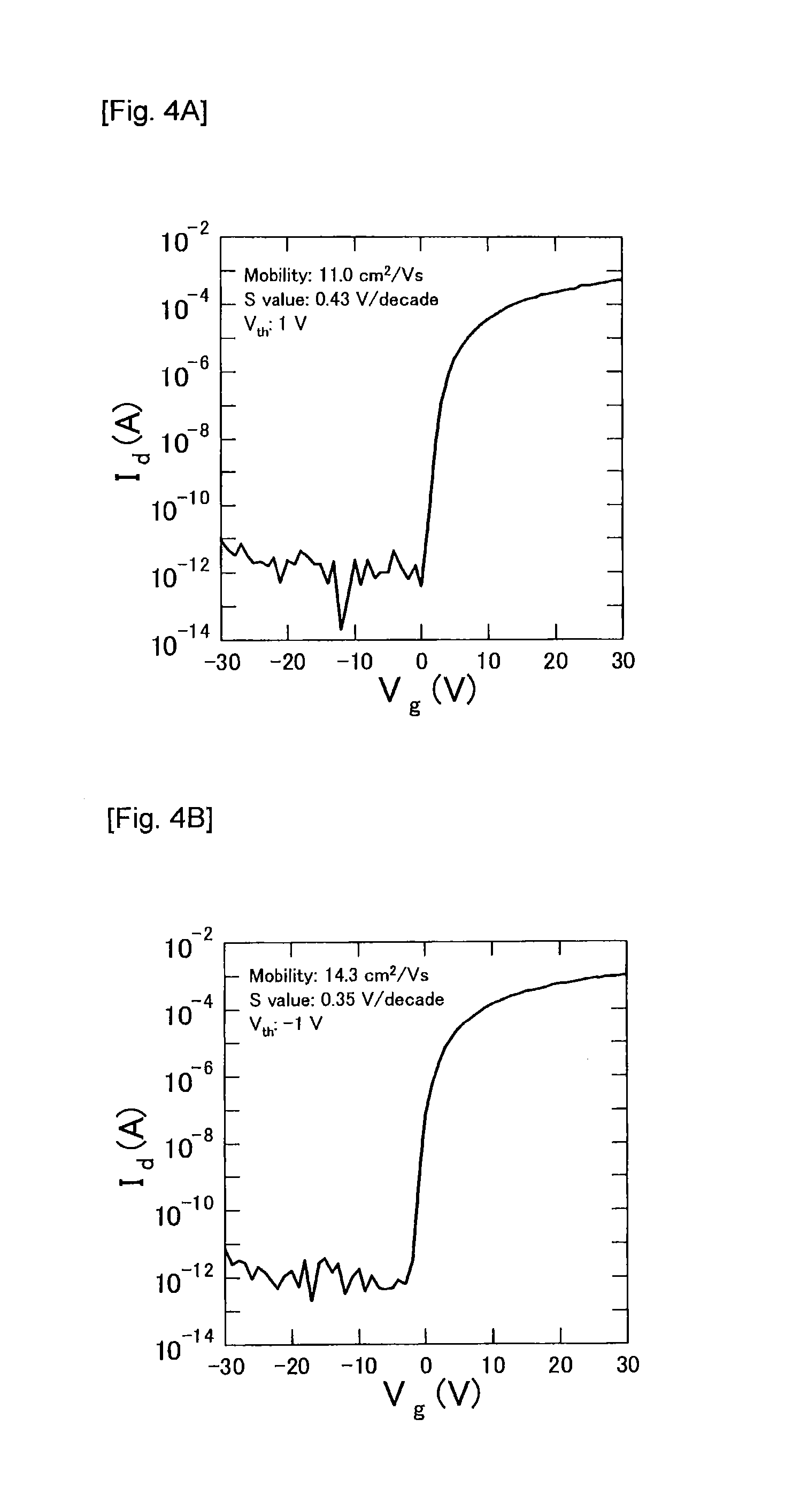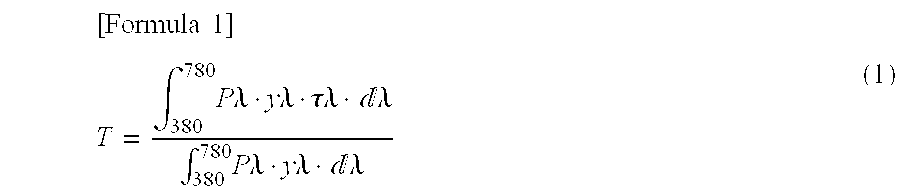Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
452results about How to "Small variation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
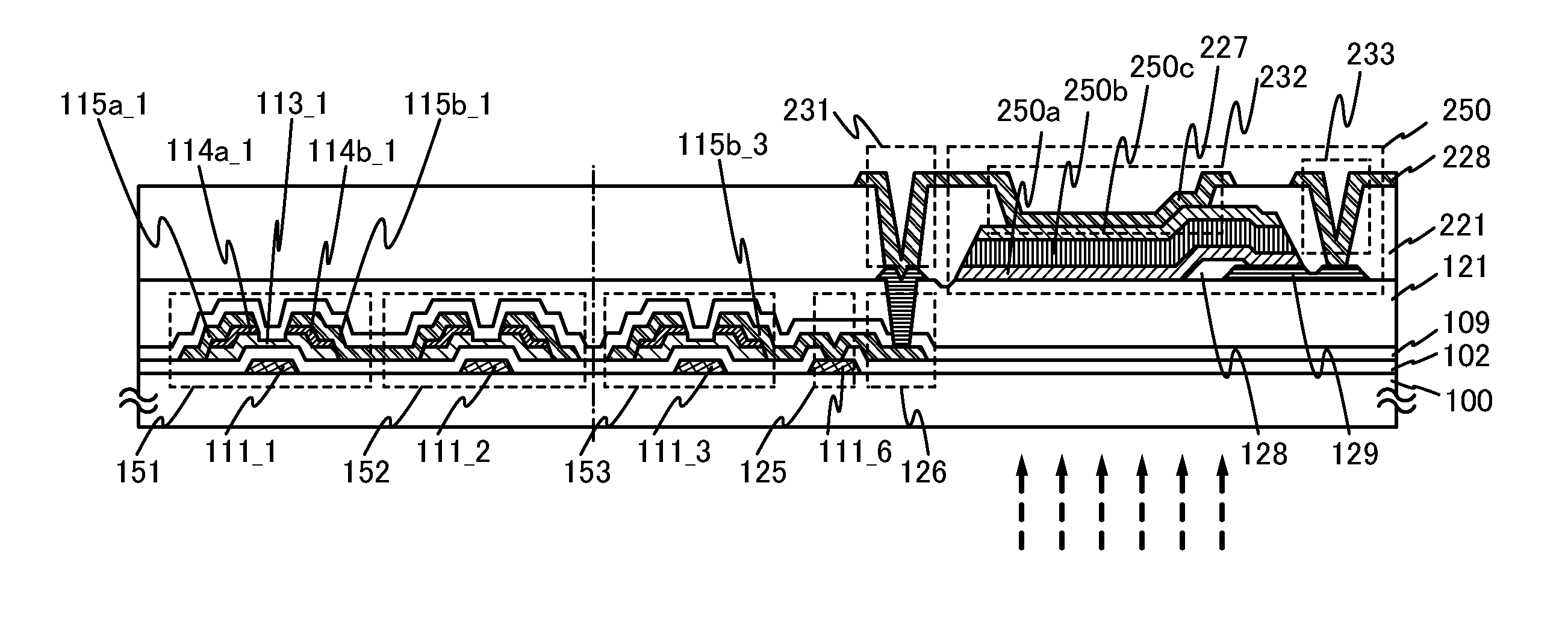
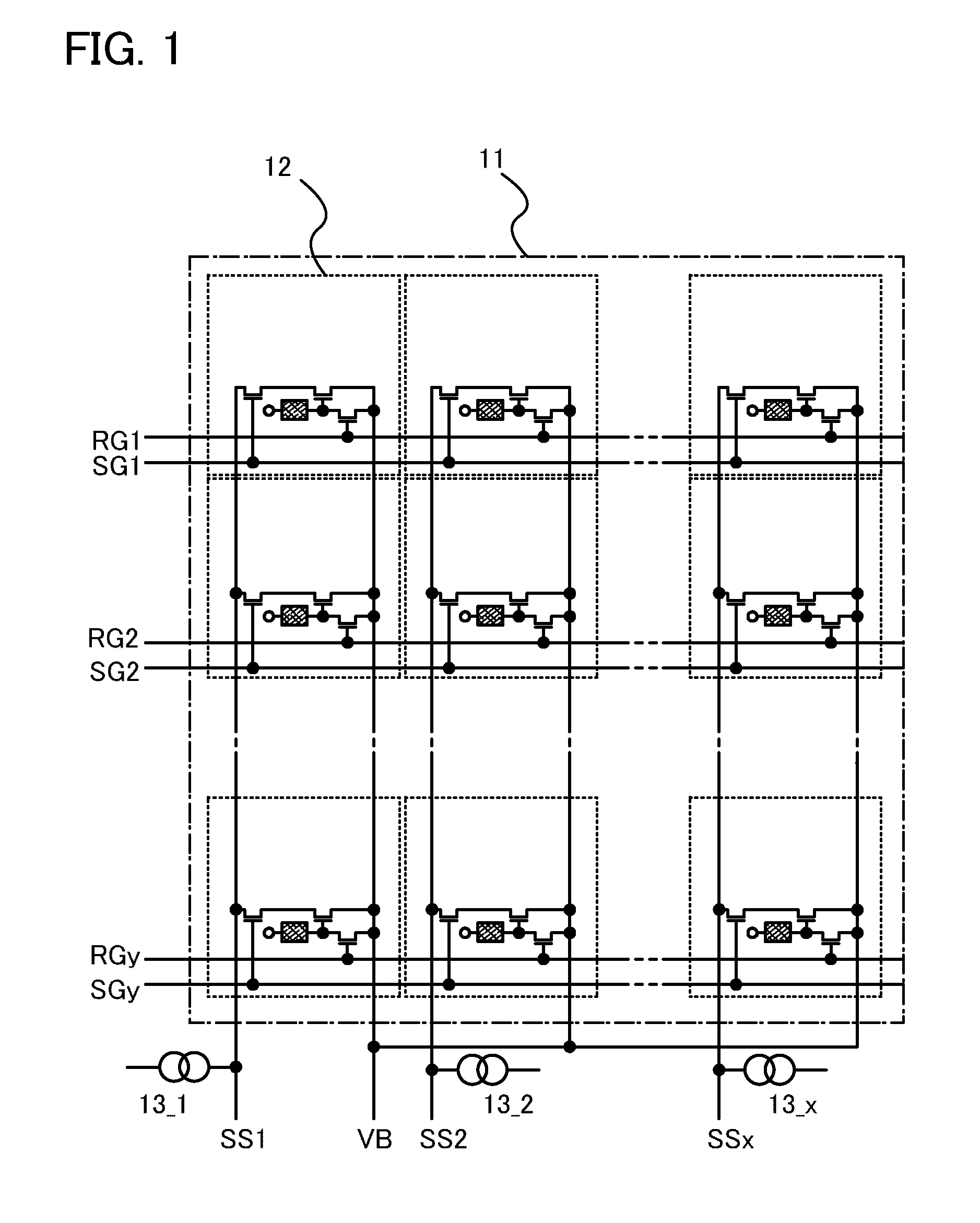
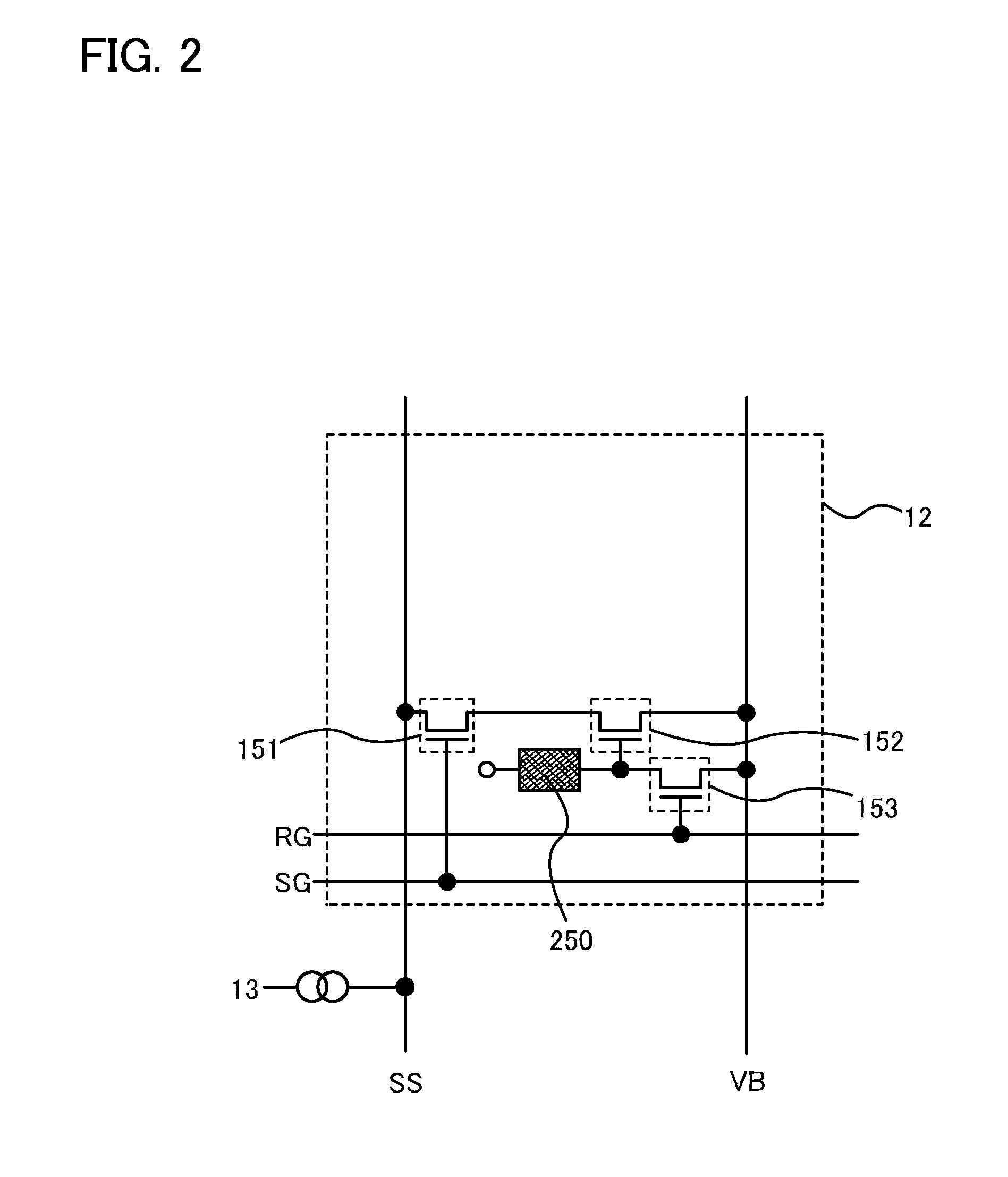
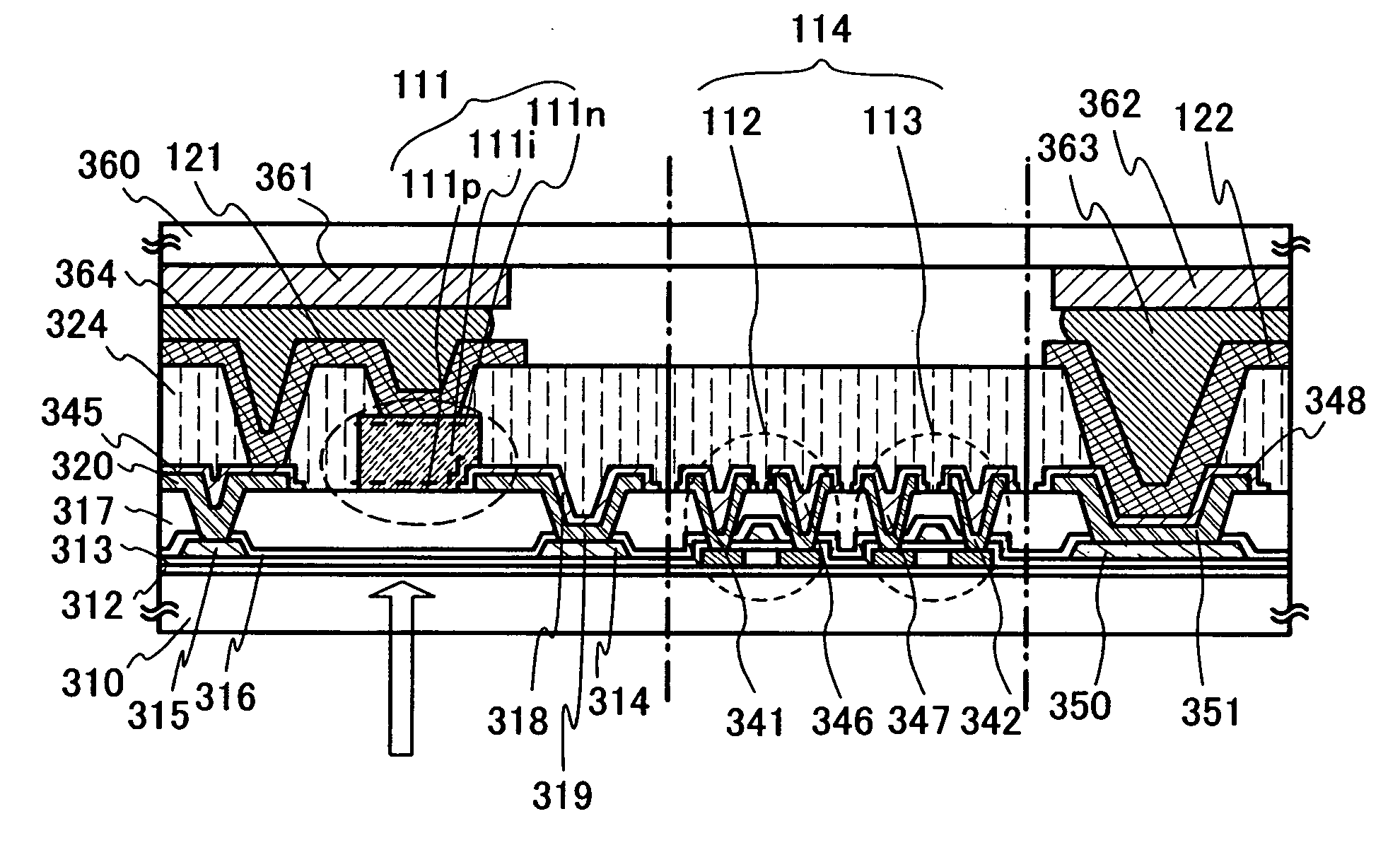
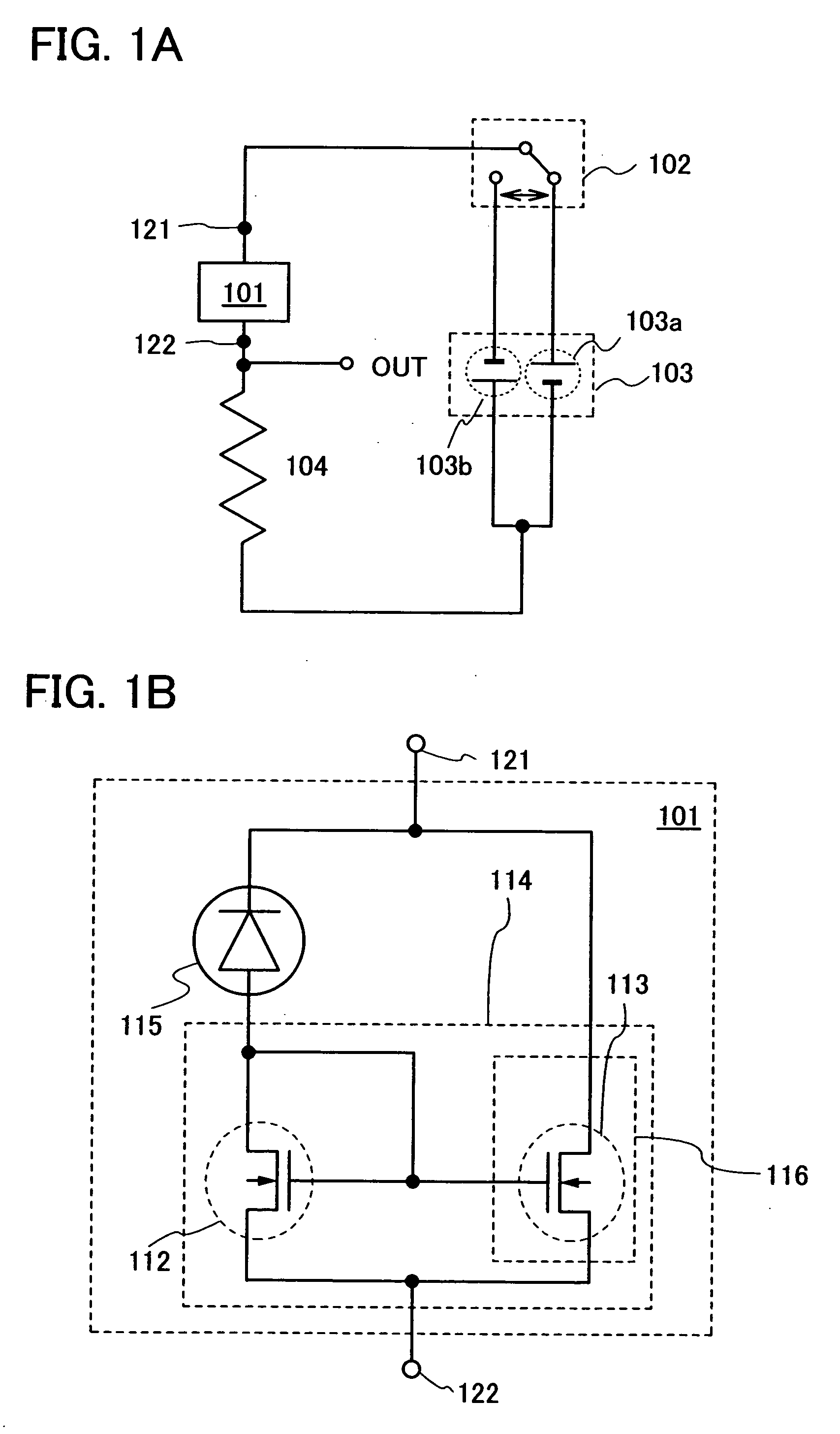
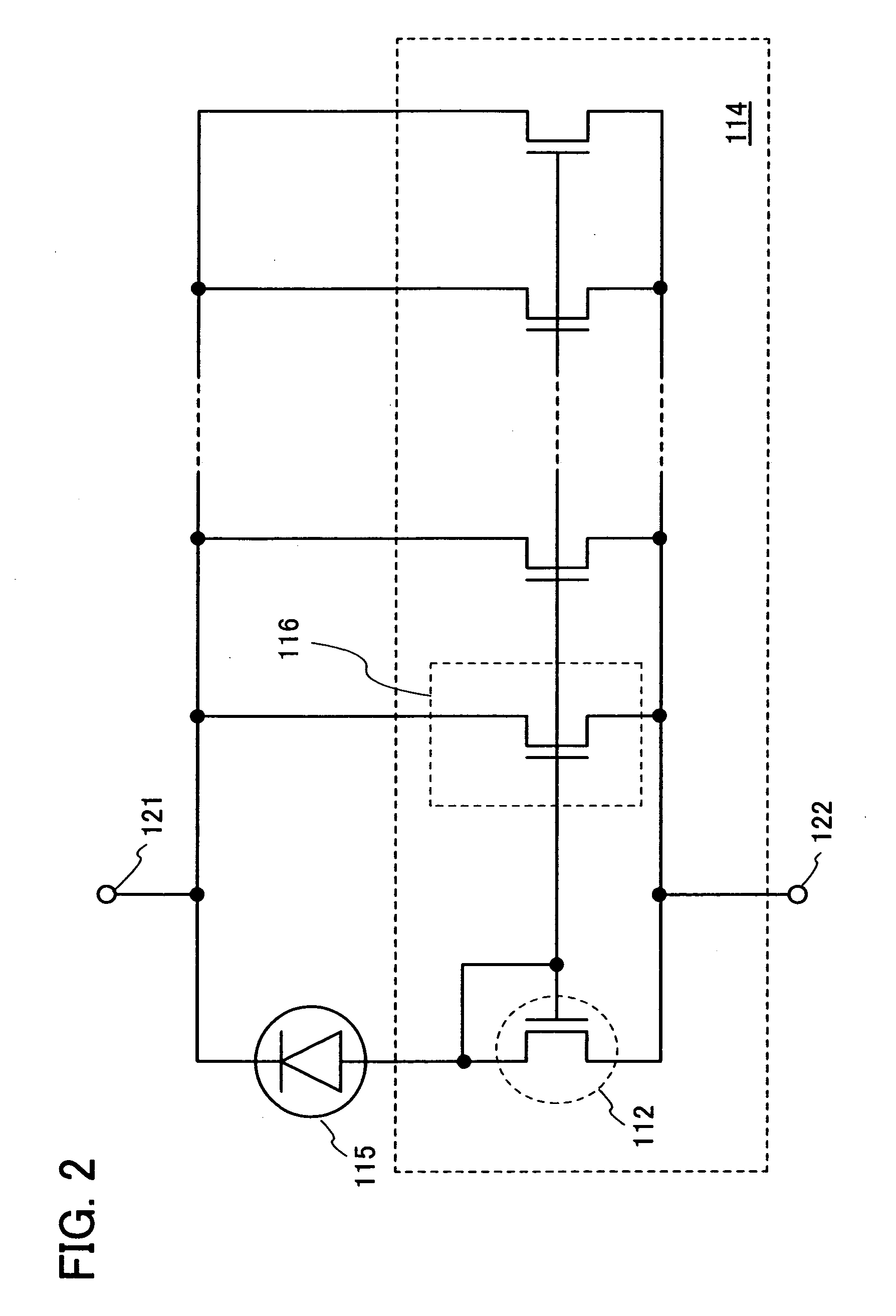
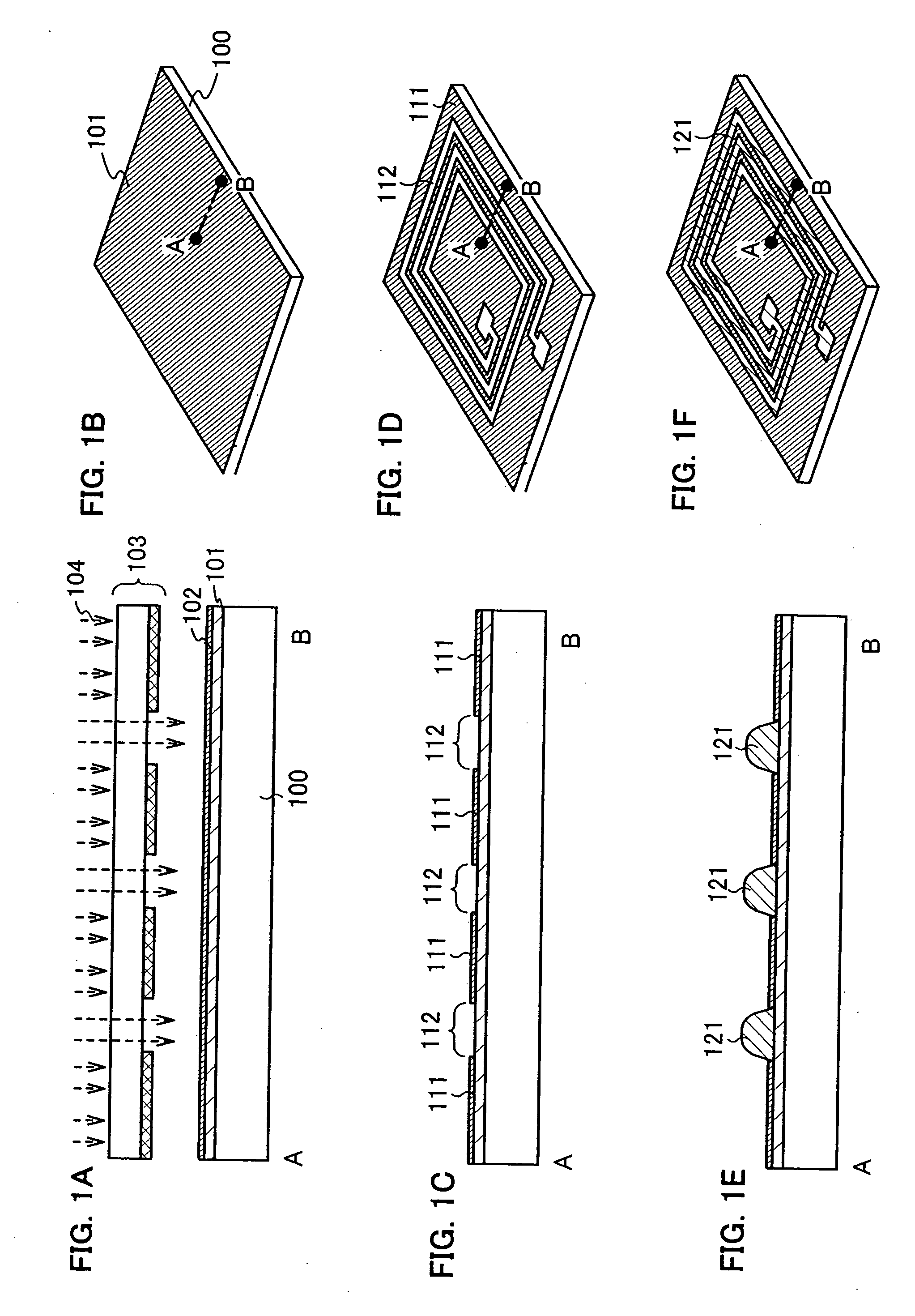
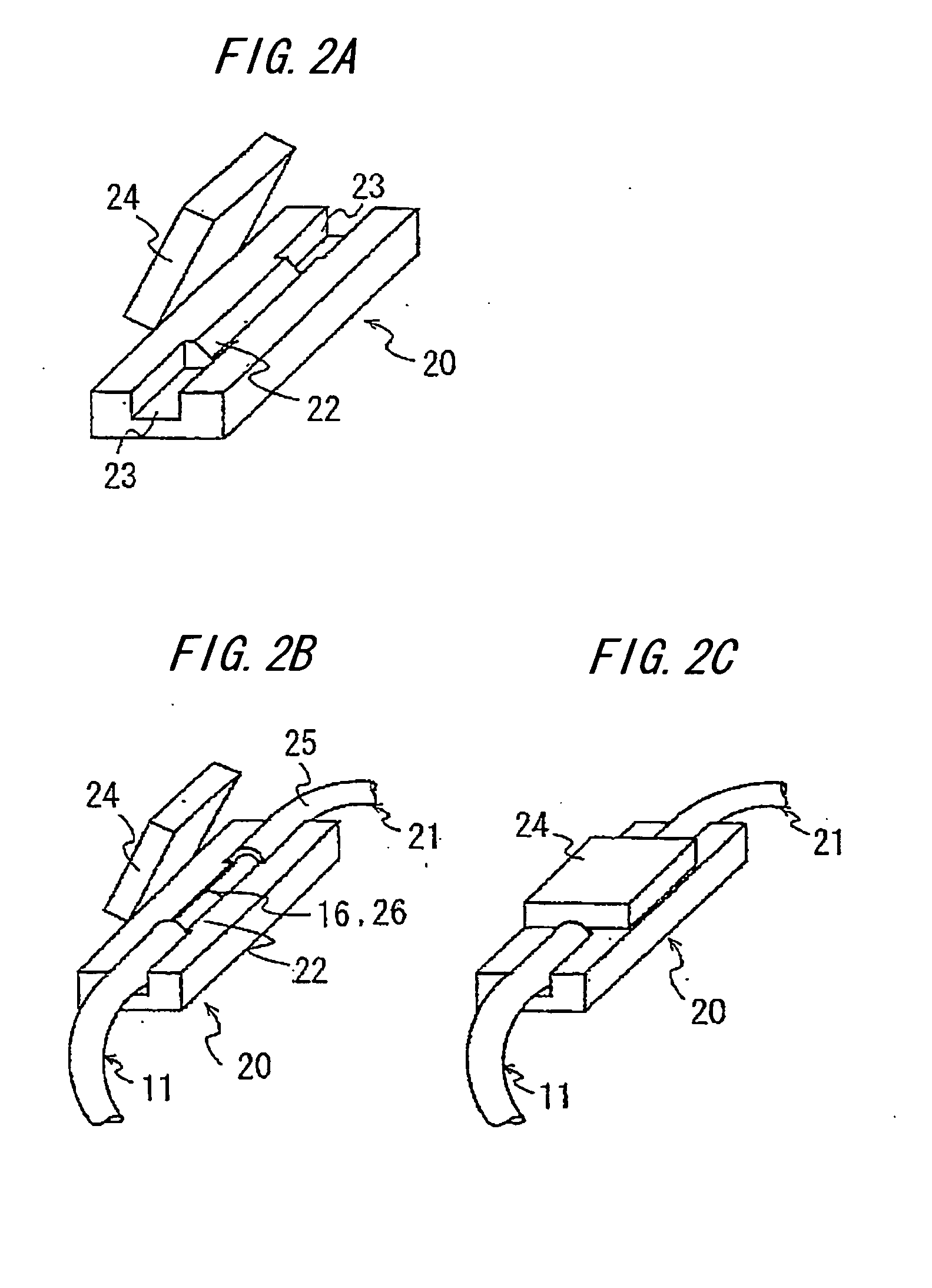
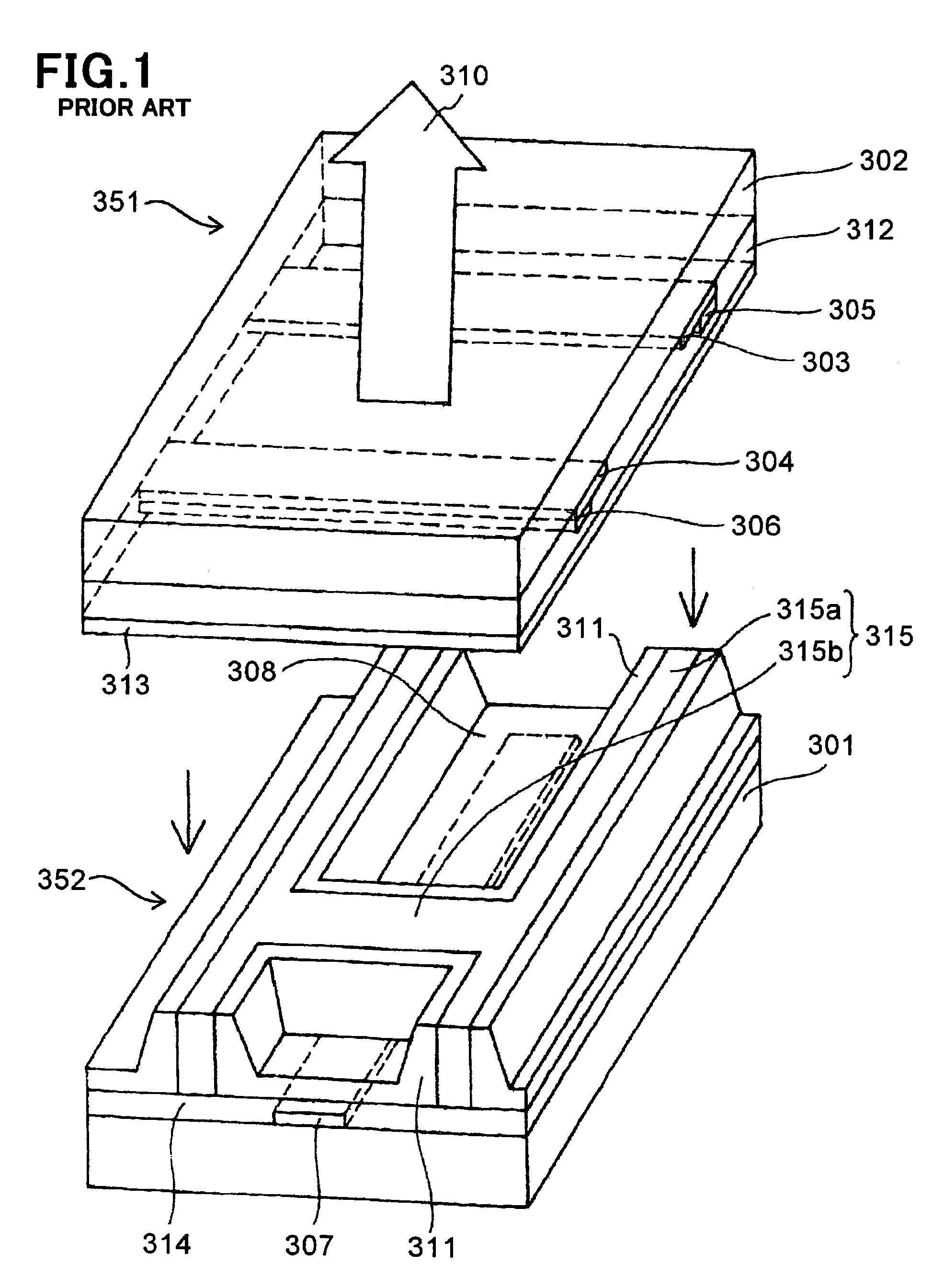
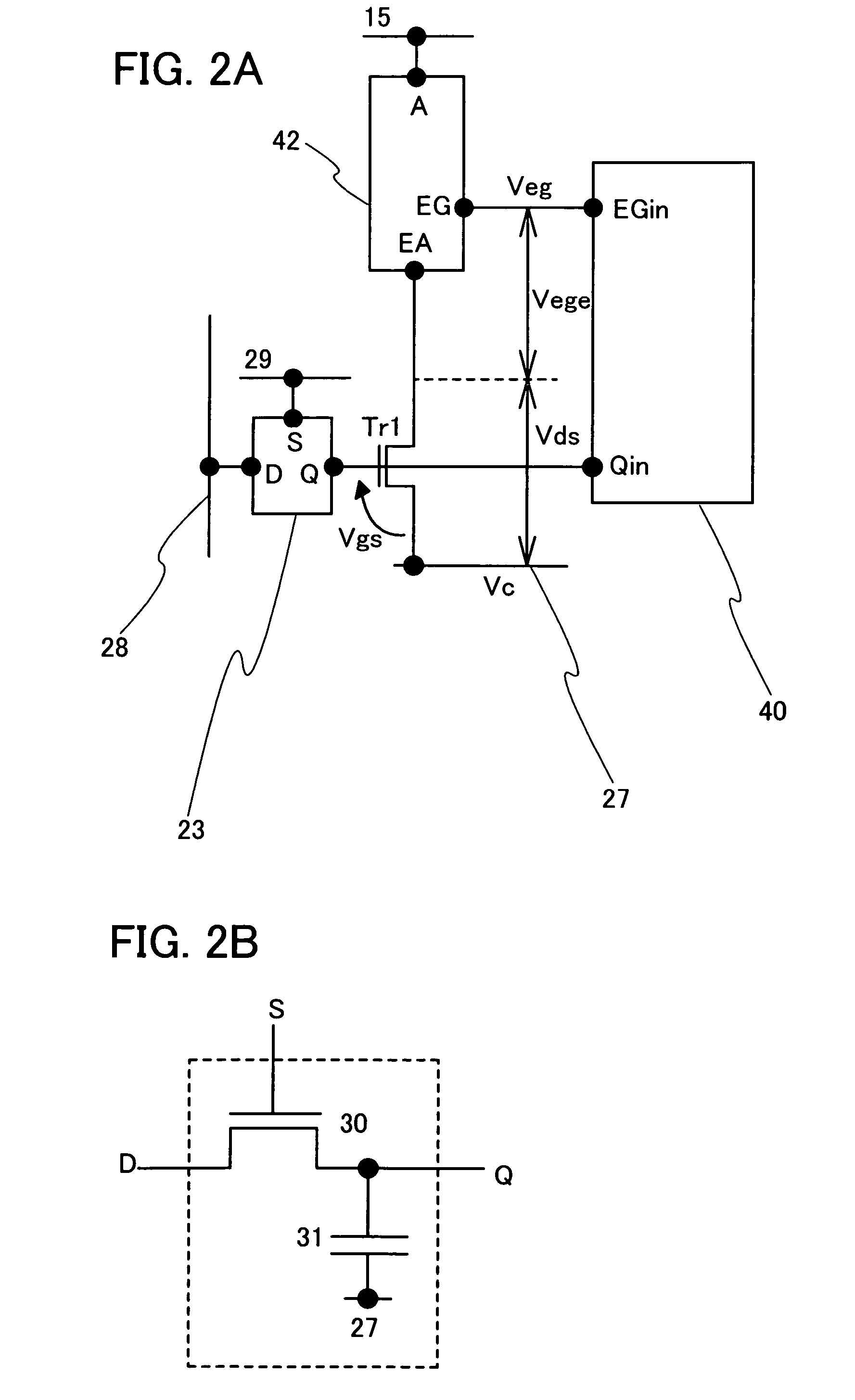
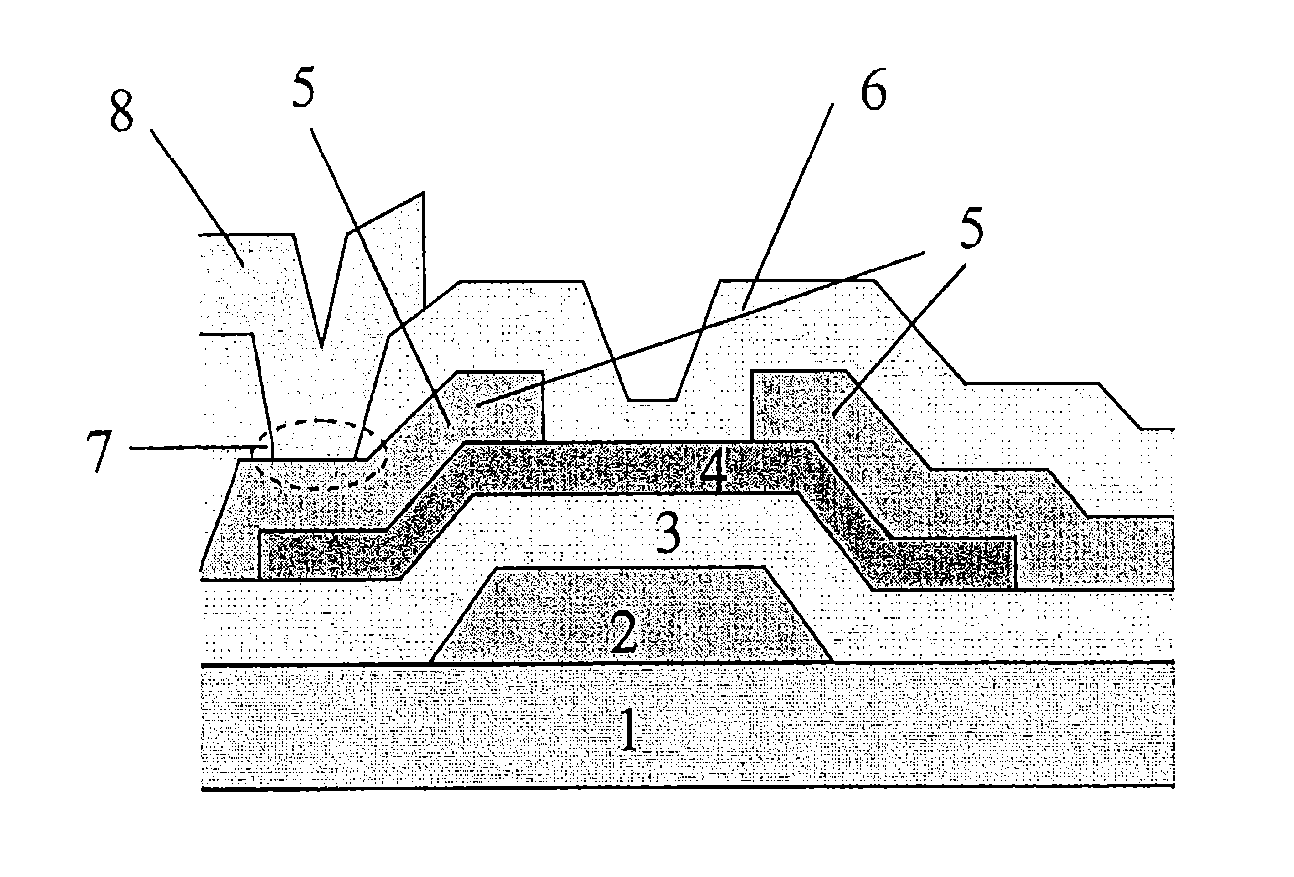
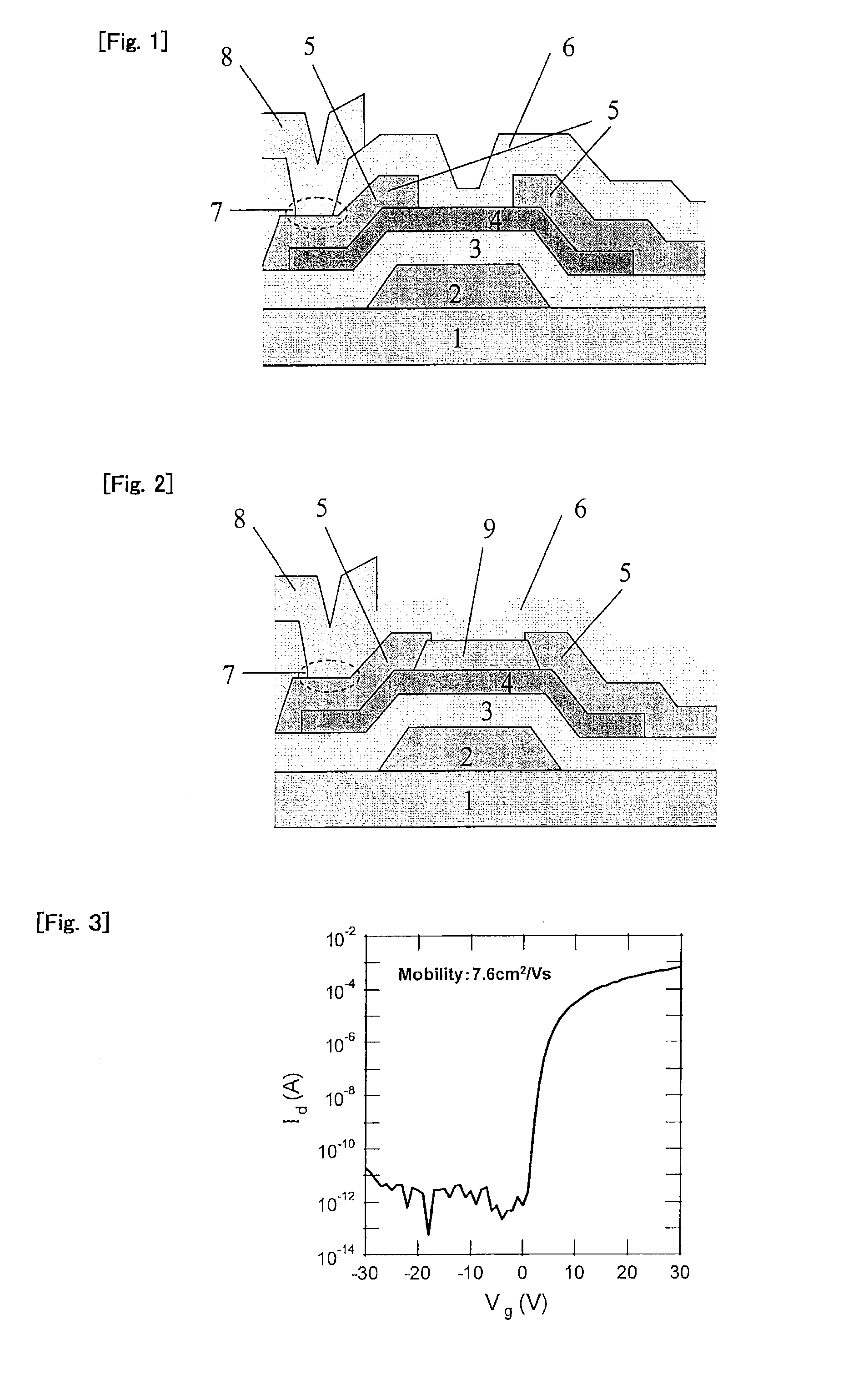
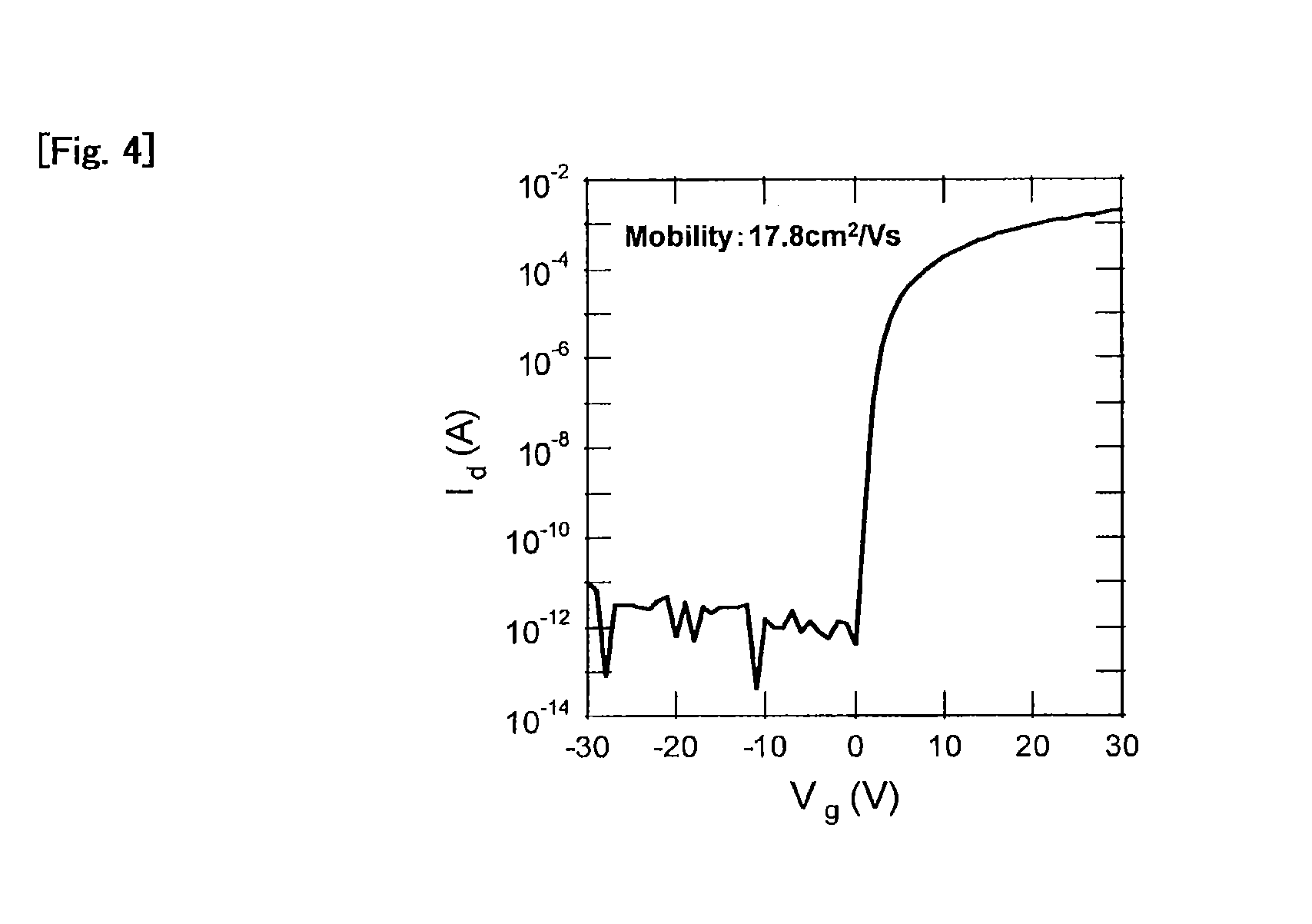
Photosensor and display device
ActiveUS20100134735A1Good reproducibilitySmall display unevennessTransistorStatic indicating devicesDriver circuitIndium
Thin film transistors including an oxide semiconductor containing indium, gallium, and zinc are easily arranged in a matrix over a large substrate and have small characteristic variations. With amplifier circuits and driver circuits of display elements which include the thin film transistors including an oxide semiconductor containing indium, gallium, and zinc with small characteristic variations, intensity distribution of light received by the photodiodes arranged in a matrix is converted into electrical signals with high reproducibility and output, and the display elements arranged in a matrix can be uniformly driven.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
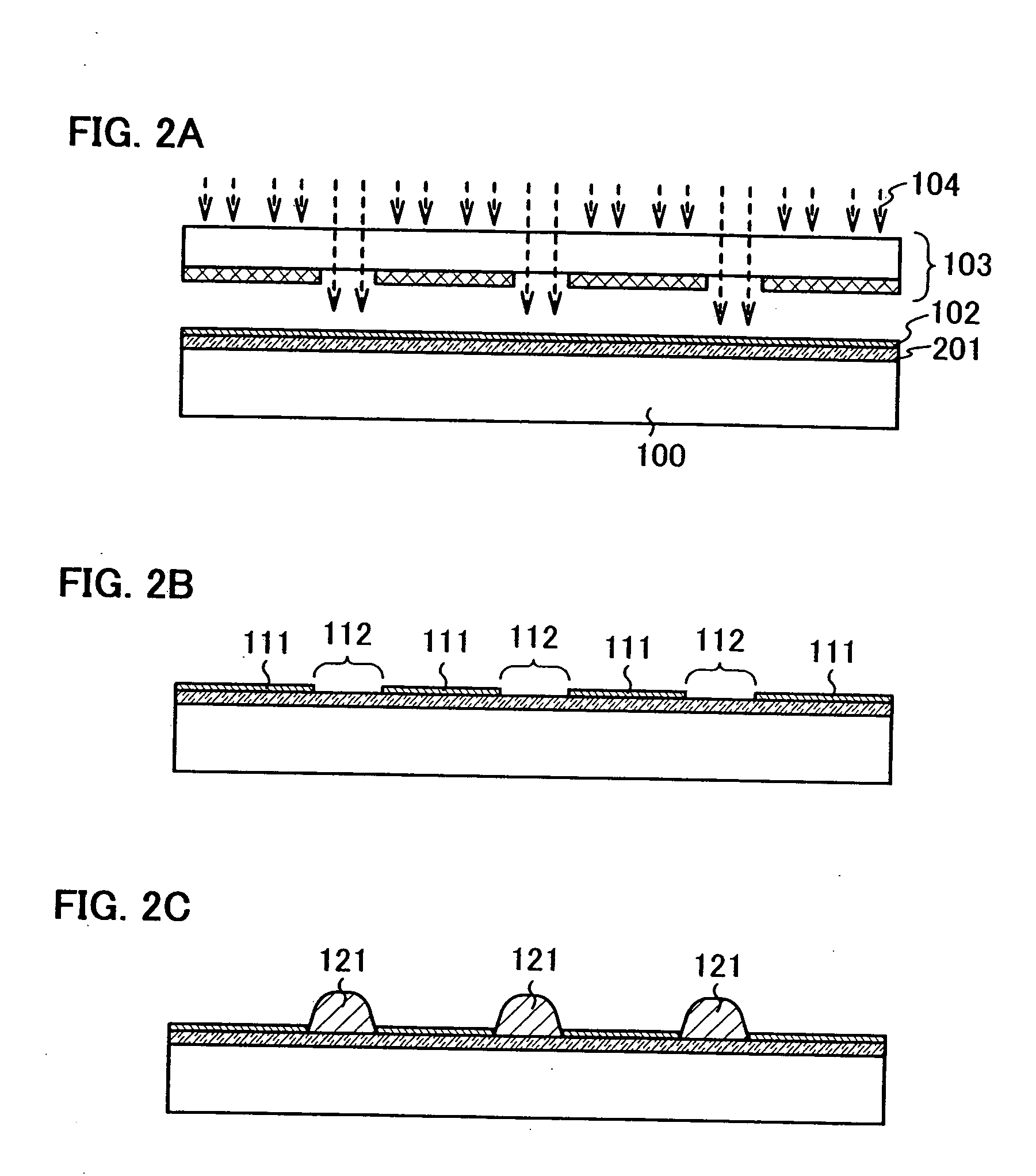
Semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080158137A1Reduce power consumptionHighly convenientStatic indicating devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansIlluminanceAudio power amplifier
A photoelectric conversion device includes a light detection circuit which includes an optical sensor to output a current signal corresponding to illuminance and a current-voltage conversion circuit to convert the current signal output from the optical sensor into a voltage signal; an amplifier to amplify the voltage signal output from the light detection circuit; a comparison circuit to compare voltage output from the amplifier and reference voltage and output the result to a control circuit; and the control circuit to determine an illuminance range to be detected depending on the output from the comparison circuit and output a control signal to the light detection circuit. The current-voltage conversion circuit has a function of changing a resistance value in accordance with the control signal.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
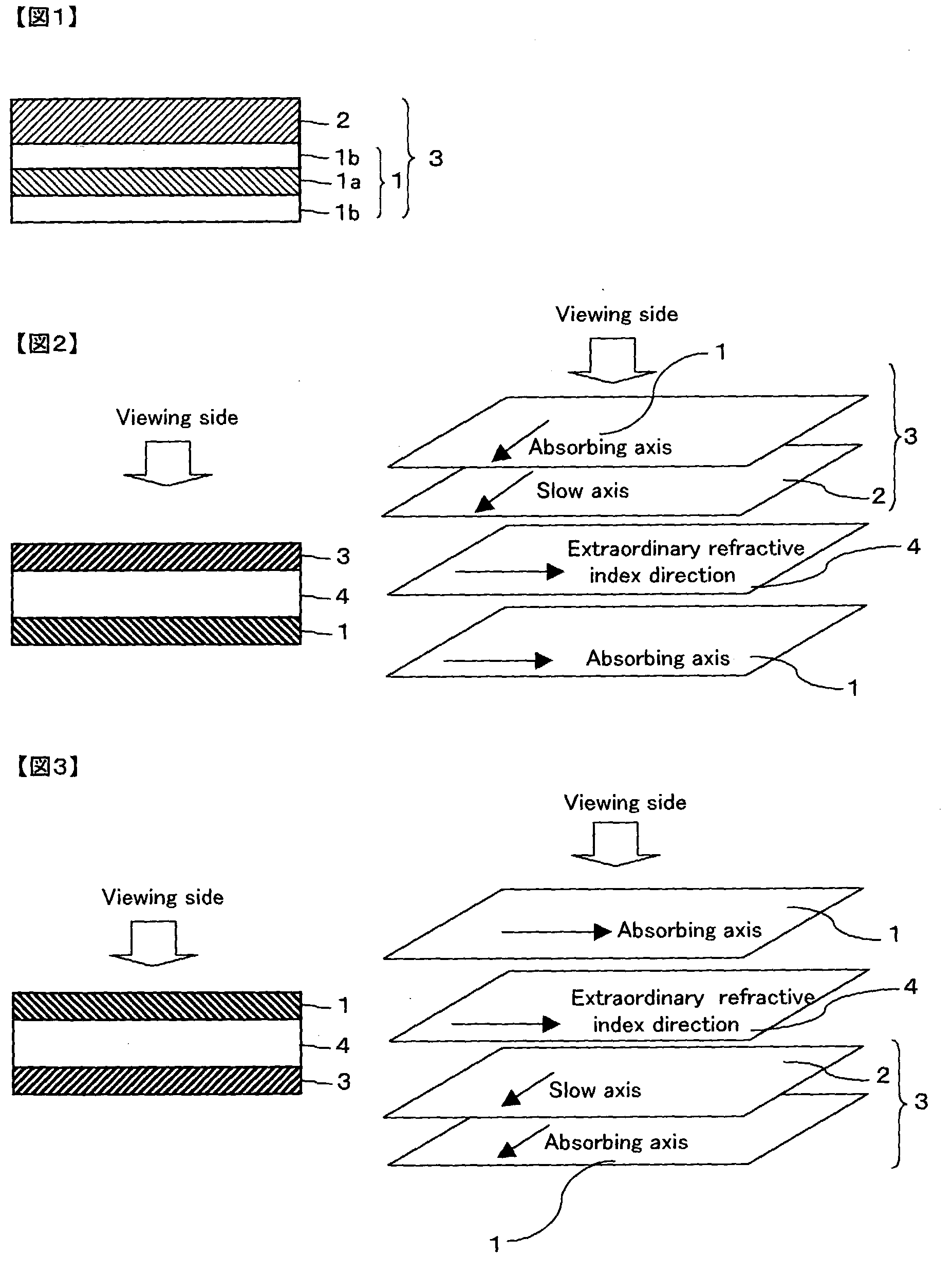
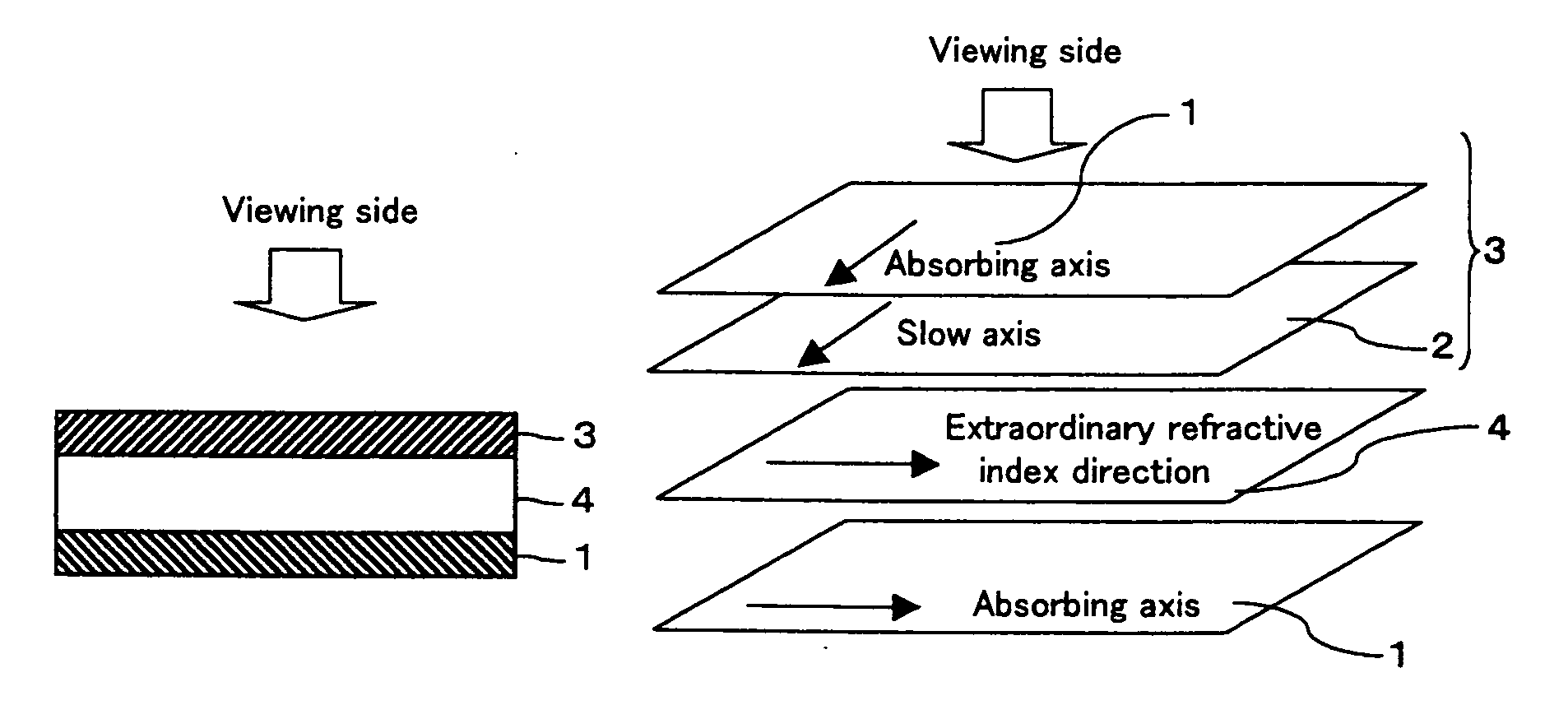
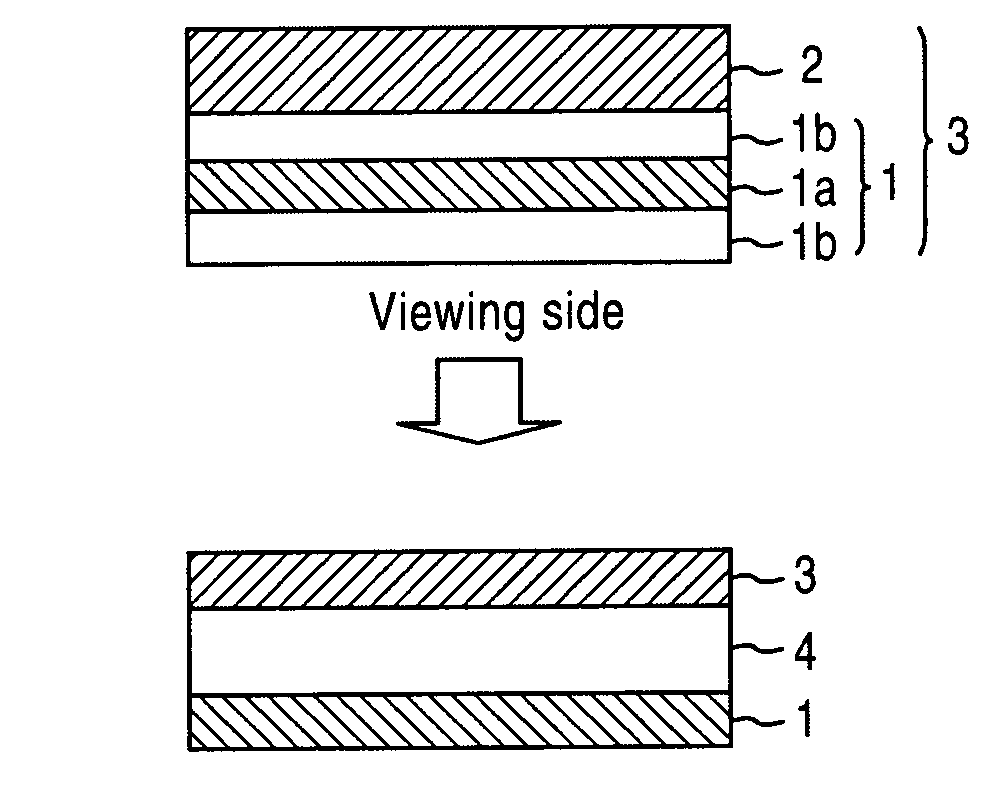
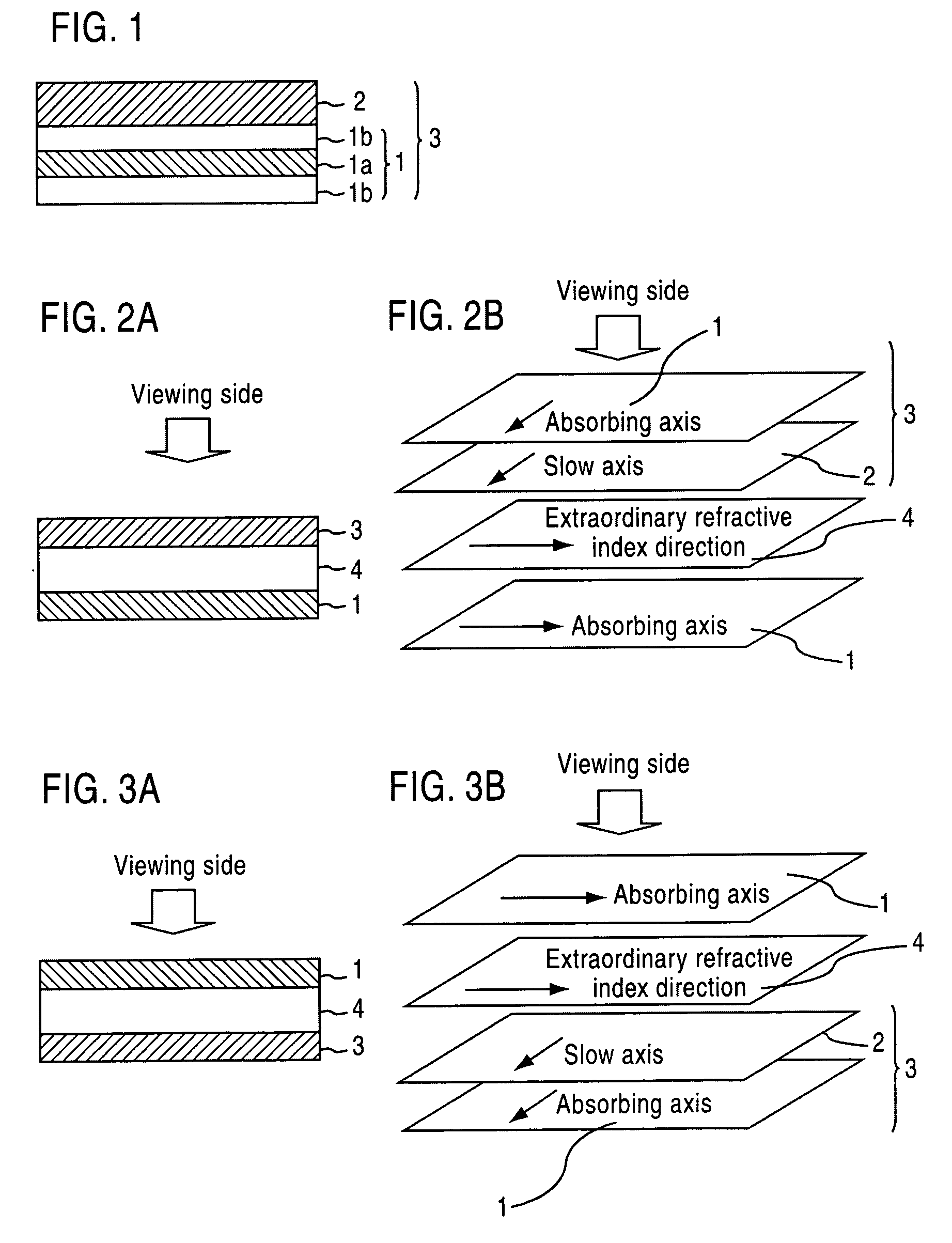
Optical film and display system
InactiveUS20030210370A1Easy to viewIncrease contrastPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planeTectorial membrane
An optical film in which a retardation film is laminated on one side of a polarizing plate, in which a transparent protective film is laminated on both sides of a polarizer, so that an absorbing axis of the polarizing plate and a slow axis of the retardation film may be perpendicular or may be parallel to each other, wherein a value Nz represented by Nz=(nx1-nzi) / (nx1-ny1) satisfies a range of 0.4 through 0.6, and an in-plane retardation Re1=(nx1-ny1)xd1 is 200 through 350 nm, where, a direction of the retardation film in which an in-plane refractive index within the film surface concerned gives a maximum is defined as X-axis, a direction perpendicular to X axis is defined as Y-axis, a thickness direction of the film is defined as Z-axis, refractive indexes in axial direction are defined as nx1, ny1, nz1, respectively, and a thickness of the film is defined as d1 (nm), and the transparent protective films comprise a thermoplastic saturated norbornene resin, may realize an easily viewable display with high contrast ratio in a wide range when applied to a display system and that may provide a retardation value stabilized under conditions of high temperature or high humidity.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
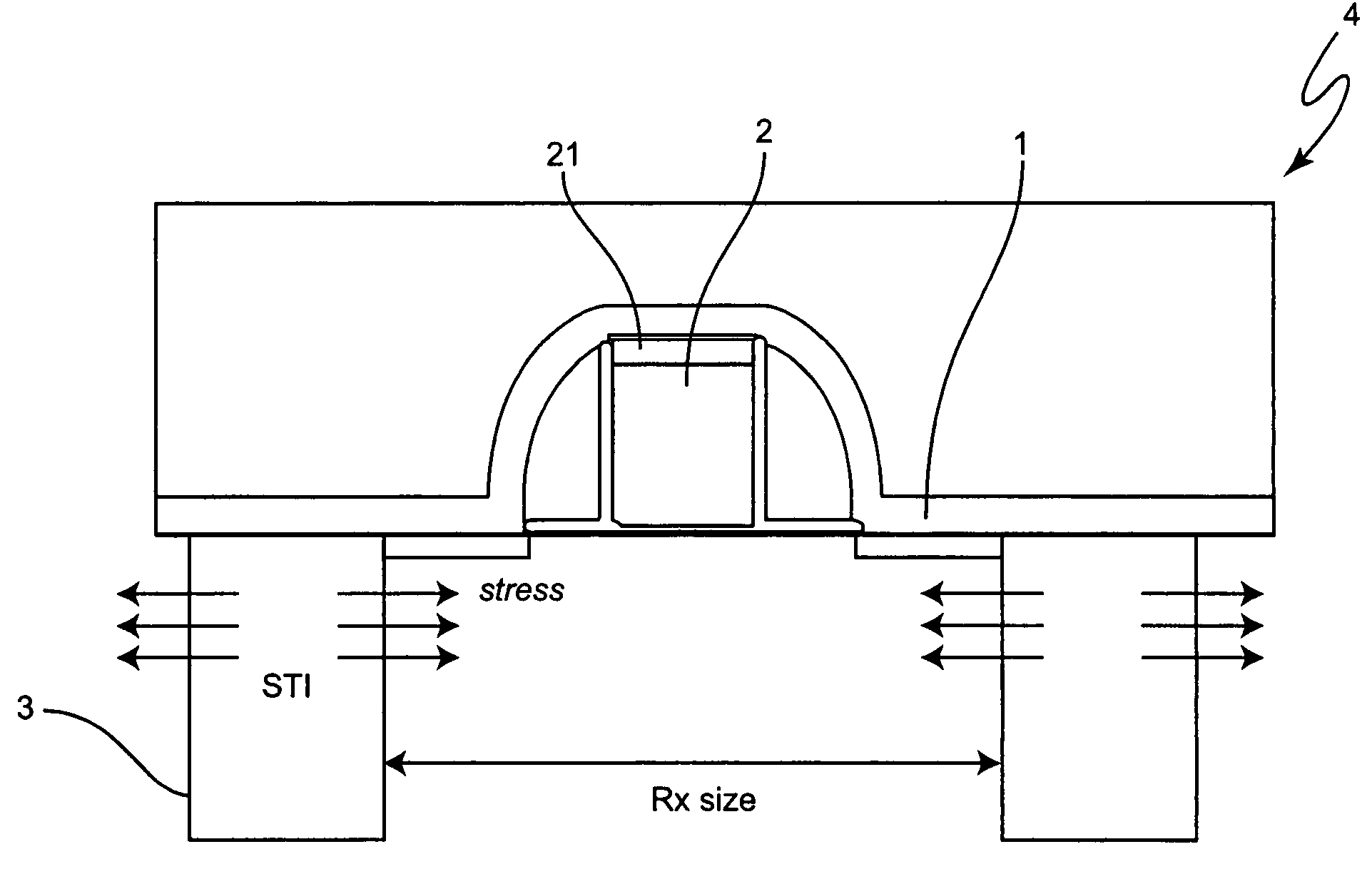
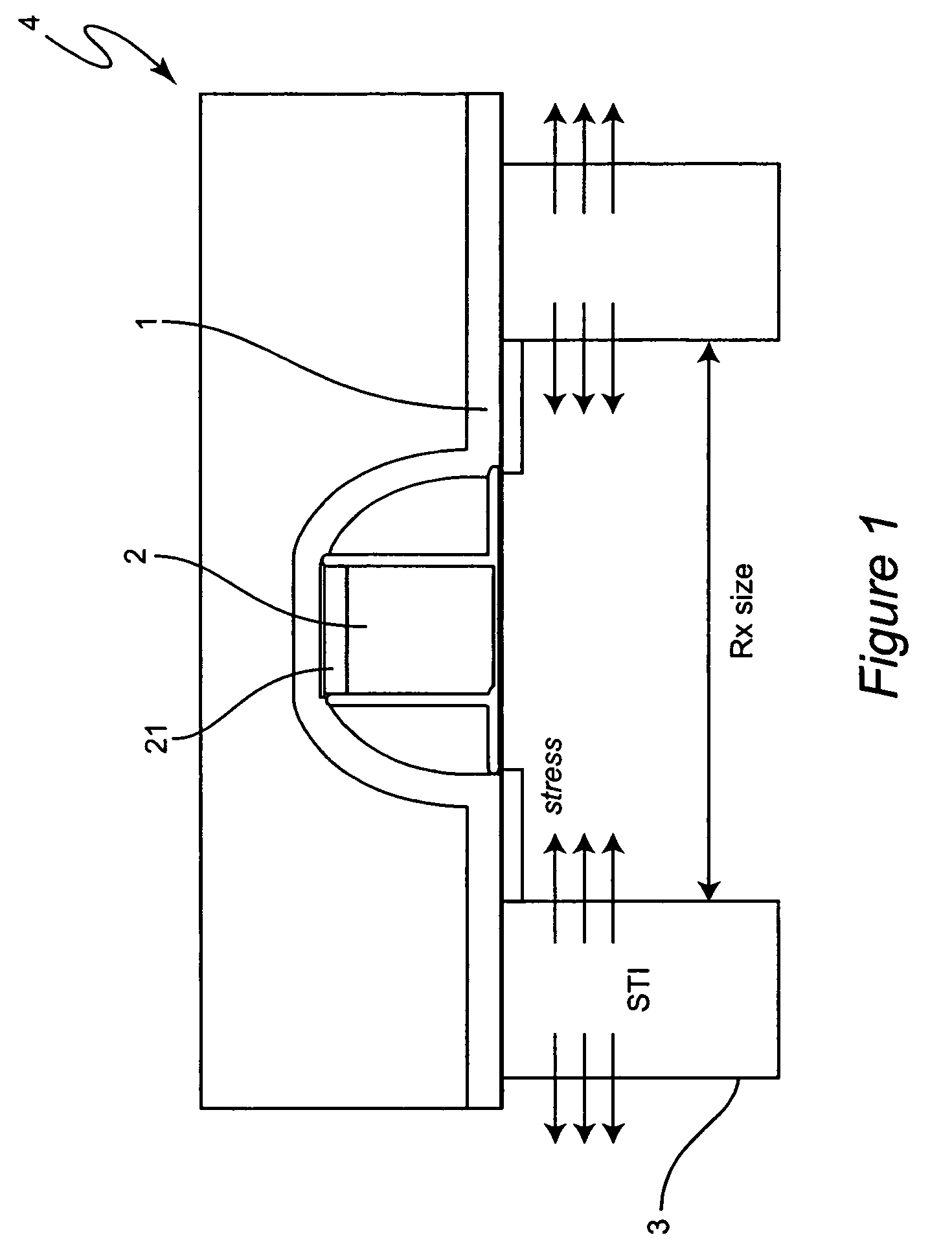
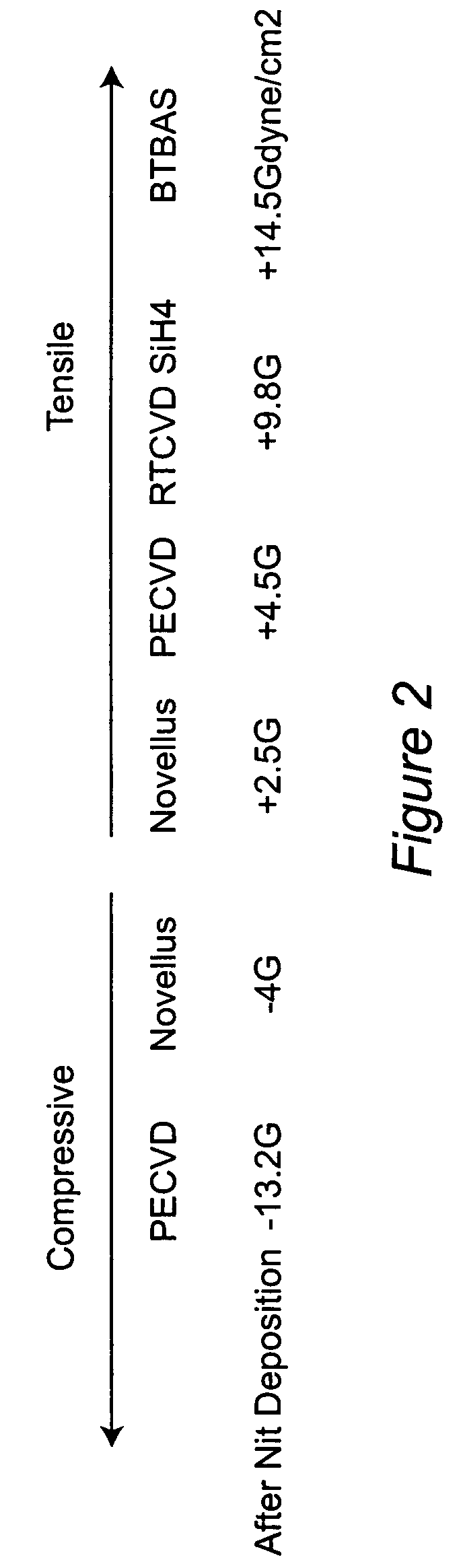
Material for contact etch layer to enhance device performance
InactiveUS7001844B2Little changeNot easy to influenceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingThermal chemical vapor depositionSilanes
Stress level of a nitride film is adjusted as a function of two or more of the following: identity of a starting material precursor used to make the nitride film; identity of a nitrogen-containing precursor with which is treated the starting material precursor; ratio of the starting material precursor to the nitrogen-containing precursor; a set of CVD conditions under which the film is grown; and / or a thickness to which the film is grown. A rapid thermal chemical vapor deposition (RTCVD) film produced by reacting a compound containing silicon, nitrogen and carbon (such as bis-tertiary butyl amino silane (BTBAS)) with NH3 can provide advantageous properties, such as high stress and excellent performance in an etch-stop application. An ammonia-treated BTBAS film is particularly excellent in providing a high-stress property, and further having maintainability of that high-stress property over repeated annealing.
Owner:IBM CORP
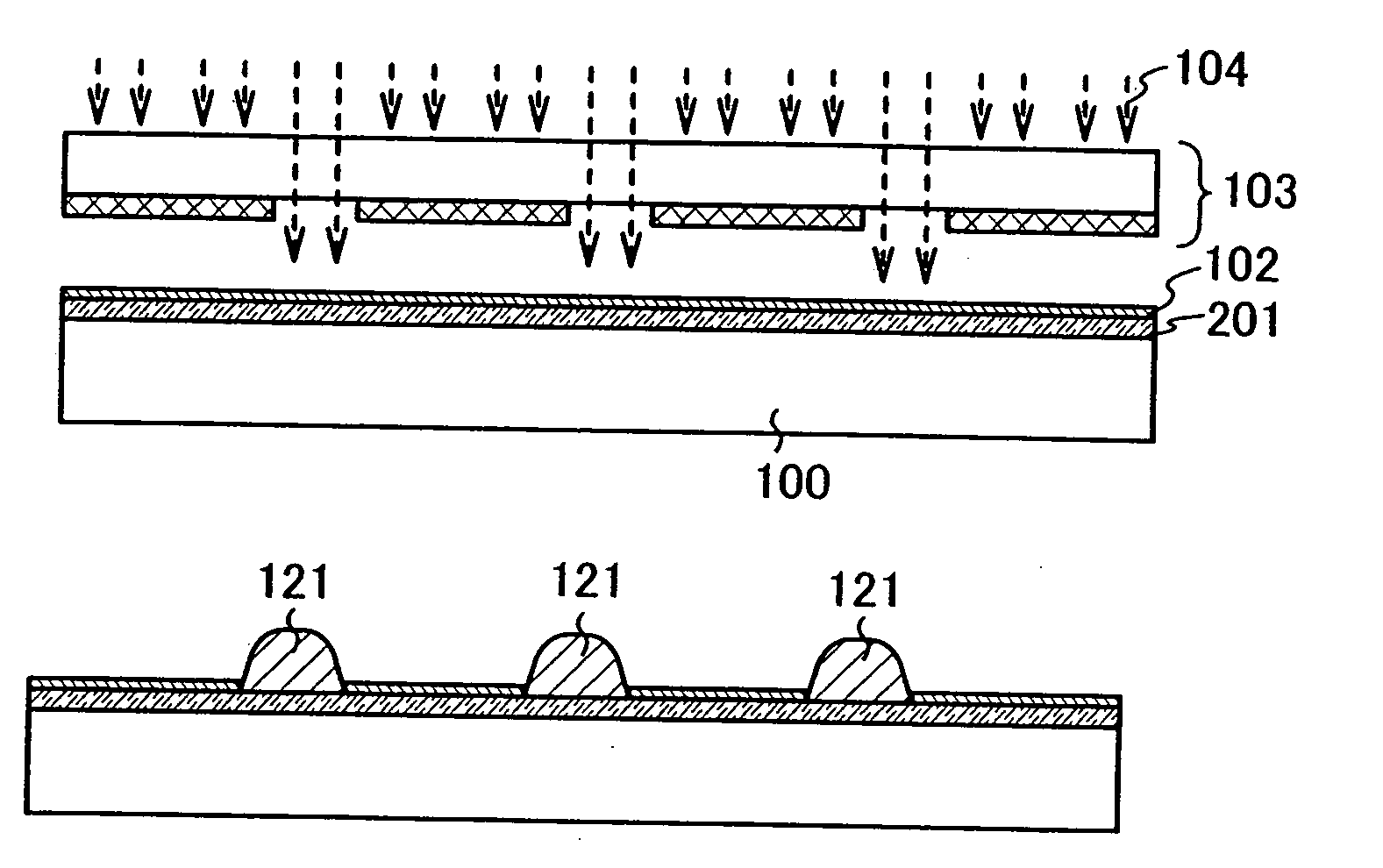
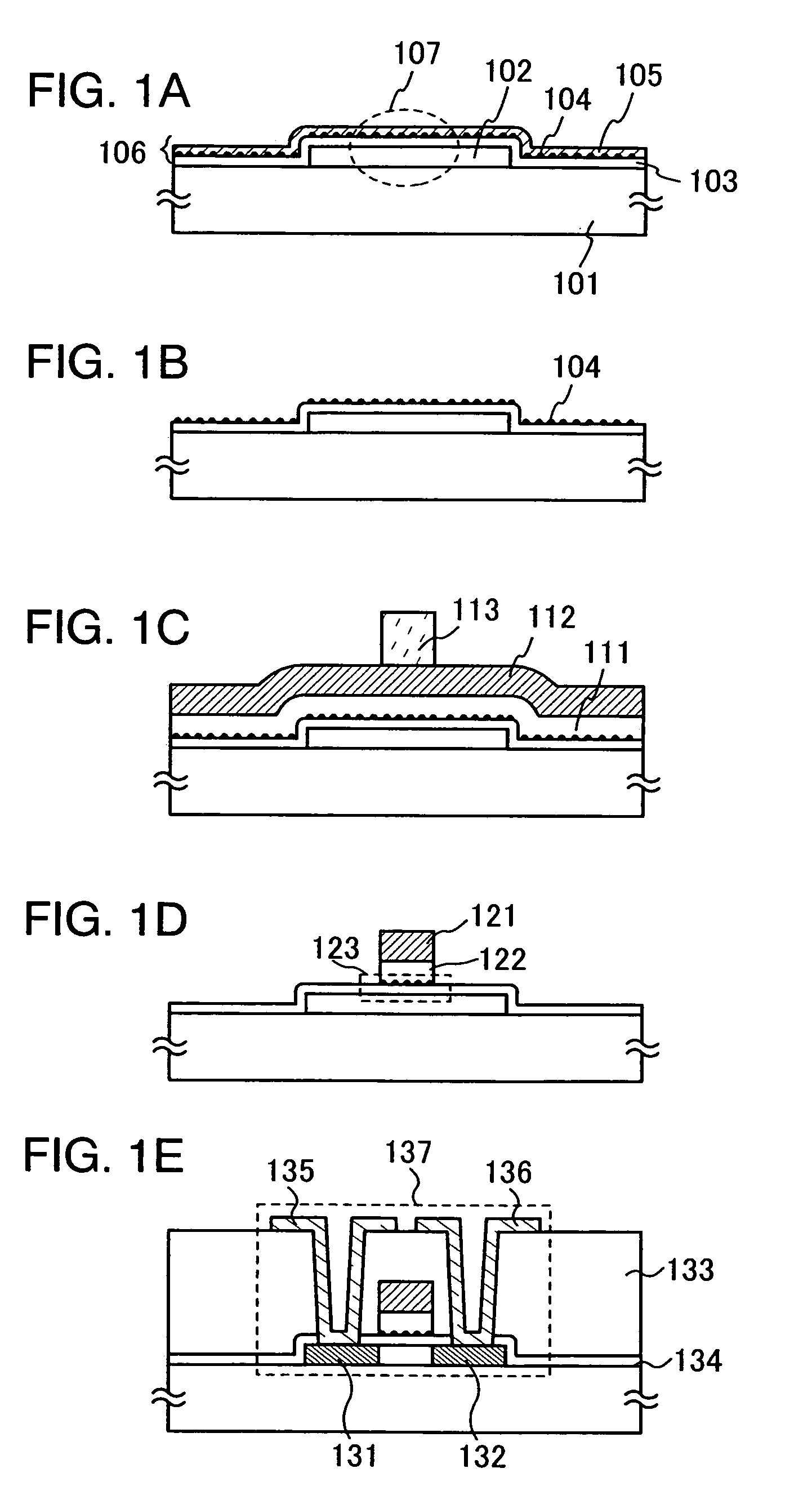
Manufacturing method of substrate having conductive layer and manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS20060134918A1Uniform thicknessLarge electromotive forceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCooking & bakingDevice material
The manufacturing method of a substrate having a conductive layer has the steps of: forming an inorganic insulating layer over a substrate; forming an organic resin layer with a desired shape over the inorganic insulating layer, forming a low wettability layer with respect to a composition containing conductive particles on a first exposed portion of the inorganic insulating layer; removing the organic resin layer; and coating a second exposed portion of the inorganic insulating layer with a composition containing conductive particles and baking, thereby forming a conductive layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
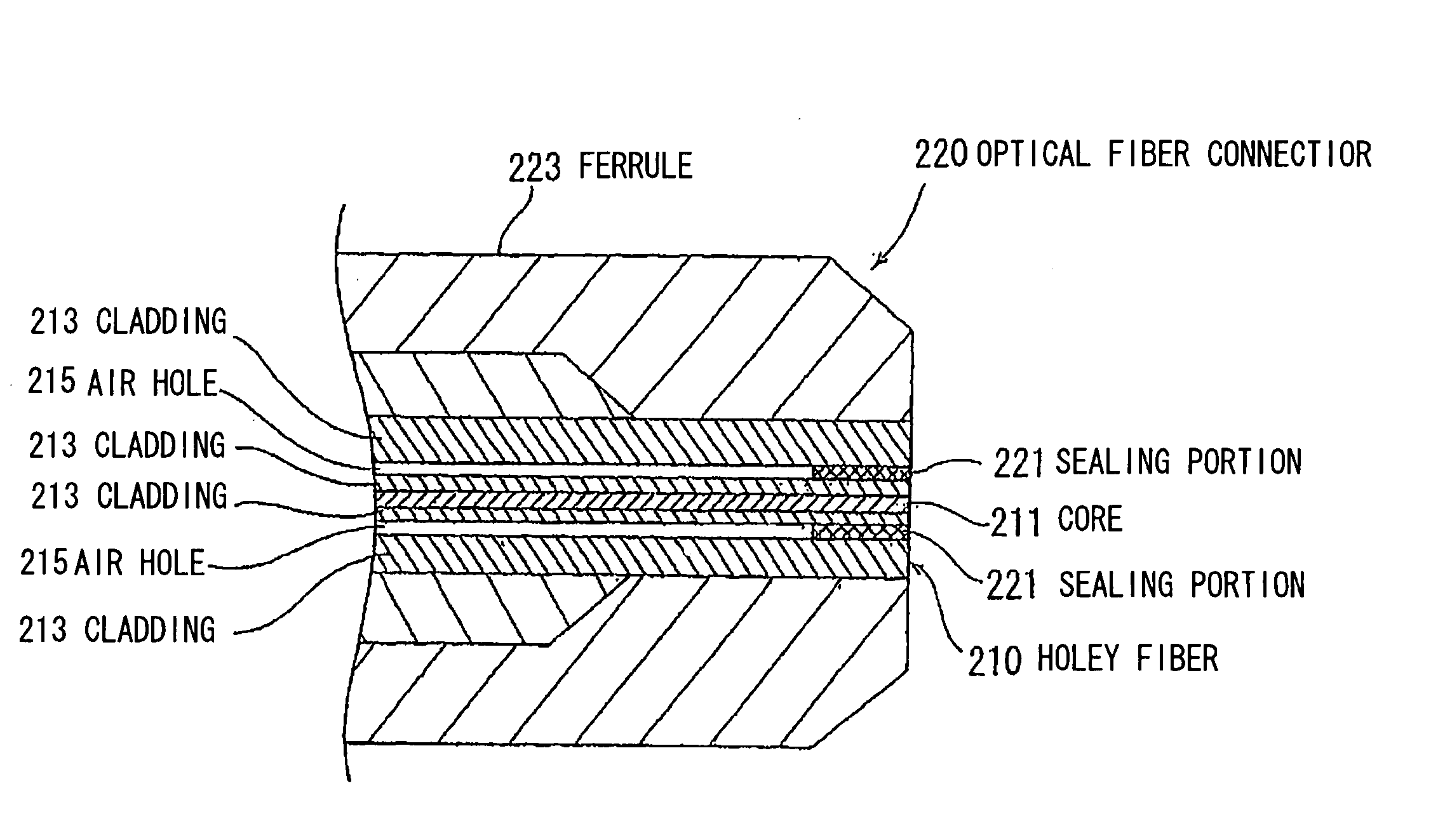
Optical fiber, optical fiber connecting method, and optical connector
InactiveUS20060204195A1Small connection loss and reflection amountSmall temperature characteristic variationOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical fiber connectorEngineering
An optical fiber which, at an optical fiber connecting end having a plurality of voids around the periphery of a core, has a light-permeable substance, such as a resin or glass whose refractive index is lower than that of quartz type substances, filled in the voids adjacent to the connecting end. An optical fiber connecting section where an optical fiber having a plurality of voids in a clad around the periphery of a core is connected to another optical fiber, wherein the optical fiber is connected end-to-end to aforesaid another optical fiber through a refractive index matching agent whose refractive index at the minimum temperature in actual use is lower than that of the core.
Owner:HITACHI CABLE +1
Enhanced hard bias in thin film magnetoresistive sensors with perpendicular easy axis growth of hard bias and strong shield-hard bias coupling
InactiveUS20080117552A1Maximize biasing fieldIncrease concentrationNanomagnetismNanoinformaticsCouplingMagnetization
A hard bias (HB) structure for longitudinally biasing a free layer in a MR sensor is disclosed that is based on HB easy axis growth perpendicular to an underlying seed layer which is formed above a substrate and along two sidewalls of the sensor. In one embodiment, a conformal soft magnetic layer that may be a top shield contacts the HB layer to provide direct exchange coupling that compensates HB surface charges. Optionally, a thin capping layer on the HB layer enables magneto-static shield-HB coupling. After HB initialization, HB regions along the sensor sidewalls have magnetizations that are perpendicular to the sidewalls as a result of surface charges near the seed layer. Sidewalls may be extended into the substrate (bottom shield) to give enhanced protection against side reading. The top surface of the seed layer may be amorphous or crystalline to promote HB easy axis perpendicular growth.
Owner:HEADWAY TECH INC
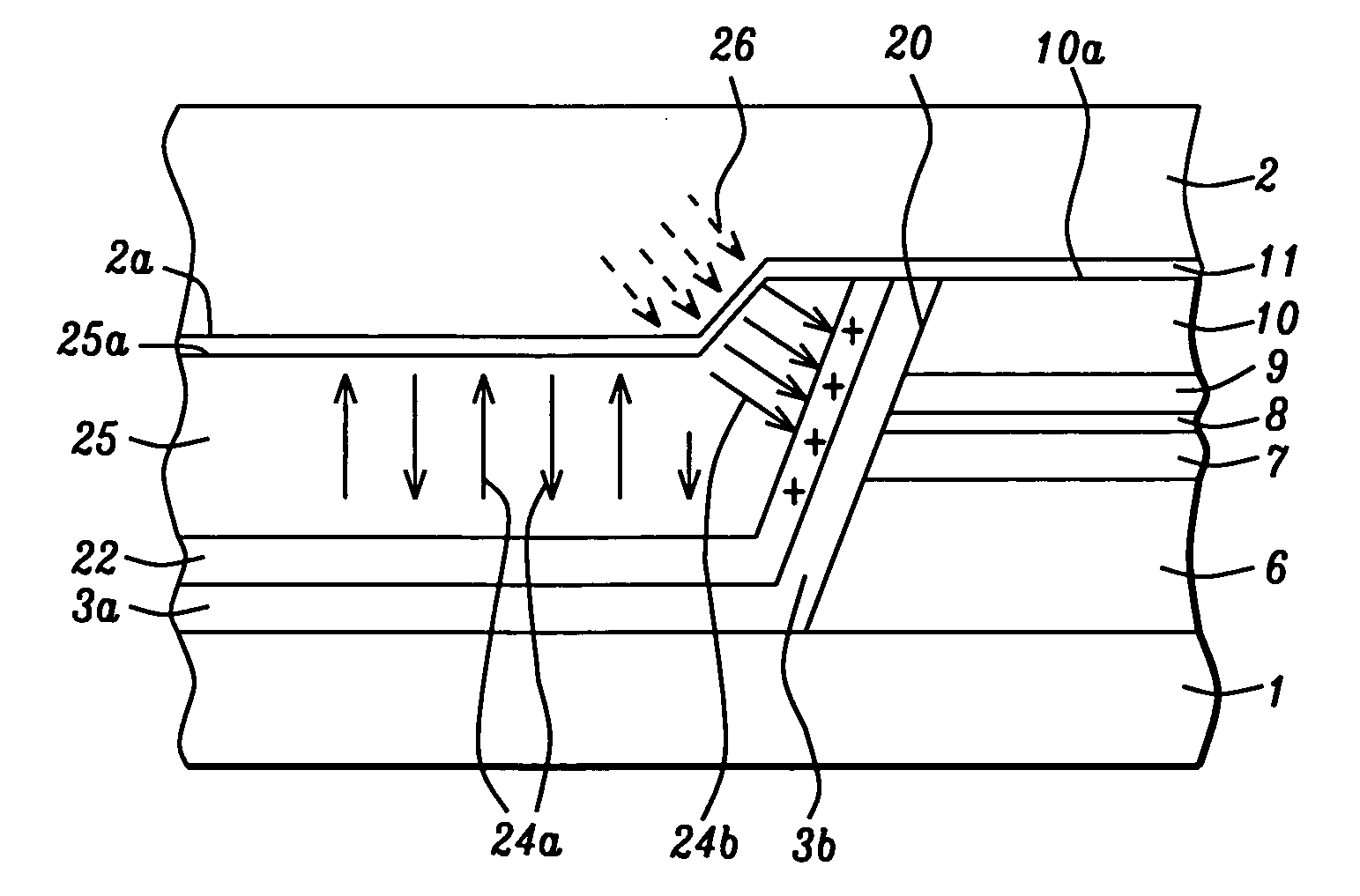
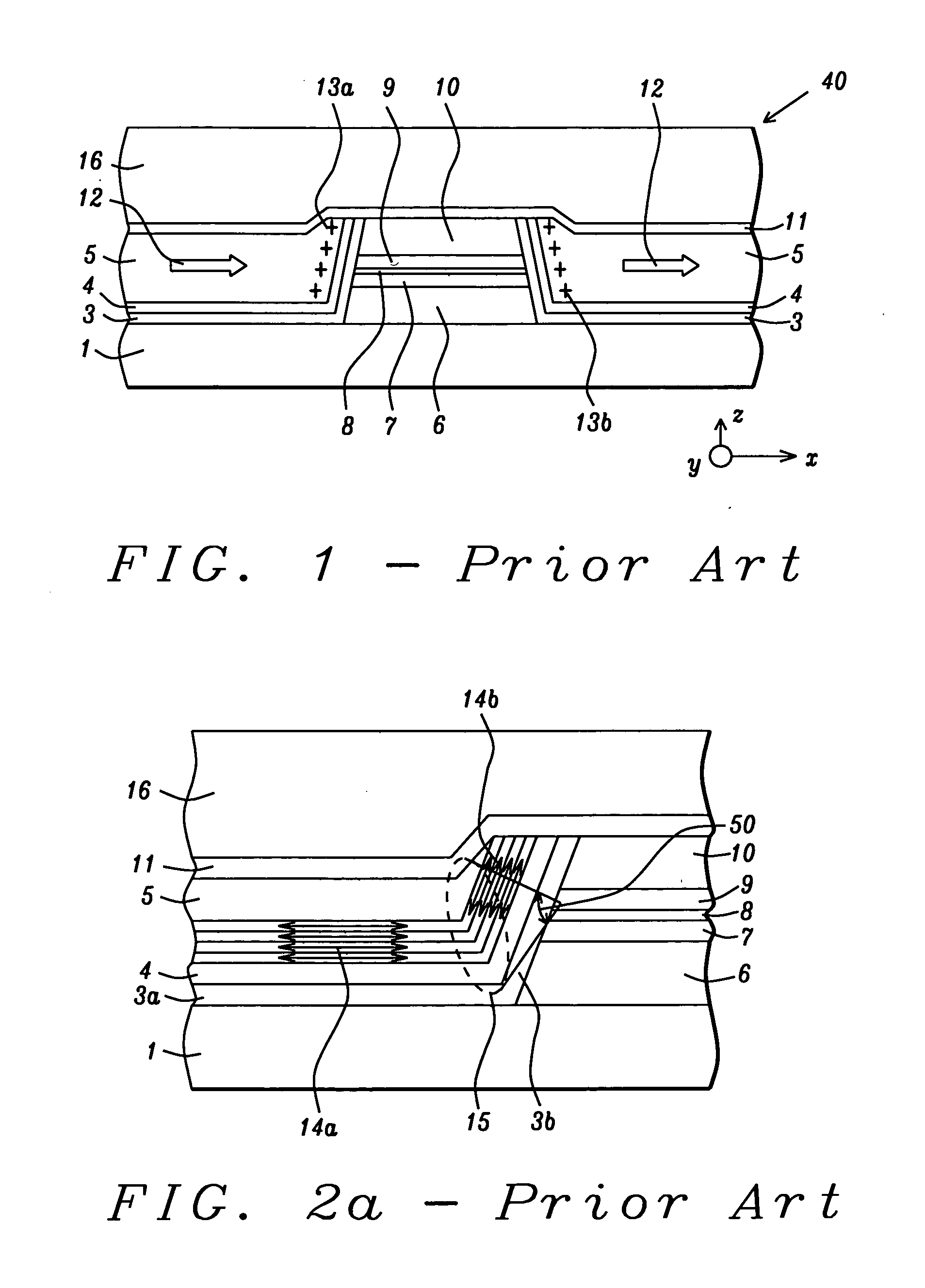
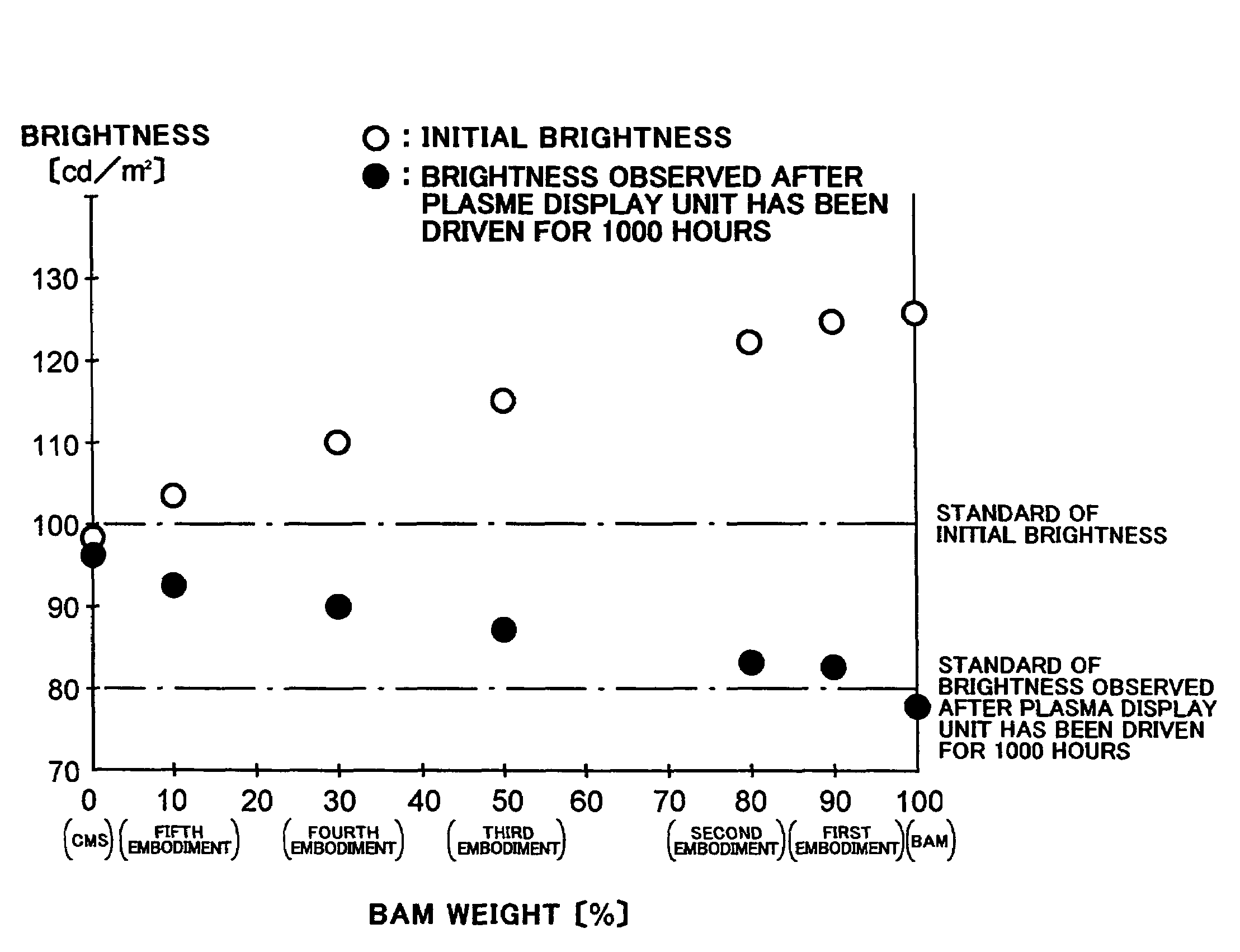
Plasma display panel
InactiveUS7239085B2Suppress brightness changesReduce brightnessAddress electrodesSustain/scan electrodesFluorescencePhosphor
A plasma display panel includes a first substrate, and a second substrate facing the first substrate. The first substrate includes a transparent substrate, a scanning electrode and a common electrode both formed on the transparent substrate, and a dielectric layer covering the transparent substrate, the scanning electrode and the common electrode therewith. The second substrate includes an electrically insulating substrate, data electrodes formed on the electrically insulating substrate, partition walls formed on the electrically insulating substrate, and a phosphor layer covering the electrically insulating substrate and the data electrodes therewith between adjacent partition walls. The phosphor layer includes a blue-phosphor layer composed of phosphor which emits a blue light. The blue-phosphor layer is composed of a mixture of two or more phosphors each of which emits a blue light and has an initial brightness and variation of brightness with the lapse of time both different from one another.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
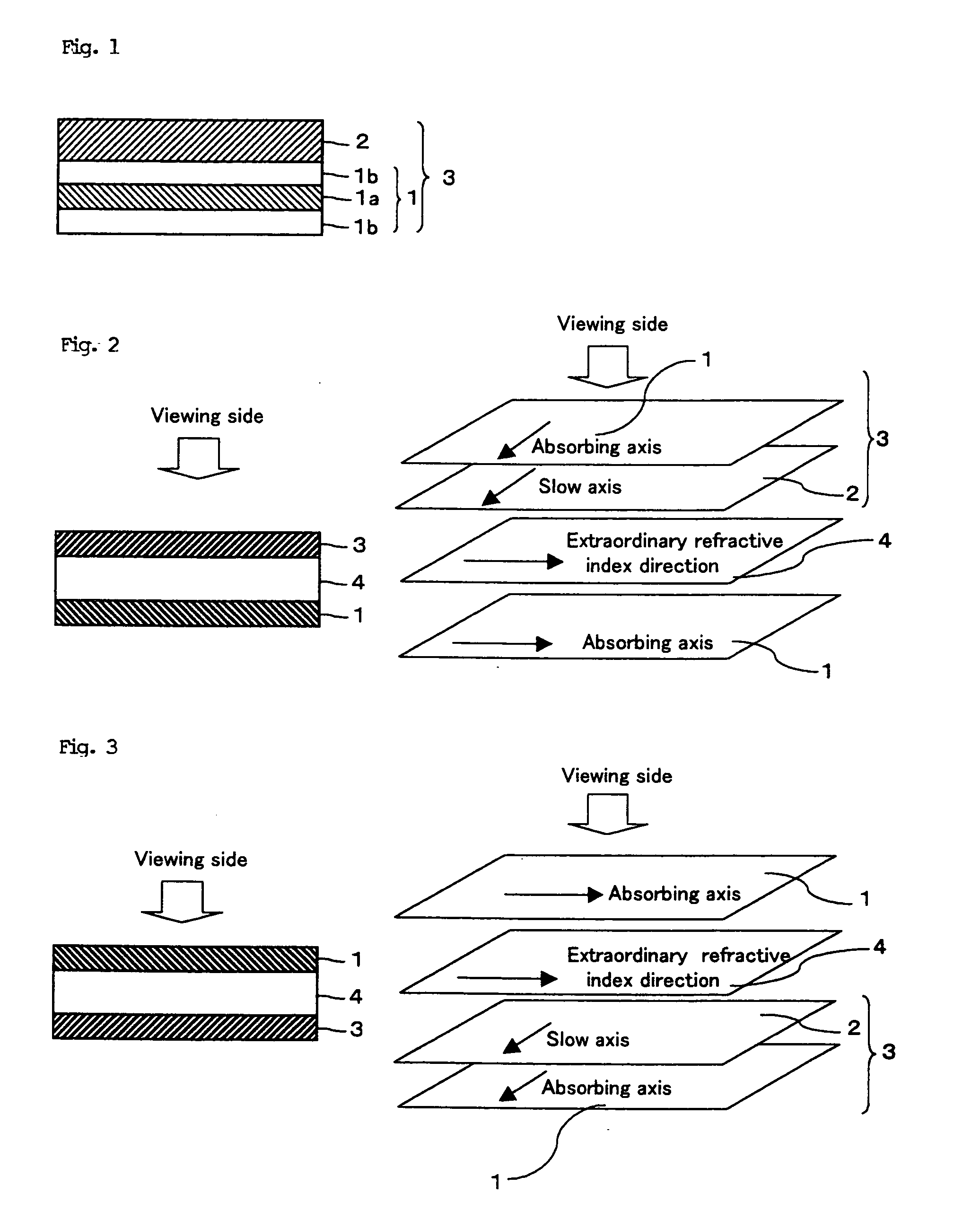
Optical film and display system
InactiveUS20040032547A1Small variationStable valuePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planeLiquid-crystal display
An optical film in which a polarizing plate and a retardation film are laminated so that an absorbing axis of the polarizing plate and a slow axis of the retardation film may be perpendicular or may be parallel to each other, wherein a value Nz represented by Nz=(nx1-nz1) / (nx1-ny1) satisfies a range of 0.4 through 0.6, and an in-plane retardation Re1=(nx1-ny1)xd1 is 200 through 350 nm, where, a direction of the retardation film in which an in-plane refractive index within the film surface concerned gives a maximum is defined as X-axis, a direction perpendicular to X axis is defined as Y-axis, a thickness direction of the film is defined as Z-axis, refractive indexes in axial direction are defined as nx1, ny1, nz1, respectively, and a thickness of the film is defined as d1 (nm), may realize an easily viewable display with high contrast ratio in a wide range when applied to a display system, preferably used for a liquid crystal display operating in IPS mode.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Pattern forming method, actinic ray-sensitive or radiation-sensitive resin composition and resist film
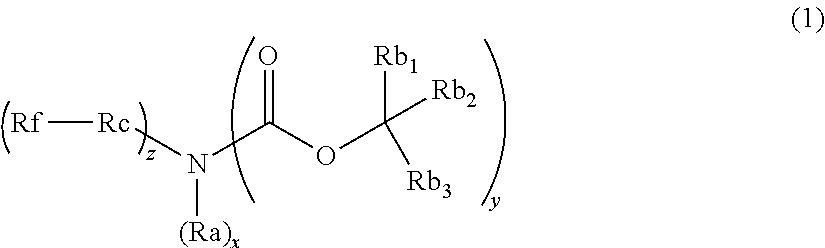
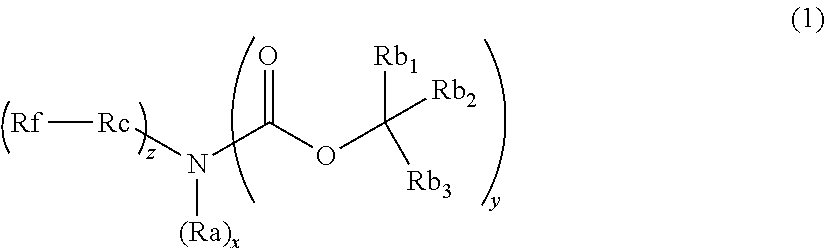
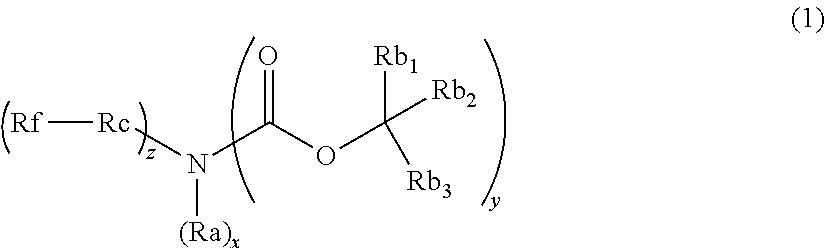
ActiveUS20120282548A1Small variationImproved profileCarbamic acid derivatives preparationOrganic compound preparationActinic RaysOrganosolv
Provided is a pattern forming method comprising (i) a step of forming a film from an actinic ray-sensitive or radiation-sensitive resin composition, (ii) a step of exposing the film, and (iii) a step of developing the exposed film by using an organic solvent-containing developer, wherein the actinic ray-sensitive or radiation-sensitive resin composition comprises (A) a resin capable of decreasing the solubility for an organic solvent-containing developer by the action of an acid, (B) a compound capable of generating an acid upon irradiation with an actinic ray or radiation, (D) a solvent, and (G) a compound having at least either one of a fluorine atom and a silicon atom and having basicity or being capable of increasing the basicity by the action of an acid.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
6-axis sensor structure using force sensor and method of measuring force and moment therewith
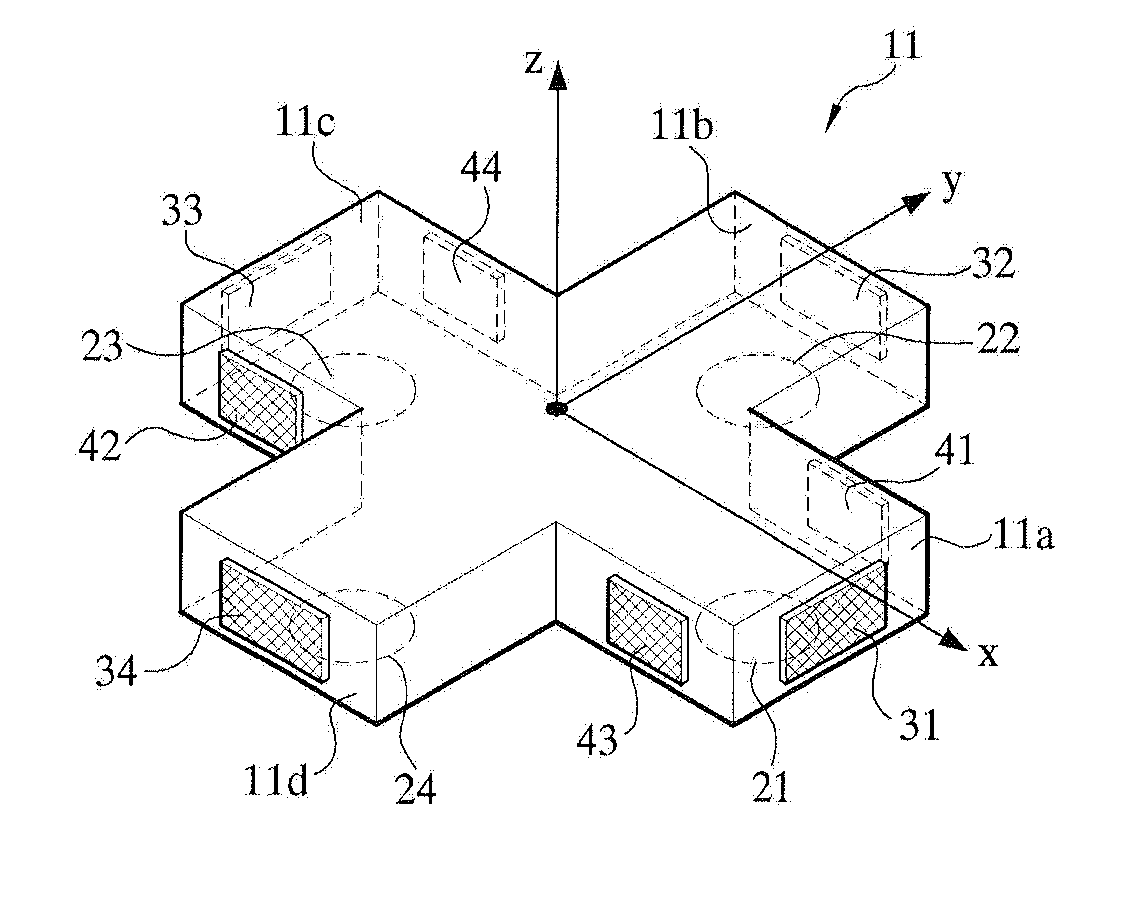
InactiveUS20110107850A1Easily processes signalSmall-sized force sensor structureForce measurement using piezo-resistive materialsTension measurementEngineeringForce sensor
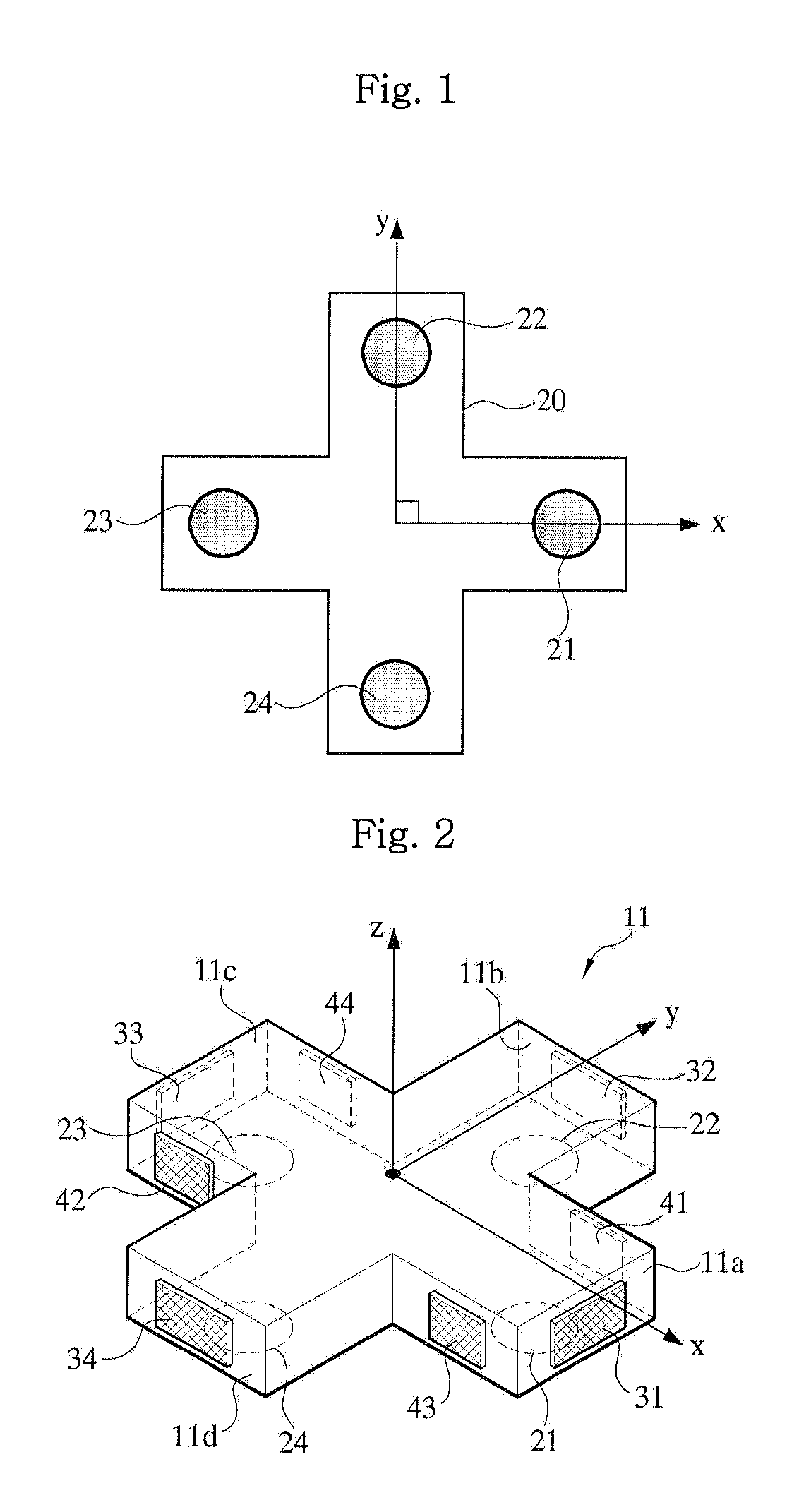
A 6-axis force sensor includes bumper 10 with bumper axis 12 and press member 11 which has four horizontal beams 11a, 11b, 11c and 11d in a cross shape with end, side and bottom faces. Sensors 31, 32, 33, and 34 on end faces sense force in one direction and sense a moment acting on opposite end faces. Sensors 41, 42, 43, and 44 on side faces sense force in a second direction transverse to the first direction and sense a moment acting on opposite side faces. A film 20 on the bottom faces has four sensors 21, 22, 23, and 24, one on each bottom face, for sensing force in a direction transverse to the first and the second directions and sensing a moment acting on opposite sensors on the film.
Owner:KOREA RES INST OF STANDARDS & SCI
Interconnect structure and sputtering target
ActiveUS20130248858A1Improve switching characteristicsImprove stress resistanceTransistorCellsGate insulatorGroup element
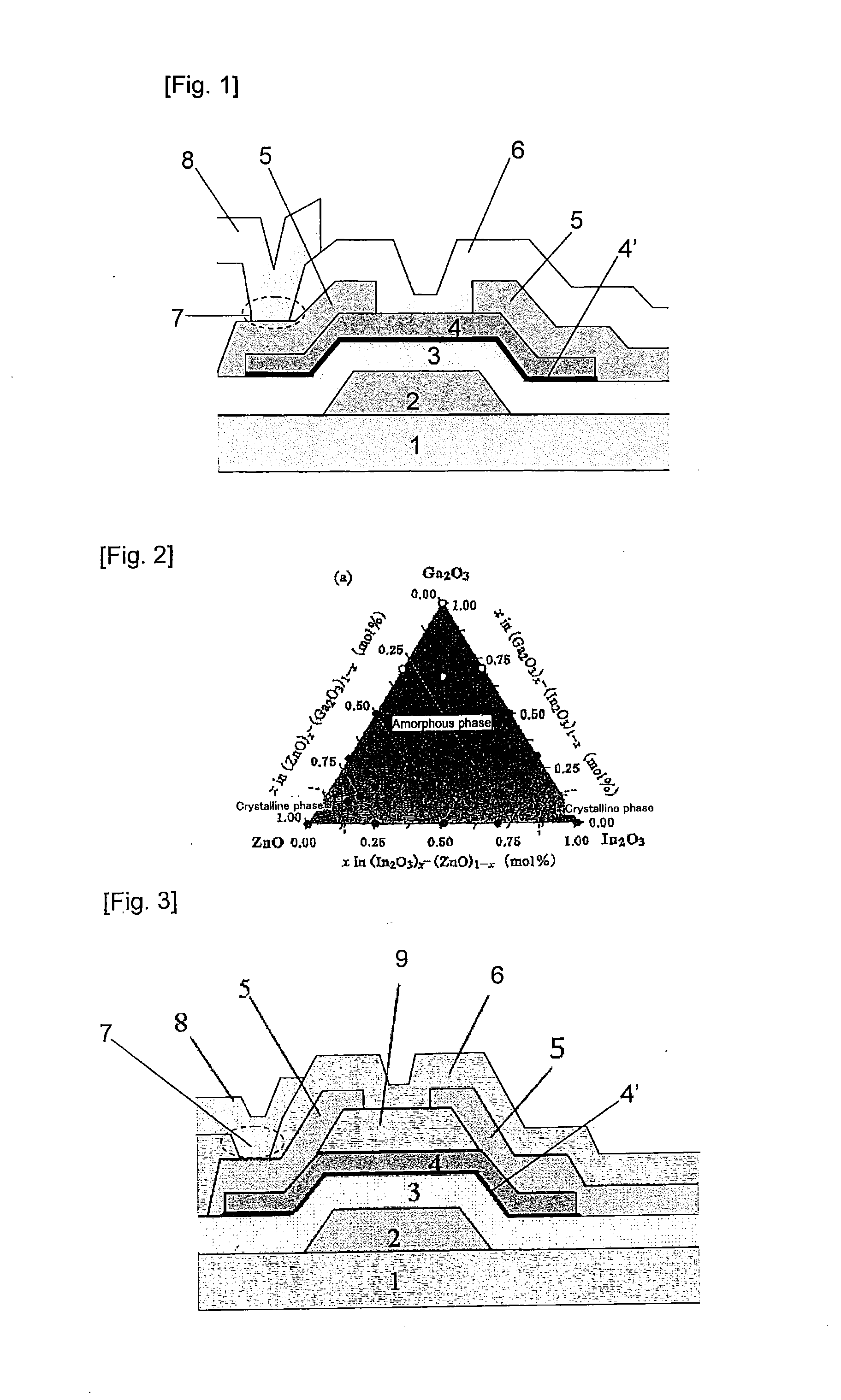
The interconnect structure of the present invention includes at least a gate insulator layer and an oxide semiconductor layer on a substrate, wherein the oxide semiconductor layer is a layered product having a first oxide semiconductor layer containing at least one element (Z group element) selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Zn and Sn; and a second oxide semiconductor layer containing at least one element (X group element) selected from the group consisting of In, Ga, Zn and Sn and at least one element (Y group element) selected from the group consisting of Al, Si, Ti, Hf, Ta, Ge, W and Ni, and wherein the second oxide semiconductor layer is interposed between the first oxide semiconductor layer and the gate insulator layer. The present invention makes it possible to obtain an interconnect structure having excellent switching characteristics and high stress resistance, and in particular, showing a small variation of threshold voltage before and after the stress tests, and thereby having high stability.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Low-loss ferrite and electronic device formed by such ferrite
ActiveUS20100085140A1Small variationReduce lossTransformers/inductances casingsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsDevice formFerric
A low-loss ferrite comprising as main components 46.5-49.5% by mol of Fe2O3, 17-26% by mol of ZnO, 4-12% by mol of CuO, and 0.2% or more and less than 1.2% by mol of CoO, the balance being NiO, and 0.03-1.4% by mass (as SnO2) of Sn based on 100% by mass of the main components, and having an average crystal grain size of 0.7-2.5 μum, and an electronic device obtained by integrally sintering pluralities of layers of this low-loss ferrite and coil-shaped electrodes formed in the laminate.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
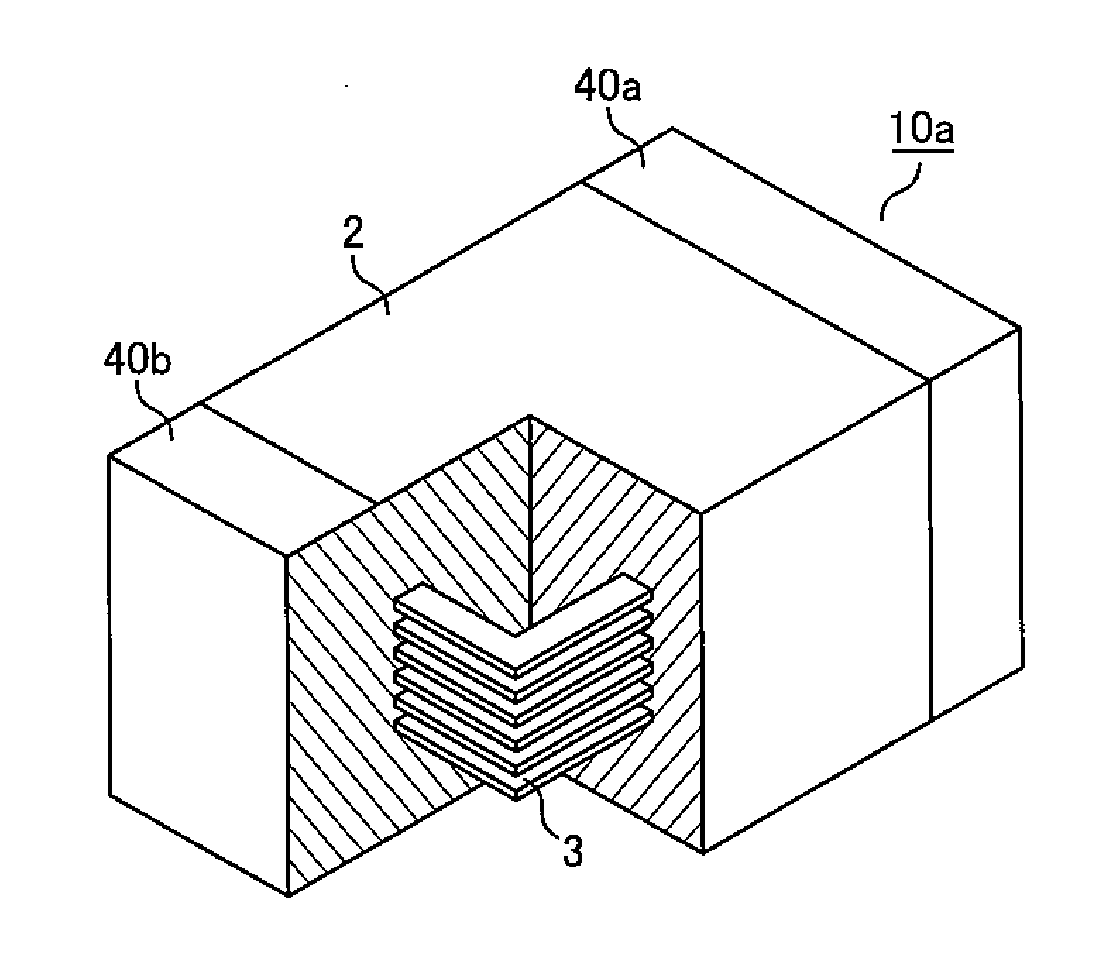
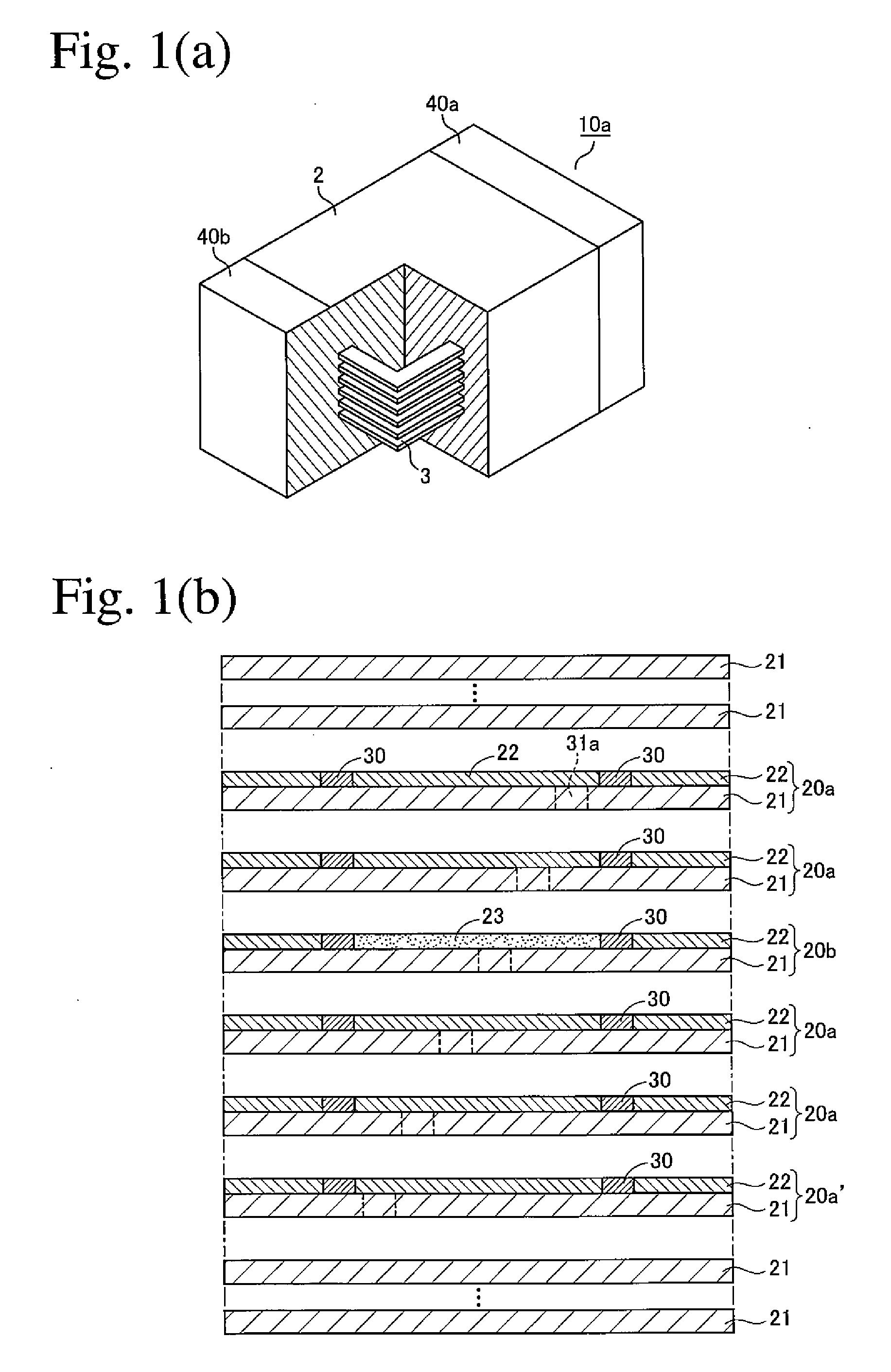
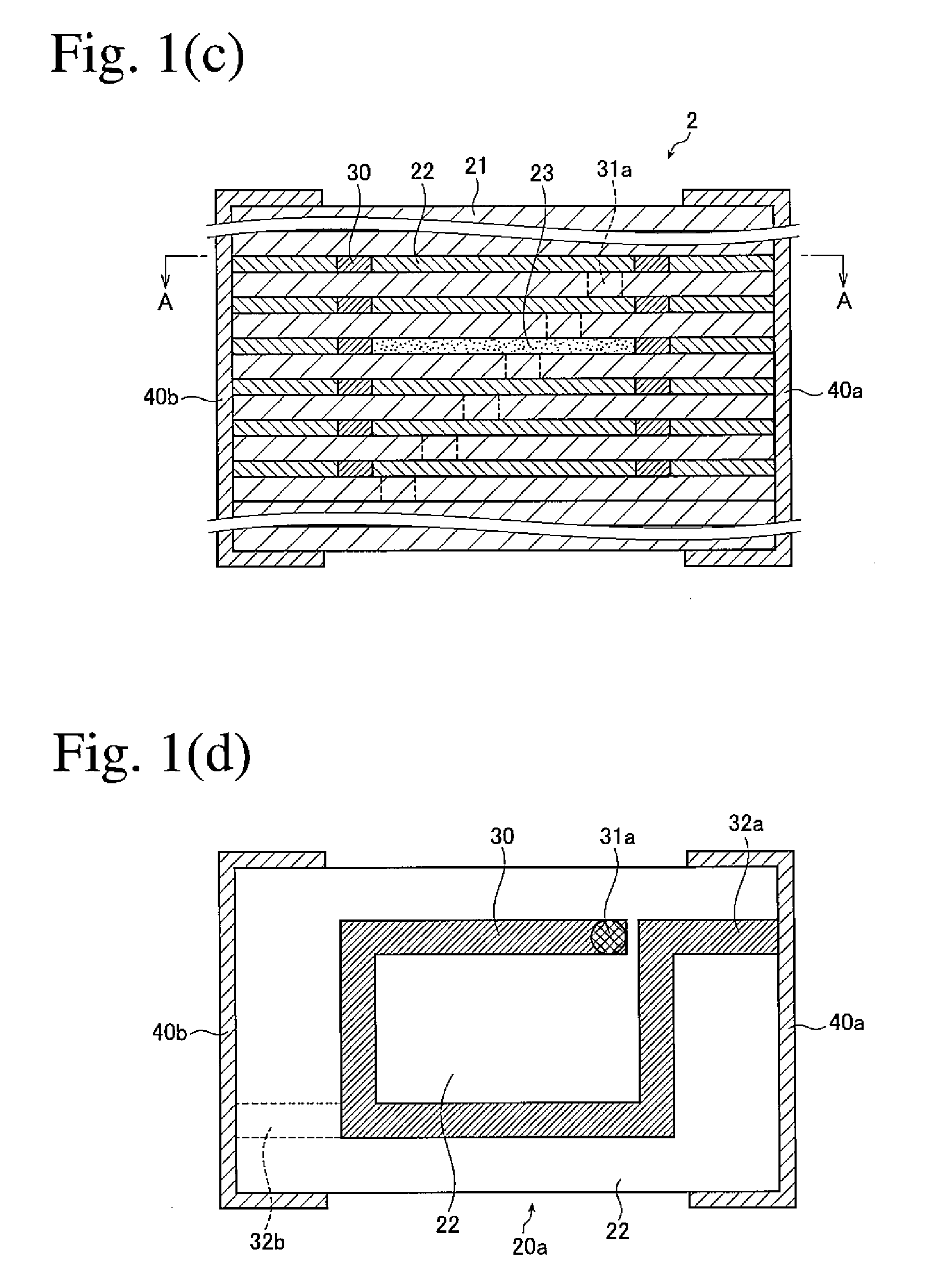
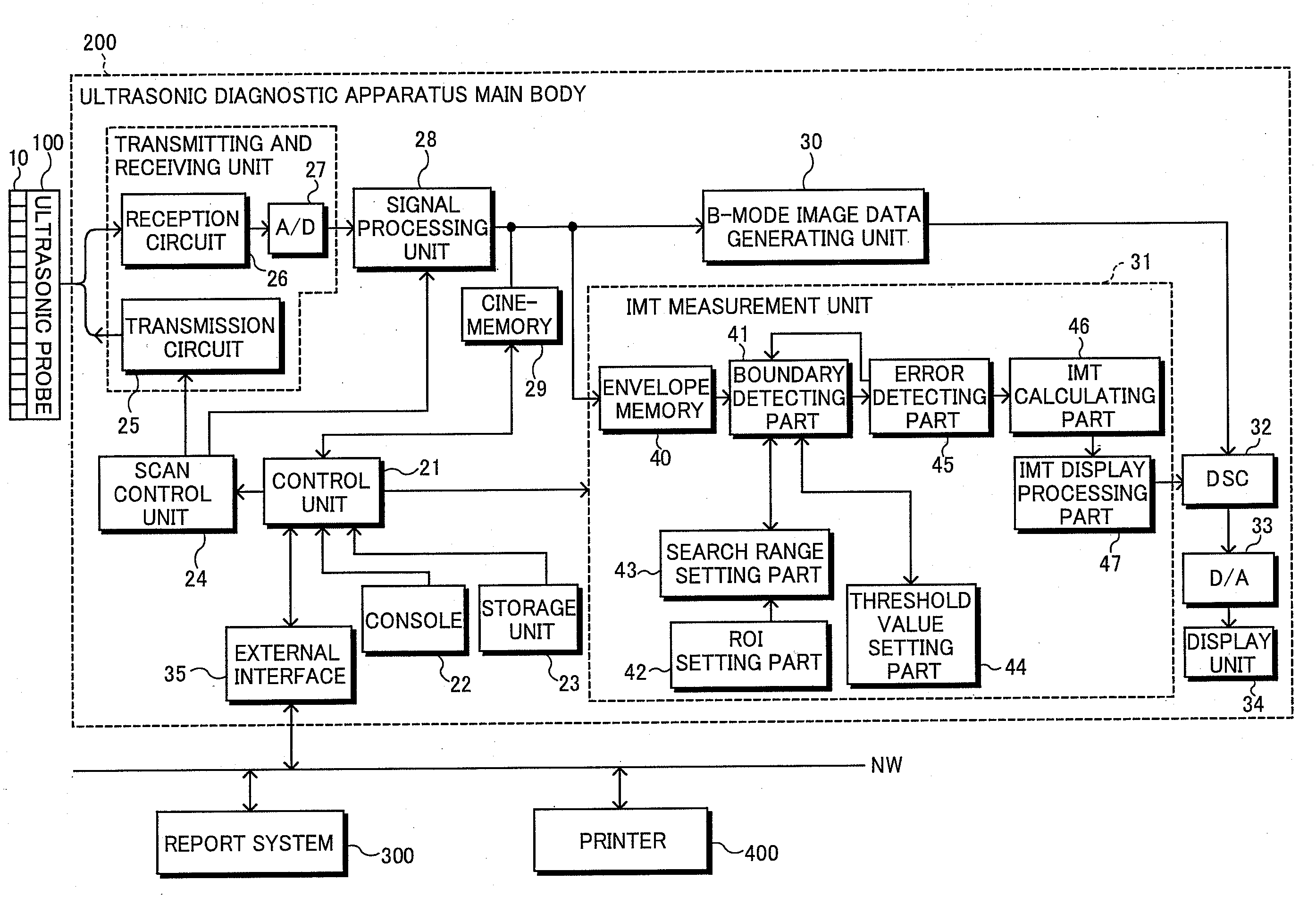
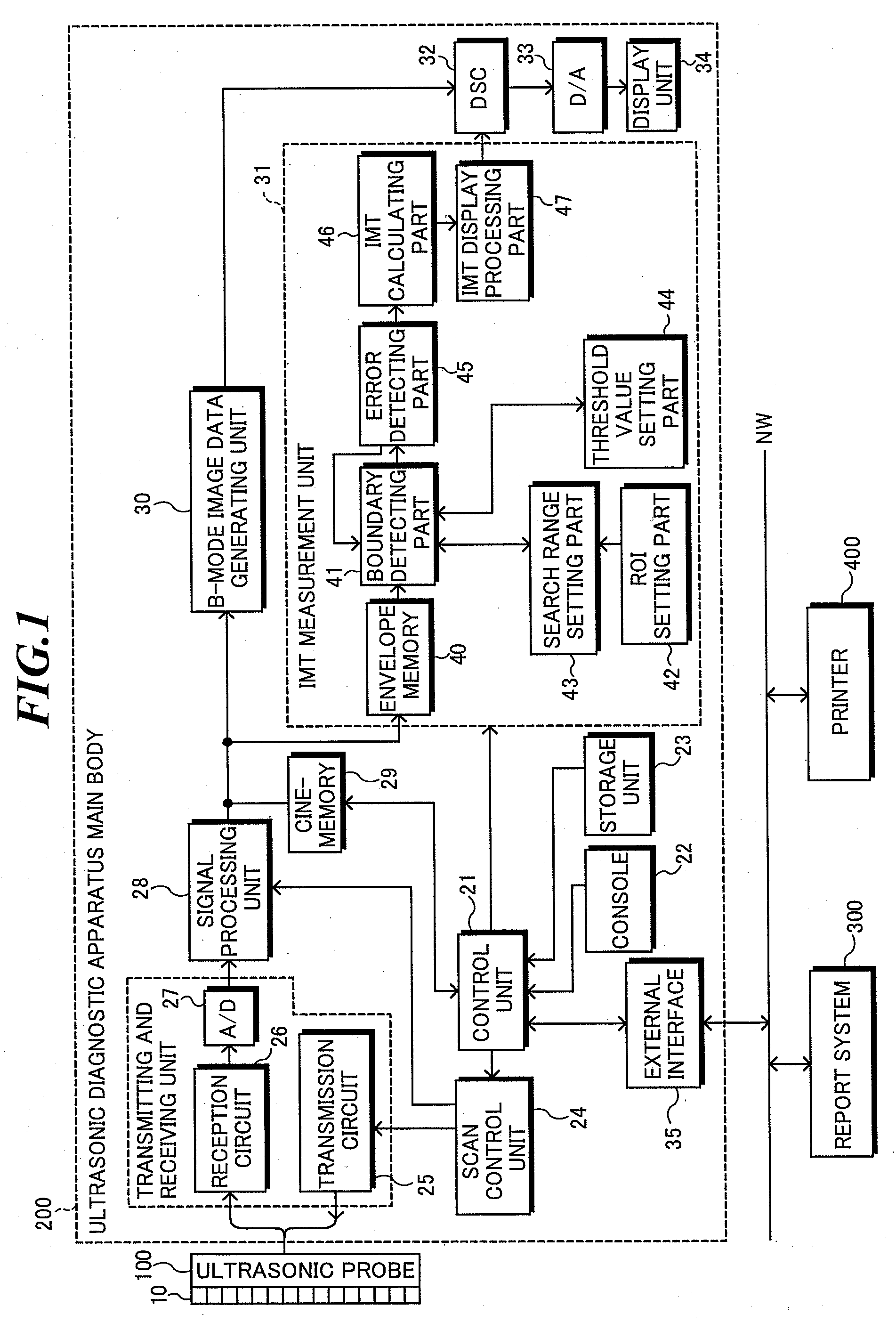
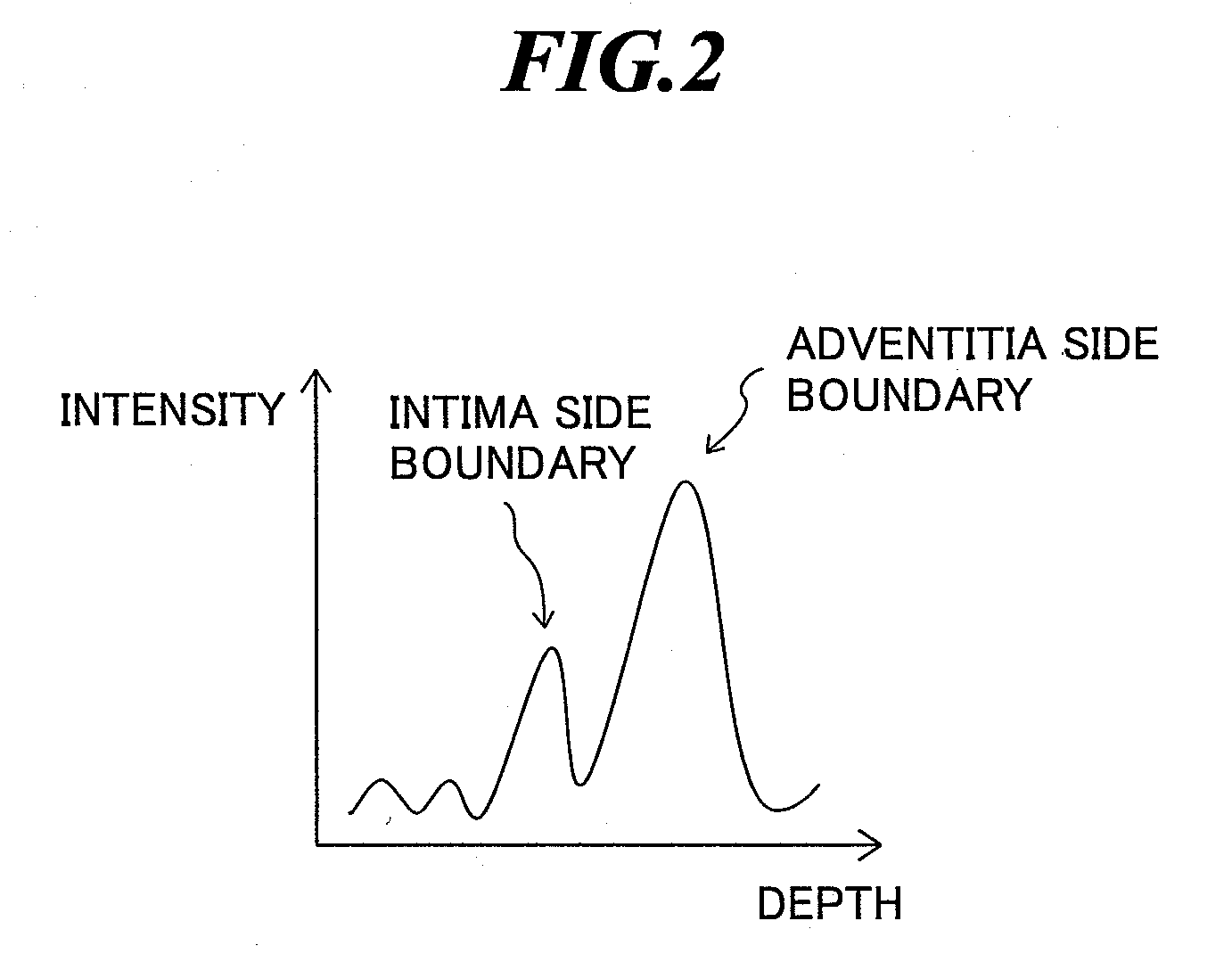
Ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus, imt measurement method, and imt measurement program
ActiveUS20080171939A1Highly quantitative IMT measurementSmall variationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementUltrasound diagnosticsBoundary detection
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Display device
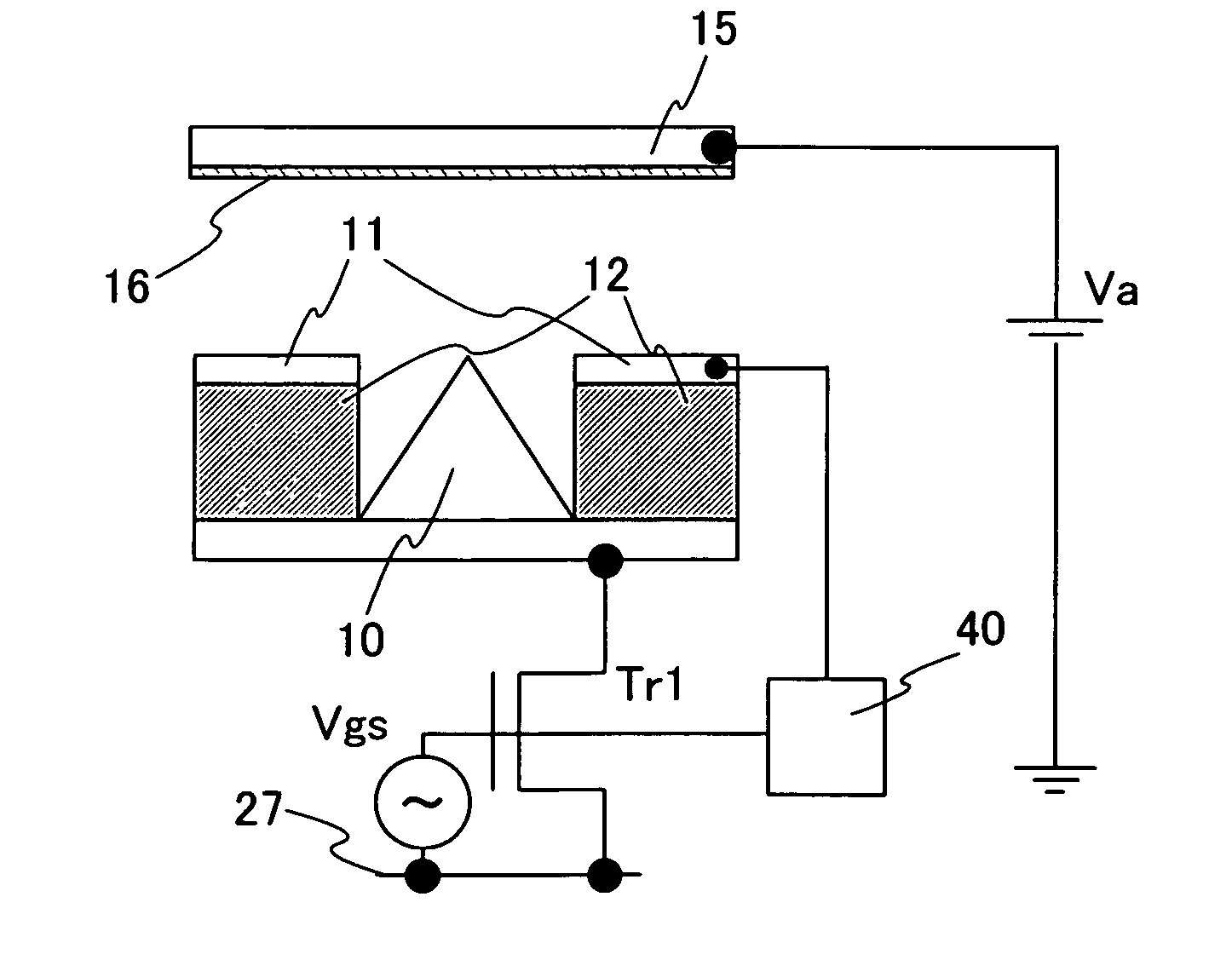
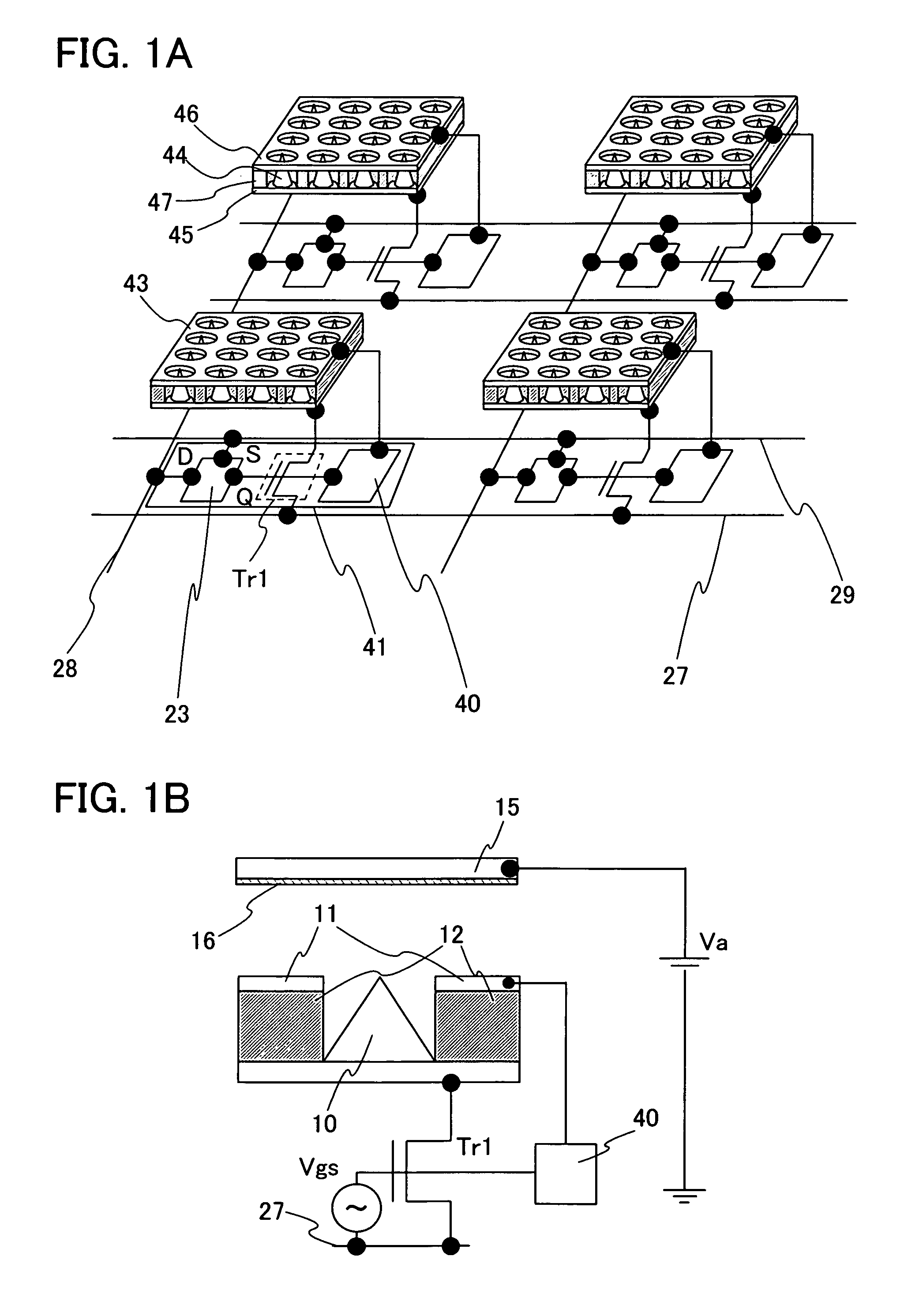
InactiveUS20070085778A1Reduce voltageSmall in luminance variationCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesStatic indicating devicesActive matrixLow voltage
To provide a highly reliable display device whose electrical element is applied with a low voltage. The display device is an active matrix FED display device whose pixel has an individual extraction gate electrode, an emitter array, a driving transistor which is connected to the emitter array in series, a potential control circuit which controls the potential of the extraction gate electrode, and a circuit which includes a switching element and a voltage holding element. By varying the potential of the extraction gate electrode in accordance with Vgs of the driving transistor, the active matrix driving method is performed by connecting a driving transistor to the emitter array in series and voltage which is applied to the driving transistor can be reduced.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Iodine Polarizing Film, a Method for Producing the Same, and a Polarizing Plate Using the Same
InactiveUS20080192345A1Stably produced industriallyExcellent polarizing filmLiquid crystal compositionsOptical articlesCross-linkOrganic acid
The present invention relates to a polarizing film obtained by stretching a polyvinyl alcohol resin film containing iodine, an iodide a cross-linking agent and / or waterproofing agent and then treating the film with a solution containing 0.0001 to 5.0 wt % of inorganic acid except for boric acid or a salt thereof and / or organic acid and having a pH of preferably 2≦pH≦5, more preferably 2.2≦pH≦5. Said polarizing film is excellent in wet heat durability and shows less decrease in polarization characteristics in wet heat test and said polarizing film obtained in a further preferable embodiment is also excellent in dry heat durability.
Owner:NIPPON KAYAKU CO LTD +1
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140103339A1Improve reliabilityStable electrical characteristicsTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor device
A semiconductor device formed using an oxide semiconductor layer and having small electrical characteristic variation is provided. A highly reliable semiconductor device including an oxide semiconductor layer and exhibiting stable electric characteristics is provided. Further, a method for manufacturing the semiconductor device is provided. In the semiconductor device, an oxide semiconductor layer is used for a channel formation region, a multilayer film which includes an oxide layer in which the oxide semiconductor layer is wrapped is provided, and an edge of the multilayer film has a curvature in a cross section.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Quantitative detection kit for neuronspecific enolase (NSE) and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102914650AImprove stabilityEasy to operate manuallyMaterial analysisBiotin-streptavidin complexAntigen
The invention relates to a quantitative detection kit for NSE and a preparation method and application of the quantitative detection kit. The kit comprises a calibrator, a magnetic separation reagent, an enzyme reactant, a stable reinforcing agent and a chemiluminiscent substrate, wherein the calibrator is obtained by treating NSE antigen through a reducing agent solution and diluting the NSE antigen to a buffer solution containing a nonionic surfactant; the magnetic separation reagent is obtained by immunofixation of a biotinylation antibody and streptavidin magnetic particles; the enzyme reactant comprises a NSE tracing antibody marked by alkaline phosphatase; and the stable reinforcing agent comprises a multicomponent immune compound interfered by an anti-heterophilic antibody. The invention further relates to a preparation method of the kit and a method of applying the kit to quantitatively detect a tumor marker NSE. The kit is reliable in performance, high in flexibility, and wide in linear range, and matched up with an automatic instrument for use. At present, the kit has already obtained a third registration certificate of a diagnostic reagent in SFDA (State Food and Drug Administration).
Owner:BEIJING DIACHA BIO ENG
Polyarylene sulfide and process for producing the same
A dehydration step is conducted by heating a mixture containing an organic amide solvent and a sulfur source including an alkali metal hydrosulfide, and a part of an overall charged amount of an alkali metal hydroxide as needed. The mixture remaining within the system after the dehydration step is mixed with a dihalo-aromatic compound, the resultant mixture is heated to conduct a polymerization reaction, and the alkali metal hydroxide is added to the mixture for polymerization reaction continuously or in portions to control the pH of the mixture for polymerization reaction within a range of from 7 to 12.5 from the beginning to the end of the polymerization reaction. The poly(arylene sulfide) according to the present invention has a nitrogen content of at most 800 ppm.
Owner:KUREHA KAGAKU KOGYO KK
Resin-filled carrier for electrophotographic developer and electrophotographic developer using the resin-filled carrier
A resin-filled carrier for an electrophotographic developer which carrier is obtained by filling a resin in the voids of a porous ferrite core material, wherein the Cl concentration of the porous ferrite core material, measured by an elution method, is 10 to 280 ppm and the resin contains an amine compound, and an electrophotographic developer using the resin-filled carrier.
Owner:POWDERTECH
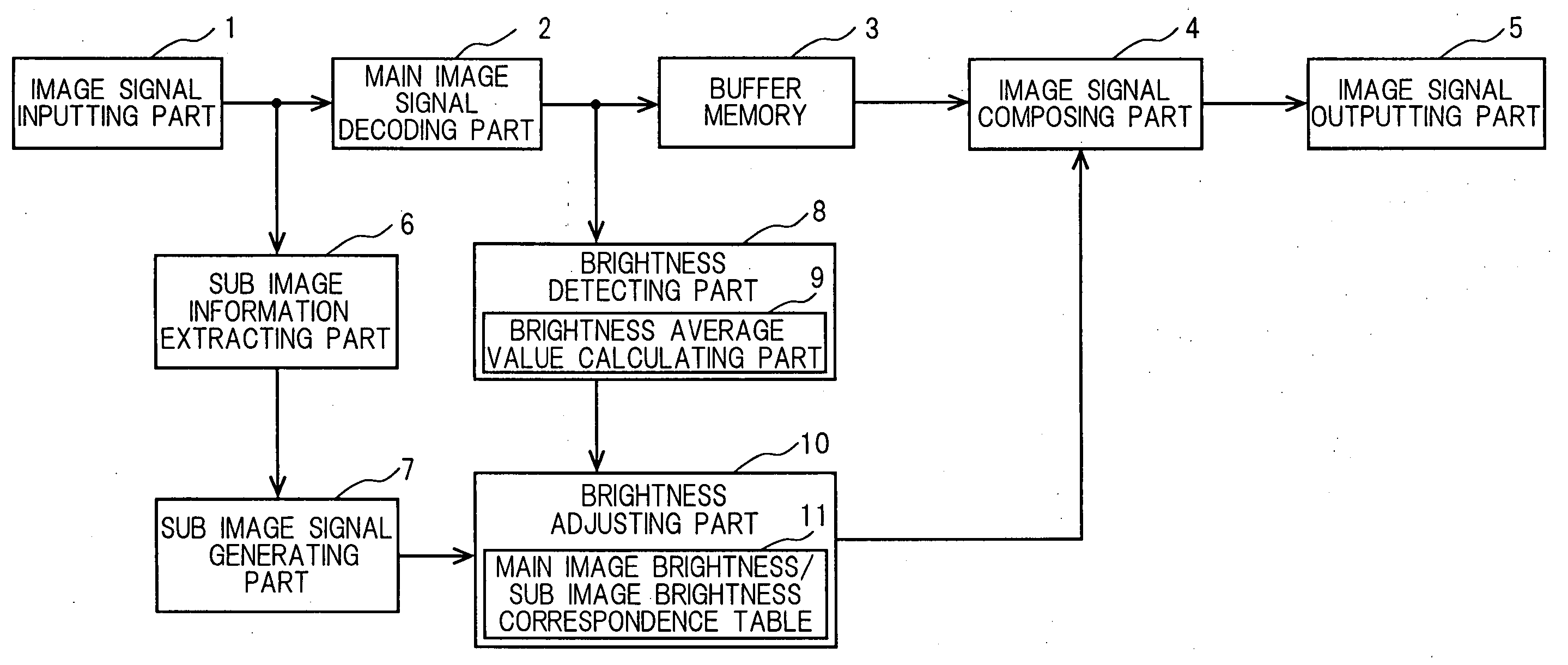
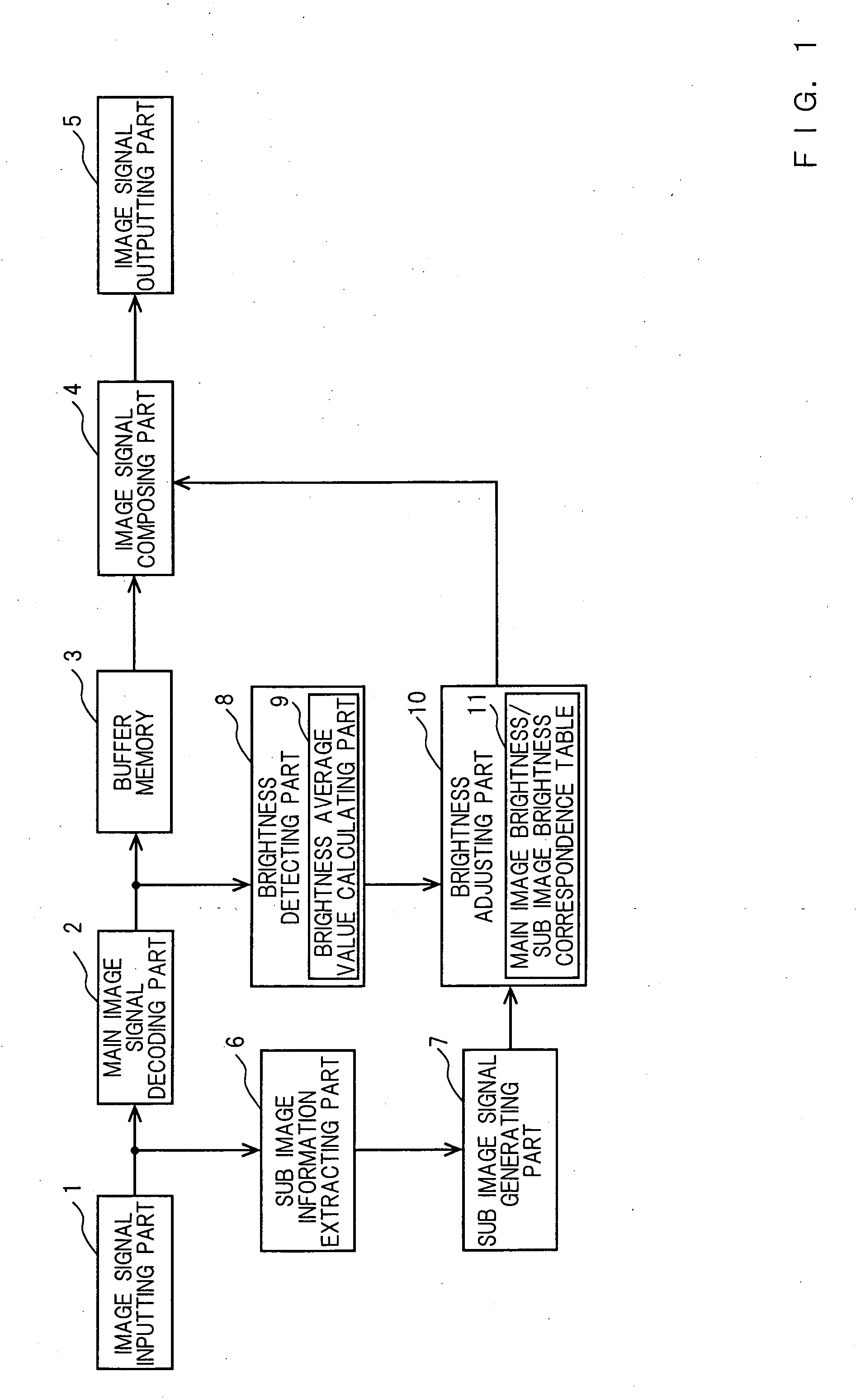
Image reproducing apparatus and image reproducing method
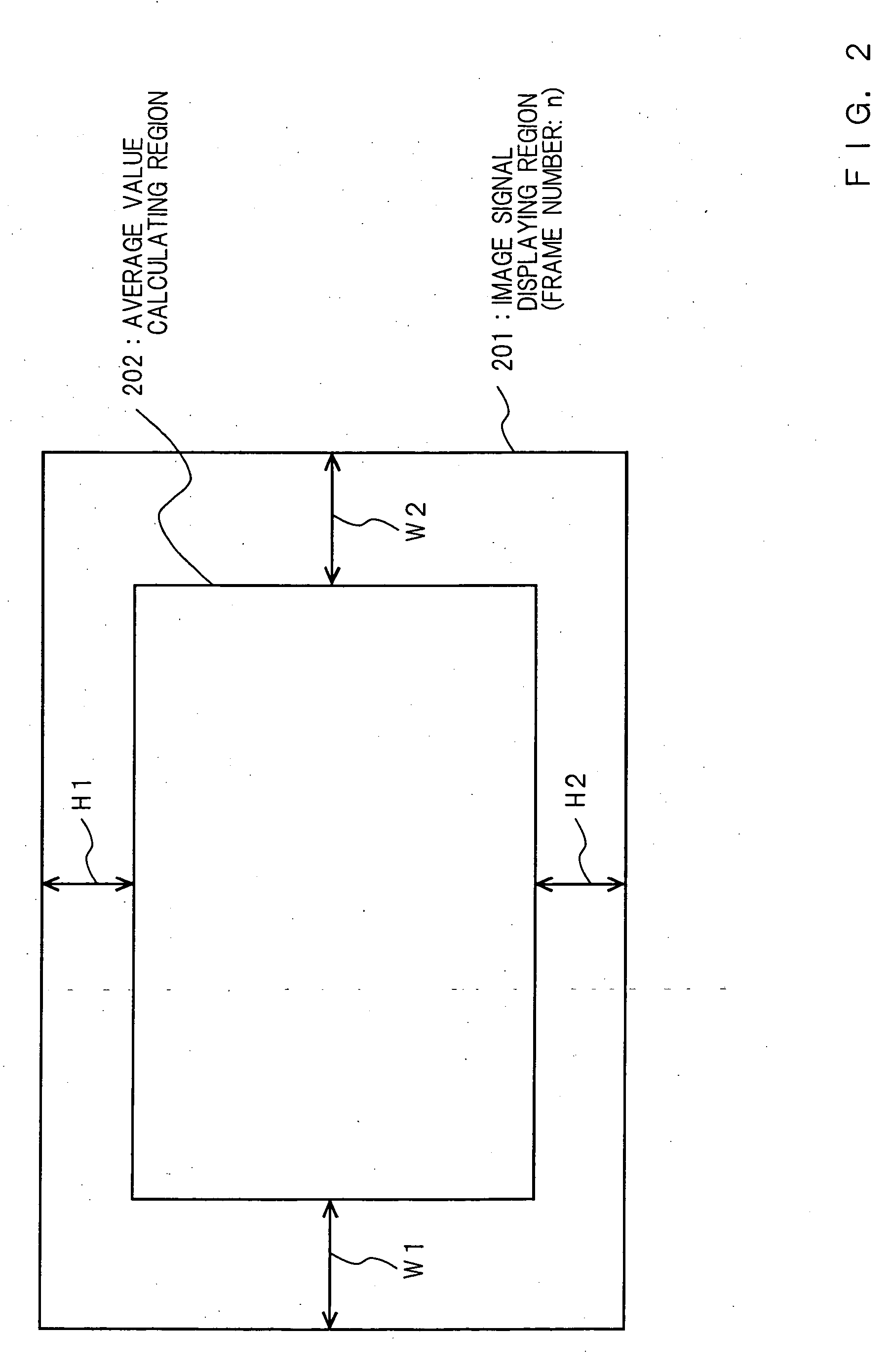
InactiveUS20050117813A1Easy to viewSuffer much eyestrainTelevision system detailsStatic indicating devicesComputer graphics (images)Image signal
An image reproducing device and an image reproducing method that can control a brightness and / or a contrast of a sub image according to a brightness and / or a contrast of a main image and minimize eyestrain of users are provided. The image reproducing device comprises an image signal inputting part for receiving input of a first image signal; a sub image signal generating part for generating a sub image signal from information on a sub image extracted from the above-mentioned first image signal; a main image signal decoding part for extracting a main image signal from the above-mentioned first image signal and decoding the above-mentioned main image signal; a brightness detecting part for detecting a brightness of the above-mentioned main image signal and calculating a brightness average value; a brightness adjusting part for adjusting a brightness of the above-mentioned sub image signal based on the above-mentioned brightness average value; an image signal composing part for synchronizing the above-mentioned main image signal and the above-mentioned sub image signal, the brightness of which is adjusted, composing them and generating a second image signal; and an image signal outputting part for outputting the above-mentioned second image signal.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Variable power relay optical system and microscope equipped therewith
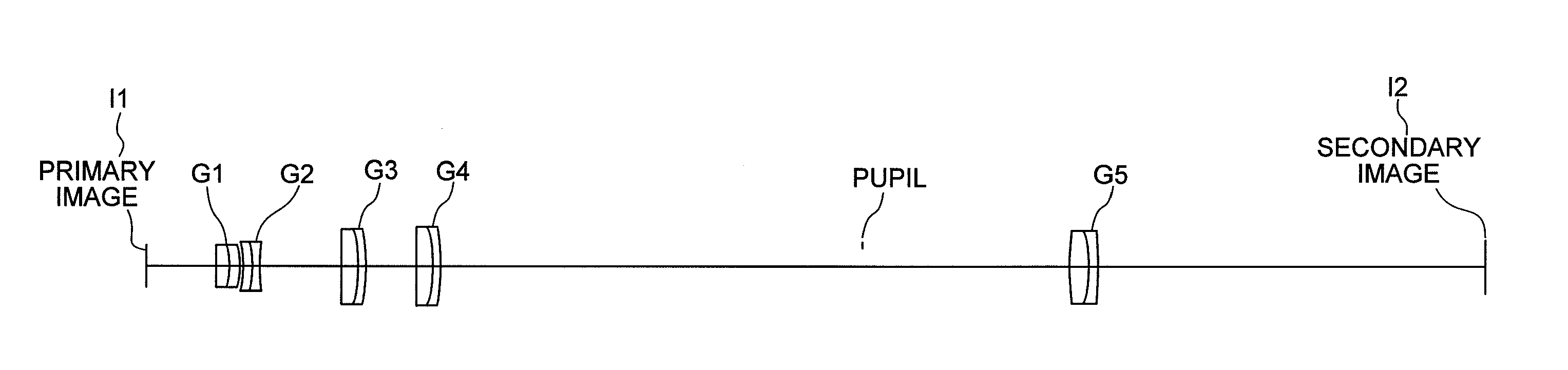
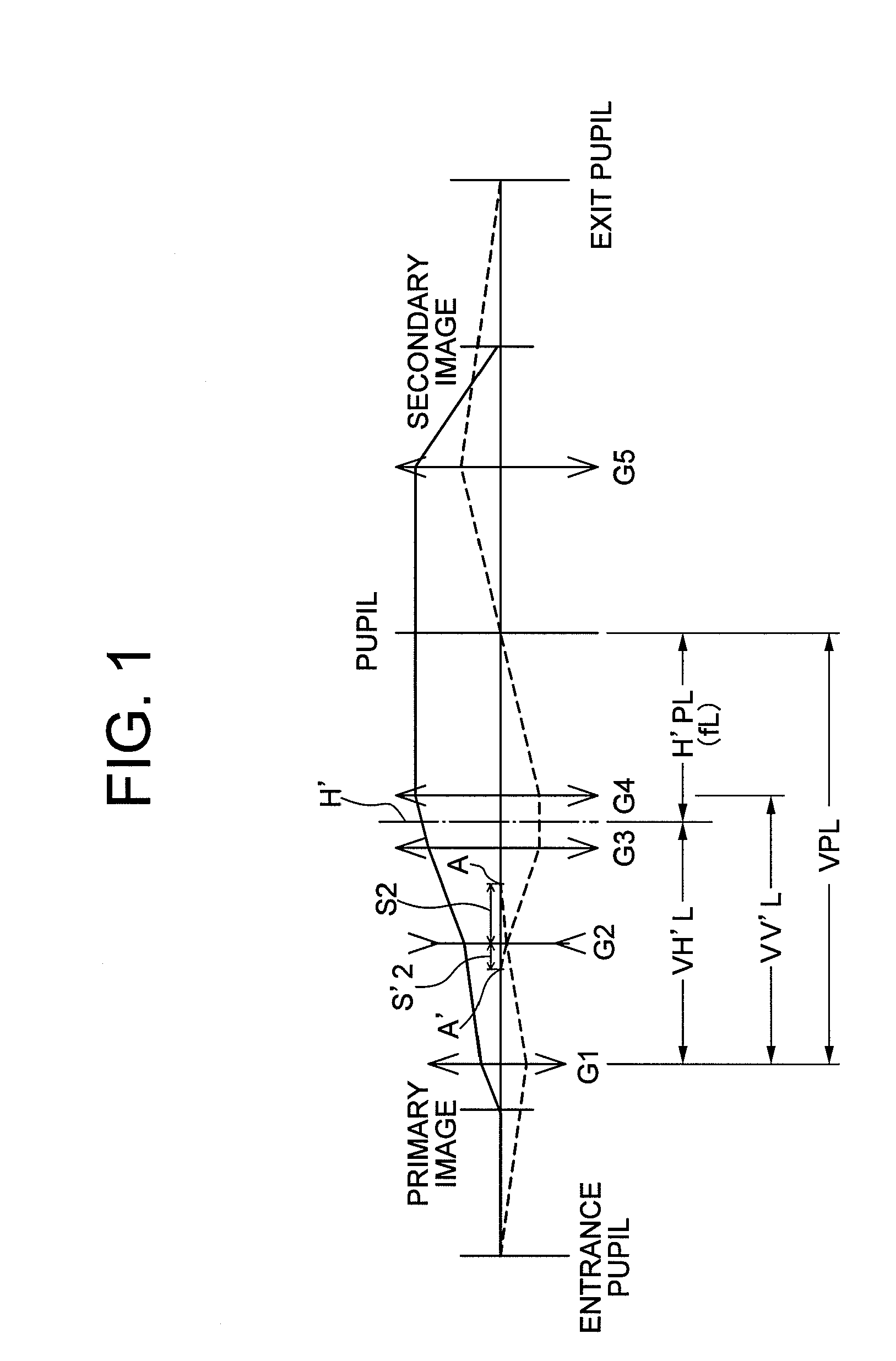
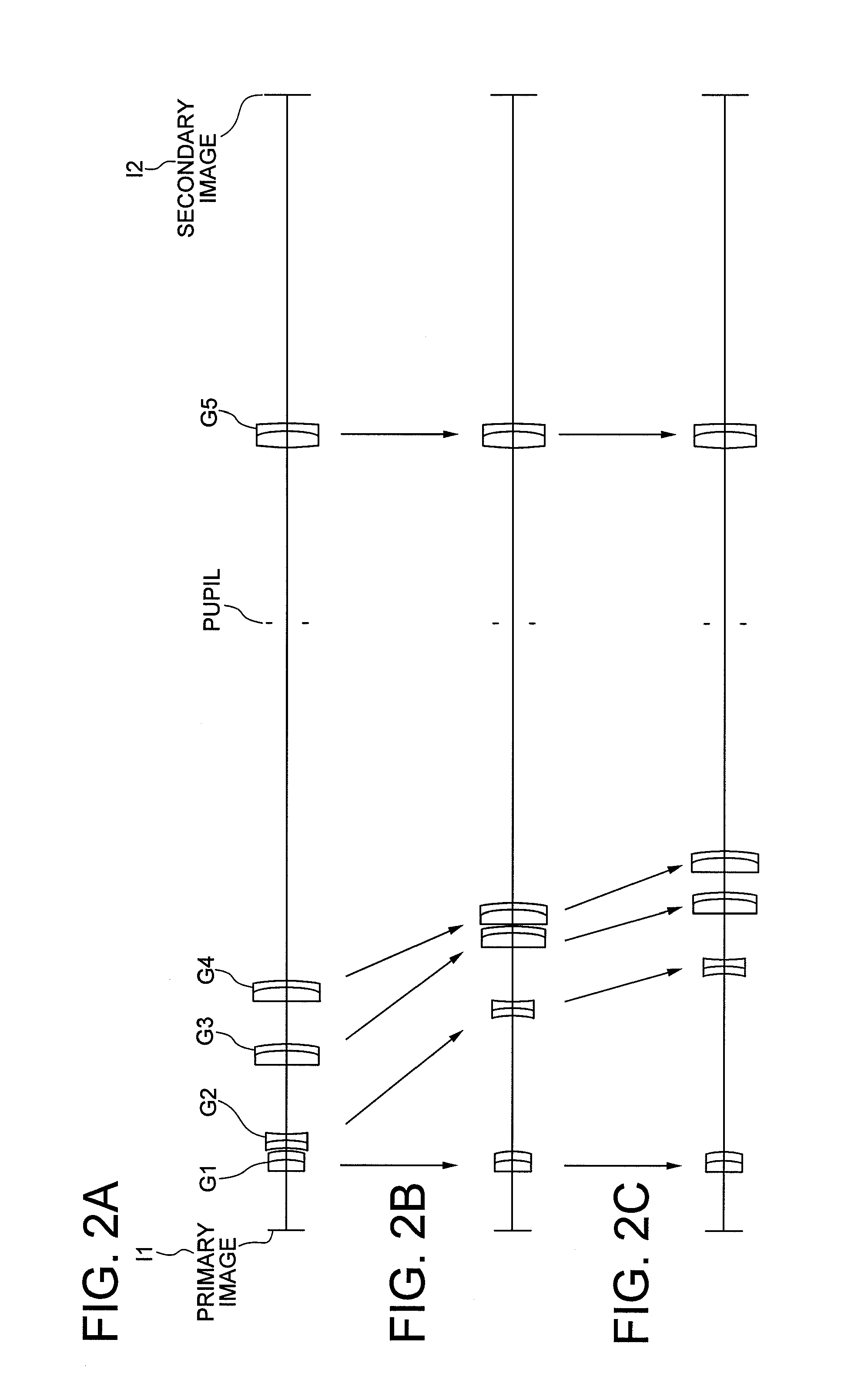
A variable power relay optical system comprising: a variable power lens performing zooming a secondary image based on light from a primary image; and a rear group forming the secondary image based on the light passing through the variable power lens; the variable power lens consisting of, in order from the primary image side, a first group having positive power, a second group having negative power, a third group having positive power, and a fourth group having positive power, upon zooming from a high magnification end to a low magnification end, the fourth group being moved to the secondary image side, and a distance between the first group and the second group increasing, positions of the primary image and the secondary image, an entrance pupil of the variable power relay optical system, a pupil of the variable power lens, and an exit pupil of the variable power relay optical system being substantially kept constant, and the pupil of the variable power lens being disposed to the secondary image side of the last surface of the variable power lens.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Oxide for semiconductor layer of thin-film transistor, sputtering target, and thin-film transistor
InactiveUS20130270109A1High reliabilityExcellent switch characteristicAluminium compoundsConductive materialOxide semiconductorOxide
The oxides for semiconductor layers of thin-film transistors according to the present invention include: In; Zn; and at least one element (X group element) selected from the group consisting of Al, Si, Ta, Ti, La, Mg and Nb. The present invention makes it possible to provide oxides for semiconductor layers of thin-film transistors, in which connection thin-film transistors with In—Zn—O oxide semiconductors not containing Ga have favorable switching characteristics and high stress resistance, and in particular, show a small variation of the threshold voltage before and after positive bias stress tests, thereby having high stability.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
Semiconductor memory device and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110216571A1Reduce voltageReduce variationTransistorSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceEngineering
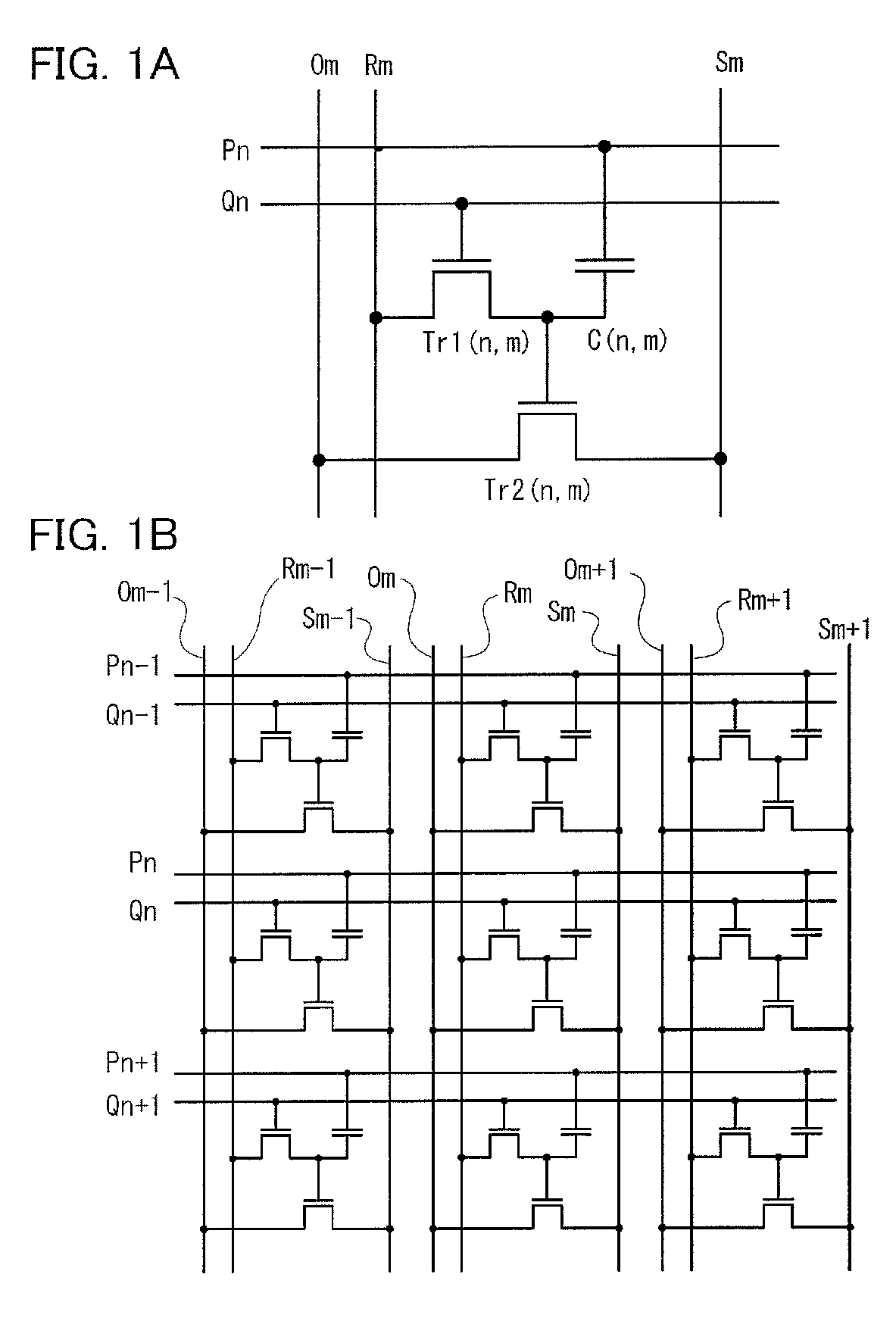
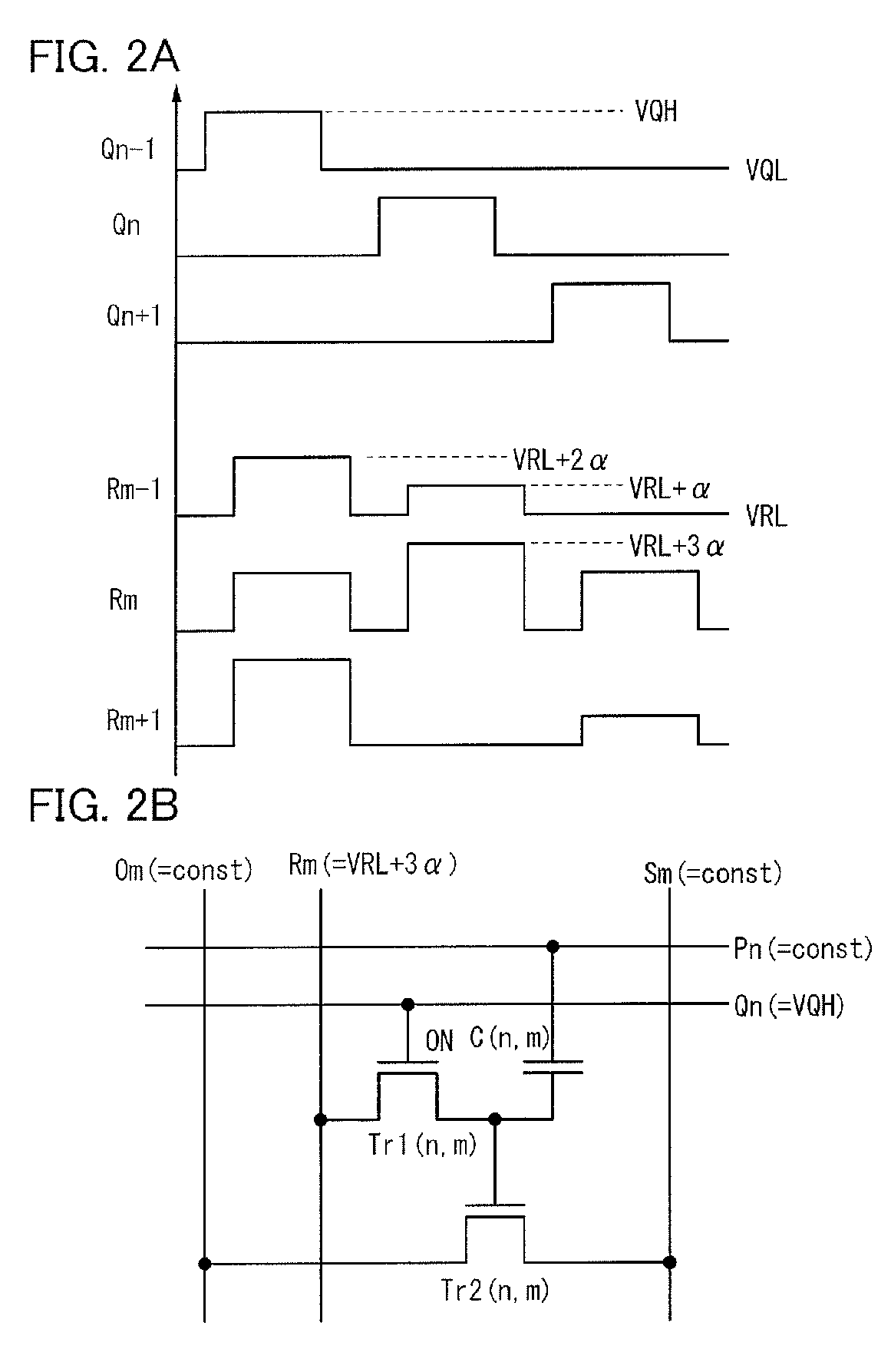
A matrix is formed using a plurality of memory cells in each of which a drain of the writing transistor is connected to a gate of a reading transistor and one electrode of a capacitor. A gate of the writing transistor, a source of the writing transistor, a source of the reading transistor, and a drain of the reading transistor are connected to a writing word line, a writing bit line, a reading bit line, and a bias line, respectively. In order to reduce the number of wirings, a writing word line to which the gate of the writing transistor is not connected is substituted for the reading word line. Further, the writing bit line is substituted for the reading bit line.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
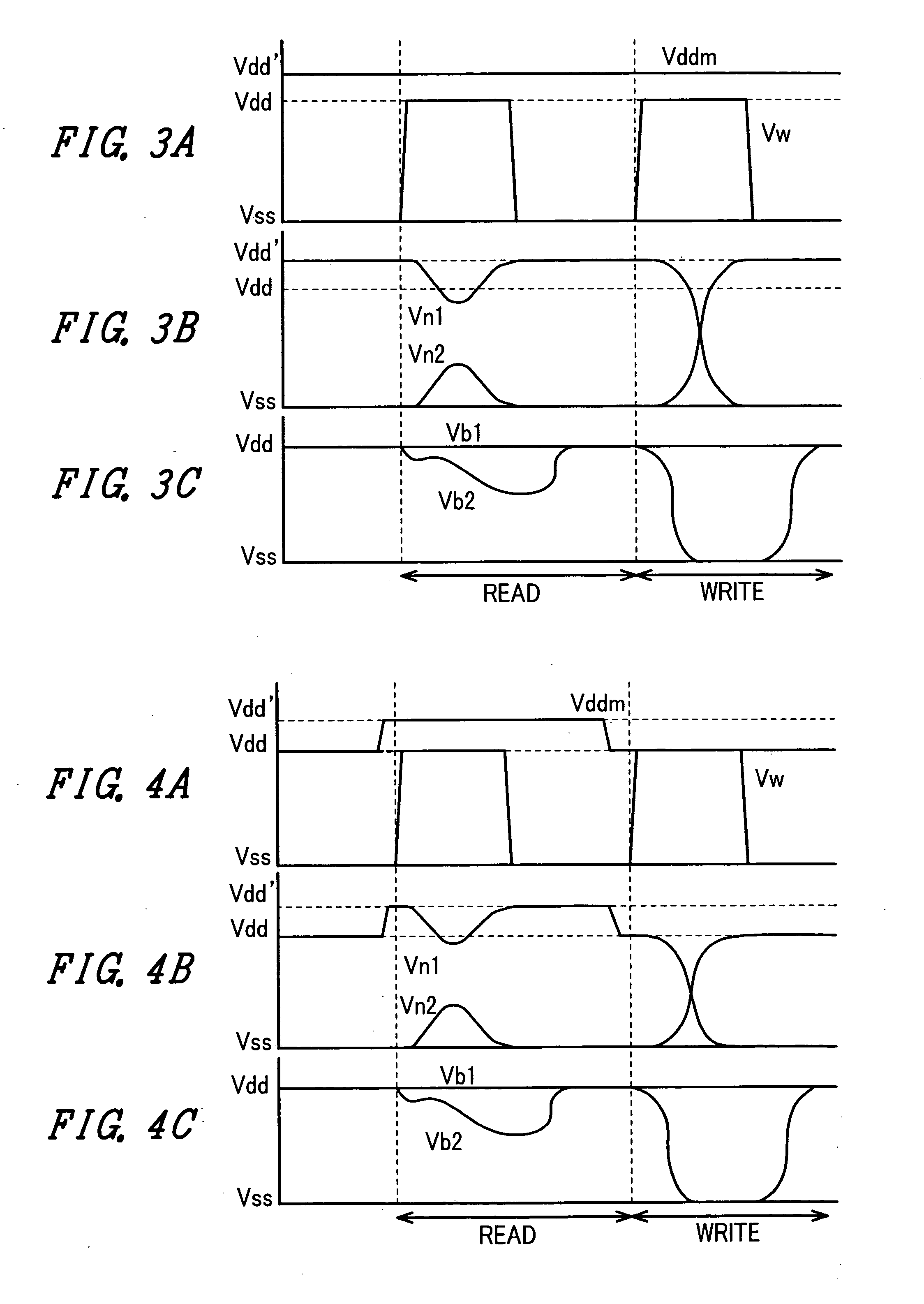
Semiconductor memory device with memory cells operated by boosted voltage
InactiveUS20050024917A1Reduced operating requirementsStatic noise marginSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLow voltageEngineering
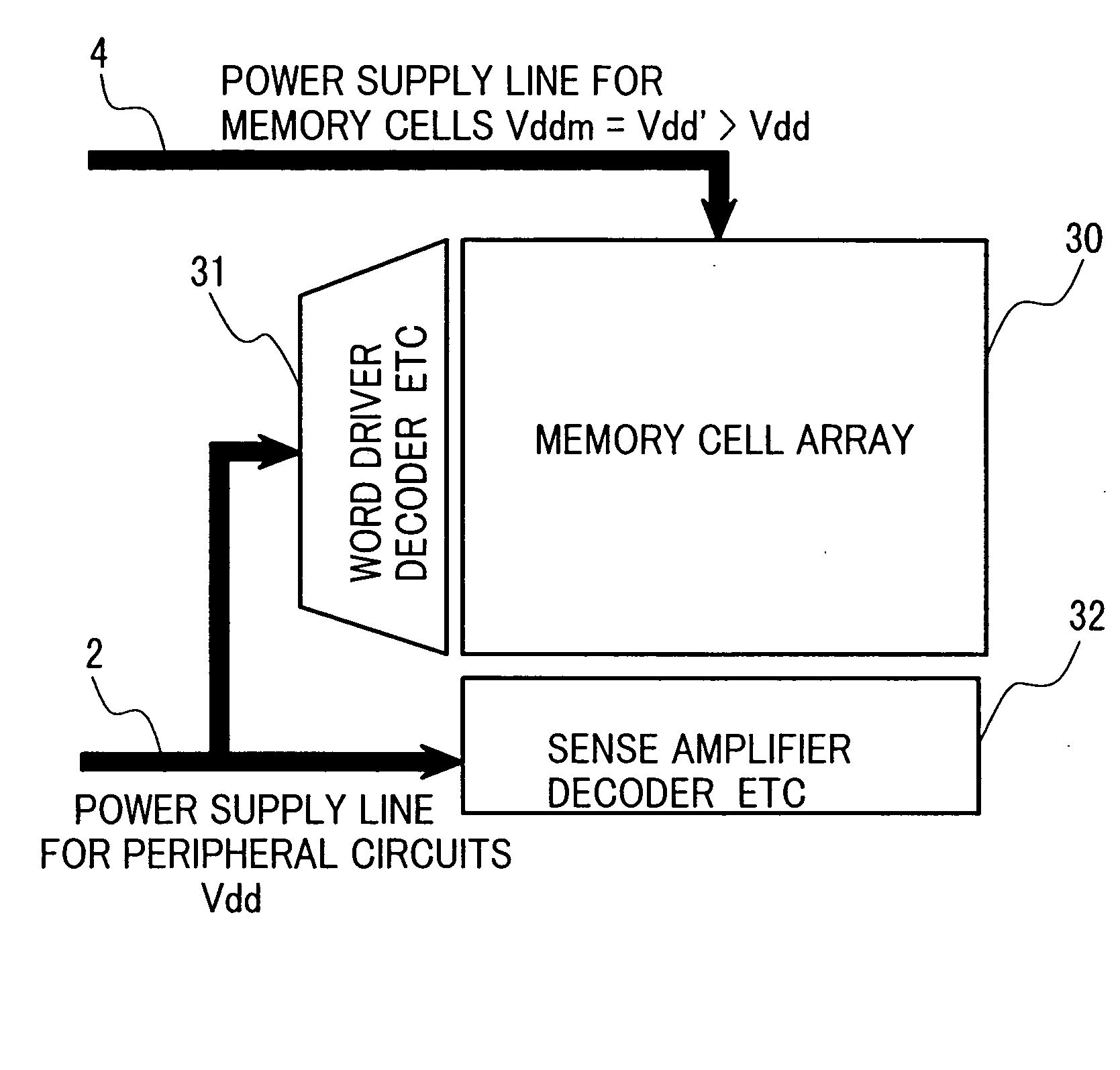
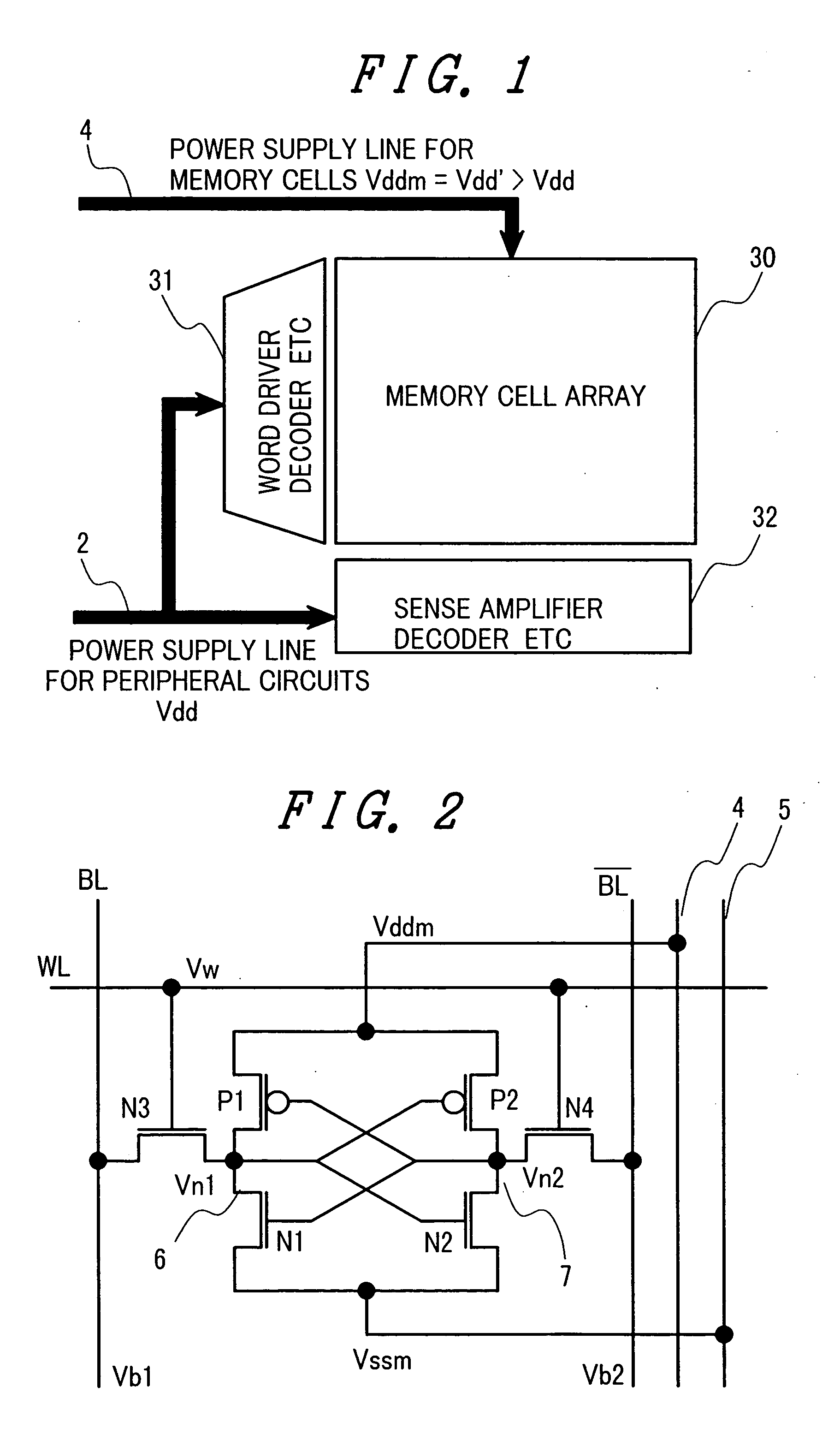
A memory using an SRAM memory cell intended for low-voltage operation is designed to decrease the threshold value of MOS transistors constituting the memory cell without substantial decrease in the static noise margin, which is the operational margin of the memory cell. To this end, a voltage Vdd′ higher than a power supply voltage Vdd of a power supply line for peripheral circuits is supplied from a power supply line for memory cells as a power supply voltage for memory cells. Since the conductance of driver MOS transistors is increased, the threshold voltage of the MOS transistors within the memory cells can be reduced without reducing the static noise margin. Further the ratio of width between the driver MOS transistor and a transfer MOS transistor can be set to 1, thereby allowing a reduction in the memory cell area.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
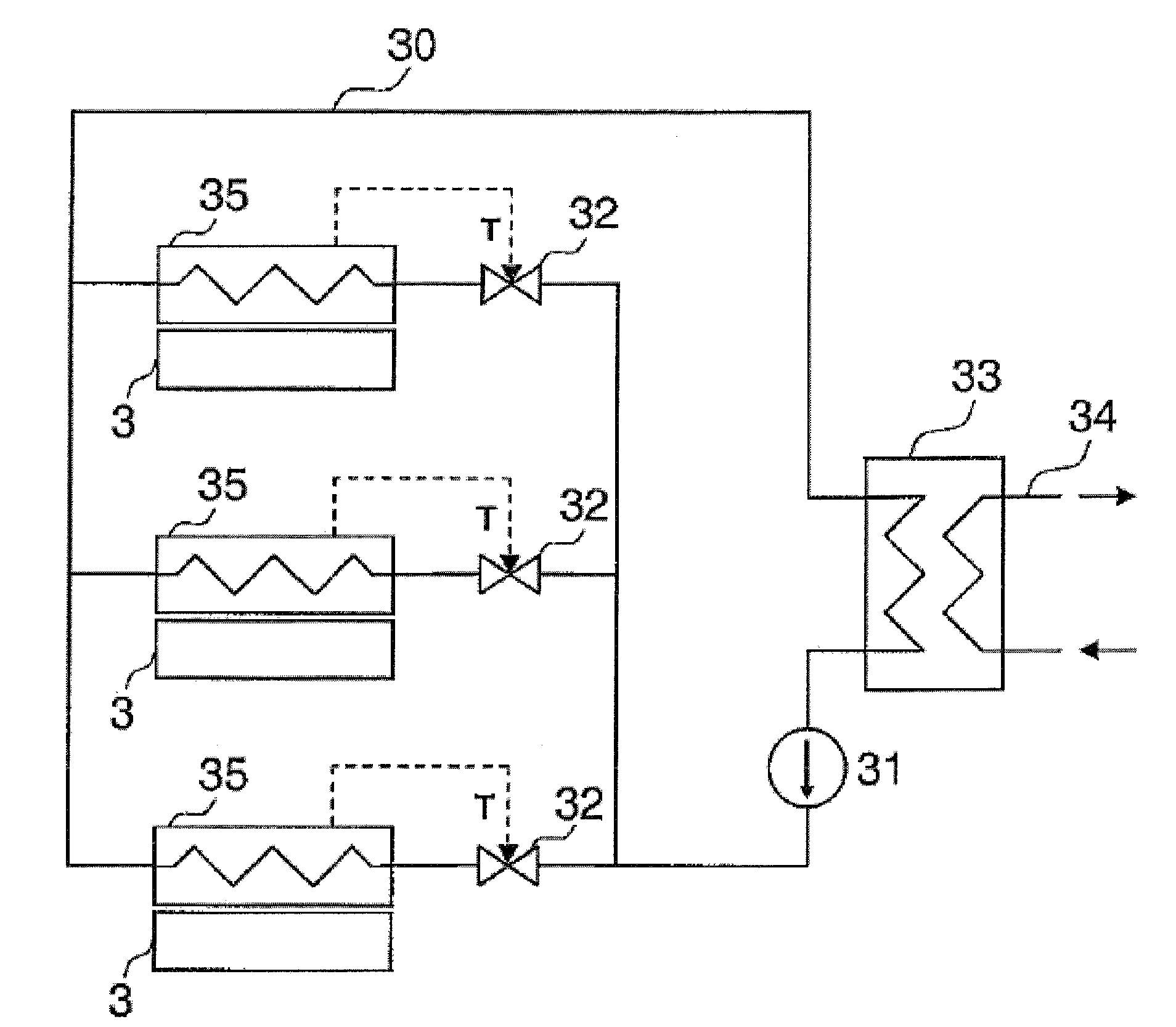
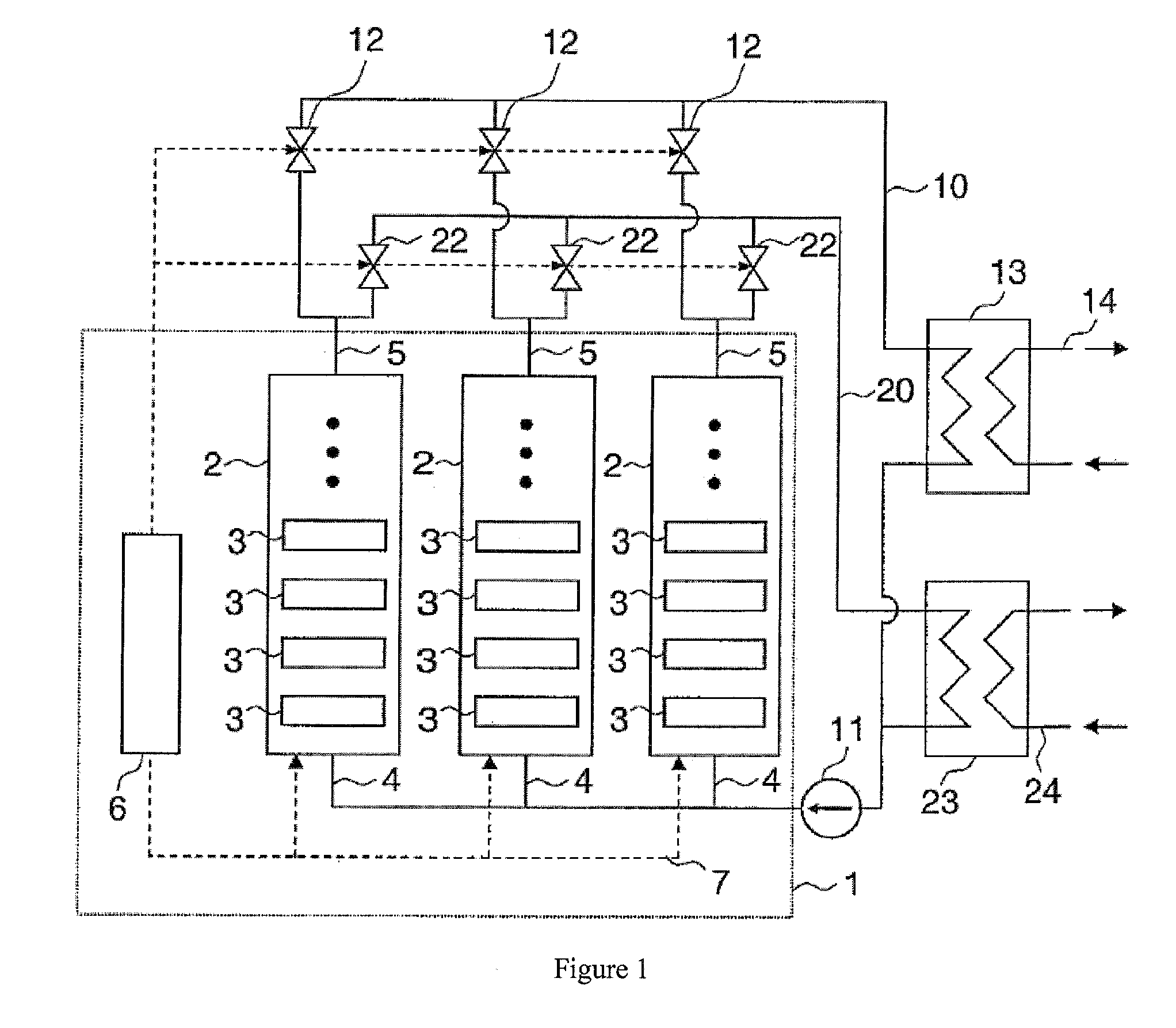
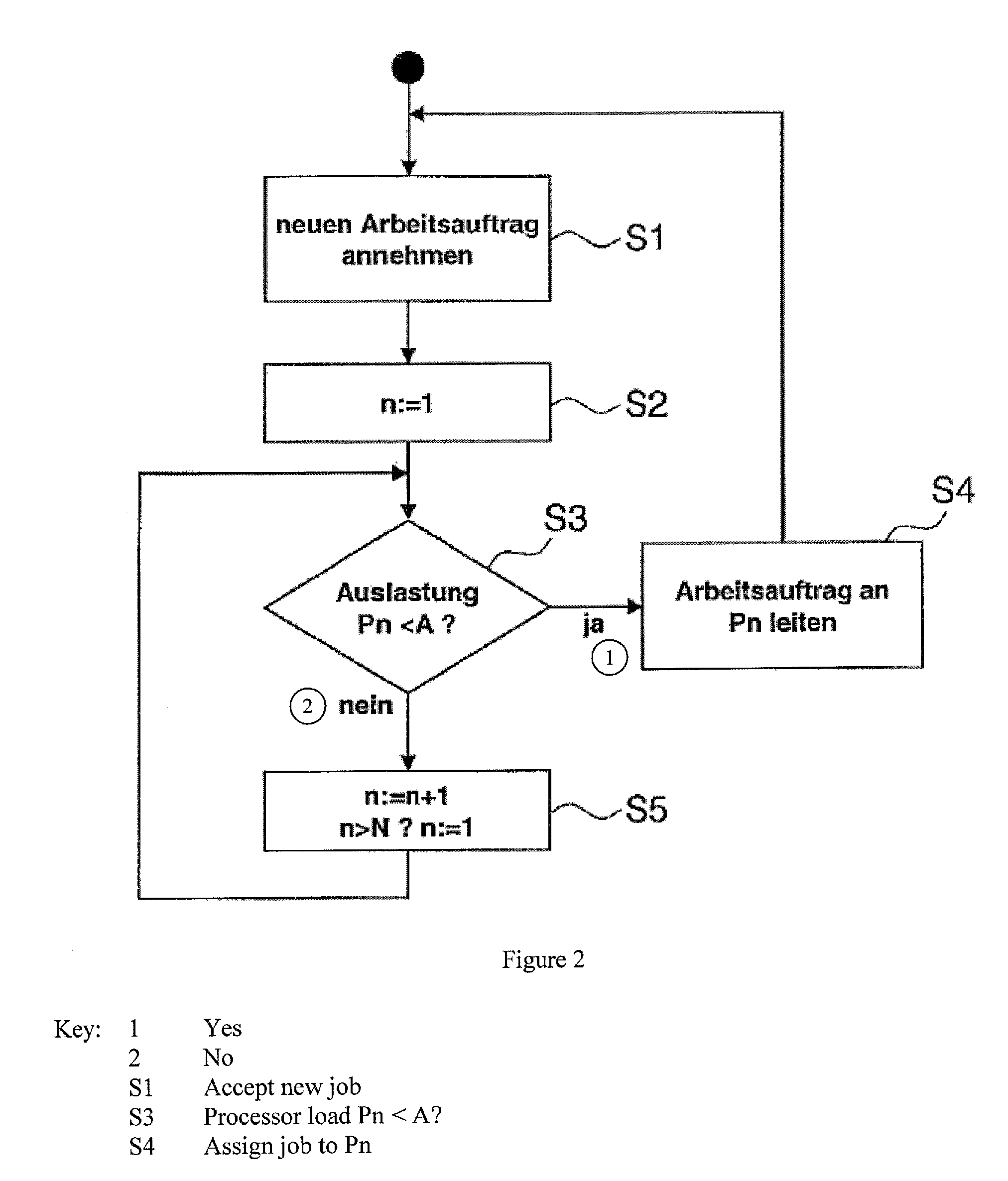
Method and system for using the waste heat of a computer system
InactiveUS20090114370A1Improve efficiencyUse waste heatDigital data processing detailsAir heatersComputerized systemWaste heat
A method for using the waste heat of a computer system with a plurality of processors comprises the following steps. Jobs in the computer system are distributed to the processors in such a way that processors of a first group of processors are operated with a high processor load and processors of a second group of processors are operated with only a minimal processor load. In another method, waste heat is dissipated from the processors by a cooling device, wherein the waste heat dissipated from the processors is regulated in such a way that the processor assumes a temperature that is greater than a given minimum temperature. In both cases, the waste heat of the processors is transferred to a device for using the waste heat.
Owner:KONIG CHRISTOPH
Optical film and display system
InactiveUS7075604B2Easy to viewIncrease contrastPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsTectorial membraneThermoplastic
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Manufacturing method of substrate having conductive layer and manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7449372B2Little changeHigh yieldTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsCooking & bakingOptoelectronics
The manufacturing method of a substrate having a conductive layer has the steps of: forming an inorganic insulating layer over a substrate; forming an organic resin layer with a desired shape over the inorganic insulating layer; forming a low wettability layer with respect to a composition containing conductive particles on a first exposed portion of the inorganic insulating layer; removing the organic resin layer; and coating a second exposed portion of the inorganic insulating layer with a composition containing conductive particles and baking, thereby forming a conductive layer.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
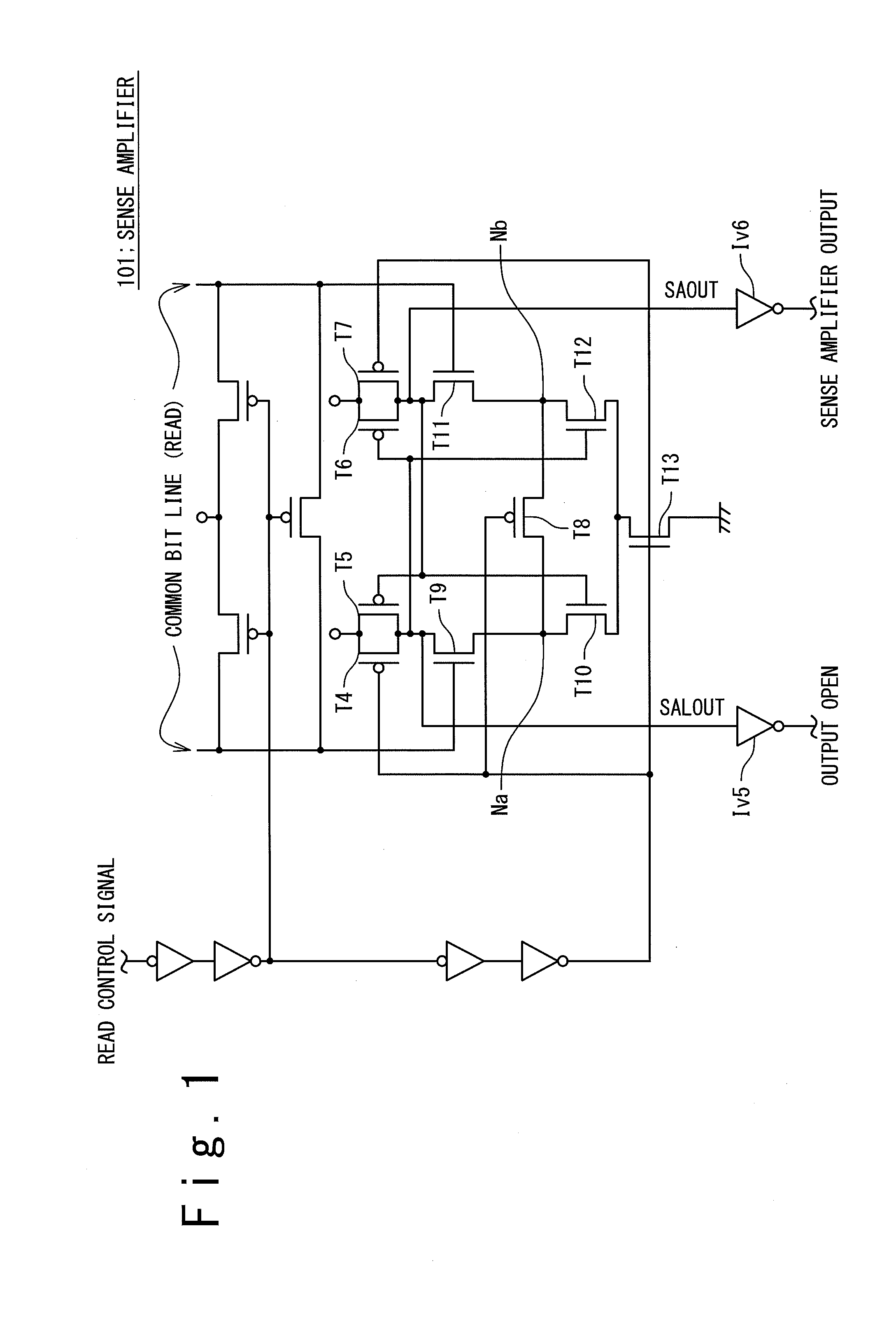
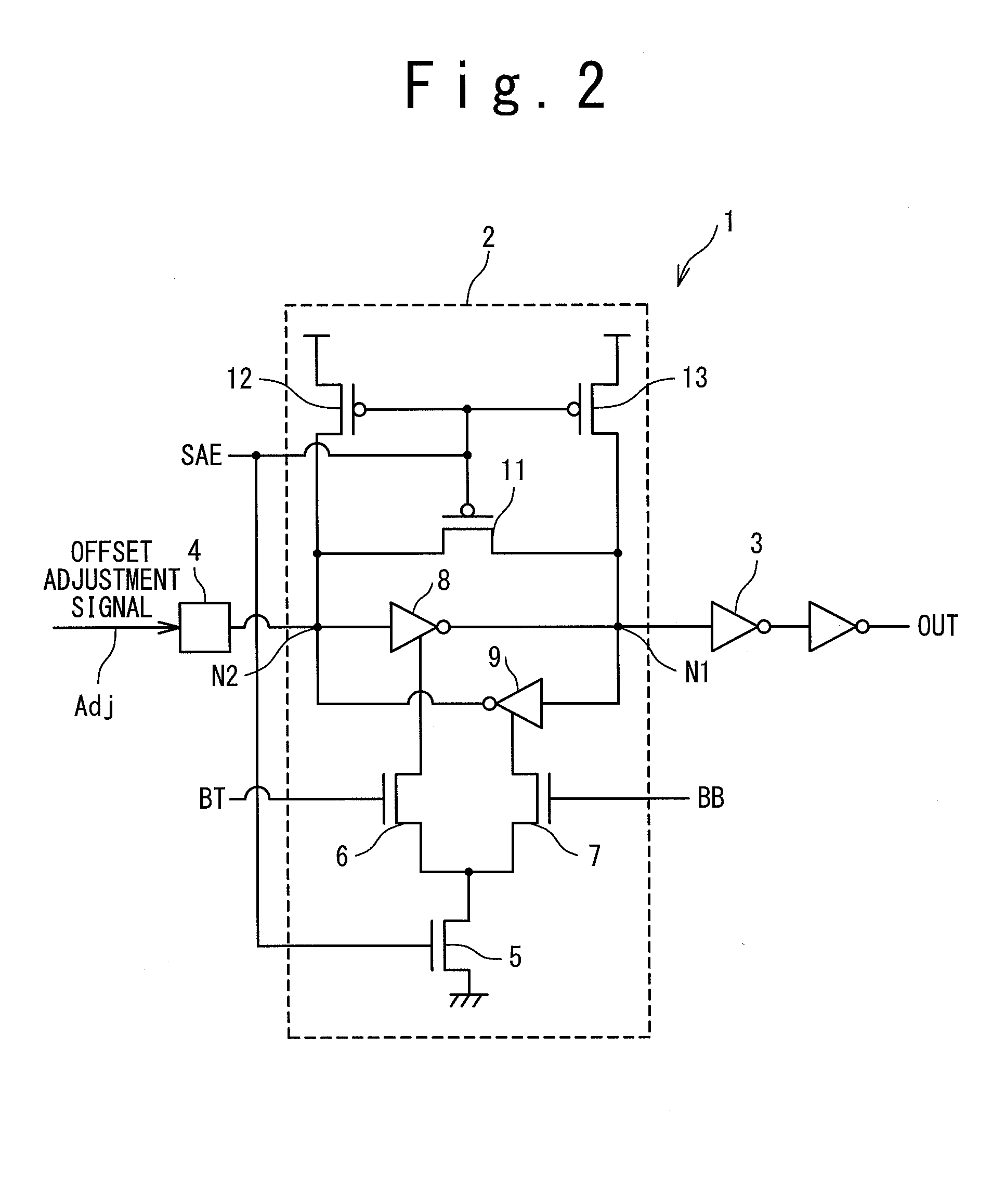
Sense amplifier and semiconductor memory device having sense amplifier
ActiveUS20100067318A1Reduce variationEasily and effectively reduce offsetCurrent/voltage measurementDigital storageCapacitanceSignal response
A sense amplifier comprises: a differential amplifier circuit configured to generate an amplified signal depending on a difference in voltage between bit lines; an output circuit receiving the amplified signal; and a load. The differential amplifier circuit comprises: a first output node supplying the amplified signal to the output circuit; and a second output node symmetrically placed with respect to the first output node and connected to the load. The output circuit comprises an output terminal for outputting an output signal generated based on the amplified signal. In response to a control signal, the load switches between a first capacitance value with which an offset voltage at the output terminal becomes a first voltage and a second capacitance value with which the offset voltage becomes a second voltage
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
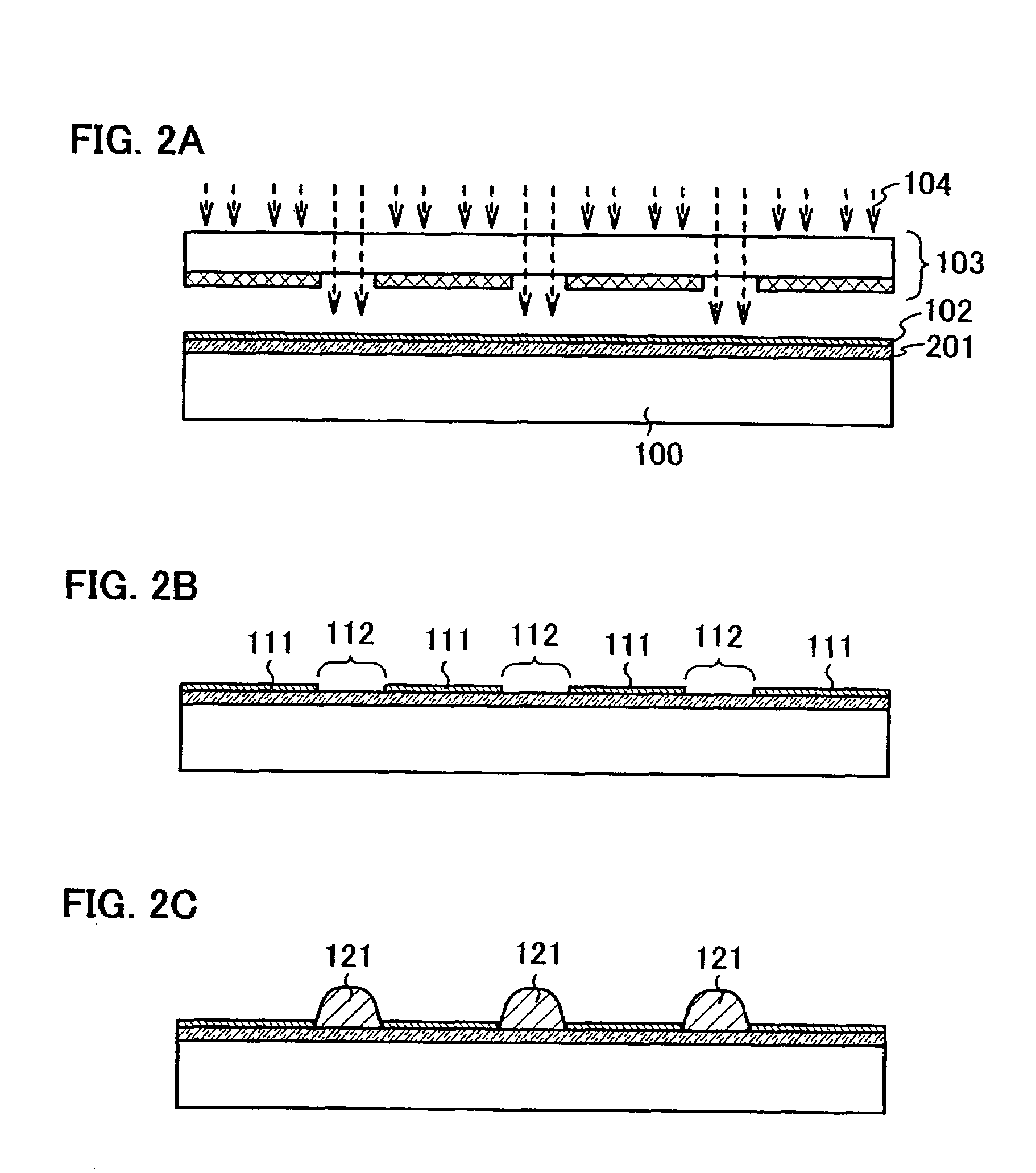
InactiveUS7335556B2Increase the number ofSmall variationTransistorNanoinformaticsSputteringEngineering
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device having a semiconductor nonvolatile memory element that is highly reliable and that can increase a variation of a threshold voltage. Further, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having a highly reliable semiconductor nonvolatile memory element using a large substrate. According to the present invention, sputtering using, as a target, a solid solution containing silicon that exceeds a solid solubility limit is conducted, so that a conductive film including a conductive layer of a metal element that is a main component of the solid solution and silicon particles is formed, and then, the conductive layer of the metal element is removed to expose silicon particles. Furthermore, a semiconductor device having a semiconductor nonvolatile memory element using the silicon particles as a floating gate electrode is manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com