Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
97results about How to "Suppression resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
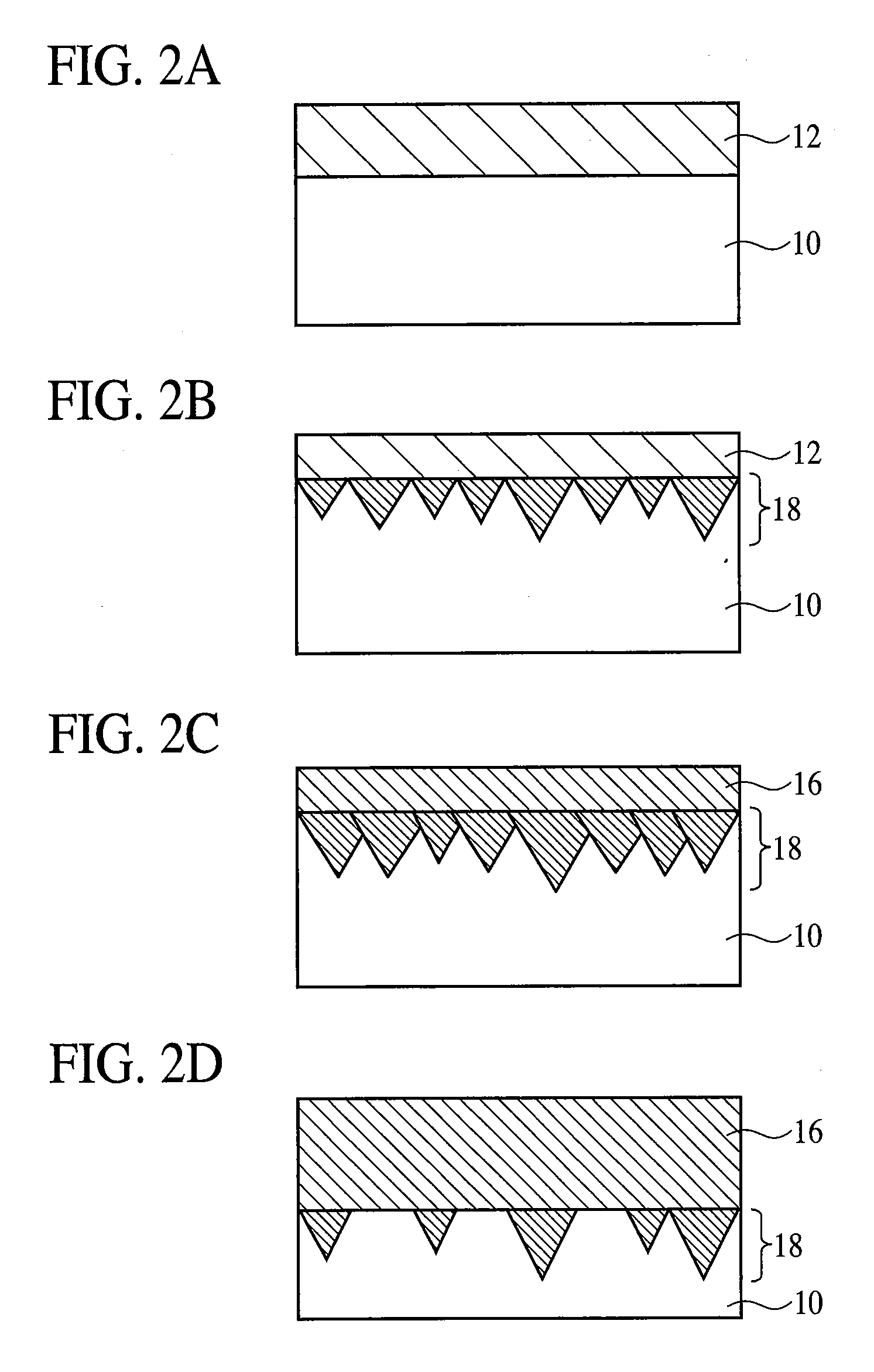
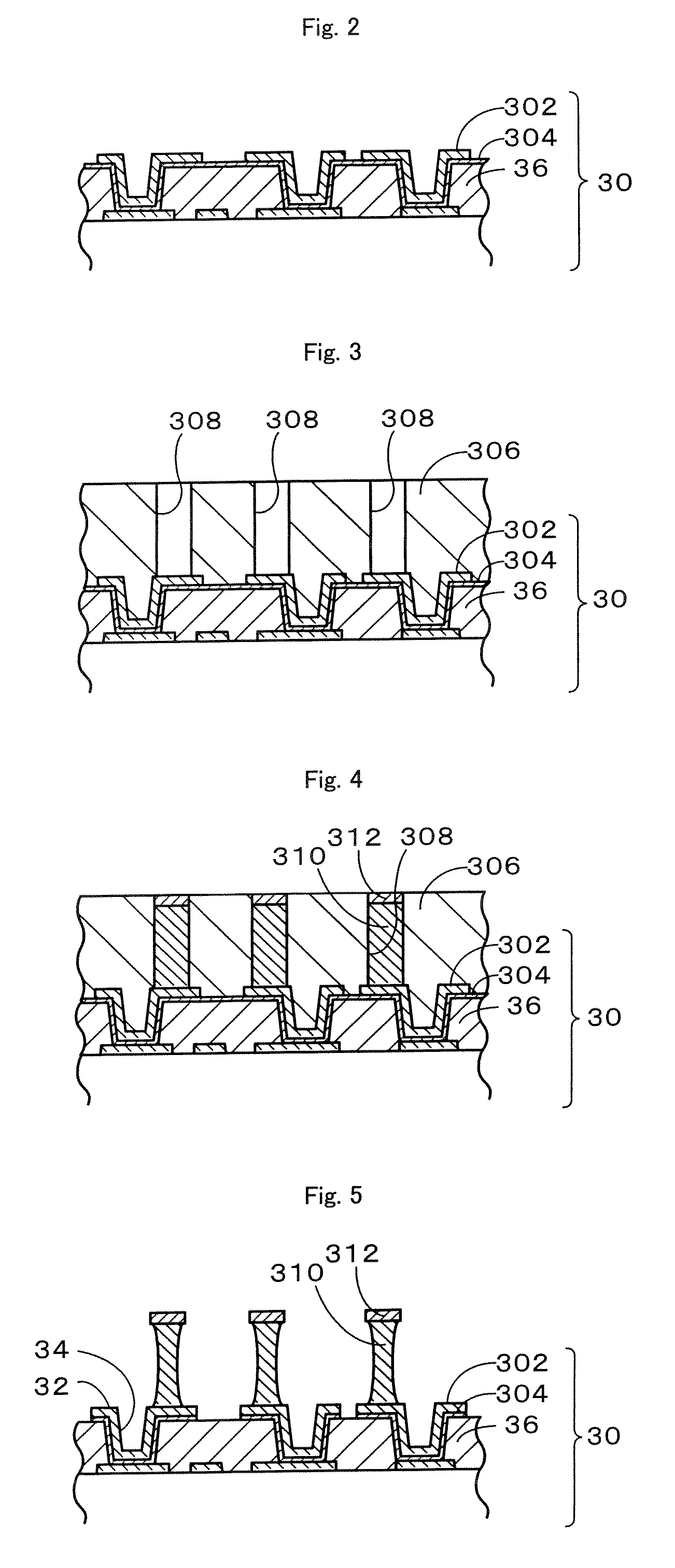
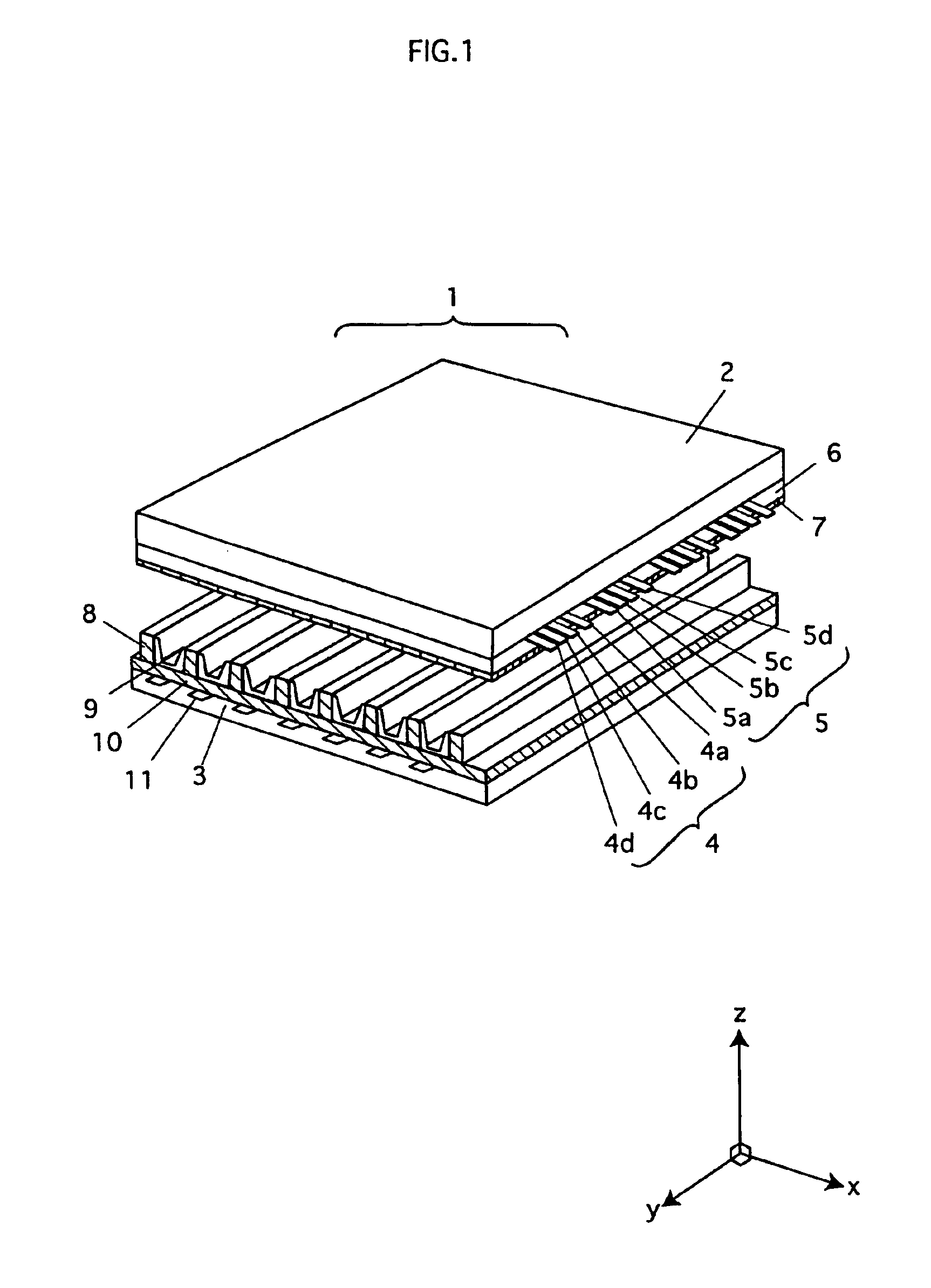
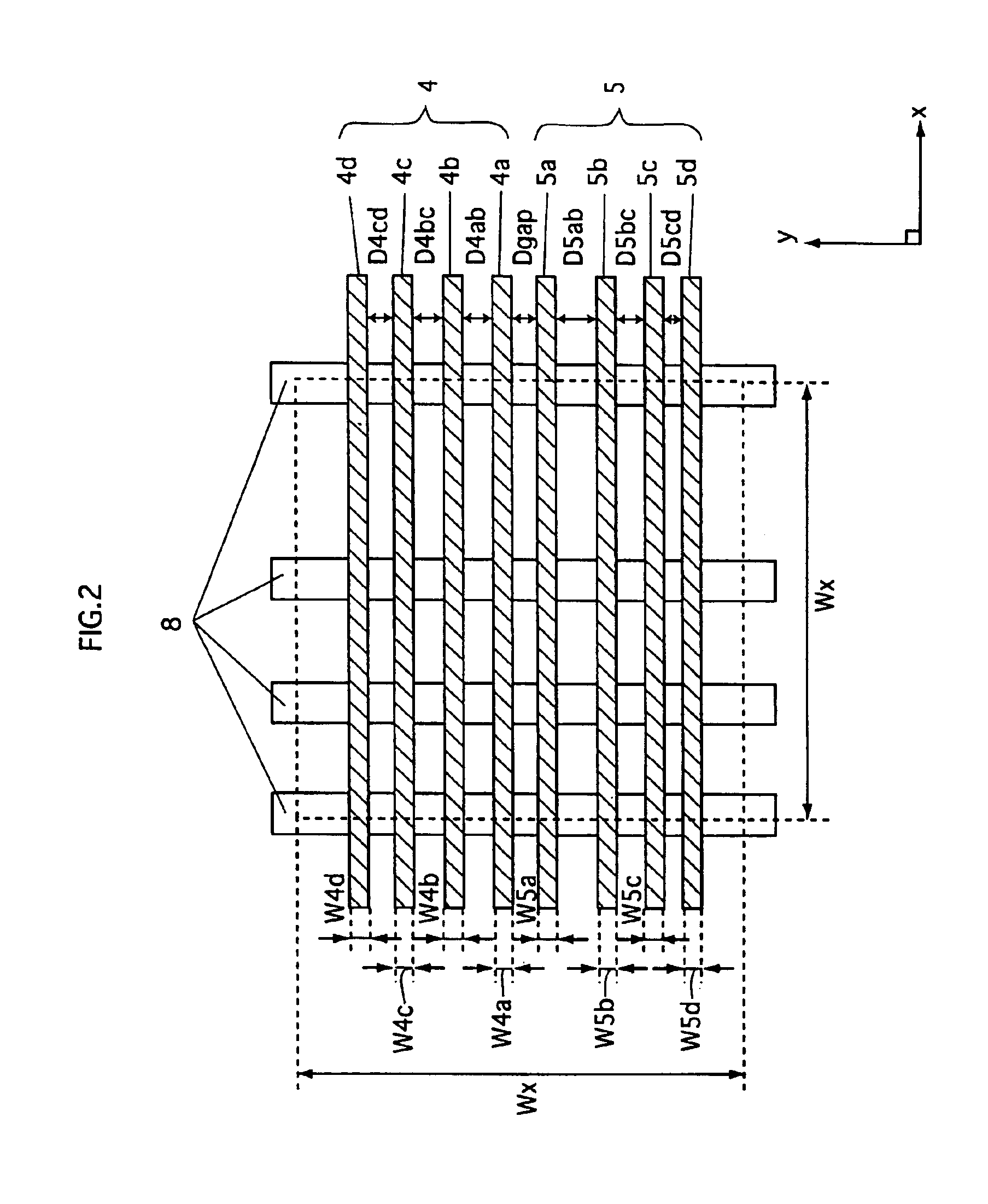
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method for the same
ActiveUS20030173671A1Improve production yieldImprove reliabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
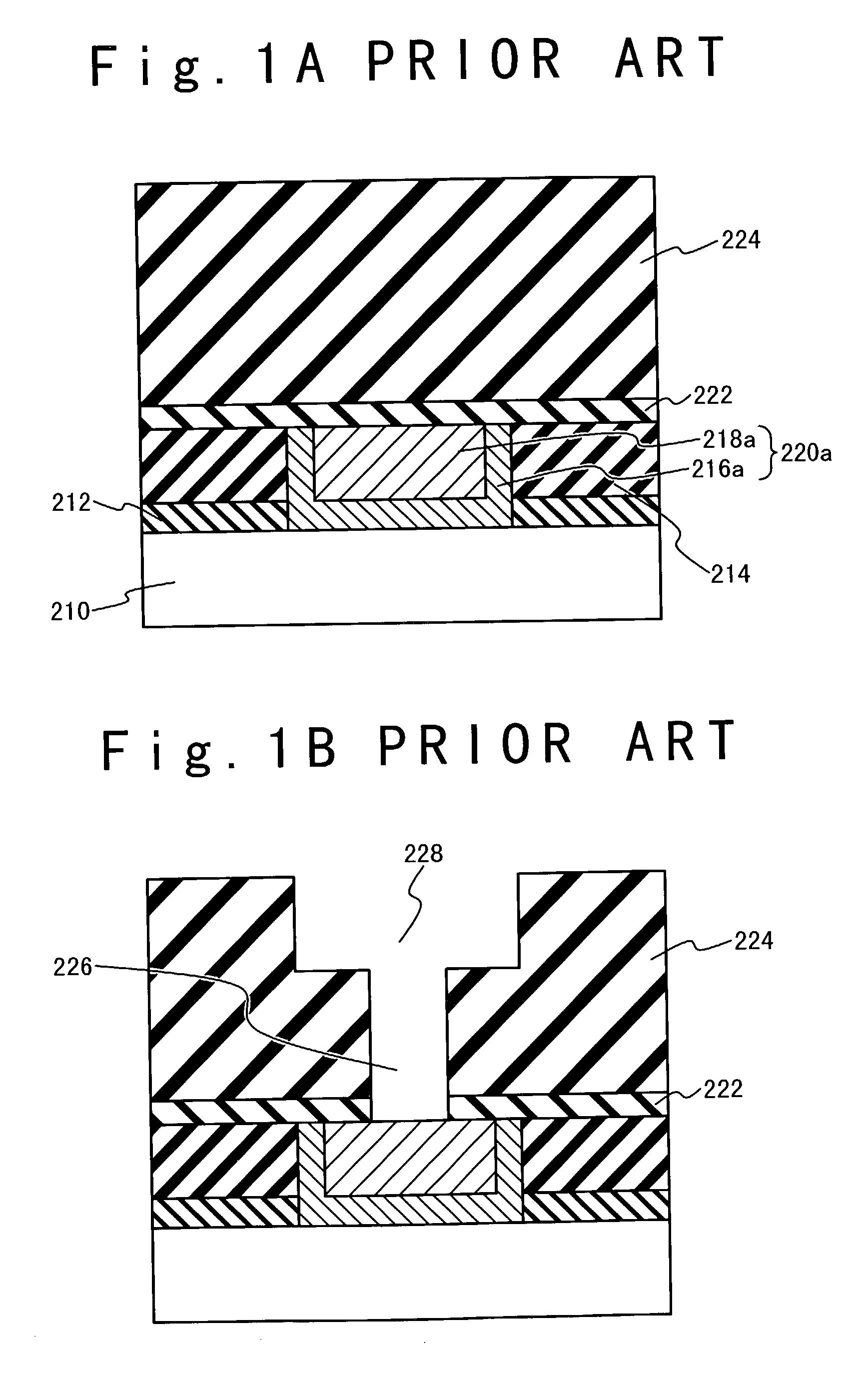
In a method of manufacturing a semiconductor device, a first wiring line composed of a copper containing metal film is formed on or above a semiconductor substrate. A first interlayer insulating film is formed on a whole surface of the semiconductor substrate to cover the first wiring line. The first interlayer insulating film is selectively removed to form a connection hole reaching the first wiring line. A barrier metal film is formed to cover an inner surface of the connection hole and then a copper containing metal film is formed to fill the connection hole. The copper containing metal film formed outside the connection hole is removed. A second interlayer insulating film is formed on a whole surface of the semiconductor substrate to cover the copper containing metal film formed in the connection hole. The second interlayer insulating film is selectively removed to form a wiring line groove such that the copper containing metal film formed in the connection hole is exposed at a bottom. A barrier metal film is formed to cover an inside of the wiring line groove and then a copper containing metal film is formed to fill the wiring line groove. Then, the copper containing metal film outside the wiring line groove is removed to form a second wiring line.
Owner:TESSERA ADVANCED TECH
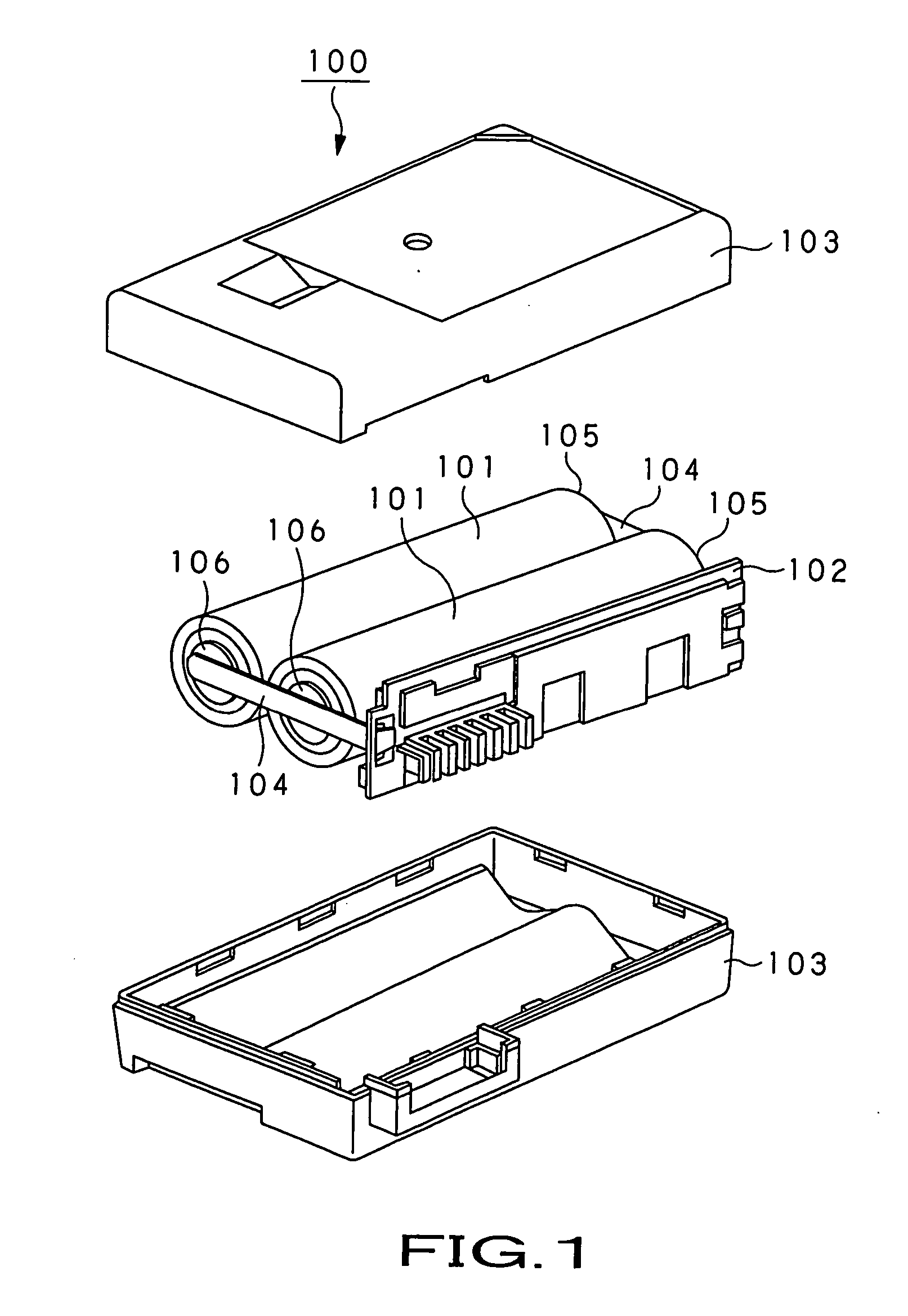
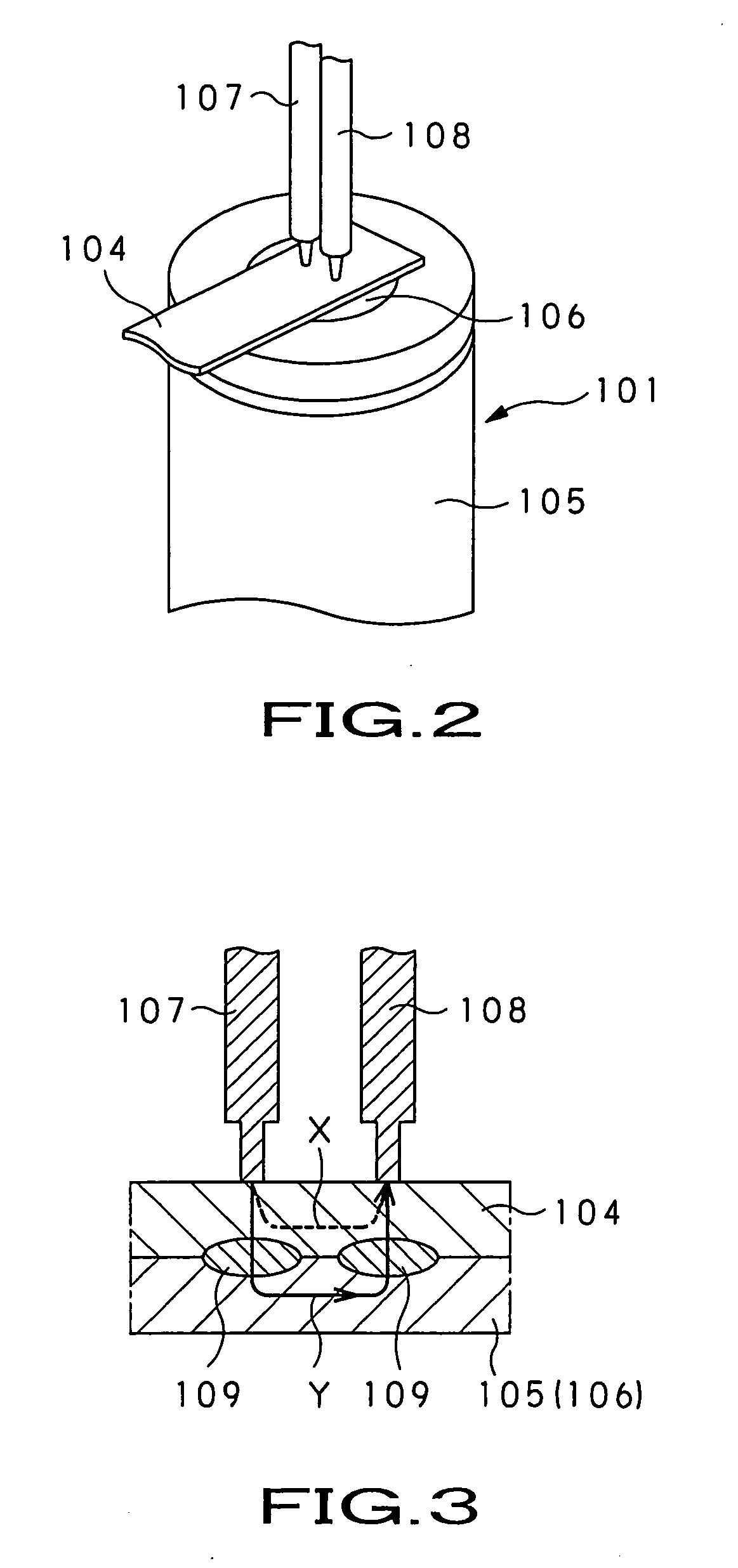
Lead terminal and power supply device
InactiveUS20060032667A1Improve welding strengthImprove electrical resistancePrinted electric component incorporationSoldered/welded conductive connectionsElectricityElectrical resistance and conductance
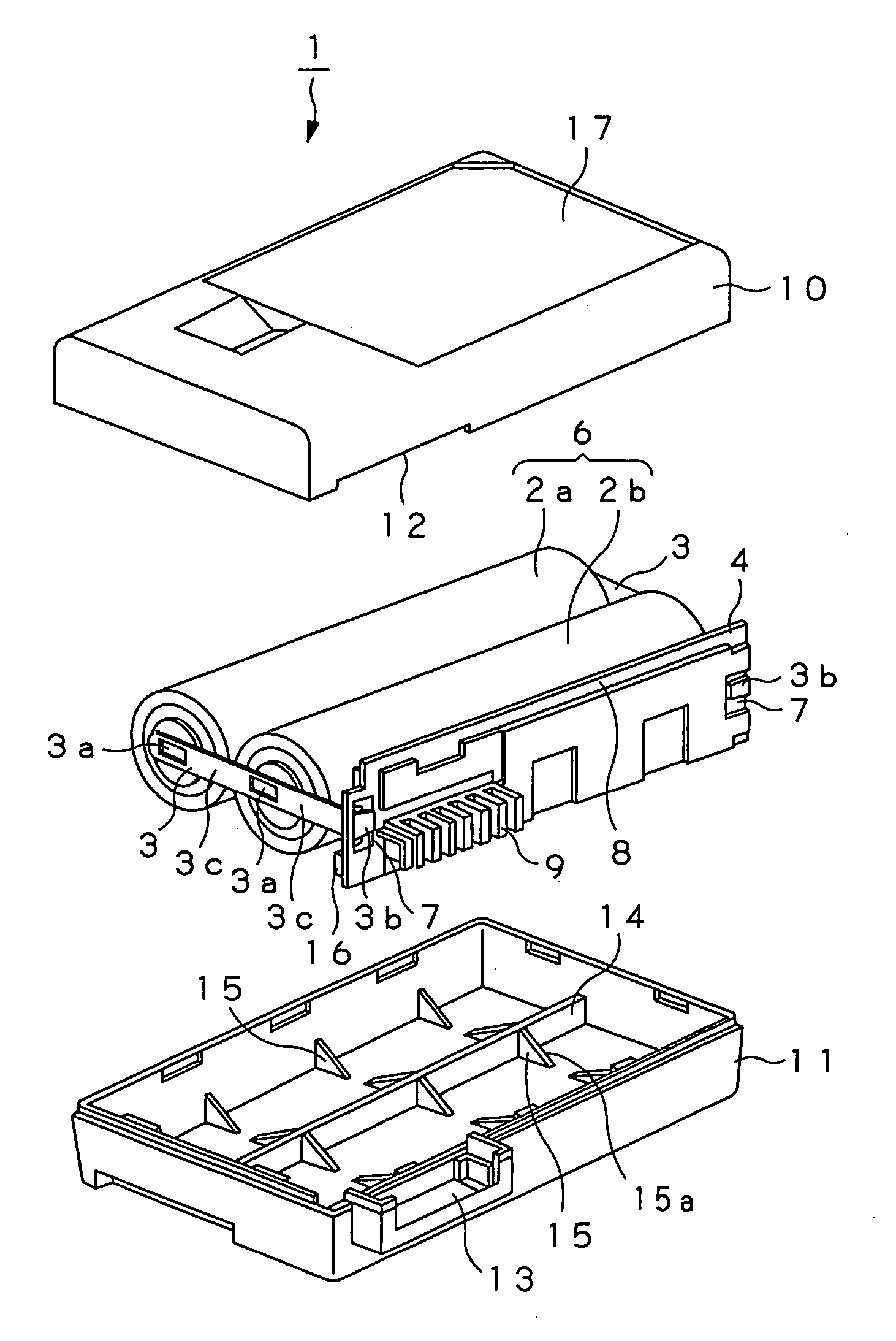
The present invention is directed to a power supply apparatus in which a battery and a circuit wiring board or boards are electrically connected by using lead terminals. The lead terminal (3) is adapted so that thickness of a welding portion (3a) is caused to be thinner than the thickness of a conductive portion (3b). Thus, current for welding flows to much degree in a thickness direction so that electric resistance of the welding portion becomes large, and heat based on the electric resistance also becomes large. From this fact, welding nugget (63) can be enlarged. As the result of the fact that large welding nugget is formed, the lead terminals are welded to terminal portions (37a) of the battery (2) with high reliability.
Owner:SONY CORP
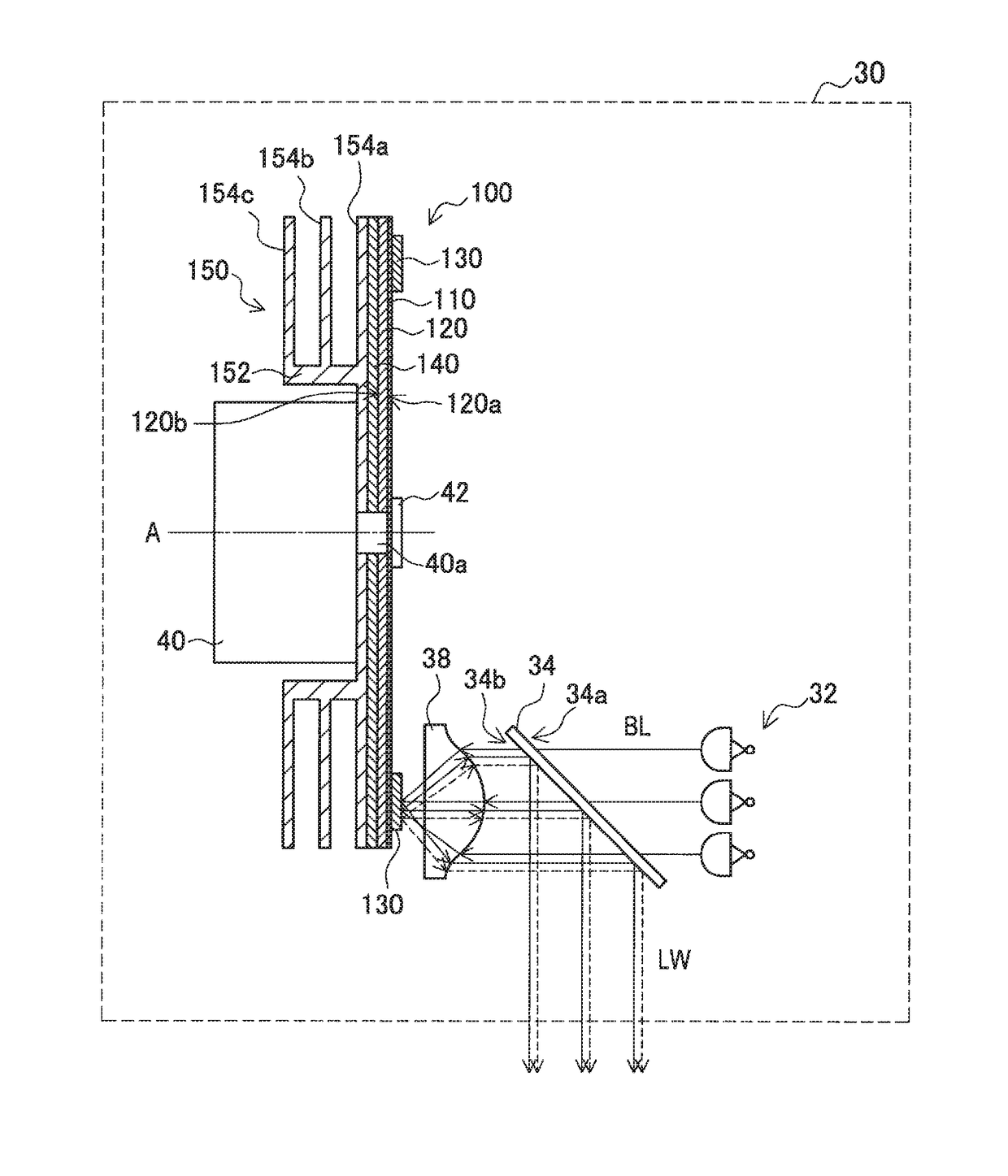
Phosphor wheel, light source apparatus, and projection-type display apparatus
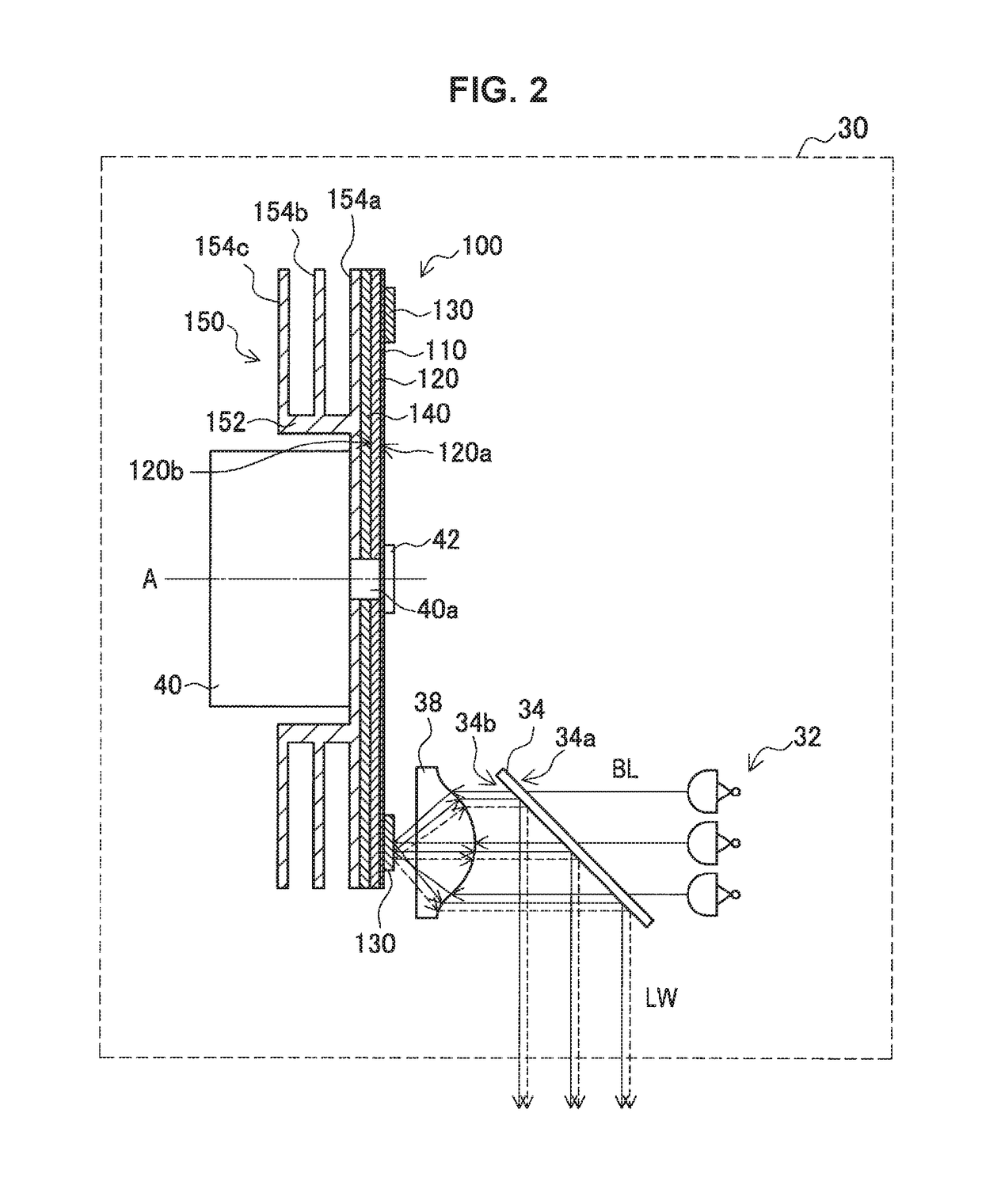
ActiveUS20170293211A1Improve efficiencySuppress air resistance and noiseLighting heating/cooling arrangementsProjectorsFluorescenceEngineering
An object of the present invention is to improve the efficiency of heat dissipation from a phosphor wheel while suppressing the air resistance and noise of the phosphor wheel during the driving of a light source apparatus. A phosphor wheel (100) according to the present invention includes: a disc-like substrate (120); a phosphor layer (130) formed on the substrate; and a plurality of heat dissipation fins (154a, 154b, and 154c) overlapping with each other when viewed in a direction orthogonal to a surface of the substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
High Corrosion Resistance Hot dip Galvanized Steel Material
InactiveUS20090053555A1Improve corrosion resistanceSuppressing degradationHot-dipping/immersion processesThin material handlingAmorphous phaseAlloy
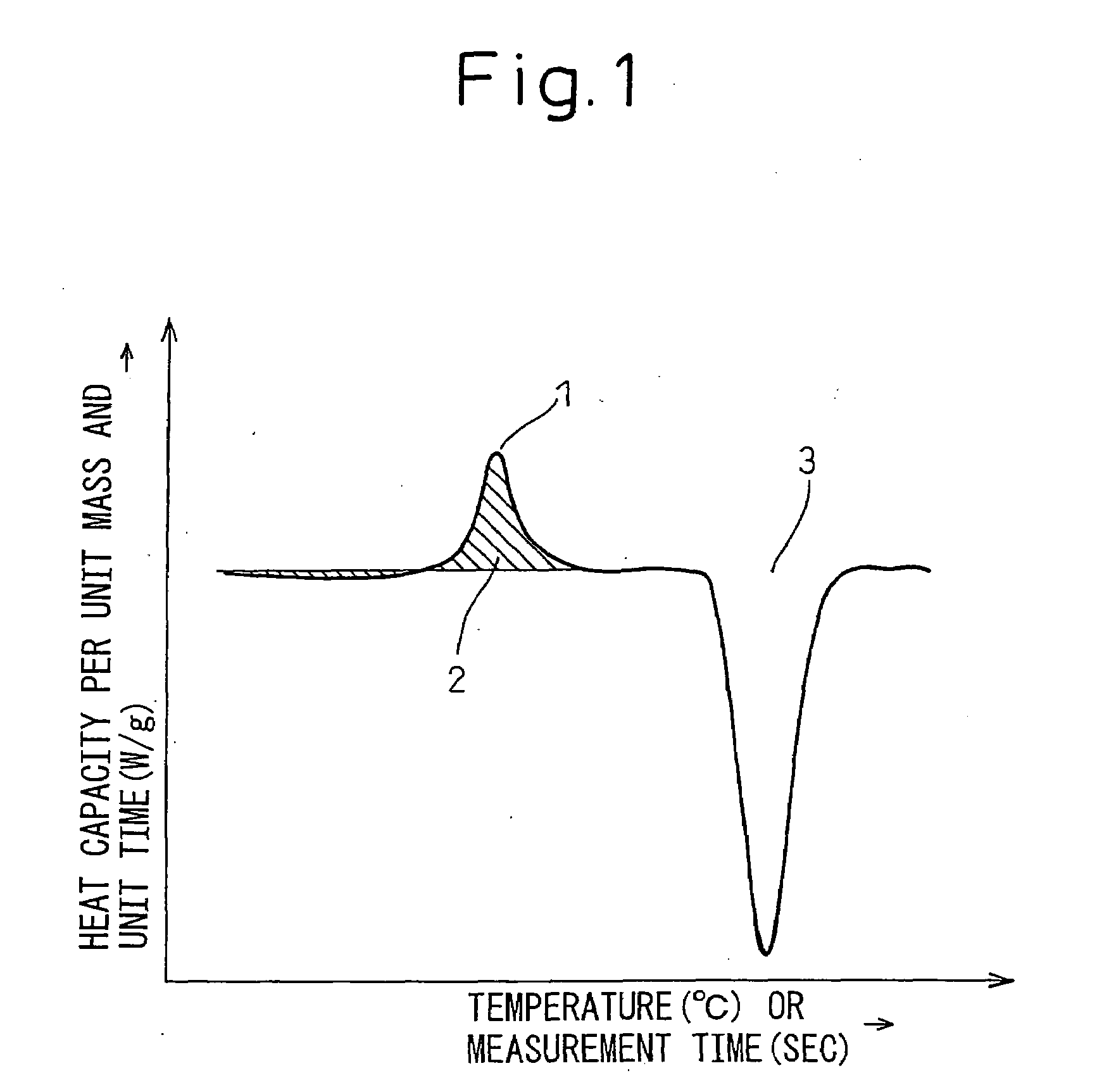
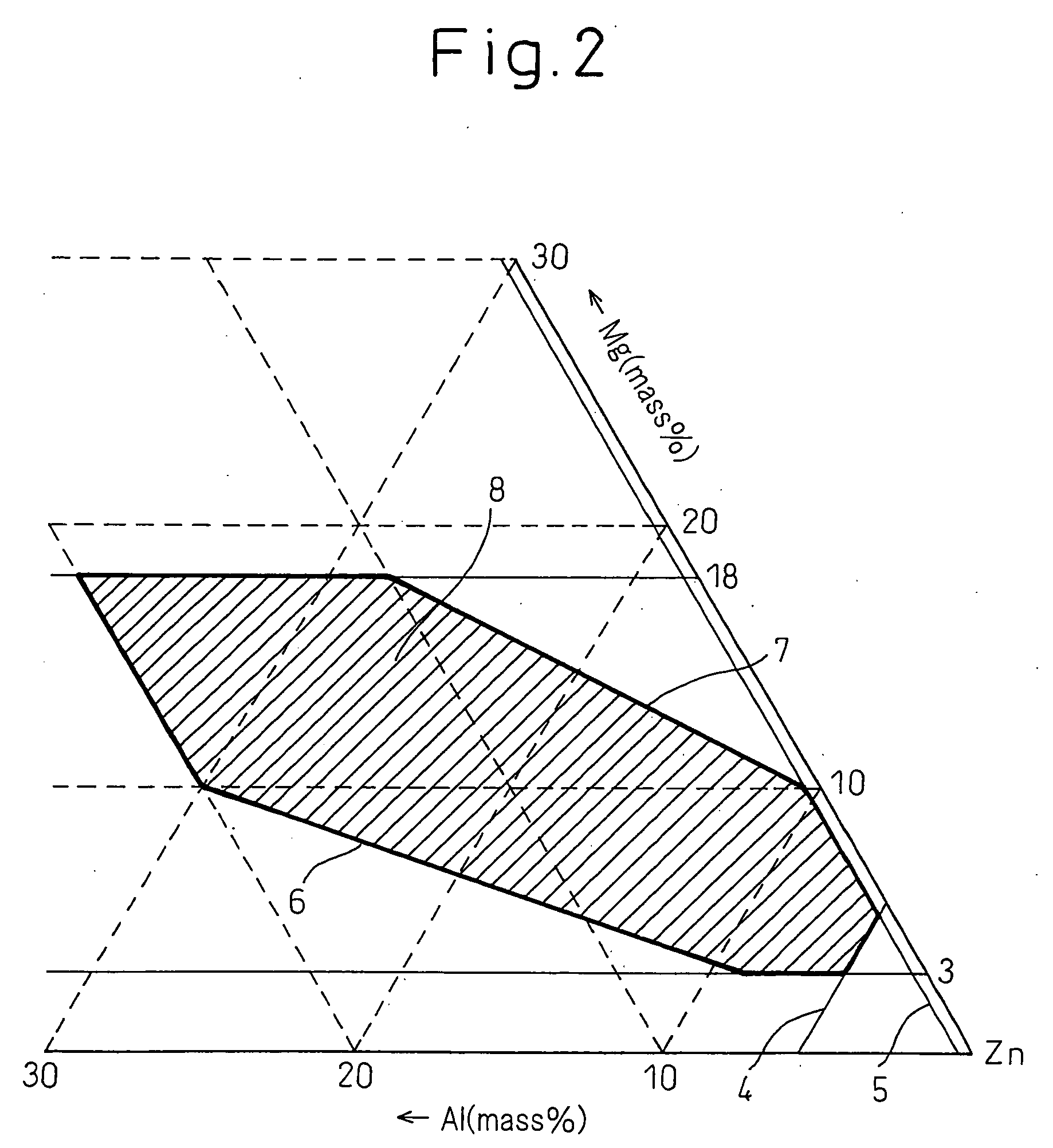
The present invention provides a high corrosion resistance hot dip galvannealed steel material comprised of a Zn-based hot dip plated steel material achieving both a higher corrosion resistance of the plated layer itself by the added elements and sacrificial protection of iron metal by the plated layer or workability free of degradation caused of formation of intermetallic compounds by added elements, that is, a high corrosion resistance hot dip Zn plated steel material characterized in that an alloy plated layer containing Zn: 35 mass % or more, preferably 40 mass % or more, contains a non-equilibrium phase having a heat capacity by differential scanning calorimetry of 1 J / g or more. Furthermore, 5% or more, preferably 50% or more in terms of vol % is an amorphous phase. The alloy layer may contain, by mass %, Mg: 1 to 60% and Al: 0.07 to 59%, may further contain one or more elements selected from Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, and Cu in a total of 0.1 to 10%, and may in addition contain one or more elements of 0.1 to 10% of La, 0.1 to 10% of Ce, 0.1 to 10% of Ca, 0.1 to 10% of Sn, 0.005 to 2% of P, and 0.02 to 7% of Si.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
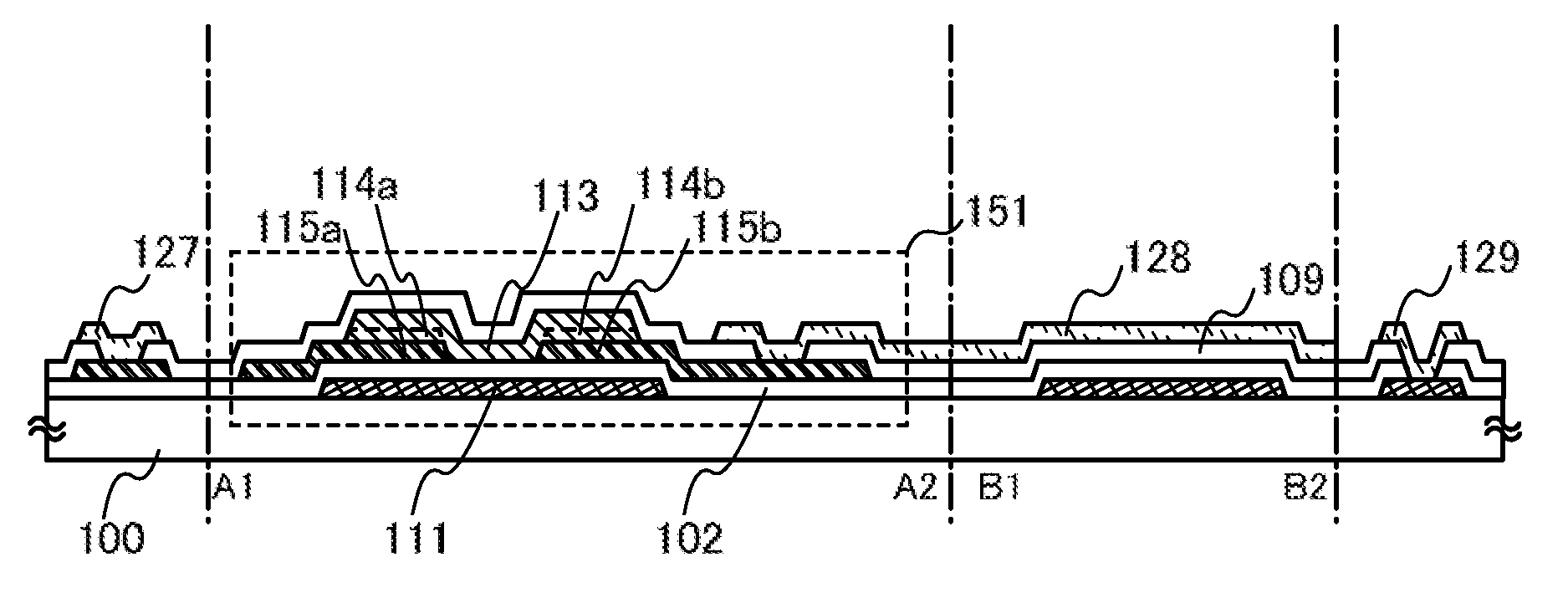
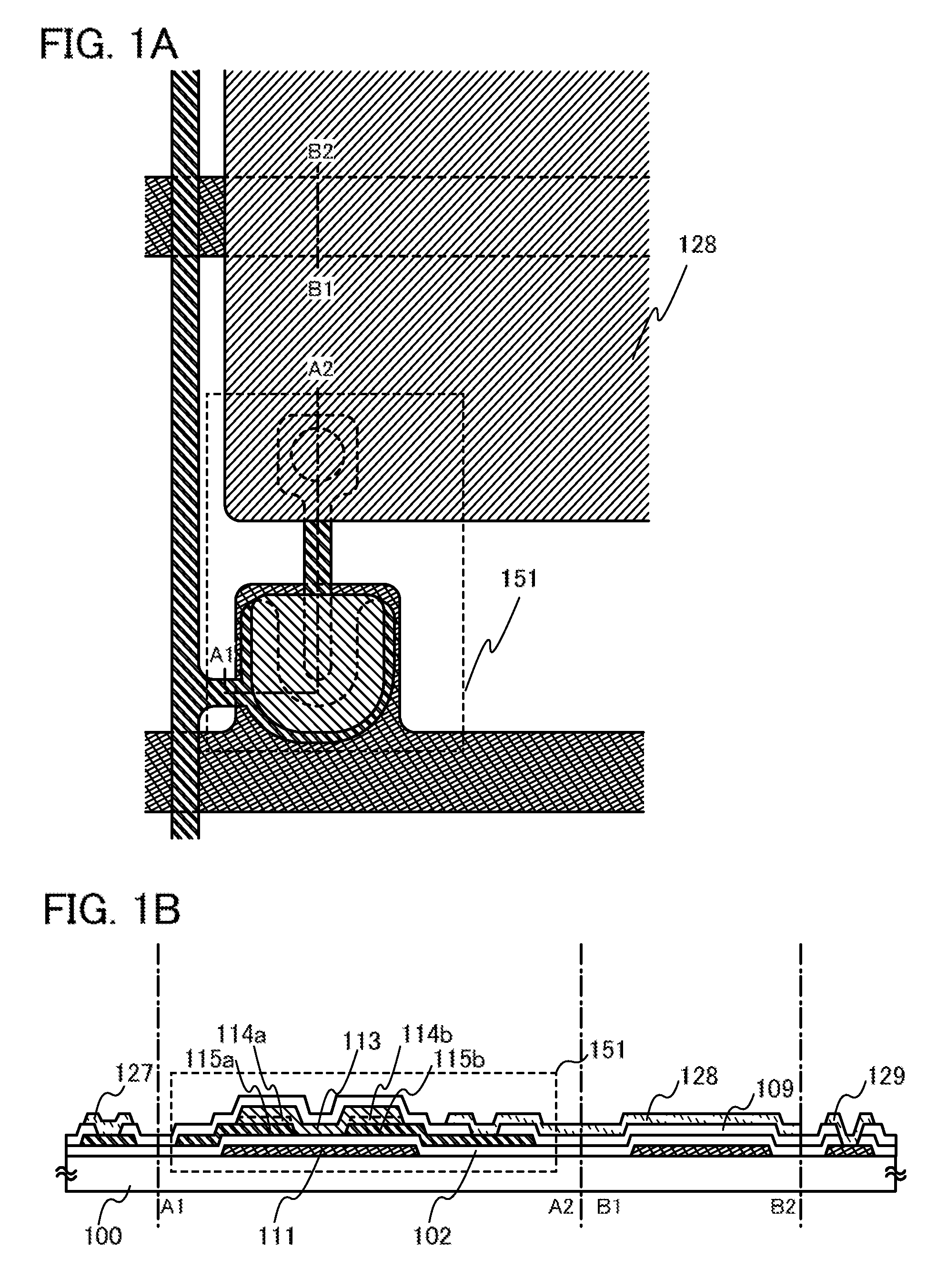
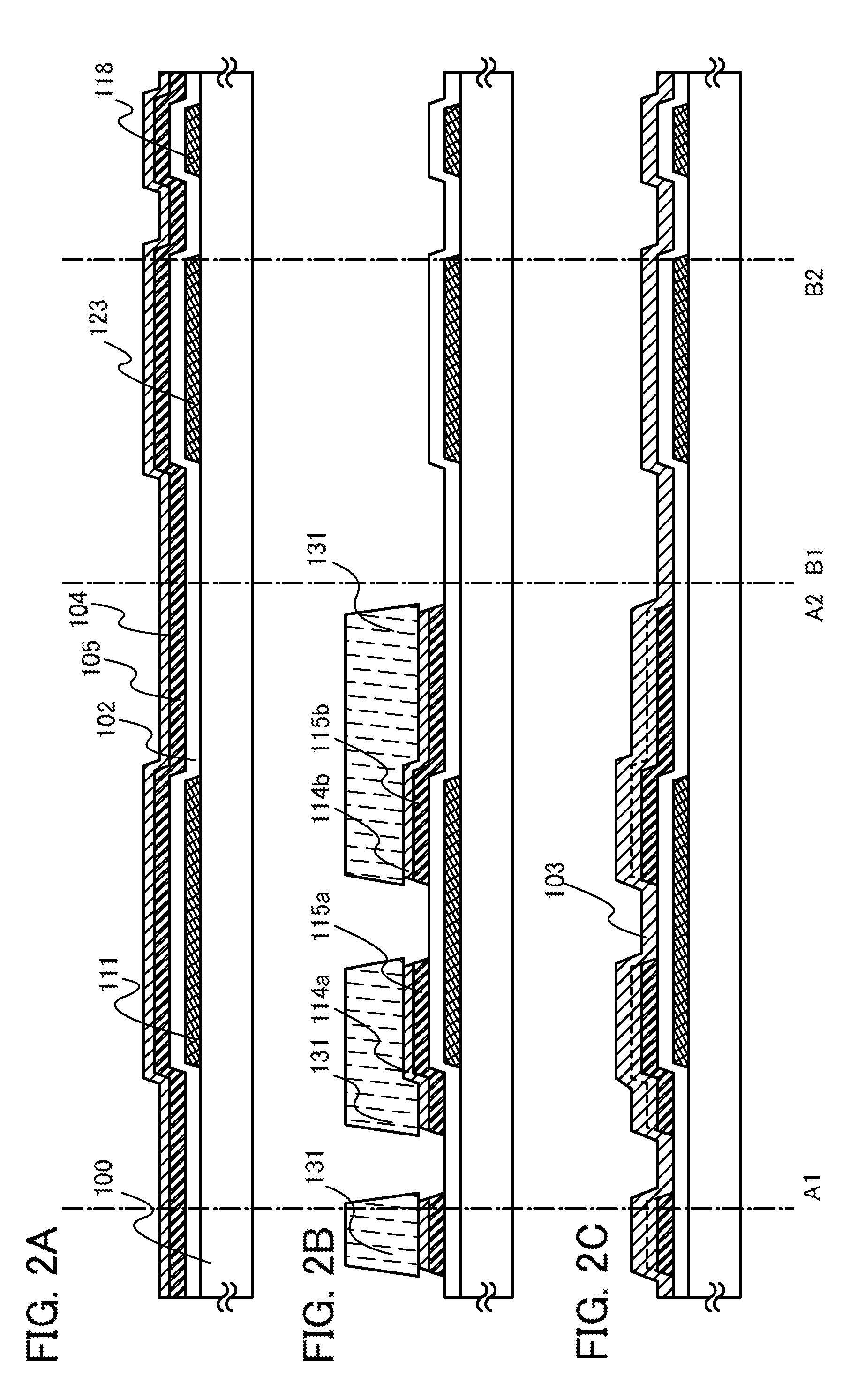
ActiveUS20100163866A1Easy to makeSolve the lack of reliabilityTransistorElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor packageContact resistance
One of factors that increase the contact resistance at the interface between a first semiconductor layer where a channel is formed and source and drain electrode layers is a film with high electric resistance formed by dust or impurity contamination of a surface of a metal material serving as the source and drain electrode layers. As a solution, a first protective layer and a second protective layer including a second semiconductor having a conductivity that is less than or equal to that of the first semiconductor layer is stacked successively over source and drain electrode layers without exposed to air, the stack of films is used for the source and drain electrode layers.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
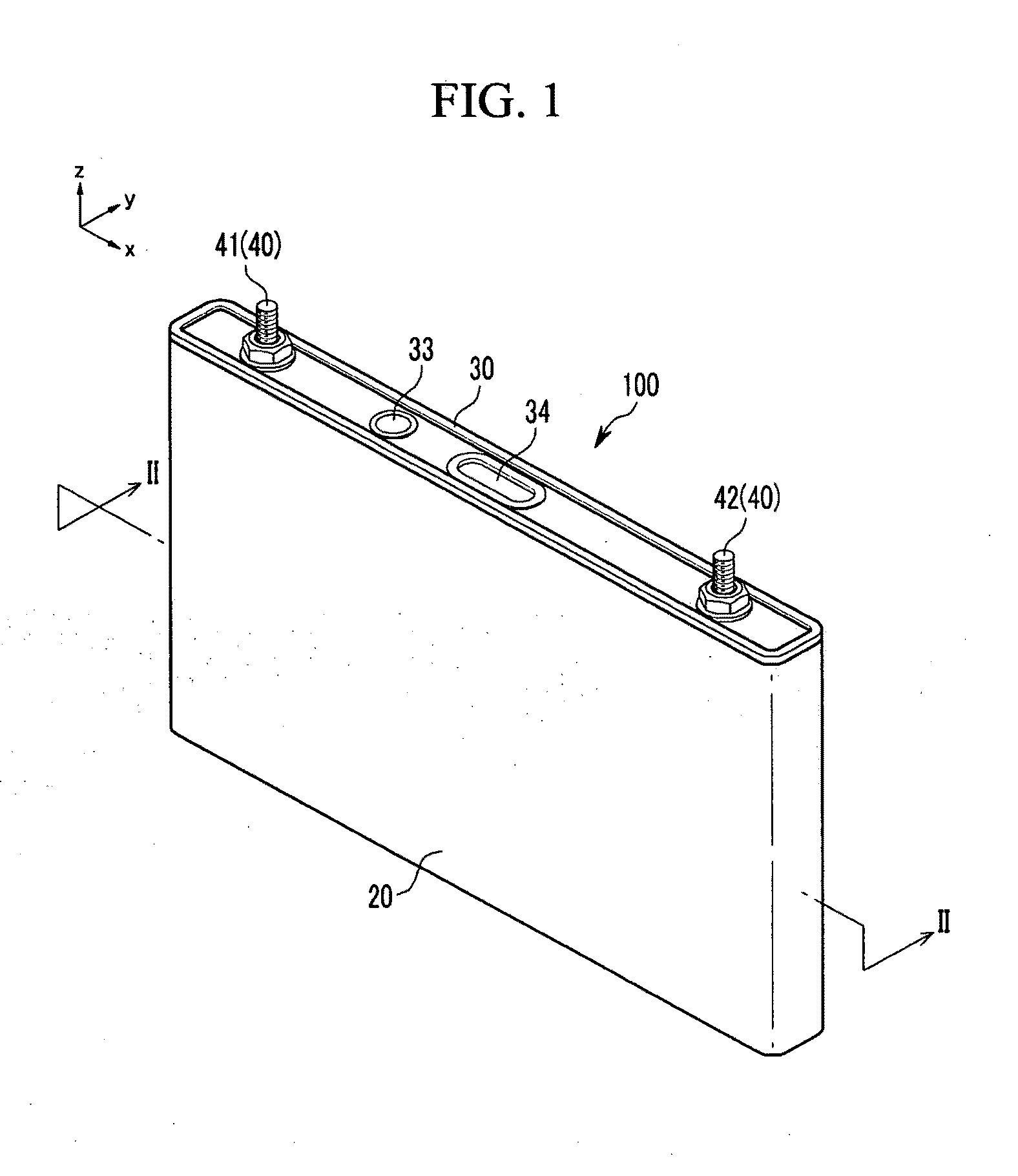
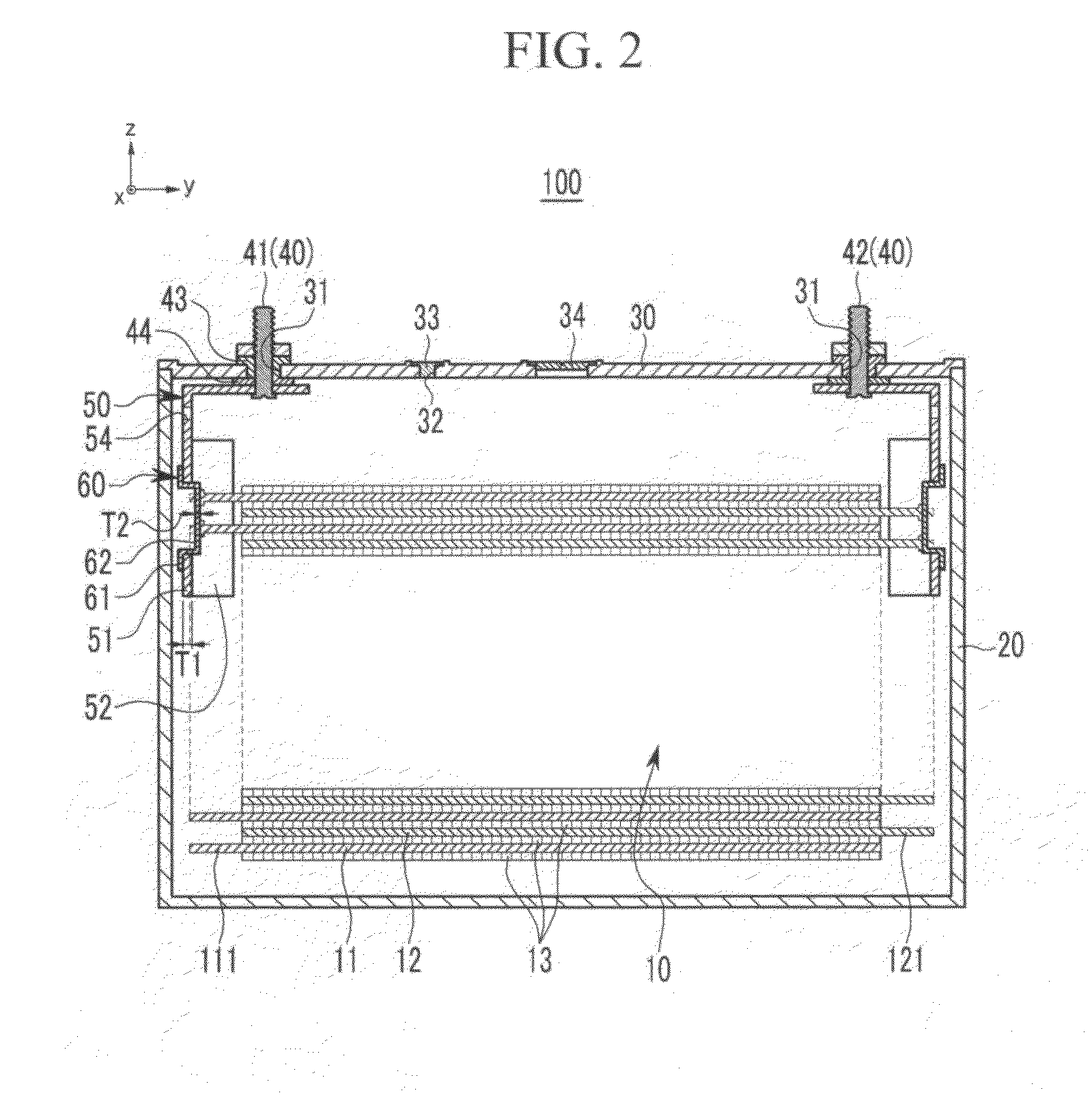
Rechargeable battery
ActiveUS20100247989A1Suppression resistanceCurrent conducting connectionsFinal product manufactureRechargeable cellElectrical and Electronics engineering
A rechargeable battery including a case containing an electrode assembly, the electrode assembly having a coated region and an uncoated region, a lead member inside the case, the lead member surrounding at least a part of the uncoated region of the electrode assembly and having a first thickness, an electrode terminal connected to the lead member, and a current collecting plate having a second thickness that is thinner than the first thickness and coupled to the lead member and to the uncoated region.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH +1
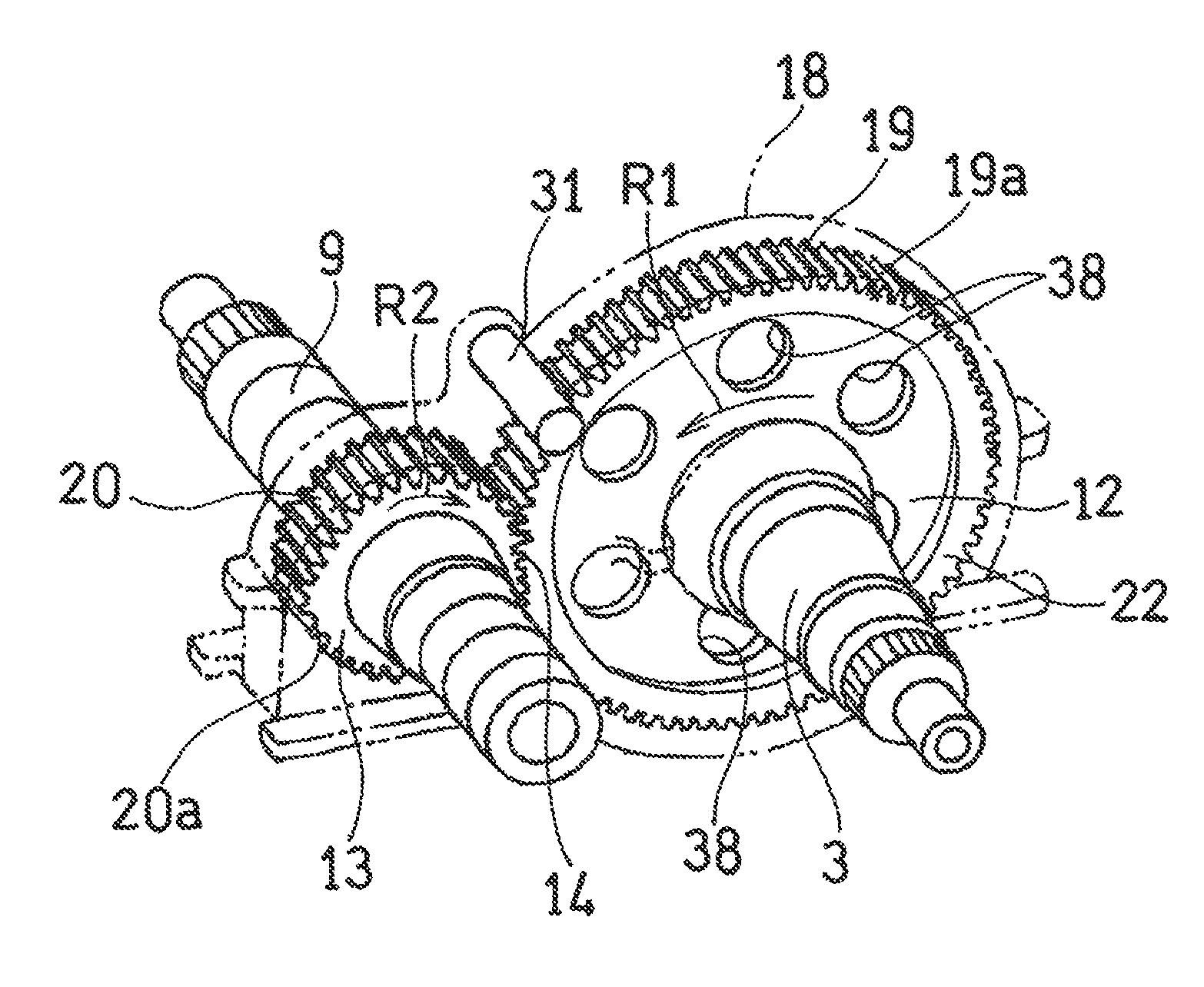
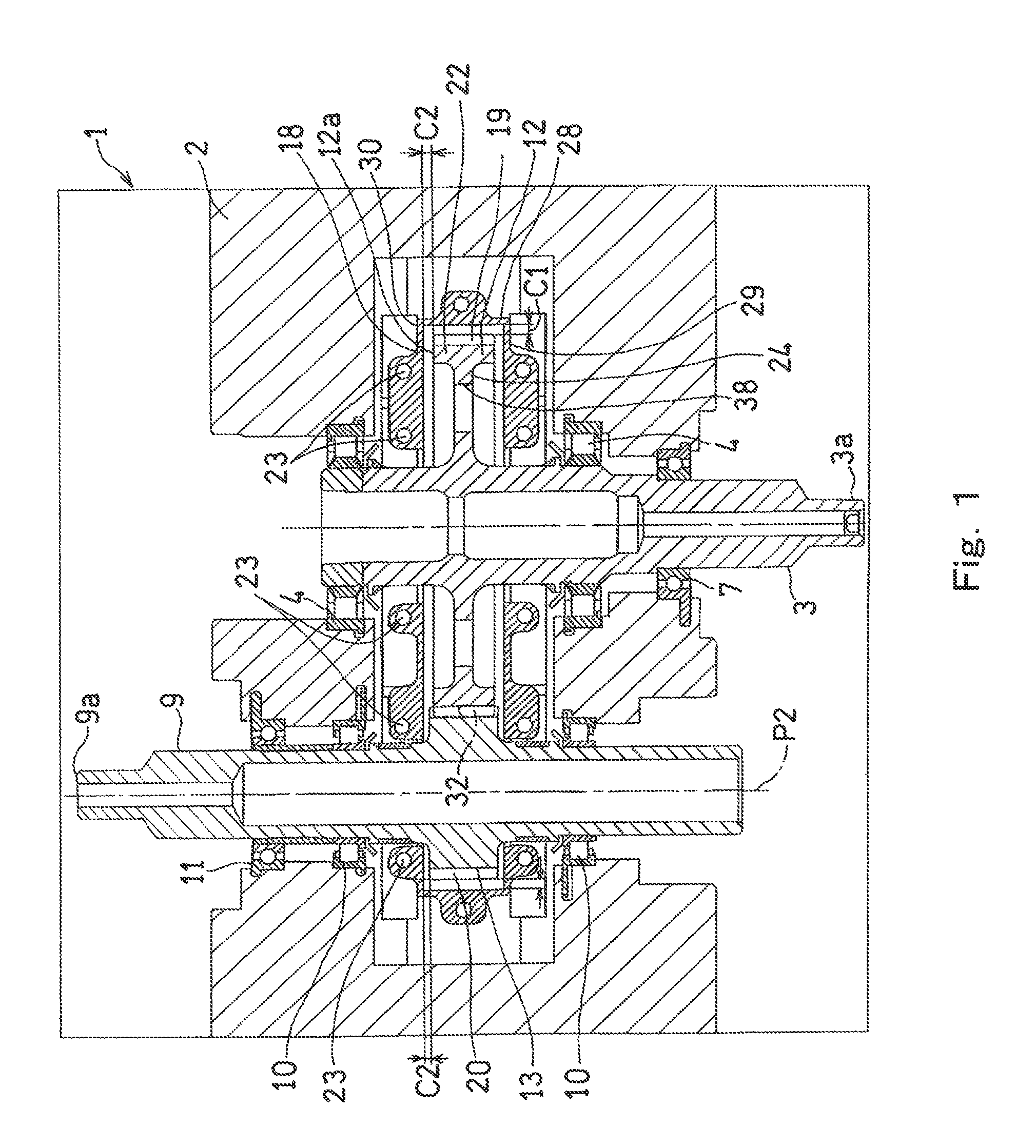
Gear train lubricating device
ActiveUS20130025405A1Reduce air resistanceSuppression resistanceGearboxesEngine fuctionsGear wheelEngineering
A gear train lubricating device configured to supply lubricating oil OL to a gear included in a gear train is provided. The gear train lubricating device includes: a shroud covering, among components constituting the gear, at least teeth of the gear; and a lubricating oil supply port through which the lubricating oil OL is supplied to a meshing position of the gear. The shroud has an outlet port formed therein, through which the supplied lubricating oil OL is discharged. The outlet port is formed in a portion of the shroud that is positioned radially outward from the gear, such that the outlet port is disposed at an angular position that is 90°±15° forward from the meshing position in a rotation direction R1 of the gear.
Owner:KAWASAKI HEAVY IND LTD
Printing device and printing method
ActiveUS20090244168A1Good colorSuppress color of color of colorMeasurement apparatus componentsPrintingComputer graphics (images)Imaging data
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080078923A1Reduce photosensitivityStable circuit operationTransistorTelevision system detailsAudio power amplifierPhotoelectric conversion
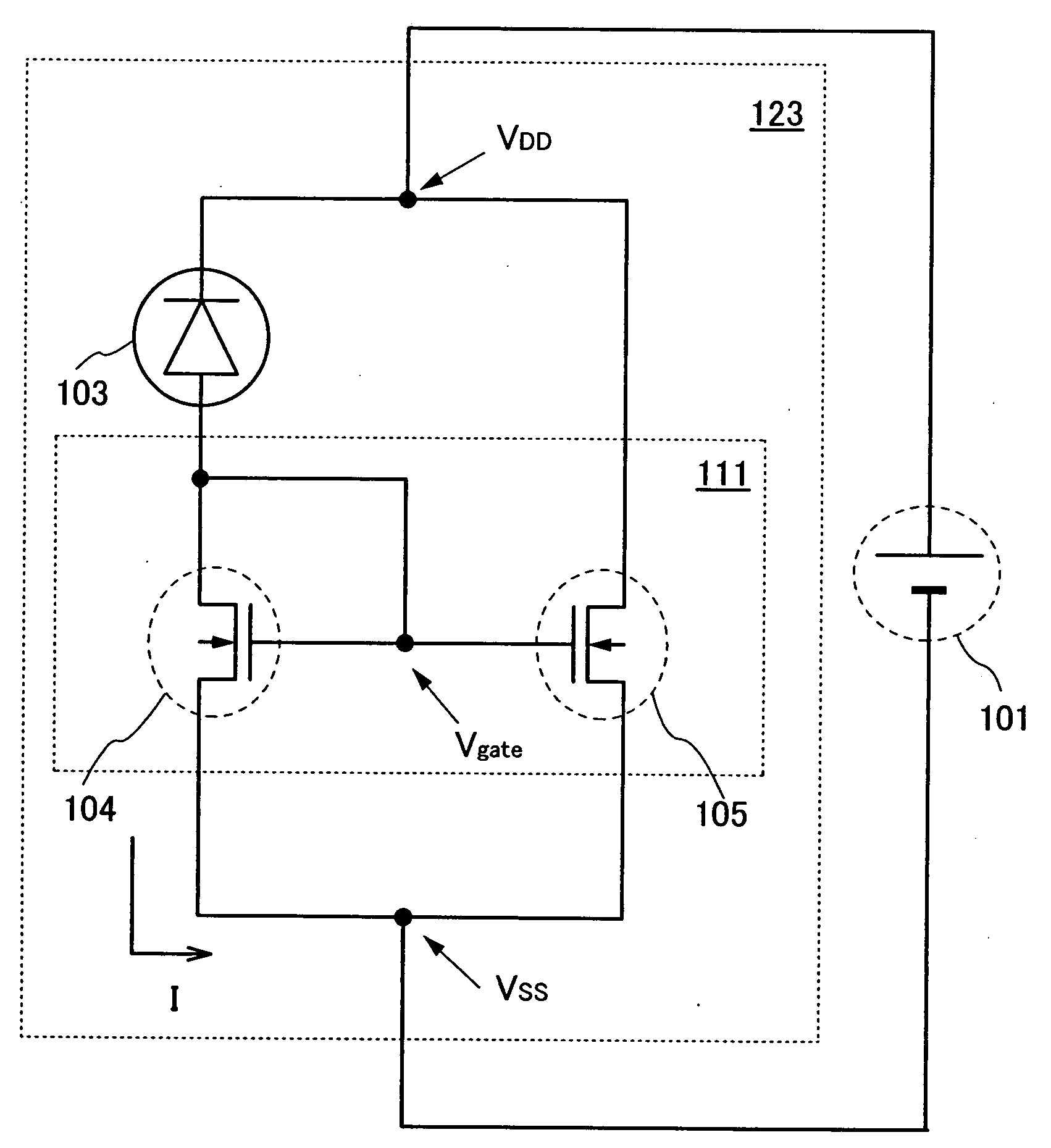
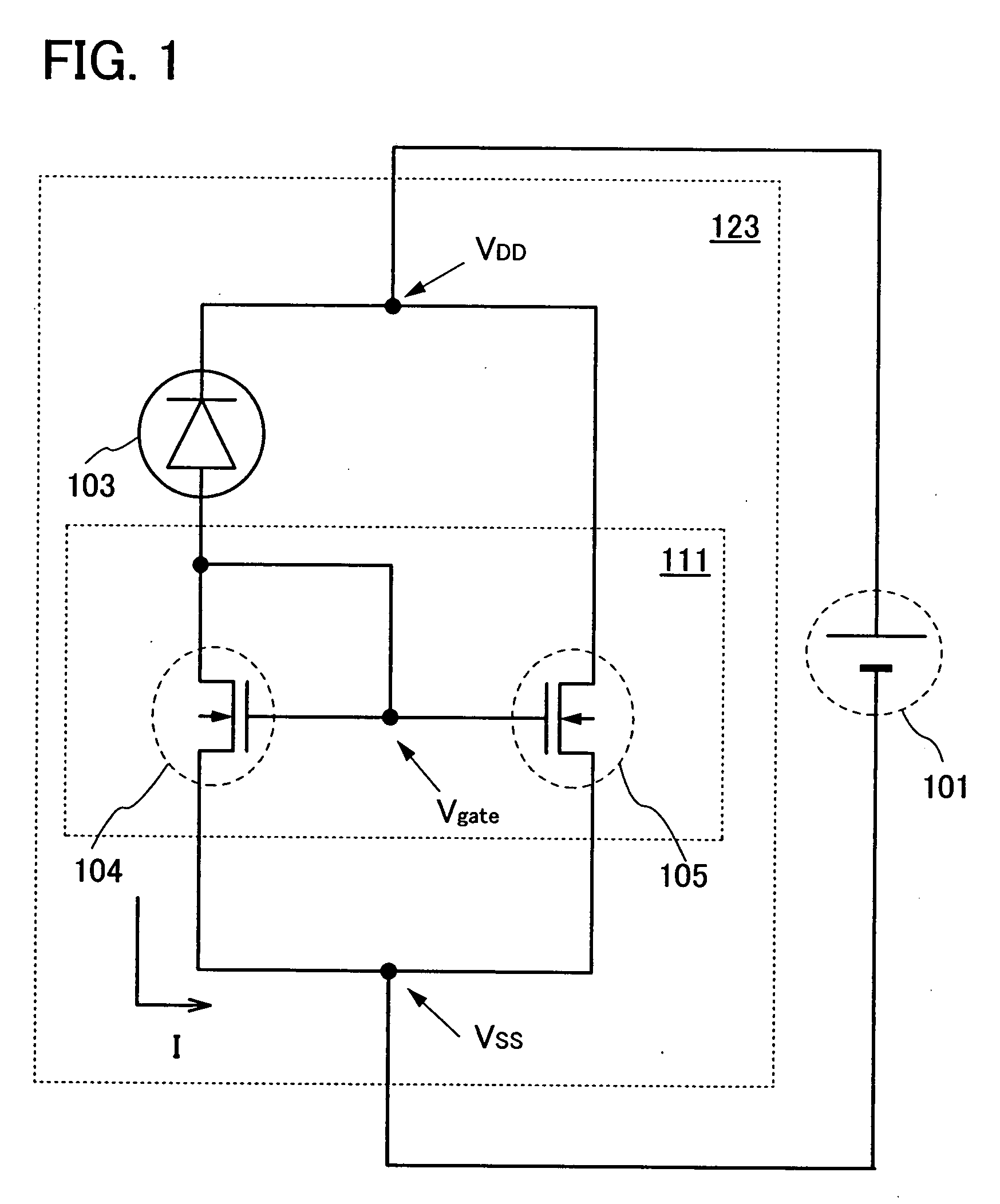
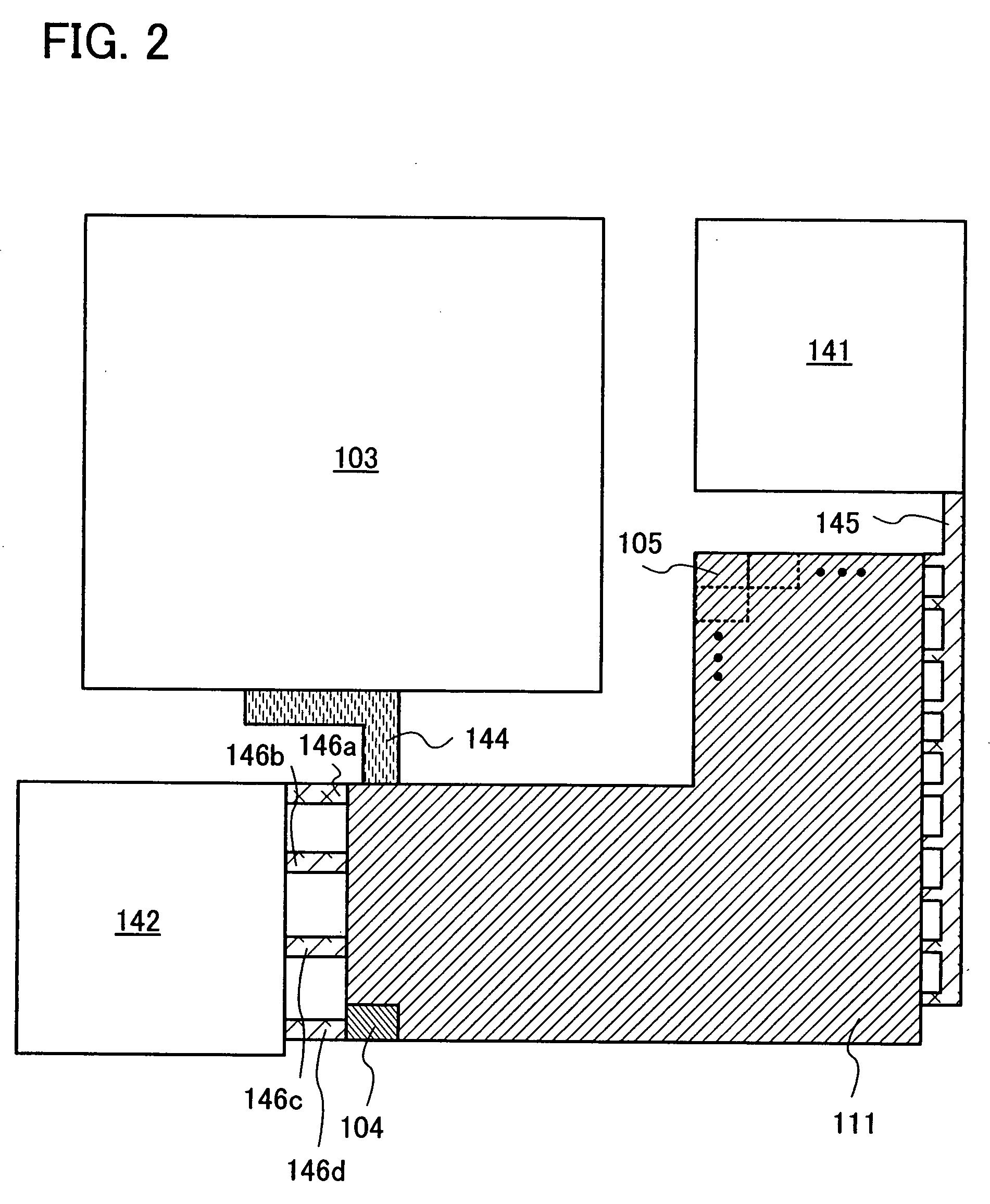
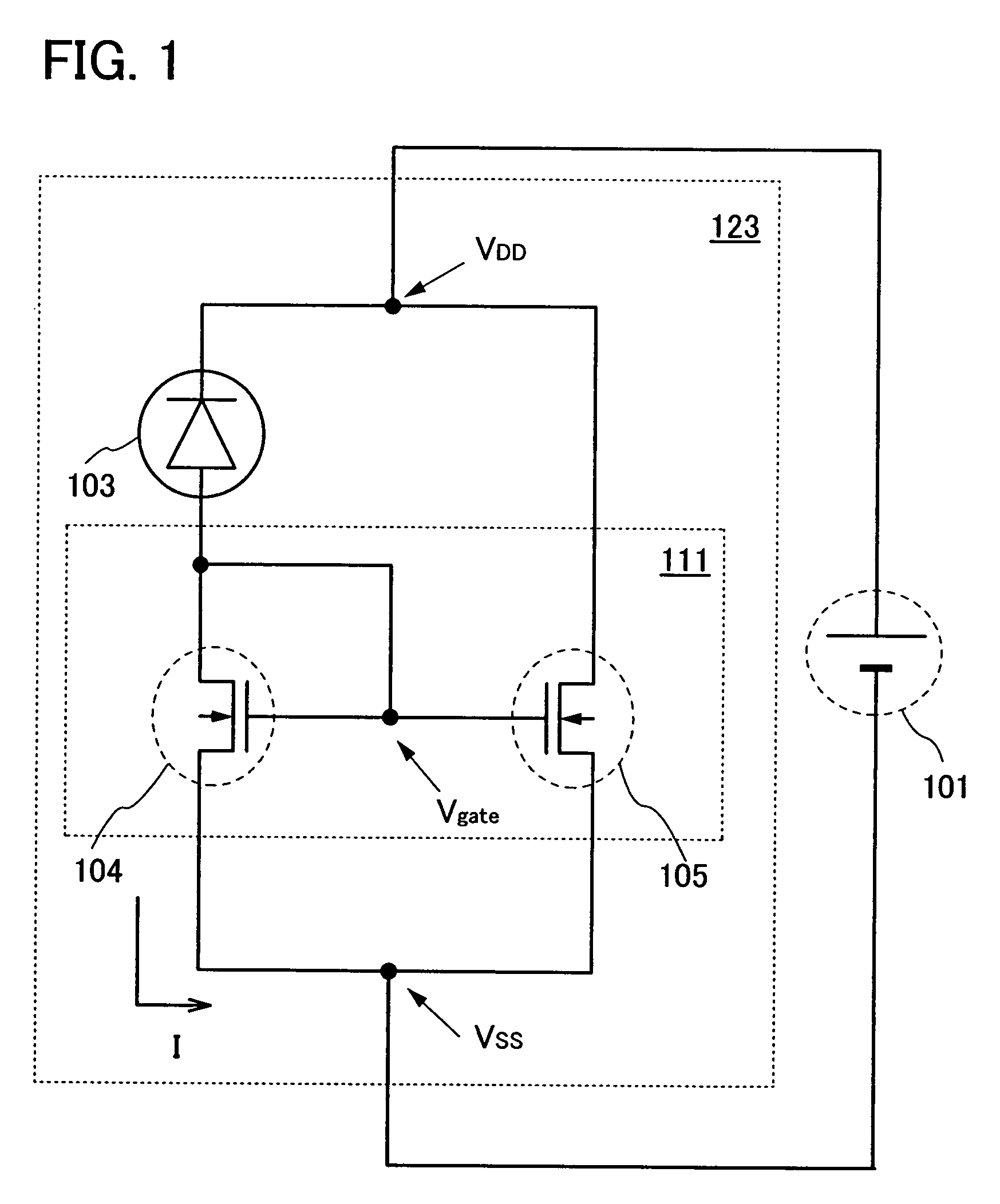
To suppress a decrease in photosensitivity of a photoelectric conversion element provided in a semiconductor device by reducing the parasitic resistance of an amplifier circuit. In addition, the amplifier circuit which amplifies the output current of the photoelectric conversion element is operated stably. A semiconductor device includes a photoelectric conversion element, a current mirror circuit having at least two thin film transistors, a high-potential power supply electrically connected to each of the thin film transistors, and a low-potential power supply electrically connected to each of the thin film transistors. When a reference thin film transistor is an n-type, the reference thin film transistor is placed closer to the low-potential power supply than an output thin film transistor is. When a reference thin film transistor is a p-type, the reference thin film transistor is placed closer to the high-potential power supply than an output thin film transistor is.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
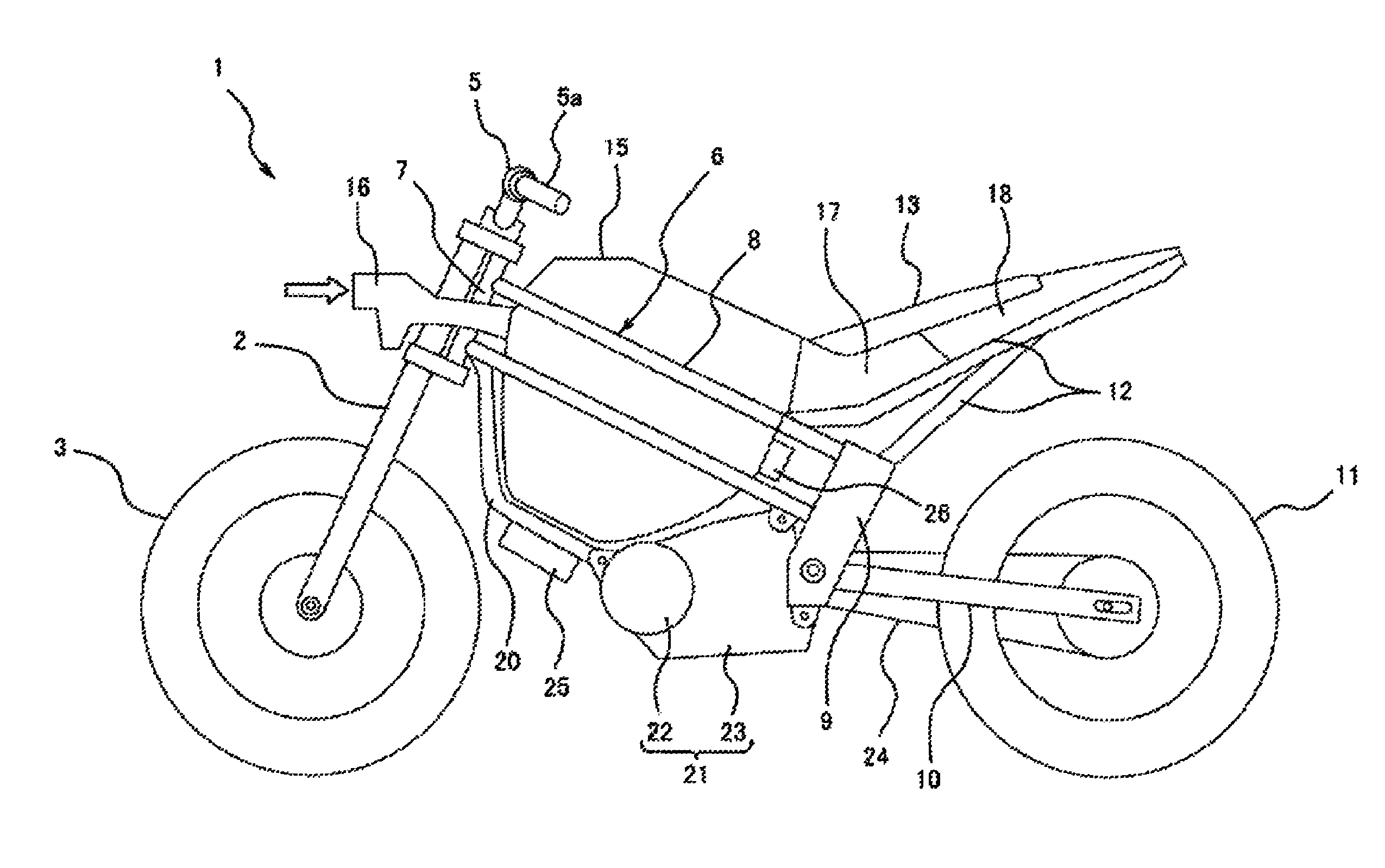
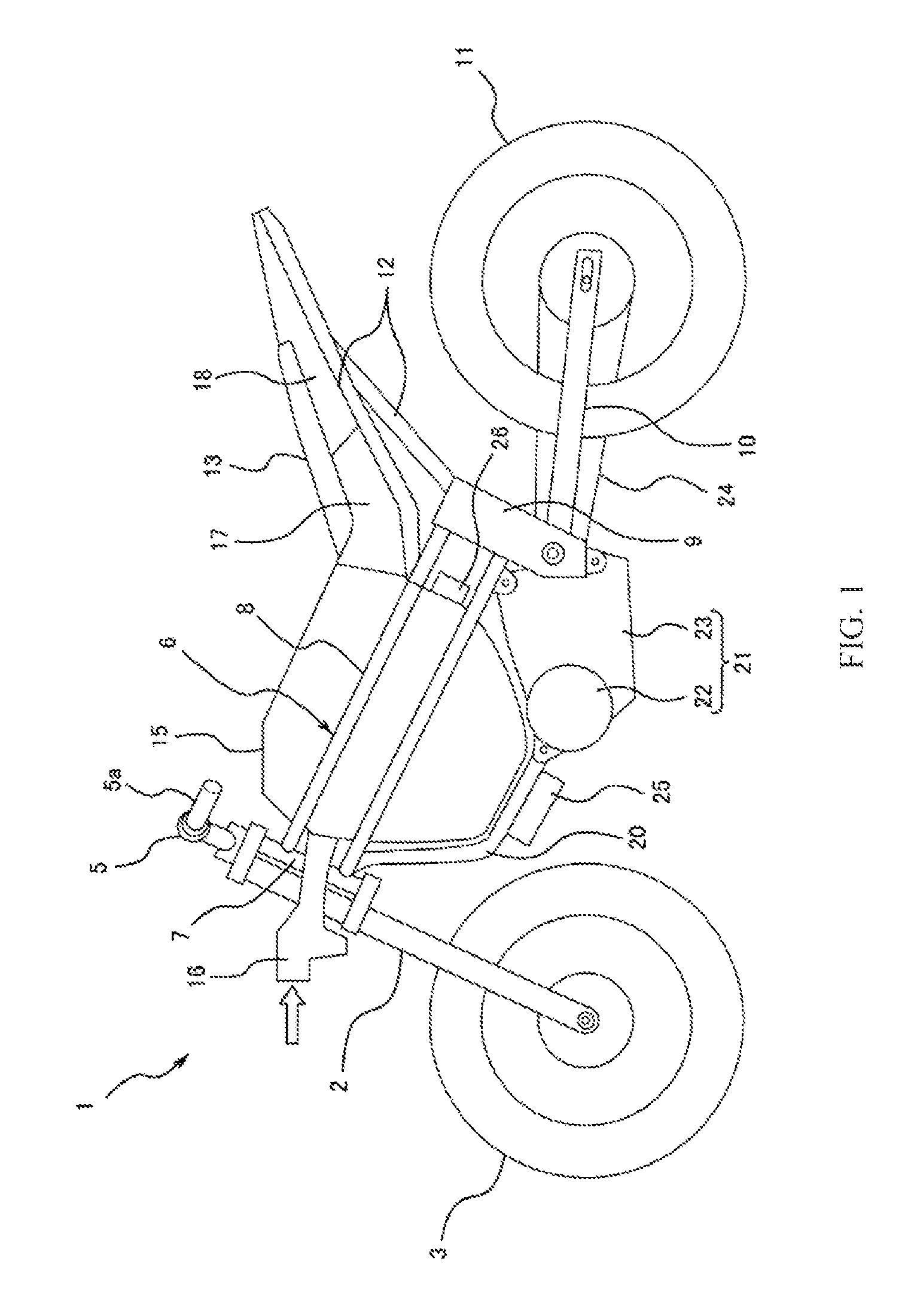
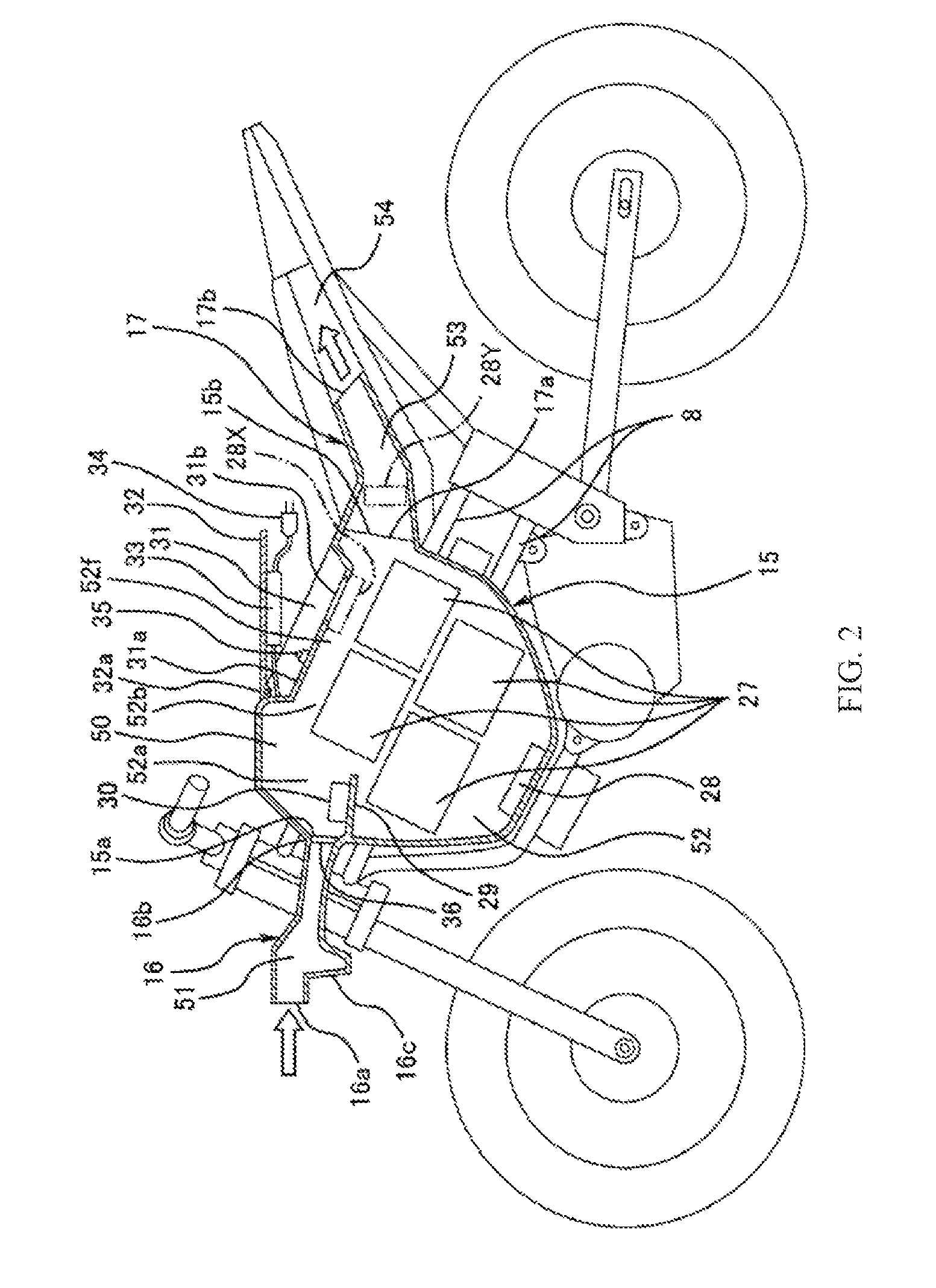
Saddle-type electric vehicle
ActiveUS8973697B2Travel efficientlySimple configurationElectric propulsion mountingCylinder headsElectric vehiclePipe support
A saddle-type electric vehicle includes a body frame having a head pipe supporting a steering shaft and a main frame portion extending rearward from the head pipe, a battery case provided on the main frame portion behind the head pipe, a battery stored in the battery case and supplying electric power to an electric motor generating traveling power, and a traveling wind path including an inner space of the battery case, wherein a traveling wind inflow port allowing traveling wind to flow in the battery case from front is formed on an upper side of a front portion of the battery case, and a traveling wind outflow port allowing the traveling wind flowing in the battery case to flow out rearward is formed on an upper side of a rear portion of the battery case.
Owner:KAWASAKI MOTORS LTD
Thin film transistor (TFT) having a protective layer and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS8383470B2Easy to makeRun at high speedElectroluminescent light sourcesSolid-state devicesMetallic materialsOptoelectronics
One of factors that increase the contact resistance at the interface between a first semiconductor layer where a channel is formed and source and drain electrode layers is a film with high electric resistance formed by dust or impurity contamination of a surface of a metal material serving as the source and drain electrode layers. As a solution, a first protective layer and a second protective layer including a second semiconductor having a conductivity that is less than or equal to that of the first semiconductor layer is stacked successively over source and drain electrode layers without exposed to air, the stack of films is used for the source and drain electrode layers.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Motor stator and manufacturing method of motor stator
InactiveUS20110260572A1Decrease coil volumeSuppress coil resistanceWindings insulation shape/form/constructionSynchronous machinesConductor CoilElectrical and Electronics engineering
A motor stator (10) is provided with a stator core (11) having a plurality of slots (16), insulation members (12) which are disposed in the plurality of slots, and coils of a plurality of phases (13) which are respectively formed by distributed-winding wires (20) in prescribed slots of the plurality of slots disposed spaced apart at intervals of a predetermined number of slots via the insulation members. The wires are disposed within the insulation members in a condition that tensions are applied to the wires. The stator core, the insulation members and the coils are physically fixed together by the tensions of the wires.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
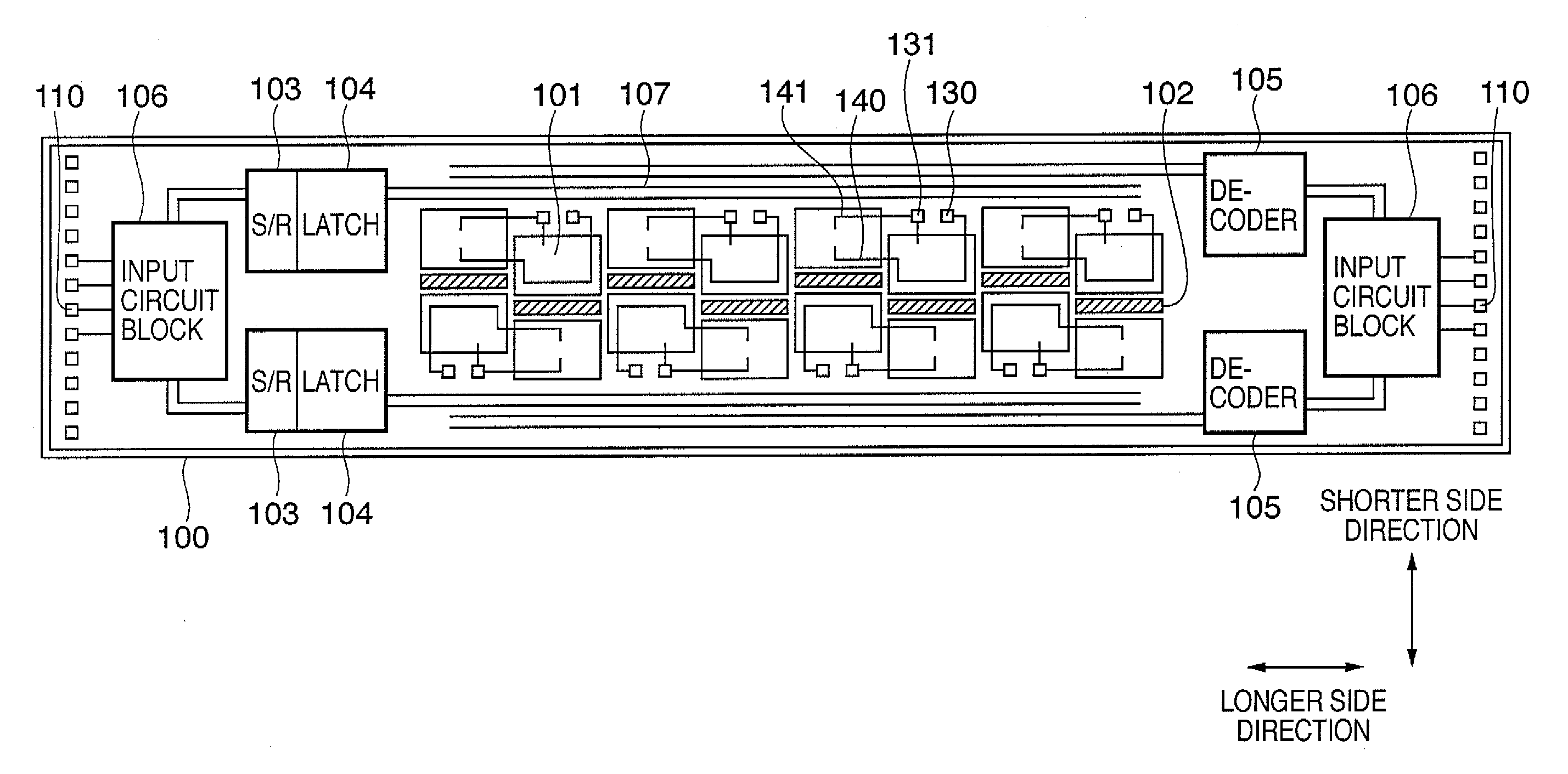
Head substrate, printhead, head cartridge, and printing apparatus
InactiveUS20080129781A1Efficient use ofReduce power lossInking apparatusElectrical and Electronics engineeringHemt circuits
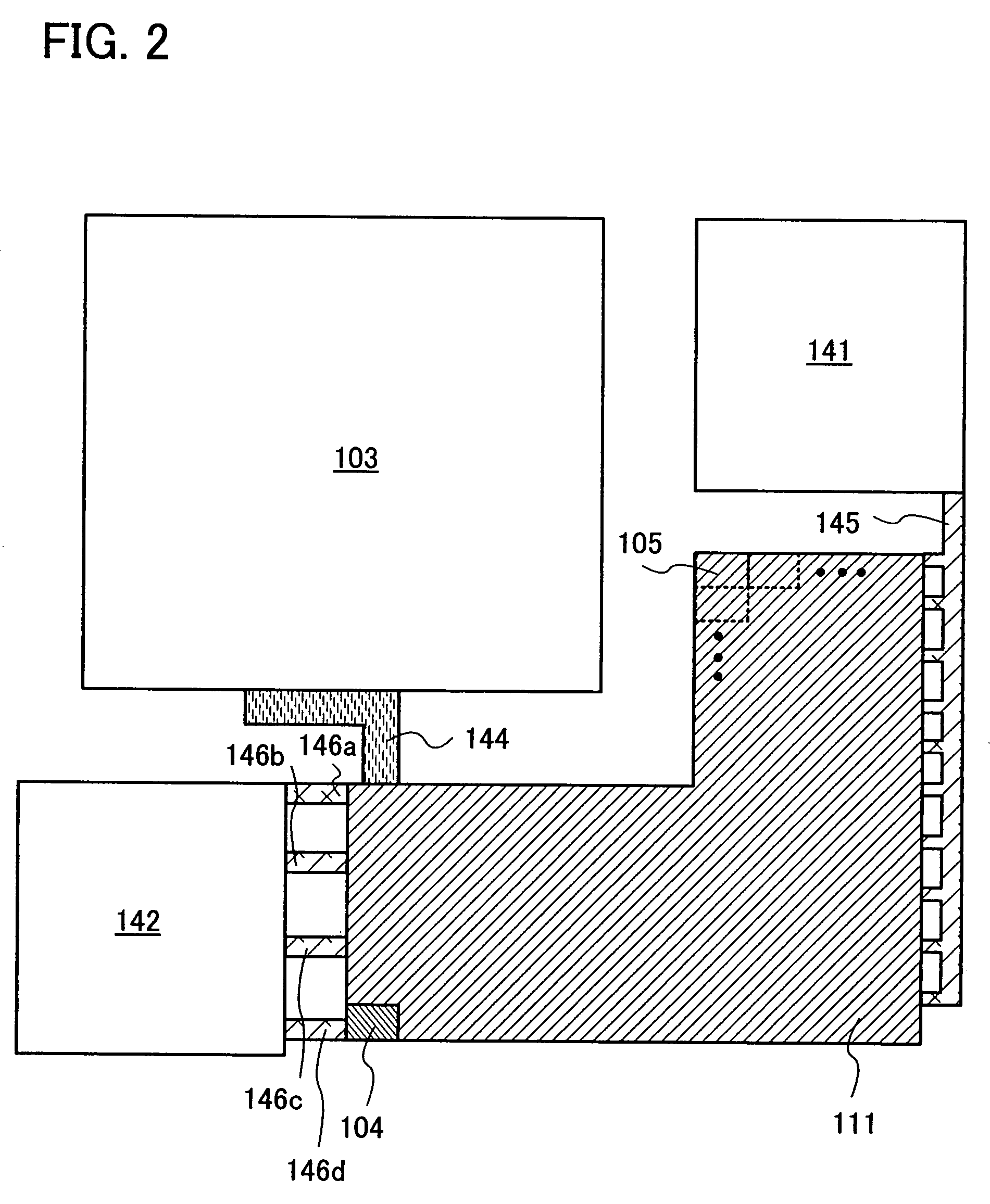
The objective of this invention is to provide a head substrate capable of increasing the layout efficiency by arranging circuit elements in a free area of the head substrate on which ink supply channels are staggered. More specifically, the circuit elements connected to a plurality of element arrays are arranged on the free area.
Owner:ABLYNX NV +1
Method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
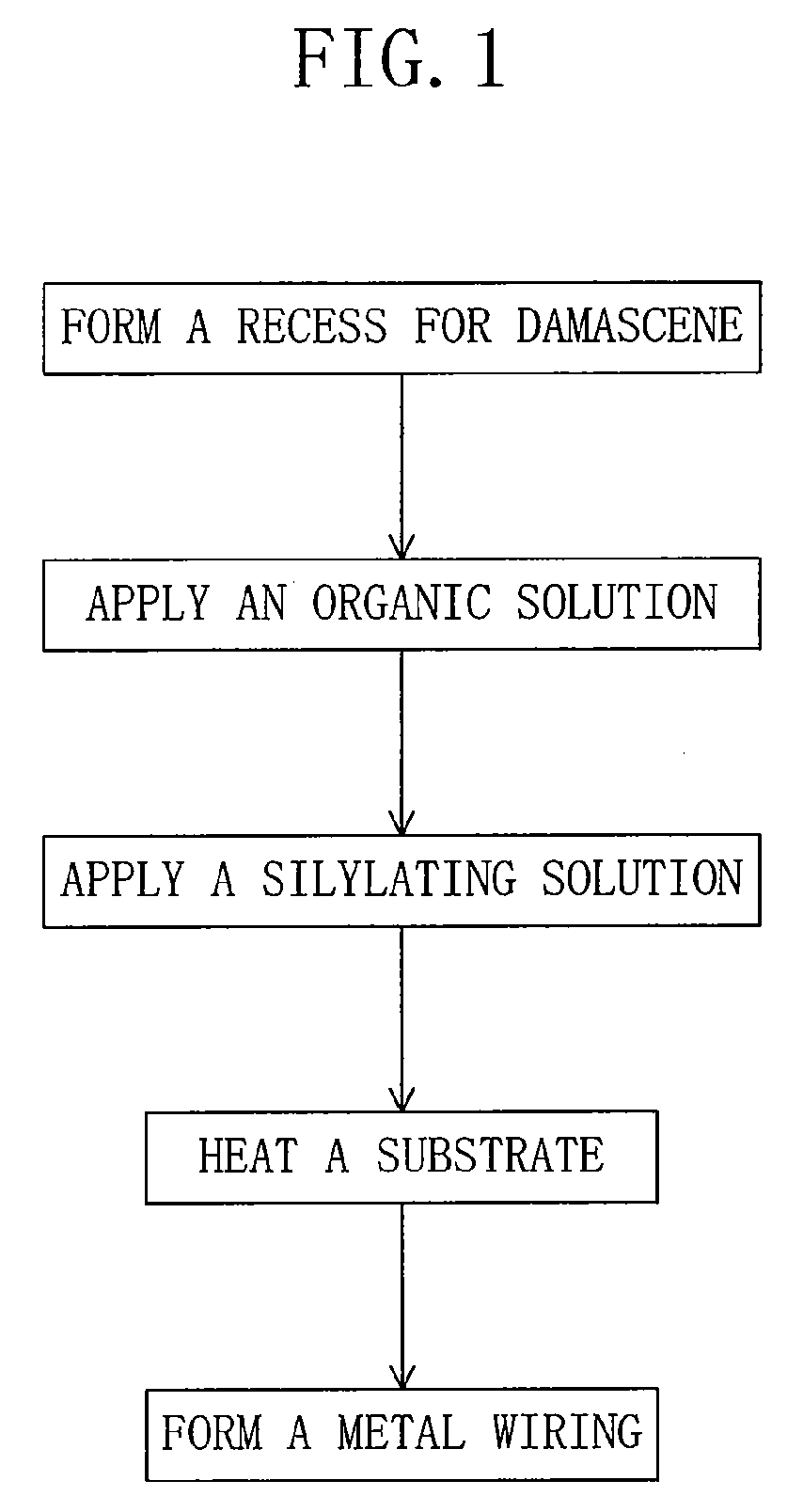
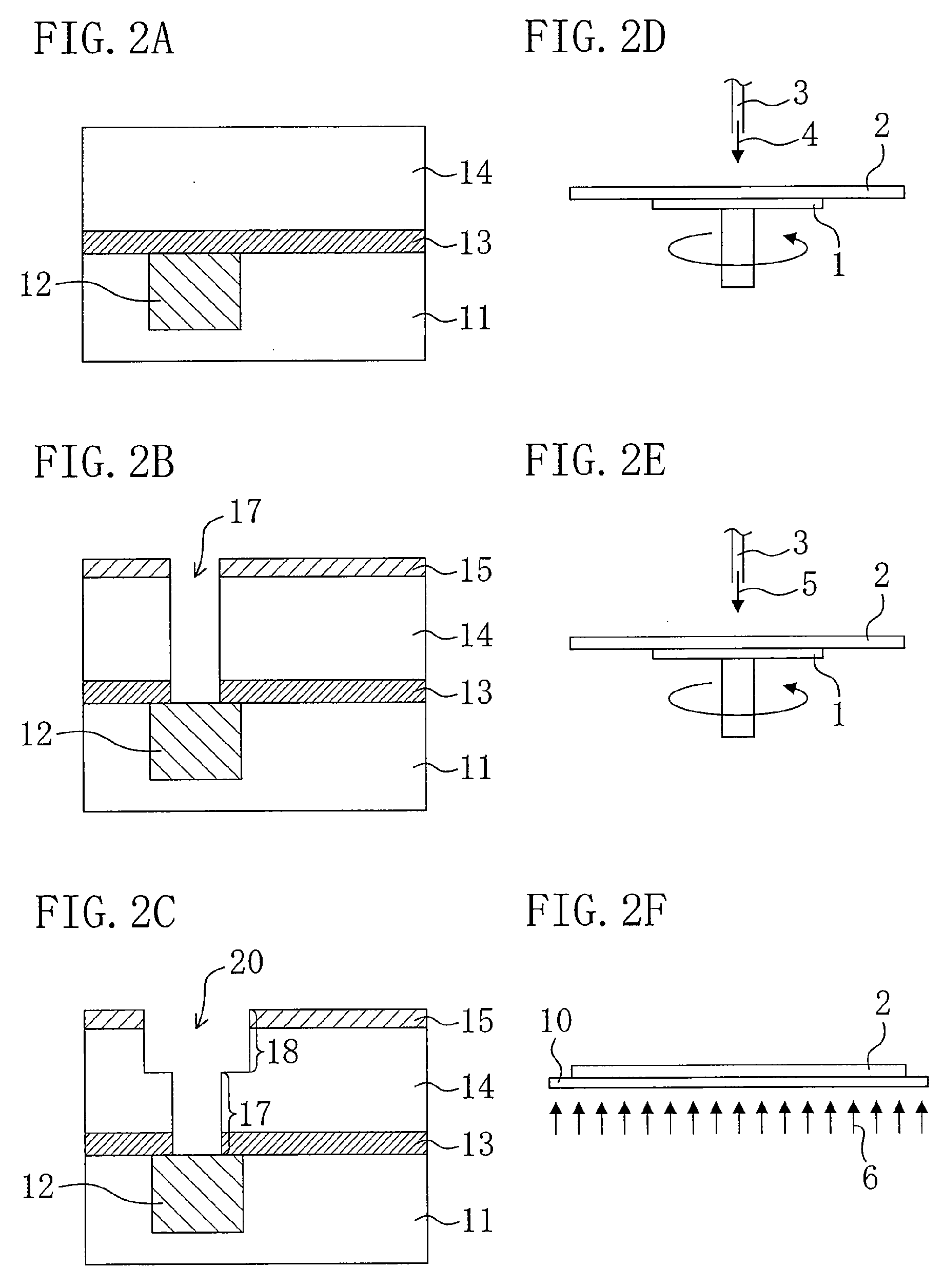
ActiveUS20090170314A1Improve abilitiesCapacity suppressedSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilylationSemiconductor
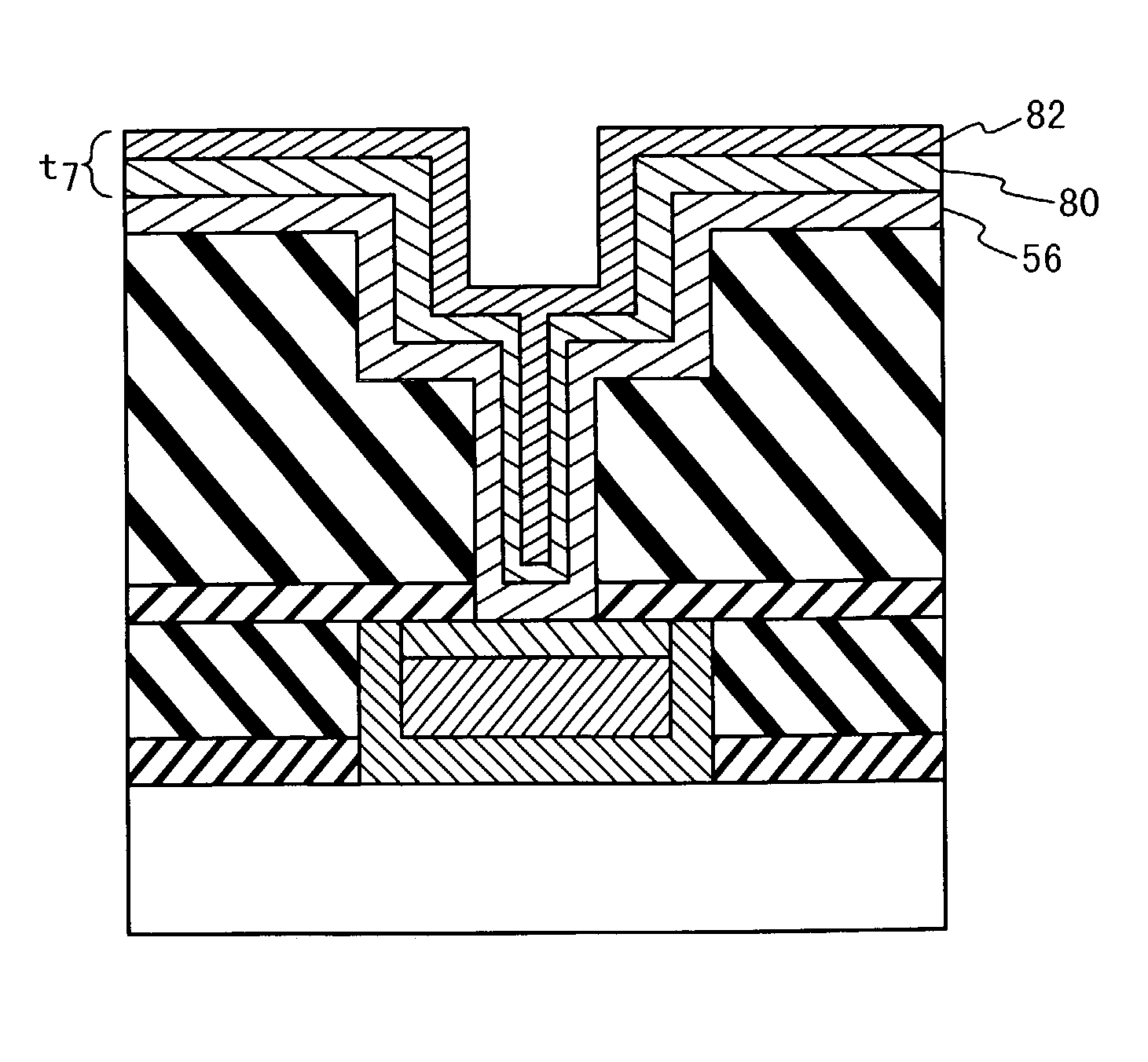
A method for manufacturing a semiconductor device includes the steps of: (a) forming a low dielectric constant film over a semiconductor substrate; (b) forming a recess in the low dielectric constant film; (c) after the step (b), sequentially performing the steps of (c1) applying an organic solution to the low dielectric constant film and (c2) silylating the low dielectric constant film with a silylating solution; and (d) after the step (c), embedding a metal in the recess to form at least one of a via plug and a metal wiring in the low dielectric constant film. Performing the step (c1) before the step (c2) improves a penetration property of the silylating solution into the low dielectric constant film.
Owner:PANNOVA SEMIC
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
InactiveUS20070018255A1Quality improvementLower resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialSemiconductor
The method for fabricating a semiconductor device according to the present invention comprises the step of forming a Ni film 66 on source / drain diffused layers 64, the step of performing a first thermal processing to react a lower part of the Ni film 66 and an upper part of the source / drain diffused layers 64 with each other to form Ni2Si films 70b on the source / drain diffused layers 64, the step of etching off selectively a part of the Ni film 66, which has not reacted, and the step of performing a second thermal processing to further react the Ni2Si film 70b and an upper part of the source / drain diffused layers 64 with each other.
Owner:FUJITSU SEMICON LTD
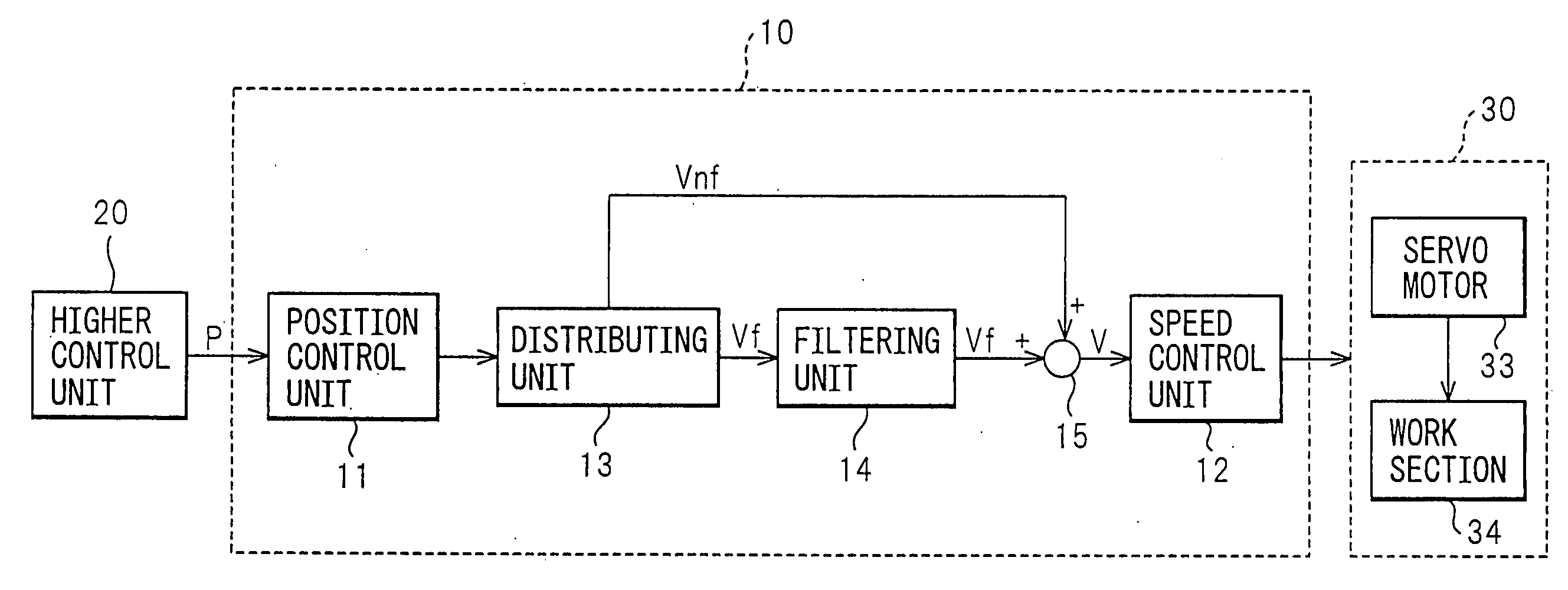
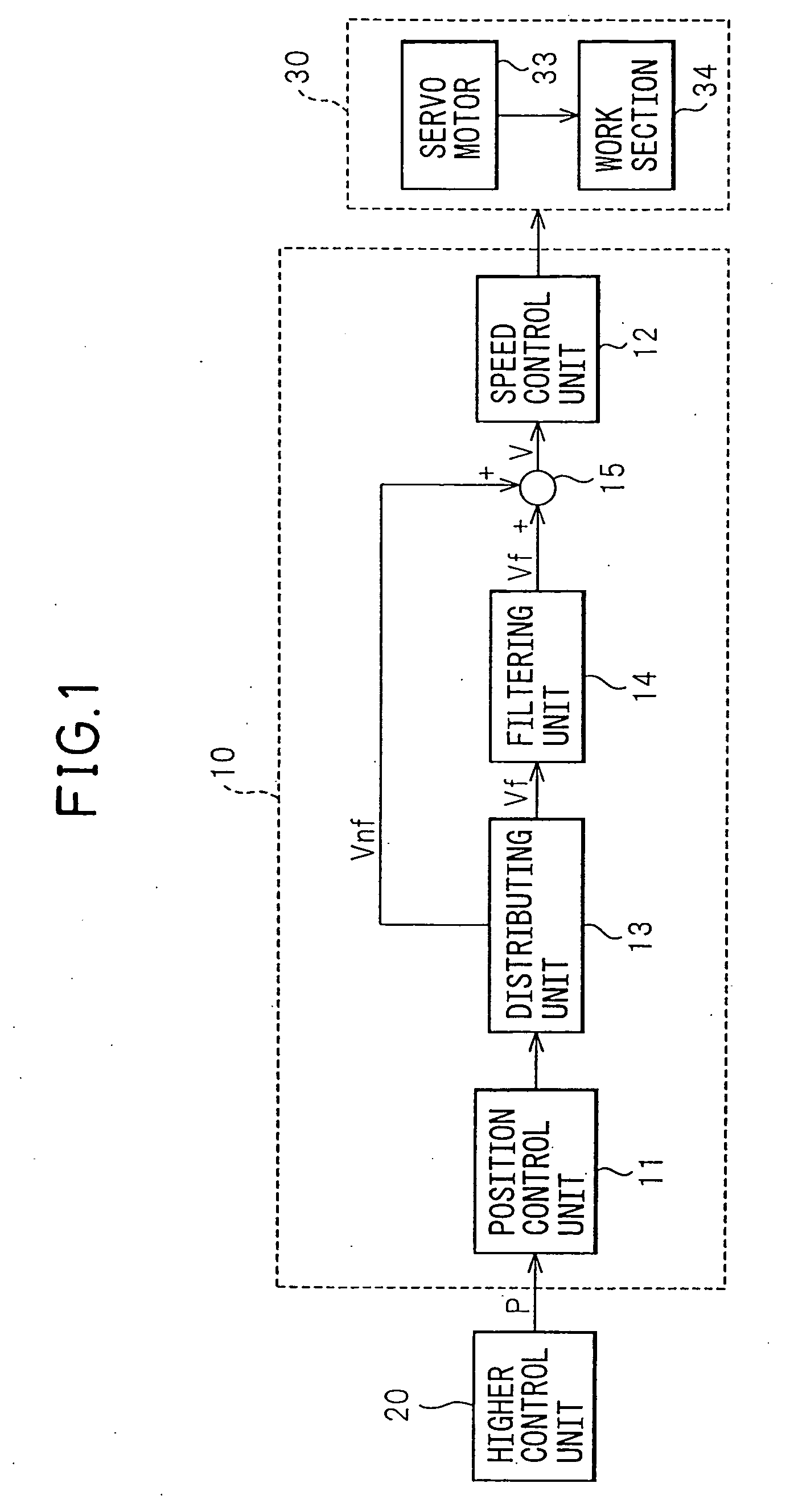
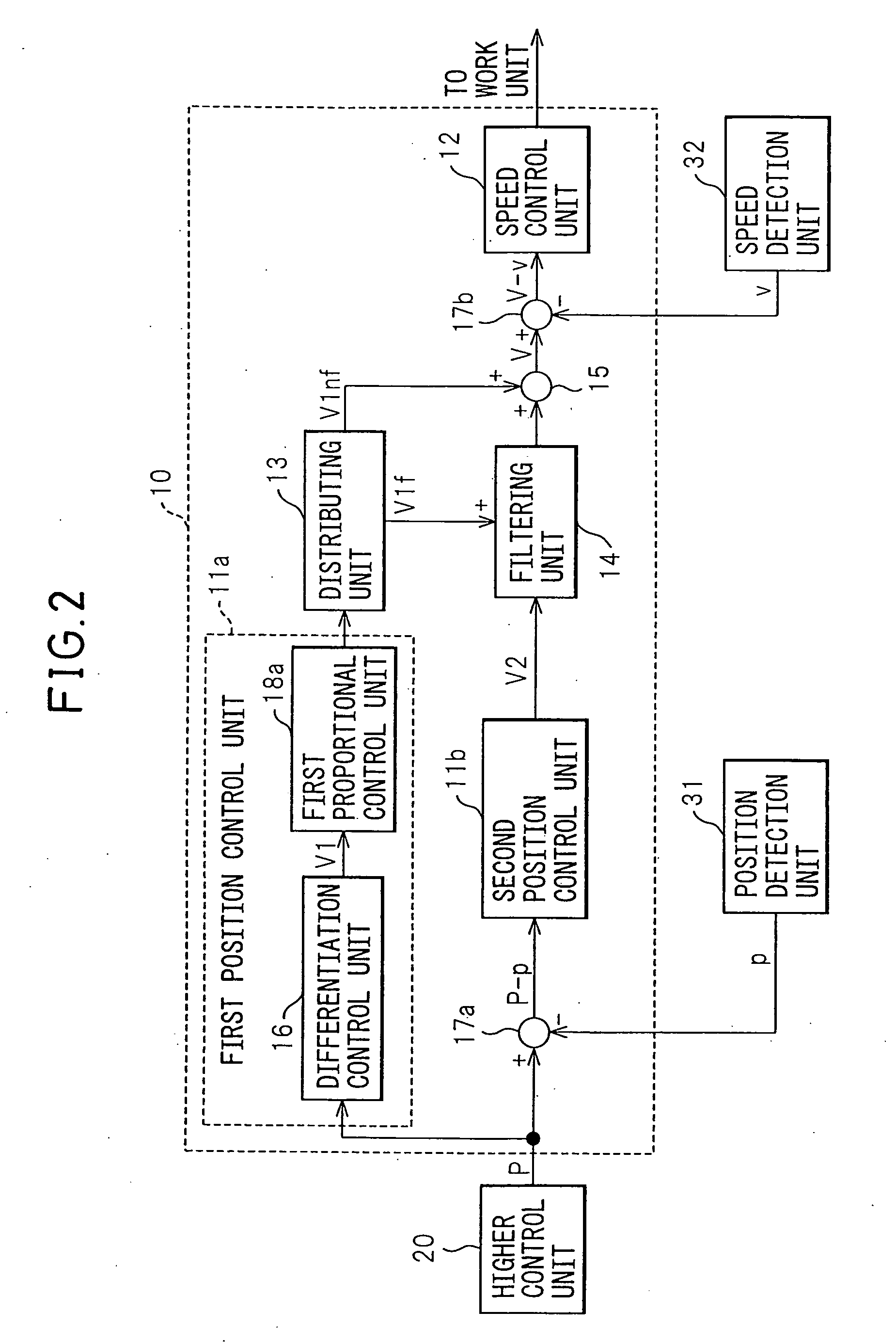
Control apparatus of servo motor
ActiveUS20080180052A1Suppressed in mechanical resistanceImprove control accuracyElectric motor controlMechanical oscillations controlPosition controlControl unit
The control apparatus 10 of a servo motor of the present invention has a position control unit 11 controlling the position of a servo motor 33, a speed control unit 12 controlling a speed of the servo motor 33, a distributing unit 13 dividing the speed command output by the position control unit 11 into a filtered part Vf which is filtered to suppress vibration and a nonfiltered part Vnf, a filtering unit 14 receiving as input the filtered part Vf and filtering and outputting the filtered part Vf, and an adder unit 15 adding the filtered part Vf filtered by the filtering unit 14 and the nonfiltered part Vnf and outputting the result to the speed control unit 12.
Owner:FANUC LTD
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and method for manufacturing same
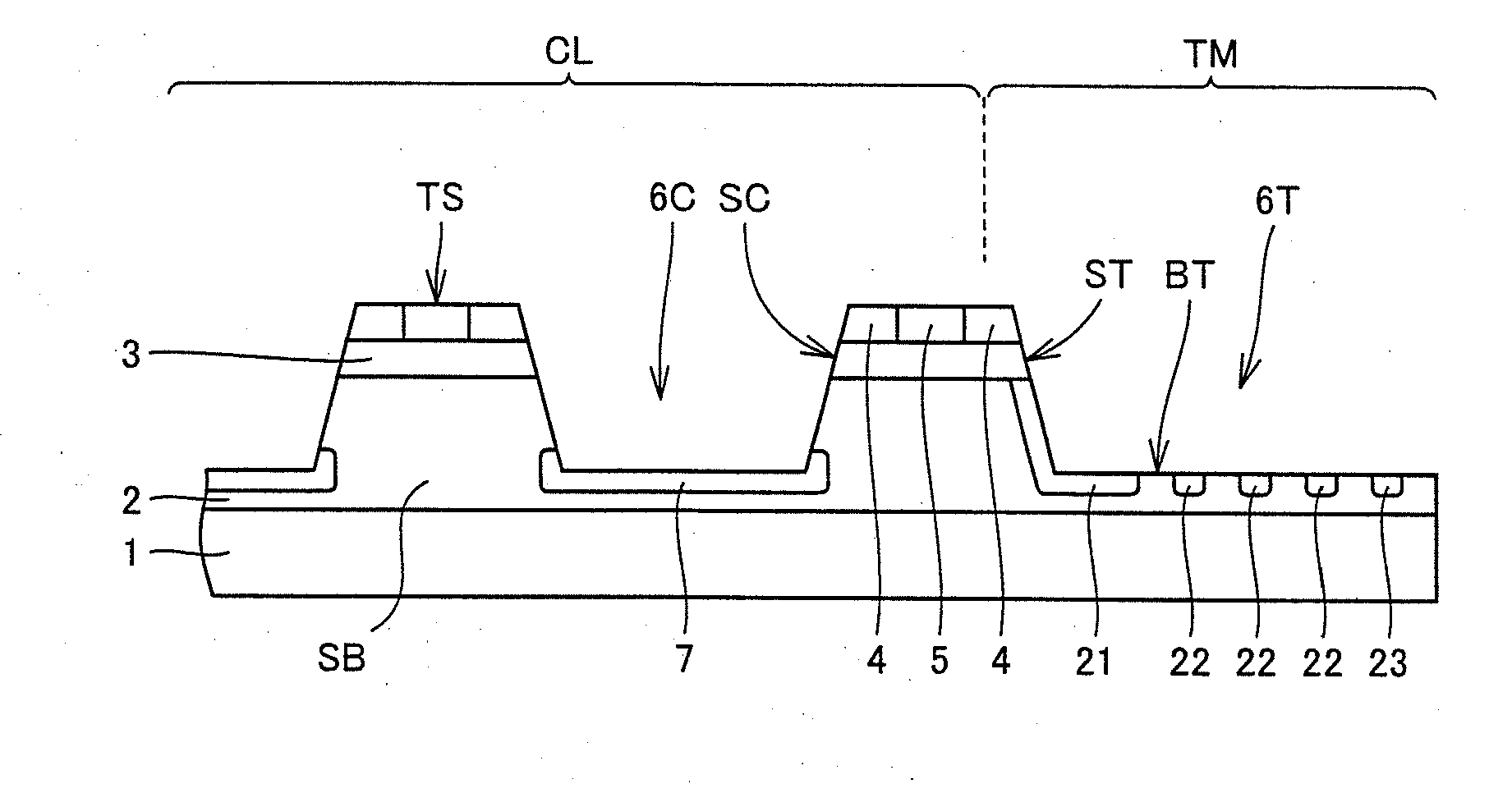
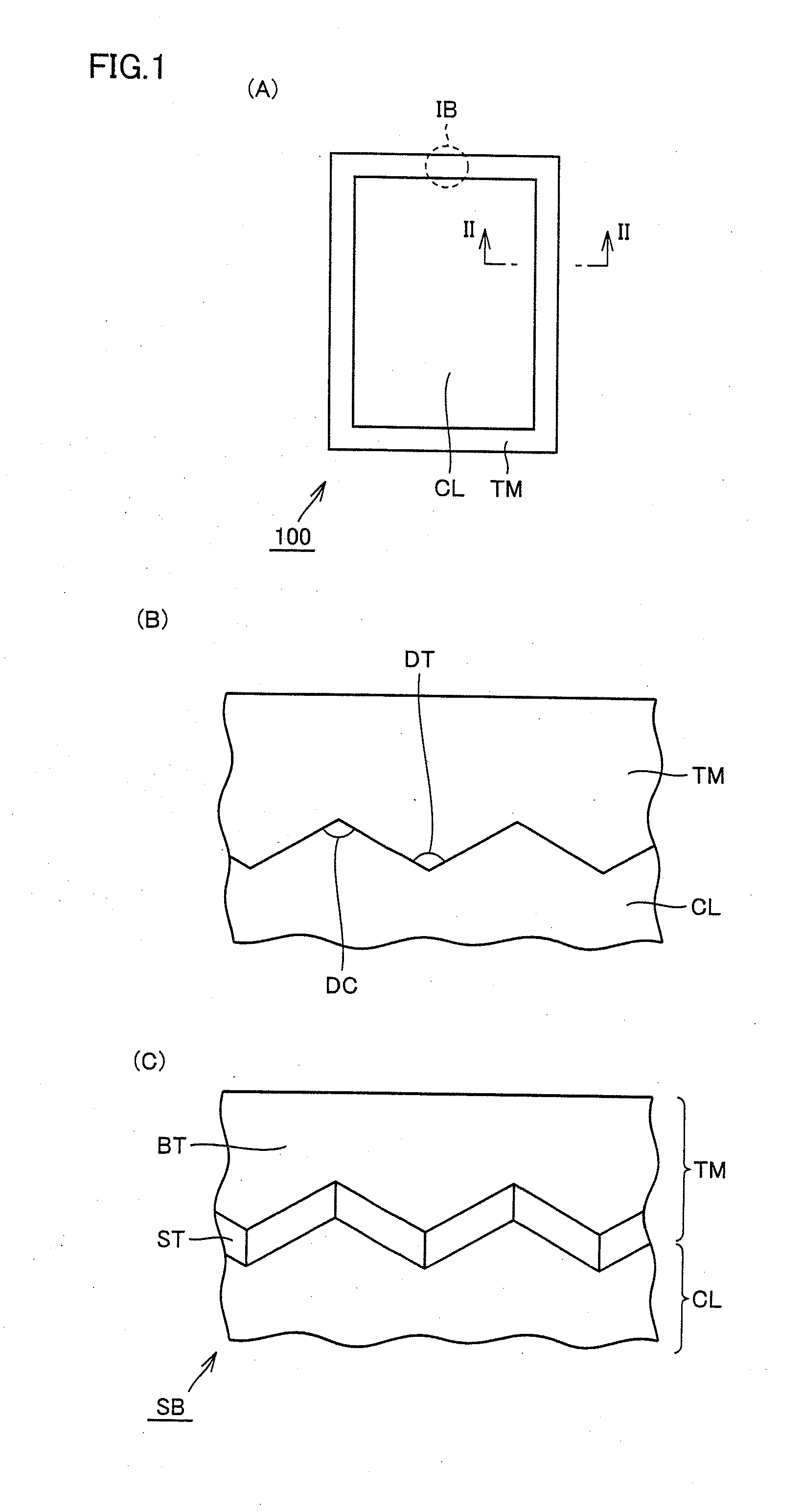
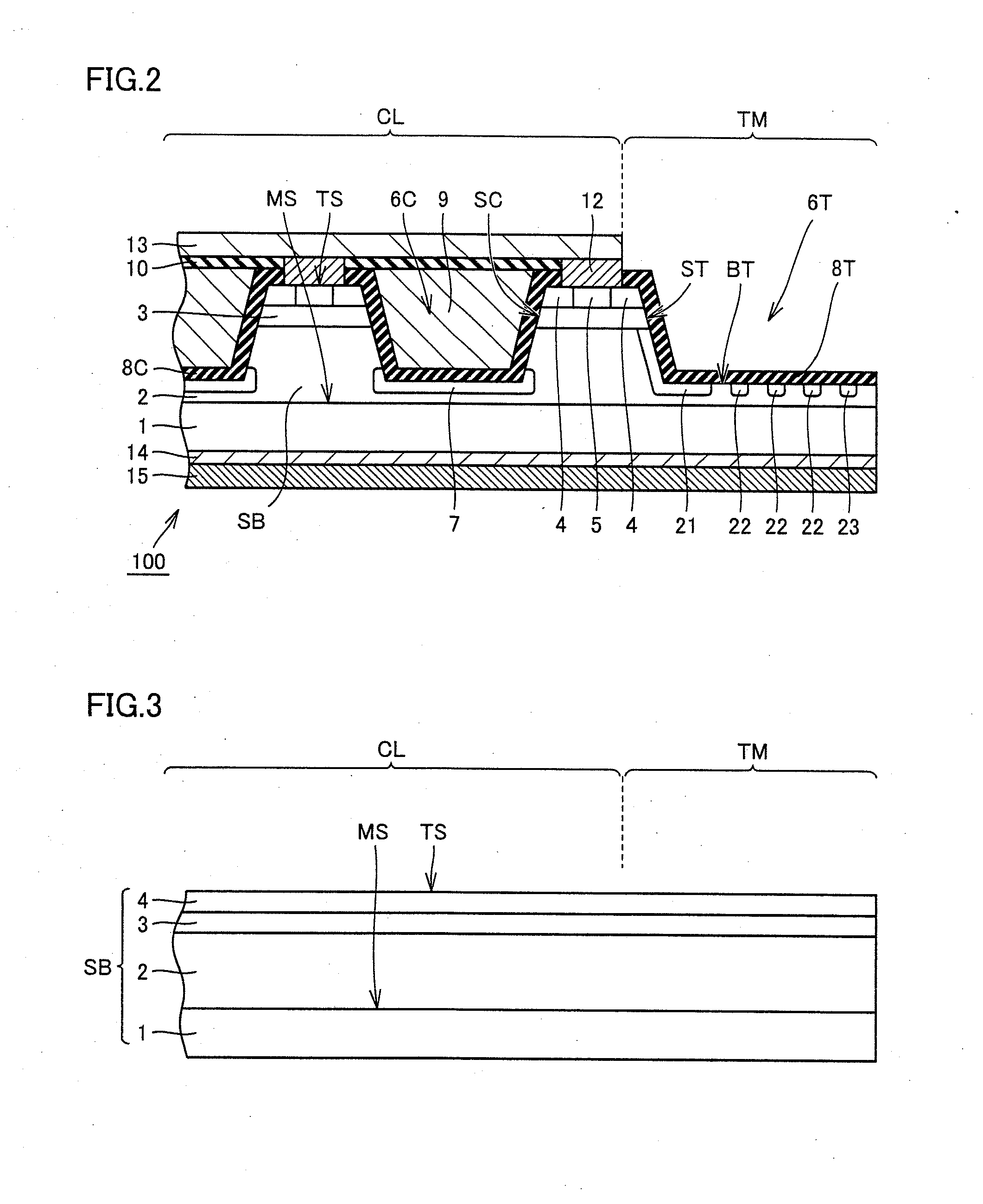
ActiveUS20130099251A1Small on-resistanceHigh carrier mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPlane orientationSemiconductor
When viewed in a plan view, a termination region (TM) surrounds an element region (CL). A first side of a silicon carbide substrate (SB) is thermally etched to form a side wall (ST) and a bottom surface (BT) in the silicon carbide substrate (SB) at the termination region (TM). The side wall (ST) has a plane orientation of one of {0-33-8} and {0-11-4}. The bottom surface (BT) has a plane orientation of {000-1}. On the side wall (ST) and the bottom surface (BT), an insulating film (8T) is formed. A first electrode (12) is formed on the first side of the silicon carbide substrate (SB) at the element region (CL). A second electrode (14) is formed on a second side of the silicon carbide substrate (SB).
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method of manufacturing semiconductor memory
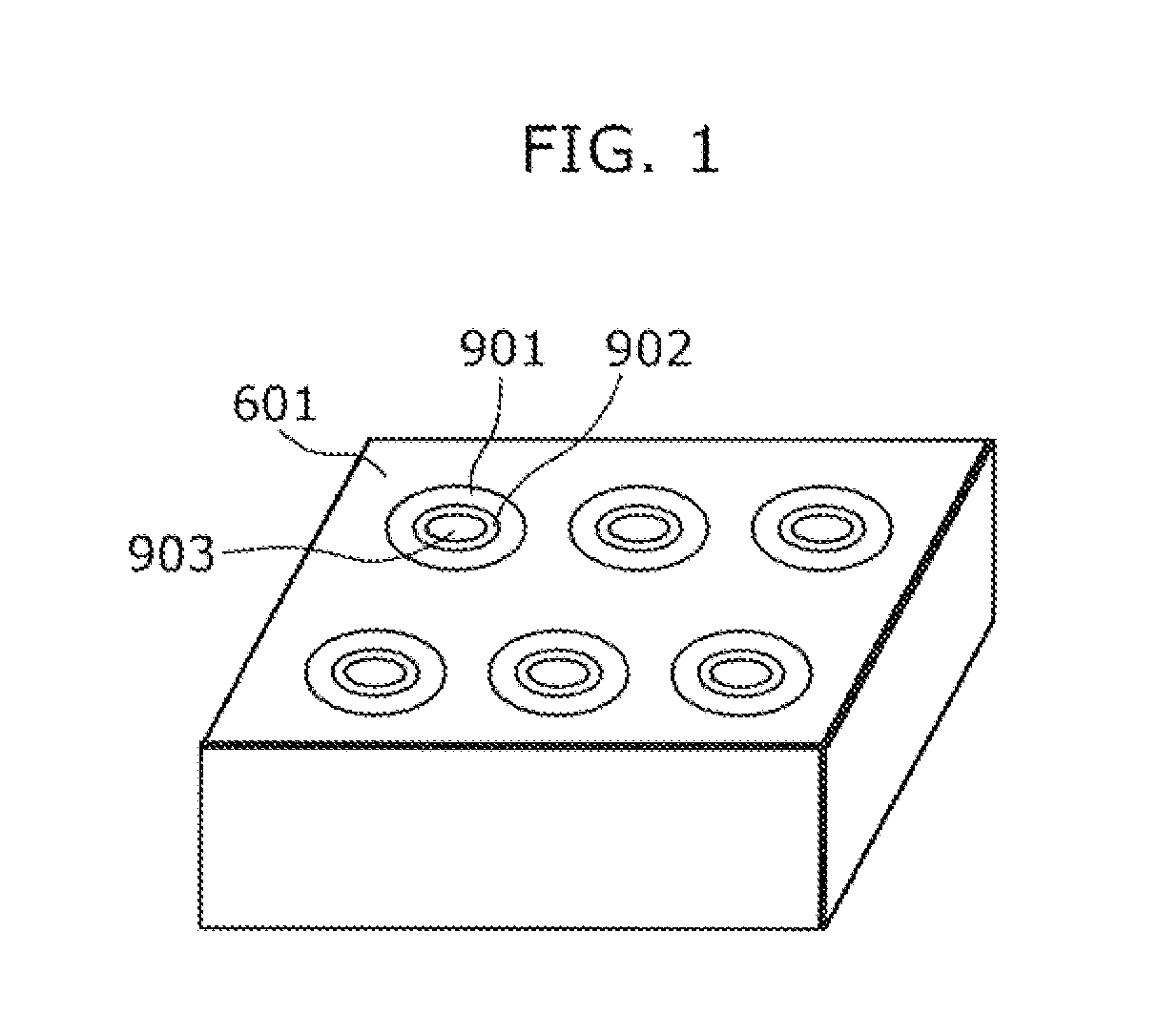
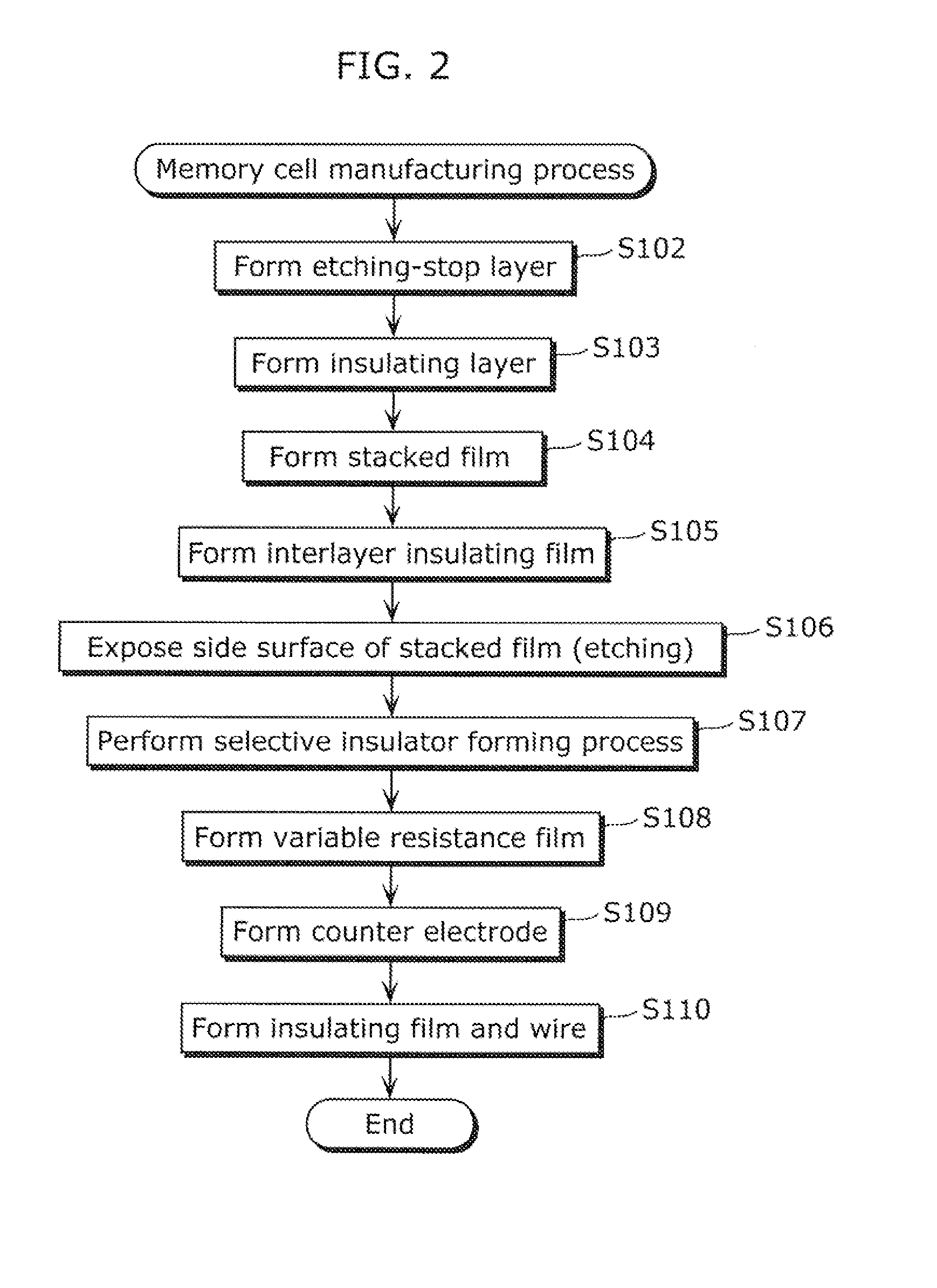
ActiveUS20110177666A1Small curvature radiusReduce curvature radiusSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical reactionConductive materials
The method of manufacturing a semiconductor memory includes a process of forming a projection by performing an insulator forming process on the exposed side surface of a reactive conductive material and a non-reactive conductive material that are stacked above a substrate so as to change a predetermined length of the side surface of the reactive conductive material into an insulator, and thereby causing the side surface of the non-reactive conductive material to project outward from the side surface of the reactive its conductive material. The insulator forming process is an oxidation process or a nitridation process, the reactive conductive material is a material that reacts chemically and changes into the insulator in the oxidation process or nitridation process, and the non-reactive conductive material is a material that does not change into the insulator in the oxidation process or nitridation process.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method of manufacturing quartz resonator element, quartz resonator element, quartz resonator, and quartz oscillator
InactiveUS20100066213A1Reduce the CI valueIncrease manufacturing costPiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblyImpedence networksQuartz resonatorQuartz substrate
To provide a method of manufacturing a quartz resonator element having a small CI value, a quartz resonator element manufactured by this method, a quartz resonator, and a quartz oscillator.In a method of manufacturing a quartz resonator element in which on a surface of a plate-shaped quartz piece, a thin film-shaped electrode in order to excite the quartz piece is provided, a first metal layer that is composed of chromium and whose thickness is not less than 20 Å nor more than 45 Å is formed on the surface of the quartz piece (P4), and next, a second metal layer that is composed of gold or silver and whose thickness is not less than 500 Å nor more than 950 Å is formed on an upper surface of the first metal layer (P5), and then, the electrode made up of the first metal layer and the second metal layer is provided (P6). Thereafter, a quartz substrate on which the electrode is formed is heated at a temperature range of not less than 200° C. nor more than 400° C., and the chromium composing the first metal layer is diffused into the second metal layer (P7).
Owner:NIHON DEMPA KOGYO CO LTD
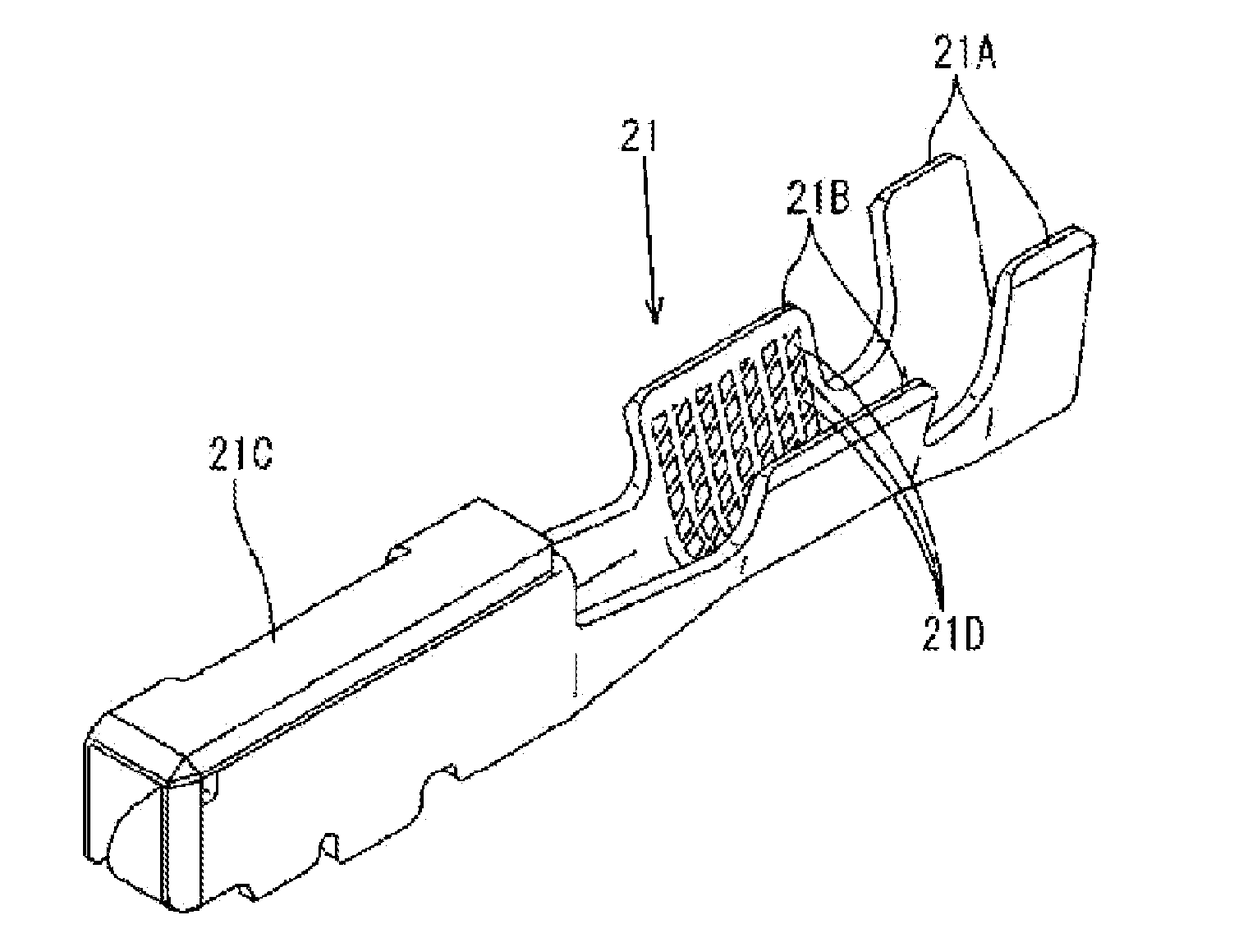
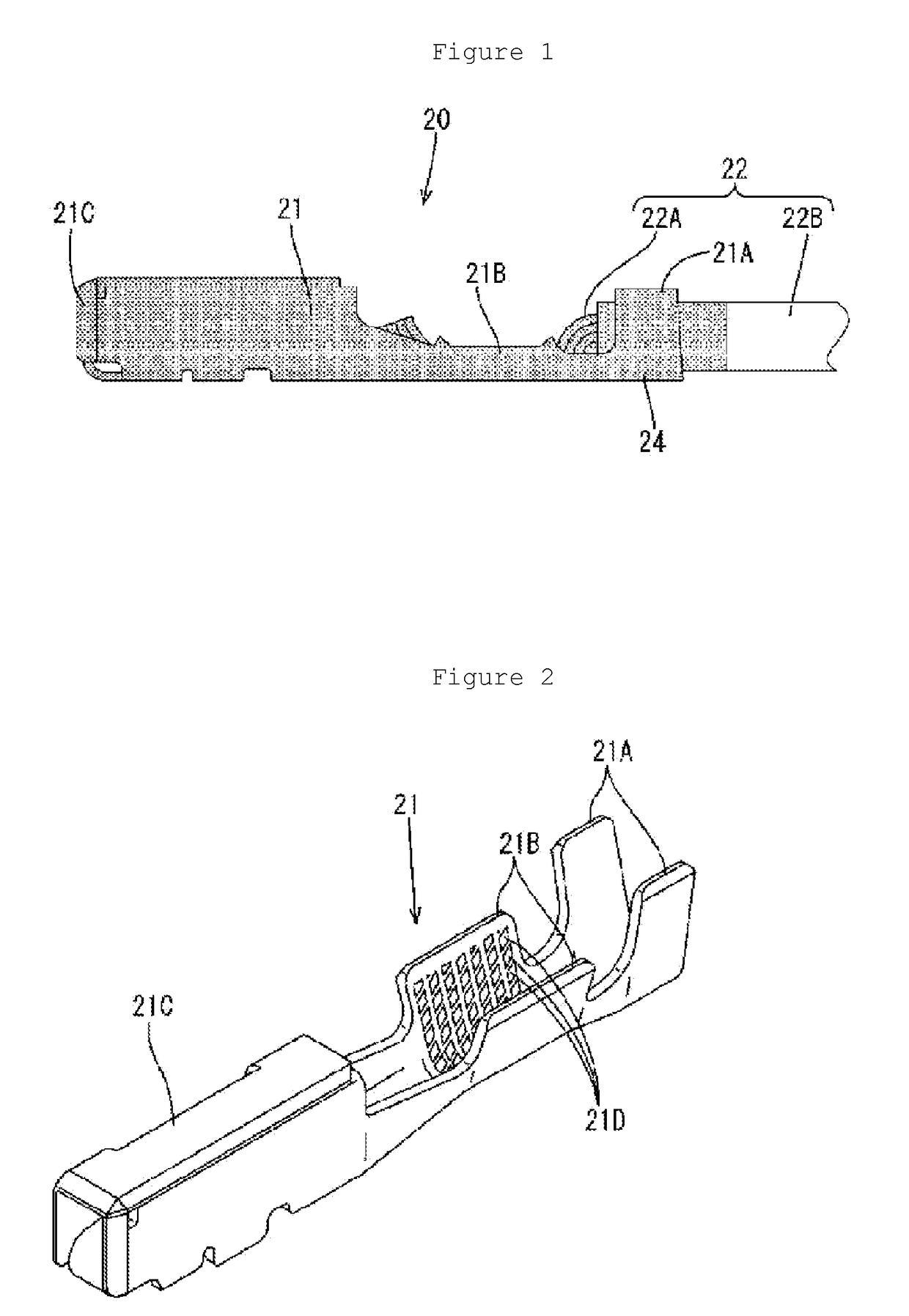
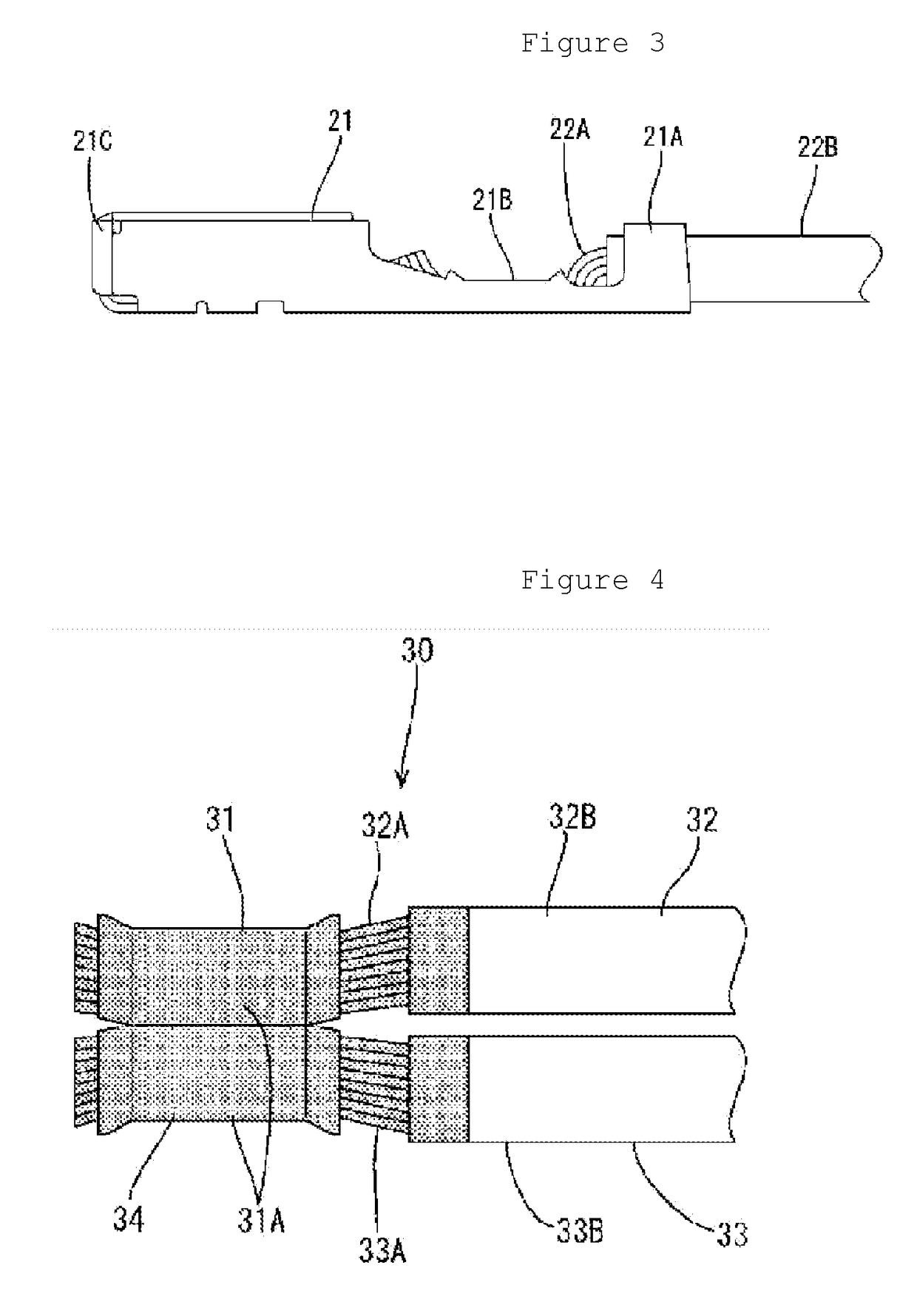
Terminal fitting
ActiveUS20140287635A1Inhibition resistanceSuppression resistanceCoupling contact membersElectric connection basesEngineeringSupport point
Owner:SUMITOMO WIRING SYST LTD
Seat belt retractor and seat belt apparatus including the same
InactiveUS20110140502A1Prevent gas pressureIncrease pressureBelt retractorsSafety beltsEnergy absorptionSeat belt
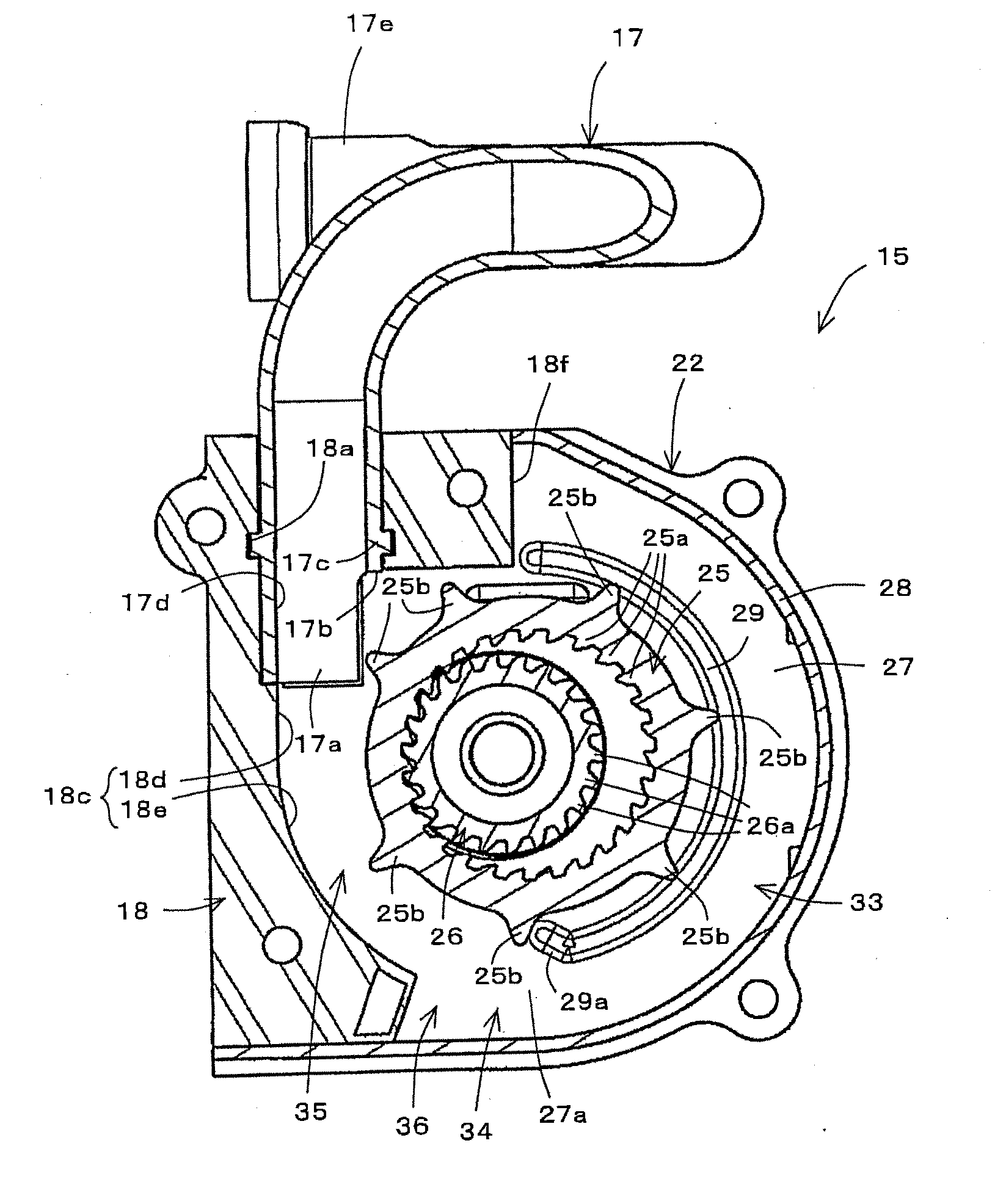
To effectively operate a pretensioner using a plurality of balls and an energy absorption mechanism, to simplify the structure of an exhaust passage in the pretensioner, and to facilitate the working process of the exhaust passage. A pretensioner 15 includes a plurality of balls 20 serving as force transmission members and a piston 21 in a pipe 17. A piston body 21a of the piston 21 includes a shaft portion 21c and a substantially hemispherical head portion 21d. The piston body 21a is provided with an exhaust hole 21e extending in the axial direction and exhaust grooves 21f communicating with the exhaust hole 21e that define an exhaust passage. The exhaust grooves 21f prevent the exhaust hole 21e from being closed even if the head portion 21d of the piston 21 contacts the ball 20. Since the exhaust hole 21e and the exhaust grooves 21f are simply provided in the piston body 21a formed as a single member, the structure of the exhaust passage is simple, and working of the exhaust passage is easy.
Owner:JOYSON SAFETY SYST JAPAN KK
Semiconductor device comprising photoelectric conversion element and high-potential and low-potential electrodes
InactiveUS7791012B2Reduce sensitivitySuppression resistanceTransistorTelevision system detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceAudio power amplifier
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
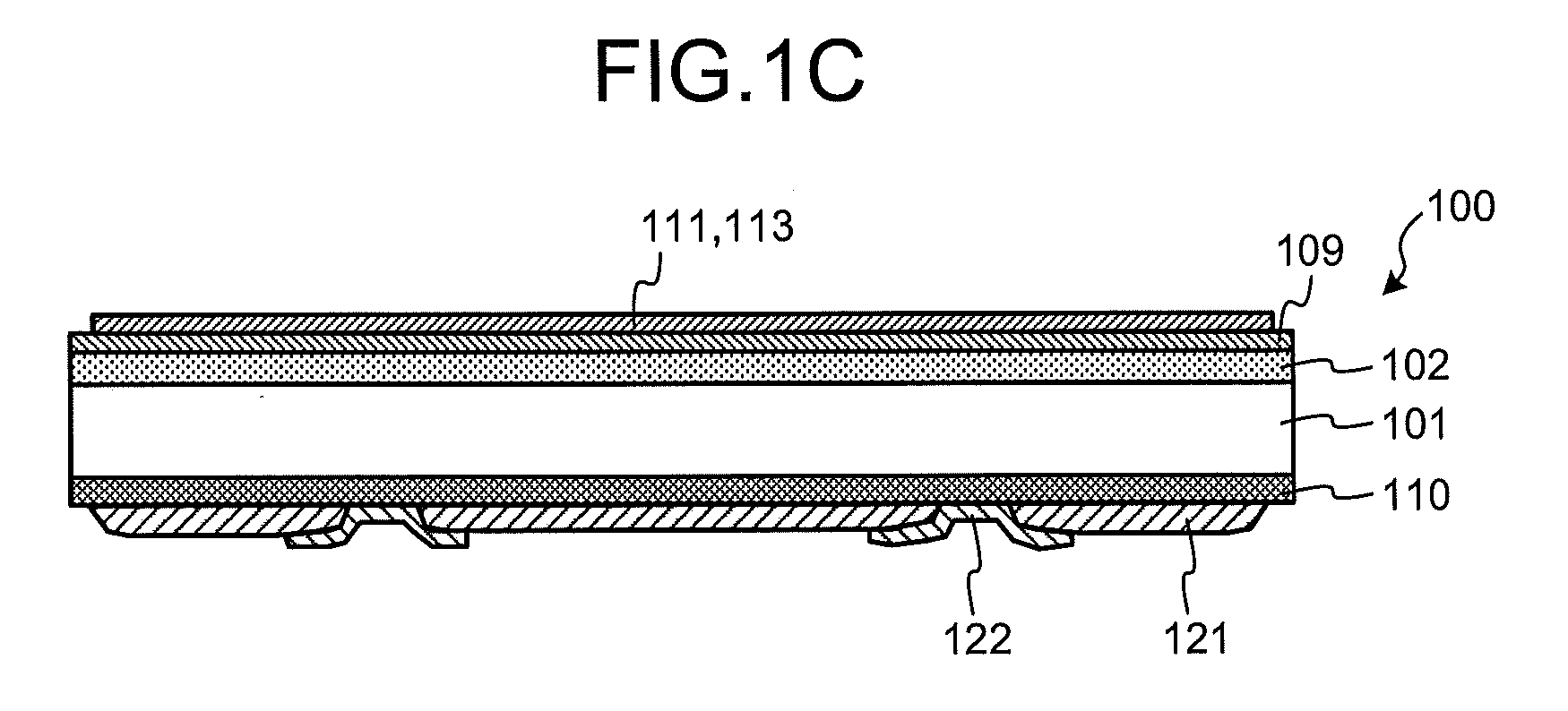
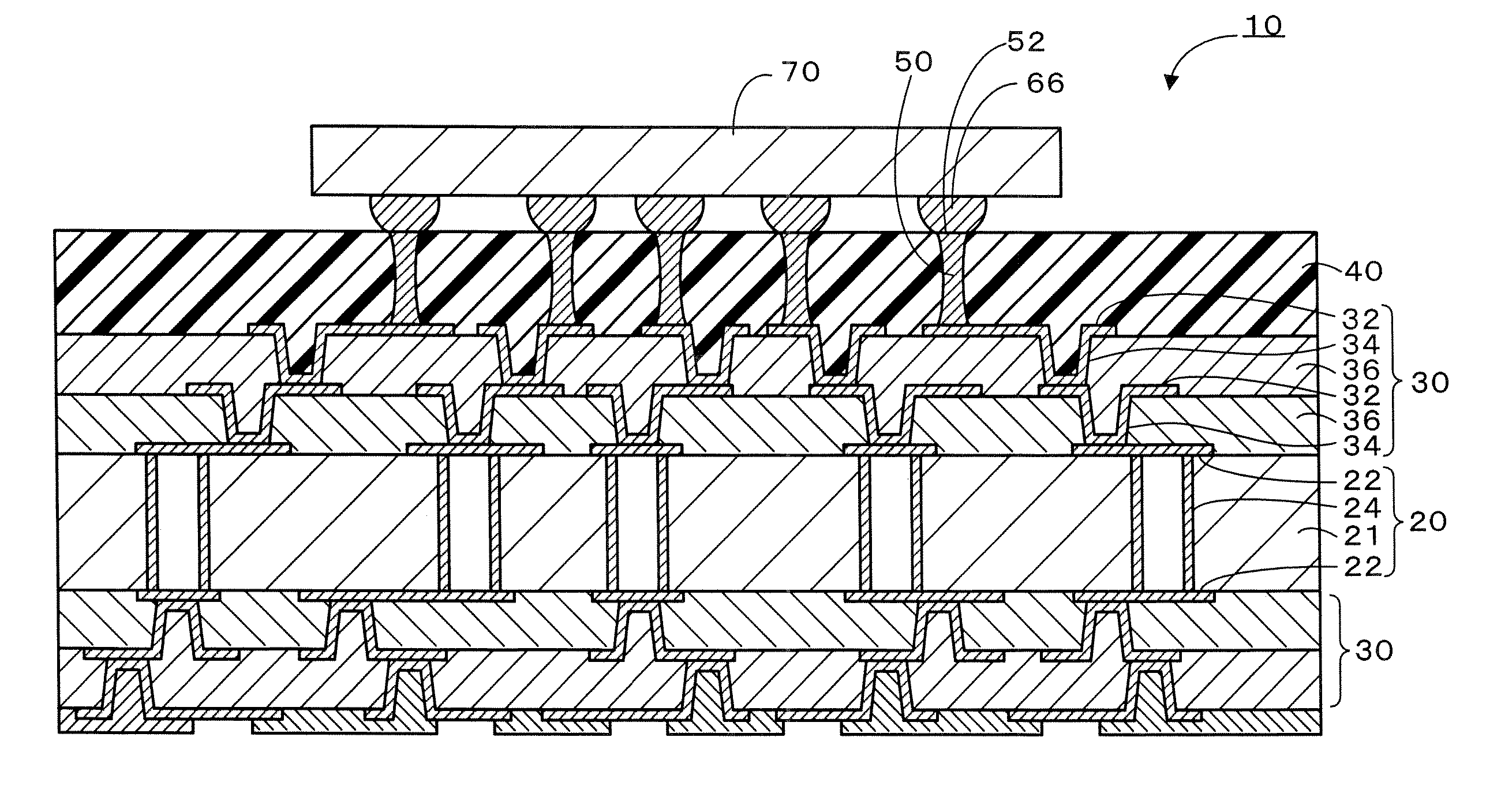
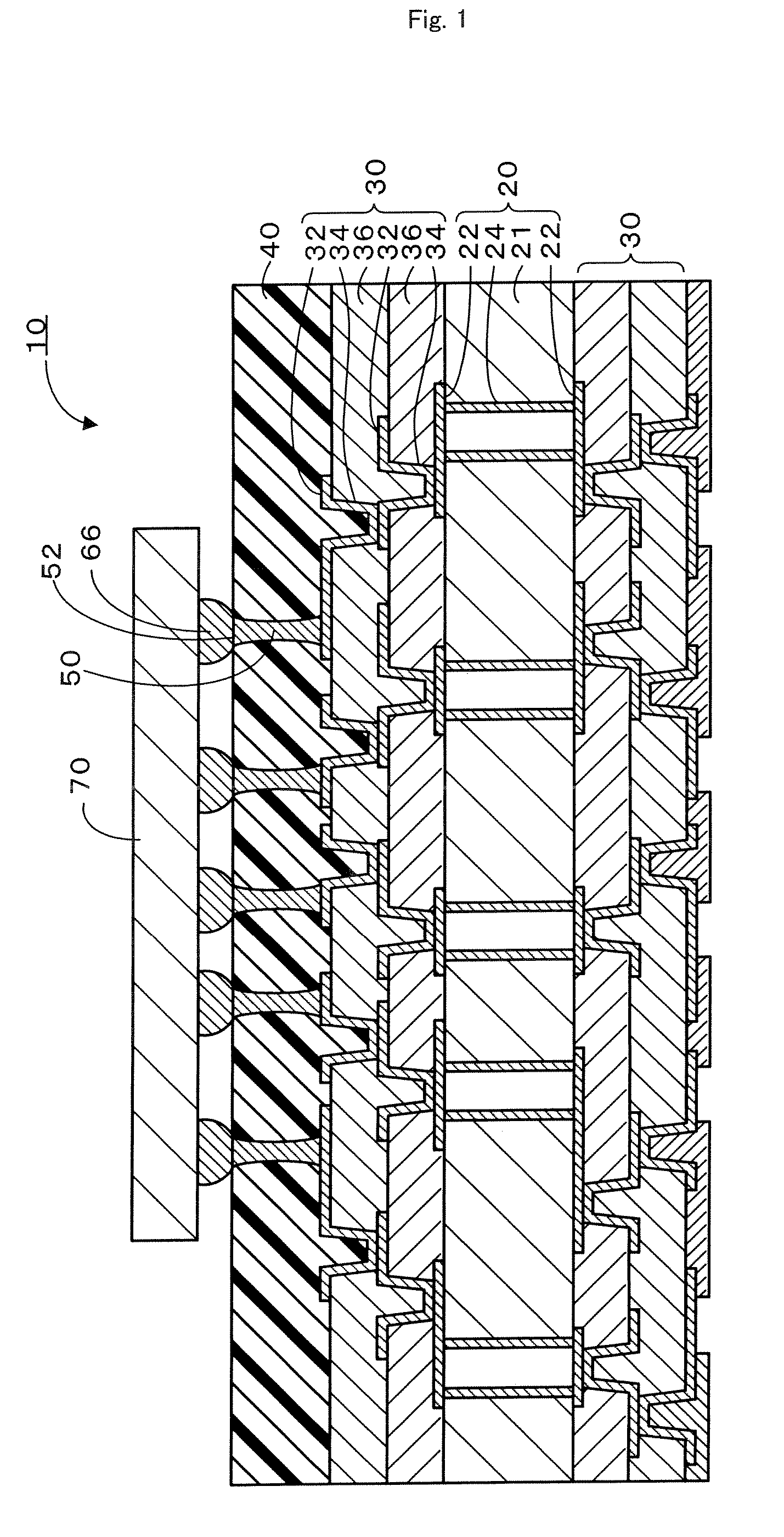
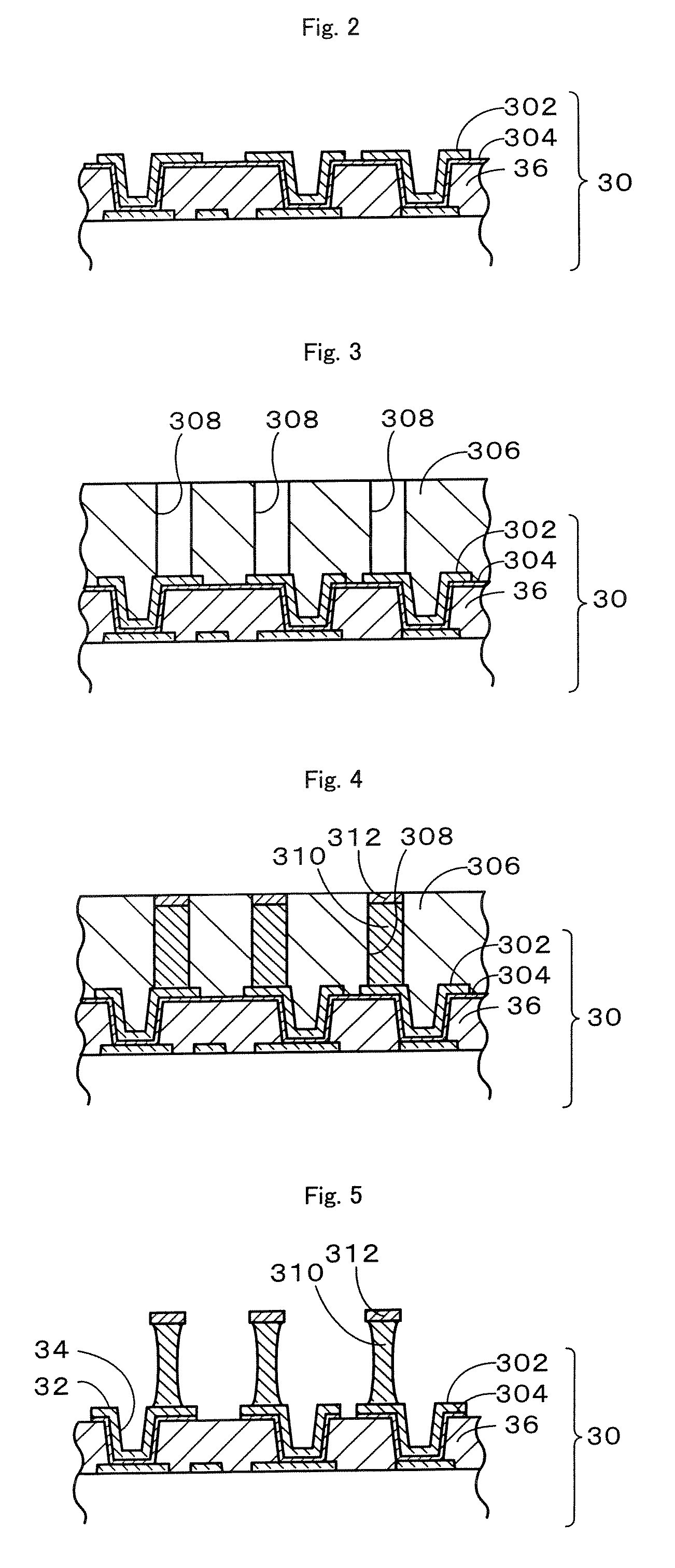
Multilayer printed wiring board
ActiveUS20070085203A1Suppression pressure dropAvoid failureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCross-linkElectrical conductor
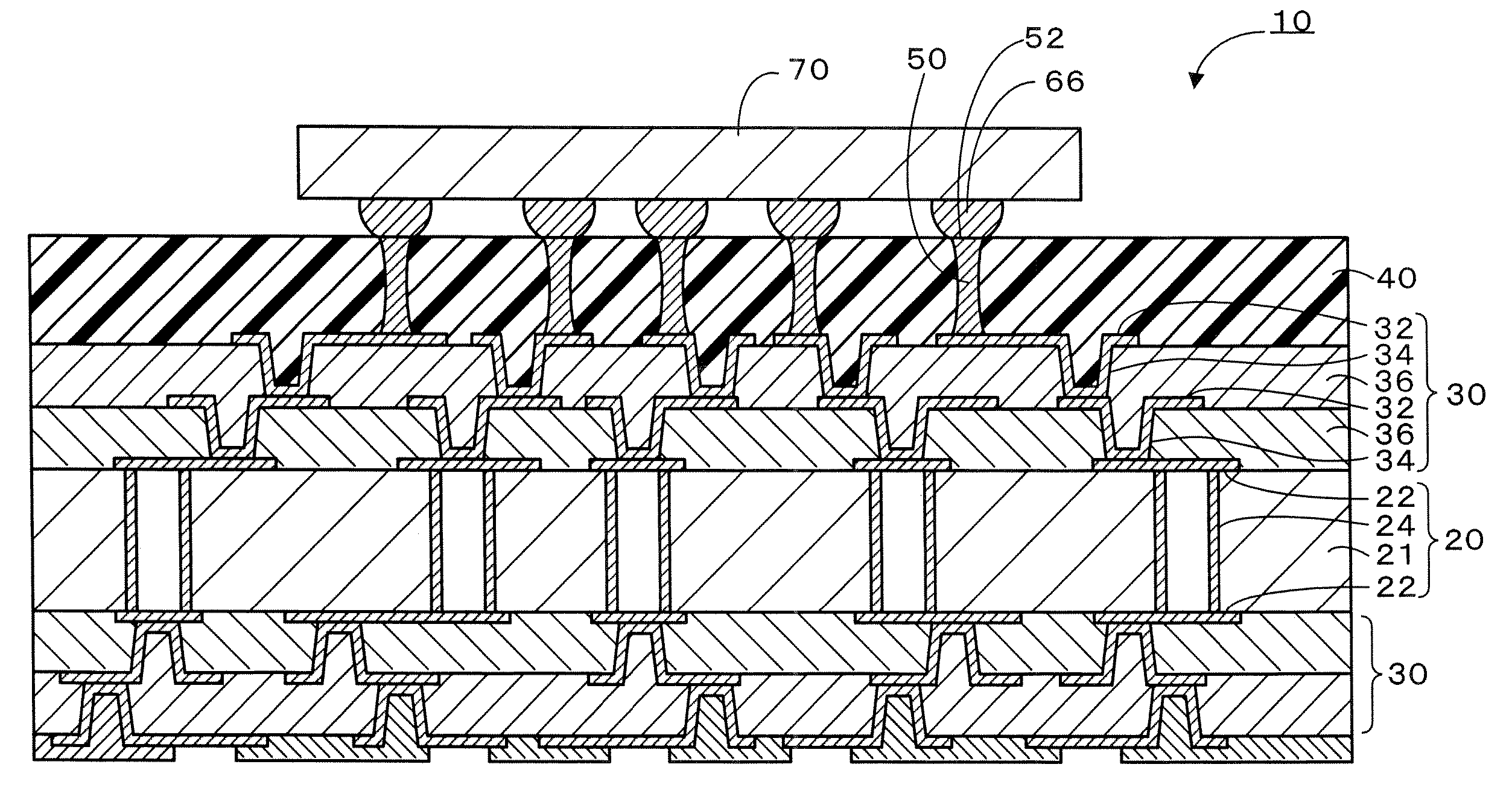
A multilayer printed wiring board is equipped with a core board 20, a build-up layer 30 formed on the core board 20 so as to have a conductor pattern 32 on the upper surface thereof, a low-elasticity layer 40 formed on the build-up layer 30, lands 52 that are provided on the upper surface of the low-elasticity layer 40 and connected to an IC chip 70 via solder bumps 66, and conductor posts 50 that penetrate through the low-elasticity layer 40 and electrically connect the lands 52 to the conductor pattern 32. The low-elasticity layer 40 is formed of resin composition containing epoxy resin, phenol resin, cross-linked rubber particles and a hardening catalyst.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD +1
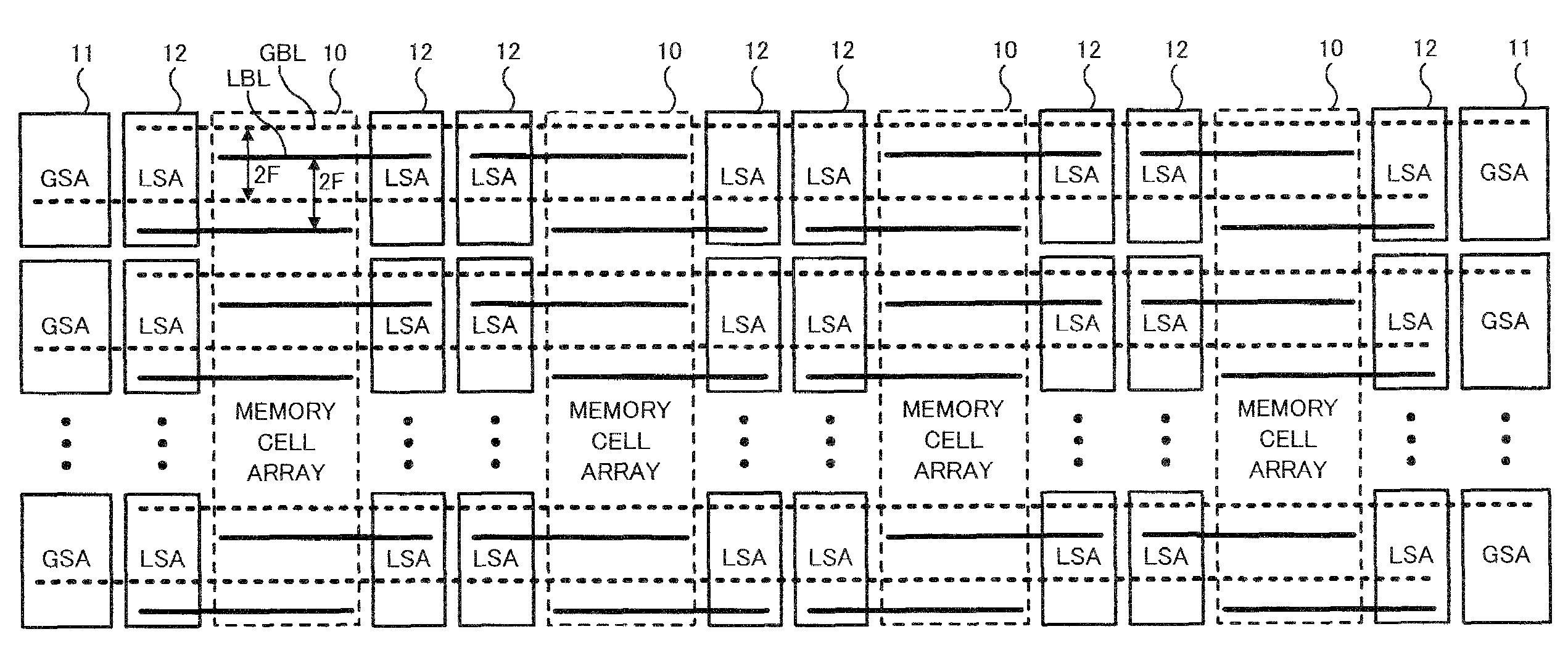
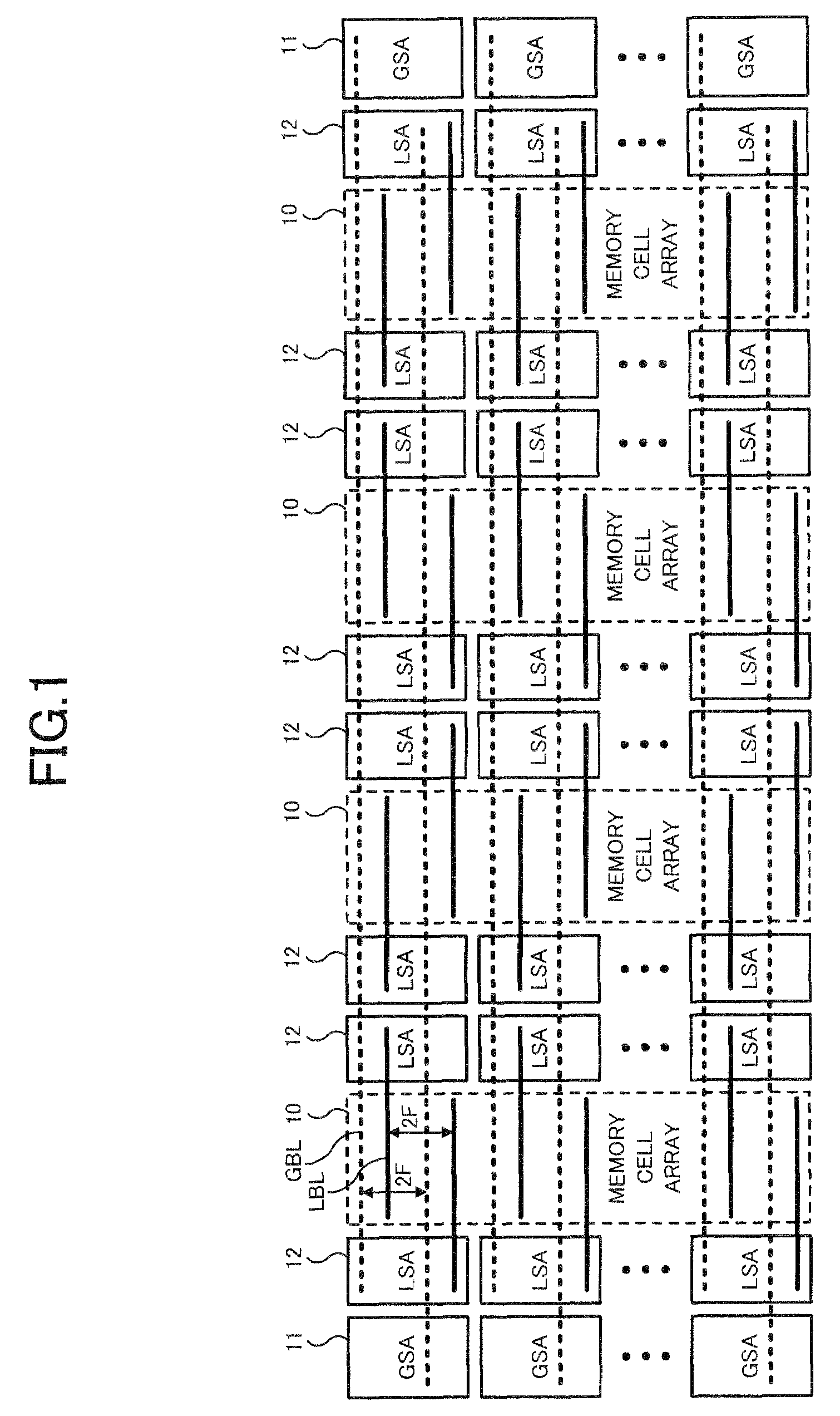
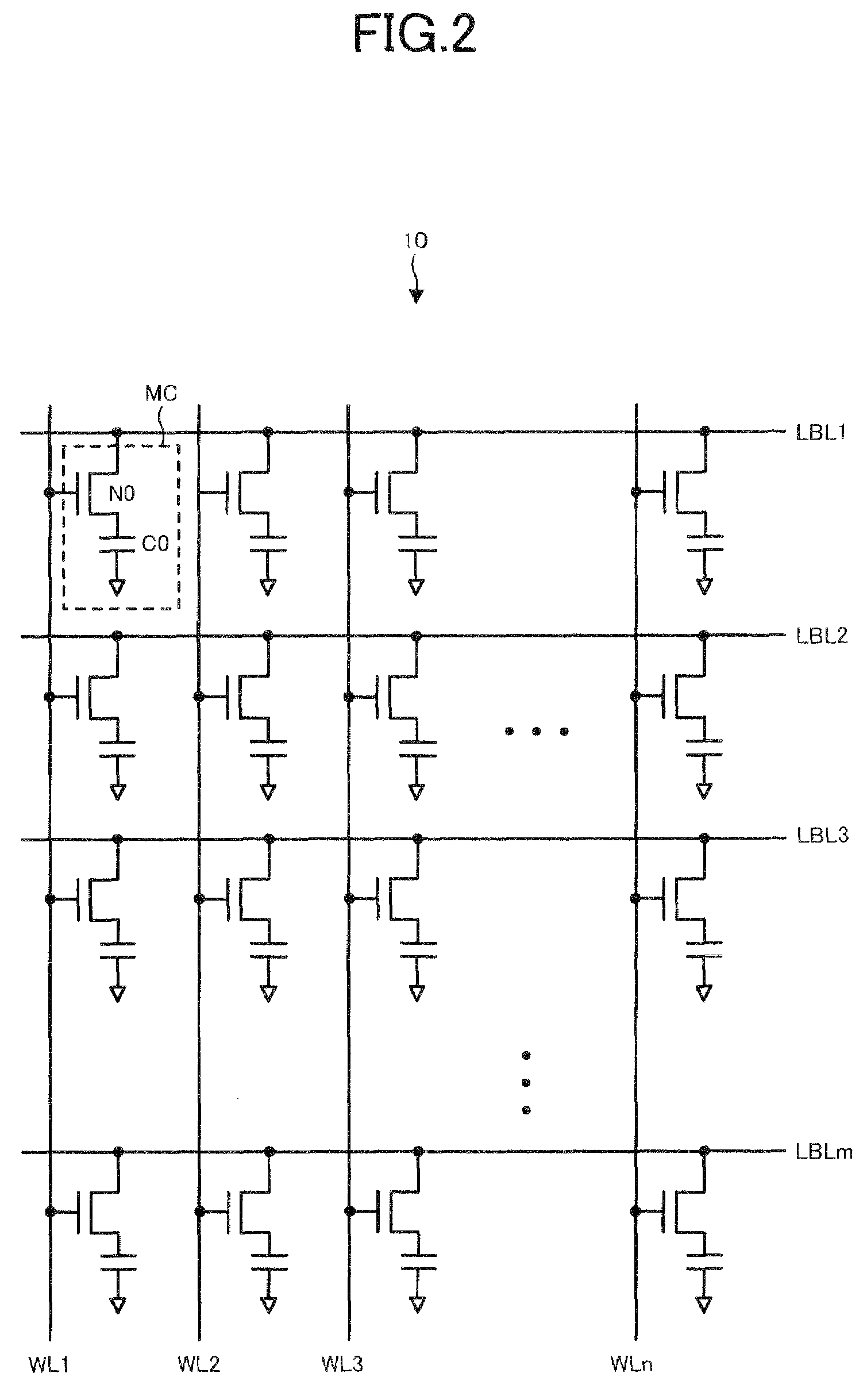
Semiconductor memory device
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
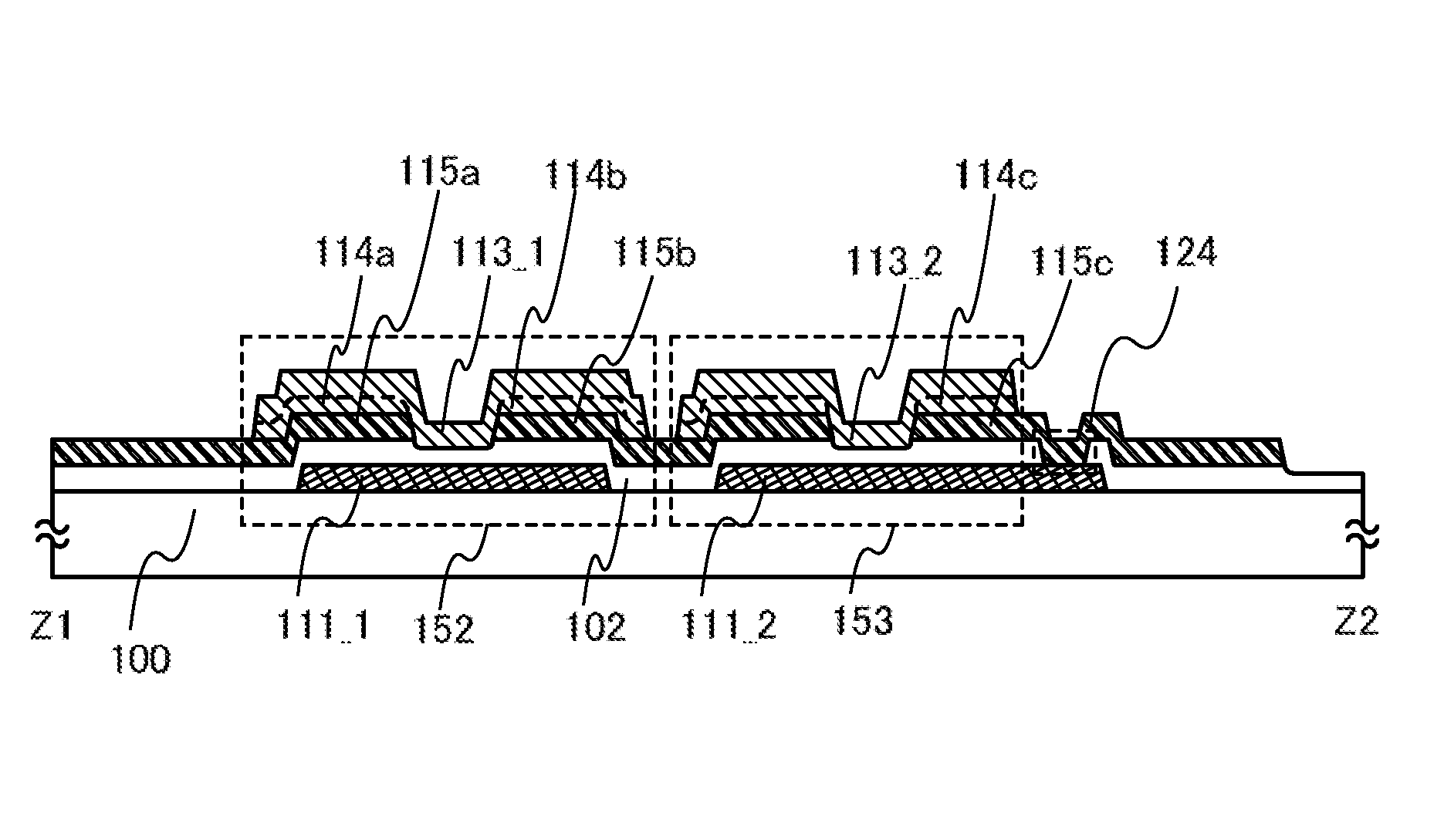
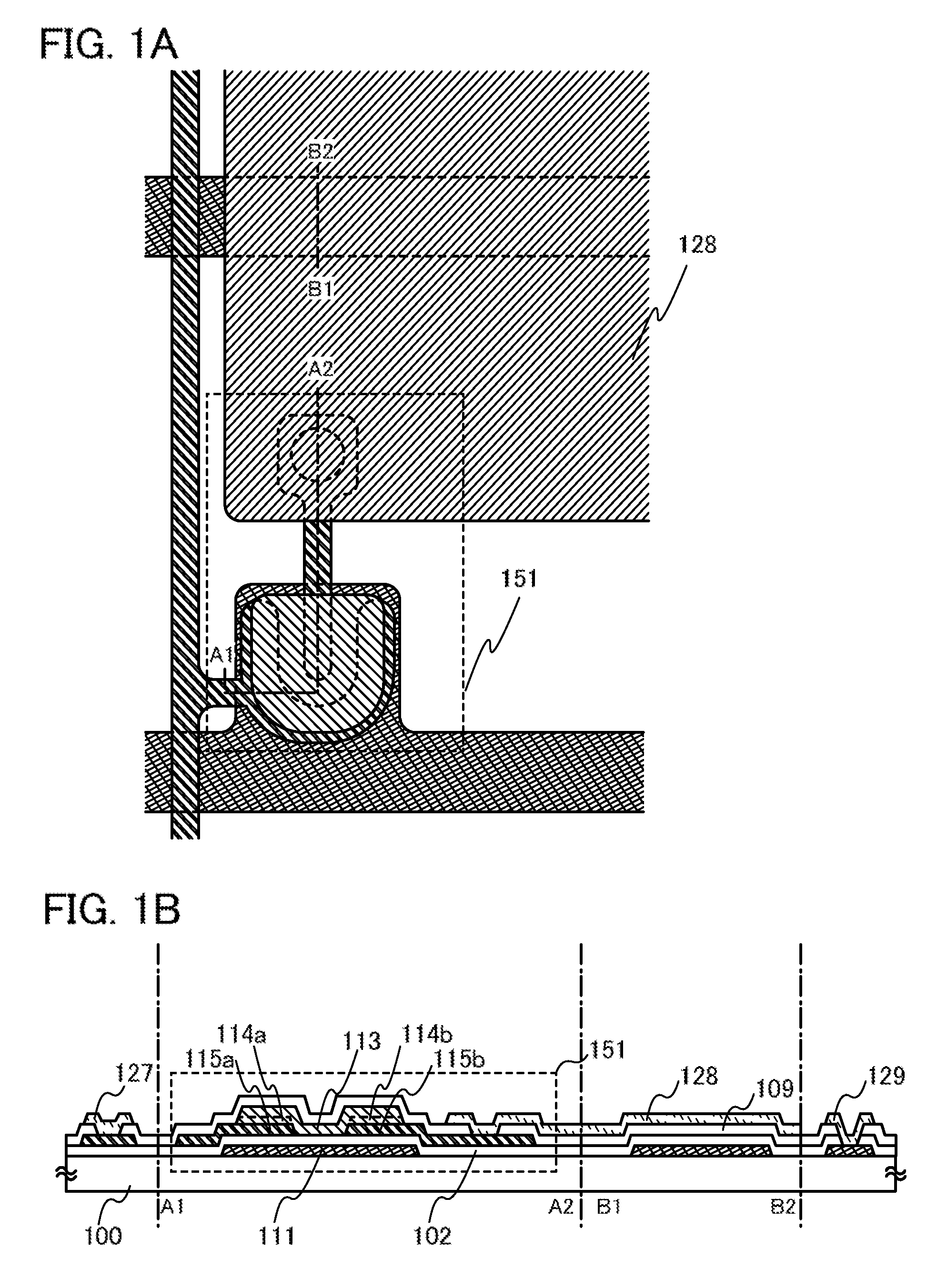
Light-emitting device and electronic apparatus
ActiveUS7855387B2Suppression resistanceSimple manufacturing processTransistorStatic indicating devicesEngineeringLight emitting device
A light-emitting device includes a drive transistor that controls a current to be supplied to a light-emitting element from a power supply line, an electrical continuity portion that electrically connects the drive transistor with the light-emitting element, an initializing transistor that is turned ON to diode-connect the drive transistor, and a connecting portion that electrically connects the drive transistor with the initializing transistor. The power supply line includes a first portion extending in a predetermined direction. The electrical continuity portion and the connecting portion are formed from the same layer as that of the power supply line and are located on one side along the width of the first portion across the drive transistor.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
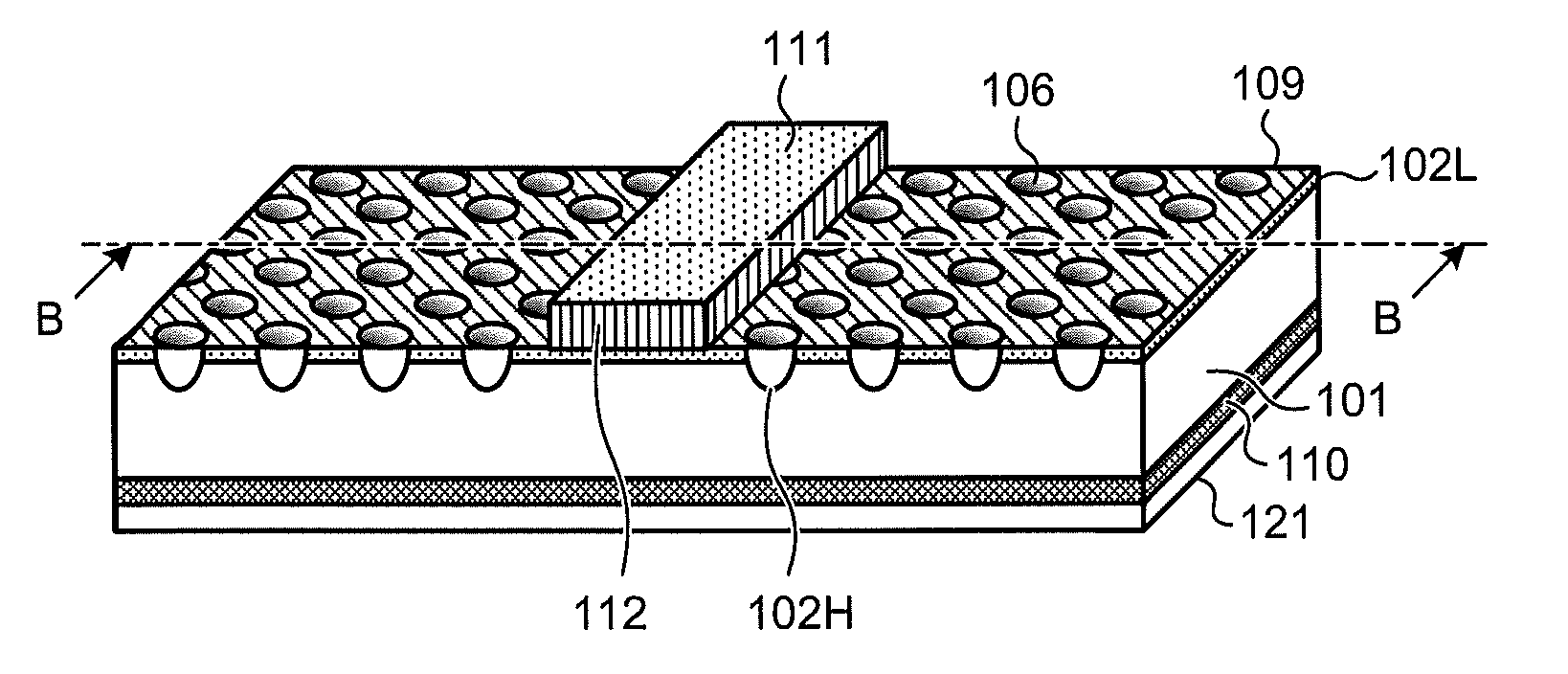
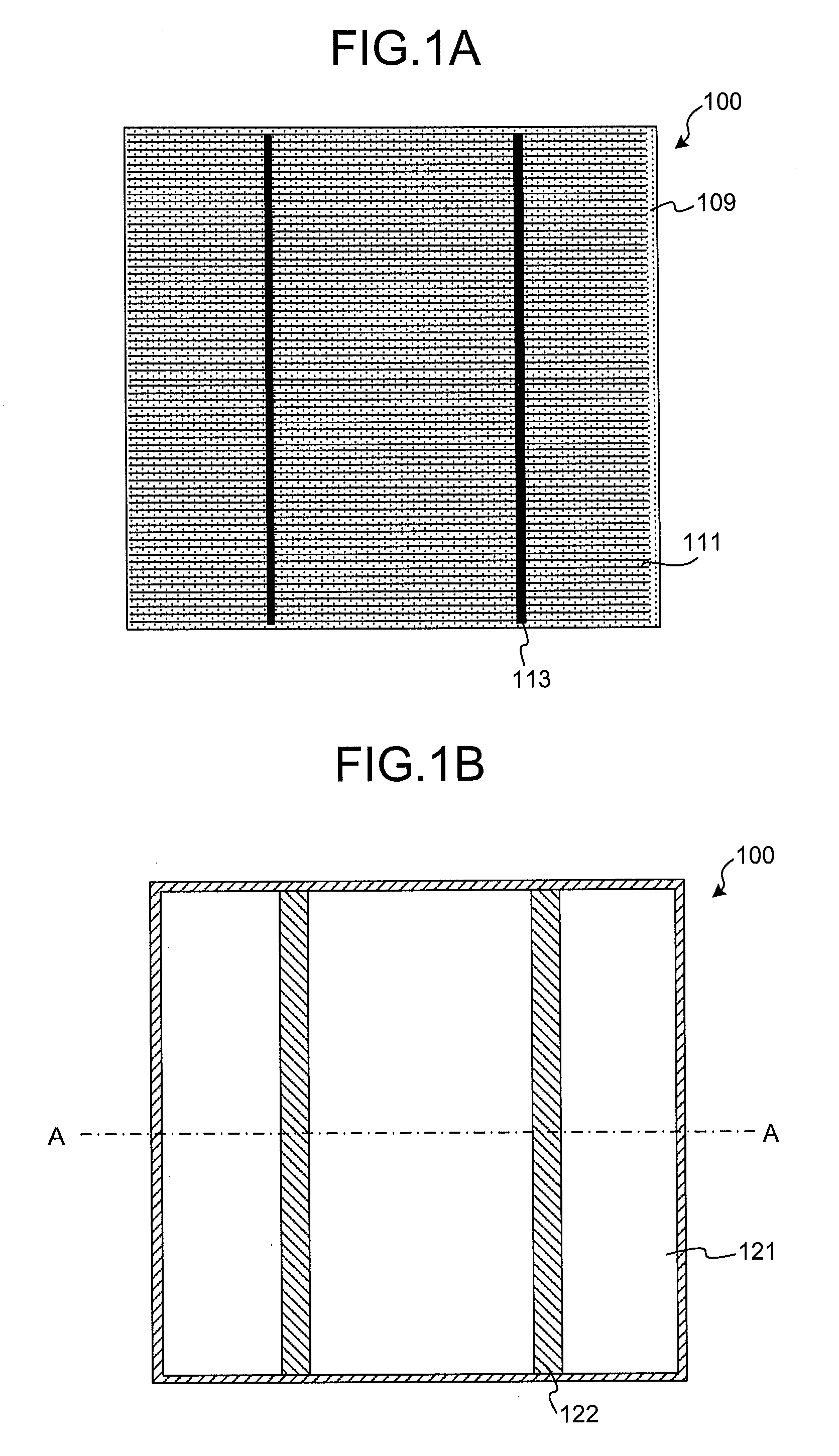
Gas discharge panel
InactiveUS6873103B2Improve the display effectImprove efficiencySustain/scan electrodesAlternating current plasma display panelsGas-discharge lampEngineering
A gas discharge panel having plural pairs of display electrodes disposed so as to extend through a plurality of cells, each pair being formed from a sustain electrode and a scan electrode. The sustain and scan electrodes each include a plurality of line parts, and an aggregate width of the line parts included in the sustain and scan electrodes is in a range of 22% to 48% inclusive of pixel pitch.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Photovoltaic power device and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20110036402A1Lower resistanceReduce reflectivityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHigh resistanceEngineering
A photovoltaic power device includes a P-type silicon substrate, a low-resistance N-type diffusion layer diffused with an N-type impurity in a first concentration formed at a light-incidence surface side, grid electrodes formed on the low-resistance N-type diffusion layer, a P+ layer formed on a back surface, and a back surface electrode formed on the P+ layer. The photovoltaic power device has concave portions provided at a predetermined interval to reach the silicon substrate from an upper surface of the low-resistance N-type diffusion layer, and an upper surface of a region between adjacent concave portions includes the low-resistance N-type diffusion layer. A high-resistance N-type diffusion layer diffused with an N-type impurity in a second concentration, which is lower than the first concentration, is formed in a range of a predetermined depth from a formation surface of the concave portions.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Multilayer printed wiring board
ActiveUS7495332B2Avoid separationAvoid failureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPrinted circuits stress/warp reductionCross-linkEpoxy
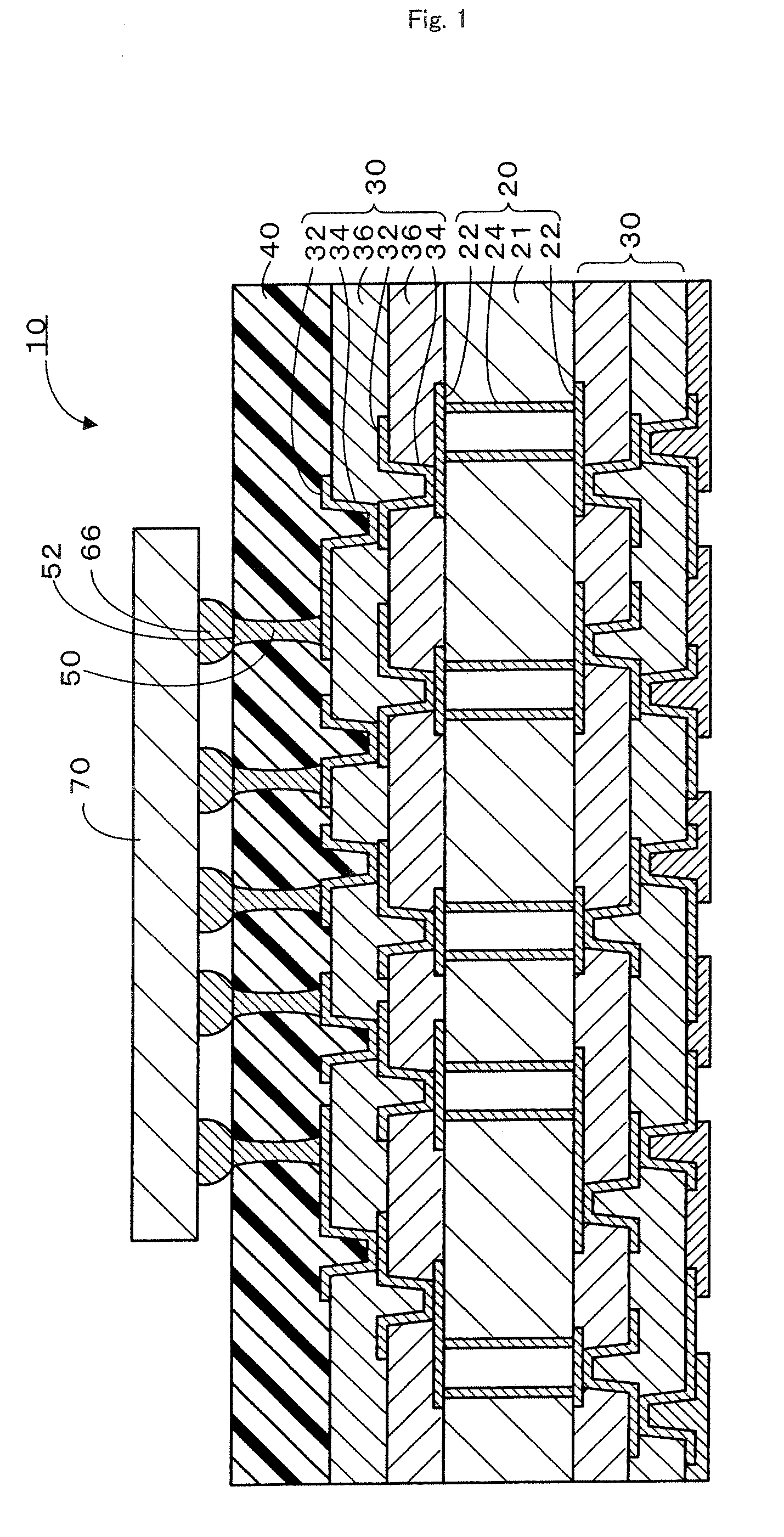
A multilayer printed wiring board is equipped with a core board 20, a build-up layer 30 formed on the core board 20 so as to have a conductor pattern 32 on the upper surface thereof, a low-elasticity layer 40 formed on the build-up layer 30, lands 52 that are provided on the upper surface of the low-elasticity layer 40 and connected to an IC chip 70 via solder bumps 66, and conductor posts 50 that penetrate through the low-elasticity layer 40 and electrically connect the lands 52 to the conductor pattern 32. The low-elasticity layer 40 is formed of resin composition containing epoxy resin, phenol resin, cross-linked rubber particles and a hardening catalyst.
Owner:IBIDEN CO LTD +1
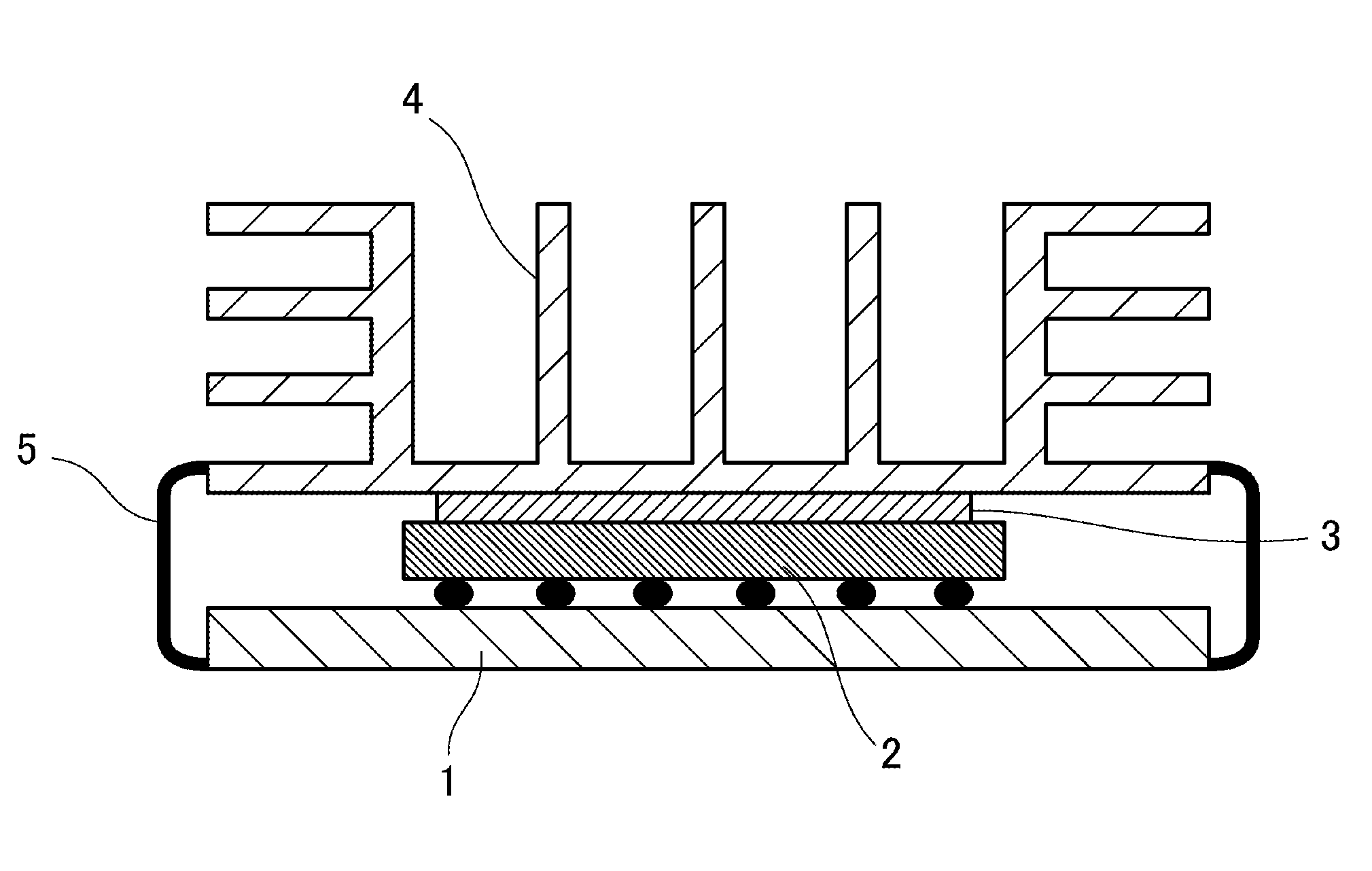
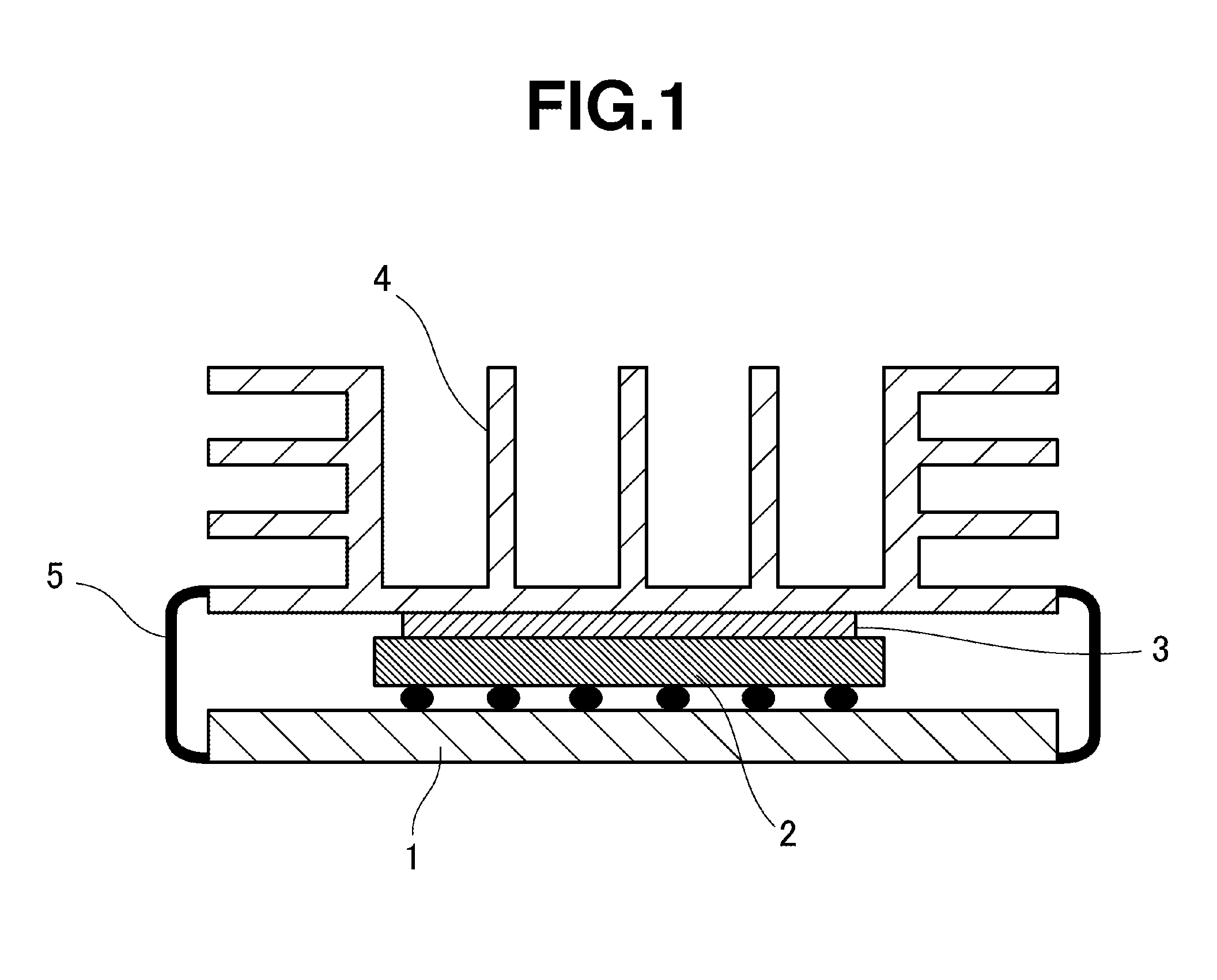
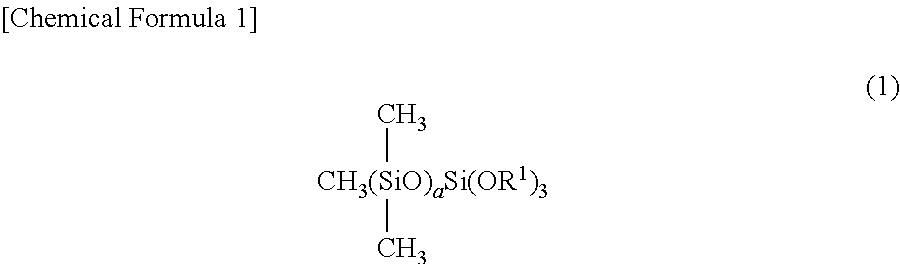
Heat conductive silicone composition, heat conductive layer, and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20150357261A1Avoid thermal resistanceSuppression resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPtru catalystDevice material
Provided is a heat conductive silicone composition disposed between a heat generating electronic component and a member for dispersing heat, wherein the heat conductive silicone composition contains (A) an organopolysiloxane having at least two alkenyl groups in one molecule and having a dynamic viscosity at 25° C. of 10 to 100,000 mm2 / s, (B) a hydrolyzable dimethylpolysiloxane having three functional groups at one end expressed by formula (1), (C) a heat conductive filler having a heat conductivity of 10 W / m° C. or higher, (D) an organohydrogenpolysiloxane expressed by formula (2), (E) an organohydrogenpolysiloxane containing a hydrogen directly bonded to at least two silicon atoms in one molecule other than component (D), and (F) a catalyst selected from the group consisting of platinum and platinum compounds. The heat conductive silicone composition provides a cured object having a storage modulus, loss modulus, and coefficient of loss within appropriate ranges; peeling and pump out during heating / cooling cycle tending not to occur, and increases in thermal resistance being suppressed.
Owner:SHIN ETSU CHEM IND CO LTD
Surface Protective Agent Composition, Electric Connection Structure Using Same, and Method for Manufacturing Electric Connection Structure
InactiveUS20170117650A1Avoid corrosionImprove metal resistanceLine/current collector detailsCoupling contact membersElectricityBase oil
To provide a surface protective agent composition that suppresses corrosion of members of different kinds of metals close to each other due to corrosion current between the metals of the members, and to provide an electric connection structure and a method for producing an electric connection structure using the same. The surface protective agent composition contains (a) a lubricant base oil; (b) a prescribed amount of at least one compound selected from the group consisting of particular phosphorus compounds and a metal salt or an amine salt thereof; and (c) a prescribed amount of an amide compound, and in the case where the component (b) does not contain the metal salt of the phosphorus compound, the surface protective agent composition further contains (d) a prescribed amount of a salicylate of a particular metal and / or a basic (or perbasic) salt thereof, and the electric connection structure containing a surface protective layer consisting of the surface protective agent composition.
Owner:JX NIPPON OIL & ENERGY CORP +4
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com