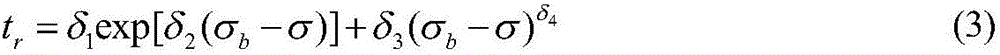Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
330 results about "Laws of thermodynamics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The three laws of thermodynamics define physical quantities (temperature, energy, and entropy) that characterize thermodynamic systems at thermal equilibrium. The laws describe how these quantities behave under various circumstances, and preclude the possibility of certain phenomena (such as perpetual motion).
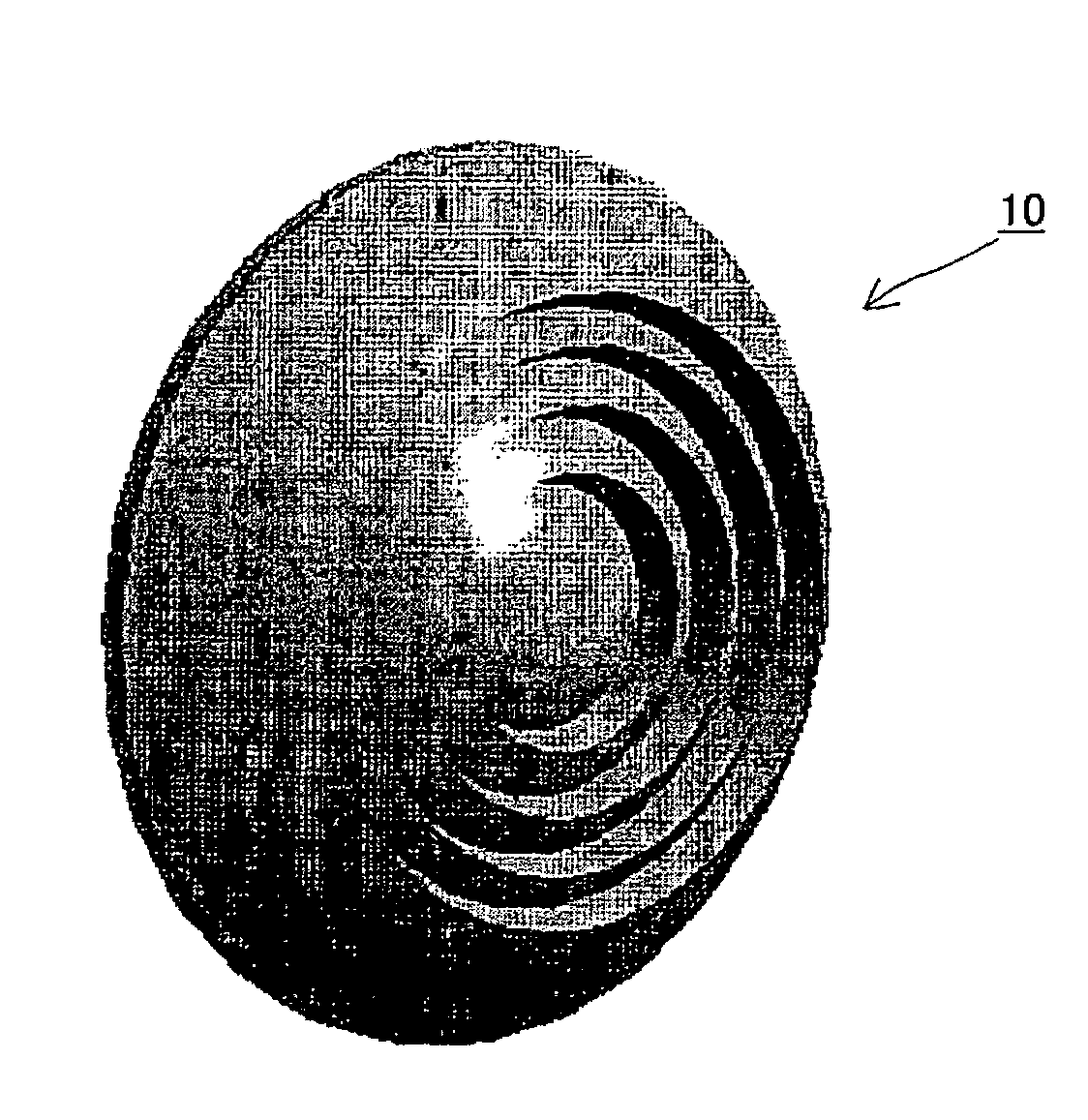
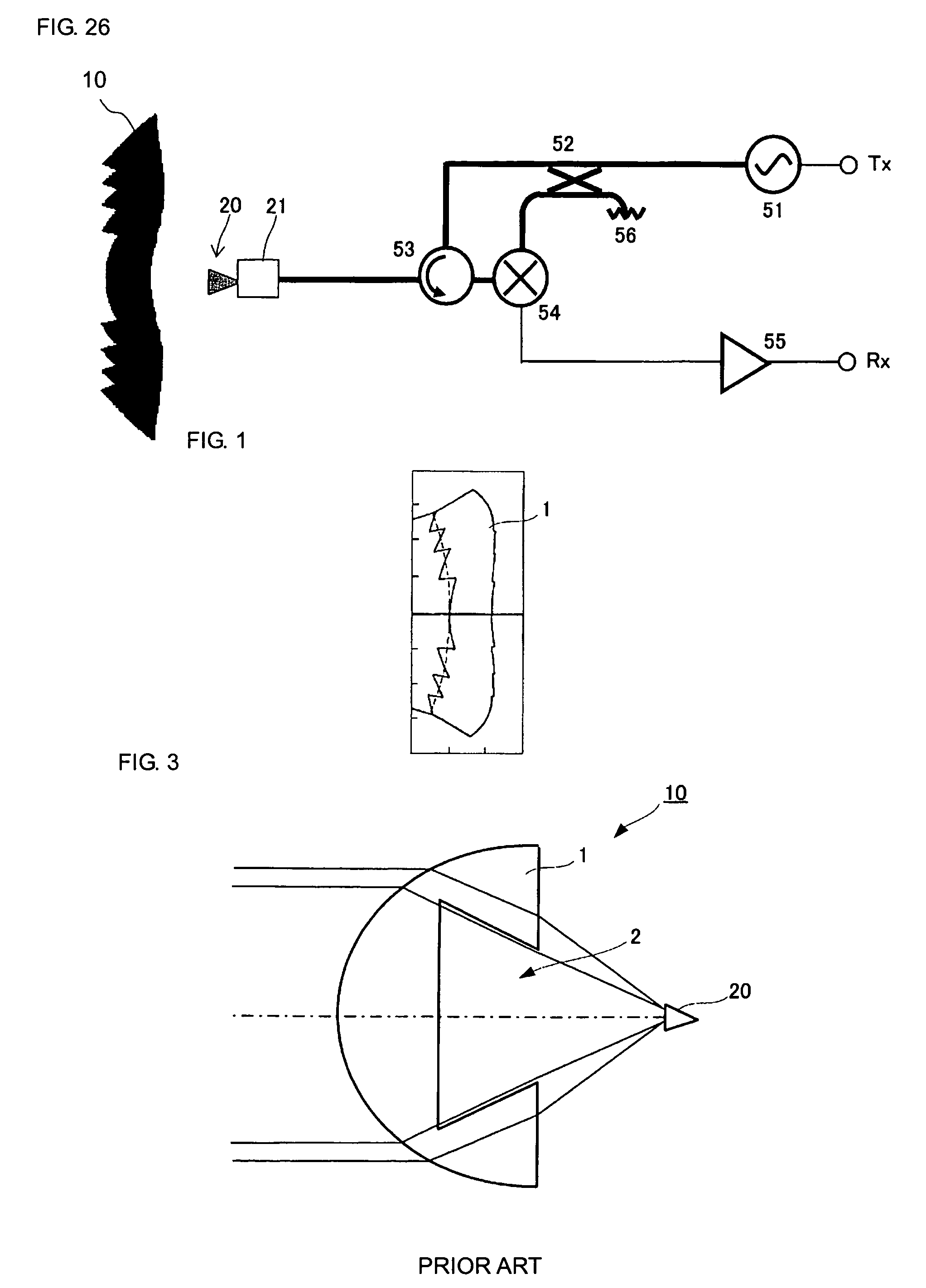
Dielectric lens, dielectric lens device, design method of dielectric lens, manufacturing method and transceiving equipment of dielectric lens
InactiveUS7355560B2Reduce weight and sizeEliminate the problemAntennasPath lengthSimultaneous equations
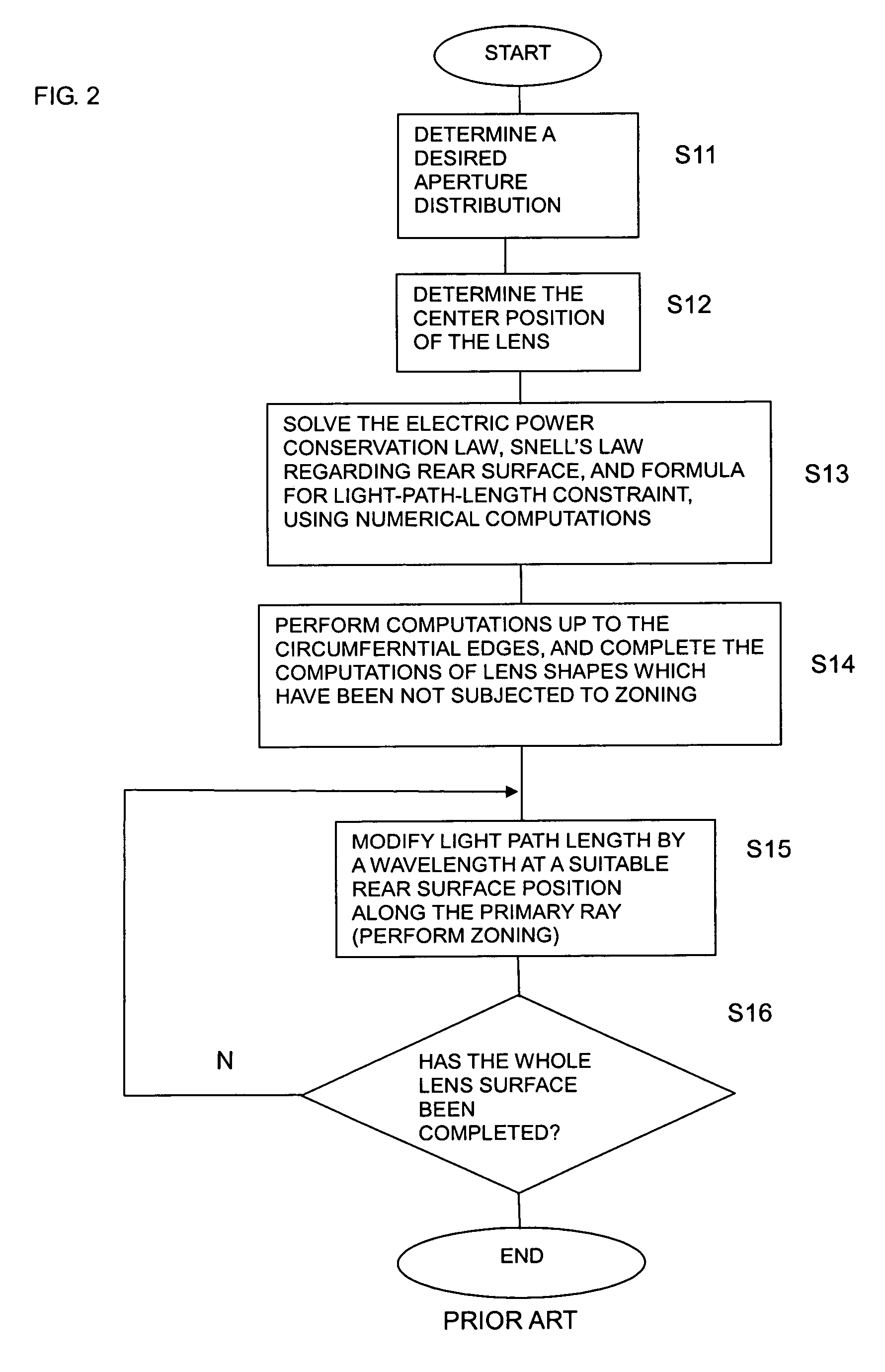
A design process first determines a desired aperture distribution, then converts the electric power conservation law, Snell's law on the rear face side of a dielectric lens, and the formula representing light-path-length constraint, into simultaneous equations, and computes the shapes of the surface and rear face of the dielectric lens depending on the azimuthal angle θ of a primary ray from the focal point of the dielectric lens to the rear face of the dielectric lens, and then reduces the light path length in the formula showing light-path-length constraint by an integral multiple of the wavelength when the coordinates on the surface of the dielectric lens reach a predetermined restriction thickness position. A dielectric lens is designed by sequentially changing the lazimuthal angle θ from its initial value, and also repeating the second and third steps. Thus, downsizing and quantification is realized by zoning while keeping antenna properties at the time of constituting a dielectric lens antenna in a good condition.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
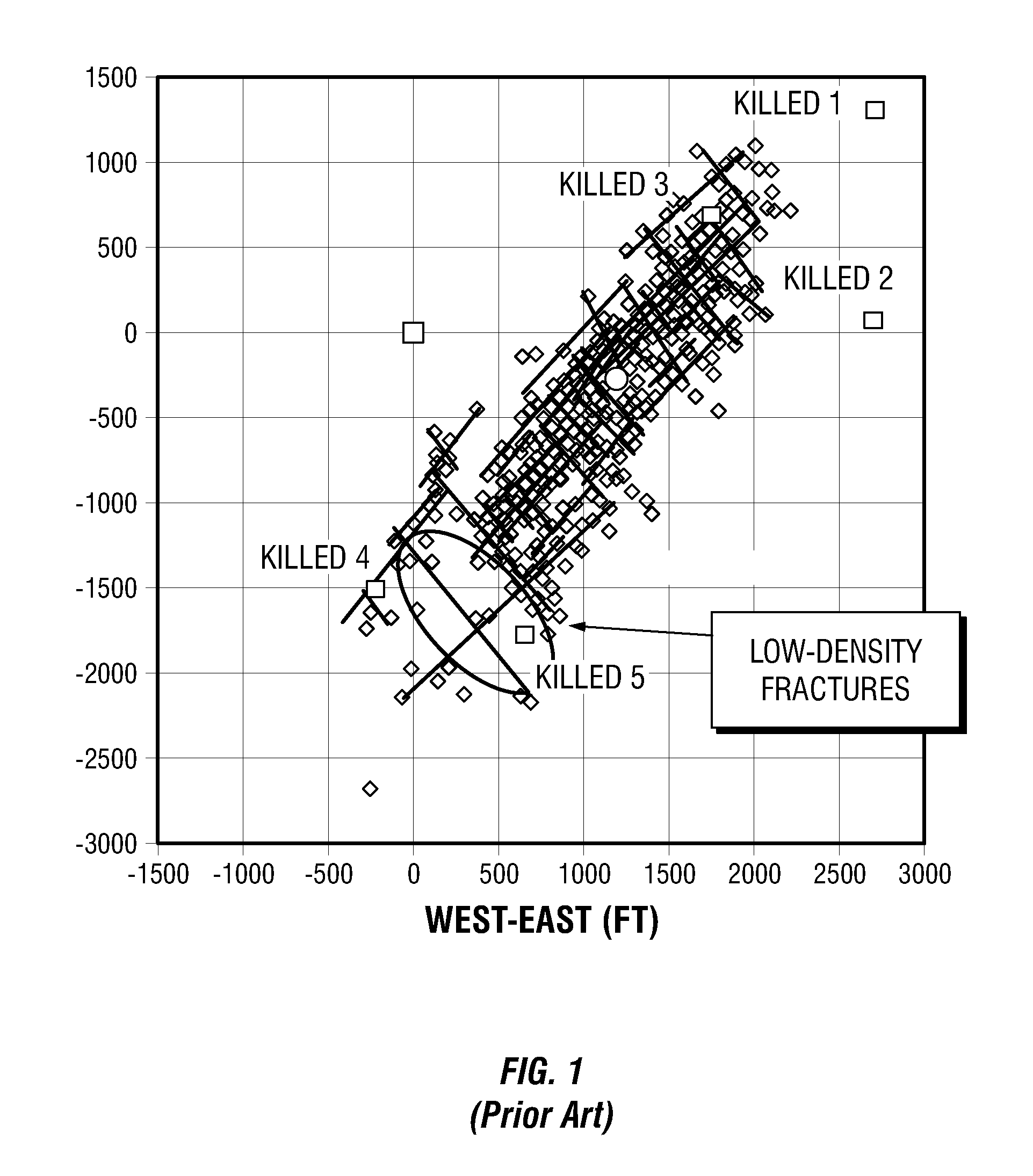
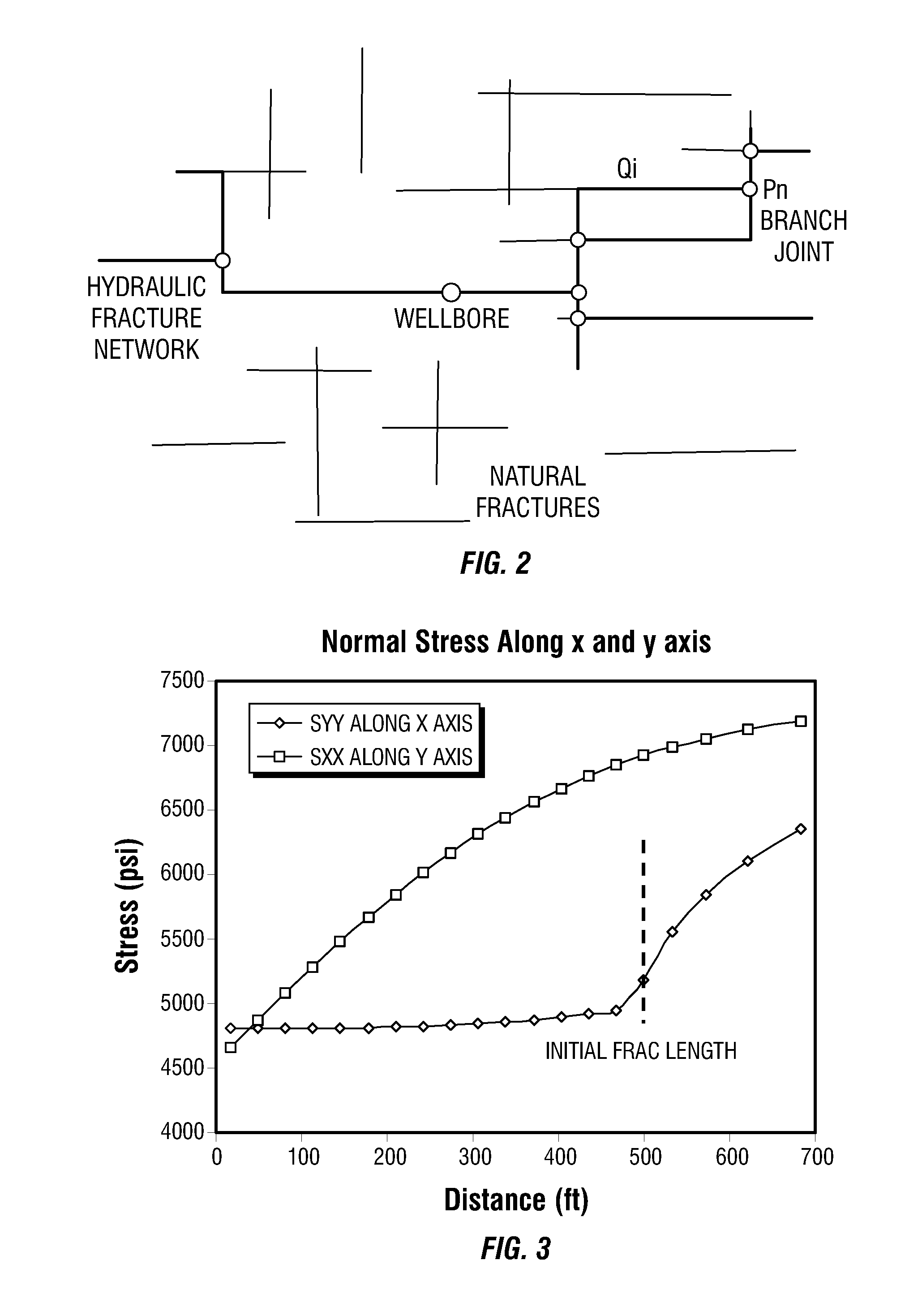
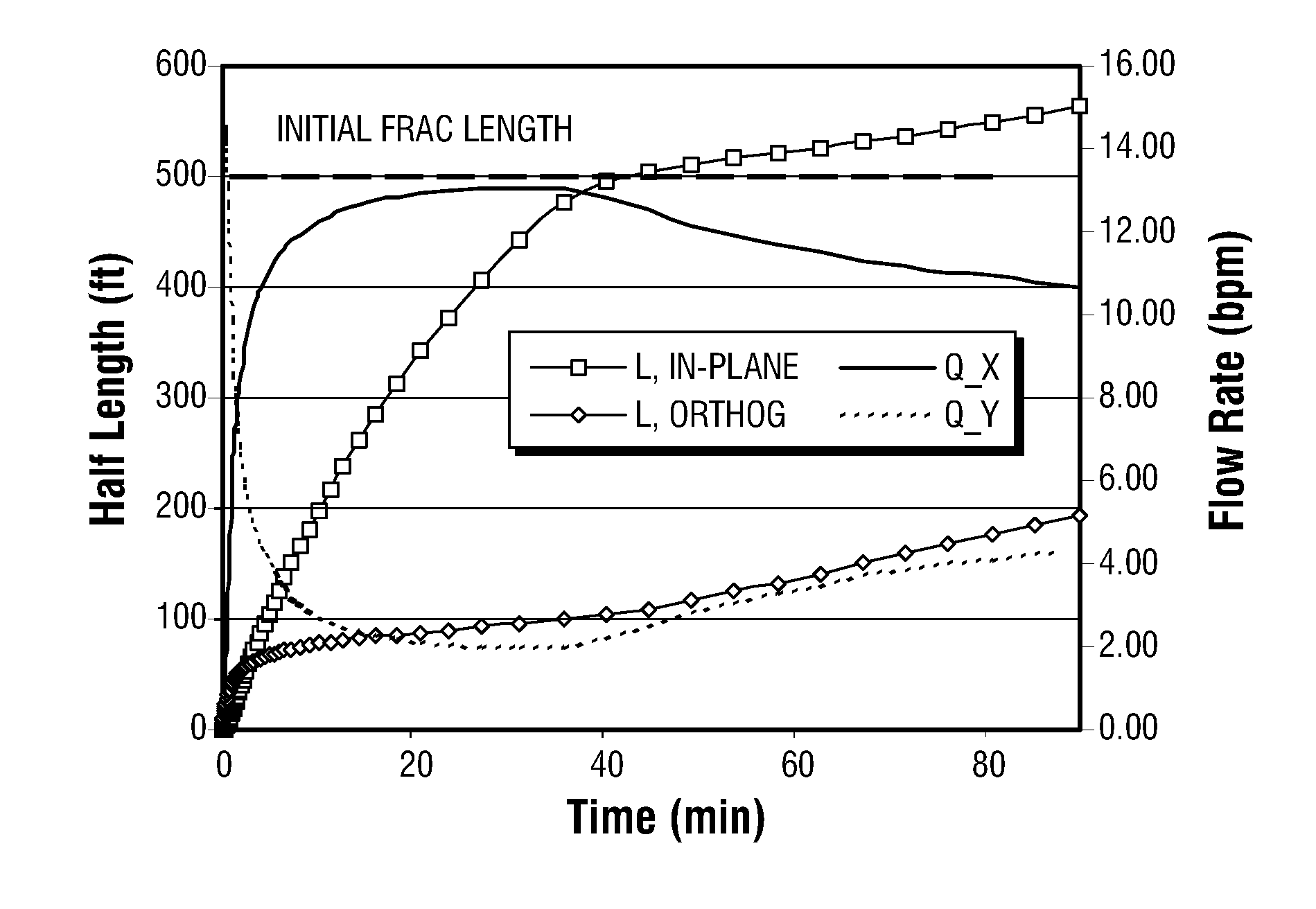
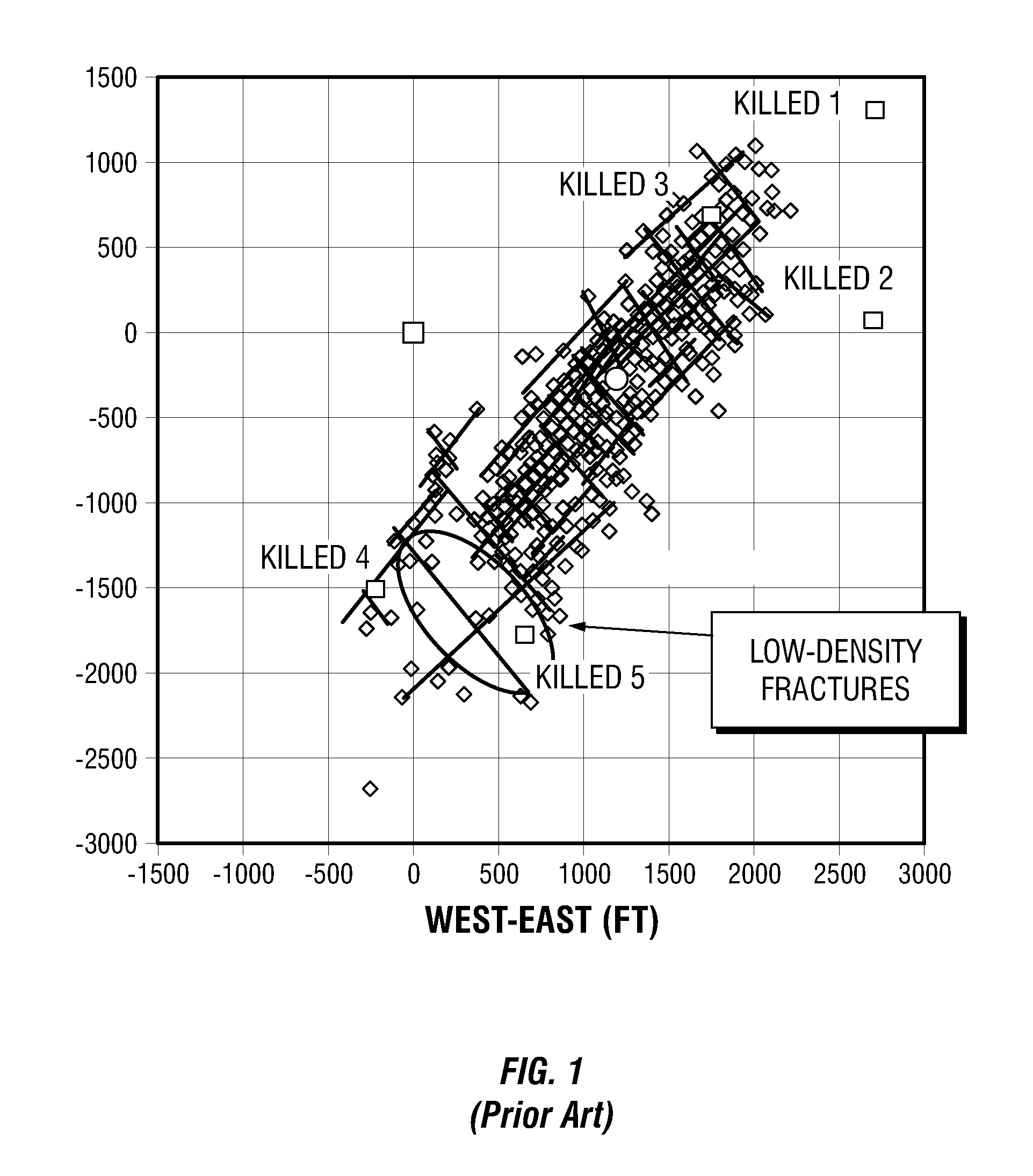
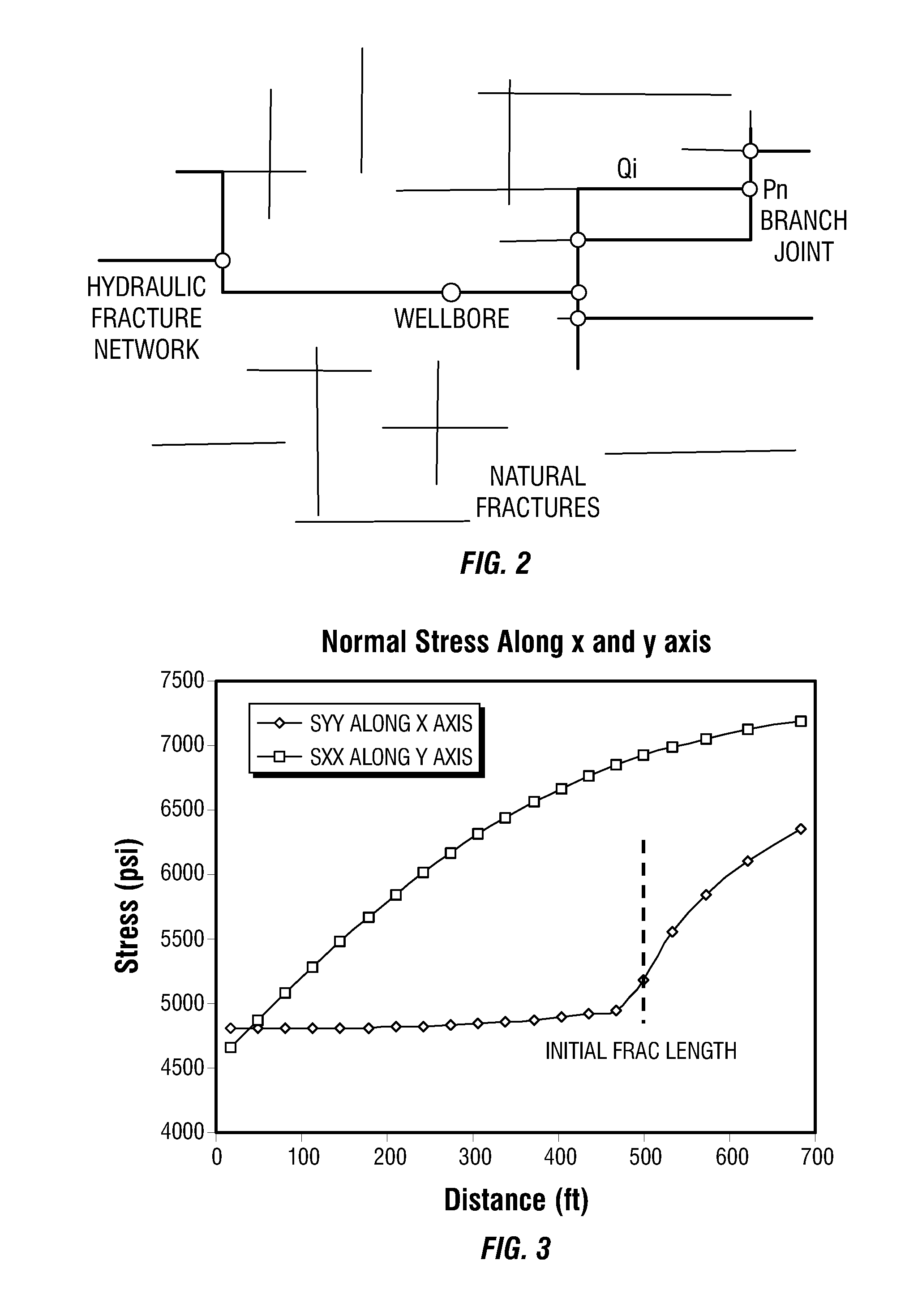
Simulations for Hydraulic Fracturing Treatments and Methods of Fracturing Naturally Fractured Formation
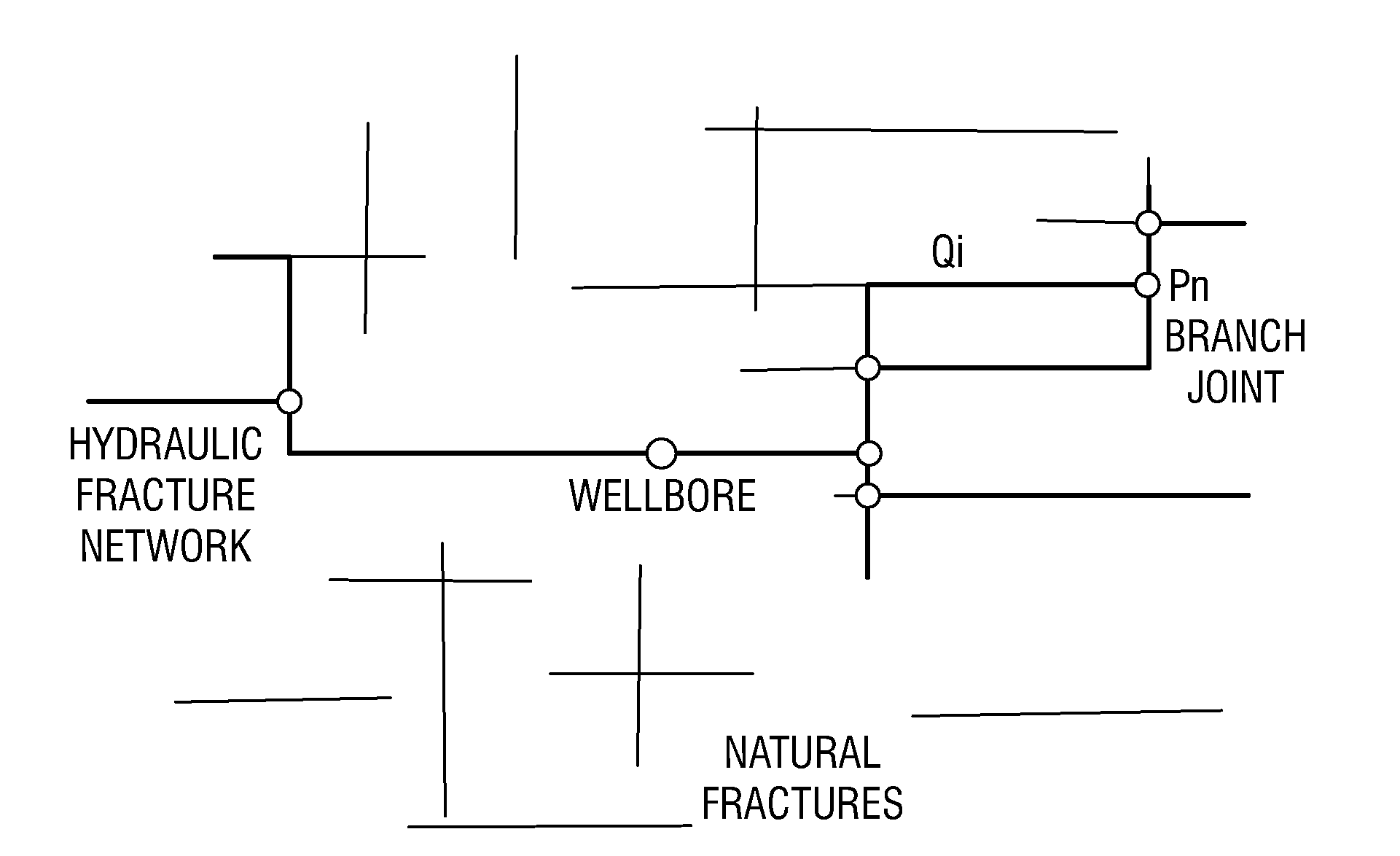
A hydraulic fracture design model that simulates the complex physical process of fracture propagation in the earth driven by the injected fluid through a wellbore. An objective in the model is to adhere with the laws of physics governing the surface deformation of the created fracture subjected to the fluid pressure, the fluid flow in the gap formed by the opposing fracture surfaces, the propagation of the fracture front, the transport of the proppant in the fracture carried by the fluid, and the leakoff of the fracturing fluid into the permeable rock. The models used in accordance with methods of the invention are typically based on the assumptions and the mathematical equations for the conventional 2D or P3D models, and further take into account the network of jointed fracture segments. For each fracture segment, the mathematical equations governing the fracture deformation and fluid flow apply. For each time step, the model predicts the incremental growth of the branch tips and the pressure and flow rate distribution in the system by solving the governing equations and satisfying the boundary conditions at the fracture tips, wellbore and connected branch joints. An iterative technique is used to obtain the solution of this highly nonlinear and complex problem.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
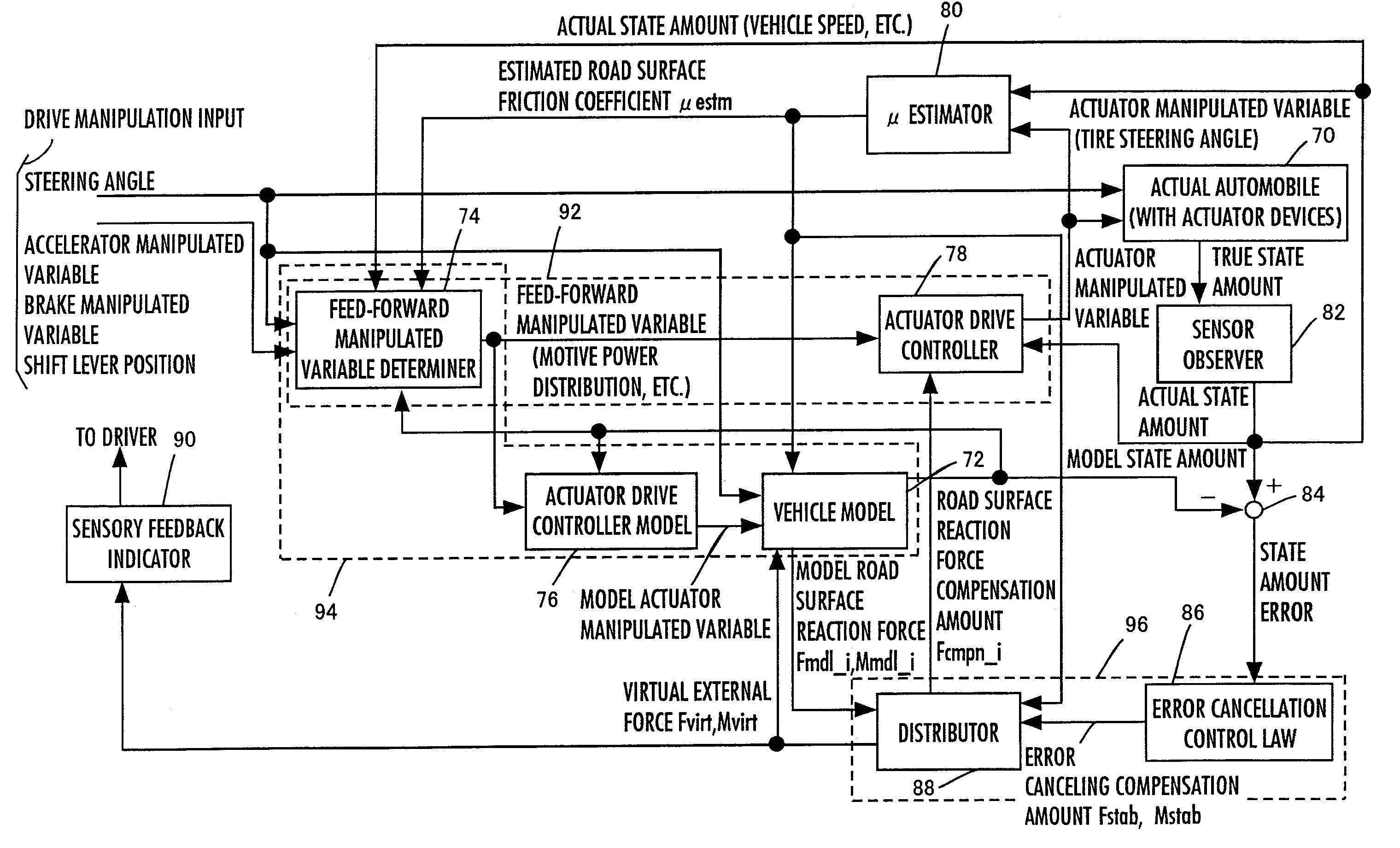
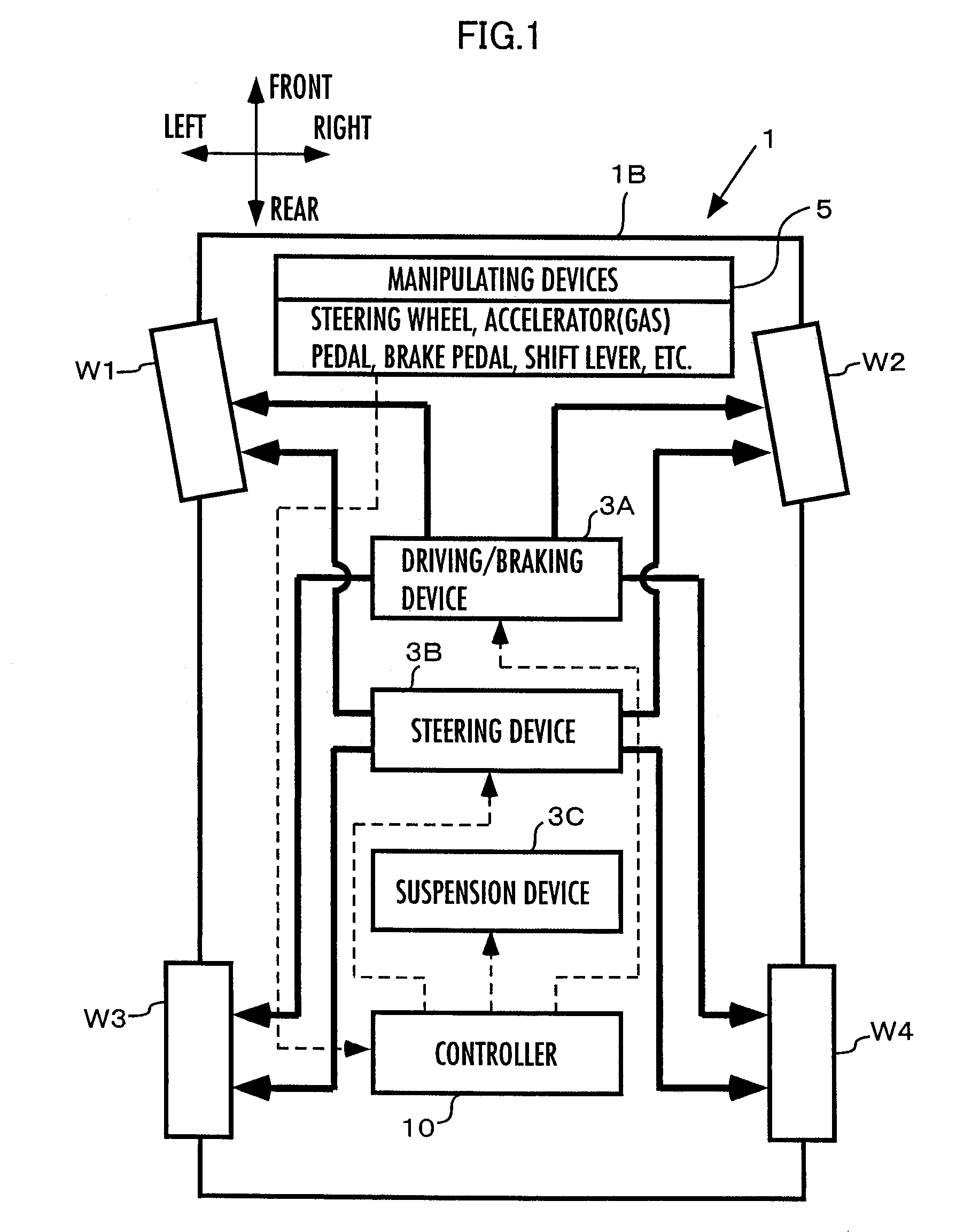
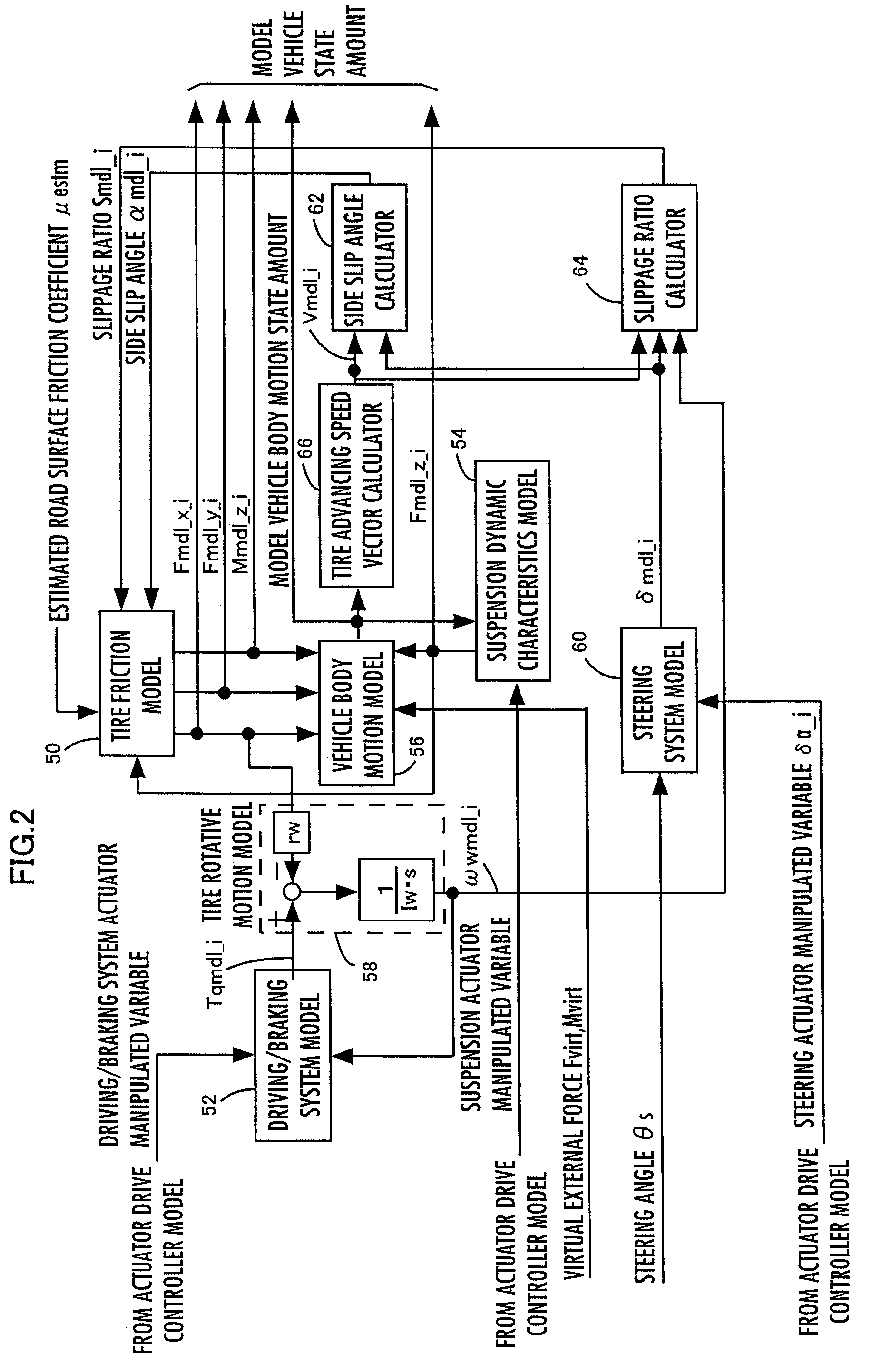
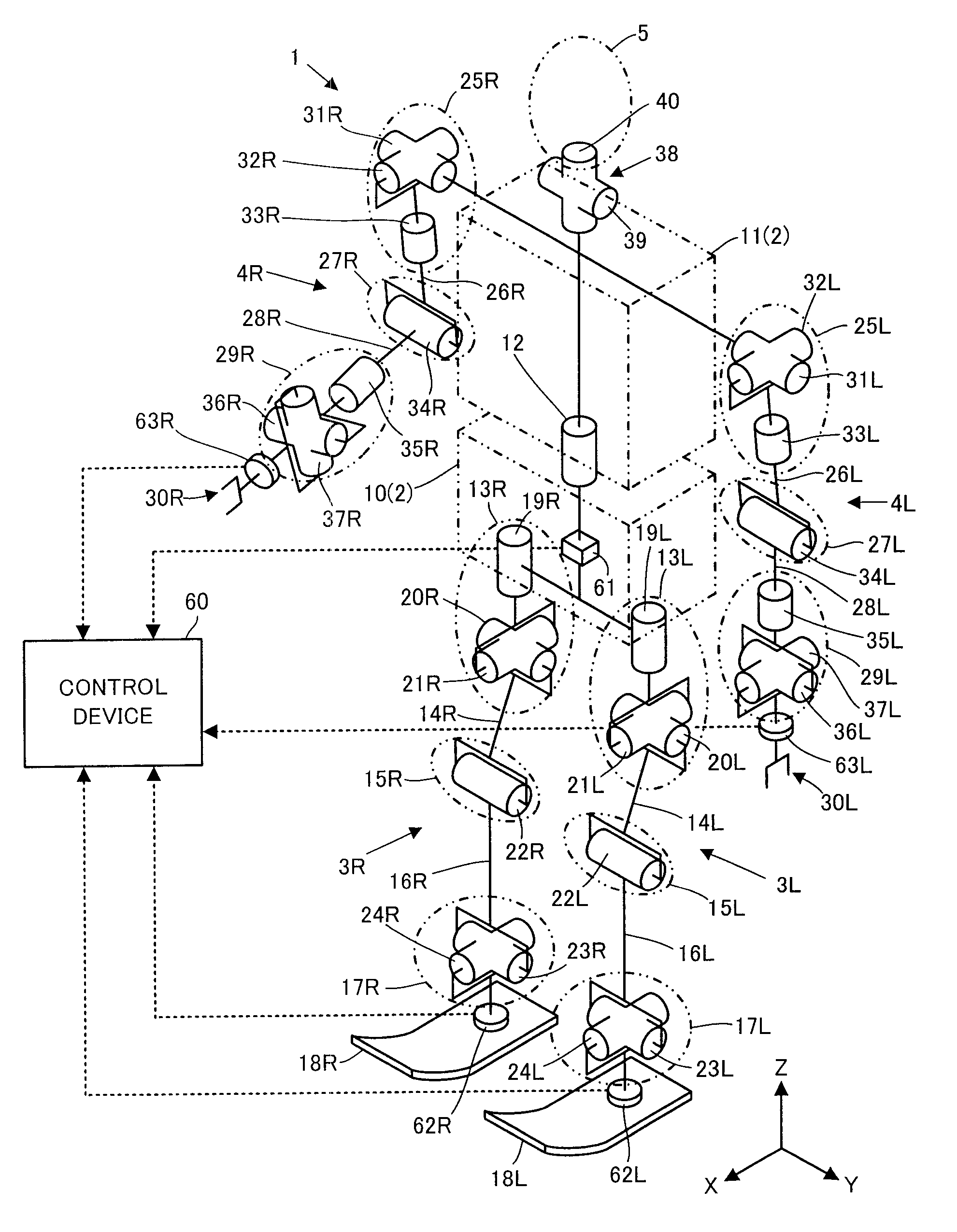
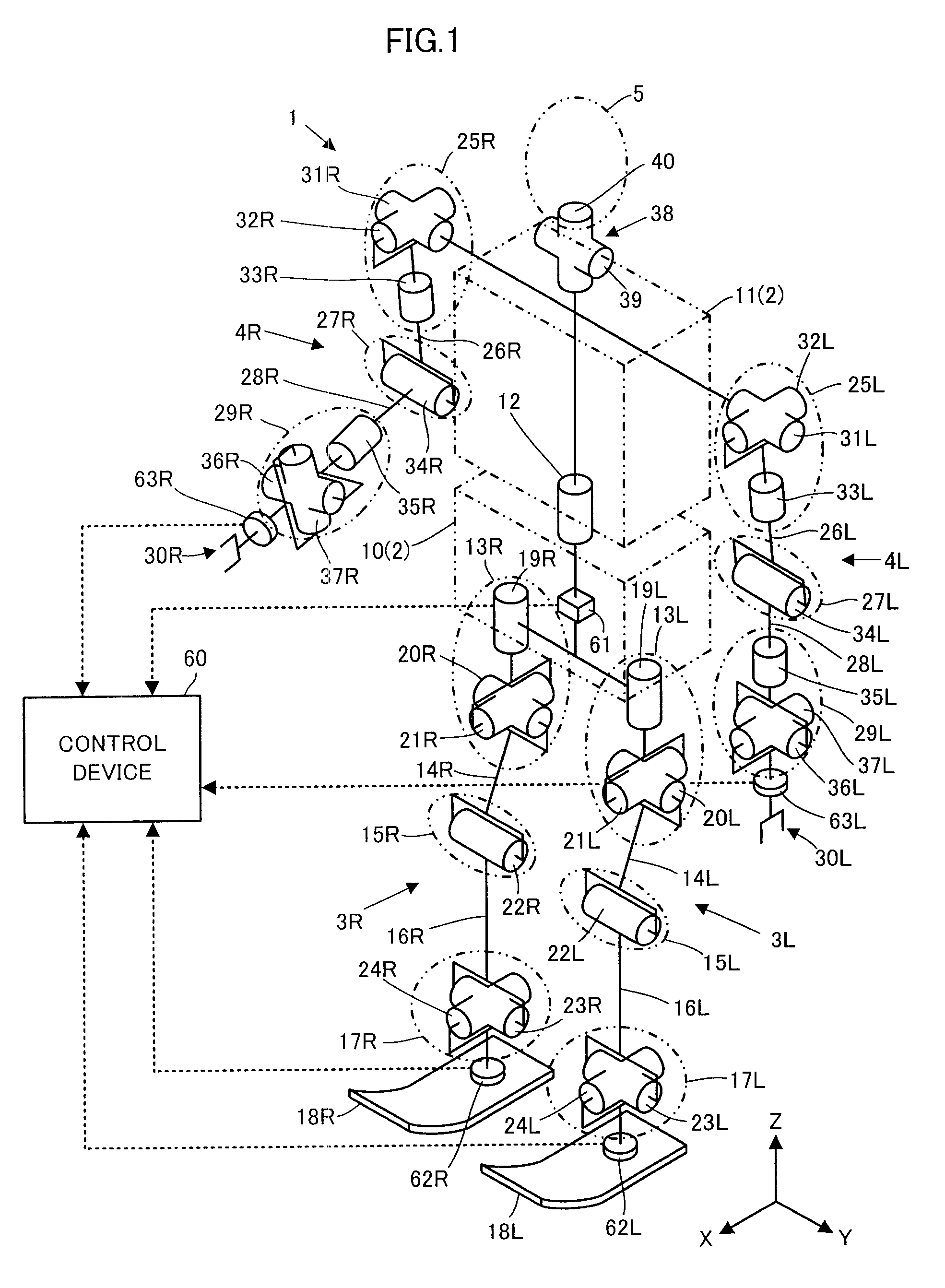
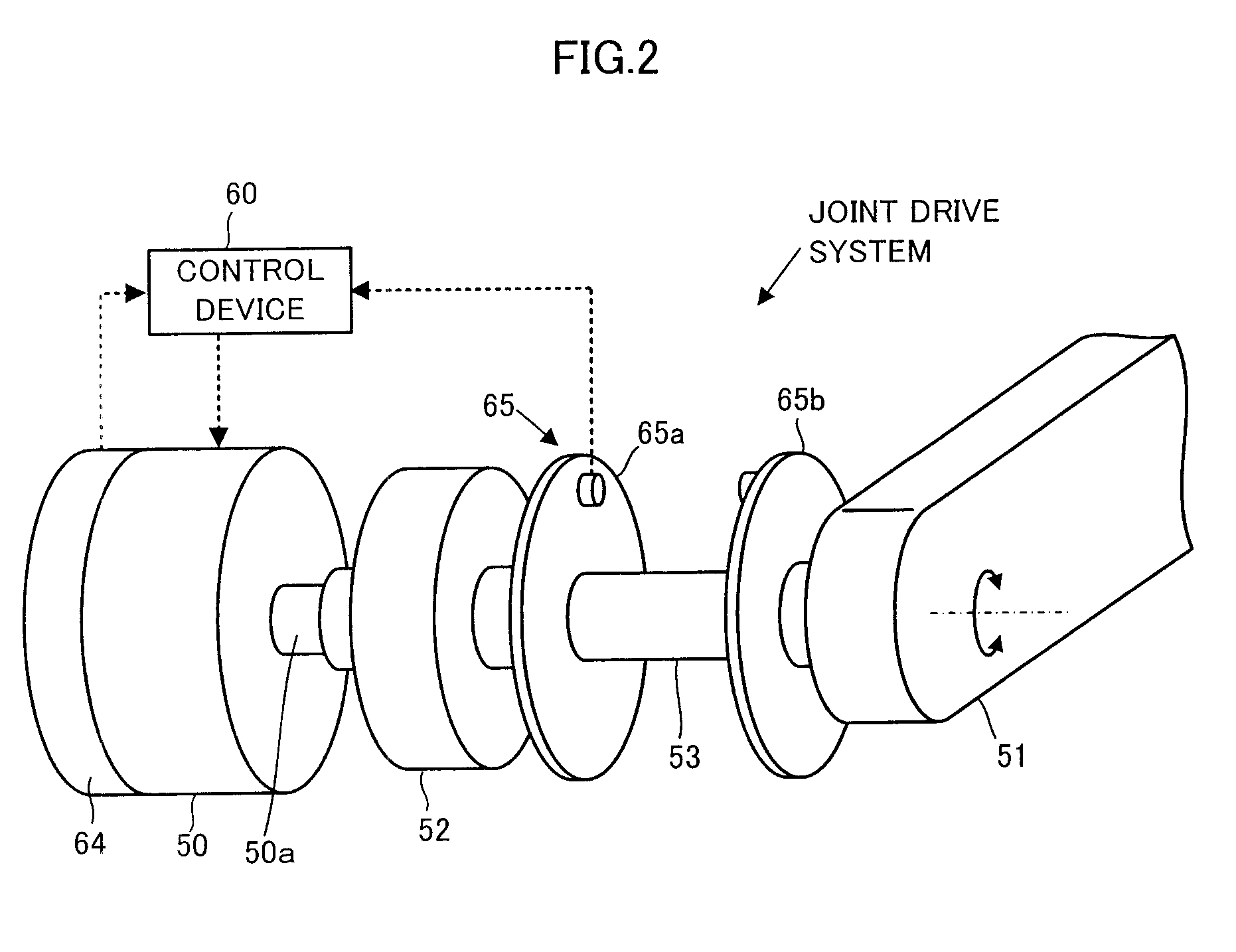
Control device for vehicle
ActiveUS7702442B2Improve control robustnessNon-rotating vibration suppressionDigital data processing detailsDriver/operatorLaws of thermodynamics
A control device for a vehicle is equipped with a vehicle model motion determining device for determining a motion of a vehicle (a vehicle model motion) on a vehicle model expressing the dynamic characteristics of a vehicle on the basis of drive manipulated variables, such as an angle of steering by a driver, and a state amount error reaction control device for determining control inputs to an actuator control device of the actual vehicle and the vehicle model motion determining device according to a feedback law on the basis of a difference between a state amount of a vehicle model motion (model state amounts, such as a position or a posture of a vehicle) and a state amount of a motion of the actual vehicle 1 (a state amount error). Based on a state amount error, not only a motion of an actual vehicle but also a vehicle model motion is manipulated, thereby enhancing robustness against disturbance factors or their changes while conducting actuator operation control that is suited to a behavior of the actual vehicle as much as possible.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Control device for mobile robot
ActiveUS20110160906A1Ensure stable implementationImprove stabilityComputer controlSimulator controlMobile robot controlMomentum
A control device for a mobile robot, in which the desired value of a motion state amount of a mobile robot includes at least the desired value of a vertical component of a first-order differential value of the translational momentum of the entire mobile robot. The desired value is determined by a state amount desired value determiner such that the observed value of the vertical position of an overall center-of-gravity point of the mobile robot is converged to a predetermined desired value according to a feedback control law. A control input determiner carries out the processing of inverse dynamics calculation, using the desired value of the motion state amount thereby to determine the desired driving force for each joint. The operation of an actuator is controlled on the basis of the determined desired driving force.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
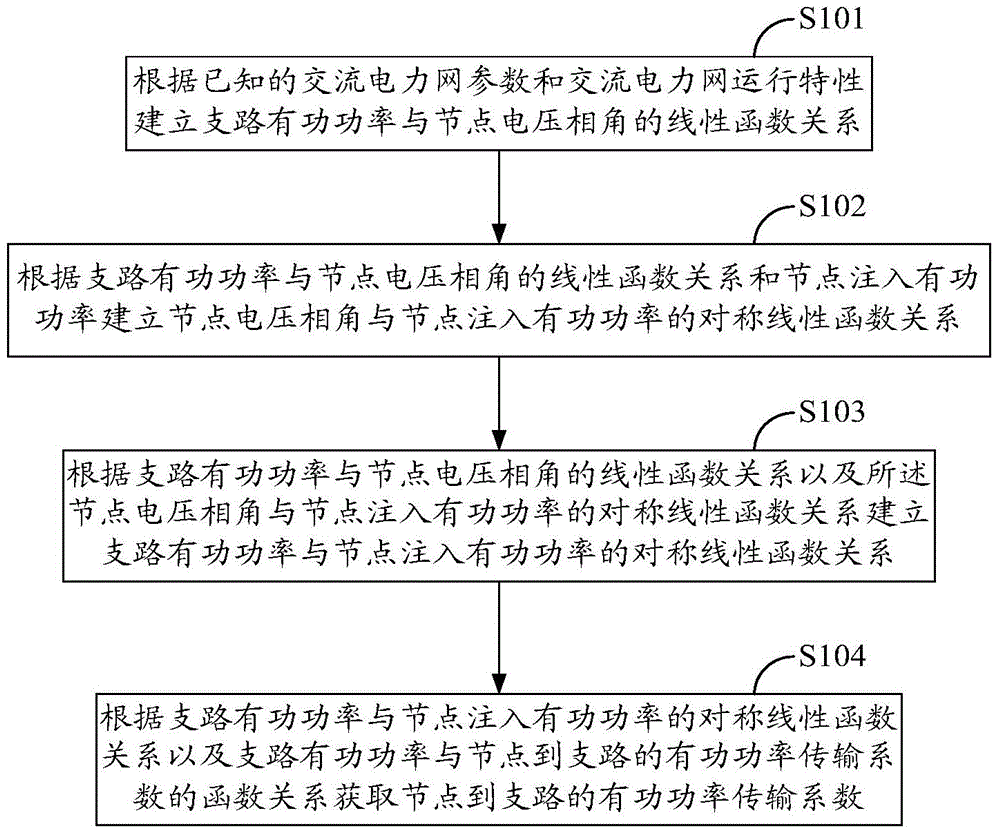
Symmetric obtaining method for coefficient of active power transmission from nodes to branches in power network
InactiveCN103956733ASpecial data processing applicationsAc network circuit arrangementsElectric power transmissionPhysical Symmetry
The invention belongs to the field of electric power engineering, and provides a symmetric obtaining method for a coefficient of active power transmission from nodes to branches in a power network. According to the method, a linear function relationship between branch active power and node voltage phase angles is established according to known alternating current power network parameters and alternating current power network running characteristics, a symmetric linear function relationship between the node voltage phase angles and node injected active power is established according to the linear function relationship and the node injected active power, a symmetric linear function relationship between the branch active power and the node injected active power is established according to the linear function relationship and the known symmetric linear function relationship, and the coefficient of the active power transmission from the nodes to the branches is obtained according to the symmetric linear function relationship and the function relationship between the branch active power and the coefficient of the active power transmission from the nodes to the branches. The problems that existing obtaining methods for the coefficient of the active power transmission from the nodes to the branches go against a physical symmetry rule and a circuital law, and cannot reflect the characteristics of the active power transmission from the nodes to the branches truly are solved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Scalable Work Load Management on Multi-Core Computer Systems
InactiveUS20100043008A1Minimize impactIncrease the number ofMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsProcessing coreAmdahl's law
Embodiments of the presently claimed invention minimize the effect of Amdahl's Law with respect to multi-core processor technologies. This scheme is asynchronous across all of the cores of a processing system and is completely independent of other cores and other work units running on those cores. This scheme occurs on an as needed and just in time basis. As a result, the constraints of Amdahl's Law do not apply to a scheduling algorithm and the design is linearly scalable with the number of processing cores with no degradation due to the effects of serialization.
Owner:EXLUDUS TECH
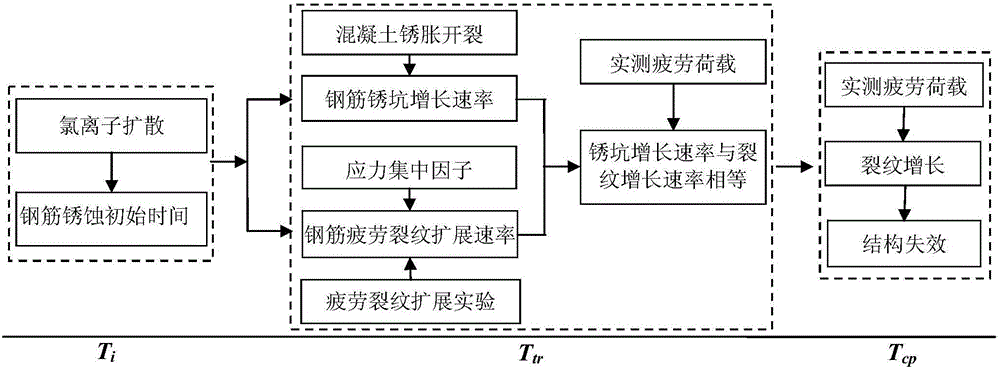
Method for evaluating fatigue life of aged reinforced concrete bridge
ActiveCN105825030AThe prediction method is reasonableGeometric CADForecastingStress concentrationCrazing
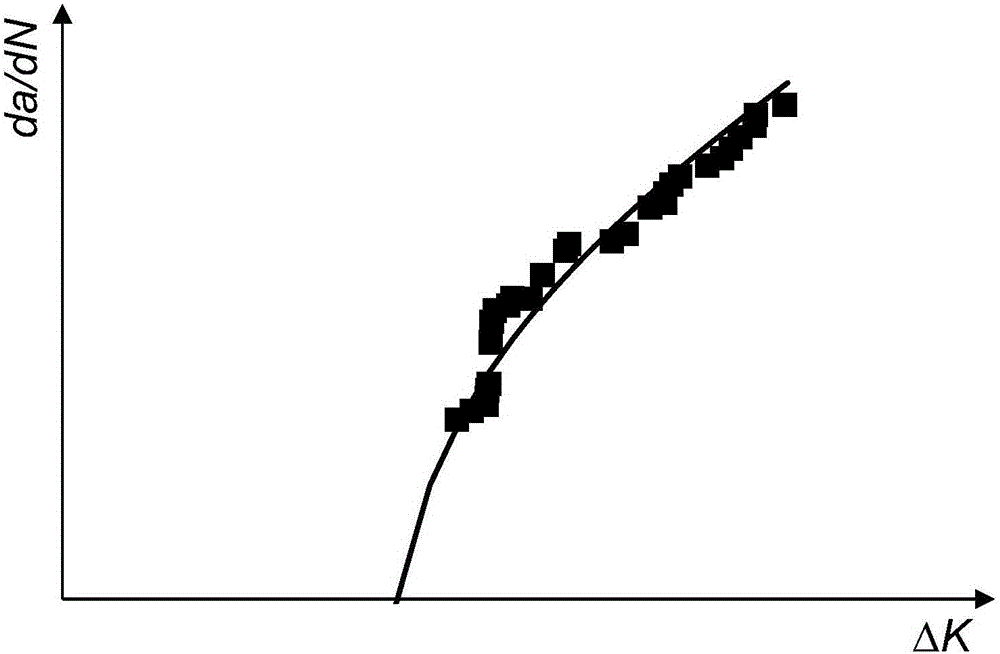
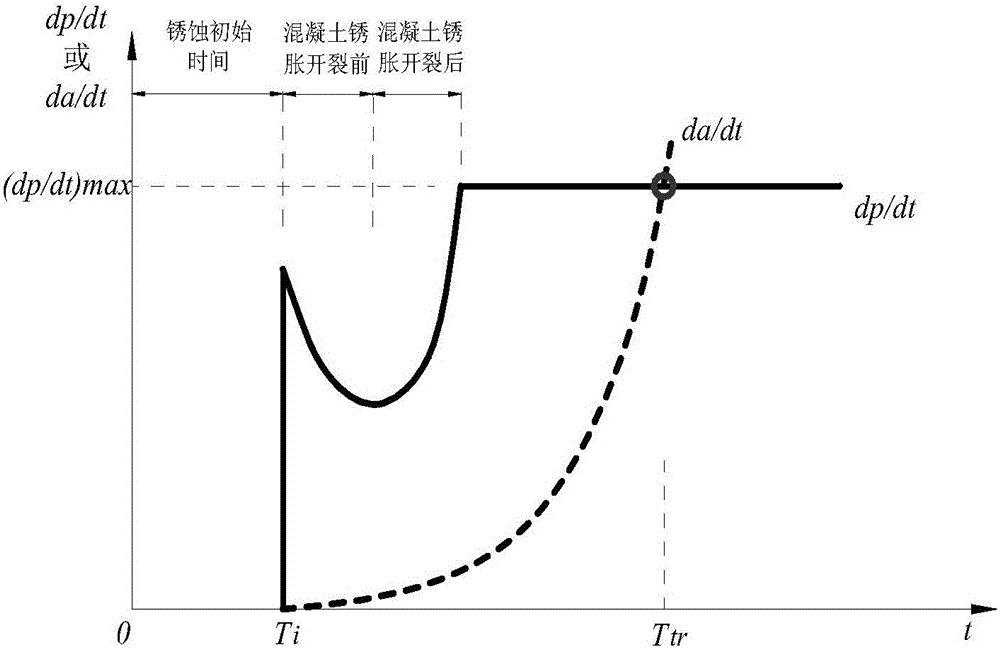
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the fatigue life of an aged reinforced concrete bridge. The method comprises the following steps of obtaining initial corrosion time of reinforcement in concrete based on the second diffusion law of Fick, and considering the influence of concrete cracking due to corrosion expansion in a corrosion rate model; adopting a small crack growth and near threshold growth analysis and determining relevant parameters of fatigue crack propagation rate of materials by developing a fatigue crack propagation test of reinforced concrete materials; performing a corrosion fatigue test or finite element analysis on corroded reinforcement to obtain stress concentration factors at different corrosion levels, and integrating into a stress intensity factor model to obtain the fatigue crack propagation rate of the reinforcement under the influence of corrosion; comparing the magnitude of a corrosion pit growth rate and the fatigue crack propagation rate and gradually converting into a single growth analysis on fatigue cracks of the reinforcement; meanwhile, combining with vehicle load observing information to realize life evaluation of a bridge at different service stages. The prediction method disclosed by the invention is reasonable and high in popularization, and can provide technical support for evaluating the life of the concrete bridges.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Brazilian split method for measuring elastic parameter of rock under extension condition
InactiveCN102183410AGain tensile strengthGet elastic parametersMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesCircular discStress conditions
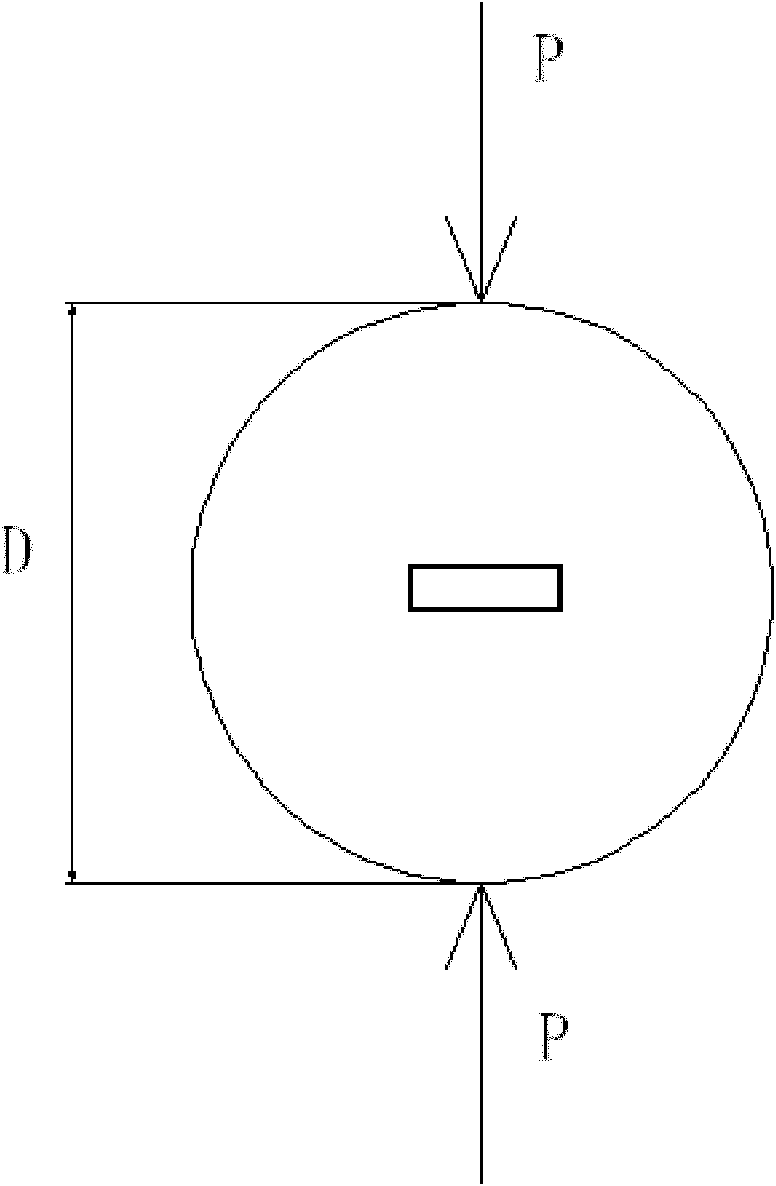
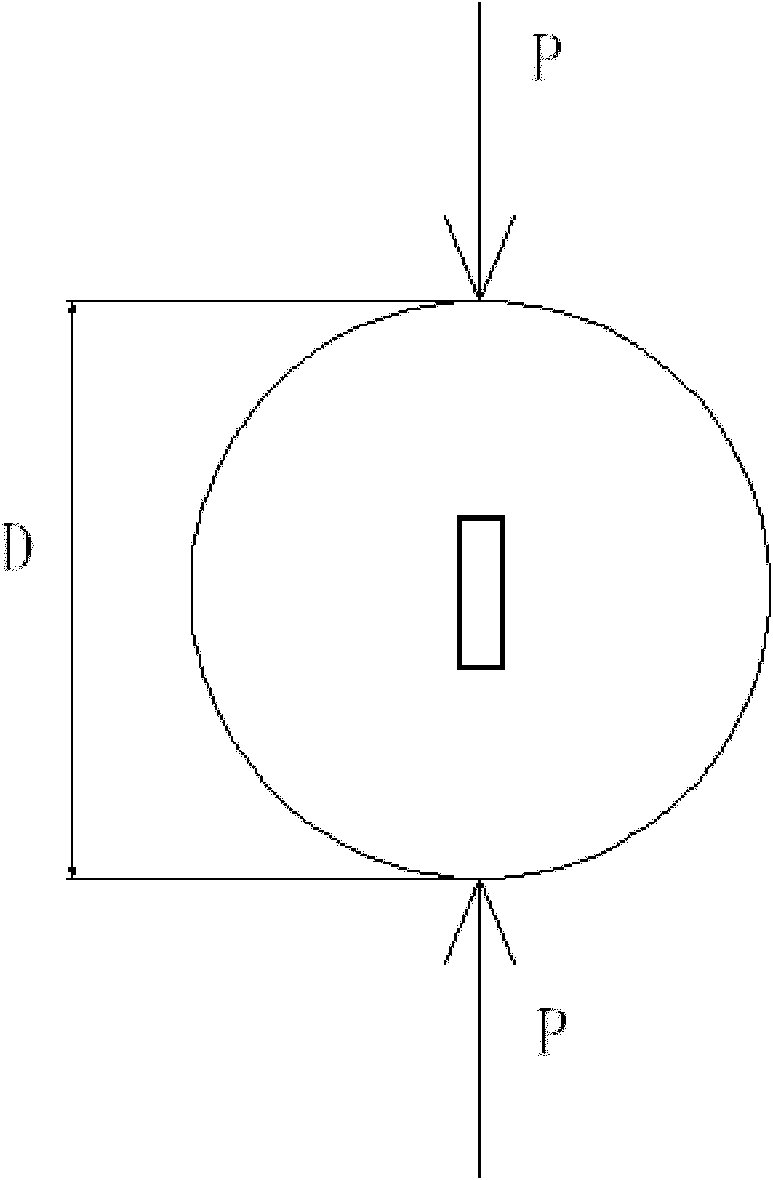
The invention discloses a Brazilian split method for measuring an elastic parameter of a rock under an extension condition, which comprises the steps of: A. horizontally putting a machined disc-shaped sample between the load bearing plates of a press machine by using a Brazilian disc split method, placing a hard steel wire respectively between the upper load bearing plate and the sample and between the lower load bearing plate and the sample, arranging a filler strip perpendicular to the symmetrical surfaces of the sample, and applying pressure on the upper load bearing plate and the lower load bearing plate to make the sample generate tension perpendicular to the action directions of an upper load and a lower load; B. carrying out analysis by using the Hooke's law in classical elasticity mechanics by combining specific conditions of the Brazilian split method; C. analyzing the stress condition of the rock and the measurement principle in the Brazilian disc split method; and D. obtaining the strain in the stress direction according to the Hooke's law from the stress condition sigma3=0, measuring epsilon1 and epsilon2, obtaining the elastic parameter of the rock sample, and arranging a strain gauge in the center position of the rock sample for measurement of epsilon1 and epsilon2. The method has the advantages of easiness for operation and use, clear principle, low material consumption, and the like. The method is suitable for wide popularization and application.
Owner:INST OF ROCK AND SOIL MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for predicting office building cooling load
InactiveCN107169606AEasy to calculateImprove accuracySpace heating and ventilation safety systemsLighting and heating apparatusFresh airLaws of thermodynamics
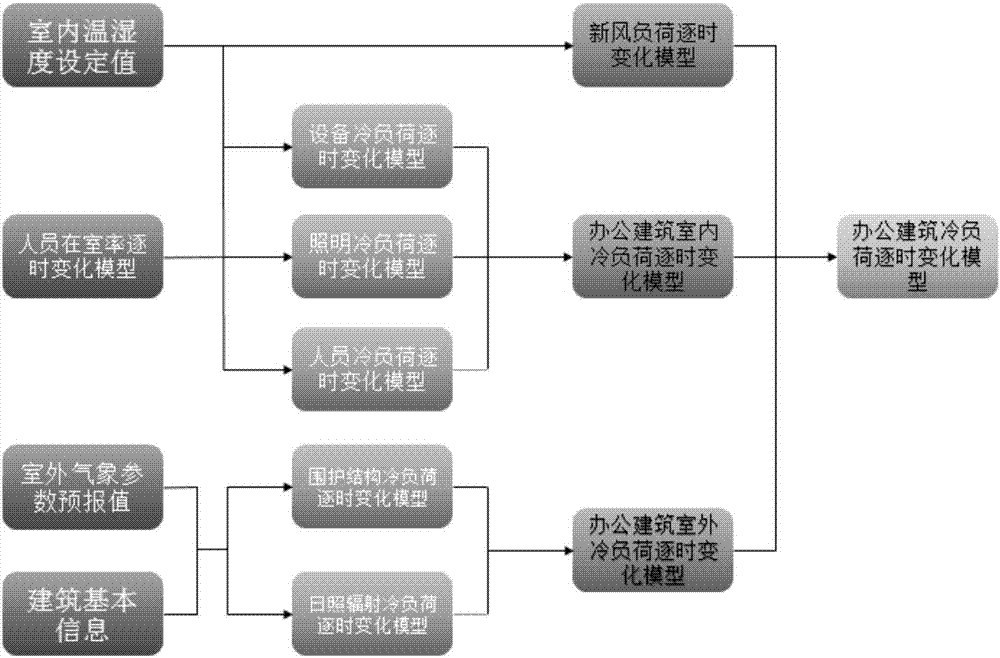
The invention belongs to the technical field of building cooling load control, relates to a method for predicting an office building cooling load, and through building an office building outdoor cooling load model, an office building indoor cooling load model and an office building fresh air load hourly variation model, an office building cooling load model is obtained. Based on the an energy conservation law and a thermal balance relation in building environment, from the point of view of variation of the number of people in an office building and personnel energy utilization modes, the interference amount of a cooling load in the office building is predicted and analyzed; and meteorological website data are utilized to predict a cooling load outside the office building and an office building fresh air load. The method for predicting the office building cooling load establishes an air conditioner enclosing structure, a solar radiation cooling load hourly variation model, and hourly variation models of personnel, equipment, illumination cooling loads and personnel indoor rate in air conditioning environment, and finally obtains a cooling load prediction model of the office building.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
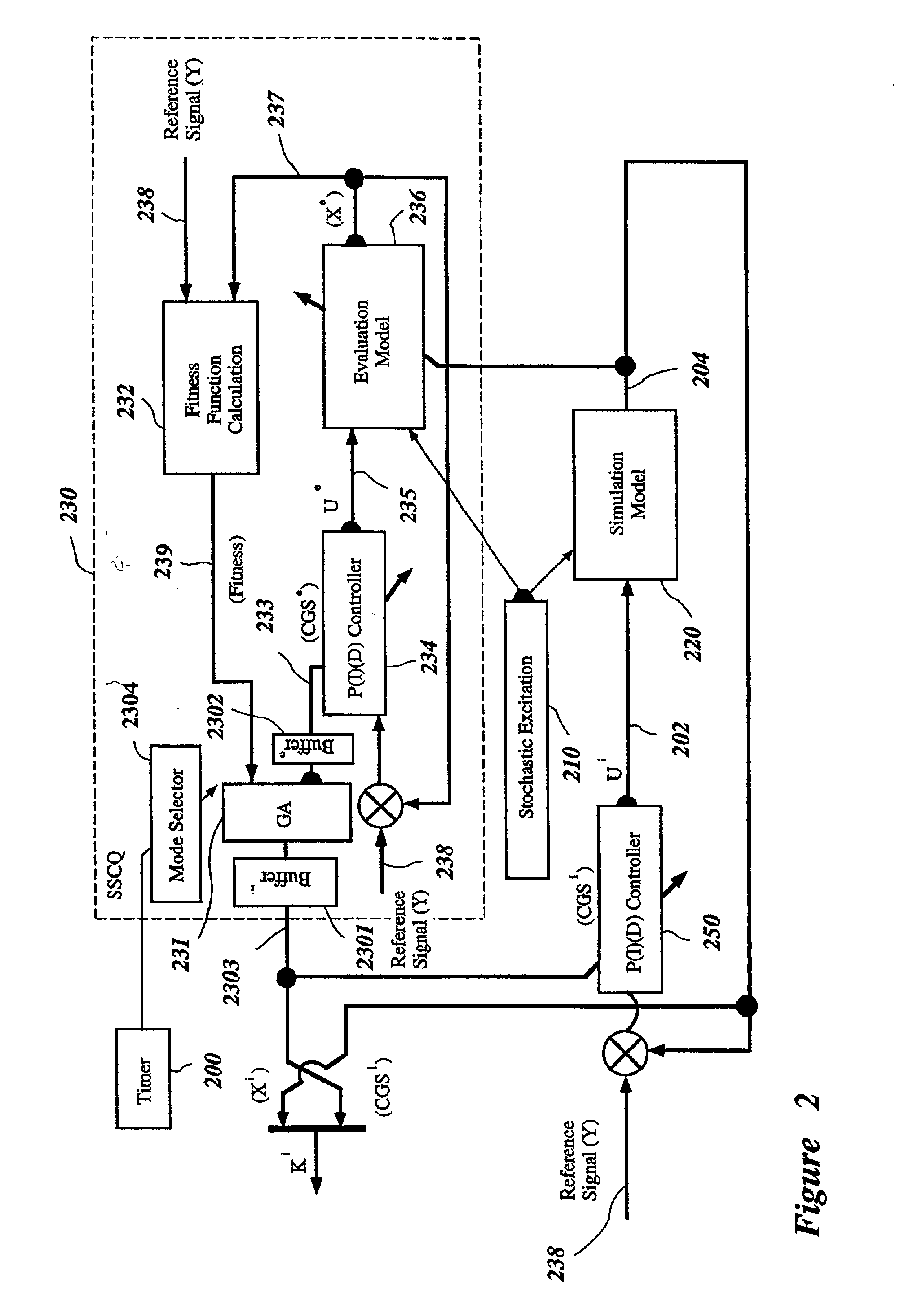
System and method for nonlinear dynamic control based on soft computing with discrete constraints
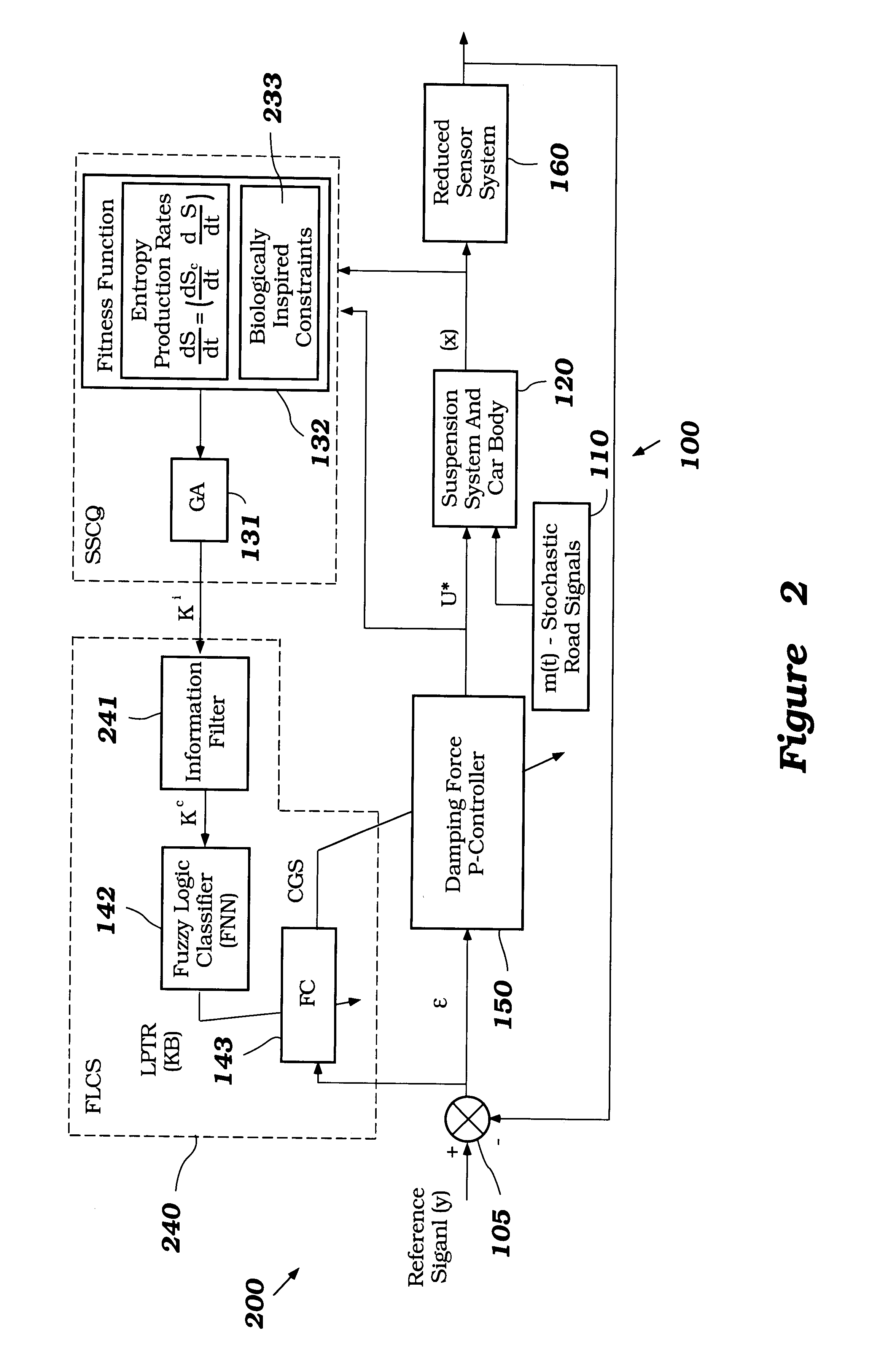
InactiveUS6950712B2Minimizes entropyMaximizes sensor information contentDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesNon linear dynamicMinimum entropy
A control system using a genetic analyzer based on discrete constraints is described. In one embodiment, a genetic algorithm with step-coded chromosomes is used to develop a teaching signal that provides good control qualities for a controller with discrete constraints, such as, for example, a step-constrained controller. In one embodiment, the control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy. In one embodiment, the genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal for a fuzzy logic classifier system that develops a knowledge base. The teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from the knowledge base. The control system can be used to control complex plants described by nonlinear, unstable, dissipative models. In one embodiment, the step-constrained control system is configured to control stepping motors.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
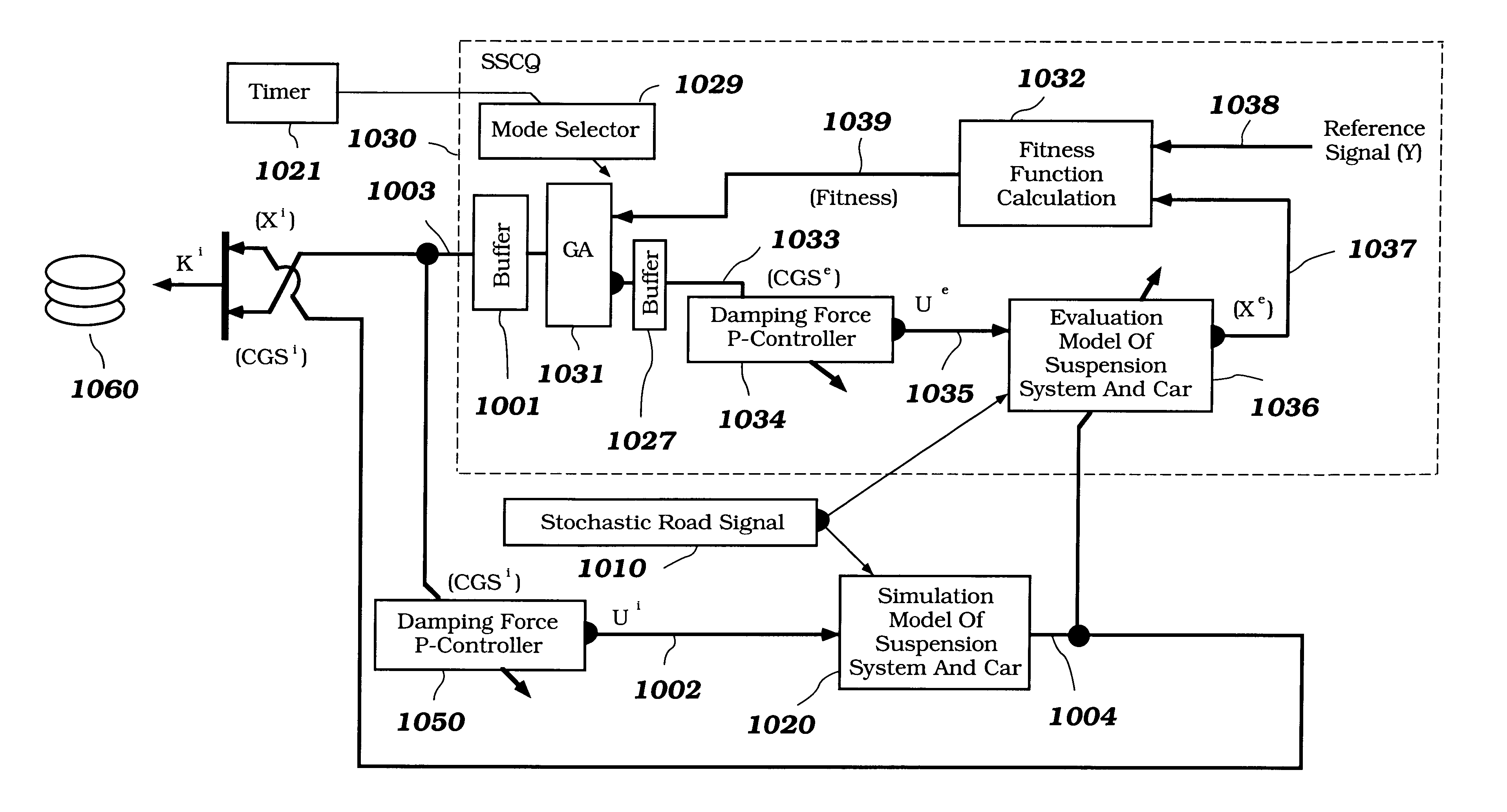
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on soft computing
InactiveUS6701236B2Maximises informationLightweight productionSpringsAnimal undercarriagesControl systemFuzzy control system
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. An information filter is used to filter the teaching signal to produce a compressed teaching signal. The compressed teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. In one embodiment, the control system includes a learning system, such as a neural network that is trained by the compressed training signal. The learning system is used to create a knowledge base for use by an online fuzzy controller. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
Material point method modeling in oil and gas reservoirs
InactiveUS20130096890A1Accurate modelingSimulation is accurateFluid removalSeismologyLaws of thermodynamicsEquation of state
A computer system and method of simulating the behavior of an oil and gas reservoir including changes in the margins of frangible solids. A system of equations including state equations such as momentum, and conservation laws such as mass conservation and volume fraction continuity, are defined and discretized for at least two phases in a modeled volume, one of which corresponds to frangible material. A material point model technique for numerically solving the system of discretized equations, to derive fluid flow at each of a plurality of mesh nodes in the modeled volume, and the velocity of at each of a plurality of particles representing the frangible material in the modeled volume. A time-splitting technique improves the computational efficiency of the simulation while maintaining accuracy on the deformation scale. The method can be applied to derive accurate upscaled model equations for larger volume scale simulations.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC +1
Predicting method for lithiumion cell heat safety performance
The core of the technique is that the method builds thermal model of lithium ion battery under condition of abuse (for ex. hot box, short circuit, and overcharge) based on law of conservation of energy and Fourier law. Using thermal insulation technique for measuring heat determines kinetic parameter of internal heat source item in model; and other parameters come from documents and experiments. Using the model can forecast safety performance of battery under condition of abuse. Modifying model parameter obtains thermo-safety factors influencing lithium ion battery so as to provide theory basis of predicting safety critical value including size of battery, application temperature and material of battery for safety design of battery. The method reduces fussy working procedures for estimating safety performance of material and new battery by making actual battery and carrying out performance test. Advantages are: avoiding waste of resources and time, quick test speed, and low cost.
Owner:TIANJIN LISHEN BATTERY
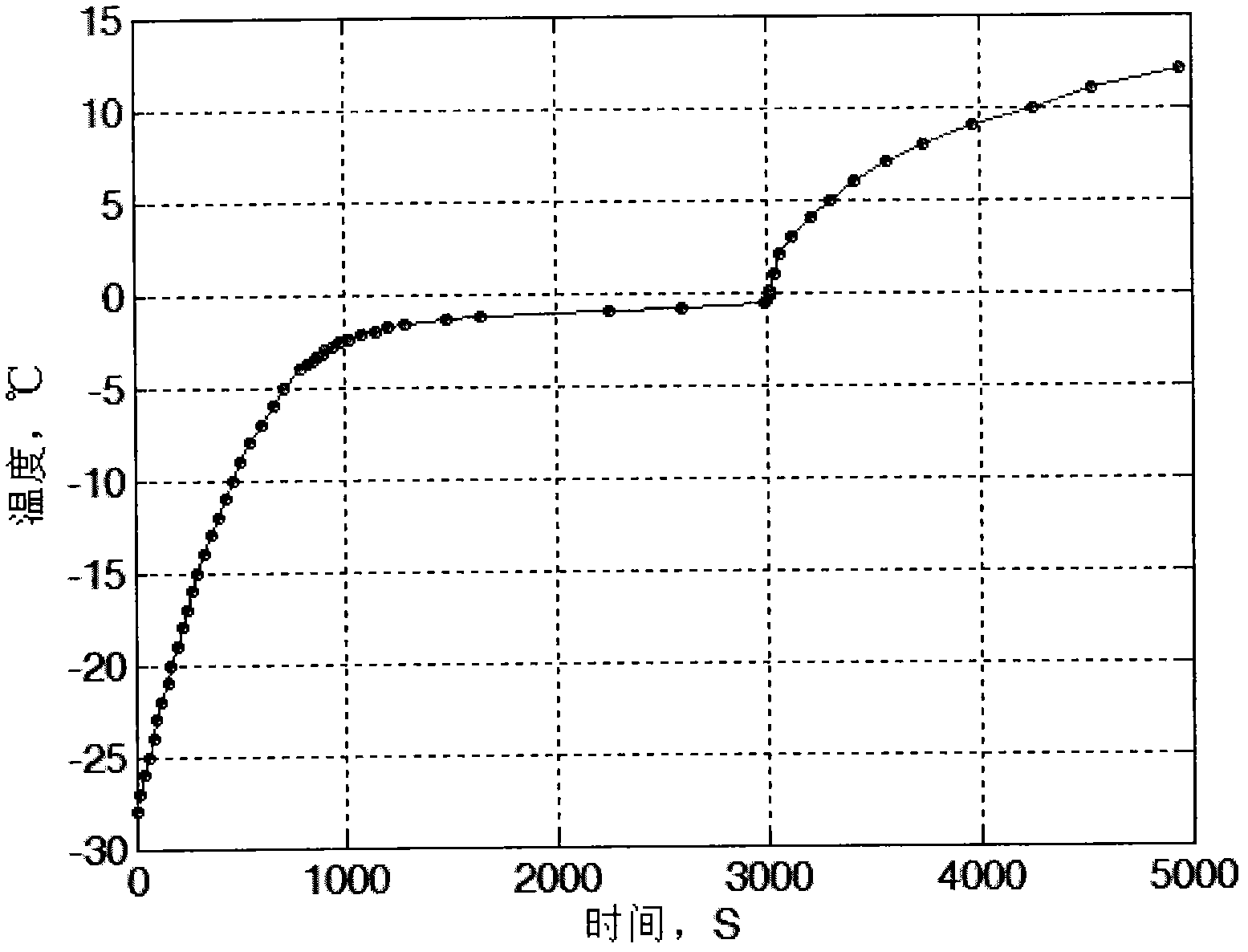
Method for testing content of unfrozen water in frozen earth
The invention provides a method for testing content of unfrozen water in frozen earth. The method is mainly applied to the testing on the content of unfrozen water in natural frozen earth and artificial frozen earth. The method comprises the steps of firstly processing the tested soil sample obtained in place according to the specified specification; subsequently freezing the tested soil sample to the low-temperature range of -30 to -15 DEG C; subsequently heating and melting the tested soil sample by natural convection under the room temperature air condition of 20 to 35 DEG C; recording thechange of the central temperature of the sample with the time; establishing a calculation model reflecting the temperature change process of the frozen earth according to a Newton cooling law; analyzing the convection heat transmission coefficient between air and soil; determining phase change time and phase change temperature so as to further calculate the content of unfrozen water under the frozen state; and finally calculating the characteristic curve of unfrozen water content during the melting process according to the test results. The method is simple and feasible and the testing resultis exact and reliable.
Owner:刘波 +1
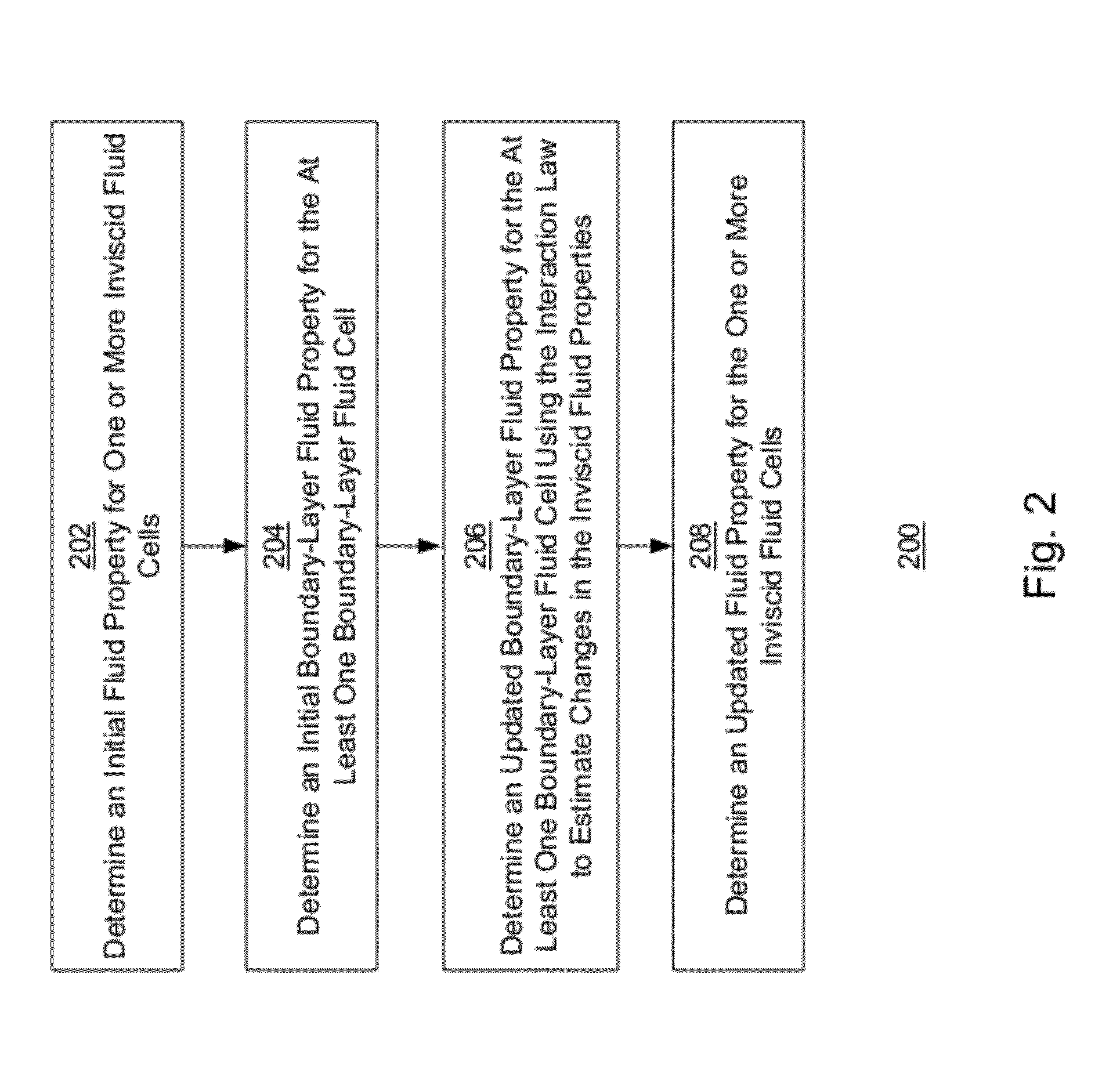
Generating inviscid and viscous fluid flow simulations over a surface using a quasi-simultaneous technique
ActiveUS20120245903A1Computation using non-denominational number representationDesign optimisation/simulationViscous effectLaws of thermodynamics
A fluid-flow simulation over a computer-generated surface is generated using a quasi-simultaneous technique. The simulation includes a fluid-flow mesh of inviscid and boundary-layer fluid cells. An initial fluid property for an inviscid fluid cell is determined using an inviscid fluid simulation that does not simulate fluid viscous effects. An initial boundary-layer fluid property a boundary-layer fluid cell is determined using the initial fluid property and a viscous fluid simulation that simulates fluid viscous effects. An updated boundary-layer fluid property is determined for the boundary-layer fluid cell using the initial fluid property, initial boundary-layer fluid property, and an interaction law. The interaction law approximates the inviscid fluid simulation using a matrix of aerodynamic influence coefficients computed using a two-dimensional surface panel technique and a fluid-property vector. An updated fluid property is determined for the inviscid fluid cell using the updated boundary-layer fluid property.
Owner:AERION INTPROP MANAGEMENT CORP
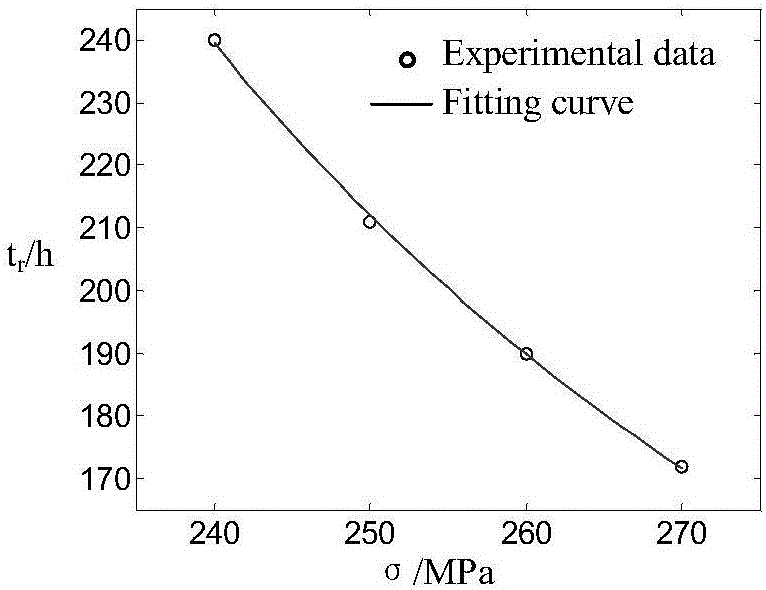
Method used for predicting creep life of heat-resisting alloy
ActiveCN106568655AReduce error rateEffective creep life predictionMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesPredictive methodsLaws of thermodynamics
The invention provides a method used for predicting the creep life of heat-resisting alloy. According to the method, a creep life predicting model is established on the foundation of Arrhenius law; tensile creep life data at different stress at a certain temperature is predicted via fitting of the creep life predicting model, model parameter values are determined, a relationship formula of the creep life at a prediction temperature with the stress is obtained, and creep life prediction is carried out based on the relationship formula. In establishment of the creep life predicting model, action of high temperature strength of alloy materials on creep performance and influence factors of stress on creep deformation mechanism are taken into consideration fully, so that obtained results are more close to practical data, and creep life prediction accuracy is increased obviously. It is shown by results of creep life prediction tests of a plurality of materials that under experiment conditions, the prediction error of the method is reduced by one magnitude order in comparing with Arrhenius law and Larson-Miller method.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Intelligent Sensor System
InactiveUS20130346009A1Improve measurement resultsMake up for deficienciesMeasurement apparatus componentsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceData limitationsIntelligent decision support system
A sensor system and method of using the system synergistically to improve the accuracy and usefulness of measured results is described. The system is comprised of electronically linked components that act as markers to trigger events, producers that gather data from sensors and aggregators that combine the data from a plurality of producers using triggers from marker devices to select the data of interest. The system is shown to be applicable to selection of data regions of interest and to analysis of the data to improve accuracy. The analysis of the data of any particular sensor within the system makes use of extrinsic data, being data generated by other sensors and intrinsic data, that is data or data limits that are known to be true from nature, laws of physics or just the particular information the user wants to acquire. The system is demonstrated on the analysis of Doppler radar measurements of a thrown object.
Owner:WINTER KIRT ALAN +1
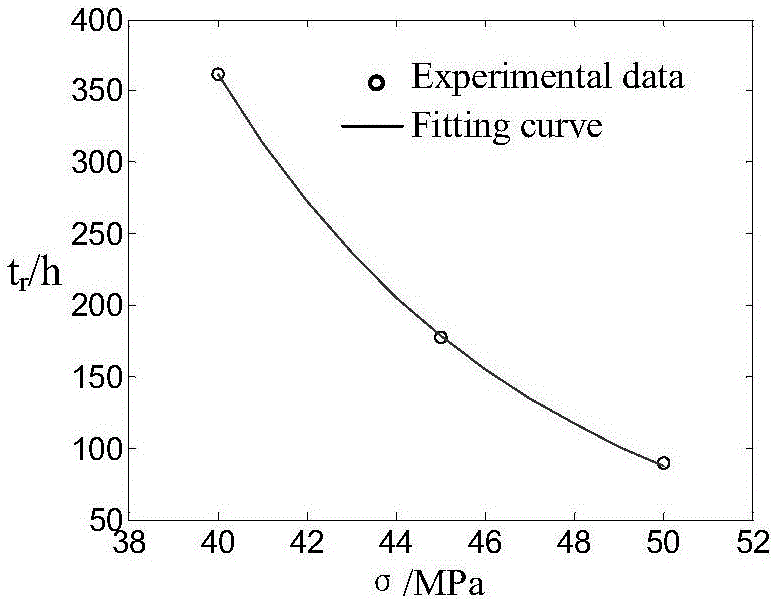
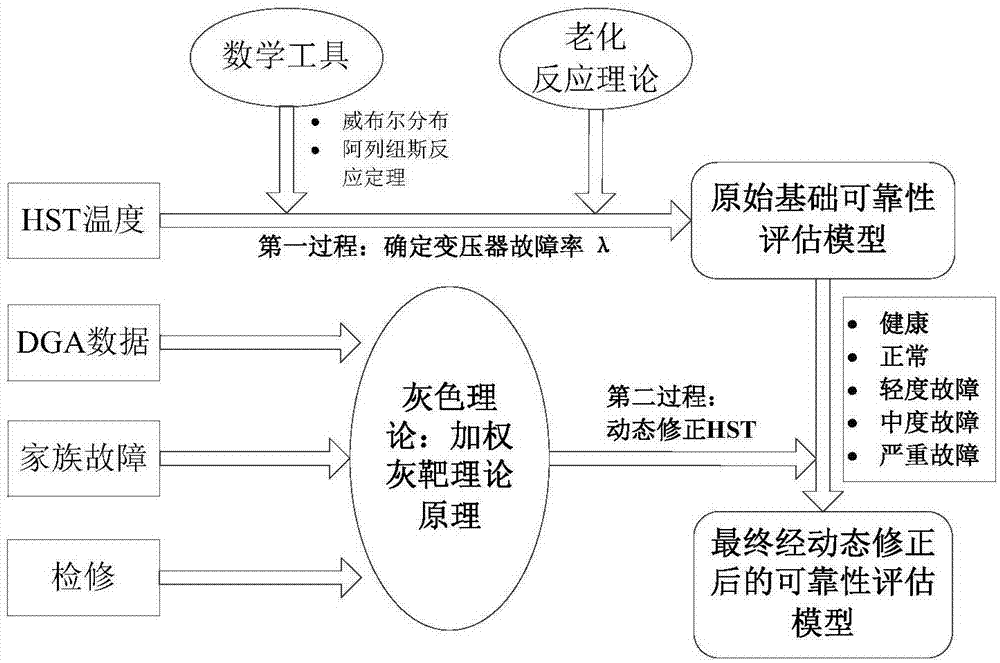
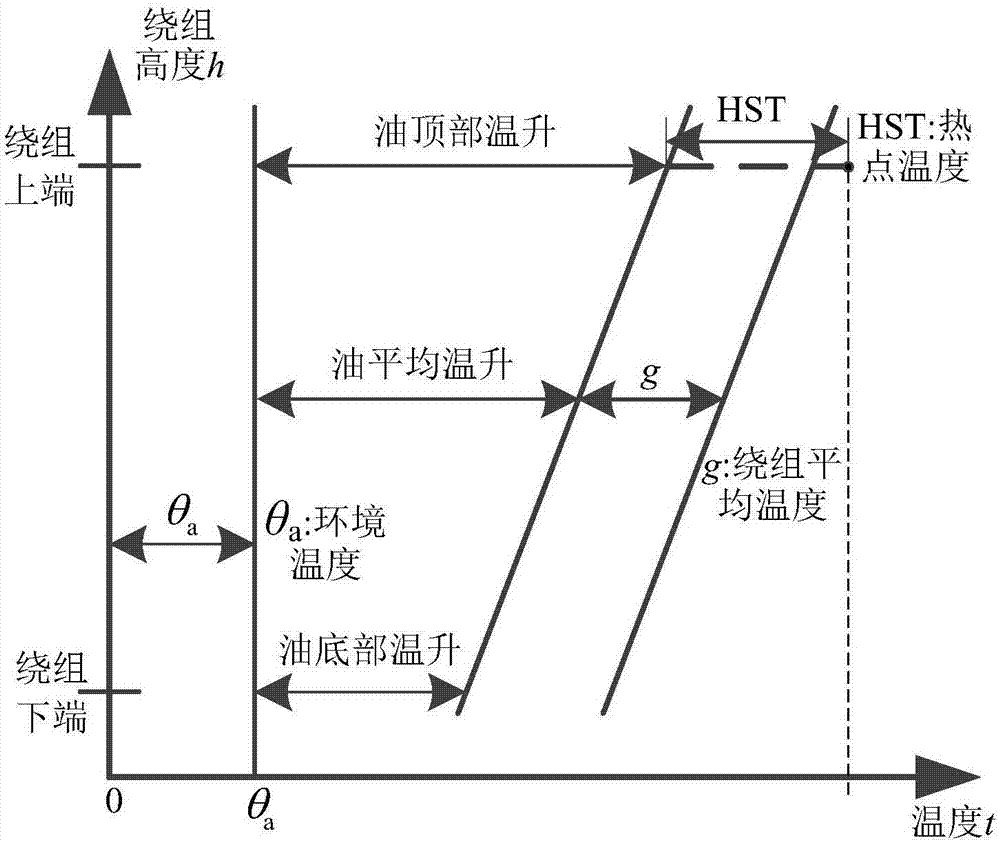
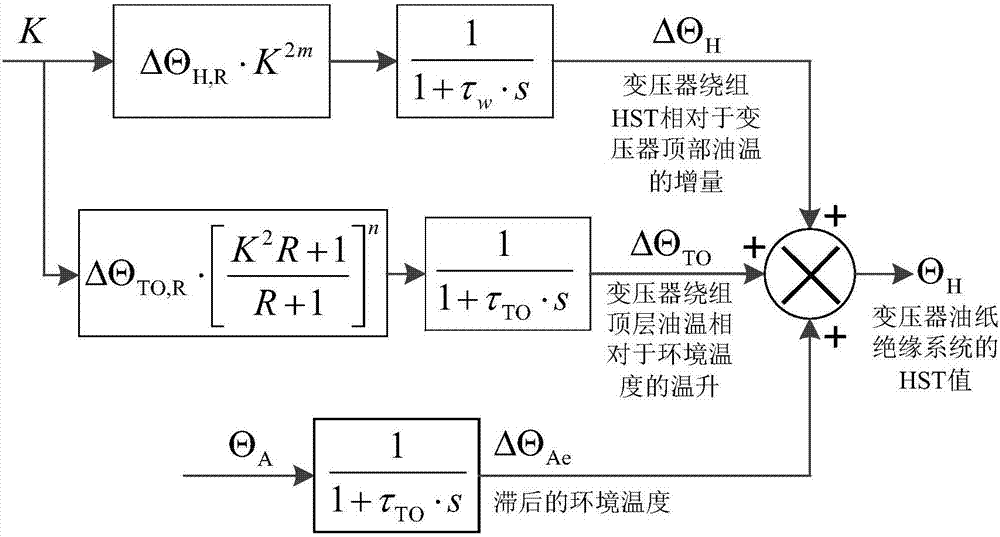
Dynamic correction method for reliability assessment of large-sized oil-immersed power transformer
InactiveCN107330286ATaking into account individual differencesEvaluation results are reliableSpecial data processing applicationsInformaticsLaws of thermodynamicsInsulation system
The invention discloses a dynamic correction method for reliability assessment of a large-sized oil-immersed power transformer; a transformer oil-paper insulating system is used as an assessment object, and two processes are involved; in the first process, with hotspot temperature calculation as the core, an HST-based (hotspot temperature) transformer aging fault model is established in conjunction with Weibull distribution and Arrhenius reaction law, winding HST is acquired by calculating, and fault rate gamma of the transformer oil-paper insulating system is solved; in the second process, with gray target correction analysis via dissolved gas in oil as the core, a relationship between transformer health state and its predicted life is established via grey theory, equivalent HST value is obtained, dynamic correction is provided for the basic model in the first process, and it is ensured that the assessment value is capable of well tracing and reflecting actual reliability level of the transformer. By using the method, it is possible to effectively solve the problems that, for instance, a transformer reliability analysis model has low accuracy and is difficult to popularize and apply.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Simulations for hydraulic fracturing treatments and methods of fracturing naturally fractured formation
A hydraulic fracture design model that simulates the complex physical process of fracture propagation in the earth driven by the injected fluid through a wellbore. An objective in the model is to adhere with the laws of physics governing the surface deformation of the created fracture subjected to the fluid pressure, the fluid flow in the gap formed by the opposing fracture surfaces, the propagation of the fracture front, the transport of the proppant in the fracture carried by the fluid, and the leakoff of the fracturing fluid into the permeable rock. The models used in accordance with methods of the invention are typically based on the assumptions and the mathematical equations for the conventional 2D or P3D models, and further take into account the network of jointed fracture segments. For each fracture segment, the mathematical equations governing the fracture deformation and fluid flow apply. For each time step, the model predicts the incremental growth of the branch tips and the pressure and flow rate distribution in the system by solving the governing equations and satisfying the boundary conditions at the fracture tips, wellbore and connected branch joints. An iterative technique is used to obtain the solution of this highly nonlinear and complex problem.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Well Modeling Associated With Extraction of Hydrocarbons From Subsurface Formations
InactiveUS20090216508A1Fluid removalSpecial data processing applicationsFirst principleLaws of thermodynamics
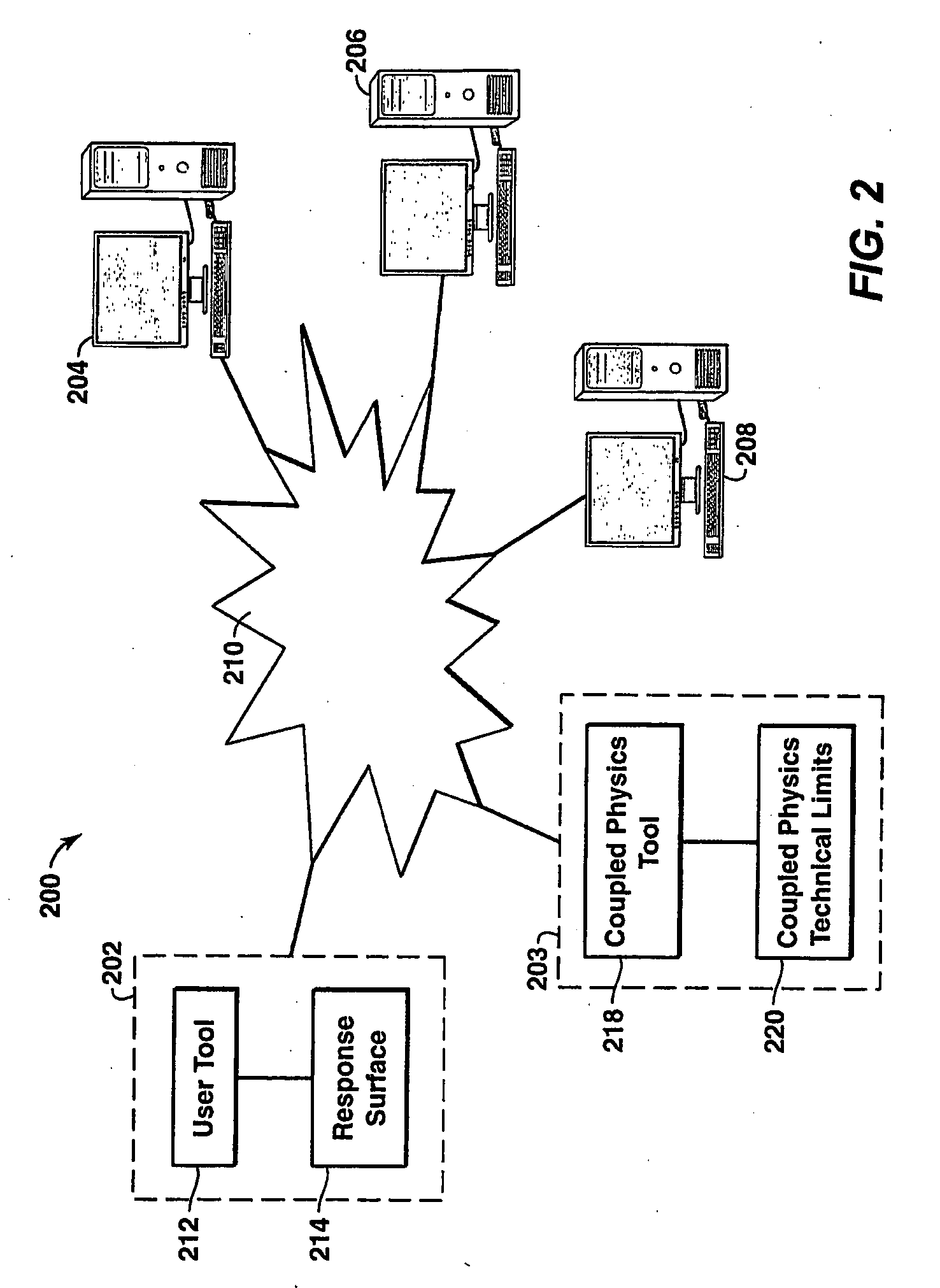
A method and apparatus for associated with various phases of a well completion. In one embodiment, a method is described that includes identifying first principle physical laws governing performance of a well completion and parameters associated with the first principle physical laws or the well. A coupled physics simulator is selected based on the first principle physical laws. Then, a coupled physics limit is generated based upon the coupled physics simulator that incorporates the first principle physical laws and the parameters.
Owner:DALE BRUCE A +3
Ionic liquid high temperature gas sensors
ActiveUS7464580B2Analysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesGas phaseElectrical polarity
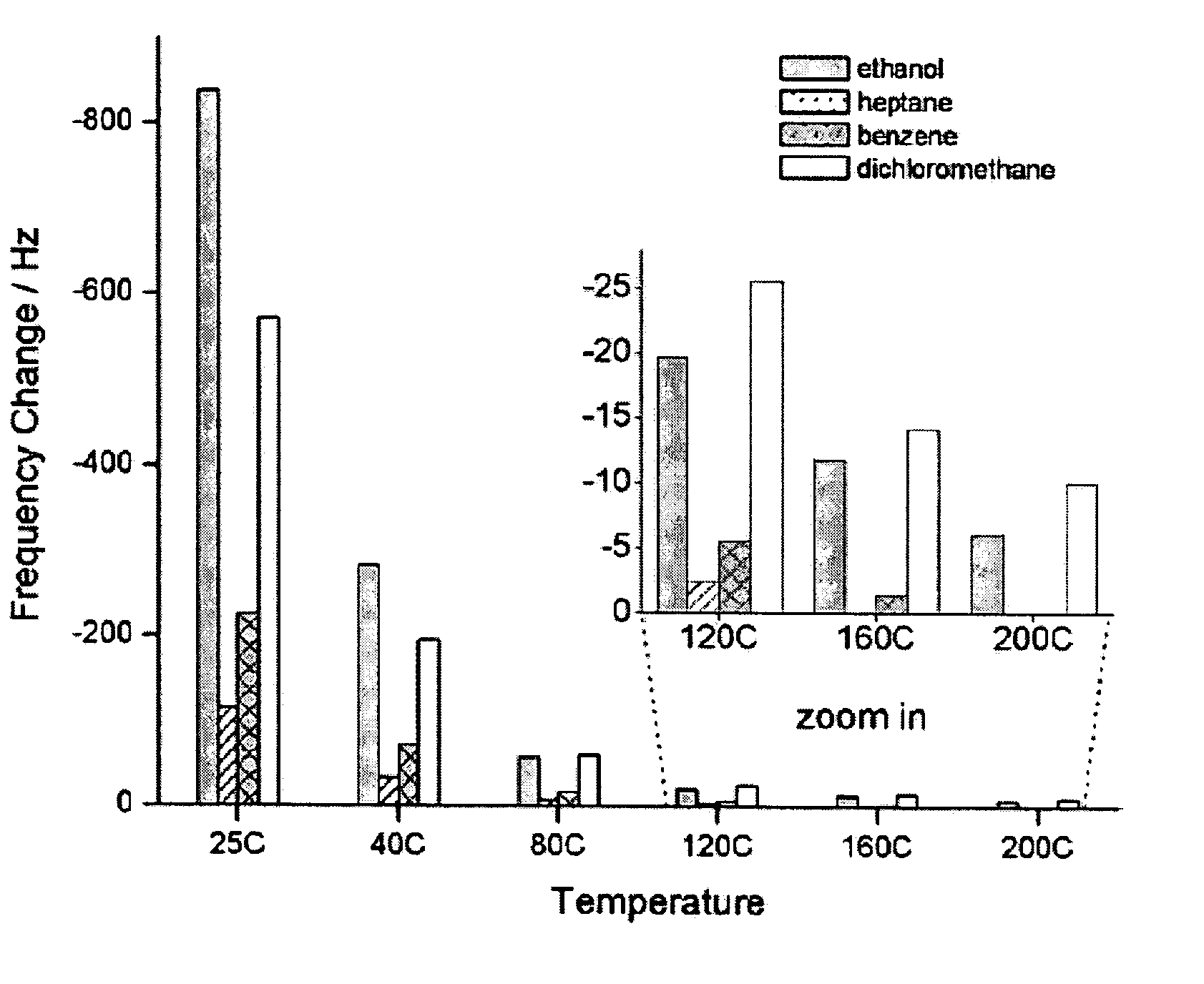
An ionic liquid piezoelectric gas sensor for the detection of polar and nonpolar organic vapors. The gas sensor can operate at high temperatures with a fast linear response which is also reversible. At high temperatures, the frequency change (Δf) versus concentration (C) curve mirrors the Henry's gas law, such that the concentration of a gas sample in liquid solvent is proportional to the concentration or partial pressure of the sample in gas phase. The gas sensor can be used for quantitative analysis of gas vapors and determination of Henry constants.
Owner:OAKLAND UNIVESITY
Unbiased code phase discriminator
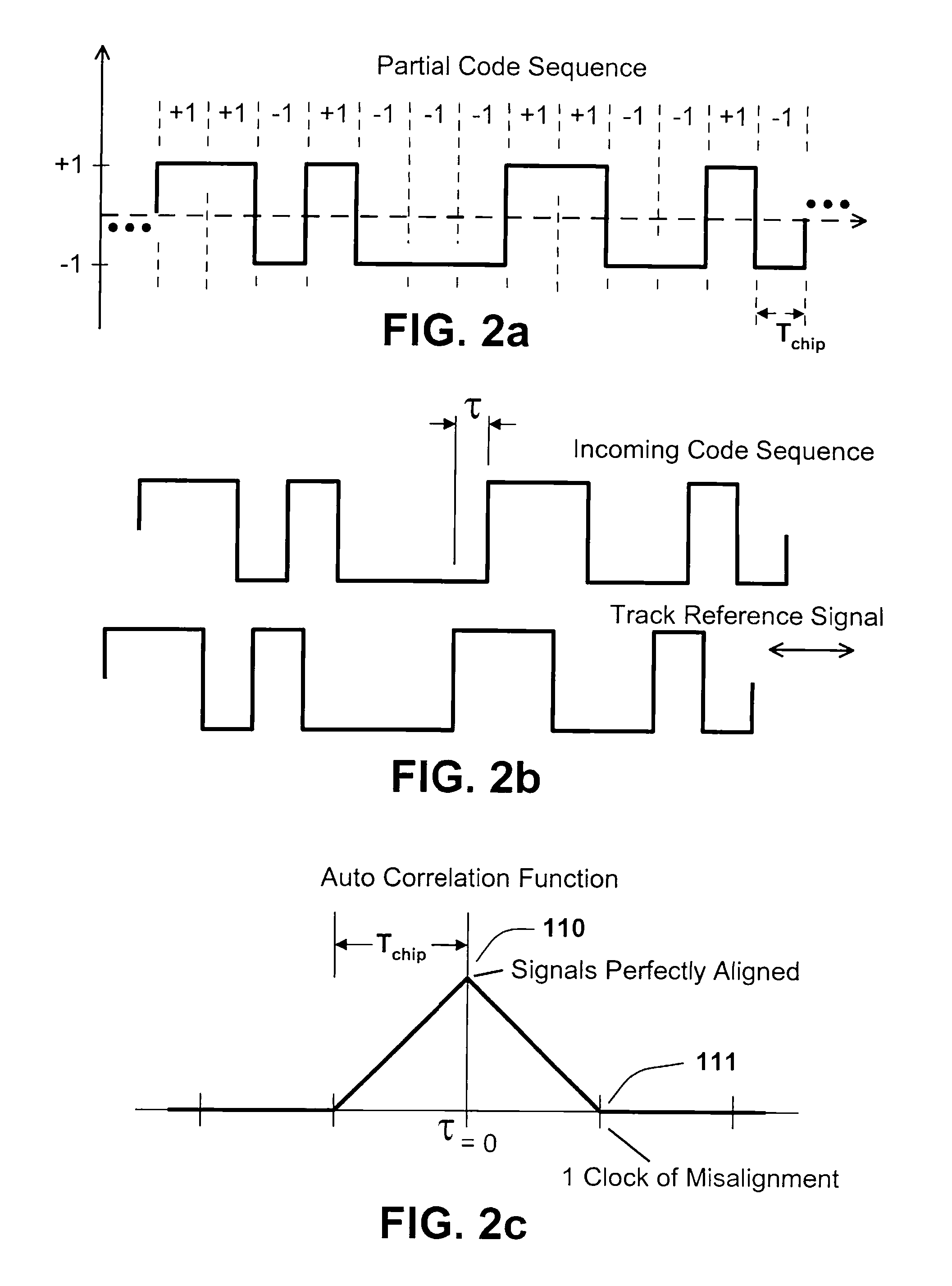
ActiveUS20080205494A1Reduce errorsAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsSatellite radio beaconingDiscriminatorCorrelation kernel
A feedback control law steers a reference phase that tracks the phase of a received code sequence. The reference phase clocks a track-reference signal consisting of a series of correlation kernels, over which data is extracted and then summed in various combinations. The correlation kernels are designed in such a manner that errors caused by multipath are eliminated or substantially reduced. Furthermore, the areas of the correlation kernels are balanced across level-transitions of a code and non-transitions to eliminate phase biases when tracking specific satellites. Extra care must be taken to balance the correlation kernels in this manner due to a little known aspect of GPS C / A codes. Specifically, not all C / A codes have the same ratio of level-transitions to non-transitions as has been assumed in prior art.
Owner:HEMISPHERE GNSS
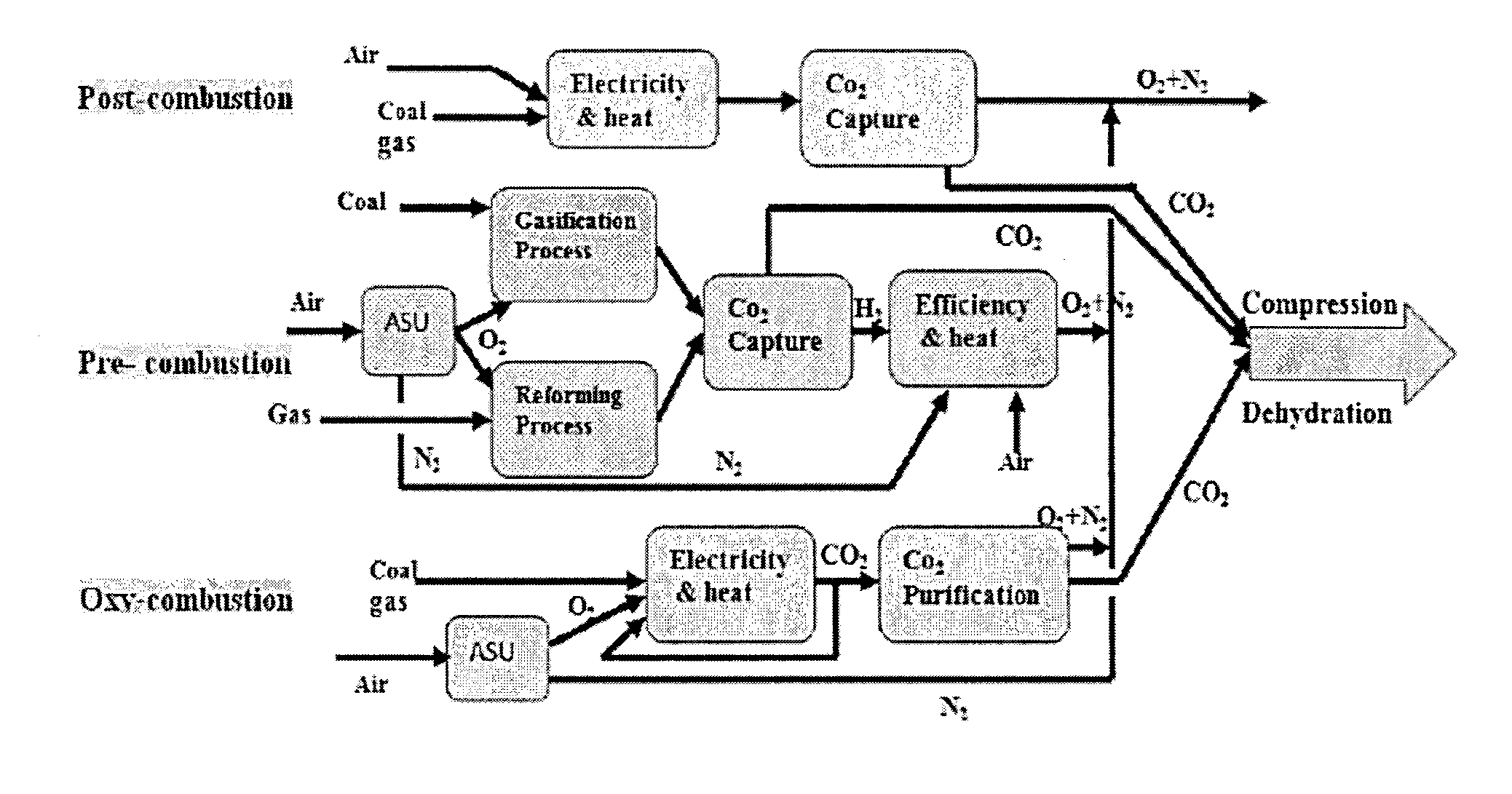
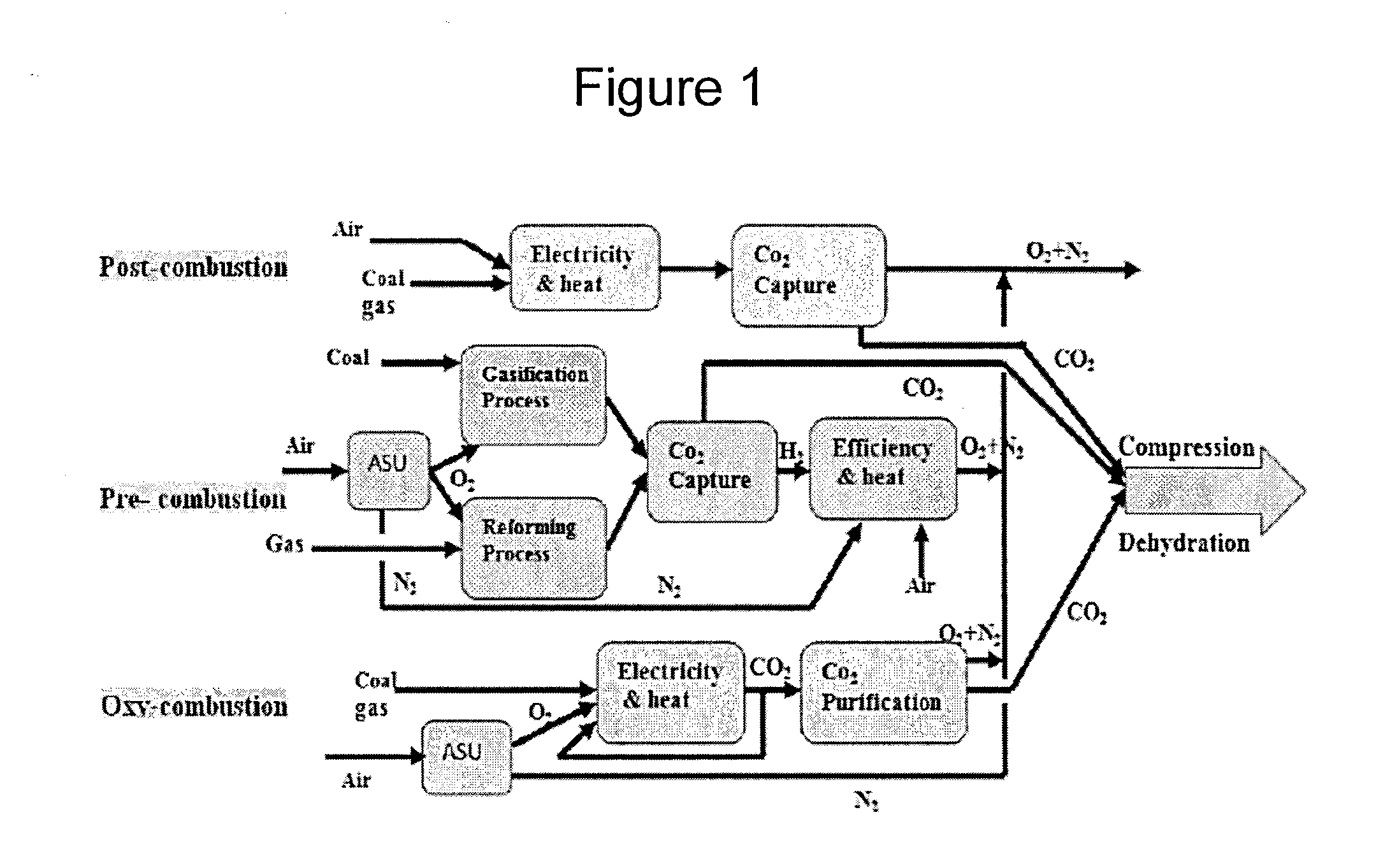
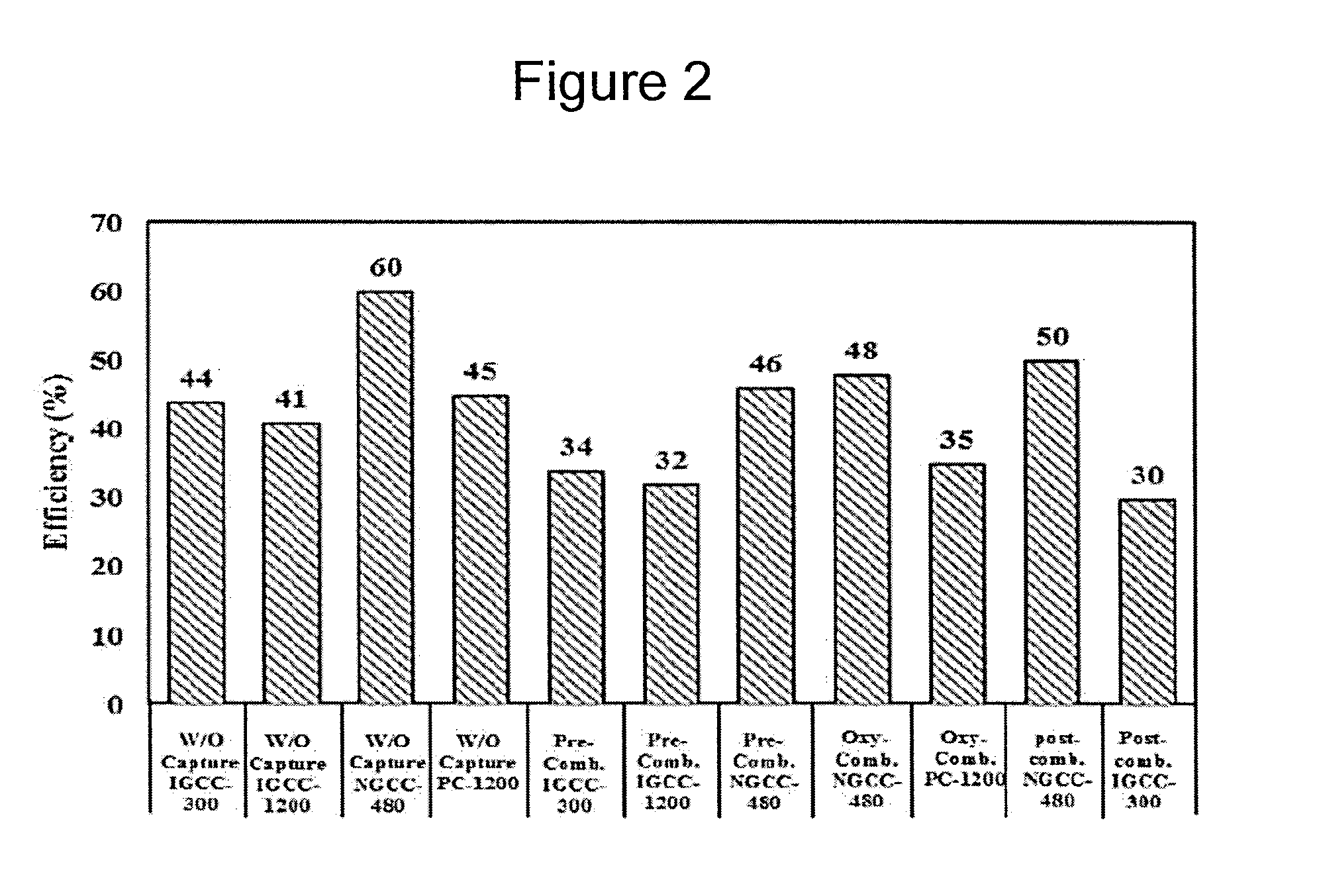
Applications of oxy-fuel combustion technology into gas turbine combustors and ion transport membrane reactors
InactiveUS20150267611A1Continuous combustion chamberTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustion chamberAtmospheric air
Experimental and numerical investigations on an atmospheric diffusion oxy-combustion flame in a gas turbine model combustor are conducted. The combustor is fuelled with CH4CH4 and a mixture of CO2 and O2 as oxidizer. The stability of the oxy-combustion flame is affected when the operating percentage of oxygen in the oxidizer mixture is reduced below 25%. A new 3D reactor design is introduced for the substitution of ITM reactors into a gas turbine combustor. A new oxygen permeation equation model has been developed by fitting the experimental data available in the literature for a LSCF ion transport membrane. The monolith structure design ITM reactor is capable of delivering power ranging from 5 to 8 MWe based on cycle first law efficiency.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Interactive system and method for rendering an object
ActiveUS9132352B1More interactiveInput/output for user-computer interactionImage enhancementMotion vectorDisplay device
A system and method for receiving an ordered set of images and analyzing the images to determine at least one position in space and at least one motion vector in space and time for at least one object represented in the images is disclosed. Using these vectors, a four dimensional model of at least a portion of the information represented in the images is formulated. This model generally obeys the laws of physics, though aberrations may be imposed. The model is then exercised with an input parameter, which, for example, may represent a different perspective than the original set of images. The four dimensional model is then used to produce a modified set of ordered images in dependence on the input parameter and optionally the set of images, e.g., if only a portion of the data represented in the images is modeled. The set of images may then be rendered on a display device.
Owner:RABIN GREGORY S +1
Systems and methods for derivative-free output feedback adaptive control
ActiveUS20120265367A1Accurate responseMinimize complexityDigital data processing detailsVehicle position/course/altitude controlLaws of thermodynamicsSelf adaptive
An adaptive control system is disclosed. The control system can control uncertain dynamic systems. The control system can employ one or more derivative-free adaptive control architectures. The control system can further employ one or more derivative-free weight update laws. The derivative-free weight update laws can comprise a time-varying estimate of an ideal vector of weights. The control system of the present invention can therefore quickly stabilize systems that undergo sudden changes in dynamics, caused by, for example, sudden changes in weight. Embodiments of the present invention can also provide a less complex control system than existing adaptive control systems. The control system can control aircraft and other dynamic systems, such as, for example, those with non-minimum phase dynamics.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Method for more rapidly producing the representative stochastic model of a heterogeneous underground reservoir defined by uncertain static and dynamic data
InactiveUS7392166B2Promote rapid formationSeismologyAnalogue computers for distribution networksPseudo dataLaws of thermodynamics
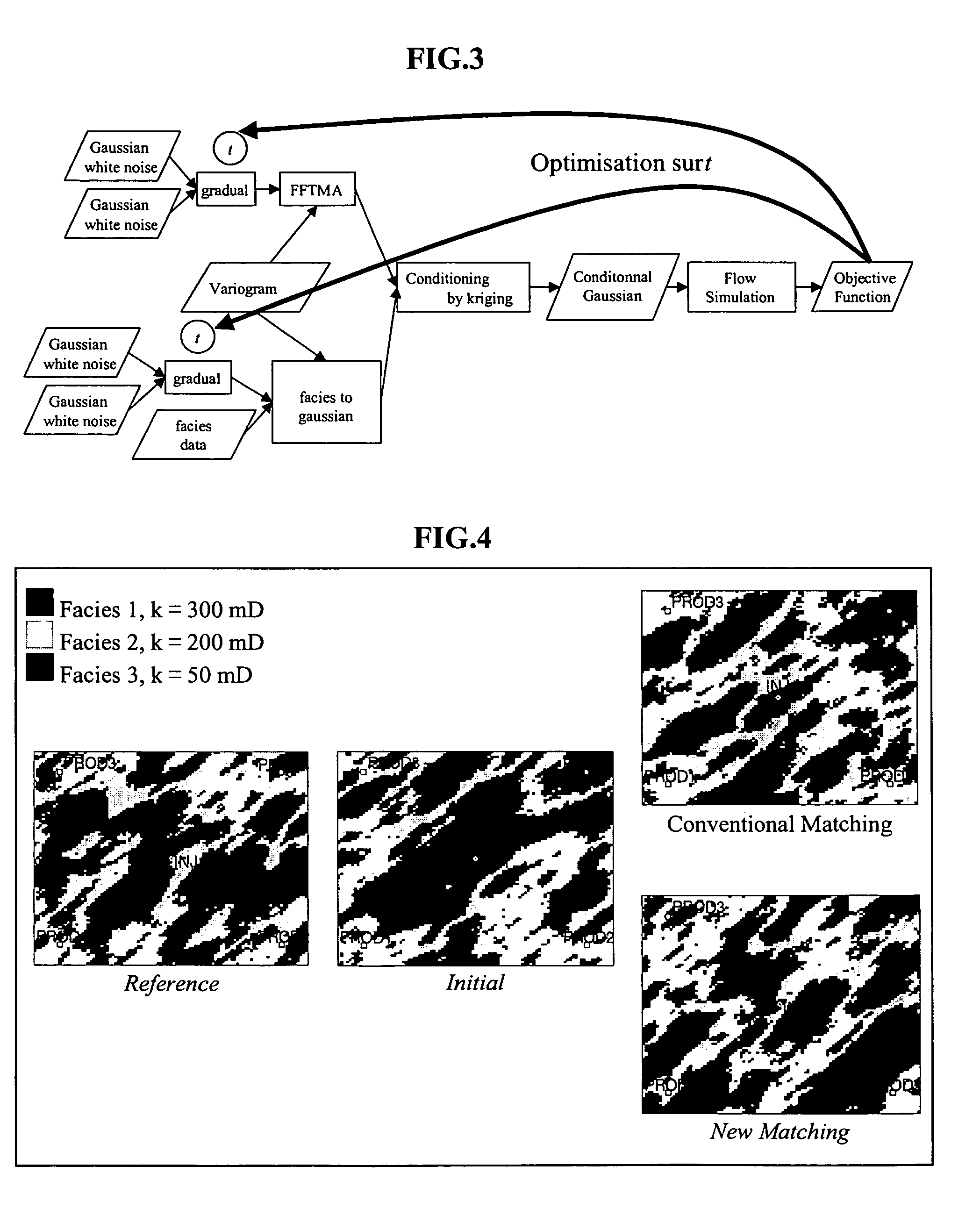
A method for more rapidly forming a stochastic model of Gaussian or Gaussian-related type, representative of a porous heterogeneous medium such as an underground reservoir, constrained by data characteristic of the displacement of fluids and punctual observations, these observations being uncertain and characterized by a probability law. The method transforms static information, given in form of probability laws, into Gaussian punctual pseudo-data which has the advantage of being compatible with a gradual deformation method. An objective function J measuring the difference between the dynamic data (production data for example) and the corresponding responses simulated for the reservoir model considered may be minimized.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Intelligent mechatronic control suspension system based on soft computing
A control system for optimizing a shock absorber having a non-linear kinetic characteristic is described. The control system uses a fitness (performance) function that is based on the physical laws of minimum entropy and biologically inspired constraints relating to mechanical constraints and / or rider comfort, driveability, etc. In one embodiment, a genetic analyzer is used in an off-line mode to develop a teaching signal. An information filter is used to filter the teaching signal to produce a compressed teaching signal. The compressed teaching signal can be approximated online by a fuzzy controller that operates using knowledge from a knowledge base. In one embodiment, the control system includes a learning system, such as a neural network that is trained by the compressed training signal. The learning system is used to create a knowledge base for use by an online fuzzy controller. The online fuzzy controller is used to program a linear controller.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
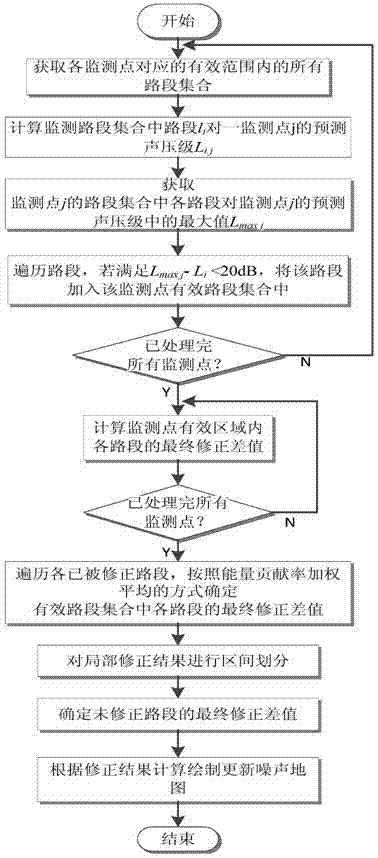
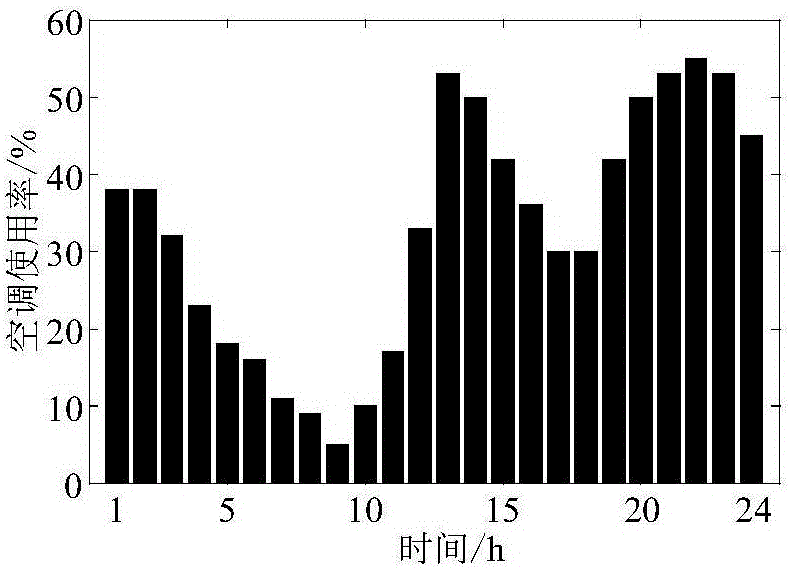
Road traffic noise map updating method based on noise monitoring data
ActiveCN104331609AGuaranteed to be scientificReduce computationSpecial data processing applicationsNoise monitoringLaws of thermodynamics
The invention provides a road traffic noise map updating method based on noise monitoring data. According to the method, noise monitoring and original traffic flow data are utilized, firstly, road section and monitoring point data are organized, and an effective road section set of each monitoring point is constructed; then, local correction is carried out, and the correcting difference value of each road section in the effective road section set of the monitoring points is calculated according to an energy conservation law; next, the local correction result is subjected to interval division; the correction difference value of other uncorrected road sections is determined according to an interval division result; finally, calculation and rendering are carried out, and an updated road traffic noise map is obtained. The road traffic noise map updating method is applied to the updating of the road traffic noise map, the calculation efficiency is high, and the updating effect is good.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Control device for mobile body
ActiveUS8204626B2Smoothly deviationEliminate biasSolid-state devicesElectric testing/monitoringLaws of thermodynamicsEngineering
A control device for a mobile body makes it possible to smoothly correct the deviation of an actual posture of a base body of a mobile body, which travels with the base body thereof moving up and down, from a desired posture of the base body while restraining an overshoot or an undershoot from occurring. To determine a required manipulated variable according to a feedback control law in order to converge a state amount deviation related to the posture of the base body of the mobile body to zero, the feedback gain of the feedback control law is determined by using the time series in a period from current time to predetermined time in the future in the time series of a desired inertial force of the mobile body or the base body. The required manipulated variable is determined by the calculation of the feedback control law on the basis of the determined feedback gain and an observed value of the state amount deviation.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Photovoltaic intelligent community electric automobile and controllable load two-stage optimization scheduling method
The invention discloses a photovoltaic intelligent community electric automobile and controllable load two-stage optimization scheduling method. A controllable load output model is established based on residential area, controllable load use characteristics and laws of thermodynamics, an electric automobile charging model is established based on electric automobile user driving characteristics, and a photovoltaic probability model is established based on the condition that photovoltaic output forecast deviations meet normal distribution; in day-ahead scheduling, time-of-use electricity price is set with profit maximization of an operator obtained after orderly charging of electric automobiles being as a target, and the electric automobiles are guided to be charged orderly through the time-of-use electricity price to reduce system valley-peak difference; taking consideration of influence of photovoltaic prediction and temperature prediction deviation on intelligent community electric automobile and controllable load co-scheduling, supply and demand unbalance due to day-ahead predication is corrected by introducing real-time scheduling; and in real-time scheduling, with the time-of-use electricity price set in day-ahead scheduling being as a basis, a day-ahead charging scheme of the electric automobiles is optimized to reduce real-time scheduling cost and stabilize load fluctuation. The method comprises day-ahead scheduling and real-time scheduling two-stage optimization.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com