Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "Reduce molybdenum content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
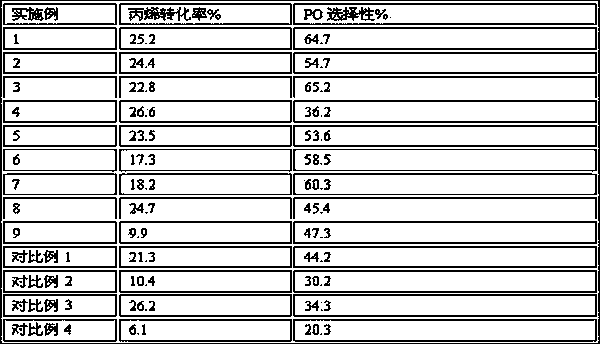
High-activity propylene gas-phase epoxidation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104128176AReduce pollutionLow costOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGas phaseMesoporous material
The invention discloses a high-activity propylene gas-phase epoxidation catalyst, TiO2-MoO3-Bi2SiO5 / SiO2, for preparing propylene oxide and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is used for a propylene gas-phase epoxidation reaction for preparing the propylene oxide, which takes molecular oxygen (O2) or nitric oxide (NO) as an oxidant; reaction conditions are moderate and no inhibitor is needed; the catalyst has high catalytic activity. The catalyst takes a SiO2 mesoporous material Bi2SiO5 / SiO2 containing bismuth silicate (Bi2SiO5) as a carrier, MoO3 as an active component and TiO2 as an auxiliary agent. The catalyst comprises following components in percentage by mass: 64.6%-98.8% of the carrier Bi2SiO5 / SiO2, 1.1%-22.8% of the MoO3 and 0.1%-12.6% of the TiO2. The mol ratio of Si to Bi in the carrier Bi2SiO5 / SiO2 is 30-200. The catalyst is synthesized by using a hydrothermal method; molybdenum and titanium precursors in the active component MoO3 and the auxiliary agent titanic oxide are immersed into the carrier by an ultrasonic-assisted immersion method to prepare the catalyst.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
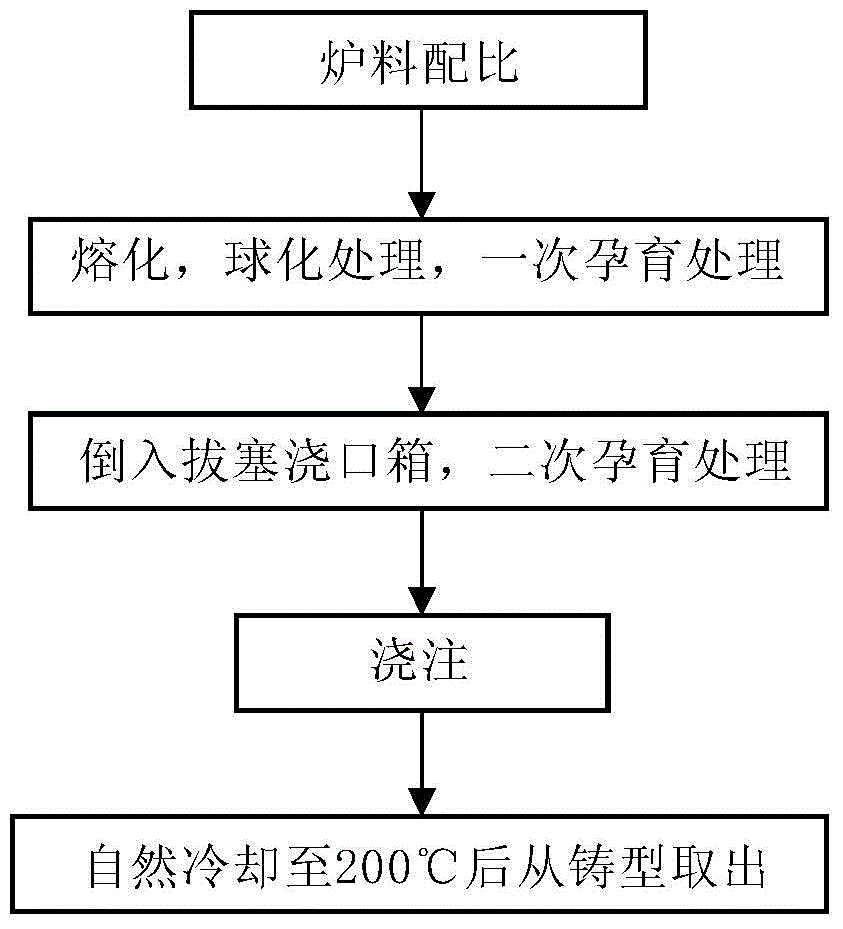
High-temperature-resistant silicon molybdenum ferrite nodular cast iron for steam turbine and preparation technology therefor
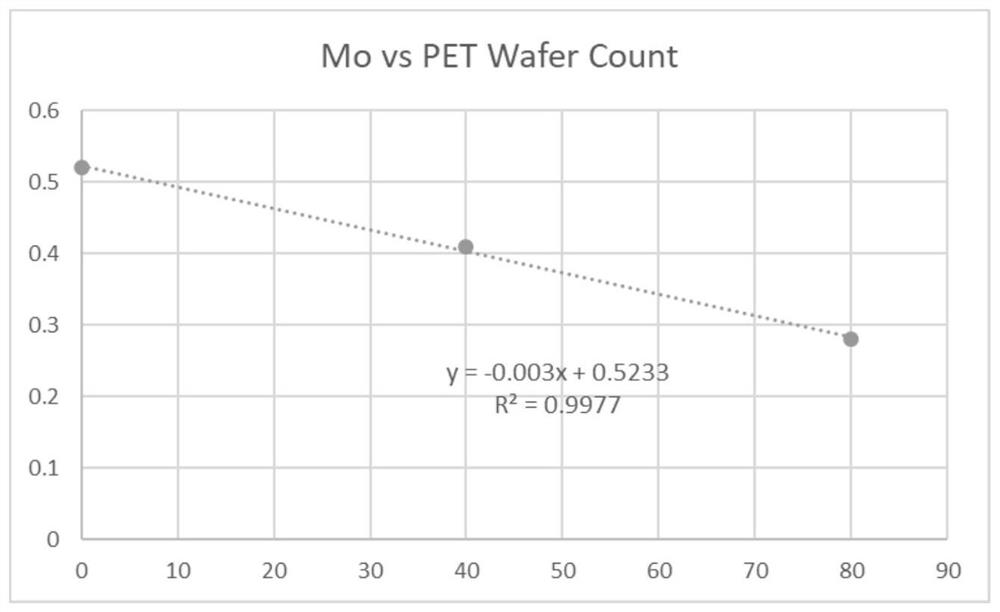
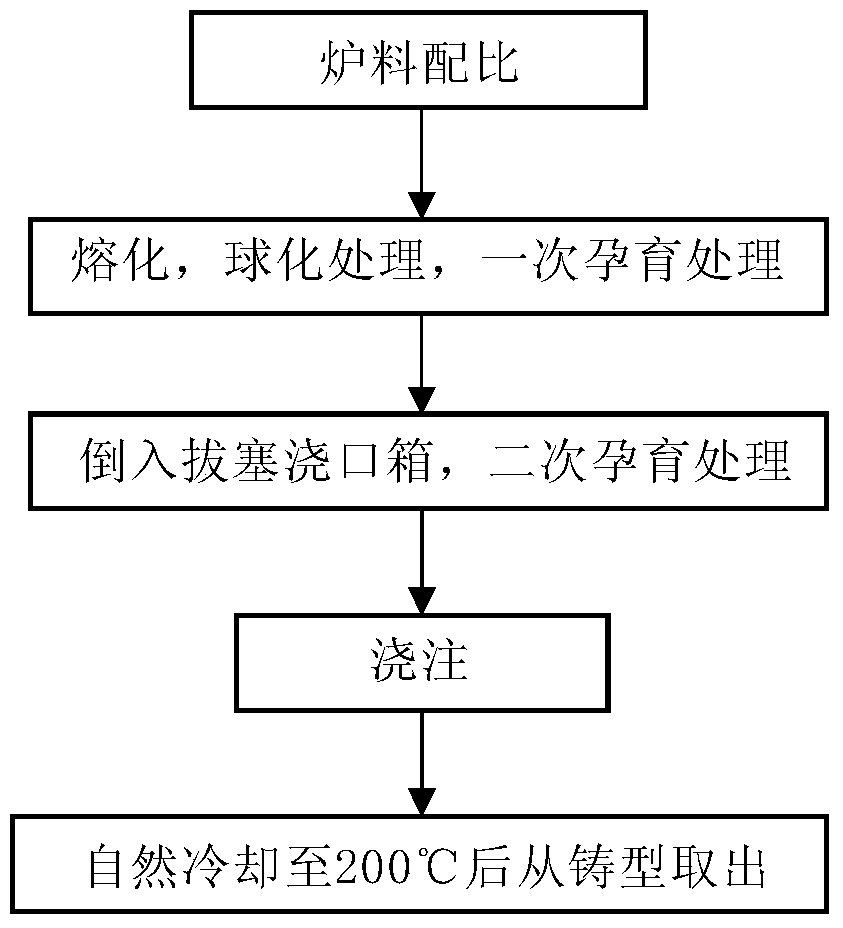
InactiveCN104911461AIncrease the brittle-ductile transition temperatureIncrease the number ofIntermediate frequencyFerrosilicon
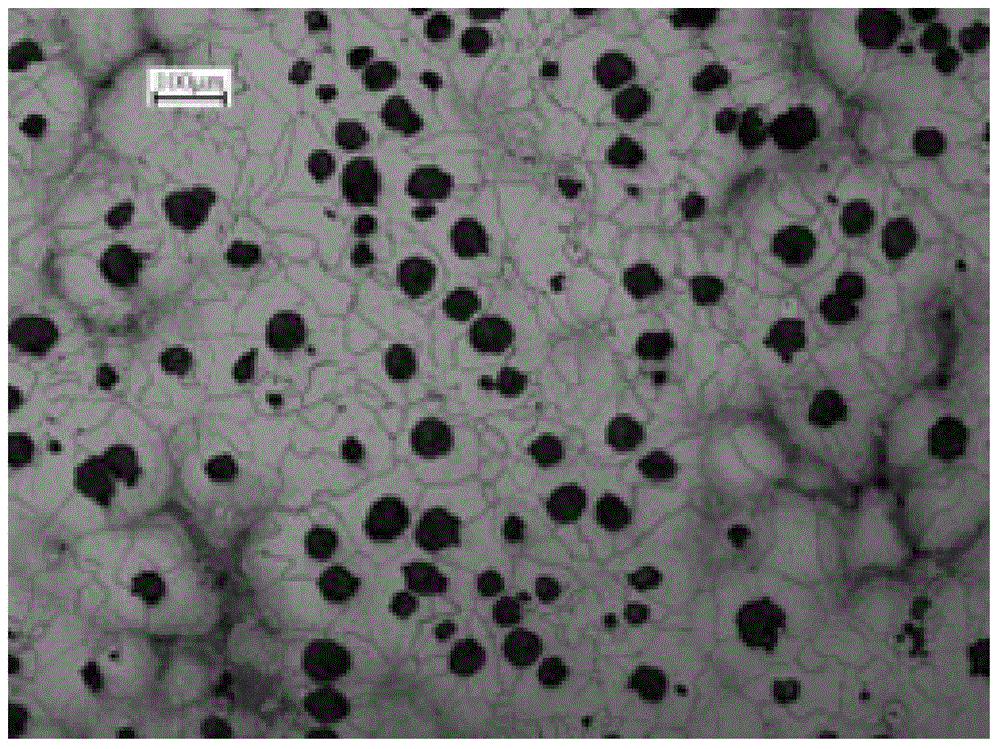
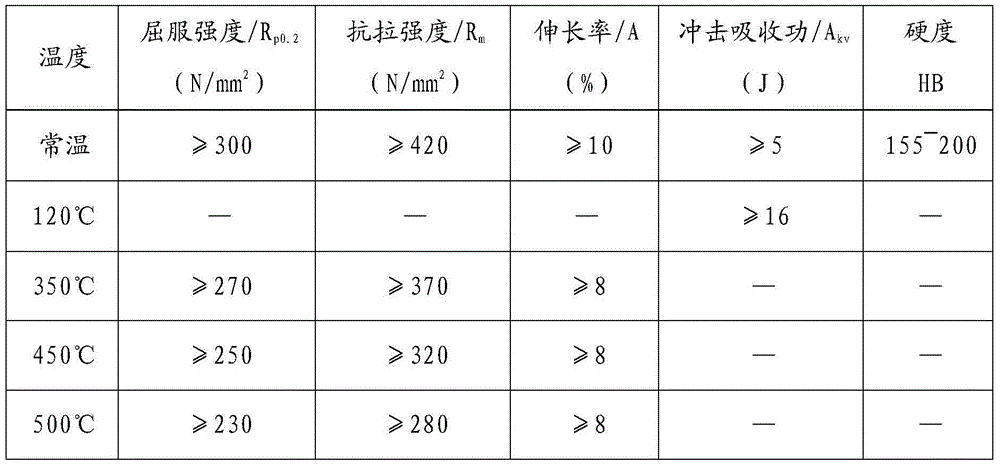
The invention discloses high-temperature-resistant silicon molybdenum ferrite nodular cast iron for a steam turbine and a preparation technology therefor. The nodular cast iron comprises components: 3.0-3.5% of C, 2.8-3.2% of Si, less than 0.2% of Mn, less than 0.040% of P, less than 0.015% of S, 0.5-0.8% of Mo, less than 0.010% of Re, 0.040-0.055% of Mg, and 0.004-0.007% of Sb, the balance being iron and residual elements. The preparation technology comprises furnace charge matching; intermediate frequency induction furnace fusing; spheroidizing and addition of first inoculation ferrosilicon; control of contents of elements; pouring into a pulling runner box for secondary inoculation; casting moulding. The obtained nodular cast iron has good combination properties and a low cost, the nodularity reaches more than 80% of the nodularity prescribed by GB / T9441-2009 nodular cast iron metallographic examination, the ferrite amount is more than 90%, and normal temperature and high temperature mechanical properties meet production requirements.
Owner:上海宏钢电站设备铸锻有限公司
Method for preparing molybdenum-containing additive and carbon disulfide by vacuum carbon thermal reduction of molybdenum concentrate
ActiveCN106498264AEasy to handleEmission reductionCarbon disulfideMaterials preparationMaterials science
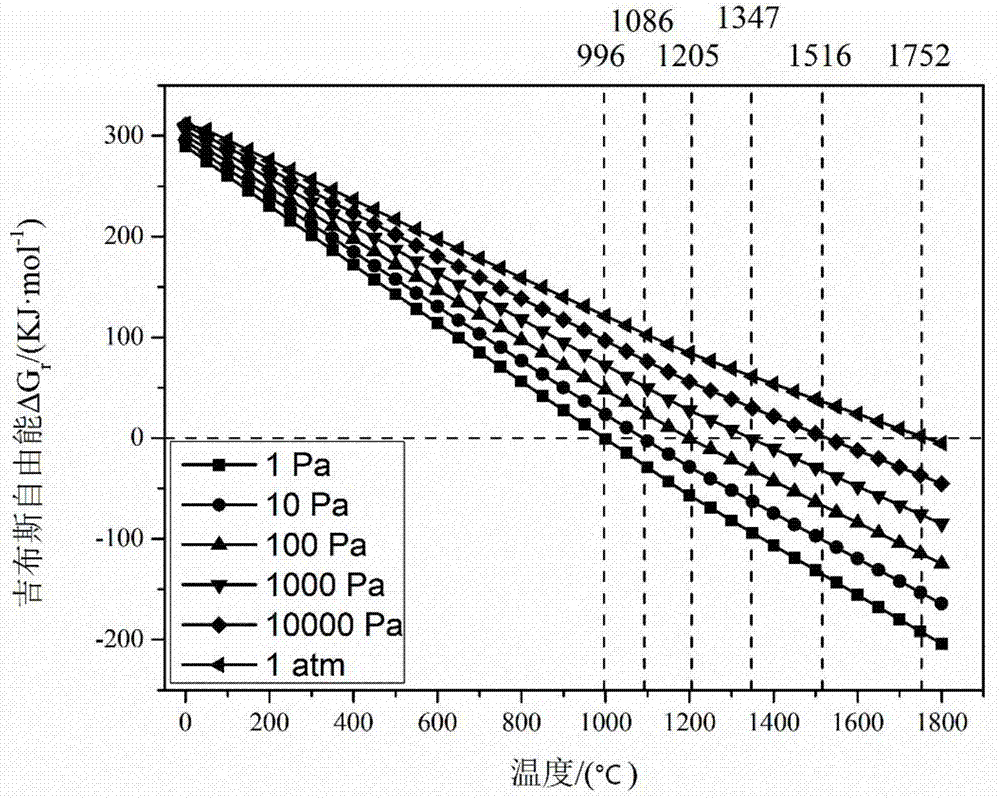
The invention discloses a method for preparing a molybdenum-containing additive and carbon disulfide by vacuum carbon thermal reduction of a molybdenum concentrate and belongs to the field of material preparation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, as raw materials, the molybdenum concentrate and carbon powder are proportioned according to a target ratio, are fully mixed and are subsequently treated at the temperature of 1200 to 1700 DEG C and at a vacuum degree of 1 Pa to 1000 Pa by adopting a vacuum carbon thermal reduction method to prepare an molybdenum-containing steel smelting additive of which the molybdenum content is as high as 90%; besides, a volatile product carbon disulfide is prepared; and the carbon disulfide is an important chemical raw material and is collected after being condensed. The method disclosed by the invention is free of generation of polluting gas sulfur dioxide and other pollutants, can be used for preparing the molybdenum-containing steel smelting additive and can also be used for preparing the carbon disulfide which has an extremely high value.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Preparation method of molybdenum-sulfur complex lubricating oil additive with high molybdenum content
The invention discloses a preparation method of a molybdenum-sulfur complex lubricating oil additive with high molybdenum content. The preparation method comprises the following steps: I, preparing a mixed liquid A from a hexavalent molybdenum compound, a sulfur-containing compound and distilled water, and then adjusting a pH value; II, adding dialkyl amine into the mixed liquid A which is subjected to pH value adjustment, then stirring, and then adding a phase transfer catalyst to obtain a mixed liquid B; III, under the protection of a nitrogen atmosphere, dropwise adding carbon disulfide into the mixed liquid B to obtain a mixed liquid C; and IV, standing the mixed liquid C till the mixed liquid C is layered, removing a water phase, washing an organic phase by virtue of an alkaline solution and an organic solvent, then distilling, and drying to obtain the high-molybdenum-content molybdenum-sulfur complex lubricating oil additive of which the mass percentage content of molybdenum is not less than 10%. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple in preparation process, and is favorable for industrial production; and the prepared molybdenum-sulfur complex lubricating oil additive has relatively high molybdenum content and good oil solubility, and after the additive is added into lubricating oil, the anti-wear and friction reduction properties of the lubricating oil can be greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
Method for lixiviating molybdenum from roasted molybdenite
ActiveCN103409624AImprove solubilityPrevent ammonia leaching reactionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionAmmonia
The invention discloses a method for lixiviating molybdenum from roasted molybdenite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, uniformly mixing the roasted molybdenite, ammonium carbonate and deionized water at a certain mass ratio, and then stirring for 40-70 minutes under the condition that the temperature is 70-90 DEG C to obtain a turbid liquid; 2, filtering to obtain a filter cake and filter liquor; 3, washing the filter cake by adopting ammonia water, then uniformly mixing the washed ammonia water with the filter liquor to obtain a mixed liquor; 4, regulating the pH value of the mixed liquor to 8.0-8.5, uniformly stirring, then carrying out sedimentation treatment, and taking a supernatant to obtain molybdenum lixivium. The process disclosed by the invention is simple, easy to operate, high in repeatability and suitable for large-scale industrial production, adopts the ammonium carbonate as a lixiviant, and can be used for greatly reducing the sludging ratio and the molybdenum content of dregs by regulating and optimizing the lixiviating process, and achieving the molybdenum lixiviating rate as high as more than 98%.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology capable of reducing slagging rate and molybdenum content in slag
The invention provides a commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology capable of reducing slagging rate and molybdenum content in slag. The commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology comprises the following steps: 1, uniformly mixing commercial molybdenum oxide, ammonium water and deionized water in certain proportions so as to obtain turbid liquid, and then stirring the turbid liquid at the temperature of 60-70 DEG C till the pH value of the turbid liquid is 6.5-7.0; 2, filtering so as to obtain filter cakes and filtrate; and 3, washing the filter cakes by adopting the ammonia water, placing the washed filter cakes in a drying cabinet so as to be dried, naturally cooling to obtain ammonia leaching slag, and uniformly mixing the ammonia water after washing and the filtrate in the step 2 so as to obtain an ammonia leaching solution. The commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology is simple and practicable, has strong repeatability and is suitable for large-scale industrial production; the reducing slagging rate and molybdenum content in slag are substantially reduced after the ammonia leaching treatment is carried out by adopting the commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Method for volatilizing and enriching molybdenum from molybdenum tailings
InactiveCN101514403AHigh volatile enrichment rateImprove high temperature stabilityProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationThermal insulation
A method for volatilizing and enriching molybdenum from molybdenum tailings relates to a process for utilizing the molybdenum tailings for enriching and recovering the molybdenum. The molybdenum tailings are firstly ground, and the water content thereof is regulated to 30-40%WT to lead the molybdenum tailings to form slurry of the molybdenum tailings. Then, hydrofluoric acid is added in the slurry of the molybdenum tailings, hydrochloric acid is further added after the bubbles disappear and the reaction is complete; after that, the slurry of the molybdenum tailings is heated to 200-250 DEG C, a cover is used for thermal insulation for 30-50min to promote the formation of chloride of the molybdenum, then the cover is removed, and the drying is carried out at 65 DEG C. Finally, the thermal treatment of the molybdenum tailings after the pretreatment with the acid is carried out at 900 DEG C, thereby generating flue gas containing the molybdenum and silicon tetrafluoride and the residues of the thermal treatment, and the residues are used as road-building materials; the collected flue gas is condensed; when the temperature is lower than 250 DEG C, substances containing the molybdenum or molybdenum compounds are recovered; the silicon tetrafluoride in the flue gas is absorbed and hydrolyzed by using water, the filtration is carried out, and filtrate is fluorosilicic acid solution. The process of the invention is simple and easy to control, the products during the process can be recovered, the cost is low, the method has no environmental pollution, and the high temperature volatilization rate of the molybdenum achieves 70 percent-98.6 percent.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
High-activity propylene gas-phase epoxidation catalyst and preparation method thereof
PendingCN111330588AReduce usageReduce pollutionOrganic chemistryHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsPtru catalystHigh activity
The invention discloses a high-activity catalyst Fe2O3-MoO3-Bi2SiO5 for preparing epoxypropane through gas-phase epoxidation of propylene and a preparation method thereof. The catalyst is used in a reaction for preparing epoxypropane through propylene gas-phase epoxidation by taking air, molecular oxygen or N2O as an oxidizing agent, the reaction condition is mild, no inhibitor is added, and the catalyst has relatively high catalytic activity. According to the catalyst, Bi2SiO5 nanosheets serve as a carrier, MoO3 serves as an active component, Fe2O3 serves as an auxiliary, the Si / Bi mole ratiois 0.1-1, the Mo / Bi mole ratio is 0.01-1, and the Fe / Mo mole ratio is 0.05-1. The carrier Bi2SiO5 nanosheet is synthesized by adopting a hydrothermal method, and for the active component MoO3 and theauxiliary agent iron oxide, molybdenum and iron precursors are impregnated on the carrier by adopting an ultrasonic-assisted impregnation method to prepare the catalyst.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Propylene gas-phase epoxidation catalyst used at ordinary pressure and preparation method of catalyst
InactiveCN108816243ALow costEasy to industrializeOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGas phaseActive component
The invention discloses a catalyst Fe2O3-MoO3-Bi2SiO5 / SiO2 for preparing propylene epoxide by propylene gas-phase epoxidation at ordinary pressure and a preparation method of the catalyst. The catalyst is applied to a reaction of preparing propylene epoxide from air, molecular oxygen or N2O as an oxidizing agent by the propylene gas-phase epoxidation, the reaction conditions are mild, inhibitors are not required, and the catalyst has higher catalytic activity. The catalyst adopts a Bi2SiO5-containing SiO2 mesoporous material Bi2SiO5 / SiO2 as a supporter, MoO3 as an active component and Fe2O3 asan auxiliary, and in terms of mole composition of the catalyst, Si / Bi is 50, Mo / Bi is 1-10, and Fe / Mo is 0.05-1. The supporter Bi2SiO5 / SiO2 is synthesized with a hydrothermal method, the active component MoO3 and the auxiliary iron oxide impregnate Mo and Fe precursor to the supporter with an ultrasonic assisted impregnation method, and the catalyst is prepared.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
A kind of highly active propylene gas phase epoxidation catalyst and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104128176BReduce pollutionEasy to industrializeOrganic chemistryMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsGas phaseMesoporous material
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
Molybdenum concentrate screening method
ActiveCN103386375AImprove resource utilizationIncrease profitVortex flow apparatusMaterials scienceMolybdenum
The invention relates to a molybdenum concentrate screening method which aims to solve the problems that a molybdenum concentrate screening method in the prior art is low in utilization rate of resources and low in recovery rate of molybdenum concentrates. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) pretreatment on molybdenum raw-ores: carrying out treatment on the molybdenum raw-ores so as to obtain fine ores; (2) ore grinding and grading: carrying out ore grinding on the fine ores so as to obtain an ore grinding product, and then carrying out closed grading on the ore grinding product by using a hydrocyclone so as to obtain an overflow object; (3) flotation: adding a flotation reagent in the overflow object subjected to ore grinding and grading in a flotation column, and carrying out molybdenum ore rough-concentration and dense grading on the obtained mixture so as to obtain a rough concentrate; (4) fine selection: after the rough concentrate obtained in the step (3) is subjected to a regrinding process, carrying out fine selection on the rough concentrate for two times, then carrying out scavenging on the obtained product for three times so as to obtain a molybdenum concentrate; and (5) concentrate dehydration; concentrating the molybdenum concentrate, and carrying out further squeezed dehydration on the molybdenum concentrate so as to obtain a molybdenum concentrate finished product. The screening method disclosed by the invention is high in utilization rate of molybdenum raw-ores; and less waste residues and waste dust are produced in a process of screening, therefore, the production environment is friendly.
Owner:ZHEJIANG TAIZHENG MOLYBDENUM IND DEVCO
Method for advancedly removing molybdenum from manganese sulfate solution
The invention discloses a method for advancedly removing molybdenum from a manganese sulfate solution. The method for advancedly removing the molybdenum from the manganese sulfate solution is carriedout according to the following steps of after a pH value of the manganese sulfate solution is adjusted, adding a molybdenum removal agent into the solution, and conducting stirring and filtering to obtain filter liquor, namely a purified manganese sulfate solution; and therefore, the requirement of purifying the manganese sulfate solution can be met, and in the molybdenum removal process, the solution does not need to be heated. The method for advancedly removing the molybdenum from the manganese sulfate solution has the advantages that the procedures are simple, the cost is low, the efficiency is high, no pollution is generated, the defects of existing methods are overcome, and the requirements of the molybdenum content of manganese sulfate for producing a high-purity manganese-bearing material are met.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV +1
Nickel-molybdenum-copper alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a nickel-molybdenum-copper alloy, which is an alloying agent used for smelting pipe line steel, stainless steel and special steel. The alloy comprises: 20 to 45 percent of nickel, 1 to 8 percent of molybdenum, 18 to 50 percent of copper, less than 0.5 percent of carbon, less than 0.05 percent of sulfur, less than 0.05 percent of phosphorus, less than 2.0 percent of silicon and the balance of ferrum. The alloy can be put at one time during the smelting of the pipe line steel and the like and reduce the labor intensity of smelters.
Owner:LIAONING JIUTONG FRICTION MATERIALS
A kind of screening method of molybdenum concentrate
ActiveCN103386375BImprove resource utilizationIncrease profitVortex flow apparatusPre treatmentMolybdenum
Owner:ZHEJIANG TAIZHENG MOLYBDENUM IND DEVCO
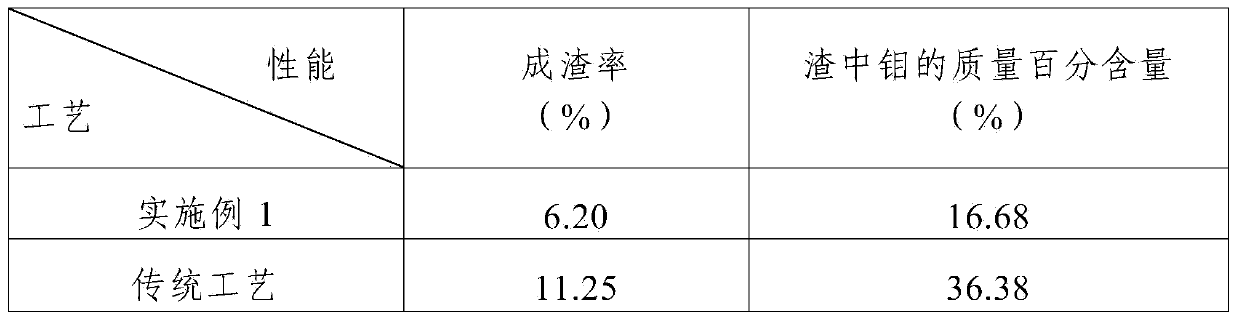
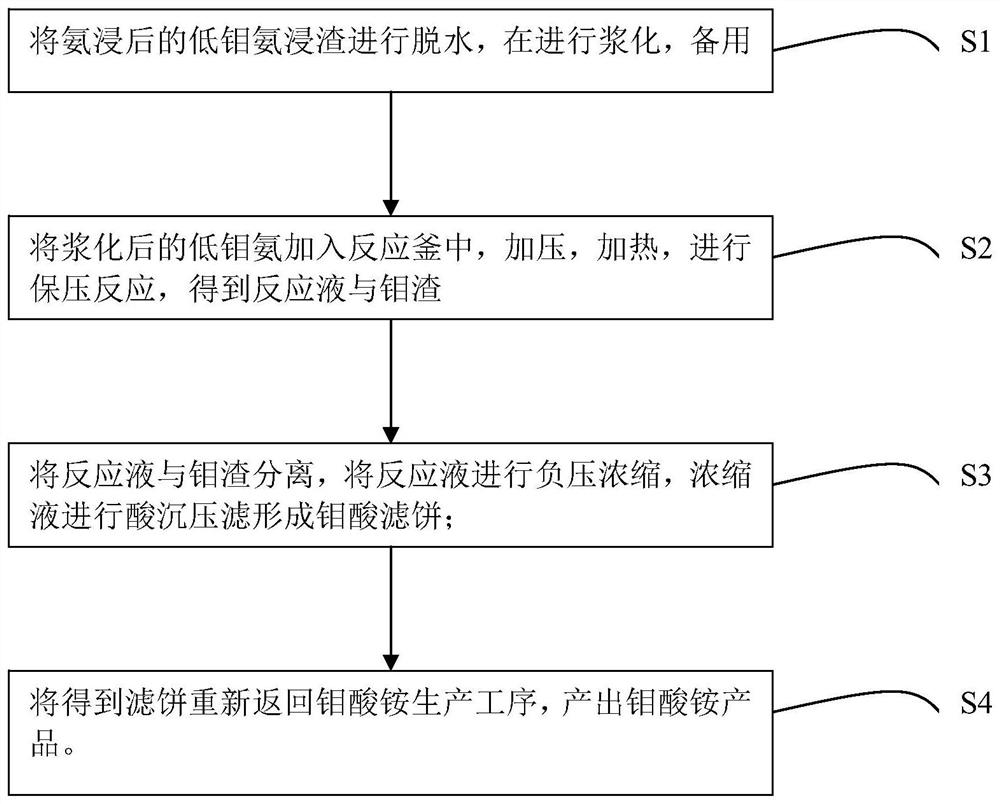
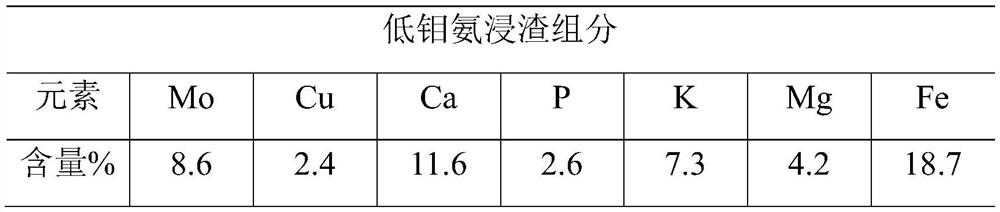
Method for recovering molybdenum from low-molybdenum ammonia leaching residues
InactiveCN111826534AHigh content of impuritiesReduce molybdenum contentProcess efficiency improvementMolybdateHydrometallurgy
The invention belongs to the field of hydrometallurgy, and relates to a method for leaching and recovering molybdenum from low-molybdenum ammonia leaching residues. The method specifically comprises the following steps that S1) the ammonia-impregnated low-molybdenum ammonia leaching residues are dehydrated and slurried for use; S2) the slurried low-molybdenum ammonia is added into a reaction kettle, pressurized and heated, and a pressure-maintaining reaction is performed to obtain a reaction solution and molybdenum slag; S3) the reaction solution is separated from the molybdenum slag, negativepressure concentration is carried out on the reaction solution, and acid precipitation filtration is carried out on the concentrated solution to form a molybdate filter cake; and S4) the filter cakereturns to the ammonium molybdate production process, and an ammonium molybdate product meeting the GB / T3460-2017MSA-1 level is produced. The method has the beneficial effects that due to the adoptionof the technical scheme, the process is simple and feasible, the ammonia leaching residues do not need to be dried and ground, the process is short, the technology is stable, the production cost is low, the leaching recovery rate is not lower than 94.98%, and the whole technological process is environmentally friendly.
Owner:JIANGXI COPPER
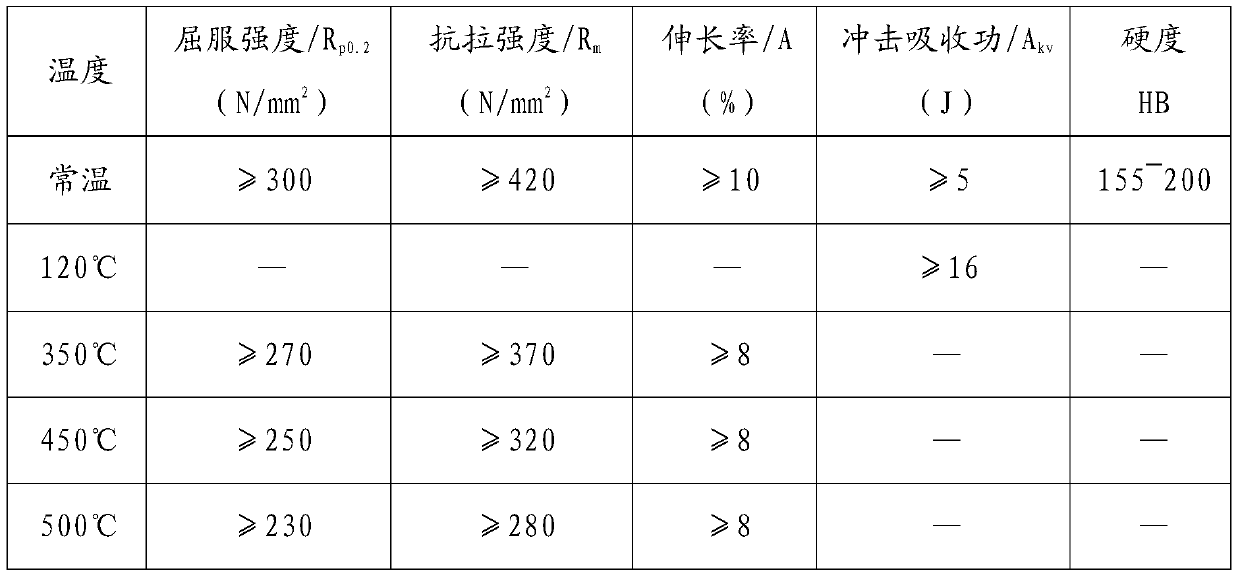
Primary material for molds adapted to mold plastics
ActiveUS20130255844A1Increase in the carbon content—madeHigh acceptanceFurnace typesProcess efficiency improvementMaterials scienceMaterial hardness
A mold material having a material hardness higher than 340 HB and a fine-grain structure. The mold material having a composition in weight percent that includes:C=0.25-0.35Si=0.04-0.20Mn=1.00-2.00Cr=1.00-2.00Ni=0.30-less than 0.90Mo=0.30-0.80V=less than / equal to 0.20Al=0.01-0.03N=0.0025-0.0150S=less than 0.15a remainder of Fe and impurities.
Owner:BUDERUS EDELSTAHL GMBH
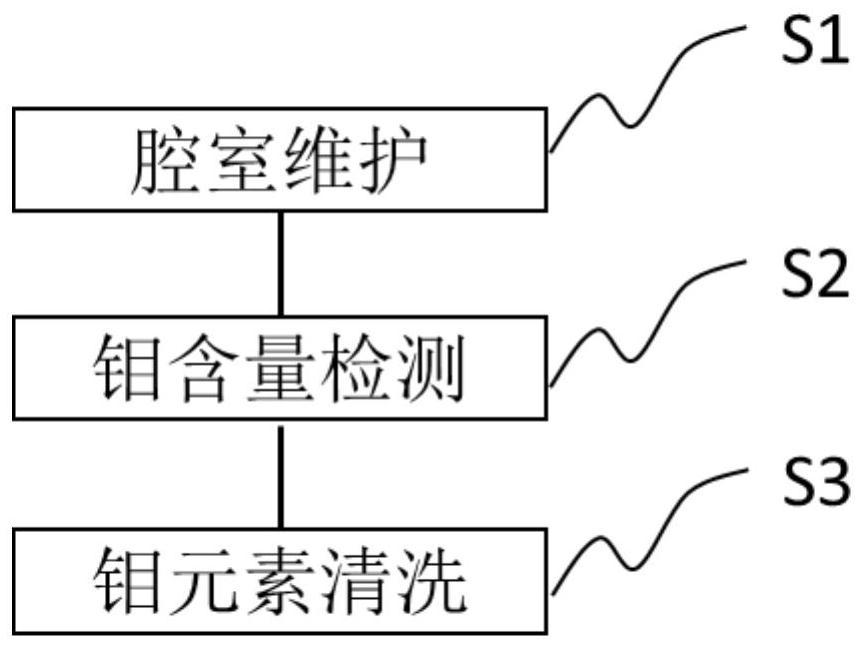
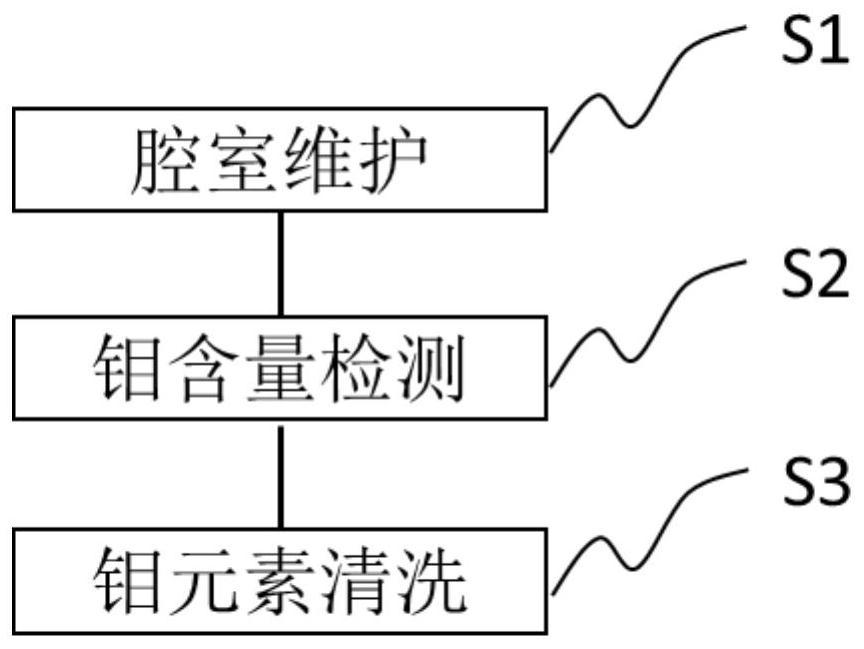
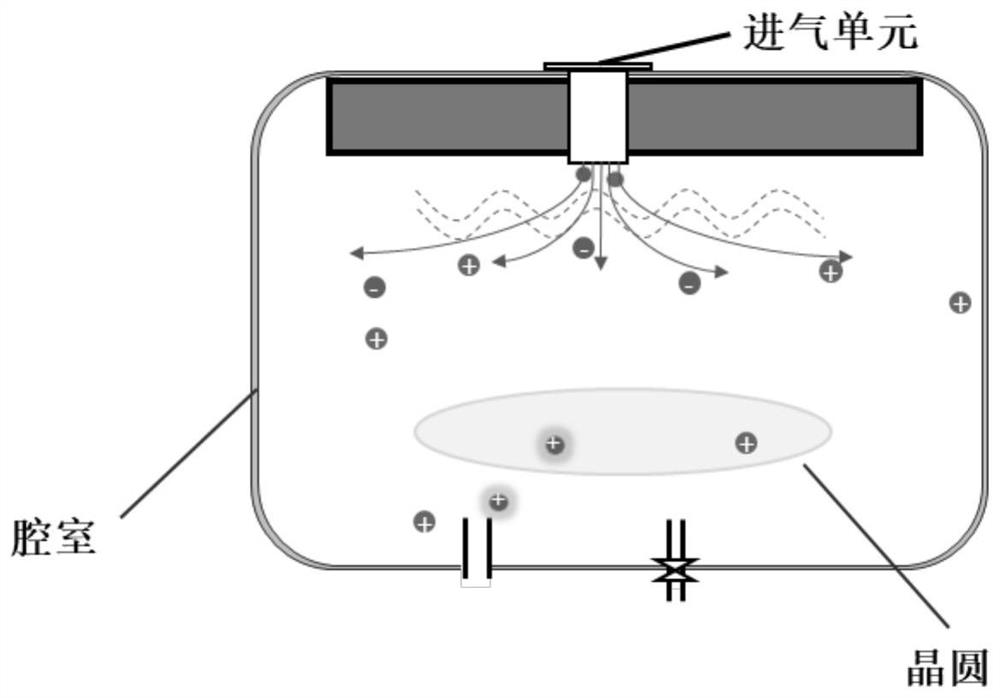
Method for reducing molybdenum content after chamber maintenance
ActiveCN113223915AImprove manufacturing yieldReduce molybdenum contentElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufacturePhysical chemistryChemical engineering
The invention discloses a method for reducing molybdenum content after chamber maintenance. The method comprises the following steps of: S1, carrying out chamber maintenance, wherein the chamber maintenance step at least comprises a cleaning substep of injecting first process gas and discharging the first process gas so as to reduce the content of metal impurity ions in a chamber, and the cleaning step is repeated for multiple times; S2, detecting the molybdenum content in the chamber to measure the content of molybdenum ions in the chamber; and S3, carrying out molybdenum element cleaning, so that the content of molybdenum ions in the cavity is reduced.
Owner:HUA HONG SEMICON WUXI LTD
Method for purifying and removing molybdenum from ammonium rhenate
The invention discloses a method for purifying and removing molybdenum from ammonium rhenate. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing a molybdenum-containing ammonium rhenate solution; 2, preparing a multi-stage series ion exchange column group, and enabling an HNO3 solution to flow through the multi-stage series ion exchange column group to obtain an H < + > type multi-stage series ion exchange column group; 3, enabling the ammonium rhenate solution containing molybdenum to flow through an H + type multi-stage series ion exchange column group to adsorb and remove molybdenum, so as to obtain a pure perrhenic acid solution; 4, the pure perrhenic acid solution is sequentially subjected to pH adjustment and evaporative cooling crystallization, and ammonium rhenate crystals are obtained. The method comprises the following steps: converting a molybdenum-containing ammonium rhenate solution into an acidic perrhenic acid solution through first-stage resin, converting molybdenum in the solution into MoO2 < 2 + > ions, removing most molybdenum through second-stage resin exchange, purifying residual trace molybdenum through third-stage and later-stage resin, neutralizing with ammonia water, evaporating, cooling and crystallizing to obtain the ammonium rhenate with low molybdenum content, and the requirement of the aeronautical material on the low molybdenum content in the metal rhenium is met.
Owner:NORTHWEST INSTITUTE FOR NON-FERROUS METAL RESEARCH
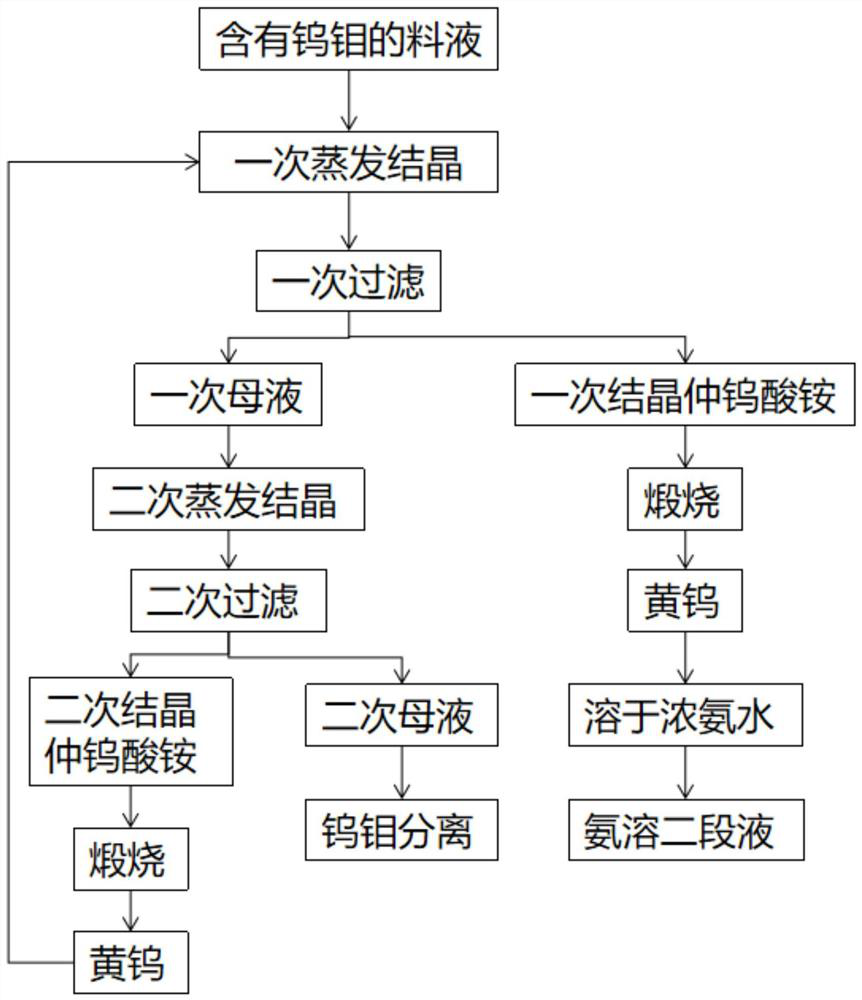
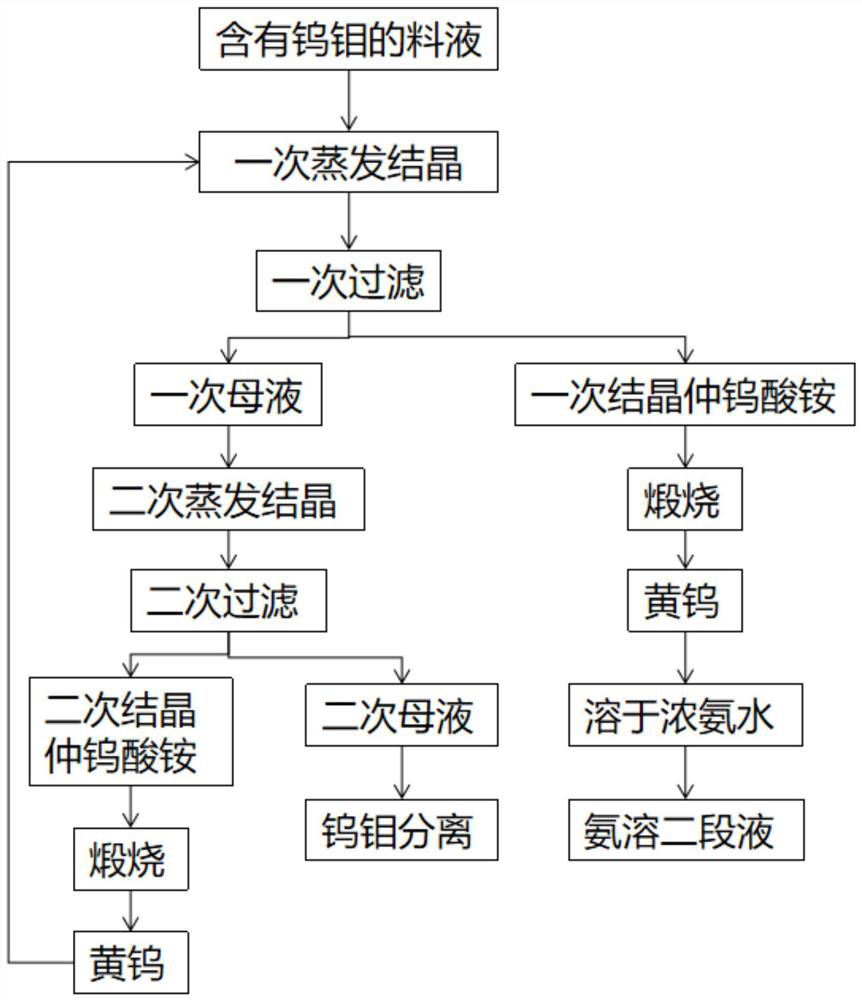
Tungsten-molybdenum separation method
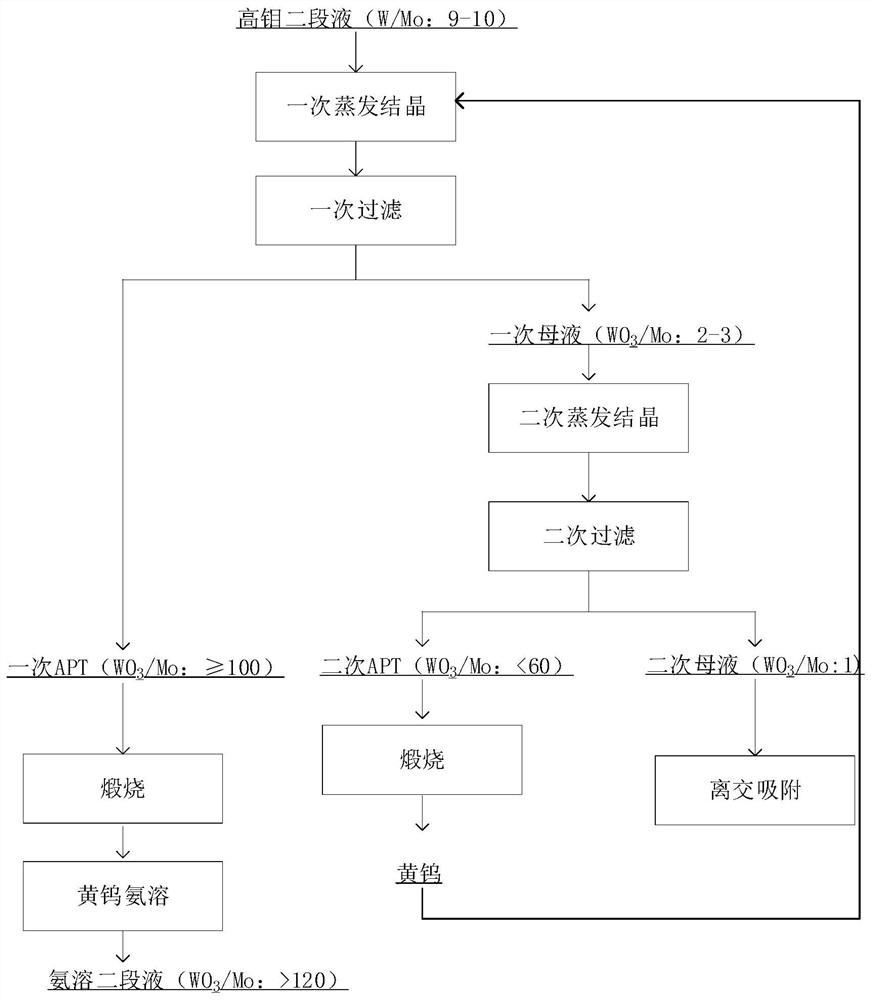
ActiveCN112877539AReduce the ratioIncrease the ratio of tungsten to molybdenumProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium paratungstatePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a tungsten-molybdenum separation method which comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out primary evaporative crystallization on a tungsten-molybdenum-containing feed liquid, and carrying out primary filtration to obtain primary mother liquor and primary crystallized ammonium paratungstate; S2, performing secondary evaporative crystallization on the primary mother liquor, and performing secondary filtration to obtain secondary mother liquor and secondary crystallized ammonium paratungstate; S3, performing tungsten-molybdenum separation on the secondary mother liquor obtained in the step S2; S4, calcining the secondary crystallized ammonium paratungstate obtained in the step S2 into yellow tungsten, and adding at least one part of yellow tungsten into the feed liquid in the step S1; and S5, calcining the primary crystallized ammonium paratungstate obtained after the yellow tungsten in the step S4 is added into the step S1 into yellow tungsten, and dissolving the obtained yellow tungsten into stronger ammonia water to obtain ammonia-soluble second-stage liquid. According to the tungsten-molybdenum separation method disclosed by the invention, a tungsten-molybdenum ratio in the evaporated and crystallized high-molybdenum ammonium paratungstate is increased by adopting a two-time evaporative crystallization mode, the proportion of molybdenum entering a subsequent molybdenum removal system is reduced, and the subsequent molybdenum removal cost is reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN TUNGSTEN
Method for lixiviating molybdenum from roasted molybdenite
ActiveCN103409624BImprove solubilityPrevent ammonia leaching reactionProcess efficiency improvementPregnant leach solutionRepeatability
The invention discloses a method for lixiviating molybdenum from roasted molybdenite. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, uniformly mixing the roasted molybdenite, ammonium carbonate and deionized water at a certain mass ratio, and then stirring for 40-70 minutes under the condition that the temperature is 70-90 DEG C to obtain a turbid liquid; 2, filtering to obtain a filter cake and filter liquor; 3, washing the filter cake by adopting ammonia water, then uniformly mixing the washed ammonia water with the filter liquor to obtain a mixed liquor; 4, regulating the pH value of the mixed liquor to 8.0-8.5, uniformly stirring, then carrying out sedimentation treatment, and taking a supernatant to obtain molybdenum lixivium. The process disclosed by the invention is simple, easy to operate, high in repeatability and suitable for large-scale industrial production, adopts the ammonium carbonate as a lixiviant, and can be used for greatly reducing the sludging ratio and the molybdenum content of dregs by regulating and optimizing the lixiviating process, and achieving the molybdenum lixiviating rate as high as more than 98%.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Method for preparing molybdenum-containing additive and carbon disulfide by vacuum carbothermal reduction of molybdenum concentrate
ActiveCN106498264BEasy to handleEmission reductionCarbon disulfideMaterials preparationSulfur dioxide
The invention discloses a method for preparing a molybdenum-containing additive and carbon disulfide by vacuum carbon thermal reduction of a molybdenum concentrate and belongs to the field of material preparation. According to the method disclosed by the invention, as raw materials, the molybdenum concentrate and carbon powder are proportioned according to a target ratio, are fully mixed and are subsequently treated at the temperature of 1200 to 1700 DEG C and at a vacuum degree of 1 Pa to 1000 Pa by adopting a vacuum carbon thermal reduction method to prepare an molybdenum-containing steel smelting additive of which the molybdenum content is as high as 90%; besides, a volatile product carbon disulfide is prepared; and the carbon disulfide is an important chemical raw material and is collected after being condensed. The method disclosed by the invention is free of generation of polluting gas sulfur dioxide and other pollutants, can be used for preparing the molybdenum-containing steel smelting additive and can also be used for preparing the carbon disulfide which has an extremely high value.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Methods to reduce molybdenum content after chamber maintenance
ActiveCN113223915BImprove manufacturing yieldReduce molybdenum contentElectric discharge tubesFinal product manufacturePhysical chemistryAnalytical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for reducing molybdenum content after chamber maintenance, comprising step S1, chamber maintenance, wherein the chamber maintenance step at least includes a cleaning step, the cleaning step injects a first process gas, and discharges the first process gas. A process gas is used to reduce the content of metal impurity ions in the chamber, and the cleaning step is repeated for several times; step S2, the detection of the molybdenum content in the chamber is used to measure the content of molybdenum ions in the chamber; step S3, molybdenum element cleaning , in order to reduce the content of the molybdenum ions in the chamber.
Owner:HUA HONG SEMICON WUXI LTD
High temperature resistant silicon molybdenum ferritic nodular cast iron for steam turbine and its preparation process
InactiveCN104911461BIncrease the brittle-ductile transition temperatureIncrease the number ofFerrosiliconDuctile iron
The invention discloses a high-temperature-resistant silicon-molybdenum-ferrite nodular cast iron for steam turbines and a preparation process thereof. The nodular cast iron is composed of 3.0-3.5% C, 2.8-3.2% Si, Mn<0.2%, P<0.040%, S <0.015%, 0.5-0.8% Mo, Re<0.010%, 0.040-0.055% Mg, 0.004-0.008% Sb, and the remainder is iron and residual elements. The preparation process includes: burden ratio; melting in an intermediate frequency induction furnace; spheroidization treatment, adding ferrosilicon for primary inoculation; controlling the content of each element; pouring into a plug sprue box for secondary inoculation; pouring molding. The ductile iron obtained by the present invention has better overall performance and lower cost, its spheroidization rate reaches more than 80% specified in GB / T9441-2009 "Metallographic Examination of Ductile Iron", and the ferrite content is greater than 90%. The mechanical properties meet the requirements of production.
Owner:上海宏钢电站设备铸锻有限公司
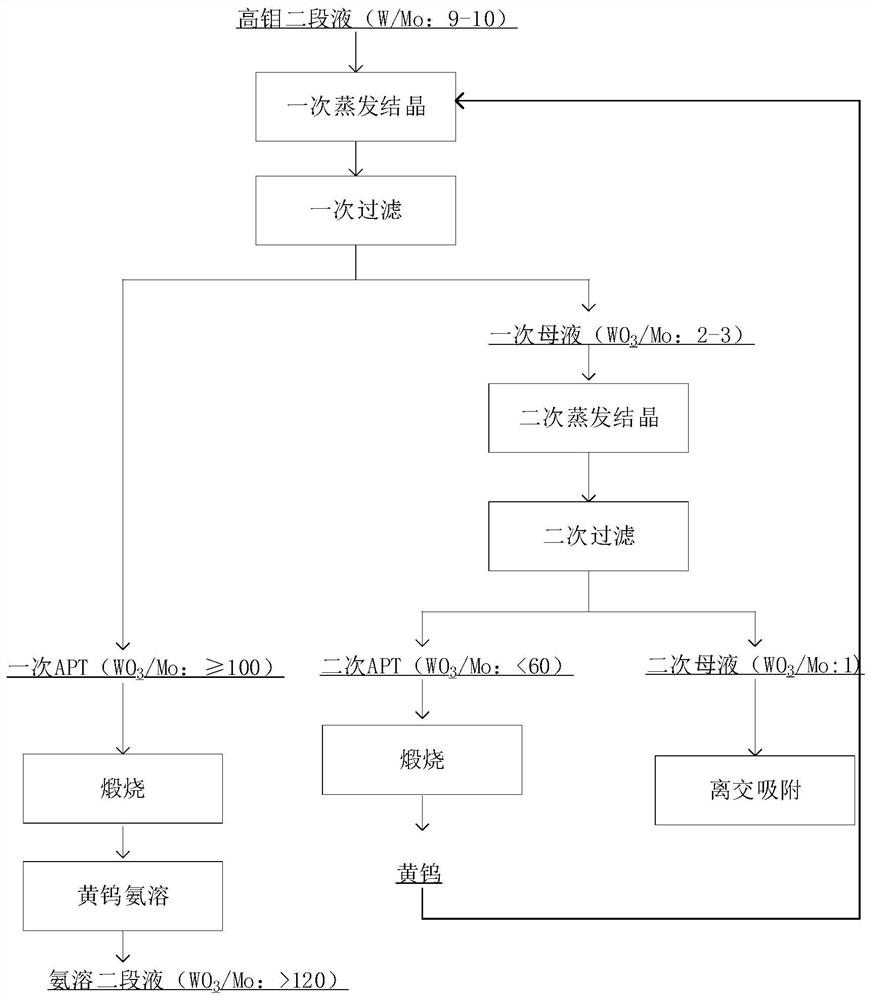
Tungsten and molybdenum separation method
ActiveCN112877539BReduce the ratioIncrease the ratio of tungsten to molybdenumProcess efficiency improvementAmmonium paratungstatePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for separating tungsten and molybdenum, which comprises the following steps: S1, performing primary evaporation and crystallization on a feed liquid containing tungsten and molybdenum, and obtaining primary mother liquor and primary crystalline ammonium paratungstate after primary filtration; S2, performing secondary evaporation on primary mother liquor Crystallization, after secondary filtration, secondary mother liquor and secondary crystalline ammonium paratungstate are obtained; S3, the secondary mother liquor obtained in step S2 is subjected to tungsten and molybdenum separation; S4, the secondary crystalline ammonium paratungstate obtained in step S2 is calcined into yellow After tungsten, at least a part of yellow tungsten is added to the feed liquid in step S1; S5, after the primary crystalline ammonium paratungstate obtained after adding the yellow tungsten of step S4 in step S1 is calcined into yellow tungsten, the obtained yellow tungsten is dissolved. In concentrated ammonia water, the ammonia-dissolved second-stage liquid is obtained. According to the tungsten and molybdenum separation method of the present invention, the tungsten and molybdenum ratio in the evaporative crystallization high-molybdenum paratungstate ammonium paratungstate is increased by two evaporation crystallizations, the proportion of molybdenum entering the subsequent molybdenum removal system is reduced, and the subsequent molybdenum removal cost is reduced.
Owner:XIAMEN TUNGSTEN
A ammonia leaching process for molybdenum calcination to reduce slag formation rate and molybdenum content in slag
ActiveCN103436695BReduce molybdenum contentReduce packageProcess efficiency improvementSlagFree cooling
The invention provides a commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology capable of reducing slagging rate and molybdenum content in slag. The commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology comprises the following steps: 1, uniformly mixing commercial molybdenum oxide, ammonium water and deionized water in certain proportions so as to obtain turbid liquid, and then stirring the turbid liquid at the temperature of 60-70 DEG C till the pH value of the turbid liquid is 6.5-7.0; 2, filtering so as to obtain filter cakes and filtrate; and 3, washing the filter cakes by adopting the ammonia water, placing the washed filter cakes in a drying cabinet so as to be dried, naturally cooling to obtain ammonia leaching slag, and uniformly mixing the ammonia water after washing and the filtrate in the step 2 so as to obtain an ammonia leaching solution. The commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology is simple and practicable, has strong repeatability and is suitable for large-scale industrial production; the reducing slagging rate and molybdenum content in slag are substantially reduced after the ammonia leaching treatment is carried out by adopting the commercial molybdenum oxide ammonia leaching technology.
Owner:JINDUICHENG MOLYBDENUM CO LTD
Method for volatilizing and enriching molybdenum from molybdenum tailings
InactiveCN101514403BHigh volatile enrichment rateImprove high temperature stabilityProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationThermal insulation
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
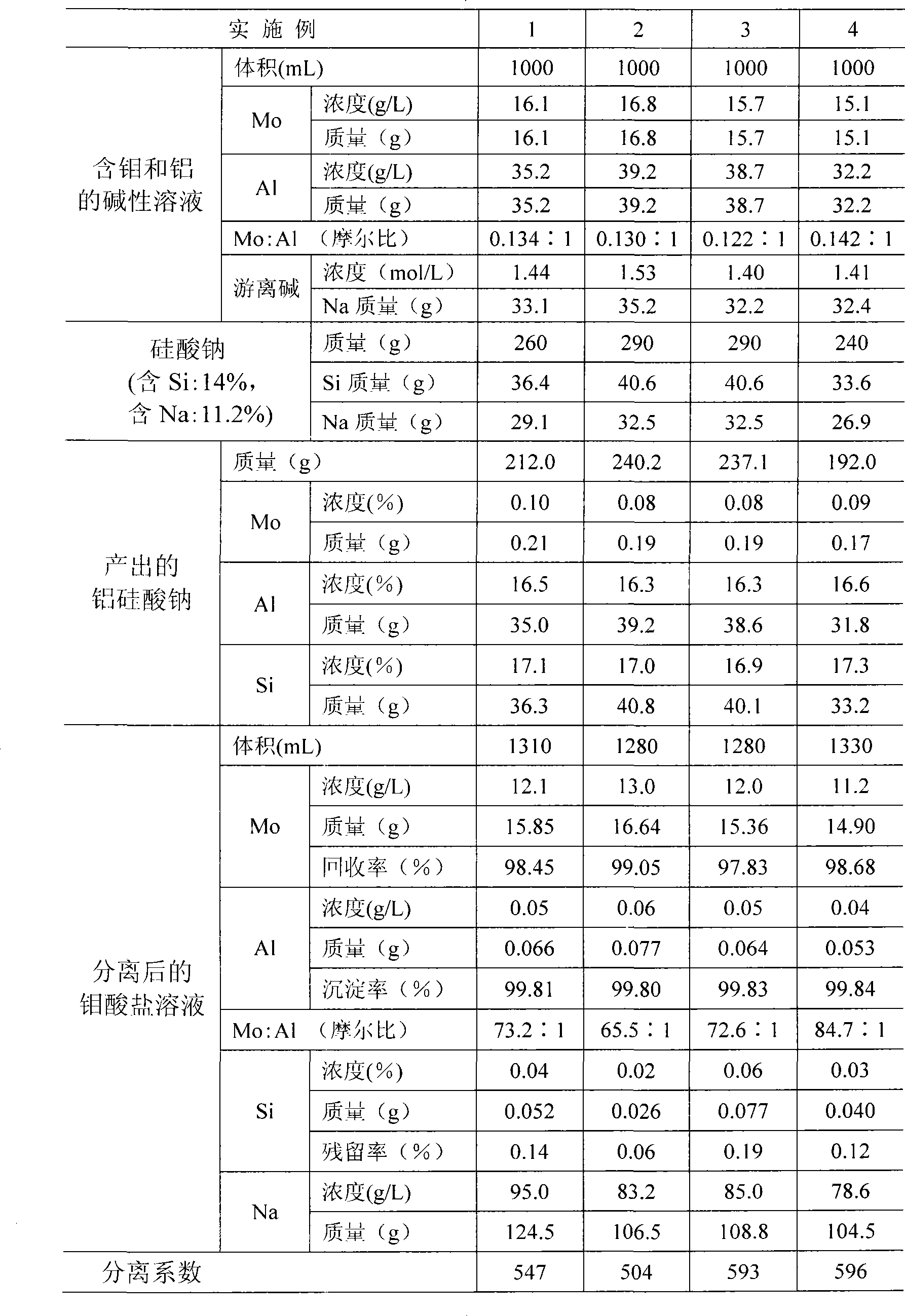
Method for separating molybdenum from aluminium in alkaline solution
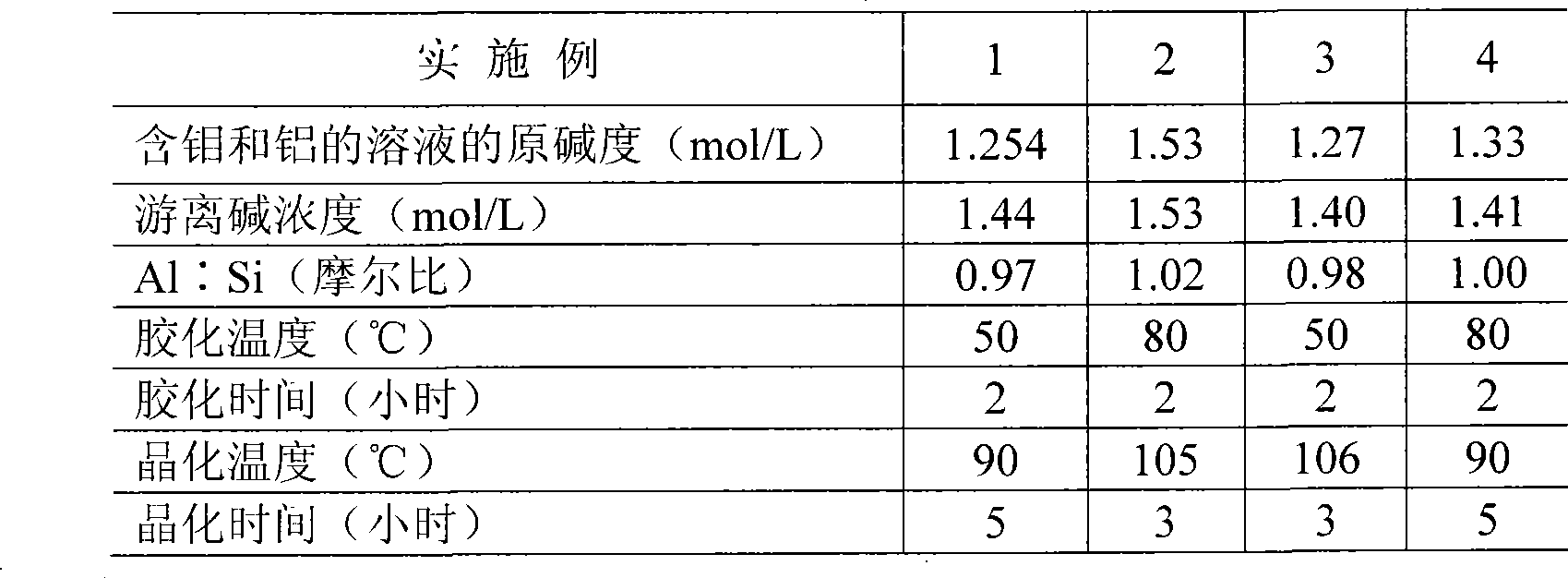
InactiveCN101445875AGood filtration and separation effectGood separation factorProcess efficiency improvementAlkali hydroxideAluminium
The invention provides a method for separating molybdenum from aluminium in alkaline solution. The method is characterized in that alkali metal hydroxide is added; the consistency of free alkali is controlled within 1.20-1.80mol / L; according to the molar ratio of 0.95-1.05 of Al:Si, alkali metal silicate solution is added under mixing condition at the normal temperature within 3 hours; the mixing condition is kept, the temperature is increased to the gelatinizing temperature of 50-80 DEG C and the gelatinizing temperature is kept for 2 hours; subsequently, the temperature is increased to the crystallization temperature of 90-110 DEG C and the crystallization temperature is kept for 3-5 hours; after filtration and separation, aluminosilicate precipitate and molybdate solution are obtained; after separation, the content of molybdenum in the aluminosilicate precipitate is reduced to below 0.2%wt, the content of aluminium or silicon in the filtrate is reduced to below 0.5g / L, the precipitation rate of the aluminium or the silicon is more than 98%. More than 98% of the soluble molybdate in the molybdenum filtrate is remained, thus achieving good separation coefficient. The method is suitable for recovering molybdenum element from waste catalyst.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RES INST OF NON FERROUS METALS
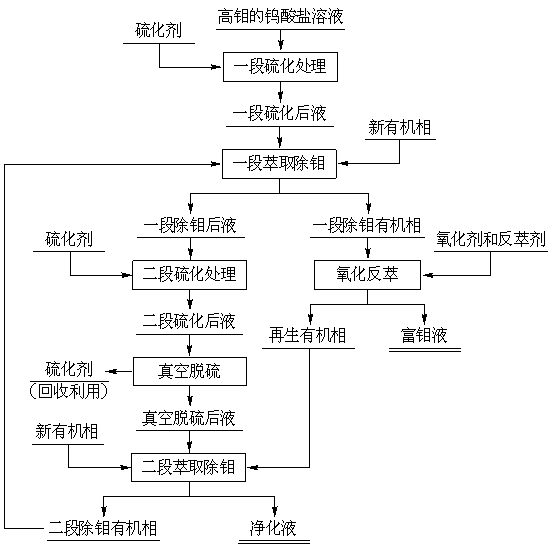
A method for extracting and removing molybdenum from tungstate solution
ActiveCN108396143BReduce total usageReduce consumptionProcess efficiency improvementDithiomolybdateSulfidation
The invention discloses a method for extracting and removing molybdenum from a tungstate solution. The method adopts two-stage sulfuration-solvent extraction to achieve deep purification of high-content molybdenum. Through the first stage of sulfidation treatment, most of the molybdenum in the solution is quickly converted into dithiomolybdate and trithiomolybdate, and then most of the molybdenum in the solution is extracted to the organic phase through a stage of extraction; the remaining small amount of molybdenum in the solution is passed through In the second stage of deep vulcanization, the molybdenum is further transformed into tetrathiomolybdate with stronger affinity with the extractant, and then the excess vulcanizing agent after vulcanization is removed and recycled by vacuum volatilization; after vacuum desulfurization treatment Solution, the molybdenum is deeply removed by two-stage extraction to obtain a purified solution. The invention has high utilization rate of the vulcanizing agent, low total consumption, less consumption of oxidant in the process of organic phase extraction, remarkably alleviates oxidation exothermic phenomenon, and is beneficial to prolonging the service life of the organic phase. There is no waste residue in the whole process of molybdenum removal, which can realize the deep molybdenum removal of high molybdenum solution.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nickel-molybdenum-copper alloy and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101775531BReasonable ingredientsReasonable ratio of ingredientsSulfurUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a nickel-molybdenum-copper alloy, which is an alloying agent used for smelting pipe line steel, stainless steel and special steel. The alloy comprises: 20 to 45 percent of nickel, 1 to 8 percent of molybdenum, 18 to 50 percent of copper, less than 0.5 percent of carbon, less than 0.05 percent of sulfur, less than 0.05 percent of phosphorus, less than 2.0 percent of siliconand the balance of ferrum. The alloy can be put at one time during the smelting of the pipe line steel and the like and reduce the labor intensity of smelters.
Owner:LIAONING JIUTONG FRICTION MATERIALS
Primary material for molds adapted to mold plastics
ActiveUS9522485B2Increase in the carbon content—madeHigh acceptanceRecovering materialsFurnace typesMaterial hardness
A mold material having a material hardness higher than 340 HB and a fine-grain structure. The mold material having a composition in weight percent that includes:C=0.25-0.35Si=0.04-0.20Mn=1.00-2.00Cr=1.00-2.00Ni=0.30-less than 0.90Mo=0.30-0.80V=less than / equal to 0.20Al=0.01-0.03N=0.0025-0.0150S=less than 0.15a remainder of Fe and impurities.
Owner:BUDERUS EDELSTAHL GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com