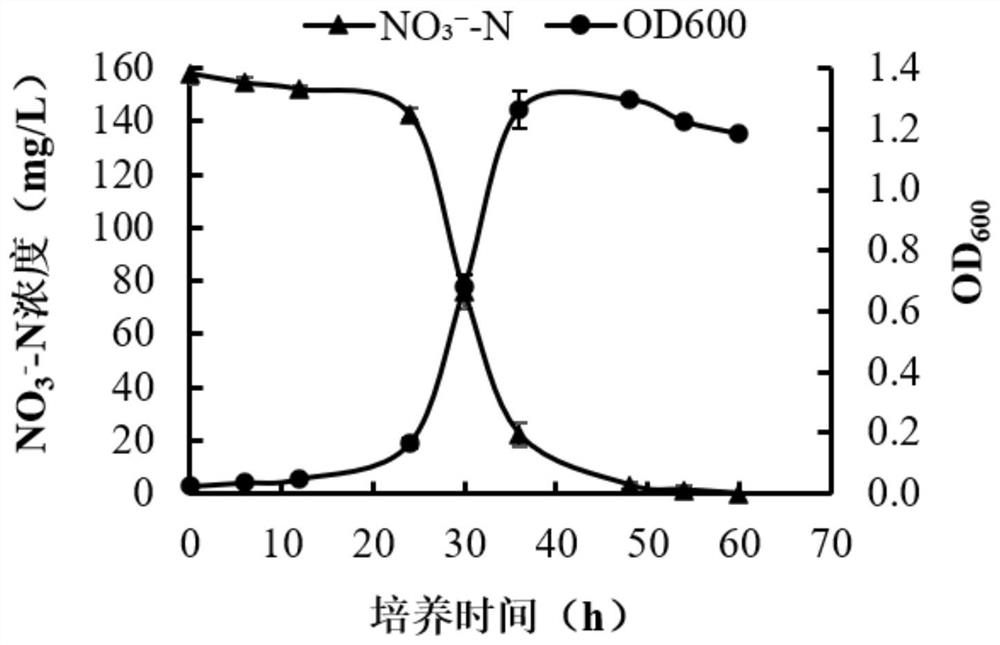
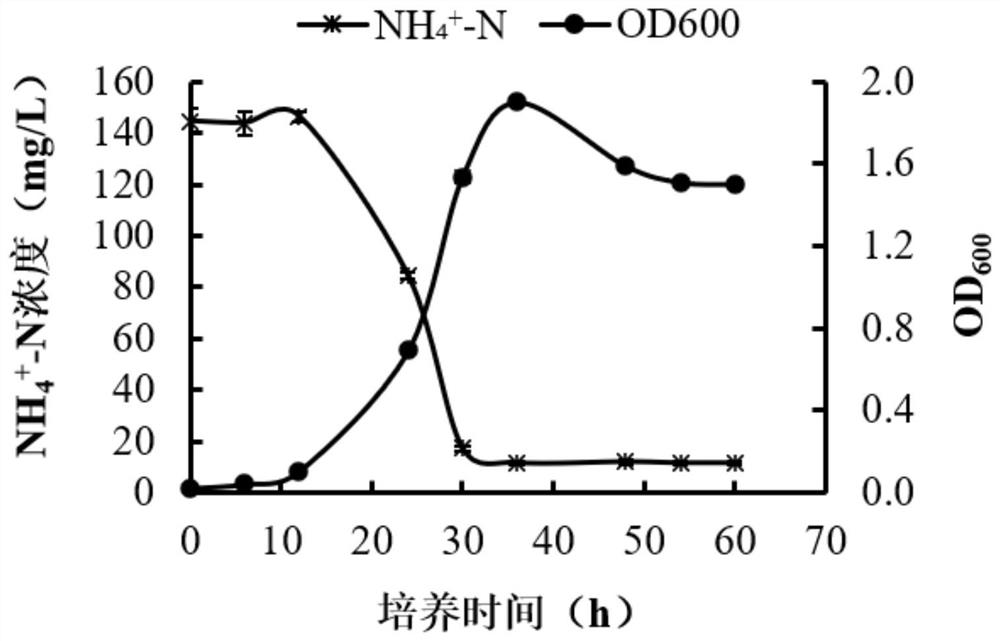
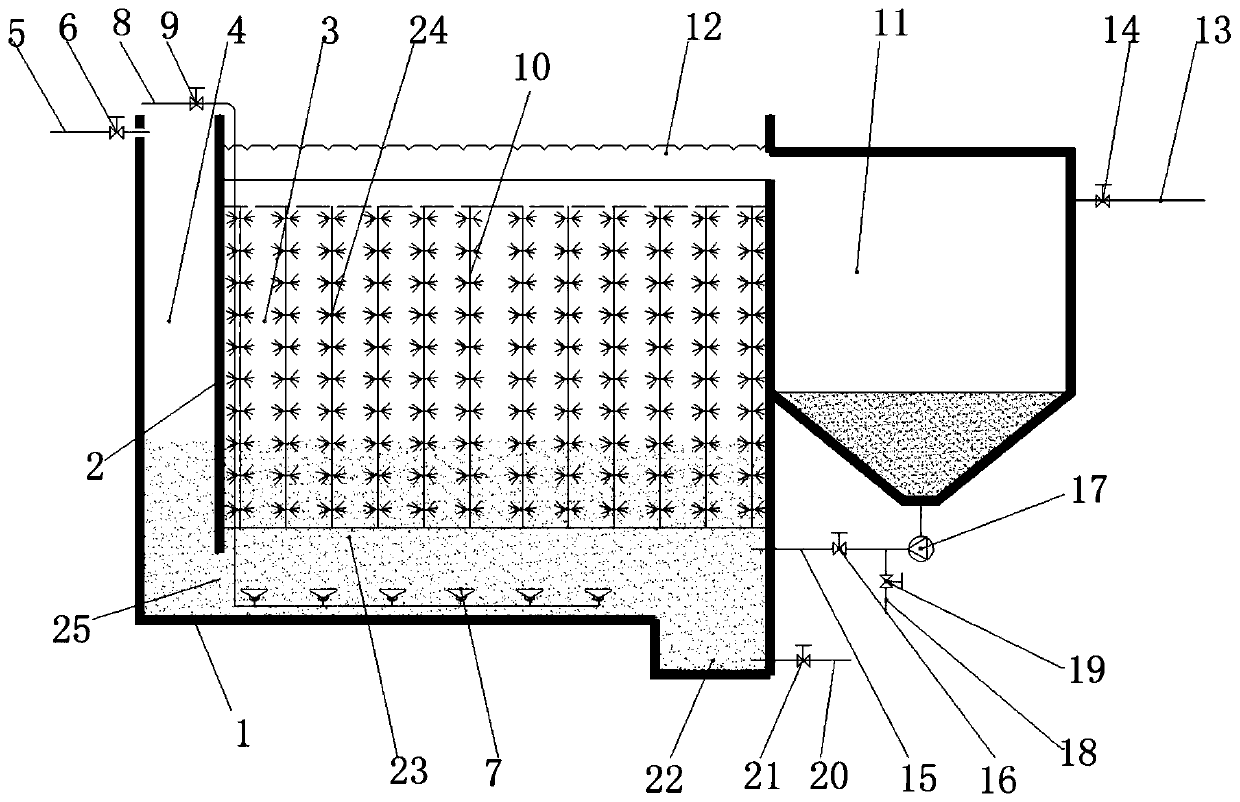
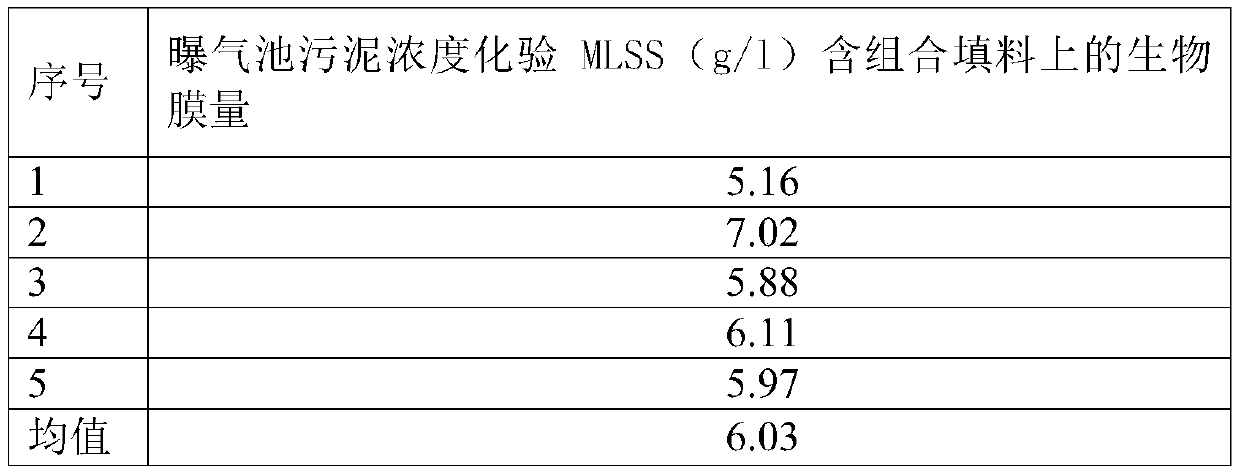
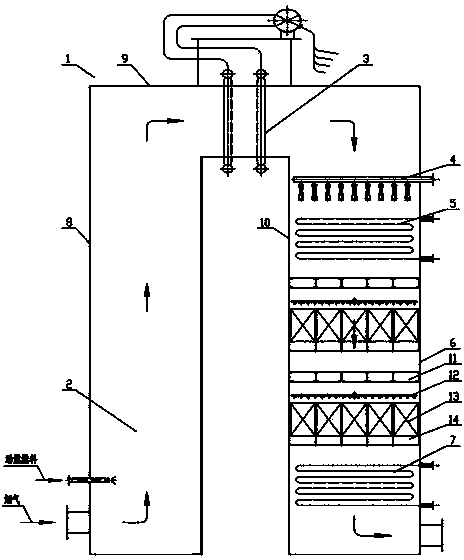
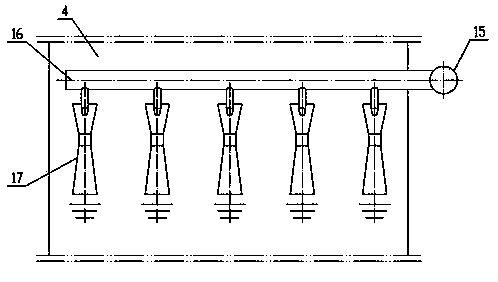
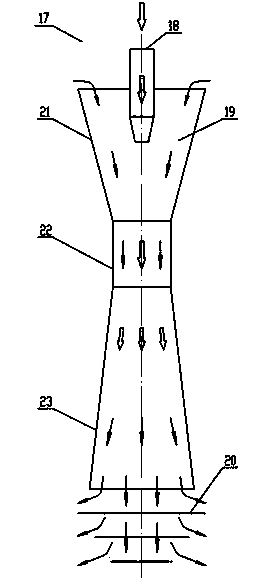
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30results about How to "With denitrification function" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Adjusting method for A/O biological denitrification reactor and nitrification process, its on-line fuzzy controller and control thereof
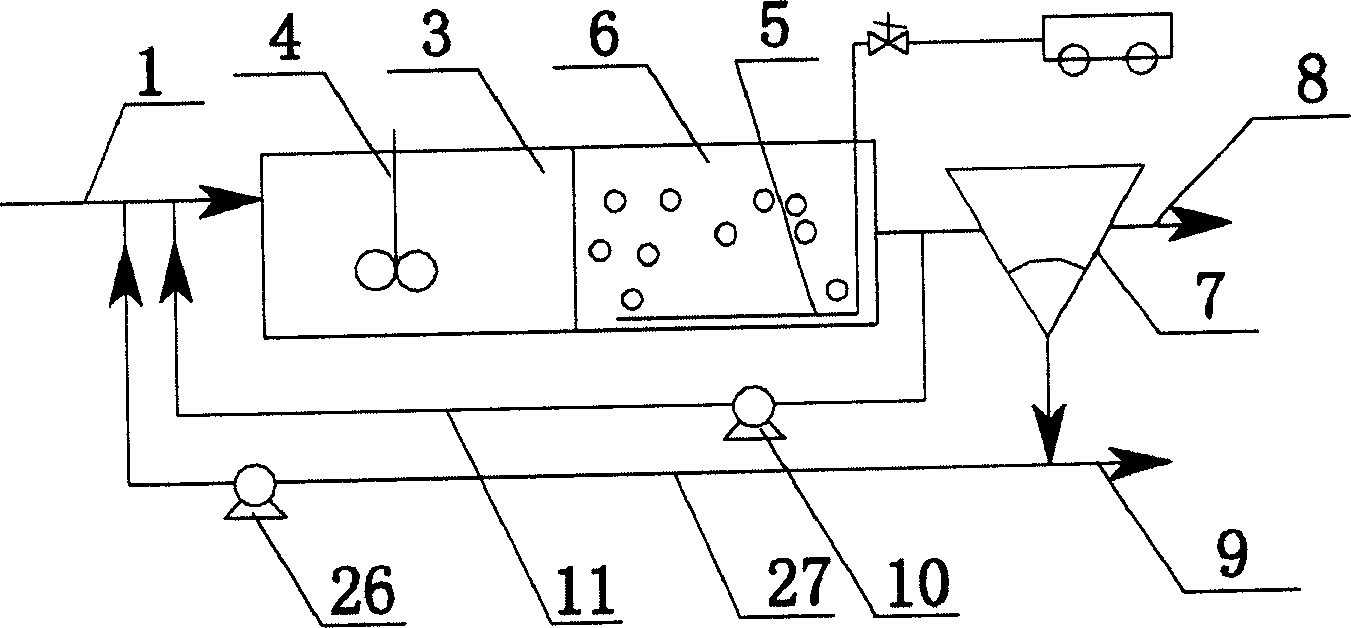
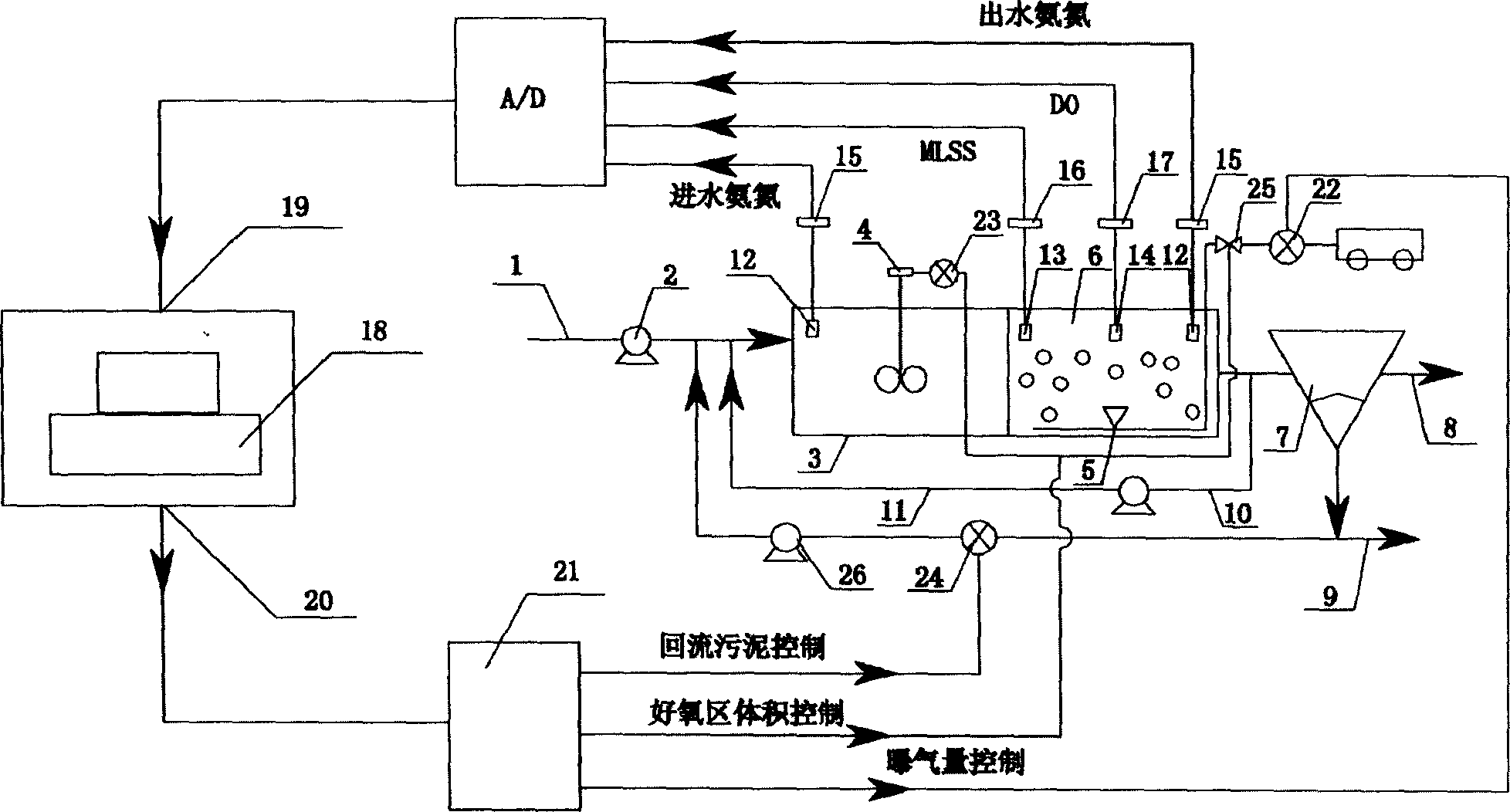
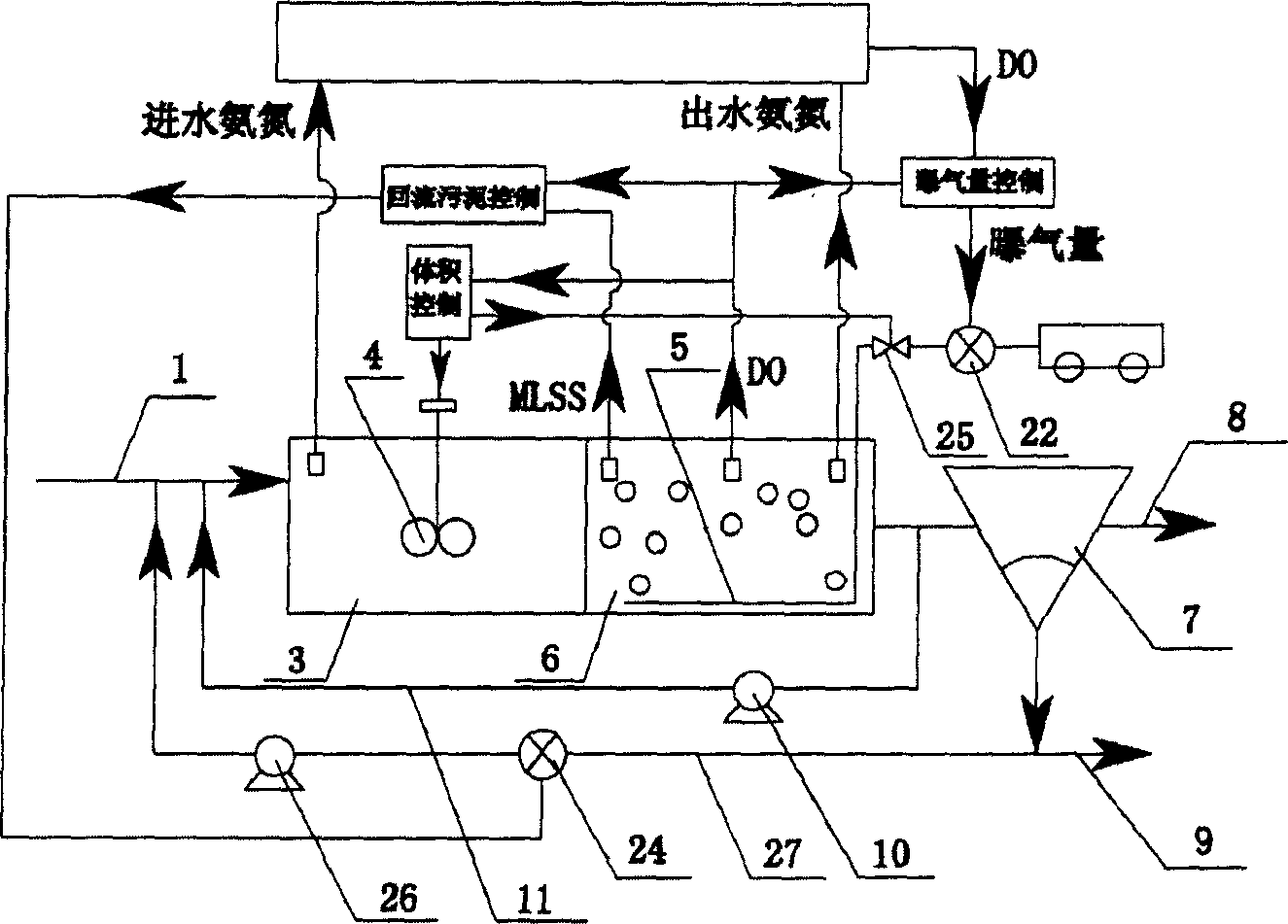
InactiveCN1778714ASave dosing costOrganic load reductionControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsChemical variable controlSludgeMarine engineering
Owner:姚宏
High-pressure electrostatic dust collection electric field device of coal-fired unit for generating ozone and simultaneously desulfurizing and denitrating
ActiveCN102949921AEasy to collectWith the function of spark cleaningDispersed particle separationExternal electric electrostatic seperatorPower control systemClosed loop
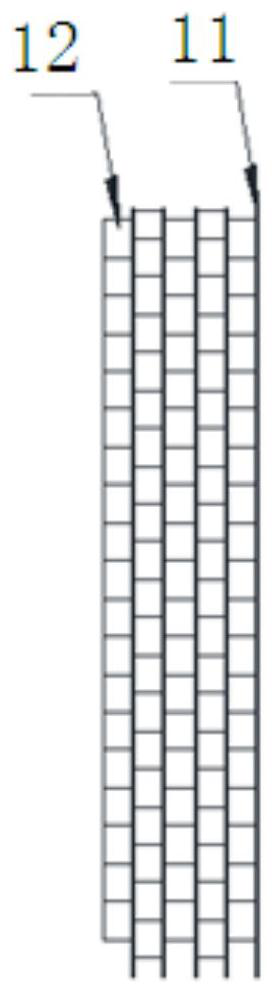
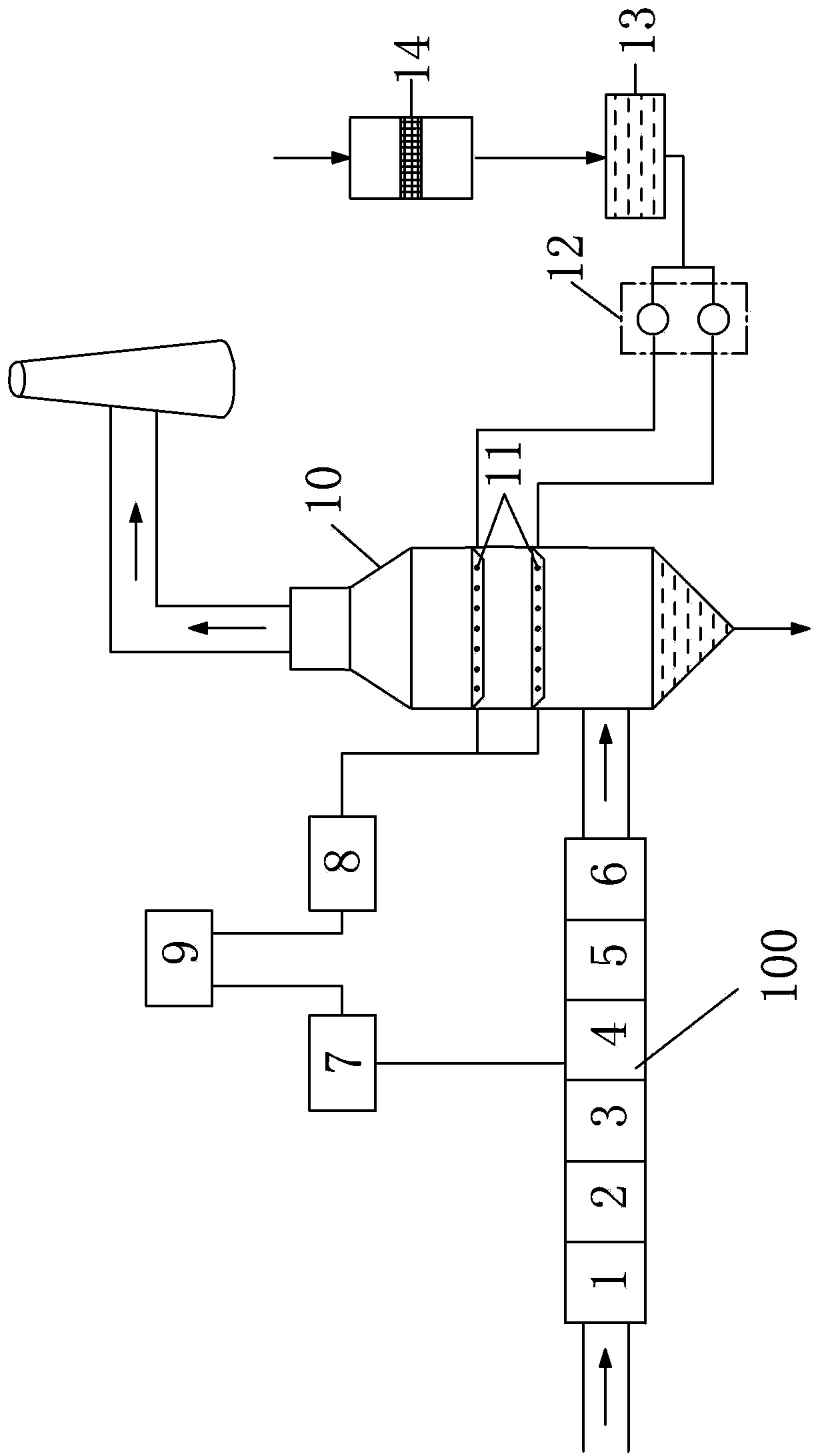
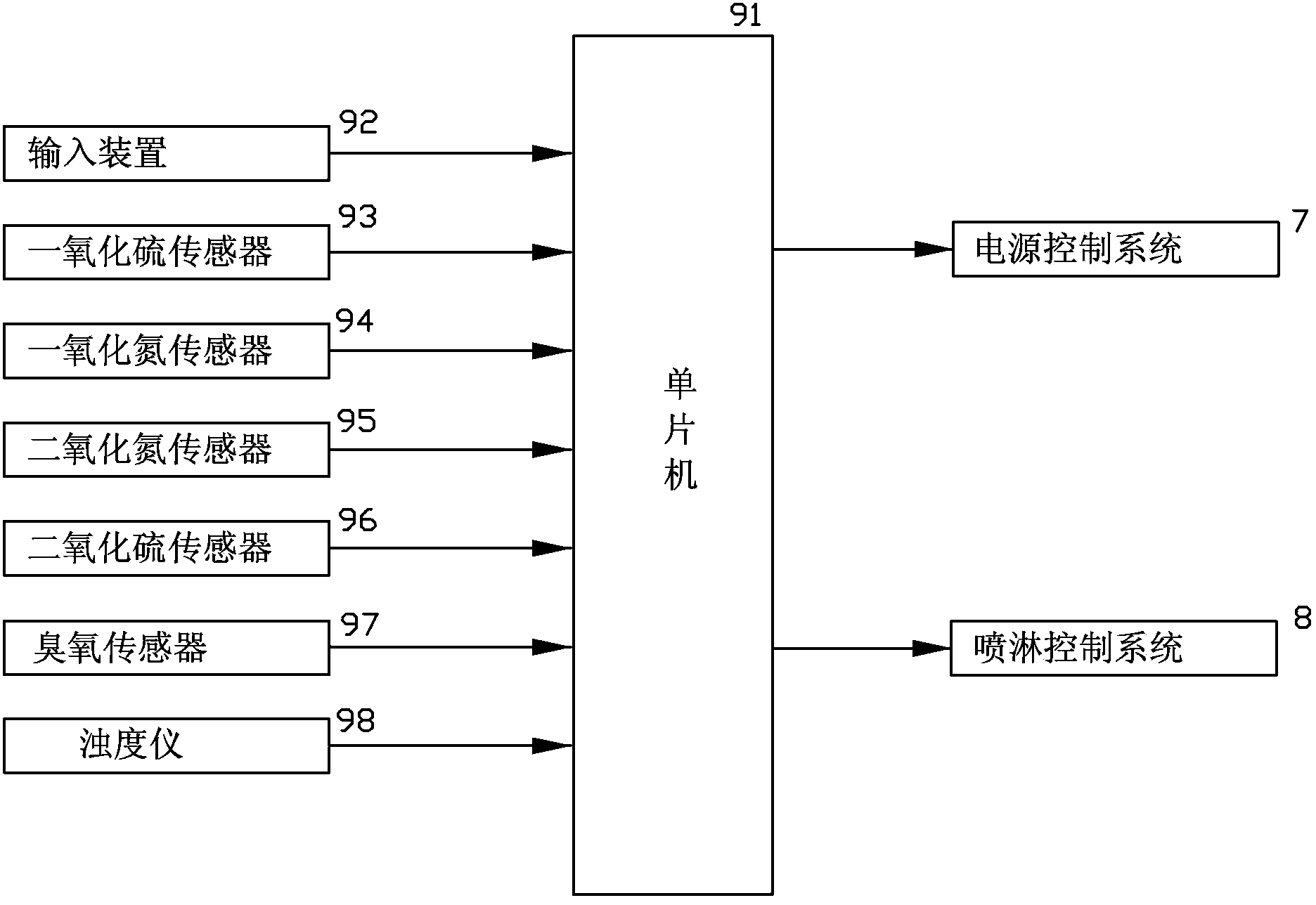
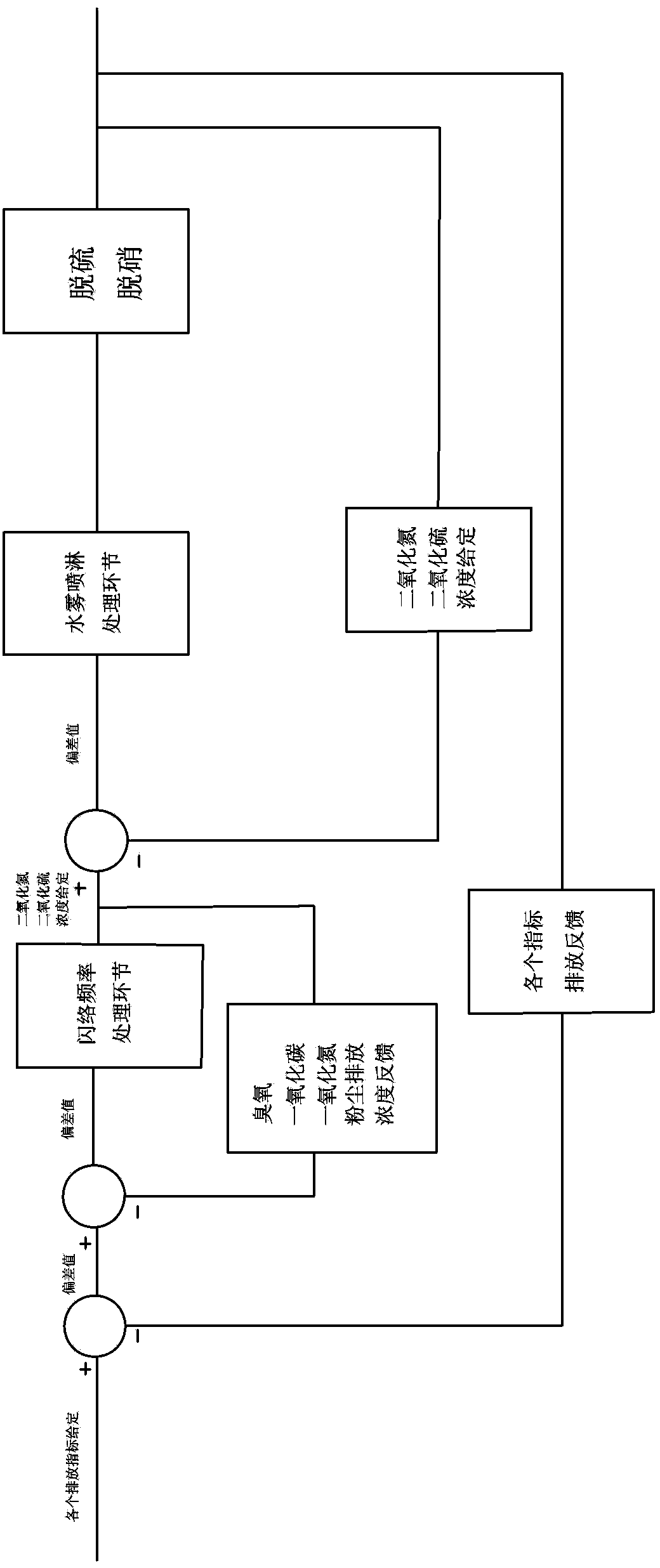
The invention discloses a high-pressure electrostatic dust collection electric field device of a coal-fired unit for generating ozone and simultaneously desulfurizing and denitrating. The device comprises an electrostatic dust collection channel which is formed by sequentially connecting a plurality of electric fields, a neutralizing tower, a water mist spray system, a water supply device, a power control system, a spray control system and an intelligent closed-loop control system, wherein the flashover frequency of the power control system is set to be 150-10000 times / minute, the water mist spray system is arranged in the neutralizing tower, the intelligent closed-loop control system is utilized to control the power control system and the spray control system is utilized to automatically coordinated with each other, so that the high-pressure electrostatic dust collection device can be added with a denitrating function on the basis of maintaining the original electrostatic dust collecting and desulfurizing functions, and nearly no investment is required for obtaining the denitrating function. On the basis of reasonably utilizing the original equipment, the environmental protection emission requirements are satisfied, and the device has the advantages of low cost, high operation effect and obvious integral economic benefit.
Owner:XIAMEN RECH TECH
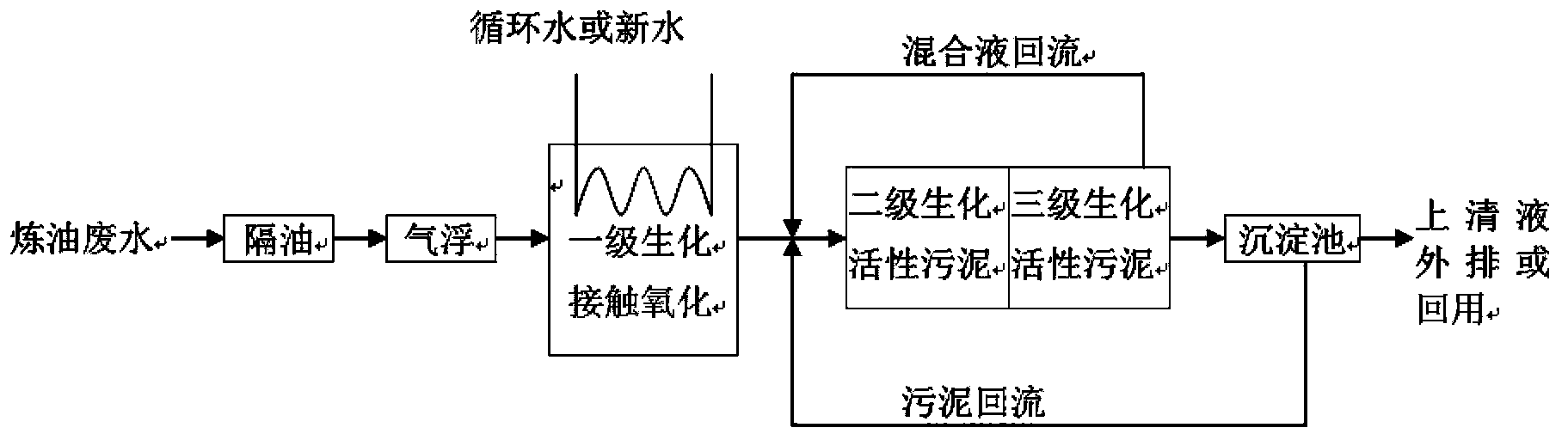
Method for treating oil refining wastewater
InactiveCN103373796AStrong removal rateAvoid inhibitionMultistage water/sewage treatmentSludgeWater quality
The invention relates to a method for treating oil refining wastewater. The method comprises the following steps: oil removal, air flotation, a first level biochemical treatment, a second level biochemical treatment, a third level biochemical treatment, and precipitation. A first level biochemical treatment unit is provided with a heat exchanger to reduce temperature of wastewater; a second level biochemical treatment unit is used for nitrogen removal by denitrification; a third level biochemical treatment unit conducts nitration of ammonia nitrogen and removal of pollutants such as residual organic compounds; and a mixed liquor from the third level biochemical treatment unit and the sludge from a precipitation treatment unit flow back to the second level biochemical treatment unit. The invention mainly solves the problem that a refining wastewater treatment facility has low efficiency of ammonia nitrogen removal or even no effect on ammonia nitrogen removal. The process has the advantages of high efficiency of ammonia nitrogen removal and nitrogen removal, high treatment efficiency, strong shock resistance, stable and standard achieved quality of outlet water, and low investment and operation cost.
Owner:CHENGDU INST OF BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF S
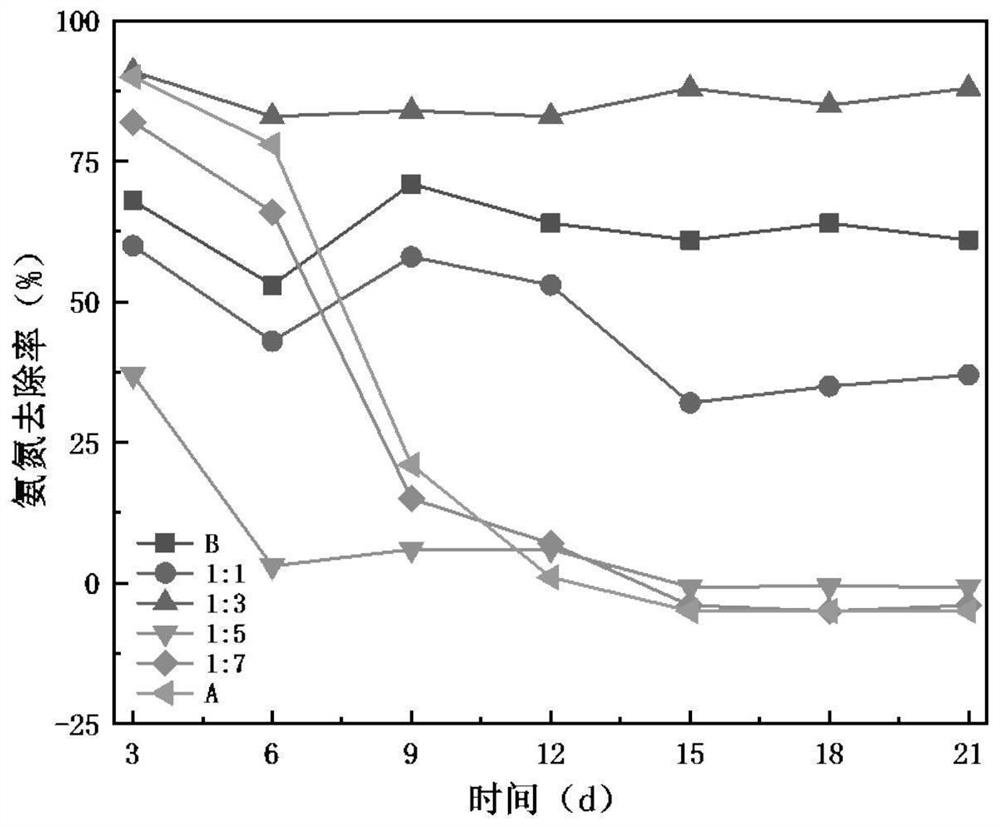
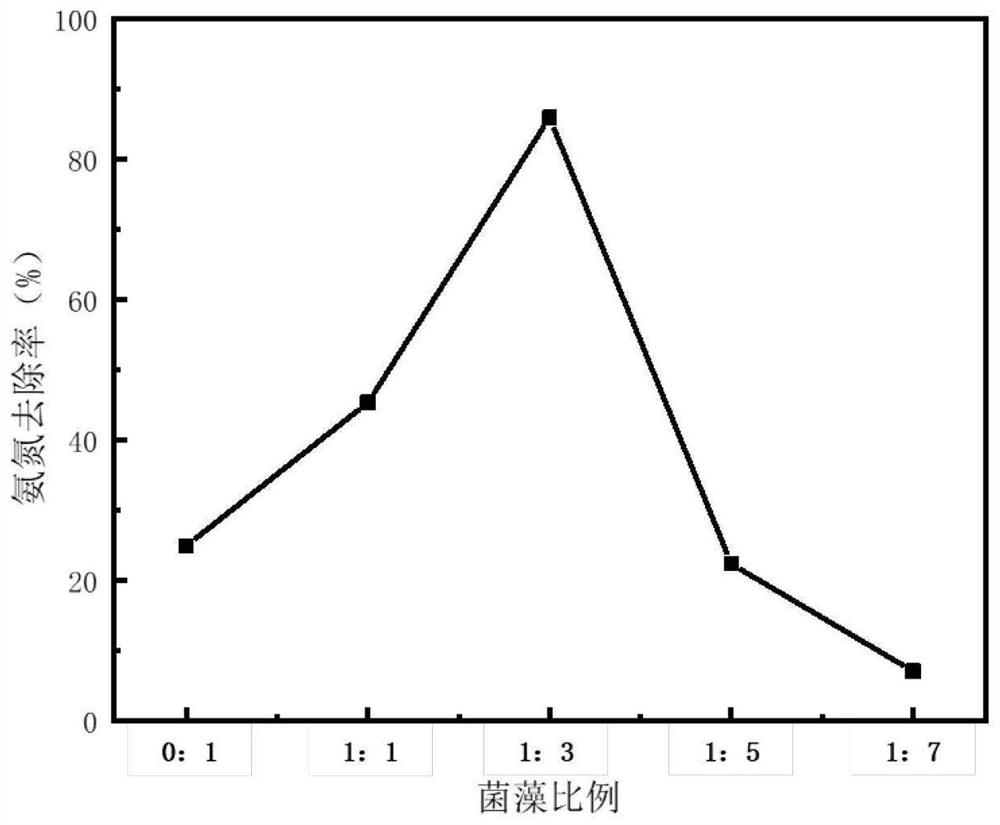
Bacteria-algae composition for synergistically degrading high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and phosphate as well as application and method thereof
PendingCN113003727AEfficient removalSolve the problem of not being able to remove phosphorusWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesTotal nitrogenP phosphate
The invention discloses a bacteria-algae composition for synergistically degrading high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and phosphate as well as application and a method thereof. The composition is prepared from a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification complex microbial inoculant and lesser chlorella, the complex microbial inoculant is formed by compounding cupriavidus, alcaligenes faecalis, acinetobacter and ochrobactrum TAC-2; chlorella is introduced into the complex microbial inoculant to form a bacterial-algae symbiotic system, chlorella generates oxygen through photosynthesis, dissolved oxygen is provided for denitrification of the complex microbial inoculant, the aeration energy consumption of the complex microbial inoculant system is reduced, and the complex microbial inoculant converts organic matters in wastewater into carbon dioxide through biological action to meet the growth requirement of chlorella. The method can improve the removal of ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen by the complex microbial inoculant, increase the phosphate removal capability, solve the problem that the complex microbial inoculant cannot remove phosphorus, and can be used for treating high-concentration ammonia nitrogen and phosphate wastewater.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF TECH
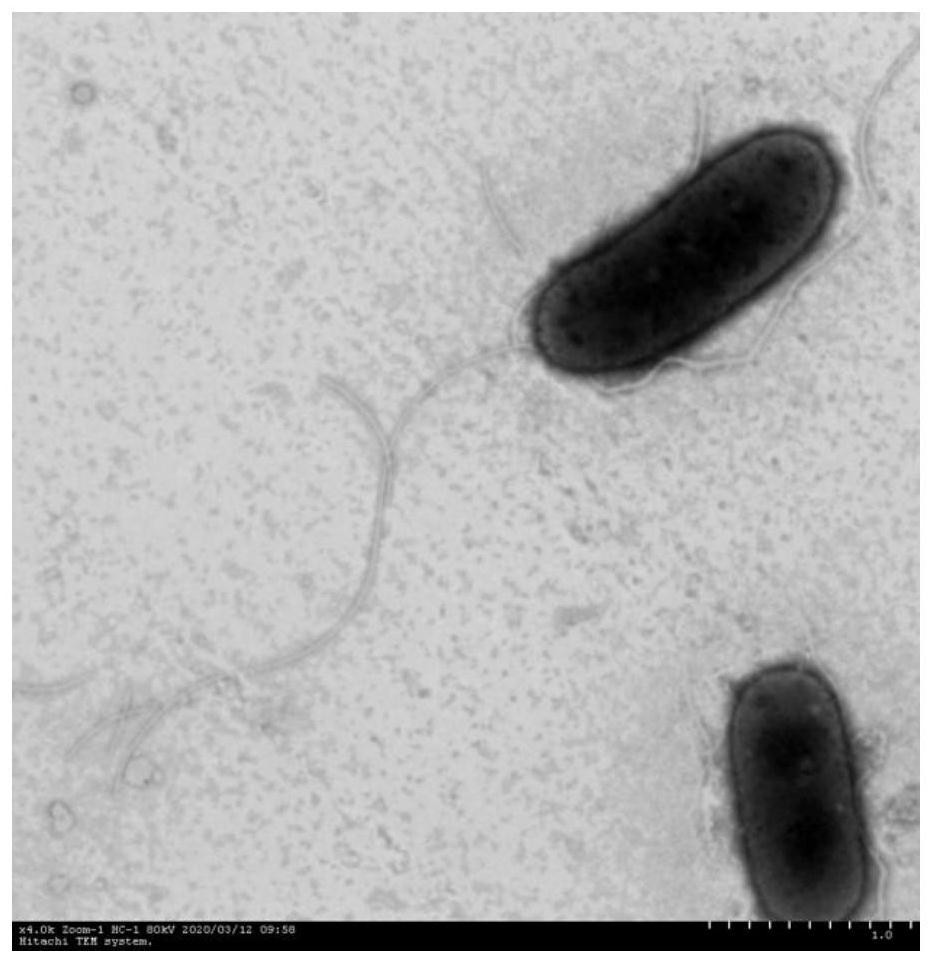
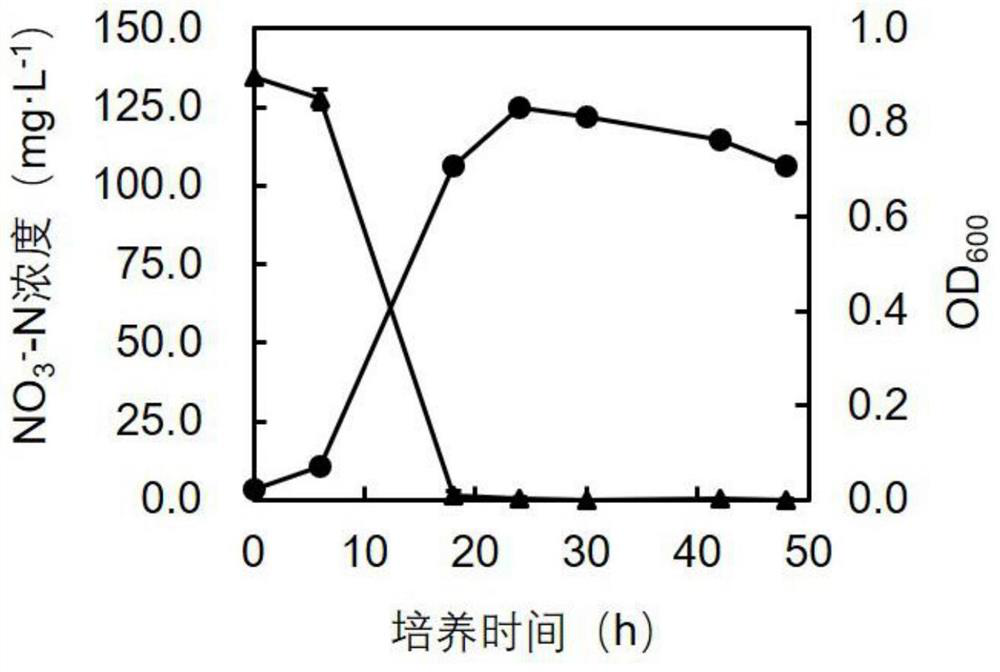
Aerobic denitrifying bacteria and application thereof
ActiveCN112625942AWith denitrification functionBacteriaWater contaminantsGenus PseudomonasDenitrifying bacteria
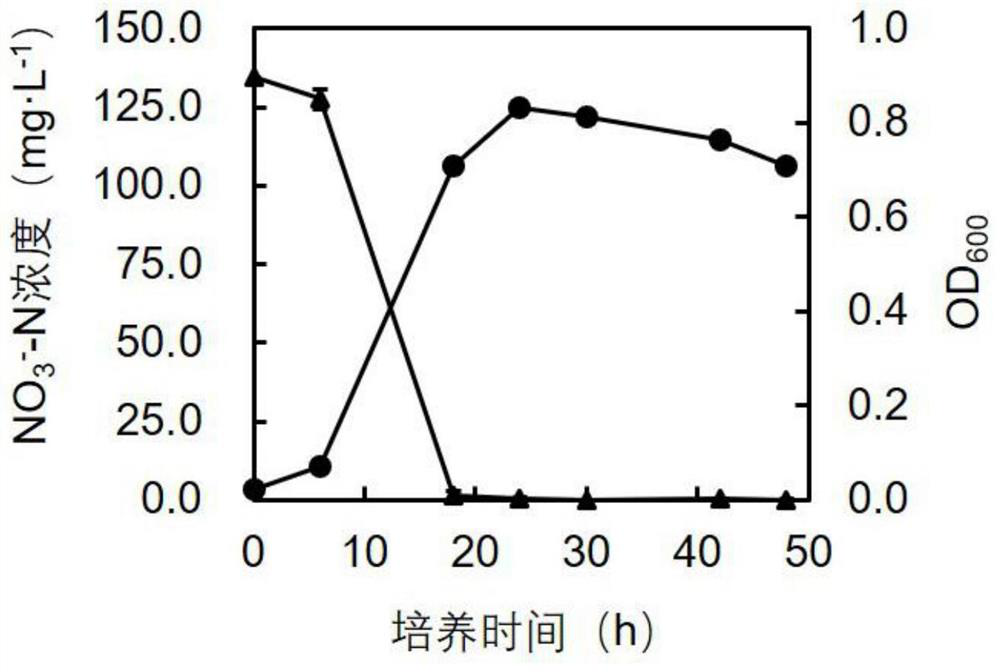
The invention discloses aerobic denitrifying bacteria and application thereof. A preservation number of pseudomonas JM22B6 disclosed by the invention is GDMCC No:61212. Integrated analysis of morphology, physiology and biochemistry, 16SrRNA sequences, genome sequences and the like shows that the strain is a new strain of pseudomonas. The strain is the novel aerobic denitrifying bacteria and can efficiently remove nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen in a water body, that is, the removal efficiency of the nitrite nitrogen and the ammonium nitrogen after culture for 12 hours is 100%; and the removal rate of the nitrate nitrogen after culture for 24 hours is 100%. In addition, the strain 22B6 has a relatively good denitrification effect under the condition that the nitrite nitrogen concentration ranges from 14 mg / L to 280 mg / L. Therefore, the pseudomonas JM22B6 has important application potential in denitrification treatment of wastewater polluted by nitrogen such as the nitrate nitrogen, the nitrite nitrogen and the ammonium nitrogen, especially various wastewater polluted by nitrite nitrogen with different concentrations.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Denitrifying bacterium and application thereof
The invention discloses a denitrifying bacterium and application thereof. The collection number of Pseudomonas sp. JM10A2A is stored with number of GDMCC No.61214. The denitrifying characteristic research result of the Pseudomonas sp. JM10A2A indicates that the strain is a heterotrophic nitrification-aerobic denitrification strain, can efficiently remove nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen in awater body, and can still efficiently remove nitrite nitrogen under the condition of low C / N. Thus, the Pseudomonas sp. JM10A2A has great application potential in the aspect of water body denitrification.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Integral flue gas denitration device filled with denitration catalyst and provided with catalyst coating
PendingCN109078495AEasy loading and unloadingReasonable structureGas treatmentDispersed particle separationFlue gasEngineering
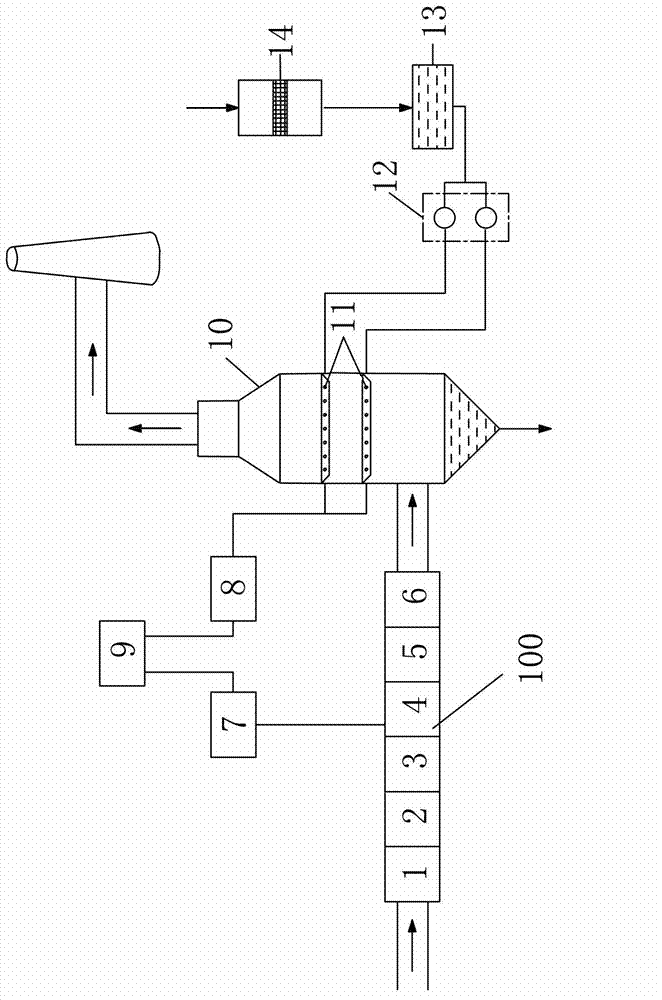
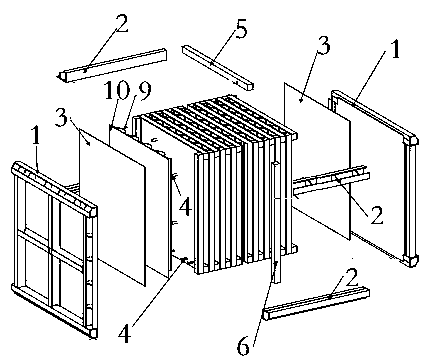
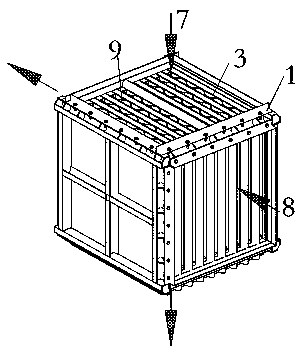
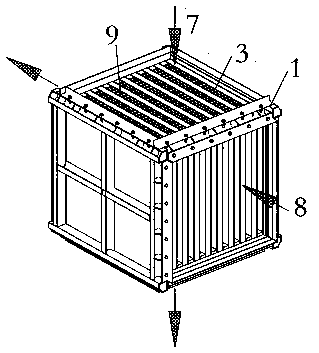
The invention discloses an integral flue gas denitration device filled with denitration catalyst and provided with catalyst coating. The integral flue gas denitration device comprises side frames anda heat-exchange core; the side frames are arranged on two opposite sides of the heat-exchange core; four corners of the heat-exchange core are positioned and fixed through corner posts correspondingly; the heat-exchange core comprises a plurality of heat-exchange plates, spoilers respectively arranged between the heat-exchange plates, edge connection bolting assemblies, corner connection bolting assemblies and edge sealing strips; the optional adjacent heat-exchange plates of the heat-exchange plates form flue gas passages and cool fluid passages, the flue gas passages and the cool fluid passages are crossed mutually but not communicated mutually; the flue gas passages is filled with the denitration catalyst, and the surfaces of the heat-exchange plates are coated with the catalyst coating. The integral flue gas denitration device is reasonable in structure and convenient to manufacture, can not only recover exhaust heat of flue gas but achieve denitration and realize denitration and heat exchanging integrally; its floor occupation is saved, and the catalyst filling the flue gas passages is convenient to load and unload.
Owner:上海孚旺炉业有限公司 +1
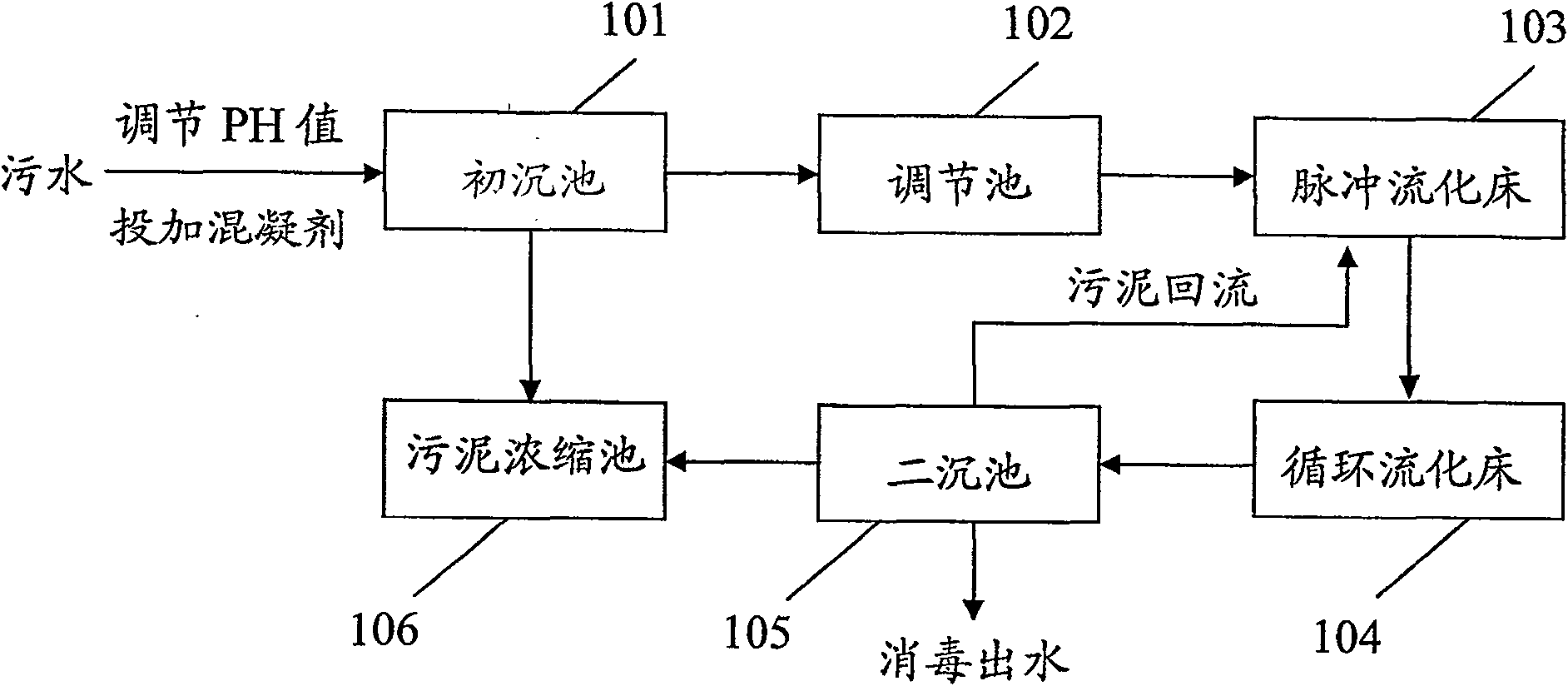
Method of processing sewage utilizing fluidized bed technique, organism compatibility filling thereof and preparing method of filling
InactiveCN100546925CLarge biomassHigh removal rateTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationFluidized bedSewage
The invention discloses an effluent disposing method through fluid bed and making method of biological affinity fill, which comprises the following steps: filling biological affinity fill in the fluid bed; making predisposed effluent into anaerobic pulse fluid bed and aerobic circulating fluid bed to do biochemical disposal; separating water from mud through two sediment pond or gas floating technique; sterilizing; discharging sludge into sludge condensing pond or refluxing sludge to anaerobic pond and aerobic pond. The biological affinity fill is composed of polyurethane, rare earth and ferric oxide.
Owner:刘德沛
Electrochemical biological rotating disc sewage treatment method for aerobic micro-organisms
ActiveCN107973403AWith denitrification functionHigh decontamination efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesChemistrySmall footprint
The invention provides an electrochemical biological rotating disc sewage treatment method for aerobic micro-organisms. The method is characterized in that an aerobic micro-organism membrane and an anaerobic electro-microorganism membrane are grow together on a three-dimensional carrier with oxygen gas reducing and catalyzing performances to form a composite biological membrane which is used for manufacturing a biological rotating disc; the anaerobic electro-microorganism membrane is grown on the inner layer which clings to the carrier, and the aerobic micro-organism membrane grows on the outer layer to package and protect the anaerobic electro-microorganism membrane. The aerobic respiration effect of the aerobic micro-organism membrane, the electrocatalytic oxidation effect and the electrocatalytic reduction effect of the anaerobic electro-microorganisms and the electro-catalytic oxygen gas reducing effect of the carrier are utilized to remove multiple pollutants in water. The electrochemical biological rotating disc sewage treatment method has the advantages as follows: (a) low material and operation cost; (b) a simple process and a small floor space; (c) high decontamination efficiency and multifunctionality; and (d) capability of being fused with a conventional aerobic biological treatment system and the like.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
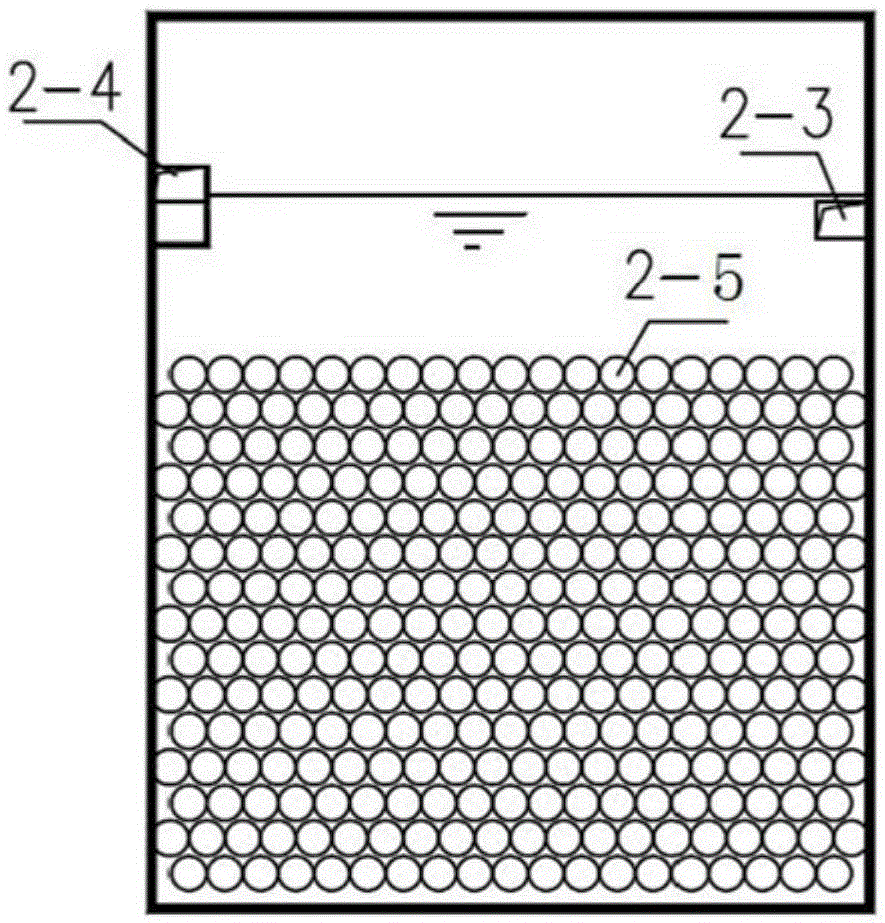
Denitrification aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor and work method thereof
PendingCN108623001AIngenious structural designSimple structural designWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSequencing batch reactorOxygen utilization rate
The invention provides a denitrification aerobic granular sludge sequencing batch reactor. An aerator system is arranged inside a tank body; a nitrification region is arranged above the aerator system; a denitrification region is arranged under the aerator system; a space from a position under the denitrification region to the tank bottom is a water distribution mixing region; a gas water separator is arranged on the top of the tank body; one end of an upper backflow pipe is connected onto the bottom of the gas water separator; the other end of the upper backflow pipe is positioned in a nitrification region and is provided with a plurality of upper backflow spray heads; one end of a lower backflow pipe is connected to the bottom of the gas water separator; the other end of the lower back flow pipe is connected to a first cross-shaped pipe; a plurality of lower backflow spray heads are arranged on the first cross-shaped pipe. Through the reasonable design of hydraulic power and mass transfer, the air lifting kinetic energy is formed by the density pressure difference generated by a reactor under the aeration work condition; the fluid is downwards discharged to be sprayed out to formcyclone mixing by using the position differences and the pressure differences; the fluid speed is accelerated; the hydraulic shearing power is enhanced; the path and dwell time of the air in the water can be improved; the oxygen utilization rate is improved; the flocculent sludge can be used for starting so as to form aerobic particle sewage.
Owner:南宁绿智环保科技有限公司
Bacillus pumilus with a denitrification function and application of bacillus pumilus
ActiveCN113293111AWith denitrification functionBacteriaWater contaminantsBacillus pumilusMicrobiology
The invention discloses bacillus pumilus with a denitrification function and application of the bacillus pumilus. The preservation number of the Marivirgasp. (Marivirgasp.) S33H4 is GDMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.61709, and the preservation number of the Marivirgasp. The bacillus pumilus S33H4 can effectively remove nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in a water body, the removal effect on the nitrate nitrogen and the removal effect on the ammonium nitrogen are both 90% or above, and in addition, the strain also has a remarkable removal effect on the nitrite nitrogen. Therefore, the bacillus pumilus S33H4 has a very good application potential in the denitrification of the water body.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Activated sludge process and biofilm process combined wastewater treatment device
PendingCN110963565AEffective congestion reductionLarge biomassWater treatment parameter controlTreatment using aerobic processesActivated sludgeAmmoniacal nitrogen
The invention relates to an activated sludge process and biofilm process combined wastewater treatment device. The device comprises a treatment tank, a partition plate is fixed in the treatment tank,a wastewater inlet pipe is connected to a water distribution cavity, and a gap is formed between a lower end of the partition plate and a bottom wall of the treatment tank. A microporous aerator is arranged at a bottom of the reaction cavity, the microporous aerator is connected with an aeration pipeline, a filler frame is arranged in the reaction cavity, a combined filler is suspended on the filler frame, a sedimentation tank is attached to one side of the treatment tank, an upper end of the reaction cavity is level with an upper end of the sedimentation tank to form an overflow port, an upper part of the sedimentation tank is provided with a water outlet, the water outlet is lower than the overflow port, a bottom of the sedimentation tank is provided with a sludge return pipeline, the sludge return pipeline is provided with a sludge pump and a return switch, and a bottom of the treatment tank is provided with a sludge outlet. The device is simple in structure and small in occupied area, the concentration of activated sludge can reach 5-6 g / l, the removal rate of COD, BOD and ammonia nitrogen is up to 90% or above, the total nitrogen removal efficiency is 60% or above, and the operation cost is low.
Owner:刘士军
Microbial electrochemical biological rotating disk for sewage treatment
ActiveCN108217915AWith denitrification functionLow running costTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsBiofilm growthElectron donor
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment, and provides a microbial electrochemical biological rotating disk for sewage treatment. The rotating disk comprises a three-dimensional carrier, a rotating shaft and a power device; the three-dimensional carrier is arranged on the rotating shaft, and the rotating shaft is connected with the power device; the rotating disk is characterized in that an anaerobic electrogenesis microbial film and an aerobiotic microbial film are adhered on the three-dimensional carrier, wherein the anaerobic electrogenesis microbial film grows on aninner layer which clings to the carrier, wherein the aerobiotic microbial film grows on an outer layer to wrap and protect the anaerobic electrogenesis microbial film; the three-dimensional carrier is partially immersed in sewage and partially exposed in the air. Electrons inside the biological rotating disk can be freely transmitted and can be used for synergistically removing electron donors and electron acceptors in water, the electron donors are prepared from organic matter and ammonia-N, and the electron acceptors are prepared from nitrate nitrogen, nitrous acid nitrogen, sulfate radicaland heavy metal ions.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
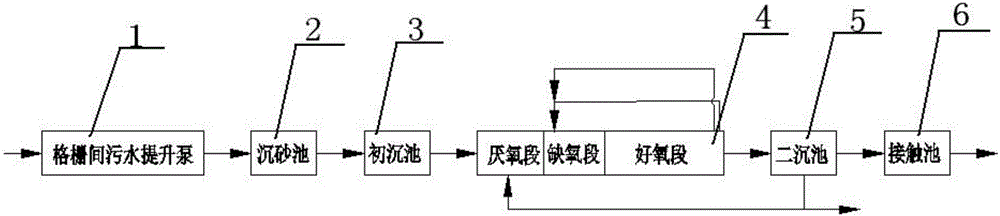
Method and device for municipal sewage treatment enhancement operation with intermittent aeration of biochemical tank
PendingCN106746383AIncrease concentrationIncrease biomassTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesMultistage water/sewage treatmentMunicipal sewageHigh load
The invention relates to a method and device for municipal sewage treatment enhancement operation with intermittent aeration of a biochemical tank belonging to the technical field of water treatment. The device is constituted by a grid, a sand setting tank, a primary settling tank, a three-zone tank, a secondary settling tank, and a contact tank. The three-zone tank comprises an anaerobic zone, an anoxic zone, an aerobic zone, a sludge return pipe, an aerator pipe, a nitrification liquor return pipe, and a return pump. A control valve is mounted on a riser of the aerator pipe at the rear end of the aerobic zone. A sludge return pump is also mounted at the tail end of the aerobic zone. An inlet of the sludge return pump is connected to a perforated sludge collecting pipe which is mounted at the bottom of the rear end of the aerobic zone, and an outlet of the sludge return pump is connected to an inner return pipe. The other end of the inner return pipe is connected to the nitrification liquor return pipe. When a sewage treatment plant operates under high load, the control valve is closed to stop aeration, and the sludge return pump is started to allow both sludge at the bottom of the settling zone and nitrification liquor to return to the anoxic zone. According to the invention, the municipal sewage is treated by increasing the sludge concentrations of the anoxic zone and the aerobic zone, thereby increasing the biomass of the biochemical tank and reducing the operation energy consumption.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF TECH
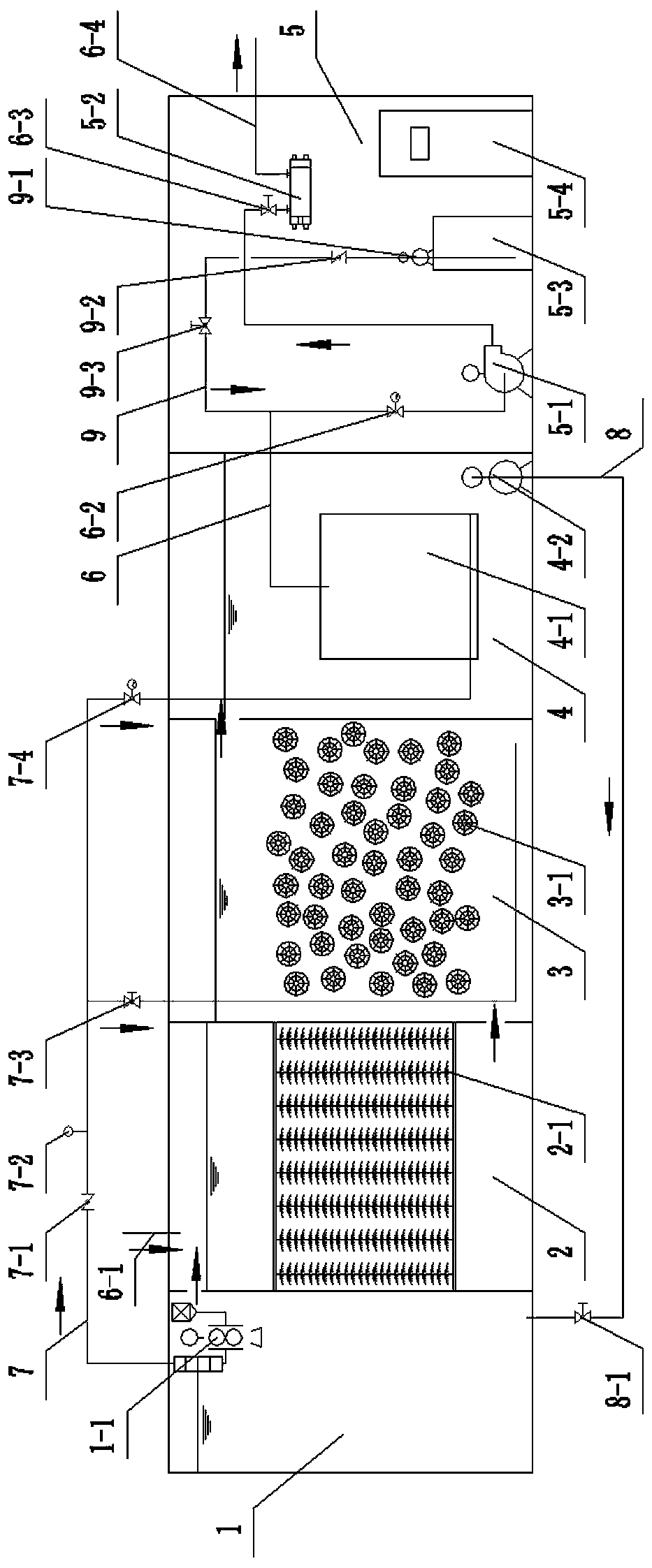
Integrated intelligent sewage treatment device and treatment method
PendingCN111153570ASave installation spaceImprove biodegradabilityWater treatment parameter controlSemi-permeable membranesSludgeSewage
The invention relates to an integrated intelligent sewage treatment device and method. The top of a hydrolytic acidification tank is connected with a device water inlet pipe. The upper part of a membrane component in an MBR membrane pool is connected with a sewage pipeline. The sewage pipeline is divided into two paths. One path is connected with a suction pump through a suction pump water inlet electric valve, the suction pump is connected with a sterilizer through a sterilizer water inlet manual valve, and the sterilizer is externally connected with a device water outlet pipe. The other pathis connected with a chemical cleaning pipeline, the chemical cleaning pipeline is sequentially equipped with a cleaning pipeline manual valve, a cleaning pipeline check valve and a cleaning pipelinemetering pump and then connected with a chemical cleaning box, and a sludge discharge pump is arranged at the bottom of the MBR membrane pool and connected with the bottom of a sludge pool through a sludge discharge pipeline with a sludge discharge manual valve. The sewage treatment device is high in impact resistance, stable in operation and high in treatment efficiency.
Owner:亚太泵阀有限公司
CO boiler having denitration function
ActiveCN103776043AWith denitrification functionImprove utilization efficiencyLighting and heating apparatusDispersed particle separationFlueCoal
The invention relates to a CO boiler having the denitration function. The CO boiler comprises a flue, a combustion chamber, steam drums, an evaporation section and an economizer section. The flue comprise a first vertical flue body, a horizontal flue body and a second vertical flue body, wherein the two ends of the horizontal flue body are communicated with the upper portion of the first vertical flue body and the upper portion of the second vertical flue body respectively, the combustion chamber is arranged in the first vertical flue body, the steam drums are arranged in the horizontal flue body, and the evaporation section and the economizer section are arranged in the second vertical flue body. The CO boiler further comprises an ammonia spraying and mixing mechanism and a denitration reactor. The ammonia spraying and mixing mechanism is arranged in the second vertical flue body and is located above the evaporation section. The denitration reactor is arranged between the evaporation section and the economizer section. The CO boiler having the denitration function can effectively improve the mixing uniformity of smoke and ammonia gas, improve the denitration efficiency and prevent ammonia escape; due to the fact that the denitration reactor is arranged in the CO boiler, an ammonia mixing grid is not needed, the utilization efficiency of smoke heat is improved, and the occupied space of the CO boiler and equipment investment are reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A kind of aerobic microbial electrochemical biological turntable sewage treatment method
ActiveCN107973403BWith denitrification functionHigh decontamination efficiencyTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesCellular respirationCatalytic oxidation
The invention provides an aerobic microbial electrochemical biological turntable sewage treatment method. The method is to use the aerobic microbial film and the anaerobic electricity-producing microbial film to grow together on a three-dimensional carrier with oxygen reduction catalytic performance to form a composite biofilm. A biological turntable is made; wherein, the anaerobic electrogenic microbial film grows on the inner layer close to the carrier, while the aerobic microbial film grows on the outer layer, wrapping and protecting the anaerobic electrogenic microbial film. It utilizes the aerobic respiration of the aerobic microbial membrane, the electrocatalytic oxidation and electrocatalytic reduction of anaerobic electricity-producing microorganisms, and the electrocatalytic oxygen reduction of the carrier itself to remove various pollutants in water at the same time. It has the advantages of (a) low material and operating costs; (b) simple process and small footprint; (c) high decontamination efficiency, multi-functionality and (d) can be integrated with traditional aerobic biological treatment systems, etc. .
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
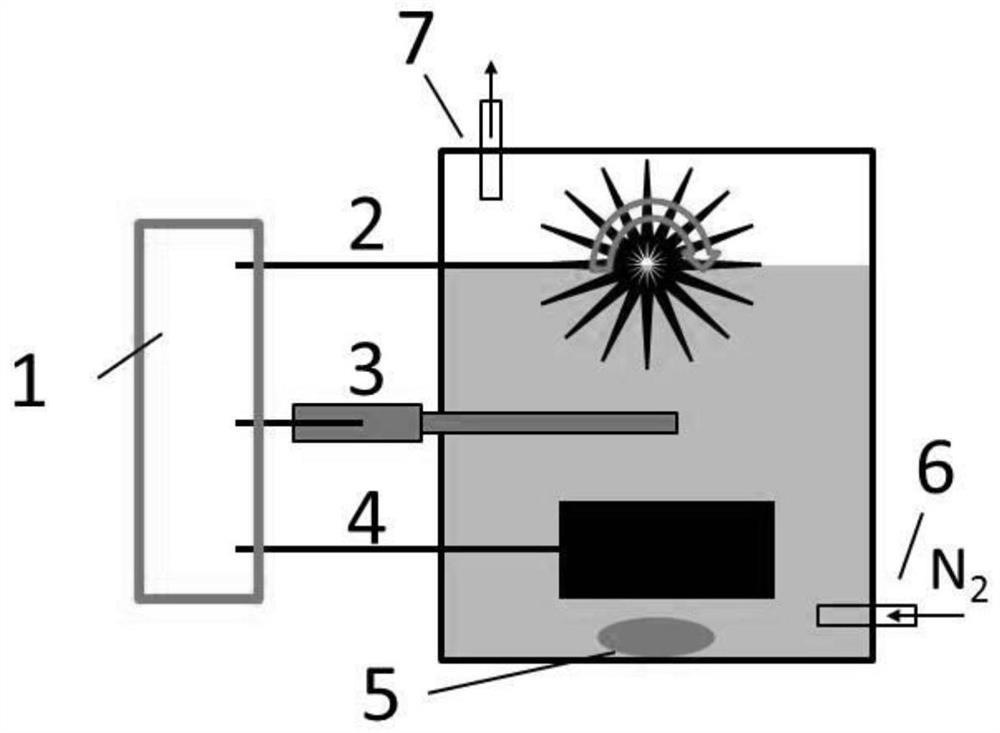
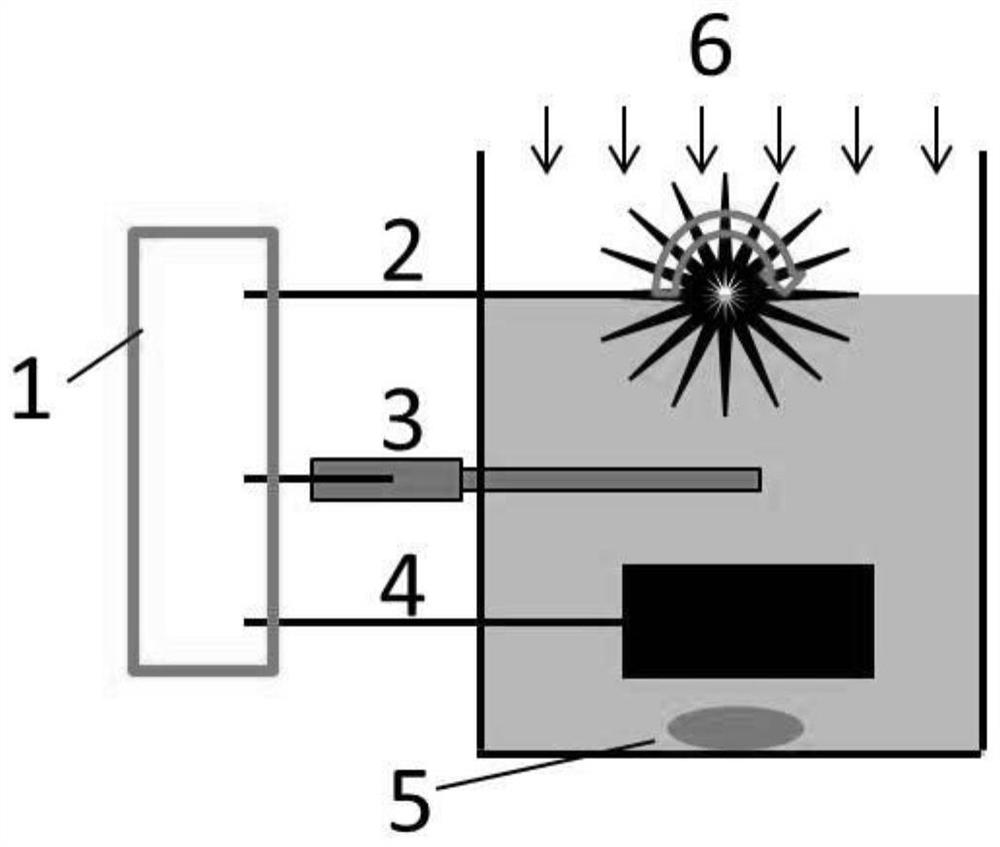
Method of advanced oxidation for NO in flue gas and device thereof
ActiveCN101785966BWith denitrification functionImprove oxidation efficiencyDispersed particle separationFerrous saltsFlue gas
The invention discloses a method of advanced oxidation for NO in flue gas and a device thereof. The flue gas after dust collection enters a vapor phase advanced oxidation device, and the method sequentially comprises the following steps of flue gas preconditioning and vapor phase advanced oxidation. The device comprises a flue gas preconditioning segment and a vapor phase advanced oxidation segment, wherein the flue gas preconditioning segment is provided with a process water spray device; and the vapor phase advanced oxidation segment is provided with a ferrous salt spray device and a hydrogen peroxide spray device. The oxidation device for NO is arranged in front of the original wet desulphurization device (or the oxidation device is directly transformed in a flue), so that the originaldesulphurization device has denitration function, and the method has the advantages of convenient transformation, less floor area and low investment and operating costs; the NO oxidation efficiency is more than 85%, the desulphurization efficiency is more than or equal to 96% after washing by a desulphurization tower, the denitration efficiency is more than or equal to 75%, and the method has a certain mercury removal efficiency.
Owner:浙江菲达环保科技股份有限公司
A kind of aerobic denitrifying bacteria and its application
ActiveCN112625942BWith denitrification functionBacteriaWater contaminantsGenus PseudomonasDenitrifying bacteria
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Vessel for purifying black odorous river water
ActiveCN107285468AImprove processing efficiencyStable waterWaterborne vesselsBiological treatment apparatusImpellerOperational costs
The invention relates to a vessel for purifying black odorous river water; the vessel comprises a hull; the hull includes an incoming water pipe, a rotary bio-treatment unit and an outgoing water pipe; an inlet of the incoming water pipe is provided with a water pump; the rotary bio-treatment unit is connected with a gear transmission device and includes three bioreactors, namely a first reactor, a second reactor and a third reactor; each bioreactor includes a bio-rotor and an oxidation tank, the bio-rotor is positioned in the oxidation tank, a plurality of bio-wheels are arranged in the bio-rotor, each bio-wheel is provided with a plurality of spiral bio-blades, and a thin bio-strip is attached to each bio-blade. The vessel provided herein has high treating efficiency, and effluent is stable and within limits; the vessel has the advantages of low operational cost, low maintenance quantity, acid and alkali tolerance, corrosion resistance, ageing resistance, low operational noise, good convenience of transport, and low transport and installation costs.
Owner:CLEAR SUZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
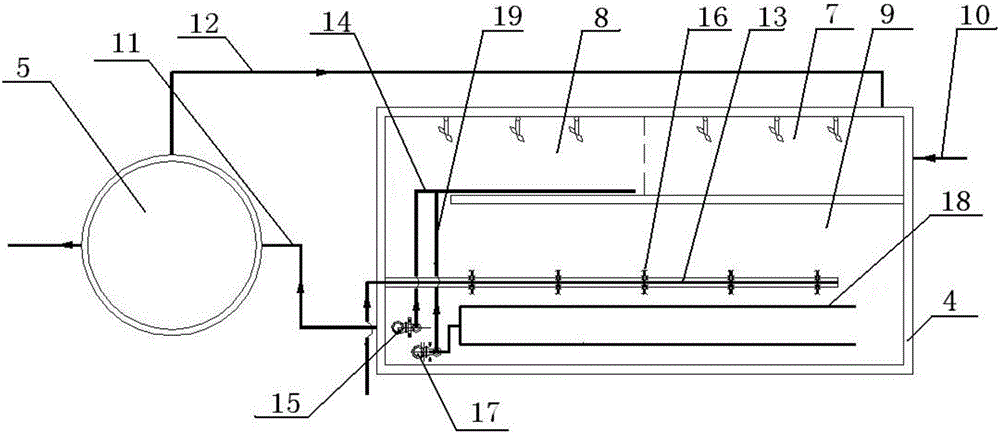
Multi-cycle self-backflow small living sewage treatment system with denitrification function
InactiveCN105417853AEfficient denitrificationSmall footprintTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesBiochemical engineeringHeight difference
The invention discloses a multi-cycle self-backflow small living sewage treatment system with a denitrification function. The system is composed of a water yield adjusting area, a biochemical treatment area and a settling area. A lifting pump is arranged in the water yield adjusting area to lift sewage to be treated to one end of the biochemical treatment area. An aerating apparatus and biochemical reaction filler are installed in the biochemical treatment area. A backflow device is arranged on the pond wall between the other end of the biochemical treatment area and the water yield adjusting area, and after the backflow device is started, sewage subjected to a biochemical reaction can flow back into the water yield adjusting area. An effluent weir is arranged on the pond wall between the other end of the biochemical treatment area and the settling area. A sufficient circular reaction of sewage can be achieved due to the design of the height difference of the bottom of the crest of the effluent weir and the bottom of the crest of a backflow weir, the pollution load impact is the smallest, and the sewage treatment efficiency is highest. The system is applicable to small-yield sewage treatment, and particularly suitable for non-uniform inflowing sewage treatment conditions with the denitrification requirement. Impact of the instantaneous water inflowing pollution load on the system is small, the ammonium-nitrogen removal rate is high, and the sewage treatment efficiency is high.
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TRANSPORTATION SCI +1
A kind of denitrification bacteria and its application
ActiveCN112251387BWith denitrification functionBacteriaWater contaminantsDenitrifying bacteriaNitration
The invention discloses a denitrification bacterium and application thereof. Pseudomonas sp. JM10A2a, the deposit number is: GDMCC No.61214. The results of the denitrification characteristics of Pseudomonas JM10A2A show that the strain is a heterotrophic nitrifying-aerobic denitrifying strain, which can efficiently remove nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen in water, and can be used at low C / N The removal of nitrite nitrogen can still be carried out efficiently under the conditions, which shows that the Pseudomonas JM10A2a of the present invention has great application potential in denitrification of water bodies.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
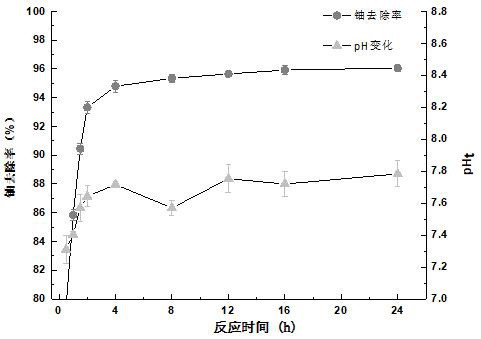
Method for removing fixed uranium by utilizing denitrification and phosphorus accumulation effects of microorganisms
ActiveCN112591893ARaise the pHReduce potential riskRadioactive contaminantsRadioactive decontaminationEnvironmental chemistryPhosphate
The invention relates to a method for removing fixed uranium by utilizing denitrification and phosphorus accumulation effects of microorganisms, and belongs to the technical field of uranium mine areapolluted water body remediation. Activated sludge is obtained from a biochemical pool of an anaerobic section of a sewage treatment plant, and sterile water is adopted for mixing to obtain a bacteria-carrying mixed solution; the obtained bacteria-carrying mixed solution is put into an LB culture medium, and grows for 24-48h at the environment temperature of 25+1 DEG C to obtain mixed solution bacteria; the mixed solution bacteria are put into a denitrification and phosphorus accumulation culture medium, and subculture is carried out for multiple times to obtain a denitrification and phosphorus accumulation microbial suspension; and the obtained denitrification and phosphorus accumulation microbial suspension is implanted into uranium-containing wastewater, and reaction is carried out at normal temperature under a sealed condition to remove fixed uranium. The denitrification and phosphorus accumulation microorganism decomposes organic phosphorus such as phytic acid into phosphate, andthen induces U-P to form scaly crystalline precipitate, so that uranium is fixed.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
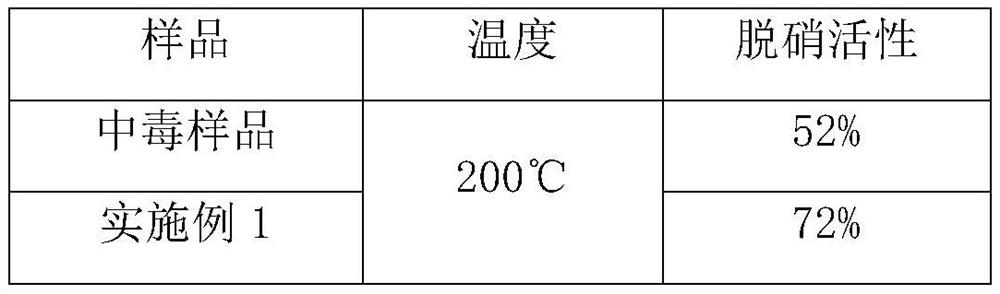
A regeneration method for dust removal and denitrification multifunctional filter material
ActiveCN108543549BEasy to cleanEfficient regenerationDispersed particle separationCatalyst regeneration/reactivationPtru catalystFlue gas
The invention provides a method for regenerating dedusting and denitrifying a multifunctional catalytic filter material. The method concretely comprises the following steps: (1) preparing a cleaning solution; (2) producing a regenerated catalyic filter membrane from polytetrafluoroethylene powder, catalyst powder, a pore forming agent, a coupling agent and a lubricant; (3) purging a poisoned or deactivated dusting and denitrifying multifunctional filter material, and washing the filter material with the prepared cleaning solution, and pretreating the filter material base cloth with a treatmentagent; and (4) performing hot press compounding on the prepared regenerated catalytic filter membrane and the pretreated filter base cloth by a hot press roller, and cooling the obtained material toobtain a regenerated dedusting and denitrifying multifunctional filter material. The method allows the regeneration of the dedusting and denitrifying multifunctional filter material to be fast completed by using an existing filter material preparation device only through matching with a simply used device, and makes the regenerated multifunctional filter material environmentally friendly and highly efficient (the denitrifying activity is more than 90%). The method has great significance to realize the industrialization and the promotion application of flue gas simultaneous dedusting and denitrifying filter bags.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Black and smelly river water purification boat
ActiveCN107285468BImprove processing efficiencyStable waterWaterborne vesselsBiological treatment apparatusGear driveEnvironmental engineering
This case involves a black and odorous river water purification ship, including a hull, the hull includes a water inlet pipe, a rotating biological treatment unit and an outlet pipe; the inlet of the water inlet pipe is provided with a pump; the rotating biological treatment unit is connected to a gear transmission device; the rotating biological treatment unit includes three bioreactors, respectively the first reactor, the second reactor and the third reactor; each bioreactor includes a biological rotor and an oxidation tank; the biological The rotor is located in the oxidation tank; a plurality of biological impellers are arranged inside the biological rotor; a plurality of spiral biological blades are arranged on each biological impeller; thin biological strips are attached to each biological blade. The black and odorous river water purification ship of the present invention has the advantages of high treatment efficiency, stable water discharge, low operating cost, small maintenance workload, acid and alkali resistance, corrosion resistance, anti-aging, low standby operation noise, convenient transportation, and low transportation and installation costs. .
Owner:CLEAR SUZHOU ENVIRONMENTAL TECH CO LTD
High-pressure electrostatic dust collection electric field device of coal-fired unit for generating ozone and simultaneously desulfurizing and denitrating
ActiveCN102949921BEasy to collectWith the function of spark cleaningDispersed particle separationExternal electric electrostatic seperatorPower control systemClosed loop
The invention discloses a high-pressure electrostatic dust collection electric field device of a coal-fired unit for generating ozone and simultaneously desulfurizing and denitrating. The device comprises an electrostatic dust collection channel which is formed by sequentially connecting a plurality of electric fields, a neutralizing tower, a water mist spray system, a water supply device, a power control system, a spray control system and an intelligent closed-loop control system, wherein the flashover frequency of the power control system is set to be 150-10000 times / minute, the water mist spray system is arranged in the neutralizing tower, the intelligent closed-loop control system is utilized to control the power control system and the spray control system is utilized to automatically coordinated with each other, so that the high-pressure electrostatic dust collection device can be added with a denitrating function on the basis of maintaining the original electrostatic dust collecting and desulfurizing functions, and nearly no investment is required for obtaining the denitrating function. On the basis of reasonably utilizing the original equipment, the environmental protection emission requirements are satisfied, and the device has the advantages of low cost, high operation effect and obvious integral economic benefit.
Owner:XIAMEN RECH TECH
A kind of sea bacillus with denitrification function and its application
The invention discloses a Bacillus hominis with denitrification function and its application. Marivirgasp. S33H4, the deposit number is GDMCCNo:61709. The Bacillus inhabitants S33H4 of the present invention can effectively remove nitrate nitrogen, ammonium nitrogen and nitrite nitrogen in water bodies, wherein the removal effects of nitrate nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen are all above 90%, In addition, the strain also has a significant removal effect on nitrite nitrogen. This shows that Bacillus coccidioides S33H4 has good application potential in water denitrification.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Sewage total-nitrogen processing apparatus and method thereof
InactiveCN106554085AGuaranteed complianceImprove denitrification efficiencyTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesSludgeWater quality
The invention relates to a sewage total-nitrogen processing apparatus and a method thereof, which belongs to the field of sewage processing. The sewage total-nitrogen processing apparatus comprises a first biochemical reaction tank, a first settling tank, a second biochemical reaction tank, a second settling tank, a sludge carbon source converter and a matched sludge backflow control system, several individual valve-controlled aeration apparatus, a filling material, a diversion trench and an air liquid level raiser are respectively arranged in the first biochemical reaction tank and the second biochemical reaction tank, a water inlet end of the diversion trench is positioned by corresponding a water outlet of the air liquid level raiser, and the backflow of outlet sewage / sludge mixed liquor is realized. The sewage total-nitrogen processing apparatus can enhance the total nitrogen removal effect of the biochemical reaction tank, and has COD removal effect, high-efficiency removal of COD, ammonia nitrogen and total nitrogen can be realized in one reaction tank, and the sewage total-nitrogen processing apparatus has the characteristics that the oxygen demand is little, power required by mixed liquor backflow is little, the removal efficiency is high, a structure is little by comparing with an A / O technology, water quality fluctuation is adapted, and the sludge output is little.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
A multi-cycle self-reflux small domestic sewage treatment system with denitrification function
InactiveCN105417853BEfficient denitrificationSmall footprintTreatment using aerobic processesTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesAmmoniacal nitrogenBiochemical engineering
Owner:CHINA ACAD OF TRANSPORTATION SCI +1
Microbial electrochemical bioturntable for sewage treatment
ActiveCN108217915BWith denitrification functionLow running costTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsSulfate radicalsElectron donor
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment and provides a microbial electrochemical biological turntable for sewage treatment. It includes a three-dimensional carrier, a rotating shaft and a power device; the three-dimensional carrier is arranged on the rotating shaft, and the rotating shaft is connected to the power device; it is characterized in that: anaerobic electricity-generating microbial film and aerobic microbial film are attached to the three-dimensional carrier, wherein the anaerobic electricity-generating The microbial film grows on the inner layer close to the carrier, while the aerobic microbial film grows on the outer layer to wrap and protect the anaerobic electricity-producing microbial film; the three-dimensional carrier is partly immersed in sewage and partly exposed to the air. The electrons inside the biological turntable can be self-transferred, and can synergistically remove electron donors and electron acceptors in water. The electron donors include organic matter and ammonium nitrogen, and the electron acceptors include nitrate nitrogen, nitrite nitrogen, sulfate and heavy metal ions.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Features
- Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com