Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
425results about How to "Reduce dynamic power consumption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
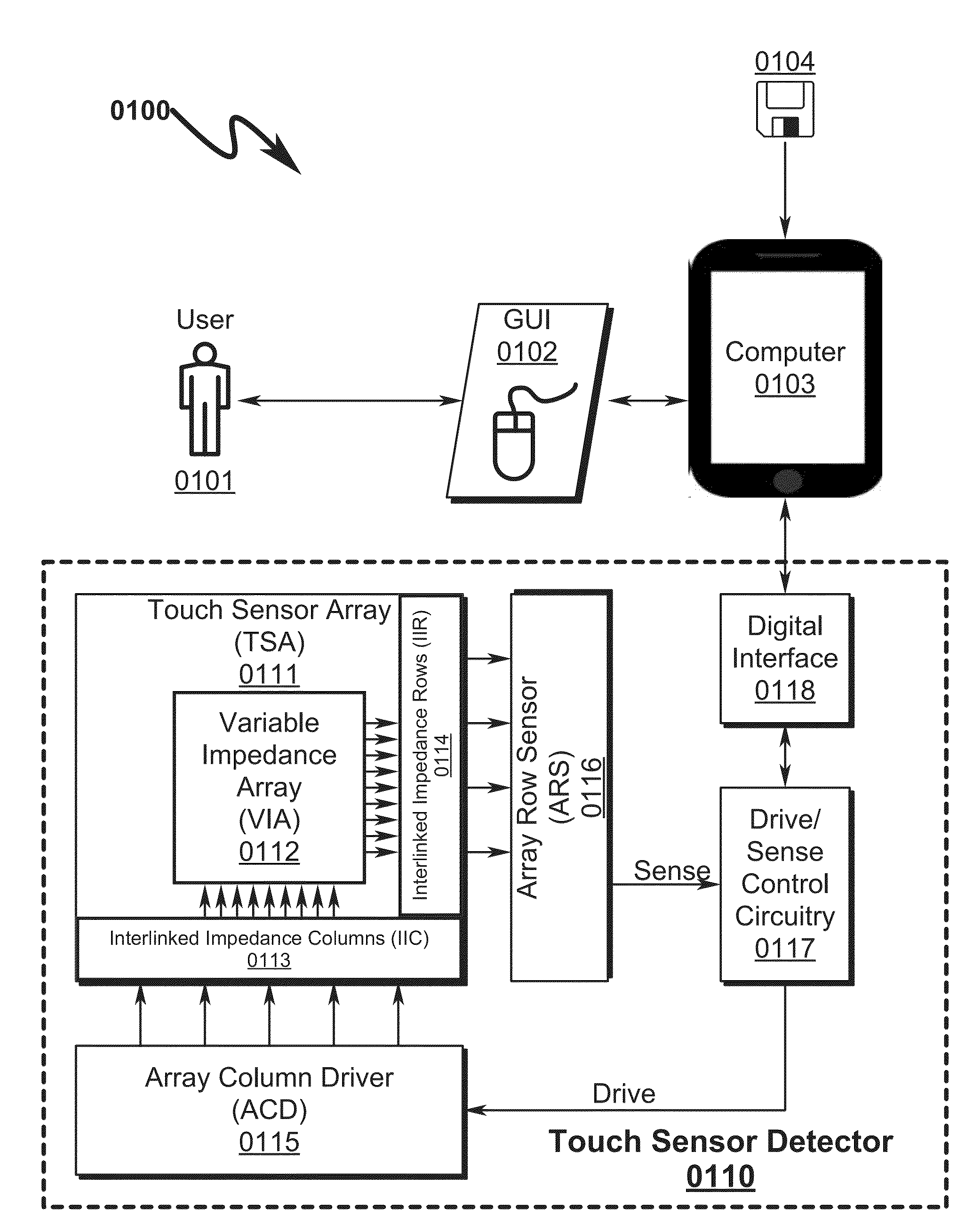
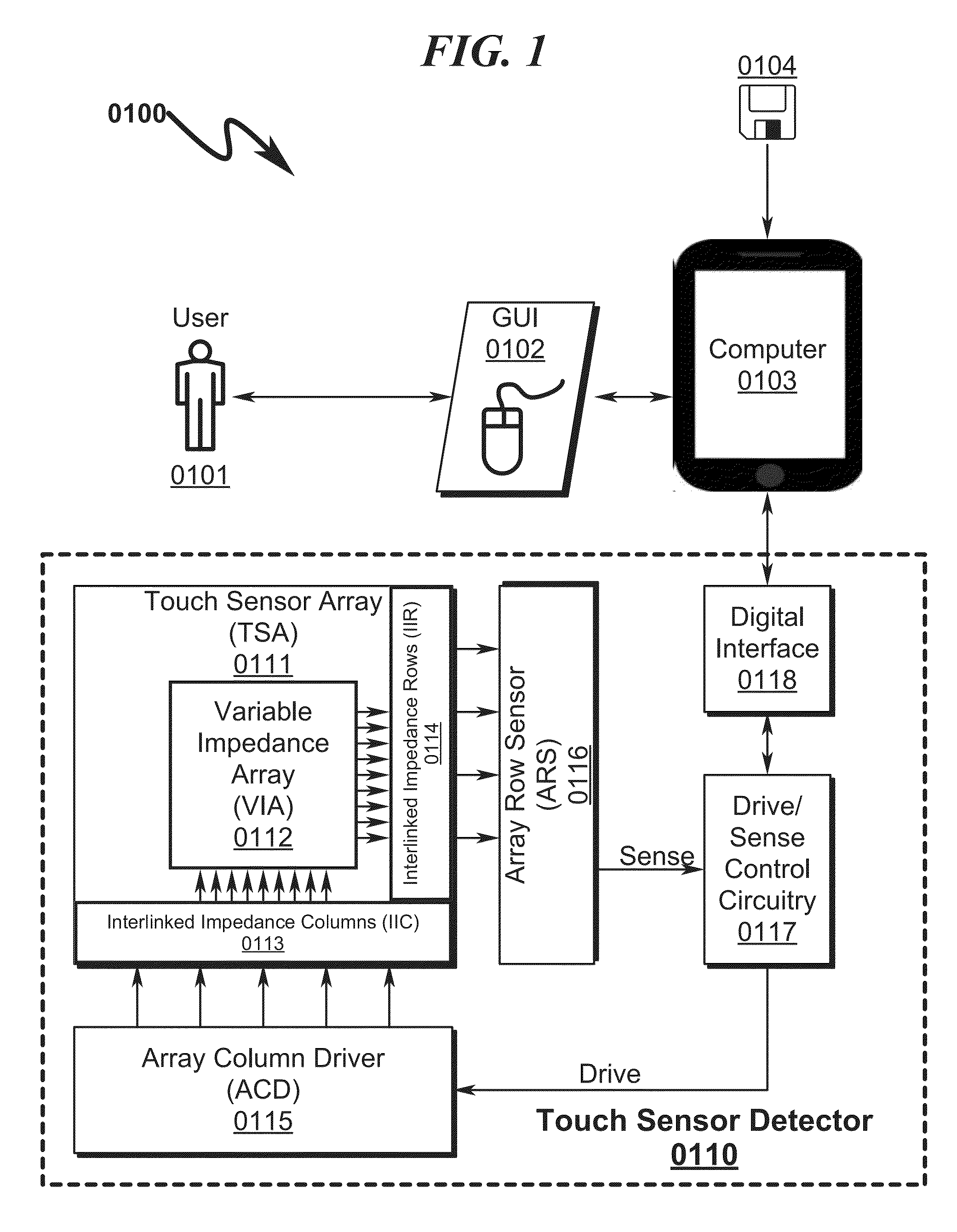
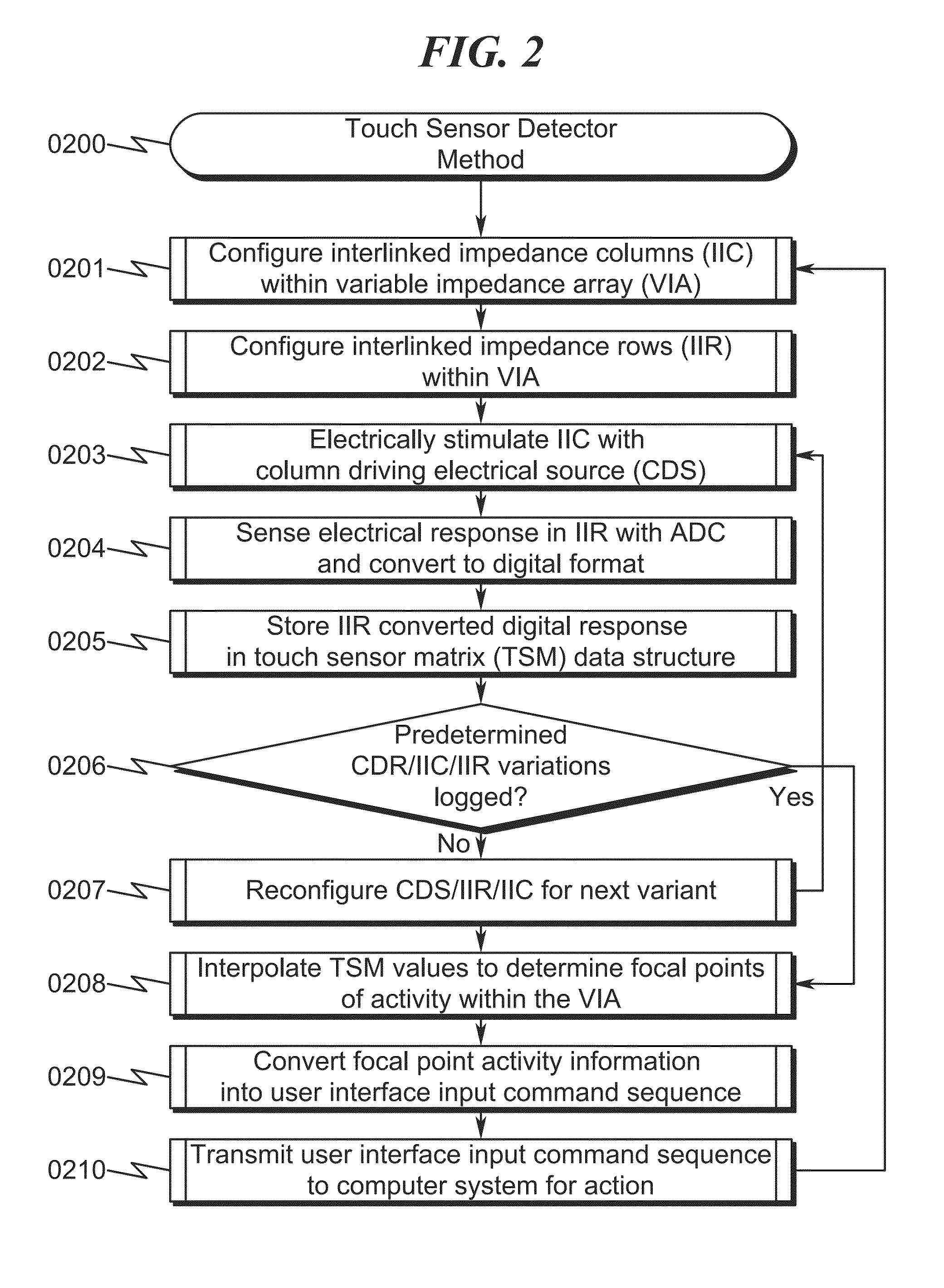
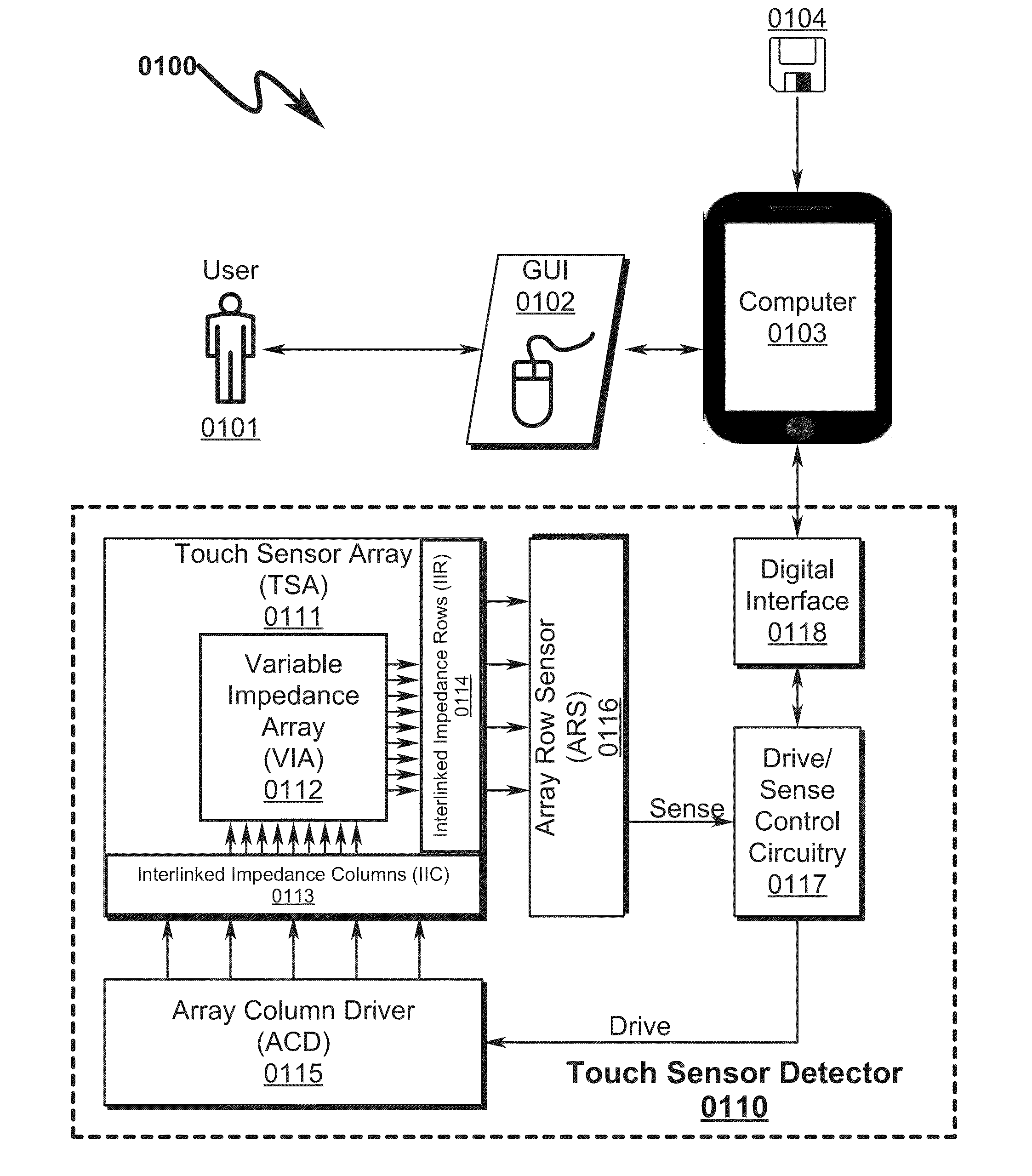
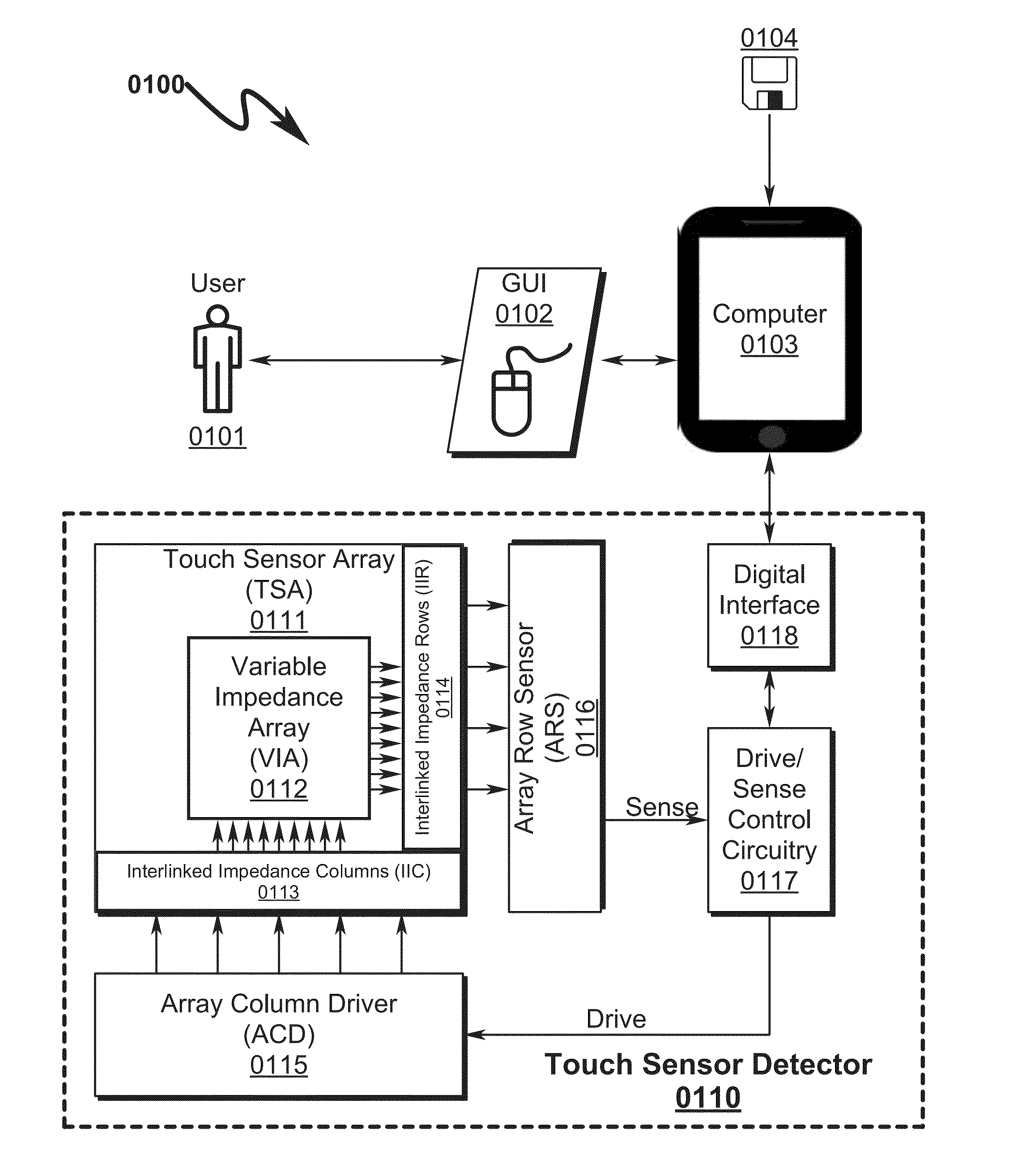
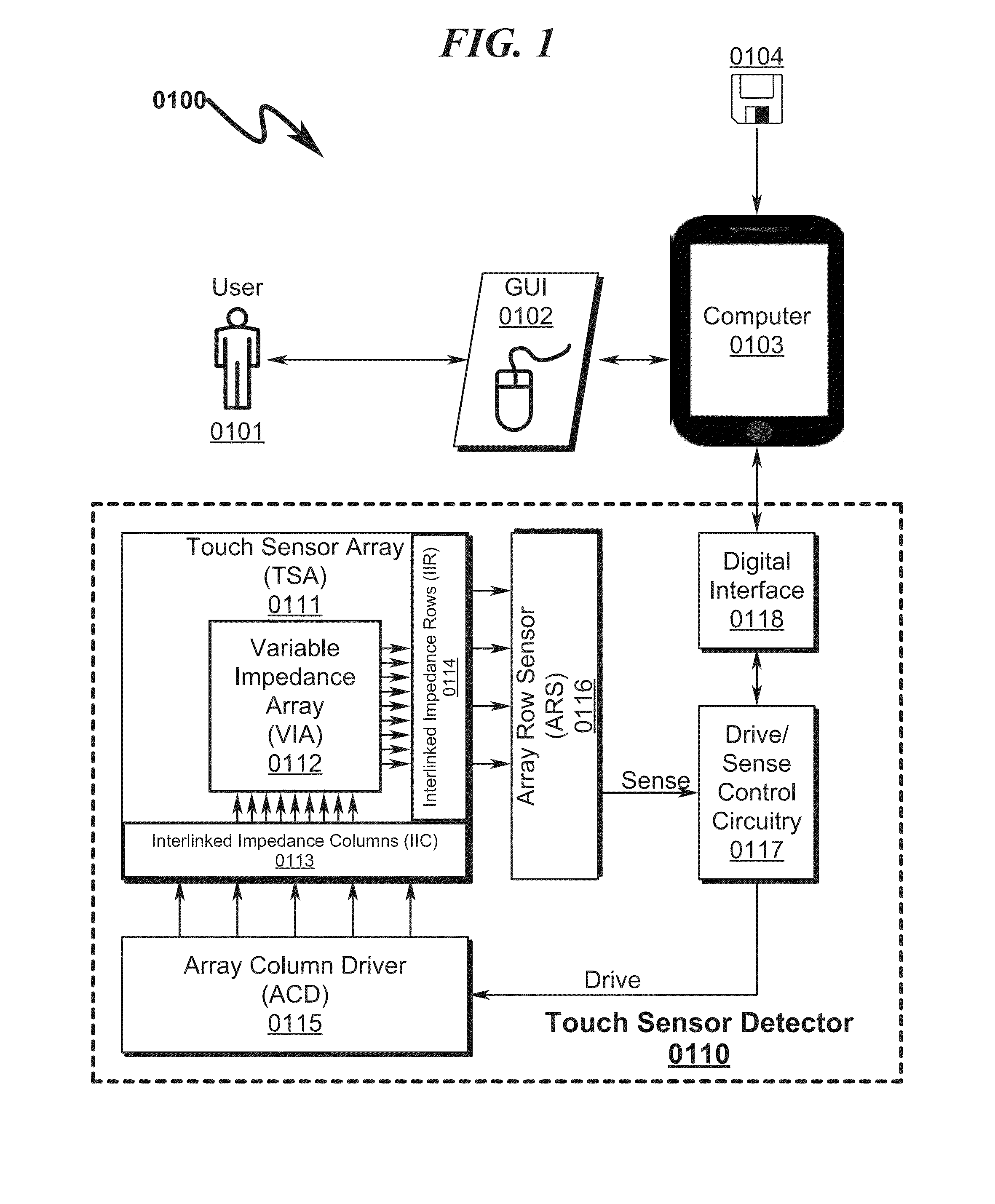
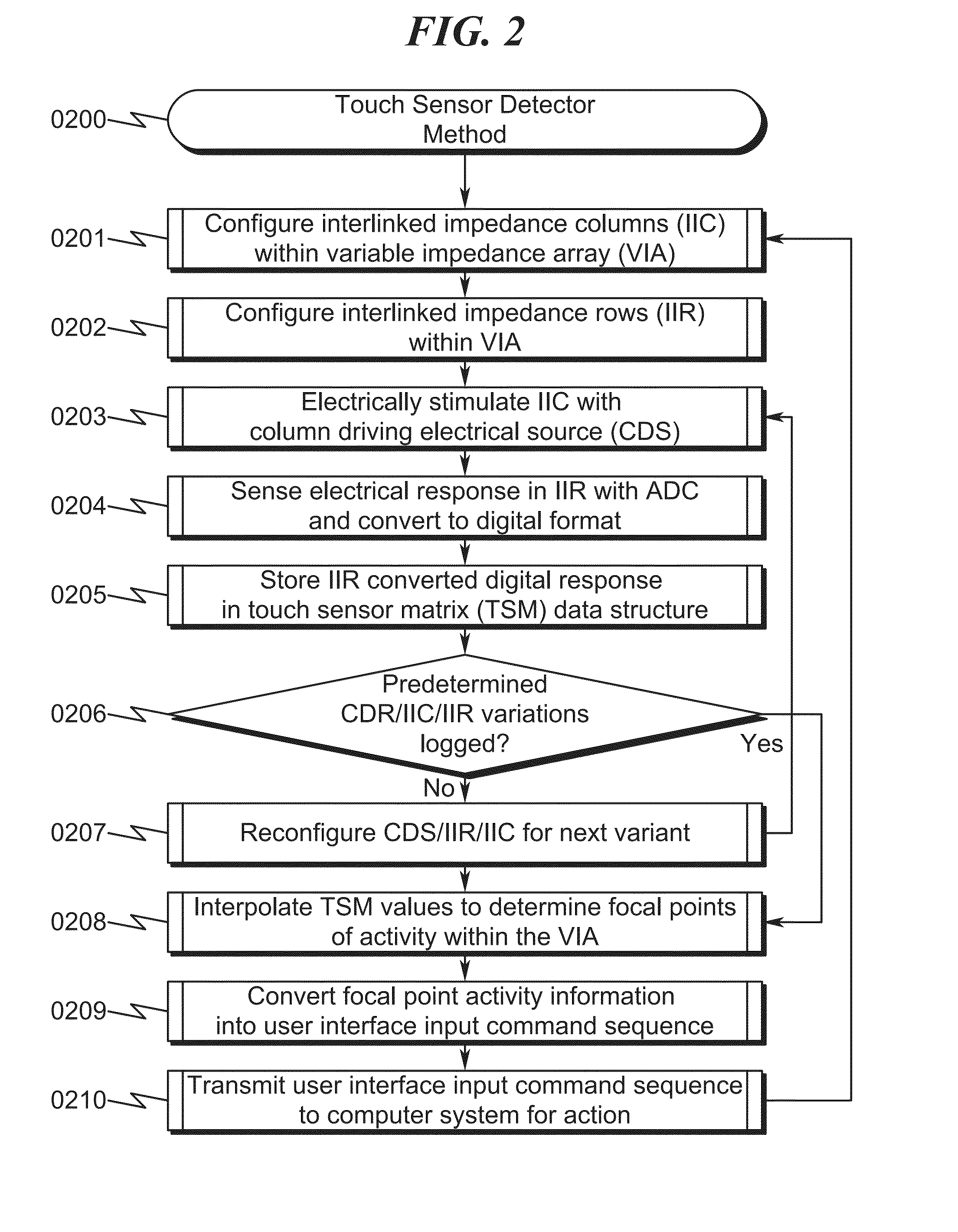
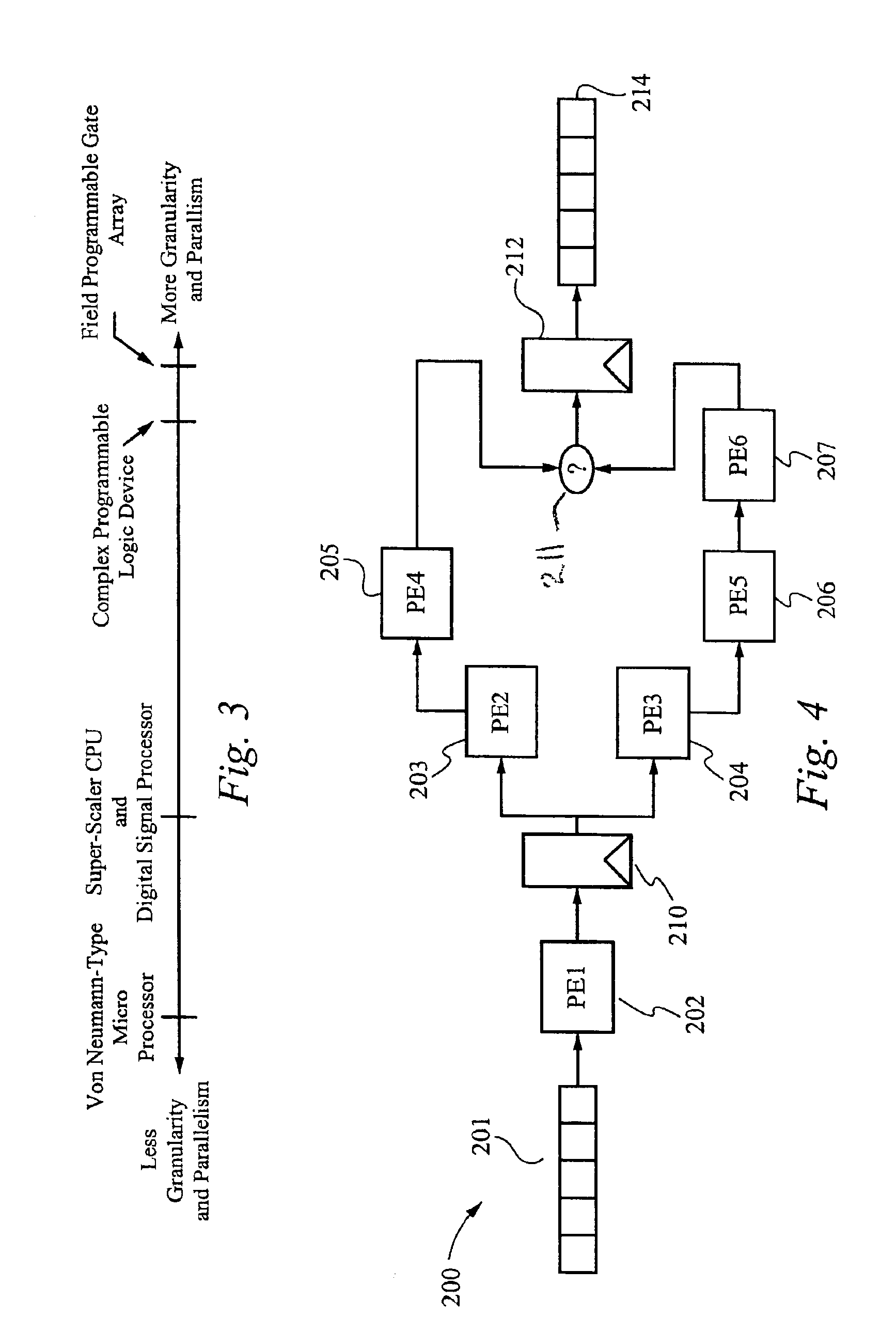
Capacitive Touch Sensor System and Method
ActiveUS20150091859A1High resolutionImprove sensor performanceForce measurementInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayElectricity
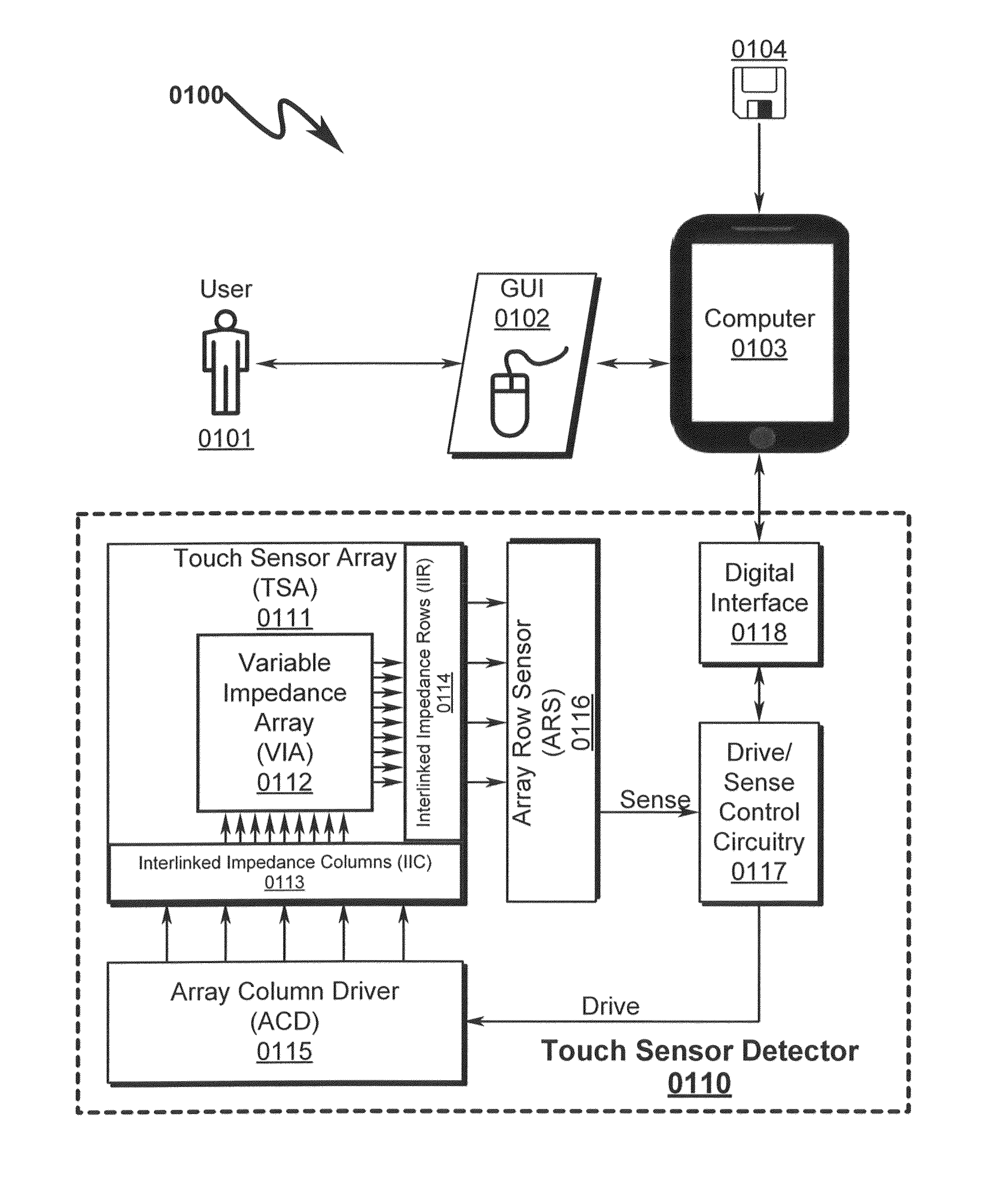
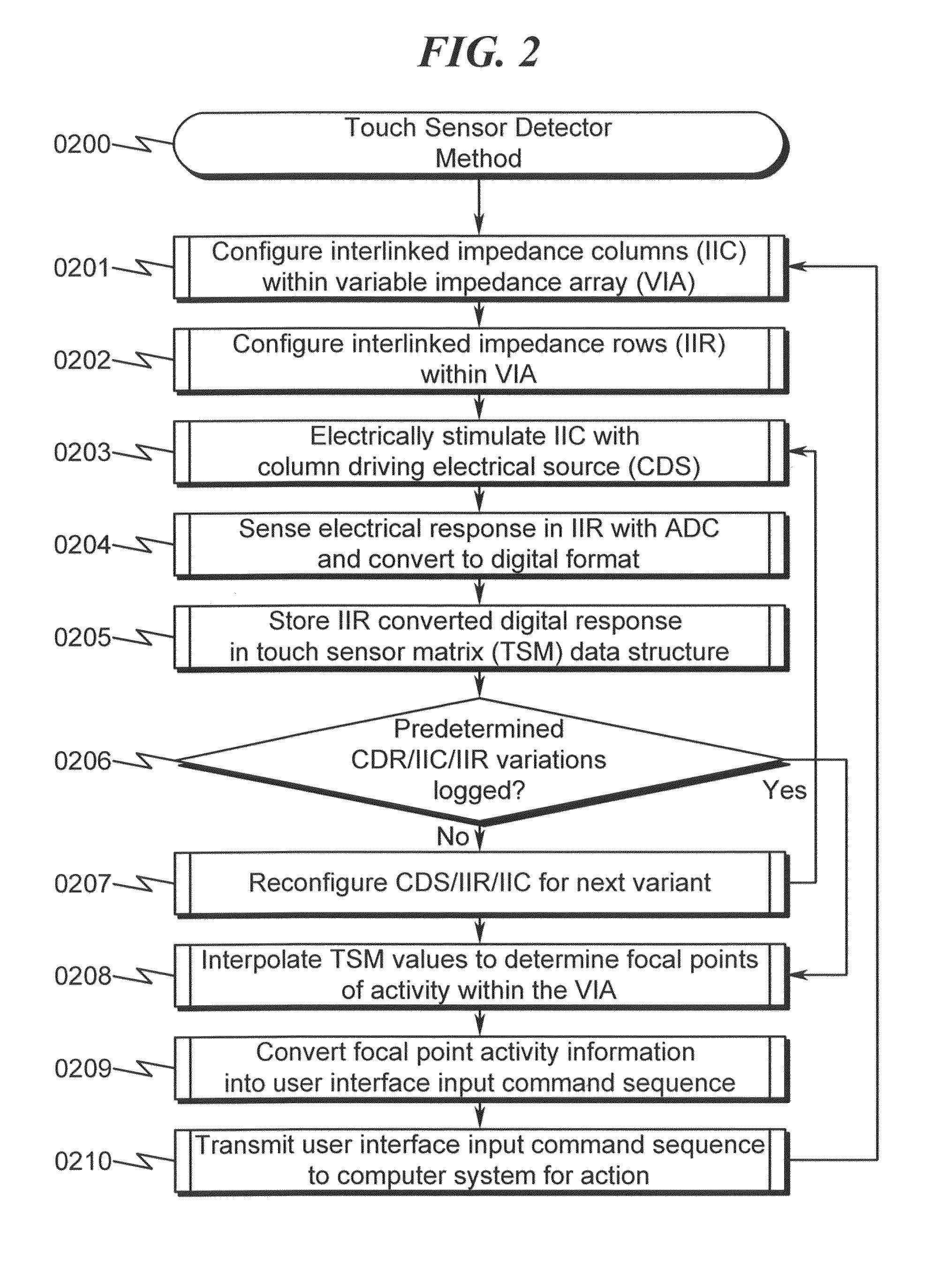
A capacitive touch sensor system and method incorporating an interpolated sensor array is disclosed. The system and method utilize a touch sensor array (TSA) configured to detect proximity / contact / pressure (PCP) via a variable impedance array (VIA) electrically coupling interlinked impedance columns (IIC) coupled to an array column driver (ACD), and interlinked impedance rows (IIR) coupled to an array row sensor (ARS). The ACD is configured to select the IIC based on a column switching register (CSR) and electrically drive the IIC using a column driving source (CDS). The VIA conveys current from the driven IIC to the IIC sensed by the ARS. The ARS selects the IIR within the TSA and electrically senses the IIR state based on a row switching register (RSR). Interpolation of ARS sensed current / voltage allows accurate detection of TSA PCP and / or spatial location.
Owner:SENSEL
Resistive Touch Sensor System and Method
ActiveUS20150091858A1High resolutionImprove sensor performanceInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayElectricity
A resistive touch sensor system and method incorporating an interpolated sensor array is disclosed. The system and method utilize a touch sensor array (TSA) configured to detect proximity / contact / pressure (PCP) via a variable impedance array (VIA) electrically coupling interlinked impedance columns (IIC) coupled to an array column driver (ACD), and interlinked impedance rows (IIR) coupled to an array row sensor (ARS). The ACD is configured to select the IIC based on a column switching register (CSR) and electrically drive the IIC using a column driving source (CDS). The VIA conveys current from the driven IIC to the IIC sensed by the ARS. The ARS selects the IIR within the TSA and electrically senses the IIR state based on a row switching register (RSR). Interpolation of ARS sensed current / voltage allows accurate detection of TSA PCP and / or spatial location.
Owner:SENSEL
Capacitive touch sensor system and method
ActiveUS9459746B2Reduce dynamic power consumptionHigh trackingForce measurementInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayElectricity
A capacitive touch sensor system and method incorporating an interpolated sensor array is disclosed. The system and method utilize a touch sensor array (TSA) configured to detect proximity / contact / pressure (PCP) via a variable impedance array (VIA) electrically coupling interlinked impedance columns (IIC) coupled to an array column driver (ACD), and interlinked impedance rows (IIR) coupled to an array row sensor (ARS). The ACD is configured to select the IIC based on a column switching register (CSR) and electrically drive the IIC using a column driving source (CDS). The VIA conveys current from the driven IIC to the IIC sensed by the ARS. The ARS selects the IIR within the TSA and electrically senses the IIR state based on a row switching register (RSR). Interpolation of ARS sensed current / voltage allows accurate detection of TSA PCP and / or spatial location.
Owner:SENSEL
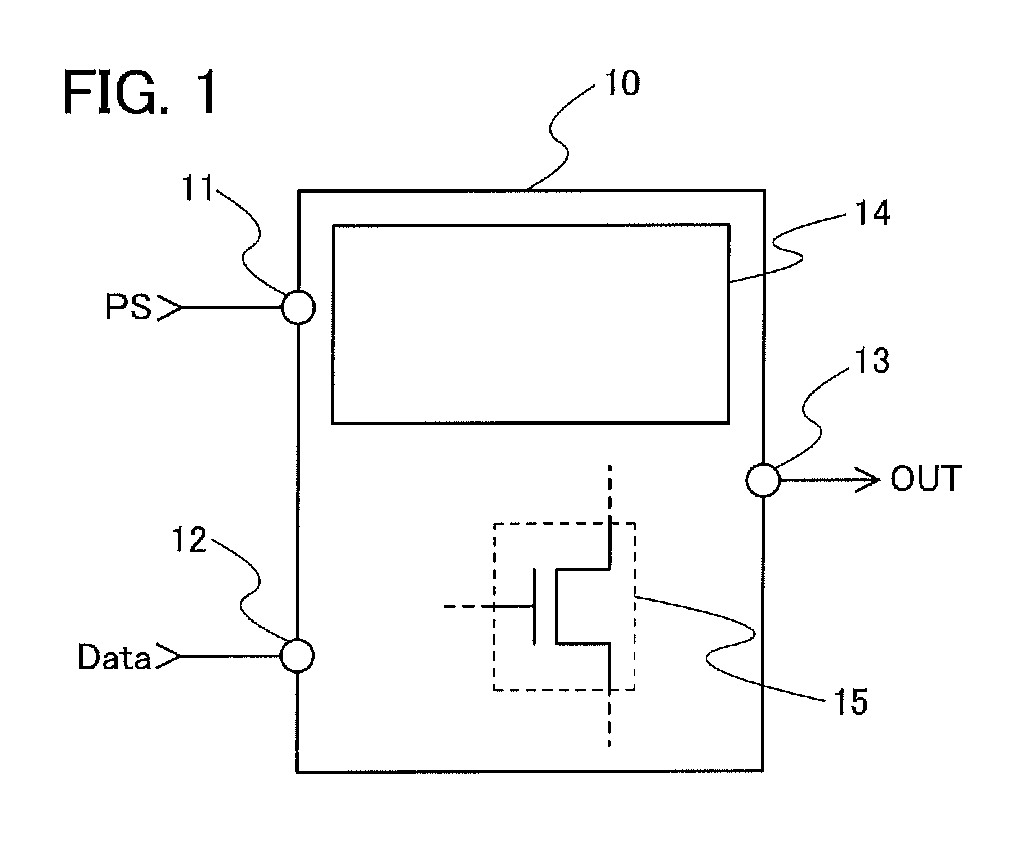
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS8207756B2Reduce dynamic power consumptionLeakage of highTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
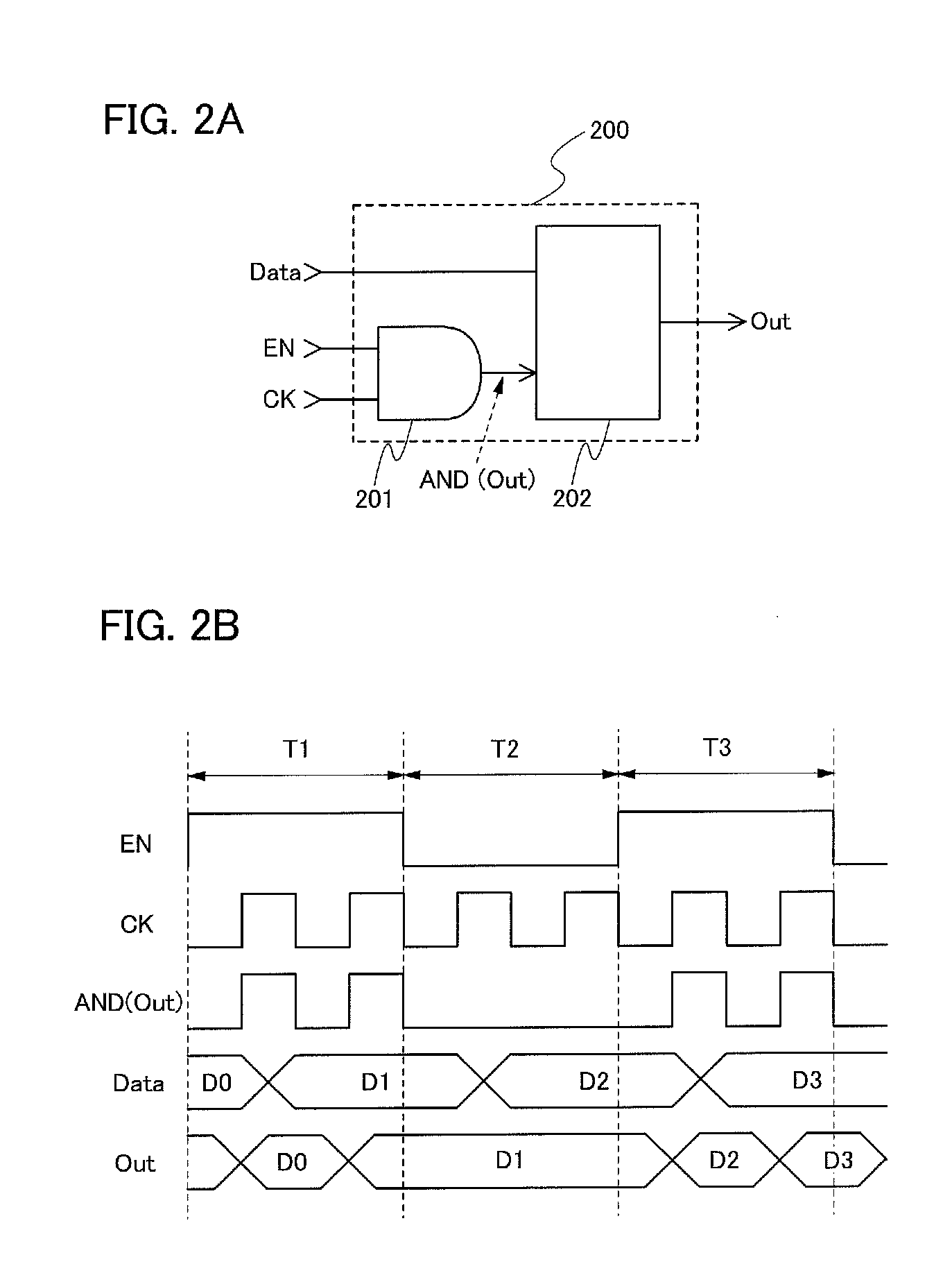
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5×1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
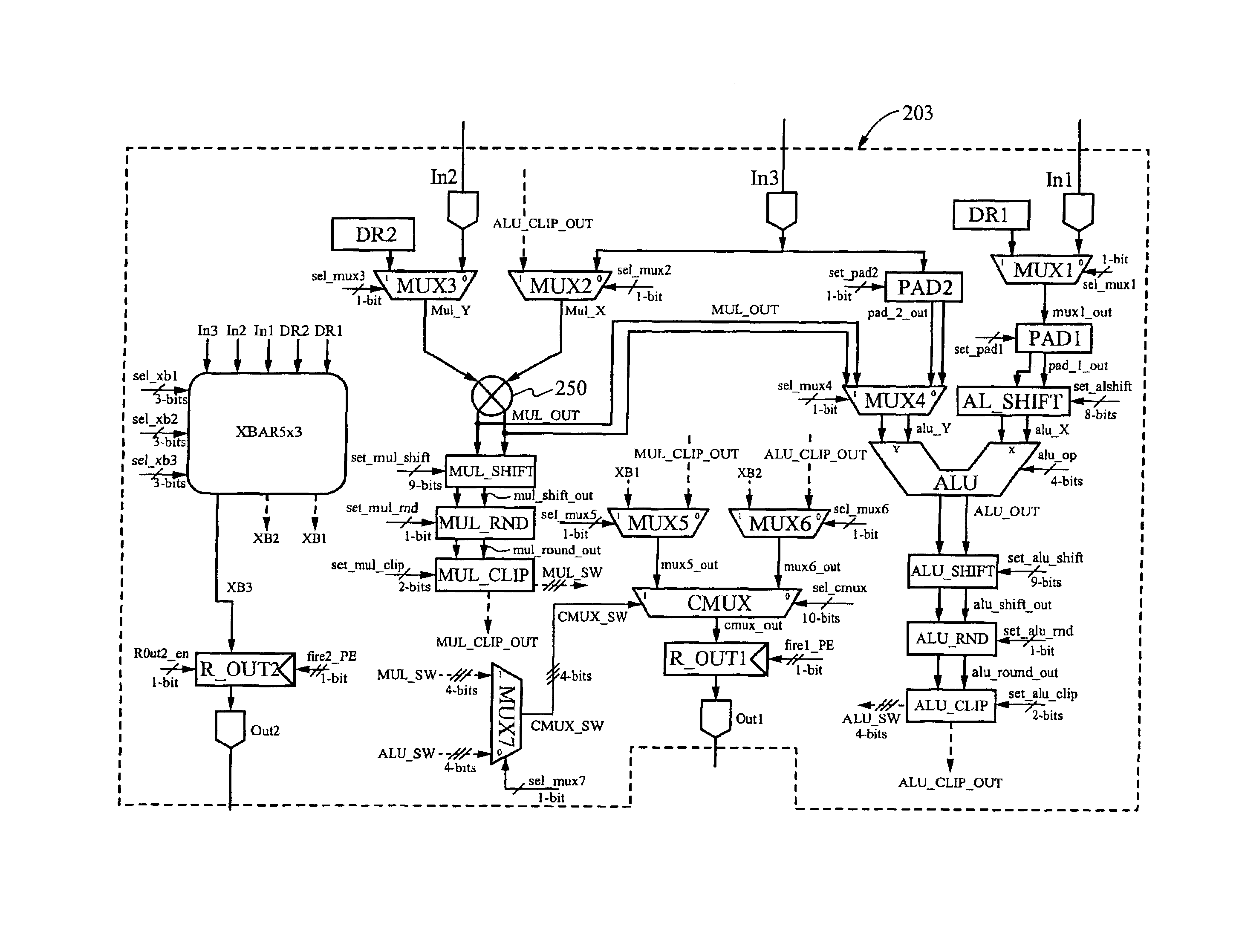
Reconfigurable data path processor
InactiveUS6883084B1Eliminates branchingCycle simpleEnergy efficient ICTConditional code generationMultiplexerProcessing element
A reconfigurable data path processor comprises a plurality of independent processing elements. Each of the processing elements advantageously comprising an identical architecture. Each processing element comprises a plurality of data processing means for generating a potential output. Each processor is also capable of through-putting an input as a potential output with little or no processing. Each processing element comprises a conditional multiplexer having a first conditional multiplexer input, a second conditional multiplexer input and a conditional multiplexer output. A first potential output value is transmitted to the first conditional multiplexer input, and a second potential output value is transmitted to the second conditional multiplexer output. The conditional multiplexer couples either the first conditional multiplexer input or the second conditional multiplexer input to the conditional multiplexer output, according to an output control command. The output control command is generated by processing a set of arithmetic status-bits through a logical mask. The conditional multiplexer output is coupled to a first processing element output. A first set of arithmetic bits are generated according to the processing of the first processable value. A second set of arithmetic bits may be generated from a second processing operation. The selection of the arithmetic status-bits is performed by an arithmetic-status bit multiplexer selects the desired set of arithmetic status bits from among the first and second set of arithmetic status bits. The conditional multiplexer evaluates the select arithmetic status bits according to logical mask defining an algorithm for evaluating the arithmetic status bits.
Owner:STC UNM +1
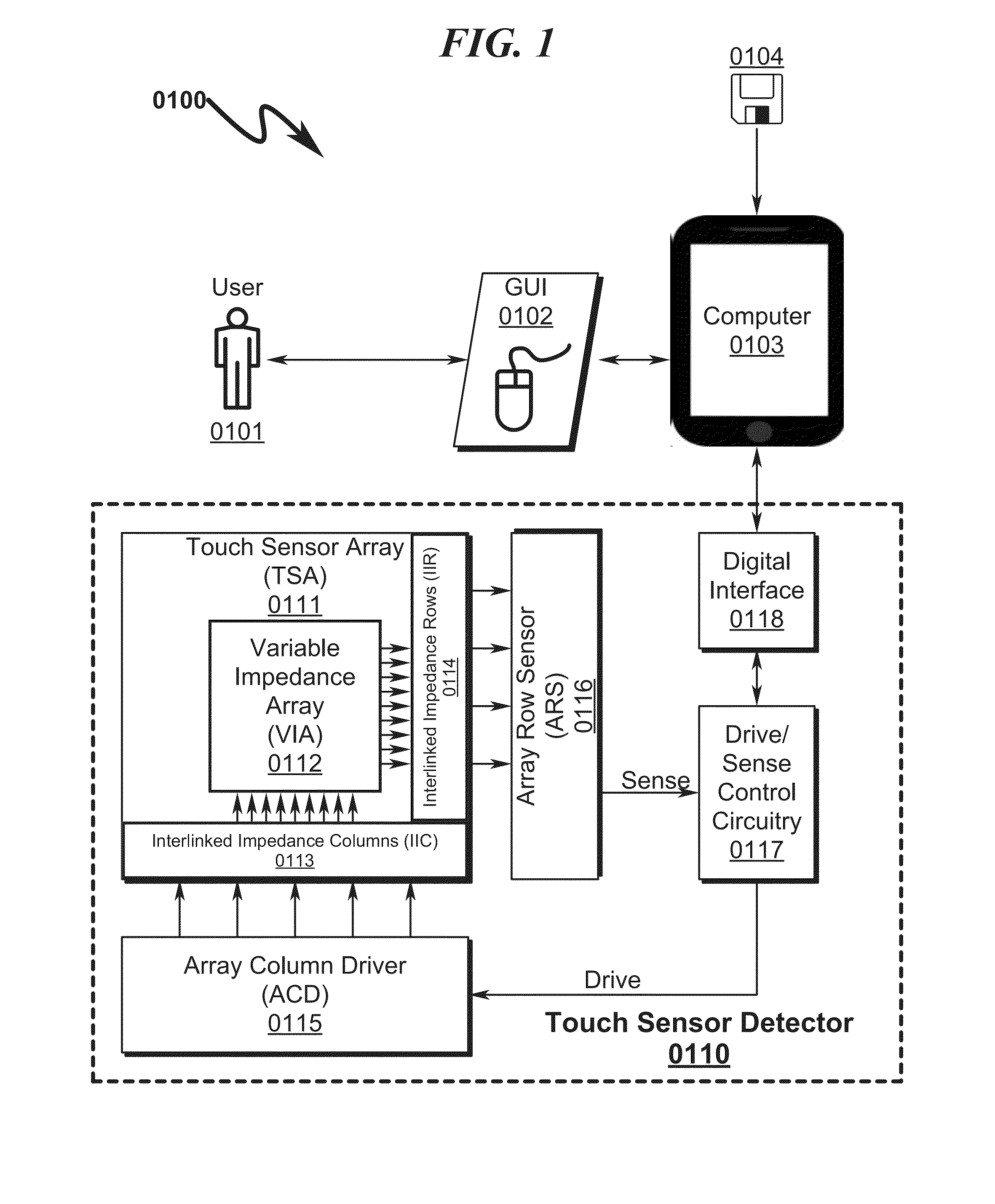
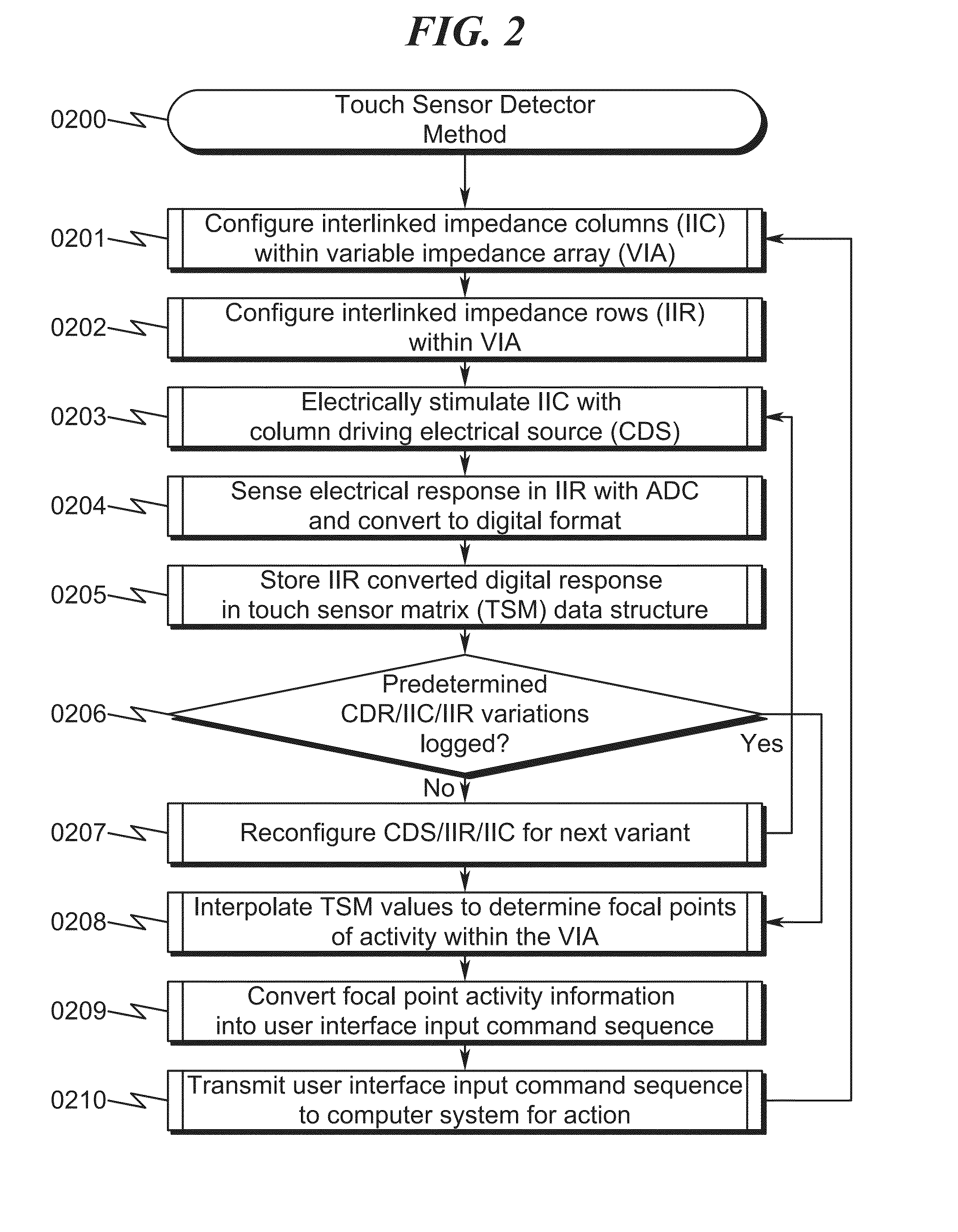
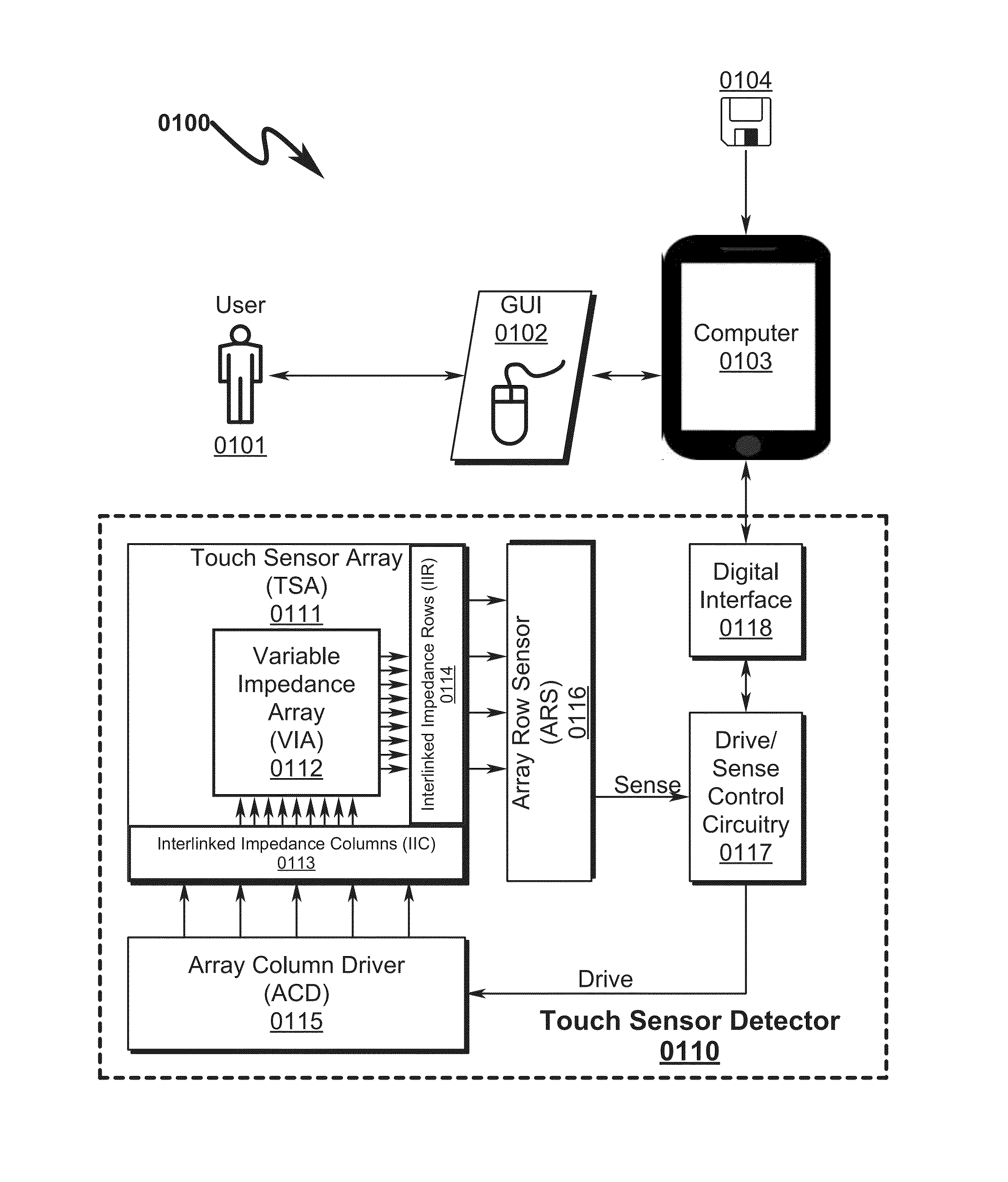
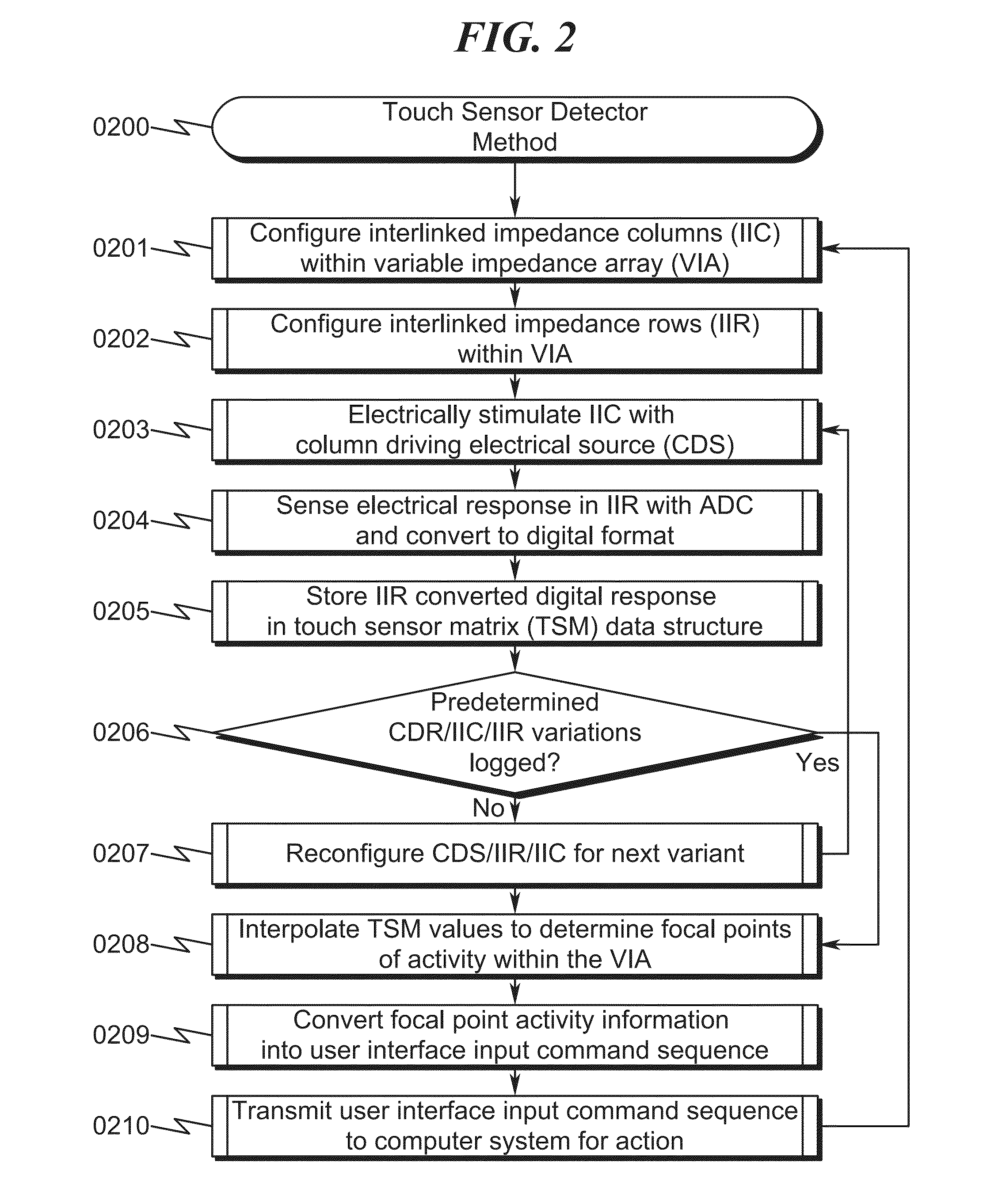
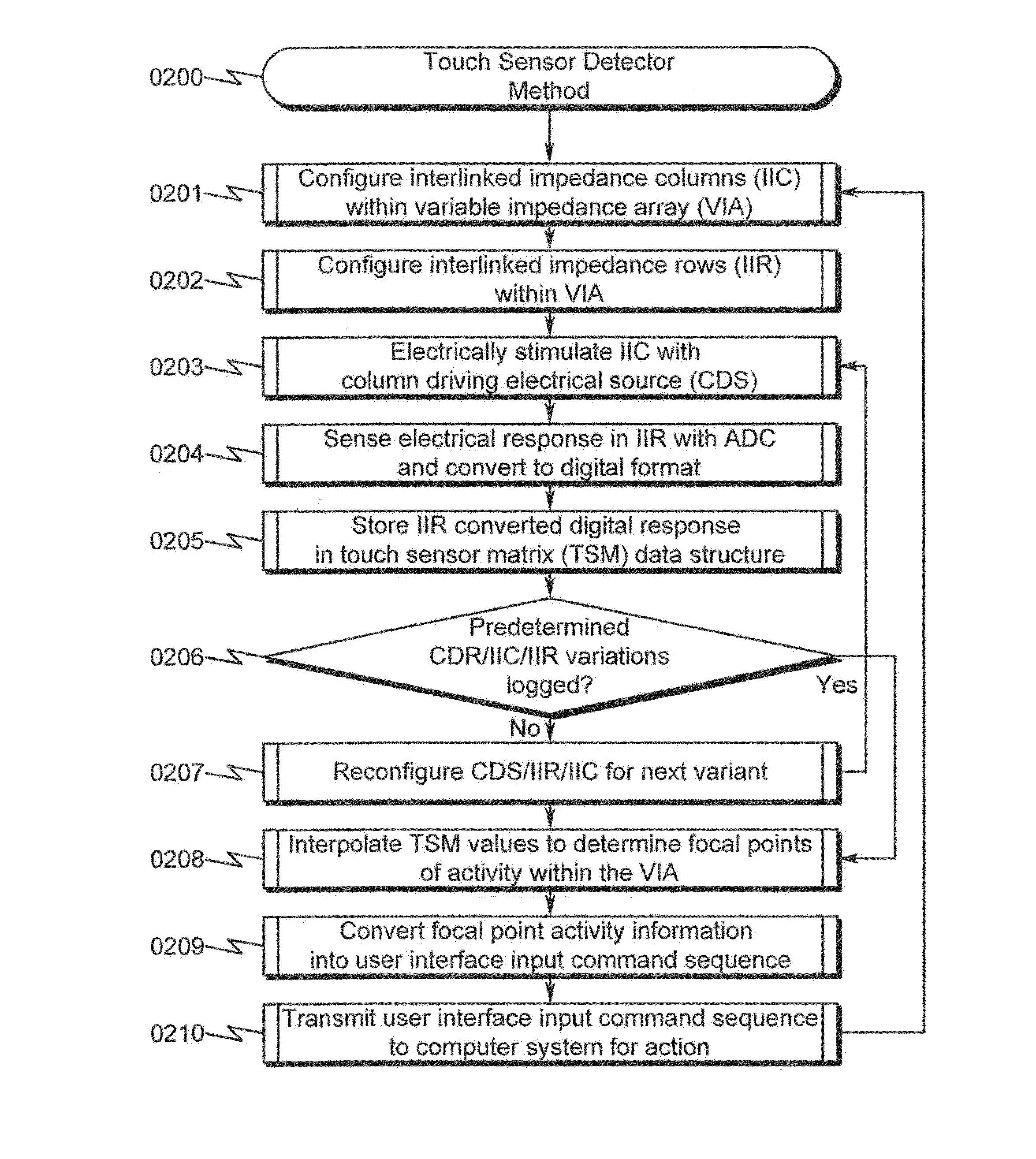
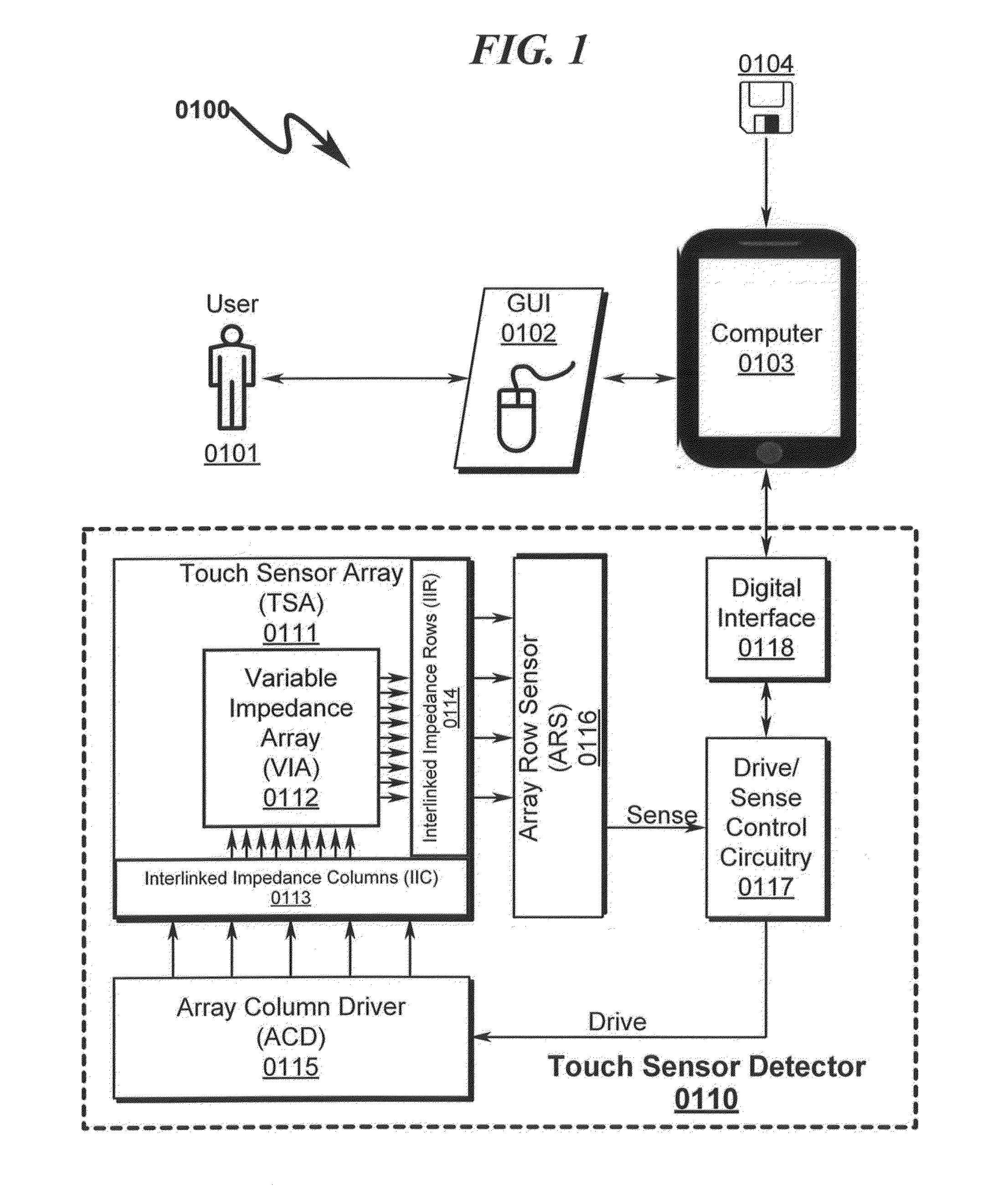
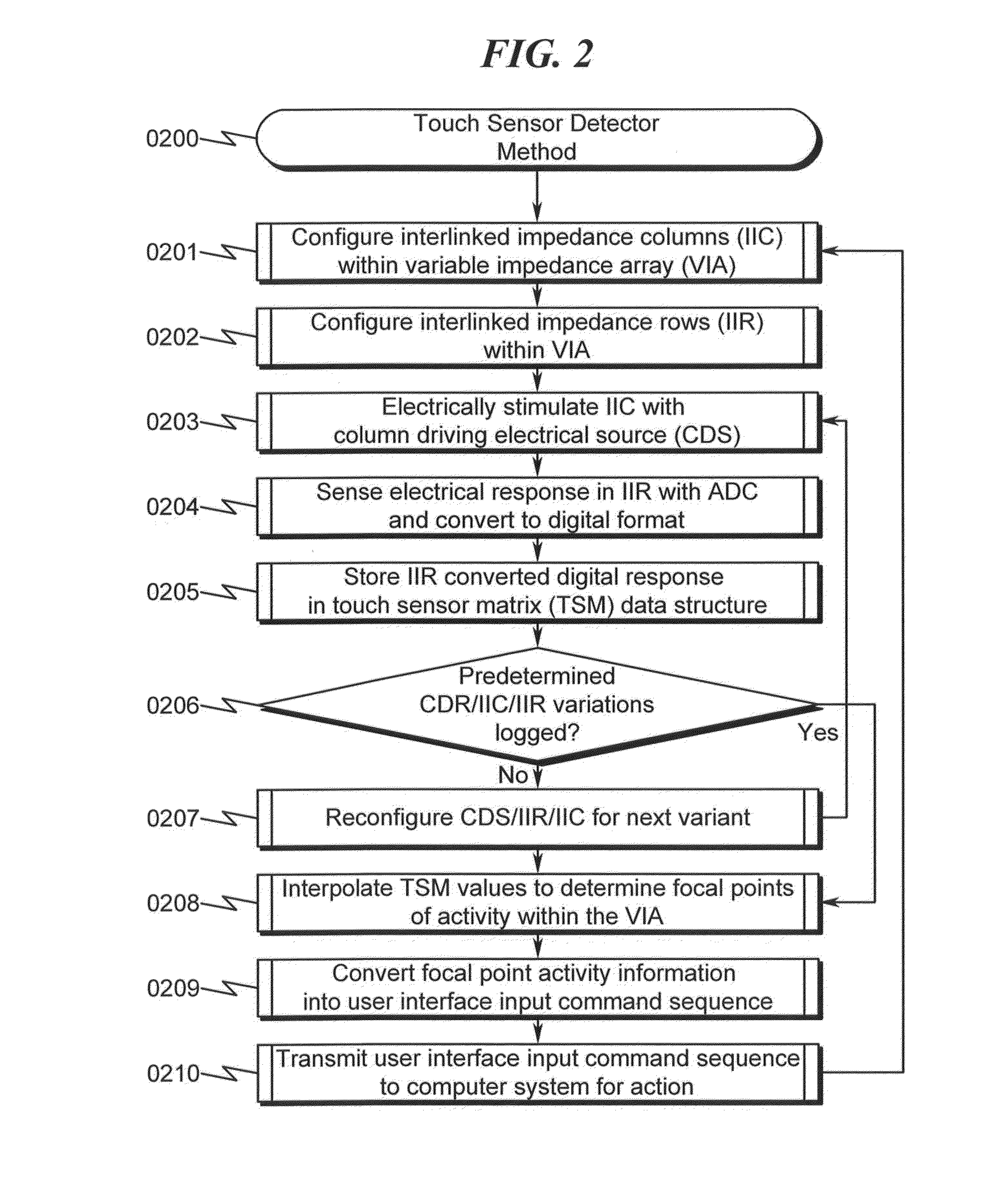
Touch Sensor Detector System and Method
ActiveUS20150091820A1High resolutionImprove sensor performanceInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayElectricity
A touch sensor detector system and method incorporating an interpolated sensor array is disclosed. The system and method utilize a touch sensor array (TSA) configured to detect proximity / contact / pressure (PCP) via a variable impedance array (VIA) electrically coupling interlinked impedance columns (IIC) coupled to an array column driver (ACD), and interlinked impedance rows (IIR) coupled to an array row sensor (ARS). The ACD is configured to select the IIC based on a column switching register (CSR) and electrically drive the IIC using a column driving source (CDS). The VIA conveys current from the driven IIC to the IIC sensed by the ARS. The ARS selects the IIR within the TSA and electrically senses the IIR state based on a row switching register (RSR). Interpolation of ARS sensed current / voltage allows accurate detection of TSA PCP and / or spatial location.
Owner:SENSEL
Active matrix device and method of driving the same
ActiveUS8173000B1Reduce dynamic power consumptionReducing voltage switchedSludge treatmentStatic indicating devicesElectricityDielectric
An active matrix electrowetting on dielectric (AM-EWOD) device which includes a plurality of array elements configured to manipulate one or more droplets of fluid on an array, each of the array elements including a corresponding array element circuit. Each array element circuit includes a top substrate electrode and a drive electrode between which the one or more droplets may be positioned; circuitry configured to write data to the corresponding array element by selectively applying to the drive electrode either: (i) a time-varying voltage waveform V1 of amplitude VB and period t0; or (ii) a time-varying voltage waveform V2, the logical inverse of V1, and applying to the top substrate electrode the time-varying voltage waveform V2+Voffset, where Voffset represents an offset voltage signal which may have AC and / or DC components and may equal zero.
Owner:SHARP LIFE SCI EU LTD
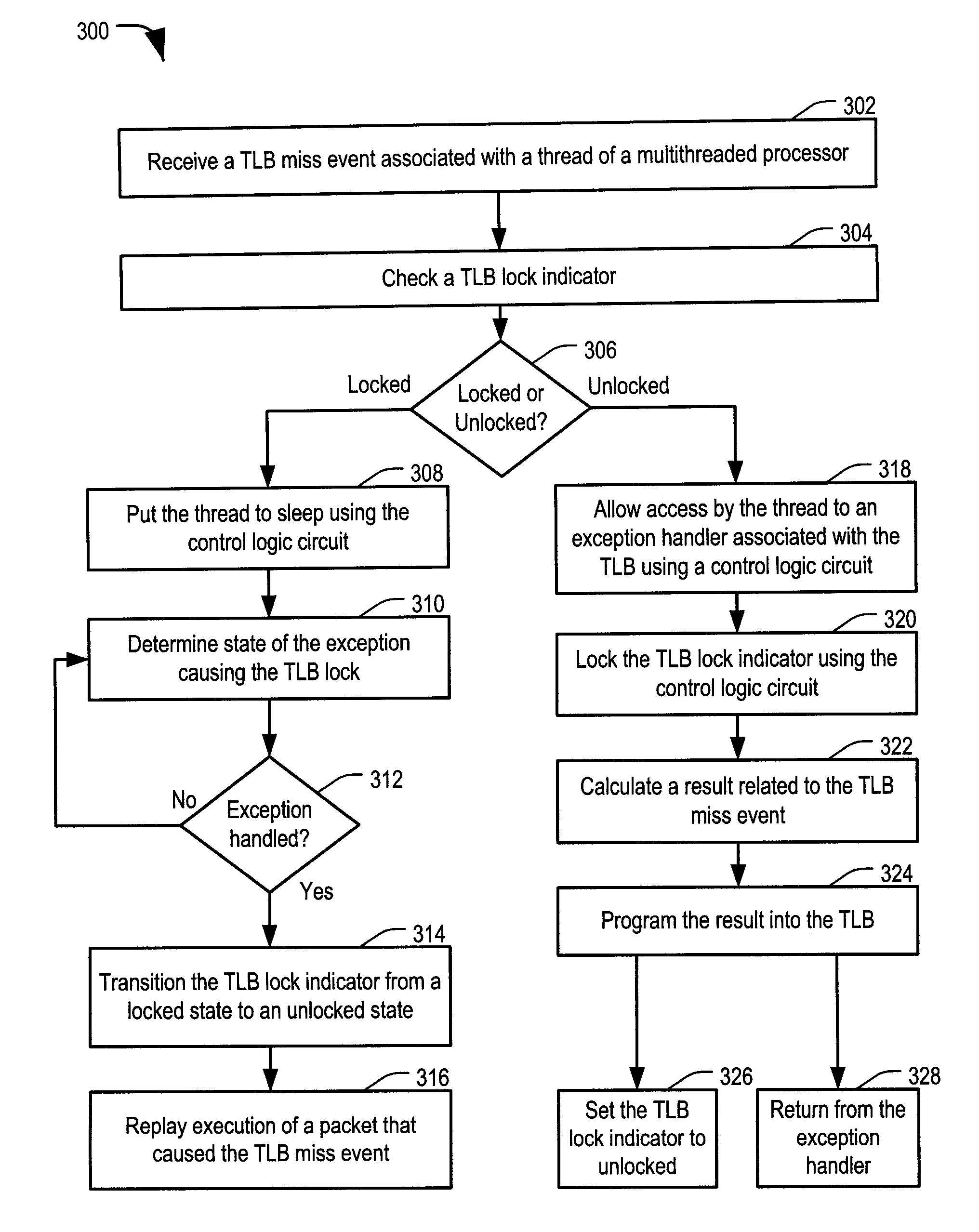
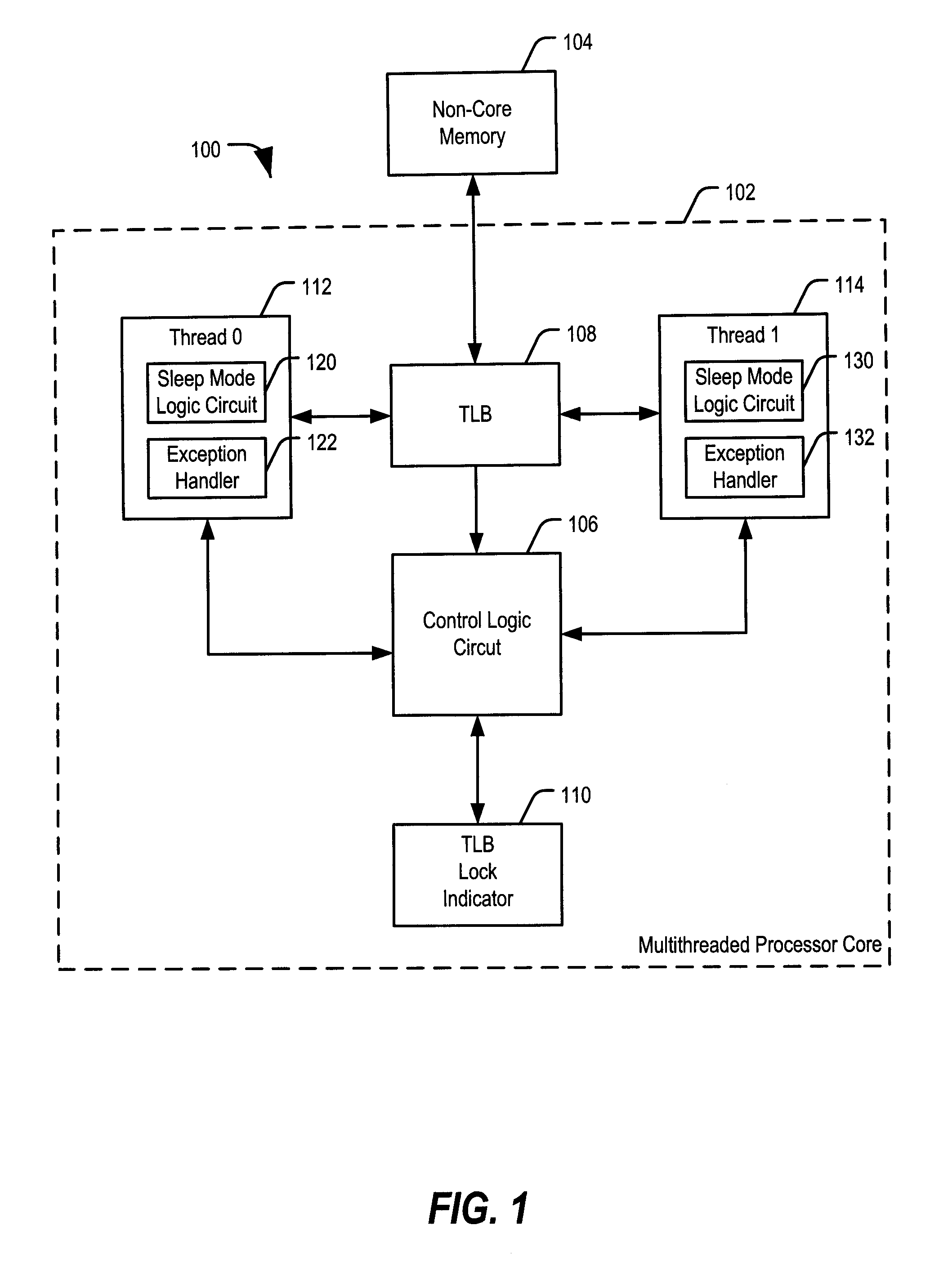
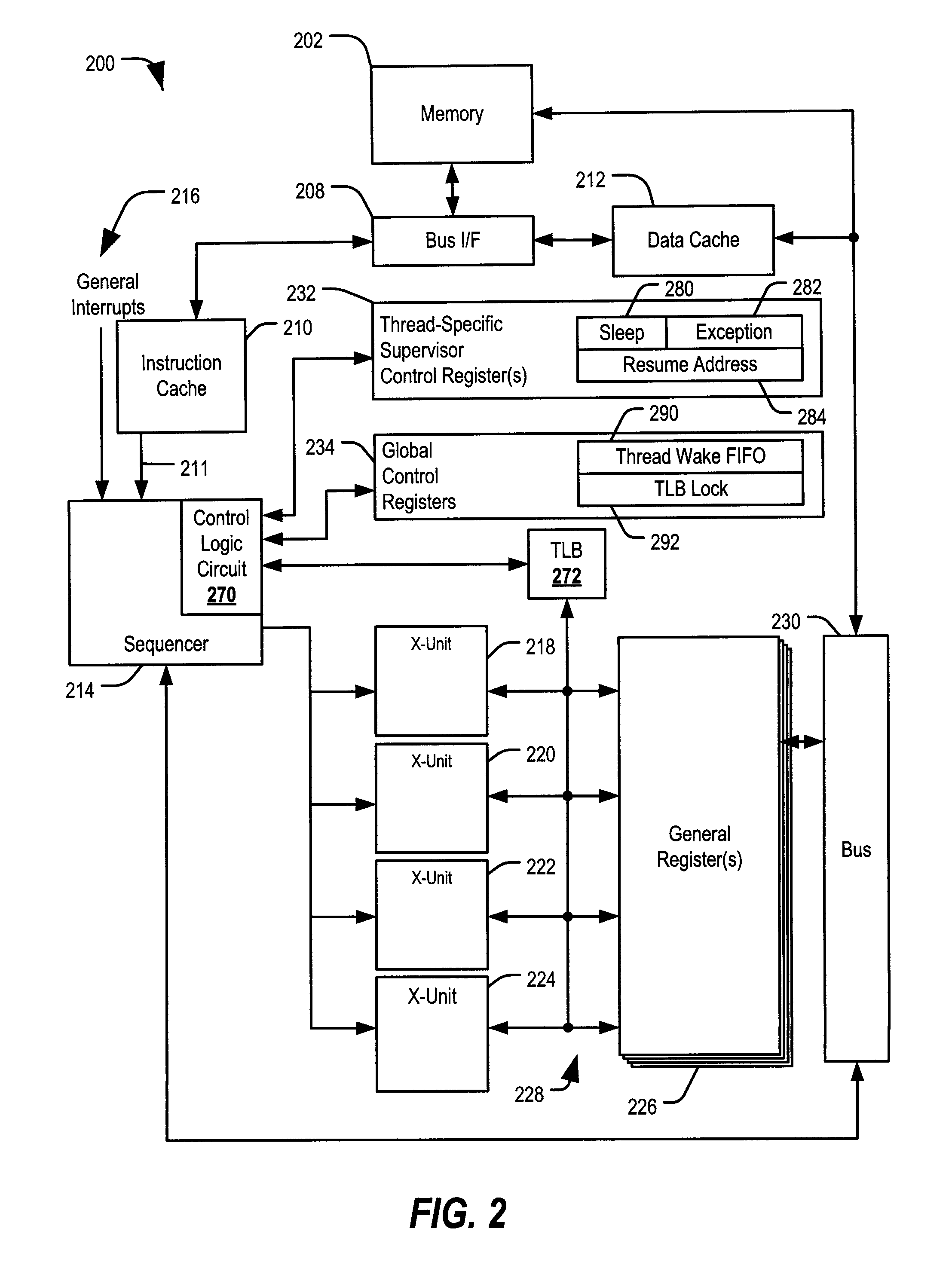
Multithreaded Processor with Lock Indicator
ActiveUS20090144519A1Faster unlock operationReduce dynamic power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsShared resourceEmbedded system
Systems and methods including a multithreaded processor with a lock indicator are disclosed. In an embodiment, a system includes means for indicating a lock status of a shared resource in a multithreaded processor. The system includes means for automatically locking the shared resource before processing exception handling instructions associated with the shared resource. The system further includes means for unlocking the shared resource.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
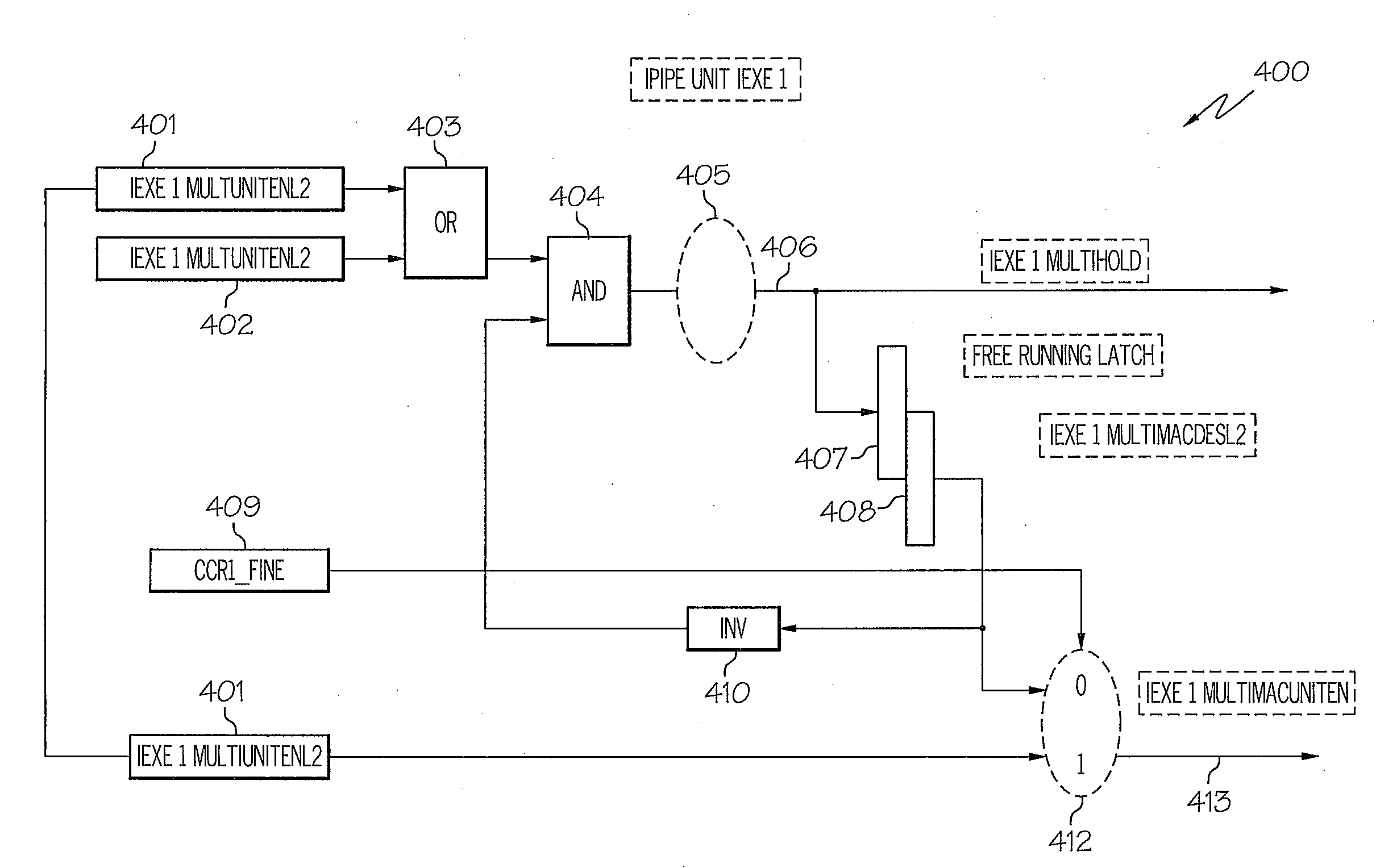
Adaptive execution cycle control method for enhanced instruction throughput
InactiveUS20090019264A1Improve throughputReduce dynamic powerEnergy efficient ICTDigital computer detailsLong latencyCycle frequency
A method, system and processor for increasing the instruction throughput in a processor executing longer latency instructions within the instruction pipeline. Logic associated with specific stages of the execution pipeline, responsible for executing the particular type of instructions, determines when at least a threshold number of the particular-type instructions is scheduled to be executed. The logic then automatically changes an execution cycle frequency of the specific pipeline stages from a first cycle frequency to a second, pre-established higher cycle frequency, which enables more efficient execution and higher execution throughput of the particular-type instructions. The cycle frequency of only the one or more functional stages are switched to the higher cycle frequency independent of the cycle frequency of the other functional stages in the processor pipeline. The logic also automatically switches the execution cycle frequency of the specific pipeline stages back from the second, higher cycle frequency to the first cycle frequency, when the number of scheduled first-type instructions has completed execution.
Owner:IBM CORP
Touch sensor detector system and method
ActiveUS9001082B1Reduce dynamic power consumptionHigh trackingInput/output processes for data processingElectrical driveElectrical current
A touch sensor detector system and method incorporating an interpolated sensor array is disclosed. The system and method utilize a touch sensor array (TSA) configured to detect proximity / contact / pressure (PCP) via a variable impedance array (VIA) electrically coupling interlinked impedance columns (IIC) coupled to an array column driver (ACD), and interlinked impedance rows (IIR) coupled to an array row sensor (ARS). The ACD is configured to select the IIC based on a column switching register (CSR) and electrically drive the IIC using a column driving source (CDS). The VIA conveys current from the driven IIC to the IIC sensed by the ARS. The ARS selects the IIR within the TSA and electrically senses the IIR state based on a row switching register (RSR). Interpolation of ARS sensed current / voltage allows accurate detection of TSA PCP and / or spatial location.
Owner:SENSEL
Logic circuit and semiconductor device
ActiveUS20110102018A1Reduce hydrogen concentrationTotal current dropTransistorPower reduction by control/clock signalHydrogen concentrationPower semiconductor device
In a logic circuit where clock gating is performed, the standby power is reduced or malfunction is suppressed. The logic circuit includes a transistor which is in an off state where a potential difference exists between a source terminal and a drain terminal over a period during which a clock signal is not supplied. A channel formation region of the transistor is formed using an oxide semiconductor in which the hydrogen concentration is reduced. Specifically, the hydrogen concentration of the oxide semiconductor is 5x1019 (atoms / cm3) or lower. Thus, leakage current of the transistor can be reduced. As a result, in the logic circuit, reduction in standby power and suppression of malfunction can be achieved.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Automatic extension of clock gating technique to fine-grained power gating
ActiveUS20070024318A1Reduce dynamic power consumptionPower reduction by control/clock signalLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsTime criticalEngineering
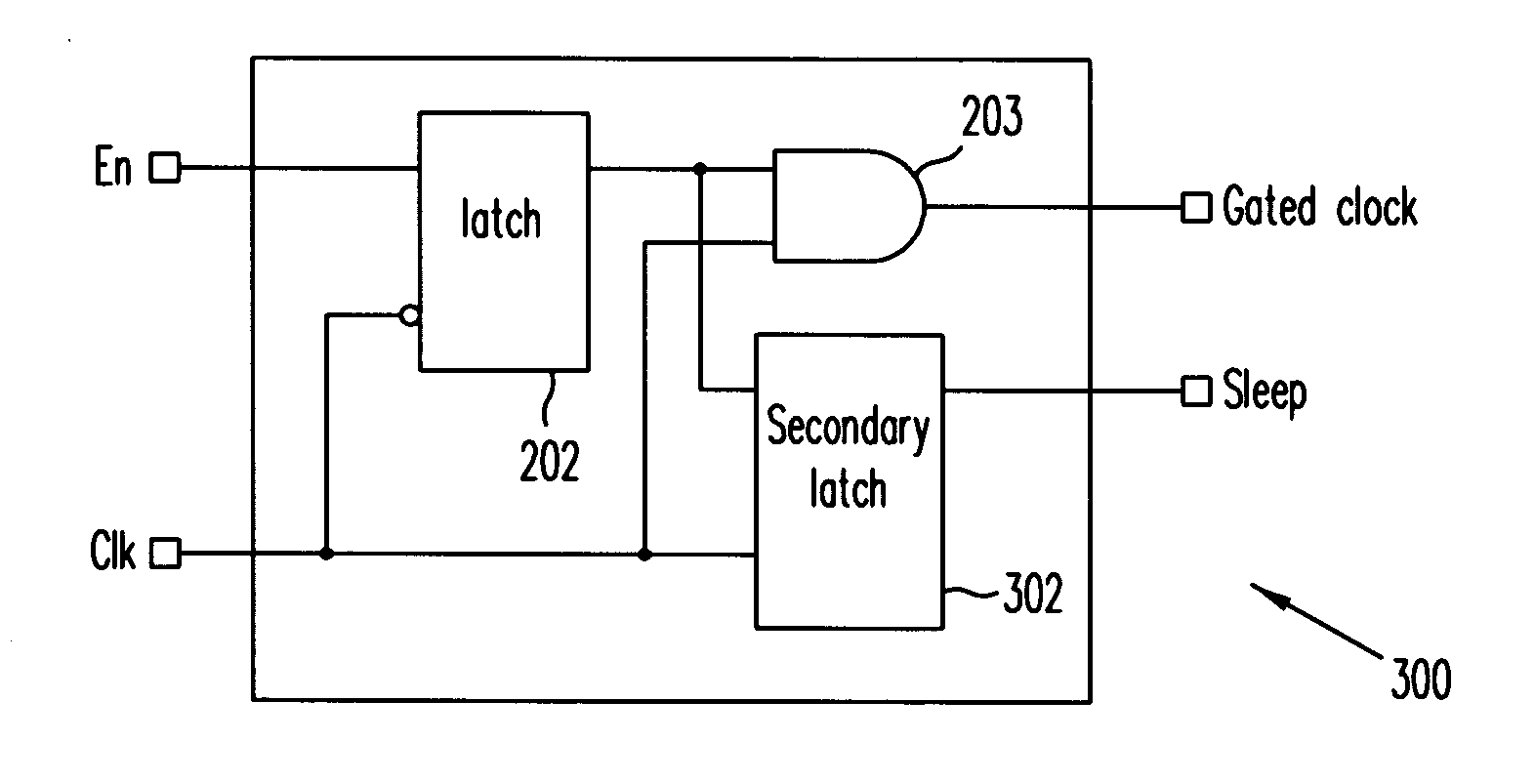
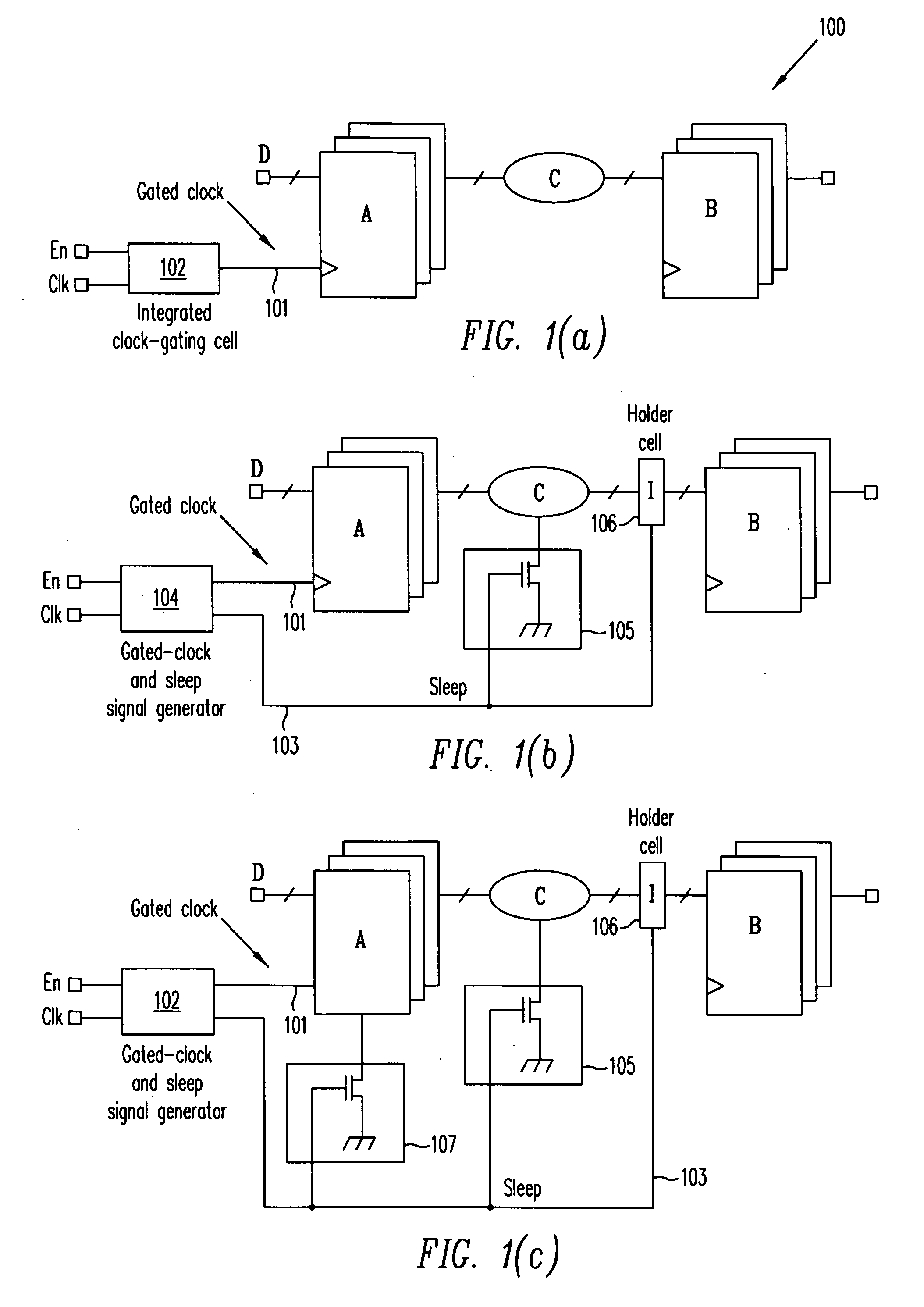
A method extends a clock-gating technique to provide a sleep signal for controlling switch circuits that reduce active leakage power. Using this extension of the clock-gating technique, fine-grained power-gating is achieved. The method automatically identifies, at an RTL or a gate level, the logic circuits that can be power-gated. The method of the present invention derives a sleep signal for fine-grained power-gating that may be applicable to both time-critical and non-time-critical designs.
Owner:ANSYS
Driving circuit unit, gate driving circuit and display device
The invention relates to a gate driving circuit and a display device. The gate driving circuit comprises multiple levels of driving circuit units connected in series. Each level of units comprises an inputting module for providing threshold voltage of a driving module, a driving module for responding to the threshold voltage and for sending a first clock signal to a signal outputting interface, a discharging module for responding to an output signal or a clock signal of an adjacent level and for coupling a control terminal of the driving module to a first voltage source, a clock feedthrough inhibiting module for stablizing the potential of the control terminal of the driving module under the control of the clock signal and the output signal of the adjacent level, and a low level maintaining module for stablizing the output signal at the potential of the first voltage source under the control of the clock signal. The driving circuit unit, gate driving circuit and display device provided by the invention employ single driving tube to realize the fast pull-up and pull-down of the output signal with sequential coordination, reducing the delay time of the rise and fall of the output signal at a low temperature, and employs the clock feedthrough inhibiting module to stablize the gate potential of the driving tube, reducing the corresponding dynamic power consumption.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
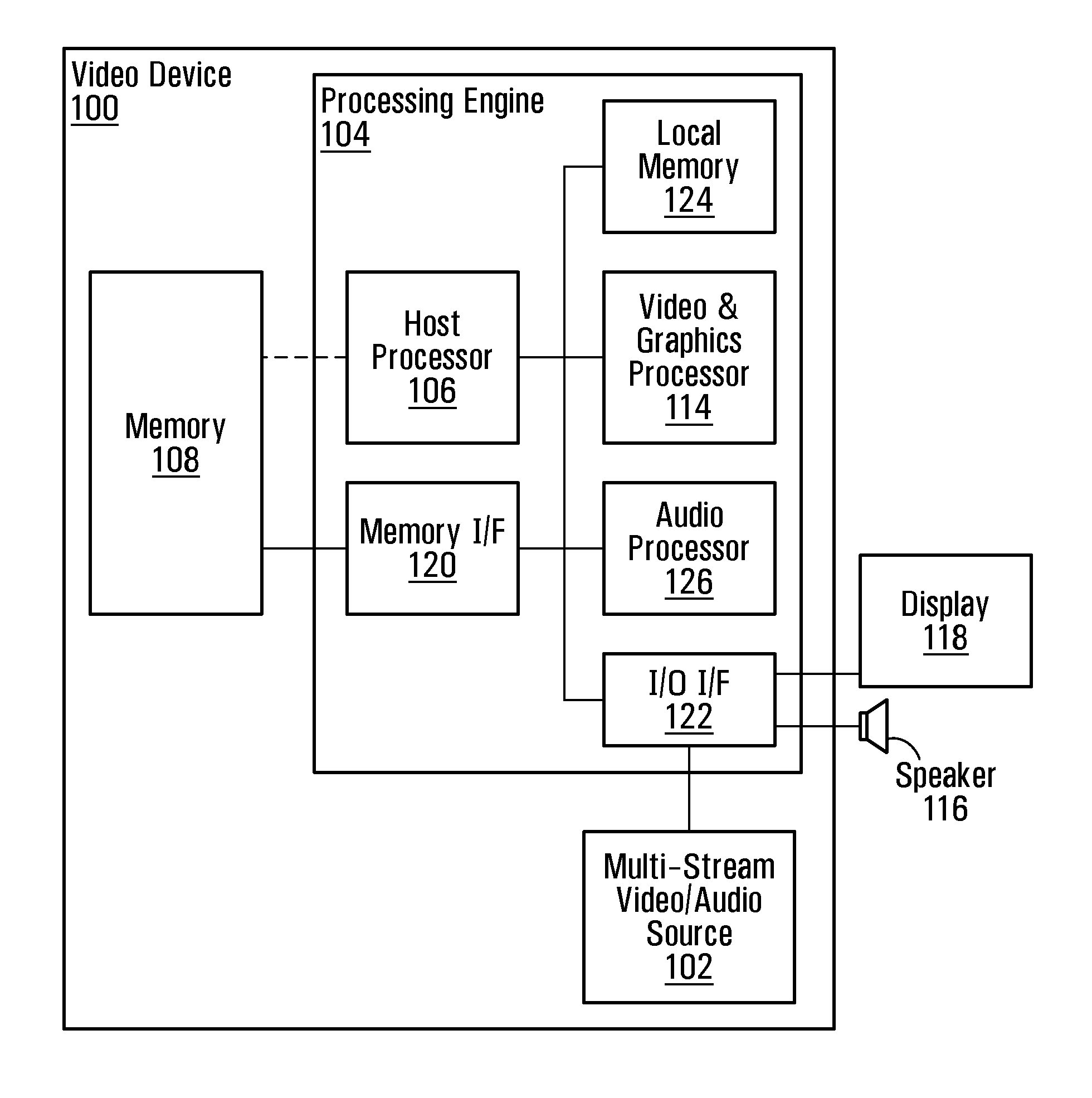
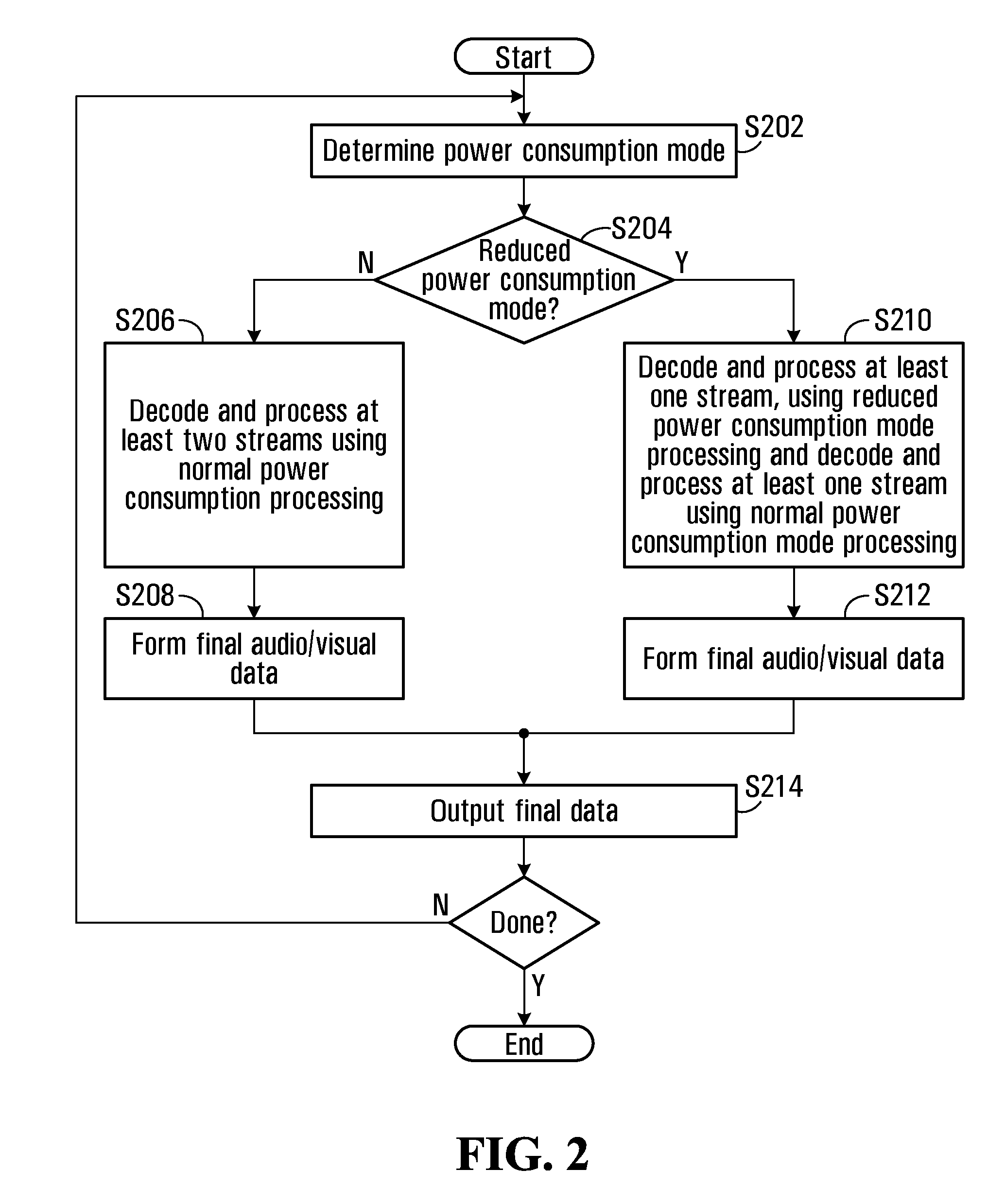
Power management in multi-stream audio/video devices
ActiveUS20110268425A1Reduce consumptionReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsComputer hardwareMulti stream
A method of managing power consumption in a video device capable of displaying encoded multi-stream video is disclosed. Power reduction is achieved by limiting the amount of video and audio decoding and processing performed on at least some of the encoded streams, by taking particular application contexts into account. In a normal power consumption mode, audio / video data from all streams are decoded and digitally processed for output. In response to detecting a reduced power consumption mode, audio / video from at least some of the streams are processed in a modified manner to reduce power consumption.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
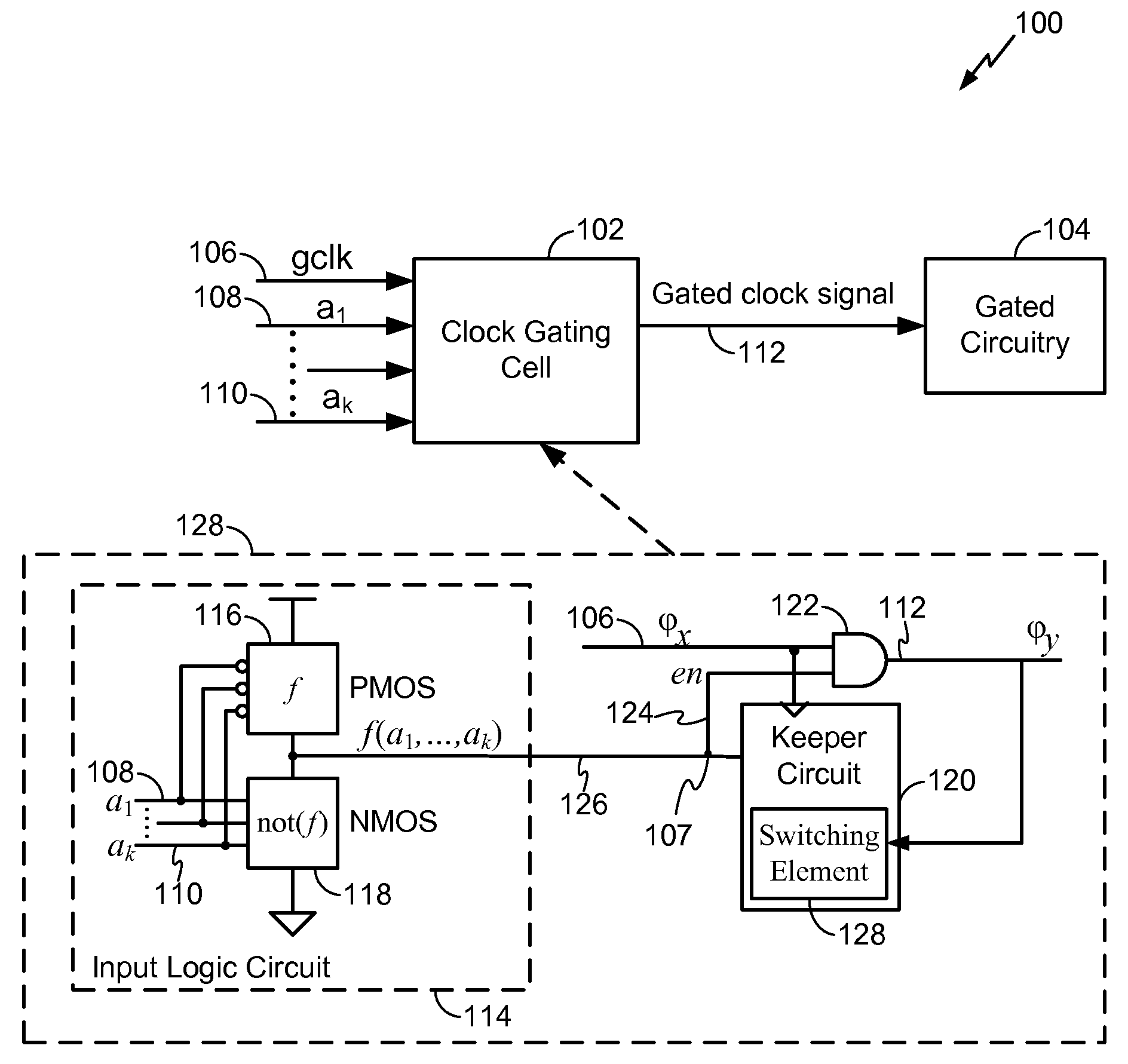
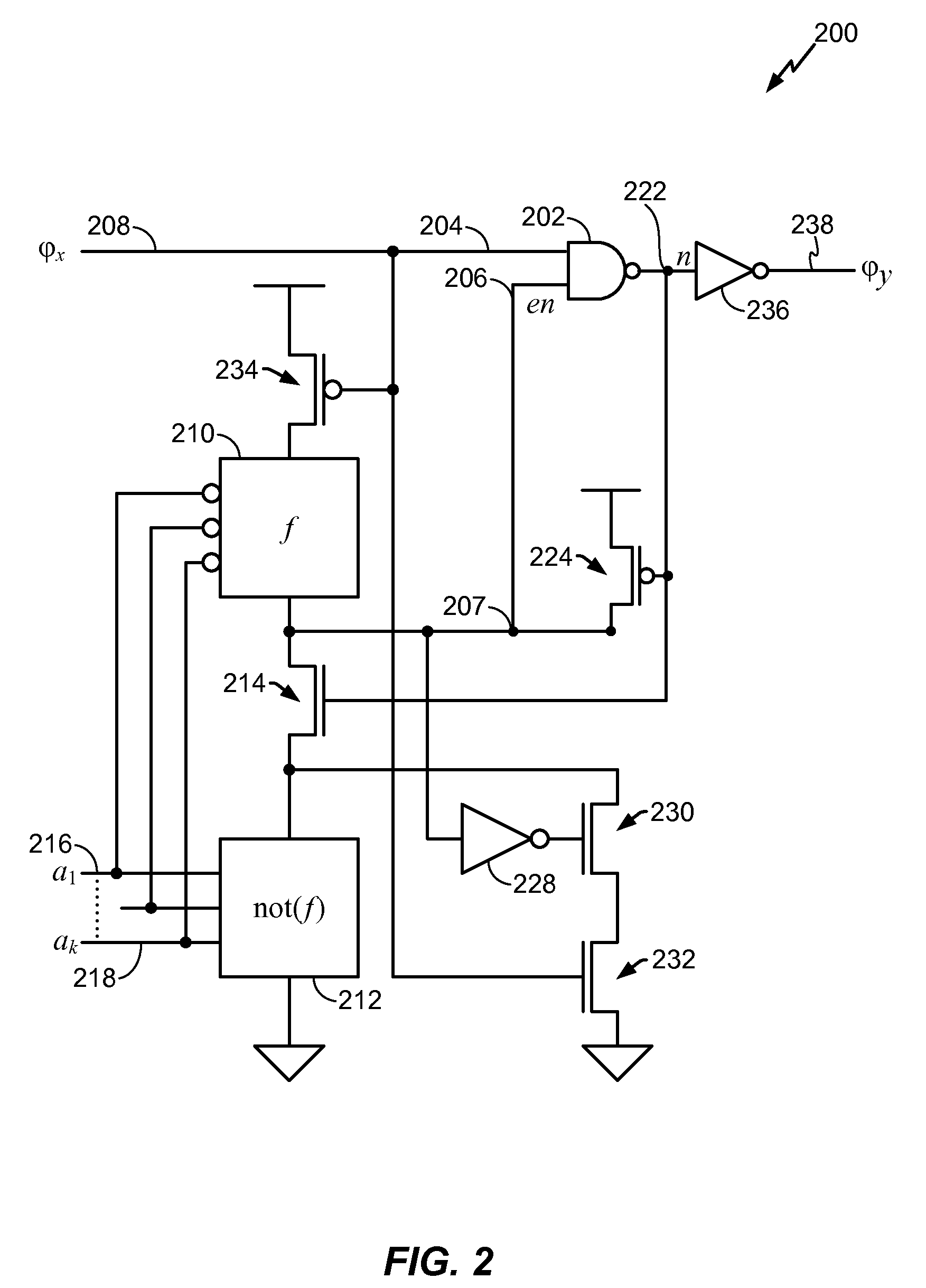
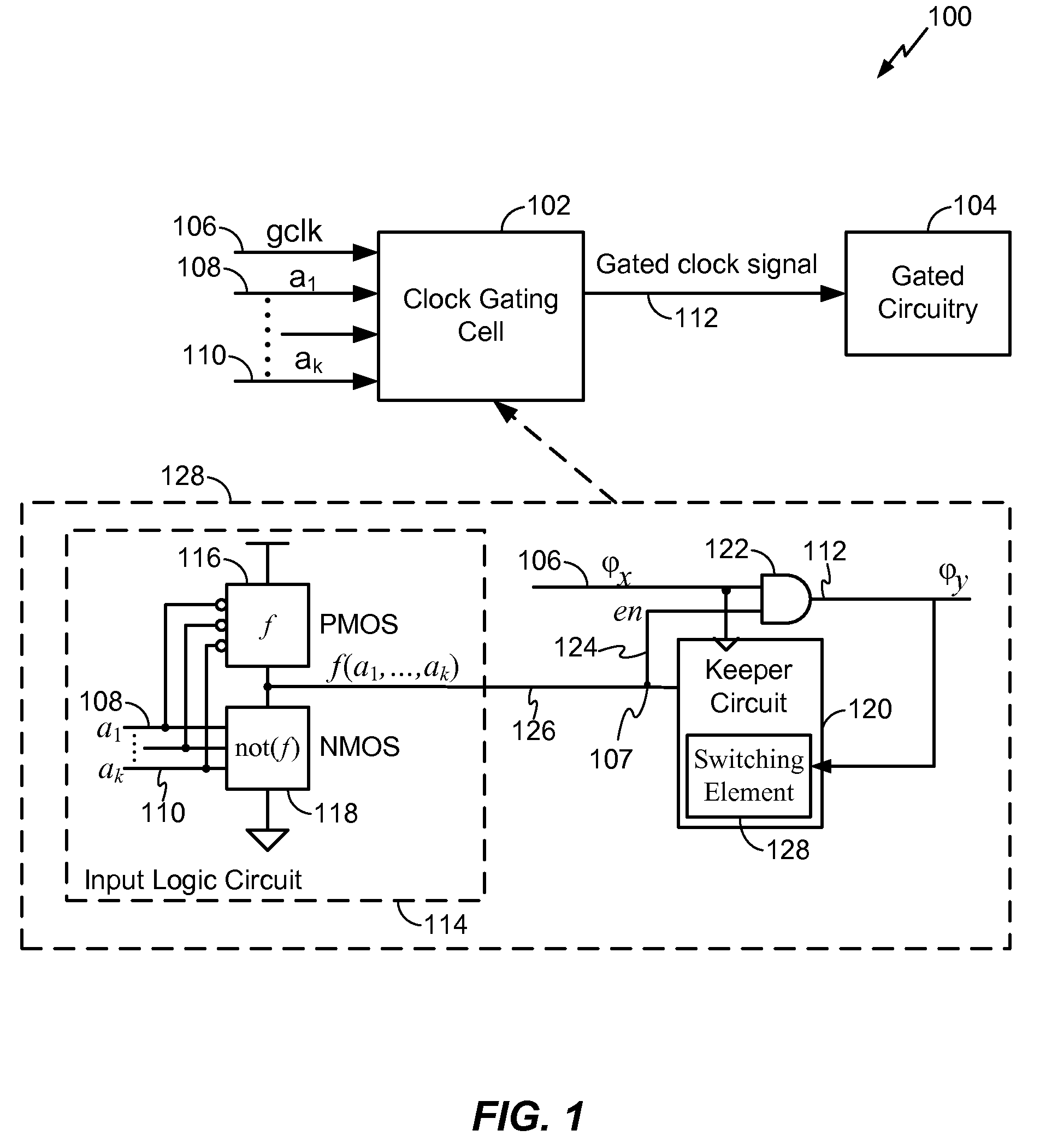
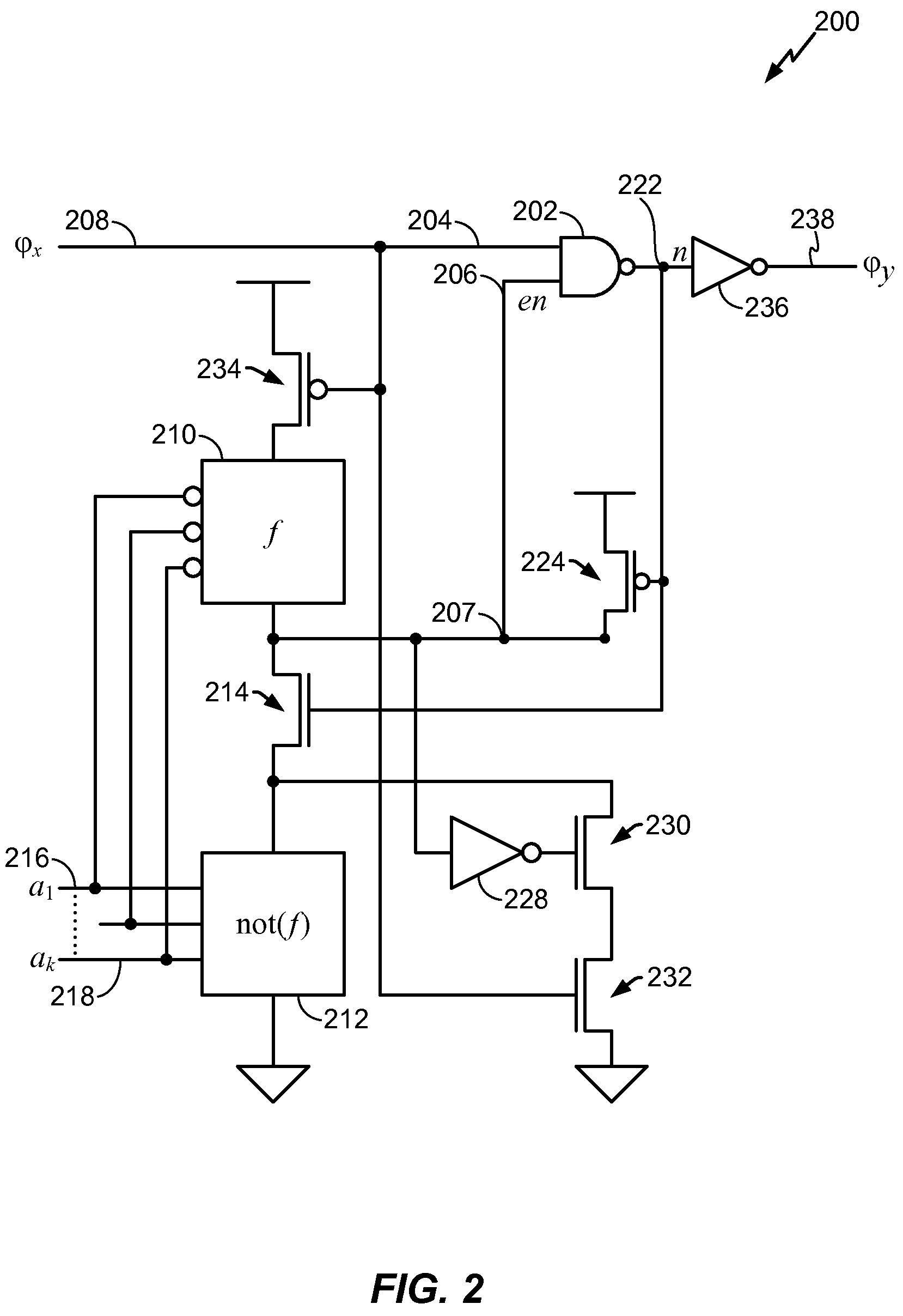
Clock gating system and method
ActiveUS7902878B2Reduce in quantityReduce areaPower reduction by control/clock signalGenerating/distributing signalsEngineeringLogic circuitry
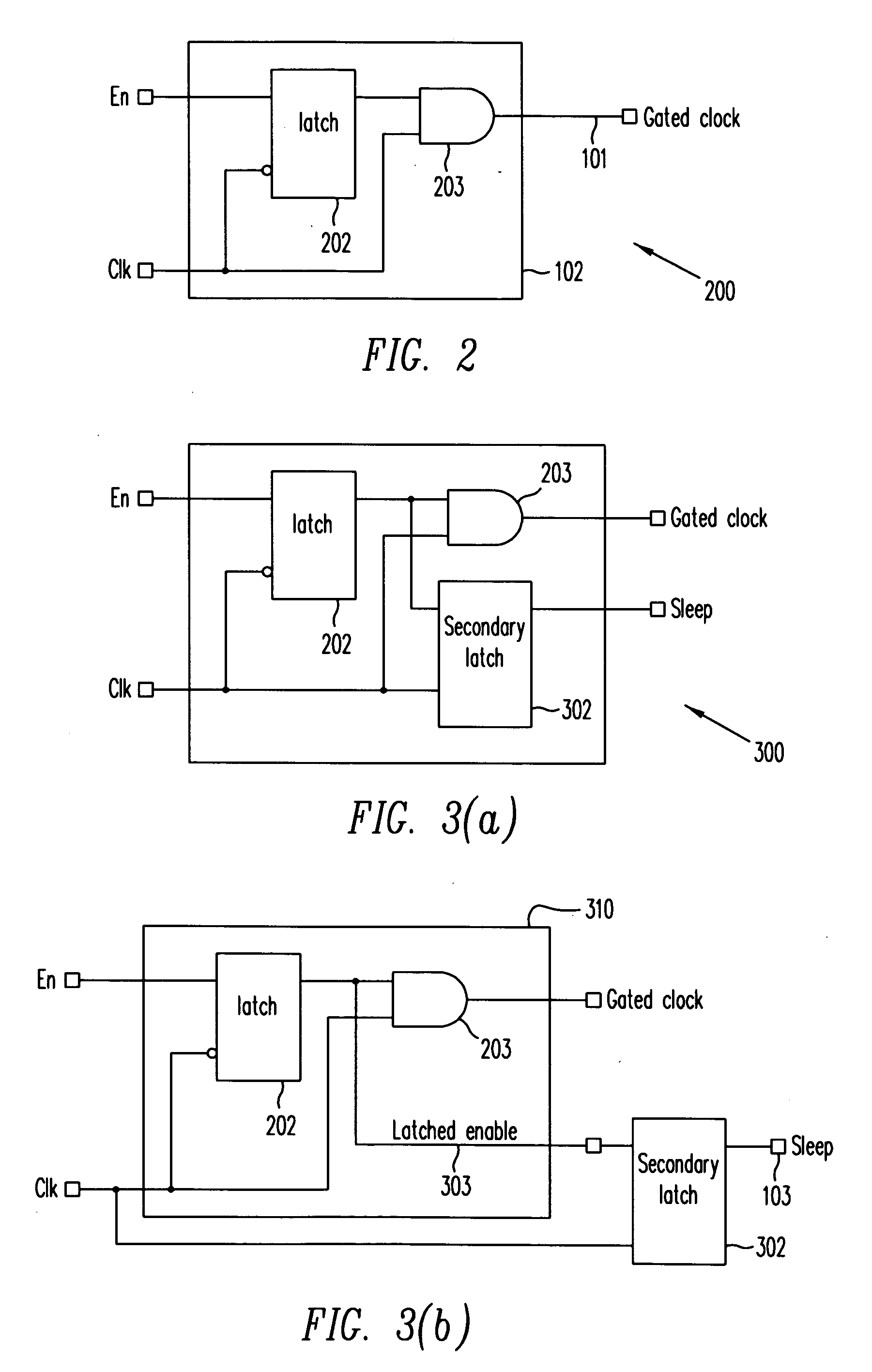
A clock gating system and method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, the system includes an input logic circuit having at least one input to receive at least one input signal and having an output at an internal enable node. A keeper circuit includes at least one switching element that is responsive to a gated clock signal and is coupled to the internal enable node to selectively hold a logical voltage level at the internal enable node. The system further includes a gating element responsive to an input clock signal and to the logical voltage level at the internal enable node to generate the gated clock signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
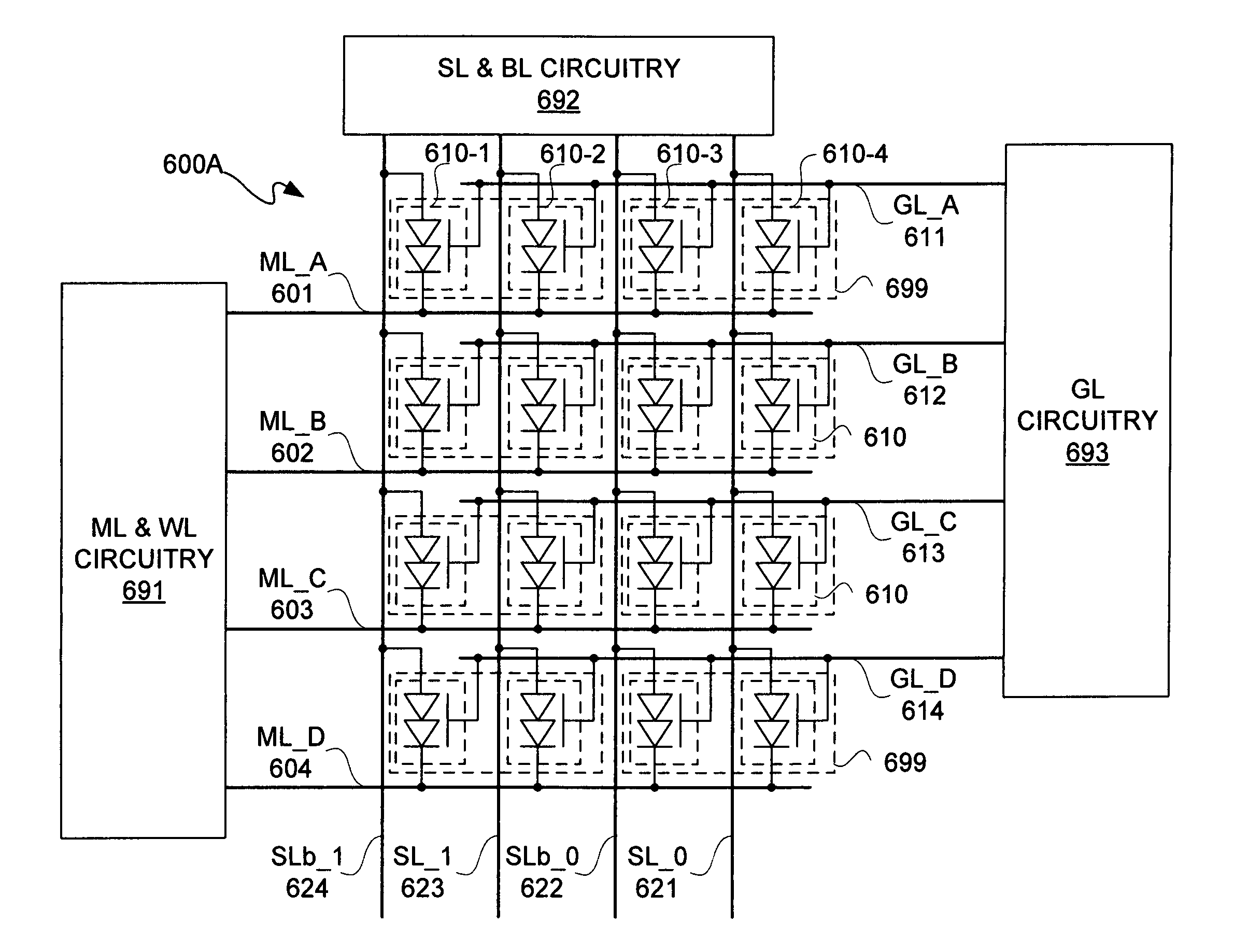
Content-addressable memory architecture
InactiveUS7738274B1Reduce power consumptionReduce dynamic power consumptionDigital storageDirect couplingThyratron
A content-addressable memory (“CAM”) architecture and method for reducing power consumption thereof are described. A CAM cell array includes CAM cells, each of which includes two thyristor-based storage elements. Each thyristor-based storage element of the CAM cells has a control gate, an anode, and a cathode for providing control gates, anodes, and cathodes of the CAM cells. The CAM cell array further includes matchlines directly coupled to the cathodes of the CAM cells; searchlines directly coupled to the anodes of the CAM cell; and gatelines coupled to the control gates of the CAM cells.
Owner:T RAM ASSIGNMENT FOR THE BENEFIT OF CREDITORS LLC +1
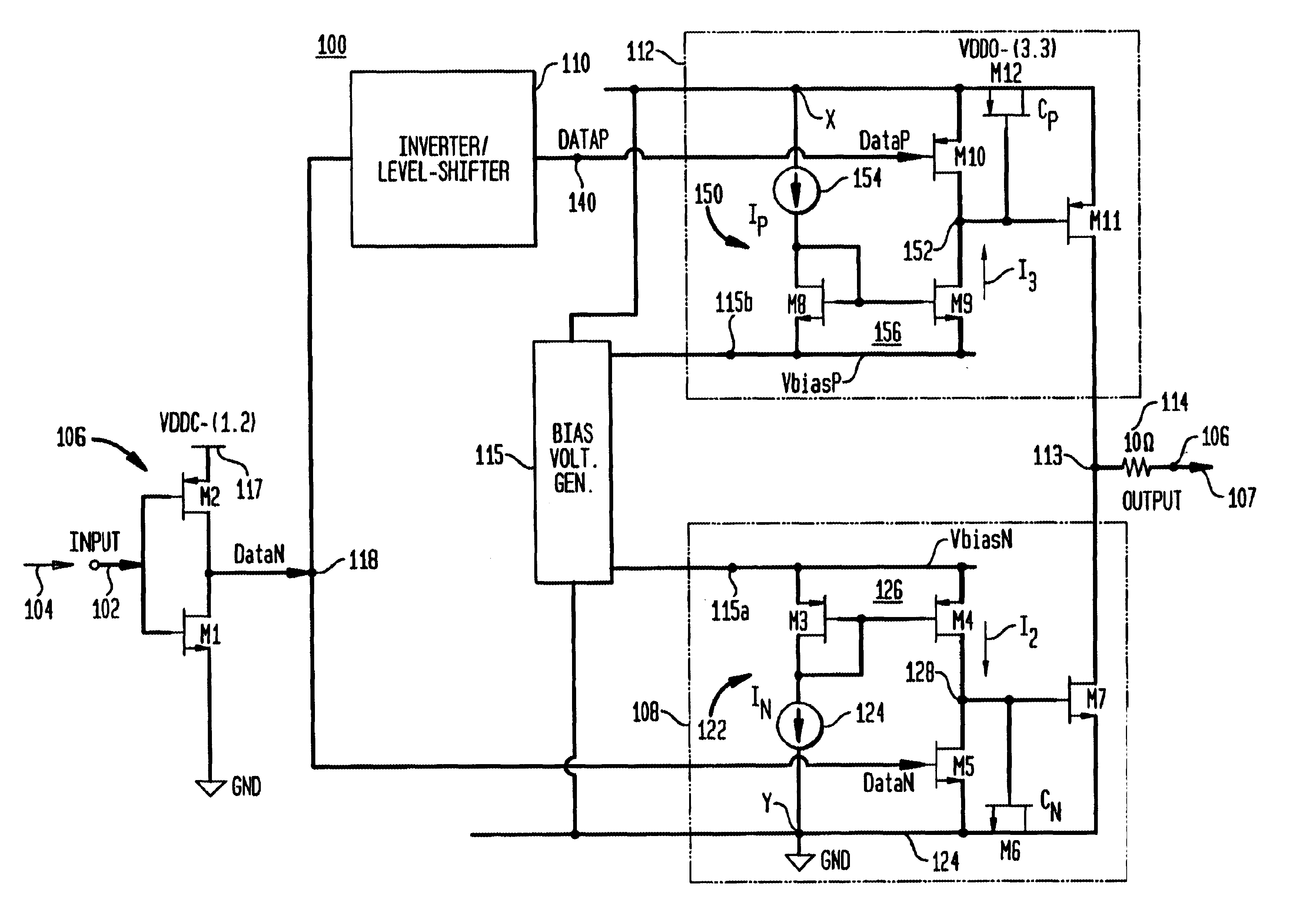
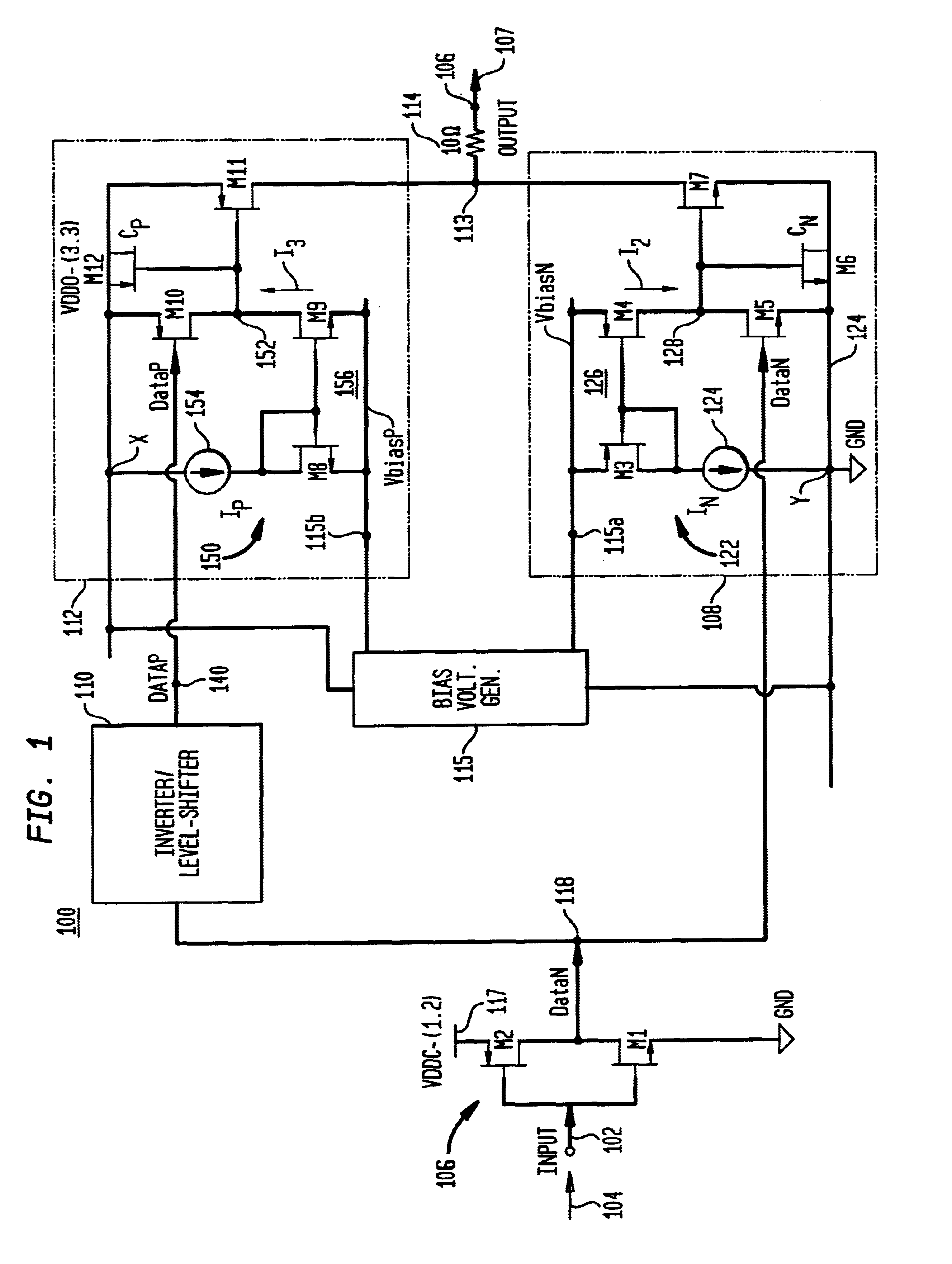
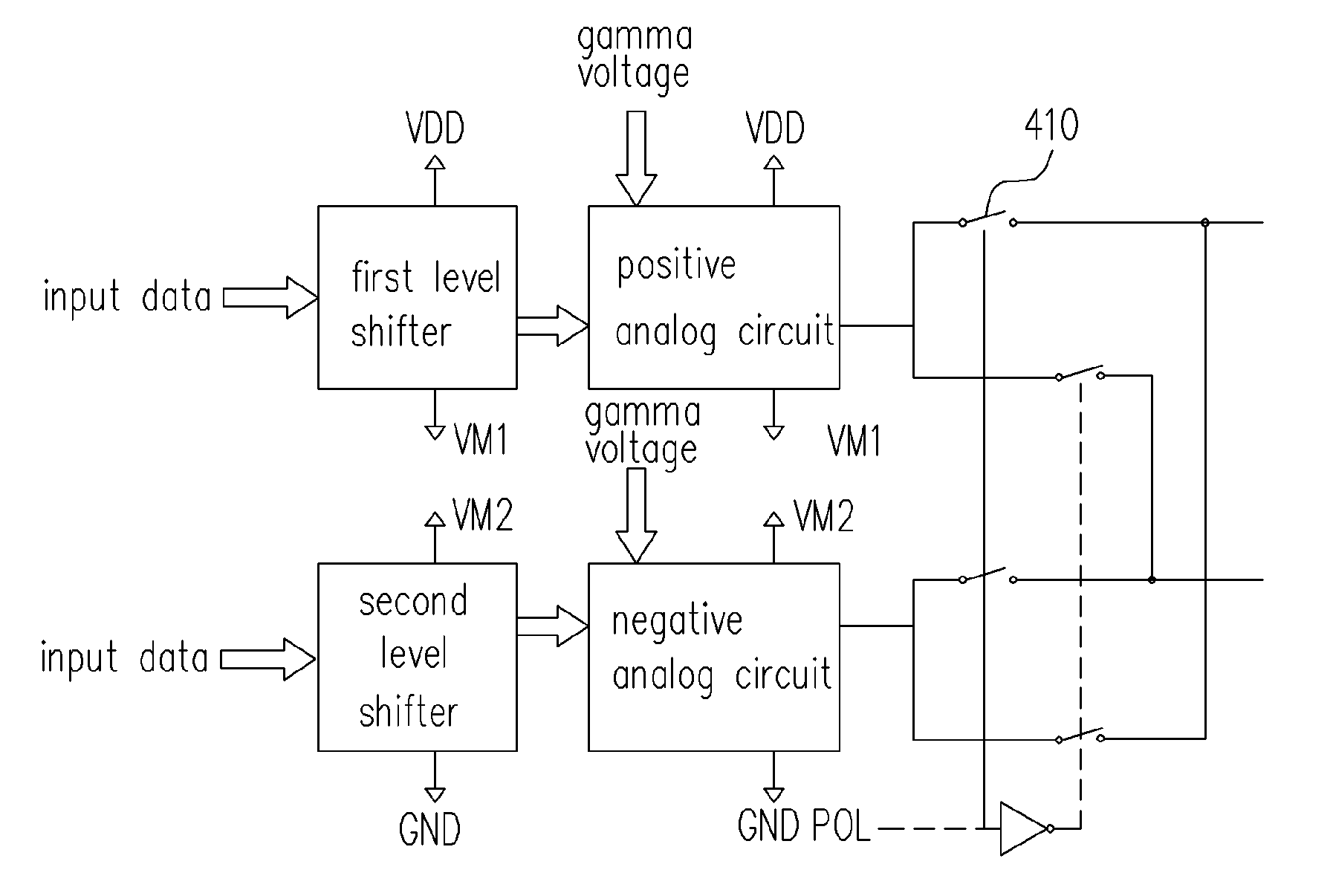
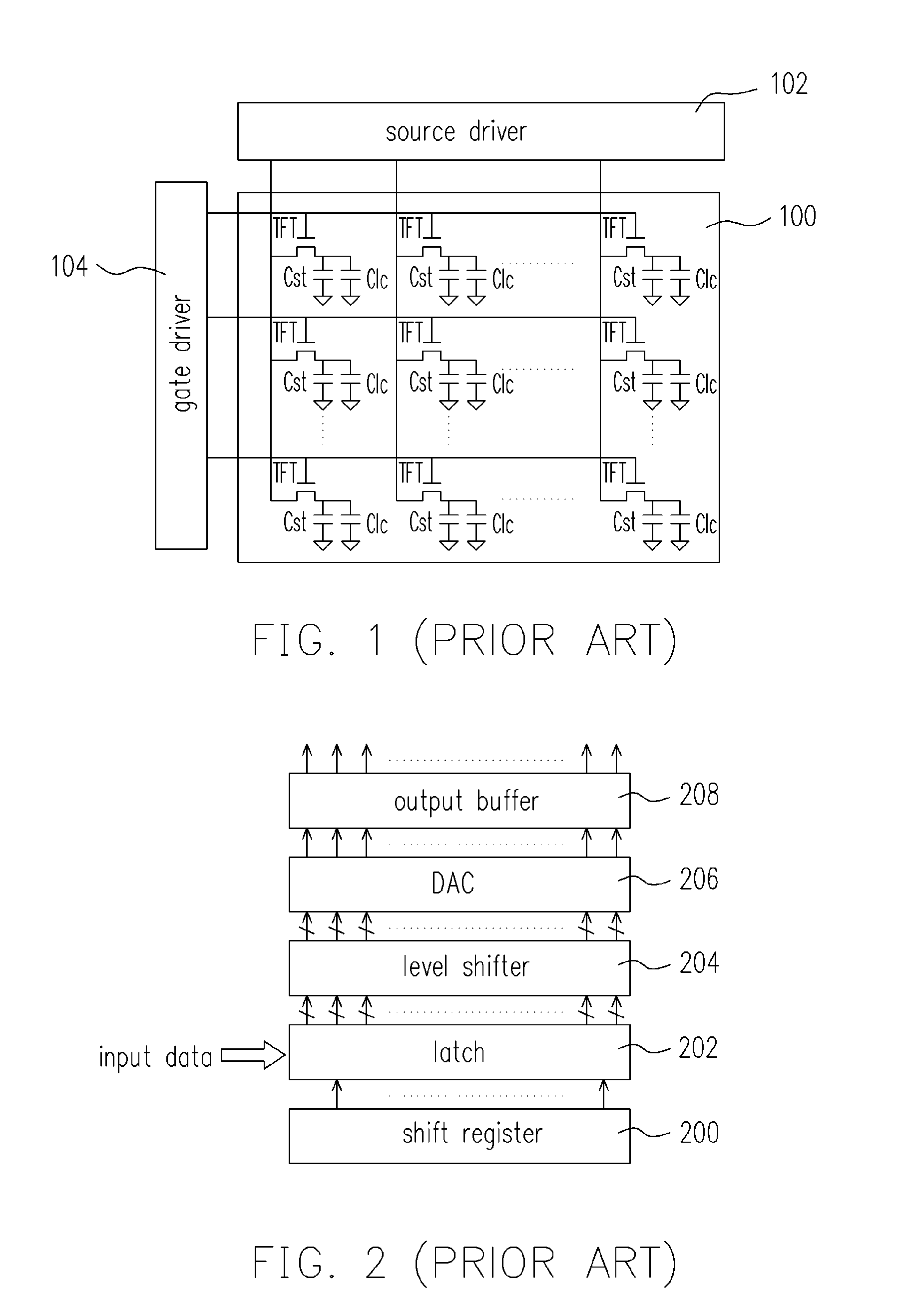
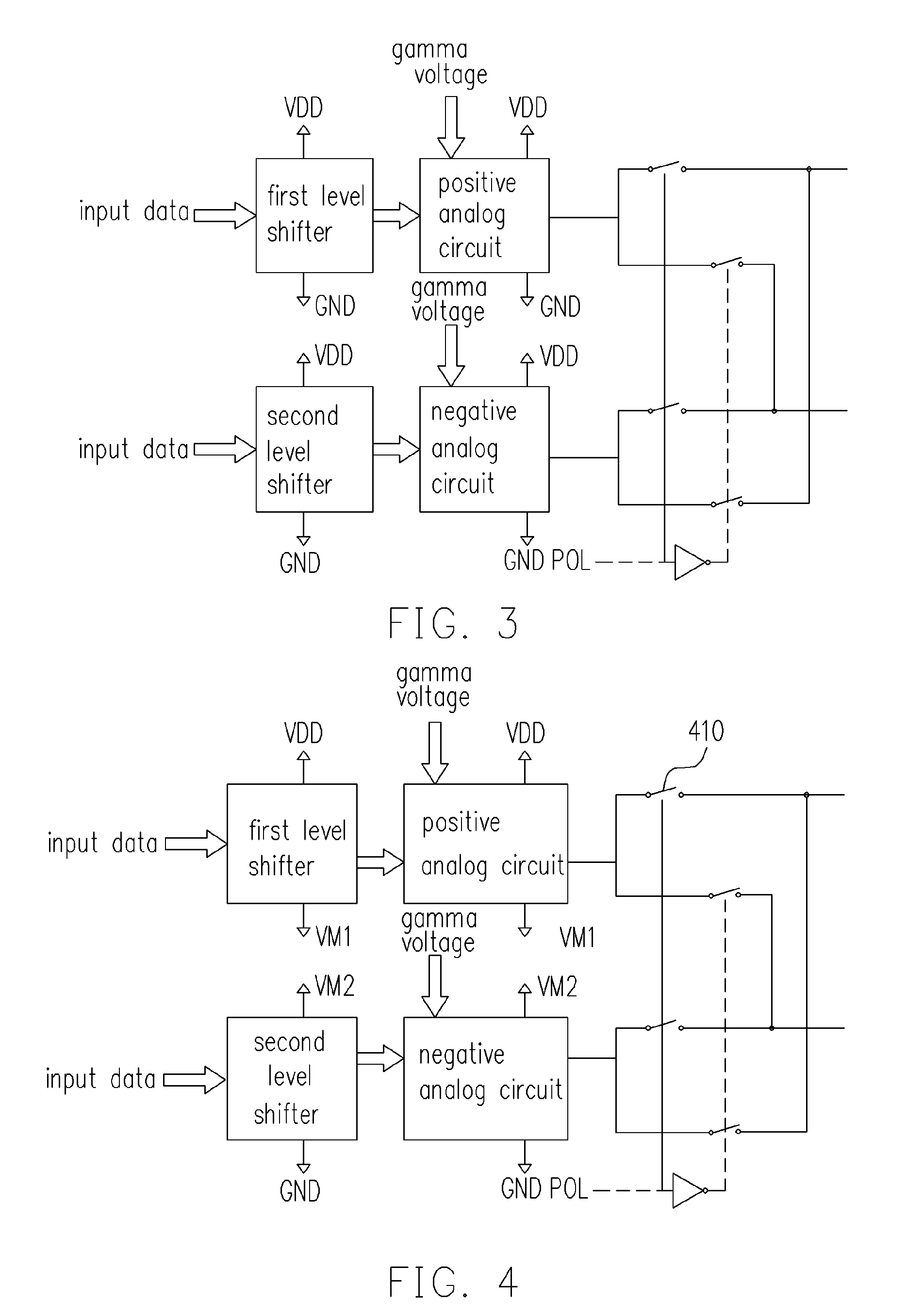
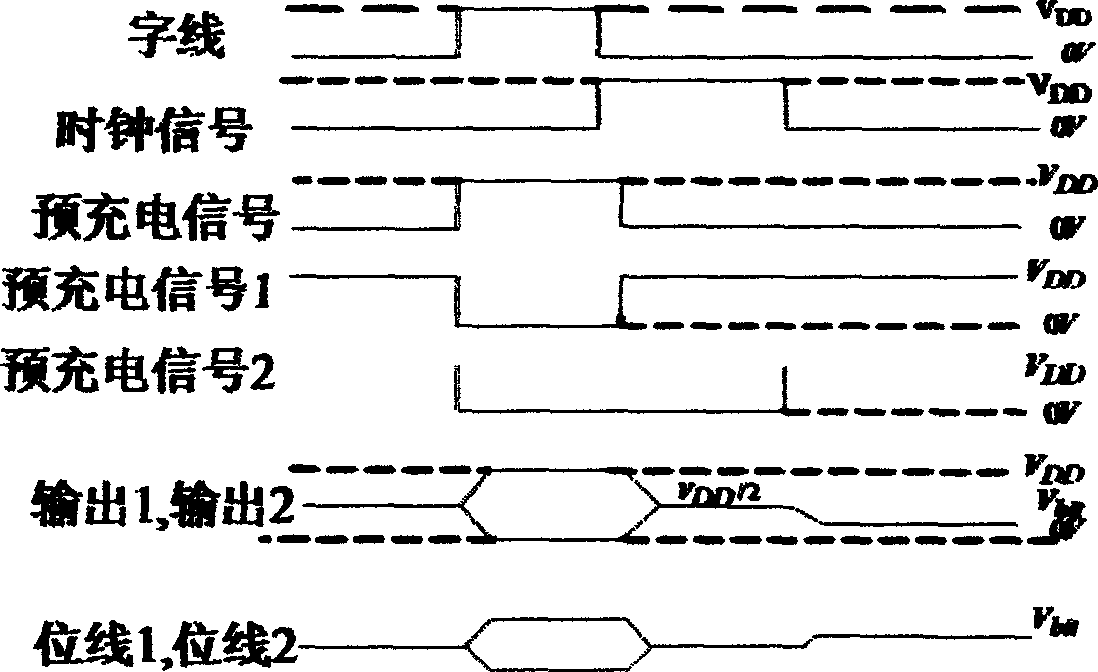
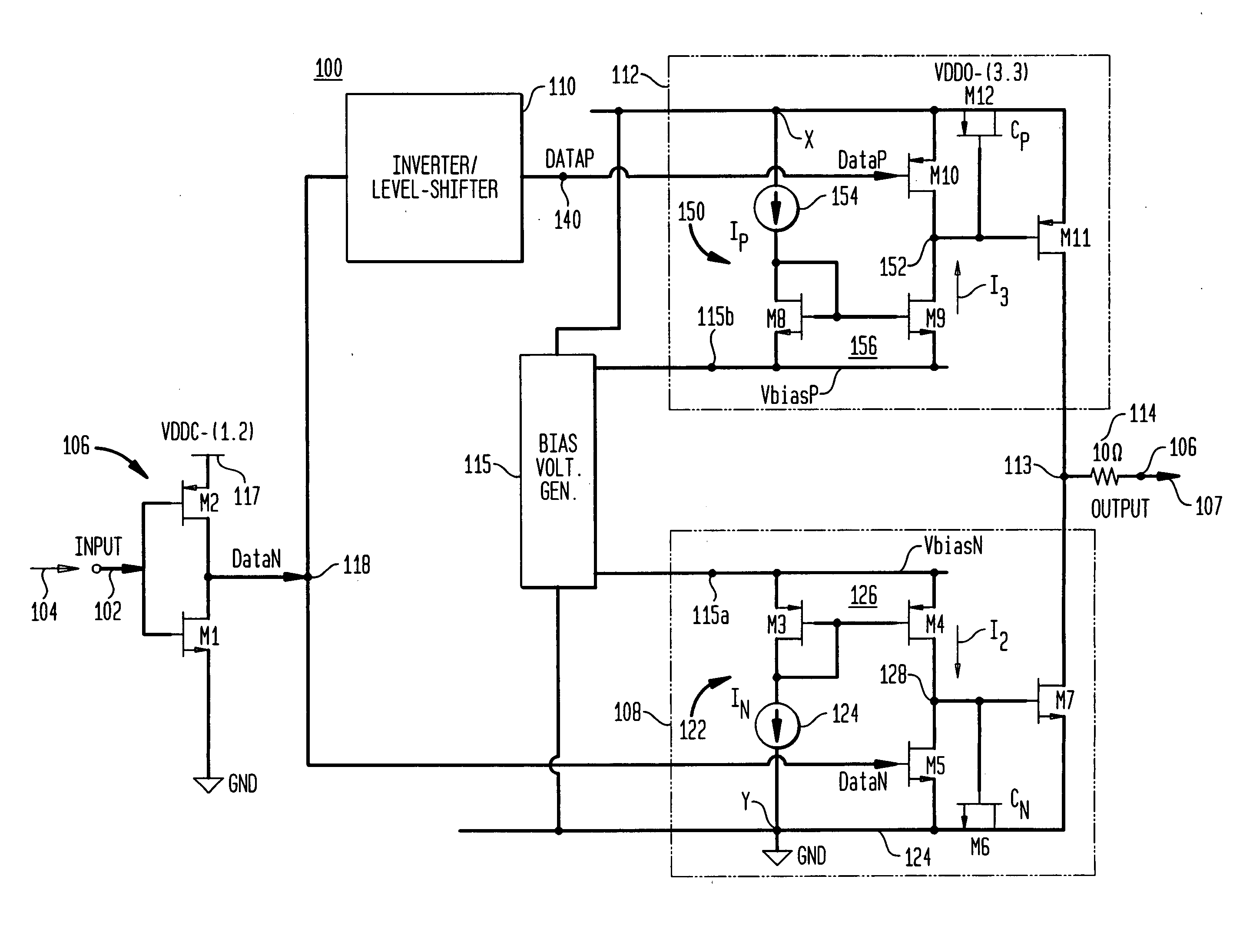
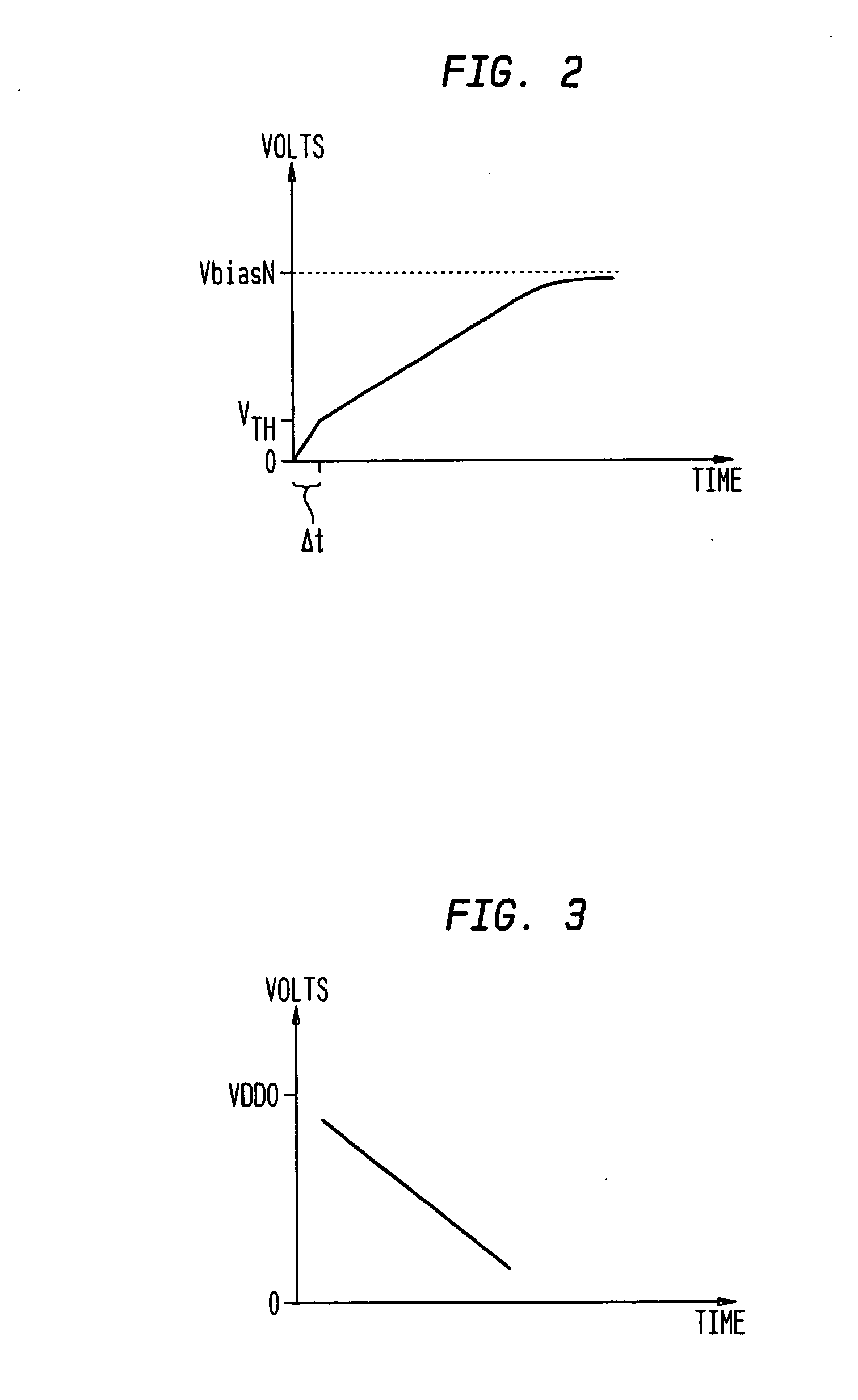
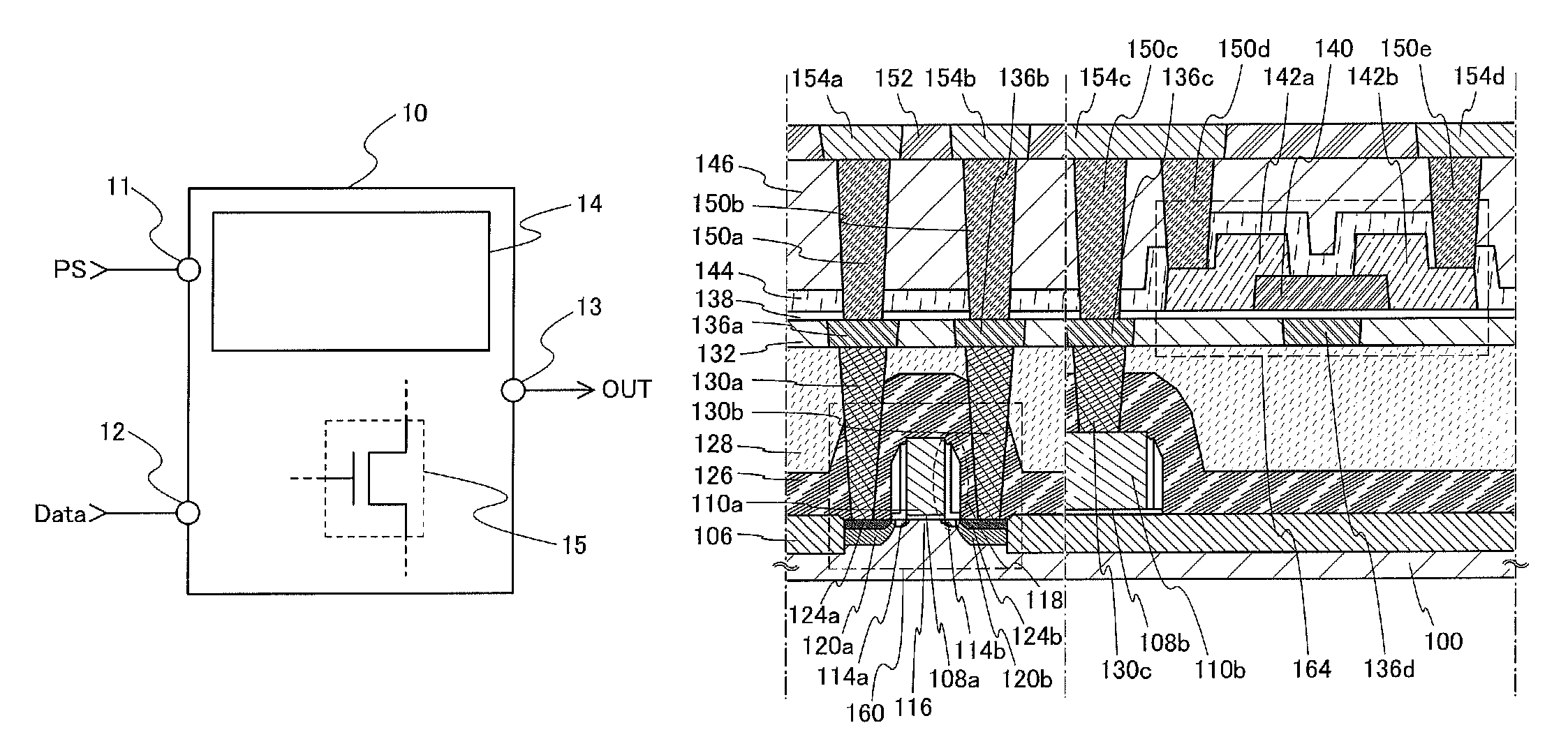
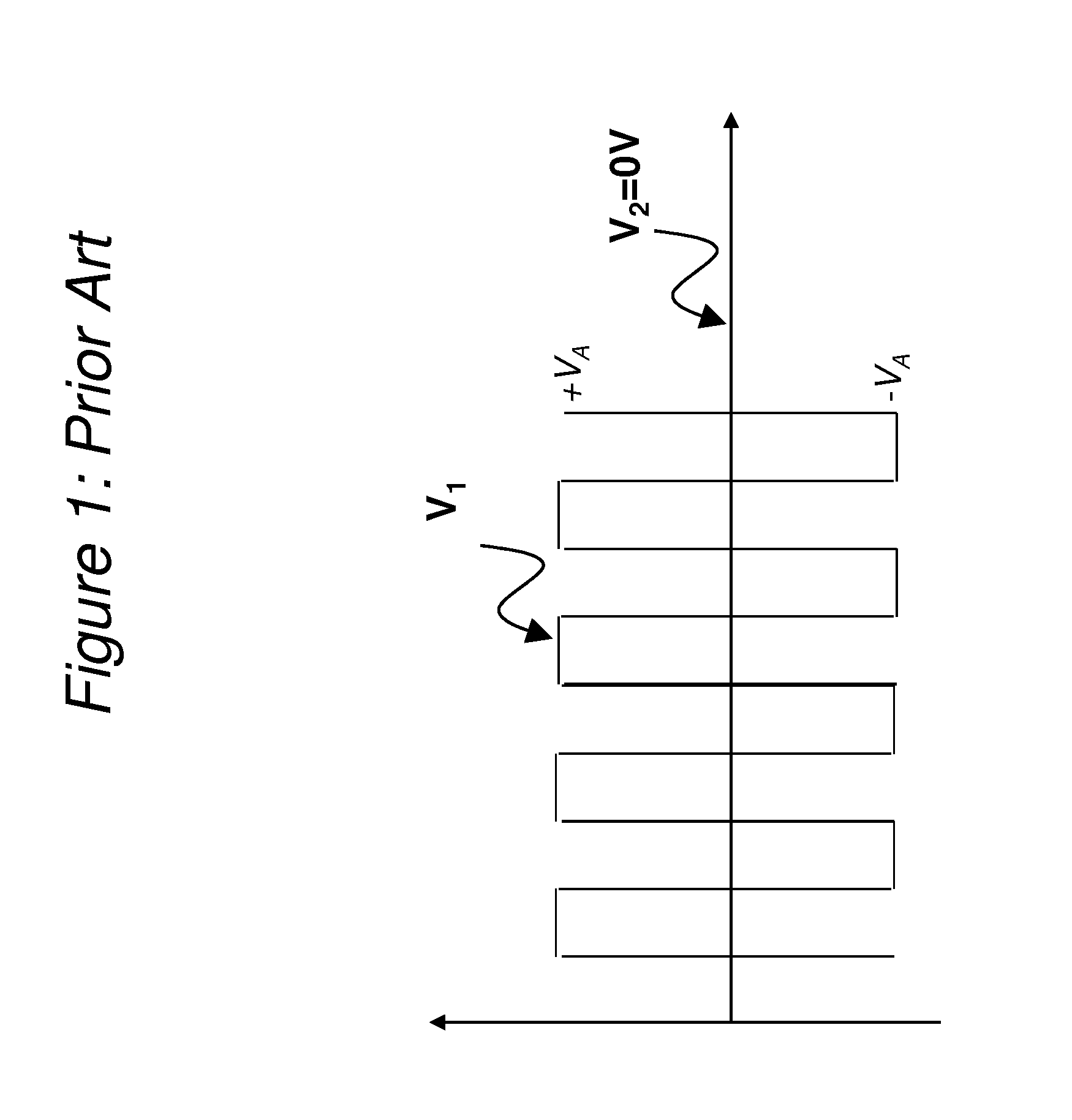
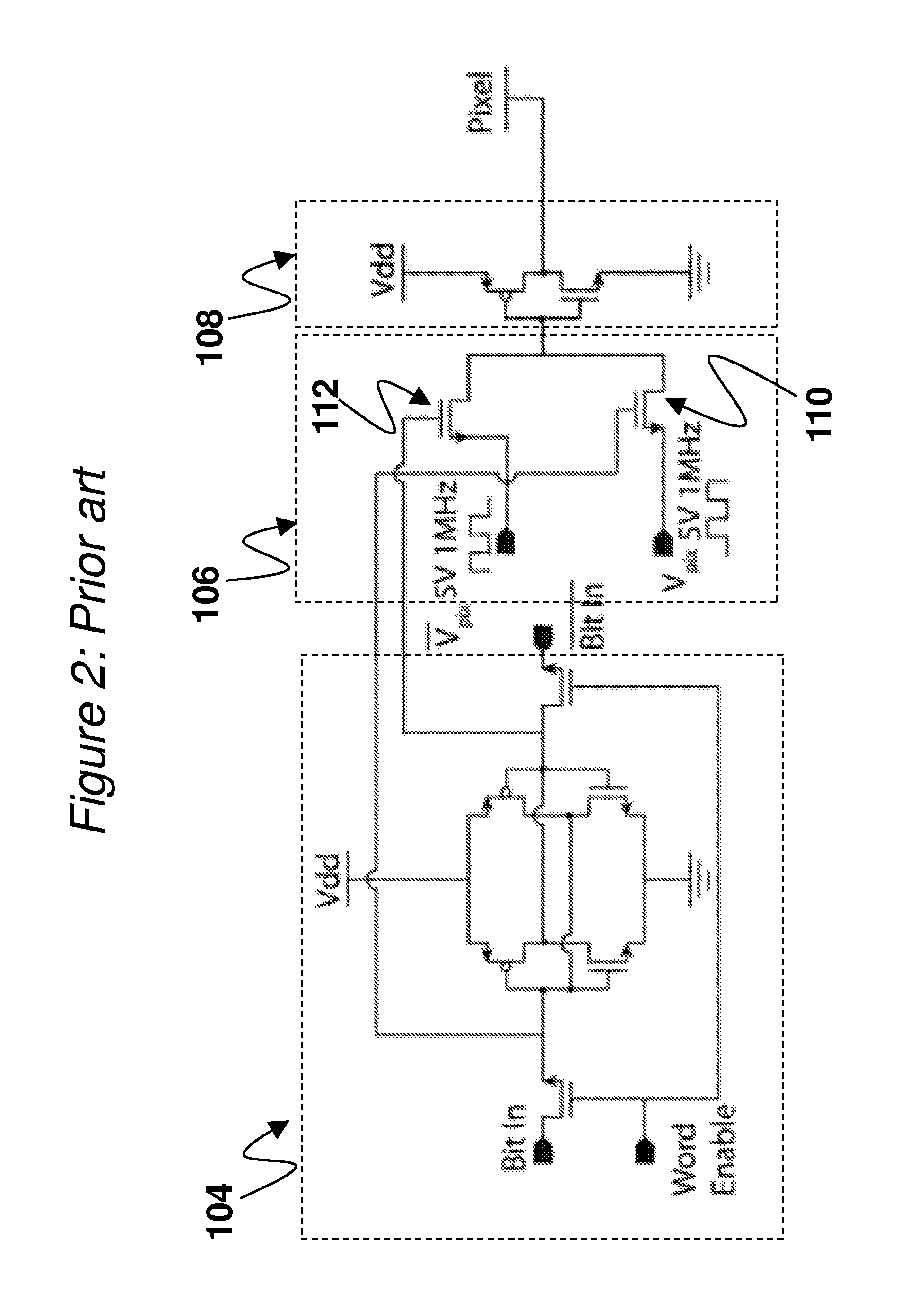
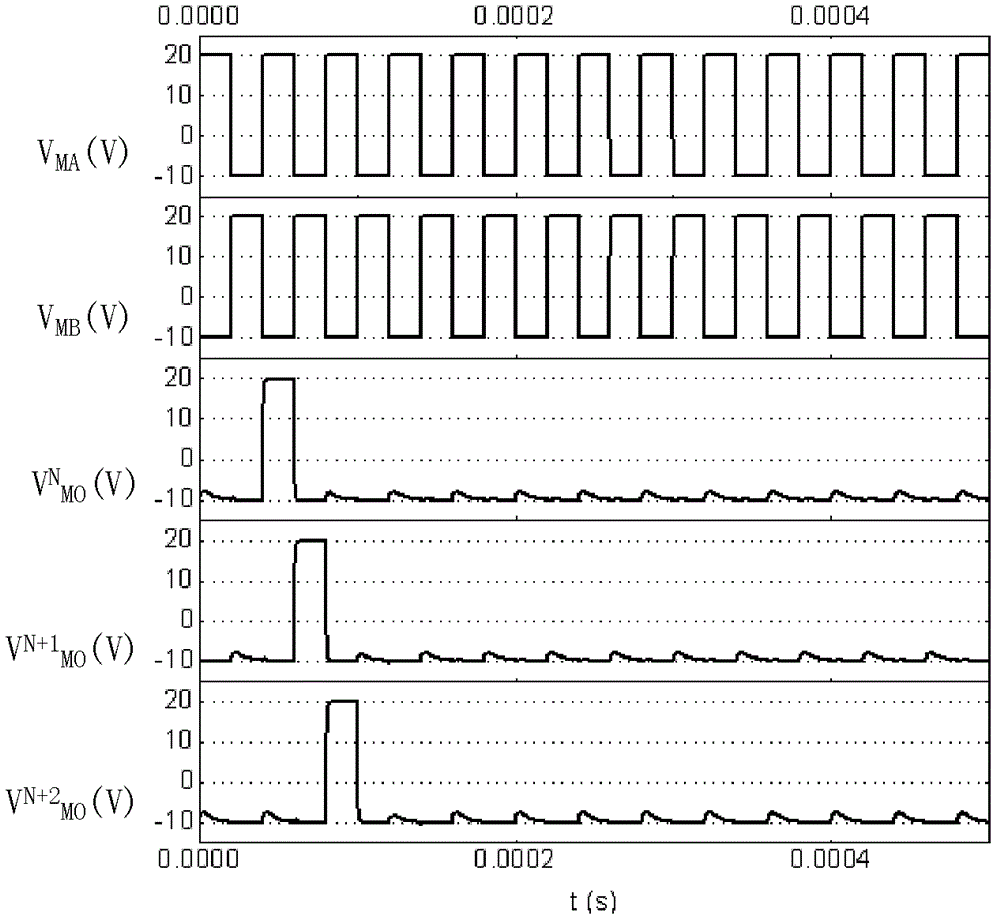
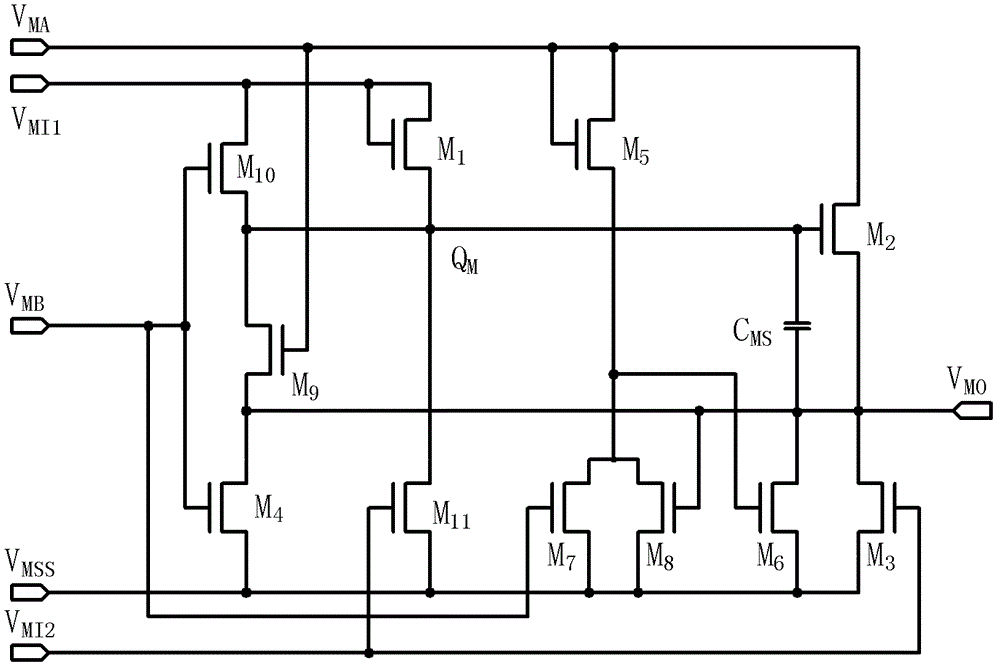
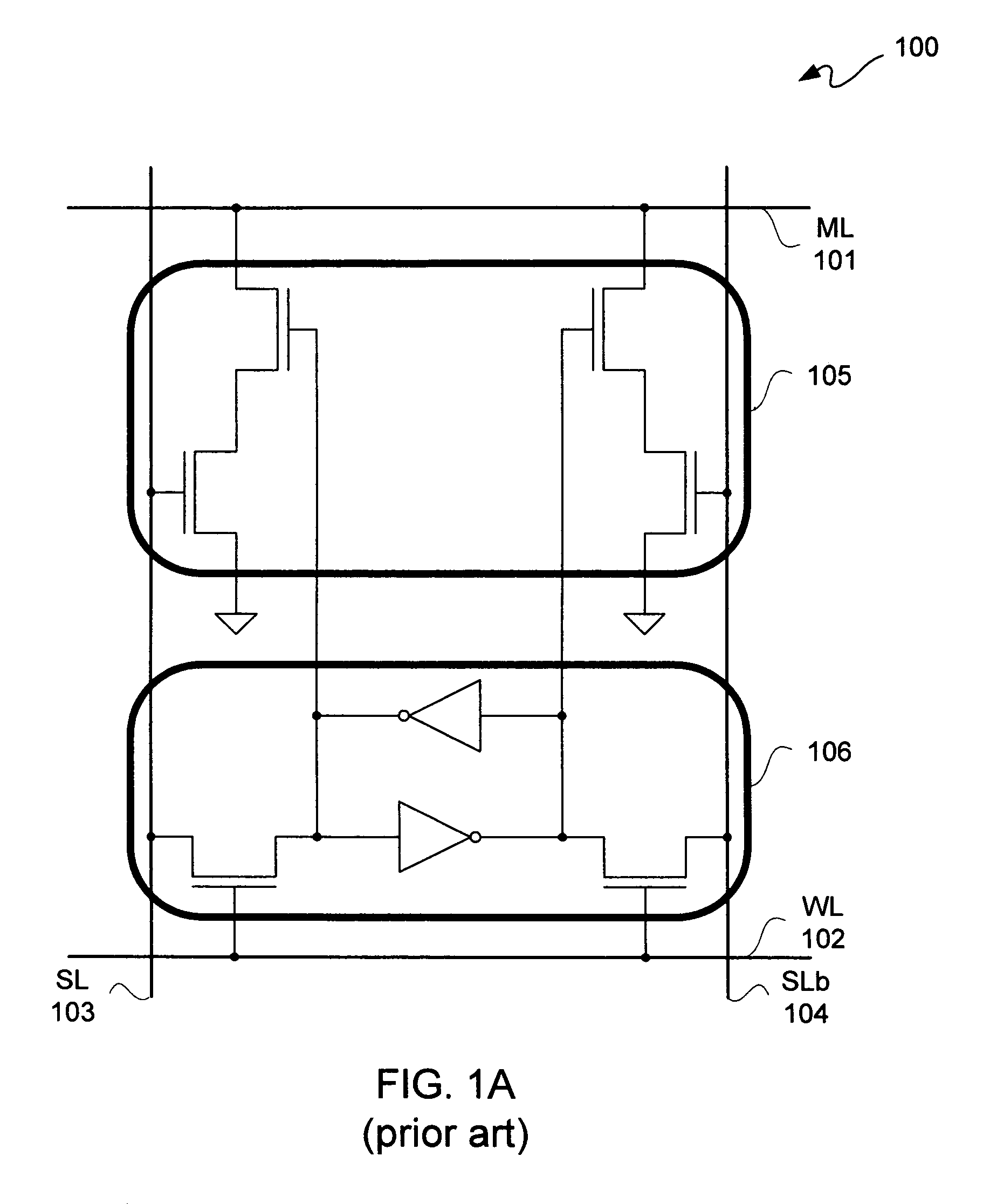
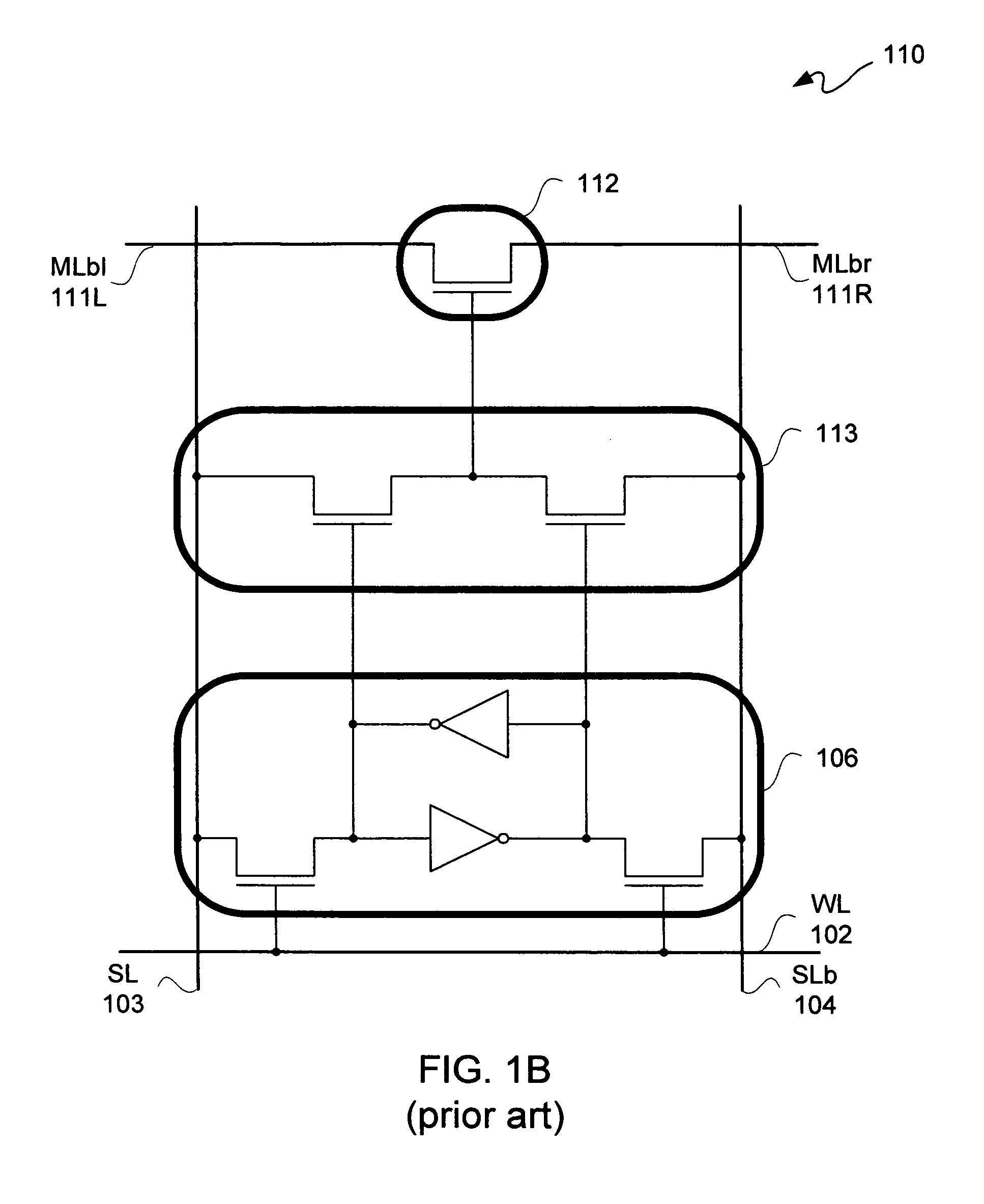
[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]
InactiveUS20050206629A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce dynamic power consumptionPulse automatic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage amplitudeLiquid-crystal display
A low-power-consumption source driver for a liquid crystal display is provided. Morethan one middle voltage level for the level shifter and the output buffer is provided, in addition to the power supply voltage level VDD and the ground level GND, to provide different voltage levels for image data of different polarities. Hence, amplitude of the operational voltage of the level shifters and the analog circuits with different polarities can be reduced. It also can reduce the amplitude of the operational voltage of the level shifter and can reduce significantly the dynamic power consumption of the level shifter and the DAC. Because the voltage amplitude of the circuit is reduced and a low-voltage tolerated device can be used, so that the present invention can further reduce the cost of the circuit.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
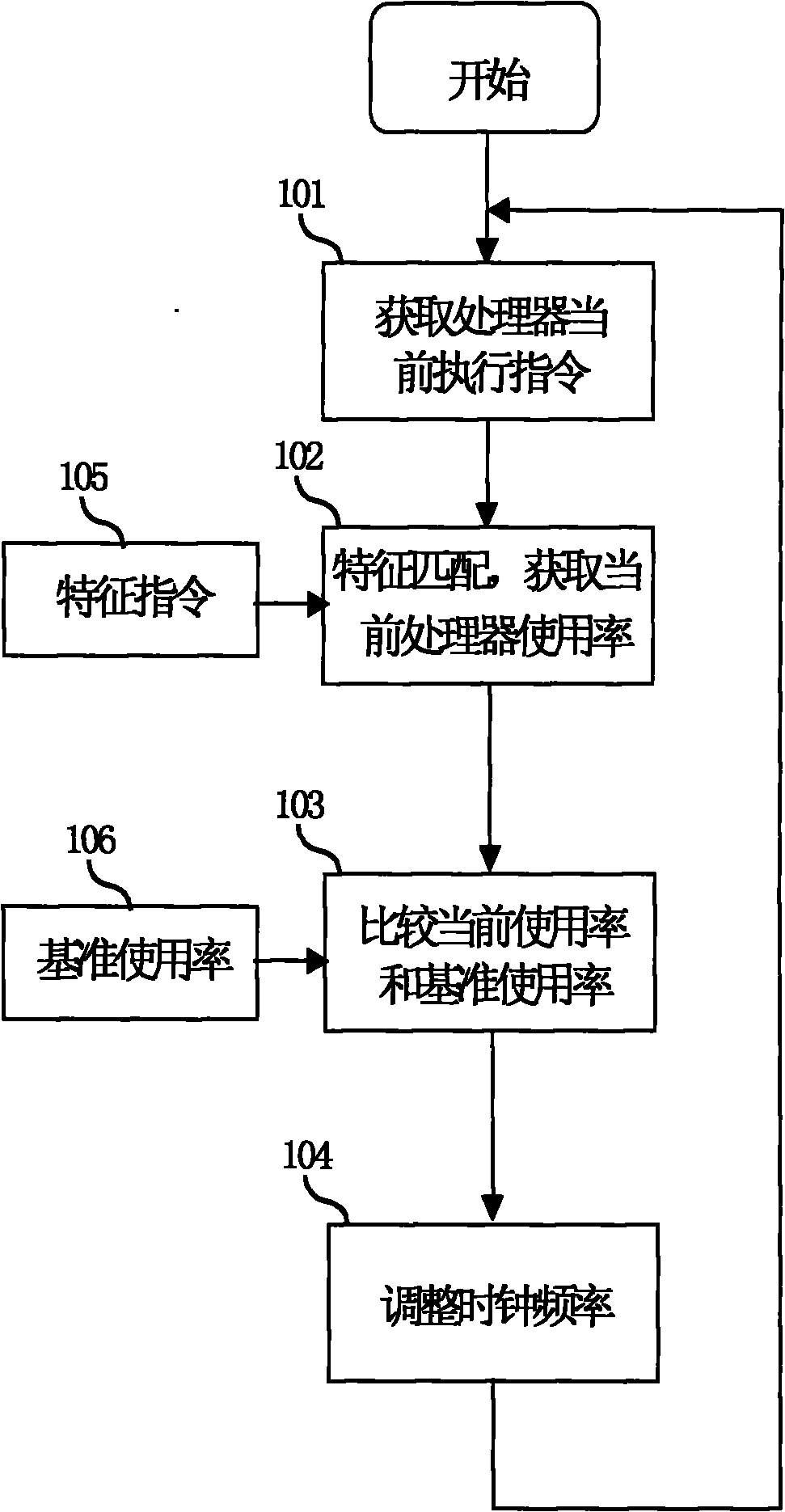
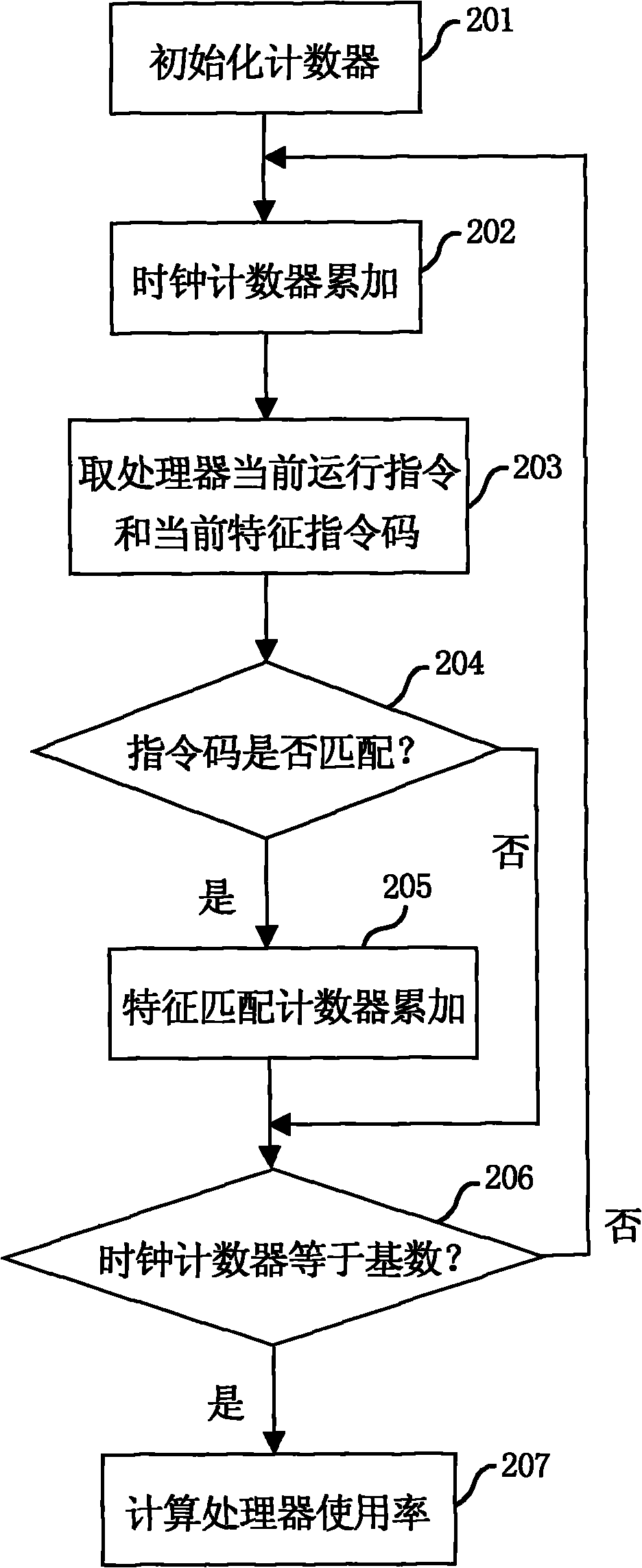
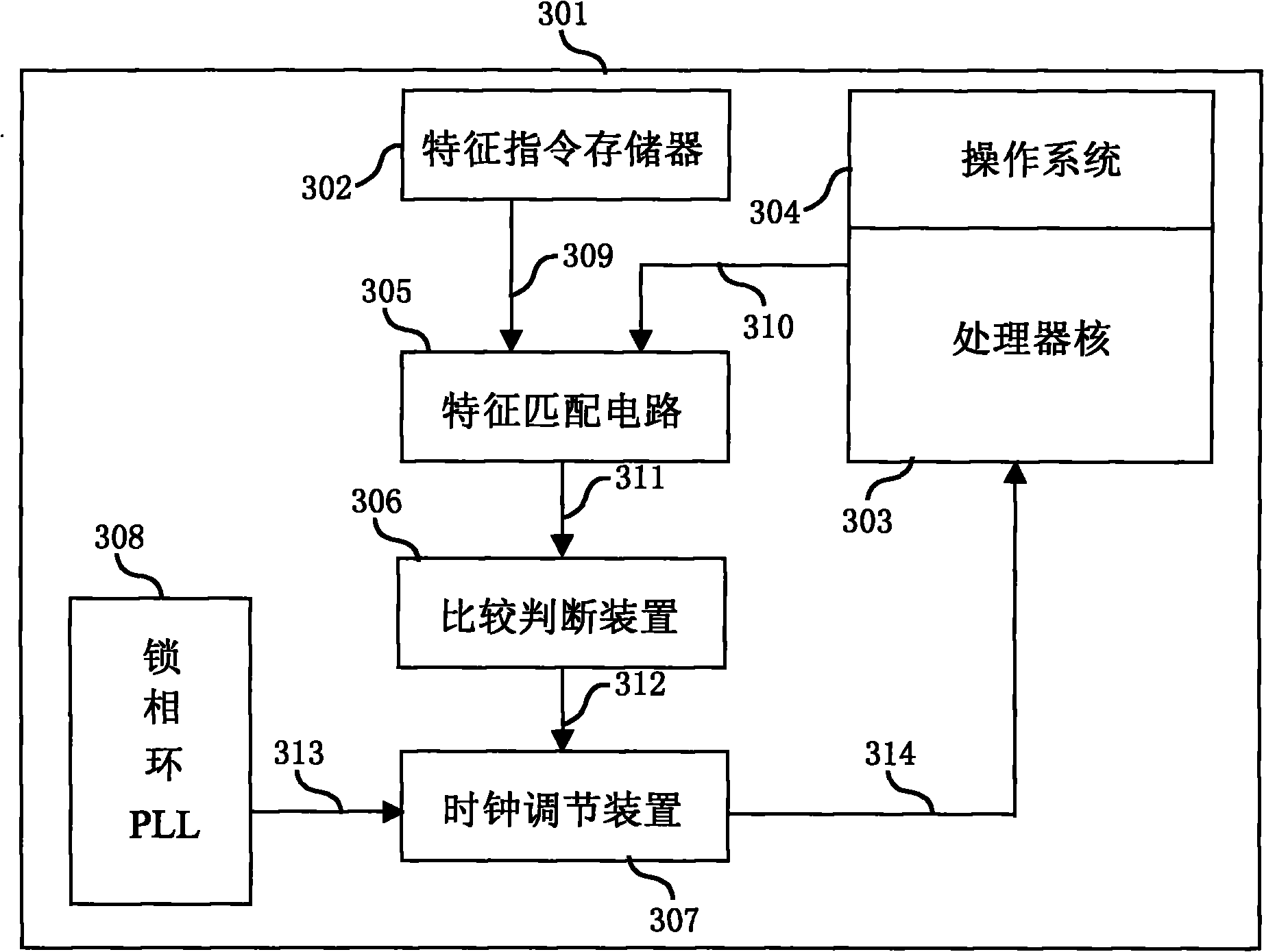
Method and device for automatically adjusting clock frequency of system in real time
InactiveCN101853066AReal-time adjustmentExtended service lifePower supply for data processingClock rateIntegrated circuit
The invention belongs to the field of integrated circuits and in particular relates to a method and a device for automatically adjusting the clock frequency or the power supply voltage of a processor system in real time. The method realizes automatic and real-time adjustment of the clock frequency or the power supply voltage of the processor system by a matching step, a judging step and an adjusting step. In the running process of a processor, the clock frequency or the power supply voltage of the processor system is automatically adjusted in real time, so that the processor runs with an optimal clock frequency or an optimal power supply voltage in real time. Therefore, normal running of the system is ensured and the power consumption of the processor can be effectively lowered.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINHAO MICROELECTRONICS
Slew rate controlled output buffer
InactiveUS6903588B2Control rateReduce degradationElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceCharge current
An output buffer includes first and second circuit portions coupled between input and output terminals. Each circuit portion includes a capacitive element; an output transistor having a gate coupled to the capacitive element, and a drain that drives a voltage at the output terminal; and a current generator configured to generate a charging current that is directed to the capacitive element responsive to a logic transition at the input terminal, wherein the charging current causes a substantially linear ramp voltage to form at the gate of the output transistor, whereby the ramp voltage controls a slew rate of the output terminal voltage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
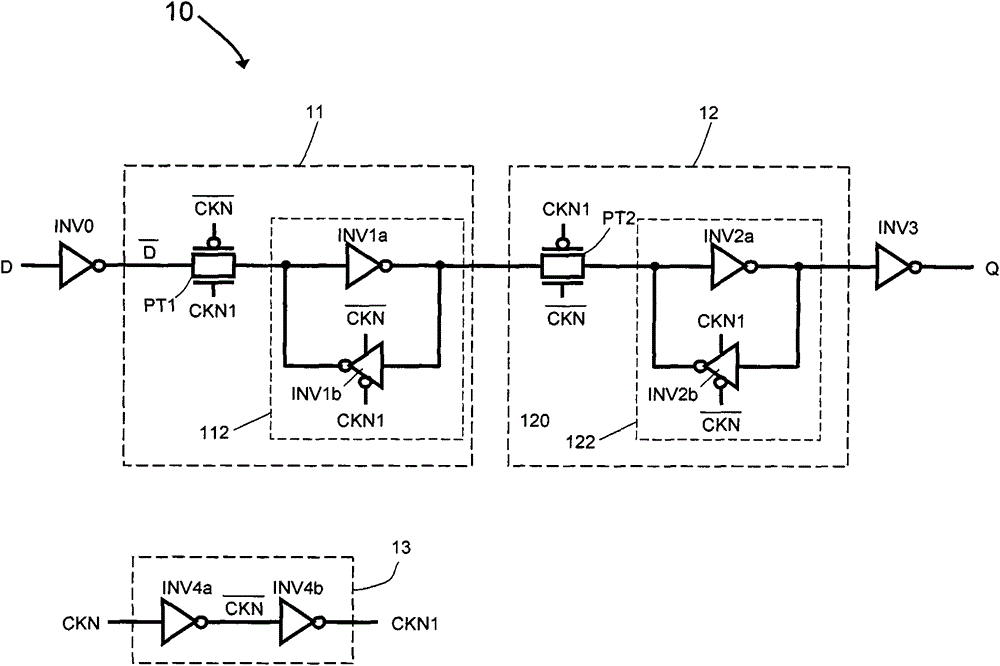
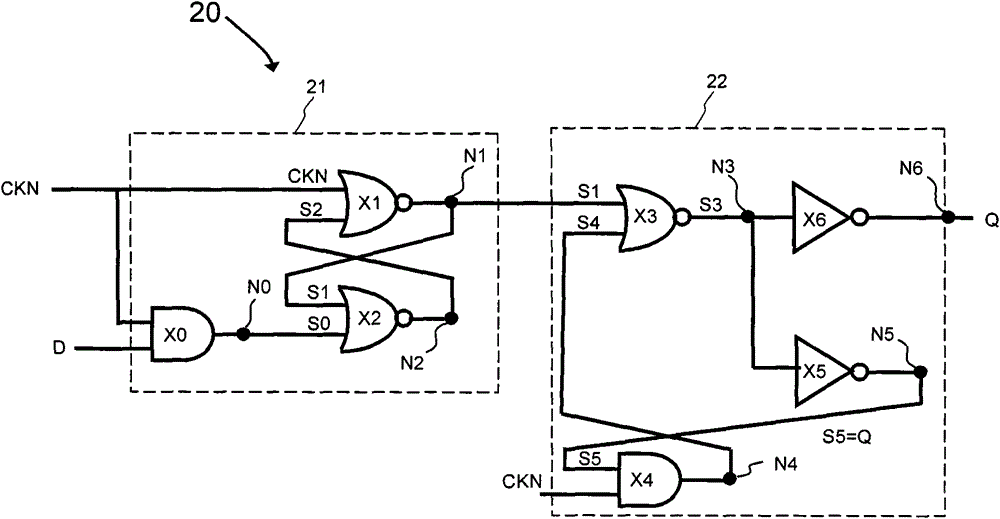
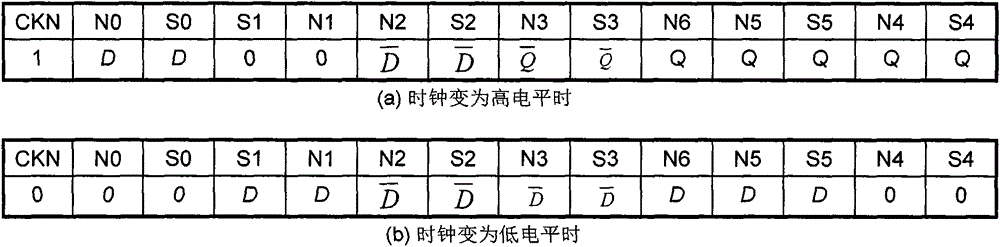
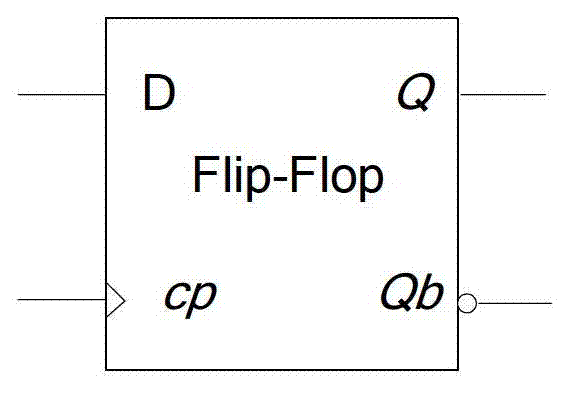
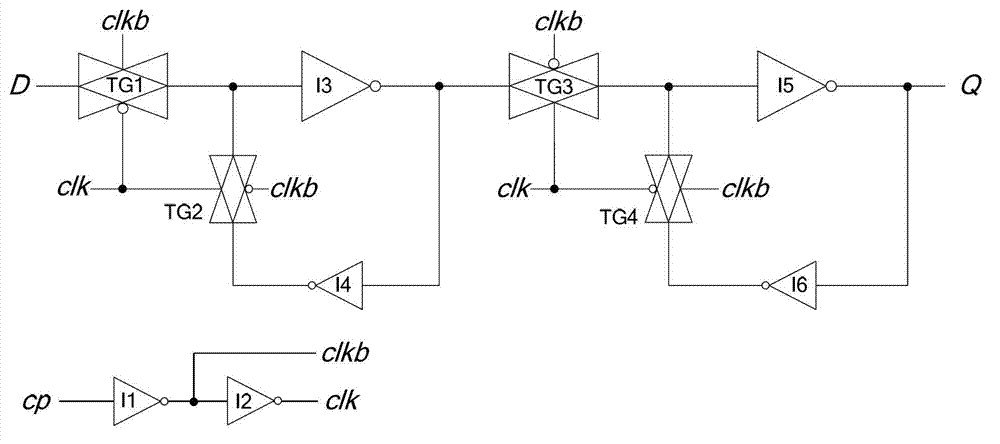
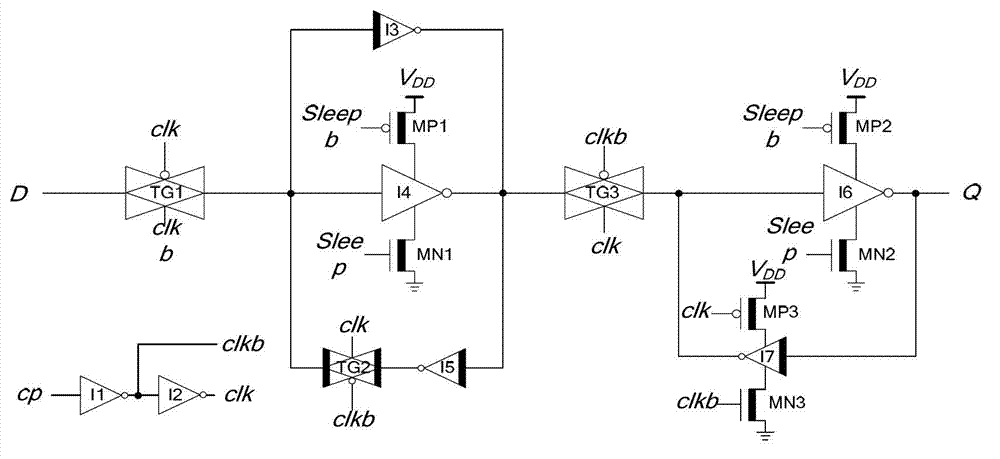
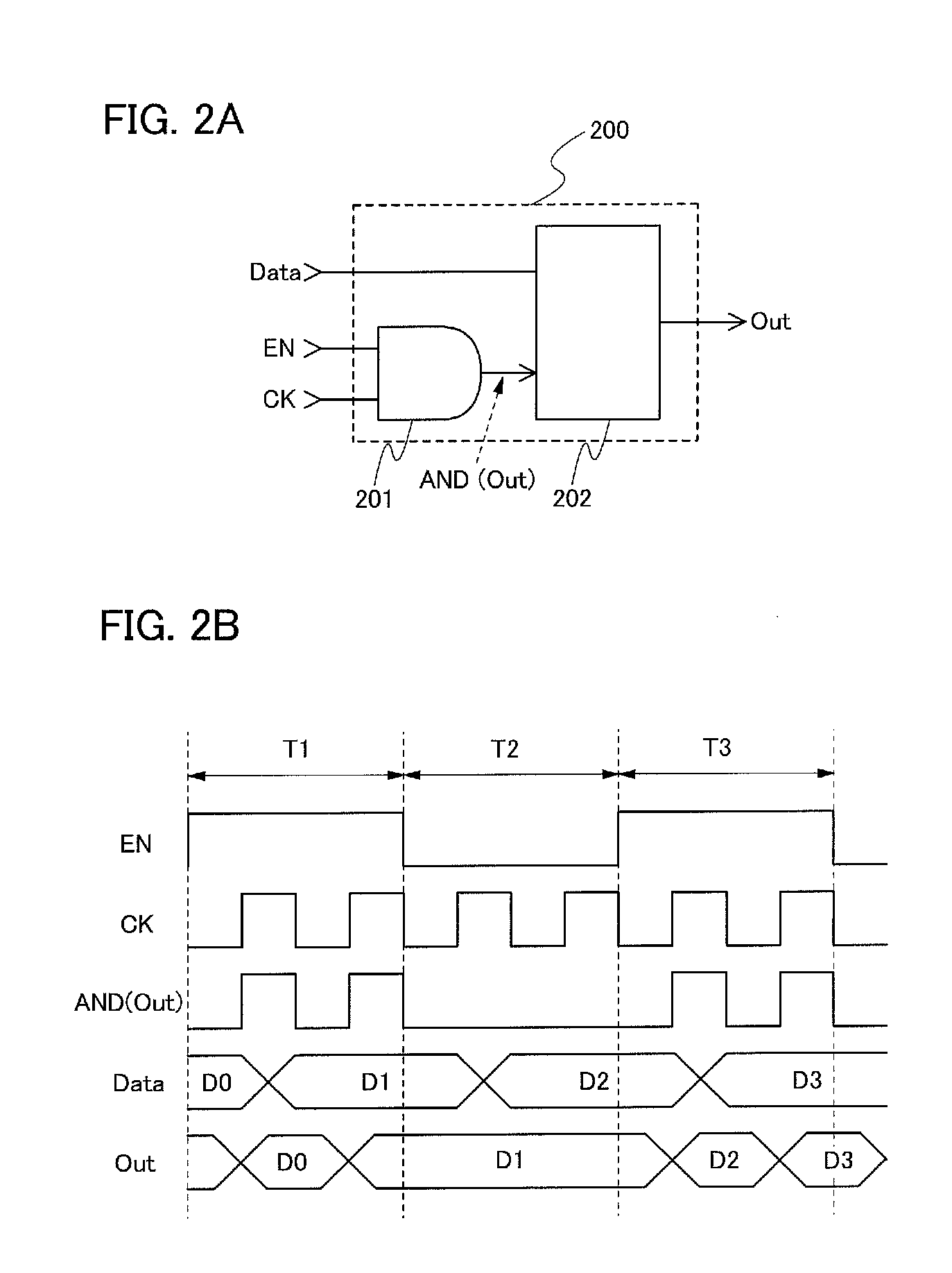
Flip-flop circuit
ActiveCN104796132ASimple structureReduce dynamic power consumptionLogic circuitsNOR logicData signal
The invention provides a flip-flop circuit, and belongs to the technical field of semiconductor integrated circuits. The flip-flop circuit comprises a master latch and a secondary latch driven by clocking signals with same phases; the master latch comprises a first logic module for selectively and at least performing AND logic processing on an input data signal and the clock signal, a second logic module for at least performing NOR logic processing on the clock signal and an output signal of a third logic module, and the third logic module for selectively and at least performing the NOR logic processing on the output signal of the first logic module and the output signal of the second logic module so as to output a result to the second logic module; the secondary latch comprises a fourth logic module for at least performing the NOR logic processing on the output signal of the second logic module and the output signal of a fifth logic module, and the fifth logic module for at least performing the AND logic processing on the clock signal and an inversion signal of the output signal of the fourth logic module. The flip-flop circuit is low in dynamic power consumption.
Owner:陈祺琦
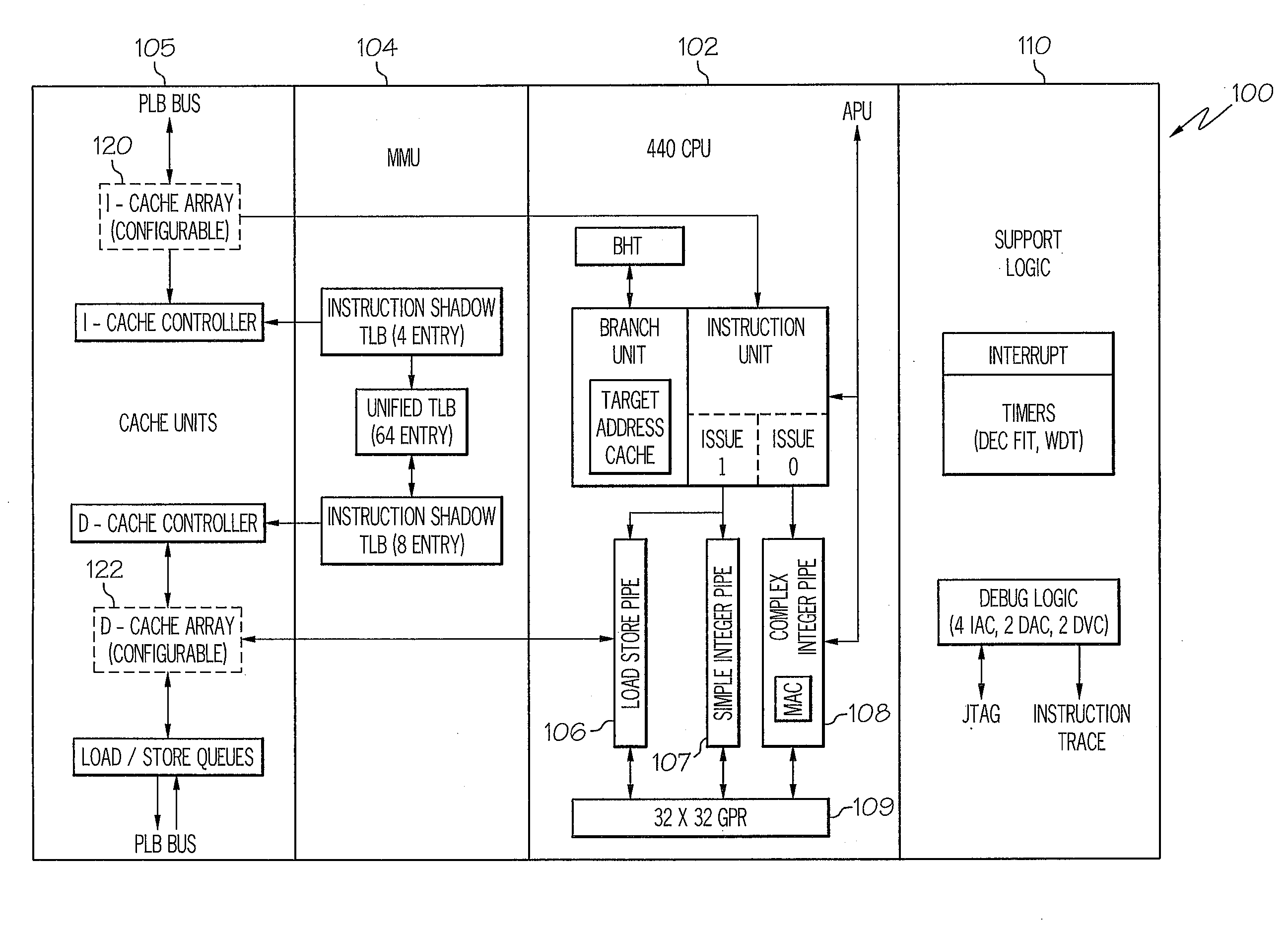
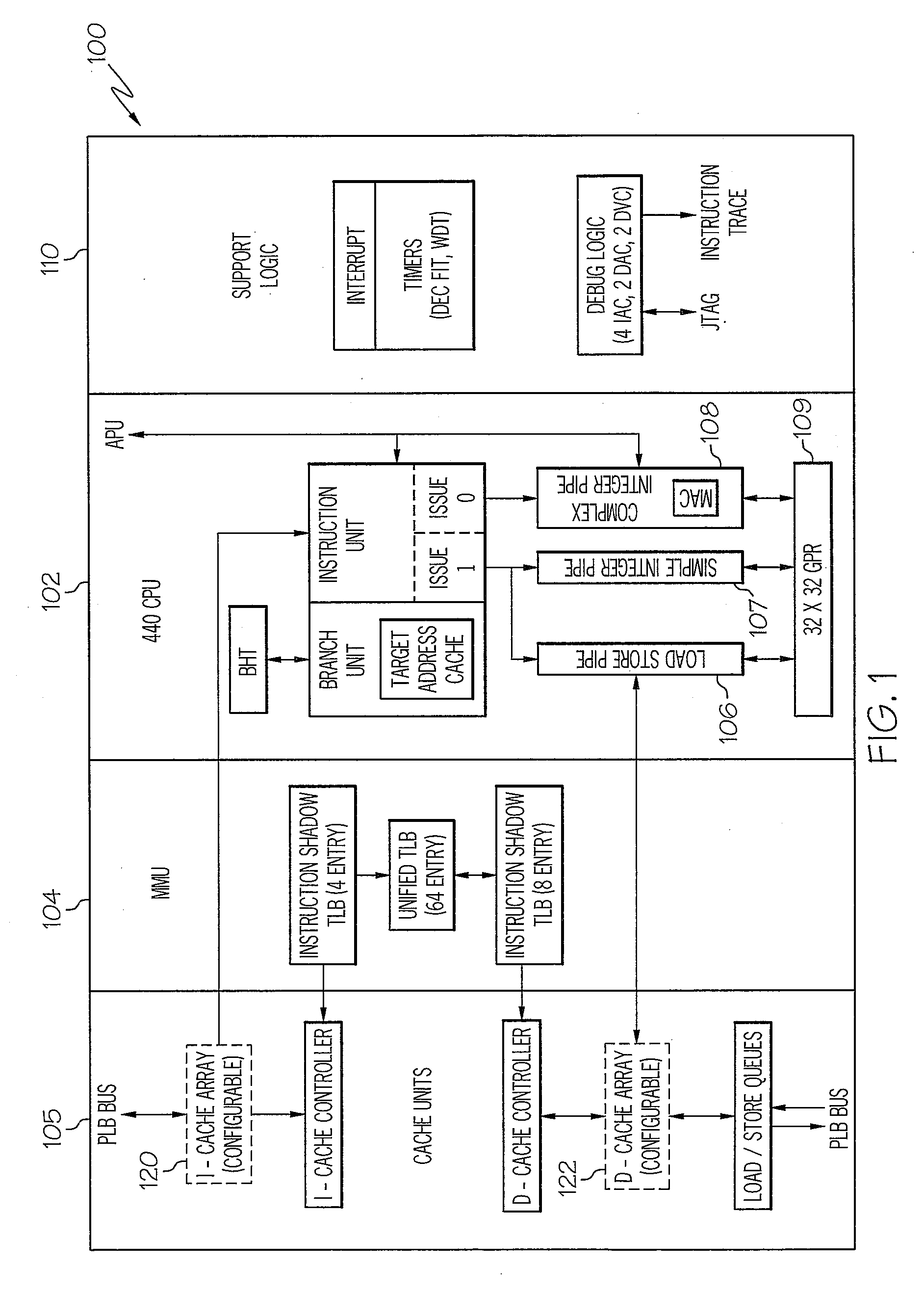
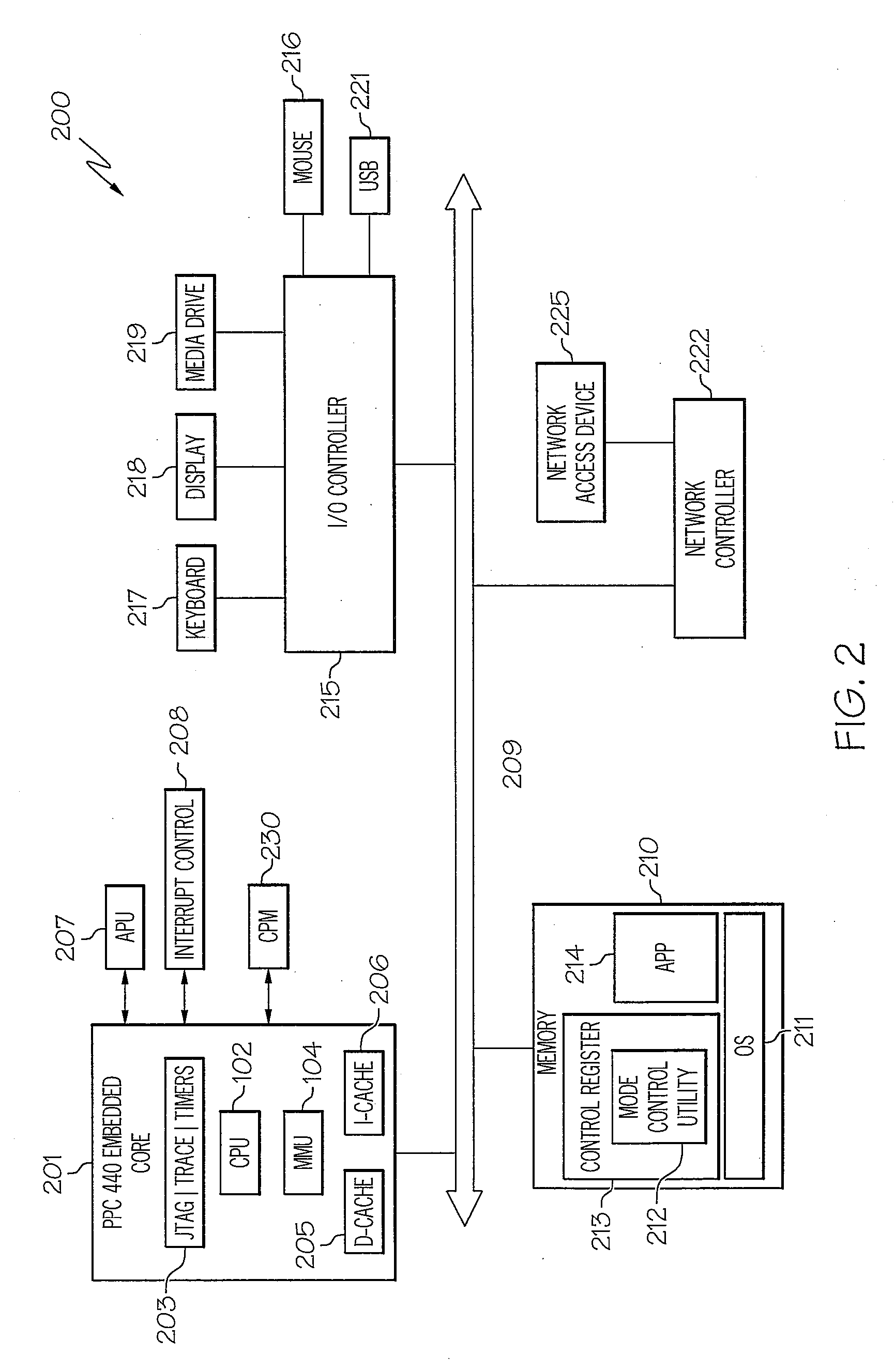
Adaptive execution frequency control method for enhanced instruction throughput
InactiveUS20090019265A1Improve CPU throughputReduce CPU dynamic power usageEnergy efficient ICTInstruction analysisCompilerSoftware
A method, system and processor for adaptively and selectively controlling the instruction execution frequency of a data processor. Processing logic or a software compiler determines when a number of first-type instructions, requiring longer execution latency, are scheduled to be executed. The logic / compiler then triggers the CPM unit to automatically switch the execution frequency of the instruction processor from a first frequency that is optimal for processing regular-type instructions to a second, pre-established lower frequency that is optimal for processing the first-type instructions, to enable more efficient execution and higher execution throughput of the number of first-type operations within the processor. When the first-type instructions have completed execution, the processor's instruction execution frequency is returned to the first optimal frequency.
Owner:IBM CORP
High-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop
InactiveCN103199823ASimple structureLow transistor countElectric pulse generatorLow leakageEngineering
The invention discloses a high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop. The high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop is characterized by comprising a clock signal inverter circuit, a master latch circuit, a slave latch circuit, an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) pipe power control switch, a P-channel Metal Oxide Semiconductor (PMOS) pipe power control switch and a maintaining inverter. The clock signal inverter circuit is connected with the master latch circuit, the clock signal inverter circuit is connected with the slave latch circuit, the master latch circuit is connected with the slave latch circuit, the slave latch circuit is connected with the maintaining inverter, the maintaining inverter is connected with the PMOS pipe power control switch, the clock signal inverter circuit, the master latch circuit and the slave latch circuit are all connected with the NMOS pipe power control switch, and the maintaining inverter is connected with the PMOS pipe power control switch. The high-performance low leakage power consumption master-slave type D flip-flop has the advantages of being simple in circuit structure, small in the number of transistors, simple in timing sequence switching of a normal working state and a sleep mode, good in working performance, low in dynamic power consumption and leakage power consumption, and suitable for being used as a standard cell of a digital circuit to be applicable to the design of a low power consumption integrated circuit in deep submicron complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor transistor (CMOS) process.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
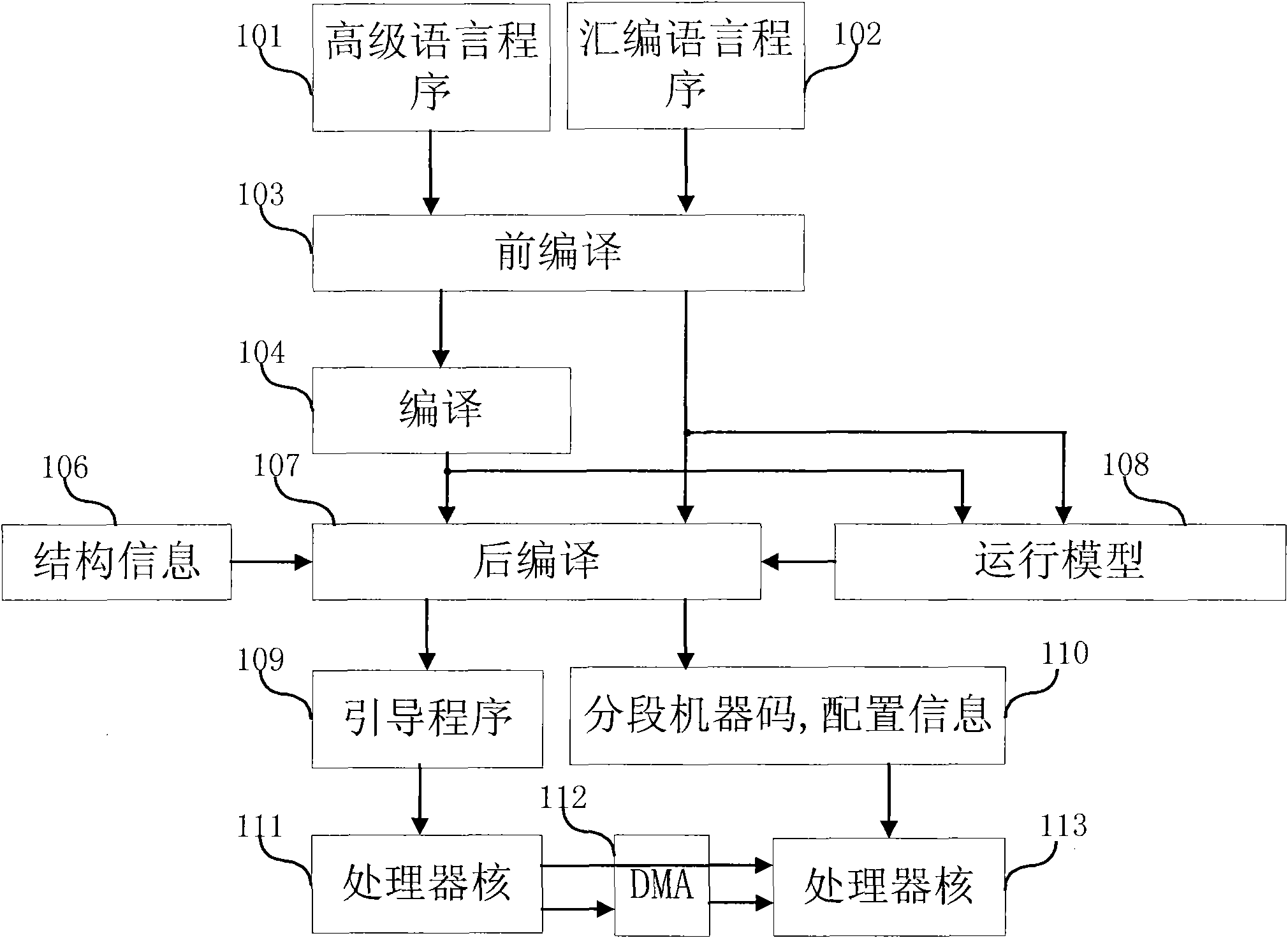
Data processing method and device
ActiveCN101799750AIncrease profitImplement multiple launchesResource allocationConcurrent instruction executionProduction lineParallel computing
The invention relates to a data processing method and a device. Program codes running on a serially connected multiprocessor nuclear structure are partitioned according to specific rules, so that the serially connected multiprocessor nuclear structure forms a serial multi-emitting and production line layered structure, and the time required for running corresponding code fragments obtained by partitioning on each nucleus is equal as much as possible, thereby realizing the load balance of internuclear workload.
Owner:SHANGHAI XINHAO MICROELECTRONICS
Storing system of integrated video decoder
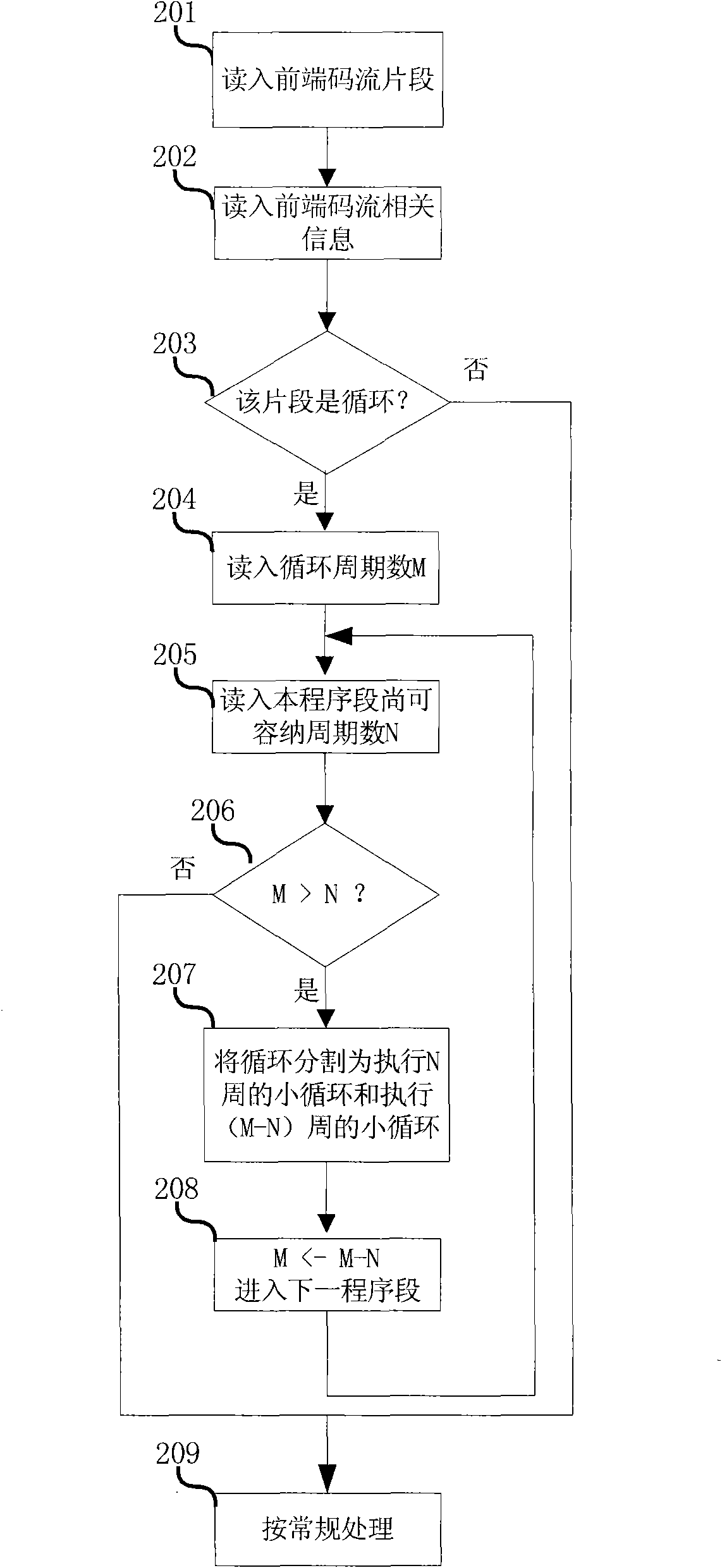
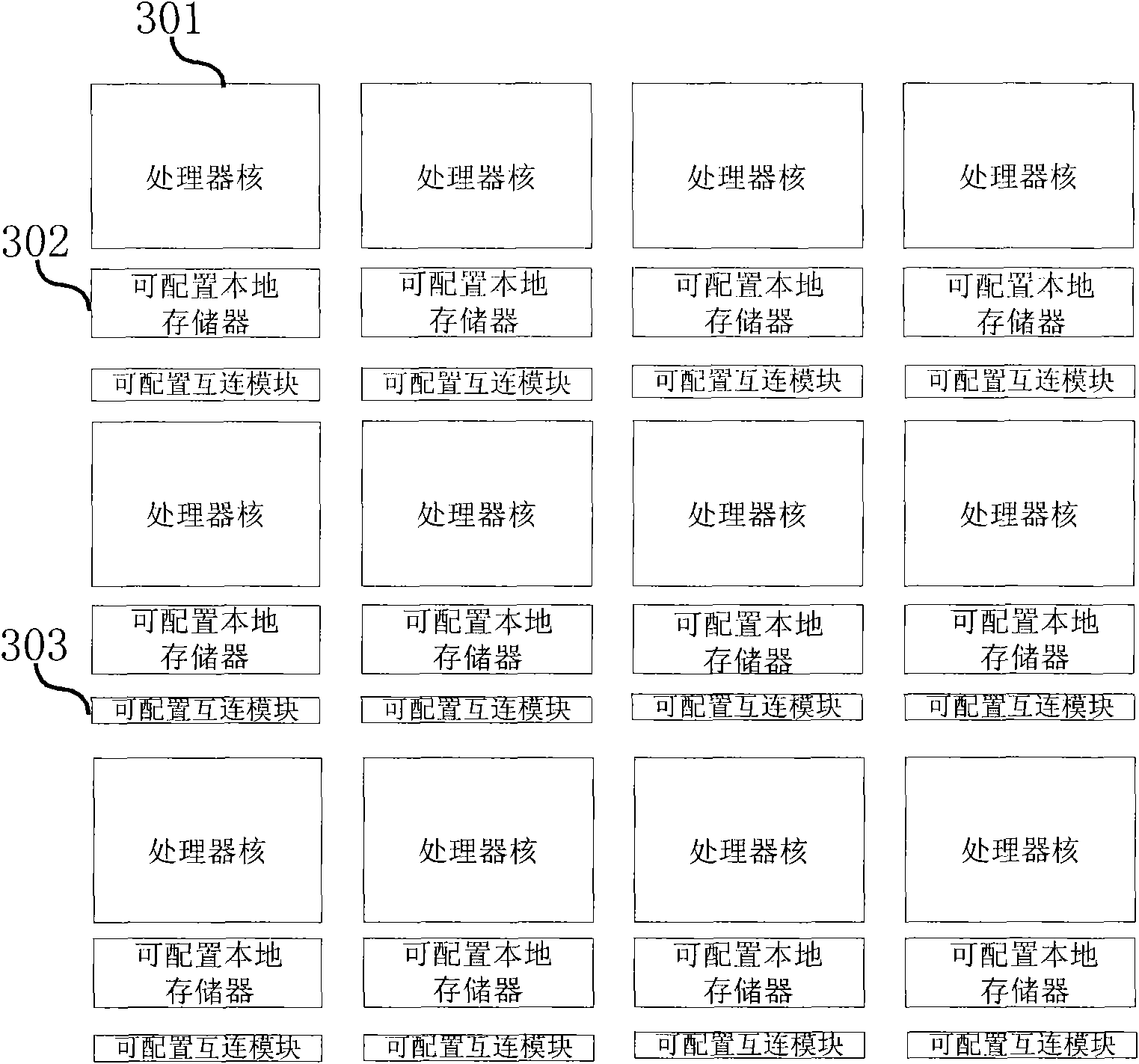
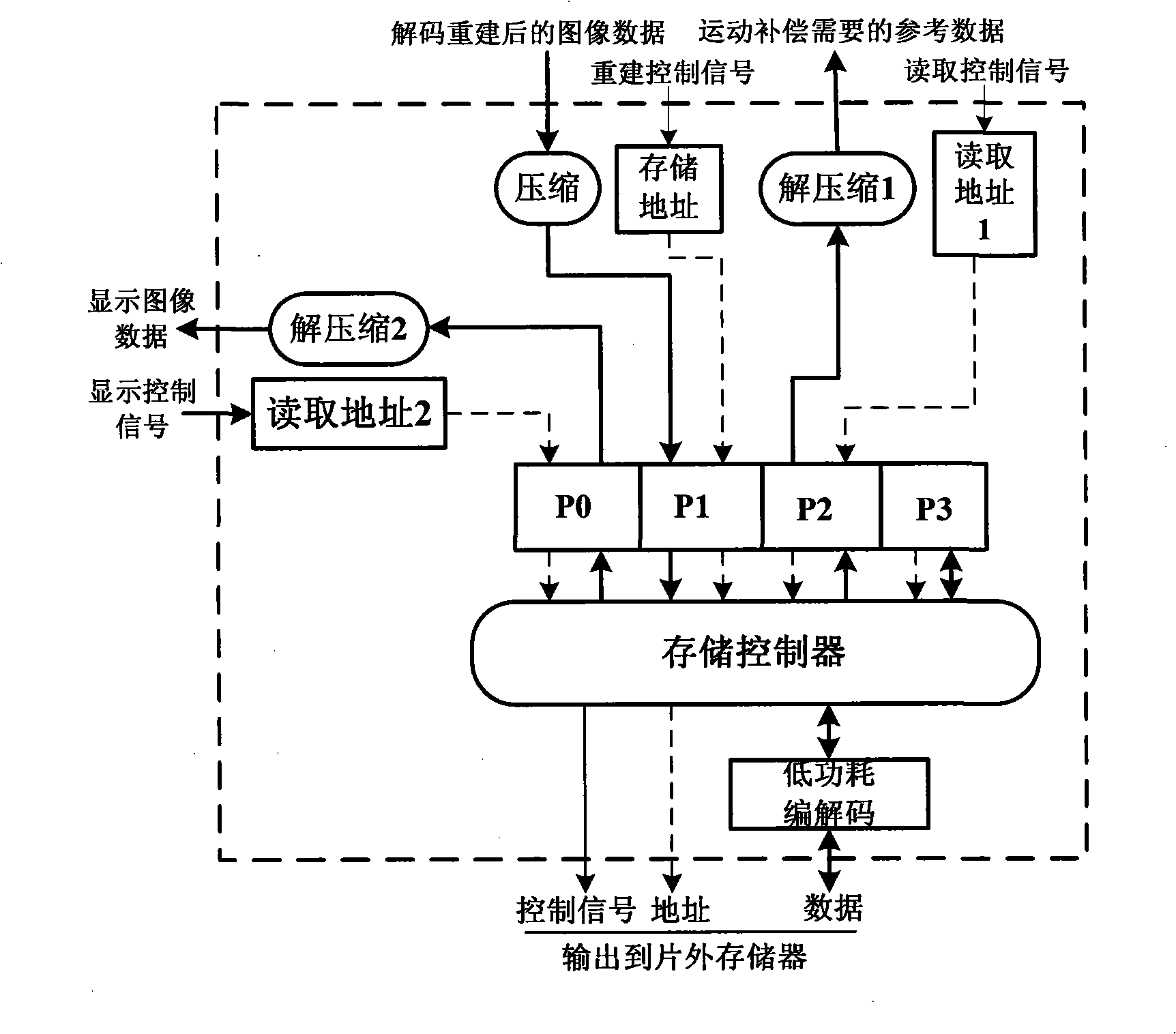
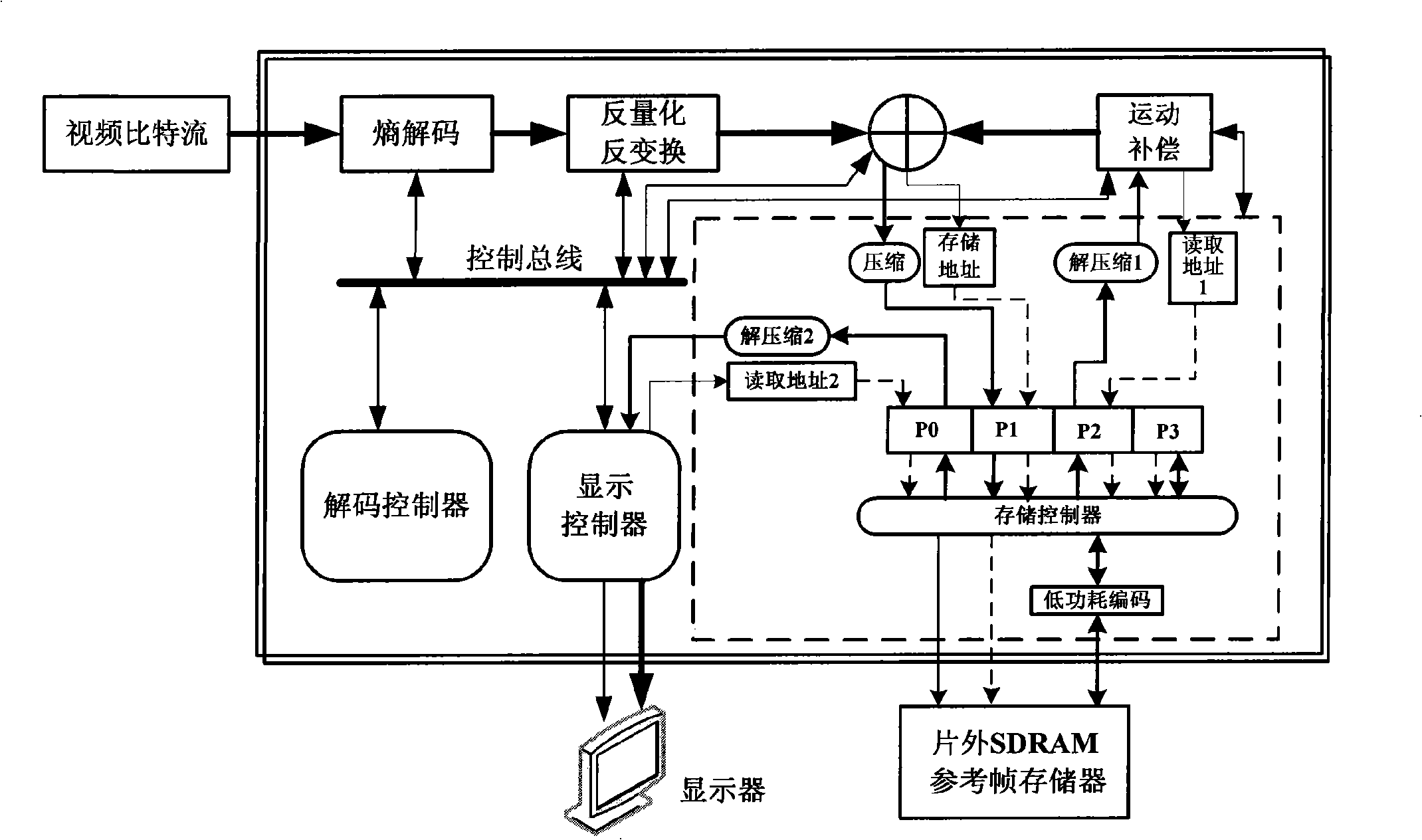
InactiveCN101527849AReduce dynamic power consumptionReduce power consumptionTelevision systemsDigital video signal modificationControl storeData exchange
The invention provides a storing system of an integrated video decoder, which can lower the power consumption and belongs to the decoder storing management field based on video coding and decoding standard of block. The storing system is characterized in that a compression module is used for the re-compression of reconstructed data, and the decompression is respectively carried out when reference data is read and displayed to reduce the data exchange amount of the decoder and a katanto memory; a storing address generating module is used for preparing a reasonable reference frame storing mapping structure to reduce row activation operation times required during a reading and writing process; a storing controller based on four storing signal ports structure is used for reducing the on-chip memory of the decoder and improving the bandwidth of the memory; the low power consumption coding and decoding is used for the low power consumption coding of stored contents. Static power consumption generated due to the leakage in the memory is lowered.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Clock Gating System and Method
ActiveUS20090267649A1Reduce power consumptionReduced footprintPower reduction by control/clock signalGenerating/distributing signalsEngineeringLogic circuitry
A clock gating system and method is disclosed. In a particular embodiment, the system includes an input logic circuit having at least one input to receive at least one input signal and having an output at an internal enable node. A keeper circuit includes at least one switching element that is responsive to a gated clock signal and is coupled to the internal enable node to selectively hold a logical voltage level at the internal enable node. The system further includes a gating element responsive to an input clock signal and to the logical voltage level at the internal enable node to generate the gated clock signal.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Source driver and liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS7292217B2Reduce the amplitudeReduce dynamic power consumptionPulse automatic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage amplitudeLiquid-crystal display
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Touch Sensor Detector System and Method
ActiveUS20150091857A1High resolutionImprove sensor performanceInput/output processes for data processingElectricitySensor array
A touch sensor detector system and method incorporating an interpolated sensor array is disclosed. The system and method utilize a touch sensor array (TSA) configured to detect proximity / contact / pressure (PCP) via a variable impedance array (VIA) electrically coupling interlinked impedance columns (IIC) coupled to an array column driver (ACD), and interlinked impedance rows (IIR) coupled to an array row sensor (ARS). The ACD is configured to select the IIC based on a column switching register (CSR) and electrically drive the IIC using a column driving source (CDS). The VIA conveys current from the driven IIC to the IIC sensed by the ARS. The ARS selects the IIR within the TSA and electrically senses the IIR state based on a row switching register (RSR). Interpolation of ARS sensed current / voltage allows accurate detection of TSA PCP and / or spatial location.
Owner:SENSEL
Method and apparatus for on-the-fly minimum power state transition
InactiveUS20080238494A1Reduce power consumptionMinimum area overheadElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionNormal modeLow leakage
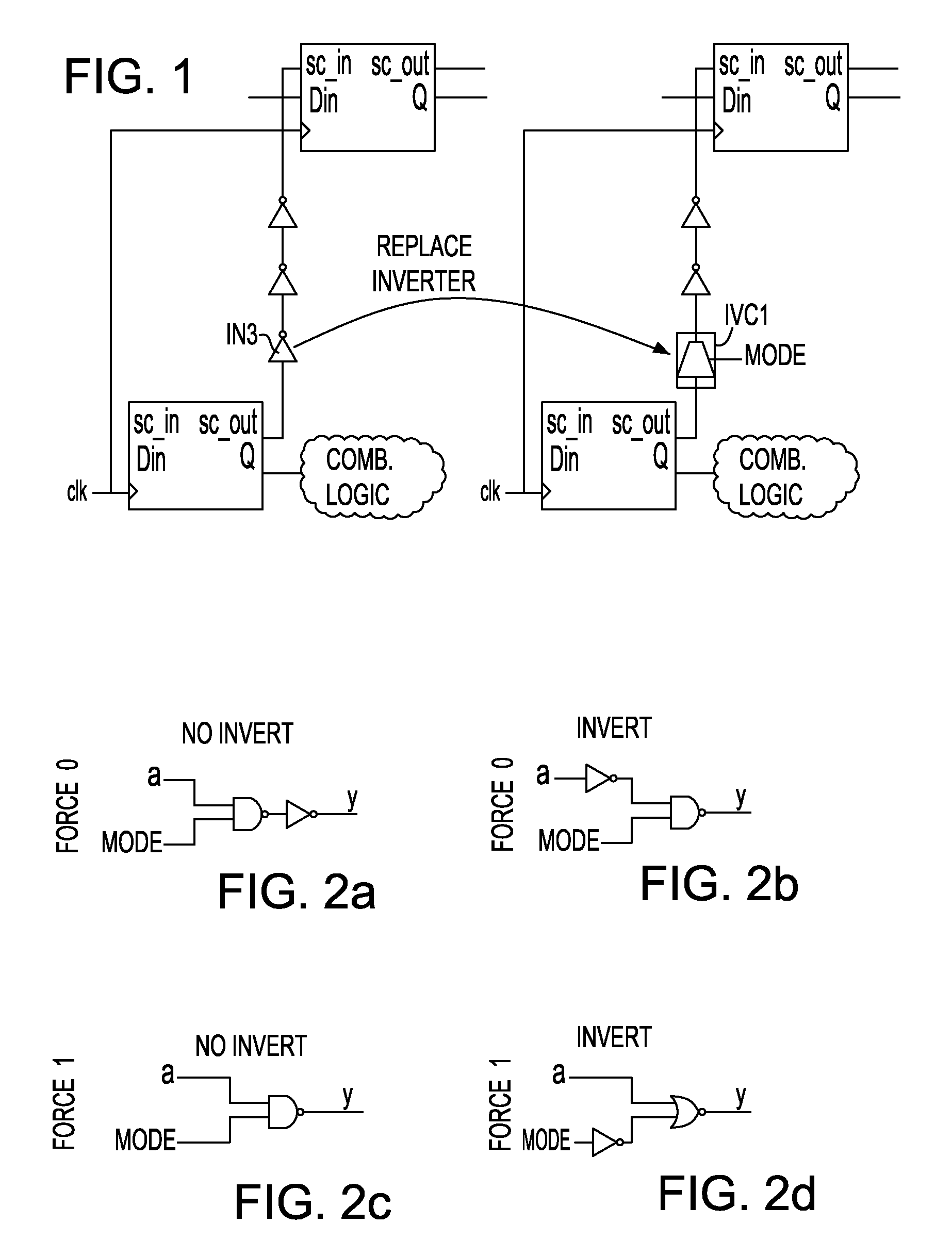
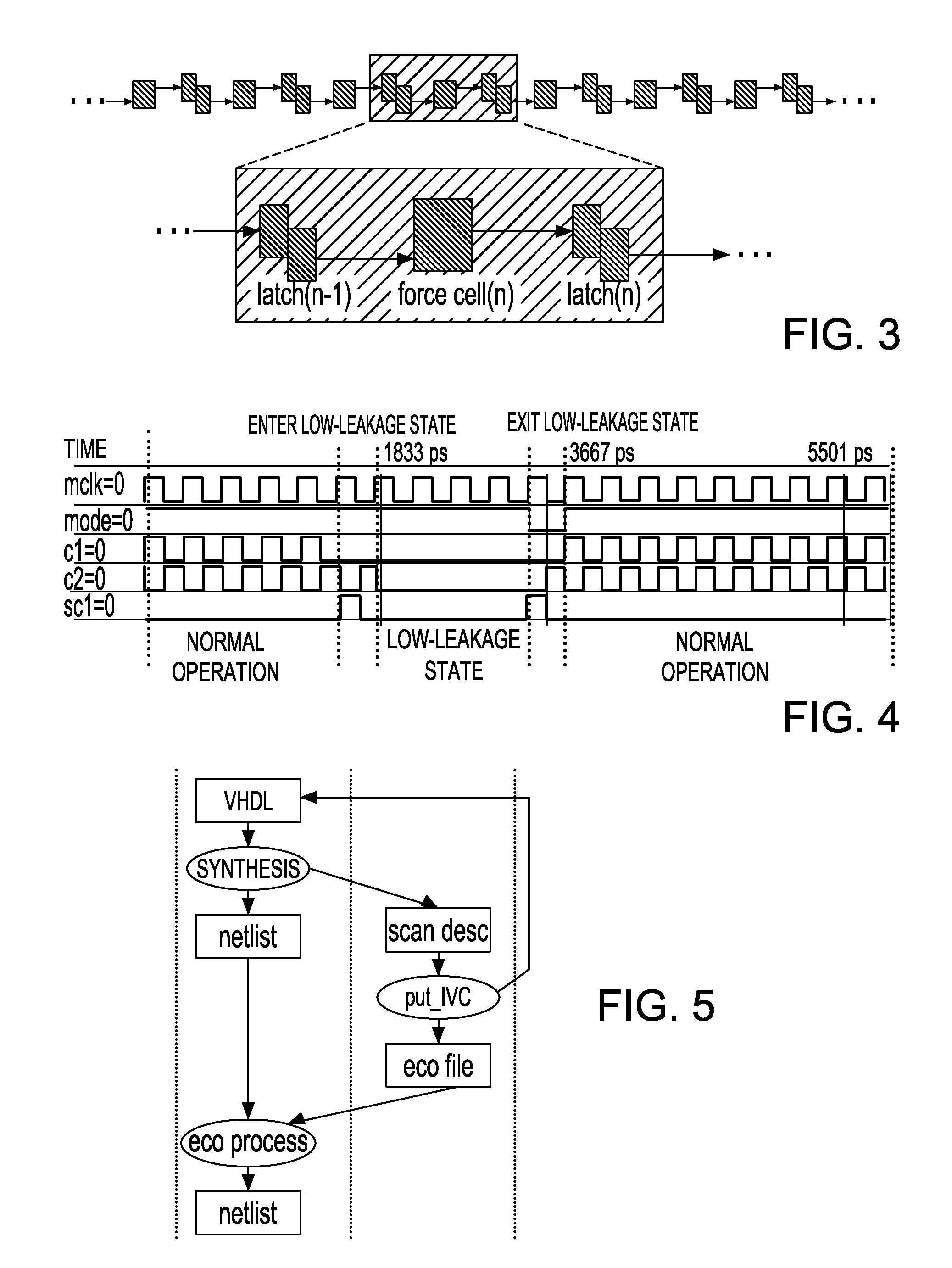
The invention includes a novel scan chain structure for LSSD or GSD IC operation. The scan chain structure includes a first flip-flop (L1) and a second flip-flop (L2) configured to operate the first flip-flop (L1) in normal mode operation, in scan mode operation, in initialization mode and in low leakage power mode operation, wherein each flip-flop within a long scan chain of latches includes a data input, data output, a clock input, a scan-in input and a scan-out output, arranged for normal mode operation. A buffer circuit is electrically connected between the scan-out output of the second flip-flop (L2) and the scan-in input of the first flip-flop (L1) for the next latch in the scan chain, the buffer circuit including a control element that controls the operation the first flip-flop (L1) to scan mode or low power leakage mode. The first flip-flop (L1) is set to a data output value upon exit from low power leakage mode that is the same value that it is set to at initialization during normal mode operation. The switching occurs in only one clock cycle.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Low power consumption static random memory with low level thread amplitude of oscillation
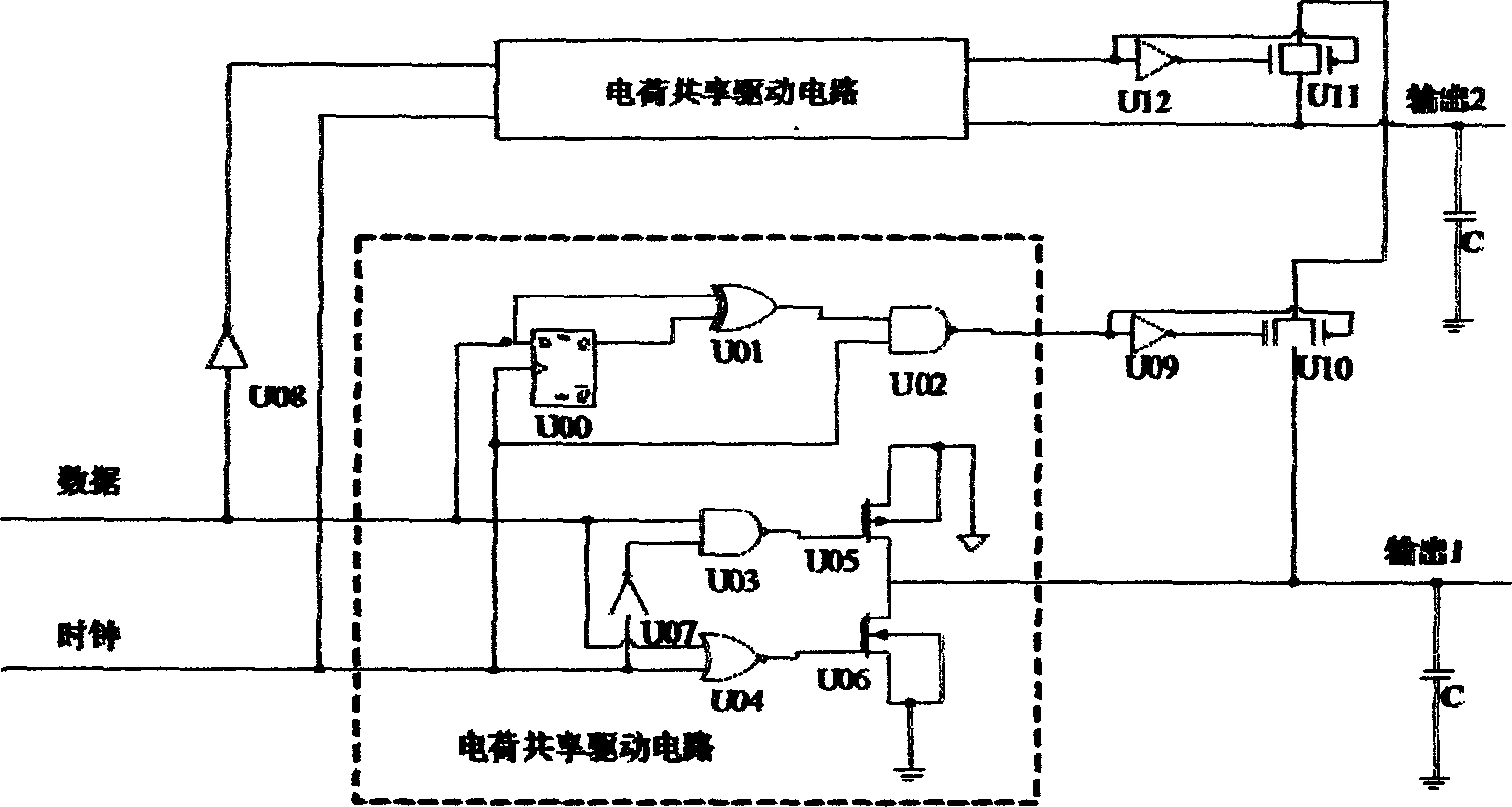
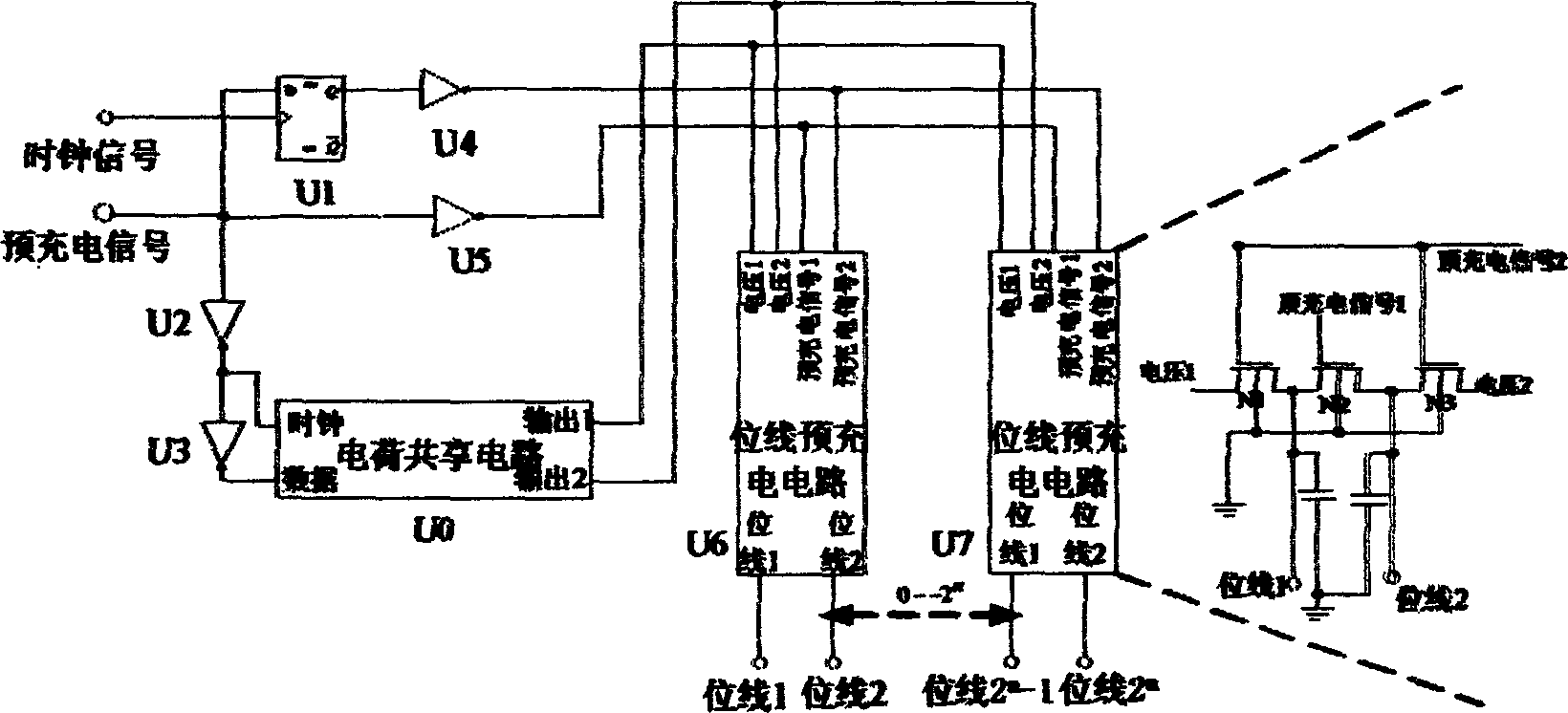
Disclosed is a low power consumption static random memory with low level thread amplitude of oscillation, wherein the memory comprises a pre-charging circuit based on electric charge sharing, a memory unit, a line decoder, a row decoder, a selector, a read-write control circuit, a sensitive amplifier and an input processing circuit, wherein the bit line end of the pre-charging circuit is connected to the bidirectional port of the selector, the output end of the input treatment circuit is connected with the input end of the sensitive amplifier and the selector.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Slew rate controlled output buffer
InactiveUS20050162191A1Control rateReduce degradationVoltage/current interference eliminationLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsCapacitanceCharge current
An output buffer includes first and second circuit portions coupled between input and output terminals. Each circuit portion includes a capacitive element; an output transistor having a gate coupled to the capacitive element, and a drain that drives a voltage at the output terminal; and a current generator configured to generate a charging current that is directed to the capacitive element responsive to a logic transition at the input terminal, wherein the charging current causes a substantially linear ramp voltage to form at the gate of the output transistor, whereby the ramp voltage controls a slew rate of the output terminal voltage.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com





![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00000.png)
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00001.png)
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00002.png)