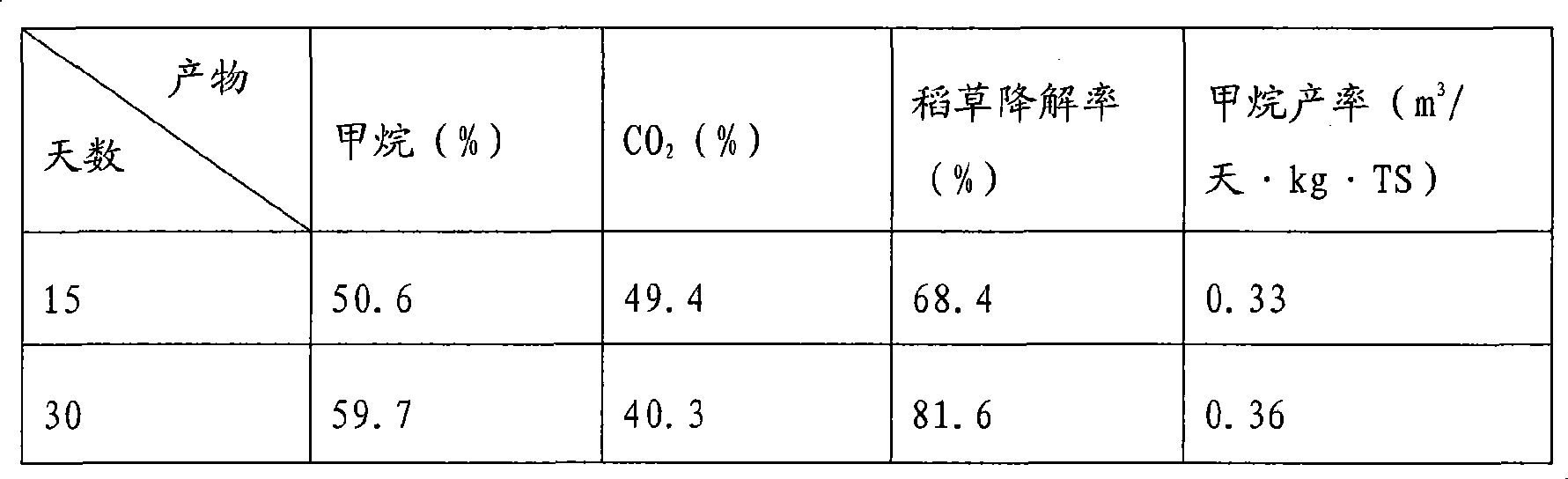
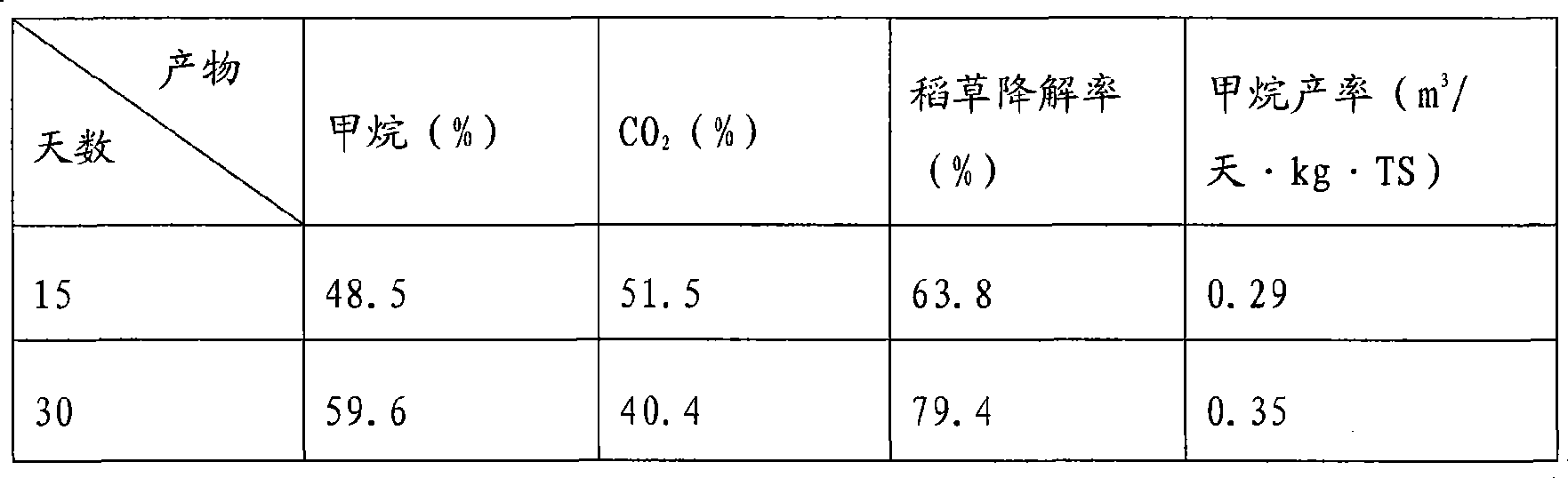
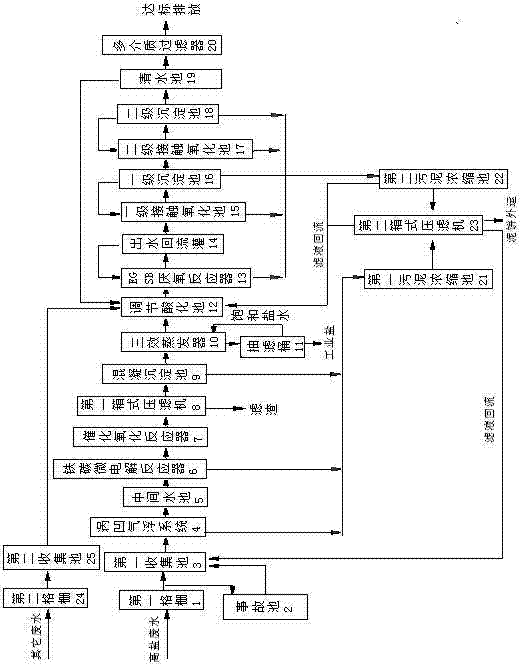
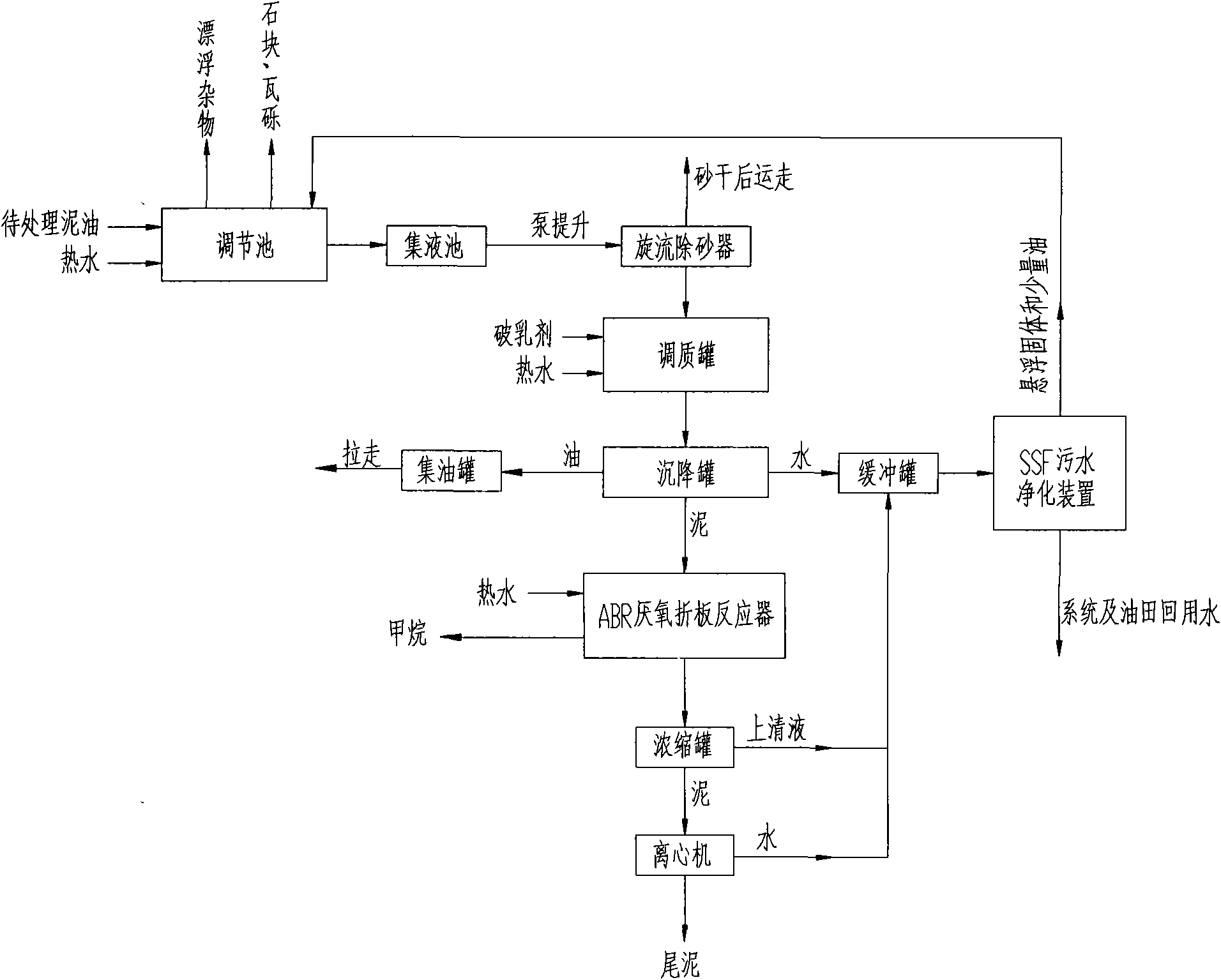
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
211 results about "Anaerobic degradation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Anaerobic Biodegradation. The degradation of compounds by microorganisms in the absence of oxygen is termed as anaerobic biodegradation. The process whereby microorganisms use a chemical other than oxygen as an electron acceptor.
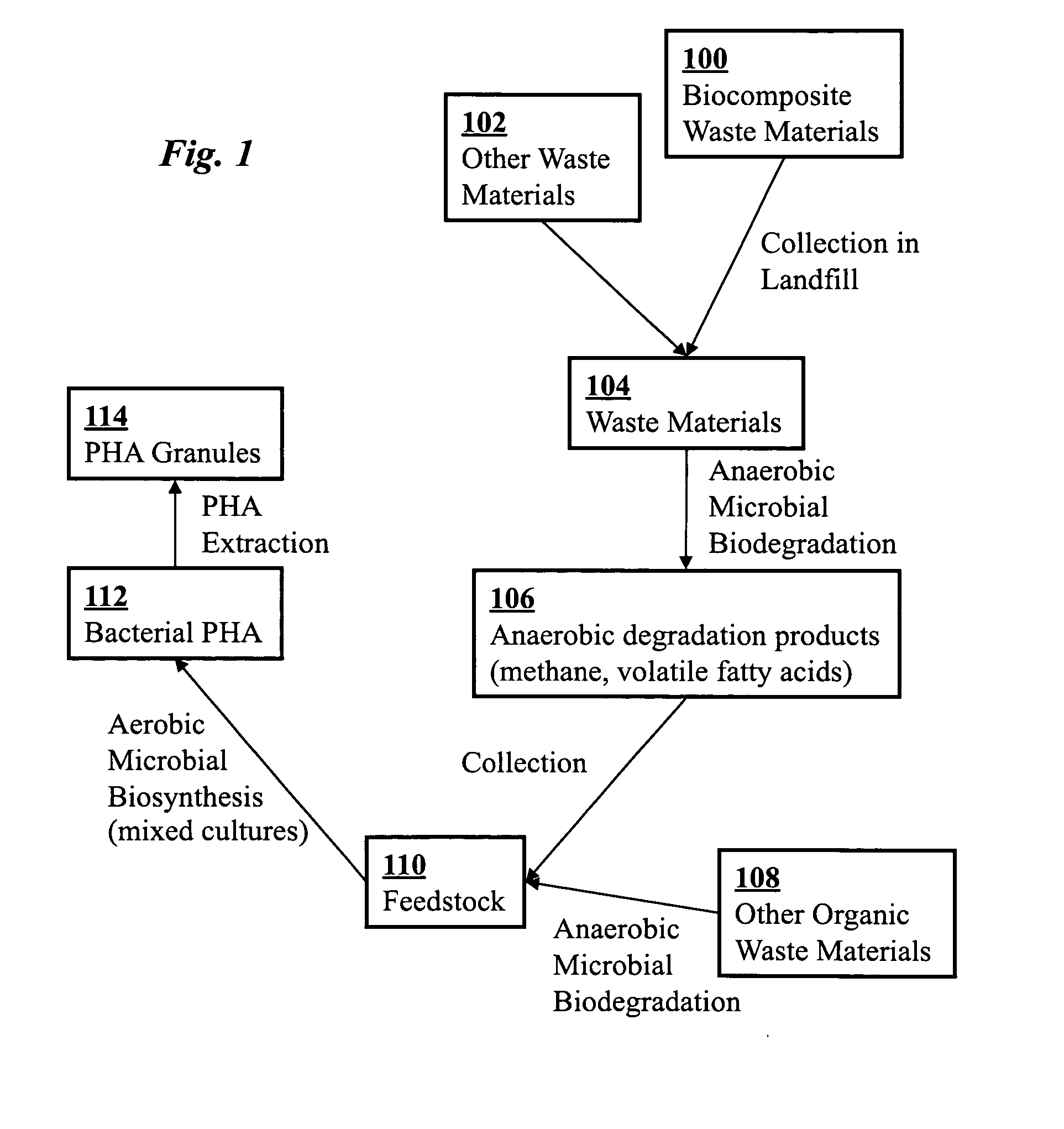
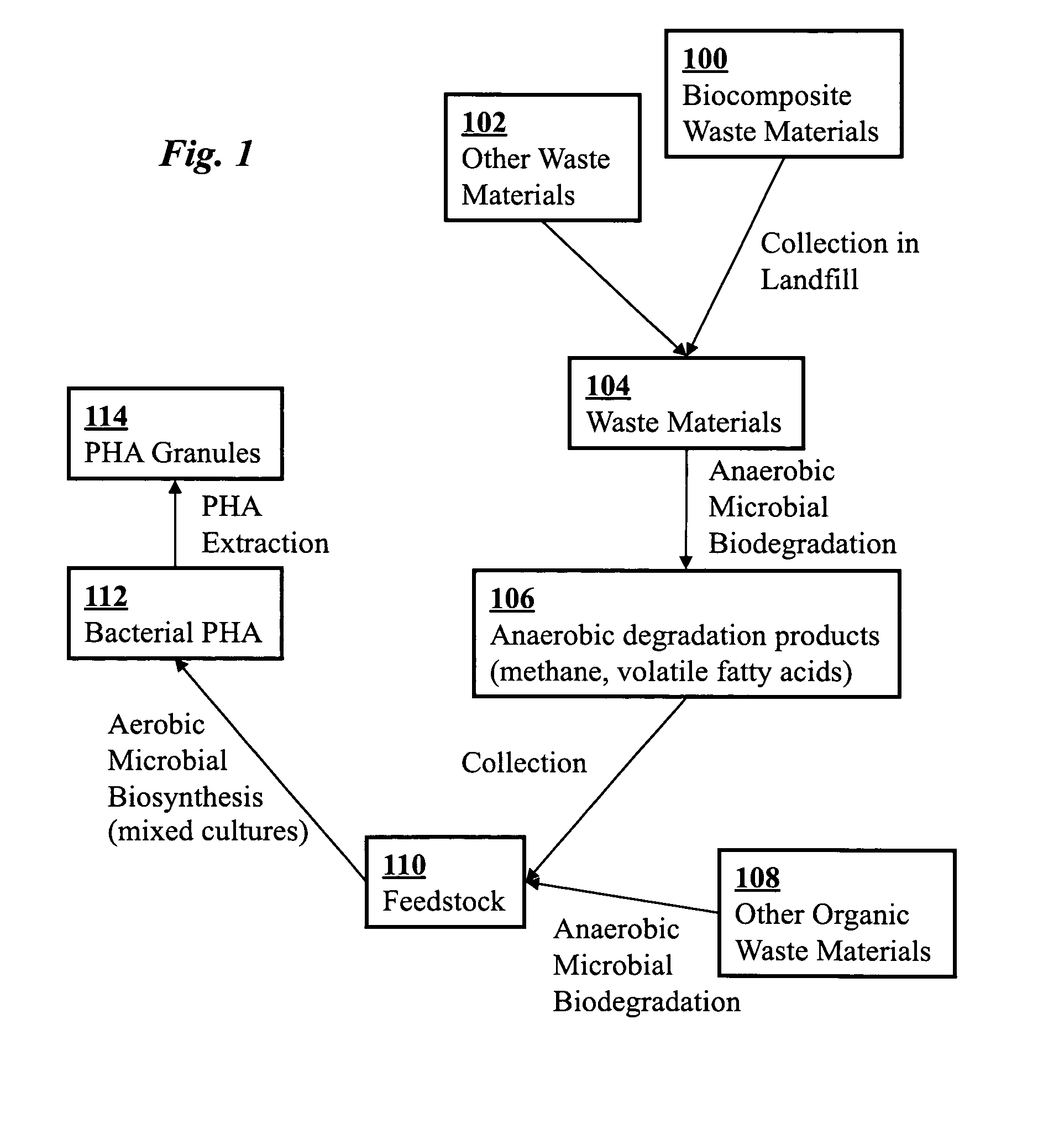
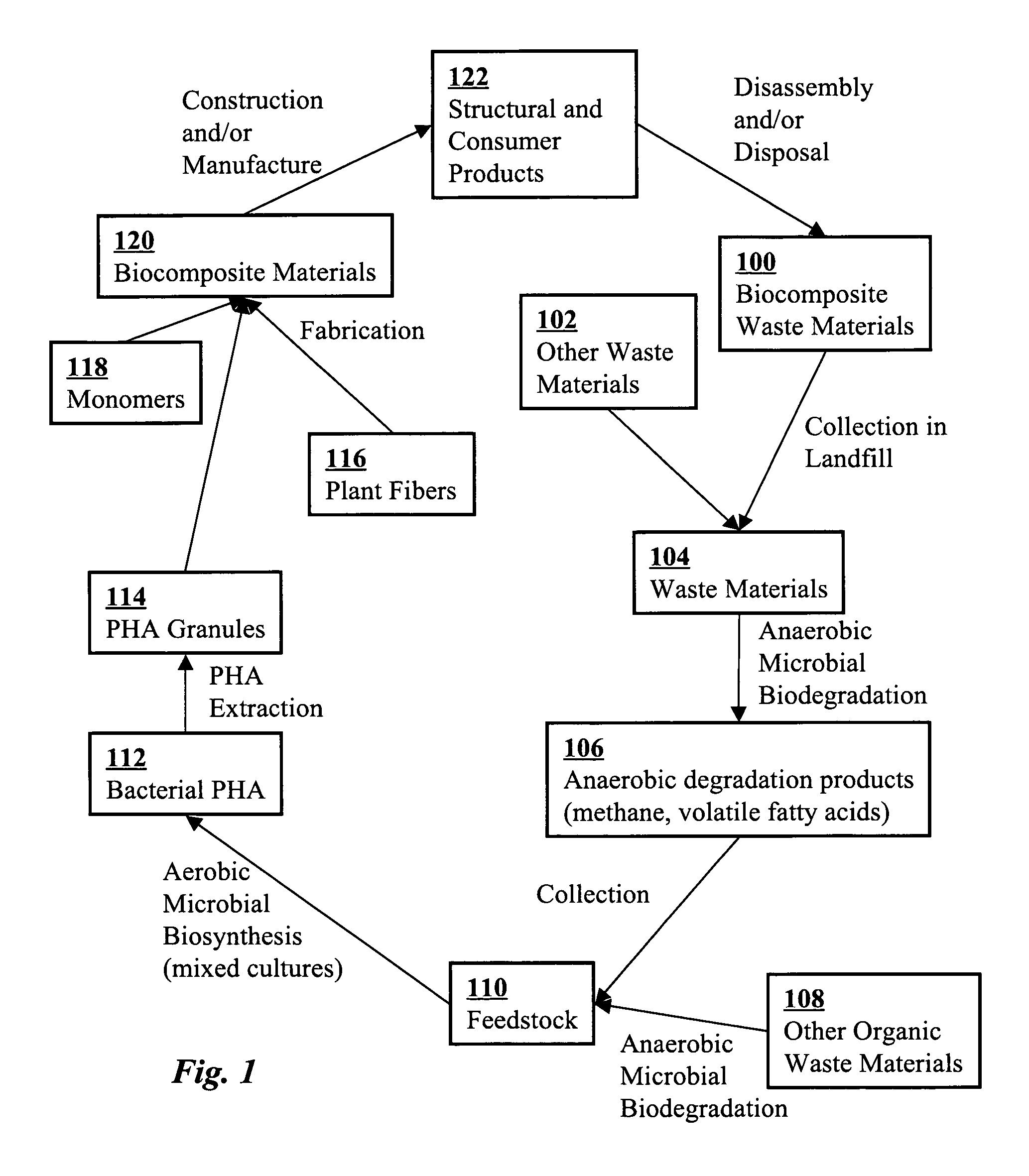
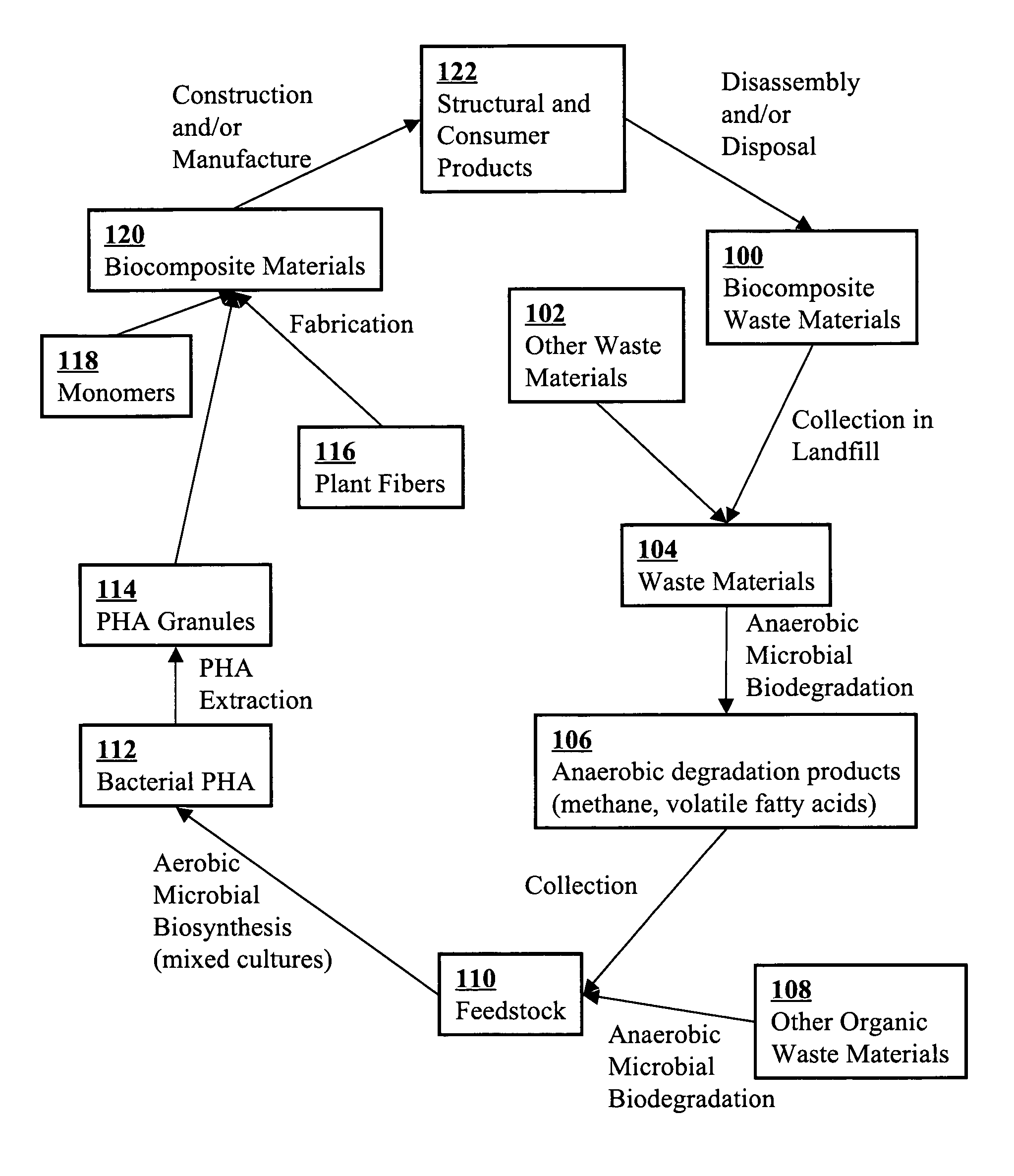
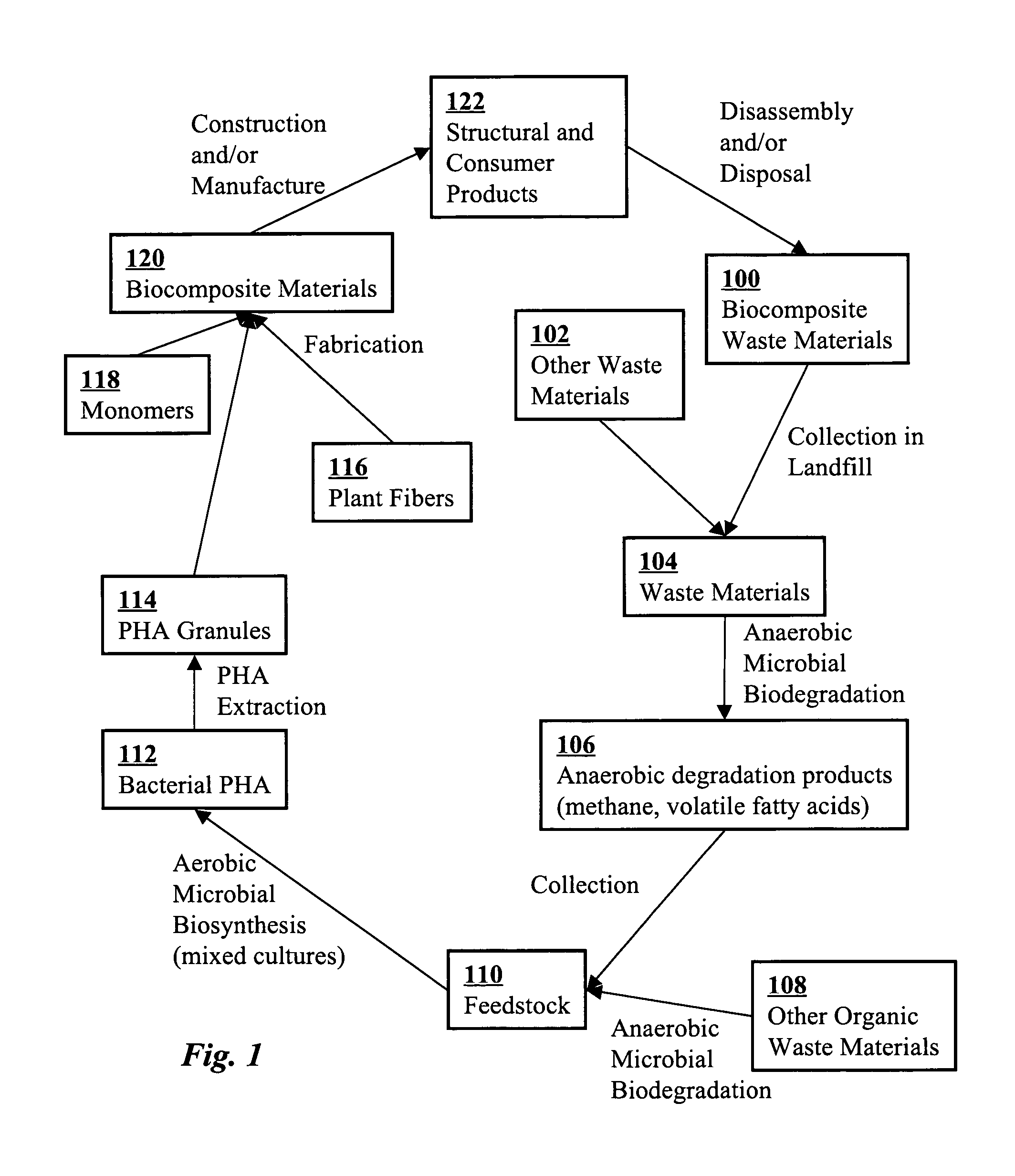
Use of selection pressures to enable microbial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from anaerobic degradation products
InactiveUS20090317879A1Cost of producingImprove the level ofWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsMethane gas
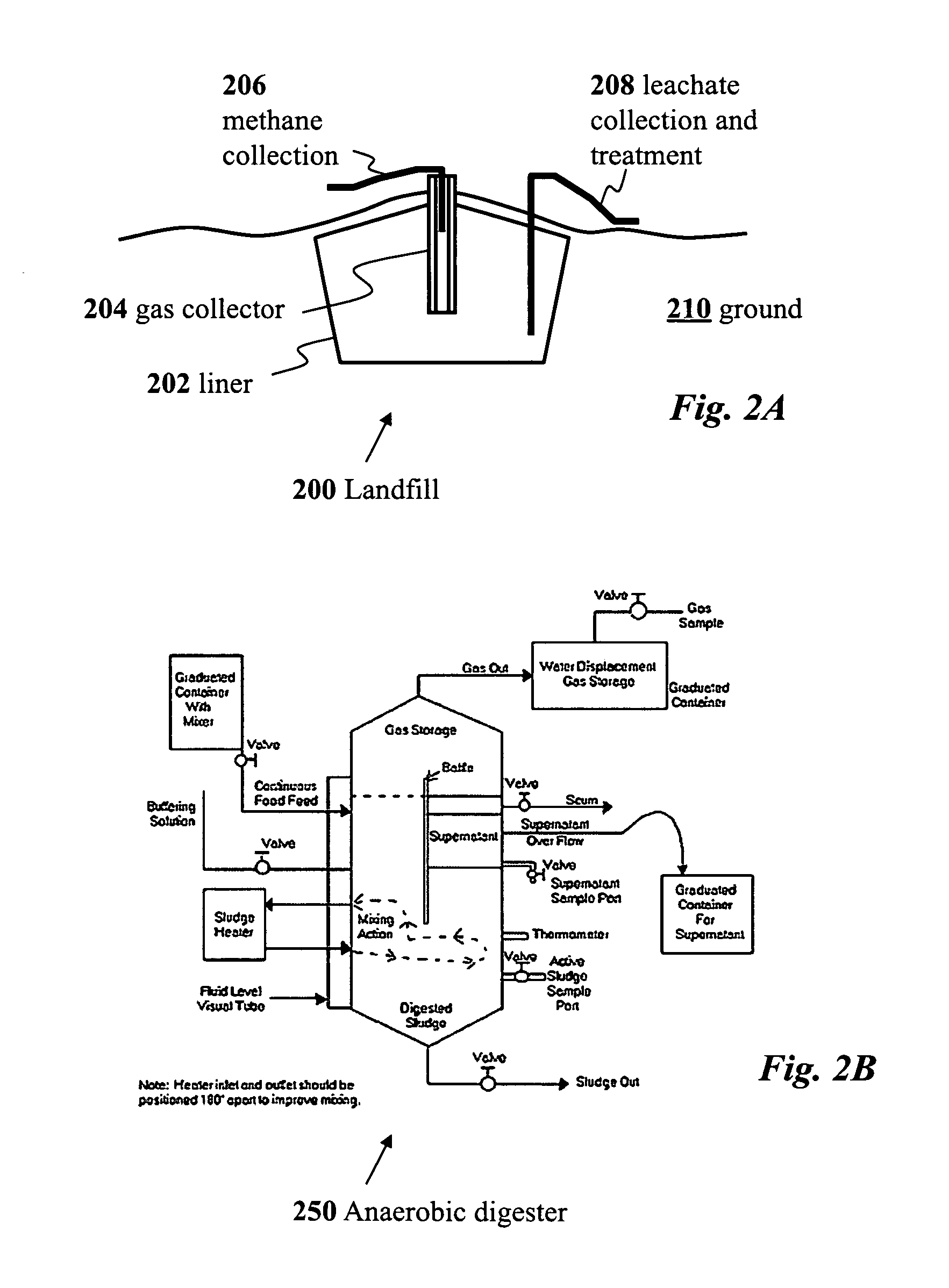
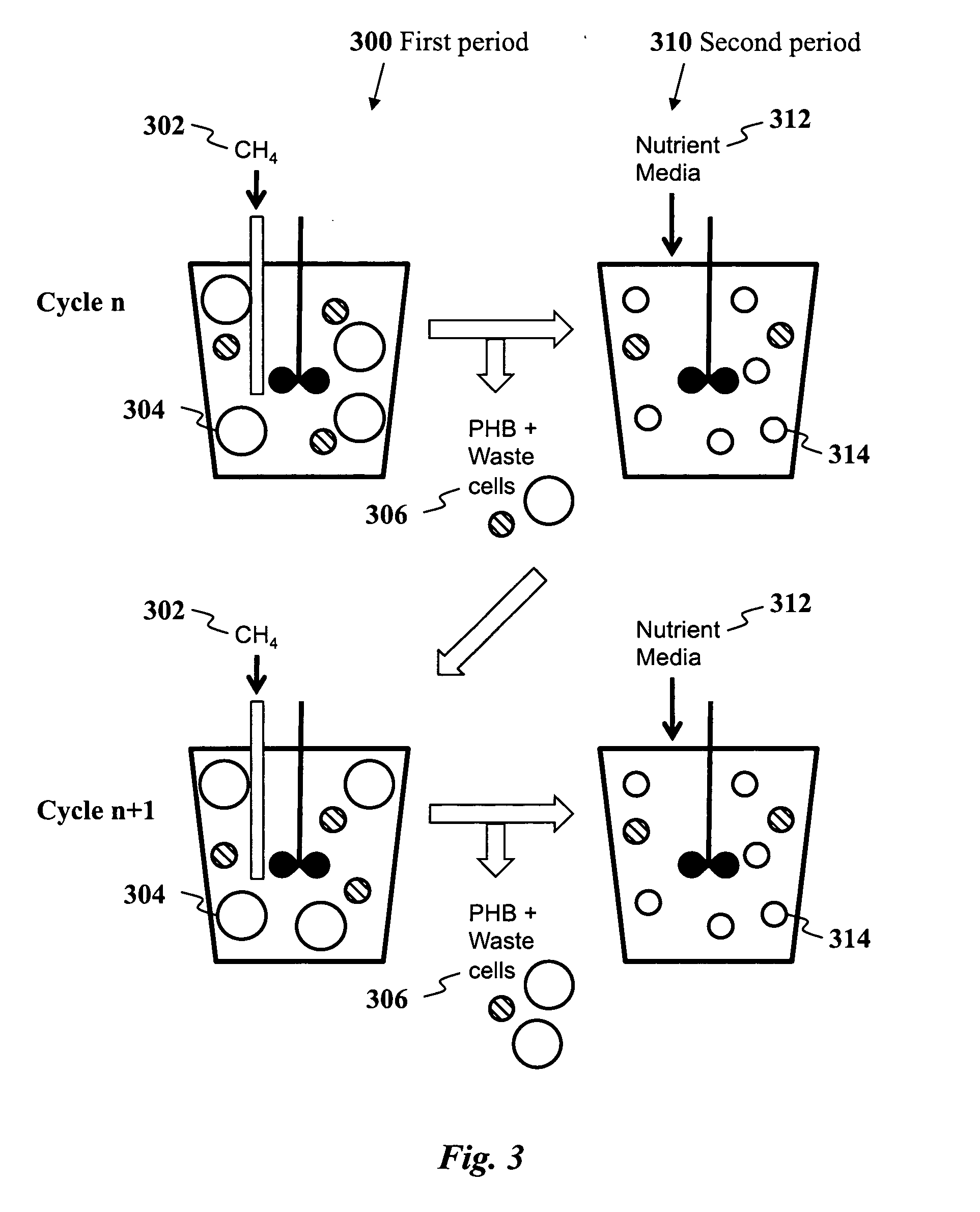
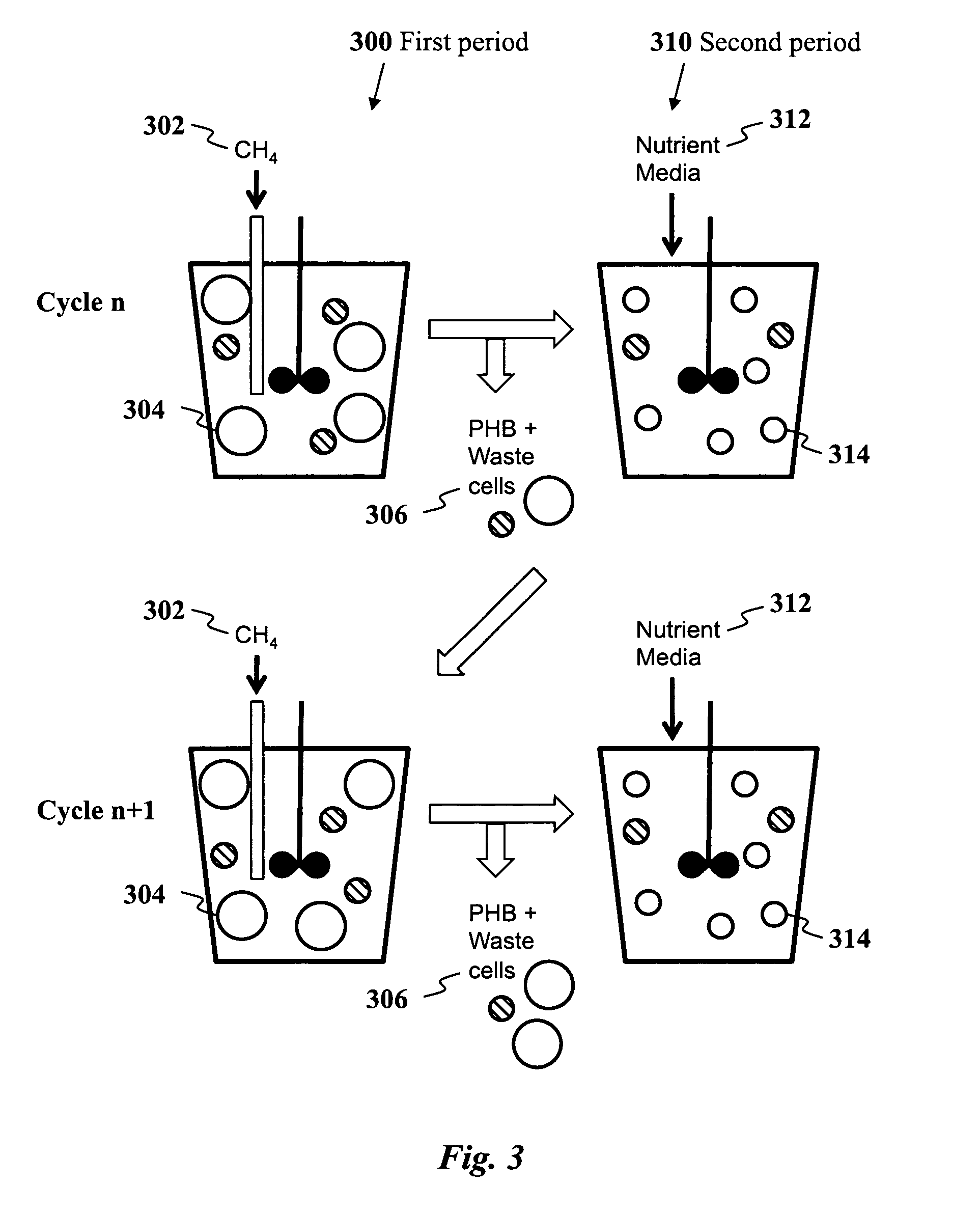
A method for inexpensive and efficient PHA biosynthesis includes operating a sequencing bioreactor in alternating phases of nutrient deprivation and carbon feedstock deprivation to select for robust PHA-producing microbes. Preferably, the bioreactor is operated in a non-sterile manner with mixed cultures of methanotrophs. The method also preferably uses periodic biomass-wasting (PHA harvesting) at the end of the carbon feed phase, gradually lengthening the time period of carbon deprivation phase to create a penalty for rapid PHA degradation and incentive for PHA accumulation. Also, bacterial enrichment cultures may be introduced periodically. The PHA-accumulating bacteria are preferably grown on common anaerobic degradation products, specifically volatile fatty acids, such as acetate and propionate, and methane gas. The PHA has useful applications in bioplastics and other products.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Flushable and anaerobically degradable films and laminates
InactiveUS20020042599A1Suitable mechanical propertyChange viscosityInfusion syringesSynthetic resin layered productsFiberPolymer science
The present invention relates to thermoplastic materials which are anaerobically degradable in an active sewage sludge. These materials are melt processable into fibers, films or laminates, and are suitable for use in an absorbent article, particularly flushable interlabial products, tampons and pantiliners.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Use of selection pressures to enable microbial biosynthesis of polyhydroxyalkanoates from anaerobic degradation products
InactiveUS8030021B2Cost of producingImprove the level ofWaste based fuelFermentationVolatile fatty acidsMethane gas
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Bacterial poly(hydroxy alkanoate) polymer and natural fiber composites
ActiveUS7887893B2Improve bindingImprove performanceLayered productsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVolatile fatty acidsResin matrix
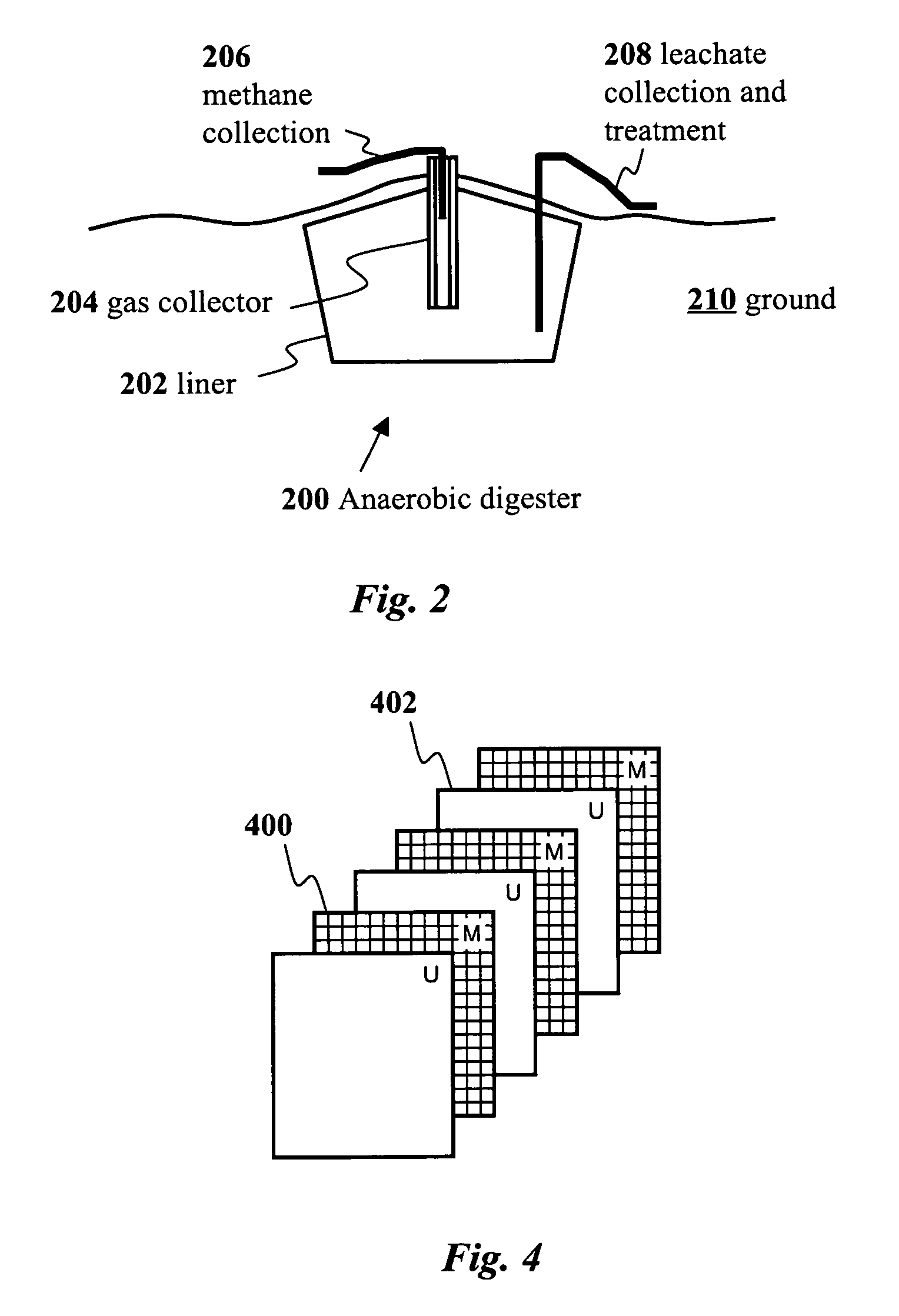
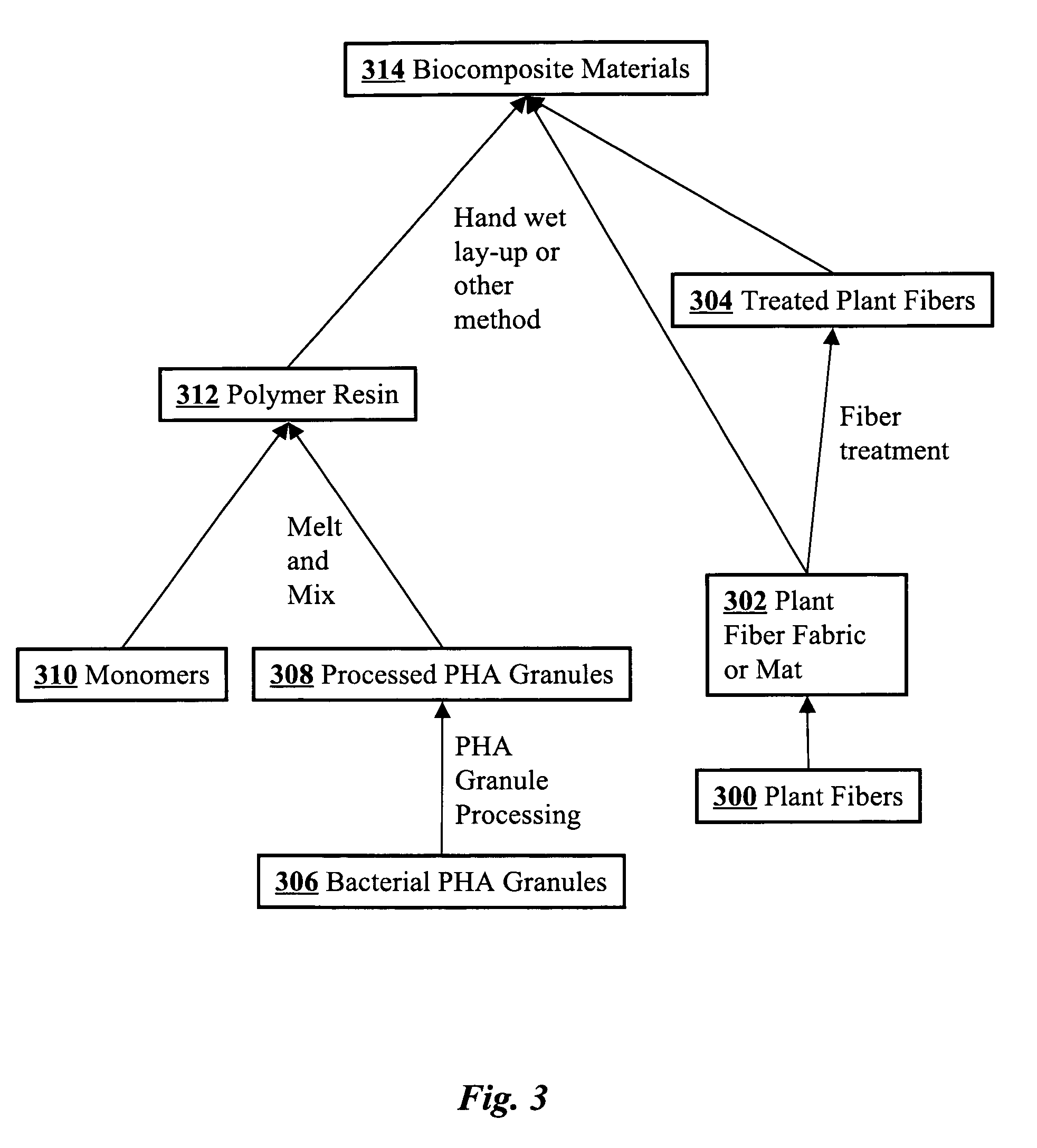
A biocomposite is produced from natural fiber fabrics embedded in a matrix of biosynthetic polyhydroxy-alkanoate (PHA) polymers. The PHA is synthesized using aerobic microbial biosynthesis using mixed bacterial cultures and a feedstock containing anaerobic degradation products such as methane and volatile fatty acids derived from microbial biodegradation of organic waste materials, which may include waste biocomposites. Monomers may be added to the synthesized PHA polymer to control mechanical properties of the resulting biocomposite. The natural fibers and / or PHA may be pretreated using various techniques to improve the bond between the fibers and the PHA resin matrix and water absorption resistance of the fibers. The composite may be a laminate of treated and untreated fabric layers, or differently treated layers, to achieve good in-service performance as well as rapid and / or optimal biogas production when taken out of service and put in an anaerobic environment to degrade.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Fixed-film anaerobic digestion of flushed waste
InactiveUS7297274B2Reduce odorMinimizing offensive odorsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryGas production bioreactorsFecesLivestock manure
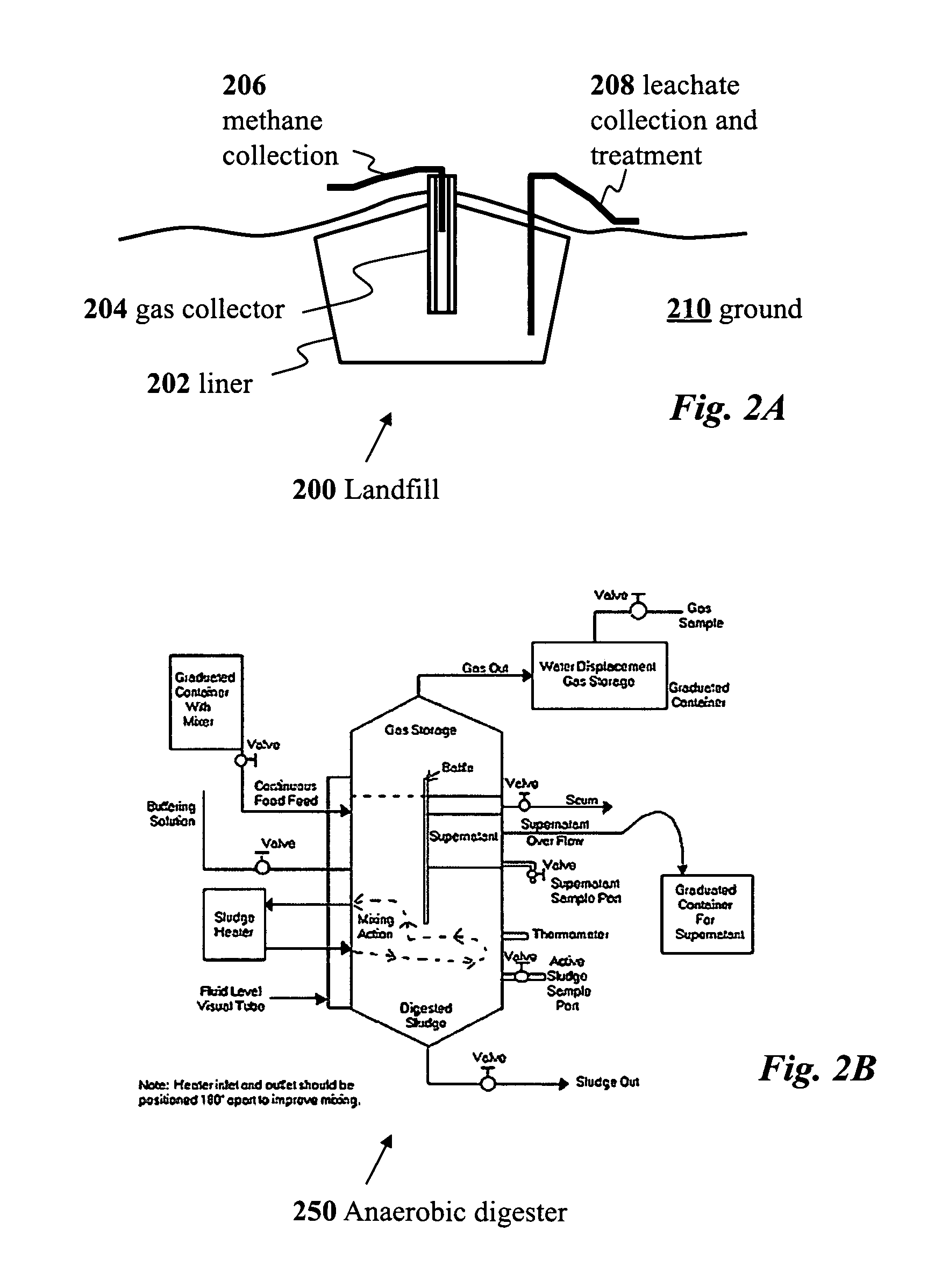
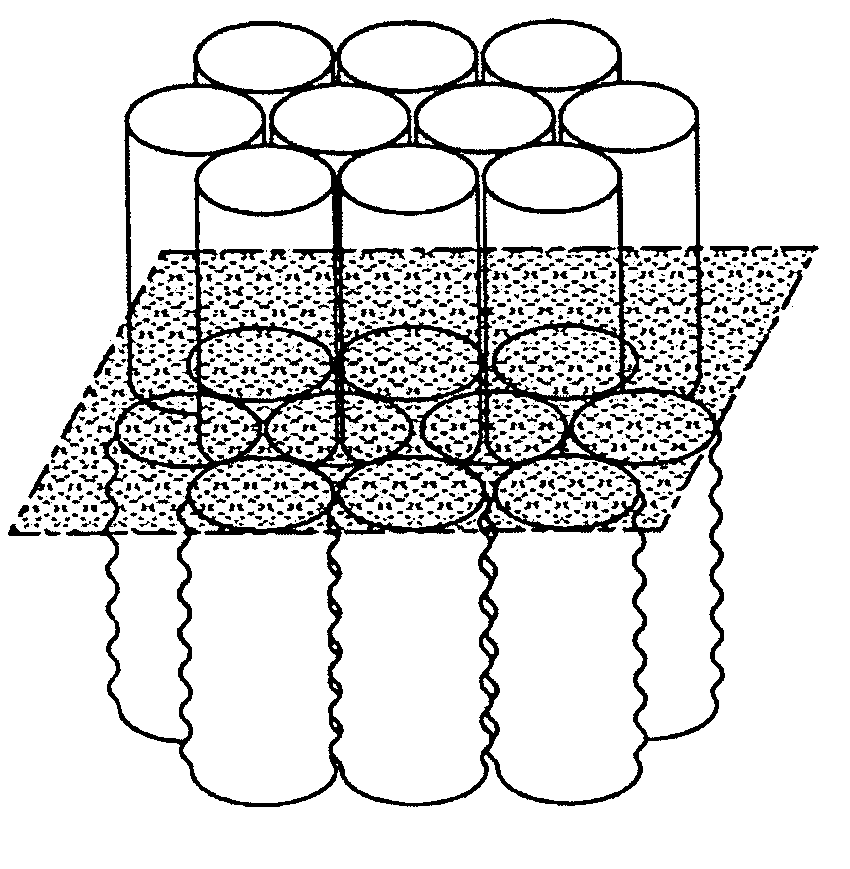
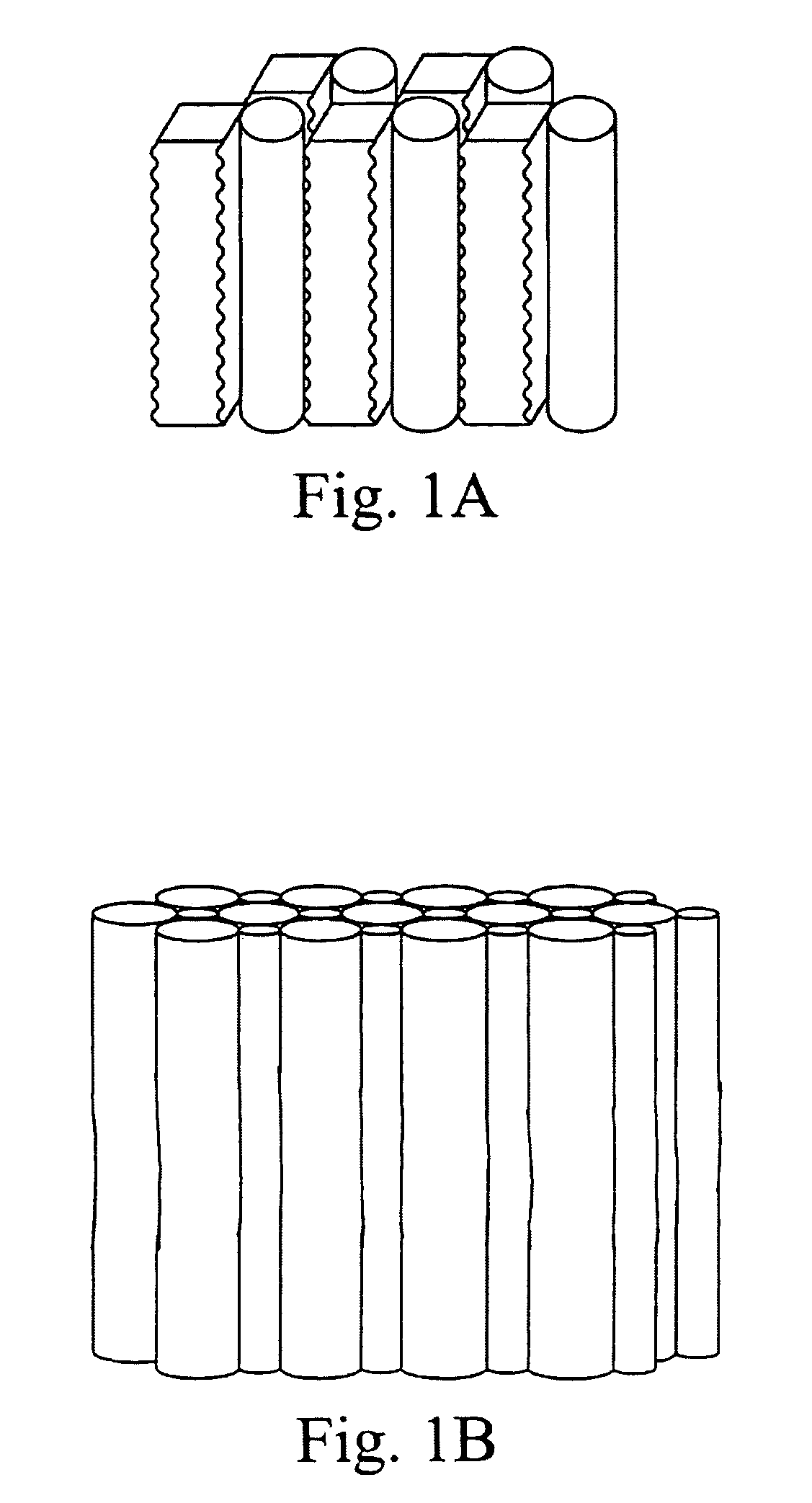
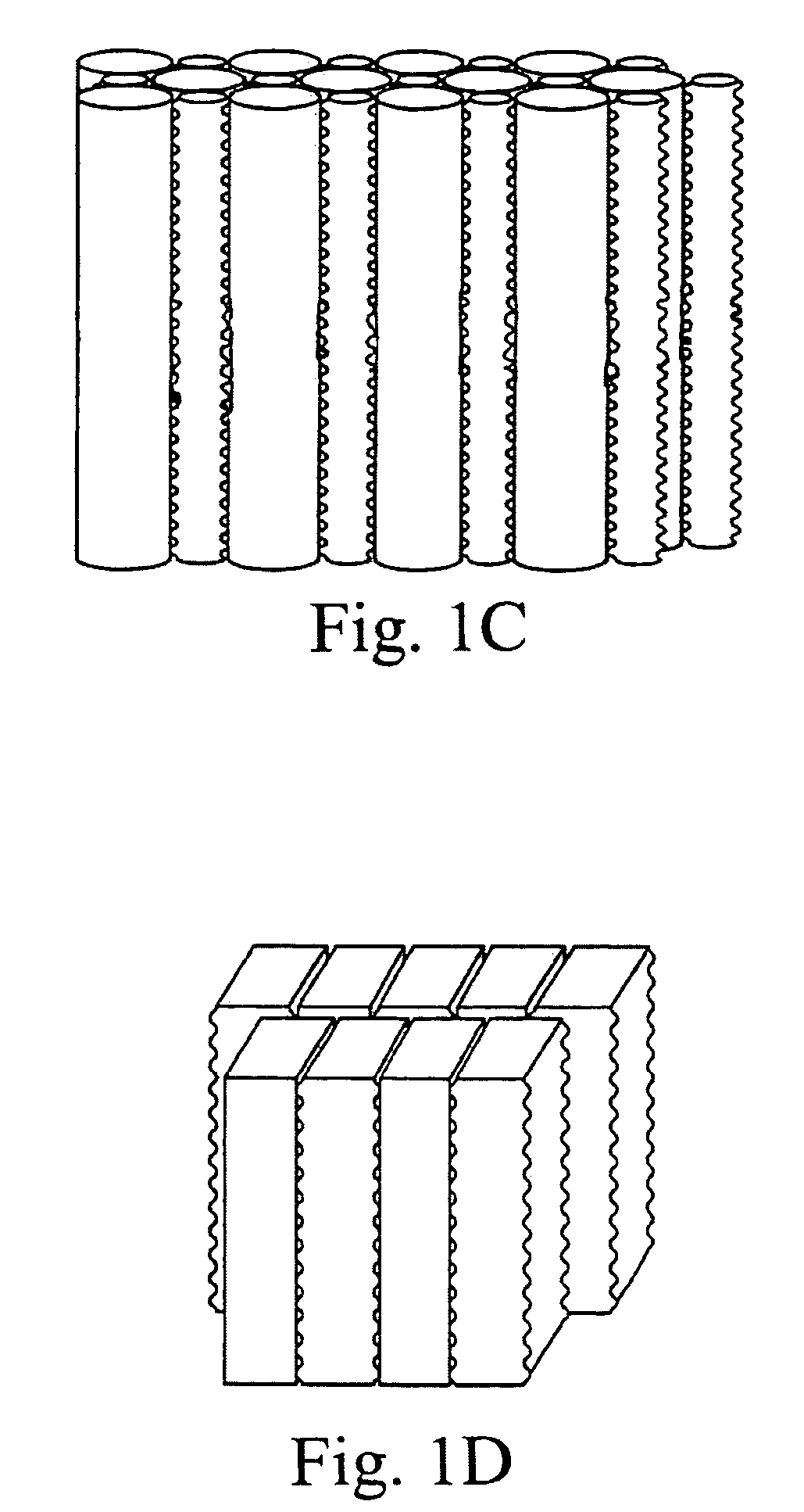
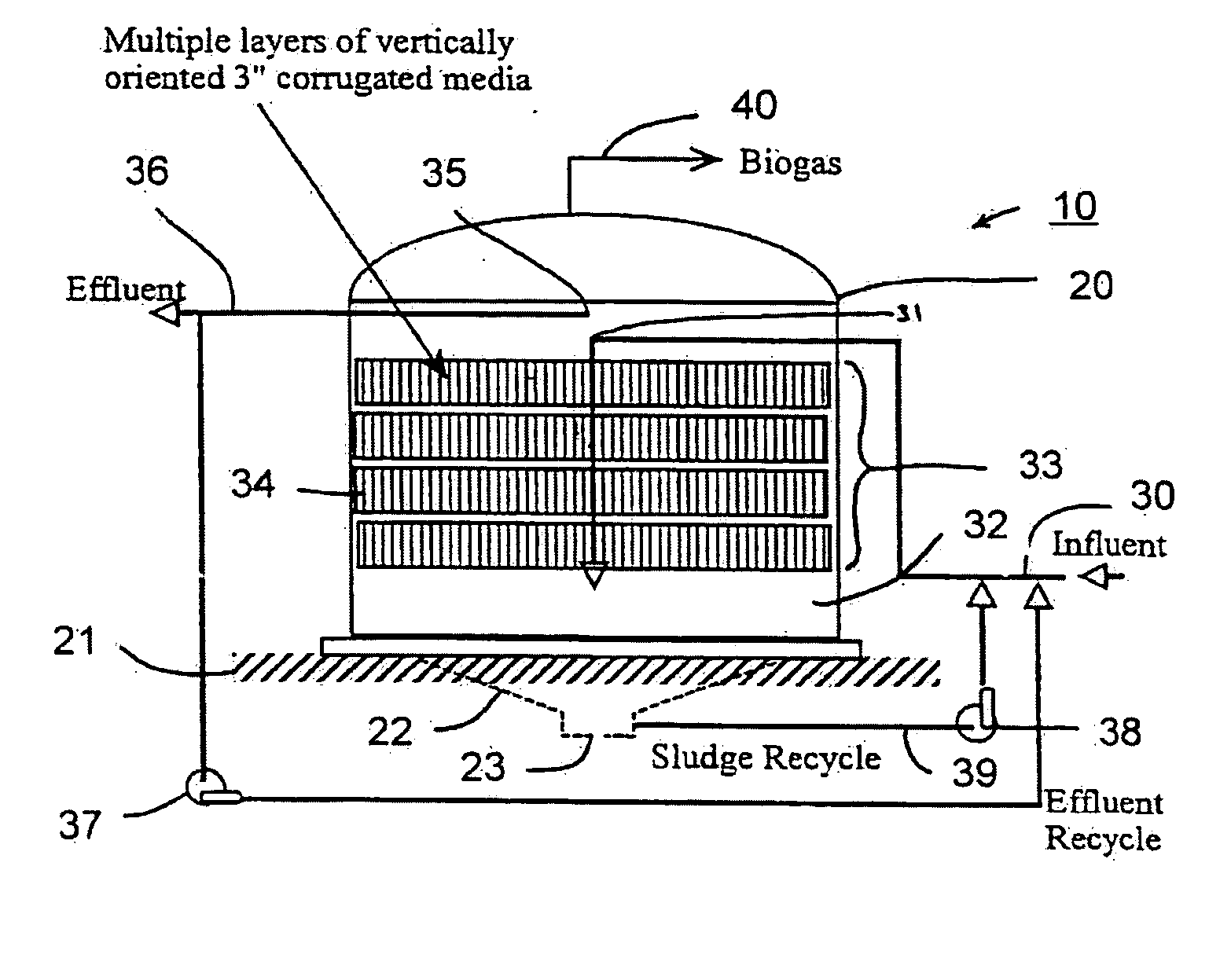
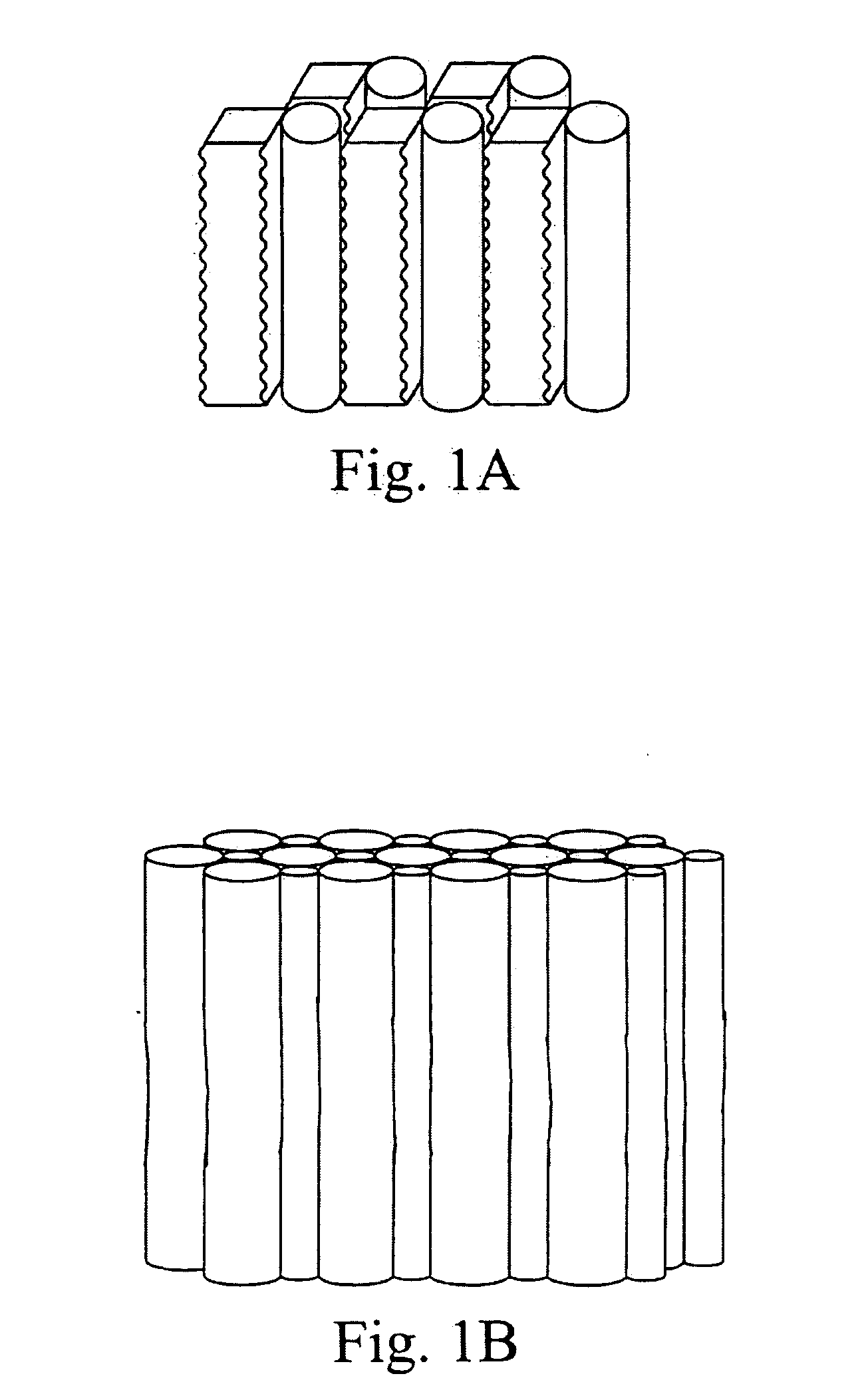
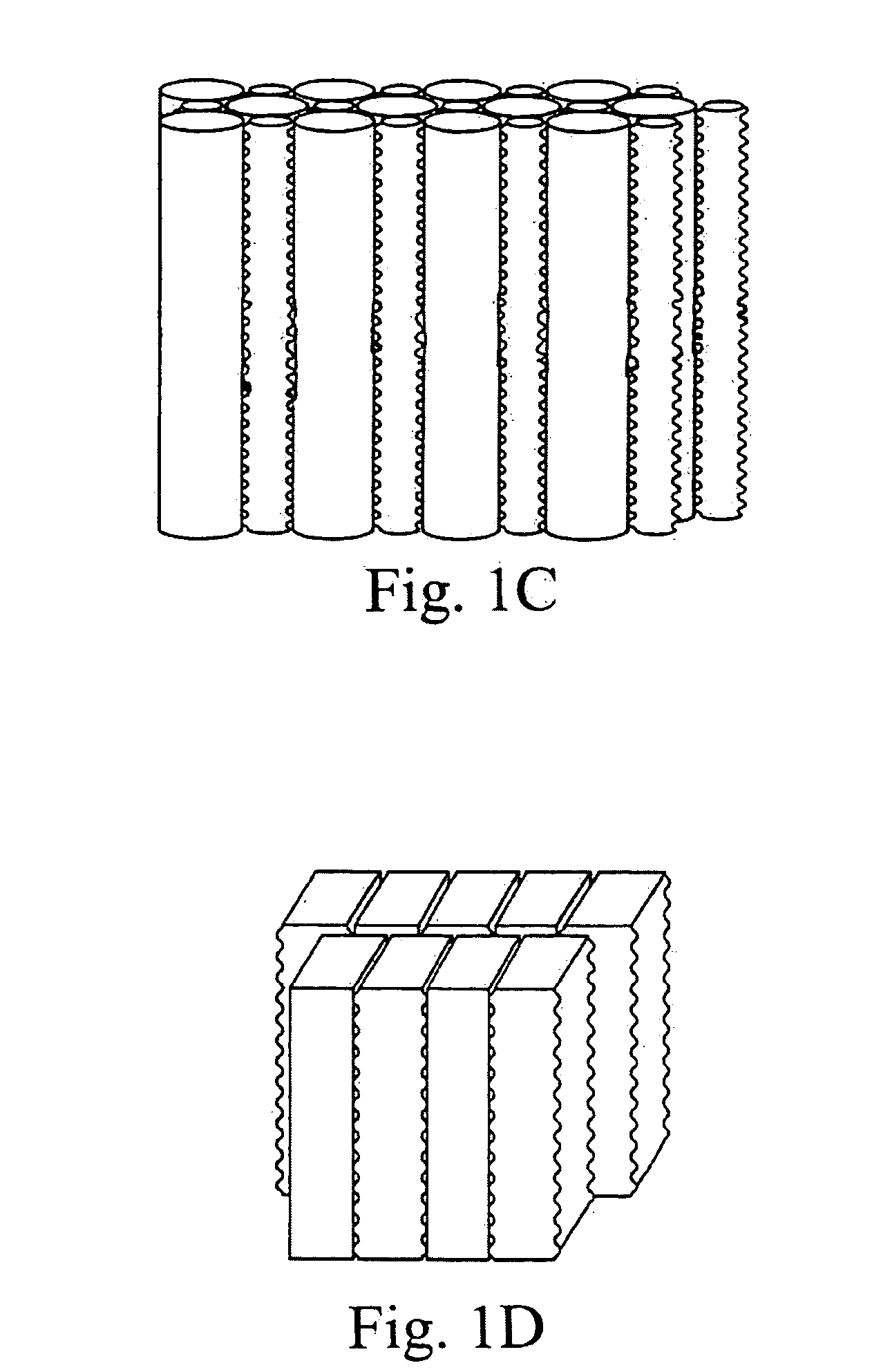
An apparatus for the fixed-film anaerobic digestion of flushed livestock manure includes an enclosed digester tank (fixed or flexible roof), internal media for biofilm development, a biogas collection and flare system, various pumps, and hydraulic control systems. The preferred media has substantially vertically-oriented, uninterrupted channels to promote enhanced bacterial attachment and biofilm development. The immobilization of microbial biomass within the reactor as a biofilm allows effective treatment of the wastewater at ambient and higher temperatures, as well as reasonable hydraulic retention times. The composition and concentration of bacterial groups in the biofilm developed on the media in the fixed-film digester result in a significantly enhanced anaerobic degradation process. This novel fixed-film digester design expands the potential application of anaerobic digestion to dilute livestock waste with significant levels of suspended solids. This holistic manure treatment system not only stabilizes the wastewater but also produces energy (biogas), controls odors, reduces pathogens, minimizes environmental impact from waste emissions, and maximizes fertilizer and water recovery for reuse.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Fixed-film anaerobic digestion of flushed waste
InactiveUS20050167359A1Reduce odorEase of inspectionGas production bioreactorsWaste water treatment from animal husbandryLivestock manureFeces
An apparatus for the fixed-film anaerobic digestion of flushed livestock manure includes an enclosed digester tank (fixed or flexible roof), internal media for biofilm development, a biogas collection and flare system, various pumps, and hydraulic control systems. The preferred media has substantially vertically-oriented, uninterrupted channels to promote enhanced bacterial attachment and biofilm development. The immobilization of microbial biomass within the reactor as a biofilm allows effective treatment of the wastewater at ambient and higher temperatures, as well as reasonable hydraulic retention times. The composition and concentration of bacterial groups in the biofilm developed on the media in the fixed-film digester result in a significantly enhanced anaerobic degradation process. This novel fixed-film digester design expands the potential application of anaerobic digestion to dilute livestock waste with significant levels of suspended solids. This holistic manure treatment system not only stabilizes the wastewater but also produces energy (biogas), controls odors, reduces pathogens, minimizes environmental impact from waste emissions, and maximizes fertilizer and water recovery for reuse.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Bacterial poly(hydroxy alkanoate) polymer and natural fiber composites
ActiveUS20080160567A1Improve bindingGood in-service performanceLayered productsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementVolatile fatty acidsResin matrix
A biocomposite is produced from natural fiber fabrics embedded in a matrix of biosynthetic polyhydroxy-alkanoate (PHA) polymers. The PHA is synthesized using aerobic microbial biosynthesis using mixed bacterial cultures and a feedstock containing anaerobic degradation products such as methane and volatile fatty acids derived from microbial biodegradation of organic waste materials, which may include waste biocomposites. Monomers may be added to the synthesized PHA polymer to control mechanical properties of the resulting biocomposite. The natural fibers and / or PHA may be pretreated using various techniques to improve the bond between the fibers and the PHA resin matrix and water absorption resistance of the fibers. The composite may be a laminate of treated and untreated fabric layers, or differently treated layers, to achieve good in-service performance as well as rapid and / or optimal biogas production when taken out of service and put in an anaerobic environment to degrade.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Anaerobic cellulose-degrading methane producing composite bacterium
InactiveCN101475926AEfficient hydrolysisFermentation starts fastBacteriaMicroorganism based processesCelluloseFacultative
The invention discloses anaerobic degradation cellulose methane composite bacteria, which is composed of 13 strains that respectively belong to facultative anaerobic and strictly anaerobic fermentative bacteria, hydrogen-production and acetic acid-production bacteria and methane-producing bacteria. The composite bacteria can not only effectively perform anaerobic degradation to the cellulose, but also can use the degradation production of the cellulose to produce methane, which can be widely used in straw biogas fermentation, compost processing, and the like conversion processes.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Process for treating epoxy resin production wastewater
ActiveCN103613244AEasy to handleHigh degree of automationMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterSuspended particlesEpoxy
The invention discloses a process for treating epoxy resin production wastewater. The process comprises: removing oils, suspended particle organic matters, a part of high polymers and toluene in high-salinity wastewater through a cavitation air flotation system, transforming macromolecular organic matters in the wastewater into micromolecular organic matters through an iron-carbon micro-electrolysis reactor, then, oxidizing non-biodegradable and non-chemical oxidable organic matters in the wastewater through a catalytic oxidation reactor under the action of an Fenton reagent, carrying out anaerobic biochemical treatment to reduce the chemical oxygen demand and the biochemical oxygen demand in the wastewater, carrying out aerobic biochemical treatment to anaerobically degrade a part of aerobic organic matters incapable of being degraded by aerobiont into biochemically degradable organic matters, finally, conveying the wastewater into a clean-water reservoir, filtering the wastewater through a multi-medium filter, and discharging the wastewater after meeting the standard. The process disclosed by the invention has the advantages of small energy consumption, high removal load and capability of recycling biogas as an energy source, and the purified water quality meets the emission standard so as to protect the ecological environment.
Owner:ANHUI GREEN TITAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
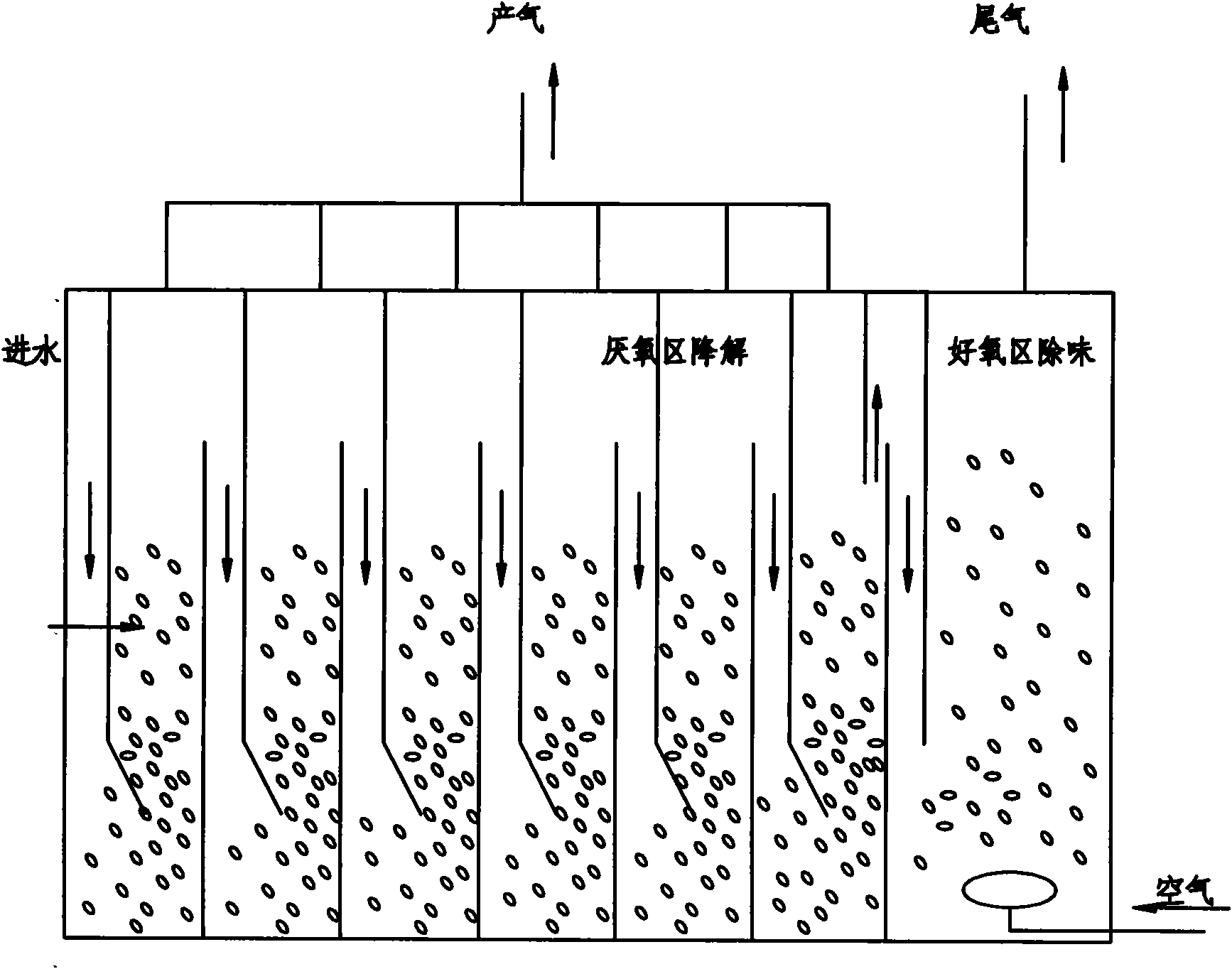
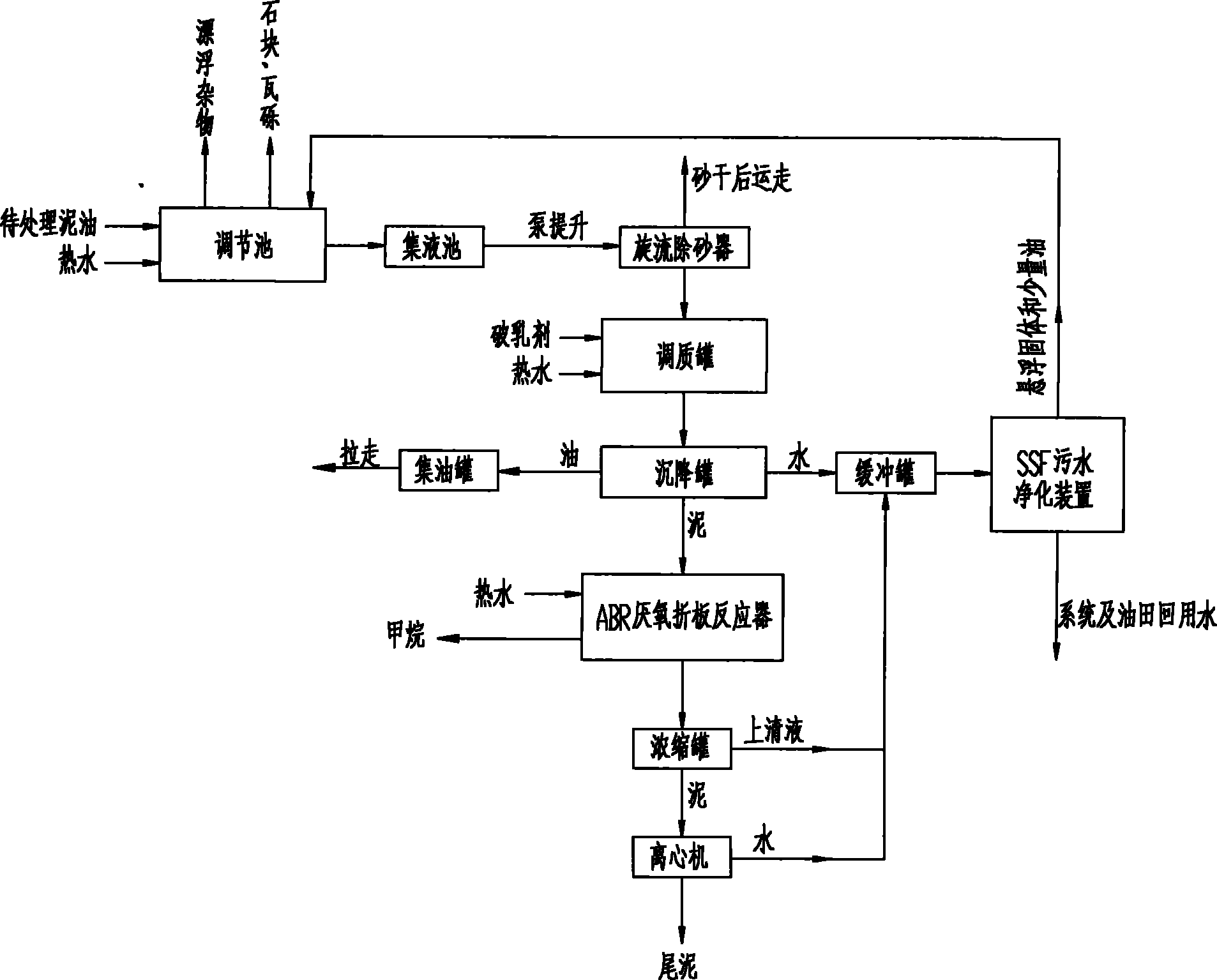
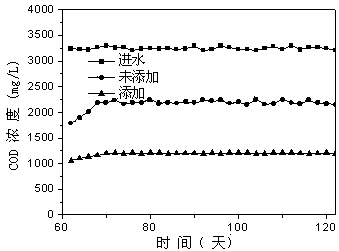
Advanced treatment process of sludge containing oil
InactiveCN101786776AIncrease biomassGuaranteed uptimeBiological sludge treatmentResource utilizationSludge
The invention discloses an advanced treatment process of sludge containing oil, belonging to the field of environment and resource utilization. The invention mainly utilizes the quenching and tempering separation technology, microorganism anaerobic degradation, floating sludge filtering and the centrifugal separation technology to ensure that moisture content is lowered by 5% after the oil is separated from the sludge so as to be recycled; and after being treated, sludge water directly reaches the oil field A3 reinjection standard, and tailing sludge reaches the agricultural standard, so that the environmental problem of the sludge containing the oil is completely solved. The process has simplified flow, reliable operation, simple equipment maintenance, low operation cost, small land occupation, investment saving and high comprehensive benefit of harmless reclamation, does not need to replace filter materials and does not have complex back wash flow and programmable logic controller (PLC) control.
Owner:BEIJING OTC ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT ENGINEERING PUBLIC LIMITED COMPANY
Method for anerobic aerobic granular sludge treating high concentration waste water from paper-making method tobacco slice production
InactiveCN101007693AHigh volume loadSmall footprintTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentHigh concentrationAnaerobic aerobic
The invention discloses a disposing method of high concentrated tobacco slice wastewater in the paper making processes through anaerobic aerobic granular sludge, which comprises the following steps: pre-processing concrete; pumping waste water into anaerobic complex reactor to get anaerobic degradation with sludge density at 30-40g / L, COD load at 12-18kg COD / m3.d and under 35-37 deg.c; adopting interval aerobic particle sludge method to get aerobic treatment; pumping water 1h with aeration of micropore aerated pipe at 8-16h; setting the density of density at 7-12g / L; making COD load at 1.2-1.5kg / (m3.d) . The invention can reach the first emission standard of nation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +2
Preparing method and application of nitrogen-doped sludge carbon-loaded nanometer ferroferric oxide
ActiveCN110171876AHigh energy recoveryEfficient and stable performanceTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesPorosityNitrogen gas
The invention discloses a method for preparing nitrogen-doped sludge carbon-loaded nanometer ferroferric oxide with waste sewage sludge as the raw material through hydrothermal and pyrolysis carbonizing, and application of the nitrogen-doped sludge carbon-loaded nanometer ferroferric oxide to enhancing wastewater anaerobic treatment technological performance. The method includes the following steps of conducting nitrogen source doping on dewatered sewage sludge through hydrothermal carbonizing, introducing nitrogen for secondary nitrogen doping in the high-temperature pyrolysis biochar preparing process to finally prepare nitrogen-doped sludge charcoal, and conducting ferric salt coprecipitation to prepare the nitrogen-doped sludge carbon-loaded nanometer ferroferric oxide. The prepared carbon material has high specific surface area and porosity, the anaerobic sludge granulation is facilitated, the conductivity of anaerobic sludge can be improved, the electron transfer of anaerobic degradation is promoted, the removal efficiency of the degradation-resistant wastewater anaerobic active sludge is enhanced, and the generation of methane is promoted. The carbon material is low in costand efficient and stable in performance, the high-additional-value resourceful utilization of the waste sewage sludge is effectively realized, and the performance of the degradation-resistant wastewater anaerobic treatment process is better improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
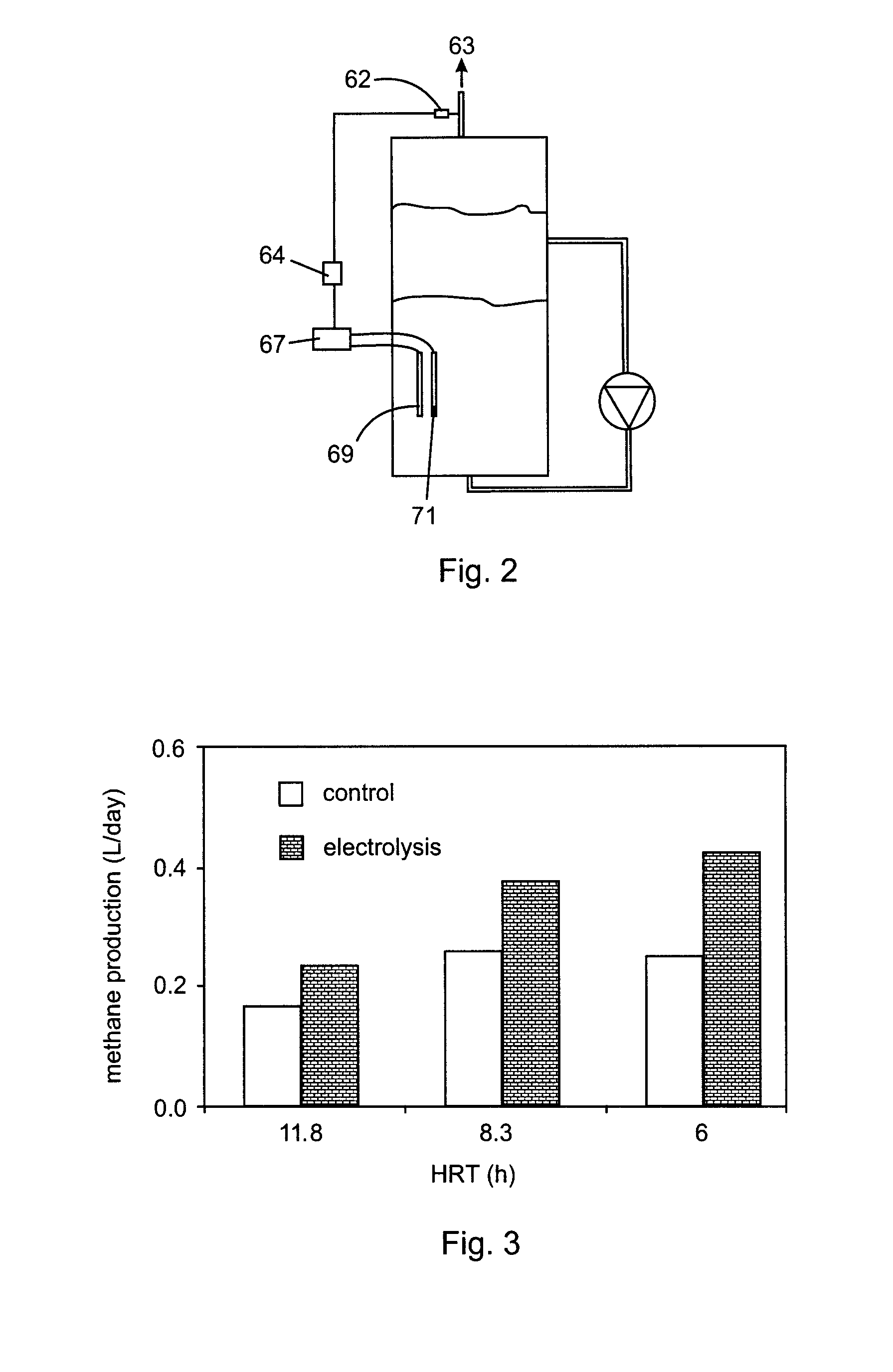
Microbially-assisted water electrolysis for improving biomethane production
InactiveUS20120100590A1Increase surface areaReduce the amount requiredBioreactor/fermenter combinationsElectrolysis componentsElectrochemistryAnaerobic microorganisms
A method of producing in a bioreactor a biogas rich in methane involves electrolyzing water in an aqueous medium at a voltage in a range of from 1.8 V to 12 V in the presence of electrochemically active anaerobic microorganisms that biocatalyze production of hydrogen gas, and, contacting a species of hydrogenotrophic methanogenic microorganisms with the hydrogen gas and carbon dioxide to produce methane. Volumetric power consumption is in a range of from 0.03 Wh / LR to 0.3 Wh / LR. Current density is 0.01 A / cmE2 or lower. The voltage is sufficient to electrolyze water without destroying microbial growth. Such a method results in improved electrolysis efficiency while avoiding the use of noble metal catalysts. Further, a combination of water electrolysis with anaerobic degradation of organic matter results in increased biogas quality and in increased biogas quantity and yield. Oxidation of hydrogen sulfide contributes to the increased quality, while an increase in the rate of organic matter hydrolysis and an increase in the production of methane from hydrogen contributes to the increased quantity and yield.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Treatment method of river polluted bed mud
InactiveCN101786720AImproved redox propertiesImprove and relieve the degree of black and odorWater contaminantsSustainable biological treatmentSalt depositOrganopónicos
The invention discloses a treatment method of river polluted bed mud, comprising: adding oxidant into a polluted river to ensure that the bed mud on the surface layer is in the oxidation state; and preferably, adding water-solubility calcium salt and ferric salt. The invention ensures that the whole self-cleaning process of the river is in the aerobic state all the time by improving the oxidation reduction property of the polluted bed mud, thus creating conditions for aerobic microorganisms, amplifying bed mud aerobic microorganisms, and leading the aerobic microorganisms to digest organic pollutants; and in addition, the organic pollutants are completely oxidized and degraded into complete oxides such as CO2, H2O, NO2, SO4<-2> and the like, blackening and odor-causing substances, such as H2S, methyl mercaptan, FeS and the like produced during the anaerobic degradation of organic matters can be quickly oxidized, and the black and odor degree of water body can be effectively improved and remitted. Meanwhile, the calcium salt, the ferric salt and phosphorus-deposited nutritive salt are simultaneously added to lower river pollution degree and eutrophy level. The method of the invention has simple operation and strong selective pertinence, can treat in situ, almost does not damage the ecological balance of the original river and has favorable treatment effect.
Owner:广州市净水有限公司 +1
Separation purification process and application of anaerobic degradation pure culture of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
InactiveCN101195811AGood anaerobic degradation performanceBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationVitamin CPurification methods
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
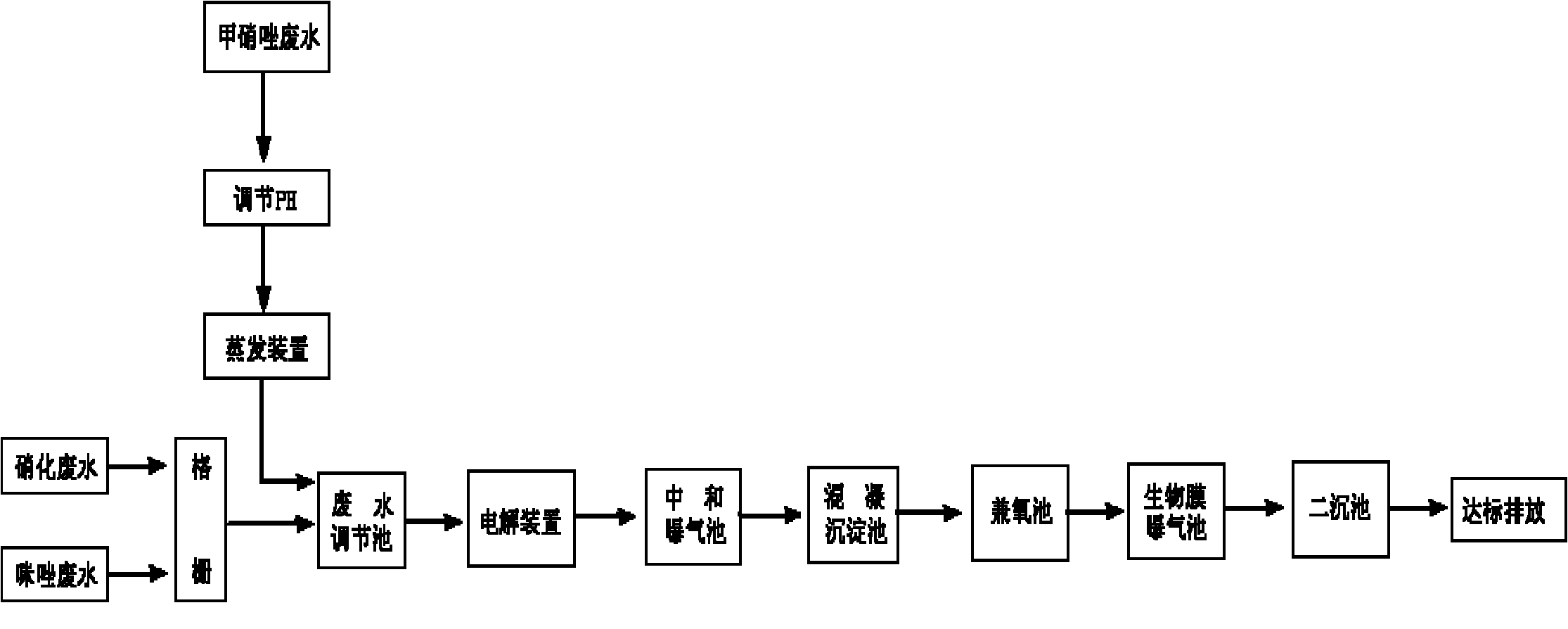
Method for treating waste water from production of metronidazole
ActiveCN102153240ALow biological toxicityReduce the concentration of pollutantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentElectrolysisEvaporation
The invention relates to a method for treating waste water from production of metronidazole. The steps of the method are as follows: adding alkali in metronidazole process waste water to adjust pH value and after evaporation, sending the metronidazole process waste water to a waste water adjusting tank; allowing imidazole process waste water and nitration process waste water to enter the waste water adjusting tank respectively through a grating; after mixture as well as water-quality and water-quantity adjustment by the waste water adjusting tank, sending the imidazole process waste water and the nitration process waste water to an electrolyzer for electrochemical catalysis water treatment; adding lime milk in the effluent of the electrolyzer to adjust pH value, sequentially removing ammonia-nitrogen by a neutralization aeration tank, adding flocculant, separating by a coagulative precipitation tank, and allowing supernatant water to enter a facultative tank for anaerobic degradation; and conducting oxic degradation by a biomembrane aeration tank and precipitation by a secondary precipitation tank on the effluent of the facultative tank for standardized discharge. Adopting a electrochemical catalysis water treatment technology for pretreating waste water, the method effectively eliminates the biotoxicity of the waste water, lowers the pollutant concentration of the waste water and greatly improves the biodegradability of the waste water, thus laying foundation for standardized biochemical treatment. The method is simple in technology and convenient in operation.
Owner:黄冈银河阿迪药业有限公司 +1
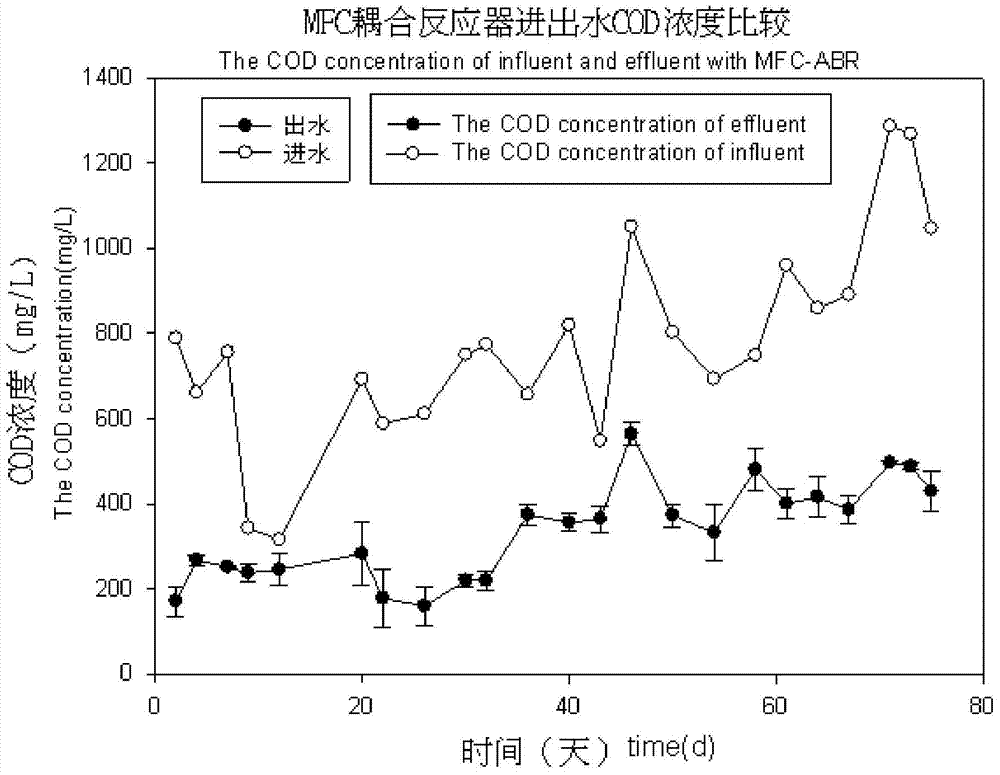
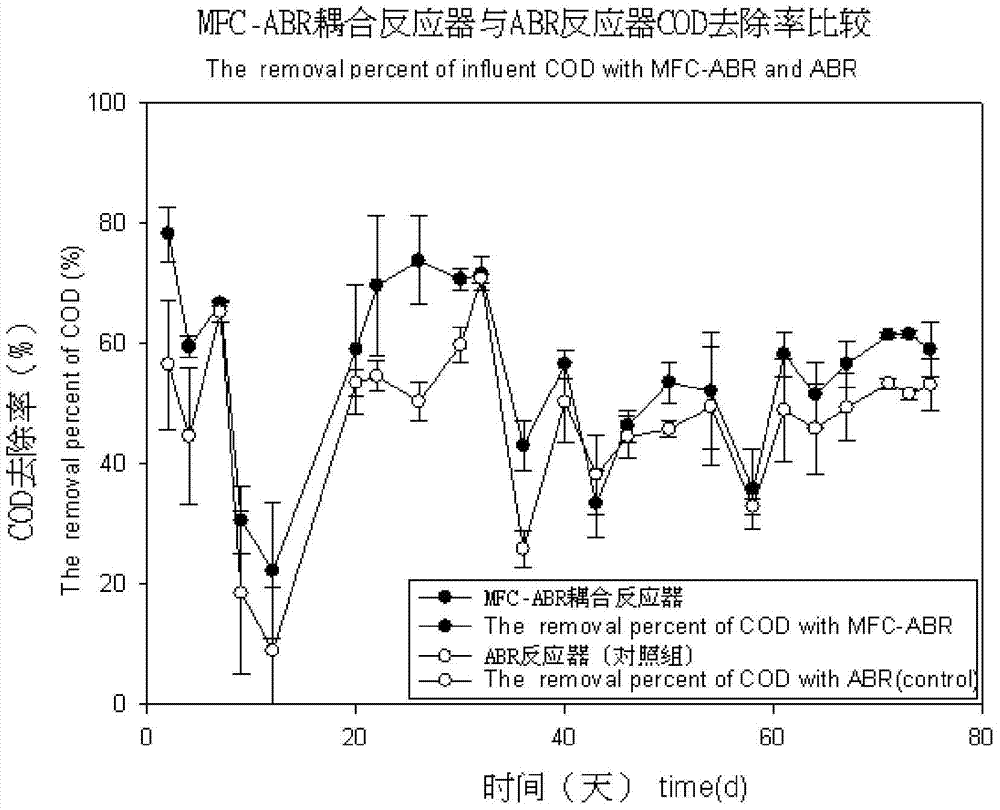
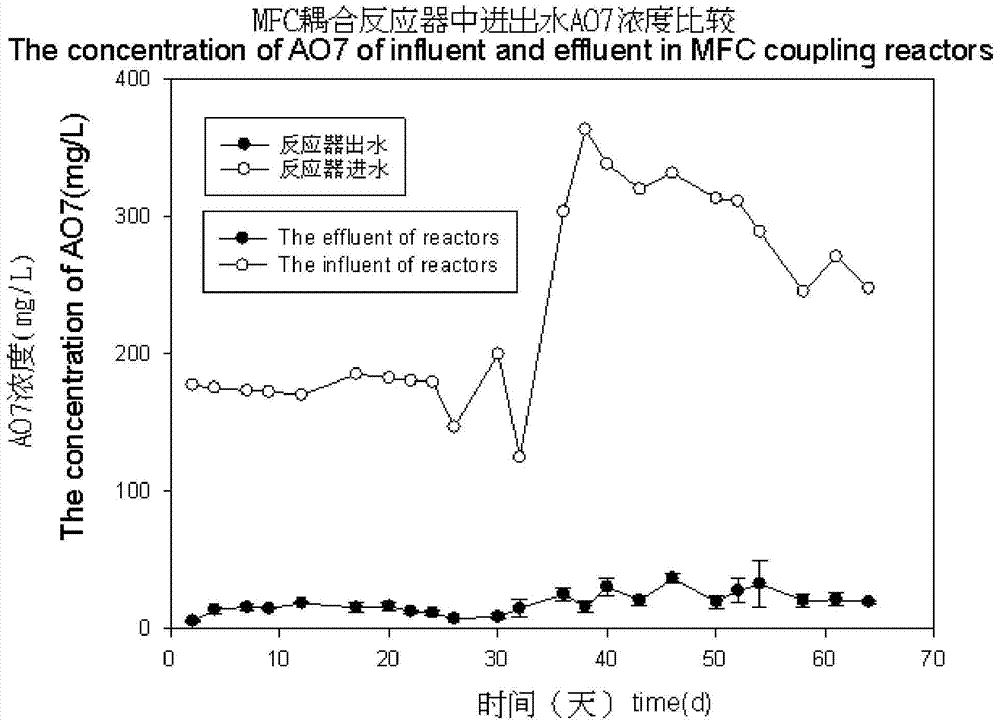
Process for intensifying anaerobic degradation and transformation of azo dyes based on breath of microbial electrode
InactiveCN104843862AAnaerobic degradation enhancementTo achieve the purpose of preliminary decolorization and degradationTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesPeristaltic pumpAnaerobic reactor
The invention discloses a process for intensifying anaerobic degradation and transformation of azo dyes based on breath of a microbial electrode. The process comprises the following steps: putting a microbial electrochemical system in an anaerobic reactor to form a coupling reactor; inoculating anaerobic sludge under the room temperature condition; after adjusting the pH value of the azo dye wastewater, the hydraulic retention time, the inflow COD concentration and the inflow azo dye concentration, filtering the azo dye wastewater and carrying out precipitating; feeding the wastewater to the coupling reactor by the action of a peristaltic pump; while decoloring being obvious after initial degradation by the anaerobic reactor in the coupling reactor, treating the wastewater by the microbial electrochemical system; and finally discharging the azo dye wastewater through a secondary sedimentation tank. The key point of the invention lies in that an efficient anaerobic reactor for intensifying biodegradation of the azo dyes based on breath of the microbial electrode is constructed;the addition of chemical agents is reduced; the consumption of electric energy is reduced; and the electric energy is recovered while the pollutants are degraded, so that the cost for treating the azo dye wastewater is effectively lowered.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Compositions of matter and uses thereof in the treatment of waste materials
ActiveUS20130005013A1Improve performanceSimple compositionBacteriaSolid waste disposalPhysical chemistryBiogas production
Disclosed are compositions of matter comprising at least one anaerobic degrading microorganism, particulate active carbon and a polymeric solid support wherein the anaerobic degrading microorganism and particulate active carbon are entrapped in the polymeric support and processes for preparing the same. The disclosed compositions of matter are used in processes of anaerobic degradation of waste materials resulting in high yields of biogas production.
Owner:AGROBICS
Method for enriching, domesticating and screening polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon anaerobic degradation mixing flora and use thereof
The invention belongs to the technical field of biodegradation treatment of contaminated soil and water, and discloses an enrichment, acclimation and screening method for an anaerobic degradation community of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and application thereof. A mixture of an electron acceptor, sodium sulfide and the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is added in the contaminated soil according to the mass ratio and is sealed and stood for 6 months, and then a mixed liquid of a basal culture medium, a micro metal liquid and a vitamin C solution is added into an anaerobic box full of nitrogen according to the proportion for soil acclimatization; the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon, the basal culture medium, the micro metal liquid, the vitamin C solution and an adsorbent are added into an anaerobic bottle in the anaerobic box full of nitrogen, the enriched and acclimatized soil is grafted into the anaerobic bottle according to the mass ratio of water to the soil, and the electron acceptor and the sodium sulfide are added according to the mass ratio. The soil is cultured for 20 to 25 days in a rotary oscillator with a temperature of between 18 and 22 DEG C and then is subjected to circular inoculation for more than 5 times to obtain a microbial community used for anaerobically degrading the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon. The method can enrich, acclimatize and screen the microbial community with good anaerobic degradation performance, and the degradation rate range of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon is between 0.01 and 1.04mg.L<-1>.d<-1>.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Process for in situ bioremediation of subsurface contaminants
InactiveUS20060263869A1Eliminate needReduce riskSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationHydrogenMulti pollutant
This invention includes methods of stimulating anaerobic degradation of subsurface contaminants. The methods include vaporizing a liquid electron donor to form a treating gas. The treating gas or hydrogen is directed to a subsurface site that includes one or more contaminants, thereby stimulating anaerobic degradation of the subsurface contaminants.
Owner:CDM SMITH
Combined process for refined cotton black liquid treatment
InactiveCN103570192AImprove water qualityReduce conductivityMultistage water/sewage treatmentWaste water treatment from plant processingChemical oxygen demandBlack liquor
The invention discloses a combined process for refined cotton black liquid treatment, which develops a treatment process mainly used for a refined cotton black liquid produced in a refined cotton production course. The combined process comprises the following steps of introducing the refined cotton black liquid produced in the refined cotton production course into a pretreatment tank for acidification; introducing an acidified supernate into an electric adsorption device for treatment so as to improve biodegradability of wastewater; introducing electric adsorption effluents into an anaerobic reactor filled with anaerobic granular sludge for anaerobic degradation of wastewater; introducing anaerobic effluents into an aerobic reactor for further removing organic matters in wastewater; and then introducing the wastewater into an ultrafiltration membrane assembly so that COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) of effluents reaches the emission standard. The combined process is developed for the black liquid produced in the refined cotton production course, namely, the combined process is designed for the cooked black liquid produced by cooking cotton linters through an alkaline method and enormous black brown wastewater produced by slurry washing. The combined process combines an acidification process, an electric adsorption process, an anaerobic and aerobic biological process and an ultrafiltration process for treating the refined cotton black liquid, solves the problem of difficult treatment of the refined cotton black liquid and is simple and easy to operate.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for use in palm oil mill effluent (POME) treatment
The present invention discloses a method for use in treating palm oil mill effluent (POME). Said method comprising the steps of: treating the palm oil mill effluents with concentrated butyrate; introducing the treated palm oil mill effluents into a reaction tank (11) with loading rate of at least 1.5 g COD / L / d and at least 4 days of hydraulic retention time; and providing microorganism biomass in the reaction tank so that anaerobic degradation of the palm oil mill effluents treated with butyrate can be performed. Preferably, the optimum condition for degradation of the palm oil mill effluents in the reaction tank is at constant temperature 37° C. with pH value of approximately 6.5-7.5.
Owner:UNIVERSITI MALAYSIA PAHANG
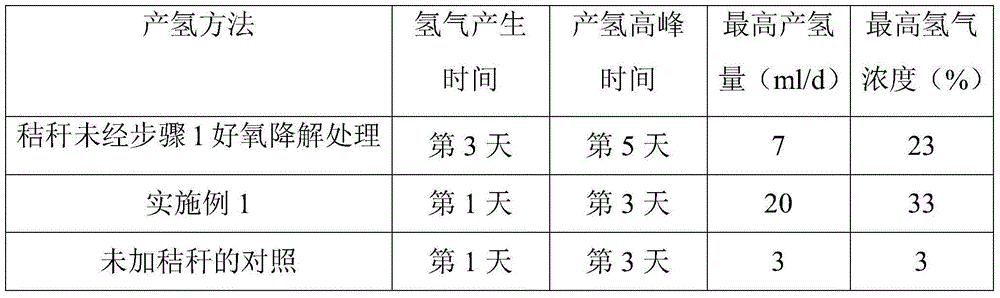
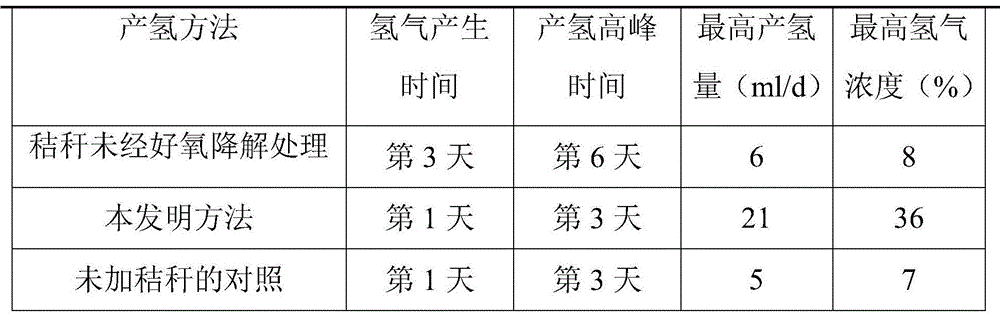
Method for preparing hydrogen from straws
InactiveCN103602715AEasily exposedImprove degradation efficiencyMicroorganism based processesFermentationNitrogenPre treatment
The invention discloses a method for preparing hydrogen from straws, which comprises the following steps: carrying out aerobic degradation on straws by using a composite microbial inoculum capable of degrading straws; cattle manure pretreatment: screening the cattle manure with a 50-mesh screen to remove granular solids and impurities, boiling for 30-60 minutes, and centrifugating to remove excessive moisture for later use; preparation of straw anaerobic degradation culture medium: preparing a liquid anaerobic degradation culture medium, and adding the straws subjected to aerobic degradation; and adding the pretreated cattle manure into the straw anaerobic degradation culture medium, charging nitrogen into the container to remove oxygen, sealing, and culturing at 60-70 DEG C at the rate of 120 r / min in a dark place. The method optimally combines anaerobic degradation and anaerobic fermentation, has the advantages of short required time for hydrogen production, low cost, no need of adding enzymes in the fermentation process and cheap raw materials, and greatly saves the cost.
Owner:四川蓉加川大环保工程咨询设计有限公司
Method for anaerobically degrading feather keratin with microbial strain 18D-TA
ActiveCN102326668AReduce energy consumptionLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention relates to a method for anaerobically degrading feather keratin with a microbial strain 18D-TA, belonging to the technical field of microorganisms. The method comprises the following specific steps of: A, treating feathers: cleaning feathers with water, putting into a drying oven of which the temperature is 45-55 DEG C, and drying for 2-3 days for later use; and B, inoculating the strain: performing high-temperature moist-heat sterilization on a culture medium and the feathers treated in the step A, inoculating the strain 18D-TA in the amount of 2-10 percent, and anaerobically standing and culturing at the temperature of 45-60 DEG C for 8-10 hours till feather down falls off, wherein the feathers are completely separated from feather stems 18-24 hours later, and the feather stems are degraded in different degrees. Compared with other aerobic bacteria, the strain used in the method has the advantages: more products can be accumulated, so that ventilation equipment is not required to be provided, and the energy consumption is lowered greatly; and meanwhile, the efficiency is high, the fermenting period is short, racemization of most amino acids is avoided, and the absorption applicability of a feather hydrolysis product is enhanced.
Owner:BIOGAS SCI RES INST MIN OF AGRI
Method of domesticating and screening benzene series anaerobic degradation flora
InactiveCN101016532AGood anaerobic degradation performancePigmenting treatmentBacteriaVitamin CTrace metal
The invention discloses a domestication screening method and appliance of benzene series anaerobic degraded flora in polluted soil and water biological degraded disposing technical domain, which comprises the following steps: adding electron acceptor, sodium sulfide and BTEX mixture into polluted soil; sealing and stewing at three months; adding basic culture medium, trace metal liquid and vitamin C solution into anaerobic box filled with nitrogen; domesticating soil; switching domestication soil into anaerobic bottle with mass ratio of water and soil in the anaerobic box; adding into BTEX, electron acceptor and sodium sulfide with mass ratio; culturing 7-9 days in rotating oscillator with the temperature at 20+-2 deg.c; circling at least 9 times; getting the degraded flora. This invention can screen good anaerobic degraded property microbe flora, which can make degraded speed range of BTEX at 1.6-3.5mg.L-1.d-1.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for promoting anaerobic degradation of estrogen NP (nonyl phenol) in sludge under combined action of surfactant and alkali treatment
InactiveCN104671627AImprove solubilityImprove degradation efficiencySpecific water treatment objectivesBiological sludge treatmentActive agentSurface-active agents
The invention belongs to the technical field of persistent refractory organic pollutant treatment for environmental protection and relates to a method for promoting anaerobic fermentation degradation of estrogen NP (nonyl phenol) in sludge. The method comprises steps as follows: adding sludge containing the estrogen NP to an anaerobic reactor, adjusting the anaerobic fermentation pH value of the sludge to enable the sludge to be alkaline, adding a surfactant, controlling the fermentation temperature, performing stirring to enable a reaction system to be evenly mixed, and leaving the reaction system to stand for a period. With the adoption of the method, anaerobic degradation of the estrogen NP in the sludge can be effectively promoted, pollution caused by the estrogen to the environment can be reduced, a foundation is laid for land utilization after anaerobic digestion of the sludge, and meanwhile, the method has important guidance and reference significance in removal of other refractory organic pollutants in the sludge.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for repairing contaminated soil in coal-to-gas plant by adopting microbe-plant combined way
InactiveCN104226679AHigh porosityPromote degradationContaminated soil reclamationPolycyclic aromatic hydrocarbonSedum alfredii
The invention discloses a method for repairing contaminated soil in a coal-to-gas plant by adopting a microbe-plant combined way. The method comprises the following steps: adding an electronic receptor preparation in the contaminated soil so as to promote anaerobic degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and analysis of heavy metals; mixing and composting the contaminated soil with pig manure and a conditioning agent for several days; eluting partial heavy metals from the soil by using clear water; planting sedum alfredii hance and festuca arundinacea in the soil in a mixed way so as to extract the heavy metals from the soil and promote microbial degradation of the polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the soil, wherein in the growth stage of plants, additives are sprayed periodically to enhance the repairing effect. Through the adoption of the method, the environment friendliness is very high, the repairing cost is low, and the ecological environment of the contaminated soil can be effectively restored, so that the method has a broad market prospect.
Owner:JINGDEZHEN CERAMIC INSTITUTE
Method for improving biological coal bed gas yield through coal bed origin fungi
The invention discloses a method for improving the biological coal bed gas yield through coal bed origin fungi. The method includes the steps that (1) target coal bed gas field data are collected, and a coal bed in-situ fungi community structure is analyzed; (2) origin fungus efficient flora cultivation is carried out; and (3) the coal bed gas production is increased through microorganisms. According to the method, the efficiency capacity of degrading macromolecular compounds through the fungi is used, origin fungus floras are cultivated from a coal bed, the microorganism increase production coal bed gas process of anaerobic degradation coal produced methane is achieved, the target coal bed environment can be better accommodated, coal bed in-site biological methane conversion is quickly achieved, the problems in biodegradation coal produced methane rate and yield are solved, the coal bed gas yield is improved, the coal bed gas well service life is prolonged, the microorganism increase production coal bed gas technical application is pushed, and the coal bed gas industrial development is promoted.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Method and system for preparing rubbish biological mulching soil material of landfill yard methane emission reduction
InactiveCN101412033AIncreased oxidation potentialEmission reductionSolid waste disposalOxygenDistributor
The invention discloses a method and a system for preparing a garbage biological earth covering material for emission reduction of methane in a landfill site. The method comprises the following steps: transferring garbage into a step-type intermittent aeration reactor, performing intermittent aeration on the reactor, and making the generated percolate pass through a water distributor to adjust humidity of the garbage, so as to further degrade organic substances in the garbage under the action of anaerobe and aerobe; at the same time, using the methane generated by anaerobic degradation of the garbage in the reactor to tame methane oxidized microbe in the garbage and improve oxidizing property of the methane; and finally twice sieving the garbage after being treated by the step-type intermittent aeration reactor to remove impurities without or with low methane oxidation activity. The method not only can tame the methane oxidized microbe in the process required by re-degradation of the garbage, and improve oxidizing property of the methane, but also use wastes after biological treatment of the garbage as raw materials, can achieve sustainability and reproducibility of biological treatment facilities for the garbage with low cost, and avoid agriculture competing soil resources.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and device for treating early urban landfill leachate
ActiveCN102491587AEasy loadingReduce outputTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentSequencing batch reactorChemical oxygen demand
The invention provides a method and a device for treating early urban landfill leachate, which belongs to the technical field of biological sewage treatment by using a biochemical method. Under the conditions that only a biological method is utilized to treat the leachate and no external carbon source is added, operating cost is greatly reduced, and more than 80% of chemical oxygen demand (COD) removal rate and more than 95% of total nitrogen removal rate are achieved. An anaerobic sequencing batch reactor (ASBR) thoroughly performs anaerobic methanogenic reaction to remove high-concentrationorganic matter in the early urban landfill leachate, and effluent of the ASBR serves as feed water of a pulse sequencing batch reactor (SBR) by adding appropriate proportion of original leachate and provides appropriate ratio of COD to NH4+-N. The pulse SBR adopts three times of the feed water equal in quantity, combines a method for controlling stirring and aeration in real time and fully utilizes at least two-thirds of organic carbon sources in the pulse SBR feed water for denitrification, and total nitrogen is removed efficiently through utilization of internal carbon sources under the condition of no external carbon sources. By means of the technology, contradiction formed by organic matter anaerobic degradation and biological denitrification is solved, running is flexible, and operation is simple.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com