Field effect transistor and application device thereof
A field effect transistor, conductive type technology, applied in the field of field effect transistors and their application devices, can solve problems such as unpredictable
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
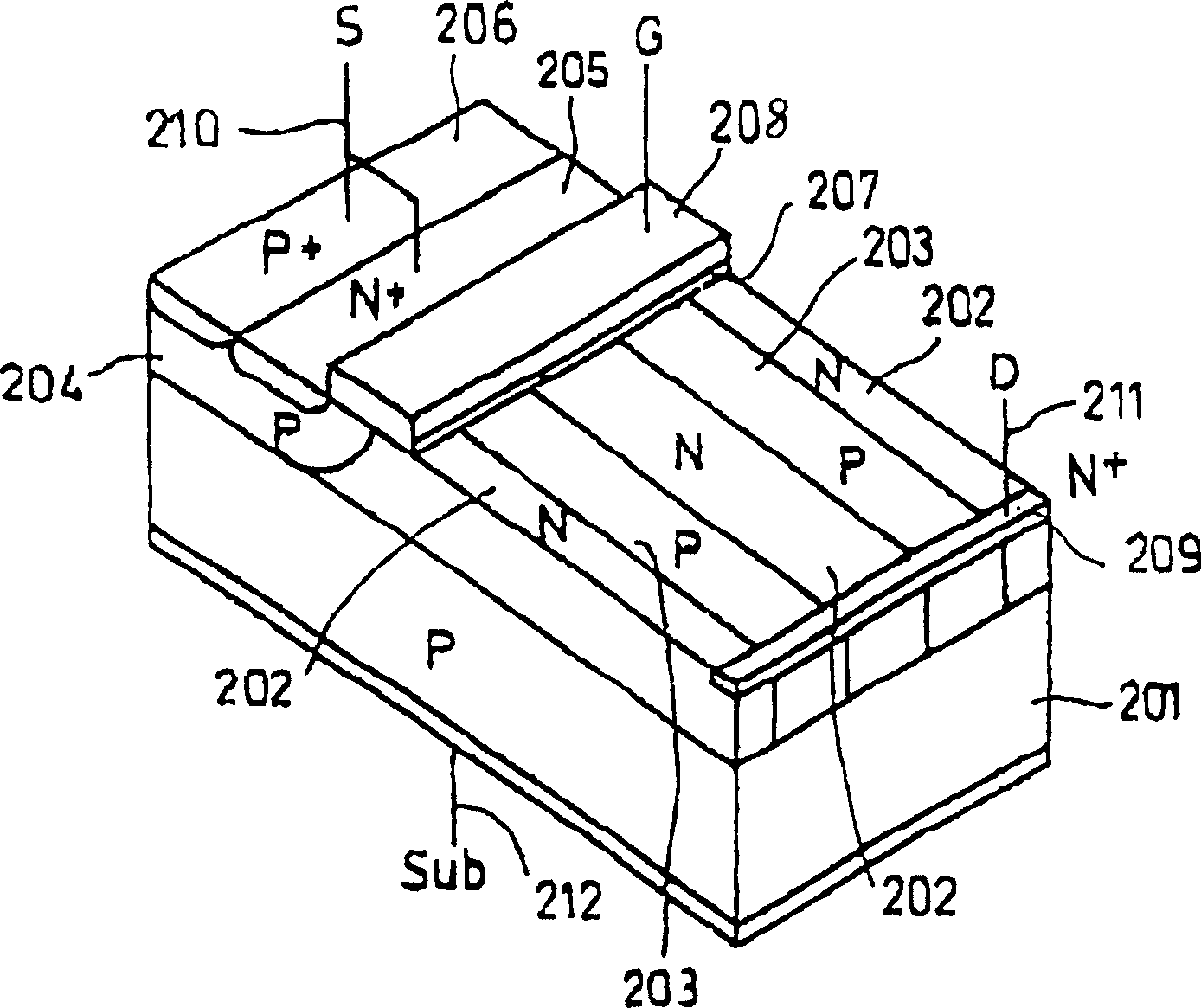
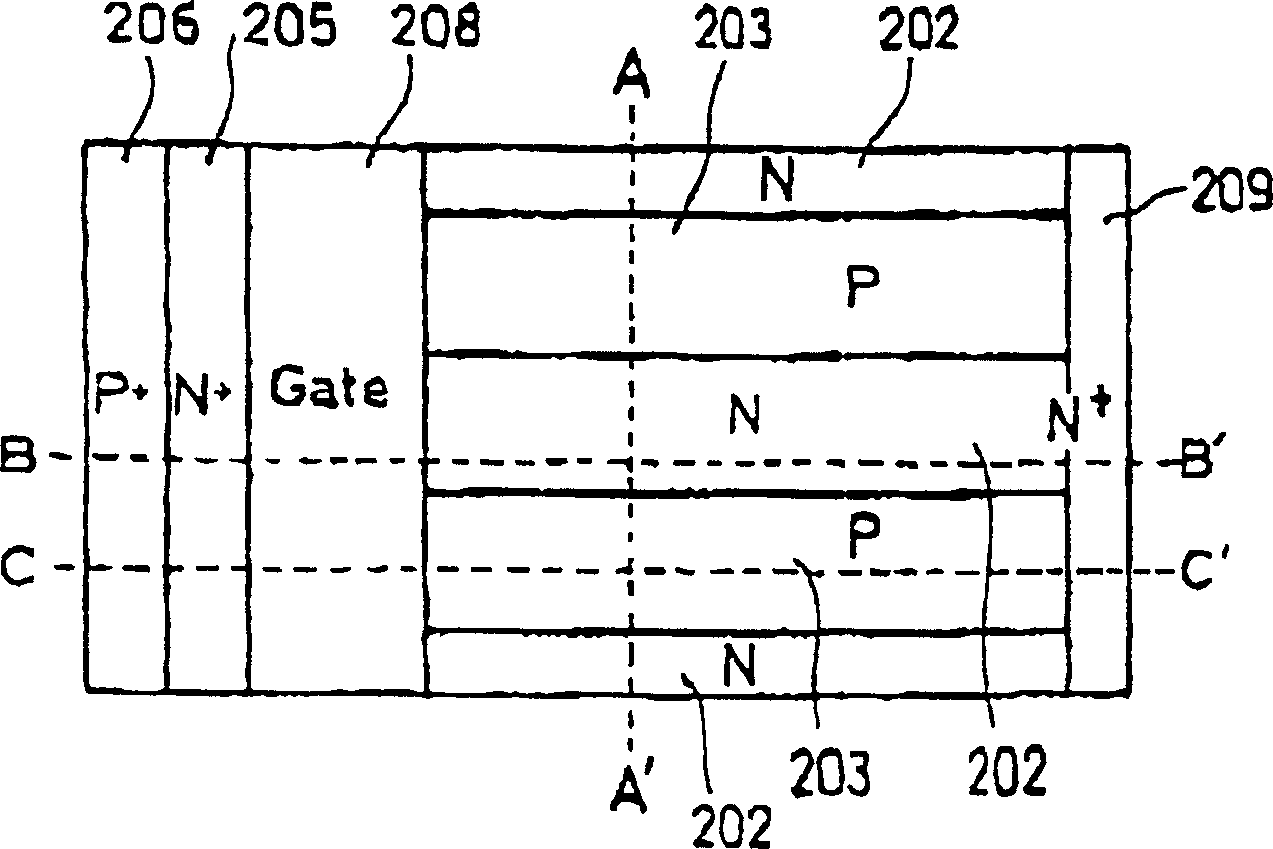
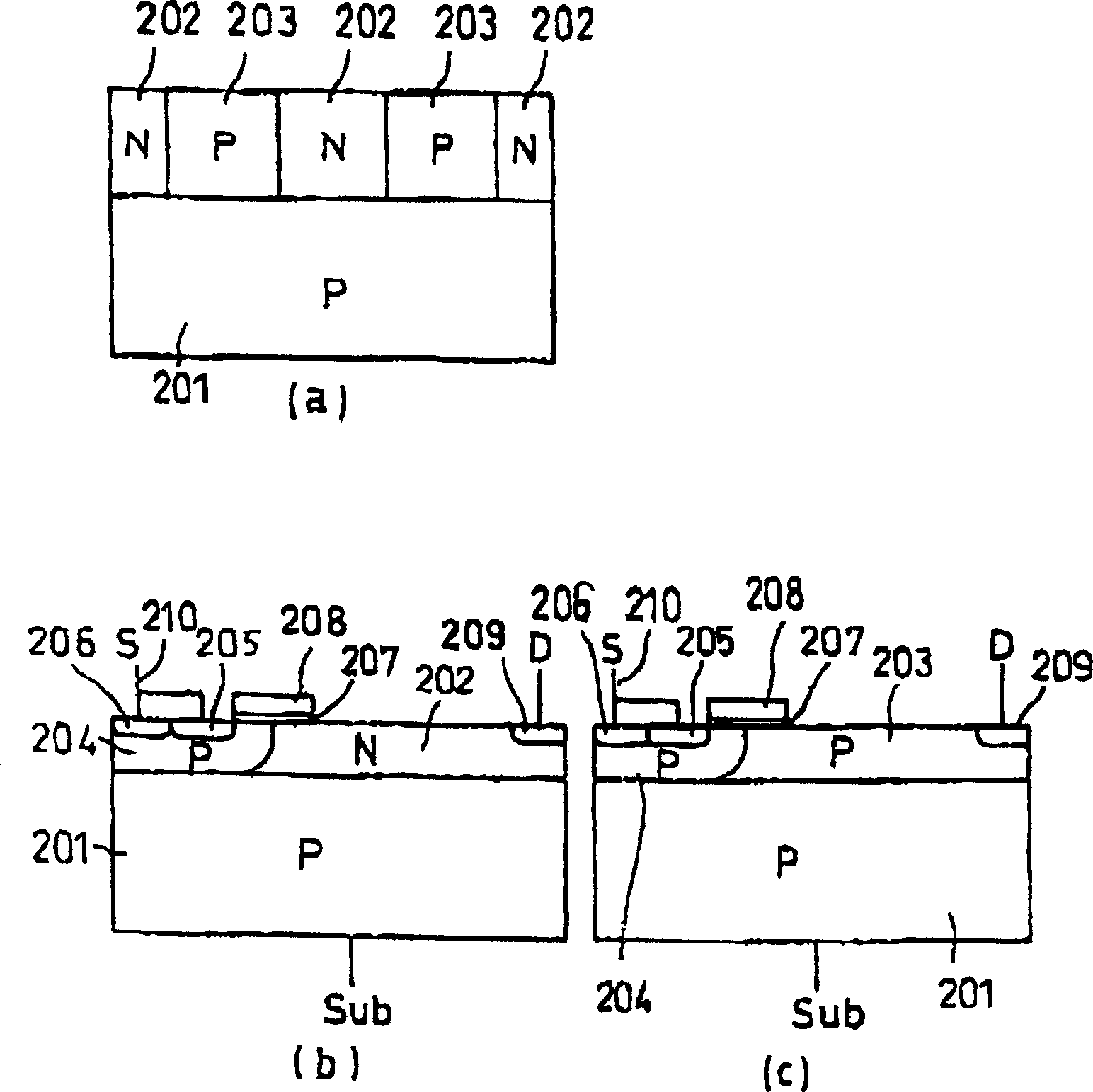
[0052] Figure 4 to Figure 7 This is Example 1 of the present invention, and is a diagram showing the structure of a lateral field effect transistor (hereinafter, the field effect transistor is simply referred to as MOSFET). Figure 4 , Fig. 5 is its three-dimensional oblique view, and Fig. 6 is its top view, Figure 7 (a) to (d) are respectively along image 3 The A-A', B-B', C-C' lines cut the cross-sectional view of the device. and, Figure 4 It is a perspective view showing part of the device shown in FIG. 5 excluding it. The horizontal MOSFET is a so-called MOSFET called a multi-resurf MOSFET or a super-junction MOSFET.
[0053] As shown in the figure, a substrate 1 is composed of a p-type (or n-type) silicon semiconductor 2 and a buried oxide film 3 stacked on its surface. On the buried oxide film 3, a p-type base layer 4 is selectively formed. On top of p-type base layer 4, high-concentration n-type source layer 5 and high-concentration p-type contact layer 6 are ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Figure 15 to Figure 18 This is Example 2 of the present invention, and is a diagram showing the structure of a lateral MOSFET. Figure 15 is its oblique view, Figure 16 is its top view, Figure 17 , Figure 18 are along Figure 16 The cross-sectional view of the A-A', B-B' line of the device.
[0069] In this embodiment, the active layer formed by the p-type base layer 4, the n-type drain layer 7, the n-type drift semiconductor layer 12 and the p-type drift semiconductor layer 13 formed between them, is formed on the SOI insulating substrate The bottom 1 is formed in a columnar shape. In addition, it is a structure in which both sides of the columnar active layer are sandwiched by gate electrodes 15 . In addition, in the active layer sandwiched by the gate electrodes 15, n-type drift semiconductor layers 12 and p-type drift semiconductor layers 13 of a superstructure structure are alternately stacked. In these figures, with Figure 4 The same parts as in FIG. ...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Figure 20 to Figure 23 It is a perspective perspective view showing the structure of a vertical trench gate MOSFET according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0073] Figure 21 It is a perspective view in which the vertical MOSFET shown in FIG. 20 is cut longitudinally and shows half thereof. As can be seen from these figures, in this embodiment, relative to Figure 15 The vertical MOSFET shown is different in that the gate electrode has a groove structure, and the n-type drift semiconductor layer 12 and the p-type drift semiconductor layer 13 are extended vertically and arranged horizontally.
[0074] in addition, Figure 22 is showing Figure 21 change example. As shown in the figure, although the n-type drift semiconductor layer 12 and the p-type drift semiconductor layer 13 are extended vertically, they are different in that they are stacked alternately from one of the two gate electrodes 15, 15' to the other. .
[0075] Again, if Figure 23 The v...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com