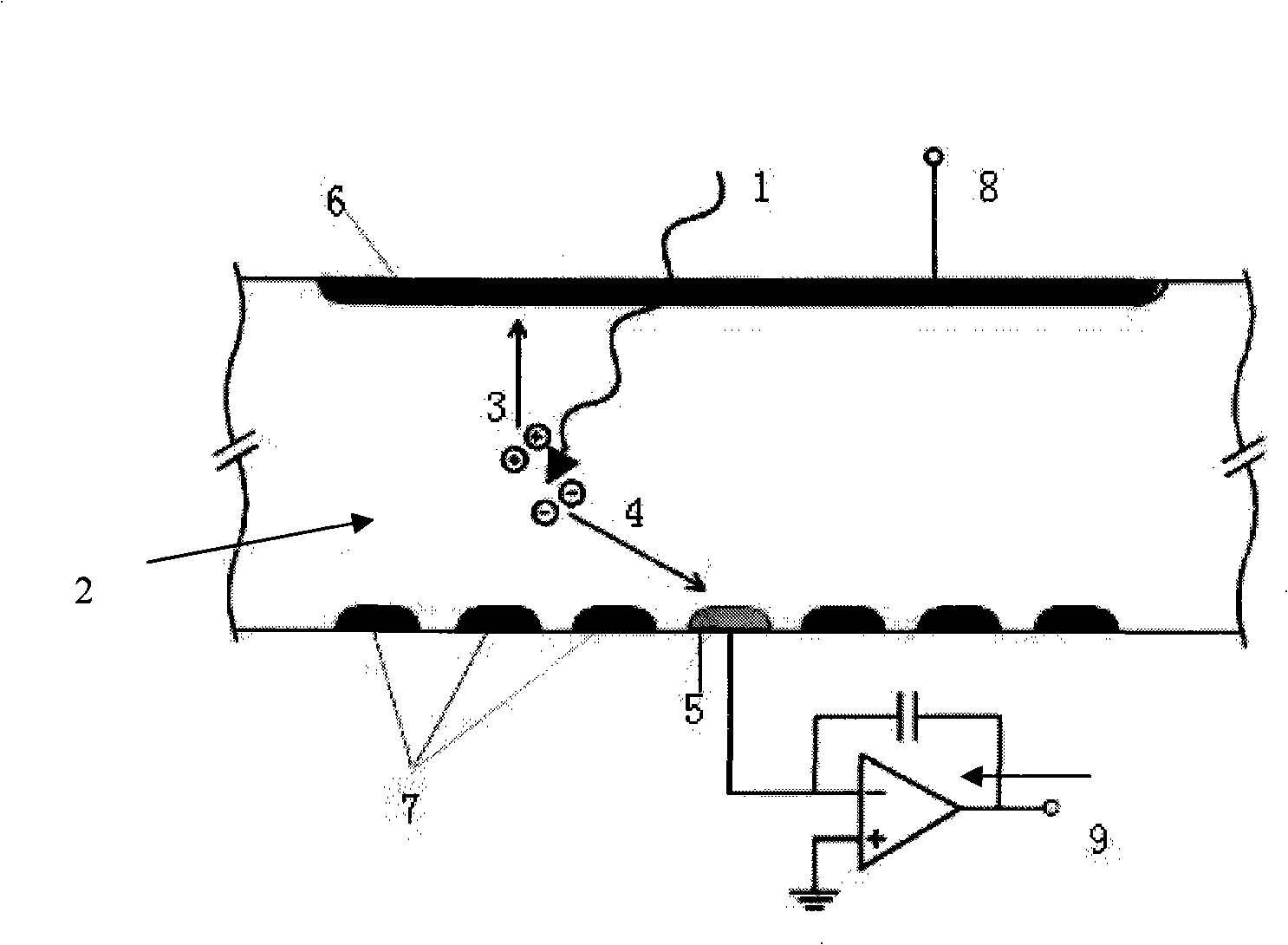
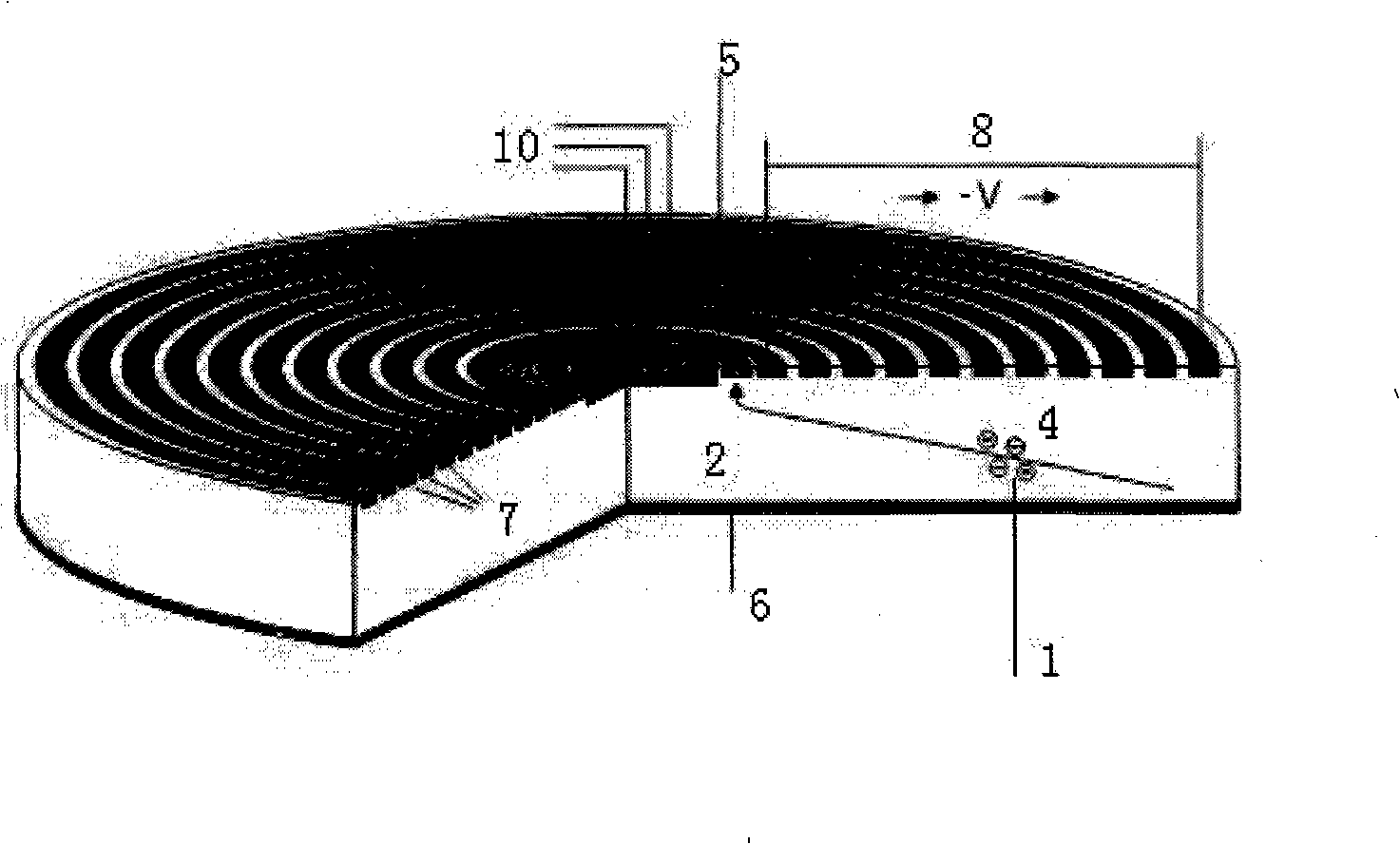
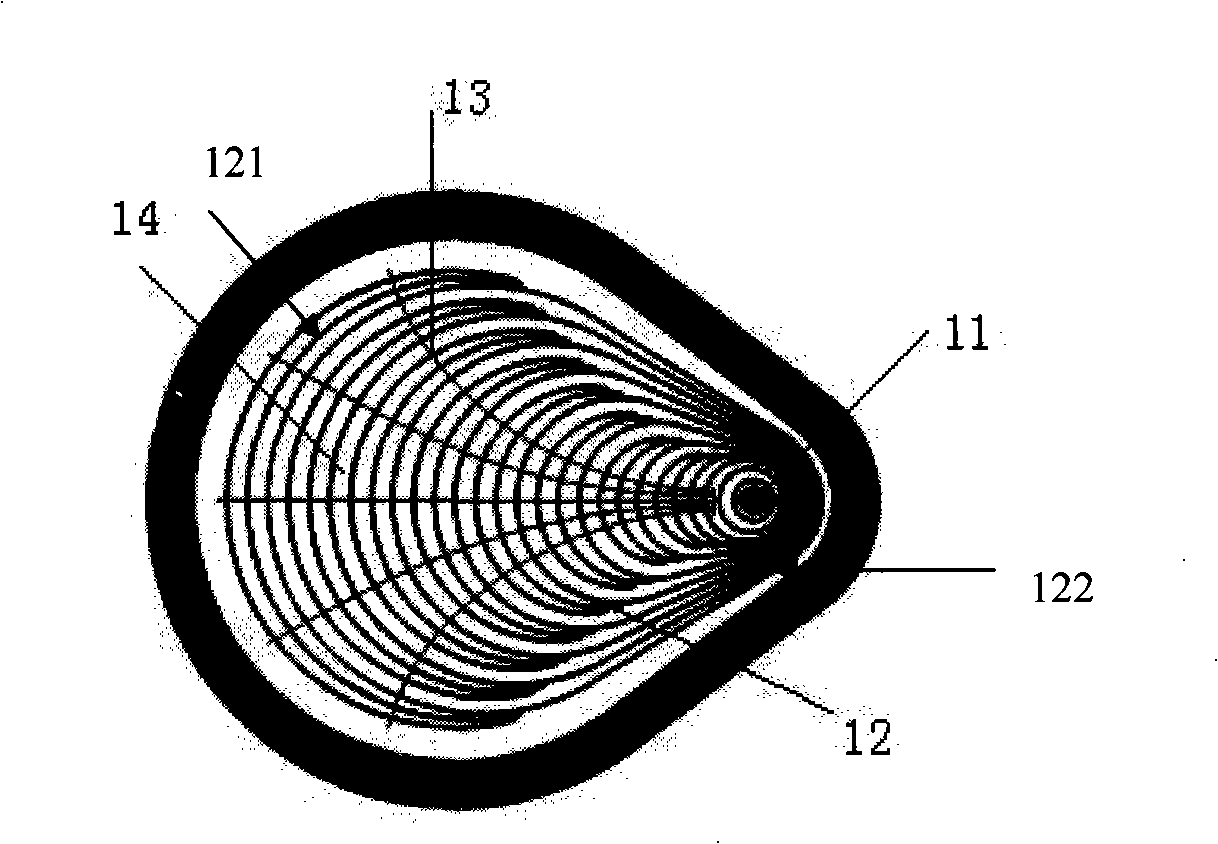
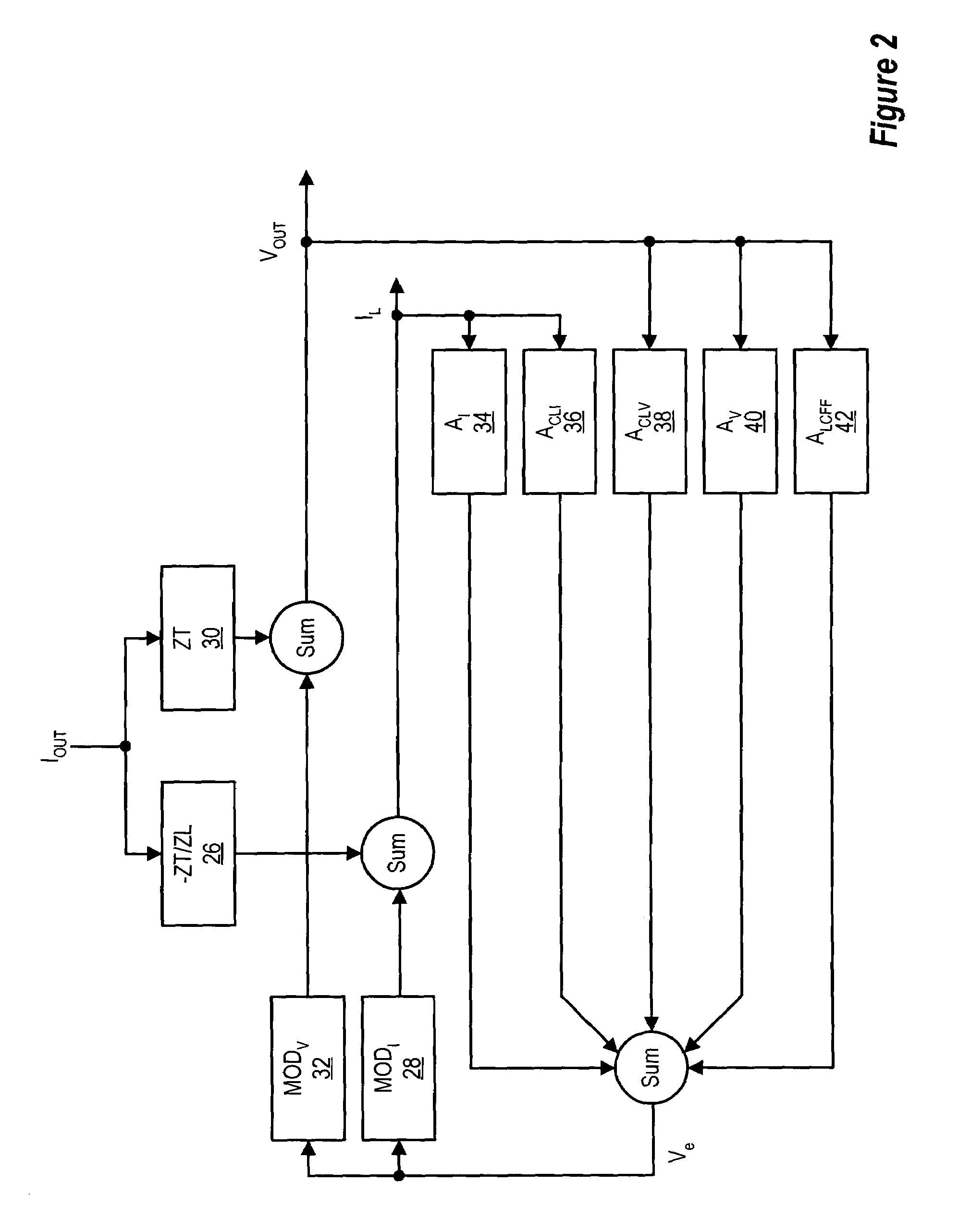
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
96results about How to "Reduce output capacitance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
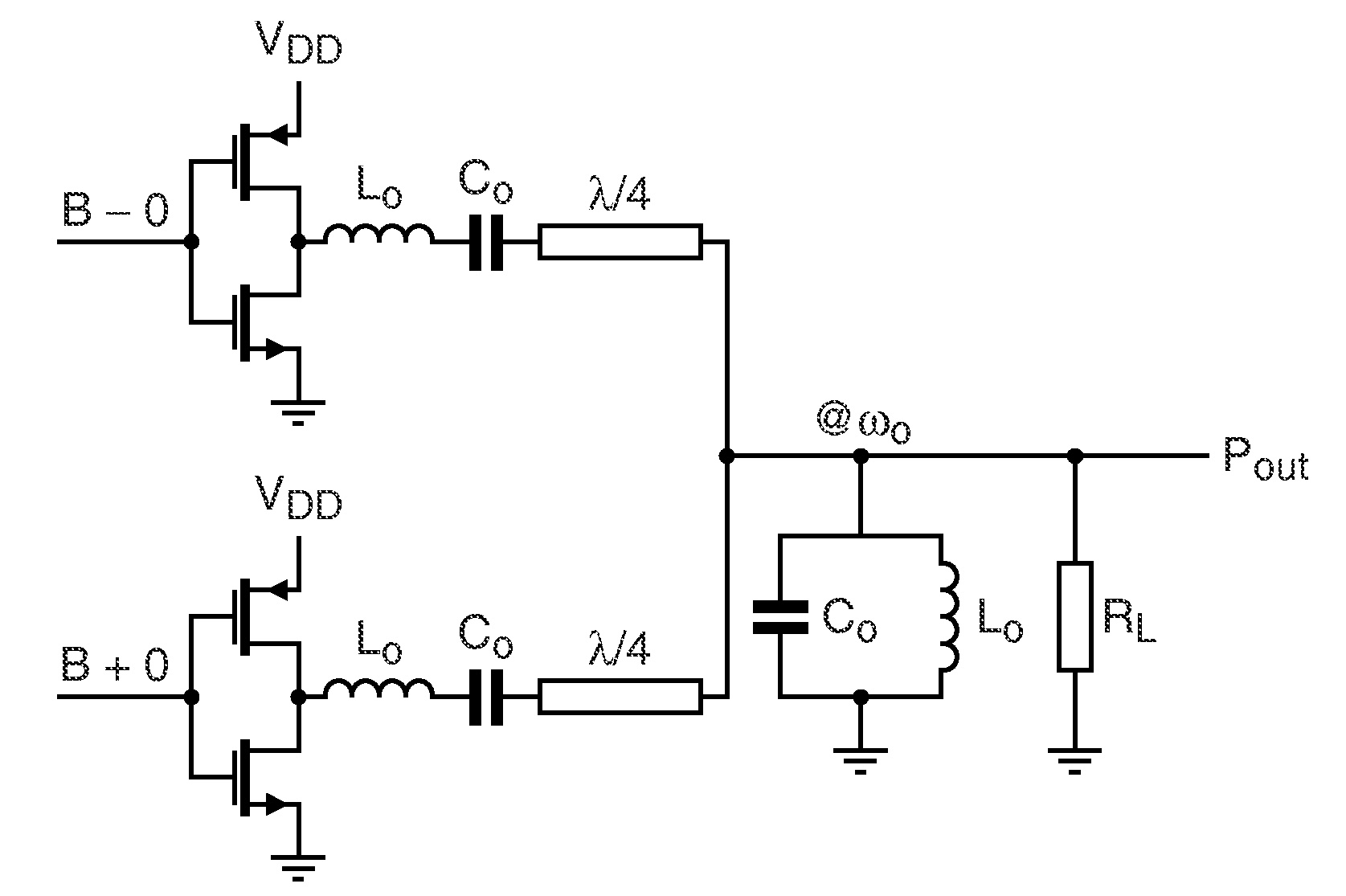
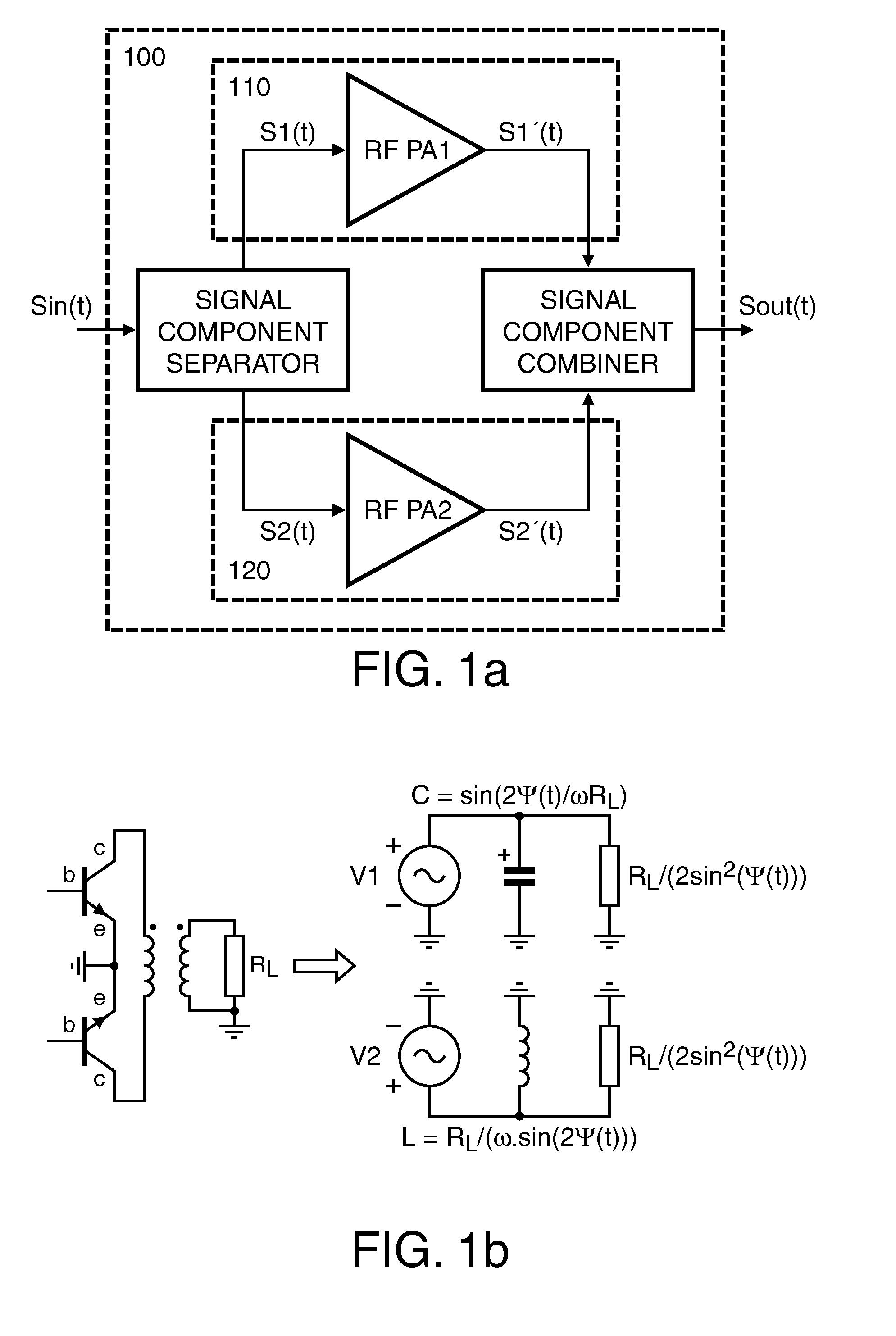
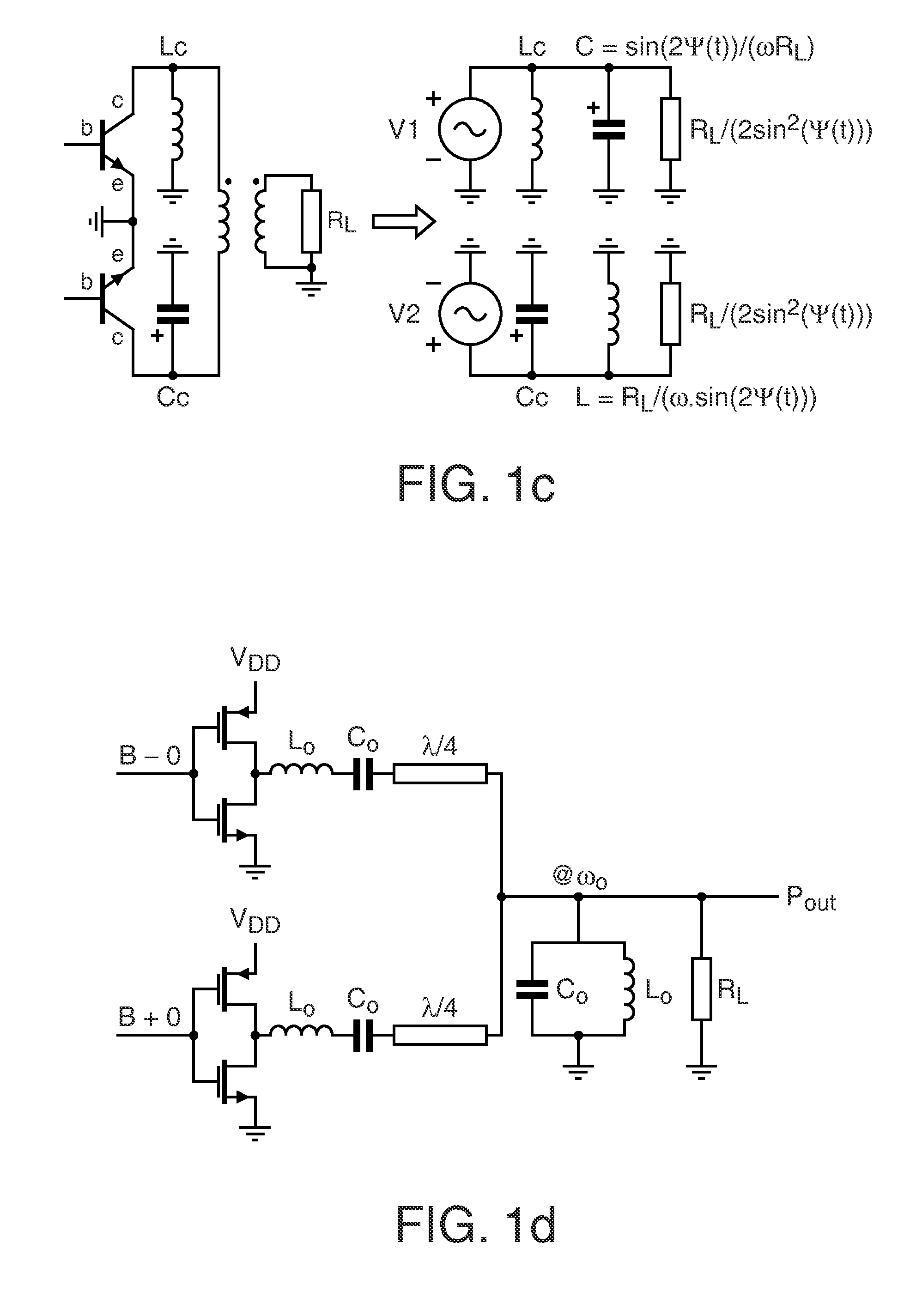
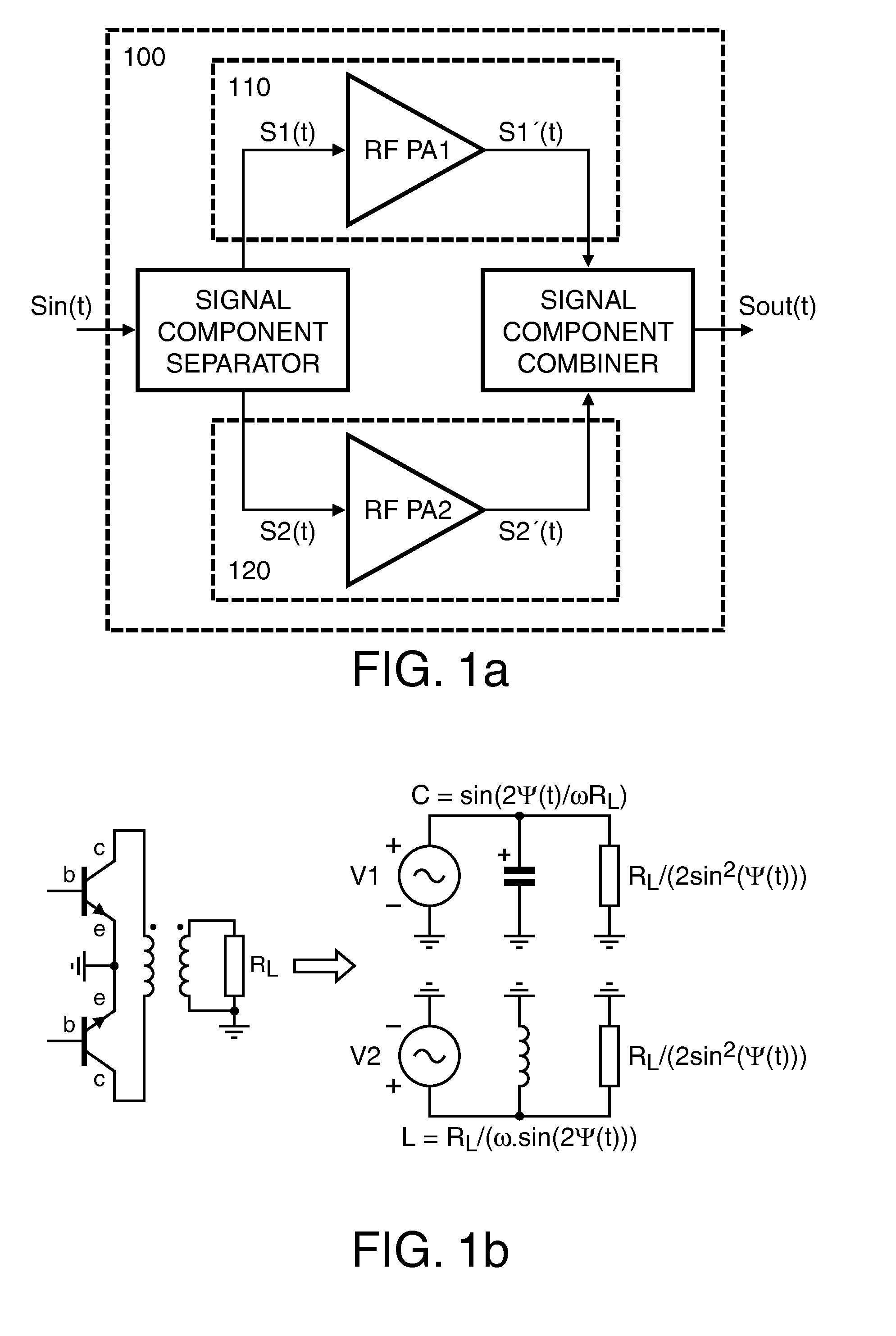
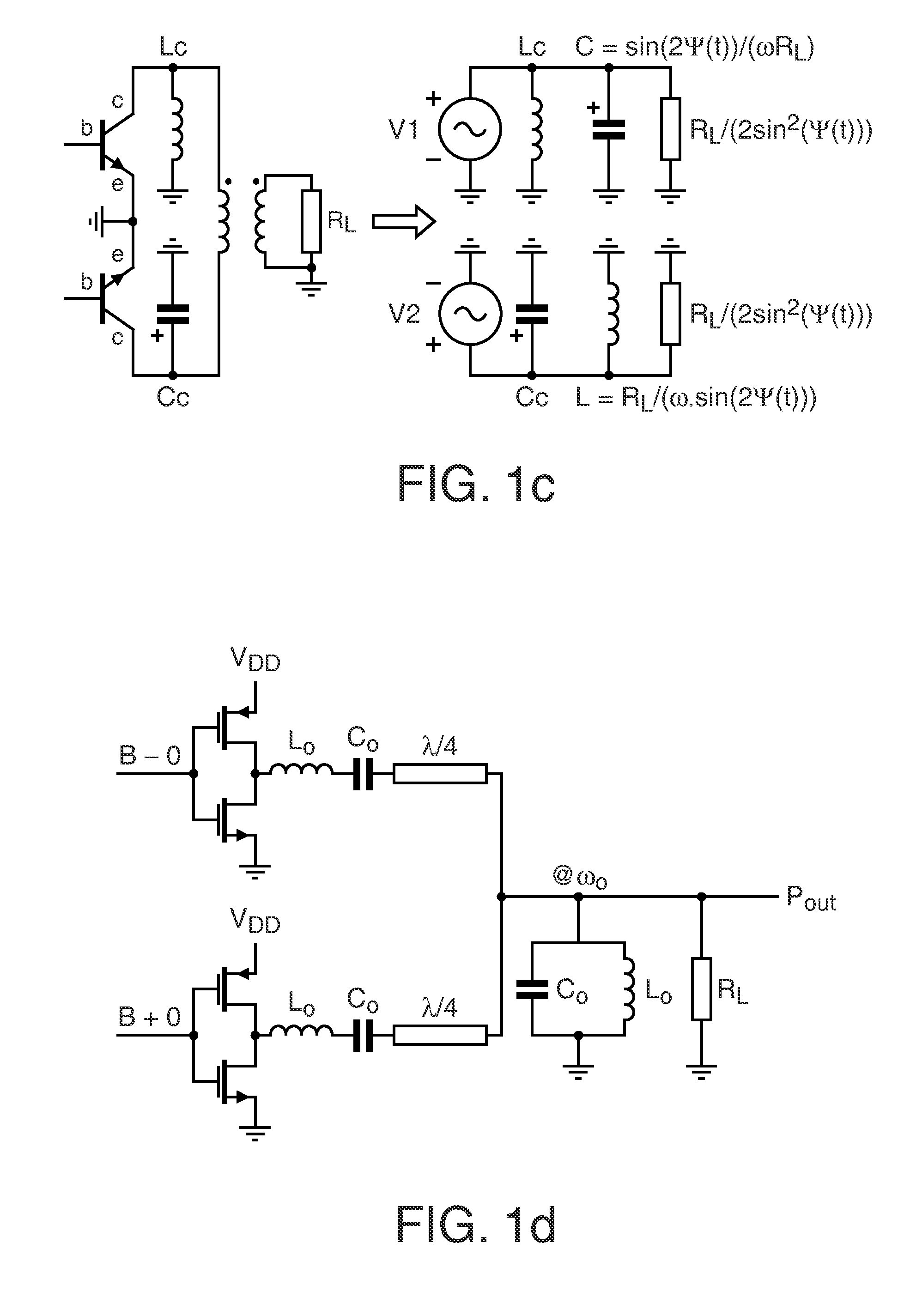
Efficient linear linc power amplifier
InactiveUS20110051842A1Improve efficiencyImproved power amplificationModulated-carrier systemsAmplifier combinationsCapacitanceDead time
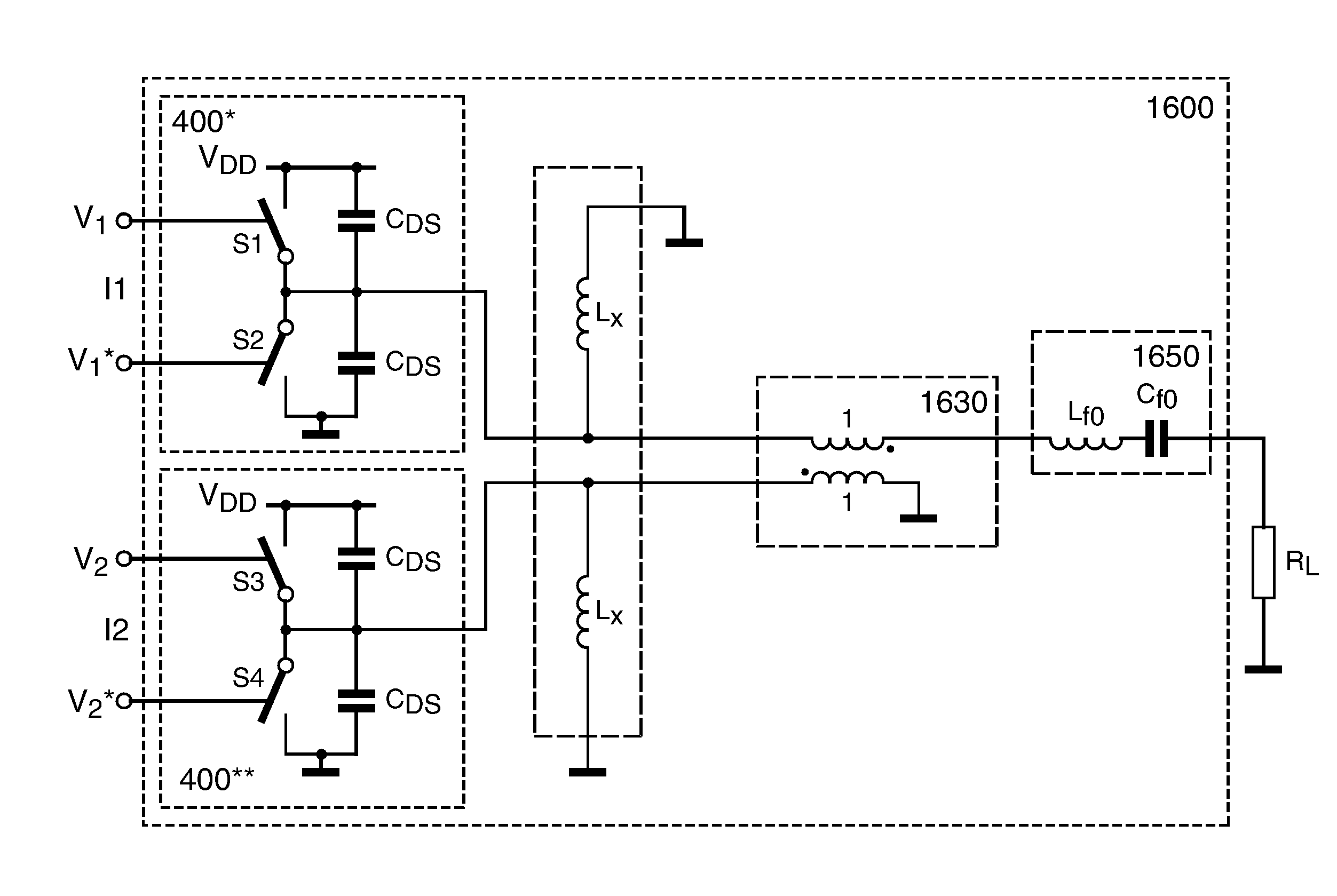
Method for setup of parameter values in a RF power amplifier circuit arrangement (200), wherein the amplifier circuit arrangement (200) comprises a first (210) and a second (220) amplification branch and is operated in an out-phasing configuration for amplification of RF input signals with modulated amplitude and modulated phase and respective circuit arrangements are disclosed. According to a first aspect a re-optimization of the dead-time or conversely the duty-cycle, respectively, the phase of the output signal after the combiner can be kept linear with respect to the out-phasing angle. Further, according to a second aspect, additionally to introduction of an optimally chosen dead-time, a non-coherent combiner (Lx, Lx*) can reduce crowbar current and switching losses due the output capacitance (Cds). Furthermore, according to a third aspect the reactive compensation can, additionally or alternatively, be controlled by operating both amplification branches at different duty-cycles.
Owner:AMPLEON NETHERLANDS
Pyroelectric sensor
ActiveUS20070108385A1Environmentally friendlyEnvironmentally robustMaterial analysis by optical meansPyrometry using electric radation detectorsHysteresisEngineering
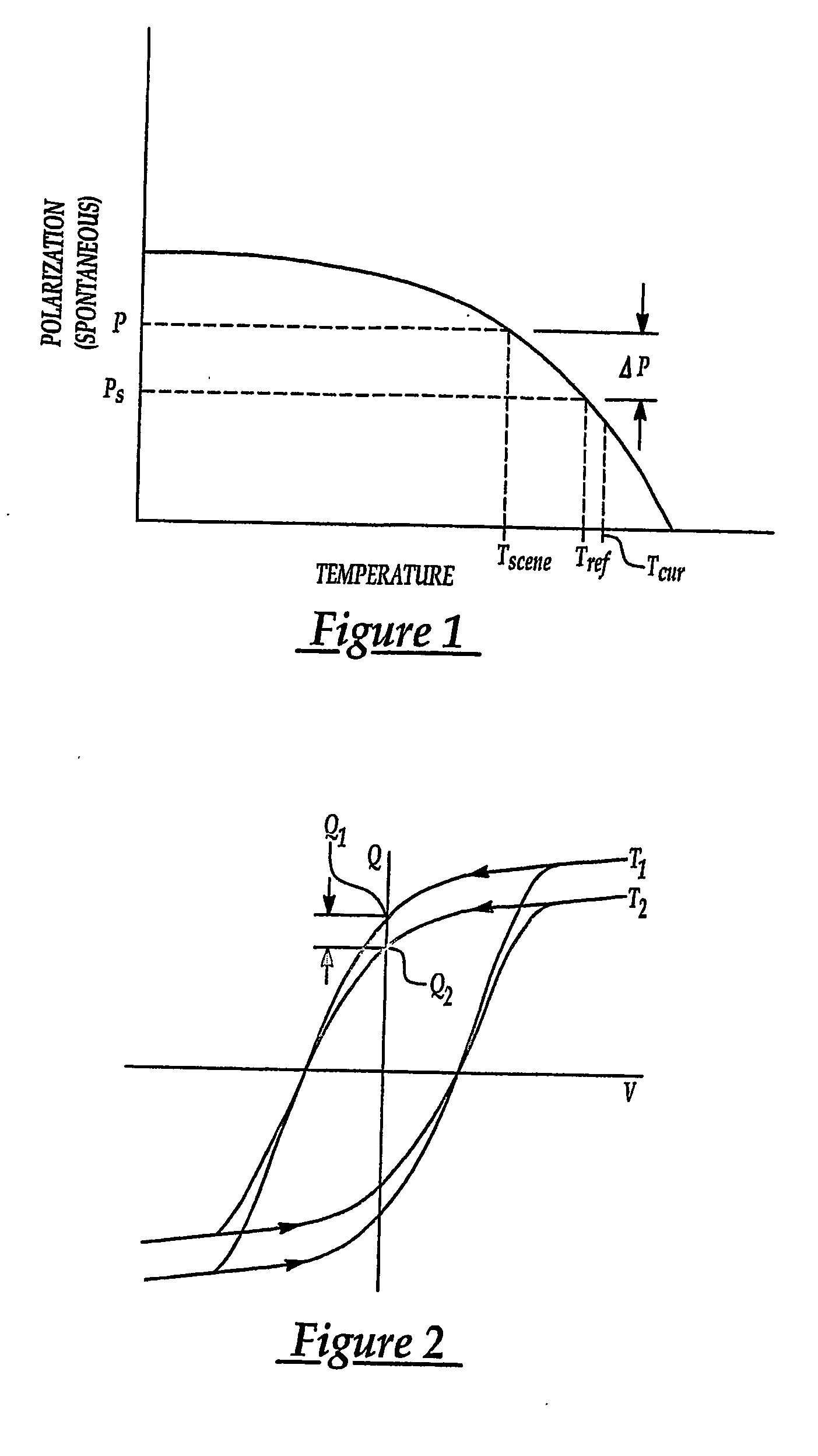
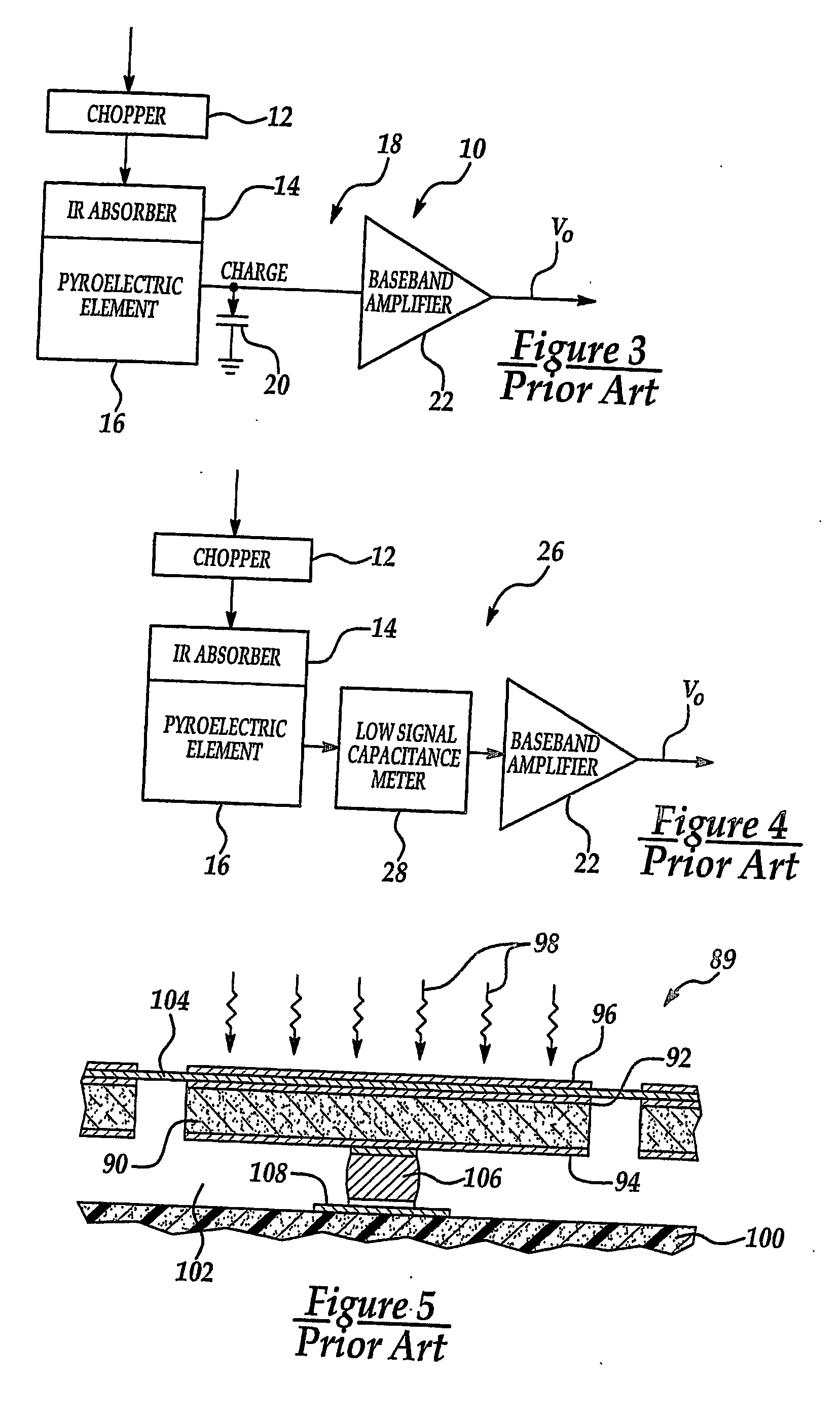
A ferroelectric / pyroelectric sensor employs a technique for determining a charge output of a ferroelectric scene element of the sensor by measuring the hysteresis loop output of the scene element several times during a particular time frame for the same temperature. An external AC signal is applied to the ferroelectric scene element to cause the hysteresis loop output from the element to switch polarization. Charge integration circuitry, such as a combination output capacitor and operational amplifier, is employed to measure the charge from the scene element. Preferably, the ferroelectric of the scene element is made of an economical and responsive strontium bismuth tantalate, SBT, or derivative thereof, disposed directly between top and bottom electrodes. Because of the frequency characteristics of the sensor, created by the external AC signal, the element need not be thermally isolated from the silicon substrate by a traditional air bridge, which is difficult to manufacture, and instead is preferably thermally isolated by spin-on-glass, SOG. To prevent saturation of an output signal voltage of the sensor by excessive charge accumulation in an output capacitor, the sensor preferably has a reference element configured electrically in parallel with the scene element. When the voltage of the AC signal is negative the output capacitor is discharged by flowing current through the reference element thus interrogating the polarization of the reference element which is compared to and subtracted from the polarization of the scene element for each cycle. The polarization difference measured for each cycle over a set time period are summed by an integrating amplifier to produce a signal output voltage.
Owner:APTIV TECH LTD +1
Multi-channel data acquisition device for submarine pipeline magnetic flux leakage internal detector
ActiveCN102495132AReduce distractionsFlexible modificationMaterial magnetic variablesOcean bottomData acquisition
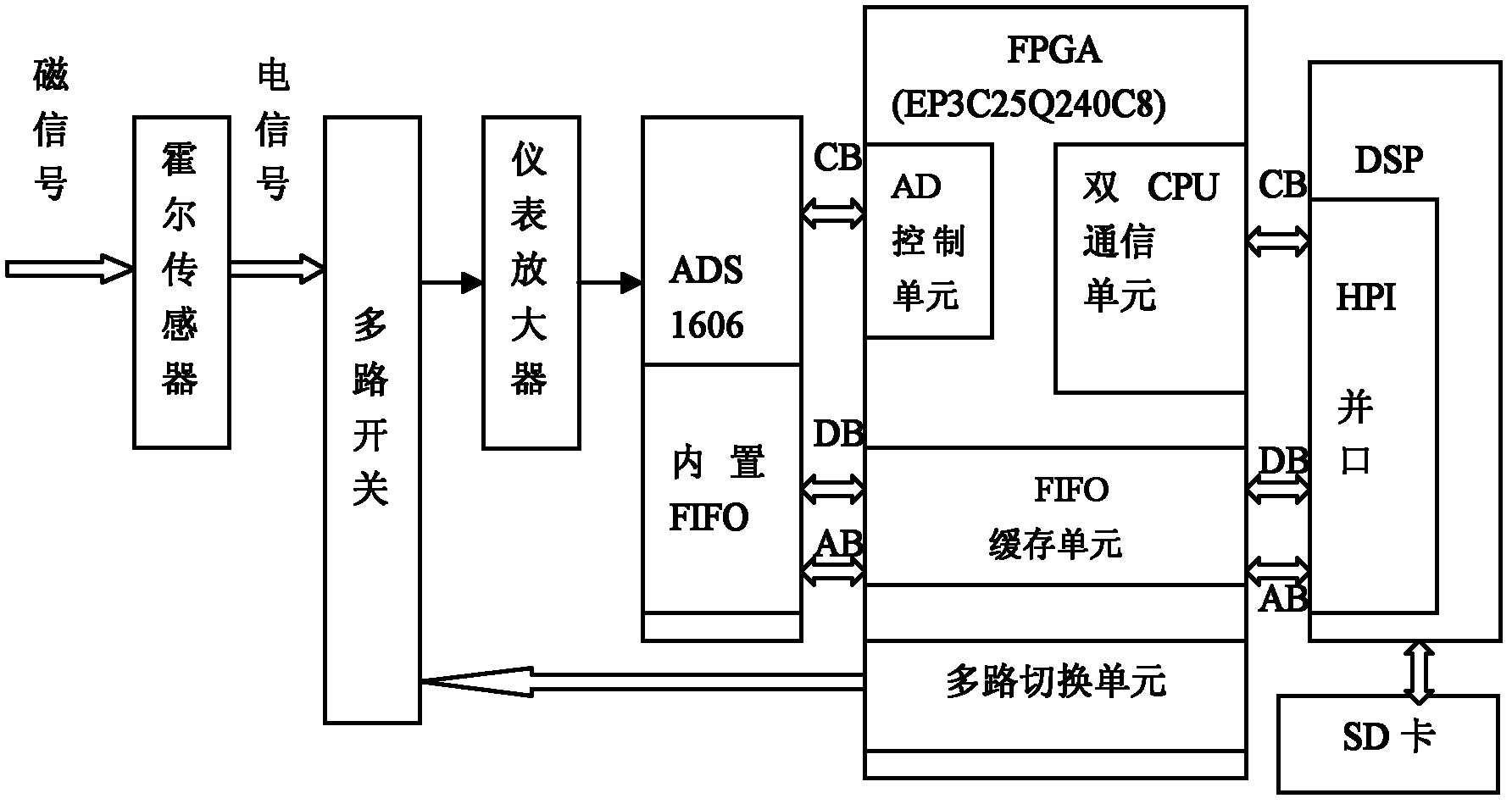
The invention discloses a multi-channel data acquisition device for a submarine pipeline magnetic flux leakage internal detector. The multi-channel data acquisition device comprises a hall sensor, a multi-path switch, an instrument amplifier, an analog-to-digital (AD) conversion module, a field programmable gate array (FPGA), a digital signal processor (DSP) and a secure digital memory (SD) card, wherein the multi-path switch has a two-stage series structure; the multi-channel data acquisition device is provided with heat insulation cotton so as to adapt to a specific high-temperature and high-corrosion environment of a submarine pipeline; the hall sensor converts the magnetic induction density into voltage; the voltage is switched by the multi-path switch, so that a signal is transmitted to the instrument amplifier; the instrument amplifier amplifies a weak signal; the AD conversion module sets sampling for eight times through software, performs analog-to-digital conversion, and transmits a digital value to the FPGA after the conversion; and the DSP receives FPGA cached data, digitally filters and compresses the cached data, and finally stores the data into the SD card. Due to a dual central processing unit (CPU) structure consisting of the FPGA and the DSP, a large amount of data can be stored and processed; the device has the characteristics of high speed, multiple channels, high resolution and the like; furthermore, pipeline transportation safety is guaranteed; and early maintenance is facilitated.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Semiconductor integrated circuit
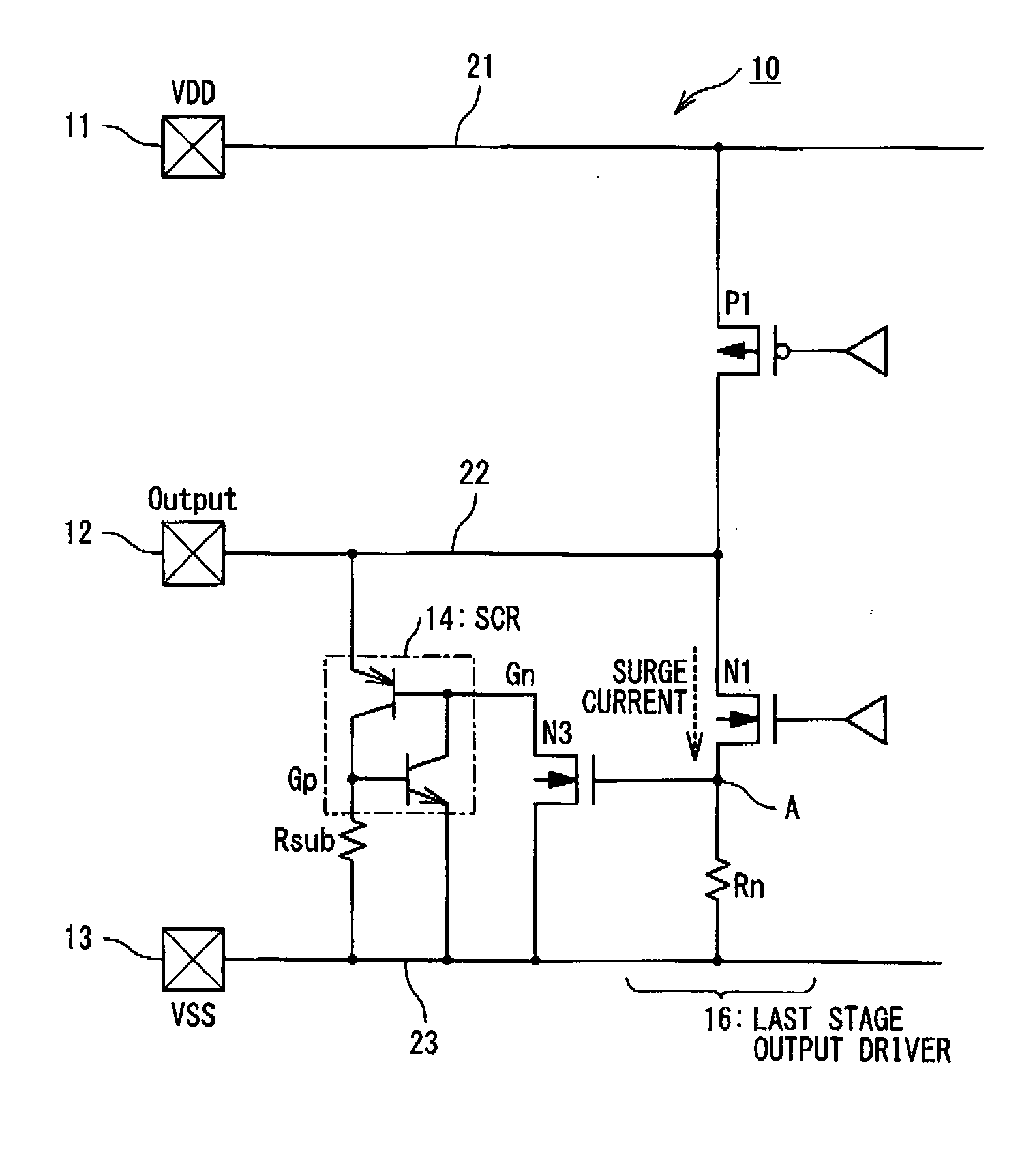
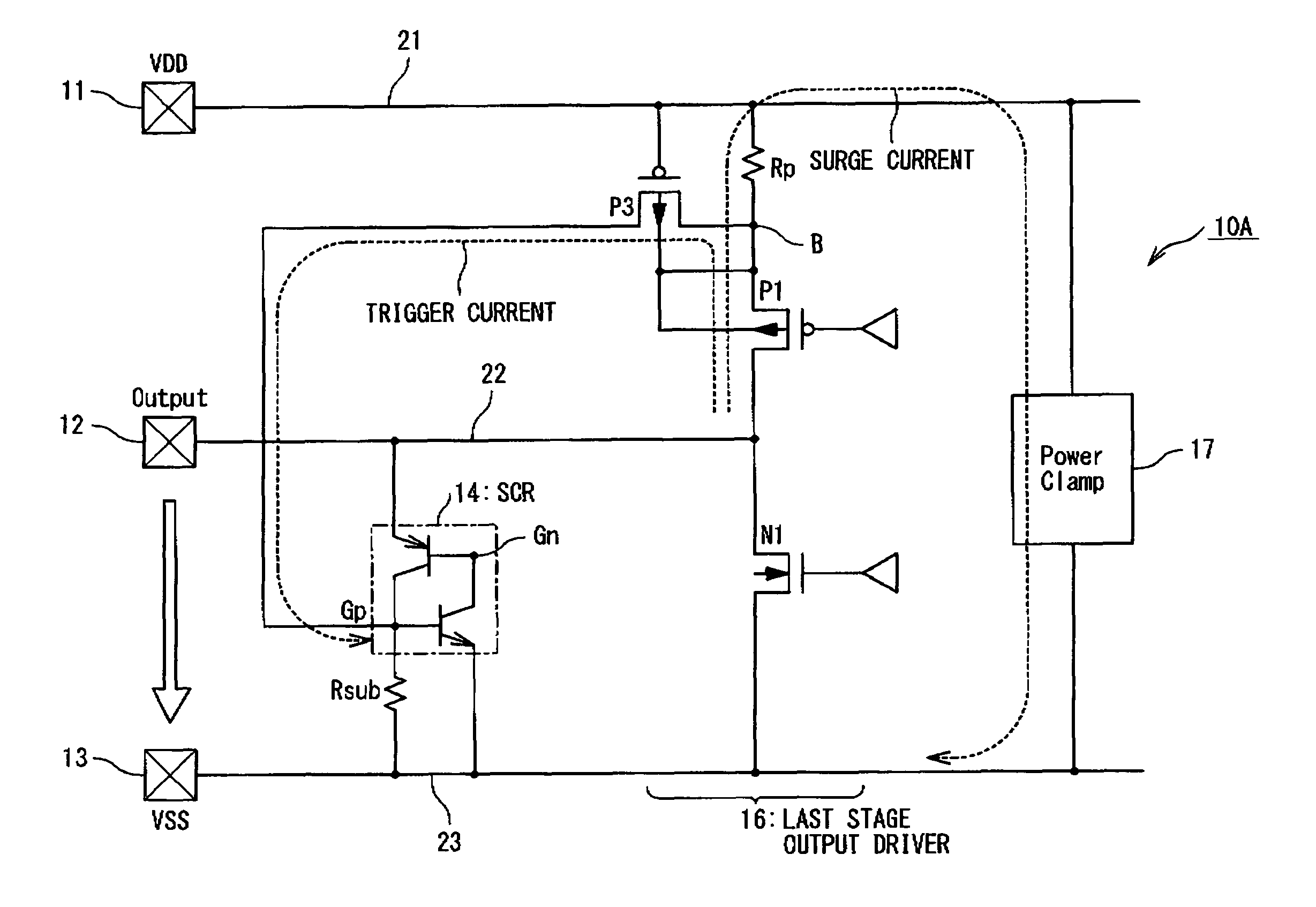
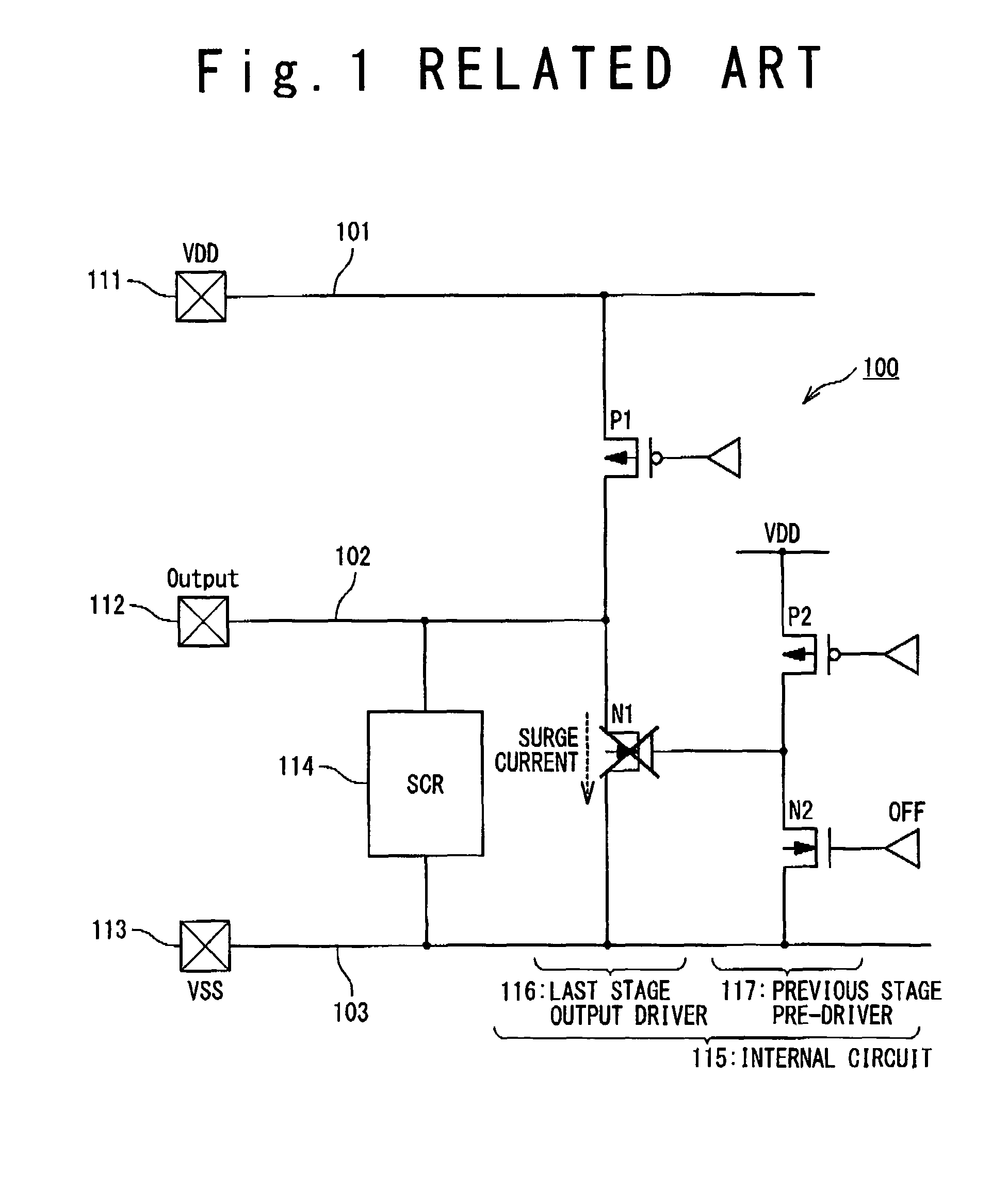
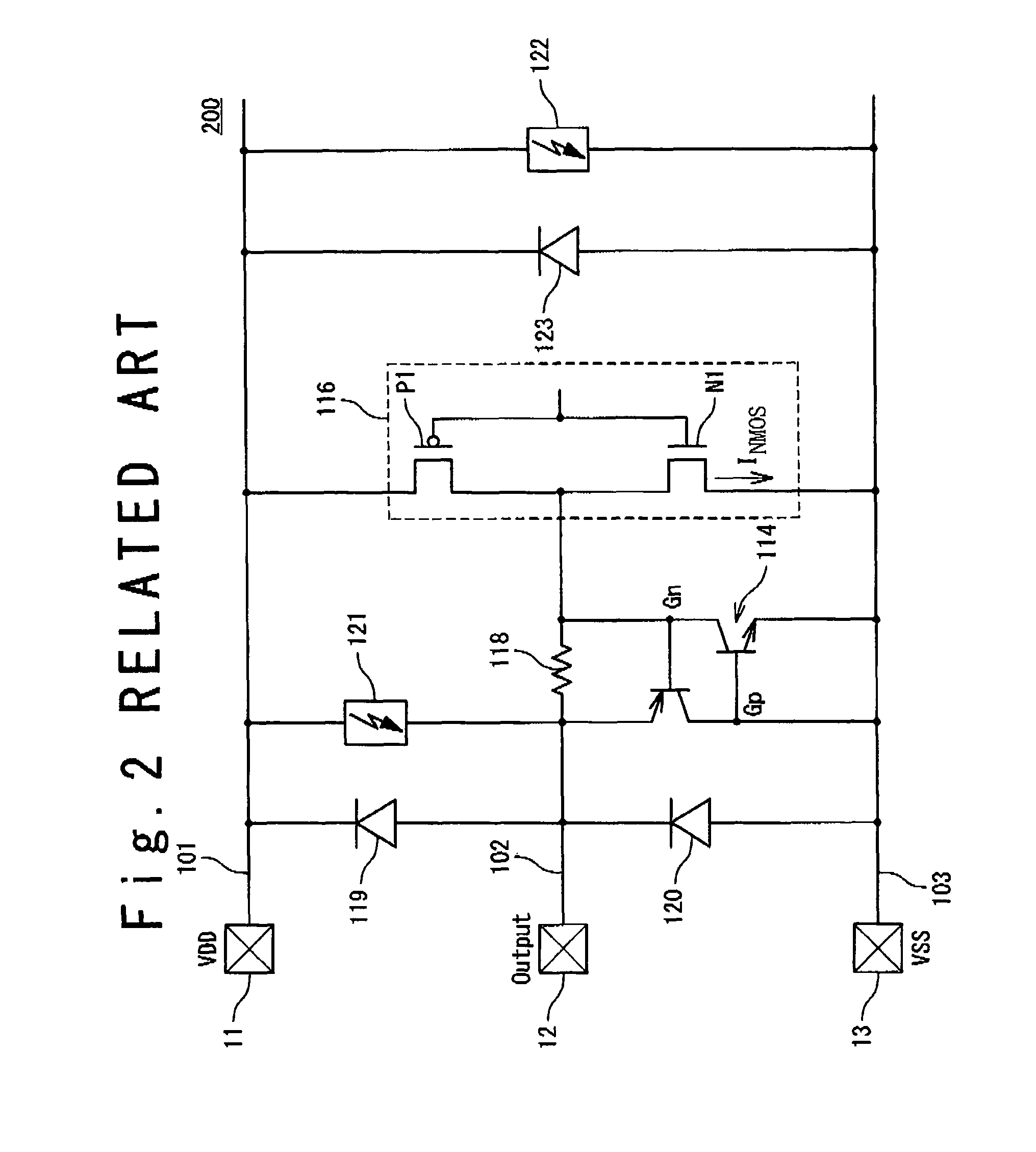
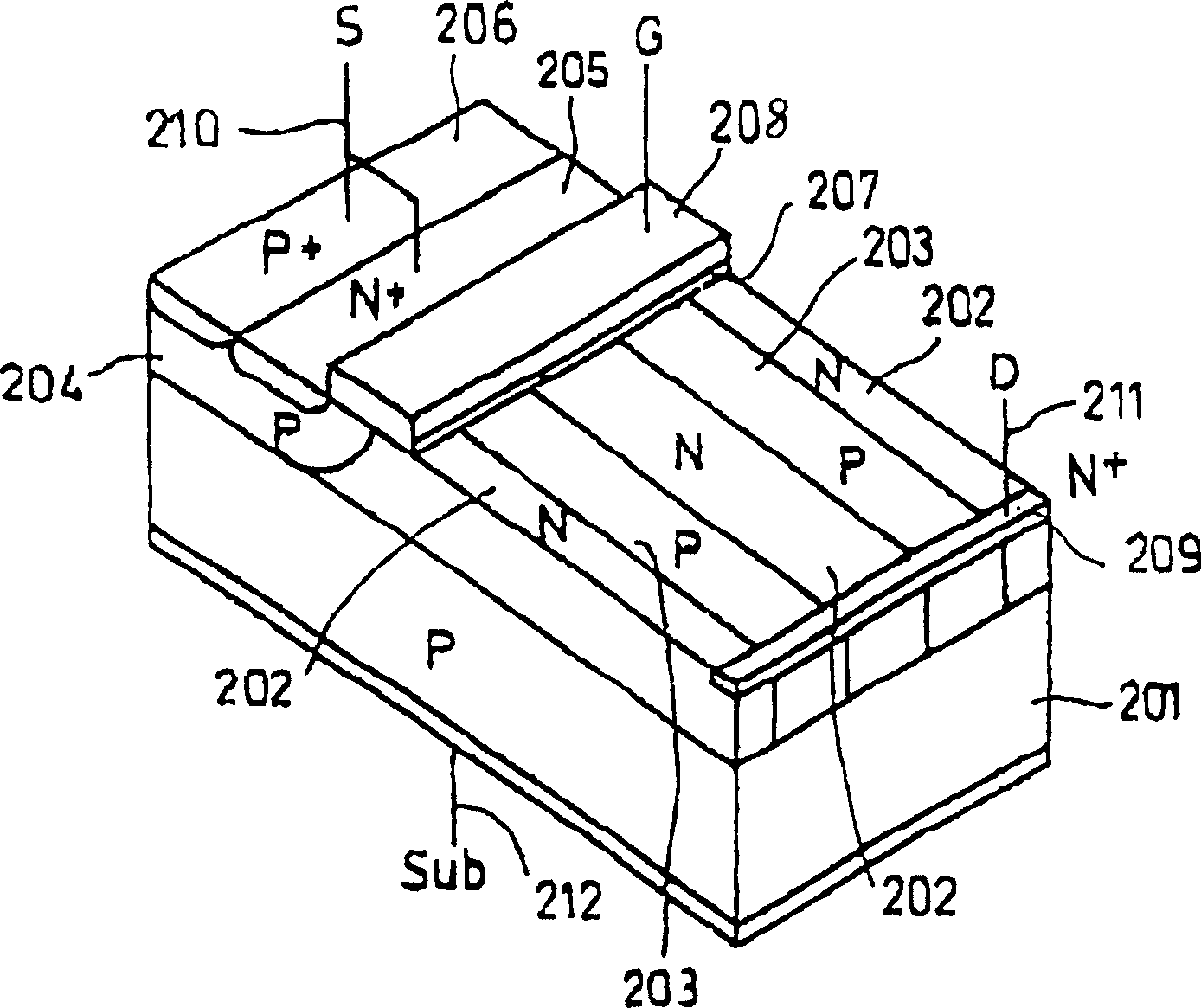
ActiveUS20090122452A1Lower the resistance valueReduce output capacitanceTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrical resistance and conductanceInterconnection
A semiconductor integrated circuit includes: an output pad from which an output signal is outputted; an output signal line connected with the output pad; a first pad configured to function as a ground terminal or a power supply terminal; a first wiring connected with the first pad; an output driver connected with the output pad and configured to generate the output signal; an ESD protection device connected with the output signal line and having a function to discharge surge applied to the output pad; and a first trigger MOS transistor used as a trigger device. The output driver includes: a first protection target device connected between the output signal line and the first interconnection; and a first resistance element connected between the first protection target device and the first interconnection. The first trigger MOS transistor configured to detect a voltage generated in the first resistance element by a gate of the first trigger MOS transistor and to allow the ESD protection device operate in response to the detected voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Vertical charge control semiconductor device with low output capacitance
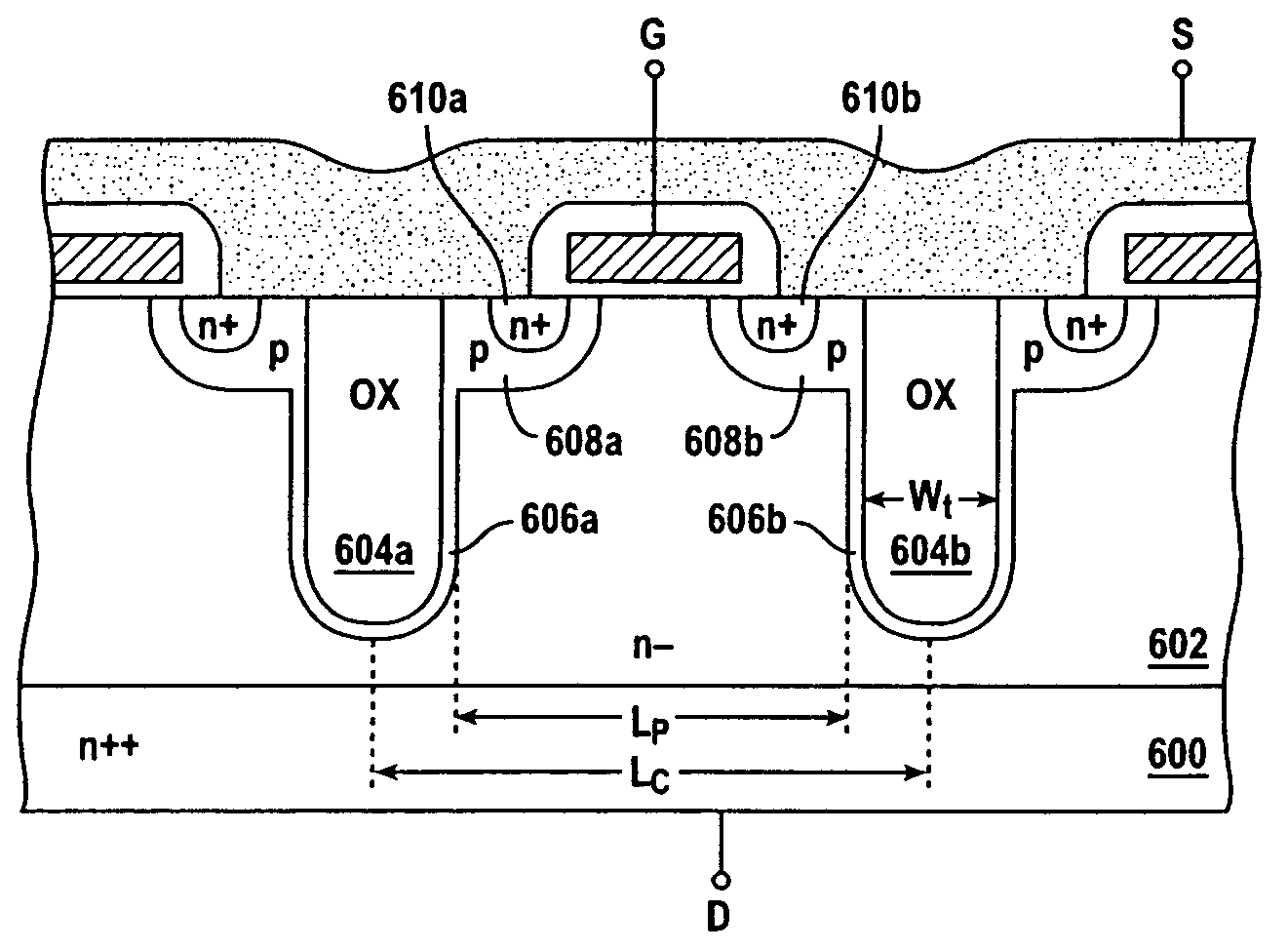
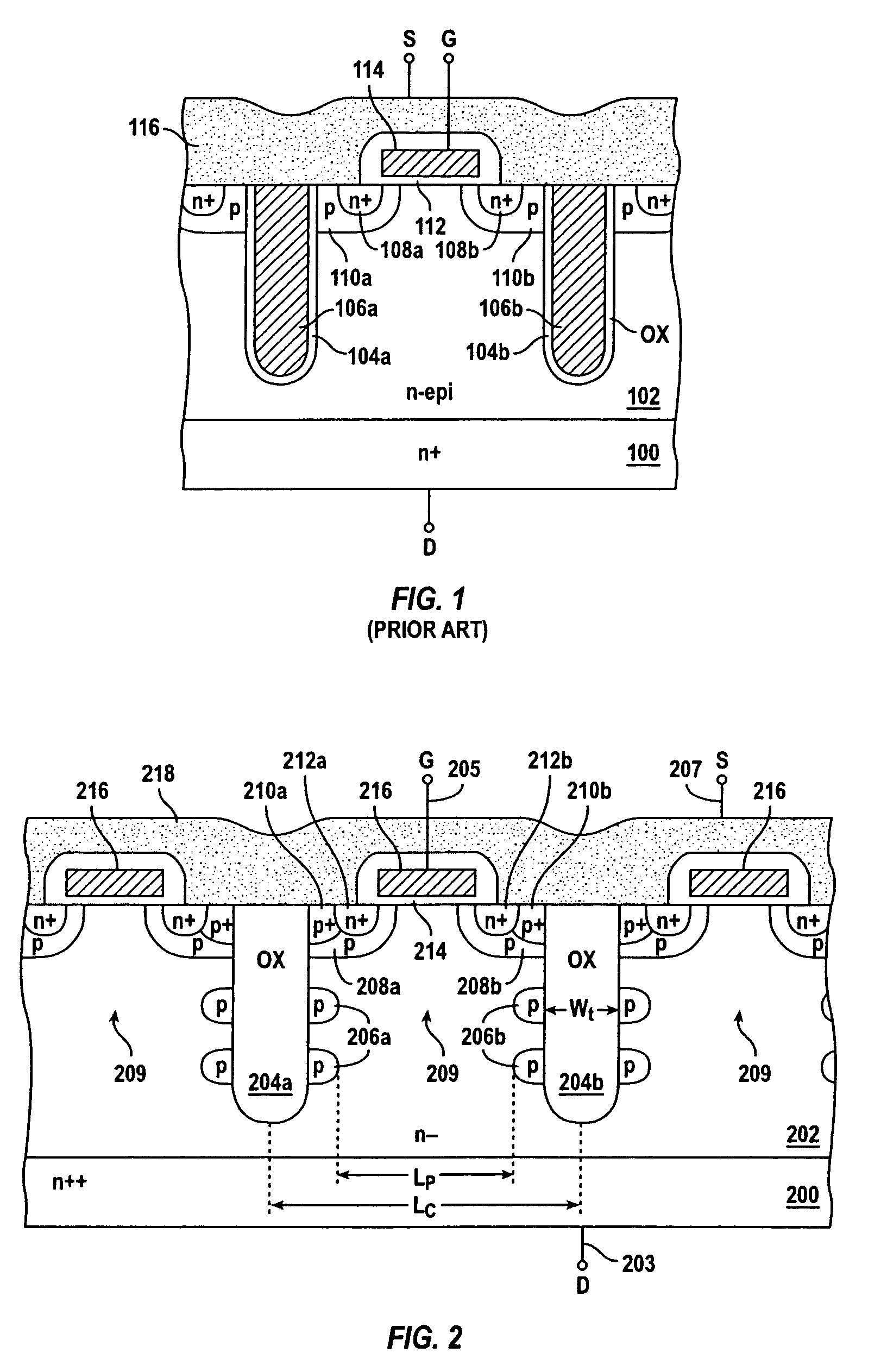
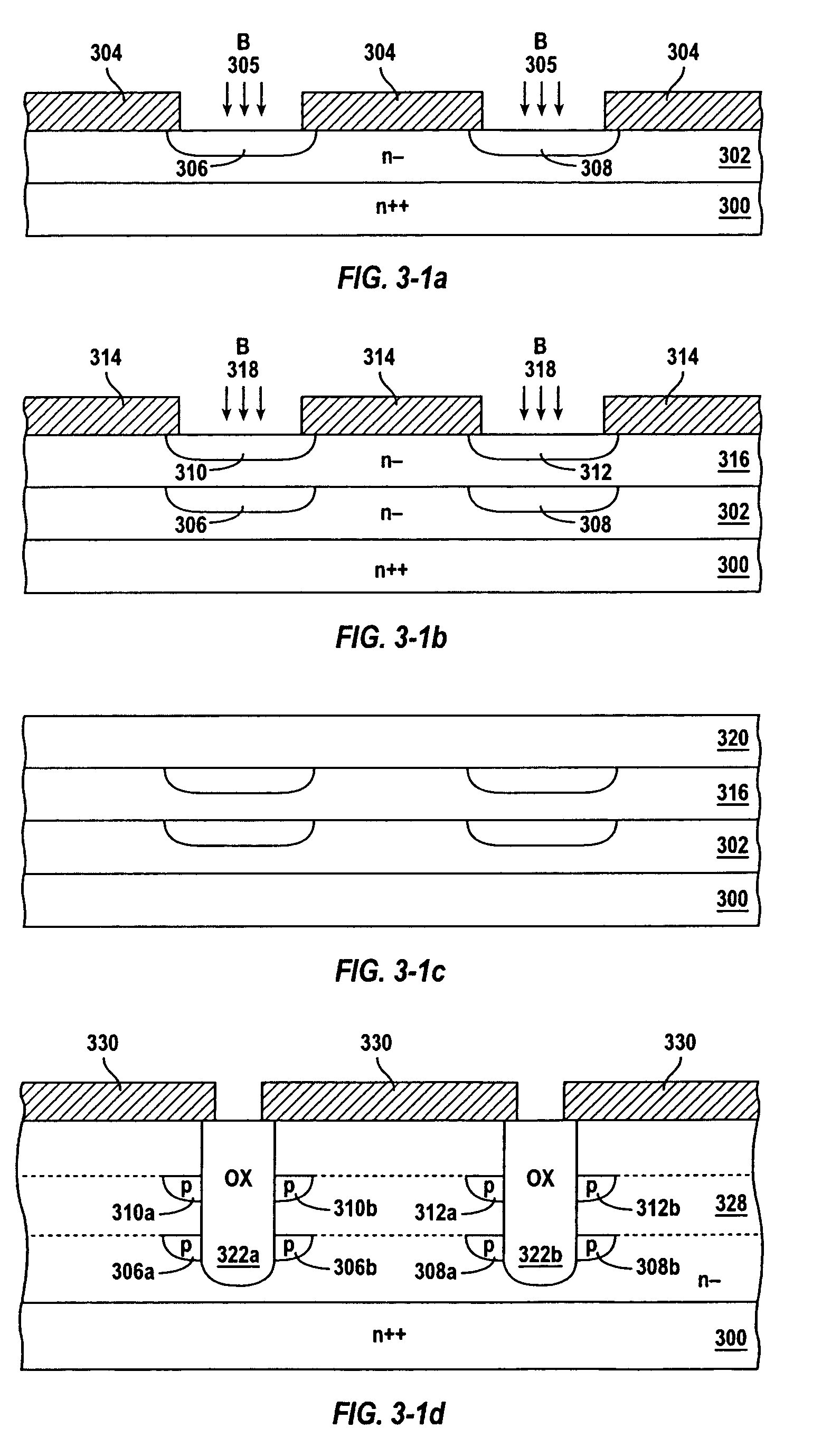
InactiveUS7291894B2Reduce output capacitanceImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETCapacitance
In accordance with an embodiment of the present invention, a MOSFET includes at least two insulation-filled trench regions laterally spaced in a first semiconductor region to form a drift region therebetween, and at least one resistive element located along an outer periphery of each of the two insulation-filled trench regions. A ratio of a width of each of the insulation-filled trench regions to a width of the drift region is adjusted so that an output capacitance of the MOSFET is minimized.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Inductive bypass, storage and release improves buck response
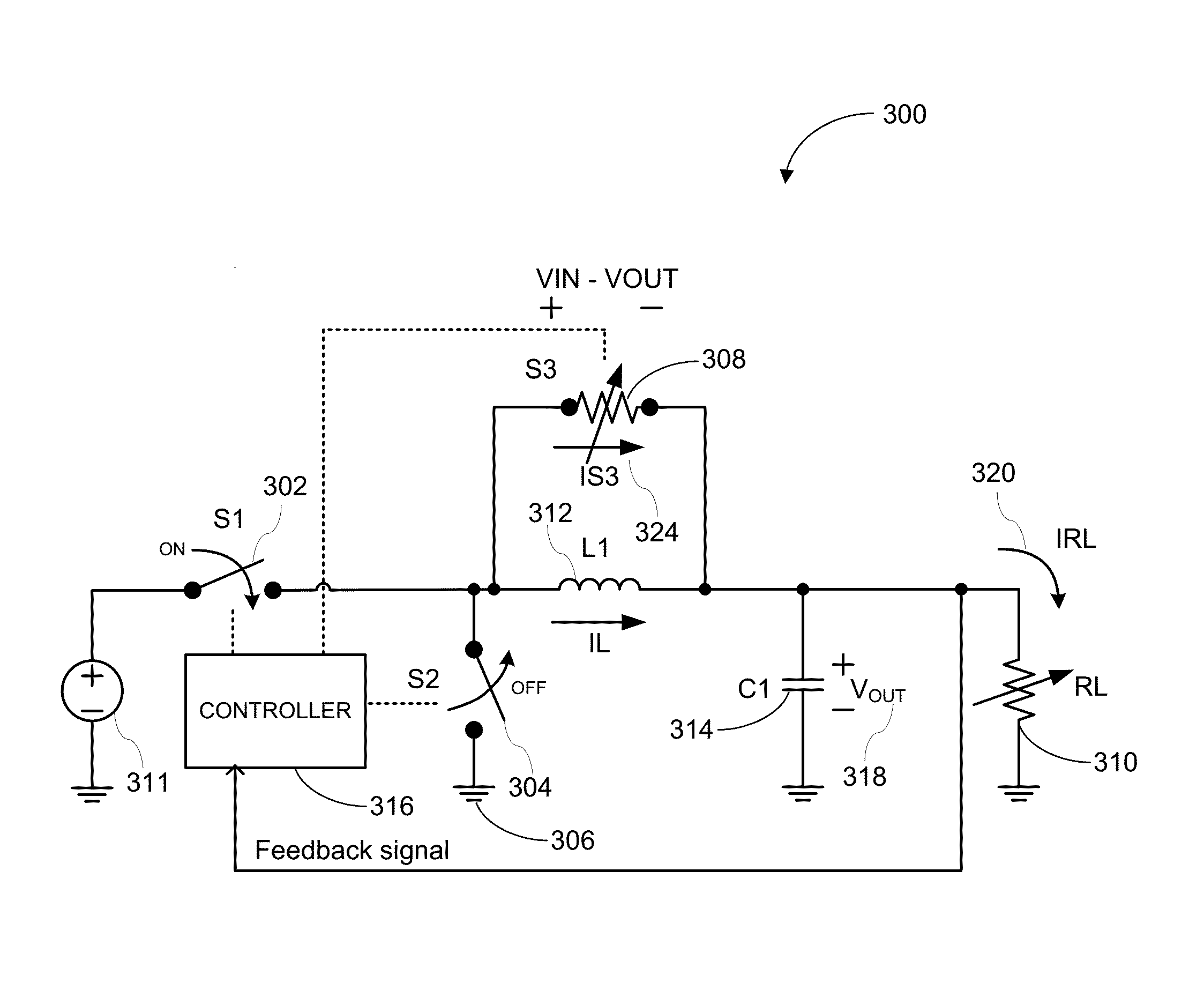
ActiveUS9178420B1Improved transient output responseImprove power efficiencyEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionEngineeringInductance
Various embodiments of the invention improve the dynamic response and output voltage accuracy in buck DC-DC converters. In certain embodiments, power efficiency is improved by storing and recycling energy that is otherwise lost during successive load transient events.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Vertical charge control semiconductor device with low output capacitance
InactiveUS20050023607A1Reduce output capacitanceImprove breakdown voltageTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMOSFETCapacitance
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Decode circuitry and a display device using the same
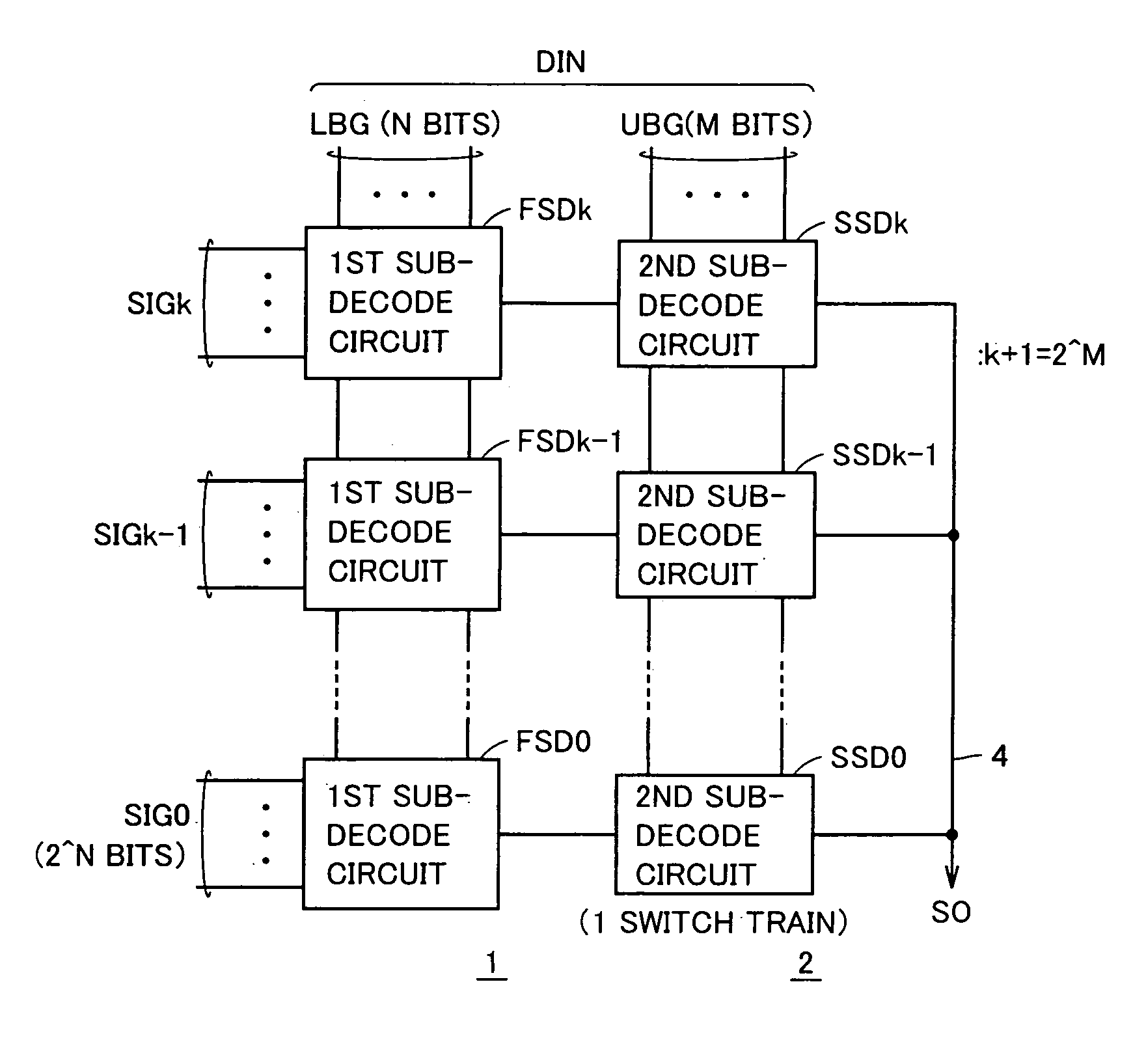
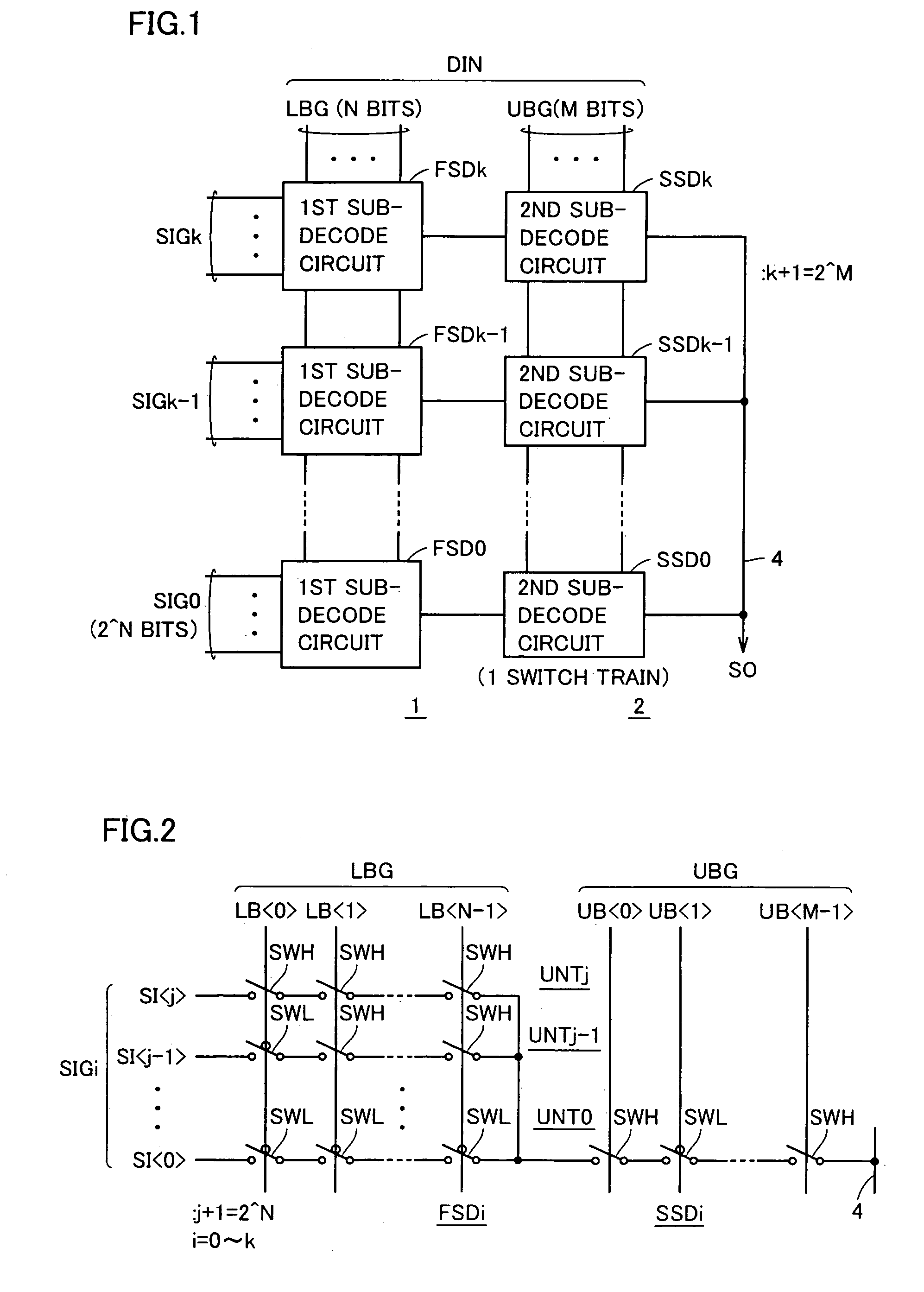
InactiveUS7209057B2Fast operationReduce areaElectric signal transmission systemsStatic indicating devicesTelecommunicationsTarget signal
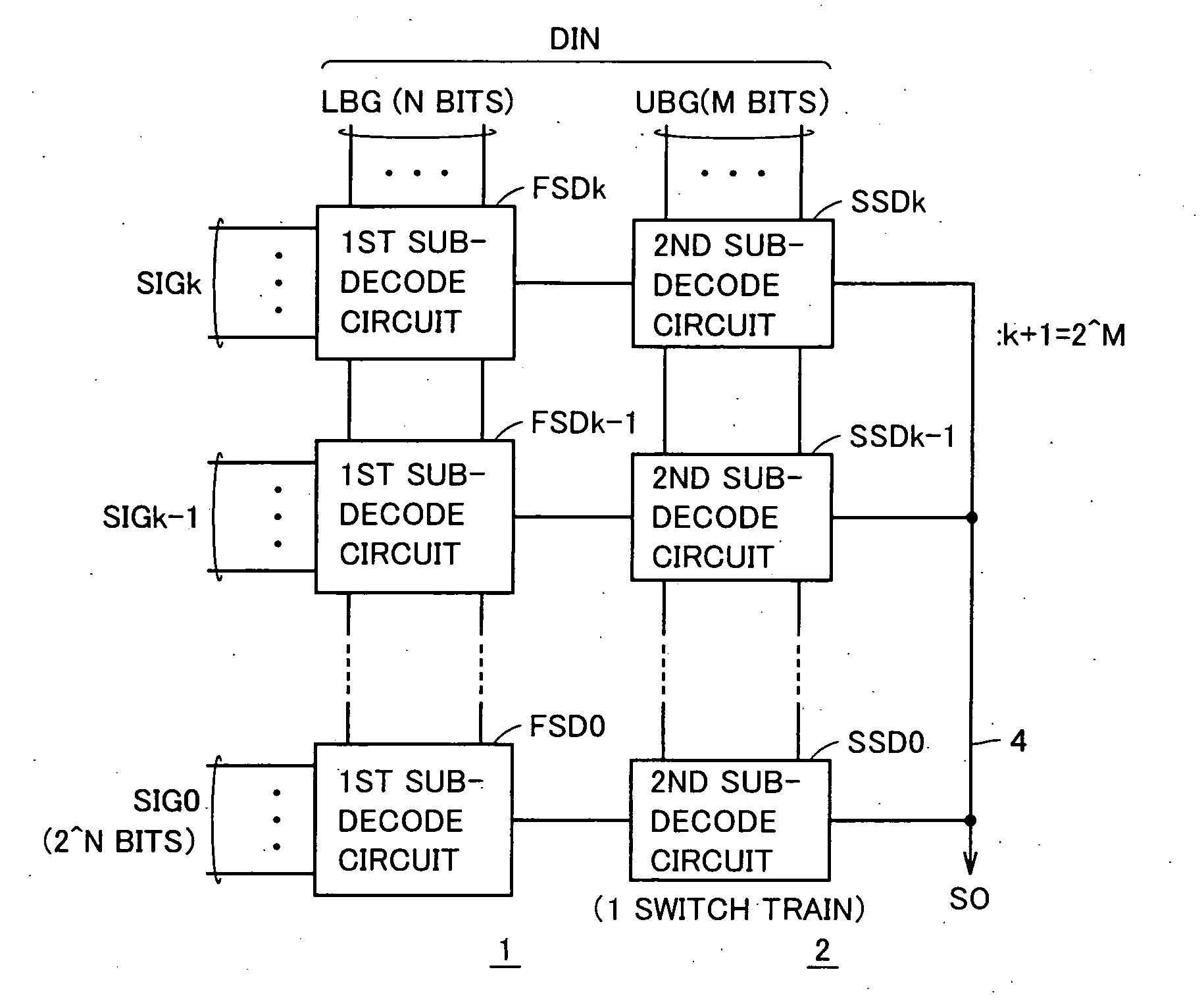
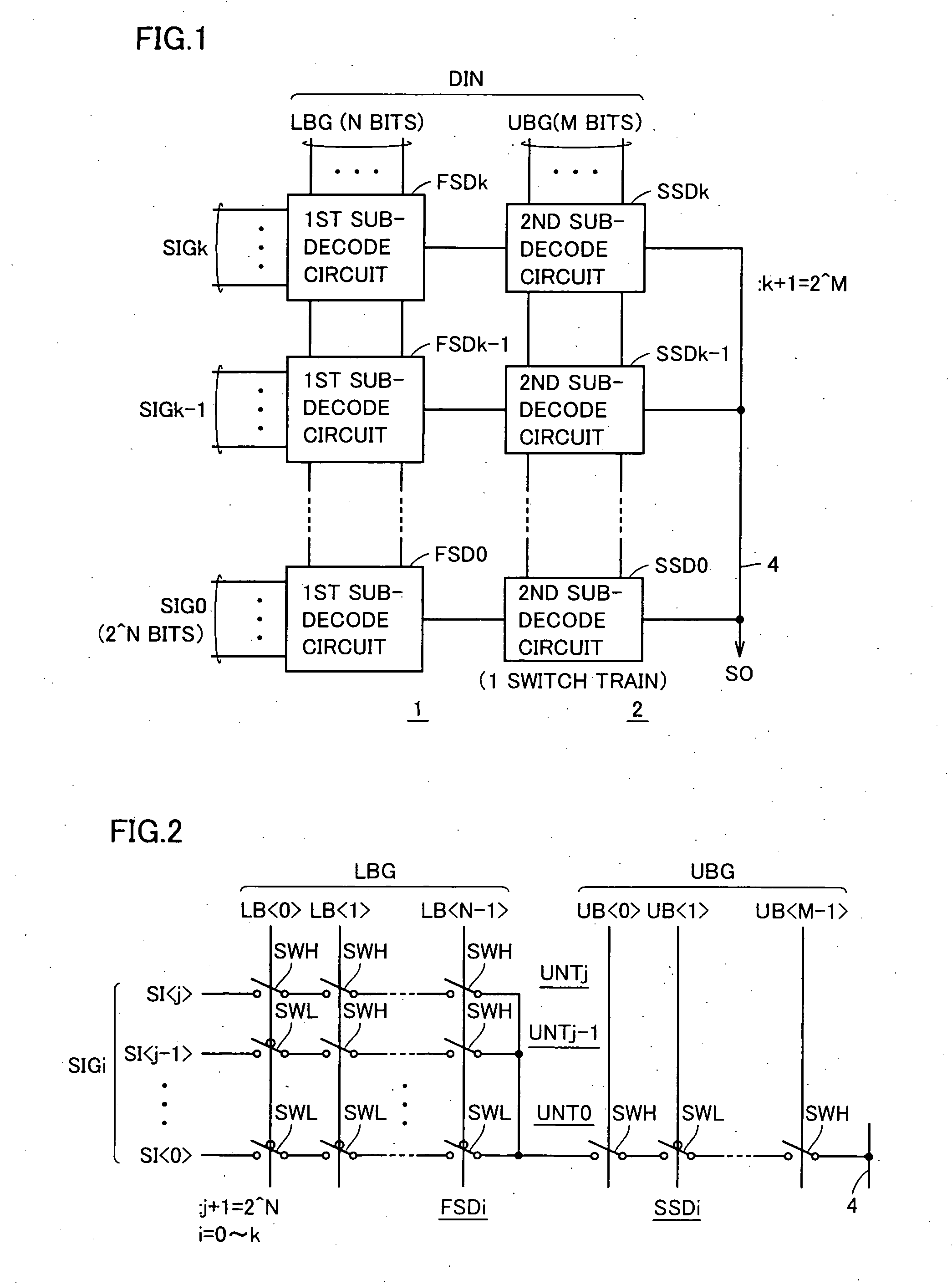
Multi-bit input data is divided into at least a first bit group and a second bit group, and each of first sub-decode circuits selects one selection target signal / voltage from selection target signal / voltage group in accordance with the first bit group. Then, one signal / voltage is selected according to the second bit group from the signals / voltages selected by the first sub-decode circuits, and is transmitted to an output signal line. Each of second sub-decode circuits is formed of a single train of series switches, and only one of the switch train is made conductive to transmit a finally selected signal / voltage to the output signal line.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Regulator for reducing power supply transient voltages
ActiveUS20060041770A1Reduces its computational workloadReduce electricity demandVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringEngineeringVoltage reference
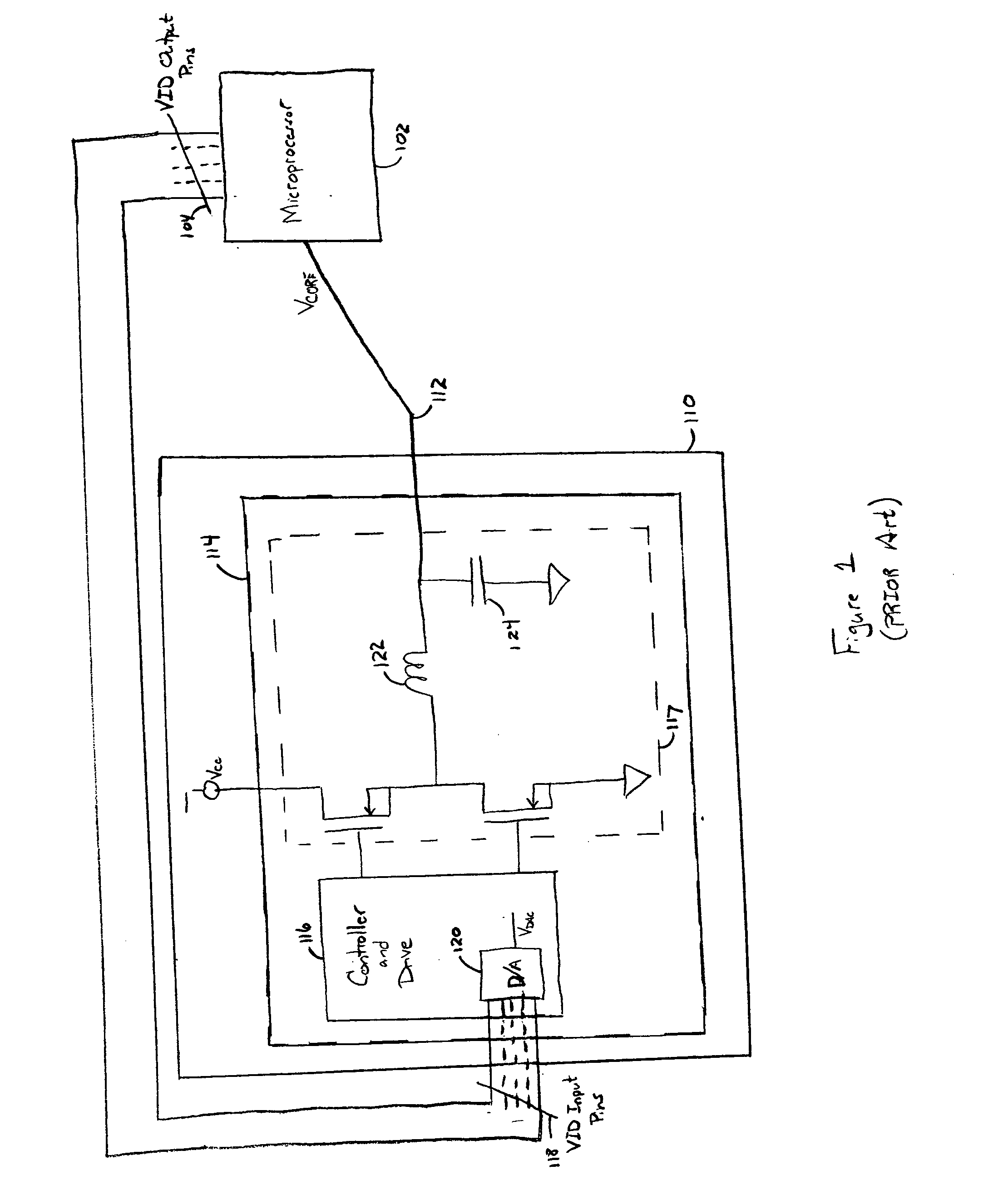
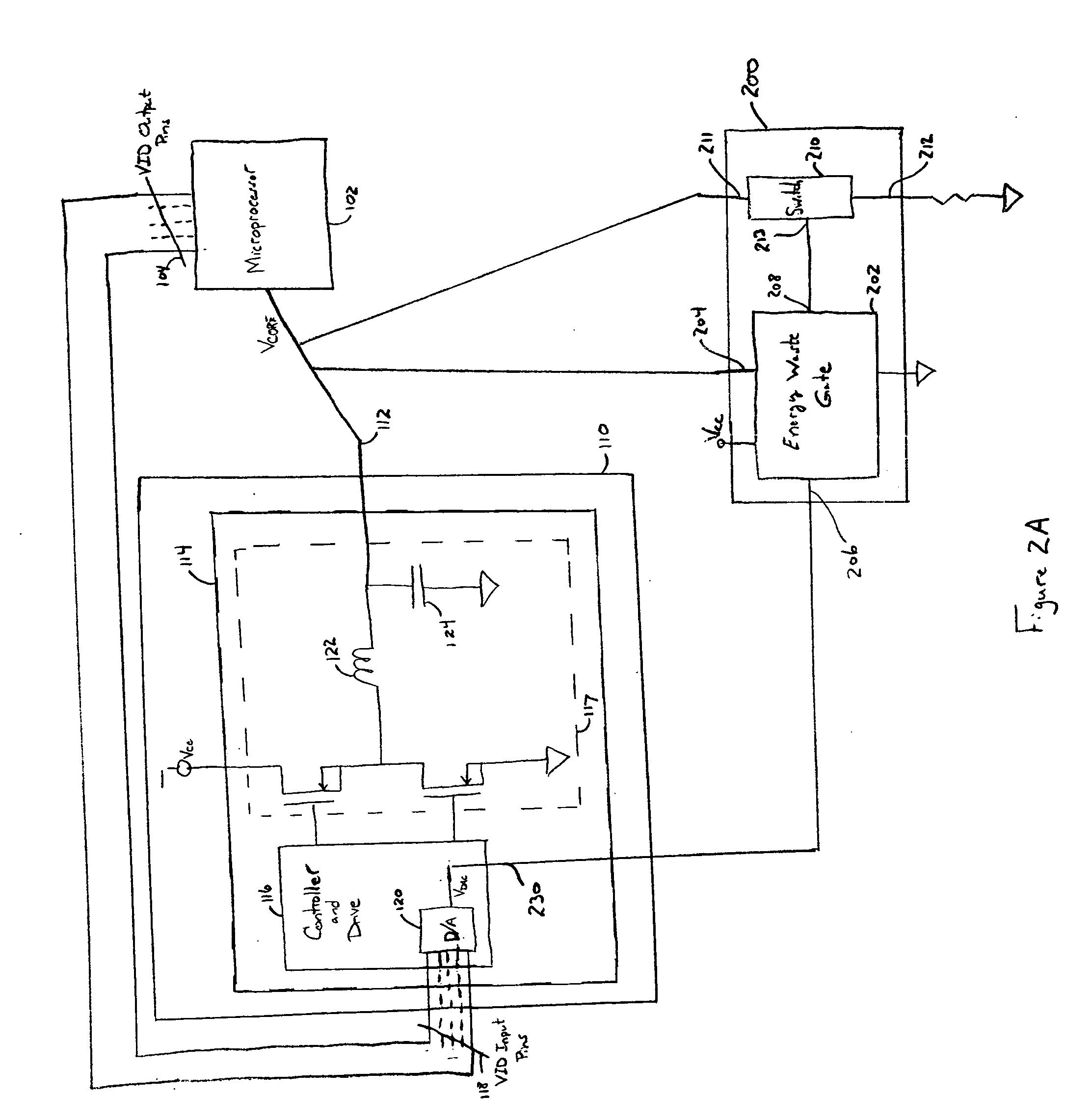
A regulator for reducing transient voltages at a power supply output includes a switch connected between ground and the power supply output and a comparator for controlling the opening / closing of the switch. The comparator includes an input for sensing a power supply output voltage and an input for receiving a reference voltage. When the output voltage exceeds the reference voltage by a threshold, for example, the comparator operates to close the switch, shunting excess energy in the power supply to ground and reducing the output voltage. As the output voltage returns to within the threshold of the reference voltage, for example, the comparator operates to open the switch, permitting the power supply to resume normal operation. The power supply may power a microprocessor that is susceptible to voltage transients that occur as the processor power demands change. The regulator compensates for these transients and maintains the power supply output voltage within desired specifications.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
LDMOS transistor
InactiveCN101238585APerformance is not affectedReduce output capacitanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesLDMOSCapacitive coupling
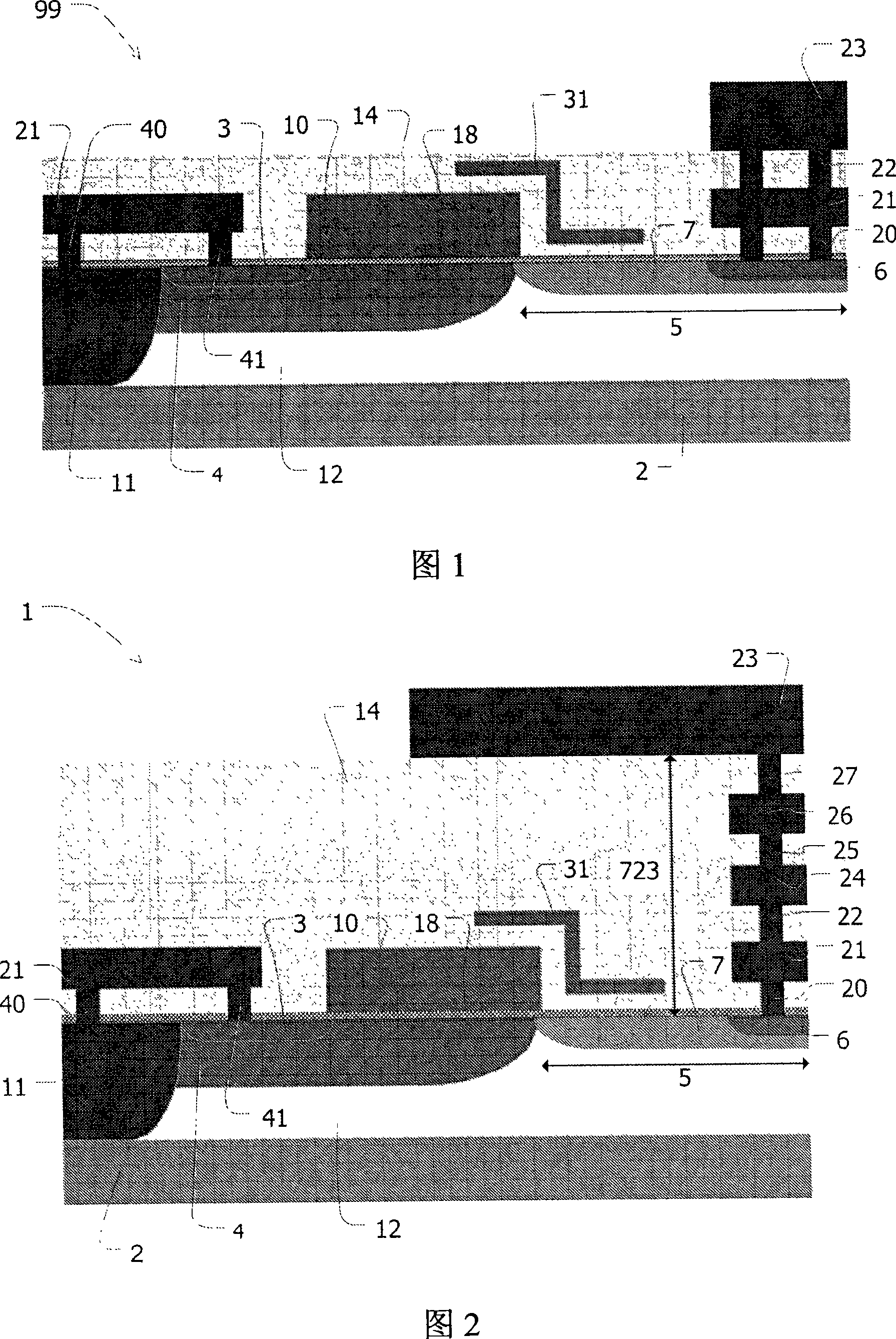
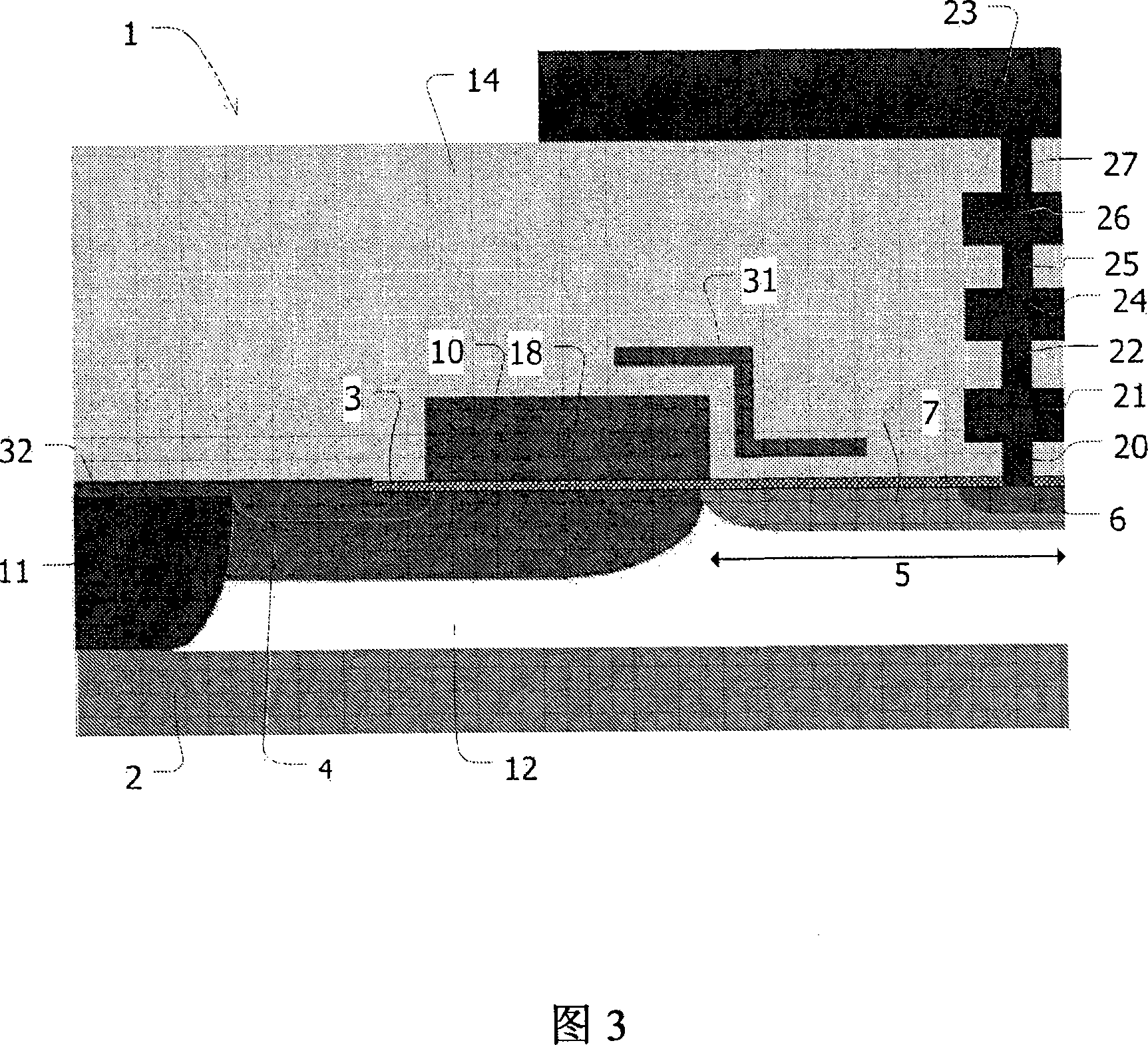
The LDMOS transistor (1) of the present invention comprises a substrate (2), a gate electrode (10), a substrate contact region (11), a source region (3), a channel region (4) and a drain region (5 ), the drain region (5) includes a drain contact region (6) and a drain extension region (7). The drain contact region (6) is electrically connected to the top metal layer (23) extending over the drain extension region (7), wherein the distance between the top metal layer (23) and the drain extension region (7) (723 ) greater than 2 μm. This reduces the area of the drain contact region (6) and increases the RF power output efficiency of the LDMOS transistor (1). In another embodiment, the source region (3) is electrically connected to the substrate contact region (11) via the silicide layer (32) instead of the first metal layer (21), thereby reducing the source region ( 3) Capacitive coupling to the drain region (5) and thereby further increasing the RF power output efficiency of the LDMOS transistor (1).
Owner:NXP BV
CMOS image sensor and method for forming same
ActiveCN101312201AFree spaceReduced output contact holesSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOptical pathCMOS
A CMOS image sensor comprises at least one CMOS image sensor pixel unit pair which comprises a first pixel unit and a second pixel unit. Each pixel unit in the CMOS image sensor comprises a photodiode area and a drive circuit area, wherein the drive circuit area comprises output transistors. Drain electrodes of the two output transistors adjacent to the first pixel unit and the second pixel unit are connected to be a common output end. The invention further provides another CMOS image sensor, wherein the amount of effective contact holes can be reduced through an output contact hole and a power contact hole of a common output transistor of the adjacent pixel units, thereby effectively decreasing the amount of the contact holes. The structure enables pixel units with smaller dimension to be designed under the condition of unreduced technical nodes without modifying a peripheral circuit and the processing parameter, which can not increase the mask and processing cost, but reduces the output capacitance and increases the filling ratio and the optical path.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
ESD protection apparatus for an electrical device
InactiveUS7196406B2Reduce capacitanceReduce inputSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectric potentialElectrical and Electronics engineering
An ESD protection apparatus for an electrical device with a circuit structure having an internal terminal, which is connected to an external terminal of the electrical device via a conductive connection, has a gas-filled cavity, through which the conductive connection extends at least partly, and a reference electrode in the cavity, wherein the conductive connection is disposed such in the cavity, that when applying a potential exceeding a predetermined threshold to the external terminal, a gas discharge occurs from the conductive connection to the reference electrode.
Owner:POLARIS INNOVATIONS
PFC circuit, PFC control circuit and switch power source
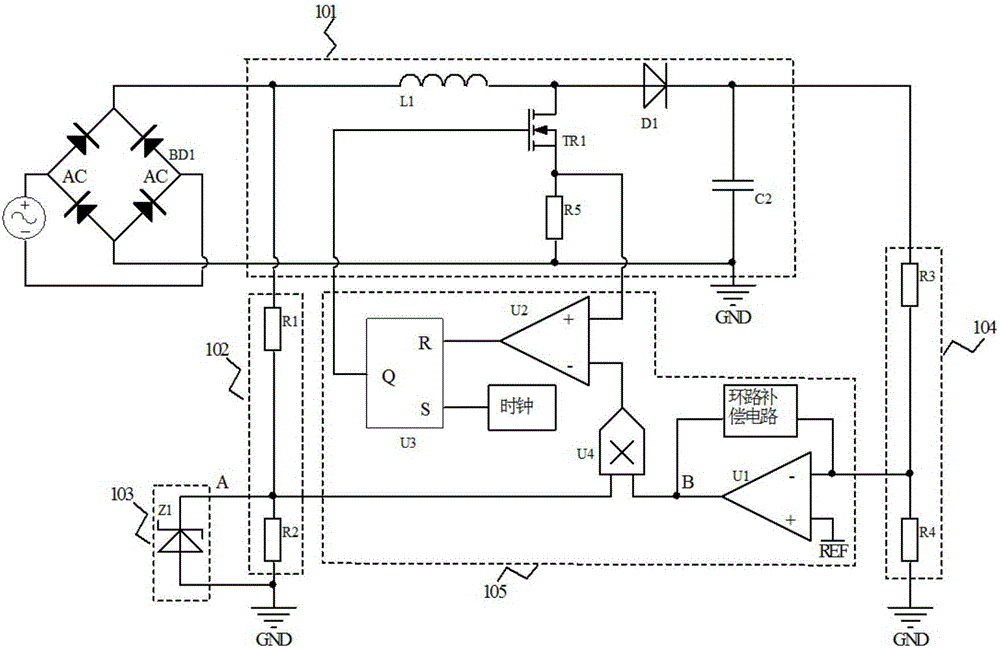
ActiveCN106208668ALow costSolve complex structuresEfficient power electronics conversionEnergy industryCapacitanceControl signal
The invention relates to the field of switch power sources and specifically relates to a PFC circuit capable of reducing output capacitance, a PFC control circuit and a switch power source in which the PFC control circuit is adopted. The PFC circuit provided in the invention comprises a PFC control chip; a feedback control circuit is integrated on the PFC control chip and is used for receiving input sampling voltage of an input detection circuit and output sampling voltage of an output detection circuit, the feedback control circuit is also used for outputting control signals for controlling a work mode of a voltage conversion circuit, the PFC control chip has a reference voltage end and is characterized by additionally comprising a waveform shaping circuit which is used for truncating a wave crest of input sampling signals, and the waveform shaping circuit is externally connected between the reference voltage end of the PFC control chip and earth. Compared with technologies of the prior art, the PFC circuit, the PFC control circuit and the switch power source are advantaged by circuit simplicity, low cost and easy-to-realize property.
Owner:MORNSUN GUANGZHOU SCI & TECH +1
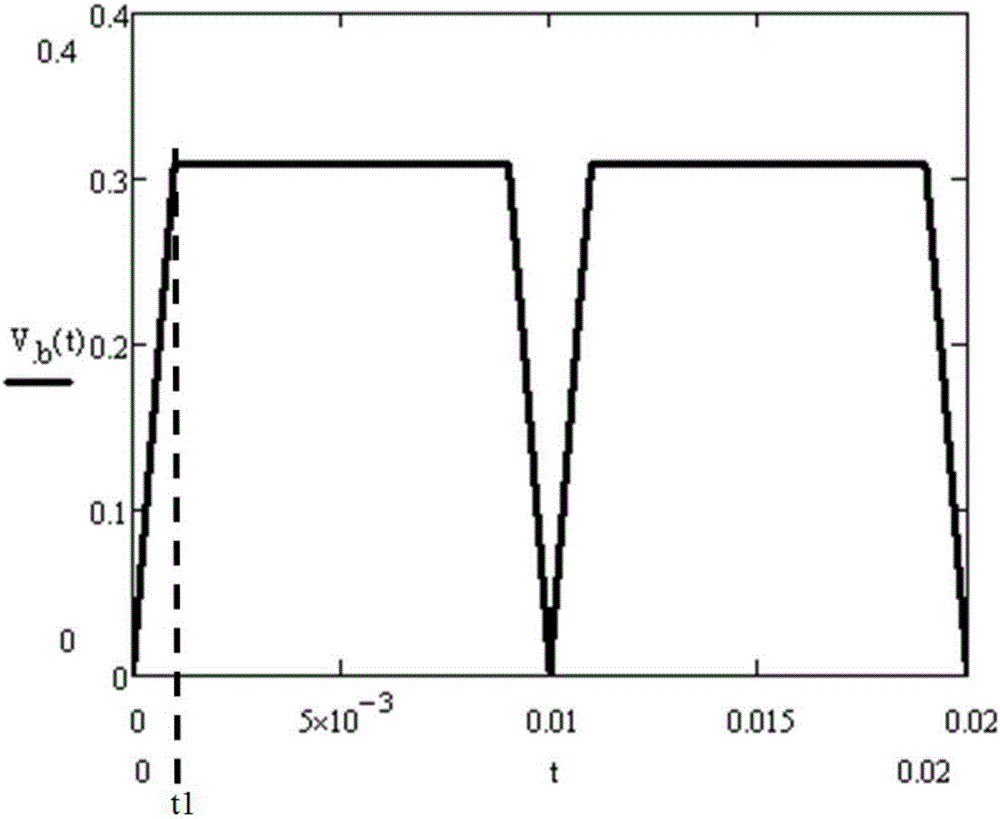
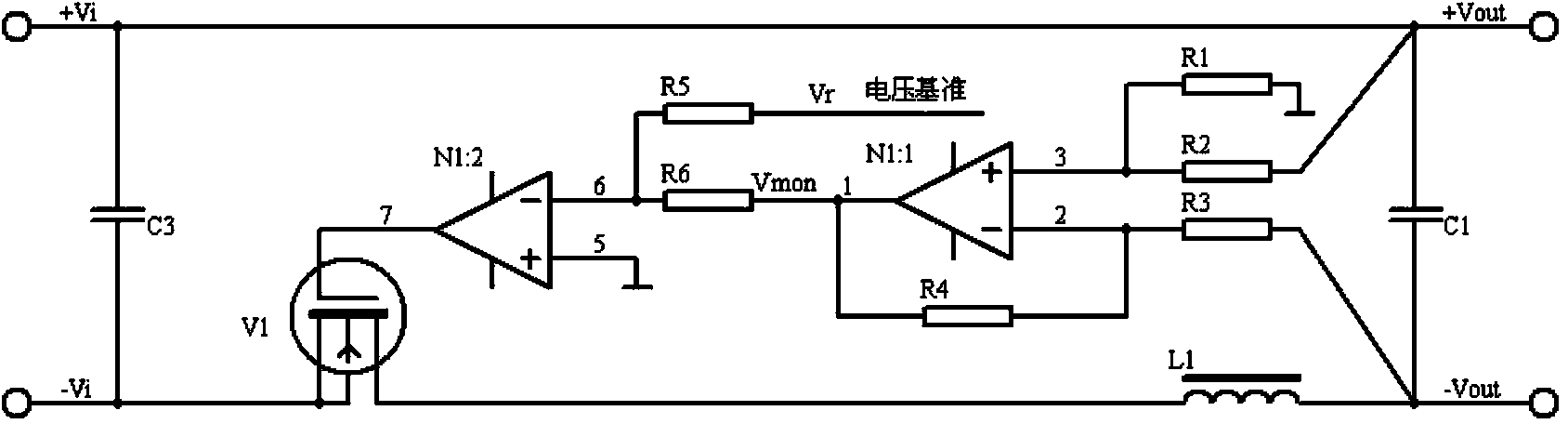
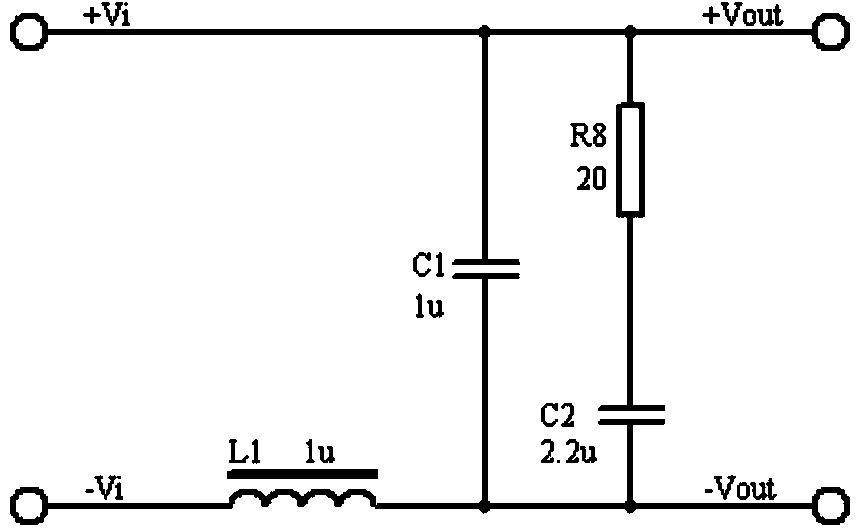
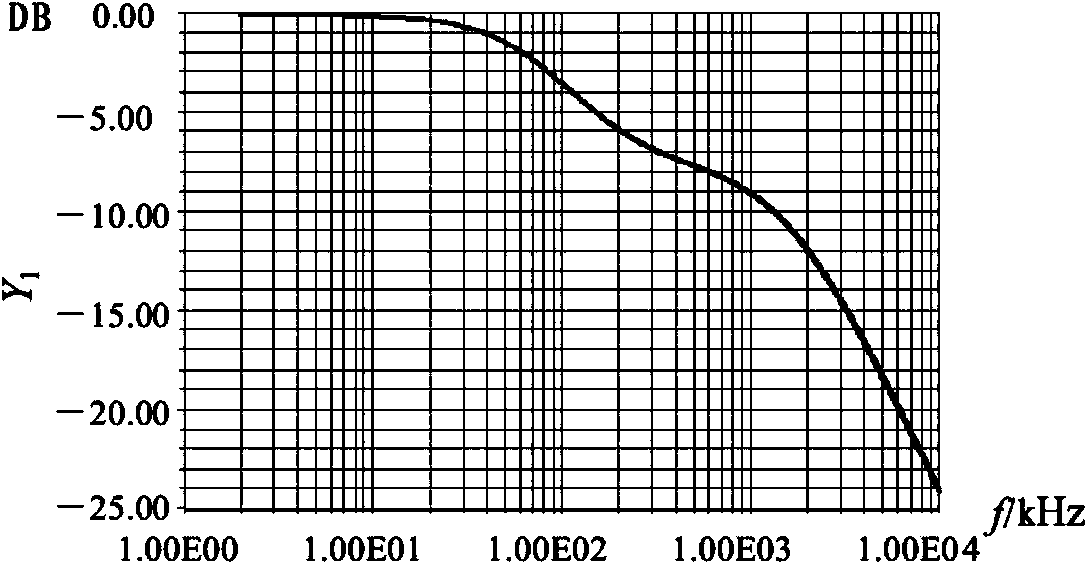
Ripple wave suppressor circuit of program-controlled direct-current power supply
ActiveCN103973086AReduce noiseFast dynamic responsePower conversion systemsCapacitanceLow-pass filter
The invention discloses a ripple wave suppressor circuit of a program-controlled direct-current power supply. According to the ripple wave suppressor circuit of the program-controlled direct-current power supply, an active low-pass filter and a passive filter are connected between a positive output line of the direct-current power supply and a negative output line of the direct-current power supply after a capacitor C3 is connected between the positive output line of the direct-current power supply and the negative output line of the direct-current power supply, the active low-pass filter comprises an N-channel high-power MOSFET V1, a front-stage operational amplifier N1:1 with a dynamic compensation function and a rear-stage operational amplifier N1:2 with a dynamic compensation function, and the passive filter comprises an inductor L1 and a capacitor C1. According to the ripple wave suppressor circuit of the program-controlled direct-current power supply, high-frequency and low-frequency ripple wave noise output by the power supply can be lowered, the dynamic response performance can be improved, and the output precision and the stability are improved. The front-stage and rear-stage synchronous tracking control is adopted, accurate adjustment enabling the voltage difference to be low can be achieved, and the conversion efficiency of the power supply is effectively improved. As a result, the ripple wave suppressor circuit of the program-controlled direct-current power supply has high application value in the aspect of design of high-precision program-controlled power supplies.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONIS TECH INSTR CO LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveUS8194369B2Reduce resistanceReduce output capacitanceTransistorEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentElectrical resistance and conductanceInterconnection
A semiconductor integrated circuit includes: an output pad from which an output signal is outputted; an output signal line connected with the output pad; a first pad configured to function as a ground terminal or a power supply terminal; a first wiring connected with the first pad; an output driver connected with the output pad and configured to generate the output signal; an ESD protection device connected with the output signal line and having a function to discharge surge applied to the output pad; and a first trigger MOS transistor used as a trigger device. The output driver includes: a first protection target device connected between the output signal line and the first interconnection; and a first resistance element connected between the first protection target device and the first interconnection. The first trigger MOS transistor configured to detect a voltage generated in the first resistance element by a gate of the first trigger MOS transistor and to allow the ESD protection device operate in response to the detected voltage.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Field effect transistor and application device thereof
InactiveCN1901226ALower on-resistanceReduce output capacitanceElectronic switchingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETCapacitance
The present invention provides a MOSFET having a low on-state resistance and a high withstand voltage as well as a small output capacitance (C(gd), etc.). The MOSFET has a p-type base layer and a n-type source layer selectively formed on the surface of the p-type base layer. A n-type drain layer is formed in a position apart from the p-type base layer . On the surface of the region between the p-type base layer and the n-type drain layer, a n-type drift semiconductor layer and a p-type drift semiconductor layer are alternately arranged from the p-type base layer 4 to the n-type drain layer. Further, in the region between the n-type source layer and the n-type drain layer, a gate electrode is formed via a gate insulating film. With the structure, the neighboring region of the gate electrode is depleted by a built in potential between the n-type drift semiconductor layer and the p-type drift semiconductor layer or by the potential of the gate electrode, when the gate electrode, source electrode, and drain electrode are at 0 potential.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Regulator for reducing power supply transient voltages
ActiveUS7441129B2Reduces its computational workloadReduce electricity demandVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringVoltage referenceComparator
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
Semiconductor radiation detector with high resolution
ActiveCN101281148AImprove shortcomingsHigh resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor radiation detectorsIntrinsics
A semiconductor radiation detectors with high-resolution, which includes a semiconductor silicon with high purity and N type, a detection intrinsic region, a N type point anodic, a P type drift electrode and a first field-effect transistor, the semiconductor silicon (namely base chip) is of square shaped, the detection intrinsic region is consist of a P-N knot which evenly placed in the ray incident surface of the semiconductor silicon with high purity and N type, the N type point anodic is located outside of the intrinsic region relative to a side, and is surrounded by the P type drift electrode whose focus is a N type electrode, the P type drift electrodes are a plurality of article round convex rings whose focus is the N type electrode, the first filed-effect transistor is arranged inside the N type electrode. A new planar construction of the P type drift electrode is used in the detector on the base of silicon drift detector SDD, and key progress is processed for maintaining high resolution in SDD, large counting region, small size, light weight, and weak points of the SDD existed in the past is quite improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SKYRAY INSTR
Digital to analog converter having fastpaths
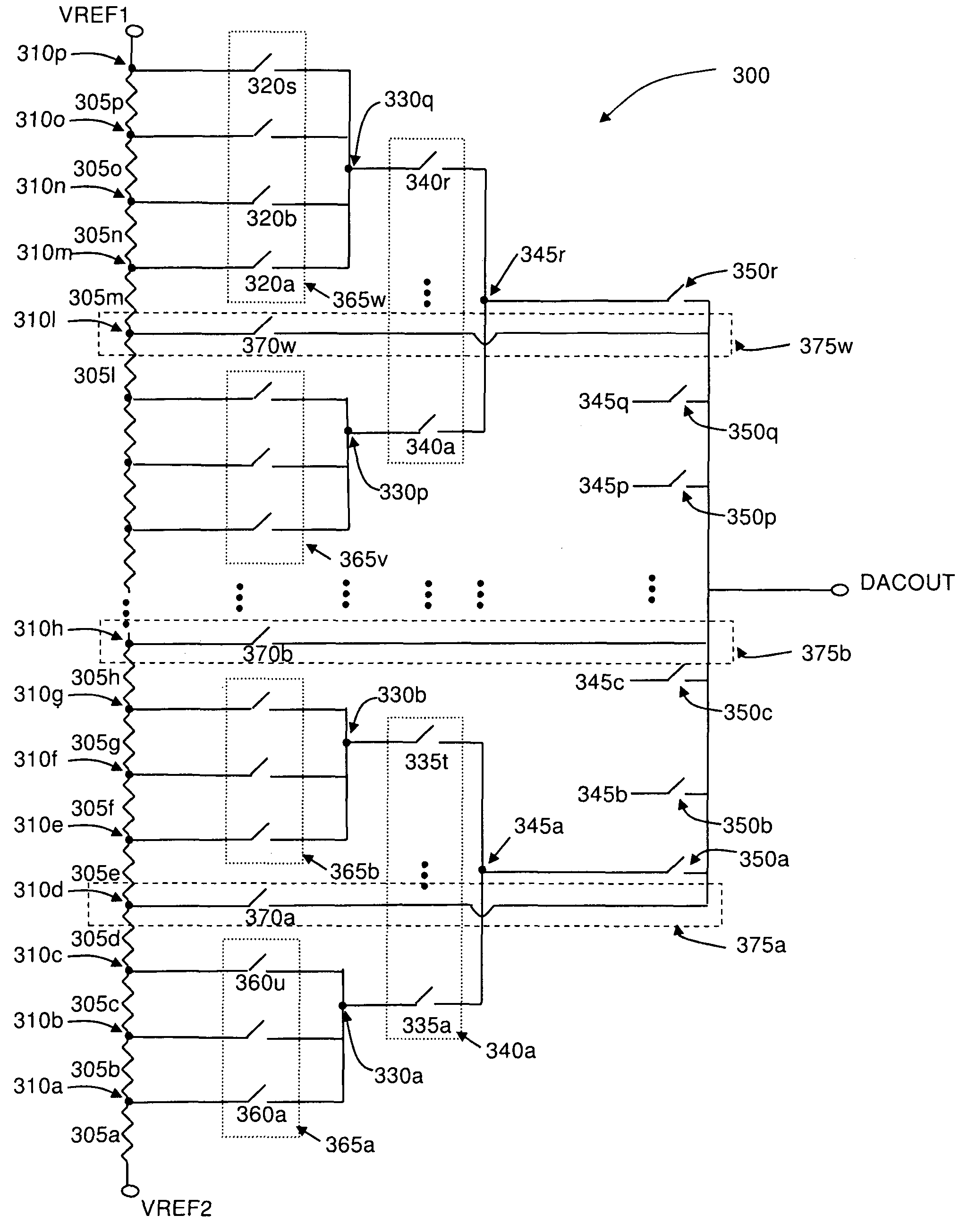
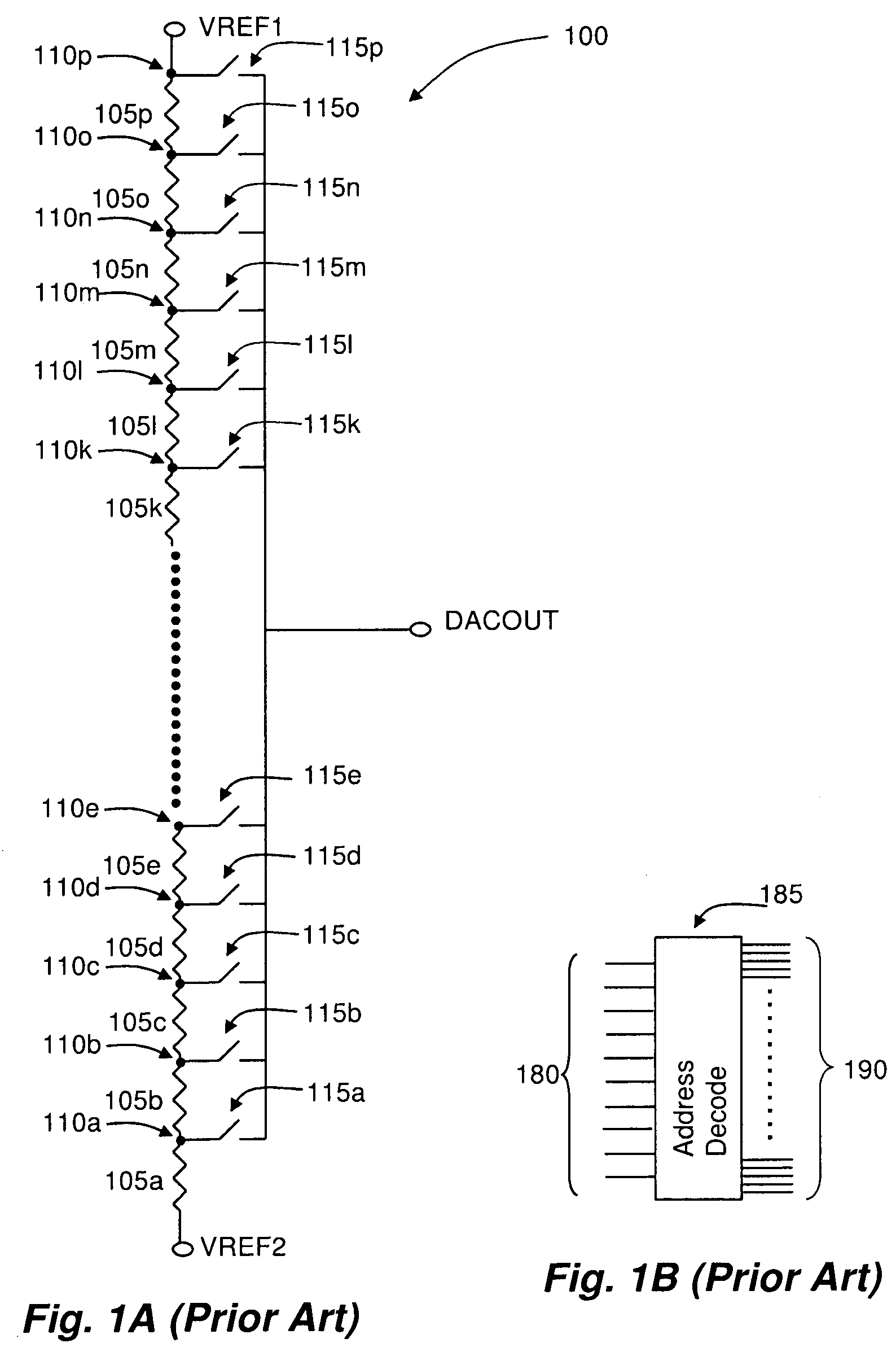
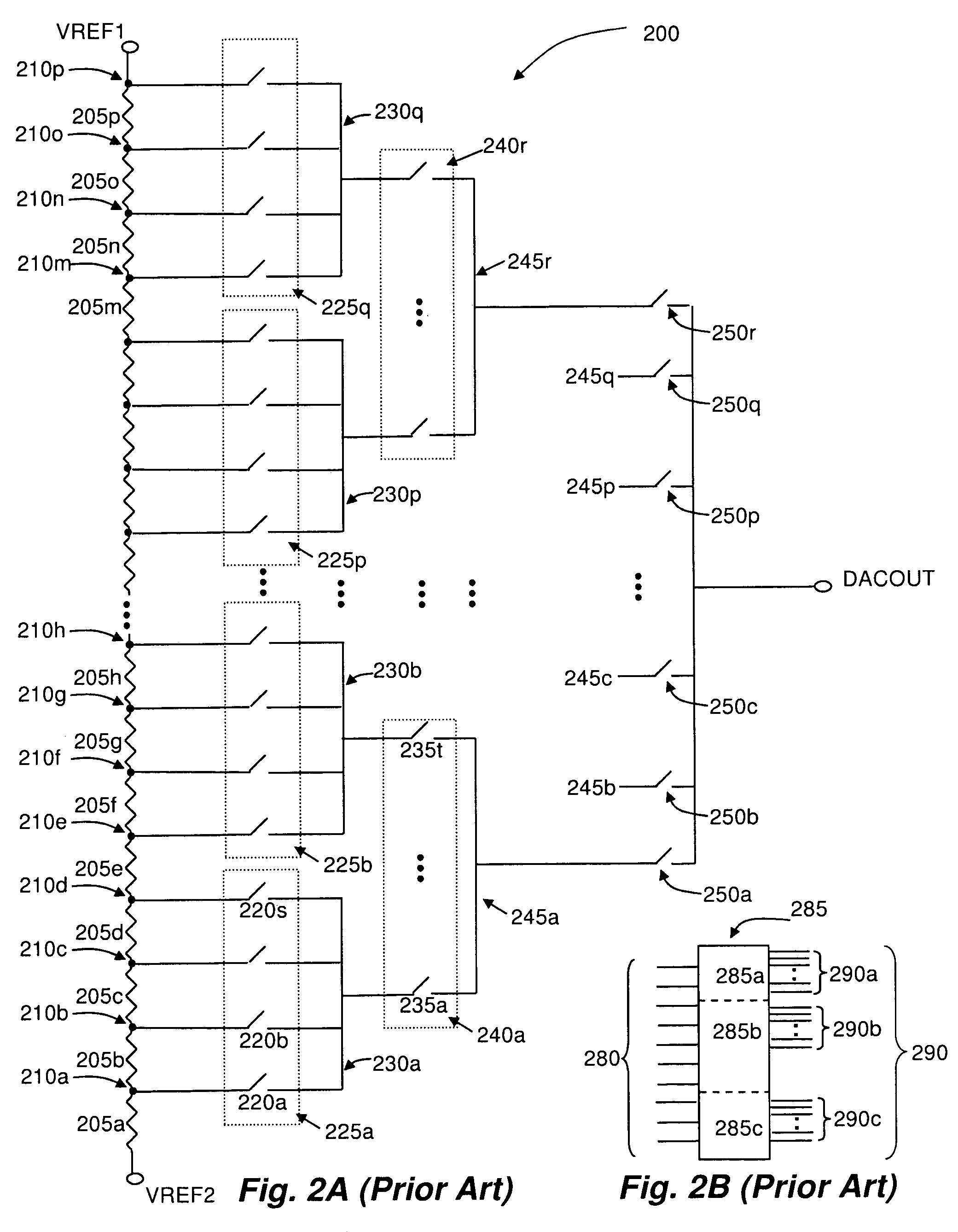
InactiveUS7868809B2Limit output resistanceReduce output capacitanceElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsMultiplexingDigital analog converter
A resistor-based digital to analog converter (DAC) having mux fastpaths, which selectively connect a subset (or an entirety) of voltage divider nodes in a DAC to either a higher level of multiplexor hierarchy, or a DAC output node, effectively bypassing one or more levels of multiplexor devices. In addition, the fastpaths may selectively connect lower levels of multiplexor hierarchy to higher levels of multiplexor hierarchy and / or a DAC output node.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
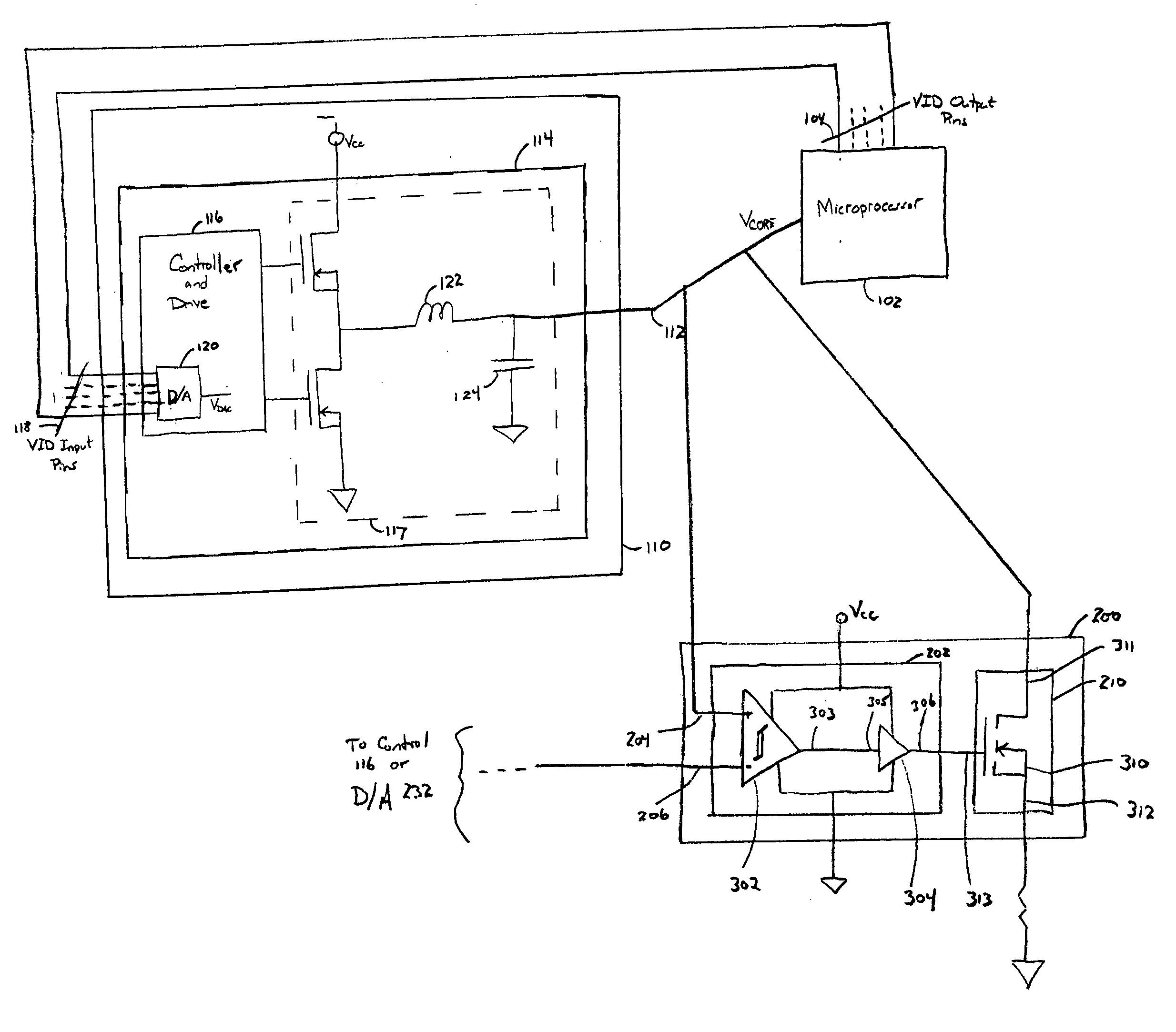
Method and system for information handling system power control
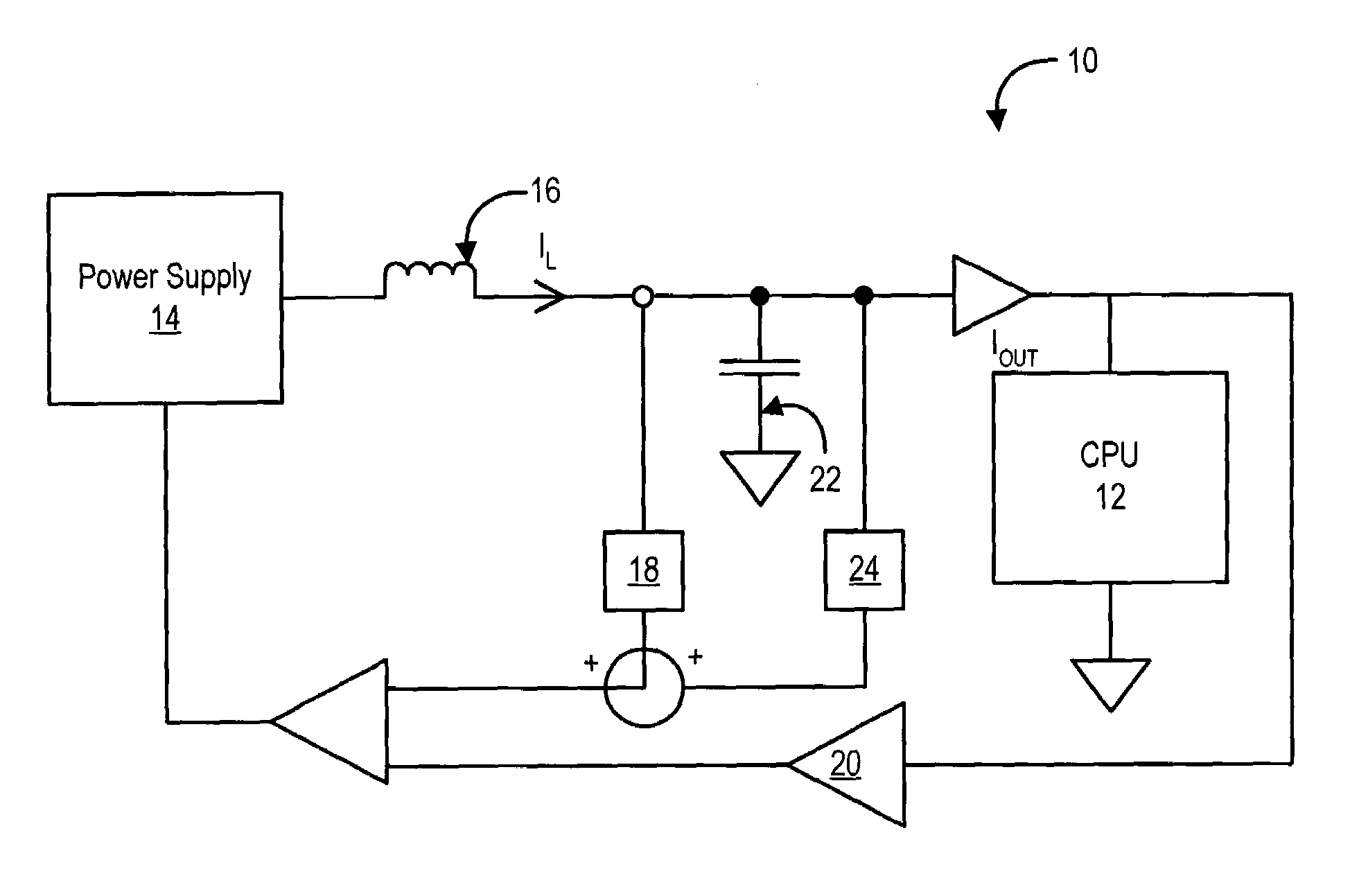
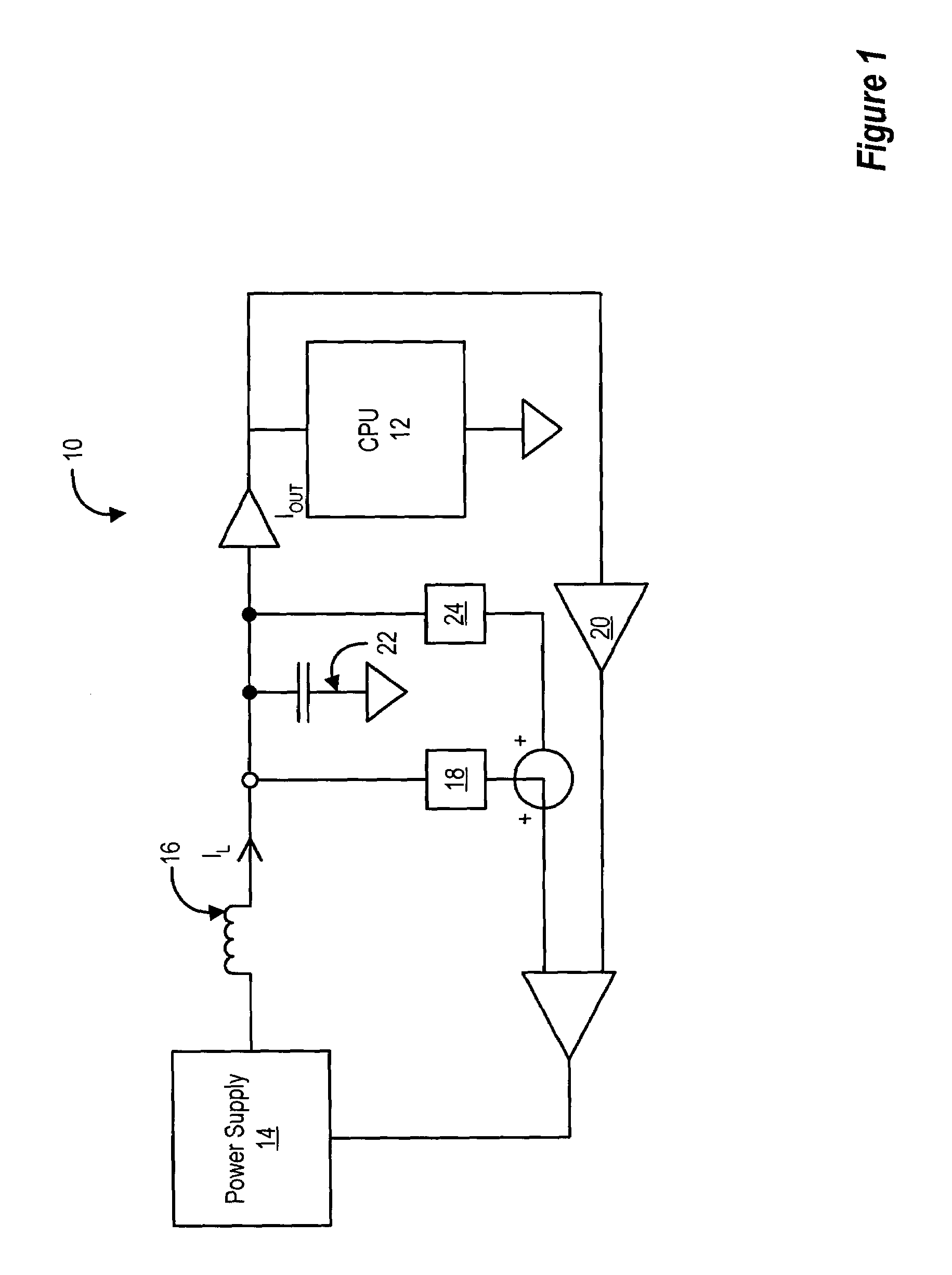
ActiveUS7162655B2Improve responseReduce output capacitanceVolume/mass flow measurementHardware monitoringCapacitanceEngineering
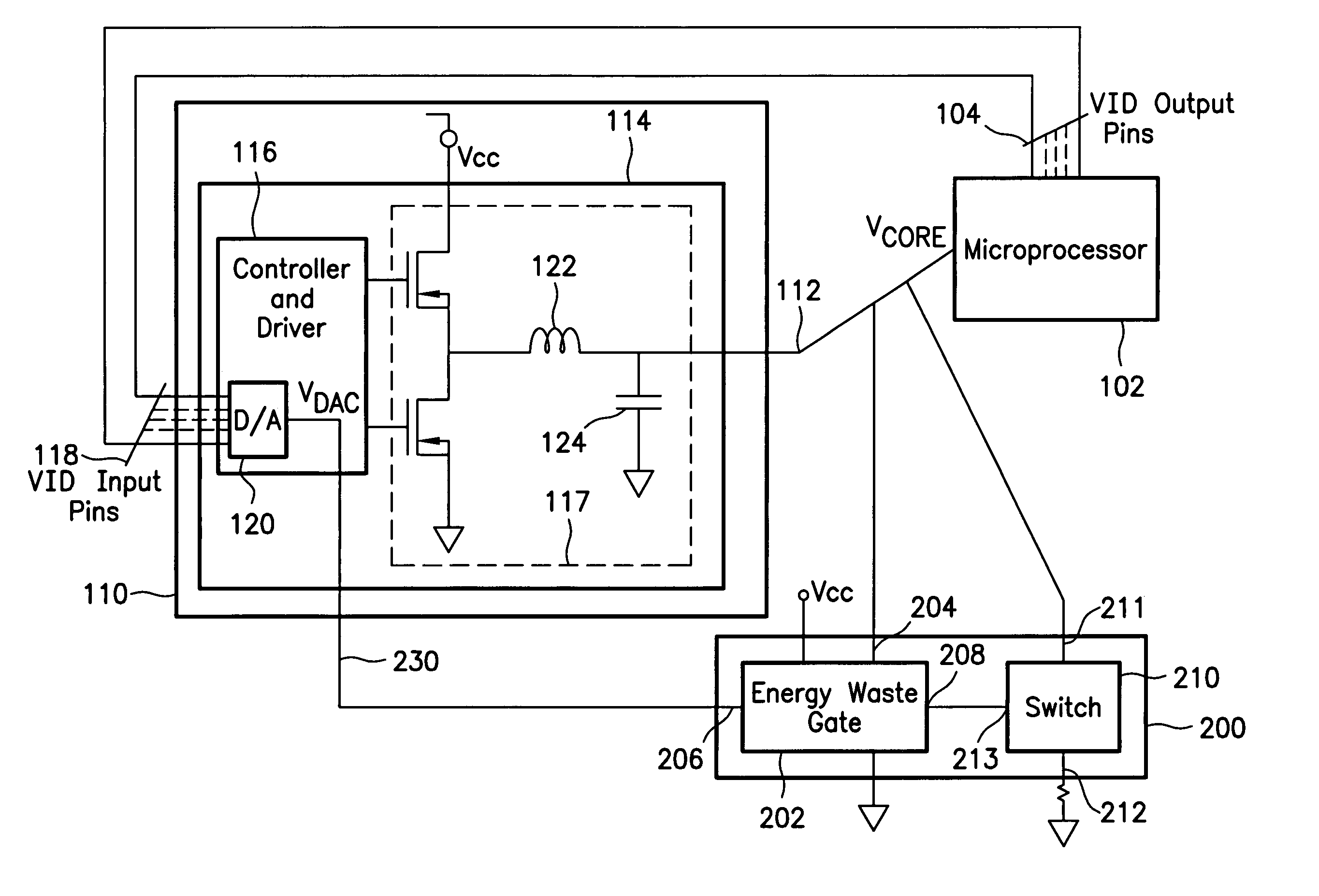
Power supply response to variations in power demand by a microprocessor is improved with a compensation loops that estimate changes in load current with improved speed. The load current estimate is performed in part with a capacitance feed forward compensation loop that senses voltage at output capacitors to replicate the current present in the capacitors and communicates the capacitor current adjusted by an optimized gain to the power supply for adjustment of power output. Capacitor current is replicated with a frequency domain filter having a pole that cancels out the zero created by power supply equivalent series resistance and capacitor capacitance. The capacitance compensation loop improves power supply response time to microprocessor power demand skews so that the size or number of output capacitors may be reduced while still maintaining power supply at the microprocessor to within desired voltage and current tolerances.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
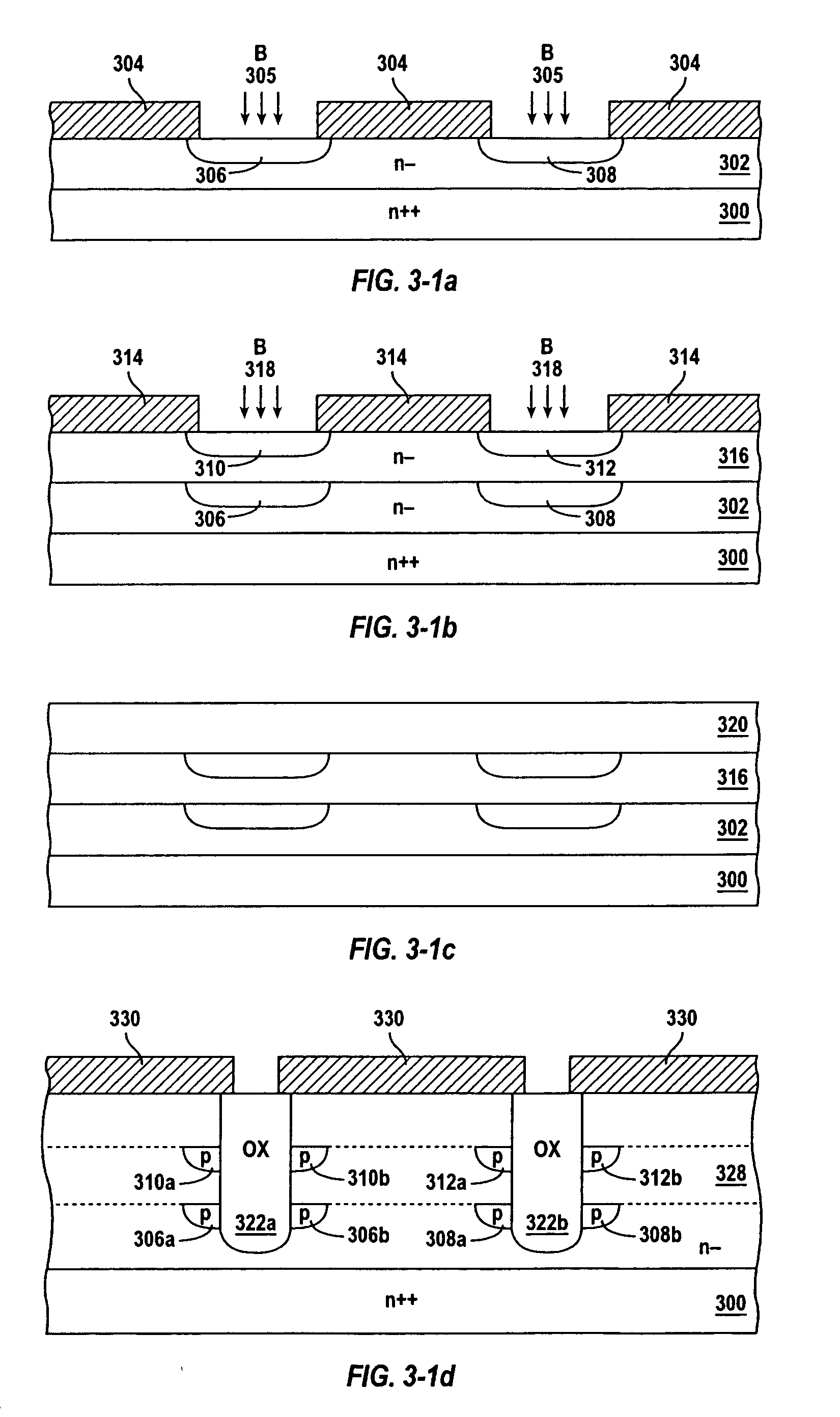
Trench step gate type IGBT chip
The invention provides a trench step gate type IGBT chip. The chip comprises a substrate and a first trench gate located in the surface of the substrate, the first trench gate is a solid grate in structure, each gate oxidation layer of the first trench gate consists of different gate oxygen thickness, and the gate oxygen thickness of the gate oxidation layer on the upper side is smaller than thatof the gate oxidation layer on the lower side. According to the trench step gate type IGBT chip, thinner gate oxidation layers are adopted in an effective trench working zone, thicker gate oxidation layers are adopted at the bottom of the trench, so that the chip density is improved, the consumption is reduced, the control capacity of the gate for a switch is improved, the voltage endurance capacity of the bottom of the trench is improved, the output capacitance is reduced, and the switch loss is reduced. Meanwhile, the P trap dosage is increased to maintain Vth at the same level, and the latching resistance of a device is enhanced, so that the electric property and reliability of the chip are optimized while the current density of the chip is improved.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CRRC TIMES SEMICON CO LTD
Radio-frequency LDMOS (Laterally Diffused Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device and technological method
ActiveCN104752500AReduce output capacitanceReduce electric field strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesBody regionPhysics
The invention discloses a radio-frequency LDMOS (Laterally Diffused Metal Oxide Semiconductor) device. A body region and an N-type light-doped drift region are arranged in a P-type epitaxial layer on a P-type substrate; a polycrystalline silicon gate and a Faraday shield layer of the LDMOS device are arranged on the surface of the epitaxial layer; the N-type drift region is divided into an upper layer and a lower layer; the concentration of the lower layer is greater than that of the upper layer; two-section P-type buried layers are arranged at a junction of the upper layer and the lower layer; and the radio-frequency LDMOS device in the structure has lower output capacitance. The invention further discloses a technological method of the radio-frequency LDMOS device.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Efficient linear LINC power amplifier
InactiveUS8269555B2Improve efficiencyIncrease powerNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsModulated-carrier systemsCapacitanceDead time
Owner:AMPLEON NETHERLANDS
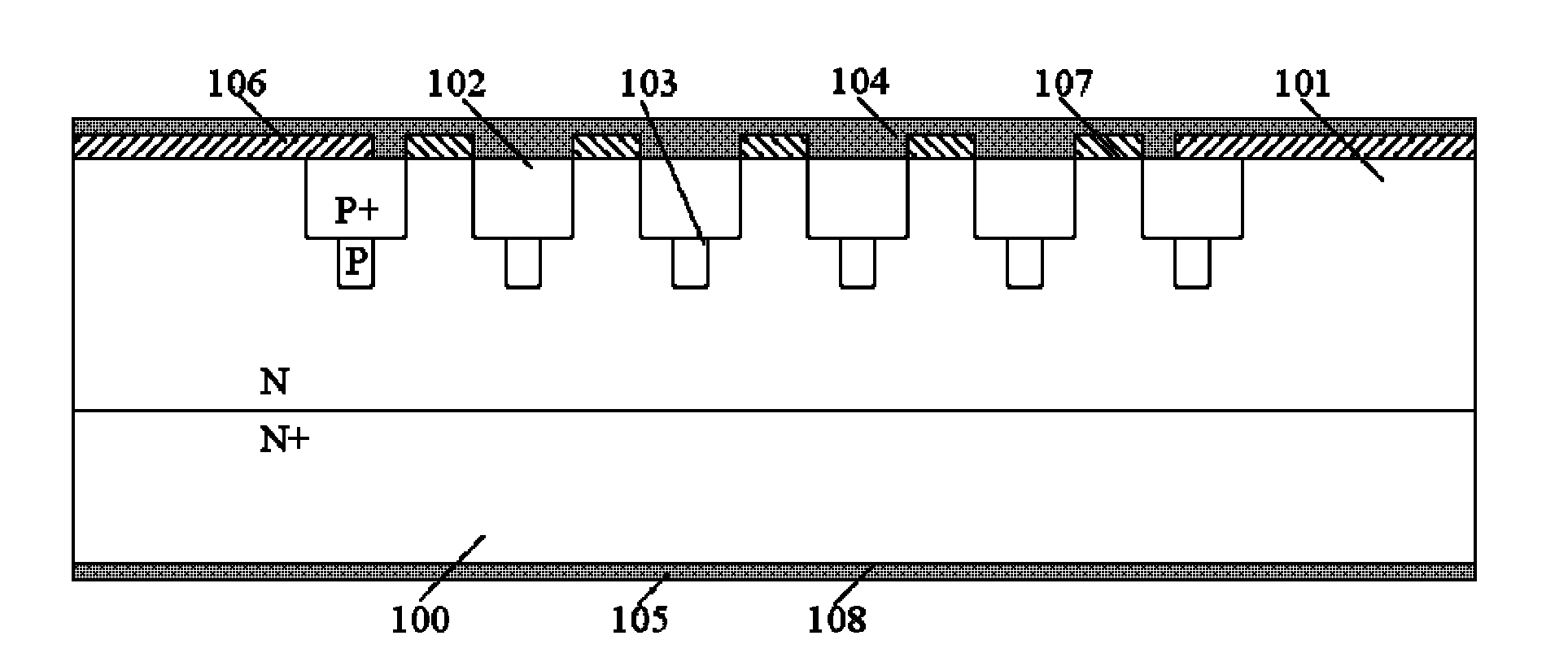
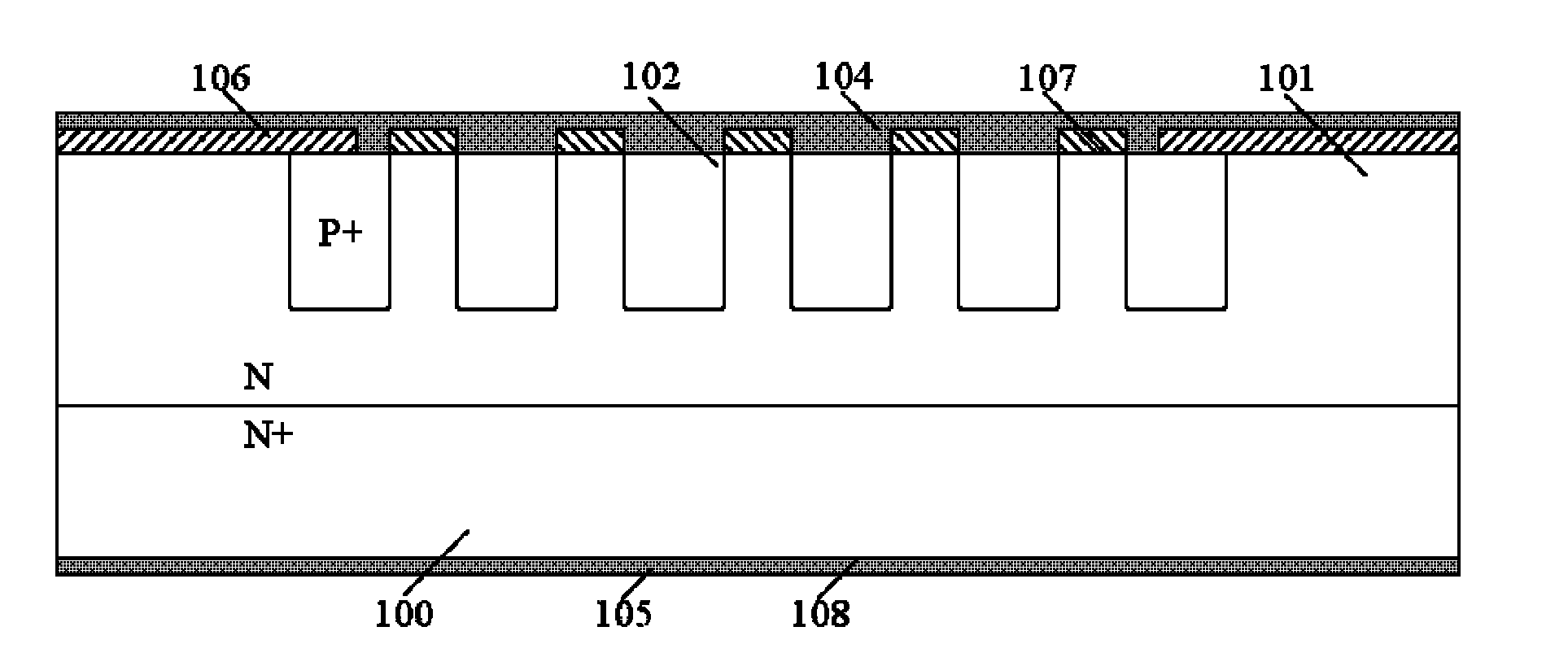
Schottky diode controlled by junction barrier having superposed P<+>-P structure
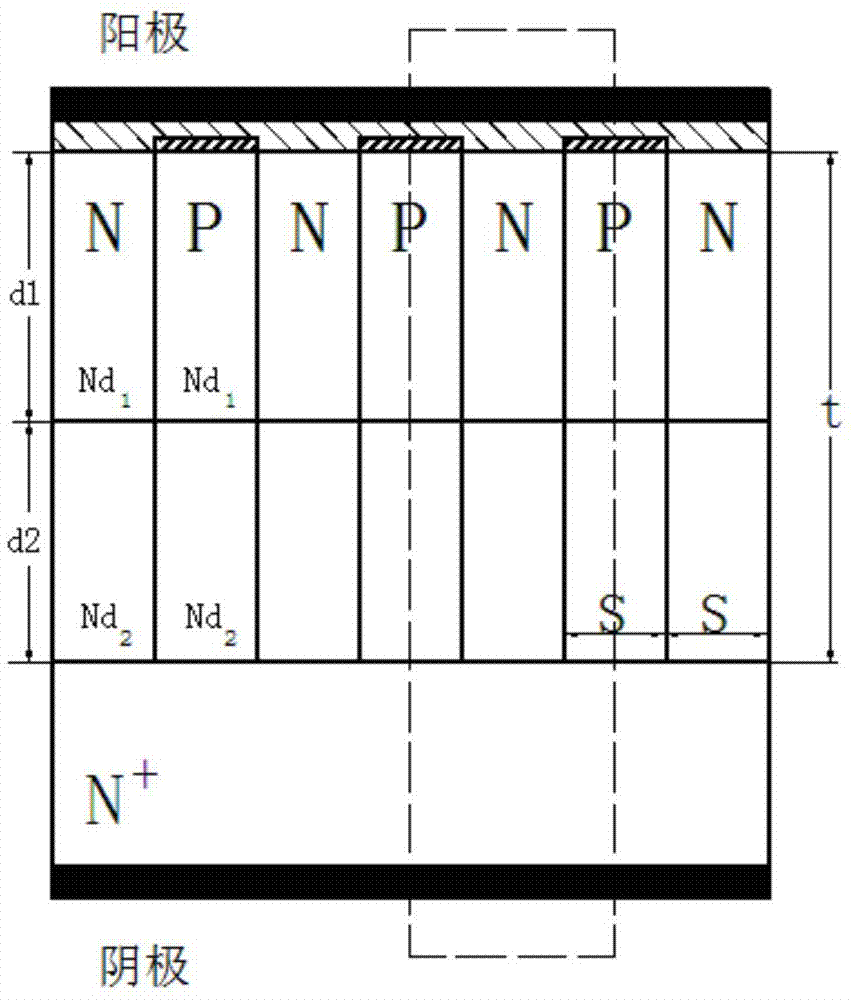
InactiveCN102208456AEasy to meet application requirementsImprove reverse withstand voltageSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceElectronic systems
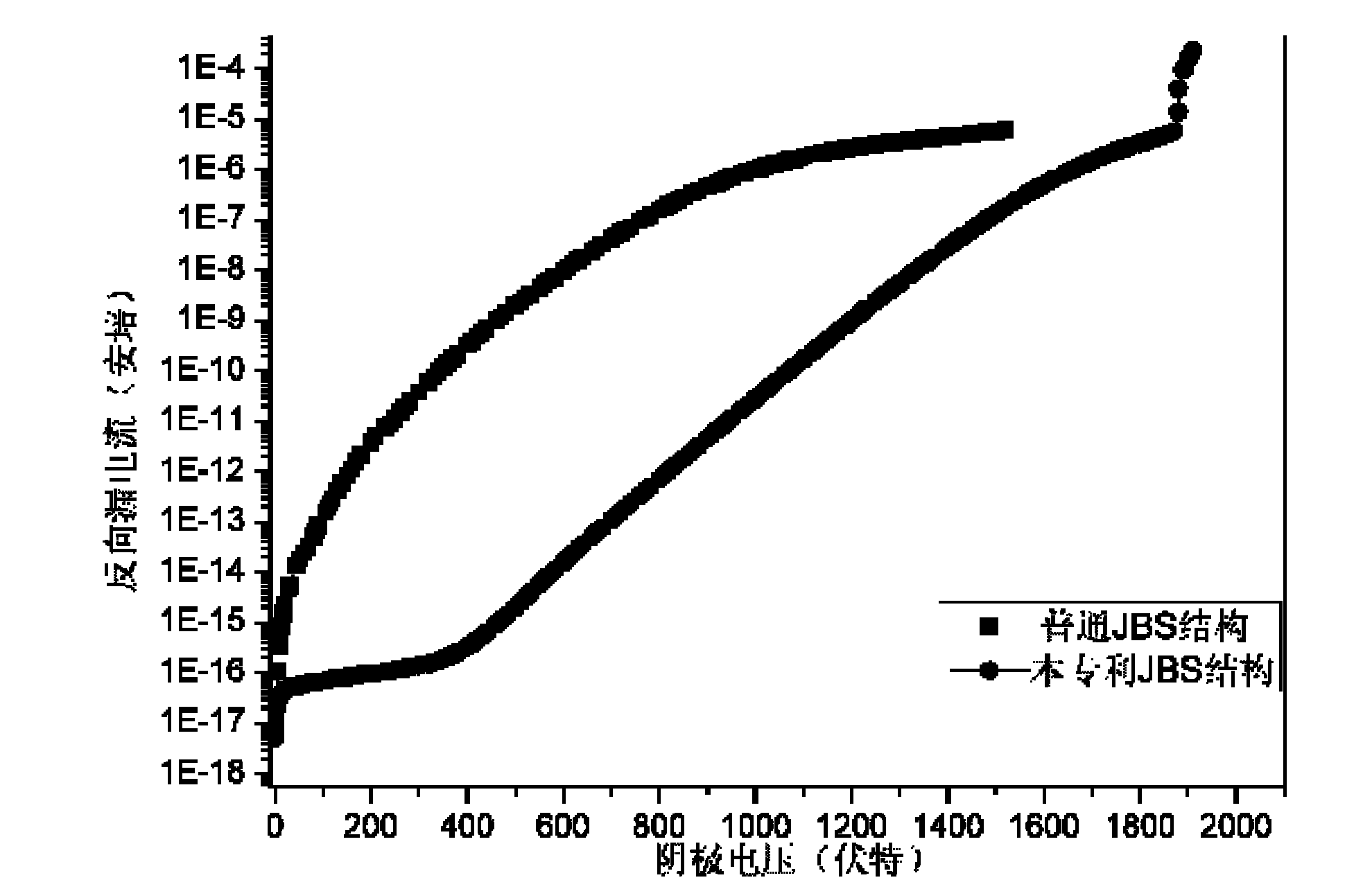
The invention provides a schottky diode controlled by a junction barrier having a superposed P<+>-P structure. The schottky diode comprises an N<+> type substrate zone (100), an N type drift region (101), P<+> portions of the superposed P<+>-P structure (102), an anodic electrode (104), a cathodic electrode (105), a silicon dioxide layer (106), a schottky contact (107), and an ohmic contact (108). Besides, the schottky diode also includes P portions of the superposed P<+>-P structure (103), wherein the P<+> window portions of the superposed P<+>-P structure (102) is on the P window portions of the superposed P<+>-P structure (103). According to the invention, before the P<+> portions of the superposed P<+>-P structure in an area are formed, the P portions of the superposed P<+>-P structure in an area are formed, wherein the P portions are separated from each other and the structure of P portions is similar to the netted structure of a junction barrier schottky (JBS). Therefore, reverse withstand voltage of the JBS diode device can be improved and the output capacitance can be reduced, on the condition that the forward conduction characteristic of the device is not sacrificed. The process of the invention has the strong feasibility of implementation, and the application requirement of the power electronic system can be satisfied easily according to the invention.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Switching adapter control method for adaptive mobile power systems
InactiveUS20110298437A1Reduce switching frequencyReduce switching lossesDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationCapacitanceMOSFET
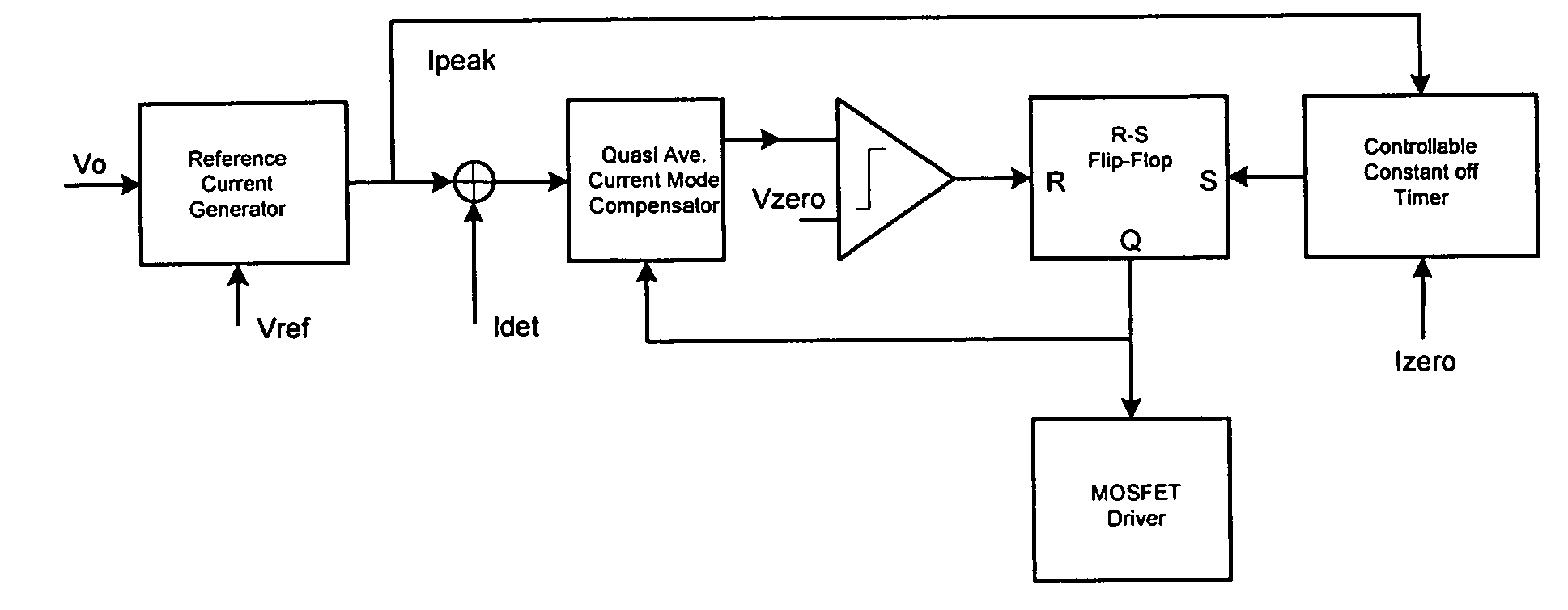
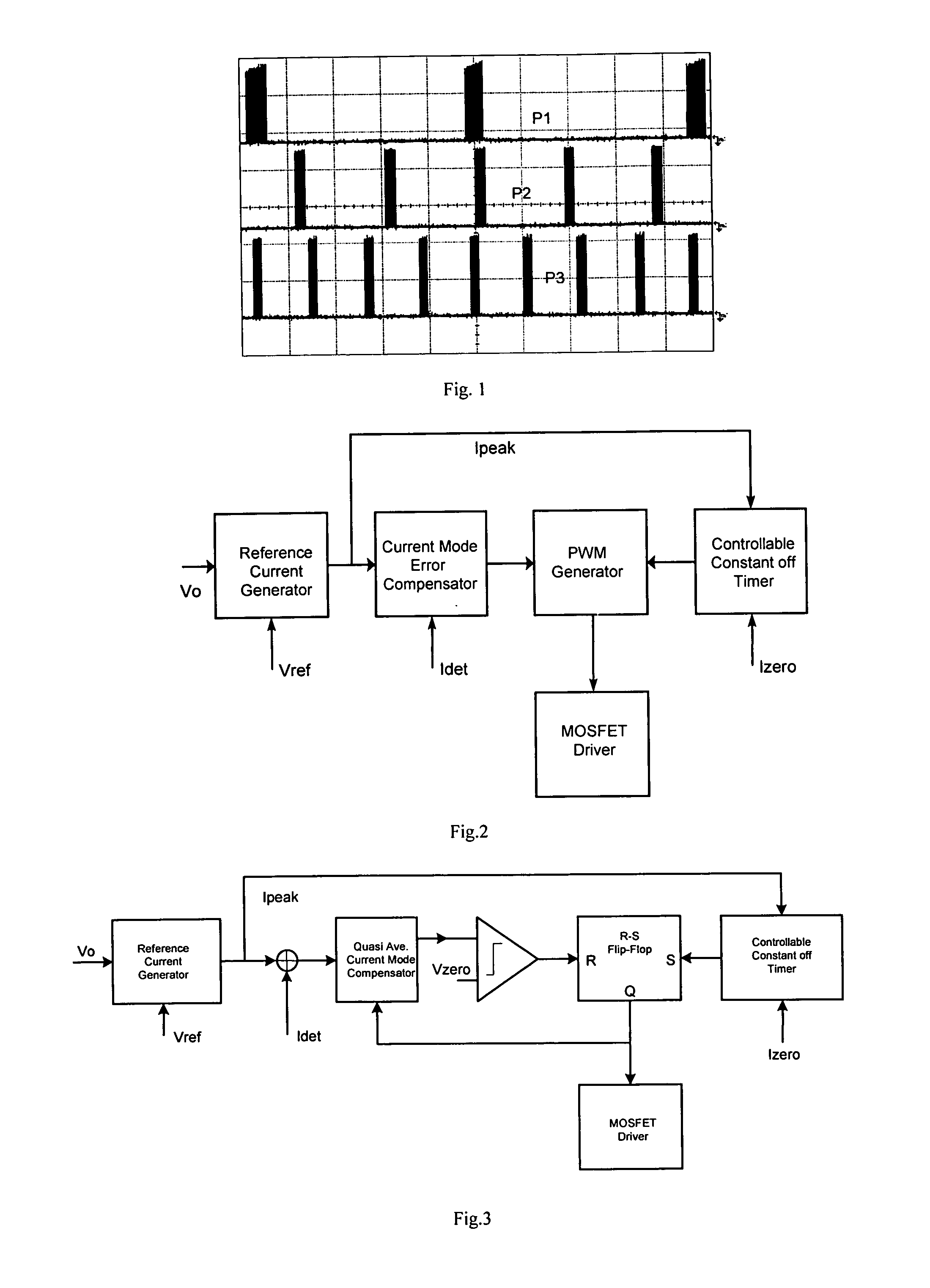
A switching adapter control method for adaptive mobile power systems is composed of reference current generator, current mode error compensator, controllable constant turn-off timer, PWM generator and MOSFET driver. The output of the switching adapter can show constant current and voltage characteristics, that means, as the DC bus voltage is over a preset voltage, the adaptor's output characteristic is converted from a constant current source into a constant voltage source with the preset voltage. For low output capacitance case, the present invention has the ability to smoothly reduce the switching frequency of the switching adaptor and reduce the switching losses and meet Energy Star 2.0 requirements under different load conditions. And the output ripple current and voltage can be in the allowed range.
Owner:WENG DA FENG
Optical semiconductor relay device
InactiveUS20090115490A1Reduce output capacitanceIncrease computing speedTransistorMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringSemiconductor
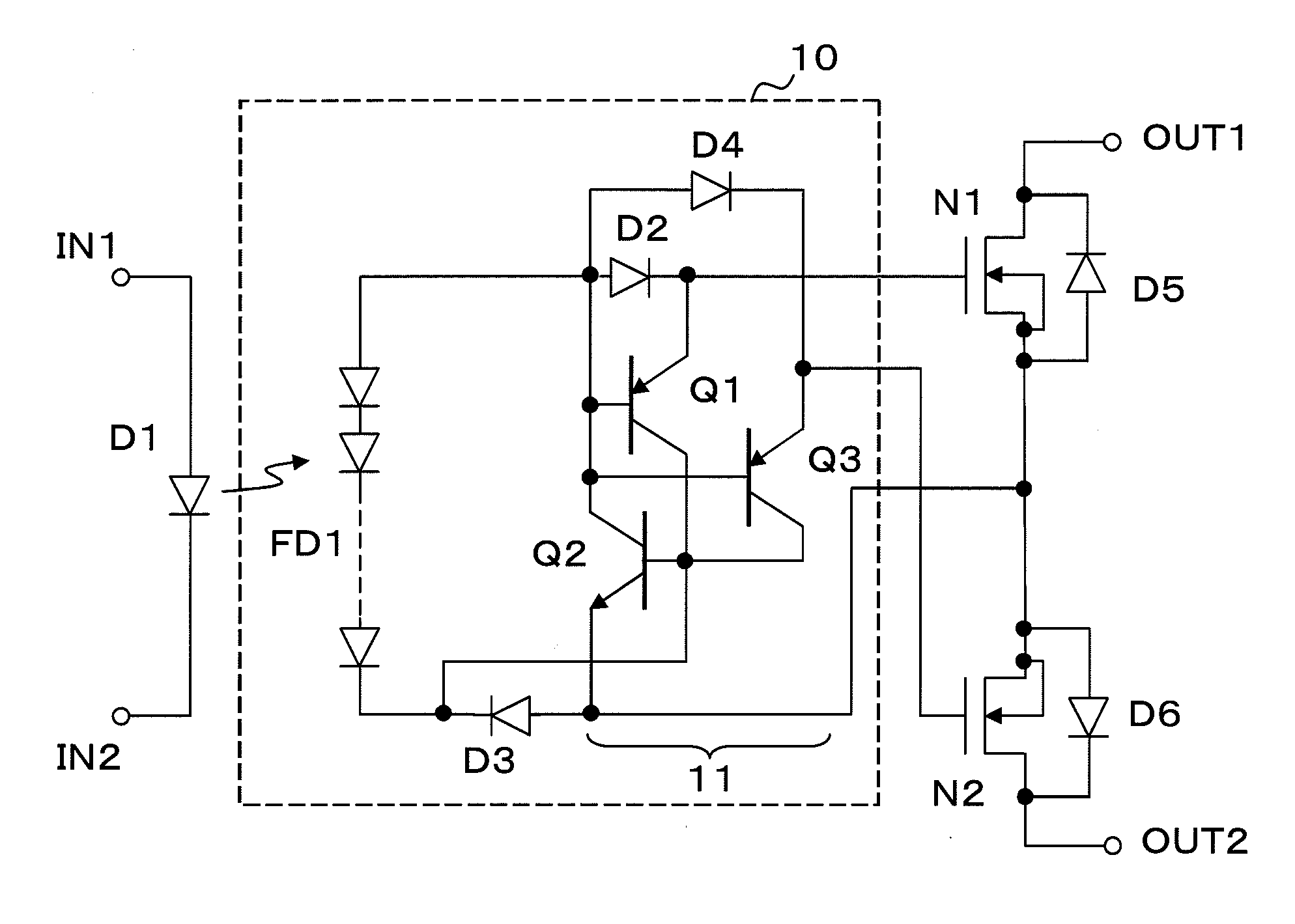
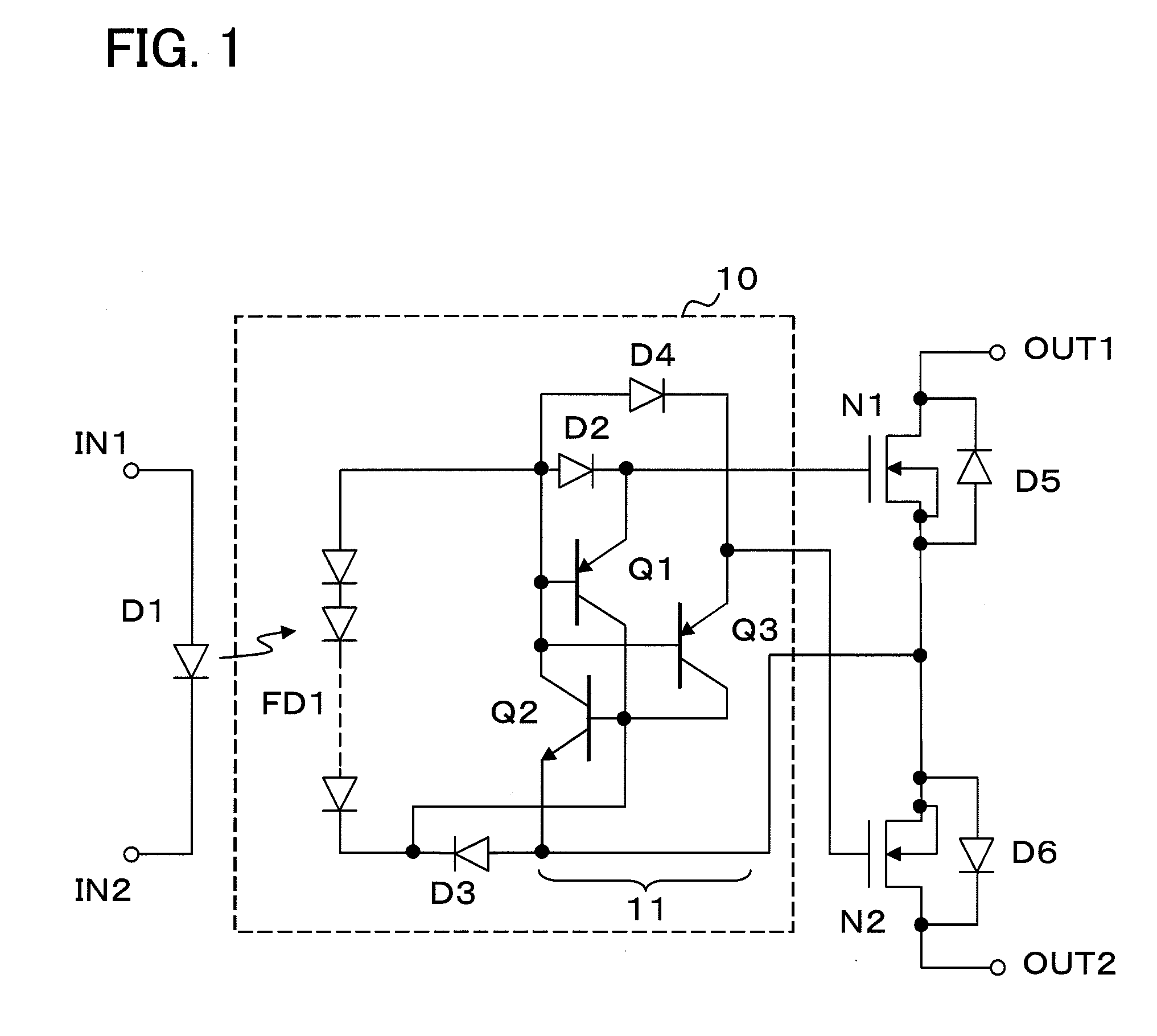
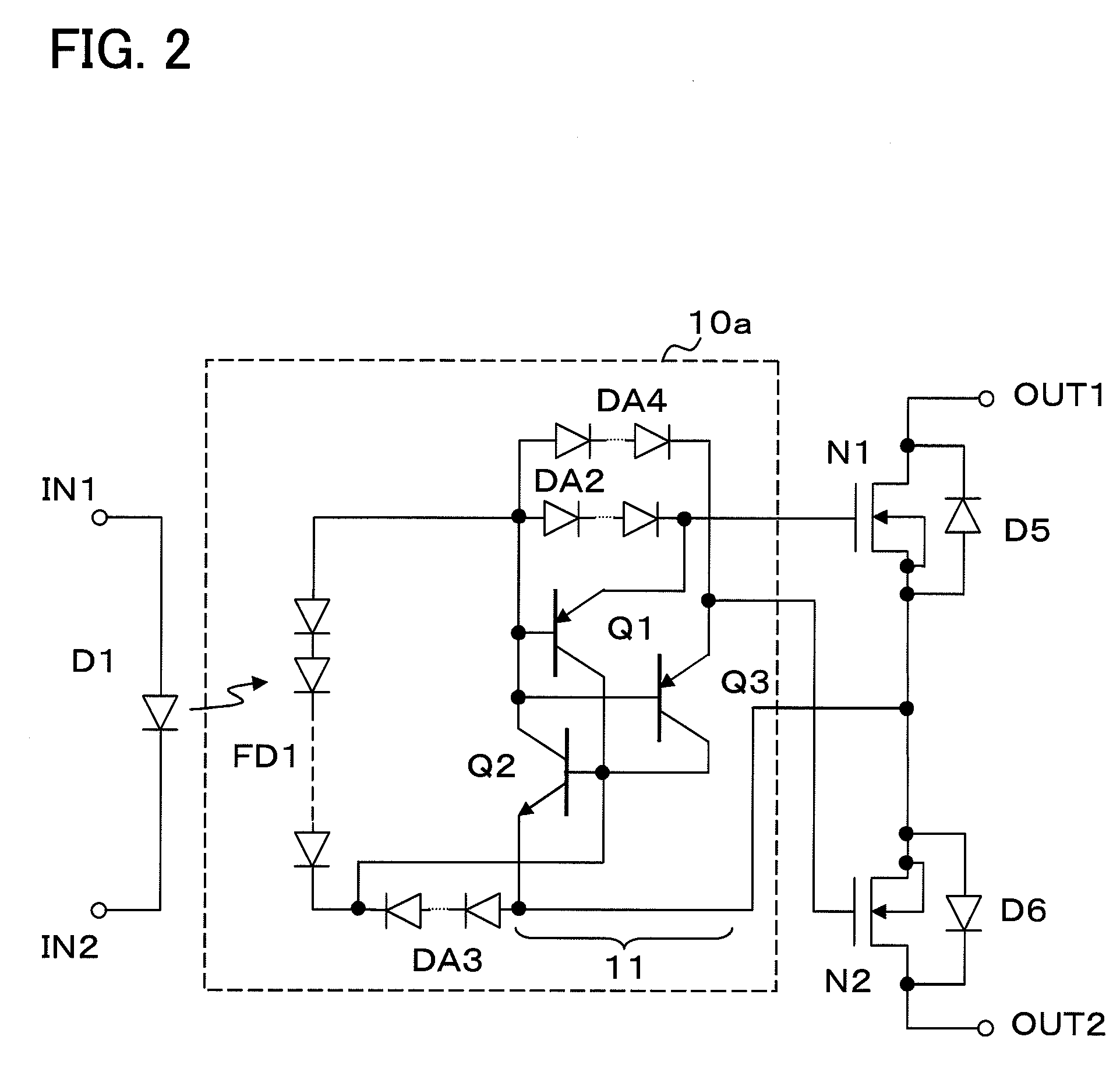
A transient voltage occurring between output terminals during ON / OFF operation is reduced. There are provided a pair of input terminals IN1 and IN2, a pair of output terminals OUT1 and OUT2, MOSFETs N1 and N2 connected between the output terminals, and a drive circuit 10 connected between the input terminals IN1 and IN2 and the MOSFETs N1 and N2. A light-emitting diode D1 is connected between the input terminals IN1 and IN2. The MOSFETs N1 and N2 have their source electrodes electrically connected to each other and their drains connected to the output terminals OUT1 and OUT2 respectively. The drive circuit 10 includes a photodiode array FD1 that supplies a drive voltage to the gates of the MOSFETs N1 and N2, and a discharge circuit 11, connected between the gate electrodes and the source electrodes of the MOSFETs N1 and N2, that discharges electric charges accumulated on each gate electrode. (FIG. 1)
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Control unit for operating a safety system for a vehicle and method for operating such a safety system for a vehicle
ActiveUS20130106179A1Easy dischargeReduce voltageBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric devicesCharge currentOperation safety
In a control device and a method for operating a safety system for a vehicle, a step-up converter is fashioned as a switching converter which converts an input voltage derived from a vehicle battery voltage into a higher charge voltage at its output. In addition, at least one energy reserve storage device is provided that is charged by the charge voltage for the operation of the safety system in an autarkic mode. Between the step-up converter and the at least one energy reserve storage device there is connected a charge current source that is programmable during operation and that defines a charge current for the at least one energy reserve storage device as a function of its programming.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
RF DMOS power device
InactiveCN1828942AReduce output capacitanceImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceDielectric
RF DMOS power device belongs to semiconductor power device technology and RF integrated circuit technique field. It contains adding doped n or P) buried layer below site partial oxidation partial oxidation insulating layer in current part SOI RF DMOS power device, making part SOI RF DMOS device having buried layer, utilizing PN node principle to increase lower pole plate junction capacitance corresponded exhaustion width of drain region / epitaxial layer junction, wherewith to reduce output capacitance, thereby raising device output power, using part air space insulation layer substituting partial oxidation insulating layer also capable of making part SON RF DMOS device, utilizing interstice relative dielectric constant being 1 property to reduce device output capacitance and raise device output power, utilizing part air space insulation layer and low doped n (or P) buried layer to make part SON RF DMOS device having buried layer capable of preferable reducing device output capacitance and raising output power. Said invented device works on microwave band frequency, at the same time having higher pressure resistance, heat dispersion and frequency response performance.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Decode circuitry and a display device using the same
InactiveUS20060232450A1Fast decoding operationReduce layout areaElectric signal transmission systemsStatic indicating devicesTarget signalDisplay device
Multi-bit input data is divided into at least a first bit group and a second bit group, and each of first sub-decode circuits selects one selection target signal / voltage from selection target signal / voltage group in accordance with the first bit group. Then, one signal / voltage is selected according to the second bit group from the signals / voltages selected by the first sub-decode circuits, and is transmitted to an output signal line. Each of second sub-decode circuits is formed of a single train of series switches, and only one of the switch train is made conductive to transmit a finally selected signal / voltage to the output signal line.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Double-layer super-junction Schottky diode
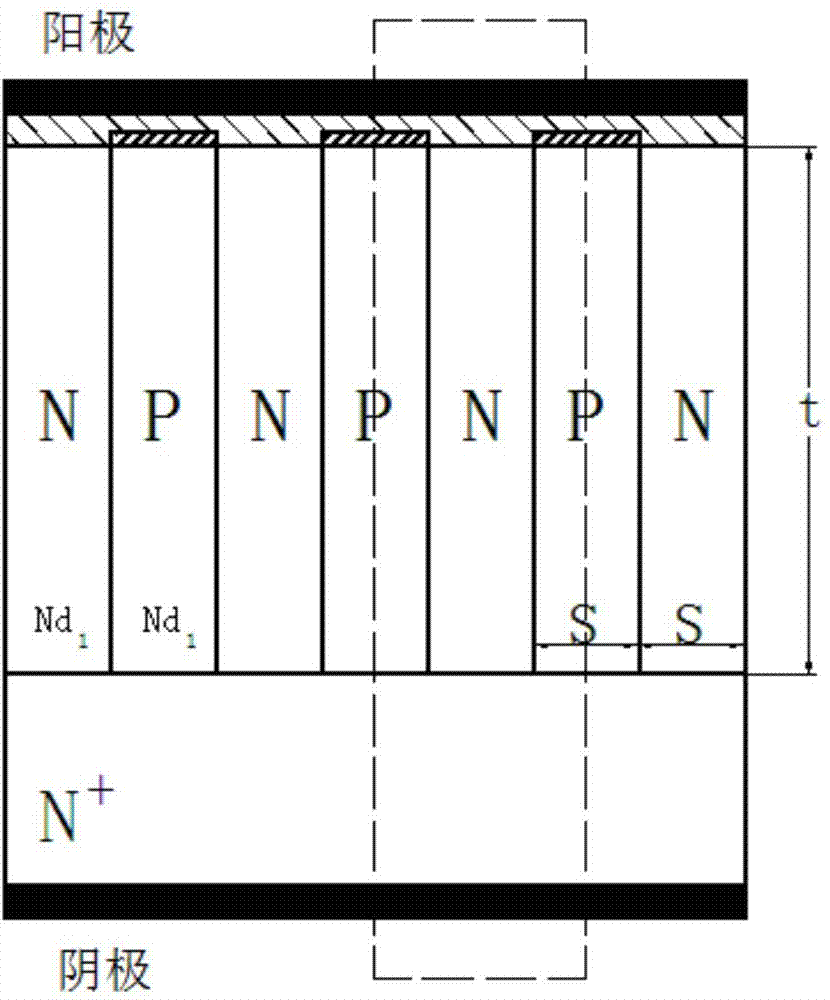
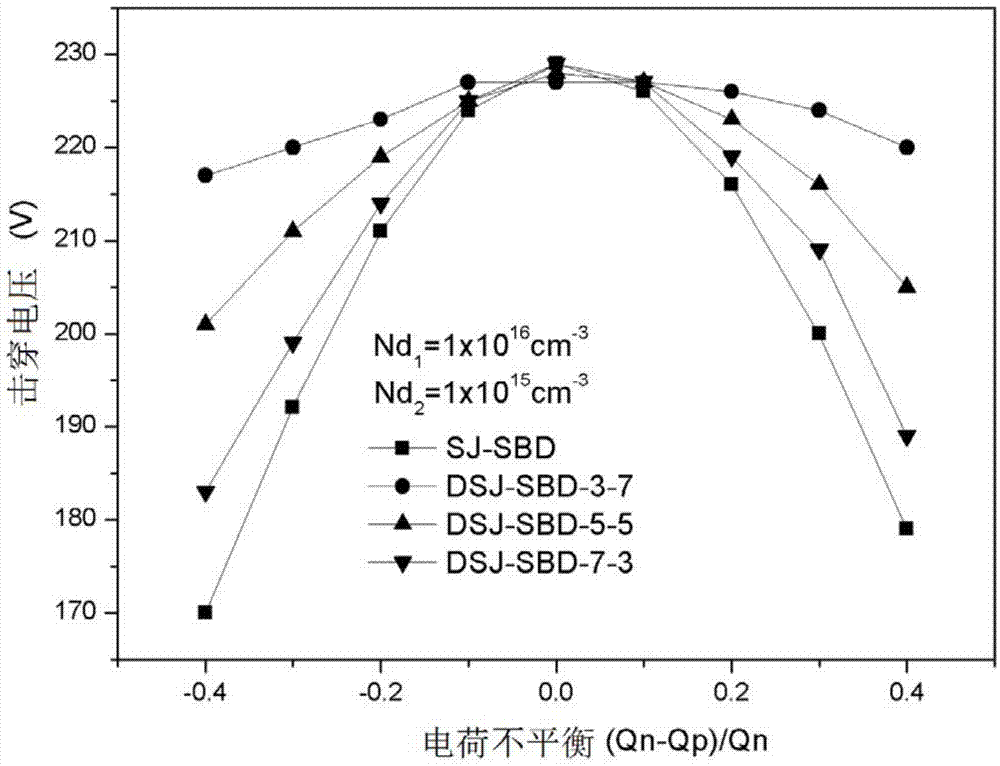
InactiveCN103594523AReduce dynamic power consumptionImprove sensitive relationshipSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceReverse recovery
The invention discloses a double-layer super-junction Schottky diode. A double-layer super-junction structure is applied to a drift region of a power Schottky device. Due to the structure, on the premise that the forward characteristics of the device are not obviously lost, the relation between the reverse breakdown characteristic and charge imbalance of an ordinary super-junction Schottky diode is well improved, the reverse recovery characteristic of the device is greatly improved, the output capacitance of the device is reduced, and the power consumption of the device is effectively reduced.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com