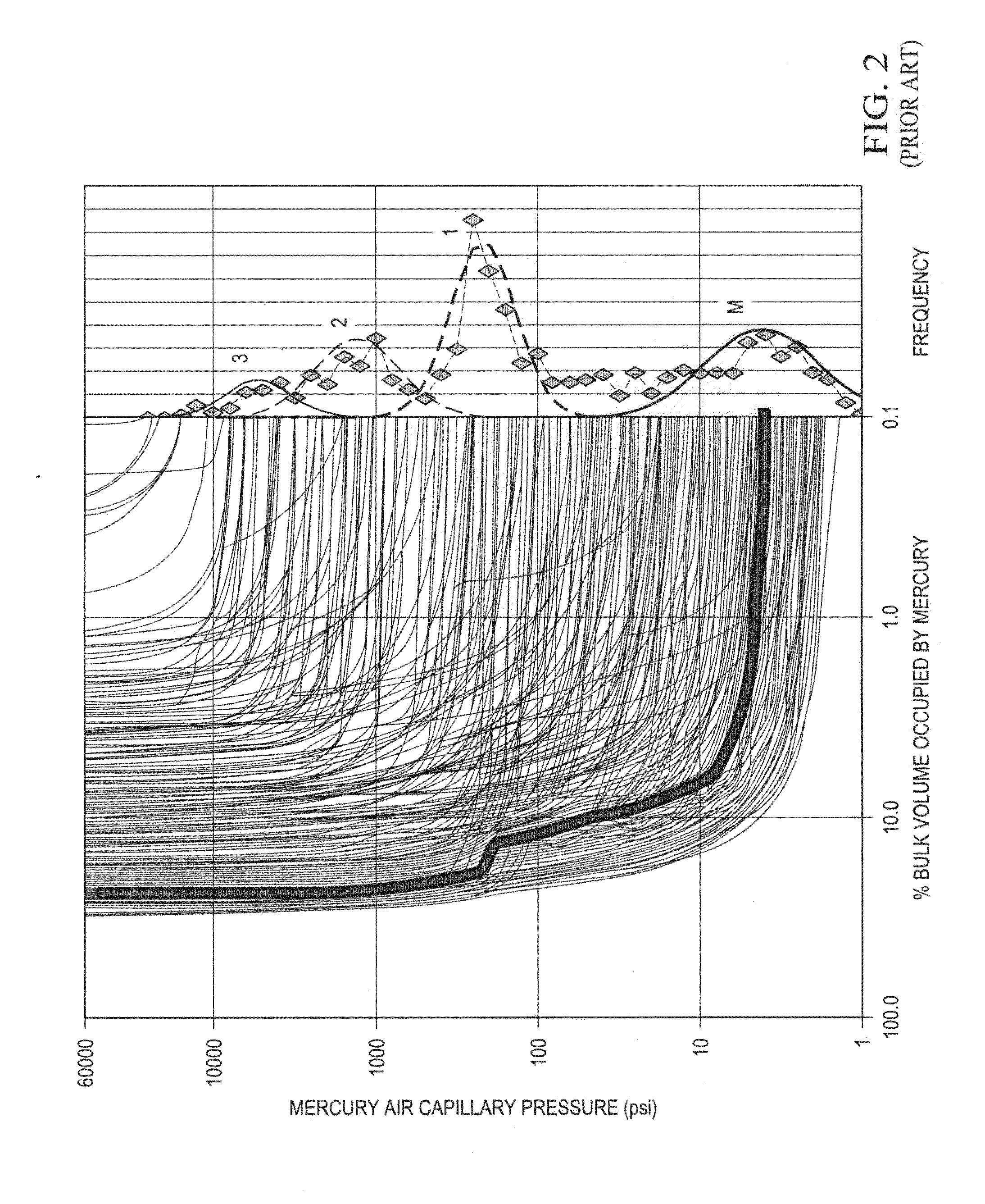
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
142results about "Analogue computers for fluid flow" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
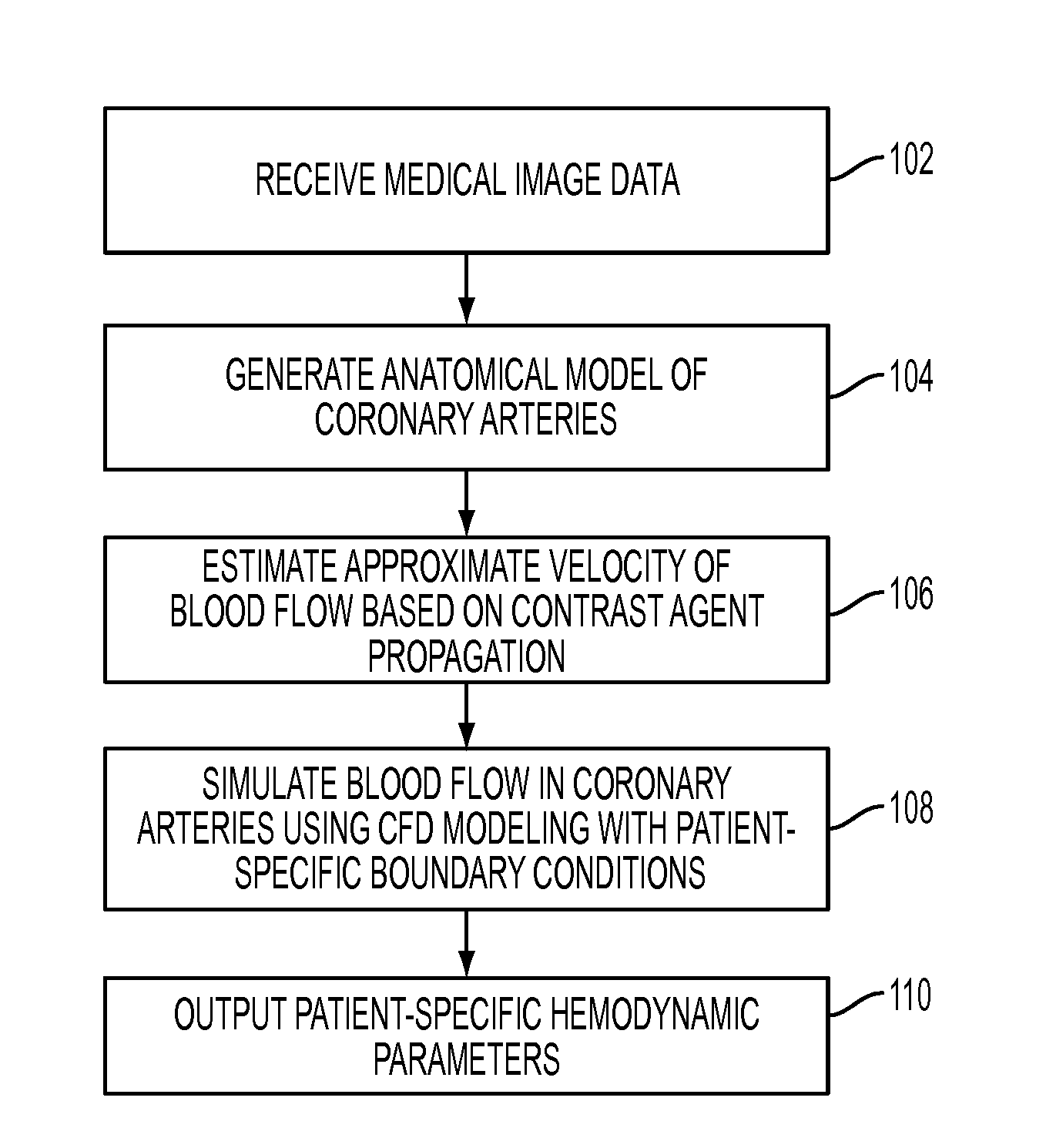
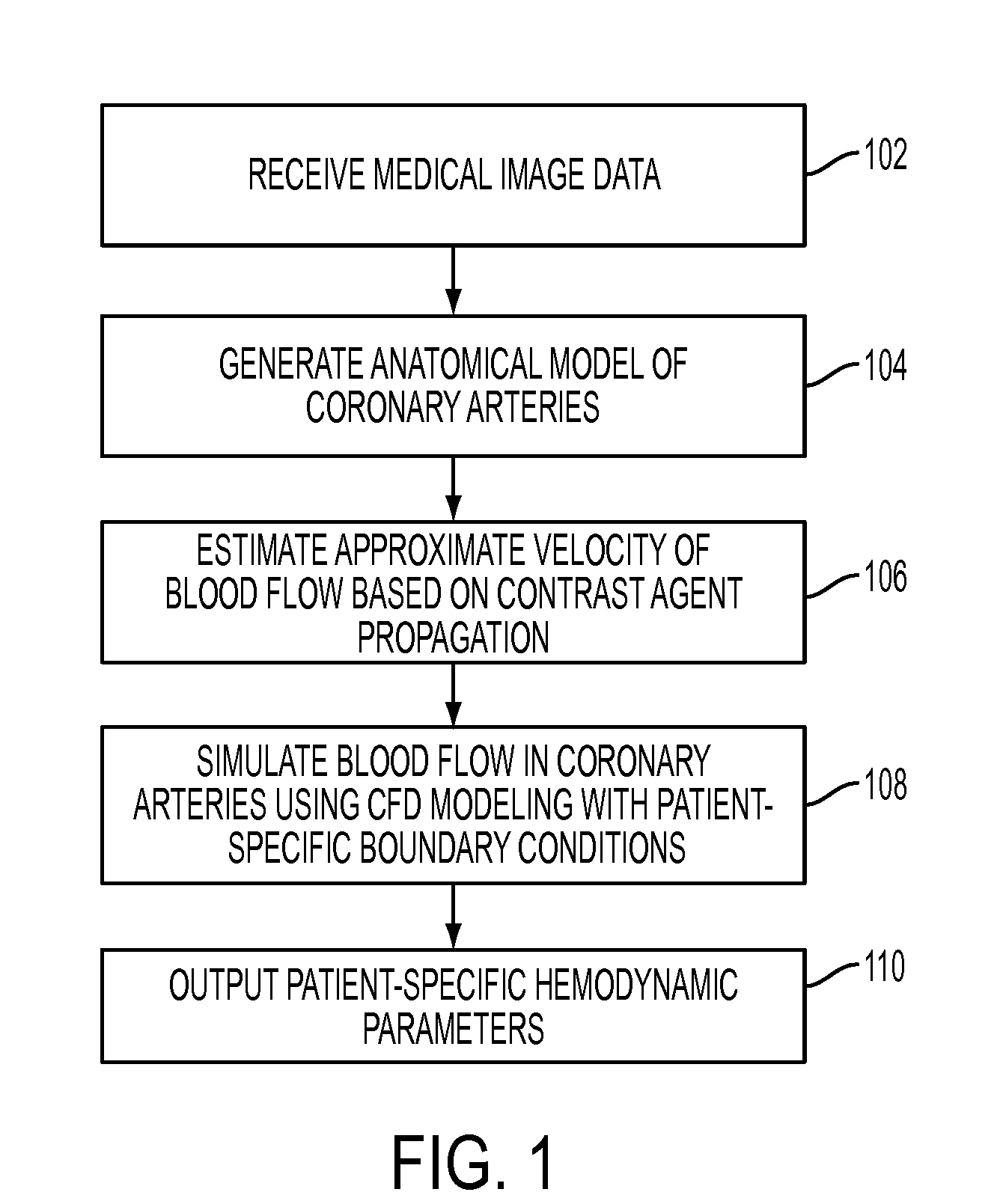
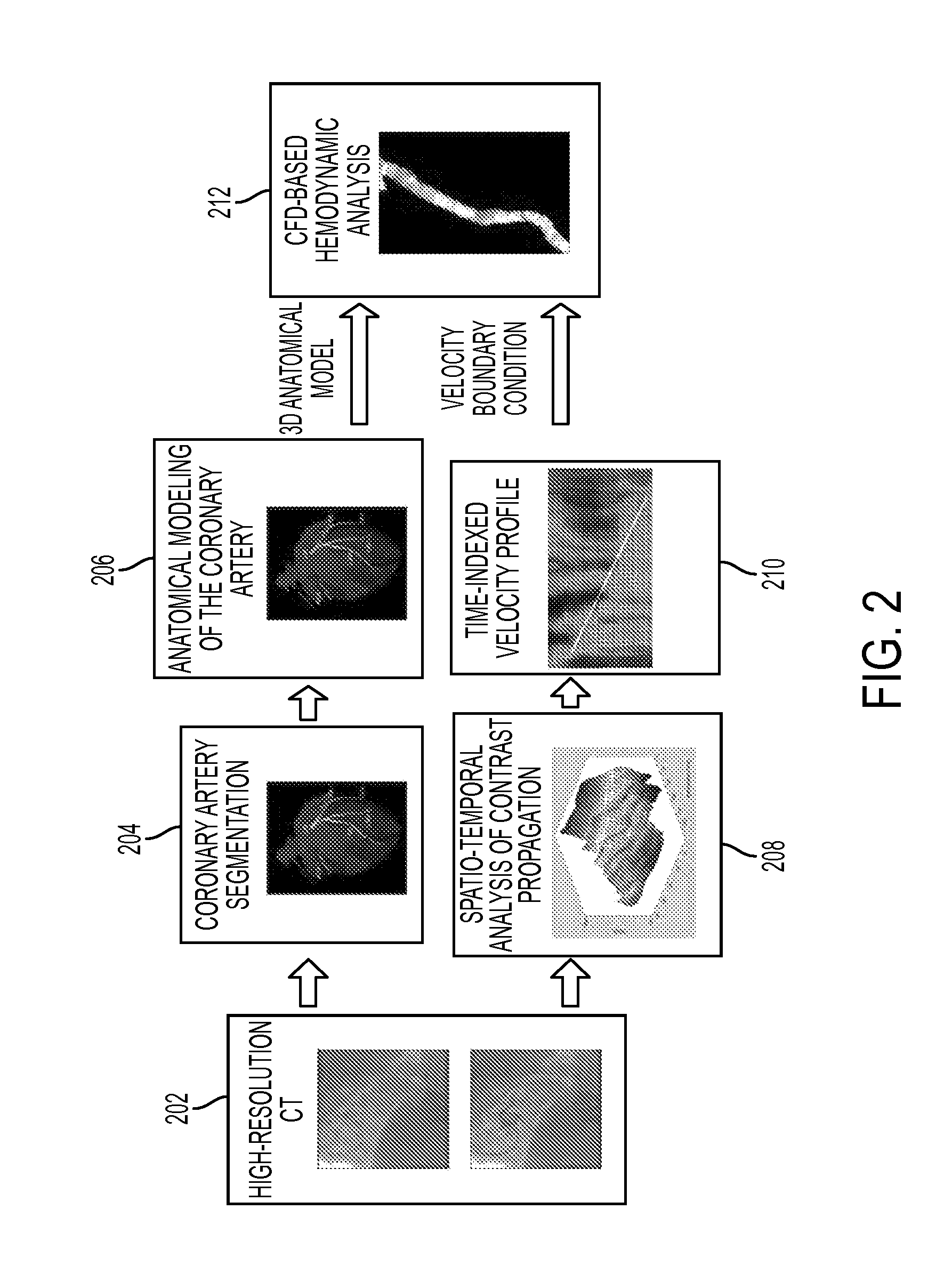
Method and System for Non-Invasive Assessment of Coronary Artery Disease
A method and system for non-invasive patient-specific assessment of coronary artery disease is disclosed. An anatomical model of a coronary artery is generated from medical image data. A velocity of blood in the coronary artery is estimated based on a spatio-temporal representation of contrast agent propagation in the medical image data. Blood flow is simulated in the anatomical model of the coronary artery using a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulation using the estimated velocity of the blood in the coronary artery as a boundary condition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
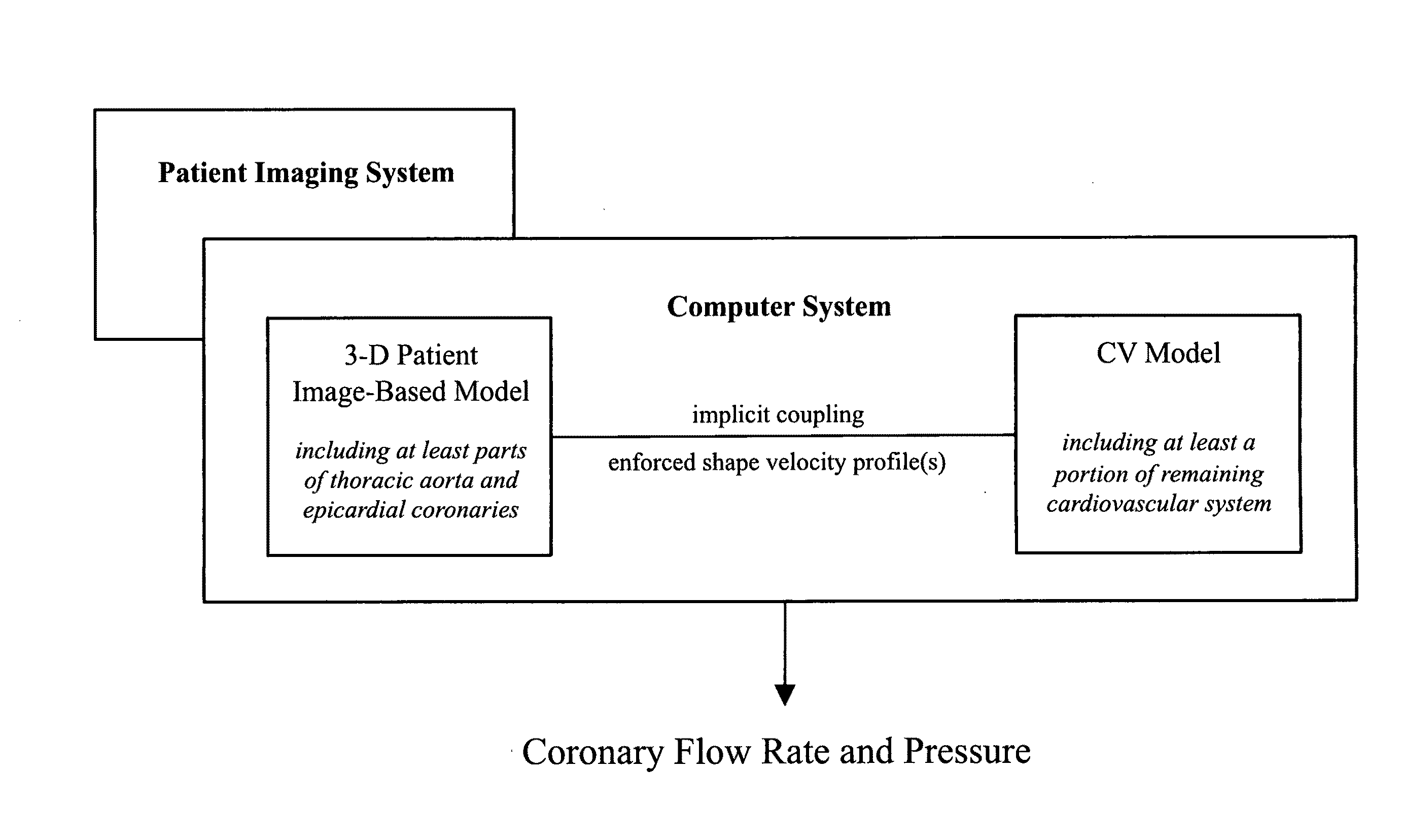
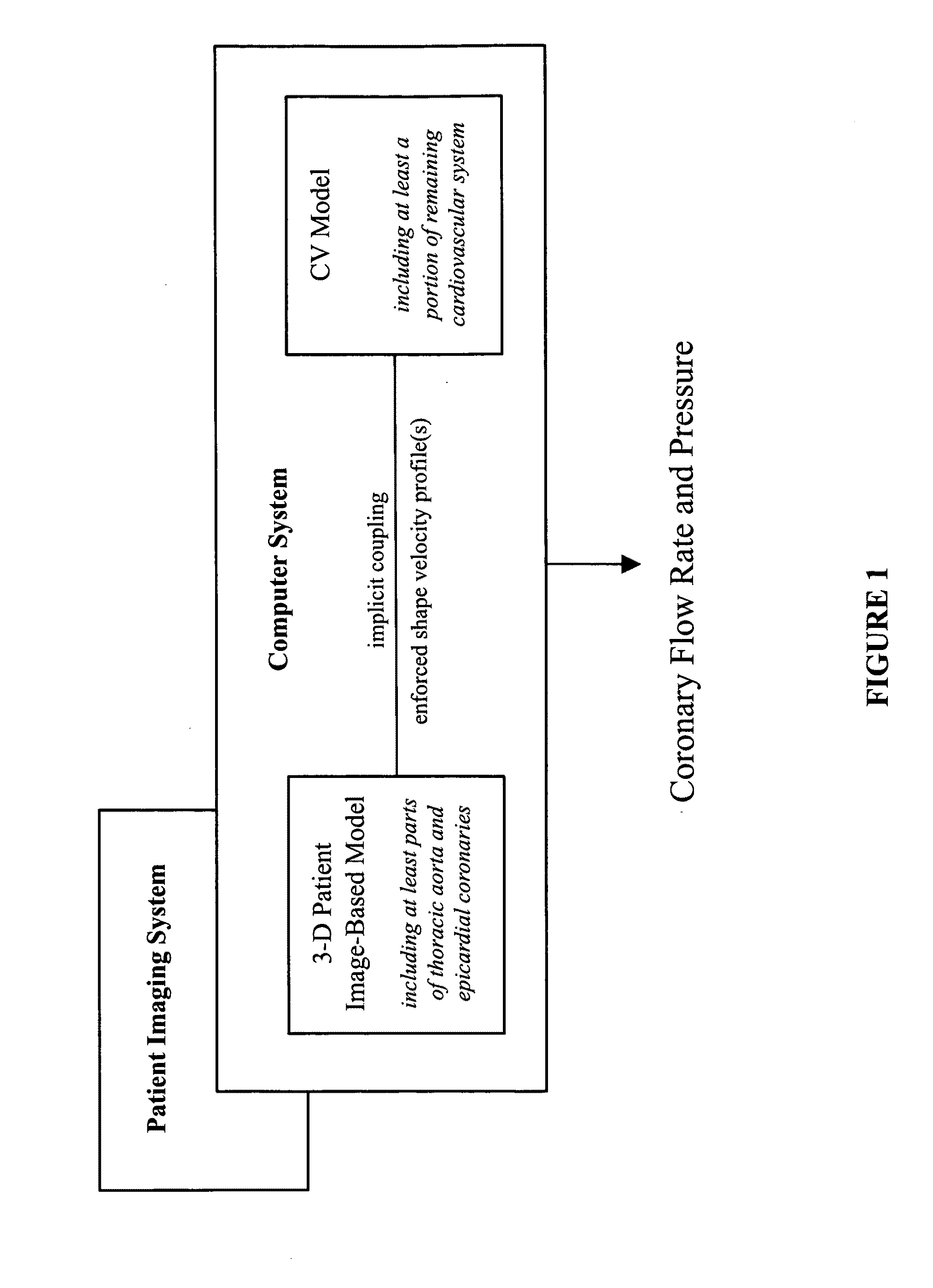
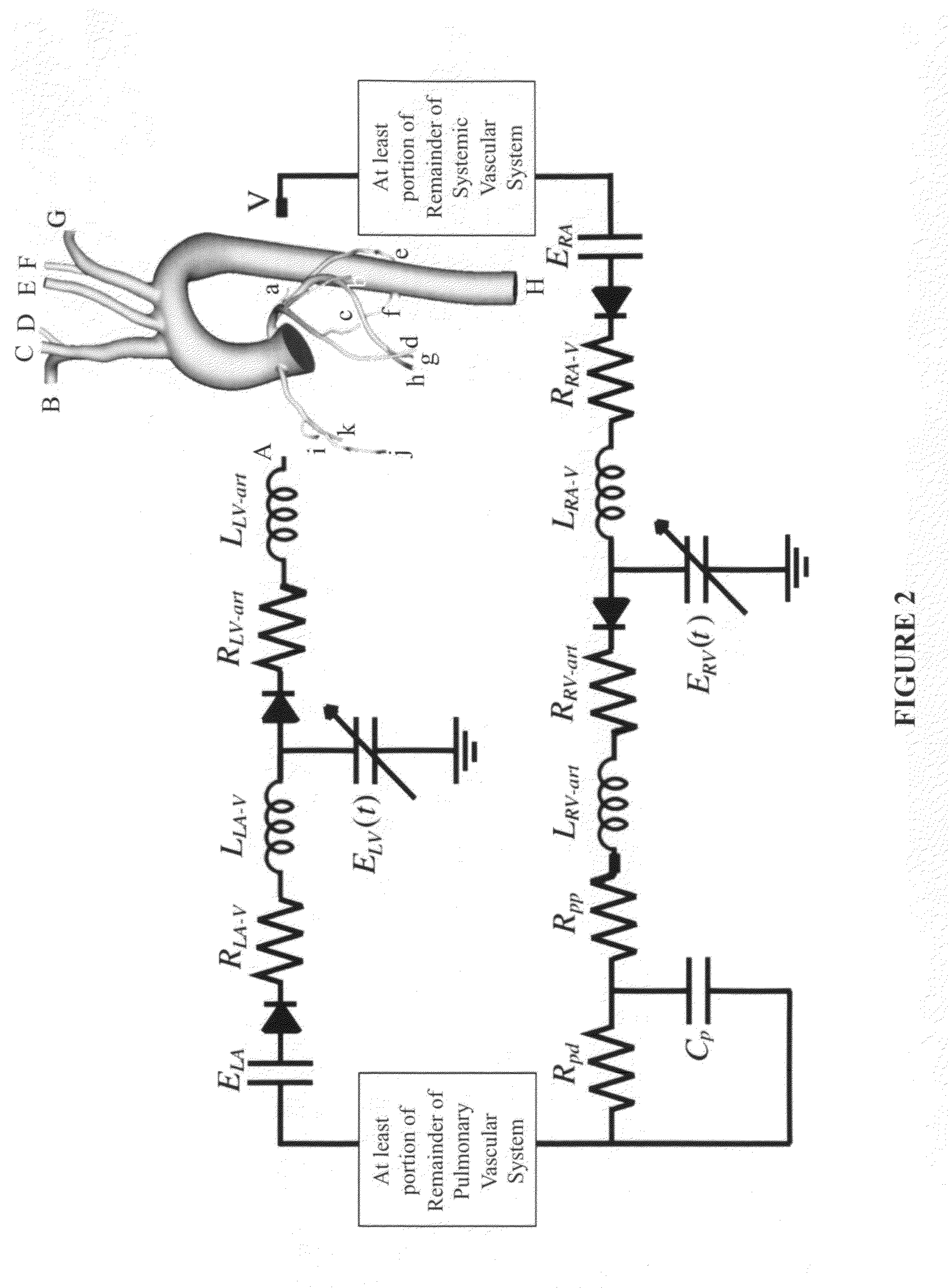
Patient-specific hemodynamics of the cardio vascular system
ActiveUS20100241404A1Minimize model instabilityMore benefitMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesInstabilityRetrograde Flow
A noninvasive patient-specific method is provided to aid in the analysis, diagnosis, prediction or treatment of hemodynamics of the cardiovascular system of a patient. Coronary blood flow and pressure can be predicted using a 3-D patient image-based model that is implicitly coupled with a model of at least a portion of the remaining cardiovascular system. The 3-D patient image-based model includes at least a portion of the thoracic aorta and epicardial coronaries of the patient. The shape of one or more velocity profiles at the interface of the models is enforced to control complex flow features of recirculating or retrograde flow thereby minimizing model instabilities and resulting in patient-specific predictions of coronary flow rate and pressure. The invention allows for patient-specific predictions of the effect of different or varying physiological states and hemodynamic benefits of coronary medical interventions, percutaneous coronary interventions and surgical therapies.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
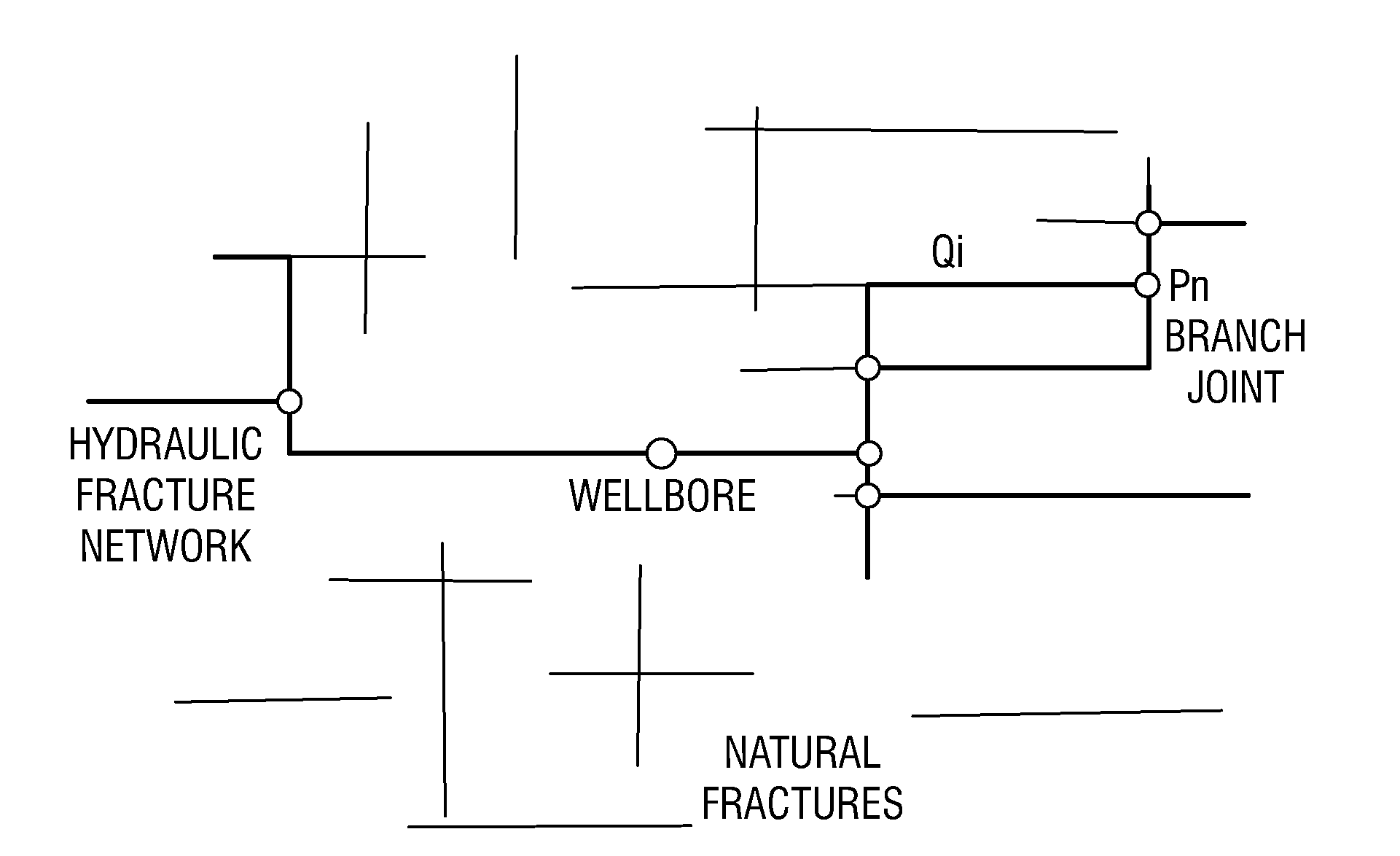
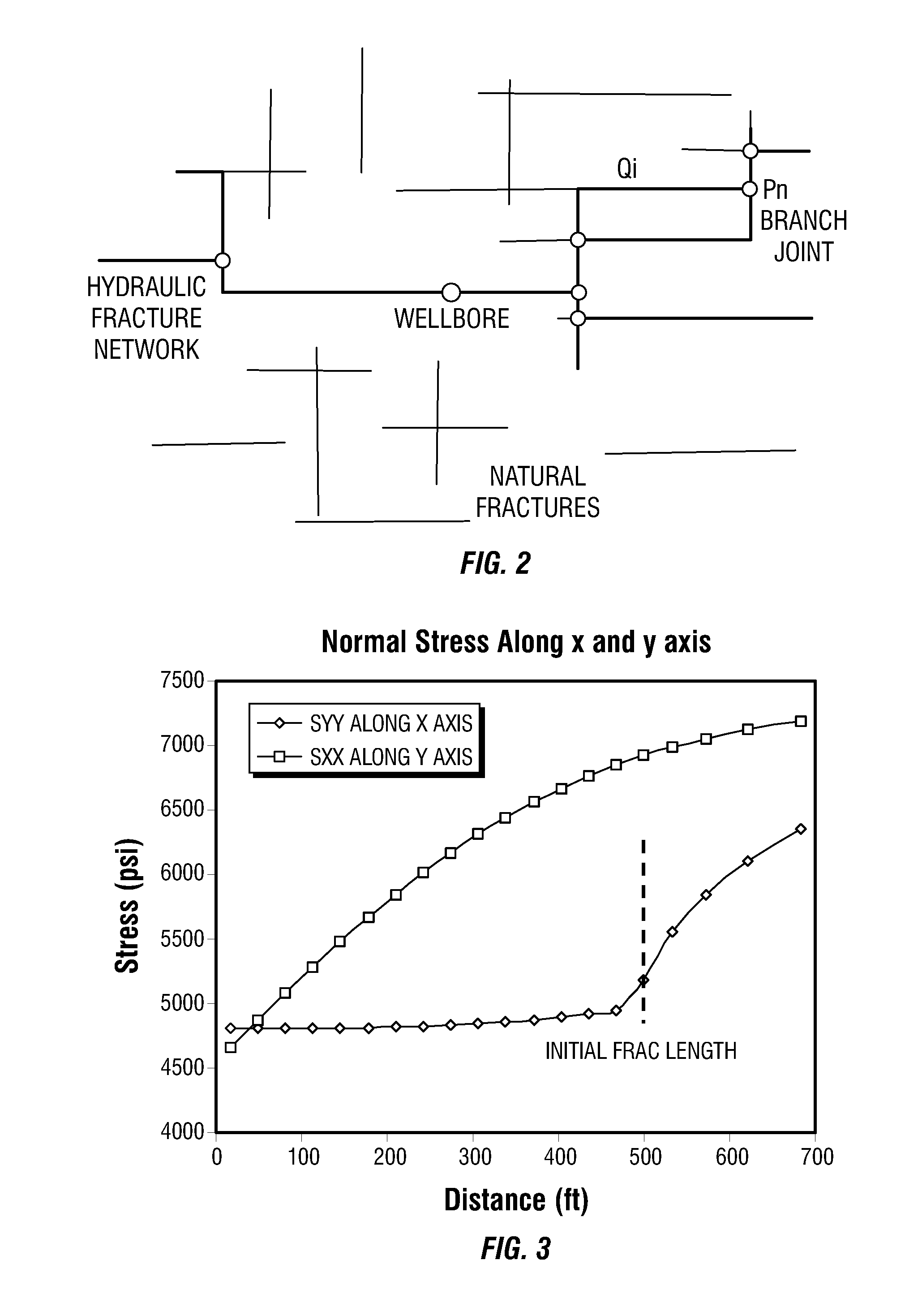
Simulations for Hydraulic Fracturing Treatments and Methods of Fracturing Naturally Fractured Formation
A hydraulic fracture design model that simulates the complex physical process of fracture propagation in the earth driven by the injected fluid through a wellbore. An objective in the model is to adhere with the laws of physics governing the surface deformation of the created fracture subjected to the fluid pressure, the fluid flow in the gap formed by the opposing fracture surfaces, the propagation of the fracture front, the transport of the proppant in the fracture carried by the fluid, and the leakoff of the fracturing fluid into the permeable rock. The models used in accordance with methods of the invention are typically based on the assumptions and the mathematical equations for the conventional 2D or P3D models, and further take into account the network of jointed fracture segments. For each fracture segment, the mathematical equations governing the fracture deformation and fluid flow apply. For each time step, the model predicts the incremental growth of the branch tips and the pressure and flow rate distribution in the system by solving the governing equations and satisfying the boundary conditions at the fracture tips, wellbore and connected branch joints. An iterative technique is used to obtain the solution of this highly nonlinear and complex problem.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
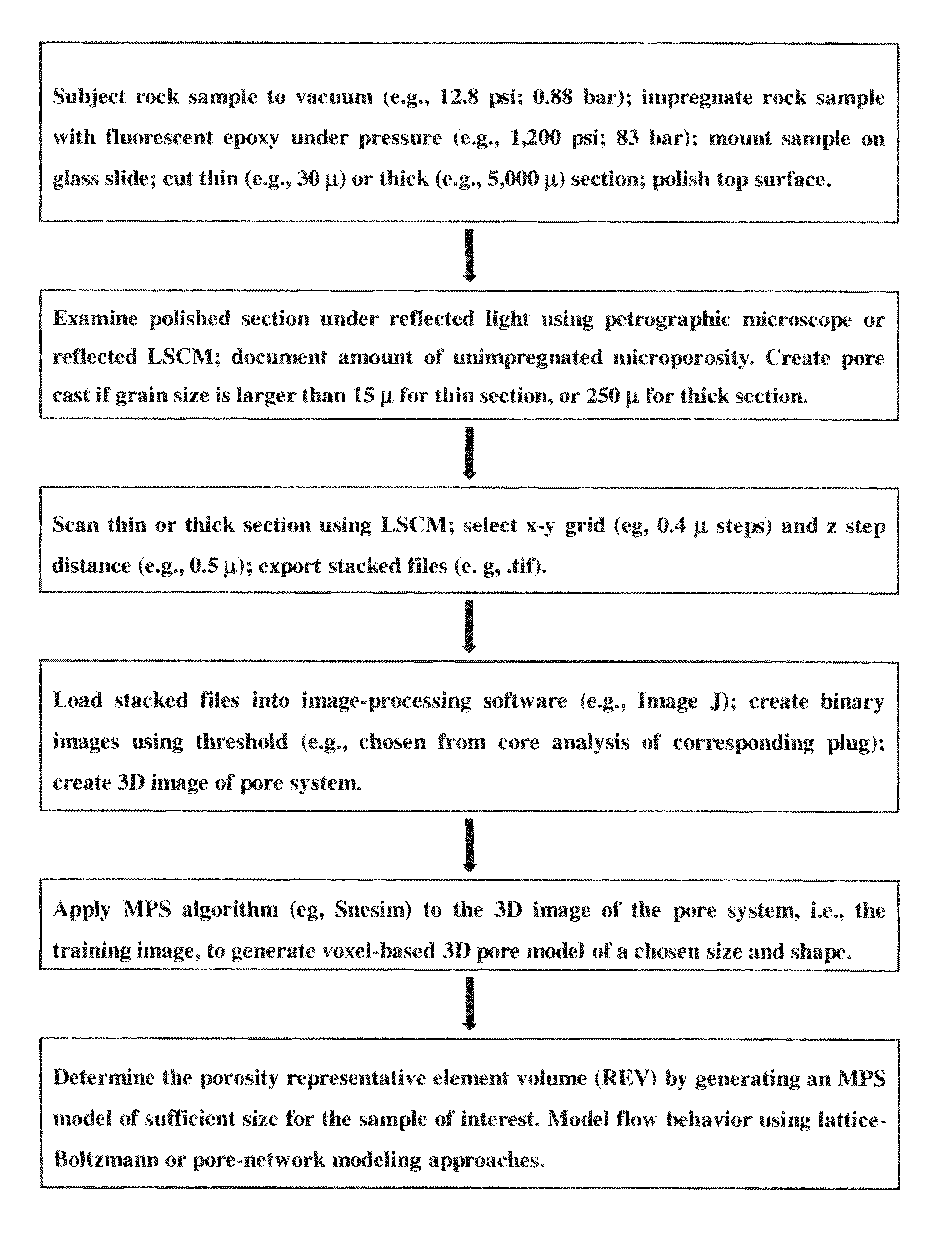
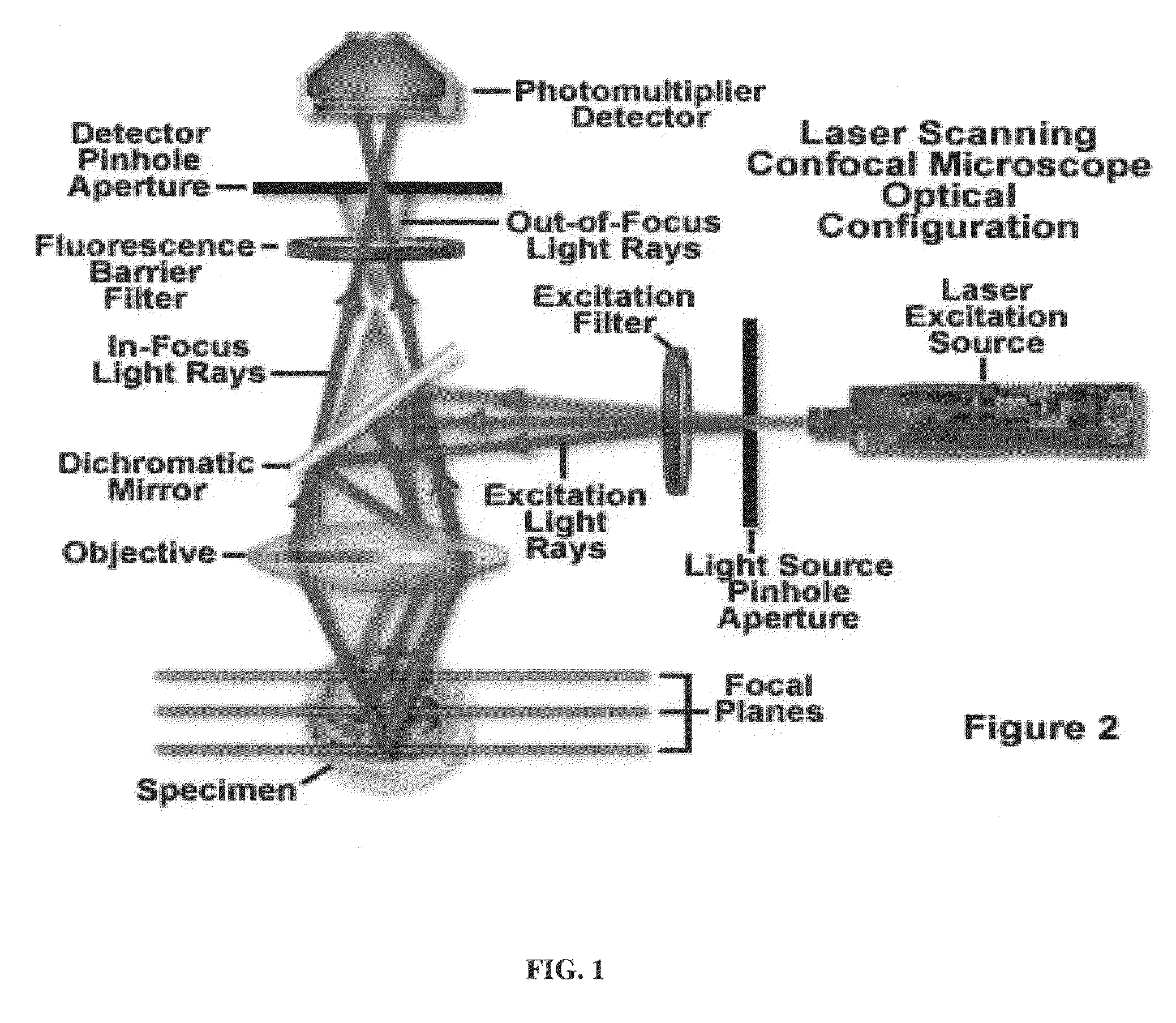
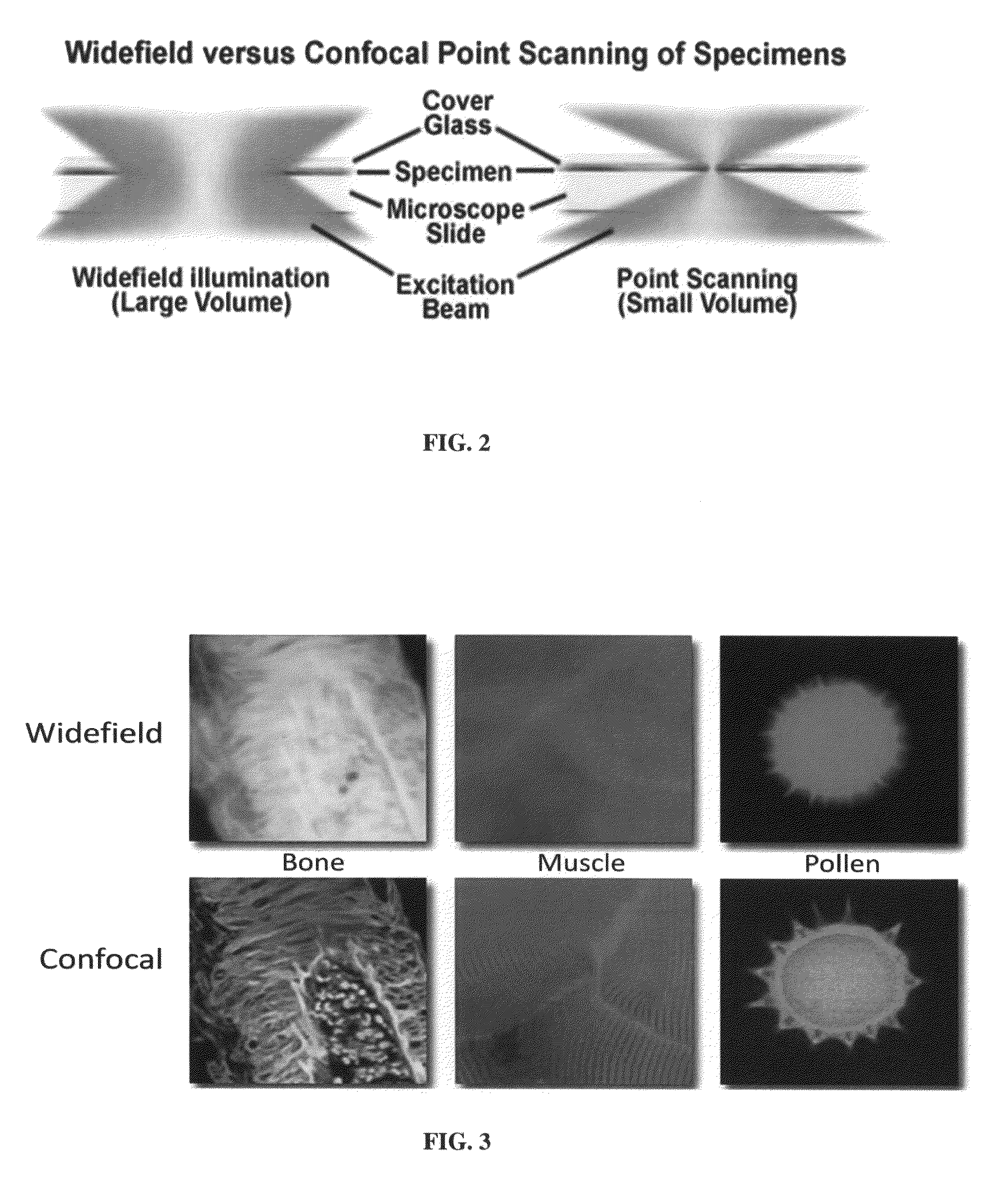
Method to build 3D digital models of porous media using transmitted laser scanning confocal mircoscopy and multi-point statistics
InactiveUS20110004447A1Reduce restrictionsReduce boundary effectsDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionPorous mediumLaser scanning
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Decentralized industrial process simulation system
ActiveUS20110131017A1Accurately solves massAccurately flow balanceProgramme controlAnalogue computers for control systemsMass storageParallel computing
A high fidelity distributed plant simulation technique includes a plurality of separate simulation modules that may be stored and executed separately in different drops or computing devices. The simulation modules communicate directly with one another to perform accurate simulation of a plant, without requiring a centralized coordinator to coordinate the operation of the simulation system. In particular, numerous simulation modules are created, with each simulation module including a model of an associated plant element and these simulation modules are stored in different drops of a computer network to perform distributed simulation of a plant or a portion of a plant. At least some of the simulation modules, when executing, perform mass flow balances taking into account process variables associated with adjacent simulation modules to thereby assure pressure, temperature and flow balancing (i.e., conservation of mass flow) through the entire simulation system. In a dynamic situation, a transient mass storage relay technique is used to account for transient changes in mass flow through any non-storage devices being simulated by the simulation modules. Moreover, adjacent simulation modules located in different drops communicate directly with one another using a background processing task, which simplifies communications between adjacent simulation modules without the need for a central coordinator.
Owner:EMERSON PROCESS MANAGEMENT POWER & WATER SOLUTIONS
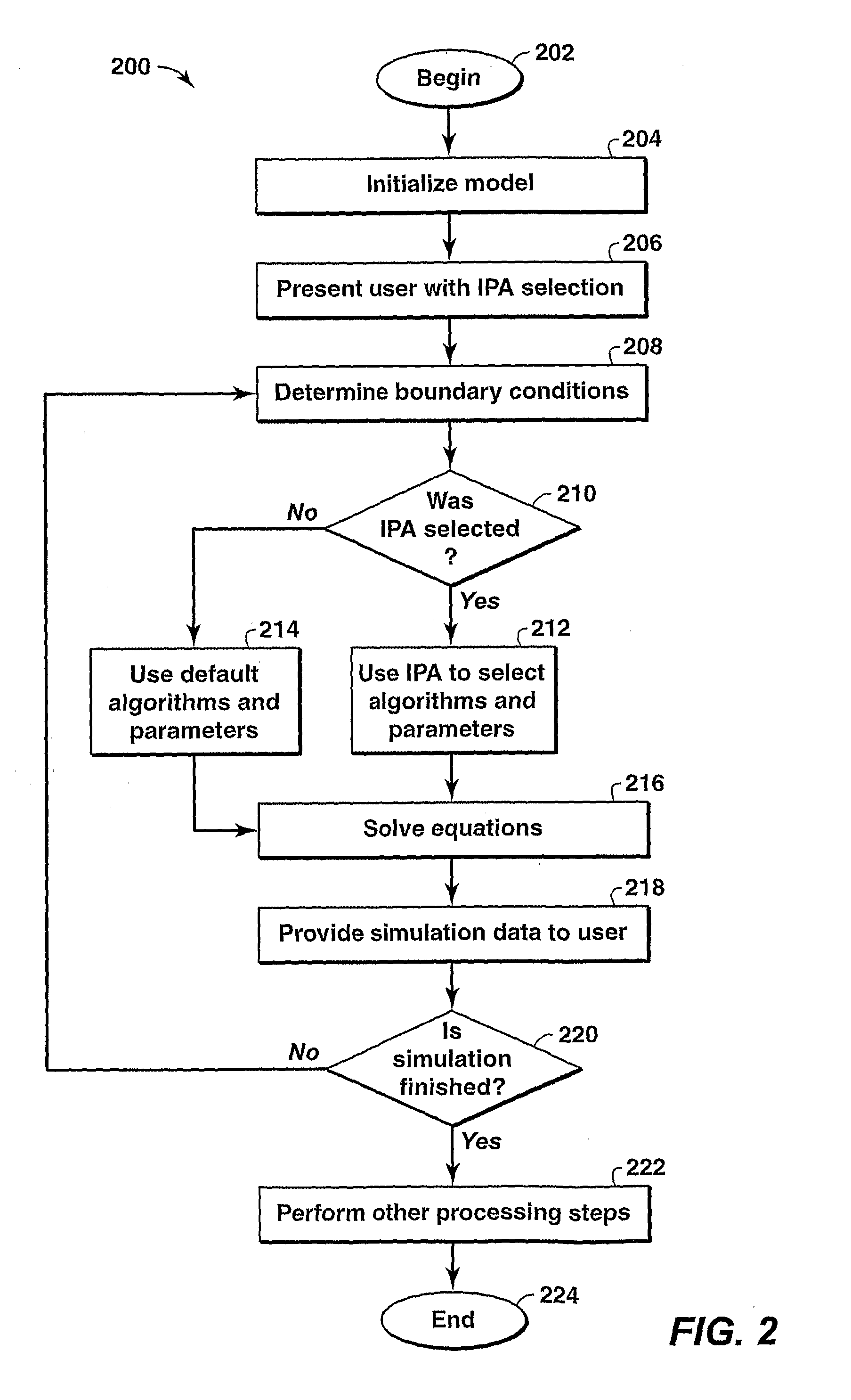
Simulation System and Method
InactiveUS20100082142A1Enhance run-time performanceImprove running stabilityComputation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationPorous mediumComputational simulation
A method and system are described that enhance the computational simulation, such as a fluid flowing through a porous media, under the present techniques. In particular, a computer implemented simulation method is described that includes initializing a simulator and utilizing an intelligent performance assistant to select a set of parameters and algorithms for the simulator. Then, equations are solved with the set of parameters and algorithms and the solution to the equations is then obtained.
Owner:USADI ADAM K +6
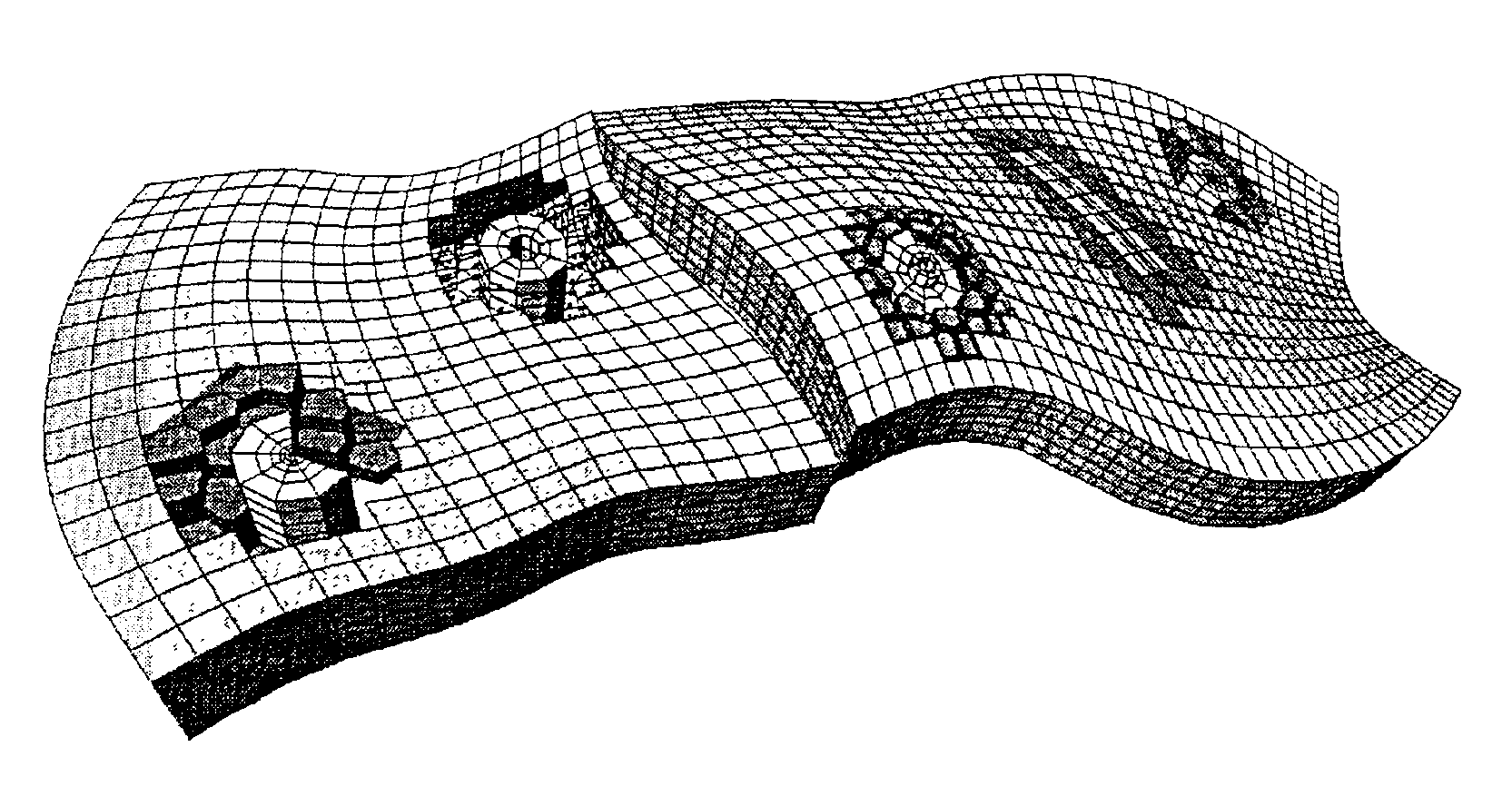
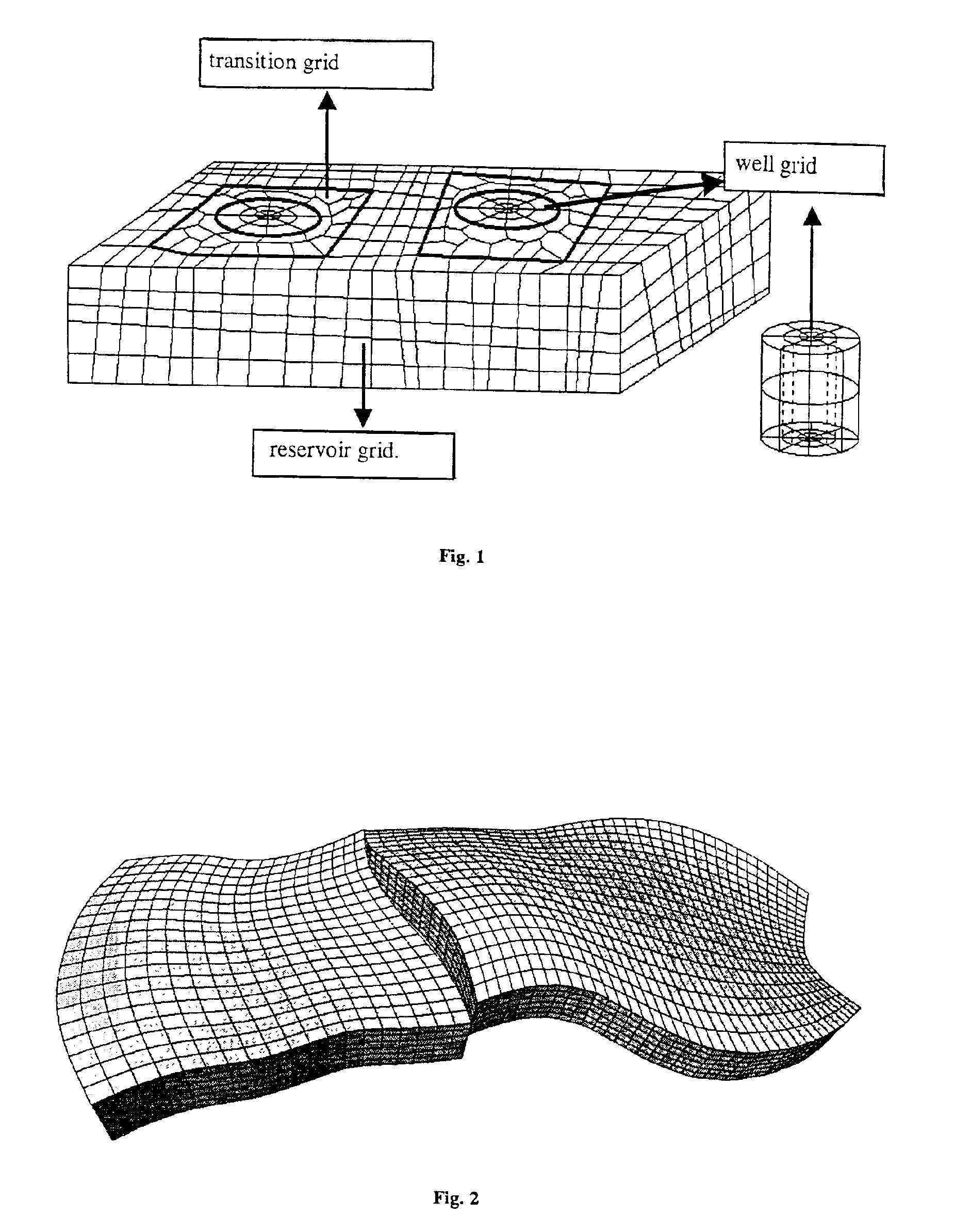
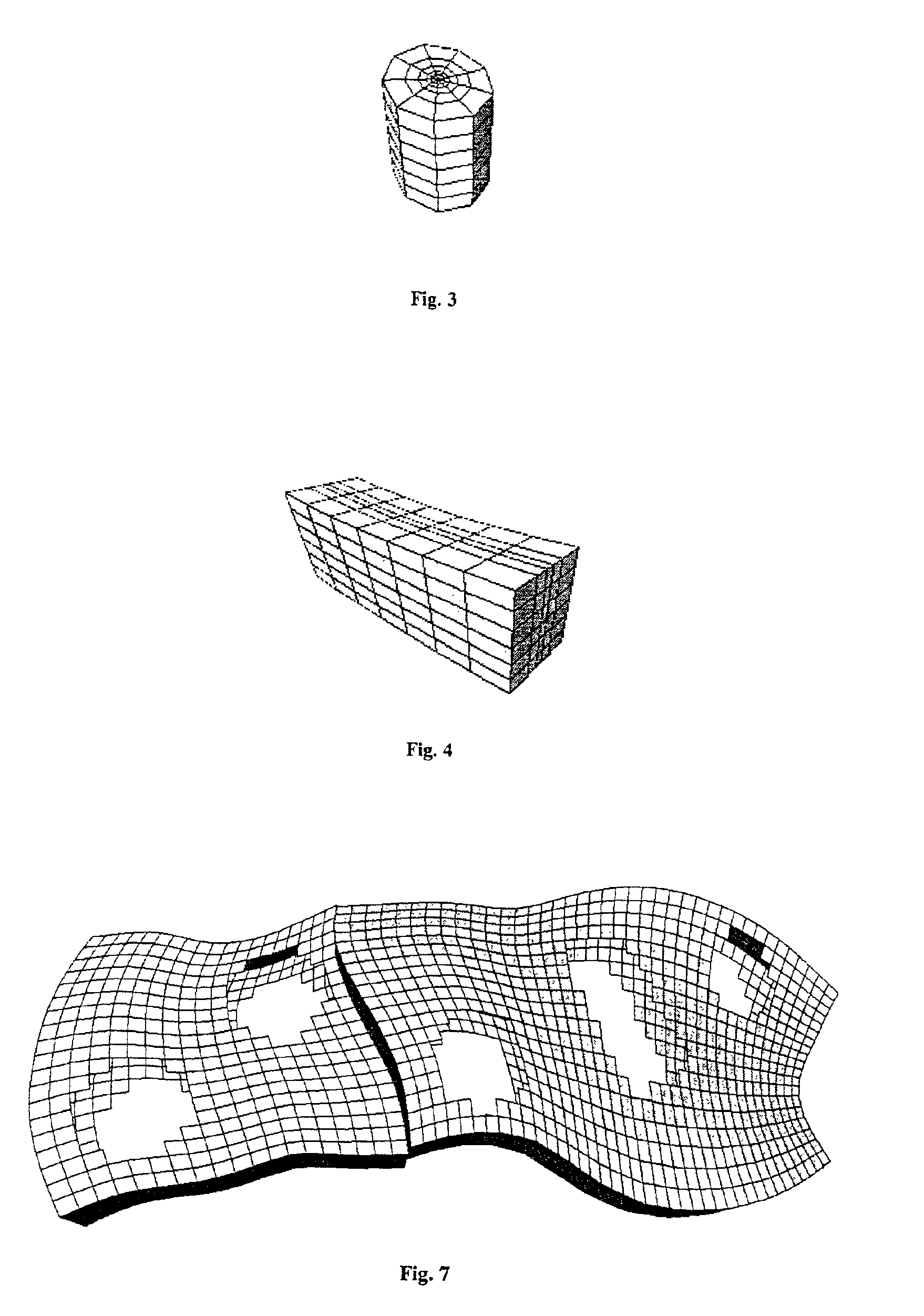
Method of generating a hybrid grid allowing modelling of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more wells
InactiveUS6907392B2Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingImage data processing detailsHybrid meshHydrocarbon
A method of generating a hybrid grid allowing modelling of a heterogeneous formation crossed by one or more pipes such as, for example, an underground formation where one or more wells have been drilled, in order to form a representative model, for example of fluid flows in the formation in accordance with a defined numerical pattern is disclosed. The method comprises associating a first structured grid for gridding of the heterogeneous medium regarding discontinuities thereof with a second structured, radial type grid for gridding of a zone around each pipe or well, which allows better constraints linked with flows in the zone, and transition of non-structured grids that are interposed between the first grid and each second well grid. Various grids are combined, each with its own formation, representation and exploration methods, structured grids which are advantageous in facilitating control and comprehension of the reservoir images formed and more flexible non-structured grids for gridding of complex zones. An application is simulation of hydrocarbon reservoirs.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
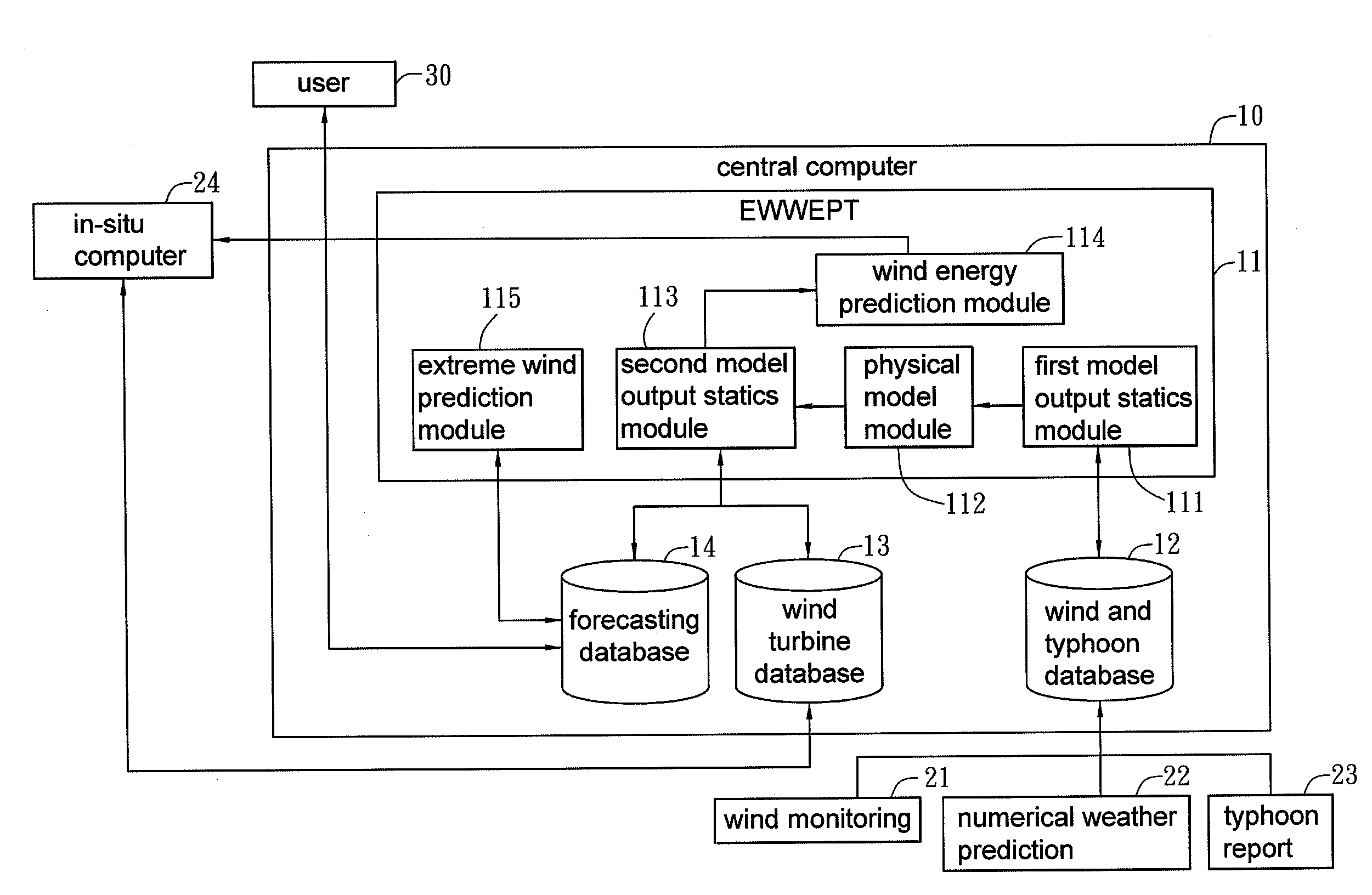
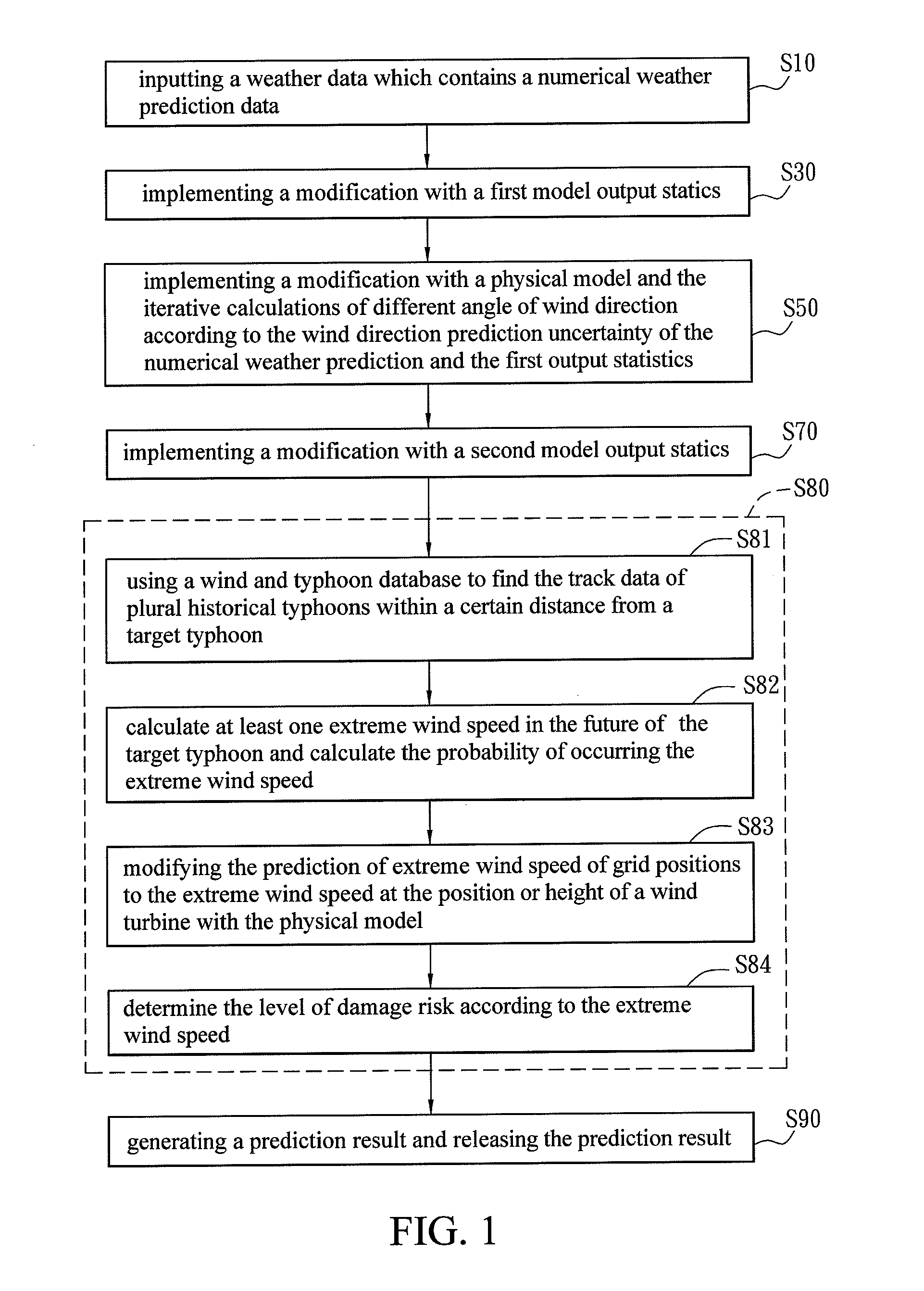
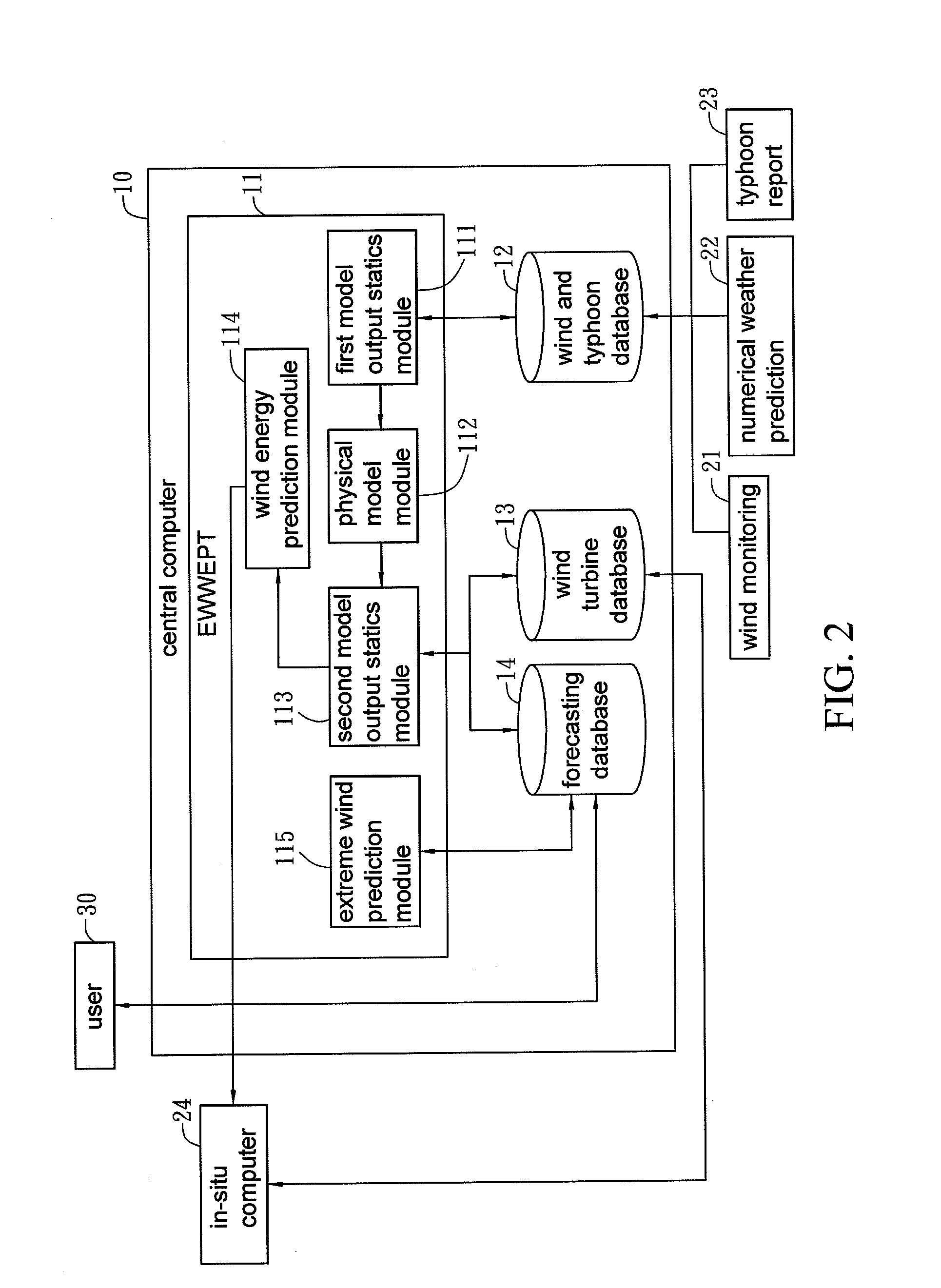
Wind energy forecasting method with extreme wind speed prediction function
InactiveUS20120046917A1Improve efficiencyProcess safetyWeather condition predictionEngine fuctionsNumerical weather predictionPhysical model
A wind energy forecasting method with extreme wind speed prediction function cooperated with a central computer, comprising the steps of: inputting a weather data which contains a numerical weather prediction data; implementing a modification with a first model output statistics; implementing a modification with a physical model in accordance with the output of the first model output statistics that can iteratively calculate the results by varying the angles of wind direction; implementing a modification with a second model output statistics; and implementing a prediction of extreme wind speed caused by typhoon, which comprises the following sub-steps of: using a wind and typhoon database to find track data of plural historical typhoons within a certain distance from a target typhoon; using an extreme wind and wind energy prediction tool to calculate at least one extreme wind speed in the future of the target typhoon and calculate the probability of occurring the extreme wind speed; and modifying the extreme wind speed with the physical model to the extreme wind speed at the position or height of a wind turbine.
Owner:INST NUCLEAR ENERGY RES ROCAEC
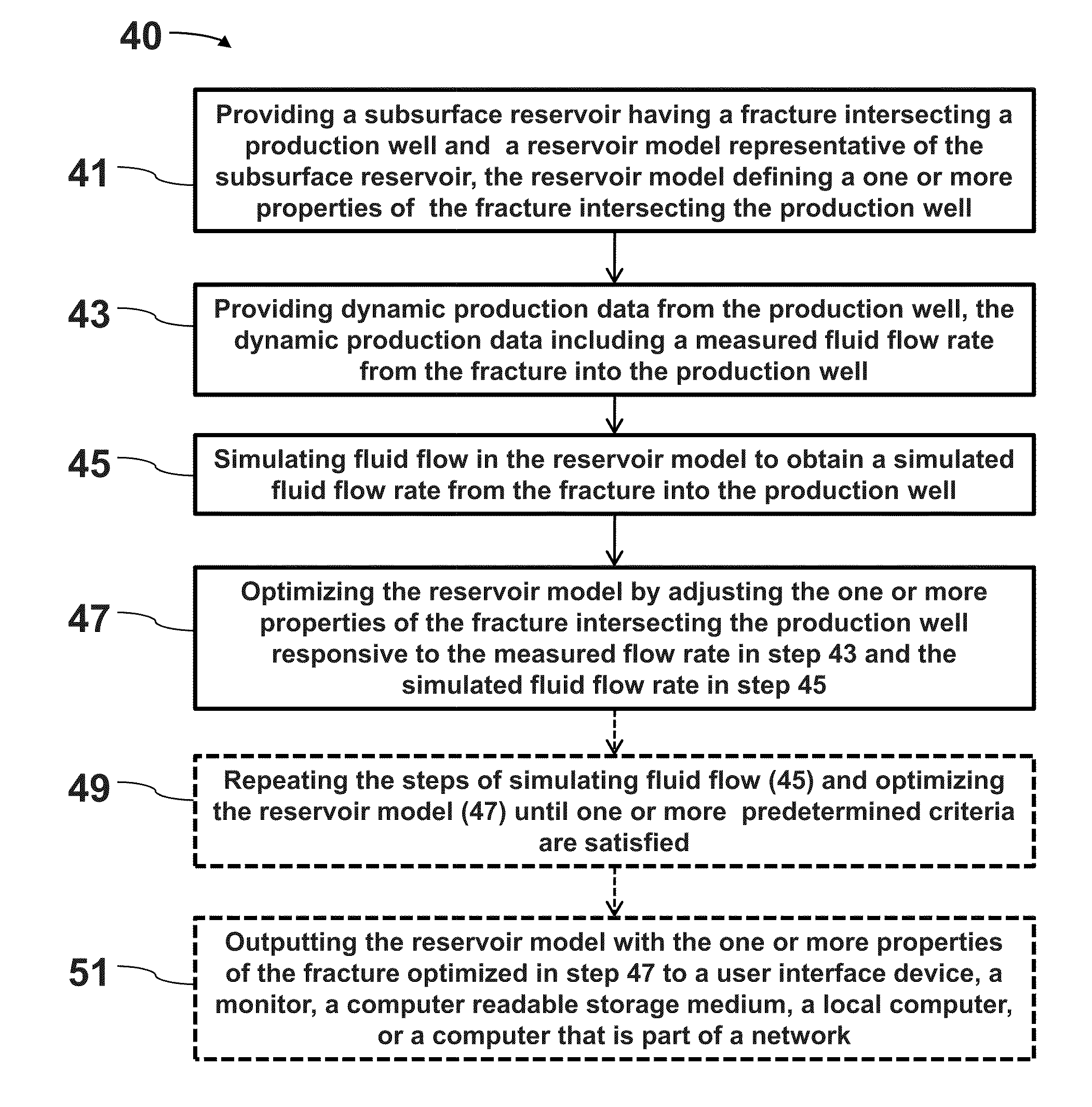
System and method for characterizing fractures in a subsurface reservoir
ActiveUS20100250216A1Fracture property can be optimizedElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingGeomodellingPressure dataDynamic data
The disclosed methods, systems, and software are described to optimize fracture characteristics and simulate fluid flow rates in a well model. The well model, which includes at least one fracture intersecting a production well, is generated with static and dynamic data. Fluid flow in the well model is simulated to obtain simulated fluid flow rates between fractures and the well. Fracture properties, such as length, height and aperture, are then updated responsive to measured and simulated fluid flow rates. Multiple simulation runs and updating of the fracture properties can be performed until the simulated fluid flow rates converge with the measured fluid flow rates. Pressure data can be used to determine gridblock permeability, which in turn helps constrain the model, thus providing more reliable fracture properties. Uncertainty ranges of the fracture properties can also be calculated.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Scalable Simulation of Multiphase Flow in a Fractured Subterranean Reservoir as Multiple Interacting Continua
ActiveUS20120179436A1GeomodellingComputation using non-denominational number representationPore systemCounter current
A subterranean reservoir where the pore space of media or formation rock is multimodal, and the media may have imbedded multiple scales of fracture networks, is simulated. The modes of the pore system and the scale of fracture networks are each represented as a separate, but interactive continuum with the other. The simulation allows multiple continua to be co-located and multi-interacting, in that each continuum may have current and counter-current multiple multiphase exchanges with other continua.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
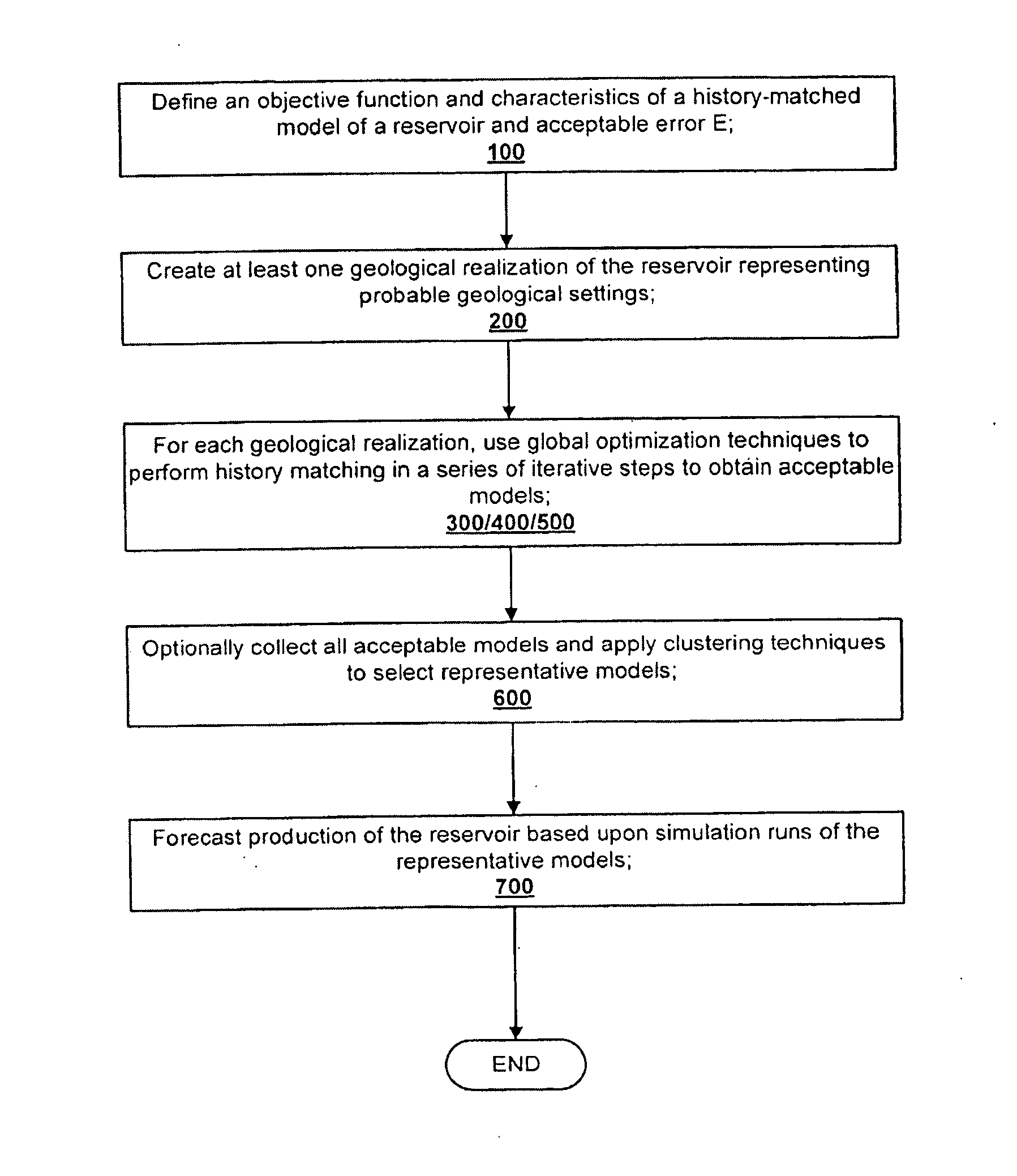
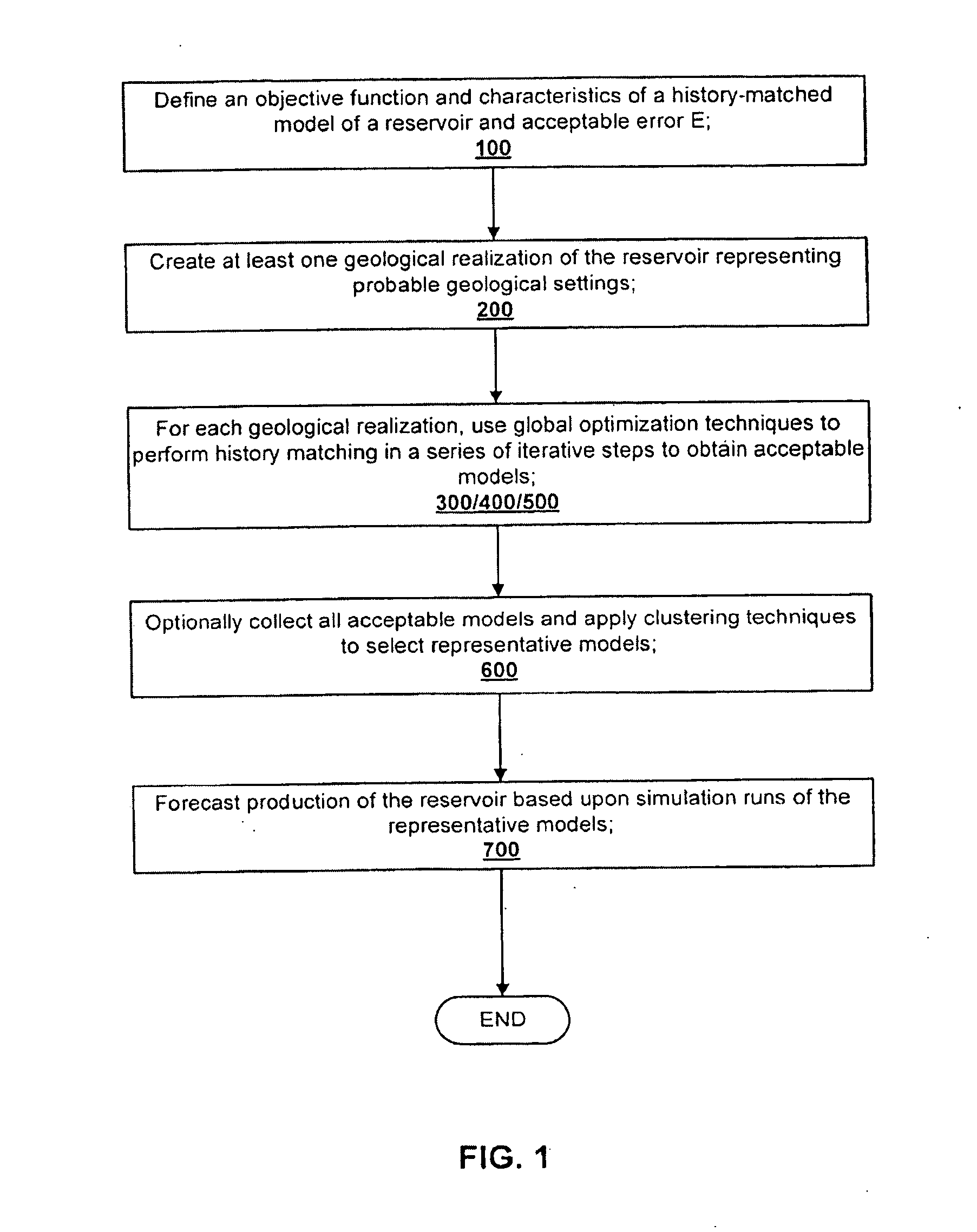
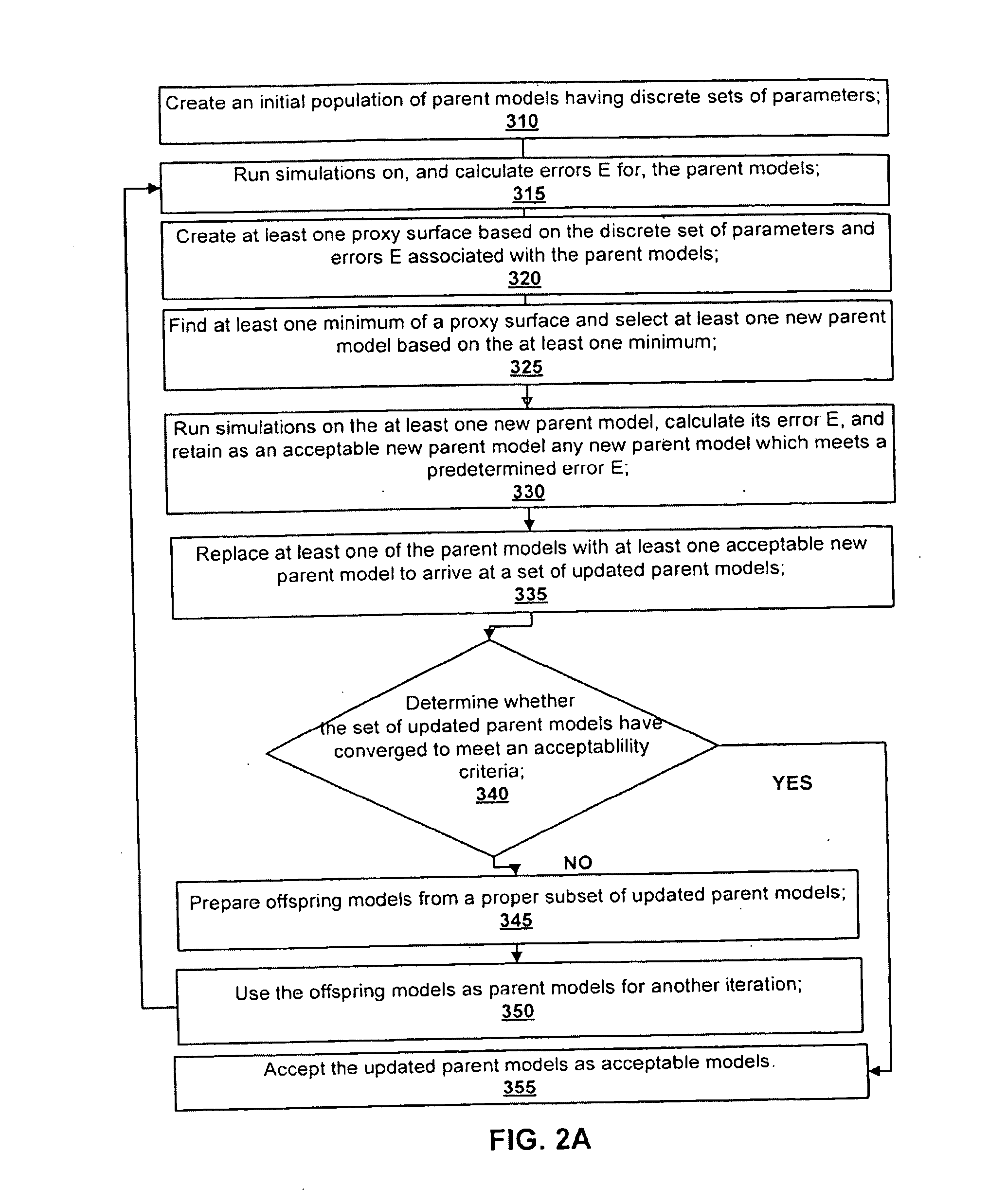
Method for history matching and uncertainty quantification assisted by global optimization techniques utilizing proxies
ActiveUS20080077371A1Improve efficiencyFluid removalSeismologyGlobal optimizationErrors and residuals
A method for forecasting production from a hydrocarbon producing reservoir, the method includes defining an objective function and characteristics of a history-matched model of a reservoir and acceptable error E. At least one geological realization of the reservoir is created representing a probable geological setting. For each geological realization, a global optimization technique is used to perform history matching in a series of iterative steps to obtain acceptable models. Production of the reservoir is forecasted based upon simulation runs of the respective models.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
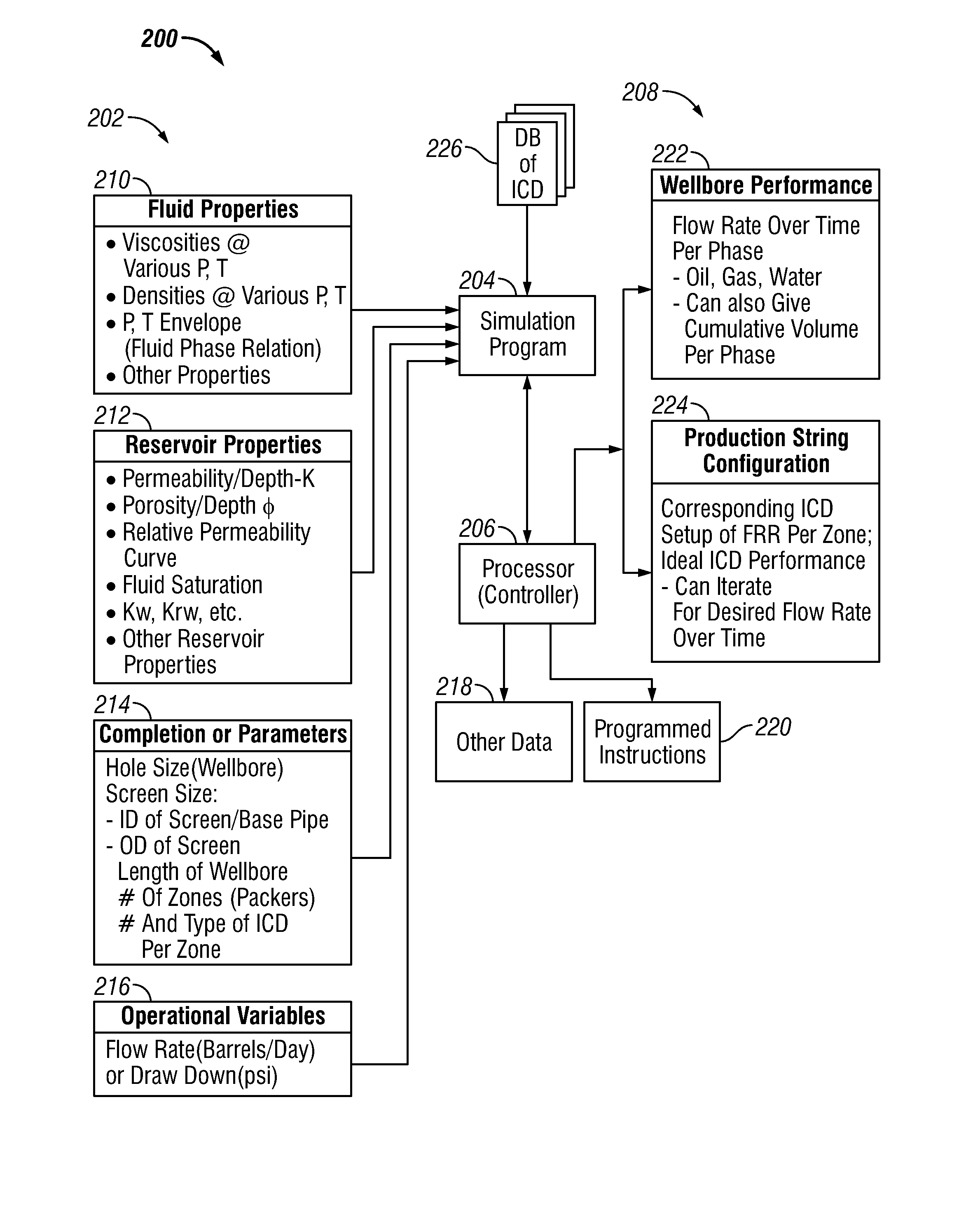
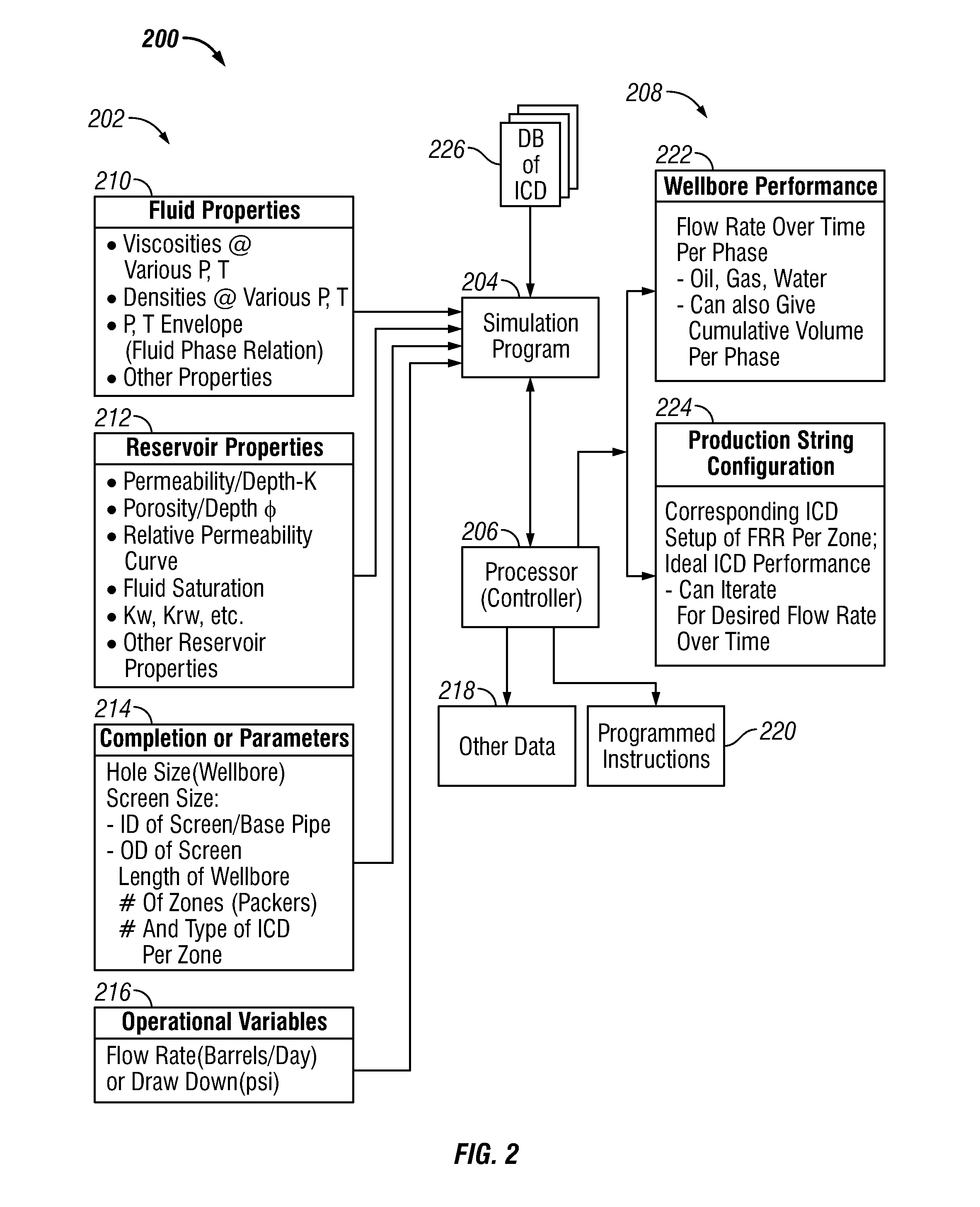
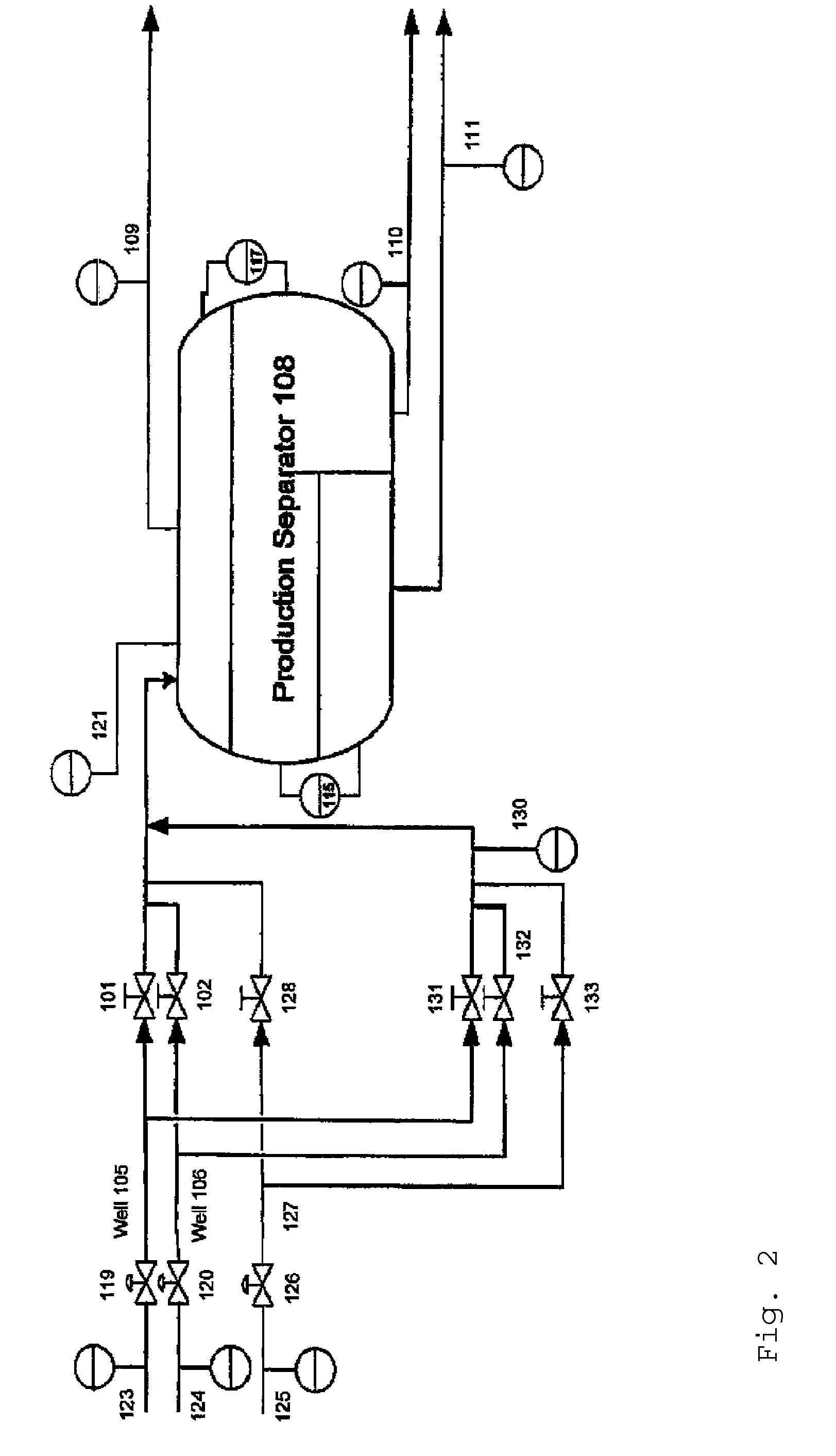
Method of Providing Flow Control Devices for a Production Wellbore
A method of providing a production string for a wellbore formed in a formation is disclosed. The method, in one embodiment may include: defining a performance criterion for flow of a fluid from a formation into a wellbore; performing a simulation using a processor, a simulation program, a parameter of the fluid, a parameter of the formation and a parameter of the wellbore to determine a first flow characteristic of the flow of the fluid from the formation into the wellbore corresponding to an initial set of flow control devices arranged in the wellbore; performing one or more additional simulations using the processor, the simulation program and the parameters of formation, fluid and wellbore to determine a new flow characteristic of the flow of the fluid from the formation into the wellbore for a new set of flow control devices until a new determined characteristic of the flow of the fluid from the formation into the wellbore meets the performance criterion; and storing results of simulation results relating to the flow control devices in a suitable storage medium.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method For Simulating Fractional Multi-Phase/Multi-Component Flow Through Porous Media
ActiveUS20130018641A1Ease of evaluationAccurate representationVolume/mass flow measurementGeomodellingPorous mediumComputerized system
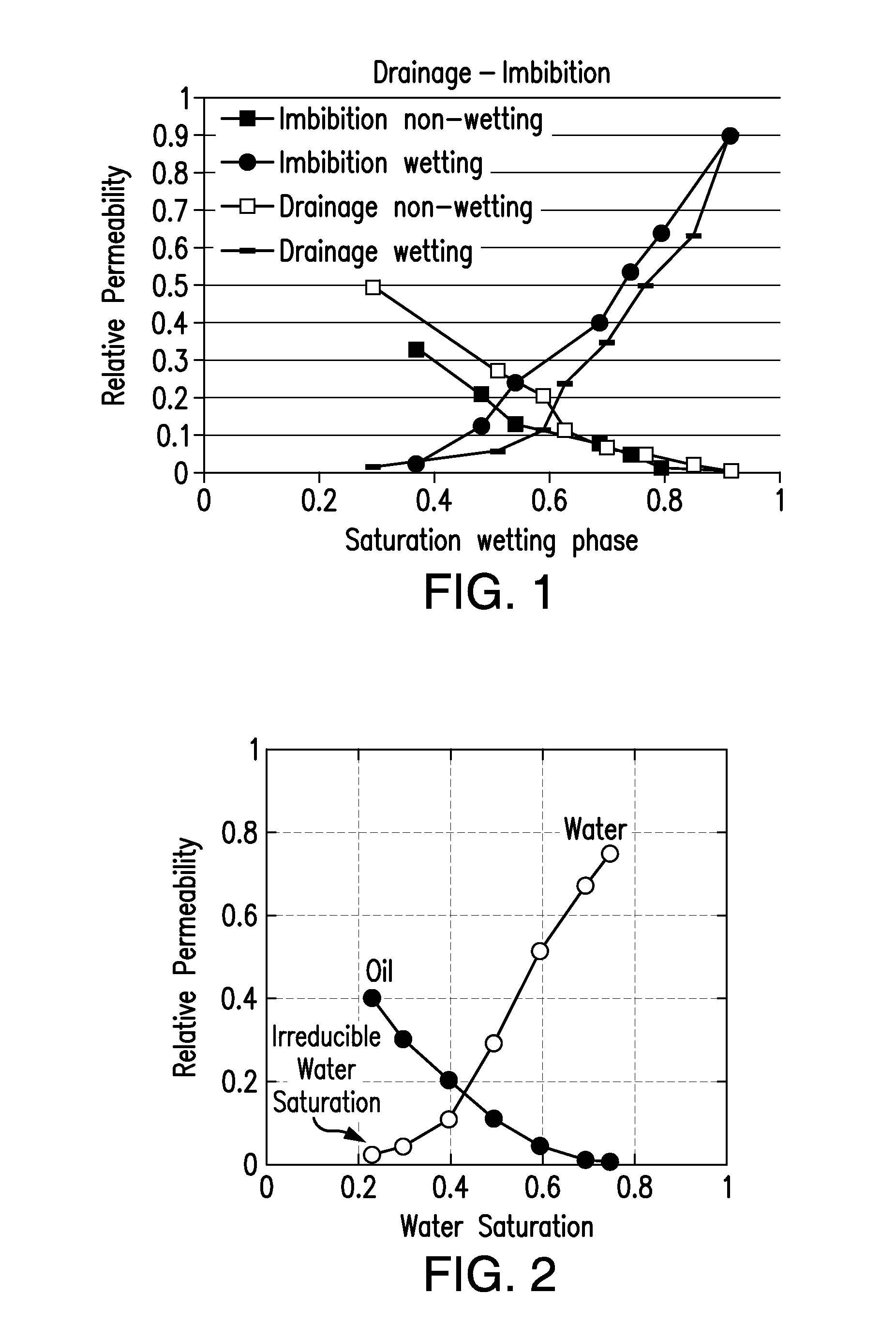
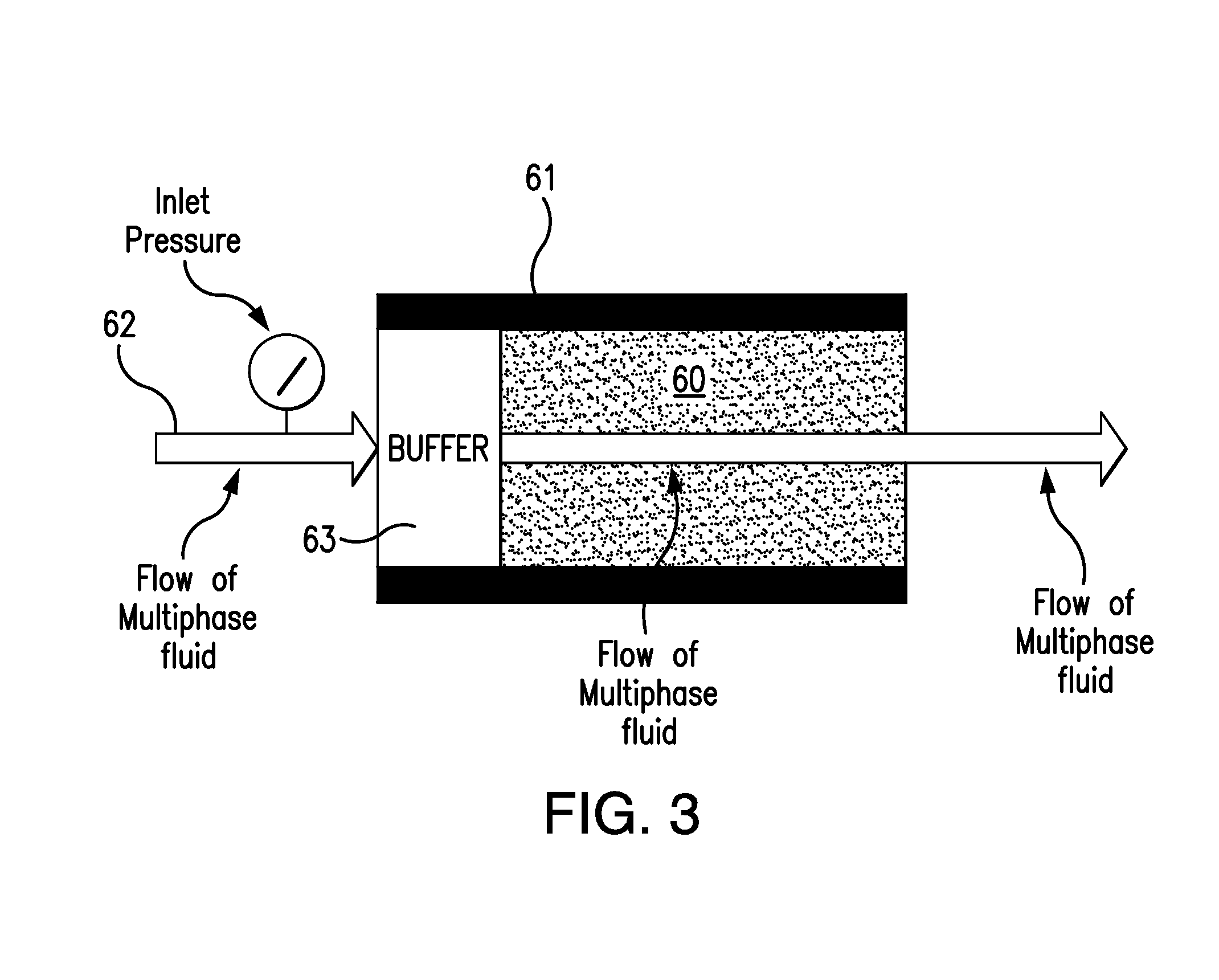
A method for computing or estimating fractional, multi-phase / multi-component flow through a porous medium employing a 3D digital representation of a porous medium and a computational fluid dynamics method to calculate flow rates, pressures, saturations, internal velocity vectors and other flow parameters is described. The method employs a unique method of introducing non-wetting and wetting fluids into the pores at the inlet face of the 3D digital representation of a porous medium and a novel process control application to achieve quasi-steady state flow at low inlet concentrations of non-wetting fluid. In addition, the method of the present invention reduces the time required to simulate to complete the fluid dynamic calculations. The resulting values of flow of non-wetting fluid, wetting fluid, saturation, and other parameters are used to generate plots of relative permeability imbibition and drainage curves. Computerized systems and programs for performing the method are also provided.
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
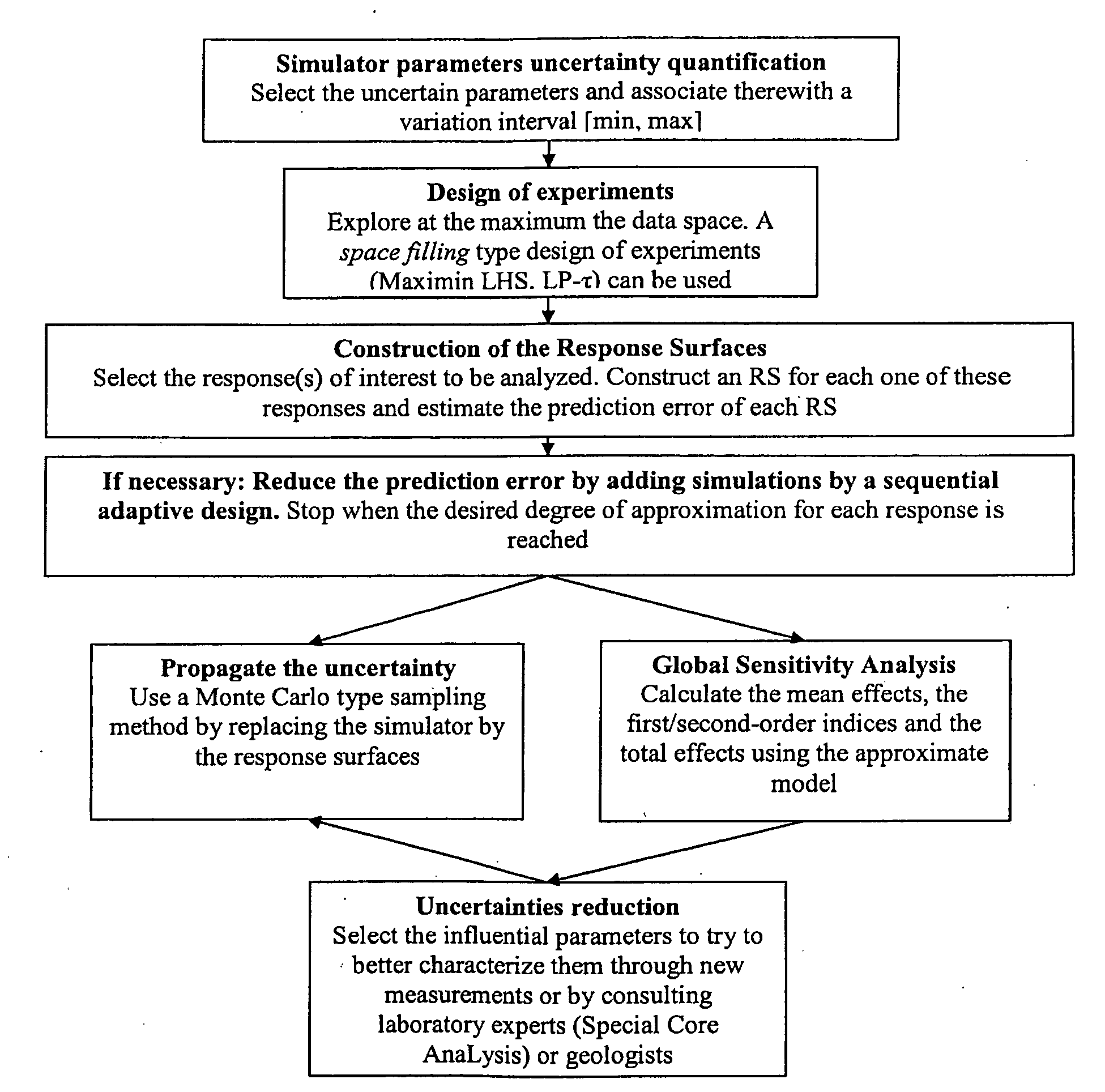
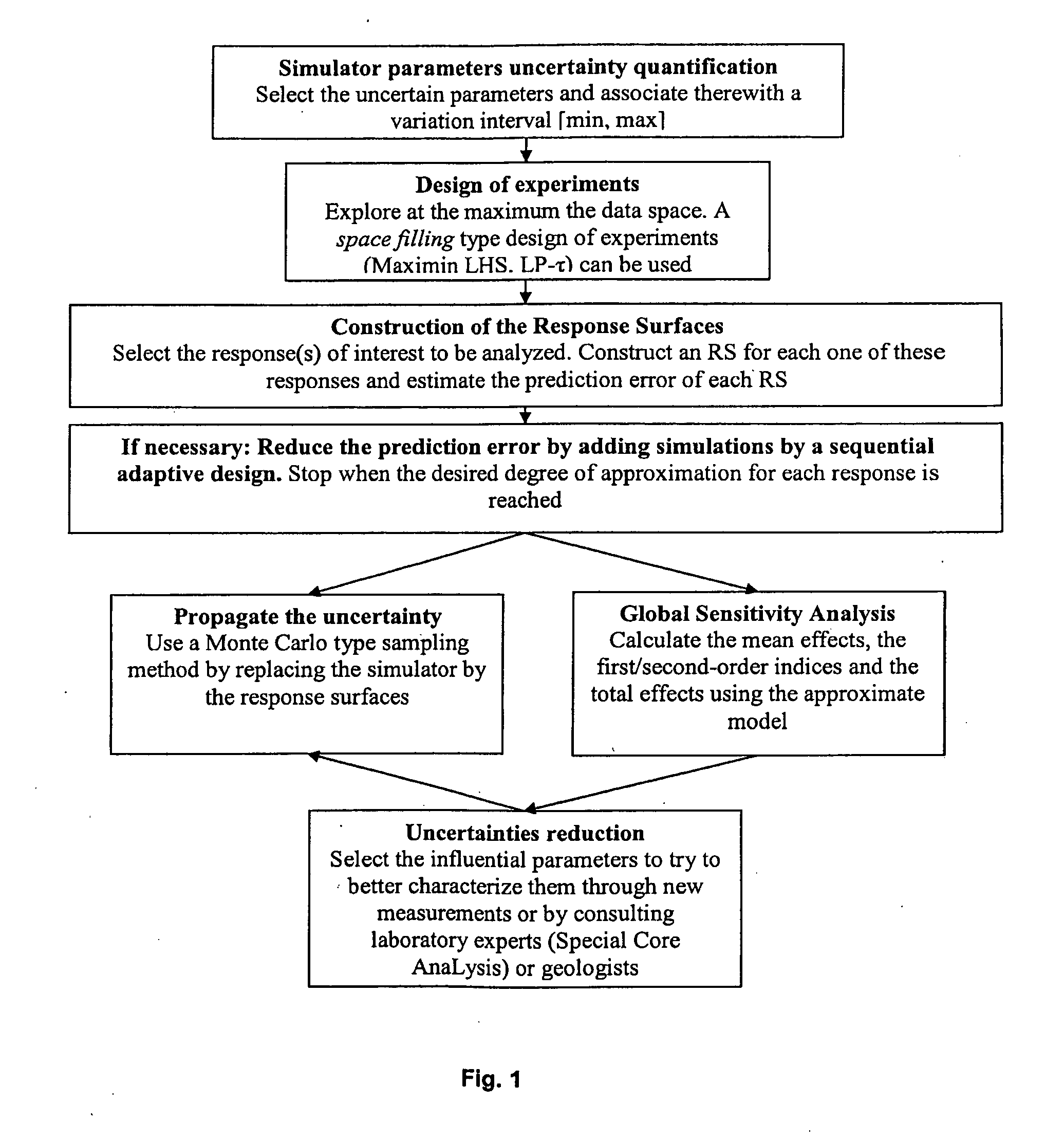
Method for Evaluating an Underground Reservoir Production Scheme Taking Account of Uncertainties
ActiveUS20090043555A1Reduce uncertaintyFluid removalComputation using non-denominational number representationComputational modelEngineering
Method for evaluating an underground reservoir production scheme taking account of uncertainties.Flow simulator input parameters characterizing the reservoir and the production scheme are selected. An approximate analytical model allowing the reservoir responses to be predicted is constructed. A desired degree of accuracy Dp is defined, this degree of accuracy Dp measuring the difference between the responses of the model and those of the simulator. The degree of accuracy Dp(M) of the predictions of the model is calculated. A design of experiments is constructed so as to select simulations to be performed, pertinent for adjustment of the model. The simulations selected by the design of experiments are carried out, then, for each response simulated by the simulator, the analytical model is adjusted by means of an approximation method. This operation is repeated until the desired degree of accuracy Dp is reached. Finally, the production scheme is evaluated by analyzing the reservoir responses predicted by the approximate analytical model.Application: notably to the development of petroleum reservoirs for example.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Using models for equilibrium distributions of asphaltenes in the prescence of gor gradients to determine sampling procedures
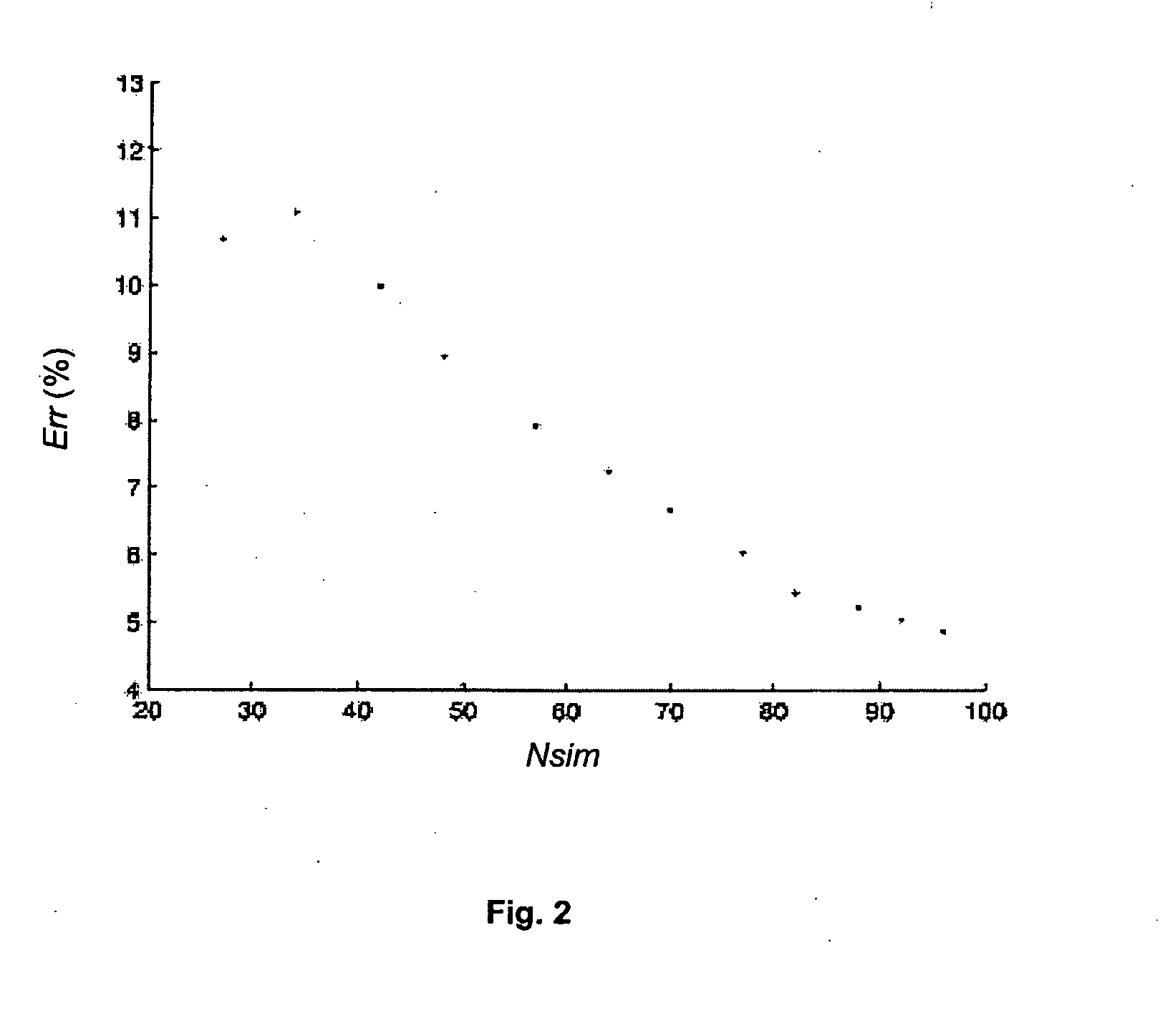
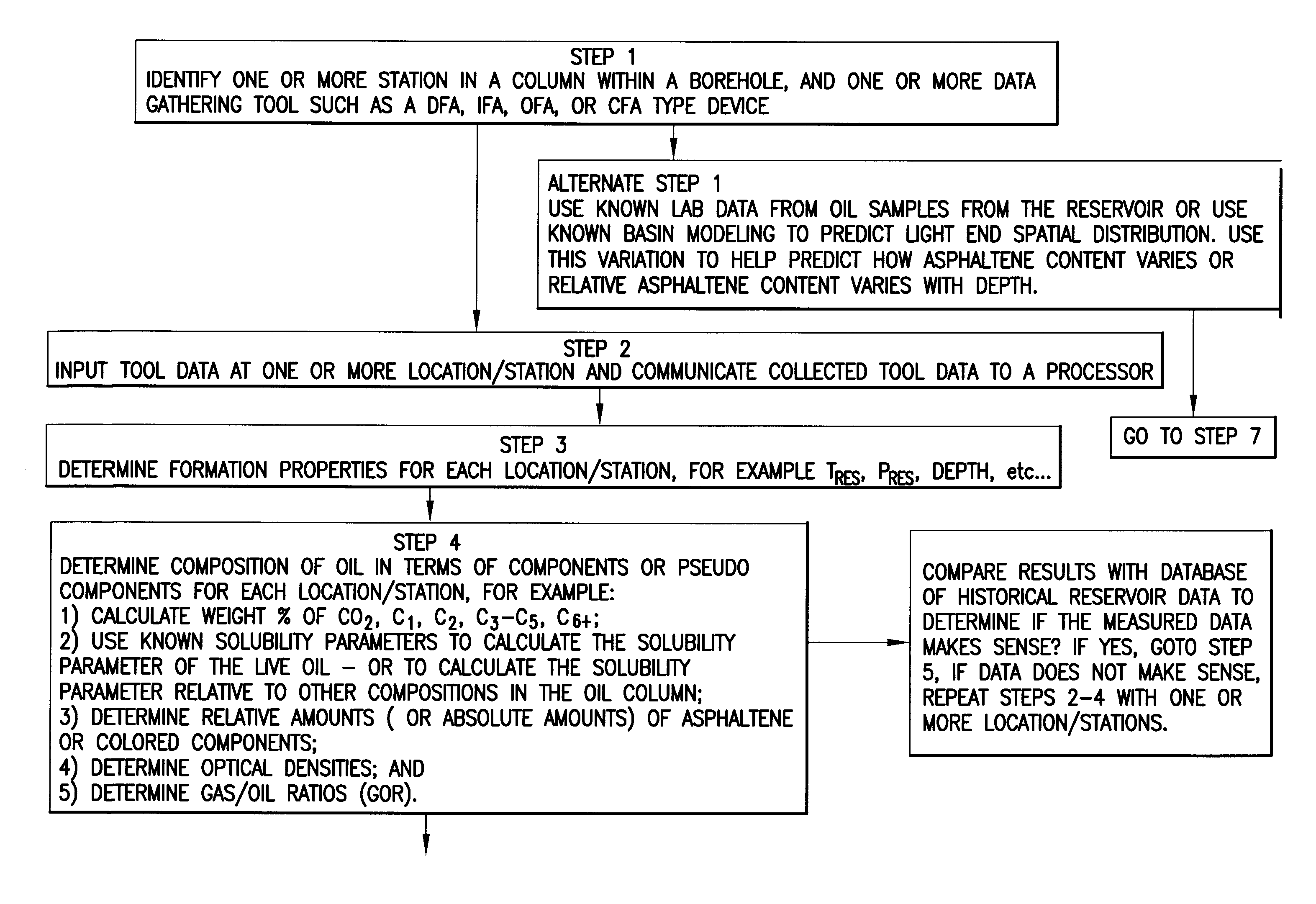
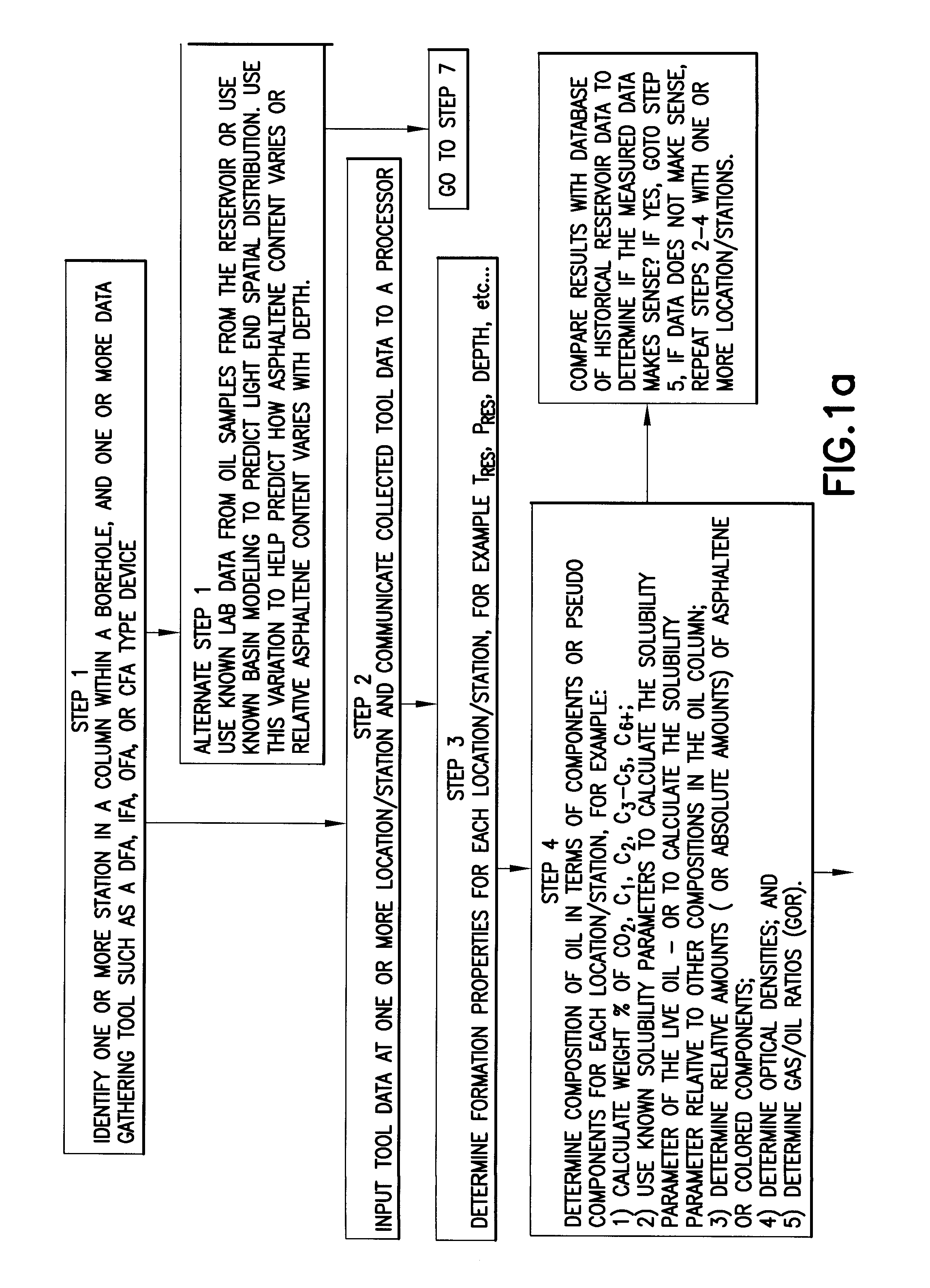
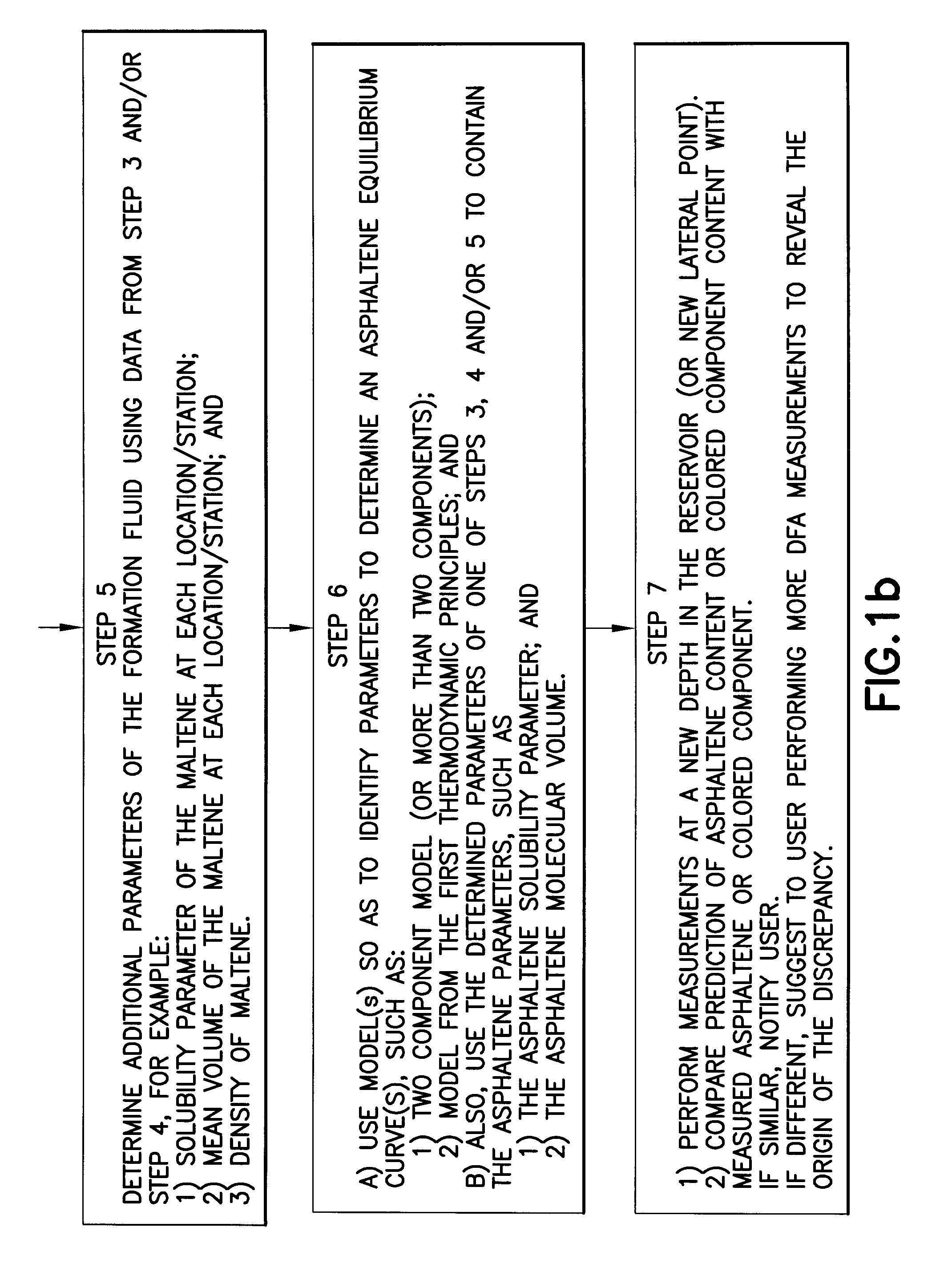
InactiveUS20090312997A1Computation using non-denominational number representationAnalogue computers for fluid flowMathematical modelAsphaltene
Methods and systems to characterize a fluid in a reservoir to determine if the fluid is in one of equilibrium or non-equilibrium in terms of one of gravity, solvency power, entropy effect or some combination thereof. The method includes acquiring tool data at each depth for each fluid sample of at least two fluid samples wherein each fluid sample is at a different depth and communicating the tool data to a processor. Determining formation properties of each fluid sample to obtain formation property data and determining fluid properties for each fluid sample to obtain fluid property data. Selecting a mathematical model based on one of gravity, solvency power or entropy, in view of a fluid property, using one of tool data, formation property data, fluid property data, known fluid reservoir data or some combination thereof, to predict if the fluid is in an equilibrium distribution or a non-equilibrium distribution.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Method for updating a geological model using dynamic data and well tests
Method for optimizing the development of an underground reservoir, wherein a geological model is updated using dynamic data and well tests.A reservoir model is constructed by performing a geological model scale change. Dynamic data are simulated from this reservoir model. Influence zones are identified within the geological model where the well tests induce a pressure variation during well testing. Well tests are then simulated for each influence zone. An objective function measuring the difference between the simulated data and the measured data is calculated. The geological model is then modified so as to reduce to the maximum the objective function using a geostatistical parametrizing technique. Finally, development of the underground reservoir is optimized by evaluating, by means of a flow simulator, the reservoir production for various production schemes.Application: notably oil reservoir development.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Method for constituting a model representative of multiphase flows in oil production pipes
InactiveUS6028992ASurveyComputation using non-denominational number representationMomentumEngineering
The invention provides a model representative of steady and transient flows, in a pipe, of a mixture of multiphase fluids, which takes account a set of variables defining the properties of the fluids and of the flow modes having separate phases which are dispersed and intermittent, and the dimensions and slope of the pipes. The modeled quantities characterizing the flow are determined by solving a set of transport equations, an equation of mass conservation per constituent and an equation of momentum of the mixture, and by using a hydrodynamic model and a hydrodynamic model of the fluids. The models are formed by considering the mixture to be substantially at equilibrium at all times and that the constituents of the multiphase mixture are variable all along the pipe. The method can be applied to hydrocarbon transportation network study and to determination of characteristics of flow of the multiphase mixture in the pipe.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
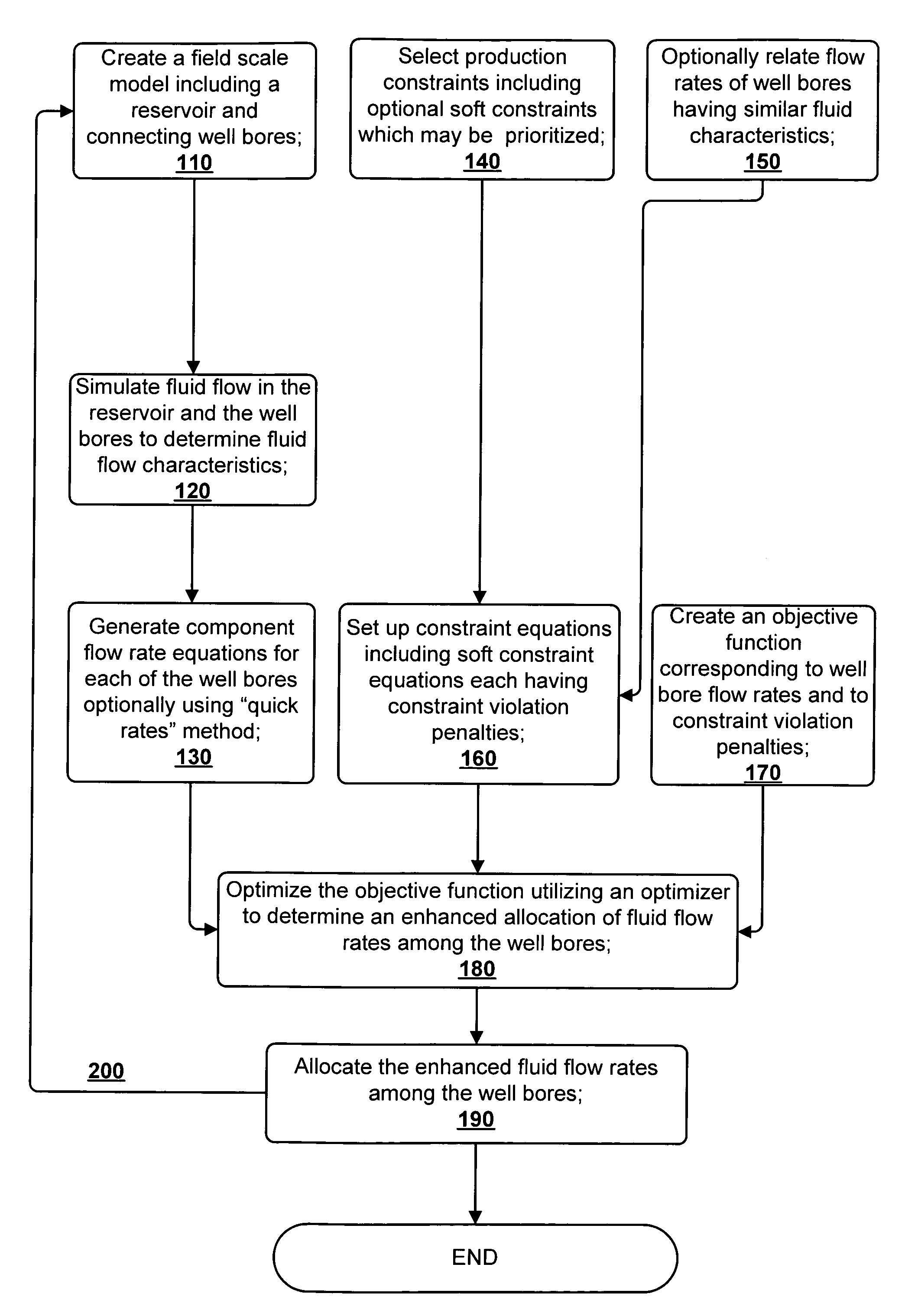
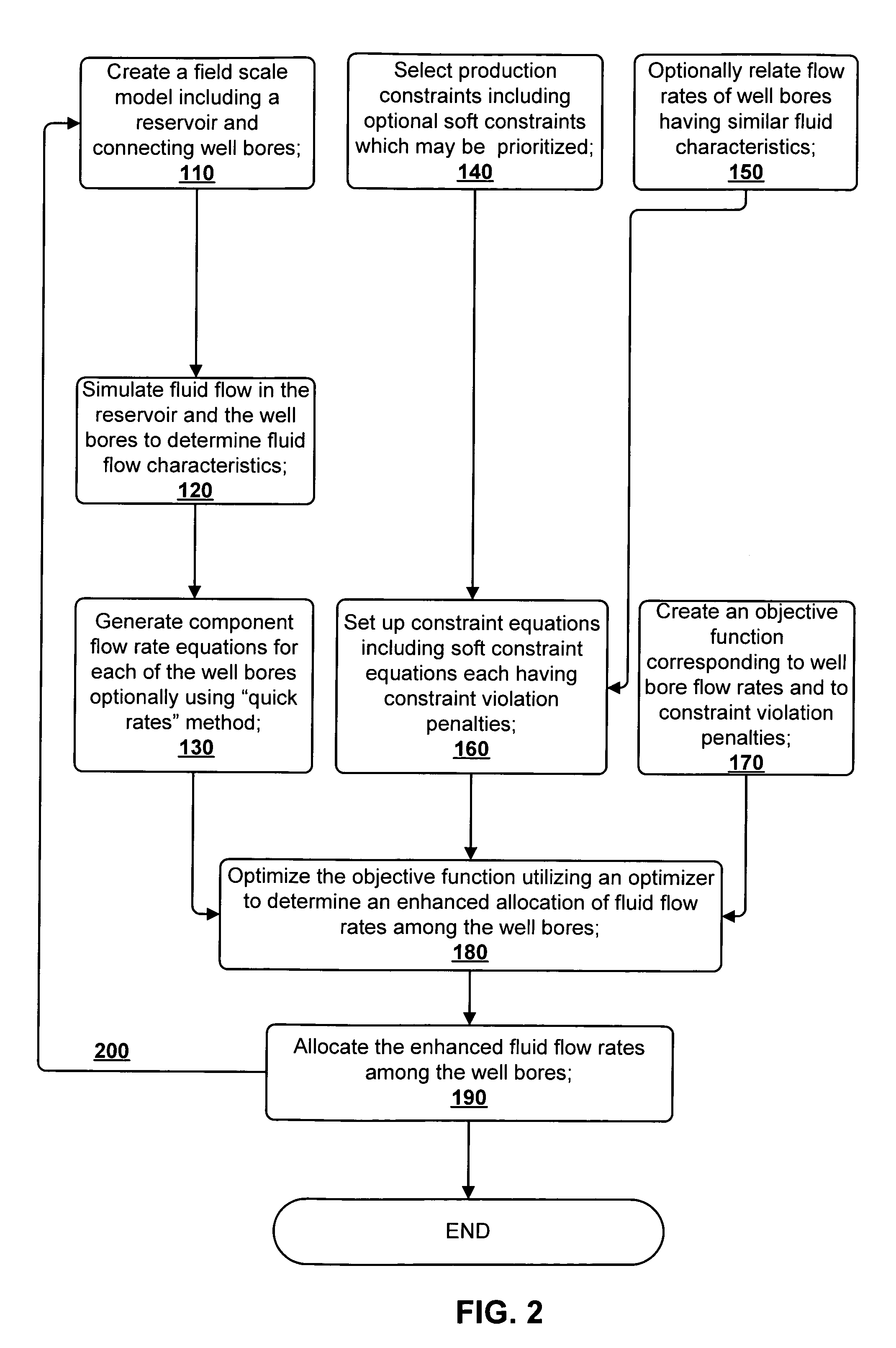
Method for field scale production optimization by enhancing the allocation of well flow rates
ActiveUS7627461B2Control flowFluid removalAnalogue computers for fluid flowProduction optimizationObject function
A method for enhancing the allocation of fluid flow rates among a plurality of well bores in fluid communication with at least one subterranean reservoir is disclosed. An objective function and system equations are generated which utilize constraint violation penalties associated with soft constraints. The soft constraints are constraints which may be violated if necessary to arrive at a feasible solution to optimizing the objective function and the system equations. The fluid flow rates are then allocated among the well bores as determined by the optimizing of the objective function and system equations. Fluid flow rates among well bores, particularly those exhibiting similar fluid characteristics, may be related to one another. Initial flow rates of components (oil, gas, and water) and pressures in the well bores may be determined by an initial simulation run. Then additional component flow rates may be estimated by scaling the original component flow rates based upon changing pressure draw downs in the well bores.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
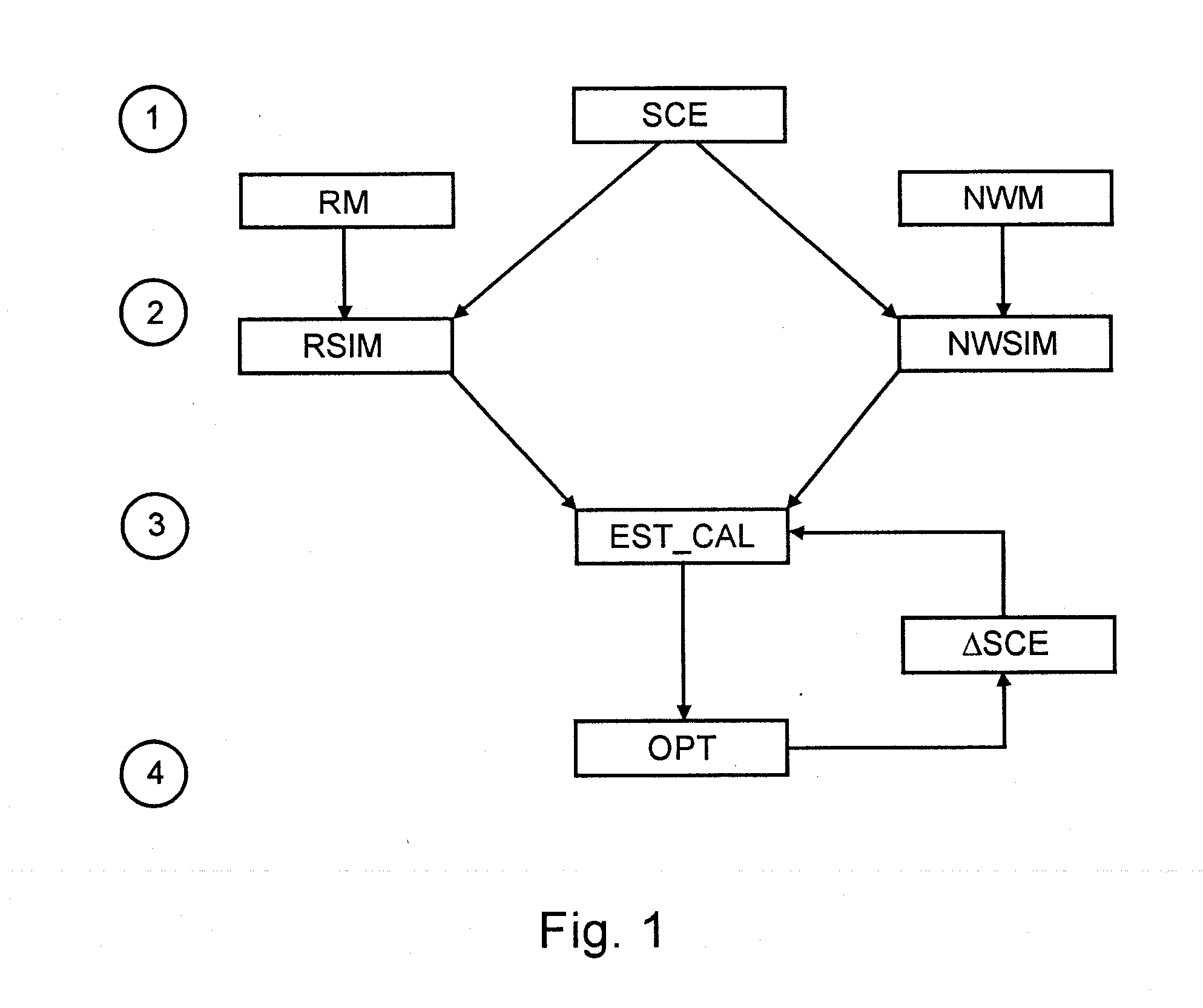
Porous medium exploitation method using fluid flow modelling
InactiveUS20100299125A1Improvement of injectivityIncrease productivityFluid removalAnalogue computers for fluid flowProduction ratePorous medium
Porous A porous medium exploitation method having application to petroleum exploitation is disclosed using coupling between a reservoir model and a near-wellbore model for modelling fluid flows. Fluid flows within the medium are simulated using a reservoir simulator and a near-wellbore simulator. At each time step, the boundary conditions used by the second simulator are calculated by means of with the reservoir simulator. Numerical productivity indices used by the reservoir simulator are calculated by means of using the near-wellbore simulator. The fluid flows within the porous medium during a given period of time are modelled by repeating the previous stages for several time steps. An optimum medium exploitation scenario is deduced determined from this modelling by taking into accounting for, for example, a well damage due to a drilling fluid, an injection of a polymer solution or of an acid solution in the well.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Modeling the transient behavior of bha/drill string while drilling
A method, system and computer program product for performing a drilling operation for an oil field, the oil field having a subterranean formation with geological structures and reservoirs therein. The method involves creating a finite-difference model to simulate behavior of a drilling assembly used to drill a wellbore in the drilling operation, performing a simulation of the drilling operation using the finite-difference model, analyzing a result of the simulation, and selectively modifying the drilling operation based on the analysis.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
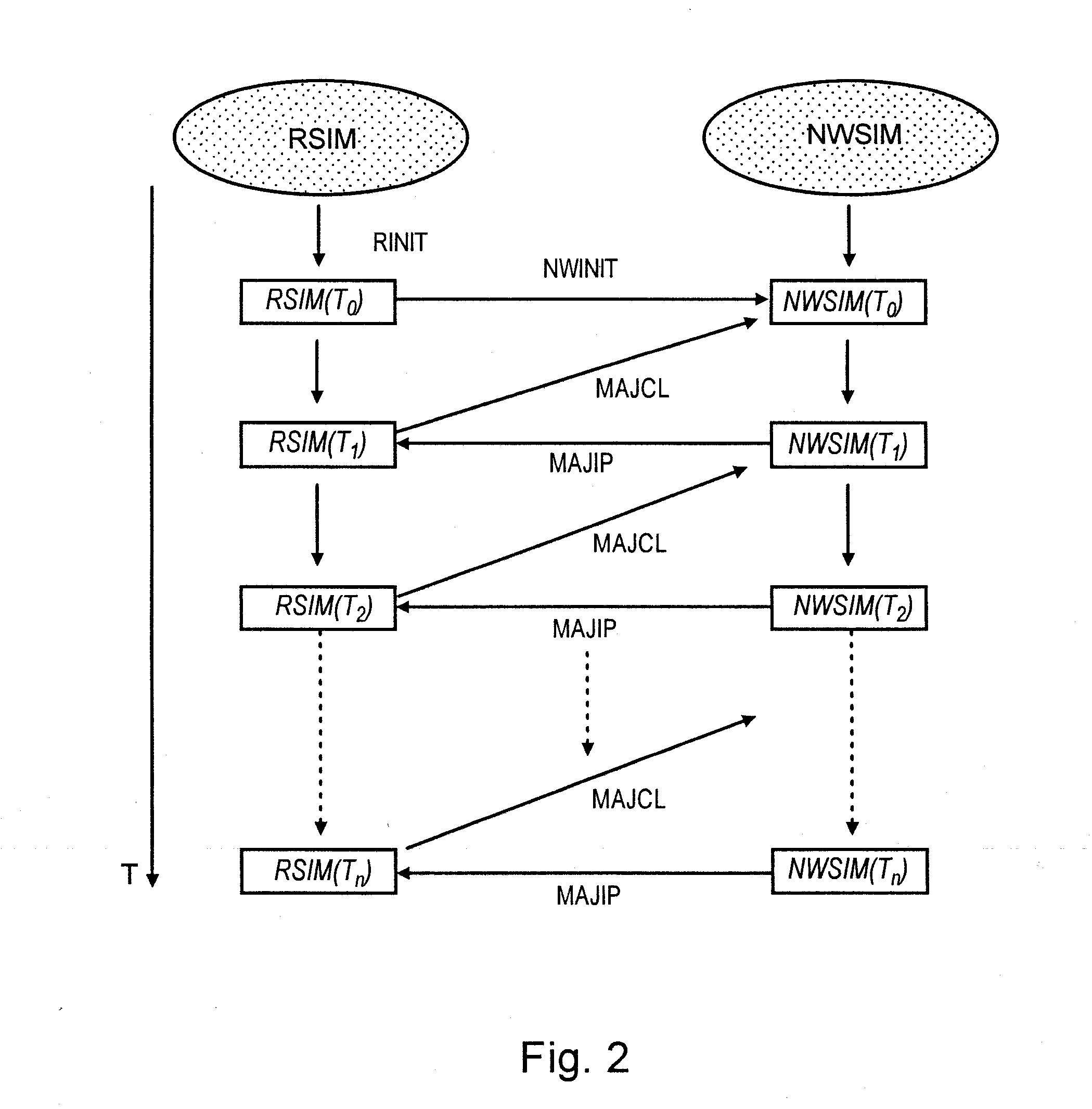
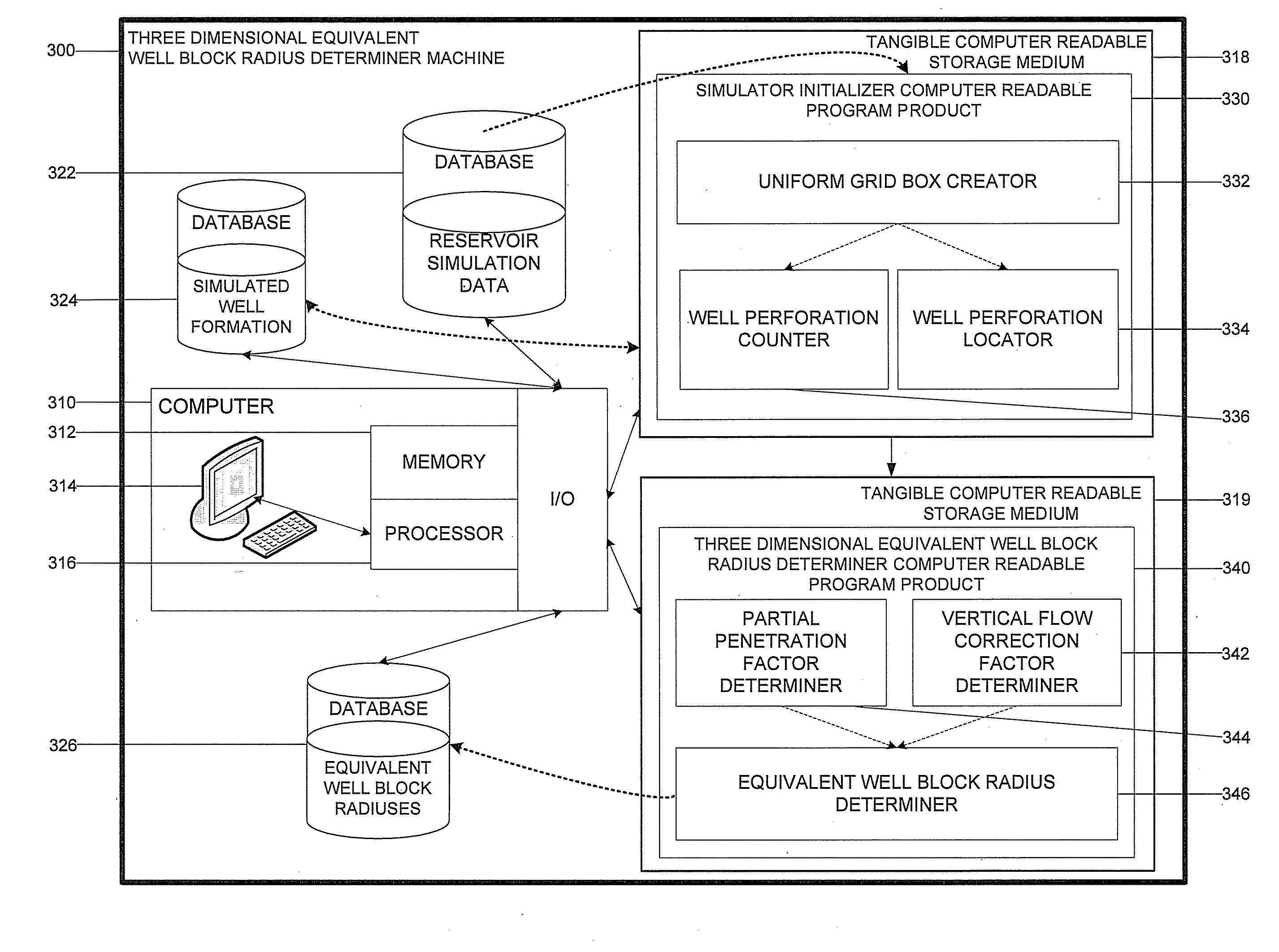
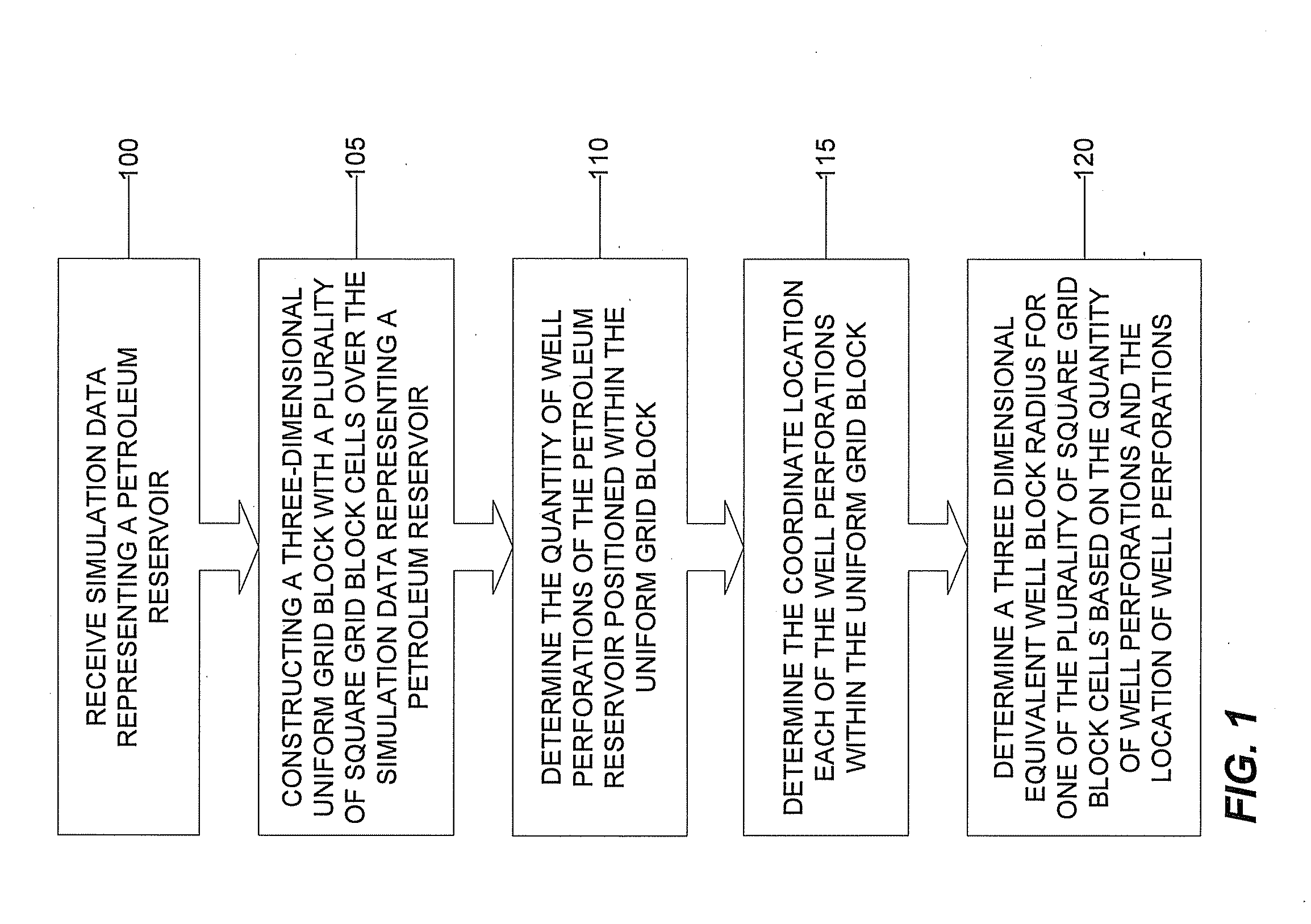
Three Dimensional Well Block Radius Determiner Machine And Related Computer Implemented Methods And Program Products
ActiveUS20100114544A1Improve accuracyLow costAnalogue computers for fluid flowGeological measurementsParallel computingPetroleum reservoir
Three dimensional well block radius determiner machines, systems, program products, and computer implemented methods are provided to determine a three dimensional equivalent well block radius of a perforated grid block cell, with three dimensional flow, of a three dimensional coordinate grid block constructed over a three dimensional simulated well formation in a finite difference petroleum reservoir simulator. Various embodiments of the invention, for example, can beneficially account for both horizontal and vertical flow of oil through a well perforation without the need for complicated, expensive, and time-consuming numerical or iterative solutions. Embodiments of the present invention, for example, can be used as a part of legacy simulators thereby providing more accurate well block radius calculations, by accounting for both horizontal and vertical perforation flow, without introducing significant implementation hurdles, development costs, or simulation runtime delays.
Owner:SAUDI ARABIAN OIL CO
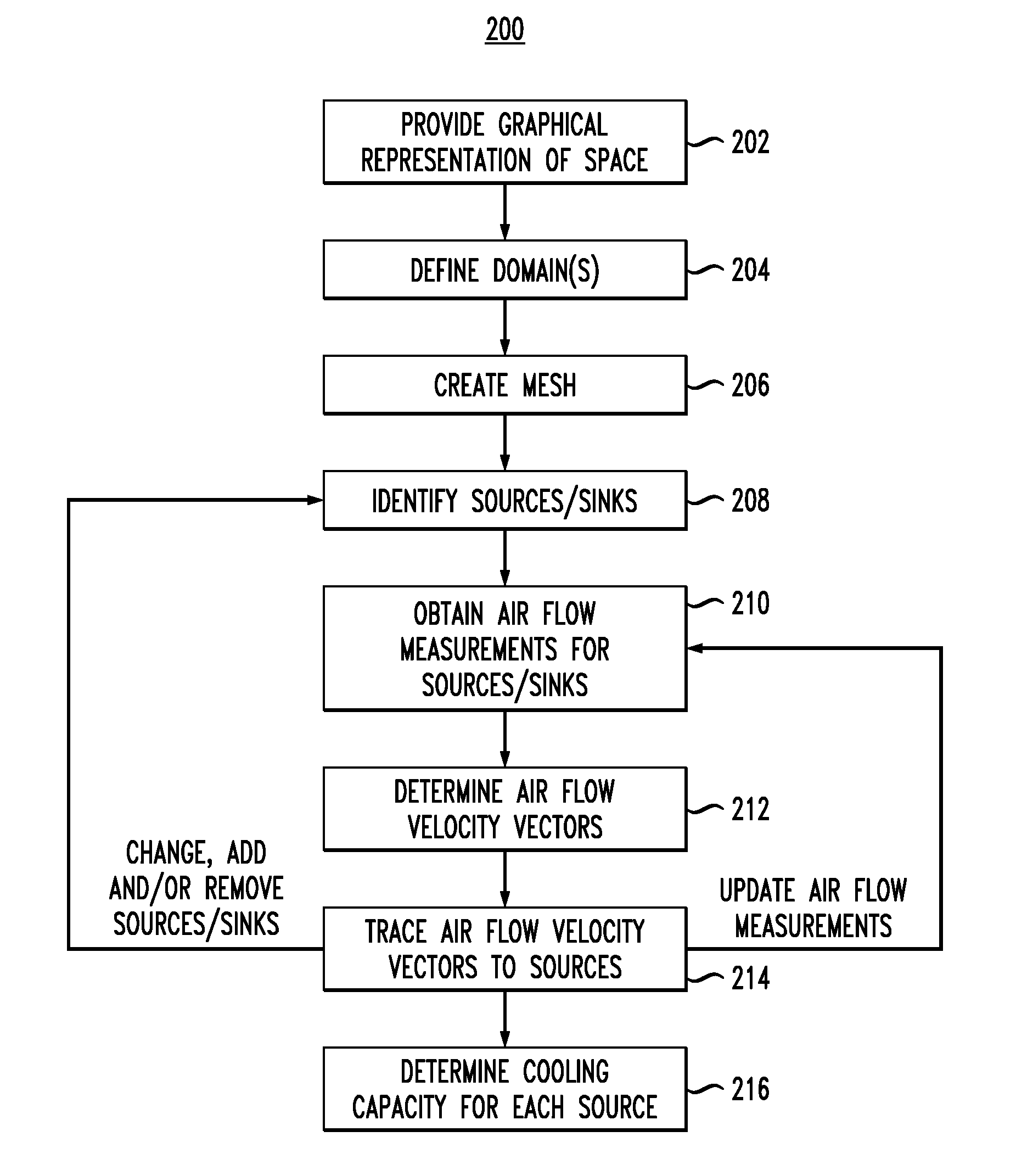
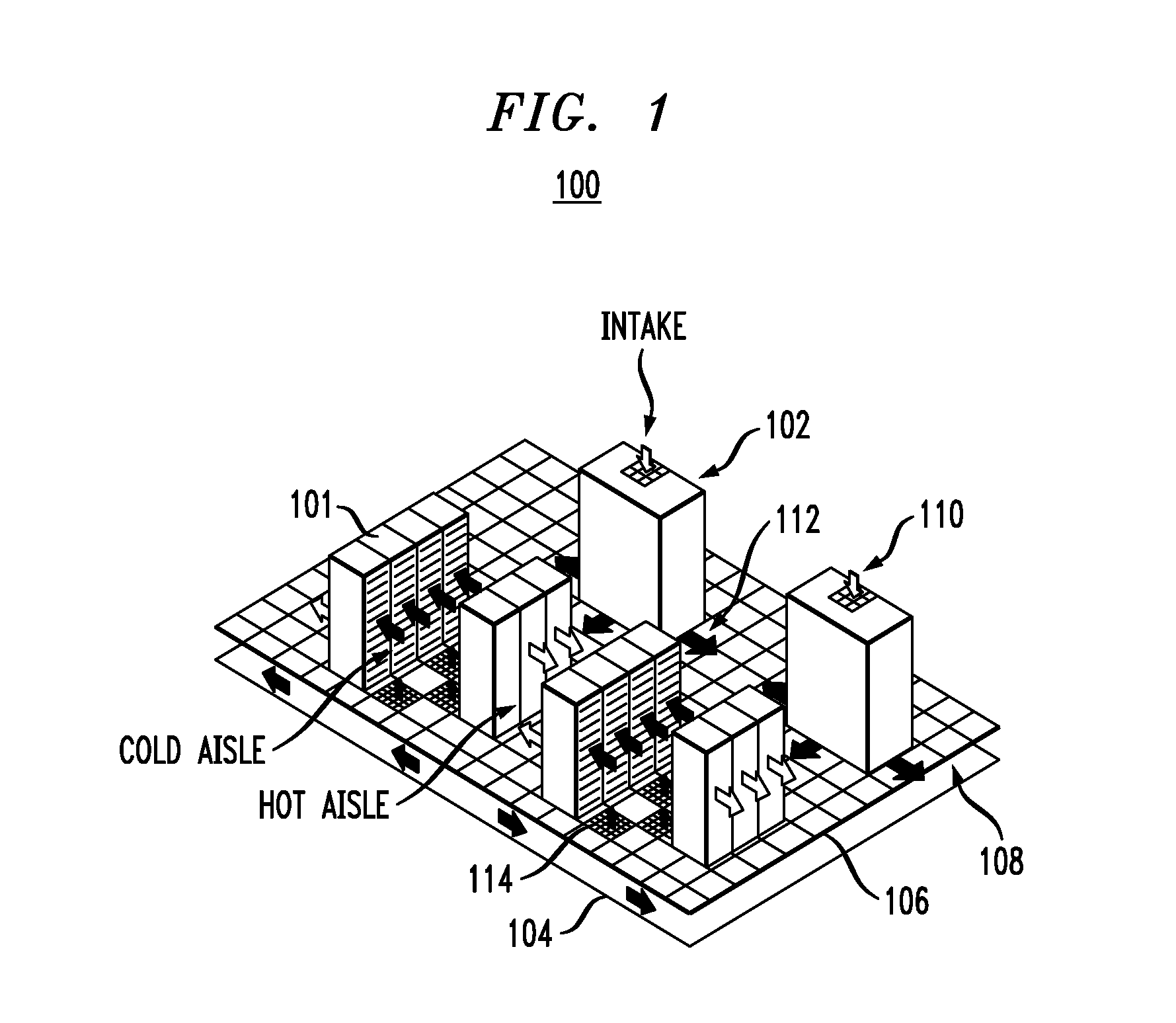
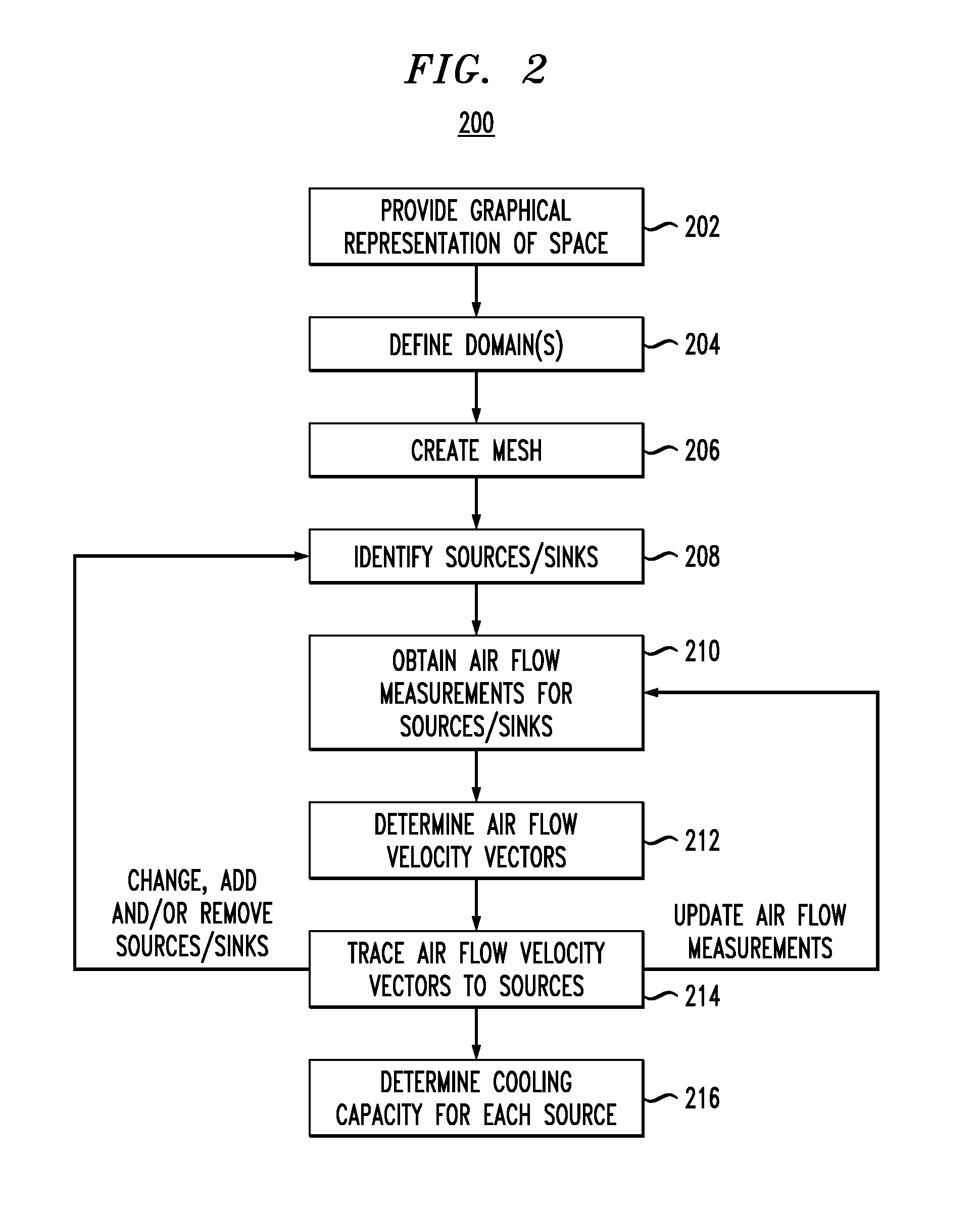
Methods and Techniques for Creating and Visualizing Thermal Zones
Techniques for using air flow analysis to model thermal zones are provided. In one aspect, a method for modeling thermal zones in a space, e.g., in a data center, includes the following steps. A graphical representation of the space is provided. At least one domain is defined in the space for modeling. A mesh is created in the domain by sub-dividing the domain into a set of discrete sub-domains that interconnect a plurality of nodes. Air flow sources and sinks are identified in the domain. Air flow measurements are obtained from one or more of the air flow sources and sinks. An air flow velocity vector at a center of each sub-domain is determined using the air flow measurements obtained from the air flow sources and sinks. Each velocity vector is traced to one of the air flow sources, wherein a combination of the traces to a given one of the air flow sources represents a thermal zone in the space.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method to improve reservoir simulation and recovery from fractured reservoirs
A method for modeling flow properties over a series of time increments of a reservoir in an earth formation having a plurality of fractures is disclosed. The method includes: building a three-dimensional stress field representing stresses in the reservoir; building a three-dimensional discrete fracture network (NFM) having fracture flow properties using information obtained from a tool or changes to the stress field; running a flow simulation of the reservoir for a time increment using the NFM to model the flow properties of the reservoir for that time increment; computing a latest change in the three-dimensional stress field from the flow simulation; and incrementing the time increment and iterating the building the NFM using the latest change in the stress field, the running of the flow simulation using the latest NFM, and the computing a latest change in the stress field from the latest running of the flow simulation.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for characterizing the fracture network of a fractured reservoir and method for developing it
ActiveUS20120116740A1Minimize the differenceFluid removalAnalogue computers for fluid flowGeomorphologyEllipse
The invention is a method for constructing a representation of a fluid reservoir traversed by a fracture network and by at least one well. The reservoir is discretized into a set of grid cells and the fractures are characterized by statistical parameters from observations of the reservoir. An equivalent permeability tensor and an average fracture opening is constructed from an image representative of the fracture network delimiting porous blocks and fractures is then deduced from the statistical parameters. A first elliptical boundary zone centered on the well and at least a second elliptical boundary zone centered on the well which form an elliptical ring with the elliptical boundary of the first zone are defined around the well. The image representative of the fracture network is simplified in a different manner for each of the zones which is used to construct the representation of the fluid reservoir.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Space-Time Surrogate Models of Subterranean Regions
Methods for creating and using space-time surrogate models of subsurface regions, such as subsurface regions containing at least one hydrocarbon formation. The created surrogate models are explicit models that may be created from implicit models, such as computationally intensive full-physics models. The space-time surrogate models are parametric with respect to preselected variables, such as space, state, and / or design variables, while also indicating responsiveness of the preselected variables with respect to time. In some embodiments, the space-time surrogate model may be parametric with respect to preselected variables as well as to time. Methods for updating and evolving models of subsurface regions are also disclosed.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Method For Prediction In An Oil/Gas Production System
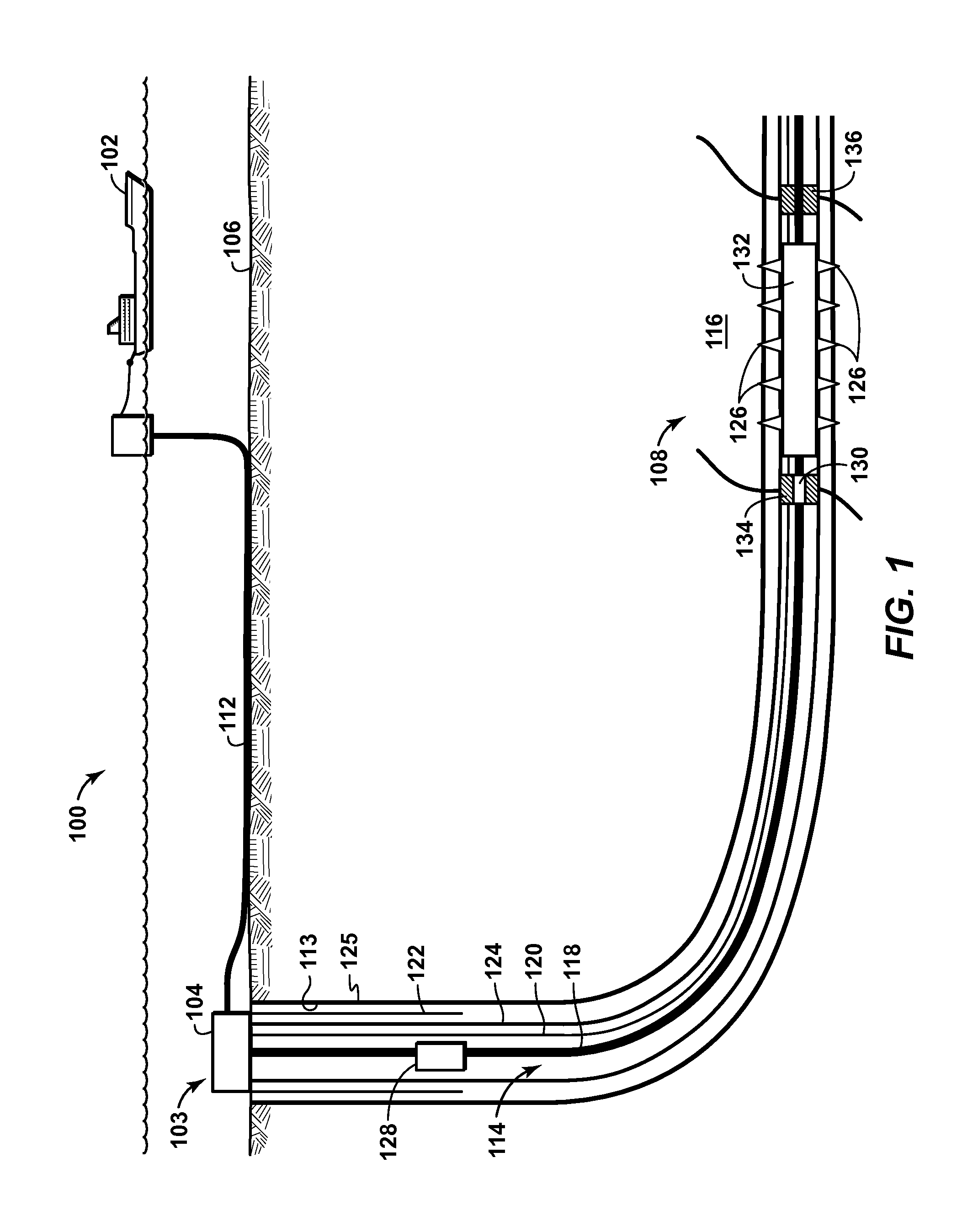
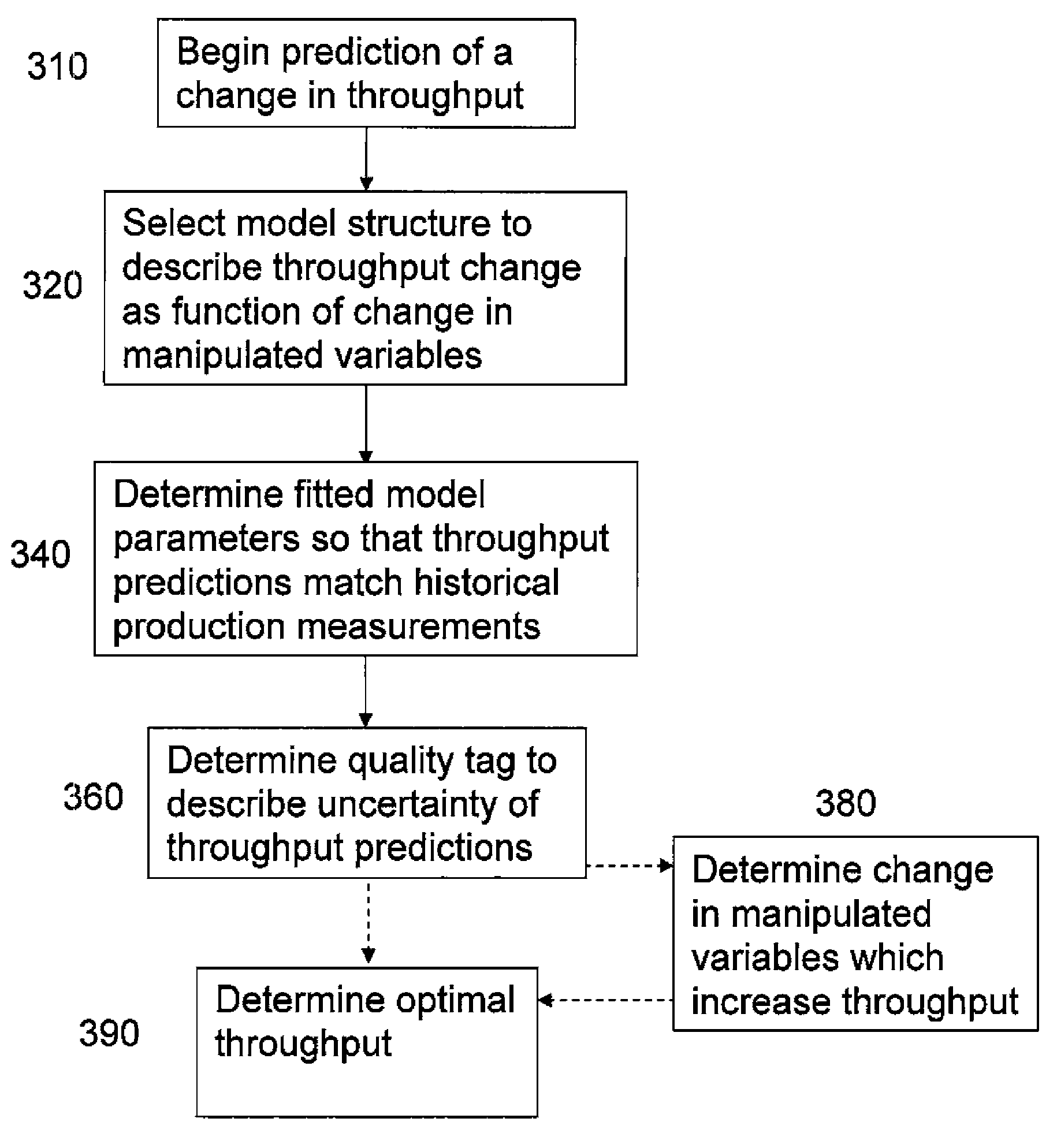
InactiveUS20100174517A1Reduce uncertaintyEasy maintenanceVolume/mass flow measurementFluid removalModel parametersProduct gas
Method in an oil and / or a gas production system including a plurality of oil and / or gas wells each producing a multiphase fluid stream, adapted for predicting change in produced fluids resulting from change in manipulated variables. Fitted model parameters which express the relationship between the change in manipulated variables and the produced fluids are determined from a set of historical production measurements. The method includes the steps of choosing a model structure which predicts change in produced fluids as a function of the change in manipulated variables, where the predicted change in produced fluids depends on the value of fitted model parameters, determining fitted model parameters so that predictions of produced fluids match said historical production measurements as closely as possible, and determining a quality tag that describes the uncertainty of the predictions of change in produced fluids.
Owner:ABB AS
Method For Geologic Modeling Through Hydrodynamics-Based Gridding (Hydro-Grids)
ActiveUS20090248378A1Accurately characterize sedimentary connectivityMaintain accuracyElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingSimulation basedSediment
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
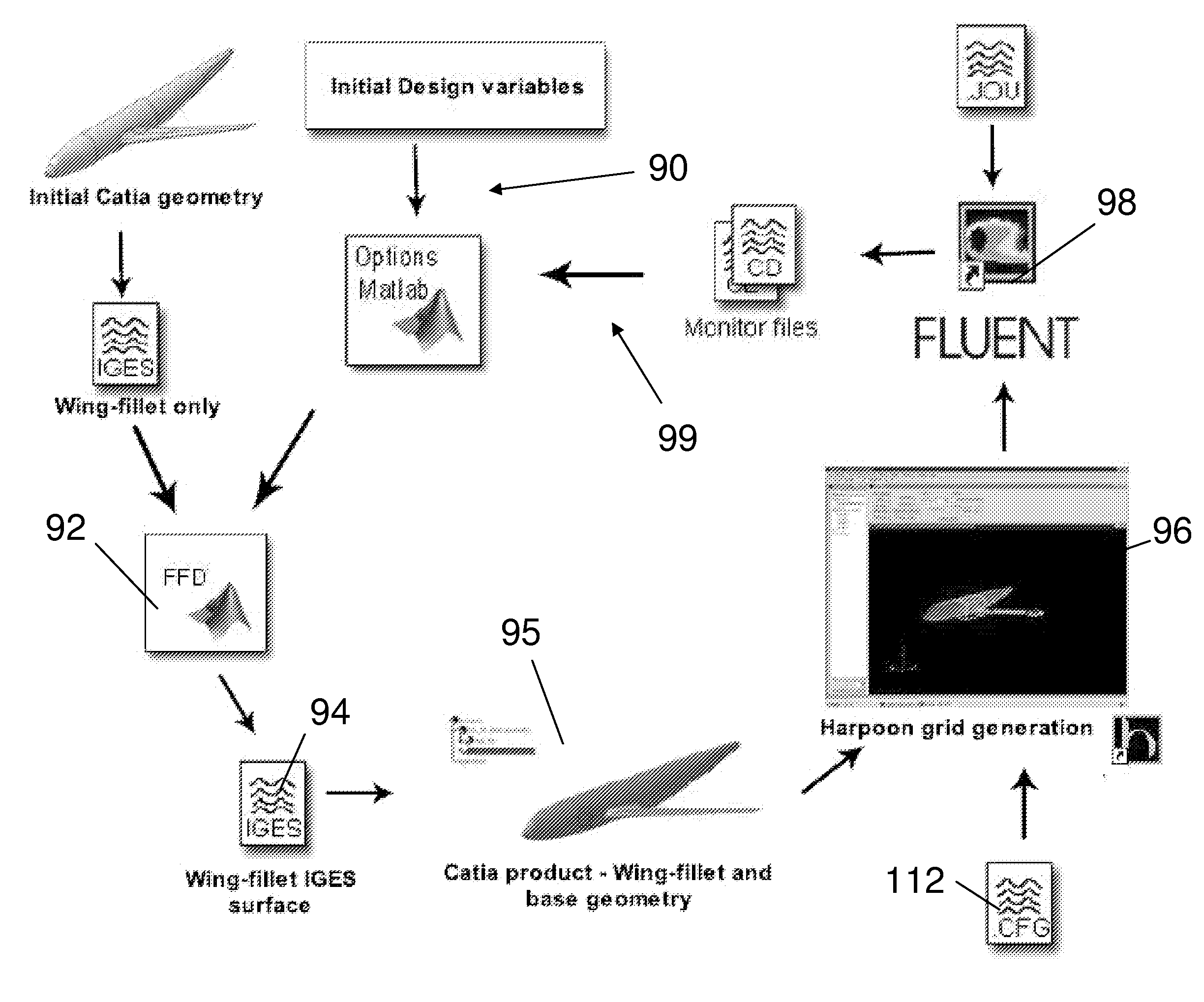
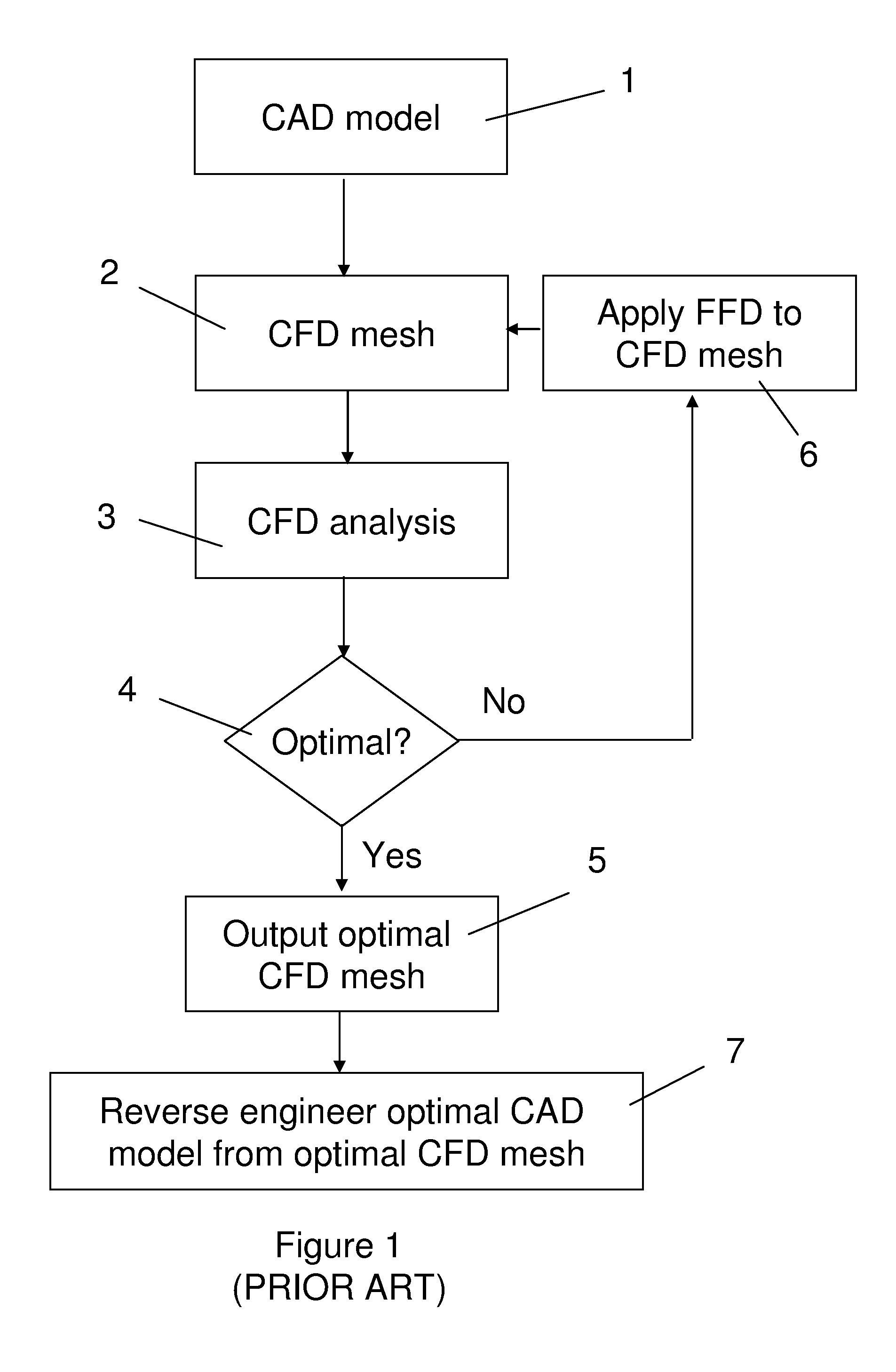
Method of design optimisation
A method of design optimization includes: a) producing a first computer model of a first geometry, the first computer model including: i) a set of nodes; and ii) a set of construction points each having a position defined by a local co-ordinate system; b) producing a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) mesh from the first computer model; c) using the CFD mesh to produce a measure of the fluid dynamic performance of the first geometry, such as drag count or lift coefficient; d) producing a new computer model of a new geometry by: i) moving one or more of the nodes; and ii) recalculating the positions of the construction points in response to movement of the one or more nodes; e) producing a computational fluid dynamics (CFD) mesh from the new computer model; f) using the CFD mesh to produce a measure of the fluid dynamic performance of the new geometry, such as drag count or lift coefficient; and g) identifying an optimal geometry using the fluid dynamic performance measurements of the first and new geometries produced in steps c and f.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS LTD
Method of modified facies proportions upon history matching of a geological model
A method of modifying a geological model representative of an underground reservoir is disclosed which respects average proportions of the lithologic facies imposed by a production data calibration process which has application to petroleum reservoir development. A geographical zone Z is defined within the geological model and an average proportion in zone Z allowing the production data to be calibrated is determined for k facies, with an optimization process. The proportions of these facies are modified using a block indicator cokriging method constrained by the average proportions to be respected. A new geological model constrained by the modified facies proportions is simulated and the development of the underground medium is optimized by the simulated model.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
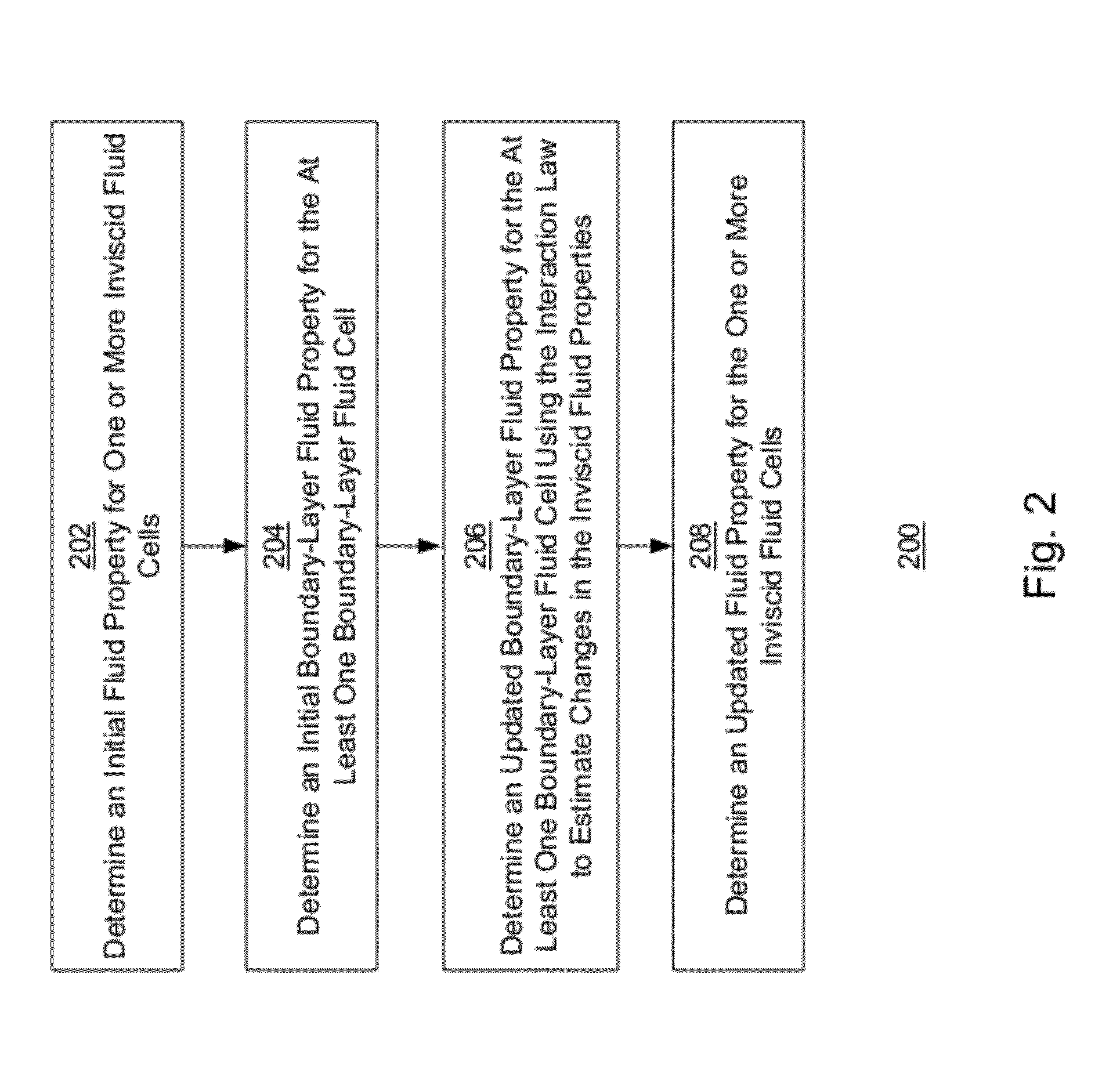
Generating inviscid and viscous fluid flow simulations over a surface using a quasi-simultaneous technique
ActiveUS20120245903A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationViscous effectLaws of thermodynamics
A fluid-flow simulation over a computer-generated surface is generated using a quasi-simultaneous technique. The simulation includes a fluid-flow mesh of inviscid and boundary-layer fluid cells. An initial fluid property for an inviscid fluid cell is determined using an inviscid fluid simulation that does not simulate fluid viscous effects. An initial boundary-layer fluid property a boundary-layer fluid cell is determined using the initial fluid property and a viscous fluid simulation that simulates fluid viscous effects. An updated boundary-layer fluid property is determined for the boundary-layer fluid cell using the initial fluid property, initial boundary-layer fluid property, and an interaction law. The interaction law approximates the inviscid fluid simulation using a matrix of aerodynamic influence coefficients computed using a two-dimensional surface panel technique and a fluid-property vector. An updated fluid property is determined for the inviscid fluid cell using the updated boundary-layer fluid property.
Owner:AERION INTPROP MANAGEMENT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com