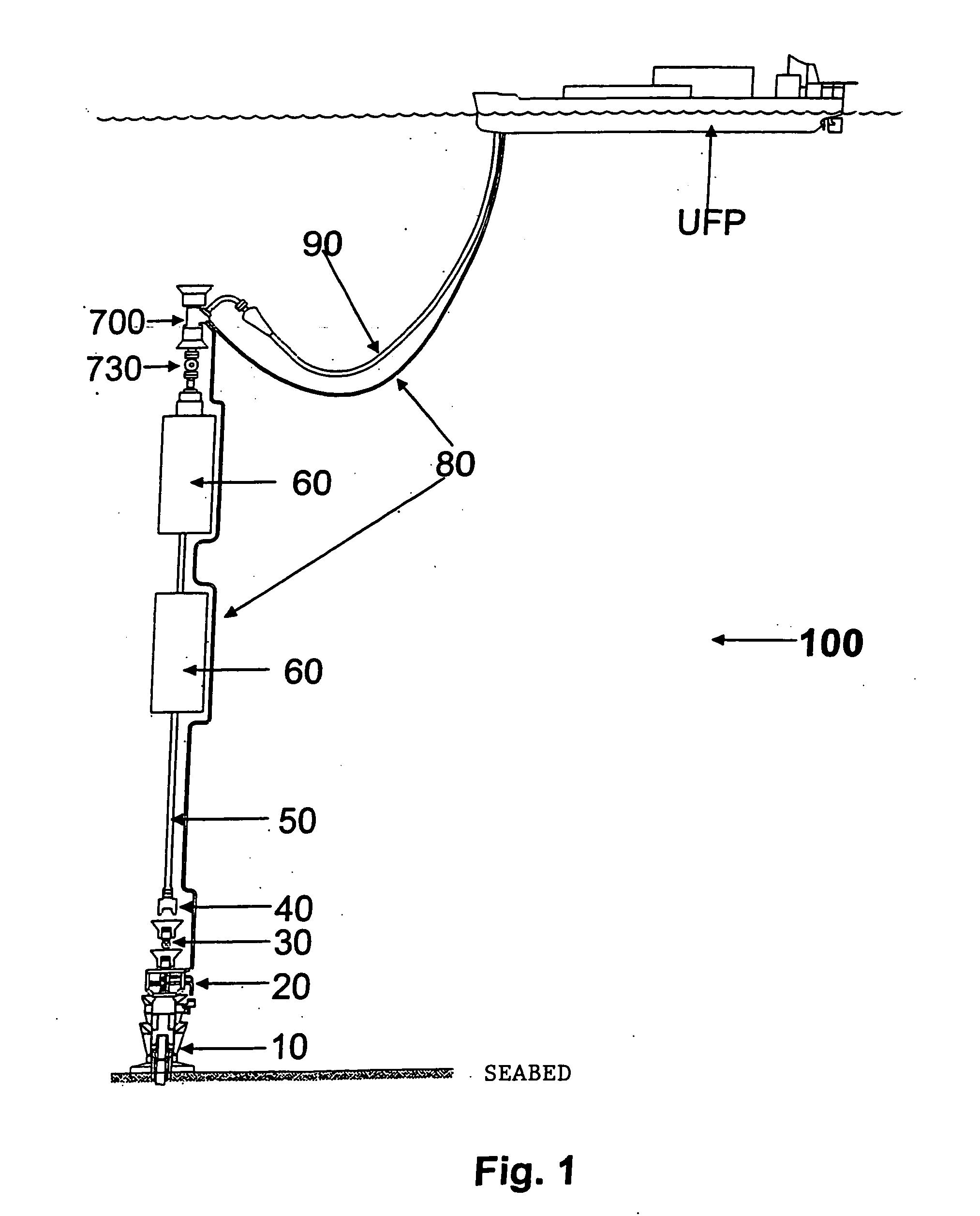
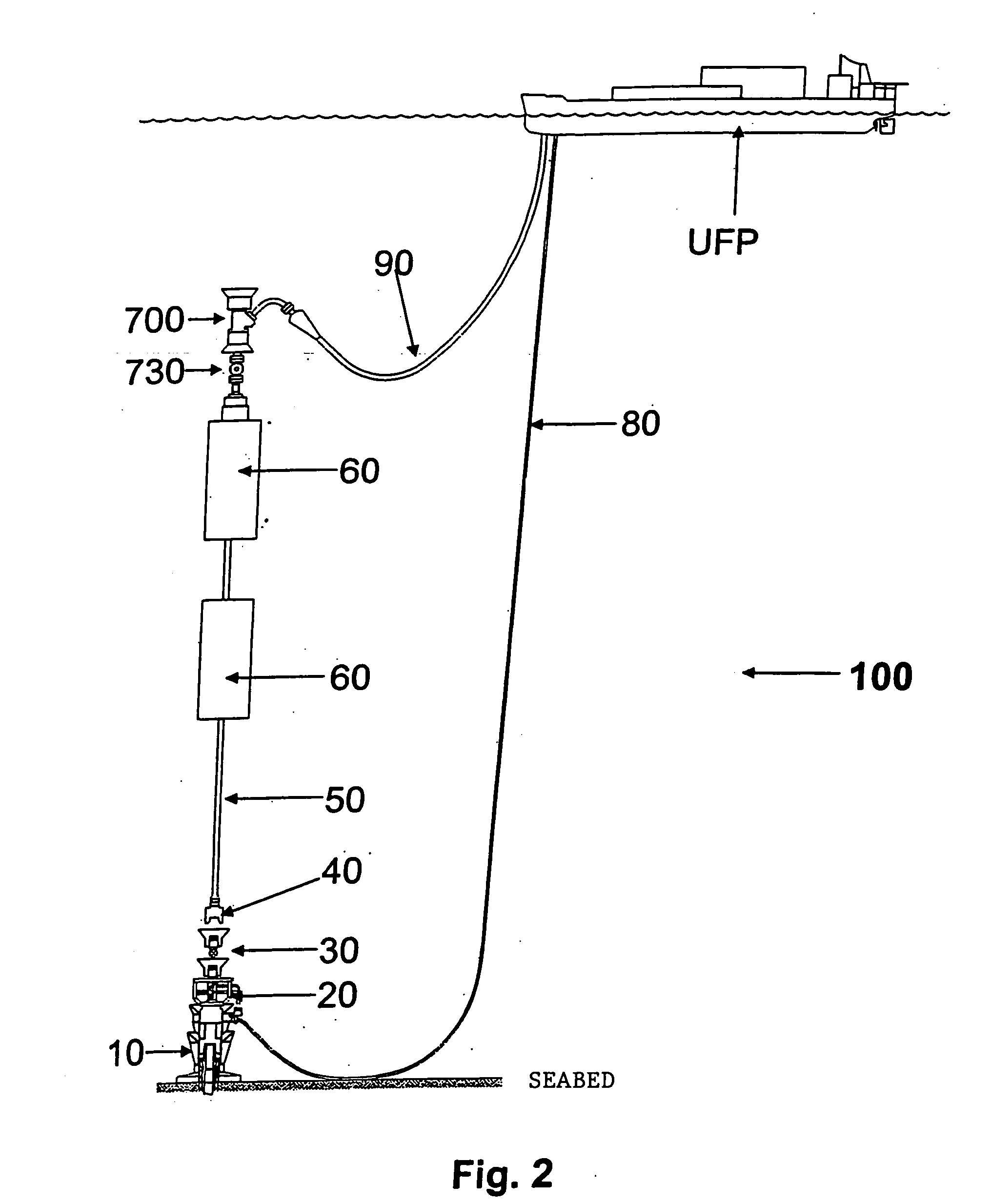
A self-supported riser system (100) for an Anticipated Production System (ASP) Test or a Long Duration Production (LDP) Test in a subsea petroleum production system, utilizing an ANM coupled to a wellhead and Floating Production Unit (FPU) is disclosed. The system includes a wellhead at the seabed, connected to an ANM (20) provided with a preventor (BOP of workover) (30). The preventor (30) is connected to a production riser (50) through a connection tool (40). The riser (50), mounted internally within a buoy assembly (60), is maintained under traction with the aid of a buoy assembly. The upper end of the riser (50) is provided with a Subsea Intervention Terminal (700), the Terminal being interlinked to the FPU by a flexible jumper (90) to carry the oil produced to the FPU. Two methods for installing the self-supported riser system (100) are also disclosed.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
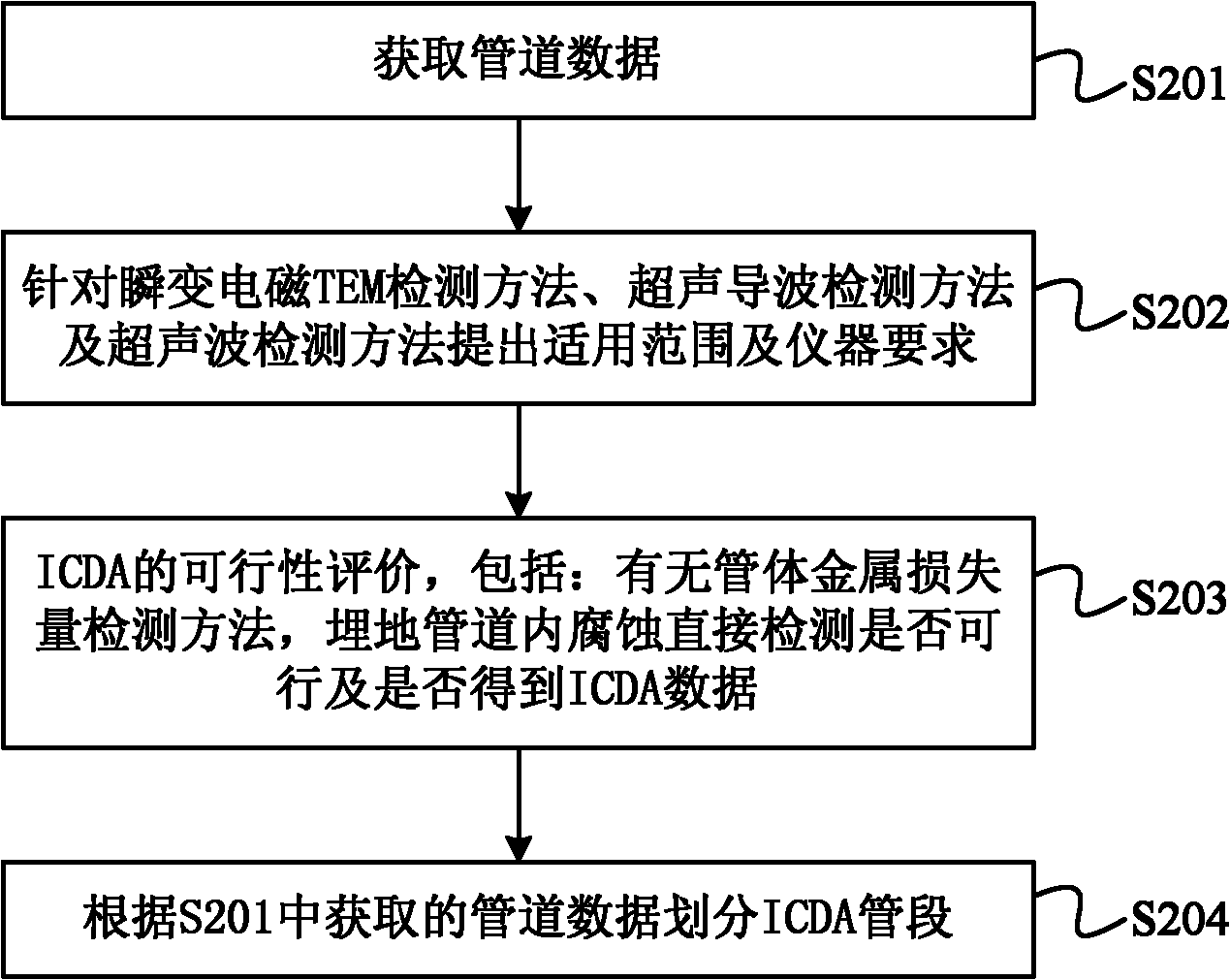
Method for evaluating corrosion in buried pipeline
ActiveCN102156089AReduce economic lossUnleash the full potential of your applicationWeather/light/corrosion resistanceDirect evaluationSafe operation
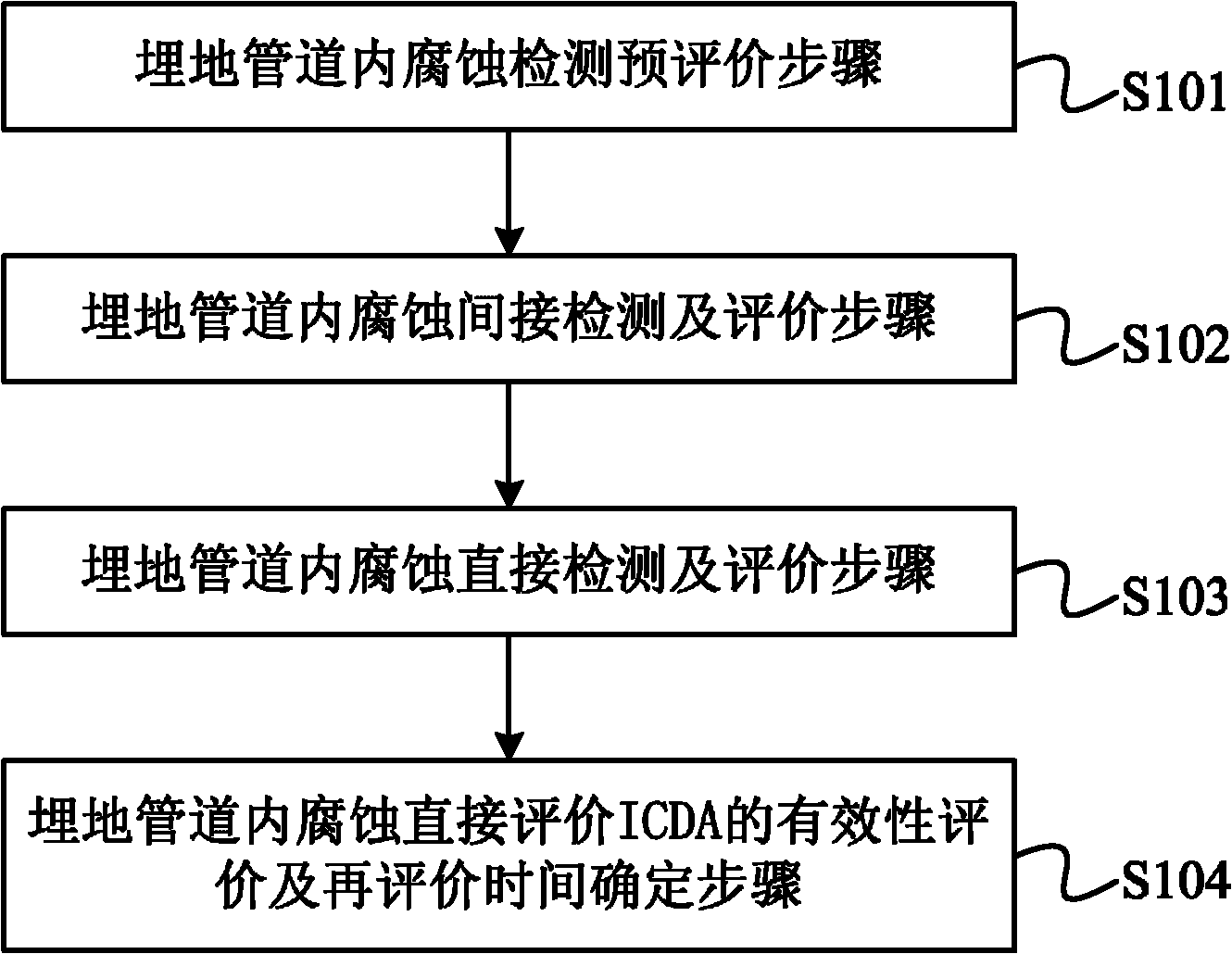
The invention provides a method for evaluating corrosion in a buried pipeline. The method for evaluating the corrosion in the buried pipeline comprises the following steps of: preliminary evaluation of corrosion detection in the buried pipeline, indirect detection and evaluation of the corrosion in the buried pipeline, direct detection and evaluation of the corrosion in the buried pipeline, and validity evaluation of direct evaluation ICDA of the corrosion in the buried pipeline and reevaluation time determination. At present, many in-service pipelines of petroleum enterprises sequentially enter a frequent accident period and an important stage of maintenance and update. By the method for evaluating the corrosion in the buried pipeline, levels of safe operation management and technology of the buried pipeline are improved, economic loss of personnel and facilities due to sudden accidents can be reduced, and safe production is ensured; the application potential of the in-service old pipelines is fully exerted, and the service life of the pipelines is prolonged; reliability and economical efficiency of pipeline engineering construction and operation are improved, and petroleum production and engineering costs are reduced; and environmental destruction caused by the sudden accidents is slowed down.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD +1
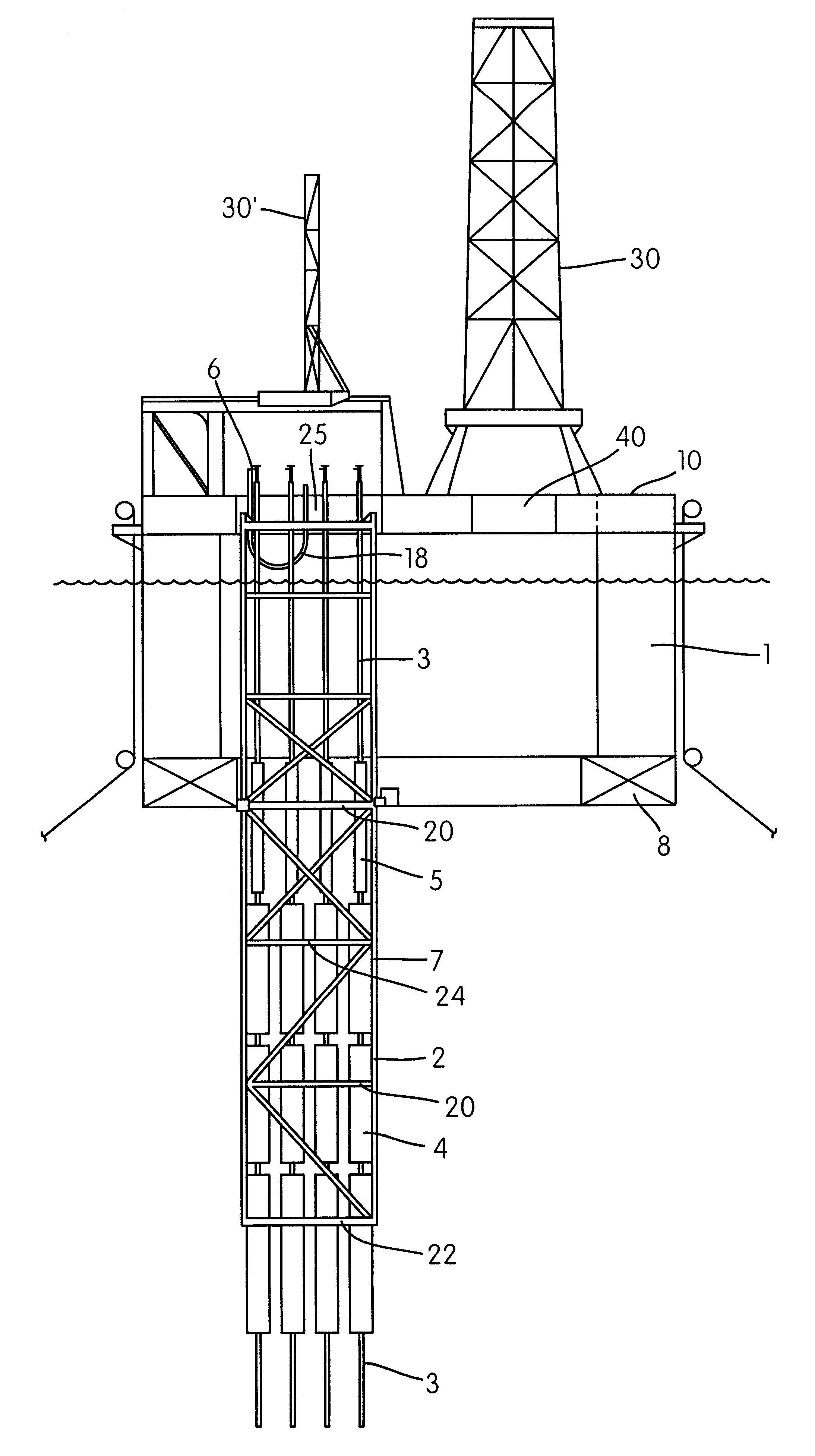
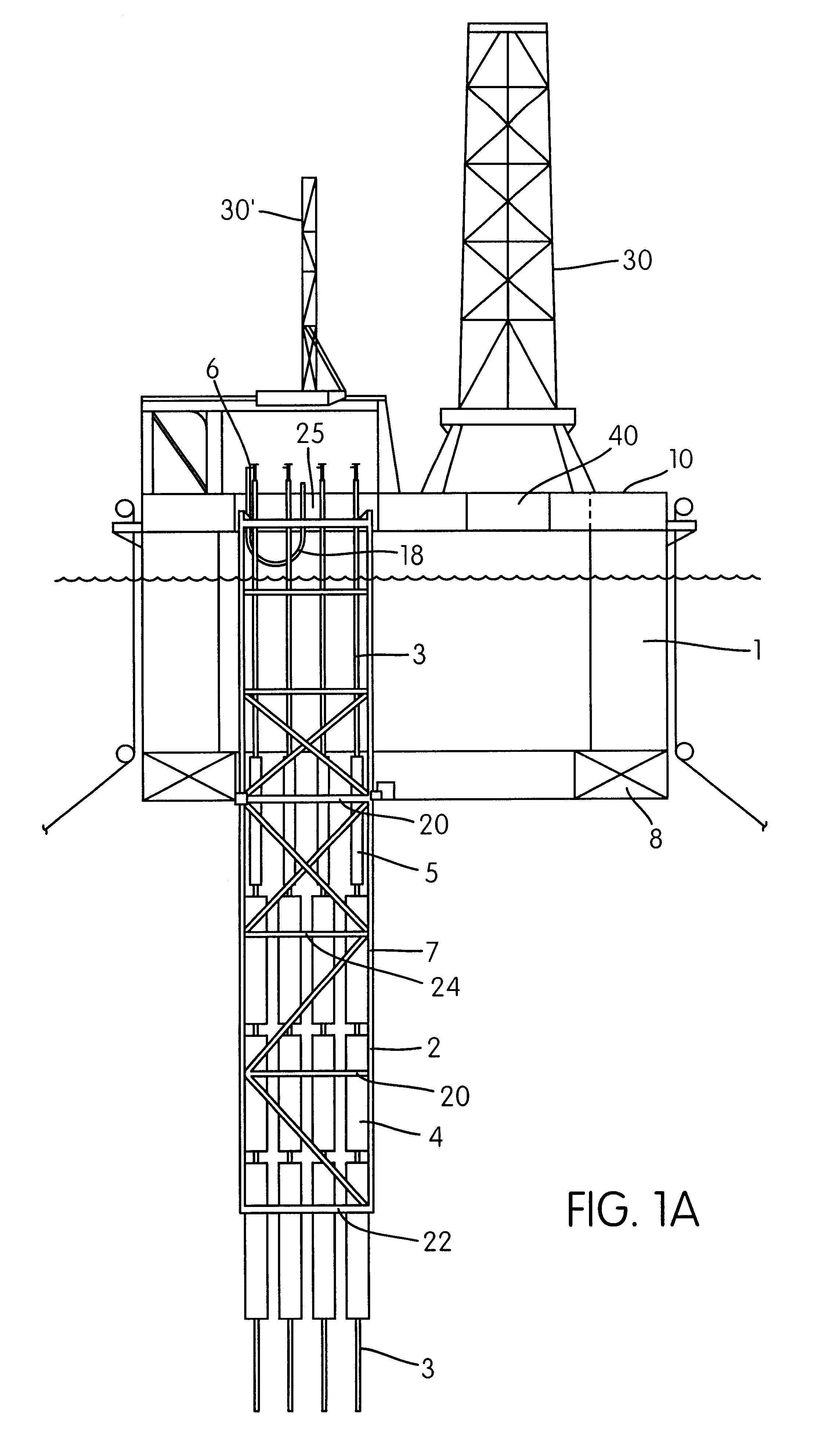
Guide device for production risers for petroleum production with a "dry tree semisubmersible" at large sea depths
A system for use in petroleum production at sea includes a guide frame for one or more riser pipes, on a semisubmersible production vessel. One or more main buoyancy member are arranged separately on at least one riser to carry the main part of the riser's weight. Each riser separately carries a Christmas tree on its top, near a main deck of the vessel. The guide frame comprises vertical main elements extending vertically downwards from the deck, through the splash zone and through the upper, more wave- and current-influenced zone of the sea. The guide frame also includes horizontal guide plates comprising vertically open cells formed of a horizontally arranged framework of beams. Lateral stabilization devices guide the risers' and the main buoyancy members' vertical movement relative to the vessel and restrict horizontal movement of the risers with respect to the guide frame. The guide plates are arranged in at least two levels on the guide frame. A lower guide plate is arranged at the lower ends of the vertical main elements', and a guide plate is arranged just below or near the splash zone. At least one main buoyancy member is held on the riser in level with, and guided by, lateral stabilization devices arranged in one or more guide plates below the upper, more wave- and current-influenced zone near the sea surface. The risers are without buoyancy elements through the splash zone, and thus are less exposed to the water forces in the upper zone of the sea.
Owner:PGS OFFSHORE TECH
Method for production and upgrading of oil
An integrated process for production and upgrading of heavy and extra-heavy crude oil, comprising (a) reforming of hydrocarbons such as natural gas to produce hydrogen, CO2 and steam (b) separating the produced hydrogen from the CO2, steam and any other gases to give a hydrogen rich fraction and a CO2 rich fraction and steam, (c) injecting the steam alone or in combination with the CO2 rich fraction into a reservoir containing heavy or extra heavy oil to increase the oil recovery, and (d) upgrading / refining of the heavy or extra heavy oil to finished products by extensive hydroprocessing, comprising several steps of hydrocracking and hydrotreating (sulfur, nitrogen and metals removal as well as hydrogenation of olefins and aromatics), using the hydrogen rich fraction.
Owner:STATOIL ASA PETRO SA (NO)
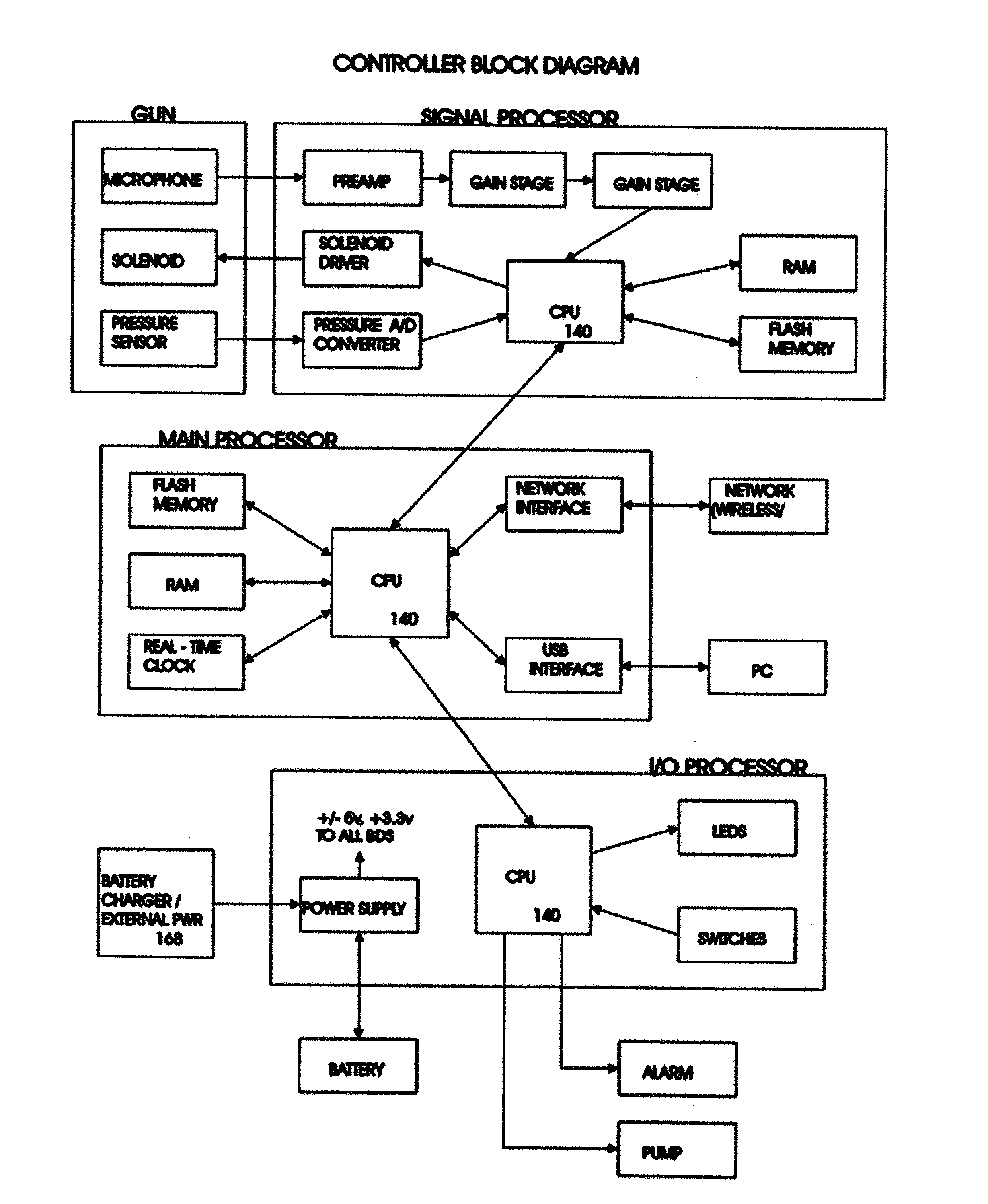
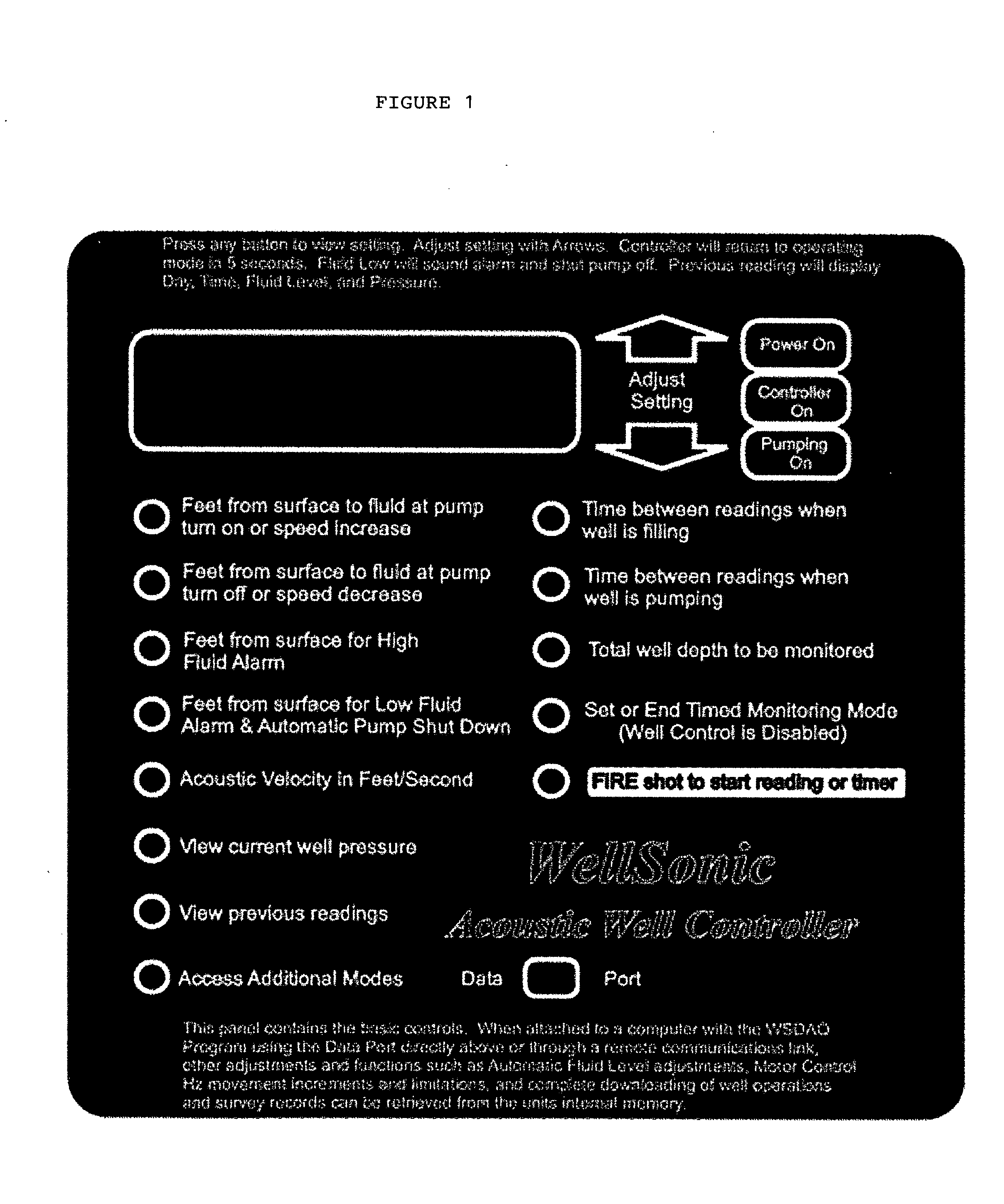
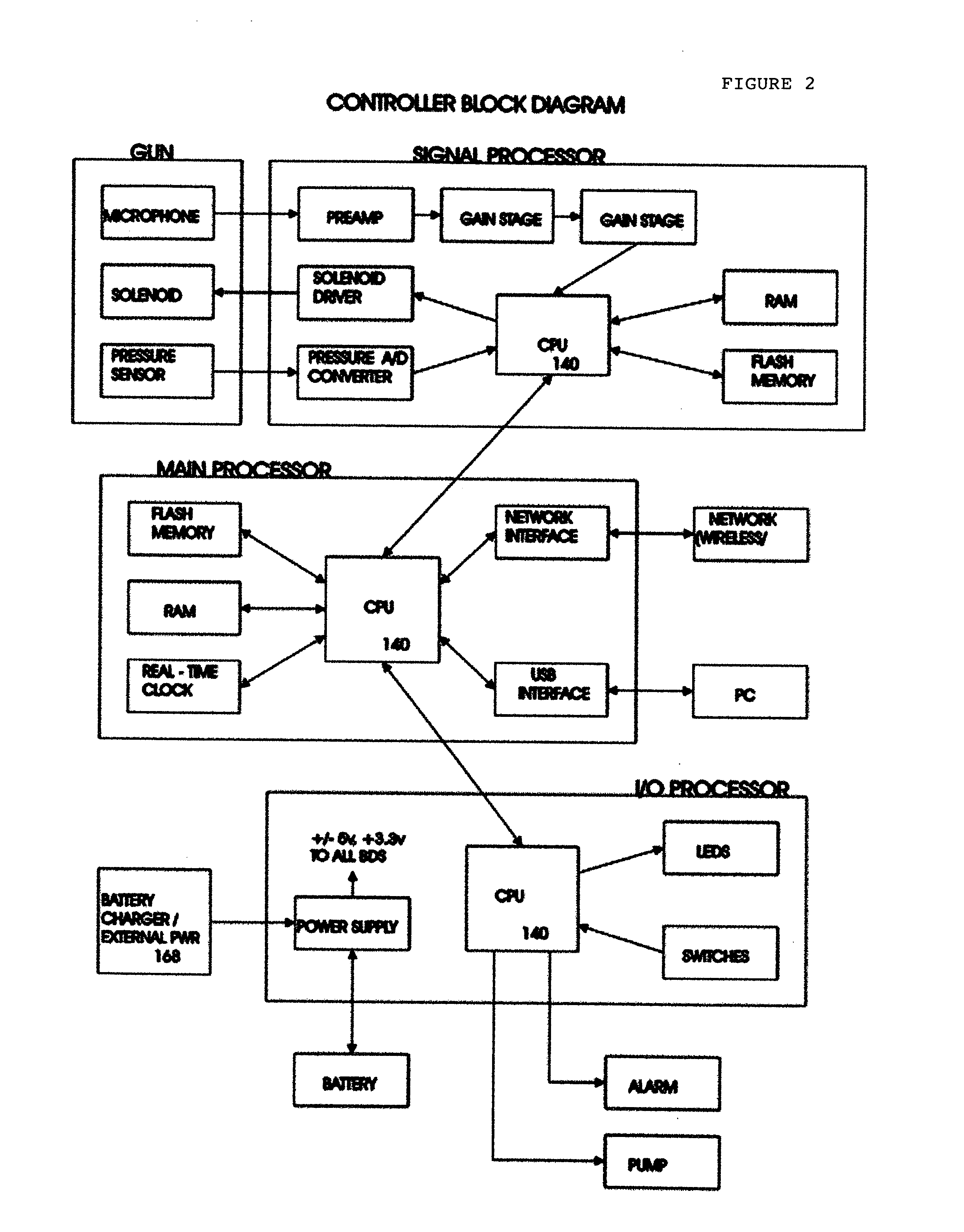
Well Pump Controller Unit
InactiveUS20060235573A1Optimizing oil productionOil production operating costSurveyFlexible member pumpsOil productionMeasurement device
In the oil production industry one objective of the field operator is to streamline their oil pumping operations for the more efficient production. The current invention is a controller device used to continuously control and optimize oil production from a well. The current invention is used in conjunction with a precise well measuring device, i.e. a device that can precisely measure characteristics of a well at a moment in time, for generating real-time information to be used by the controller device to optimize the rate of oil production.
Owner:GUION WALTER FRANKLIN
Well injection and production method and system
InactiveUS20150369023A1Fluid removalWell/borehole valve arrangementsPetroleum engineeringPetroleum production
A method and system for enhancing petroleum production are provided, in which petroleum is displaced from a fractured formation by selectively injecting fluid into selected fractures in the formation without injecting into the other non-selected fractures. The injected fluid flows out into the fractured formation and enhances recovery from the non-selected fractures. Petroleum is selectively collected from the non-selected fractures.
Owner:NCS MULTISTAGE
Well injection and production methods, apparatus and systems
A method and system for enhancing petroleum production are provided, in which a fracturing operation can be conducted in a formation through a string and then petroleum is displaced from the fractured formation by selectively injecting fluid into selected fractures in the formation while other non-selected fractures remain without fluid injection. The injected fluid flows out into the fractured formation and enhances recovery from the non-selected fractures. Petroleum is selectively collected from the non-selected fractures.
Owner:NCS MULTISTAGE
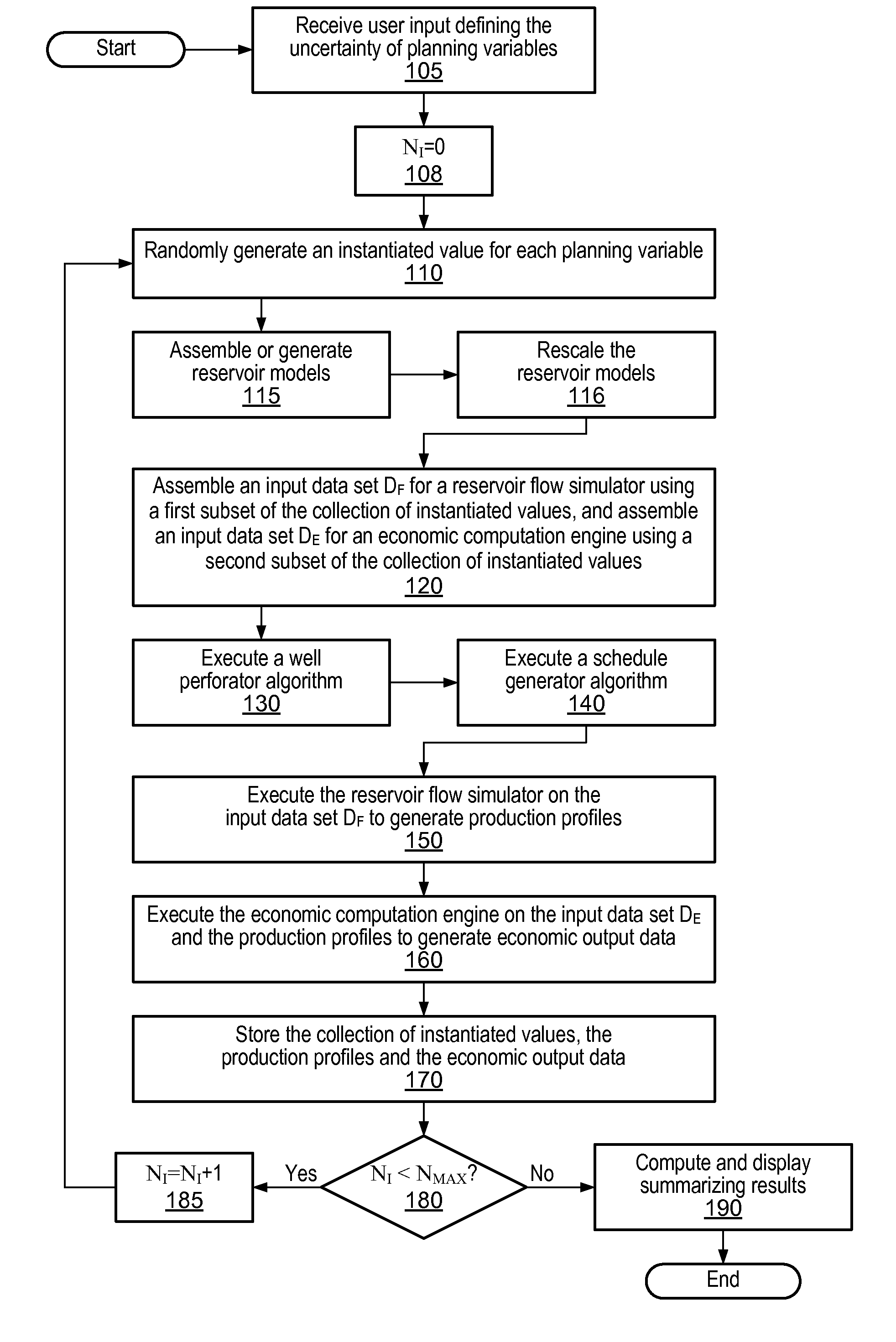
Method and system for scenario and case decision management
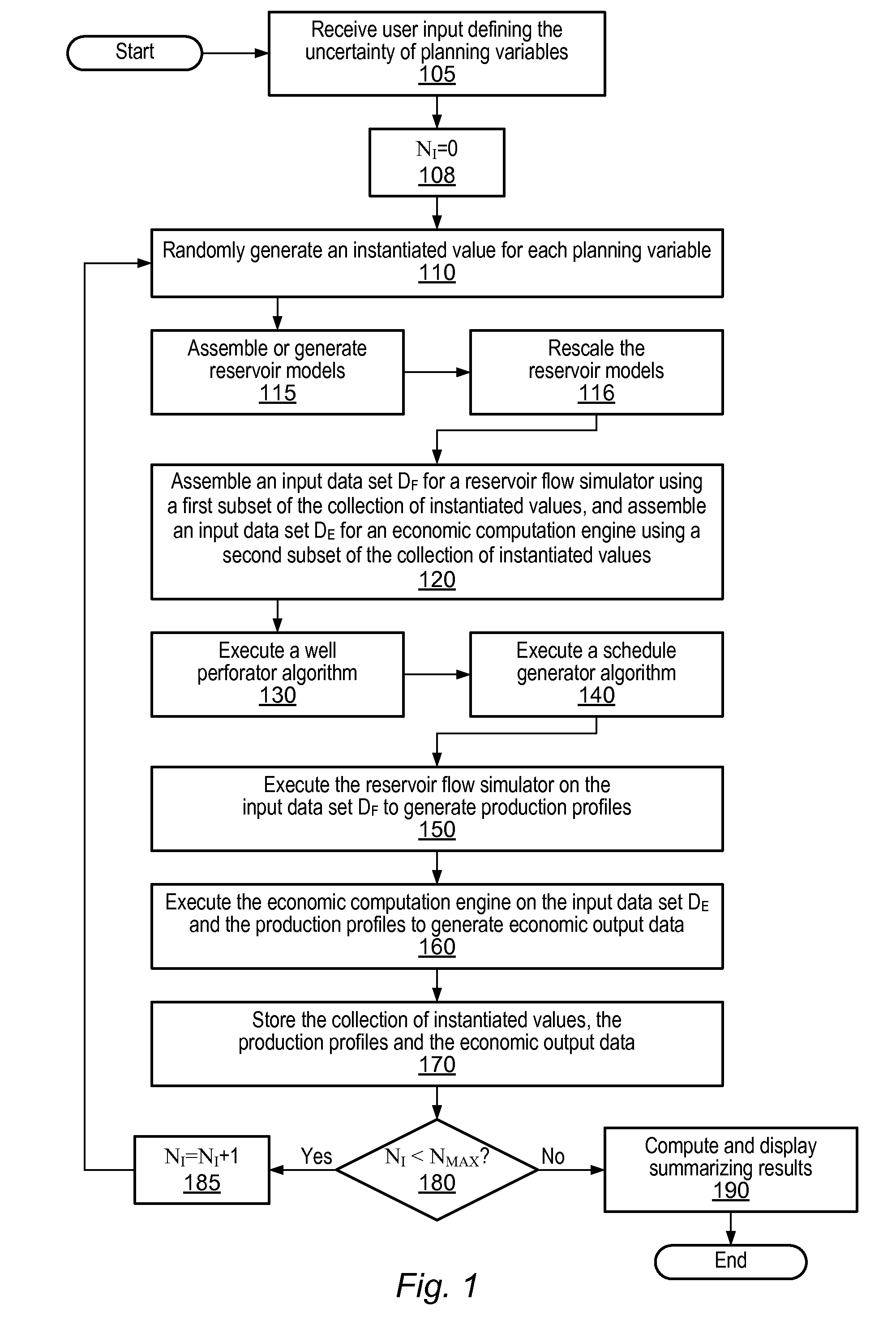
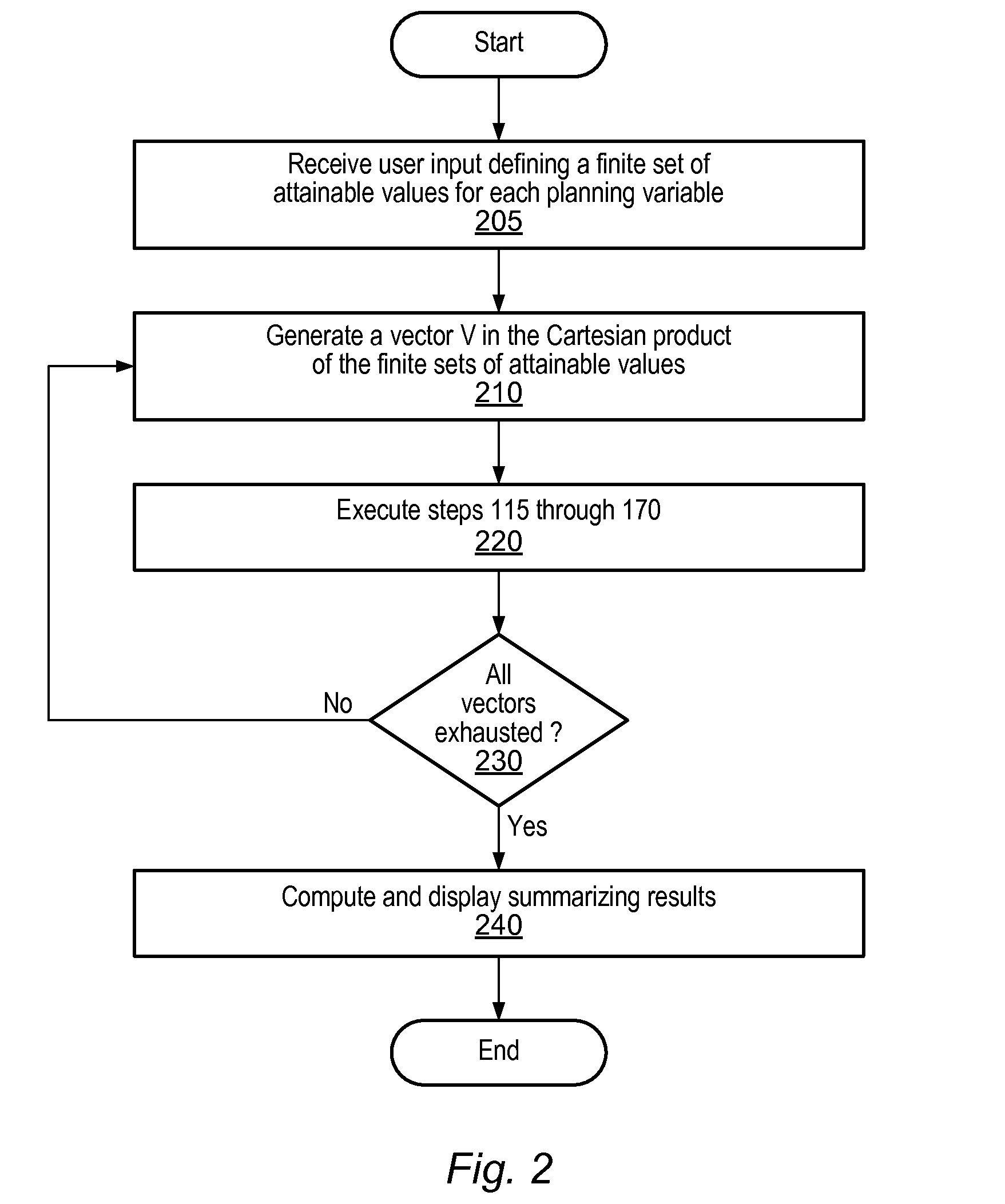
A system and method may be configured to support the evaluation of the economic impact of uncertainties associated with the planning of a petroleum production project, e.g., uncertainties associated with decisions having multiple possible outcomes and uncertainties associated with uncontrollable parameters such as rock properties, oil prices, etc. The system and method involve receiving user input characterizing the uncertainty of planning variables and performing an iterative simulation that computes the economic return for various possible instantiations of the set of planning variables based on the uncertainty characterization. The system and method may (a) utilize and integrate highly rigorous physical reservoir, well, production flow, and economic models, and (b) provide a mechanism for specifying constraints on the planning variables. Furthermore, the system and method may provide a case manager process for managing multiple cases and associated “experimental runs” on the cases.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS
Swellable polymer with anionic sites
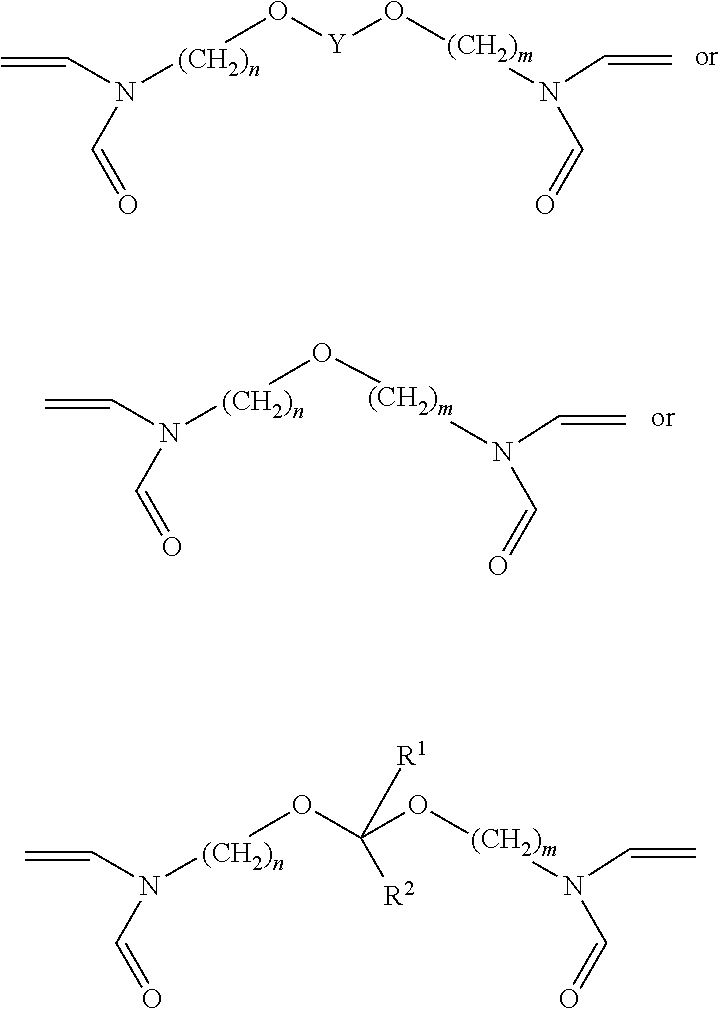
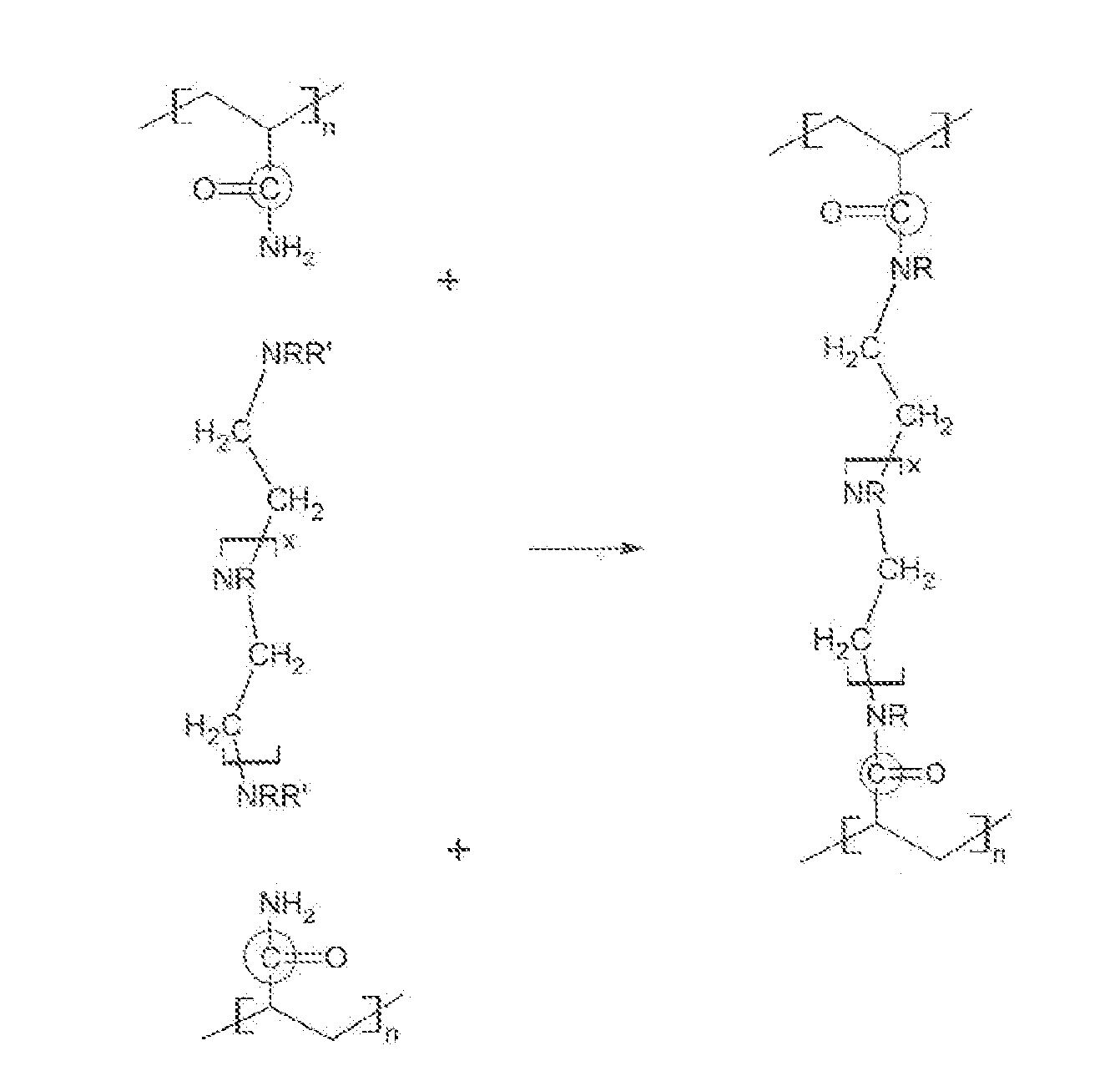
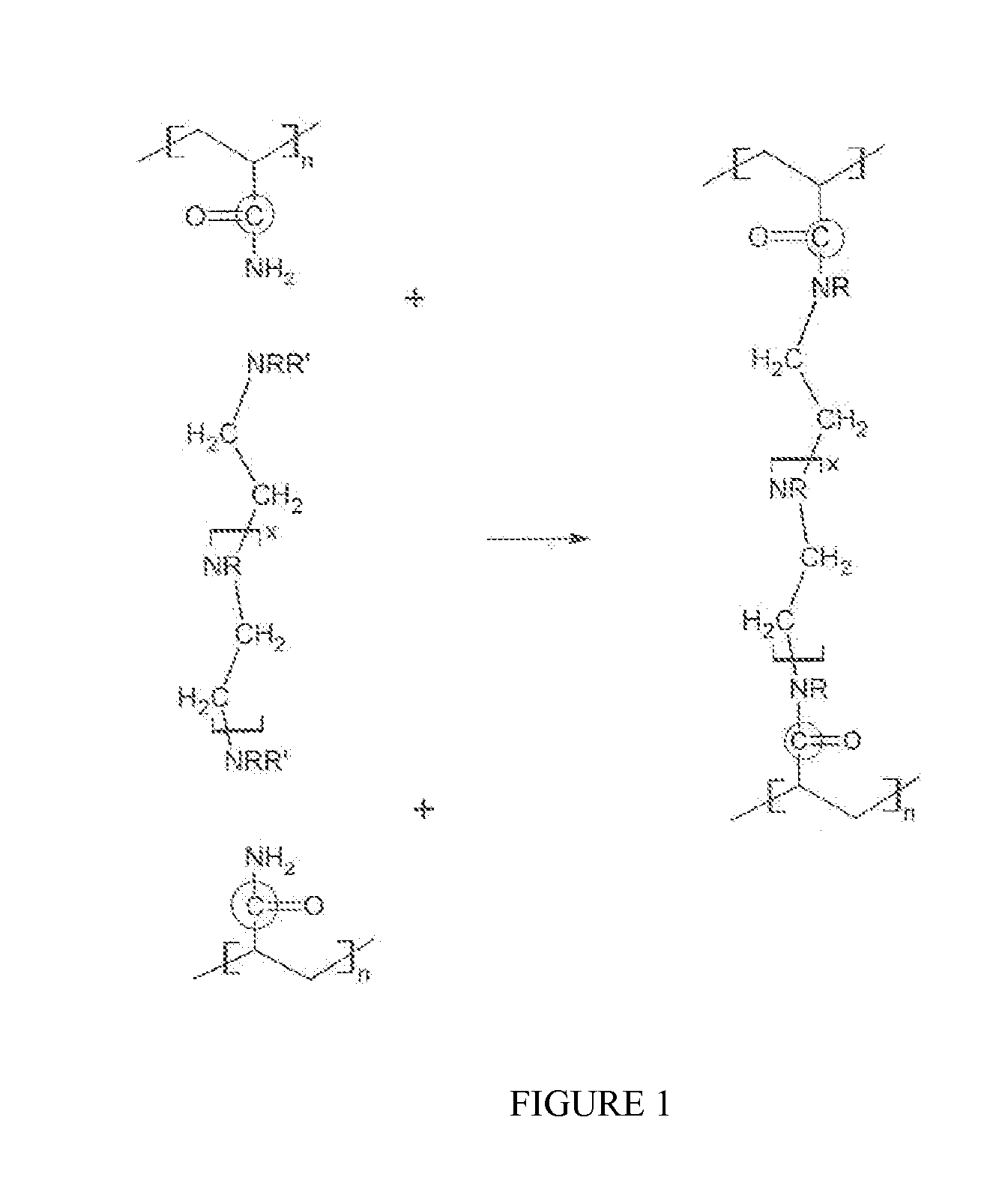
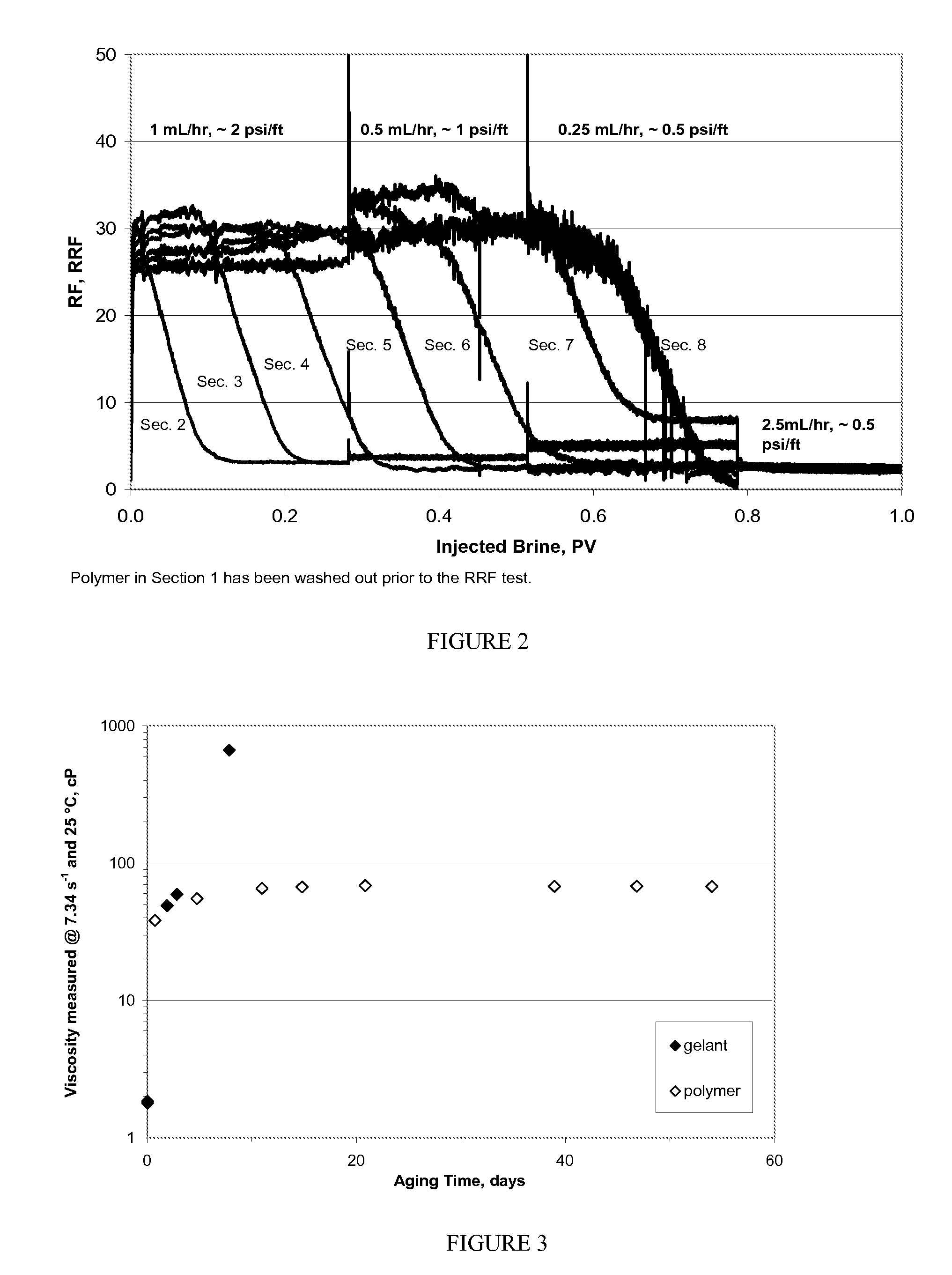
ActiveUS20100314114A1Promote recoverySmall diameterFluid removalDrilling compositionWater solublePolymer
The invention is directed to stable crosslinked water-soluble swellable polymers and methods for making same. More particularly, the invention relates to a composition comprising expandable polymeric particles having anionic sites and labile crosslinkers and stable crosslinkers, said particle mixed with a fluid and a cationic crosslinker that is capable of further crosslinking the particle on degradation of the labile crosslinker and exposure of the anionic sites so as to form a gel. A particularly important use is as an injection fluid in petroleum production, where the expandable polymeric particles are injected into target zone and when the heat and / or suitable pH of the target zone cause degradation of the labile crosslinker and the particle expands, the cationic crosslinker crosslinks the polymer to form a gel, thus diverting water to lower permeability regions and improving oil recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
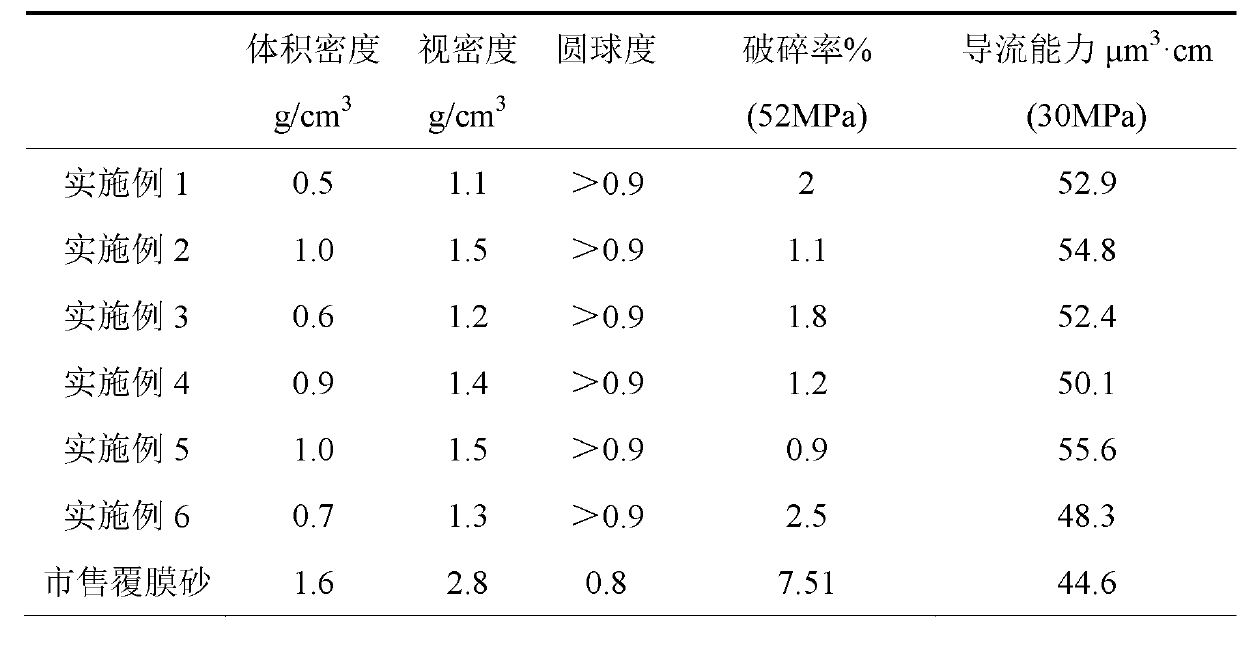
Clean-water-carrying petroleum proppant for petroleum production of low-permeability petroleum reservoir and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a clean-water-carrying petroleum proppant for petroleum production of a low-permeability petroleum reservoir. The proppant is prepared through coating macromolecular polymer particles with the particle sizes of 3-100 meshes by using macromolecular resin, wherein the macromolecular polymer particles are white polymer balls formed through polymerizing olefin monomers or polymer microspheres formed through compounding after a silane coupling agent modified mineral material is added; and the proppant has the volume density of 0.5-1.0 g / cm<3> and the apparent density of 1.1-1.5 g / cm<3>. The invention simultaneously provides a preparation method of the petroleum proppant. The clean-water-carrying petroleum proppant prepared by adopting the preparation method can greatly reduce the viscosity of sand carrying liquid, reduce the damage to strata and pumps and even realize clean fracturing. Through the low-density proppant, the entire construction cost can be reduced, and the phenomenon of proppant discharging or crack emptying is difficult to occur.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
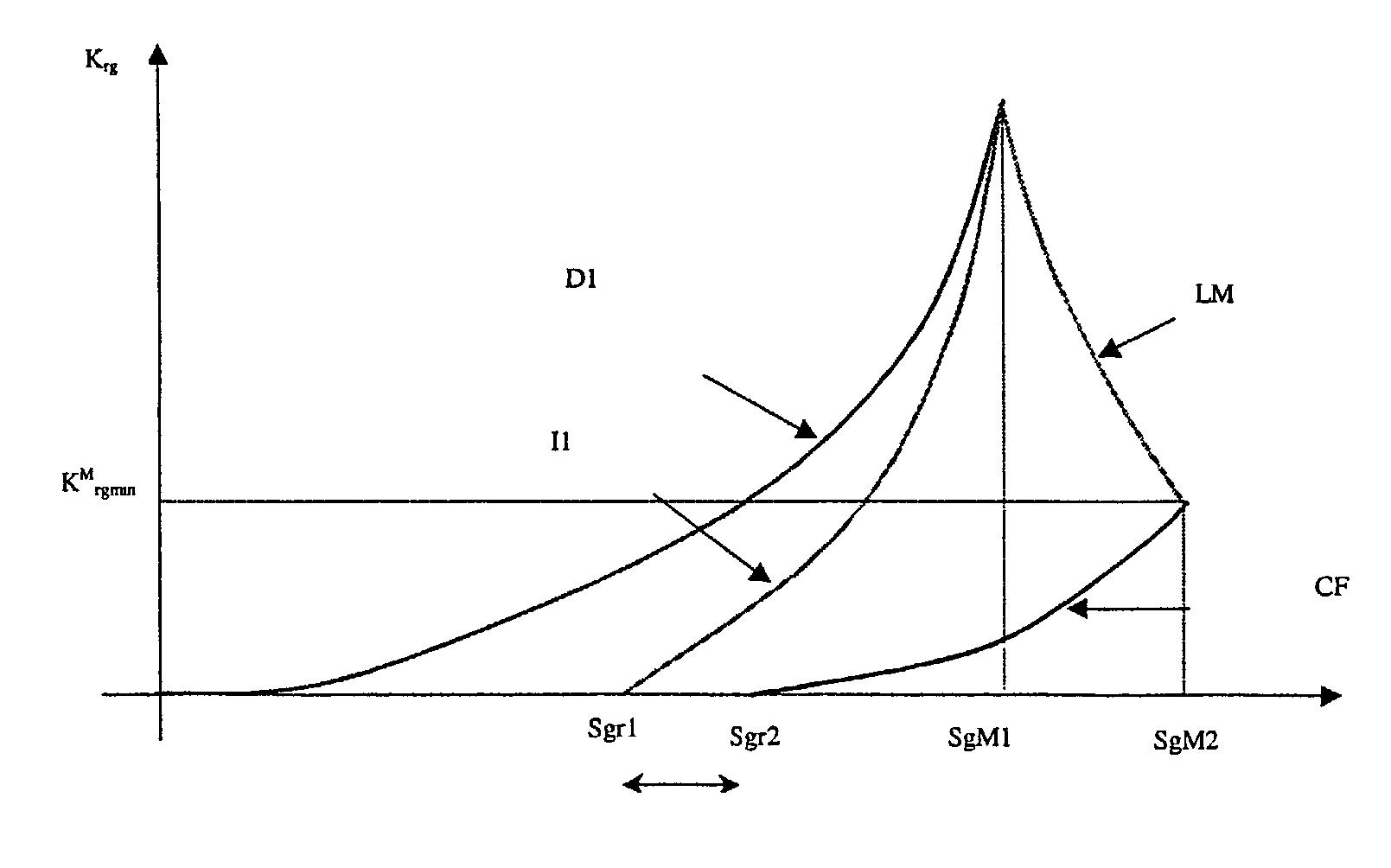
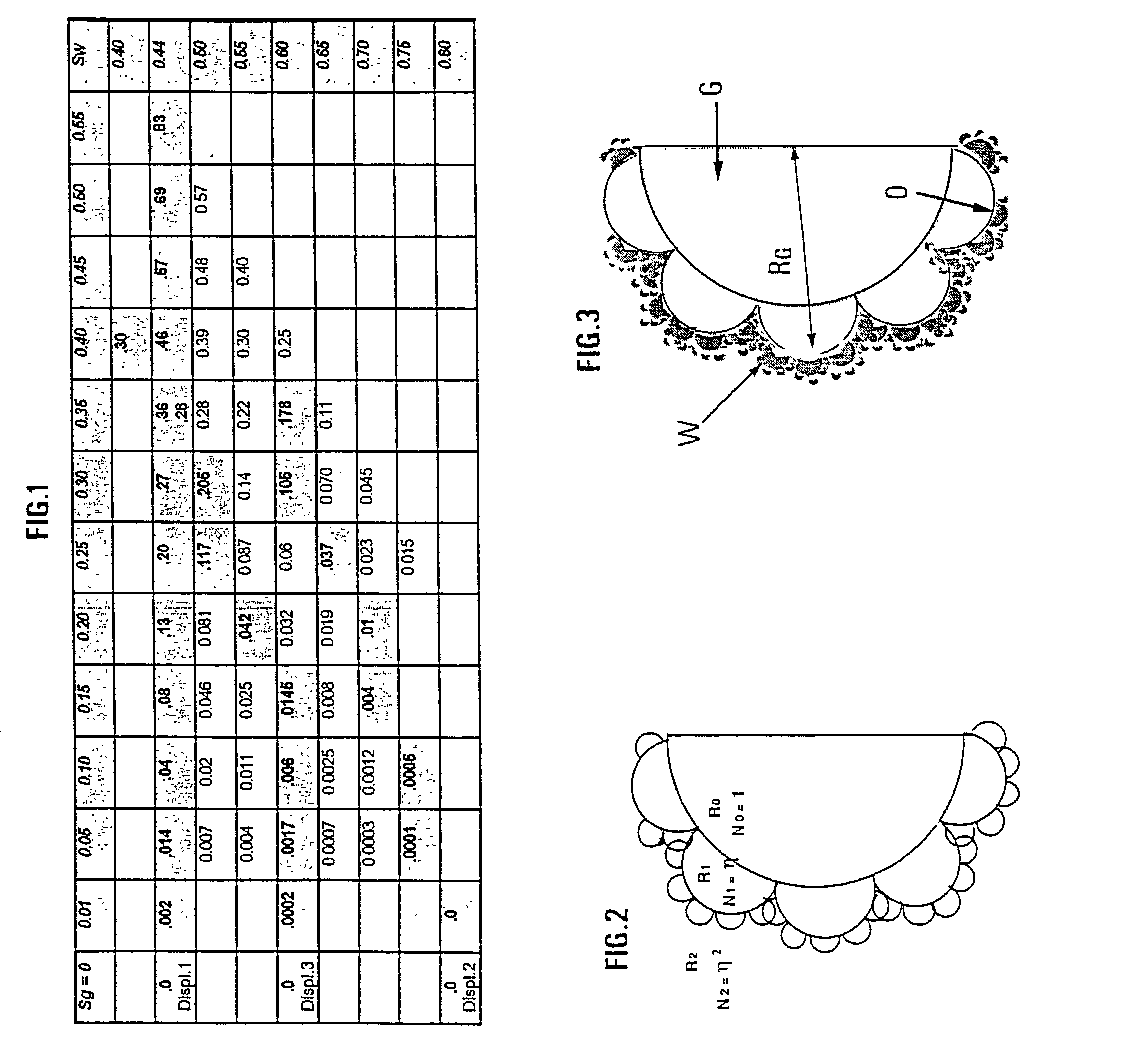
Method for modelling fluid displacements in a porous environment taking into account hysteresis effects
InactiveUS7072809B2The process is convenient and fastMore and more conditionElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingEarth material testingHysteresisNon wetting
A modelling method having application to petroleum production, soil cleaning, etc. for optimizing faster and more realistically the displacement conditions, in a porous medium wettable by a first fluid (water for example), of a mixture of fluids including this wetting fluid, another, non-wetting fluid (oil for example) and a gas. The method comprises experimental determination of the variation curve of the capillary pressure in the pores as a function of the saturation in the liquid phases, modelling the pores of the porous medium by means of a distribution of capillaries with a fractal distribution by considering, in the case of a three-phase water (wetting fluid)-oil-gas mixture for example, a stratification of the constituents in the pores, with the water in contact with the walls, the gas in the center and the oil forming an intercalary layer, determination, from this capillary pressure curve, of the fractal dimension values corresponding to a series of given values of the saturation in the liquid phase, modelling the hysteresis effects that modify the mobile saturations of the fluids effectively displaced in the sample, that vary during drainage and imbibition cycles.
Owner:GAZ DE FRANCE +1
Growth functions for modeling oil production
ActiveUS20170177992A1Improve predictabilitySurveyFluid removalFinite difference modelSimulation based
The present disclosure describes the use of growth models and data driven models that are combined for quickly and efficiently modeling SAGD reservoir oil production. Growth function surrogate models are used for efficient and reliable reservoir modeling and production forecasting as opposed to CPU intensive simulations based on finite difference models. A data-driven technique can then compare the growth function surrogate model with real field data to find discrepancies and inconsistencies between the two, allowing for an updates and improvements of the growth function model.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Crosslinked swellable polymer
ActiveUS20100234252A1Stable and labile crosslinkersAdvantageously employedFluid removalFlushingFlocculationPapermaking
The invention is directed to stable crosslinked water-soluble swellable polymers, methods for making same, and their various uses in the hygiene and medical arts, gel electrophoresis, packaging, agriculture, the cable industry, information technology, in the food industry, papermaking, use as flocculation aids, and the like. More particularly, the invention relates to a composition comprising expandable polymeric microparticles having labile crosslinkers and stable crosslinkers, said microparticle mixed with a fluid and an unreacted tertiary crosslinker that is capable of further crosslinking the microparticle on degradation of the labile crosslinker so as to form a stable gel. A particularly important use is as an injection fluid in petroleum production, where the expandable polymeric particles are injected into a well and when the heat and / or pH of the well cause degradation of the labile crosslinker and when the particle expands, the tertiary crosslinker crosslinks the polymer to form a stable gel, thus diverting water to lower permeability regions and improving oil recovery.
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
Swellable polymers with hydrophobic groups
The invention is directed to crosslinked water-soluble swellable polymers, methods for making same and their various uses. More particularly, the invention relates to a composition comprising expandable polymeric particles being made with 0.1-5% hydrophobic monomers and labile crosslinkers and stable crosslinkers, said particles mixed with a fluid. A particularly important use is as an injection fluid in petroleum production, where the expandable polymeric particles are injected into a well and when the heat and / or pH of the target zones in the formation cause degradation of the labile crosslinker and when the particle expands, the hydrophobic groups associate to form a hydrophobically associative polymer, thus diverting water to lower permeability regions and improving oil recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
Subsea petroleum production system method of installation and use of the same
ActiveUS20060118310A1Long transportLow costFluid removalUnderwater drillingProduction lineOcean bottom
A subsea production system for producing petroleum by artificial elevation, assisted by submersible centrifugal pumps (SCPs) upstream of the WCT and installed on the seabed, includes a pumping module having one of more SCPs, installed in series or in parallel, with an inclination of up to 85 degrees in relation to the vertical, the module being connectible to a flow base to permit the “bypass” of production and wherein the pumping module and the flow base may be linked to installation and recovery by cable. A production line is connected upstream to the pumping module upstream and another production line is connected downstream to the pumping module. A method of installing the system in a new wellhead is described, as well as a method for installing the system in an existing wellhead. The uses of the subsea production system for boosting multiphase flow, injection of water in an injector well and the transfer of oil between two points of collection are also described.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Wellbore plug isolation system and method
A wellbore plug isolation system and method for positioning plugs to isolate fracture zones in a horizontal, vertical, or deviated wellbore is disclosed. The system / method includes a wellbore casing laterally drilled into a hydrocarbon formation, a wellbore setting tool (WST) that sets a large inner diameter (ID) restriction sleeve member (RSM), and a restriction plug element (RPE). The WST is positioned along with the RSM at a desired wellbore location. After the WST sets and seals the RSM, a conforming seating surface (CSS) is formed in the RSM. The CSS is shaped to engage / receive RPE deployed into the wellbore casing. The engaged / seated RPE isolates heel ward and toe ward fluid communication of the RSM to create a fracture zone. The RPE's are removed or left behind prior to initiating well production without the need for a milling procedure. A large ID RSM diminishes flow constriction during oil production.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
Subsea petroleum production system method of installation and use of the same
ActiveUS7516795B2Low costFast replacementFluid removalUnderwater drillingOcean bottomArtificial lift
A subsea petroleum production system for artificial lift, including a pumping module coupled to a flow base, the system being installed downstream of a Wet Christmas Tree (WCT) on the seabed. The pumping module includes at least one submersible centrifugal pump (SCP) inclined with respect to the vertical direction at an inclination of up to 85 degrees from the vertical direction, wherein a flow in said at least one pump is ascending.
Owner:PETROLEO BRASILEIRO SA (PETROBRAS)
Swellable polymer with cationic sites
ActiveUS20100314115A1Promote recoverySmall diameterFluid removalDrilling compositionWater solublePolymer
The invention is directed to long lasting crosslinked water-soluble swellable polymers, methods for making same, and their uses. More particularly, the invention relates to a composition comprising expandable polymeric particles having cationic sites as well as labile crosslinkers and stable crosslinkers, said particle mixed with a fluid. A particularly important use is as an injection fluid in petroleum production, where the expandable polymeric particles are injected into a target zones in the reservoirs and when the heat and / or a suitable pH in the reservoir cause degradation of the labile crosslinker and when the particle expands, the cationic sites in the polymer adsorb to negative sites of the rock in the formation, thus diverting water to lower permeability regions and improving oil recovery. However, many other uses are possible.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
Method for predicting petroleum expulsion
ActiveUS8352228B2Analogue computers for chemical processesFluid removalChemical fractionationComputer science
A method for predicting petroleum production is provided. An exemplary embodiment of The computer-implemented comprises computing a first approximation of an amount of generated petroleum that is retained with a complex organic product using a Threshold and a Maximum Retention value. The exemplary method also comprises revising the first approximation by approximating a process of chemical fractionation using at least one partition factor to create a revised approximation and predicting petroleum production based on the revised approximation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
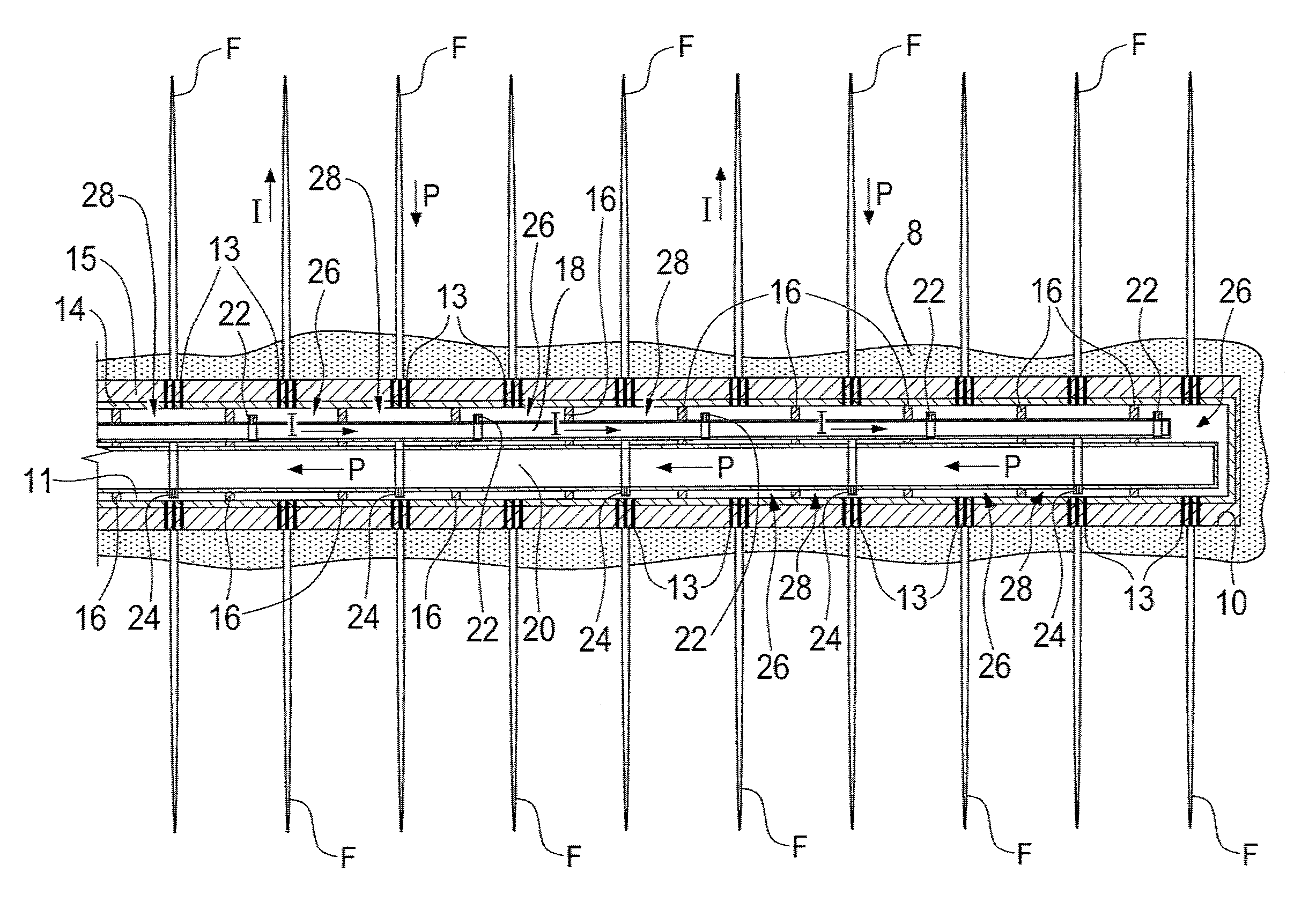
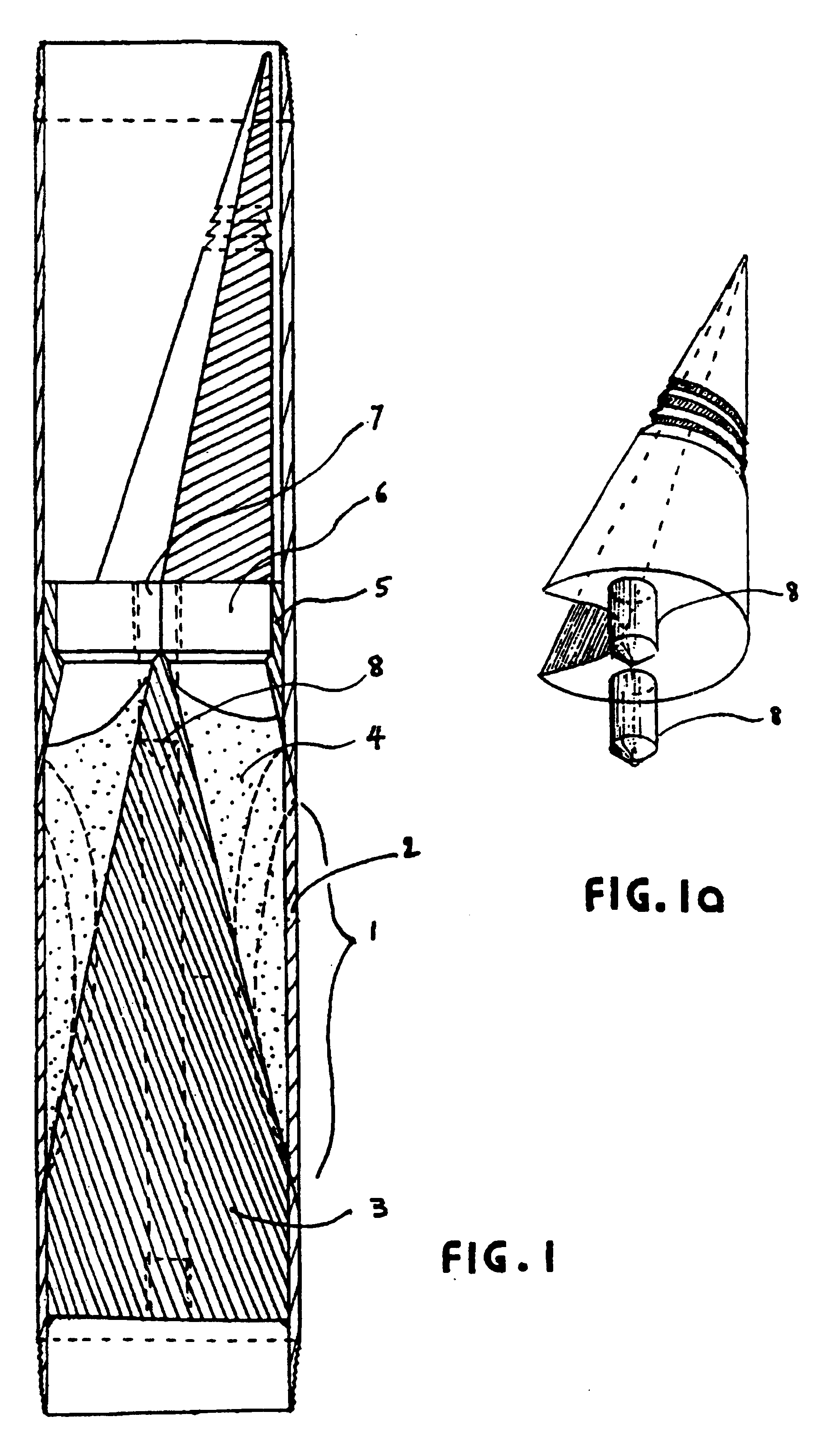
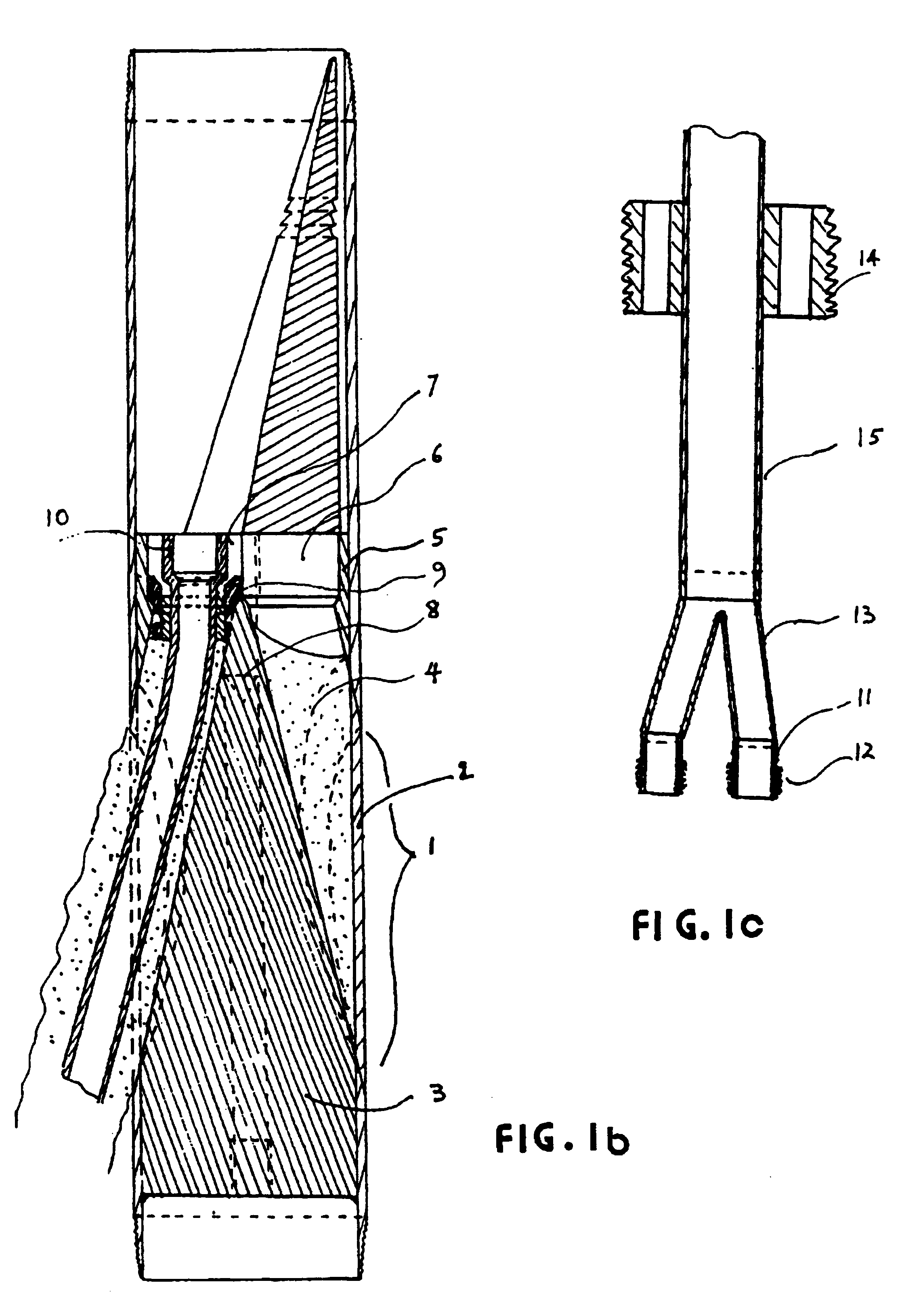
Downhole equipment, tools and assembly procedures for the drilling, tie-in and completion of vertical cased oil wells connected to liner-equipped multiple drainholes
Single horizontal wells drilled through heterogeneous reservoirs are capable of greater oil productivity than vertical wells, often with lower produced GOR and WOR. Multiple drainholes tied-in to a vertical cased well are even more beneficial. Completion of such drainholes in many sandy reservoirs must use cemented liners. Well configurations comprising multiple drainholes liners, each of them tied-in to a vertical casing by pressure-tight connections require novel technologies making use of some novel downhole equipment, tools and procedures for drilling, tie-in and completion of such wells. These may be for newly-drilled wells or may be obtained by re-entry into an existing vertical cased well. Specific equipment, including novel casing joints, whipstocks, intermediate liners and tubing completion assembly components applicable to new wells are described herein. Equipment comprising novel casing inserts and patches applicable to re-entry wells, and the corresponding tubing completion assembly components for a variety of well exploitation modes are also described, together with the required tools and procedures. The liners of the drainholes are such that known well logging and cleaning tools may be used throughout the well's life. The various tubing completion assemblies can all be run-in and installed in a single trip. They allow either commingled flow from all drainholes or selective injection into some drainholes while others are under production. They are adapted to a variety of reservoir pressure conditions and of oil types, including heavy oil produced by sequential "huff and puff" steam injection.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
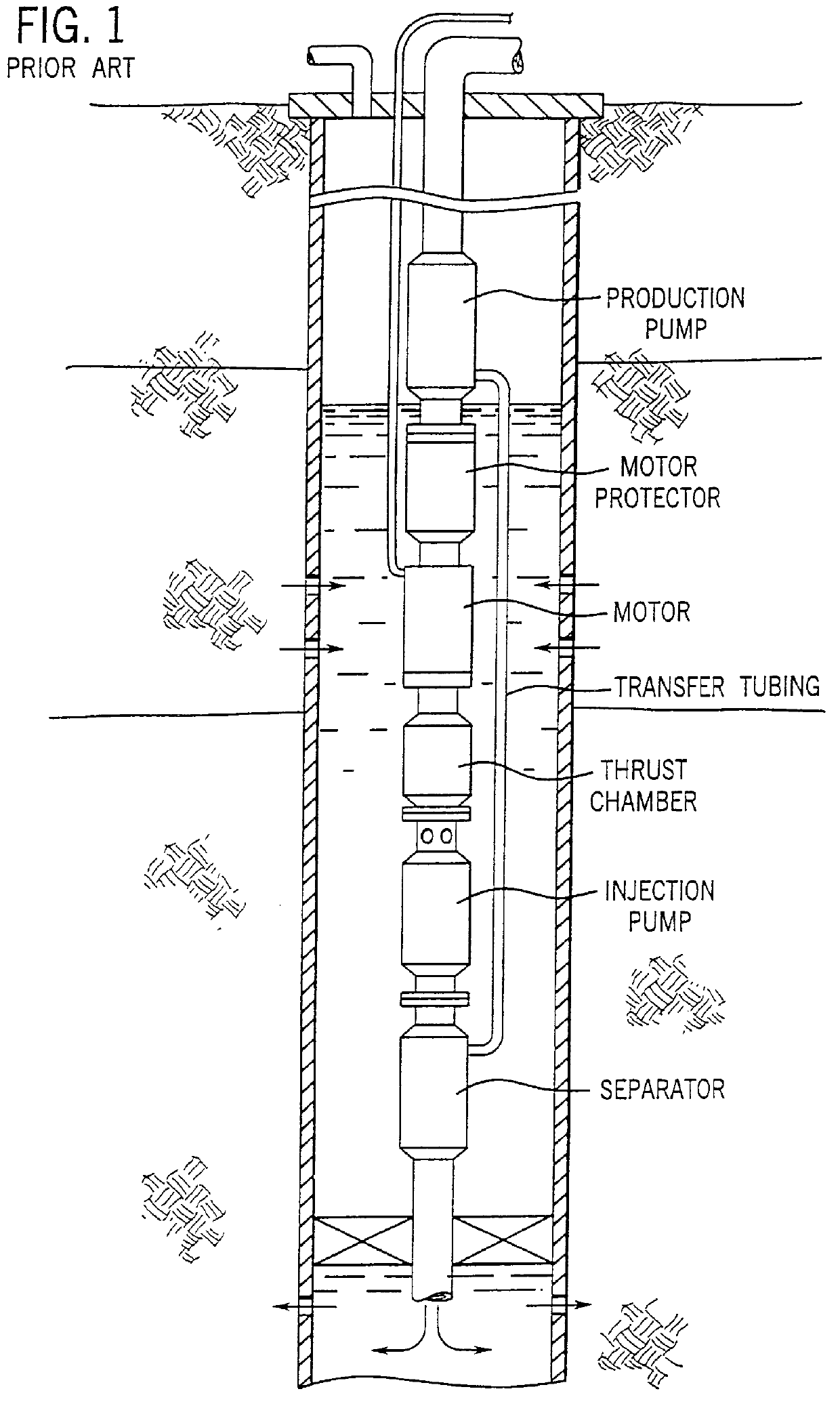
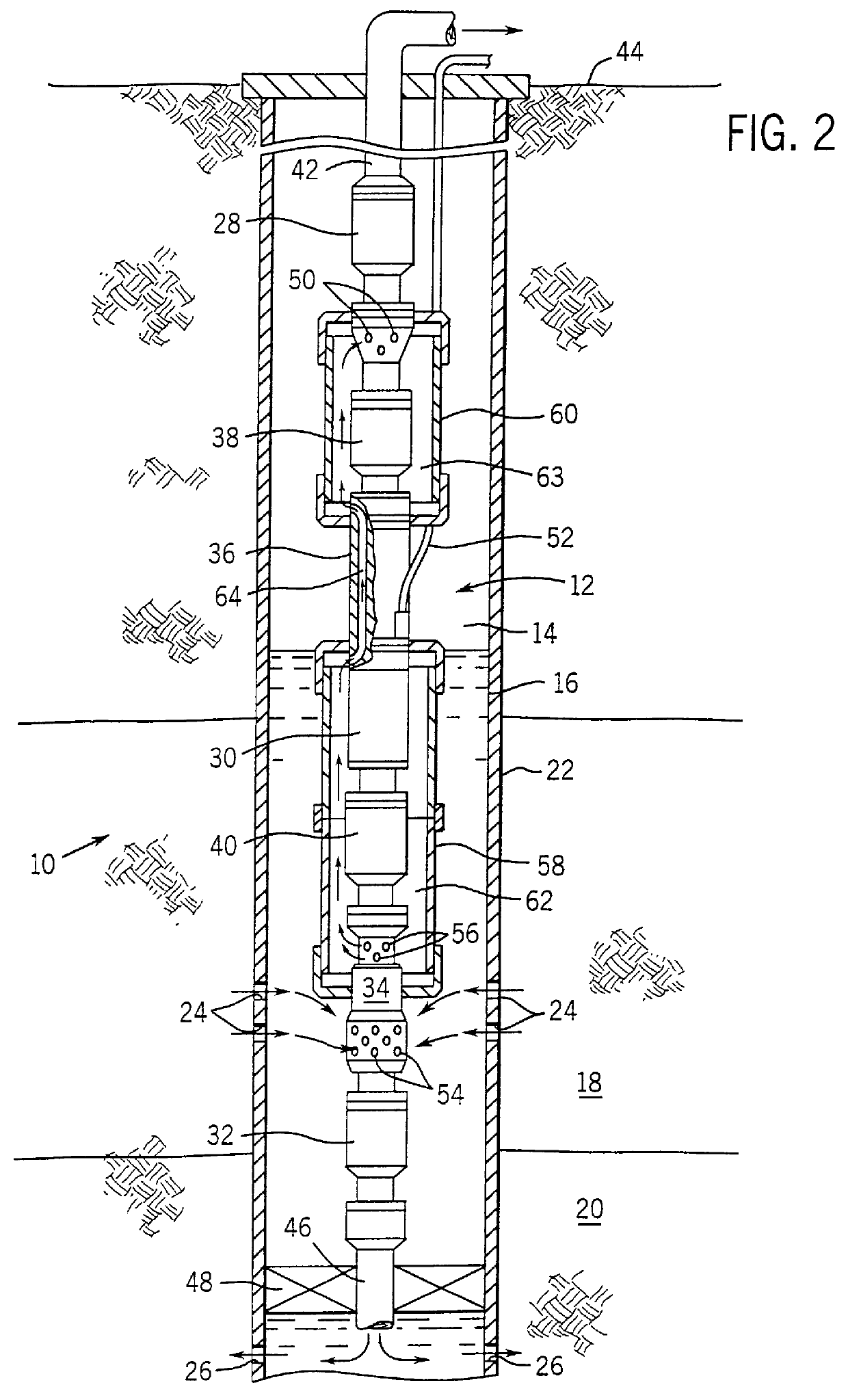
Adjustable shroud for a submergible pumping system and pumping system incorporating same
An adjustable shroud arrangement is disclosed for a submergible pumping system. The pumping system is of the type used to raise fluids from wells, such as petroleum production wells. The systems include a plurality of interconnected components, including a motor and a pump driven by the motor. The systems may also include a separator for separating production fluids from non-production fluids. The shroud serves to transfer fluids between system components, such as around the motor to promote convective cooling of the motor during operation. The shroud fits around a portion of the pumping unit to define a fluid flow path. The shroud is adjustable with respect to the pumping unit to permit relative thermal expansion and contraction of the shroud and the pumping unit components. In a preferred embodiment, the shroud has one end fixed to the pumping unit and a second end slidingly seals against a component of the pumping unit. In another embodiment, both ends of the shroud are fixed to the unit and an adjustable seal is provided along the length of the shroud.
Owner:CAMCO INT
Crosslinking of swellable polymer with pei
InactiveUS20140144628A1Stable and labile crosslinkersResist erosionFluid removalFlushingFlocculationPapermaking
The invention is directed to stable and labile crosslinked water swellable polymeric microparticles that can be further gelled, methods for making same, and their various uses in the hygiene and medical arts, gel electrophoresis, packaging, agriculture, the cable industry, information technology, in the food industry, papermaking, use as flocculation aids, and the like. More particularly, the invention relates to a composition comprising expandable polymeric microparticles having labile crosslinkers and stable crosslinkers, said microparticle mixed with a fluid and an unreacted tertiary crosslinker comprising PEI or other polyamine based tertiary crosslinker that is capable of further crosslinking the microparticle on degradation of the labile crosslinker and swelling of the particle, so as to form a stable gel. A particularly important use is as an injection fluid in petroleum production, where the expandable polymeric microparticles are injected into a well and when the heat and / or pH of the well cause degradation of the labile crosslinker and when the microparticle expands, the tertiary crosslinker crosslinks the polymer to form a stable gel, thus diverting water to lower permeability regions and improving oil recovery.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF KANSAS +1
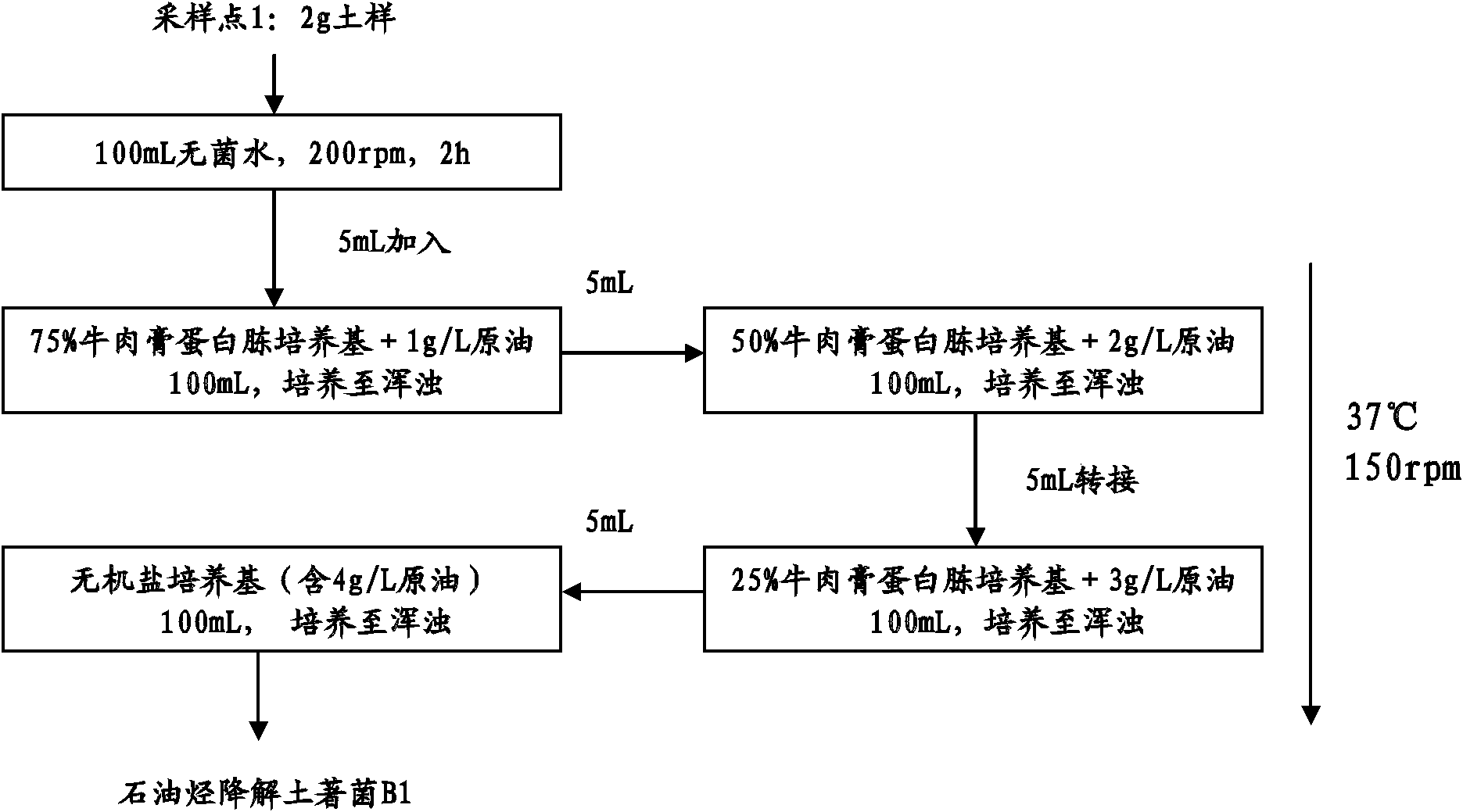
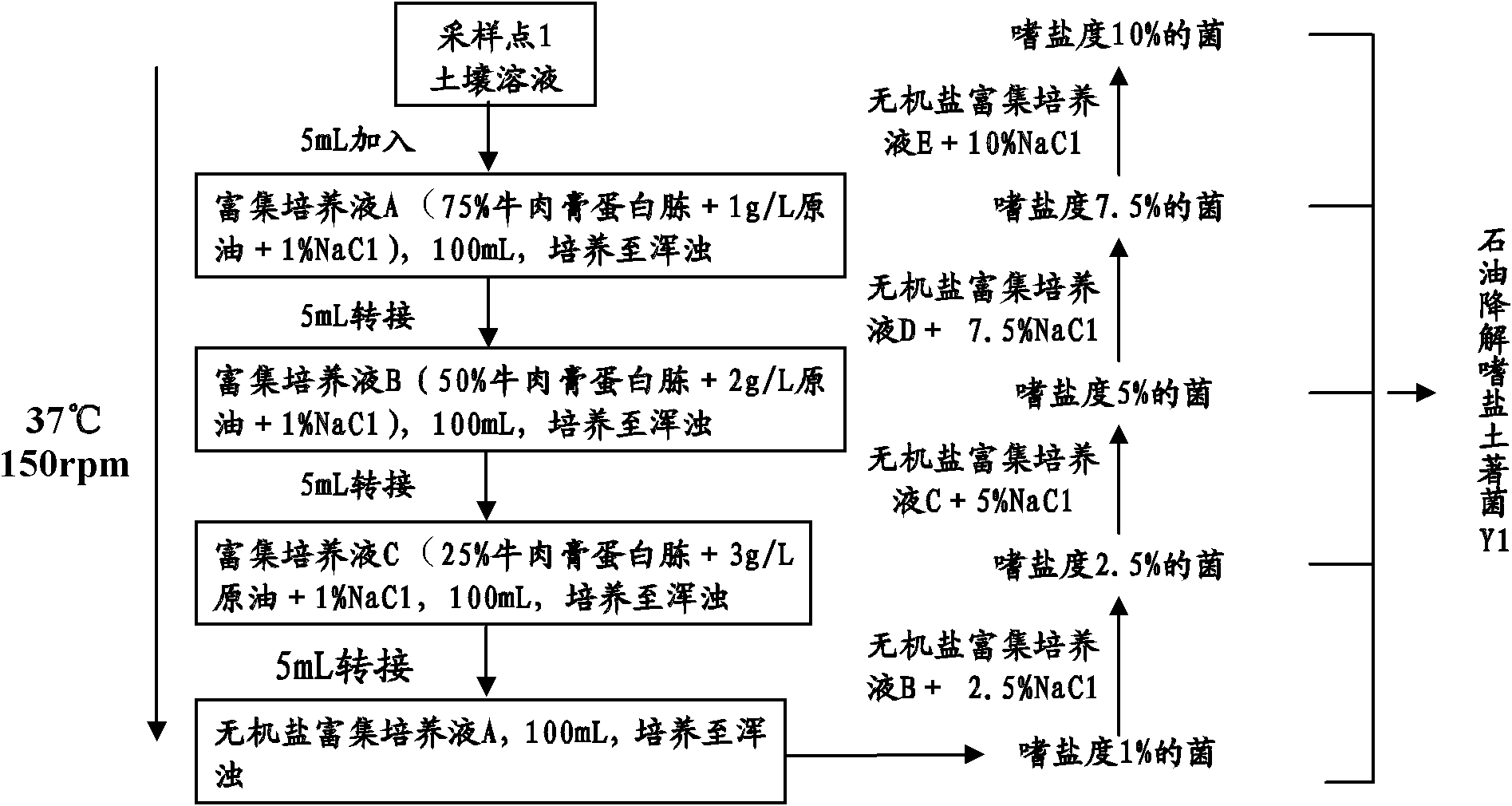
Method for screening and remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil bioremediation agent
InactiveCN102021132APromote growthImprove repair effectBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationSalt contentWastewater
The invention provides a method for the screening and remediation of a petroleum-contaminated soil bioremediation agent, which specifically comprises the following six steps of: collecting a petroleum degradation autochtonous bacterium source and a halophilic bacterium source, screening petroleum degradation autochtonous bacteria, screening halophilic bacteria, screening the petroleum degradation halophilic bacteria, screening a high-efficiency agent for the remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil and selecting optimal conditions for the remediation of the high-efficiency degradation agent by utilizing an orthogonal remediation experiment. The bioremediation agent screened by the screening and remediation method can be applied to the bioremediation of the petroleum-contaminated soil with the salt content of 10 to 20 g / Kg. The method for the screening and remediation of the petroleum-contaminated soil bioremediation agent has high practical value, and can be widely applied in the fields of bioremediation of the petroleum-contaminated soil, beaches, petroleum production wastewater and the like.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method For Predicting Petroleum Expulsion
ActiveUS20100161302A1Improve the level ofAnalogue computers for chemical processesFluid removalCompound organicChemical fractionation
A method for predicting petroleum production is provided. An exemplary embodiment of the method comprises computing a first approximation of an amount of generated petroleum that is retained with a complex organic product using a Threshold and a Maximum Retention value. The exemplary method also comprises revising the first approximation by approximating a process of chemical fractionation using at least one partition factor to create a revised approximation and predicting petroleum production based on the revised approximation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Silicon rubber self-adhesive tape
InactiveCN101921550AExcellent electrical performanceGood chemical stabilityFilm/foil adhesivesVulcanizationManufacturing technology
The invention provides a silicon rubber self-adhesive tape which belongs to the technical field of chemical product manufacturing. The silicon rubber self-adhesive tape is made from methyl vinyl silicon rubber, fume silica, tackifier, vinyl silicon oil and iron red; the production technology comprises the steps of mixing the raw materials and placing the mixture in a gamma ray irradiation field of 60Co for radiation vulcanization. The product not only satisfies the manufacturing need of a special engine, but also can serve as an insulation protection product under high temperature and high pressure for electric insulation protection of a large-scale motor, an electromotor, special machines, and the like, and can satisfy the strong insulation sealing requirement on the industries such as shipbuilding, mining, petroleum production, chemical engineering, steel making and the like under severe environments of specially high temperature and high pressure.
Owner:长春中科应化特种材料股份有限公司
Method using particulate chelates to stimulate production of petroleum in carbonate formations
InactiveUS20060142166A1Increasing hydrocarbon productionLow level of stabilityReciprocating drilling machinesOther chemical processesParticulatesDissolution
A method and composition for stimulating petroleum production from carbonate reservoirs by employing chelating agents, such as EDTA, which are in particulate form rather than aqueous solutions of chelating agents. The use of particulate chelants, which are relatively unstable in acidic solutions, results in a stimulation fluid with a very high dissolution capability.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
Decision Management System and Method
A system and method may be configured to support the evaluation of the economic impact of uncertainties associated with the planning of a petroleum production project, e.g., uncertainties associated with decisions having multiple possible outcomes and uncertainties associated with uncontrollable parameters such as rock properties, oil prices, etc. The system and method involve receiving user input characterizing the uncertainty of planning variables and performing an iterative simulation that computes the economic return for various possible instantiations of the set of planning variables based on the uncertainty characterization. The system and method may (a) utilize and integrate highly rigorous physical reservoir, well, production flow, and economic models, and (b) provide a mechanism for specifying constraints on the planning variables. Furthermore, the system and method may provide a case manager process for managing multiple cases and associated “experimental runs” on the cases.
Owner:LANDMARK GRAPHICS CORP
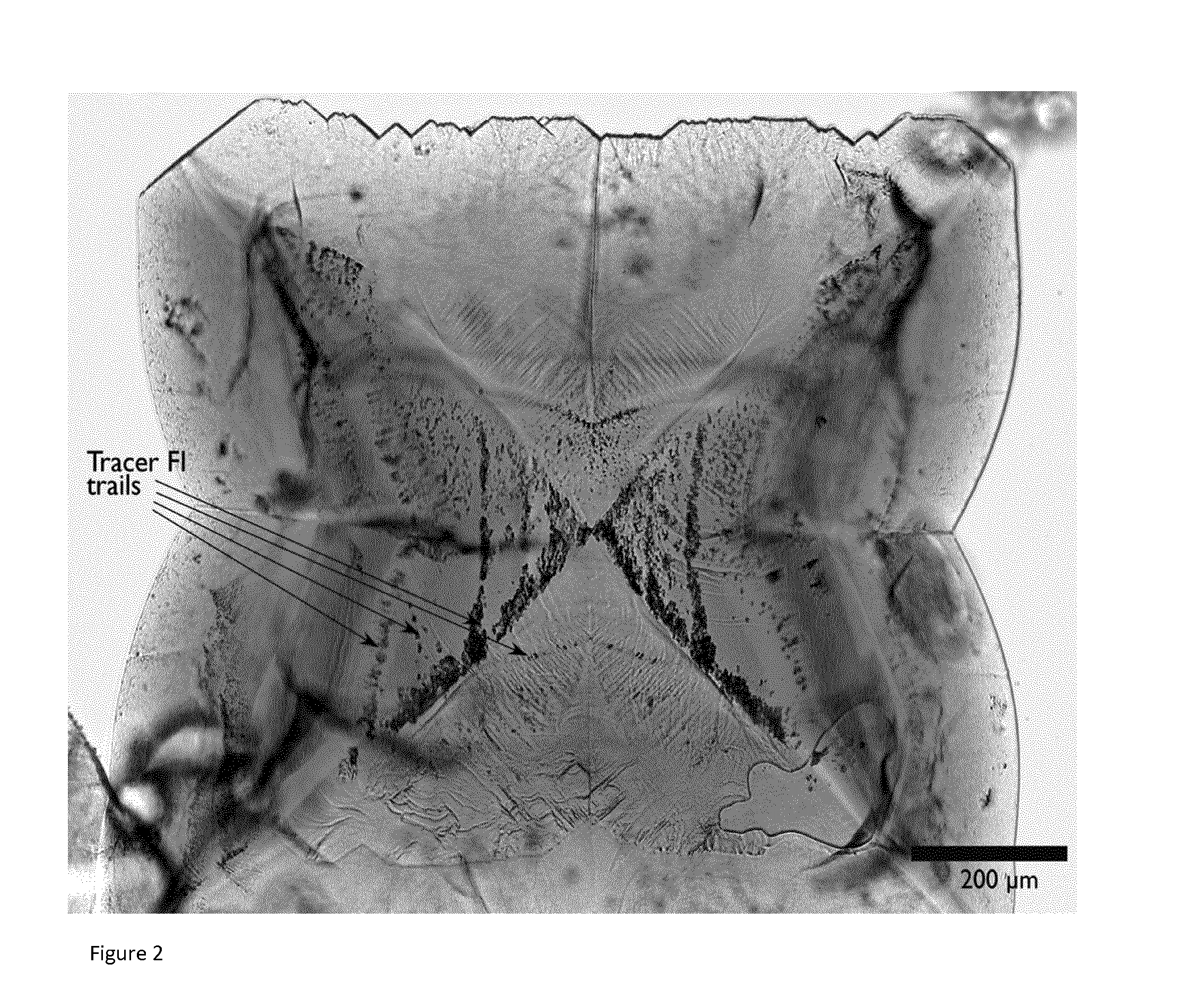
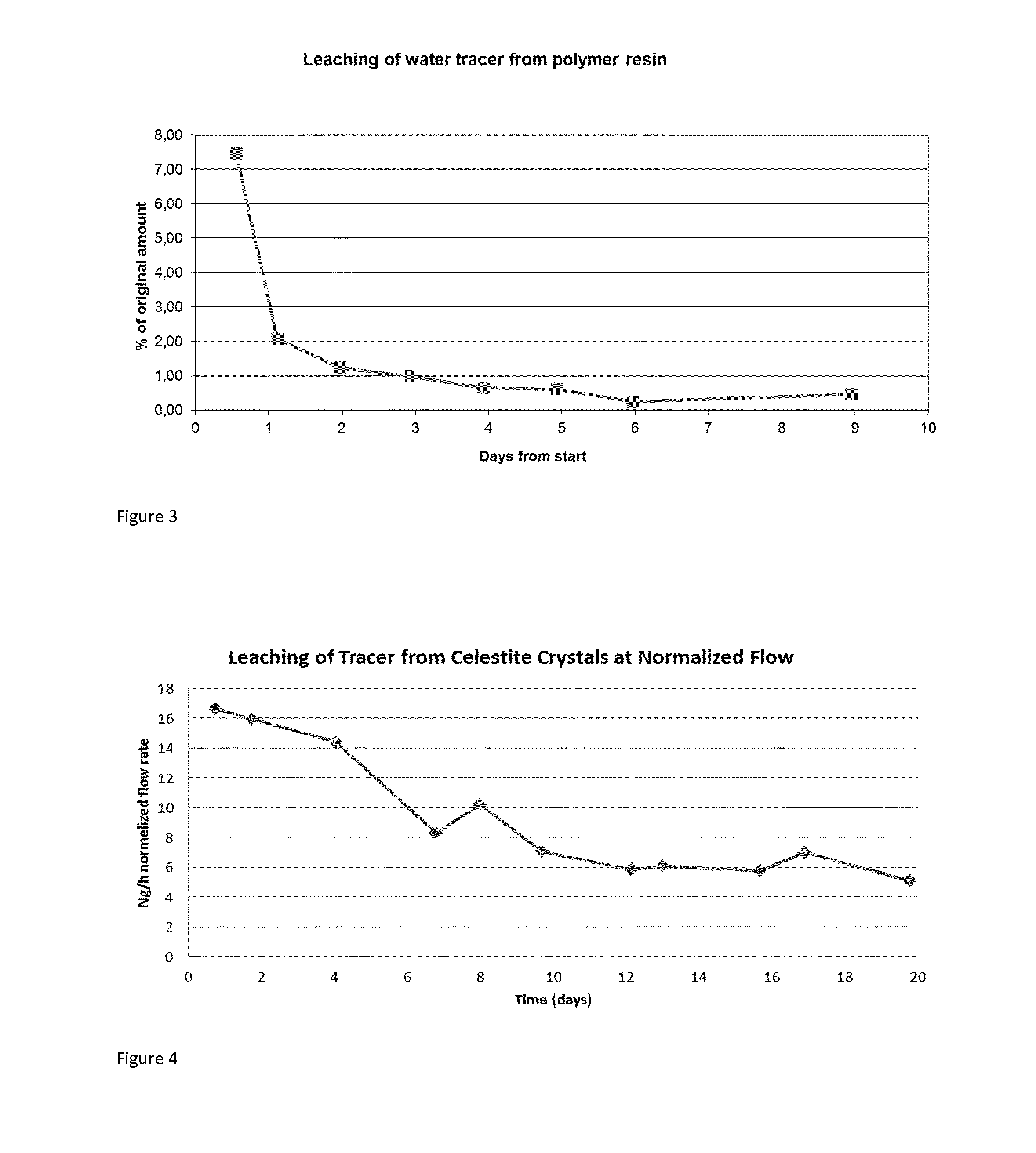
Mineral-Encapsulated Tracers
InactiveUS20160272882A1Increase volumeSuitable solubilitySurveyConstructionsControlled releaseCompound (substance)
The invention provides controlled-release compositions comprising at least one encapsulating compound and at least one tracer and / or oil-field chemical, wherein the encapsulating compound is in the form of synthetic crystals having inclusions, and wherein said tracer and / or oil-field chemical is encapsulated within said inclusions. The invention further provides methods for the use of such composition including in tracking the flow, pH and / or salinity of at least one fluid within a geothermal reservoir or a reservoir for petroleum production, as well as in monitoring the integrity of cap and other barriers to fluid flow within the reservoir. Methods for the formation of such compositions are also provided.
Owner:INSTITUTT FOR ENERGITEKNIKK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com