Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
106results about How to "Keep the same performance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
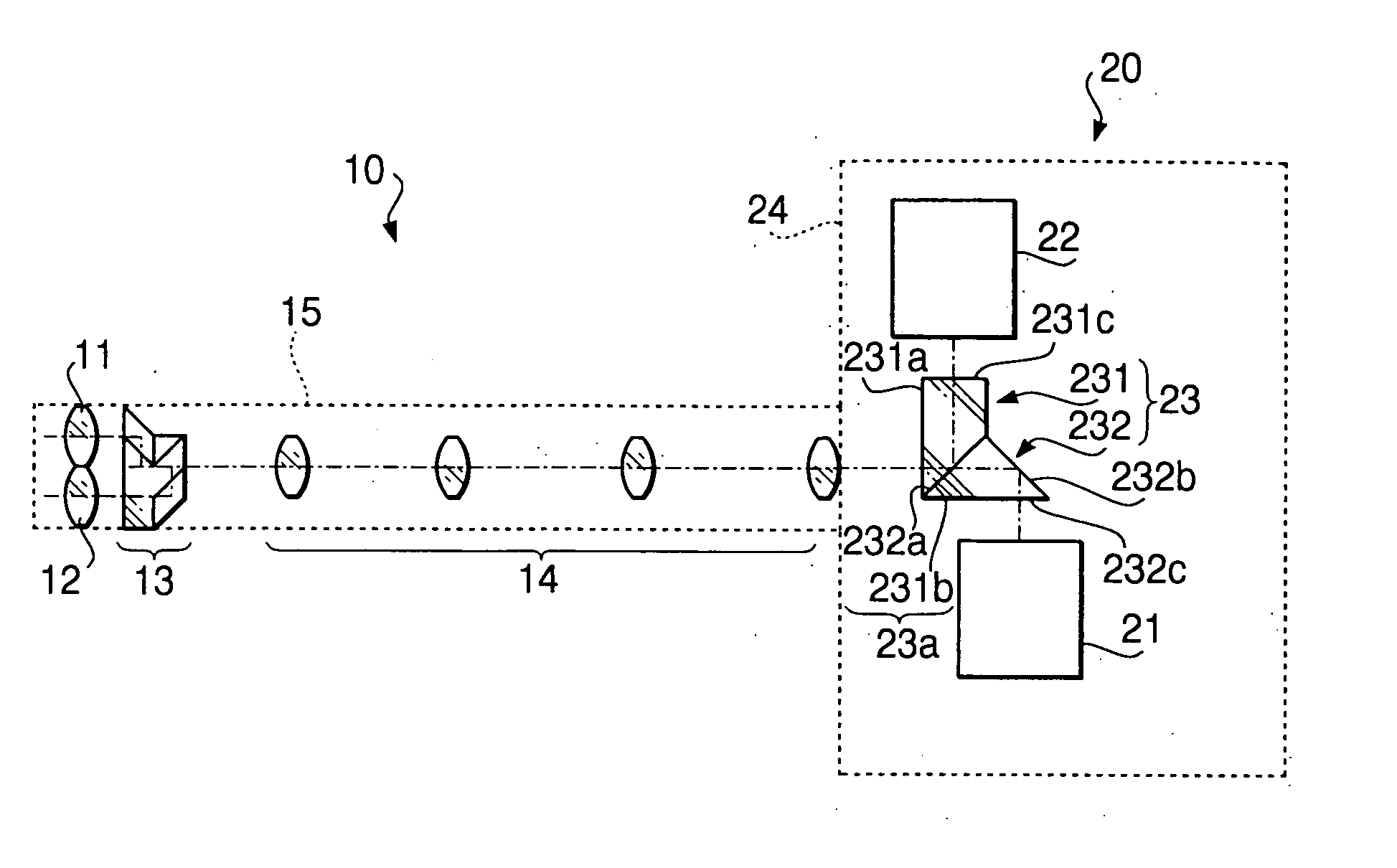
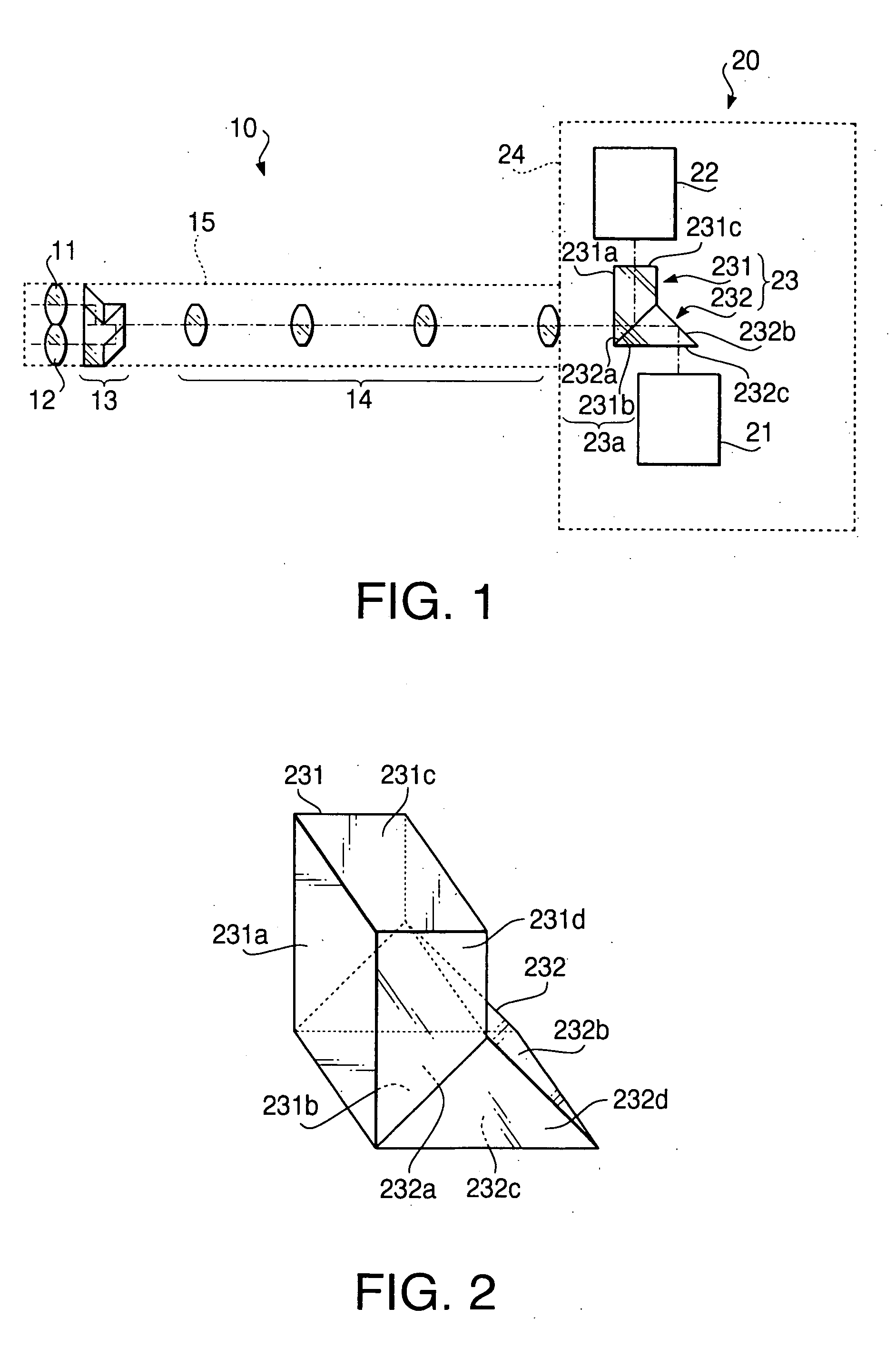
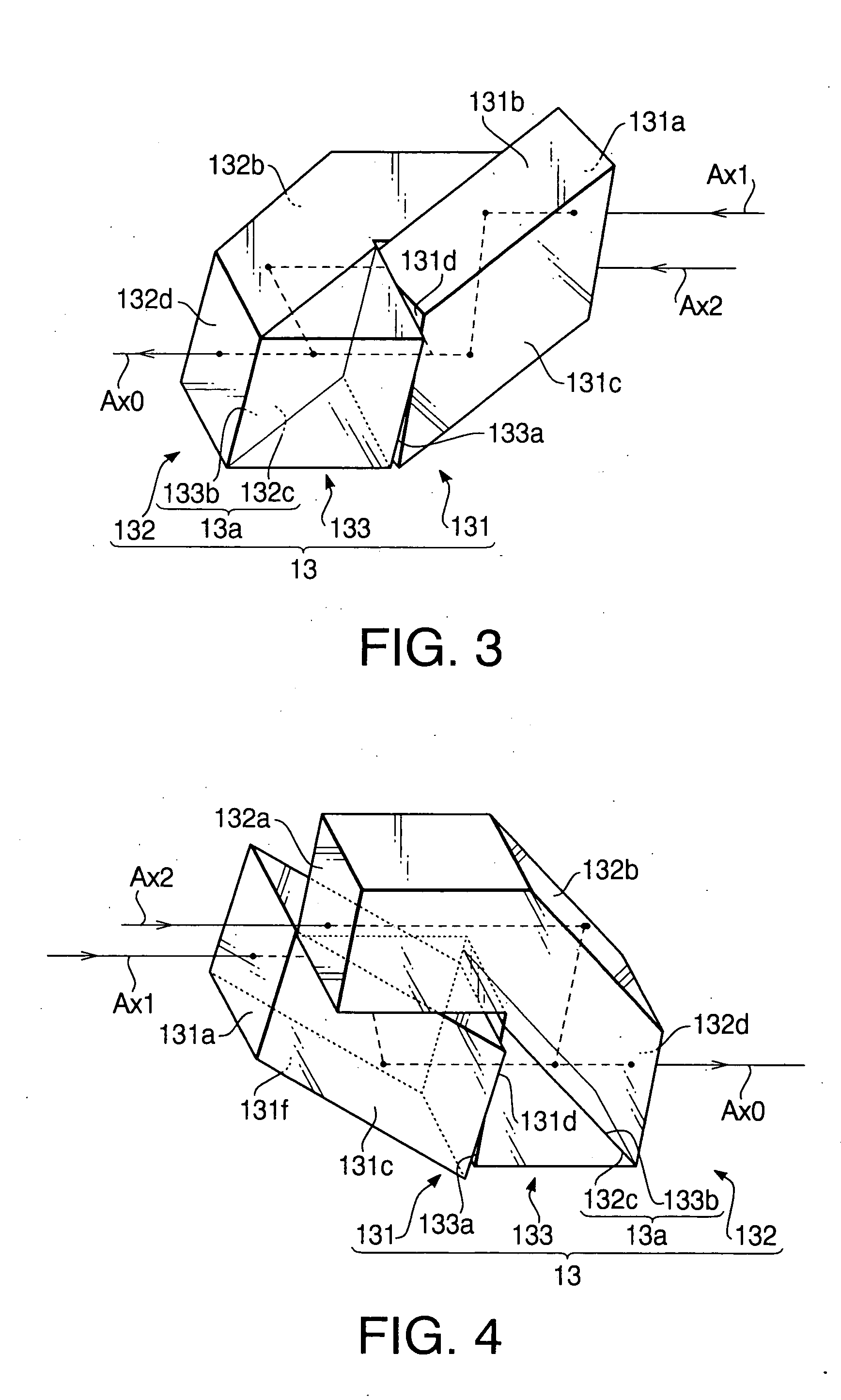
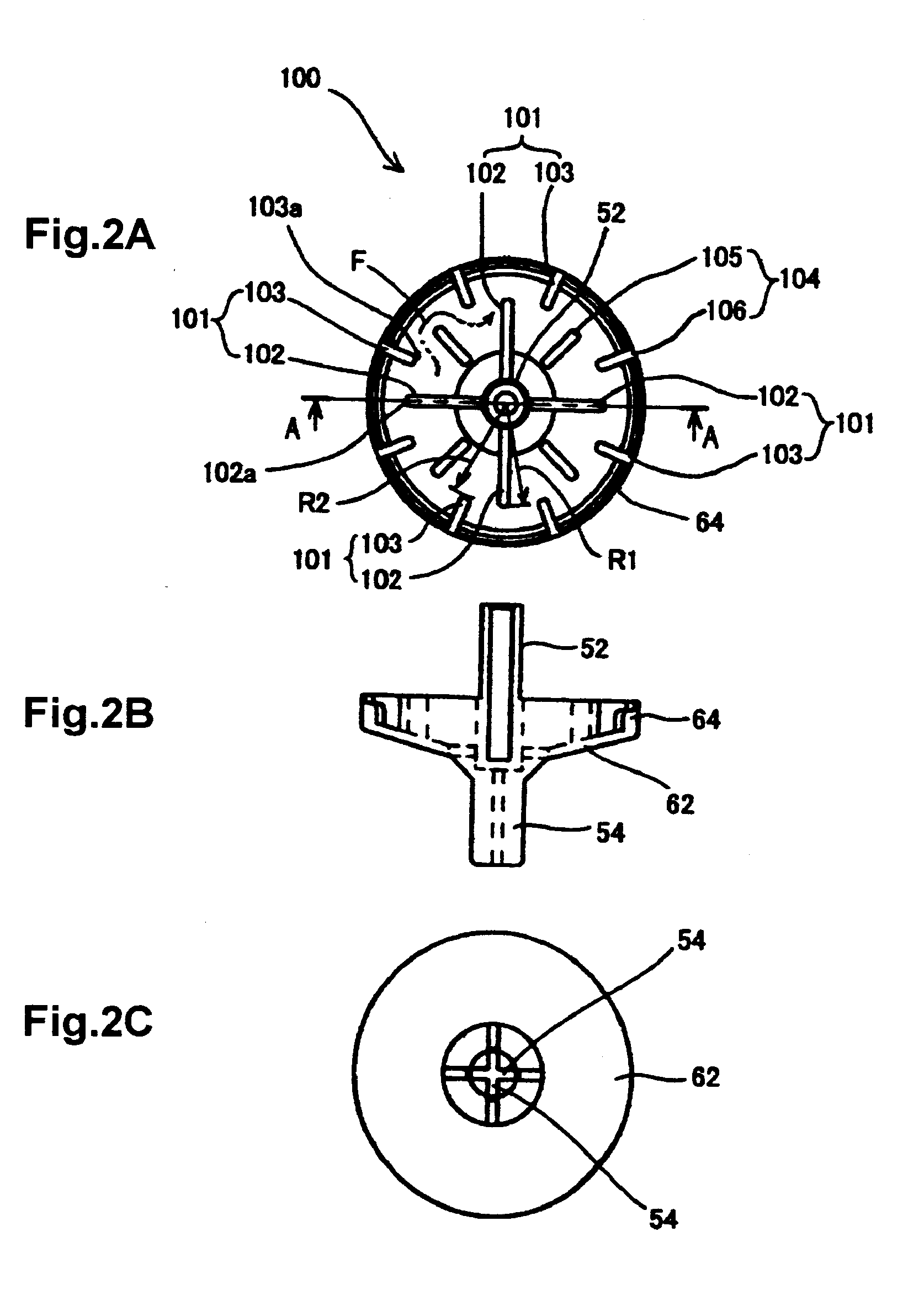
Optical system for stereoscopic rigid endoscope
InactiveUS20050159641A1Easy to optimizeAvoid insufficient lengthSurgeryEndoscopesPhysicsOptical path
An optical system for stereoscopic rigid endoscope is provided with first and second objective optical systems arranged to have a predetermined clearance therebetween and an optical path combining system that polarizes light passed through the first and second objective optical systems in directions perpendicular to each other. The optical path combining system parallelly shifts the optical axes of the first and second objective optical systems so that they coincide with each other. The shifting directions of the optical axes form an angle less than 90 degrees. A relaying optical system is provided inside the insertion unit of the endoscope. An optical axis of the relaying optical system is coaxial with the combined optical axes. An optical image separating system separates the light passed through the relaying optical system into first and second components that passed through the first and second objective optical systems and polarized by the optical path combining system, respectively.
Owner:HOYA CORP
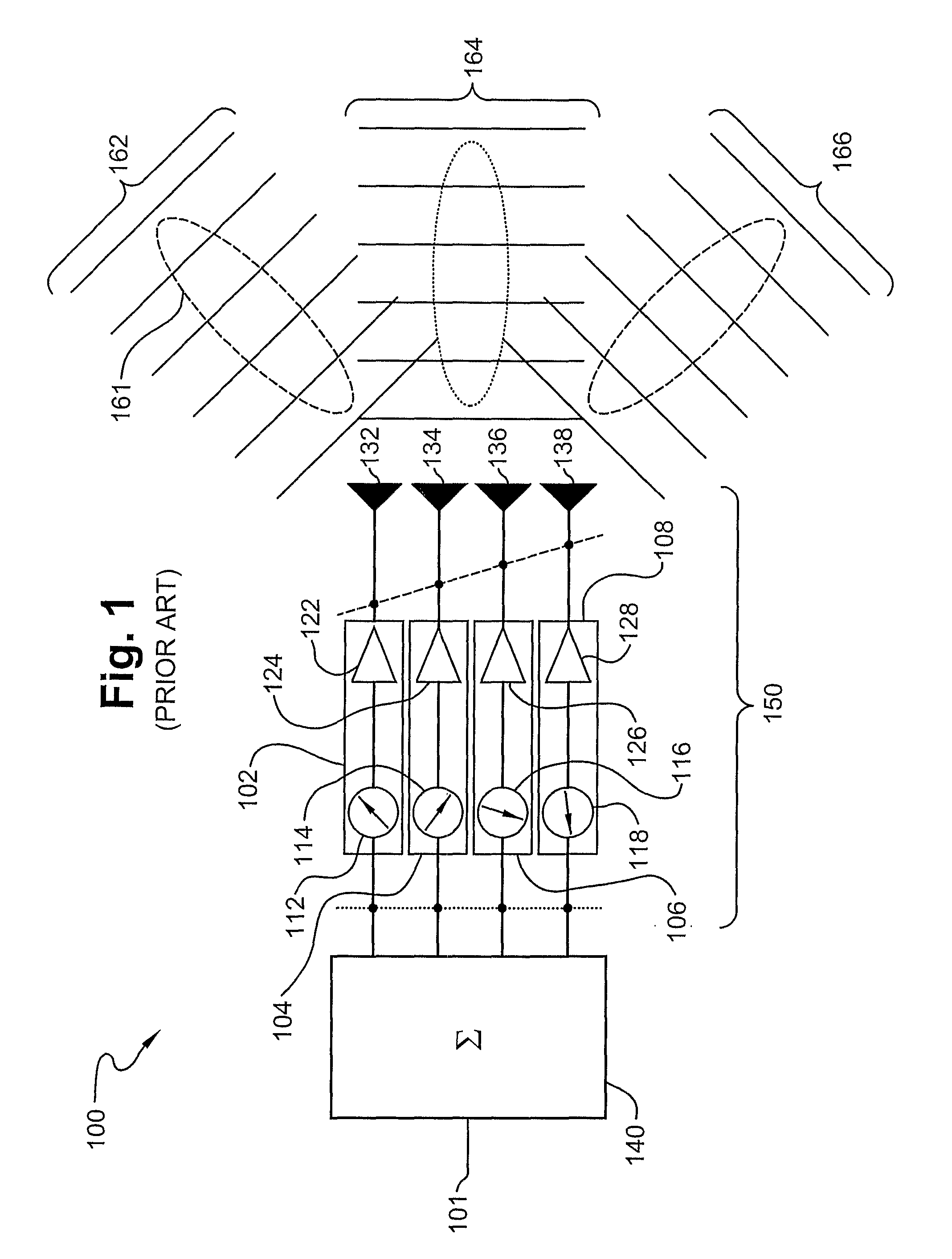
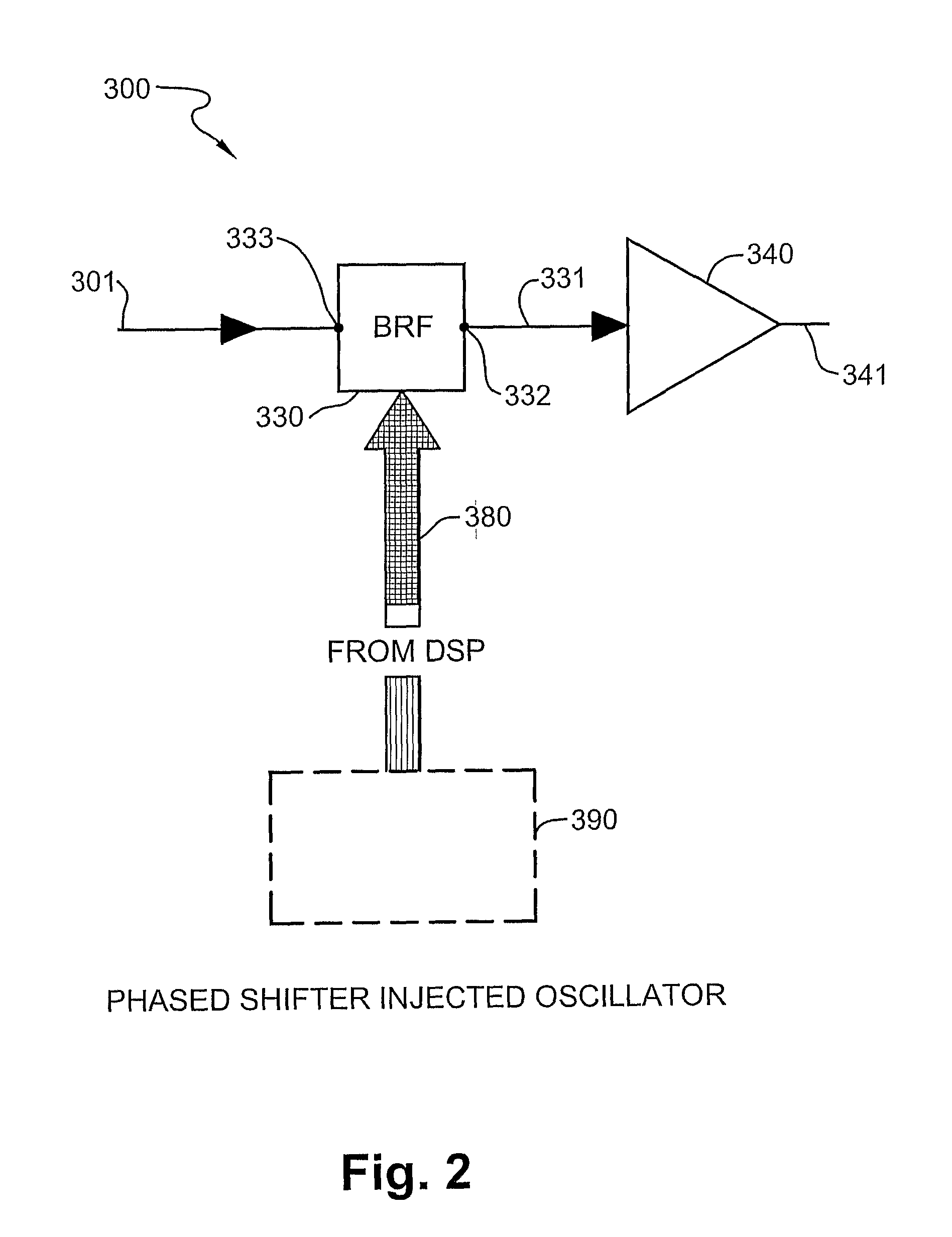
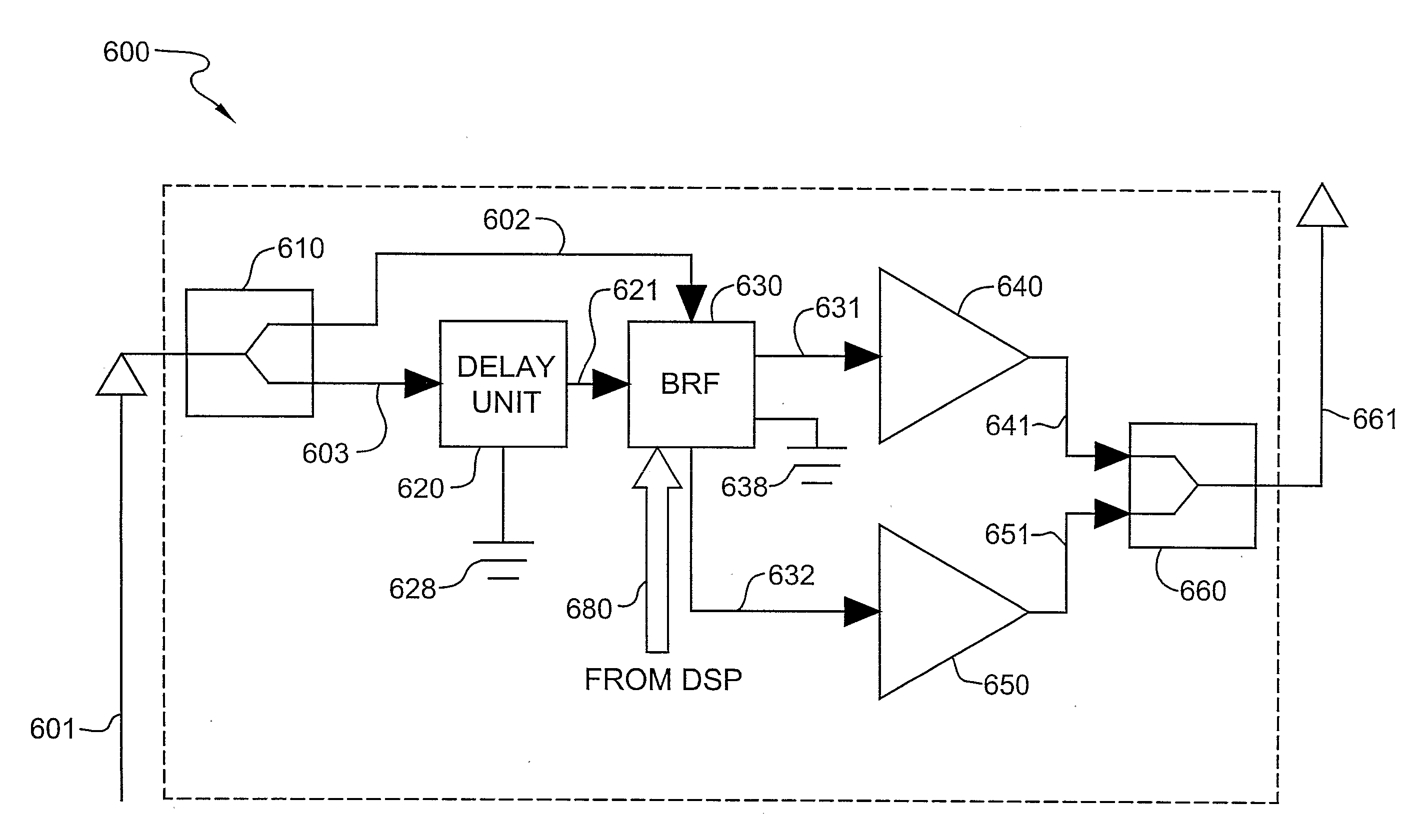
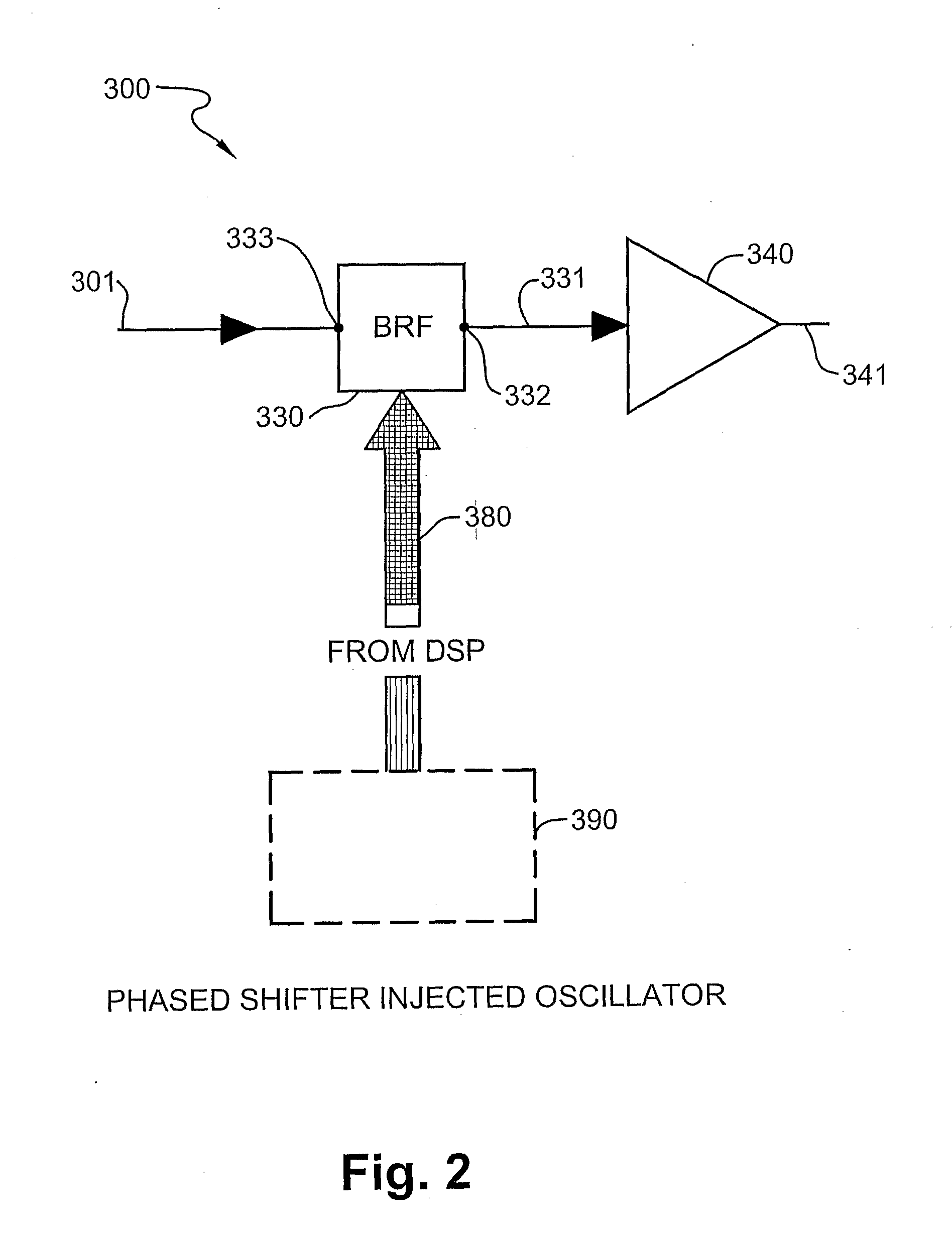
Phased shifted oscilator and antenna
ActiveUS8183935B2Low costKeep the same performancePulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsInjection lockedPhase shifted
This invention describes new and improved phased shifted injection oscillator, a phased shifted injection locked push-push oscillator and a phased array antennas (PAA). The PAAs in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention are low cost, and therefore can be used in various commercial applications, such as wireless communication or satellite mobile television.
Owner:BEAM NETWORKS
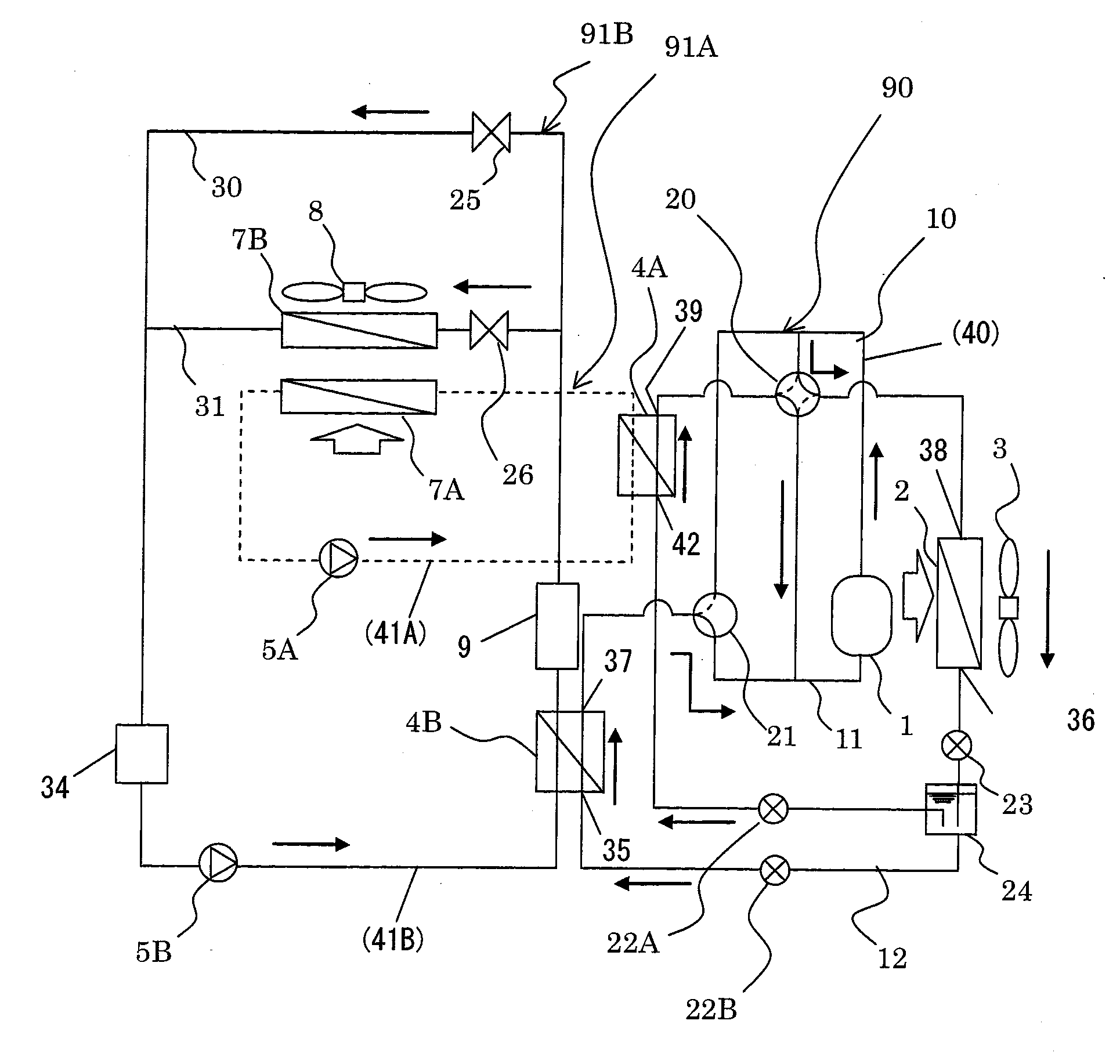
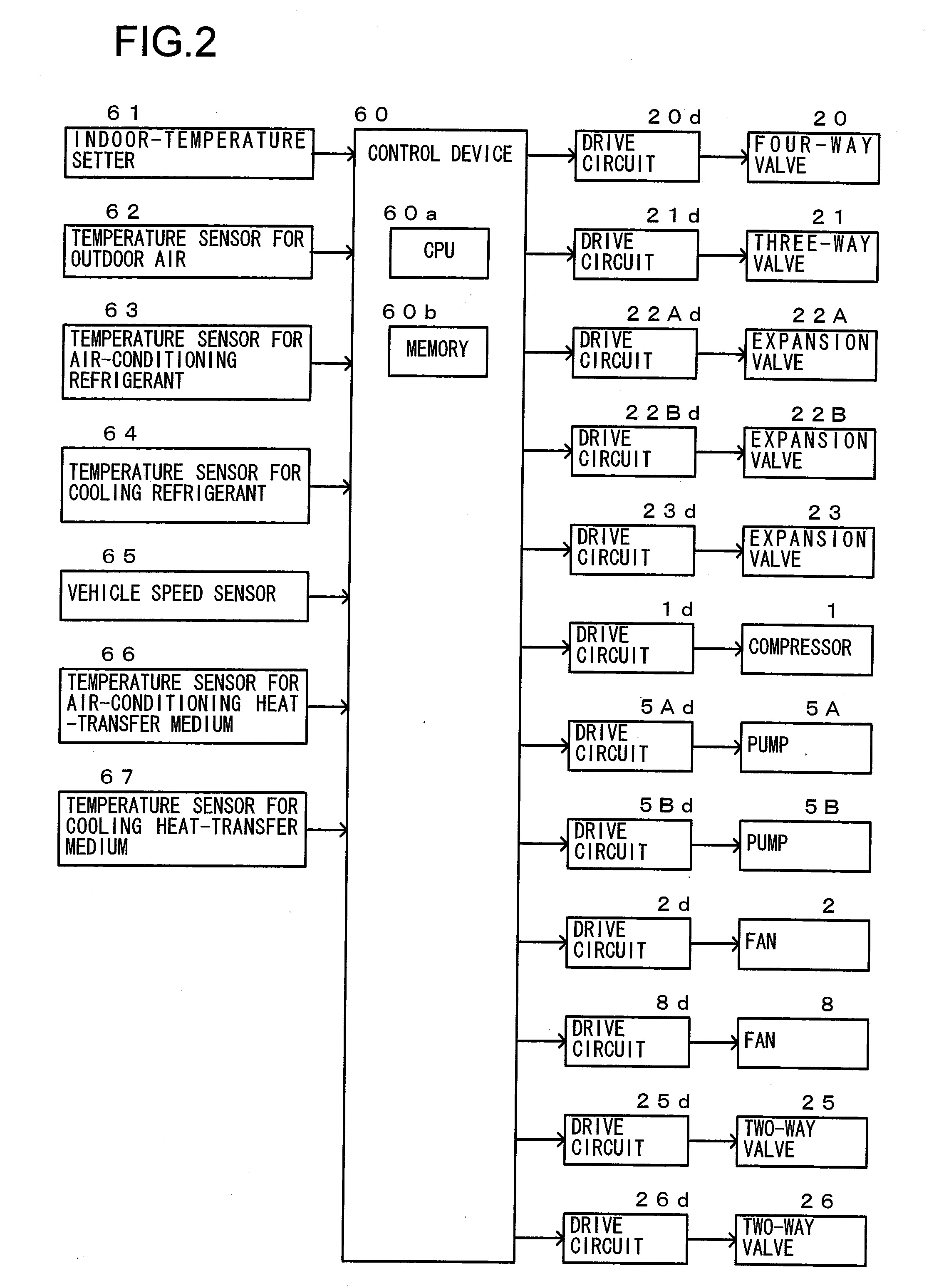
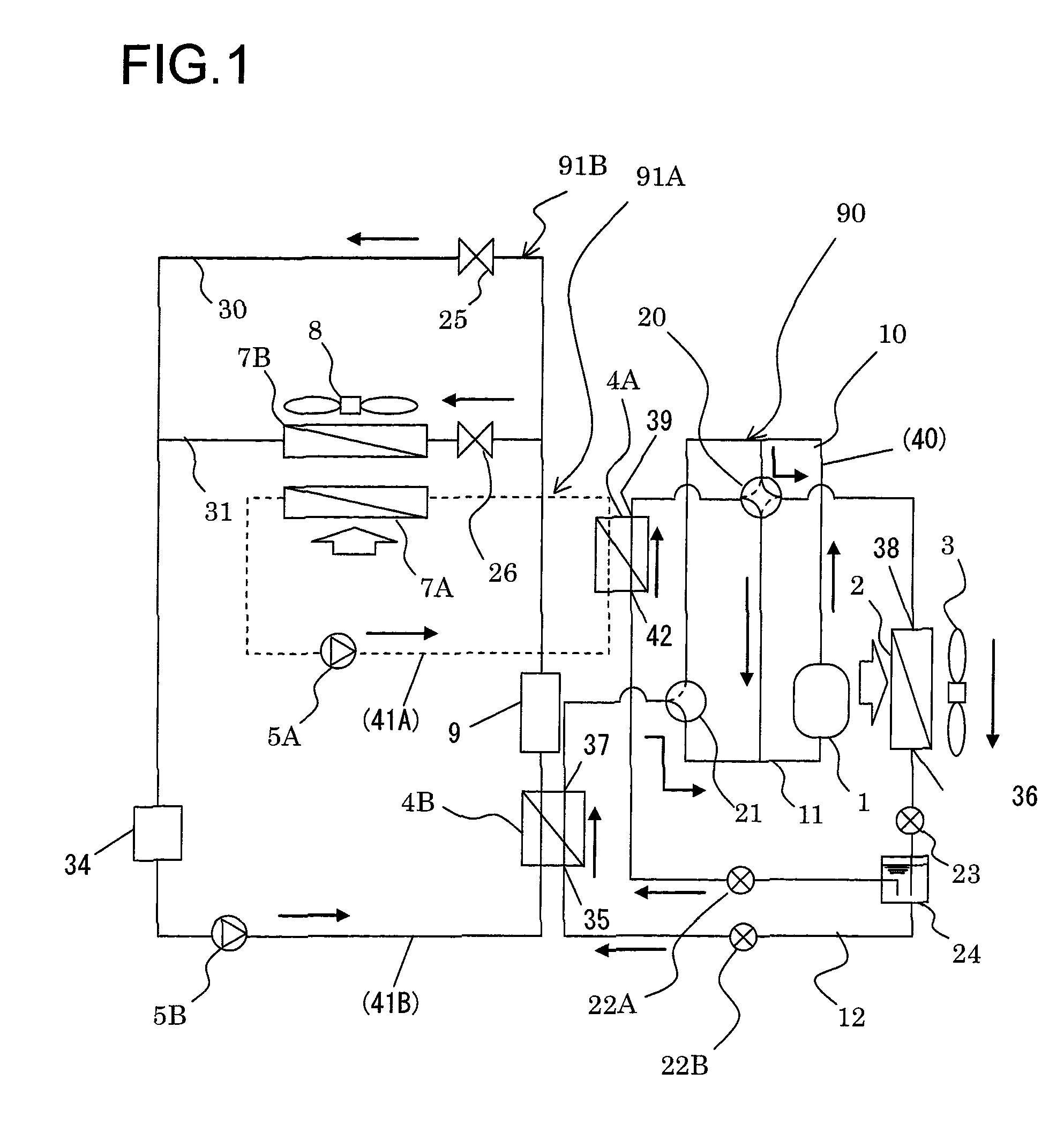
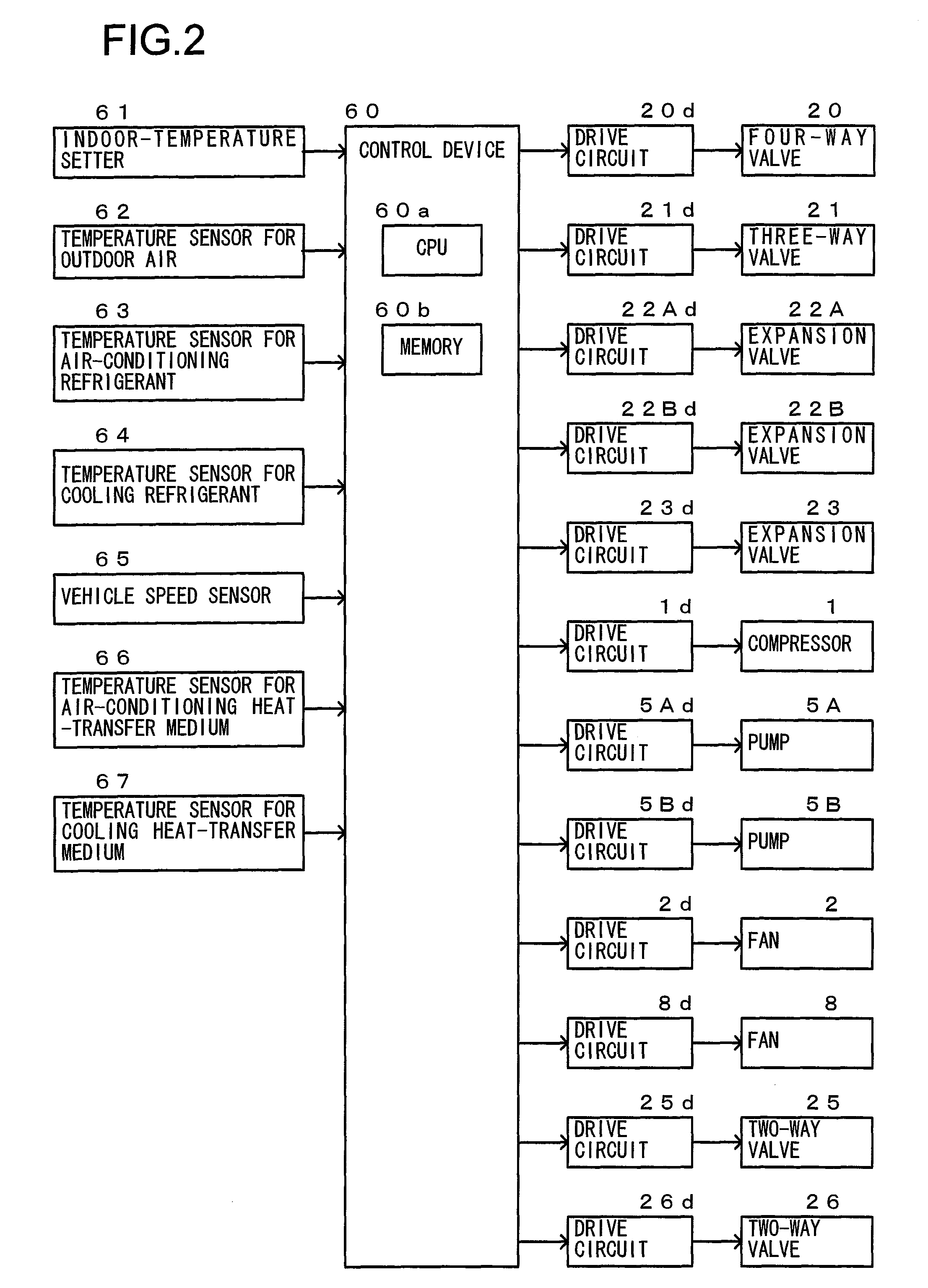
Vehicle Air-Conditioning Apparatus
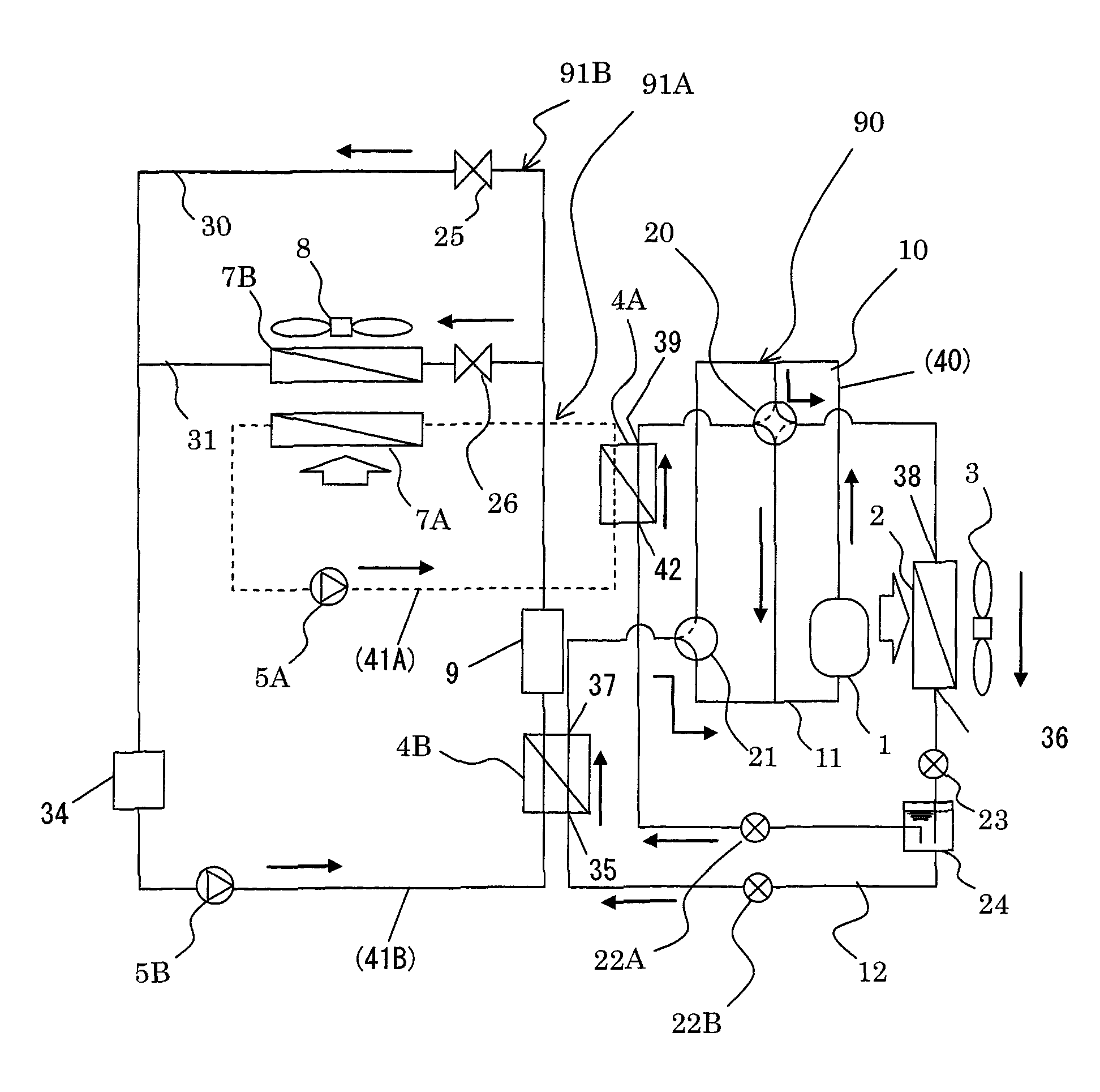
ActiveUS20110113800A1Minimize power consumptionIncreased power consumptionCompression machines with non-reversible cycleDomestic refrigeratorsIn vehicleEngineering
A vehicle air-conditioning apparatus, including: a refrigerant circulation channel that flows a refrigerant, the refrigerant circulation channel provided in a refrigeration cycle system including, as connected in a cyclic pattern, a compressor for the refrigerant, an outdoor heat-exchanger exchanging heat between the refrigerant and an outdoor air, an expansion valve reducing pressure of the refrigerant, and an air-conditioning heat-exchange circuit exchanging heat between the refrigerant and air to be introduced into a vehicle interior; and an equipment heat-exchange circuit connected in parallel to the circuit and exchanging heat between the refrigerant and in-vehicle equipment. The circuit includes a cooling heat-transfer medium circulation channel that circulates a heat-transfer medium for cooling. The cooling channel has a cooling heat-exchanger exchanging heat between the refrigerant in the channel and a cooling heat-transfer medium for cooling the in-vehicle equipment and a cooling circulation pump for circulating the cooling heat-transfer medium.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
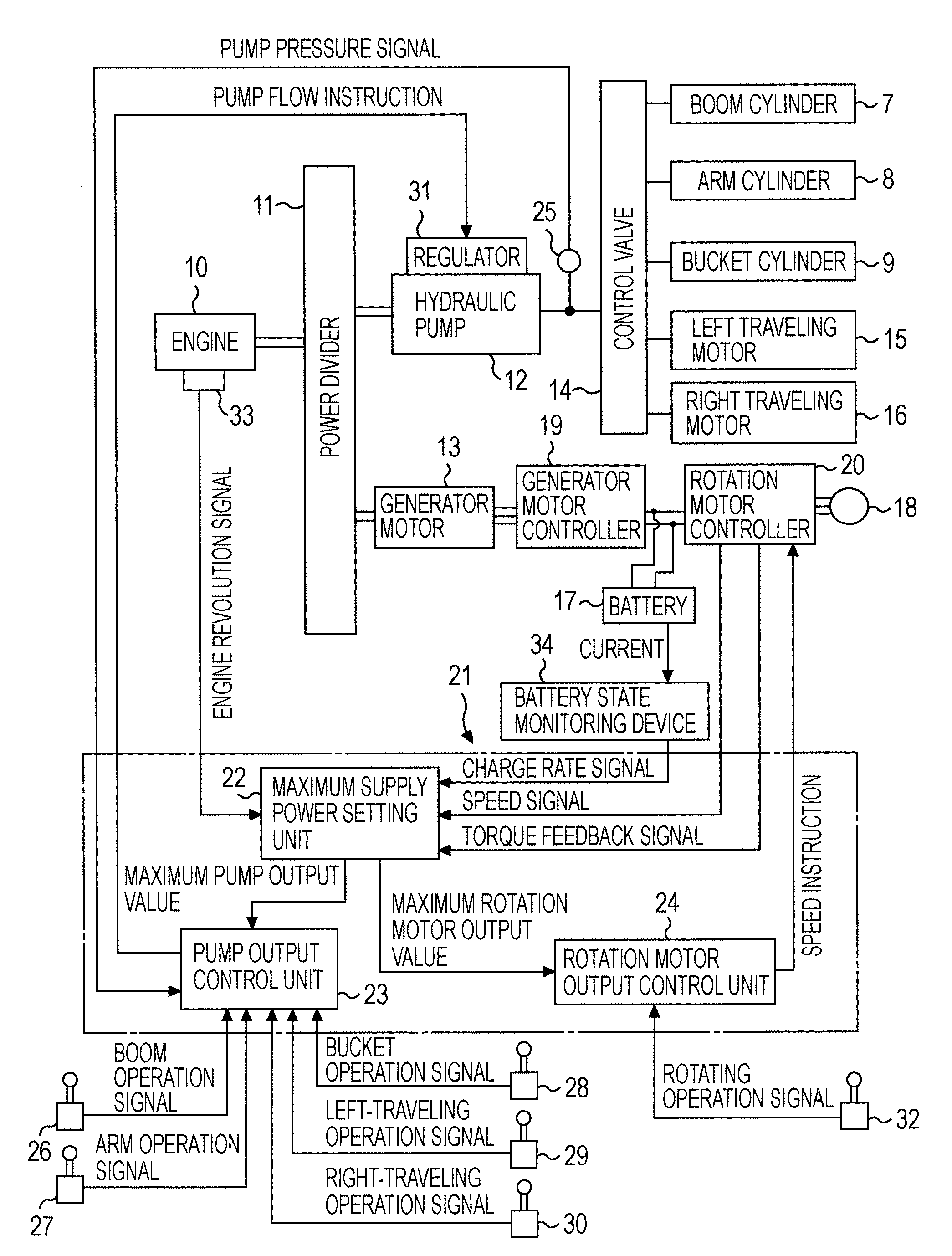
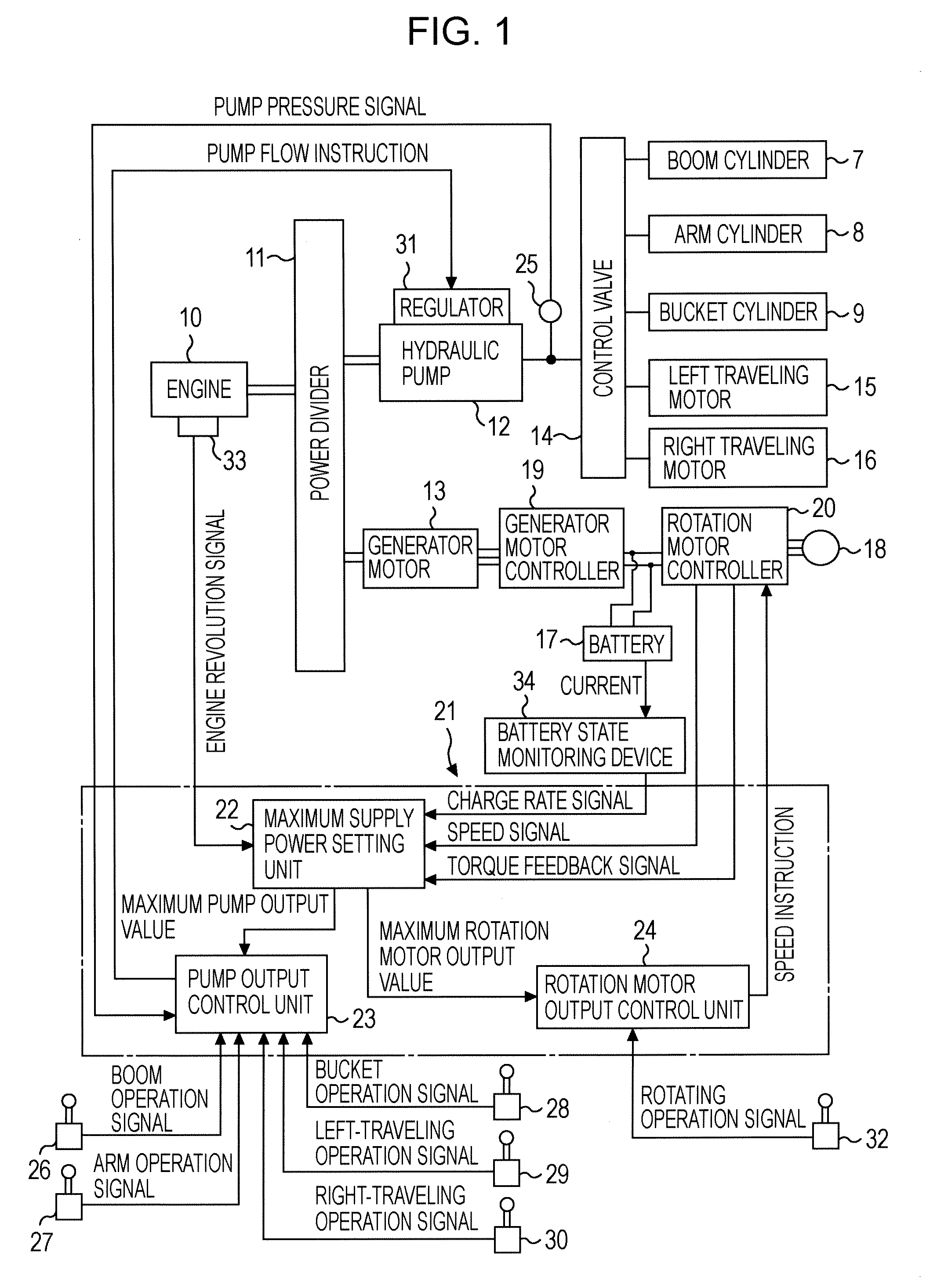
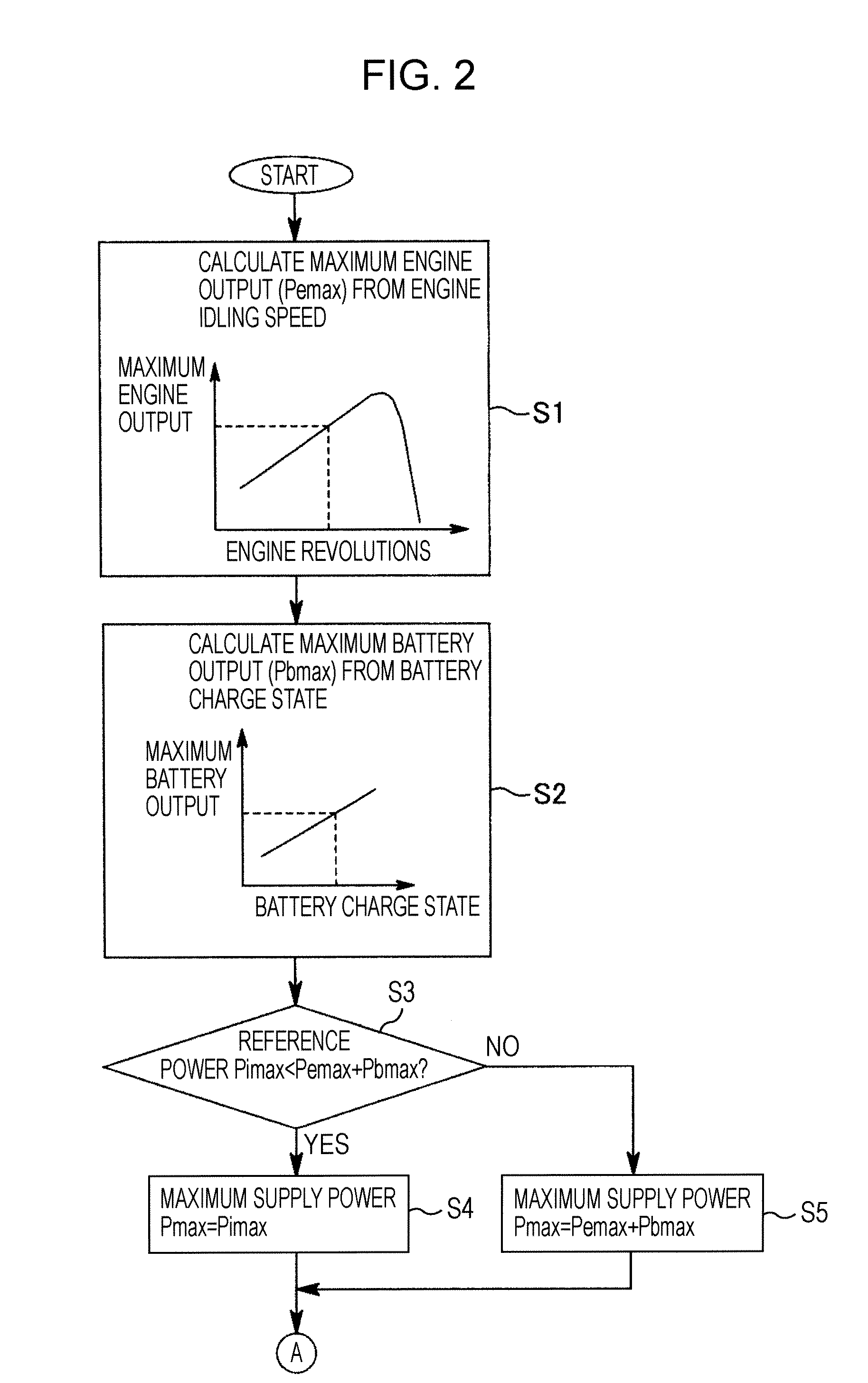
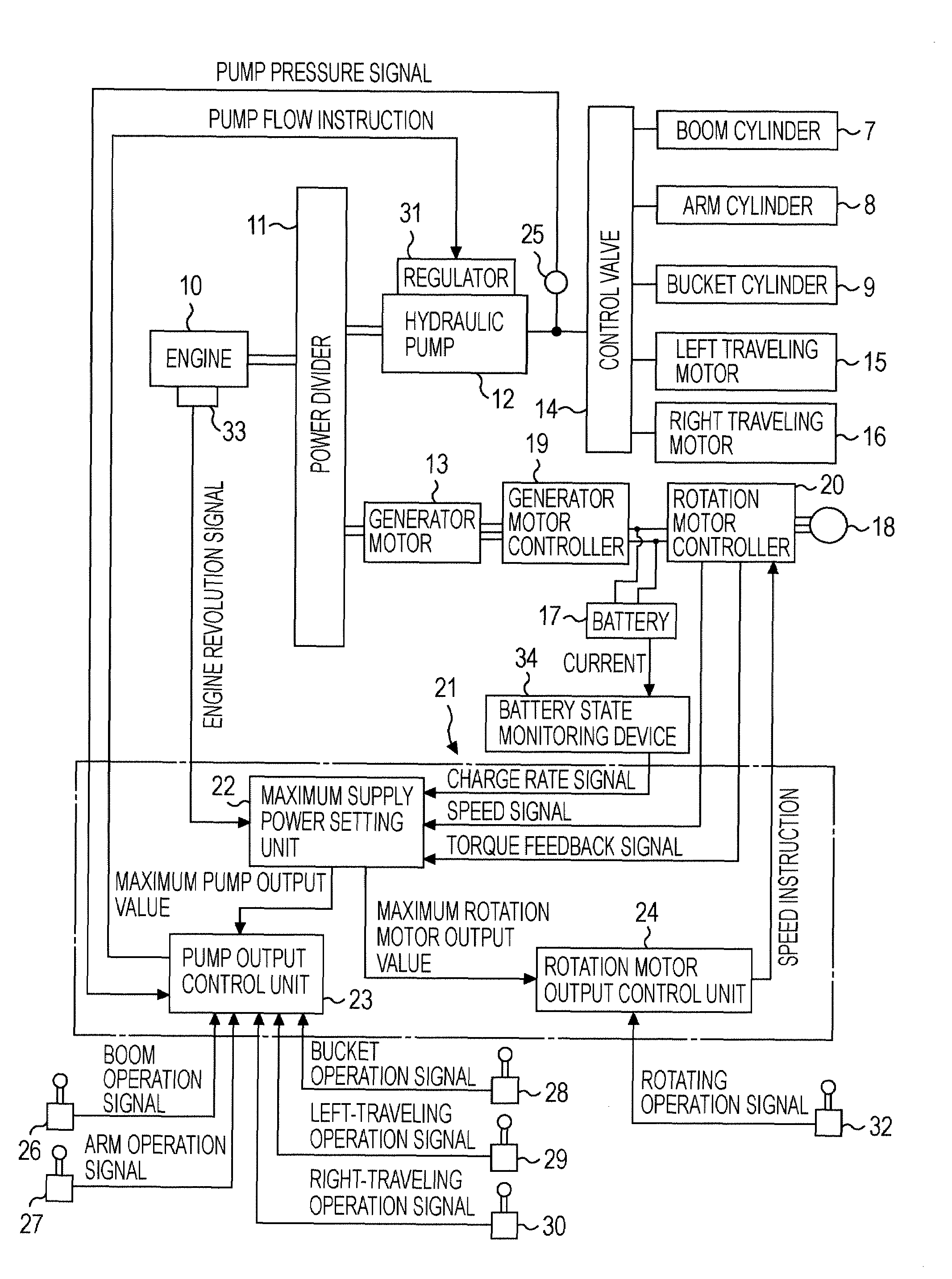
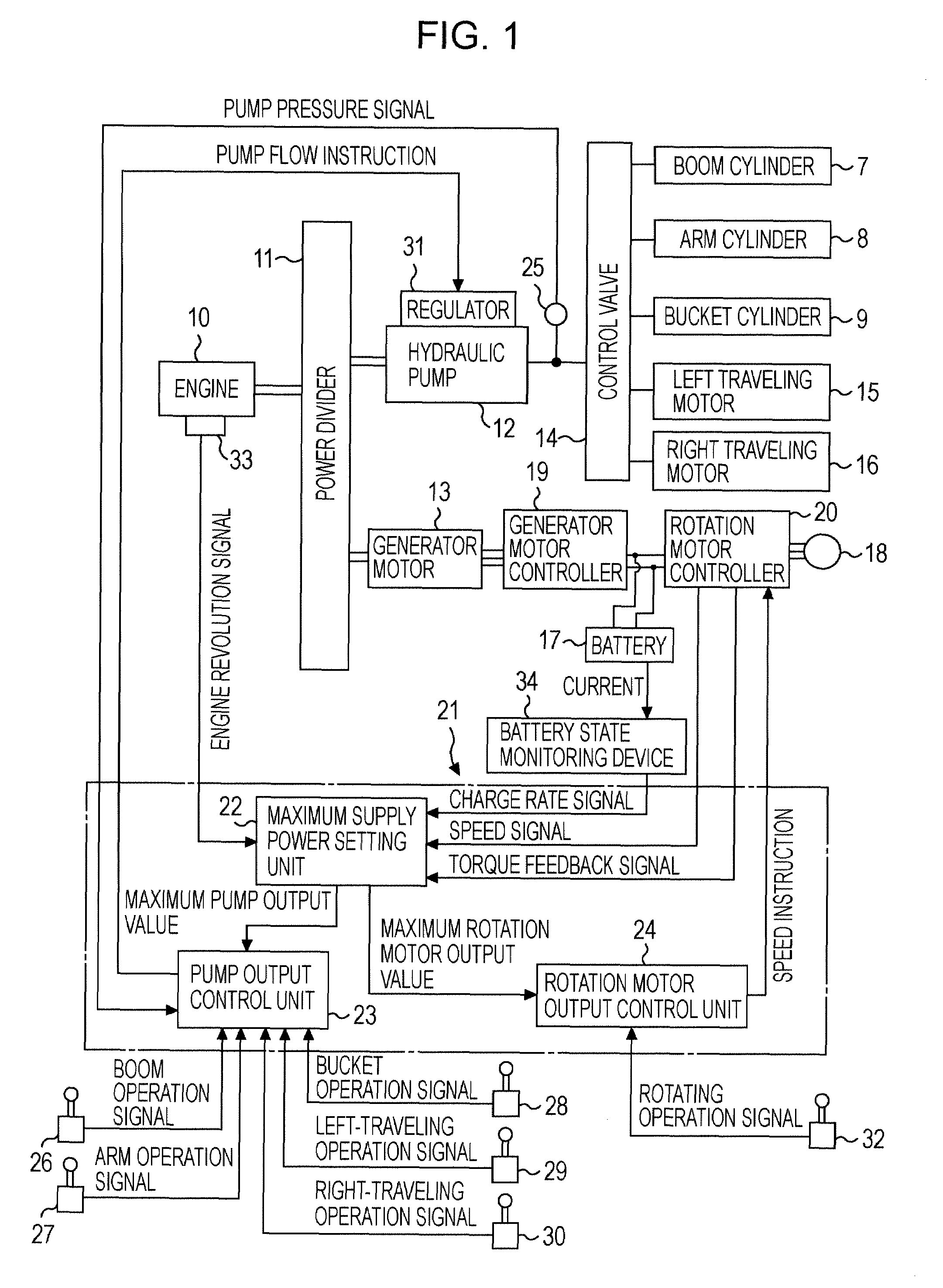
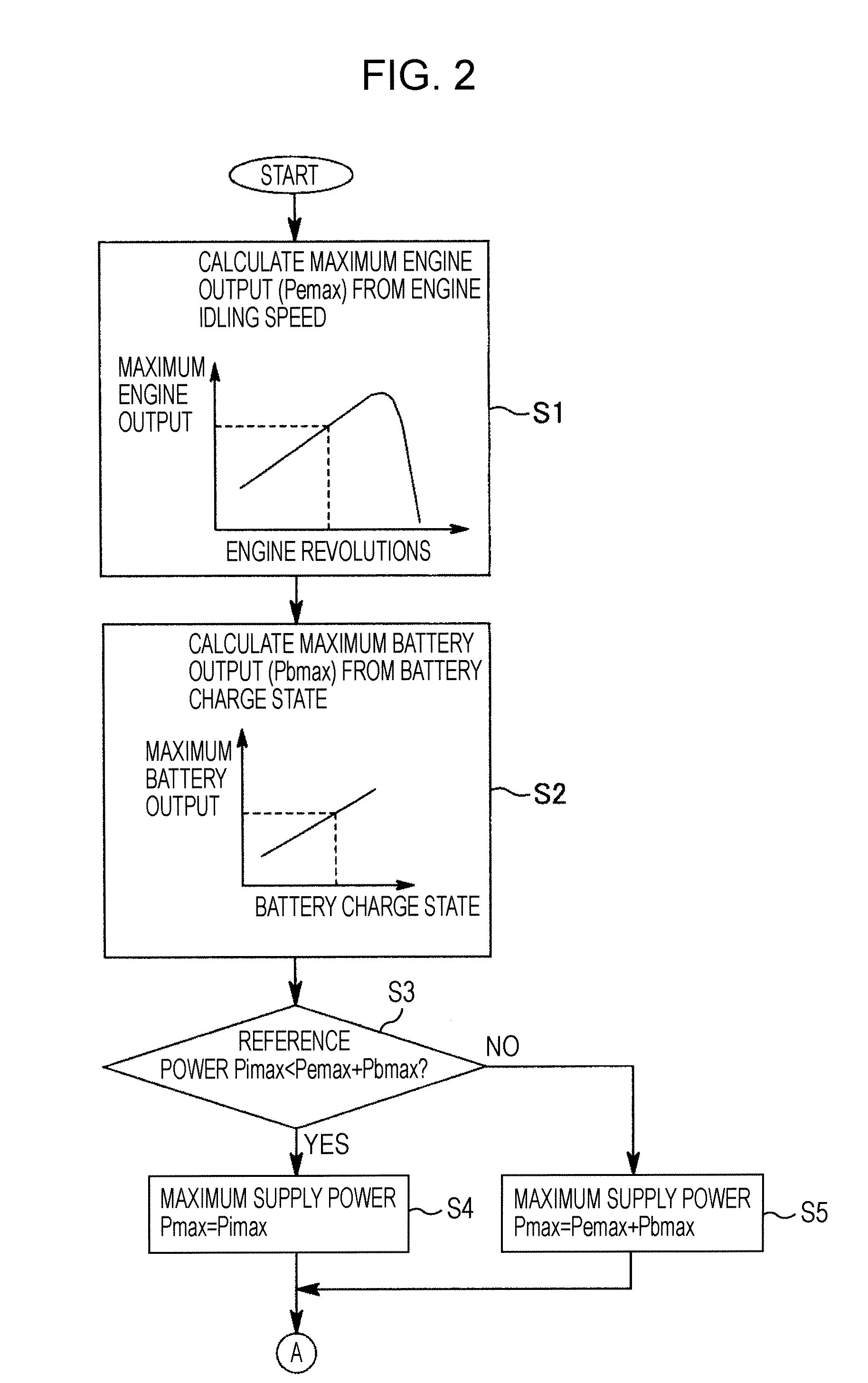
Hybrid construction machine
ActiveUS20070214782A1Adverse effectSimilar operating capabilityFluid couplingsElectric machinesHydraulic pumpMotor function
In a hybrid excavator, a hydraulic pump and a generator motor are connected in parallel to an output shaft of an engine and a rotation motor is driven by a battery. The generator motor assists the engine by performing a motor function. Power consumption of each of the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor is detected. The output of the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor is controlled such that the sum of the detected power consumption does not exceed maximum supply power set as the sum of power that can be supplied to the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor.
Owner:KOBELCO CONSTR MASCH CO LTD
Process and system for laser crystallization processing of film regions on a substrate to provide substantial uniformity within arears in such regions and edge areas thereof, and a structure of film regions
ActiveUS20060060130A1Reduce perceptionKeep the same performanceTransistorPolycrystalline material growthLaser crystallizationThin membrane
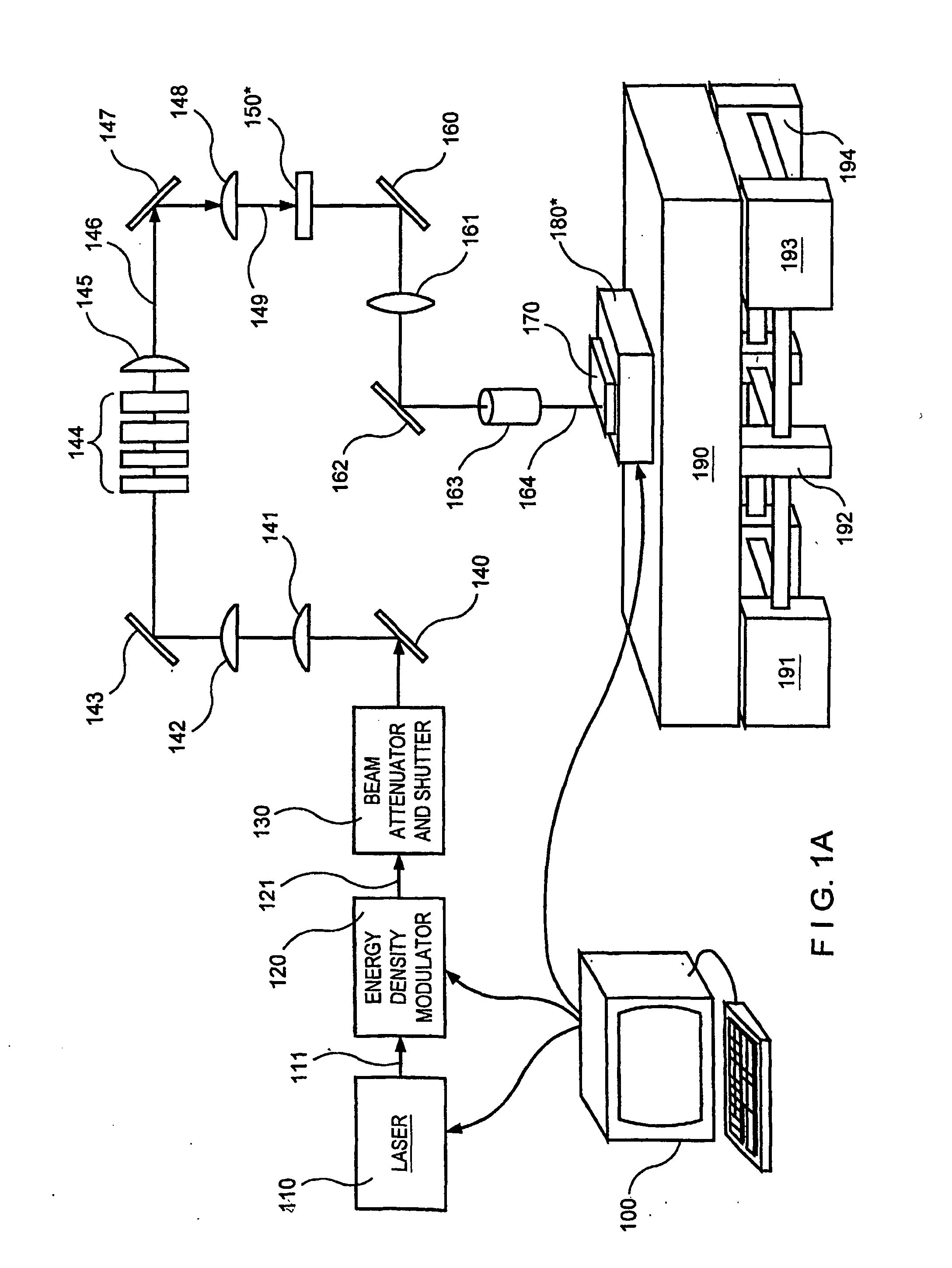
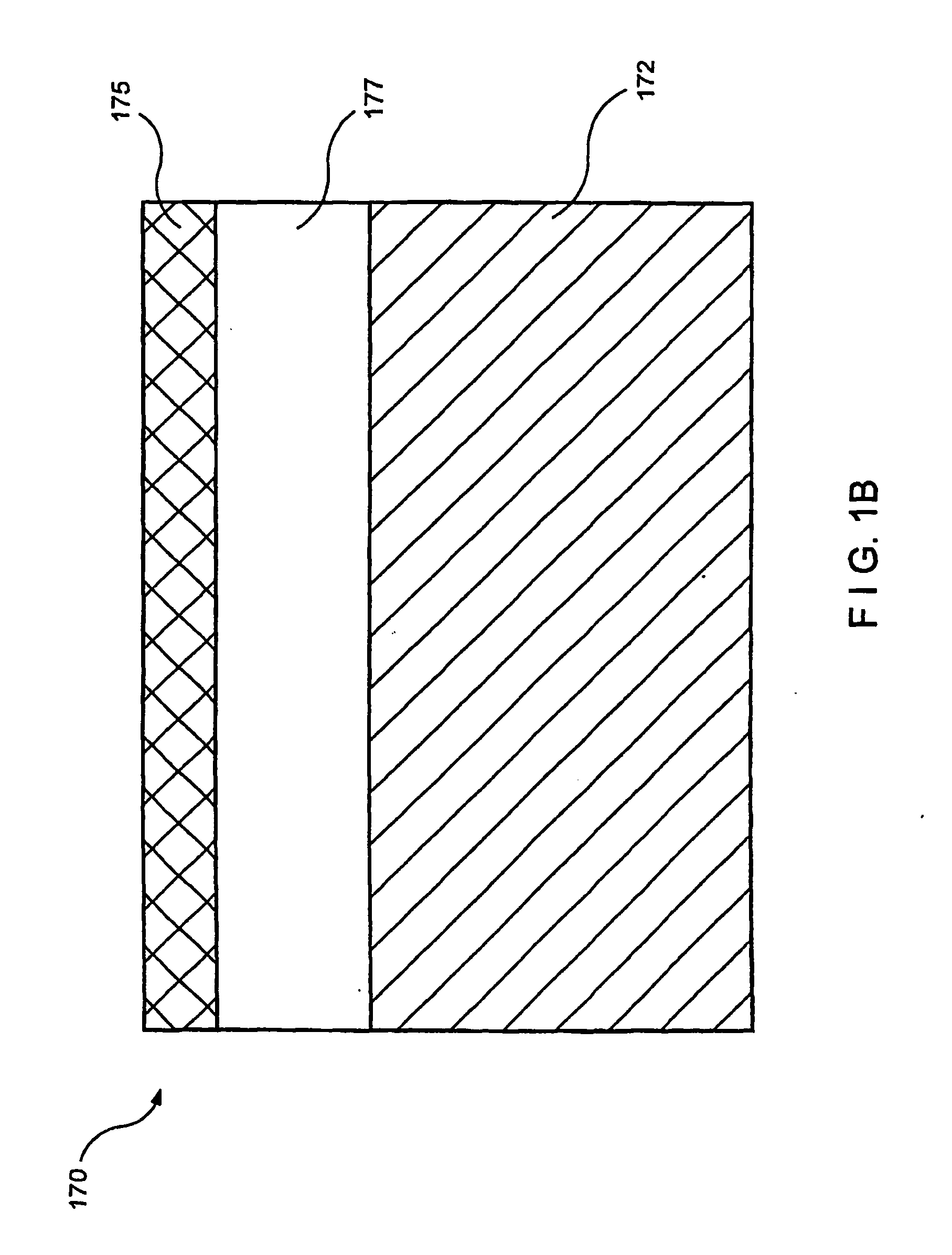
A process and system for processing a thin film sample, as well as the thin film structure are provided. In particular, a beam generator can be controlled to emit successive irradiation beam pulses at a predetermined repetition rate. Each irradiation beam pulse may be masked to define a first plurality of beamlets and a second plurality of beamlets. The first and second plurality of beamlets of each of the irradiation pulses being provided for impinging the film sample and having an intensity which is sufficient to at least partially melt irradiated portions of the section of the film sample. A particular portion of the section of the film sample is irradiated with the first beamlets of a first pulse of the irradiated beam pulses to melt first areas of the particular portion, the first areas being at least partially melted, leaving first unirradiated regions between respective adjacent ones of the first areas, and being allowed to resolidify and crystallize. After the irradiation of the particular portion with the first beamlets, the particular portion is again irradiated with the second beamlets of a second pulse of the irradiated beam pulses to melt second areas of the particular portion, the second areas being at least partially melted, leaving second unirradiated regions between respective adjacent ones of the second areas, and being allowed to resolidify and crystallize. The first irradiated and re-solidified areas and the second irradiated and re-solidified areas are intermingled with one another within the section of the film sample. In addition, the first areas correspond to first pixels, and the second areas correspond to second pixels.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
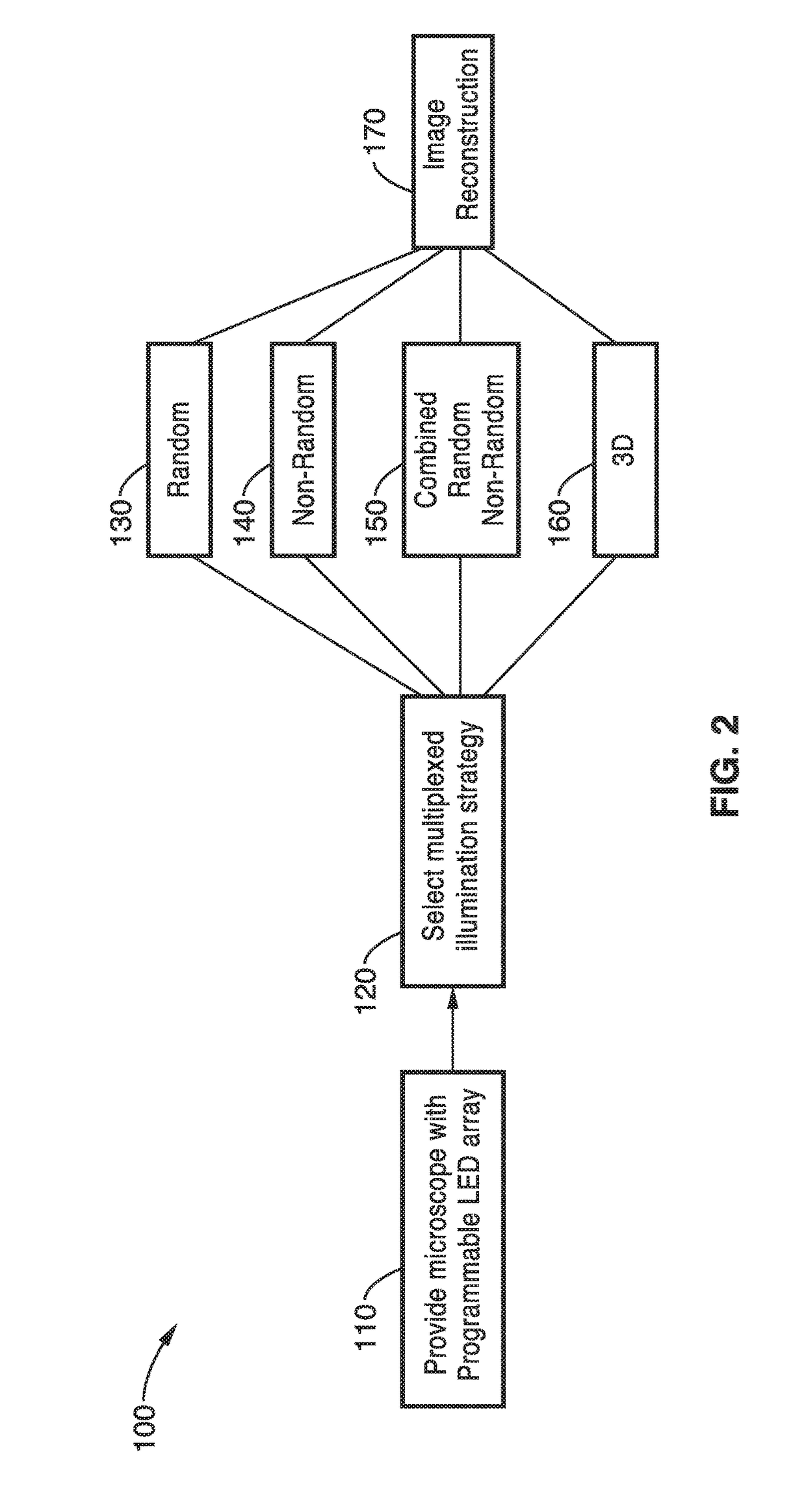
Fourier ptychographic microscopy with multiplexed illumination
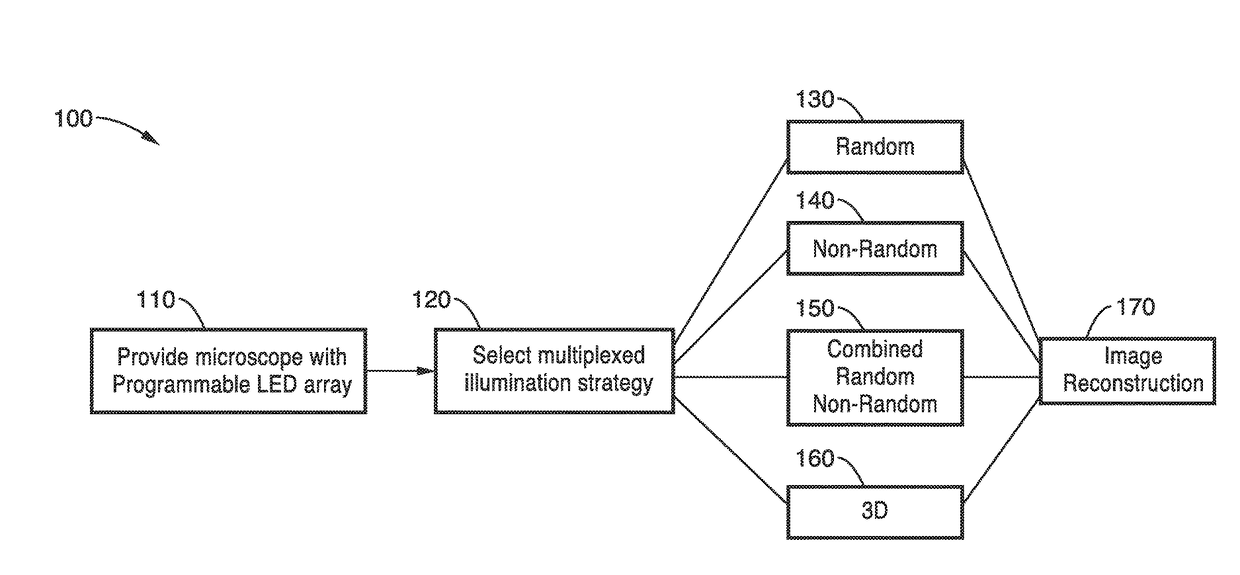
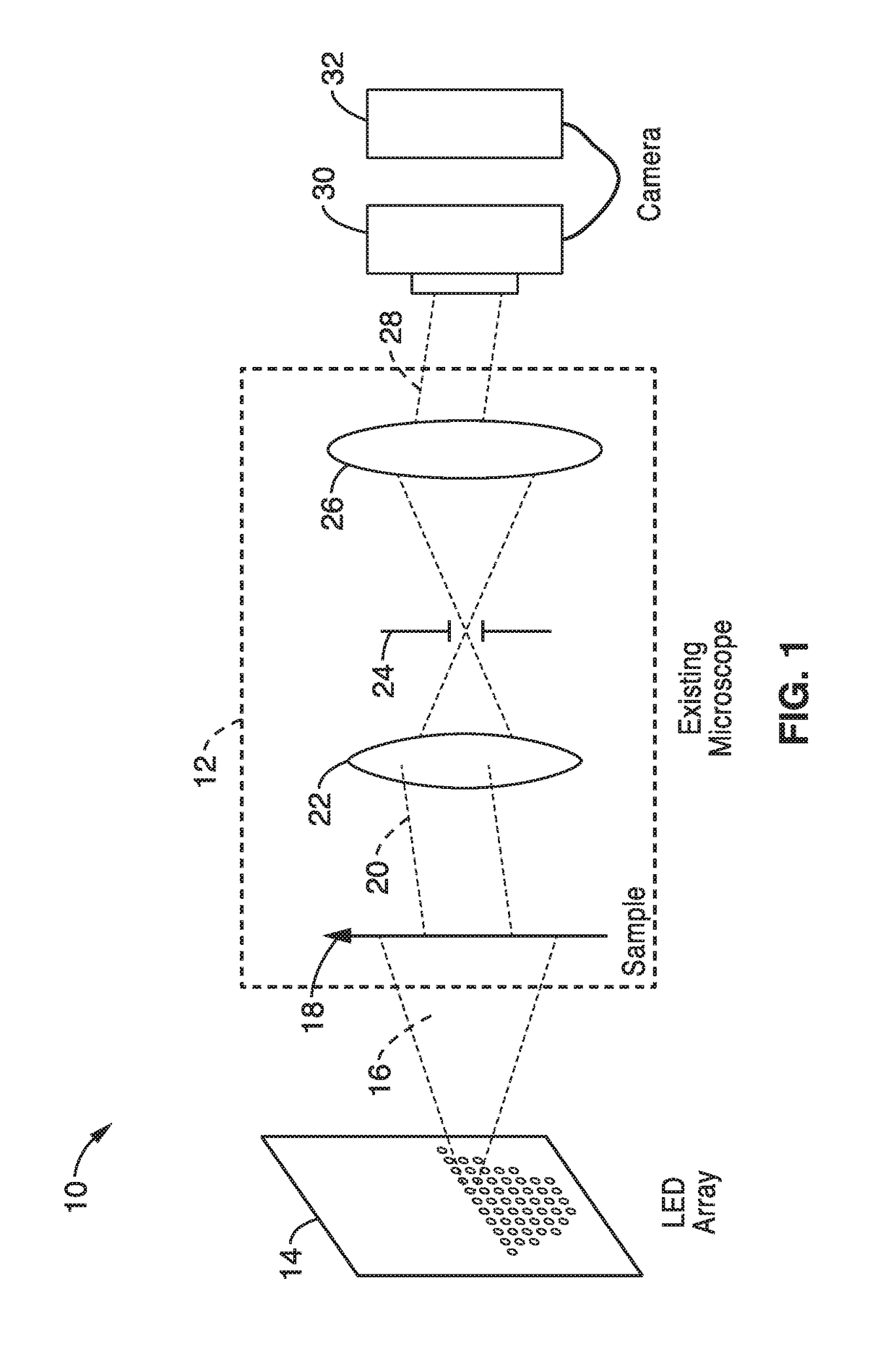
InactiveUS20170146788A1Exploits redundancyFaster sample dynamicImage enhancementTelevision system detailsMicroscopic imageWide field
A system and methods for wide field of view, high resolution Fourier ptychographic microscopic imaging with a programmable LED array light source. The individual lights in the LED array can be actuated according to random, non-random and hybrid random and non-random illumination strategies to produce high resolution images with fast acquisition speeds. The methods greatly reduce the acquisition time and number of images captured compared to conventional sequential scans. The methods also provide for fast, wide field 3D imaging of thick biological samples.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Hybrid construction machine
ActiveUS7669413B2Same operabilityKeep the same performanceFluid couplingsElectric machinesHydraulic pumpMotor function
In a hybrid excavator, a hydraulic pump and a generator motor are connected in parallel to an output shaft of an engine and a rotation motor is driven by a battery. The generator motor assists the engine by performing a motor function. Power consumption of each of the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor is detected. The output of the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor is controlled such that the sum of the detected power consumption does not exceed maximum supply power set as the sum of power that can be supplied to the hydraulic pump and the rotation motor.
Owner:KOBELCO CONSTR MASCH CO LTD
Two-mode radar level gauge system
ActiveUS7345622B2Simplified feeding meanSame capacityLevel indicatorsAntenna detailsRadarFilling materials
A radar level gauge system for gauging the level of a filling material in a container is disclosed. The system comprises a waveguide extending towards the surface of said filling material; a transmitter for transmitting a microwave signal of a first mode of propagation in the waveguide; and a receiver for receiving the microwave signal reflected against the surface of the filling material and propagating back through the waveguide. Further, it comprises a processing circuitry for determining the filling level of the container based on the reflected microwave signal; and a transition element connecting the waveguide and the transmitter, wherein the transition element is configured to allow a part of the transmitted microwave signal to leak into a second mode of propagation. The first and second modes of propagation are within a frequency band which admits propagation of said microwave signal in the two different modes of propagation in the waveguide, wherein the receiver is arranged to receive the microwave signal in the at least two different modes of propagation.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Two-mode radar level gauge system
ActiveUS20070085729A1Simplified feeding meanSame capacityLevel indicatorsAntenna detailsRadarFilling materials
A radar level gauge system for gauging the level of a filling material in a container is disclosed. The system comprises a waveguide extending towards the surface of said filling material; a transmitter for transmitting a microwave signal of a first mode of propagation in the waveguide; and a receiver for receiving the microwave signal reflected against the surface of the filling material and propagating back through the waveguide. Further, it comprises a processing circuitry for determining the filling level of the container based on the reflected microwave signal; and a transition element connecting the waveguide and the transmitter, wherein the transition element is configured to allow a part of the transmitted microwave signal to leak into a second mode of propagation. The first and second modes of propagation are within a frequency band which admits propagation of said microwave signal in the two different modes of propagation in the waveguide, wherein the receiver is arranged to receive the microwave signal in the at least two different modes of propagation.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT TANK RADAR
Laser crystallization and selective patterning using multiple beamlets
ActiveUS7300858B2Reduce perceptionKeep the same performanceTransistorPolycrystalline material growthLaser crystallizationLight beam
A process and system for processing a thin film sample, as well as the thin film structure are provided. In particular, a beam generator can be controlled to emit successive irradiation beam pulses at a predetermined repetition rate. Each irradiation beam pulse may be masked to define a first plurality of beamlets and a second plurality of beamlets. The first and second plurality of beamlets of each of the irradiation pulses being provided for impinging the film sample and having an intensity which is sufficient to at least partially melt irradiated portions of the section of the film sample. A particular portion of the section of the film sample is irradiated with the first beamlets of a first pulse of the irradiated beam pulses to melt first areas of the particular portion, the first areas being at least partially melted, leaving first unirradiated regions between respective adjacent ones of the first areas, and being allowed to resolidify and crystallize. After the irradiation of the particular portion with the first beamlets, the particular portion is again irradiated with the second beamlets of a second pulse of the irradiated beam pulses to melt second areas of the particular portion, the second areas being at least partially melted, leaving second unirradiated regions between respective adjacent ones of the second areas, and being allowed to resolidify and crystallize. The first irradiated and re-solidified areas and the second irradiated and re-solidified areas are intermingled with one another within the section of the film sample. In addition, the first areas correspond to first pixels, and the second areas correspond to second pixels.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
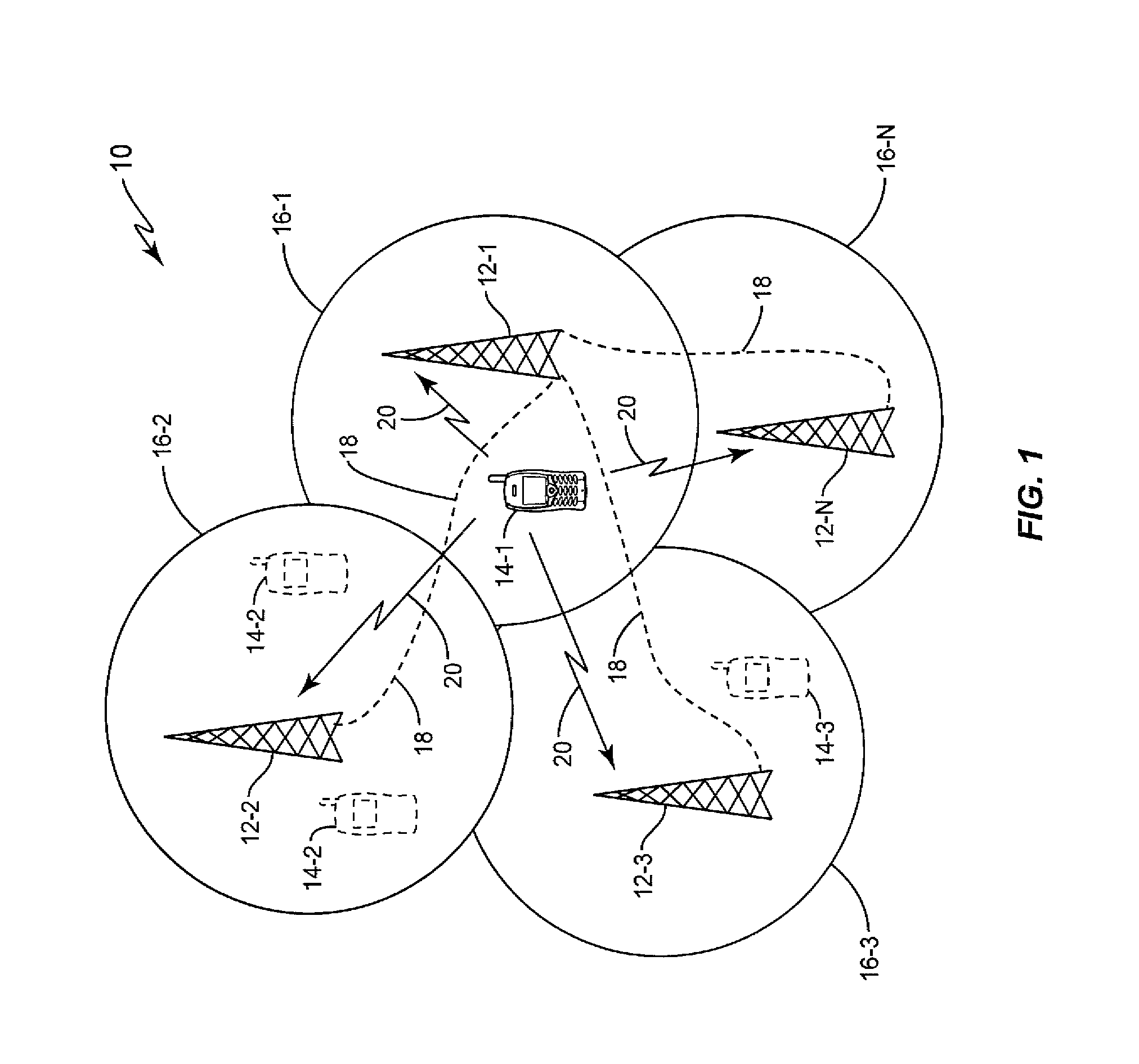
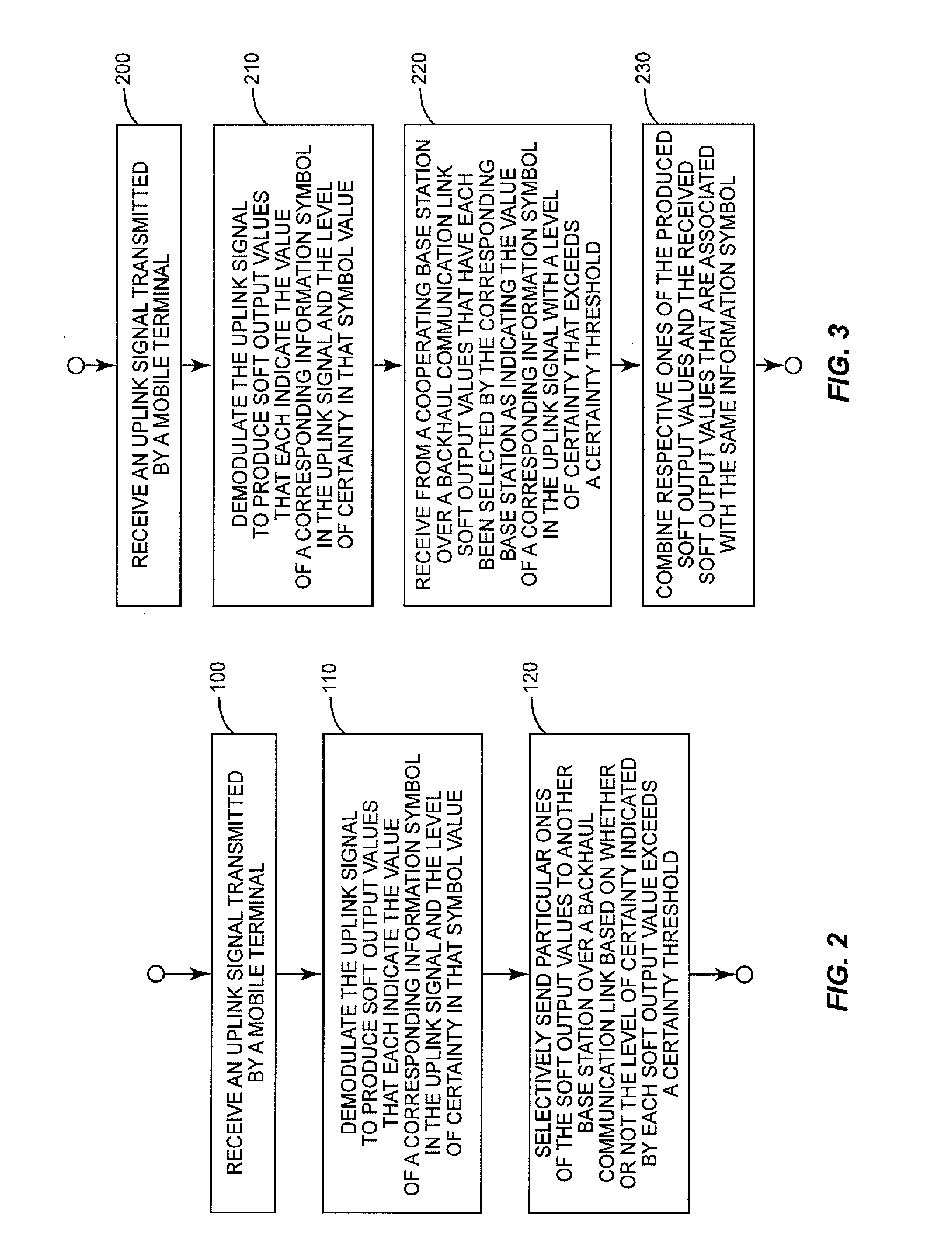
Reduced Bandwidth Backhaul for Coordinated Multi-Point Reception
InactiveUS20120184218A1Reduced backhaul bandwidth requirementImprove certaintySite diversityNetwork traffic/resource managementTelecommunications linkCommunication link
Embodiments herein provide reduced backhaul bandwidth requirements for Coordinated Multi-Point reception of an uplink signal. A cooperating base station receive and demodulates the uplink signal to produce soft output values that each indicate the value of a corresponding information symbol in the uplink signal and the level of certainty in that symbol value. The cooperating base station then selectively sends particular ones of the soft output values to a serving base station over a backhaul communication link based on whether or not the level of certainty indicated by each soft output value exceeds a certainty threshold. The serving base station likewise receives and demodulates the uplink signal to produce its own soft output values. The serving base station then combines respective ones of the soft output values it received from the cooperating base station and the soft output values it produced itself that are associated with the same information symbol.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
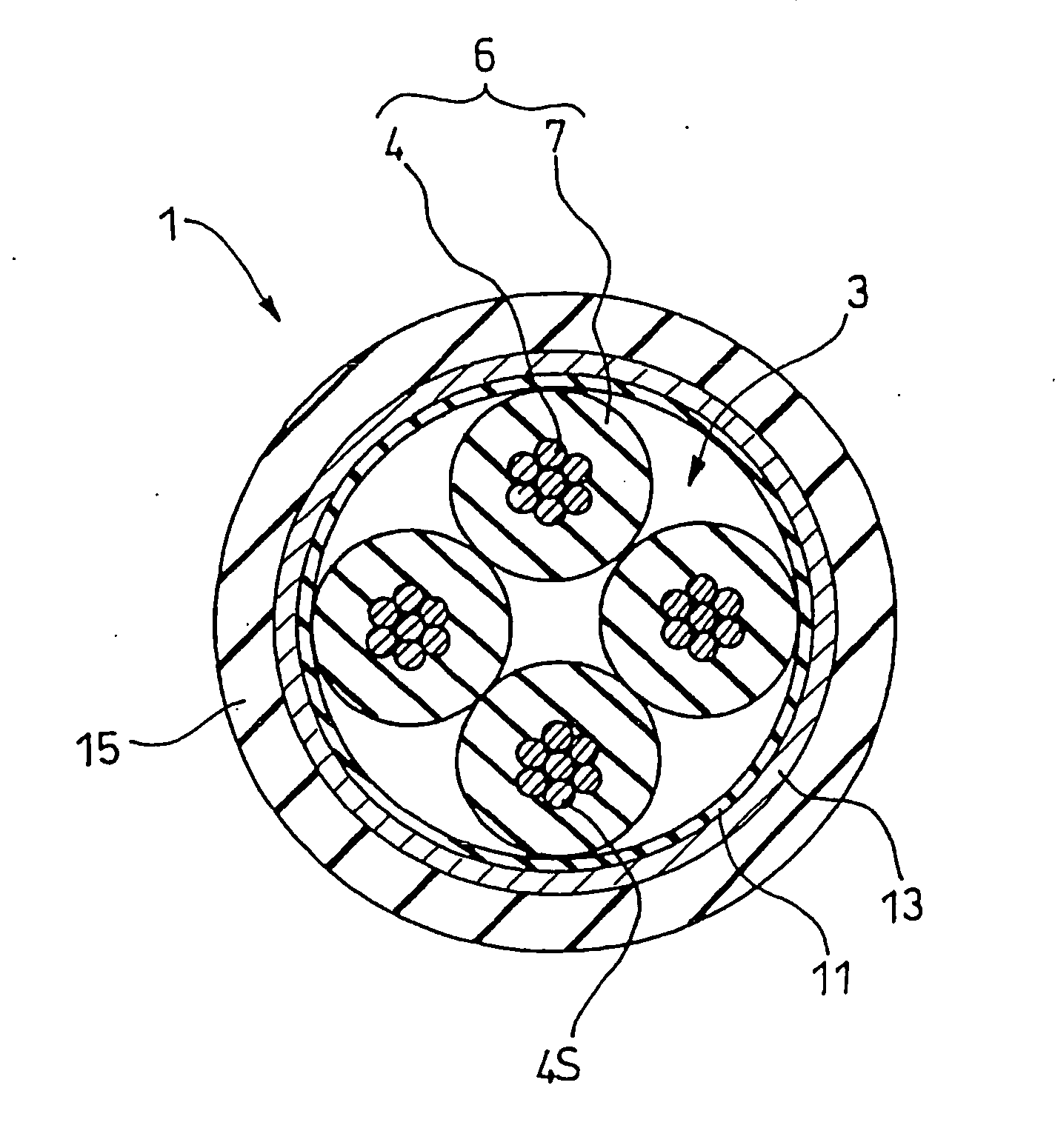
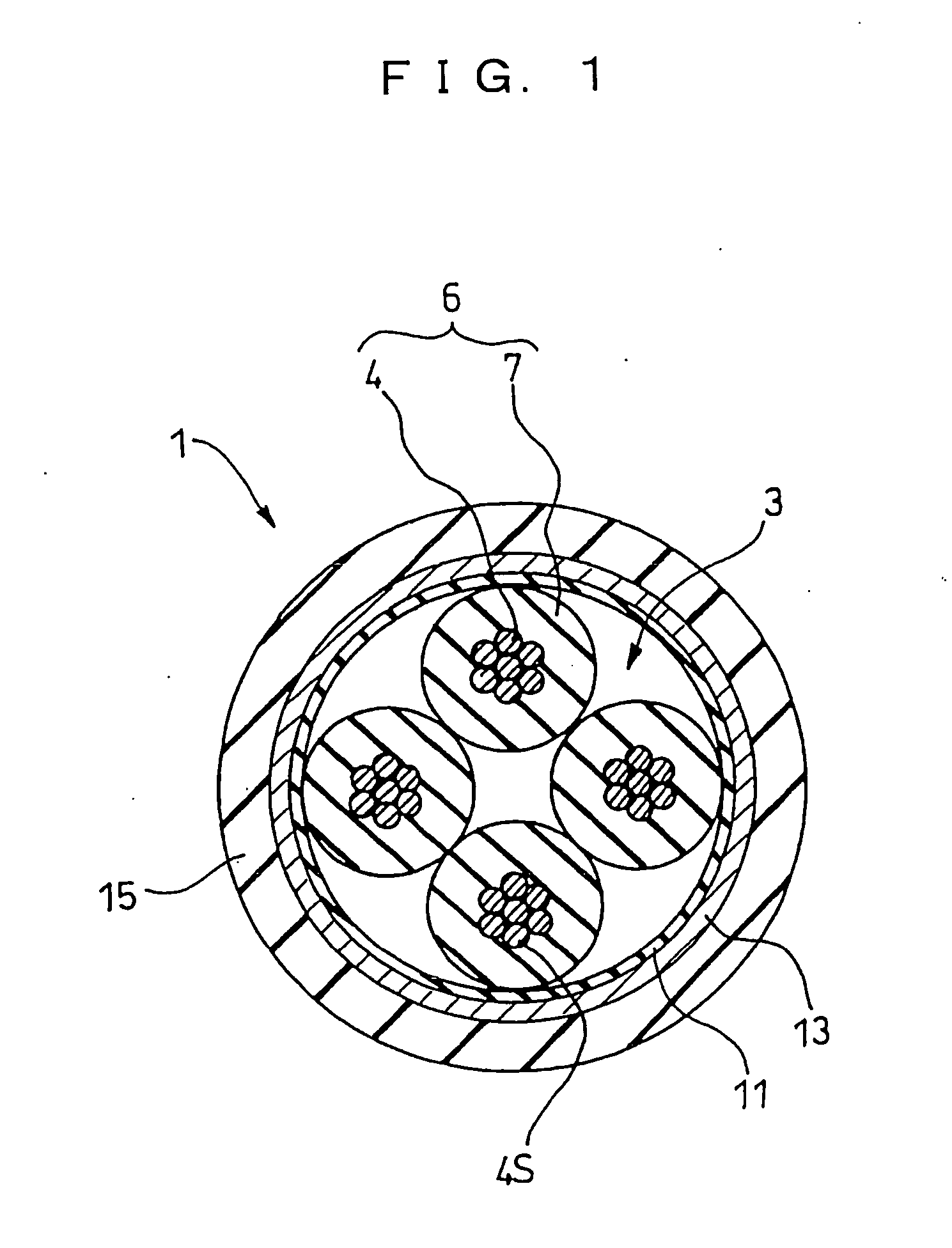
Signal transmission cable terminal device and data transmission method using signal transmission cable
InactiveUS20050029006A1Reduced footprintHigh mechanical strengthQuad constructionsPower cables with screens/conductive layersUltrasound attenuationElectrical conductor
It is intended to provide a high-speed differential signal cable having a small diameter and high strength. A 4-conductor cable includes four insulation-coated insulated wires (center conductors) bundled together, and a wire mesh and an insulating sheath which cover a periphery thereof, and this cable is characterized in that a conductor size of center conductor wires is thinned so as to satisfy a specified value of attenuation with a cable length of 2.5 m, and also twisted pair wires are replaced by a quad-structure wire, so that the outer diameter is not larger than 3 mm.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
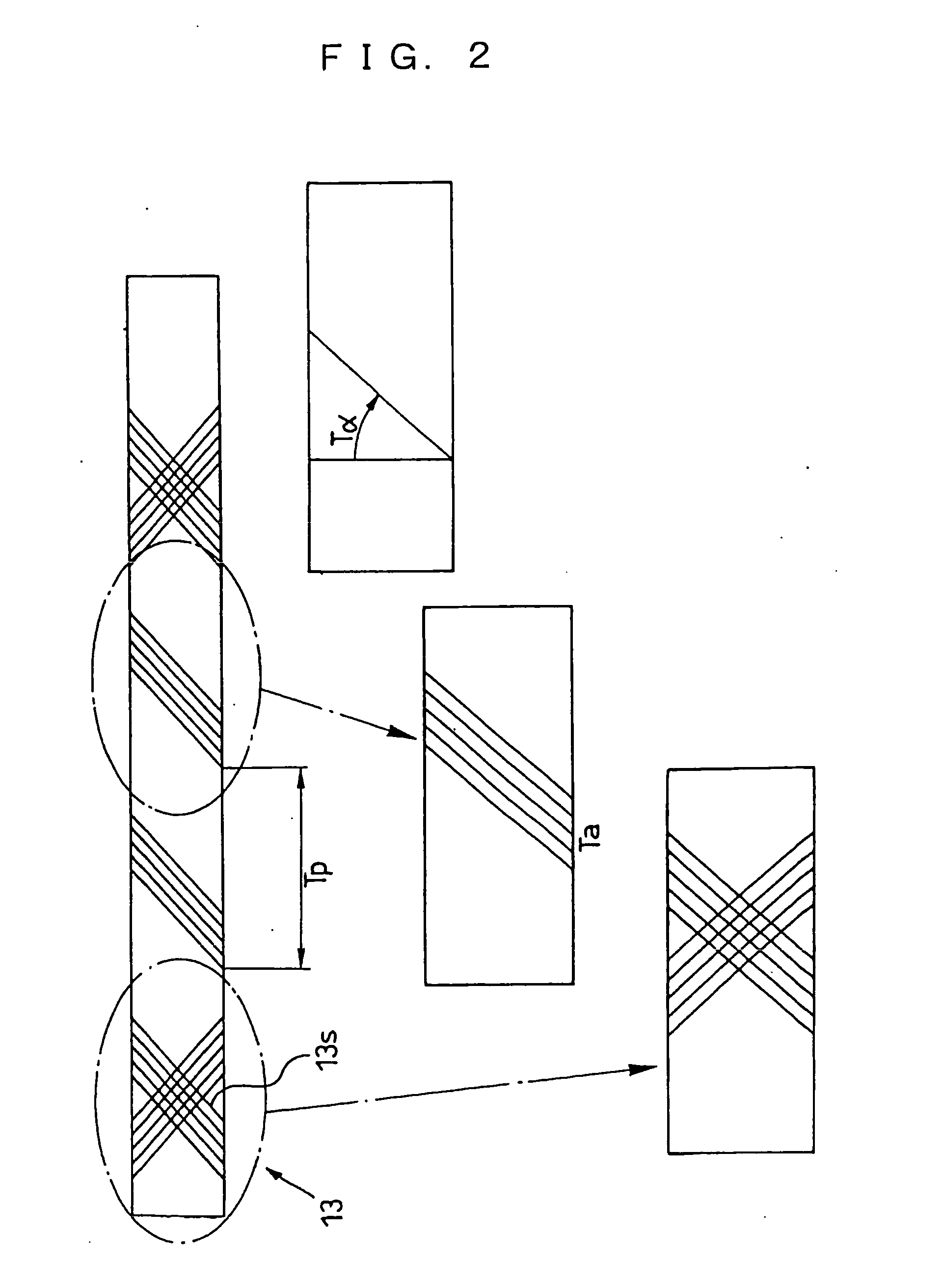
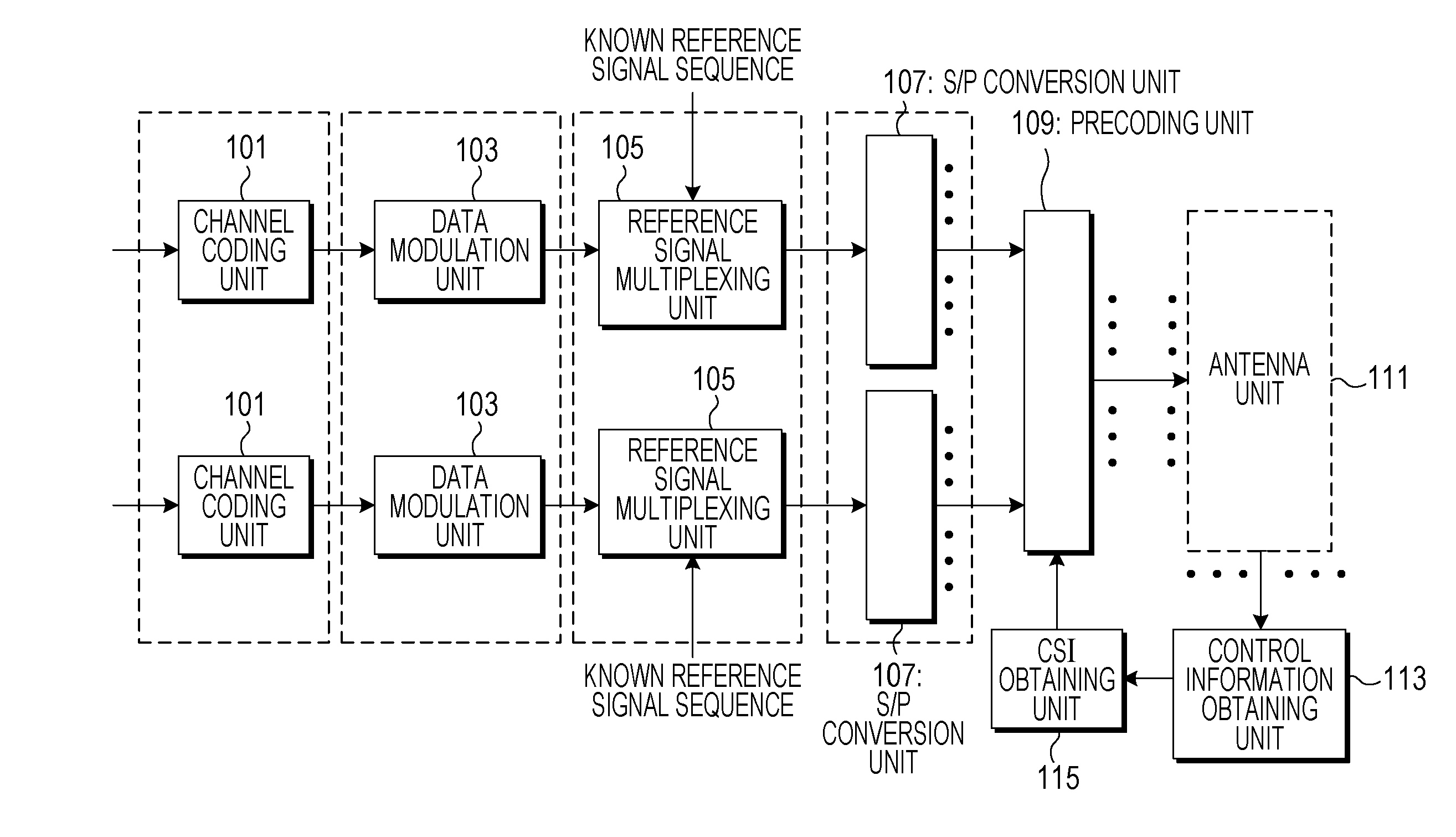
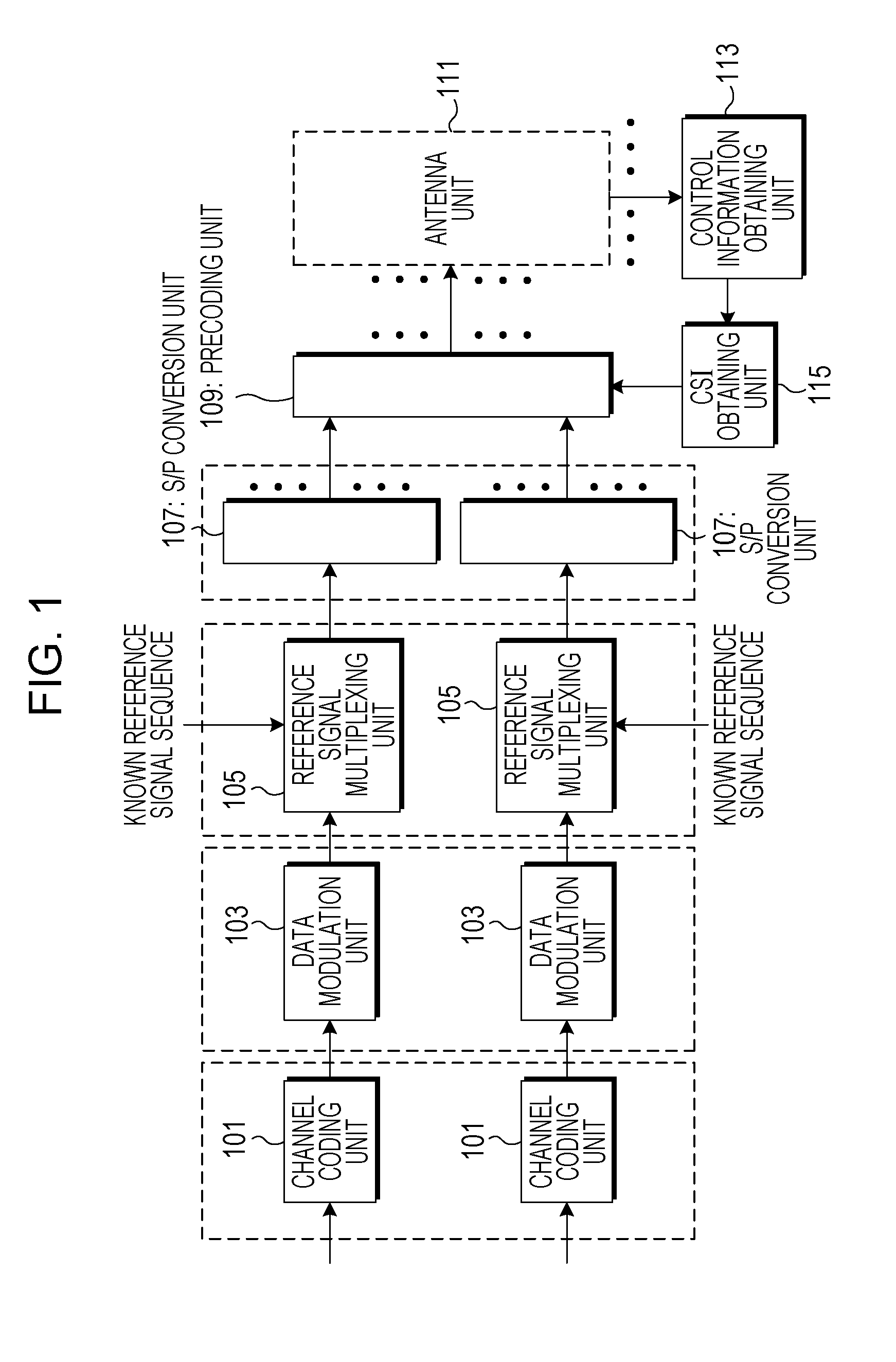
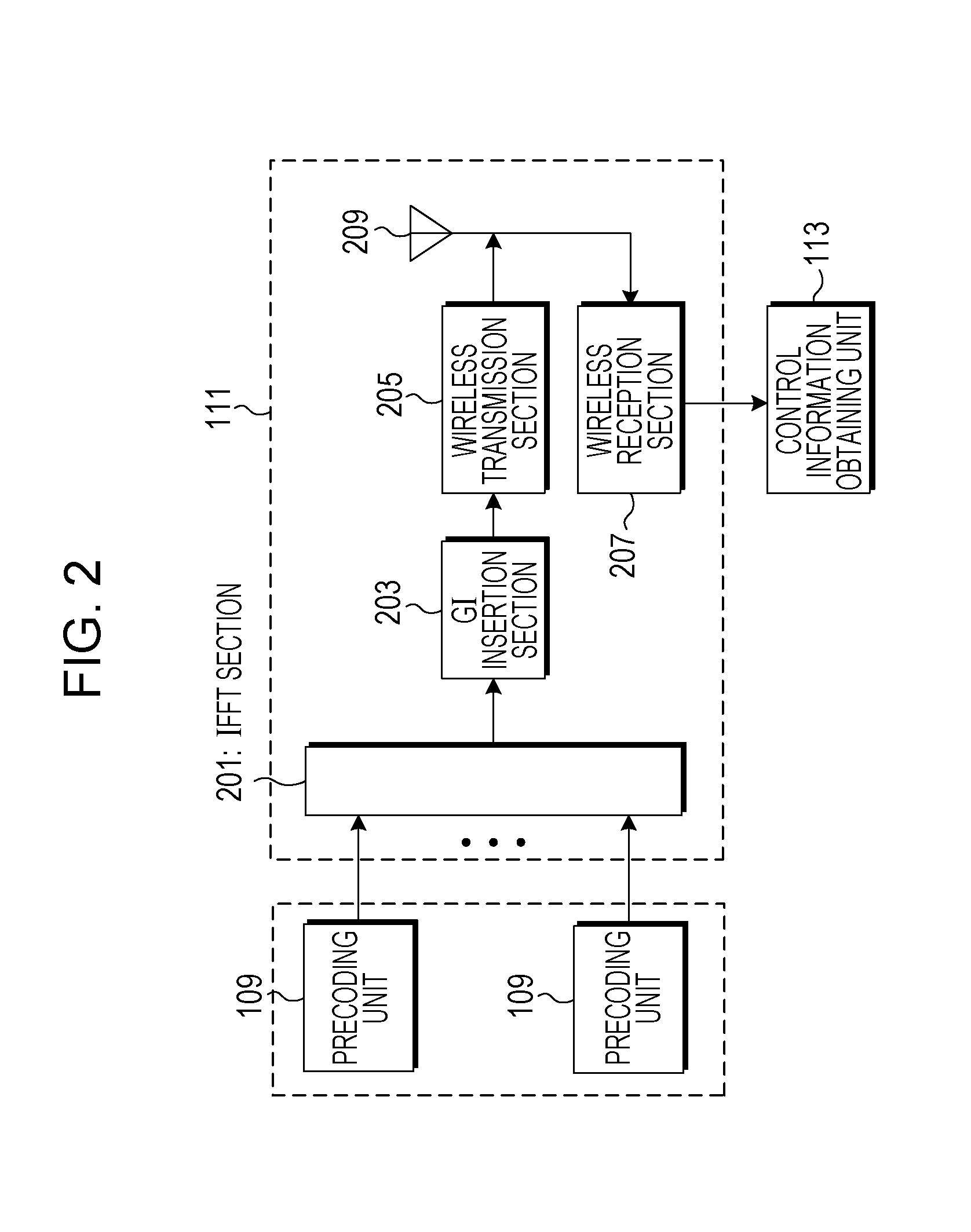
Precoding apparatus, program for precoding, and integrated circuit
ActiveUS20140177751A1Improve spectral efficiencyIncrease in amount of operationError preventionRadio transmissionPrecodingWireless transmission
More reduction of the amount of operation than in QRM-VP is realized while maintaining transmission performance that can be achieved by VP. A precoding apparatus 109 that performs preliminary processing on transmission data transmitted from a wireless transmission apparatus including a plurality of antennas to a wireless reception apparatus includes a linear filter generation section 301 that generates a linear filter on the basis of a result of estimation of a channel between an antenna unit 111 and the wireless reception apparatus, a signal conversion section 303 that expands perturbation term candidates of a perturbation vector to be added to a transmission data vector and a reference signal associated with the transmission data in a complex plane, and a perturbation vector search section 305 that searches for the perturbation vector to be added to the transmission data vector by performing a quadrant search on the basis of the perturbation term candidates and the reference signal expanded in the complex plane. A transmission signal vector is calculated by adding a found perturbation vector to the transmission data vector and multiplying the transmission data vector by the linear filter.
Owner:SHARP KK
Method for high speed machining and coated cutting tool
InactiveUS7416778B2Guaranteed high speed operationLower performance requirementsPigmenting treatmentWorkpiecesCemented carbideTotal thickness
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
Methods of achieving optimal communications performance
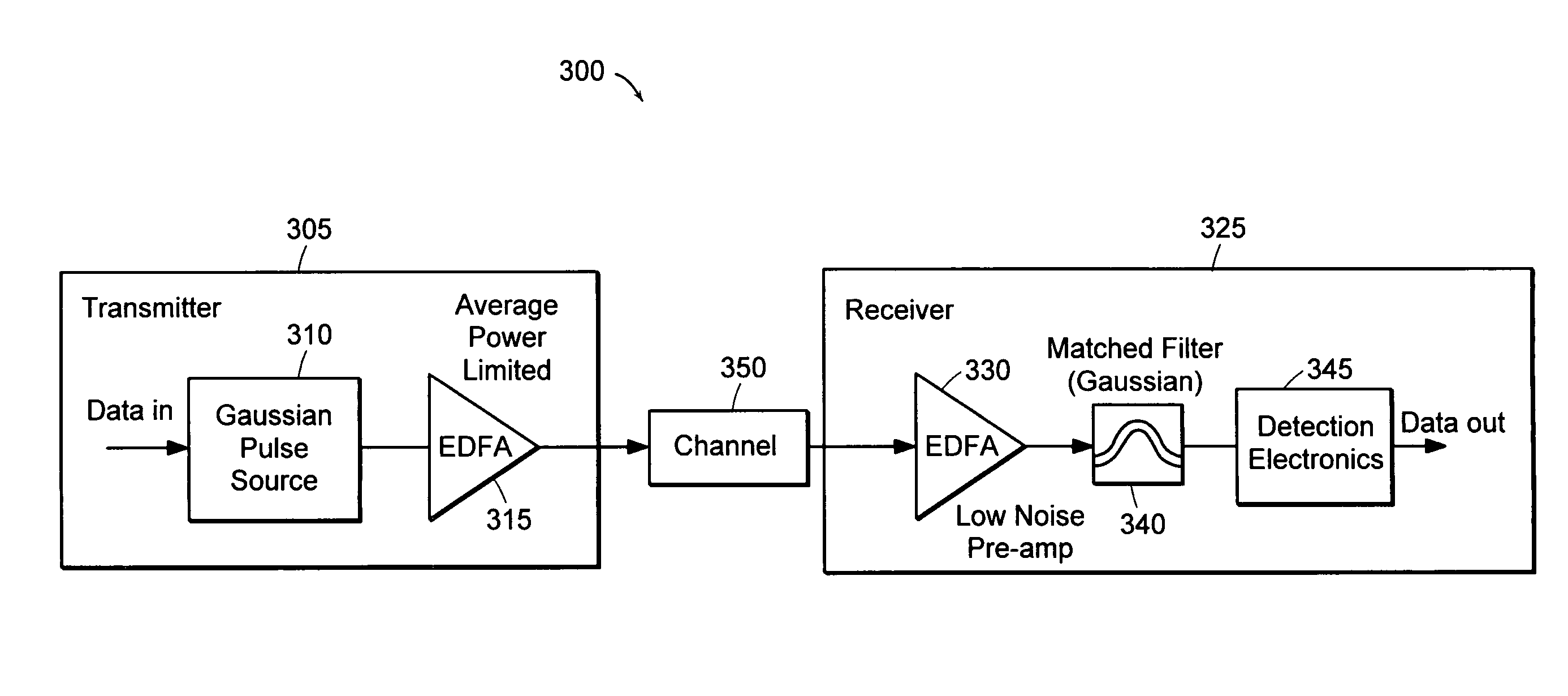
InactiveUS7181097B2High bandwidthImprove measurement resolutionCoupling light guidesElectromagnetic transmissionErbium dopingPower limits
A system includes an optical transmitter that outputs an optical signal having a substantially Gaussian waveform and an optical receiver that is optically coupled to the optical transmitter and has an impulse response essentially matching the waveform. The impulse response and waveform preferably match in the time domain. The transmitter and receiver may be average-power-limited, using, for example, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier. To achieve a high signal-to-noise ratio, the waveform may be designed to minimize jitter, sample duration, matching parasitics, and inter-symbol interference (ISI). Such a waveform may be a return-to-zero (RZ) Gaussian or Gaussian-like waveform and may be transmitted in a variety of modulation formats. Further, the system may be used in WDM or TDM systems. A method for characterizing the time domain impulse response of an optical element used in the optical receiver is provided, where the method is optionally optimized using deconvolution and / or cross-correlation techniques.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
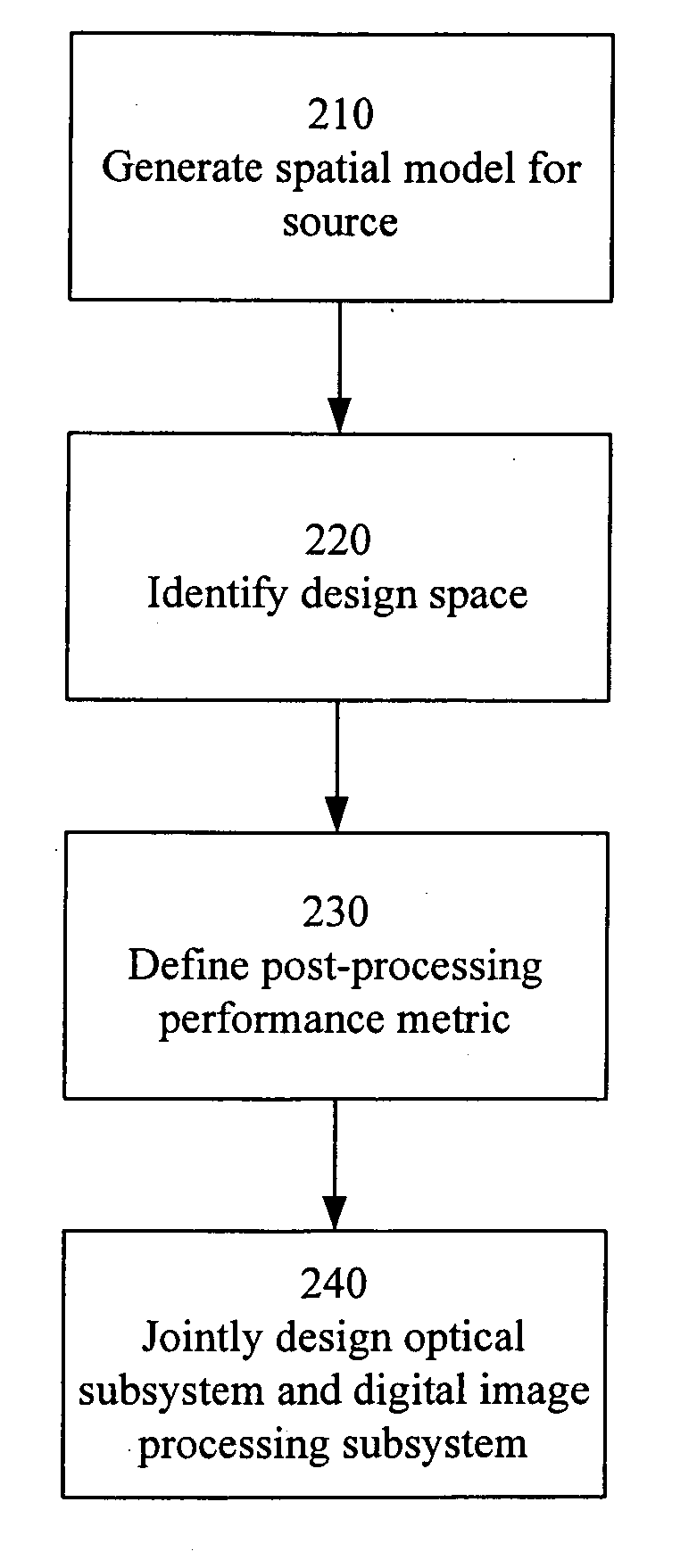
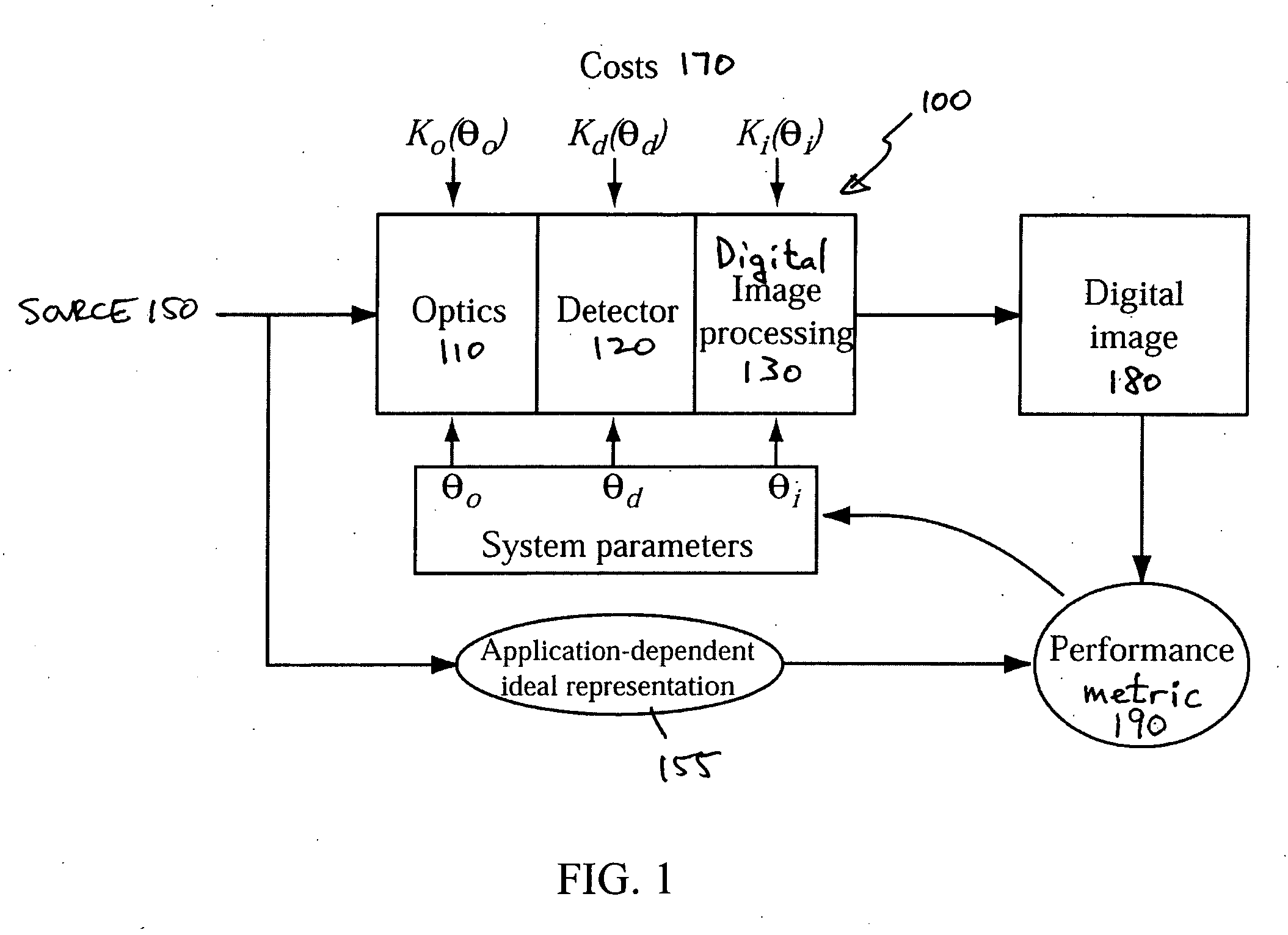
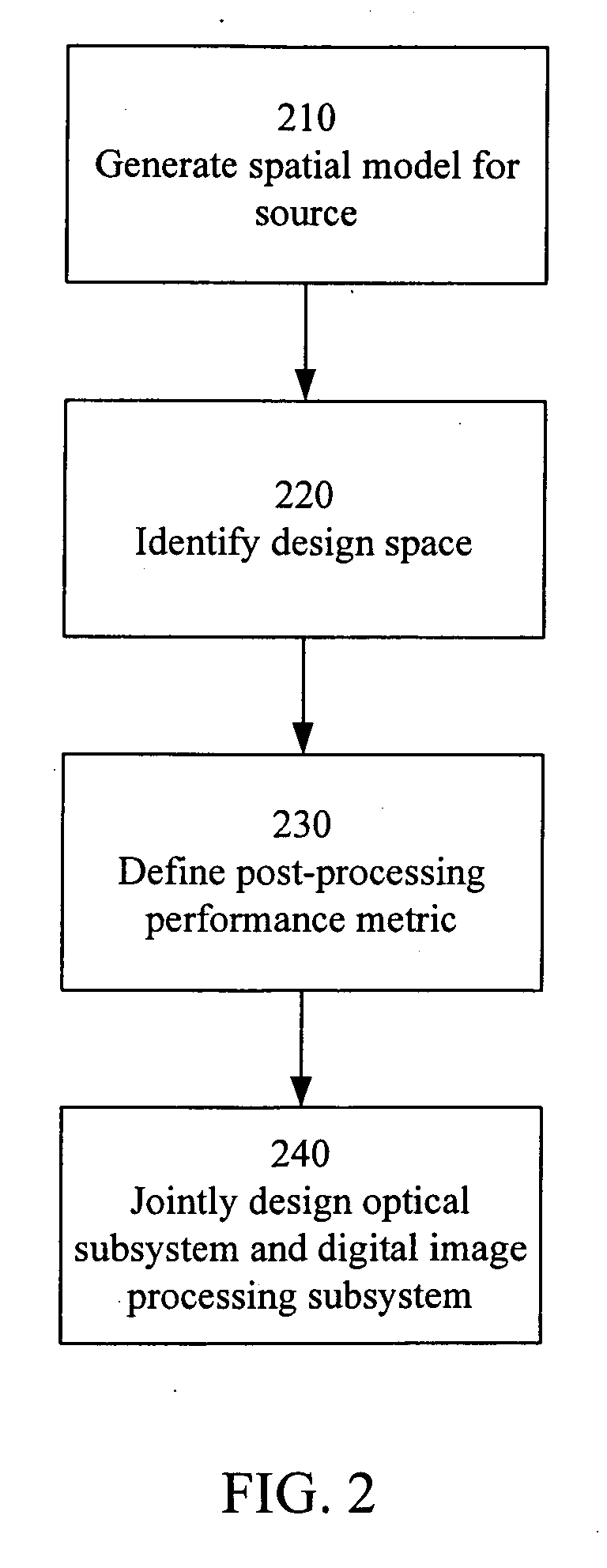
End-to-end design of electro-optic imaging systems with constrained digital filters
ActiveUS20070002158A1Improve image qualitySmall sizeTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionIntermediate imageDigital filter
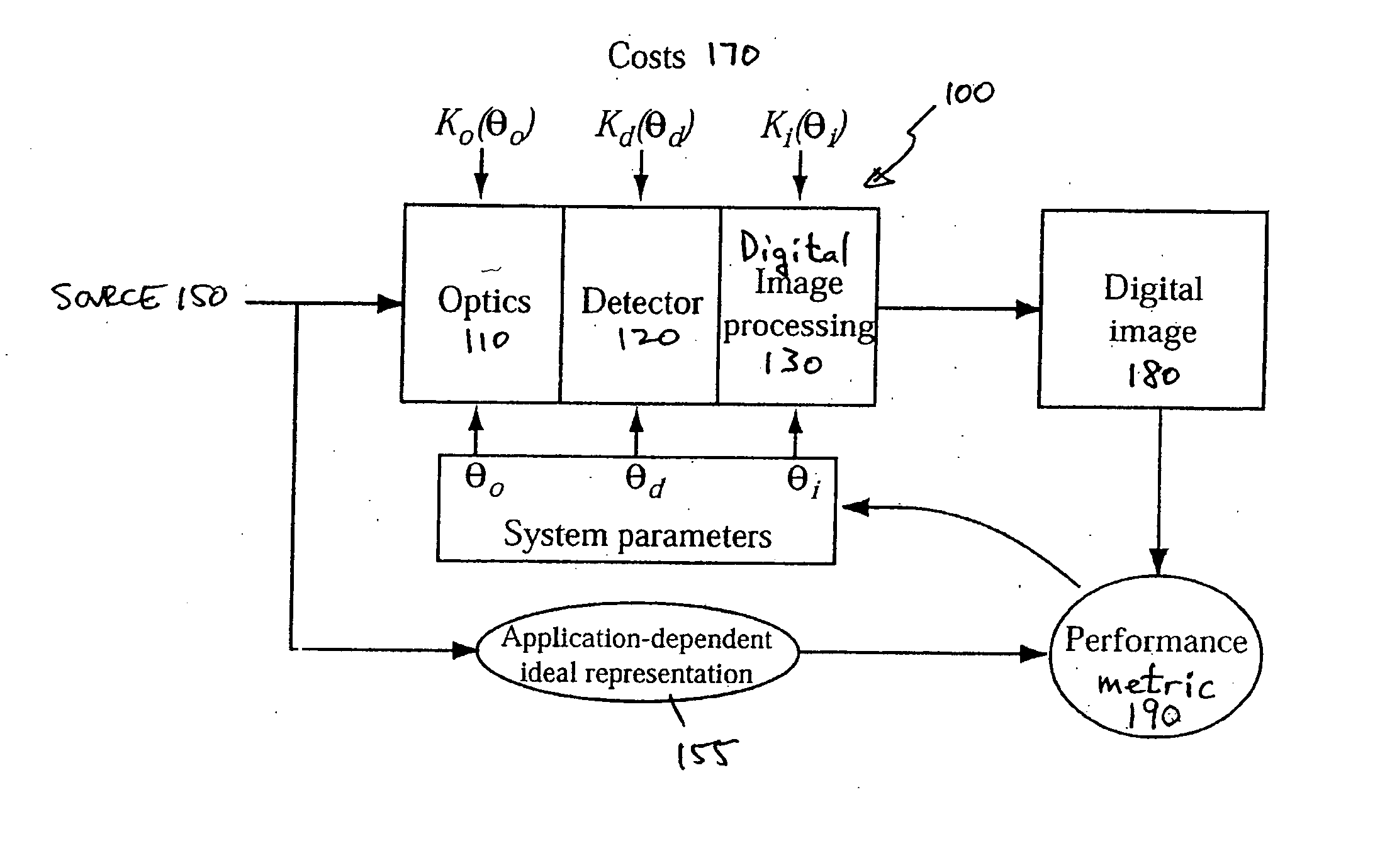
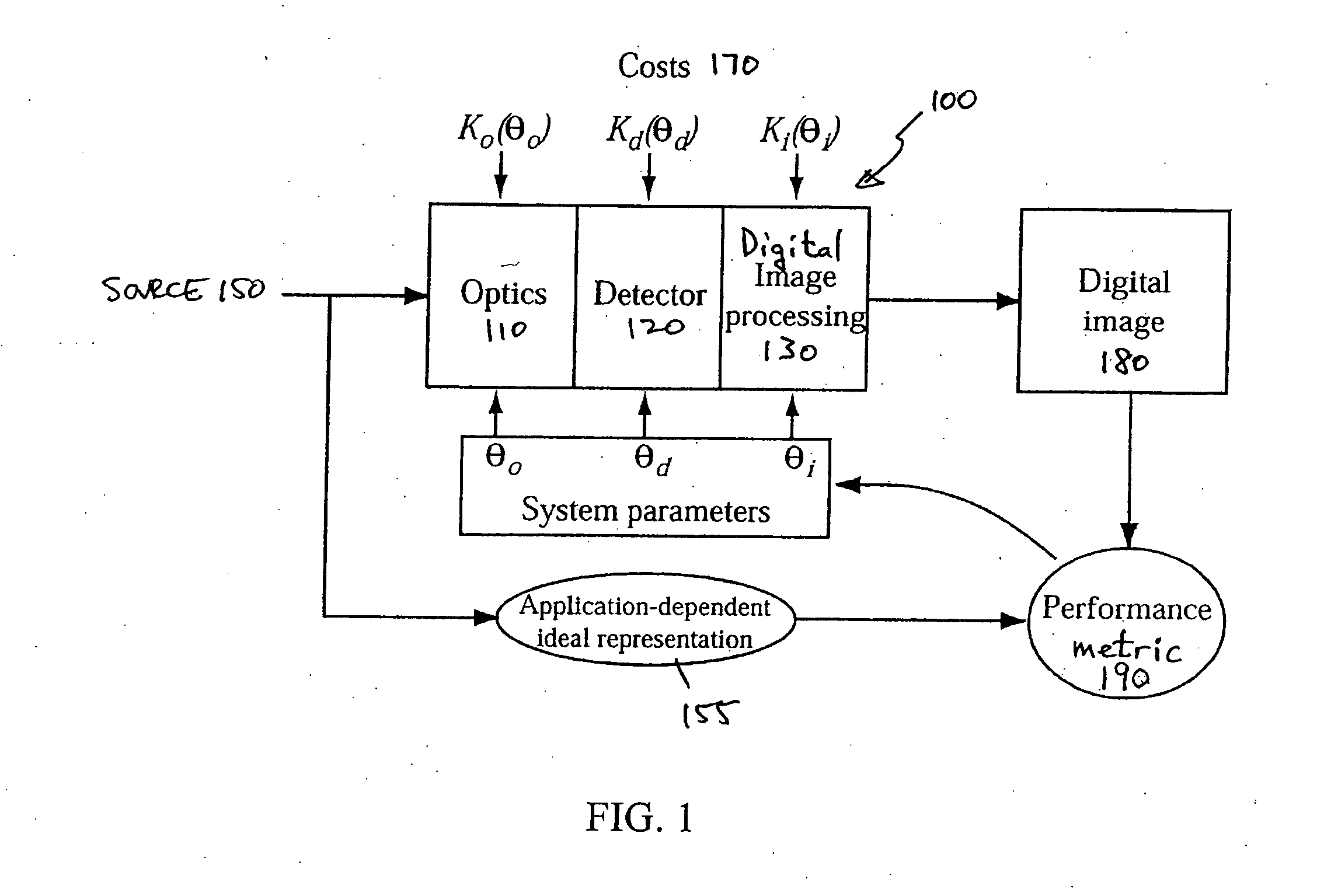
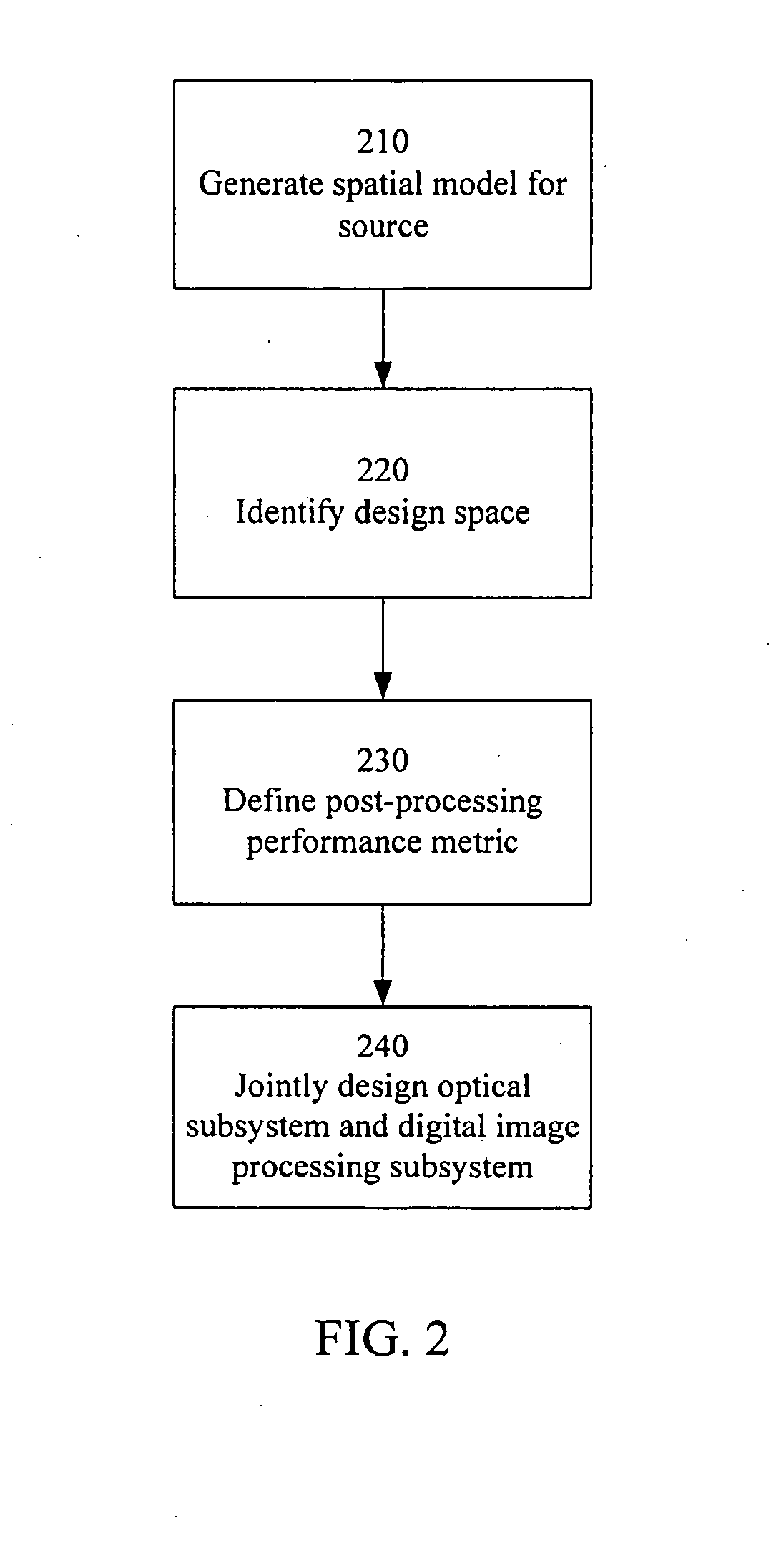
A unified design strategy takes into account different subsystems within an overall electro-optic imaging system. In one implementation, the design methodology predicts end-to-end imaging performance using a spatial model for the source and models for the optical subsystem, the detector subsystem and the digital image processing subsystem. The optical subsystem and digital image processing subsystems are jointly designed taking into account the entire system. The intermediate image produced by the optical subsystem is not required to be high quality since, for example, the quality may be corrected by the digital image processing subsystem.
Owner:RICOH KK
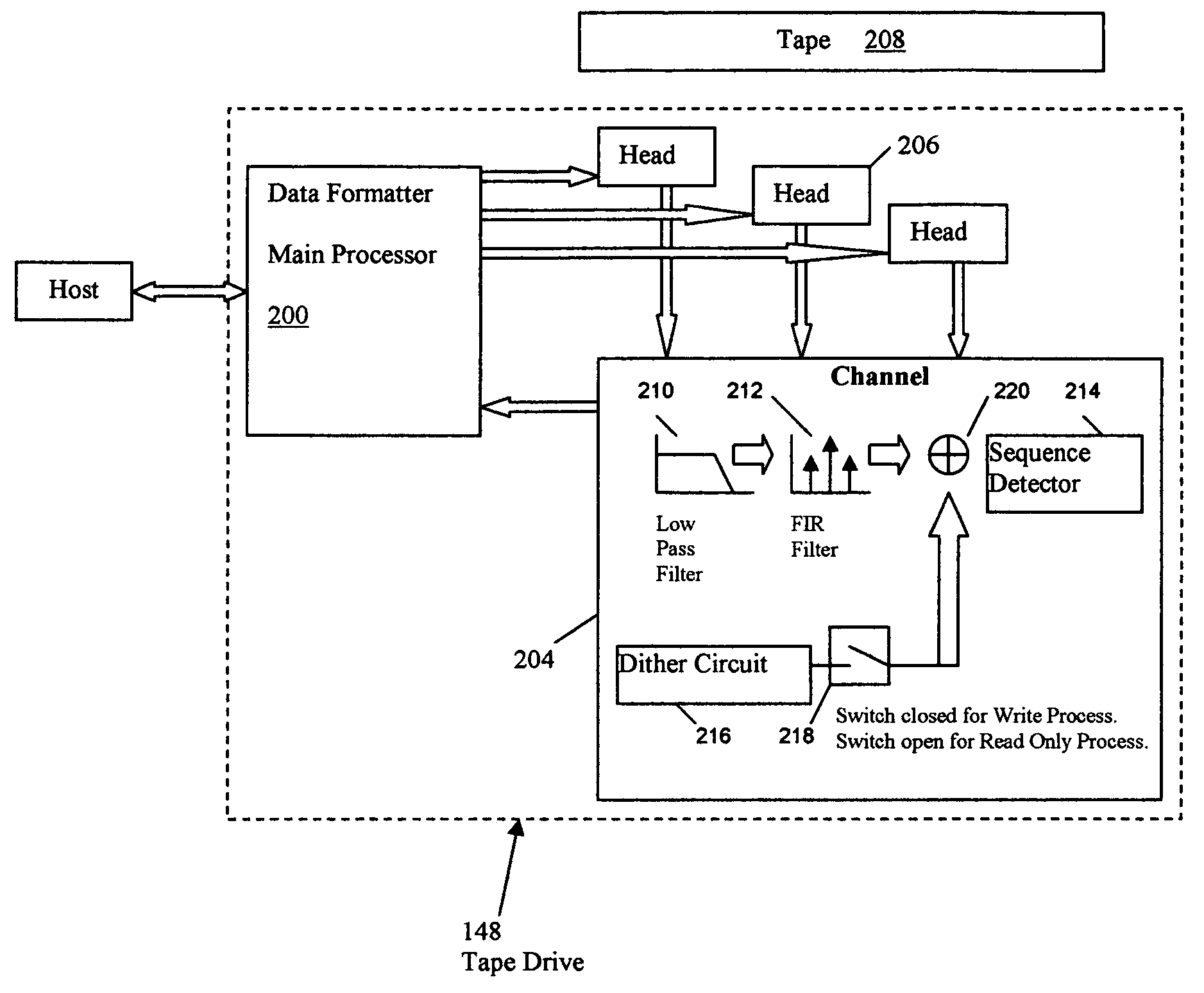
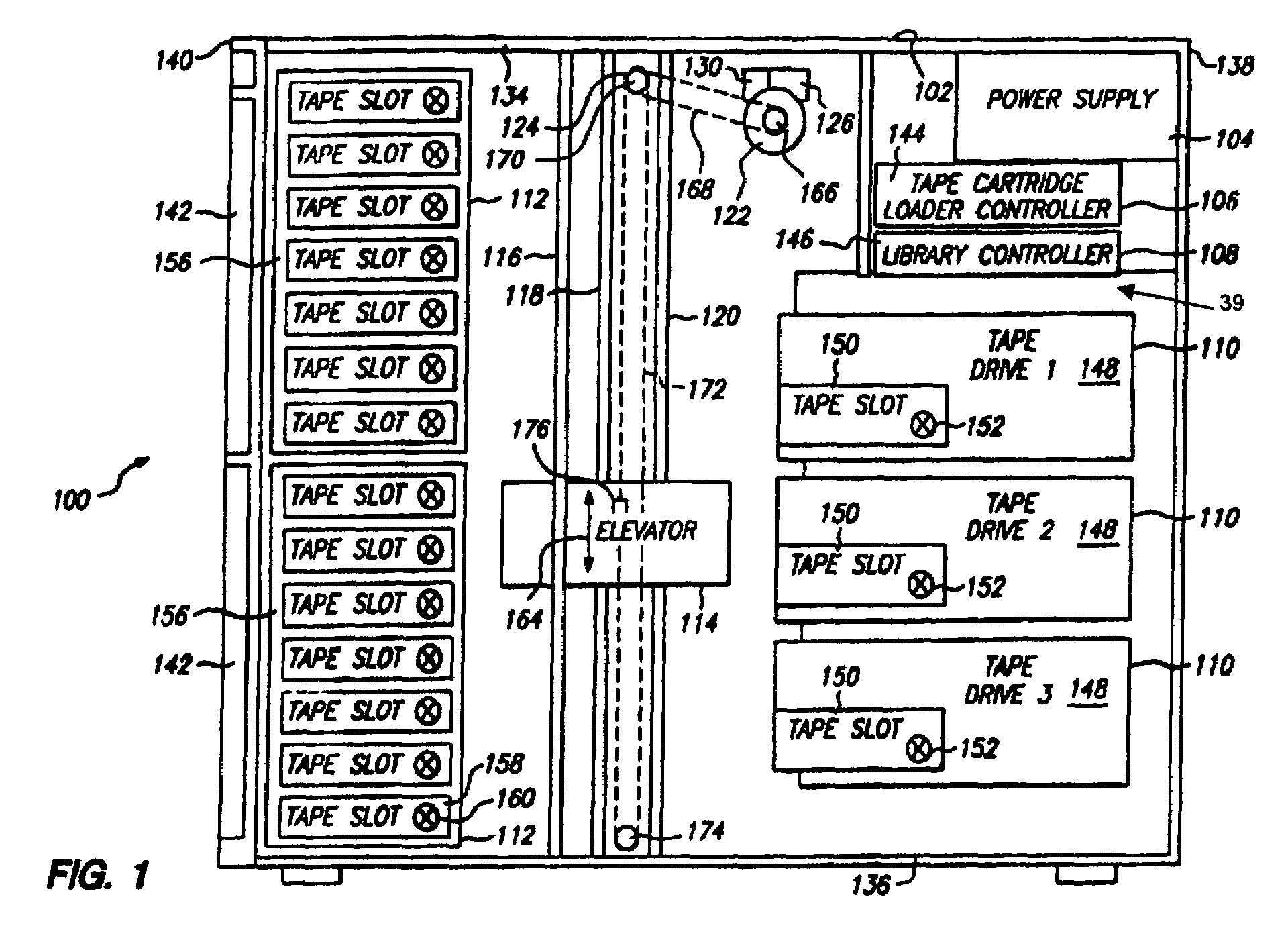
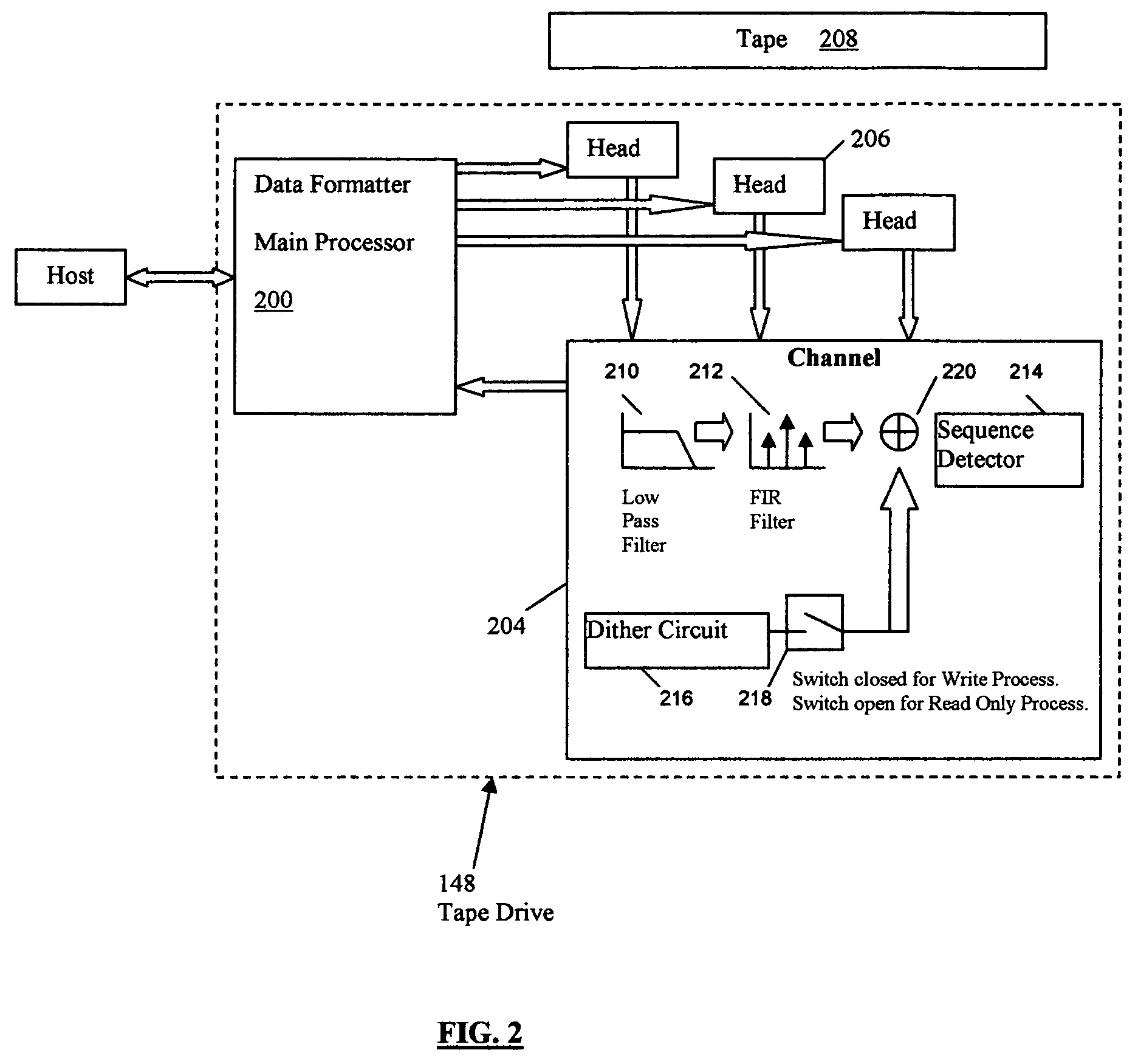
Enhanced read margining using dither enhanced write marginalization for mass data storage applications
InactiveUS7064913B2Improve error performanceSame read/write error performanceFilamentary/web carriers operation controlModification of read/write signalsComputer hardwareComputer science
A recording target error rate is selected for one or more of data storage devices, and for each data storage device, a dither value is determined for each read / write head in the data storage device, wherein for each head, using a dither value for writing data, essentially provides the selected recording target error for all the heads.
Owner:QUANTUM CORP
End-to-end design of electro-optic imaging systems
ActiveUS20060285002A1Less componentsSmall “ footprint ”Television system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionIntermediate imageSpatial model
A unified design strategy takes into account different subsystems within an overall electro-optic imaging system. In one implementation, the design methodology predicts end-to-end imaging performance using a spatial model for the source and models for the optical subsystem, the detector subsystem and the digital image processing subsystem. The optical subsystem and digital image processing subsystems are jointly designed taking into account the entire system. The intermediate image produced by the optical subsystem is not required to be high quality since, for example, the quality may be corrected by the digital image processing subsystem.
Owner:RICOH KK
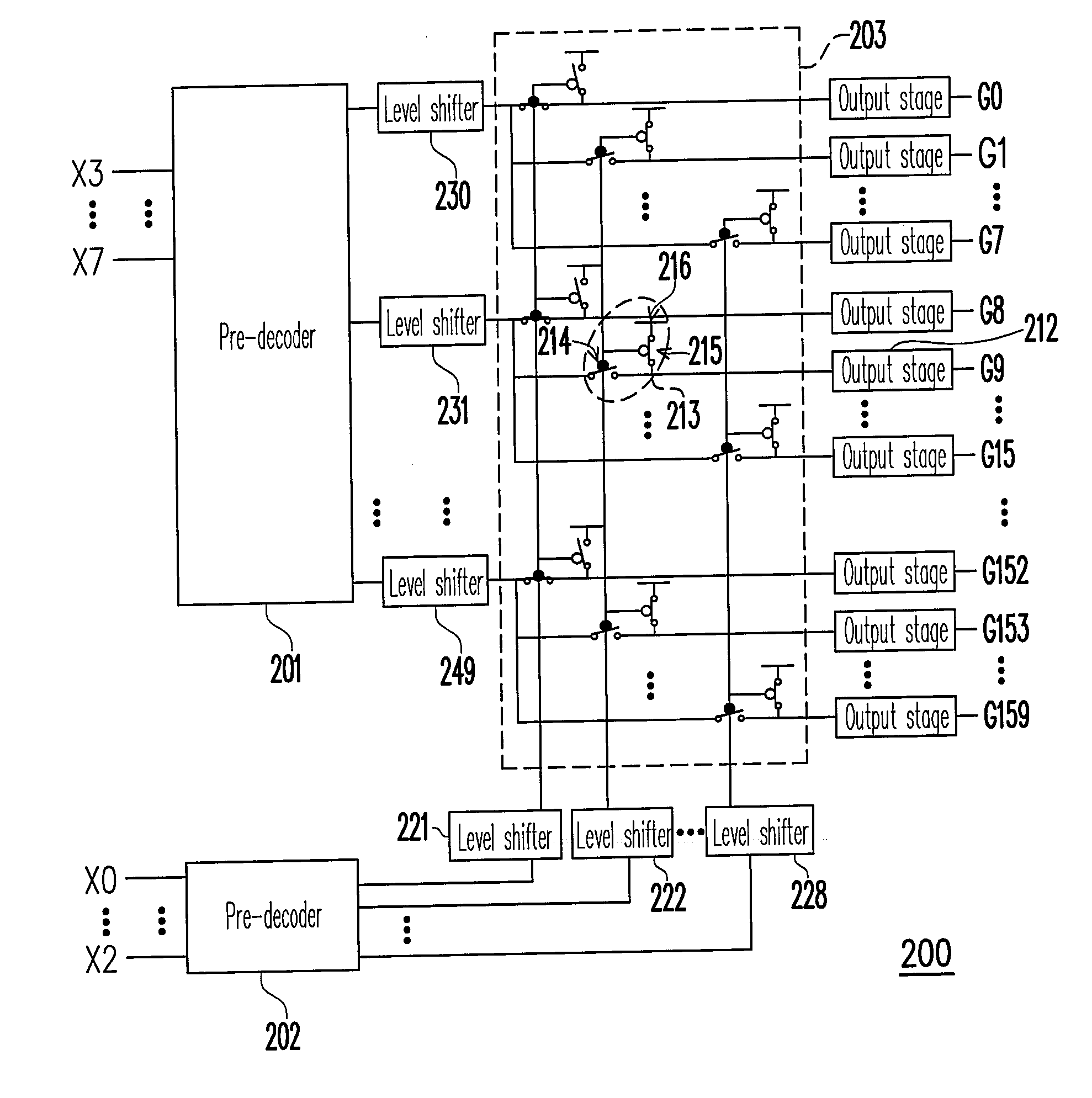
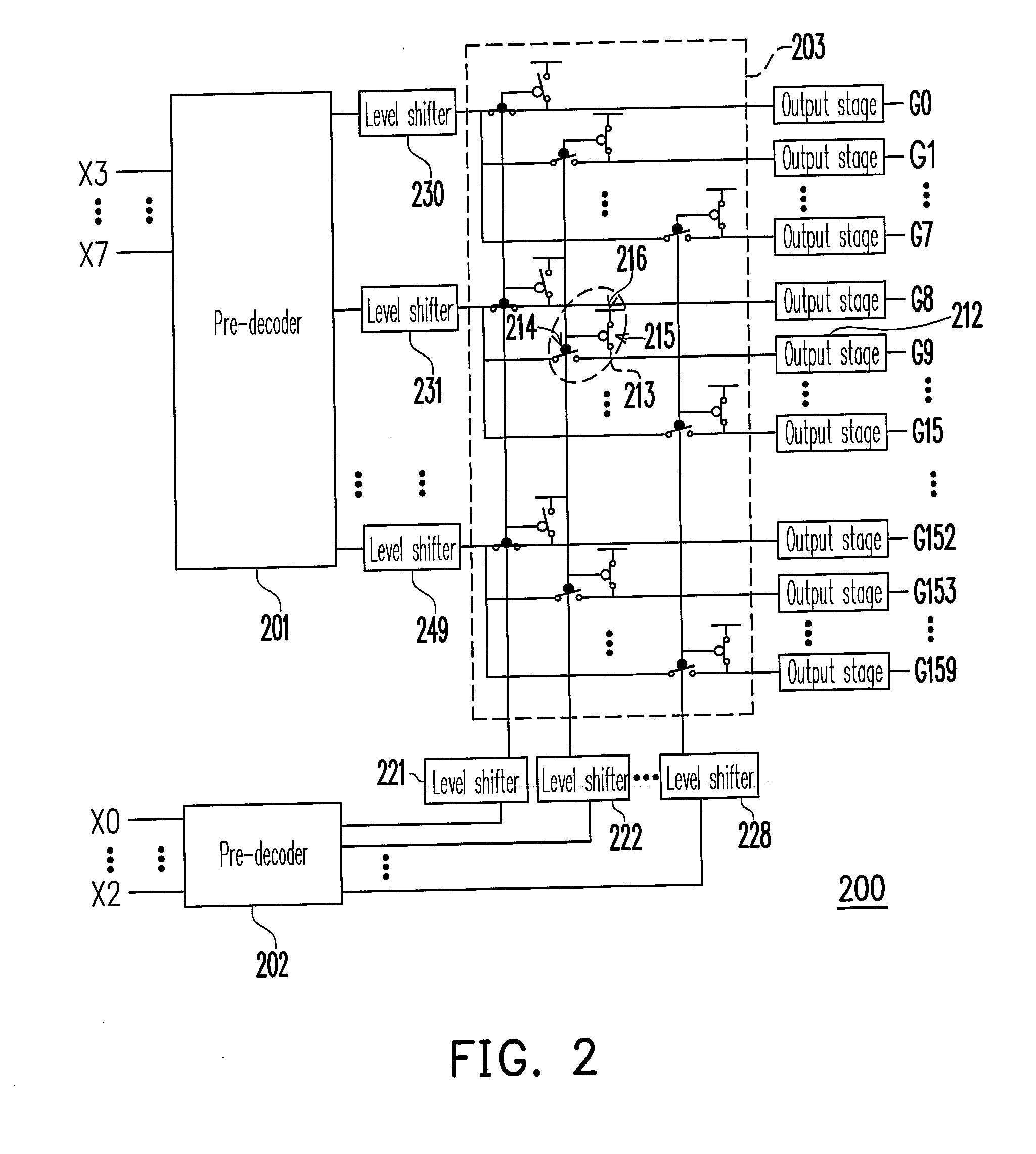
Matrix decoder
InactiveUS20070103346A1Minimize overall surface areaReduce in quantityStatic indicating devicesCode conversionEngineeringLogic state
A matrix decoder is provided, which includes a plurality of first level shifters, a plurality of second level shifters, and a demultiplexer. The first level shifters and the second level shifters boost the voltages of inputted signals to the voltages required by high voltage components and output the boosted signals. One of the first level shifters receives a first logic state and outputs a fifth logic state. Each of the other first level shifters receives a second logic state and outputs a sixth logic state. One of the second level shifters receives a third logic state and outputs a seventh logic state. Each of the other second level shifters receives a fourth logic state and outputs an eighth logic state. The demultiplexer outputs a ninth logic state and a plurality of tenth logic states according to the logic states outputted by the first level shifters and the second level shifters.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
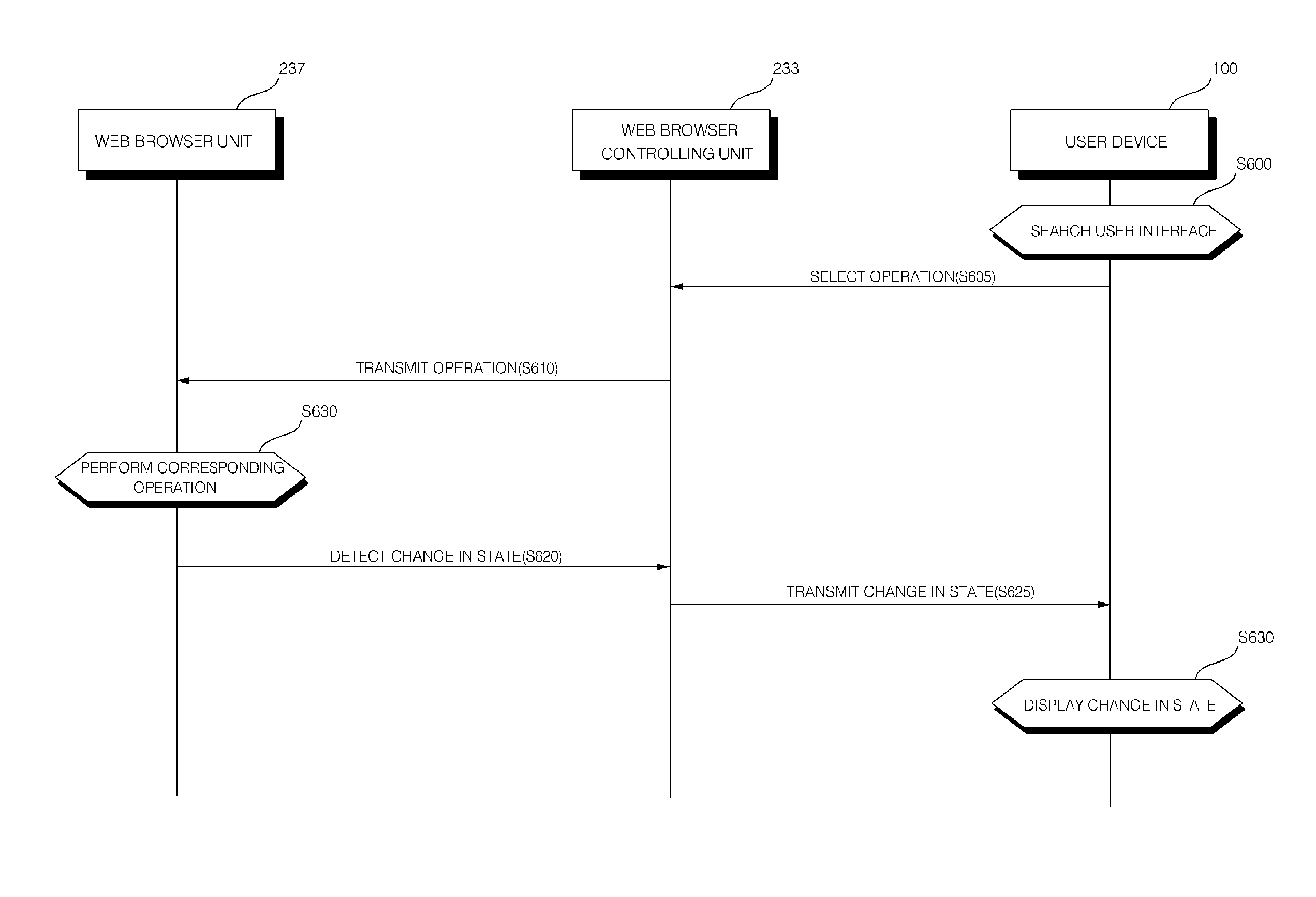
Web browsing environment provider system for multiple users and control method thereof
InactiveUS20110083067A1Same and high performancePerfectly compatibleSpecial data processing applicationsInput/output processes for data processingComputer compatibilityPersonal computer
Provided are a web browsing environment provider system for multiple users, in which a remote server computer is used, and a method of controlling the system. The system includes a user device on which a user interface is displayed for reading a web page and controlling web browsing, and a web browsing environment server efficiently generating and managing an independent web browsing environment for each respective user device, notifying the user device about a state of the independent web browsing environment, rendering a web page, executing active contents contained in the web page, transmitting a web page image that is rendered to the user device, and controlling an operation requested by the user device to operate in the web browsing environment, thereby saving on resources related to performance. Thus, multiple users can perform the same level of web browsing operation as in a personal computer (PC) that is a main device of web browsing by using a user device having lower performance than the PC or low compatibility with the PC.
Owner:LOGICPLANT
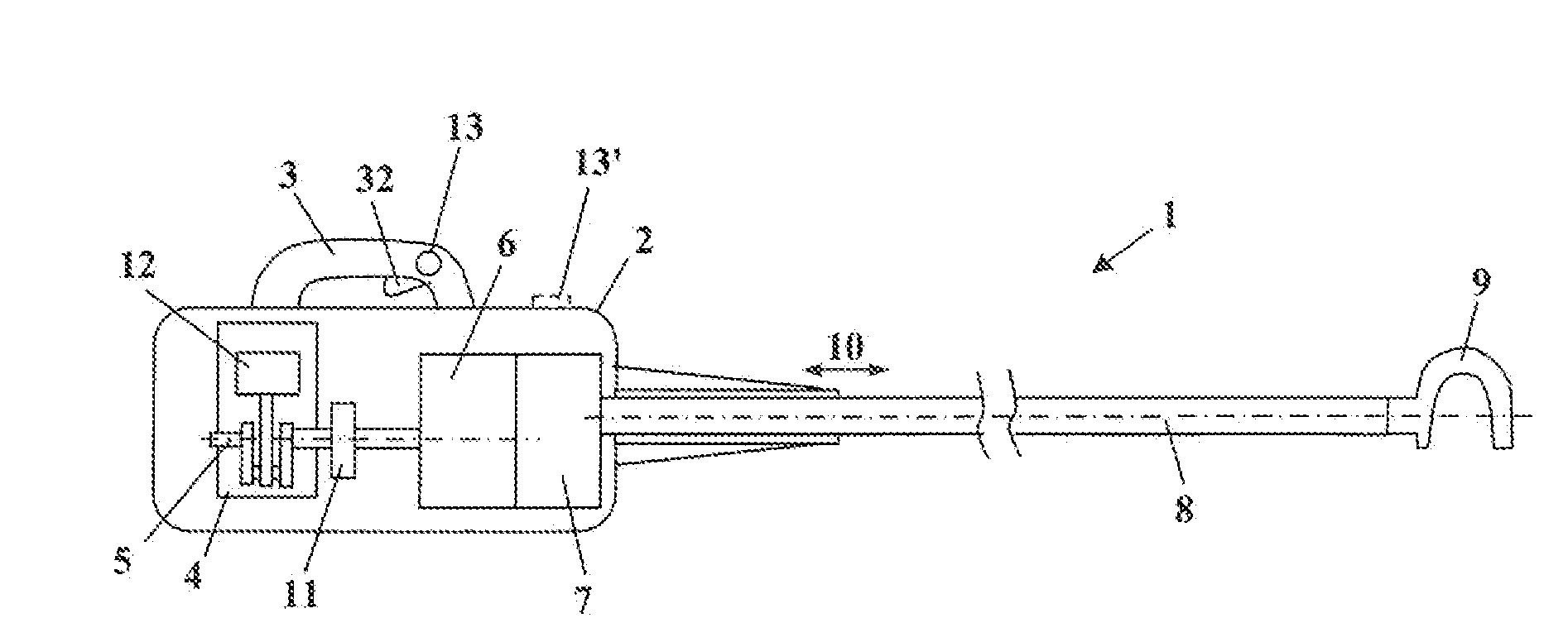
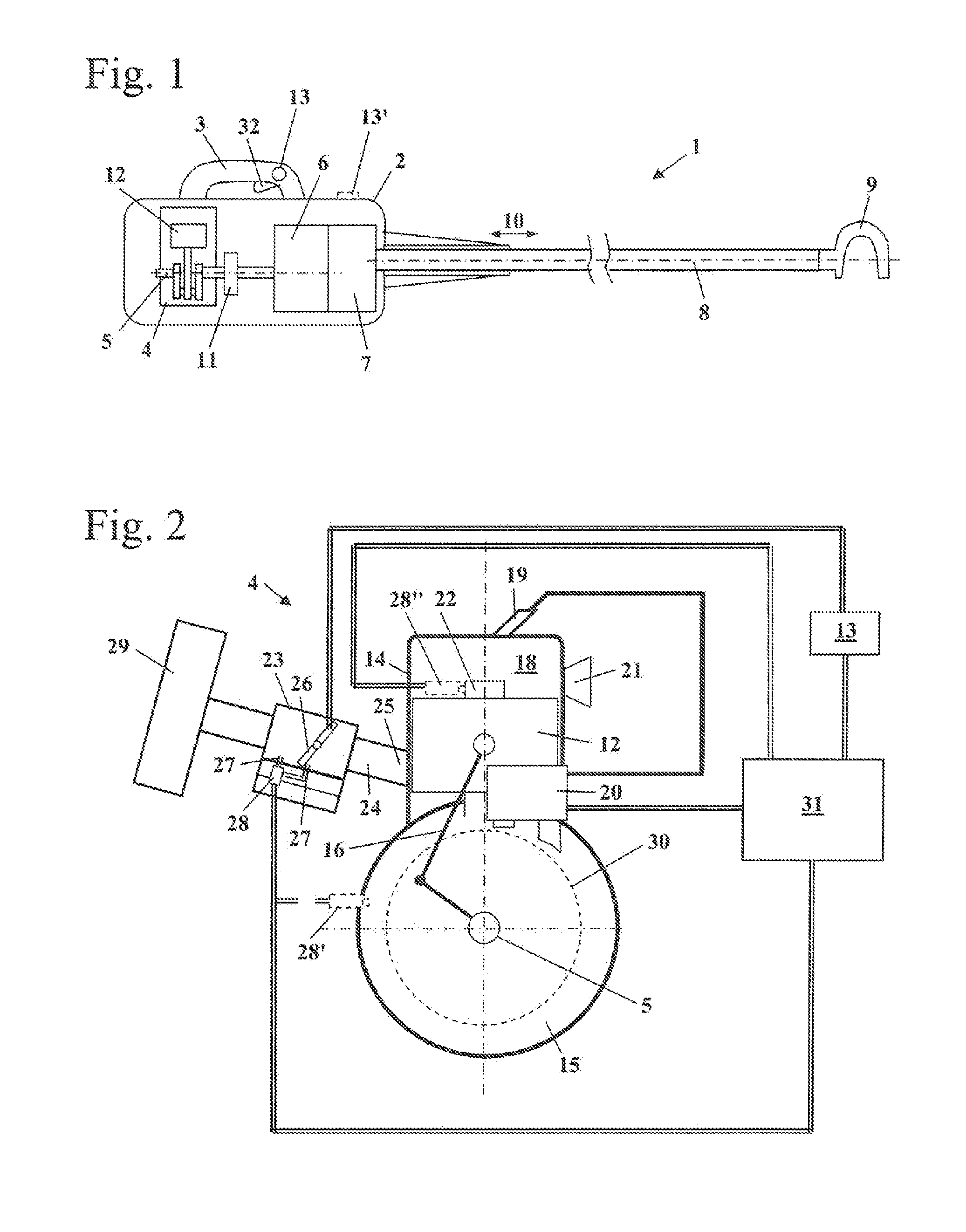
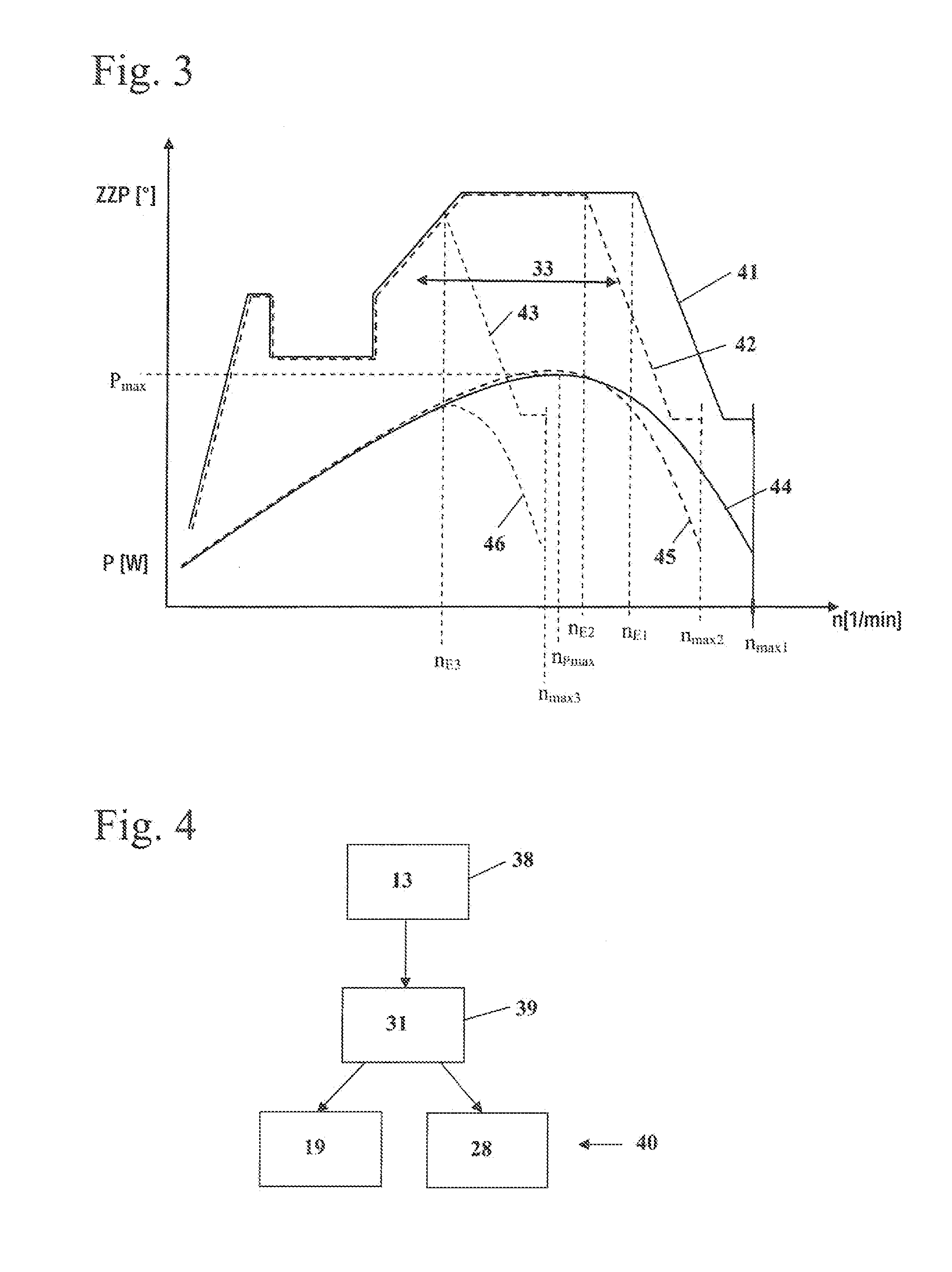
Handheld work apparatus
ActiveUS20130199812A1Set speed in easyEasily set speedElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesCombustionHand held
A handheld work apparatus has a combustion engine (4) for driving a tool. The combustion engine (4) has an ignition device, a device for metering fuel and a control device (31). The control device (31) engages when an engagement speed (nE1, nE2) is reached, in order to limit the speed (n) of the combustion engine (4). In order to allow the speed (n) to be set in an easy manner at full throttle, the work apparatus has a device for setting the engagement speed (nE2) by the user.
Owner:ANDREAS STIHL AG & CO KG
Membrane structures and their production and use
InactiveUS20100006503A1The process is compact and efficientKeep the same performanceMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPorous substratePolymer science
A method is provided for forming zeolite membranes in internal surfaces of a plurality of conduits in a cylindrical porous ceramic monolith, the conduits extending from one end of the monolith to the other, said method including a step of: flowing a pre-treatment liquid including a zeolite initiating agent into the conduits; causing at least part of a carrier liquid component of the treatment liquid to flow from the conduits into and through the body of the monolith to the exterior; and causing zeolite crystals to be deposited in the porous internal surfaces of the conduits as the carrier liquid component flows into the monolith. The substrates may be pre-conditioned for membrane formation by a method which comprises: (a) forming an aqueous suspension of zeolite particles; and (b) passing the suspension alternately (i) through the tubular conduits and (ii) out through the walls of the tubular conduits so as to deposit a layer of zeolite particles on the inner surfaces of the tubular conduits; wherein the porous substrates are treated in chambers arranged e.g in annularly and the suspension is supplied to the chambers from a first common manifold via respective delivery tubes and is recovered via recovery tubes leading to a second common manifold, the first and second manifolds and the supply and recovery tubes being configured so that the branch path to and from each chamber is substantially the same. After pre-conditioning, formation of membranes may be by depositing or crystallizing a zeolite membrane on the zeolite particles by gel crystallization. A membrane structure is also provided which comprises a tubular porous ceramic monolith having tubular conduits each having an internal diameter of (5) to (9) mm formed within the monolith with a zeolite membrane formed on the internal surface of each of the conduits, wherein either there are four conduits and the monolith is longer than 600 mm or there are five or more conduits. The invention also provides methods for removal of water from organic liquids and methods for the purification of water using the above membrane structures e.g. to remove residual water from ethanol or butanol or to produce high purity water.
Owner:PHOENIX IPR LTD
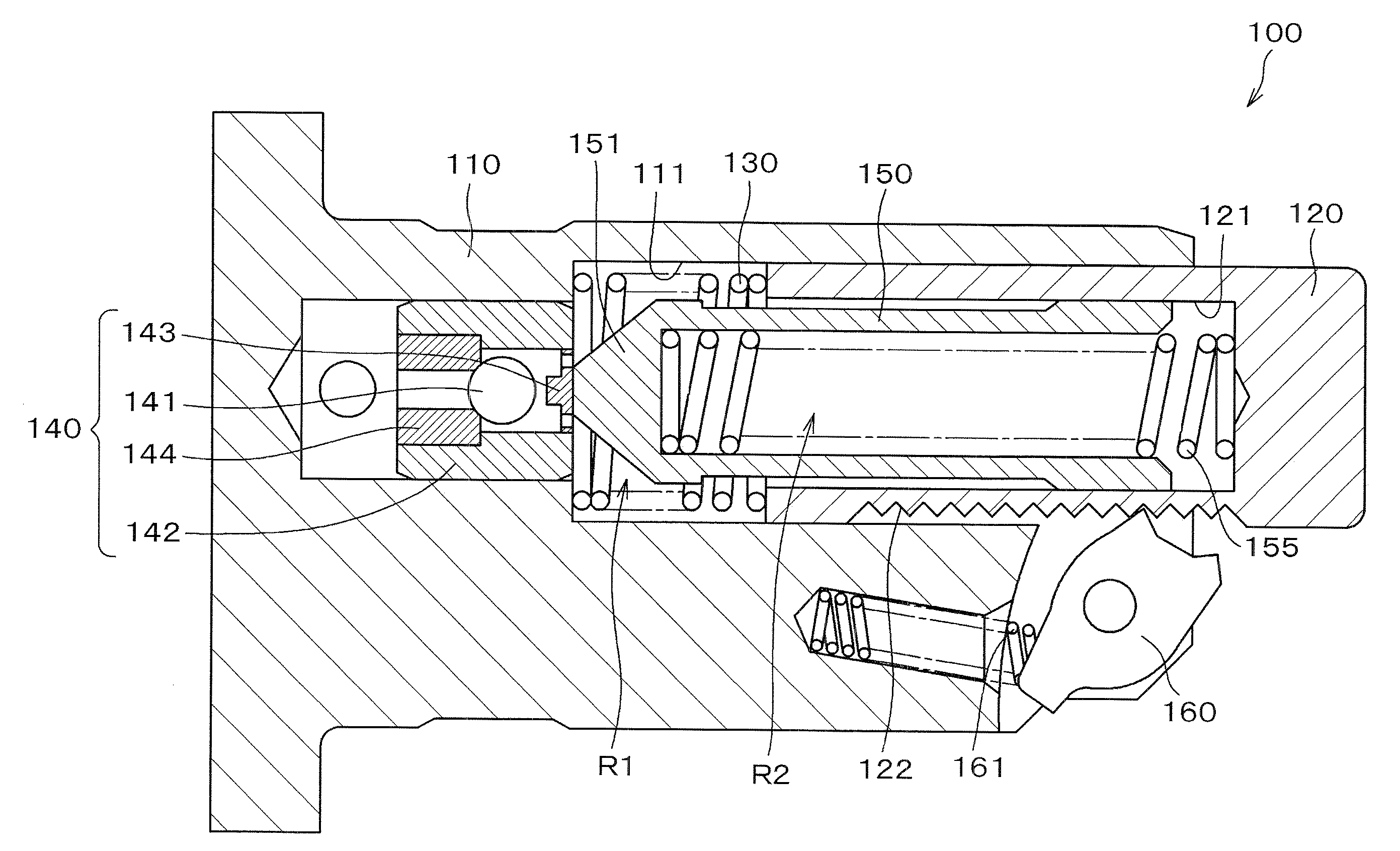
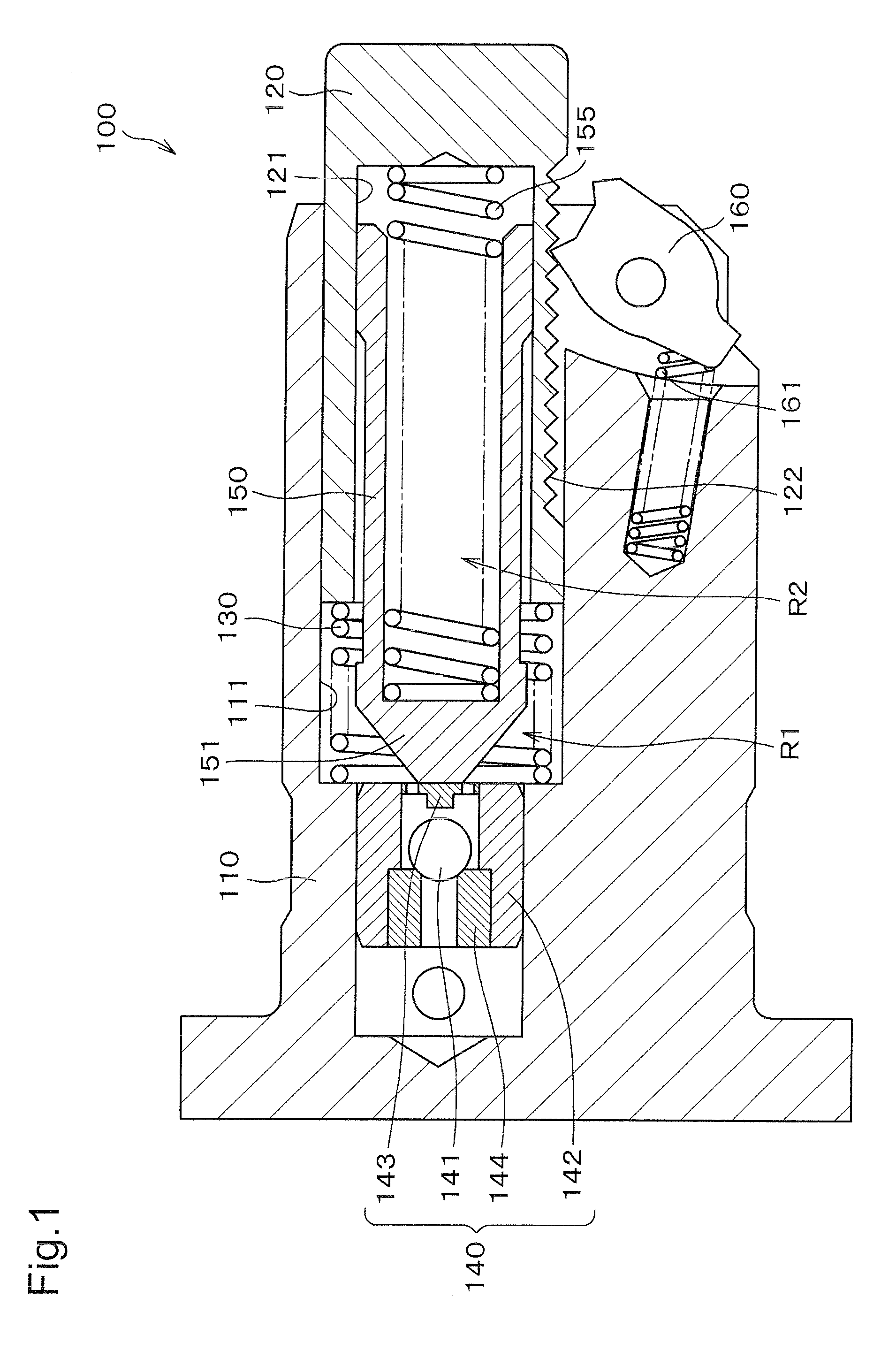
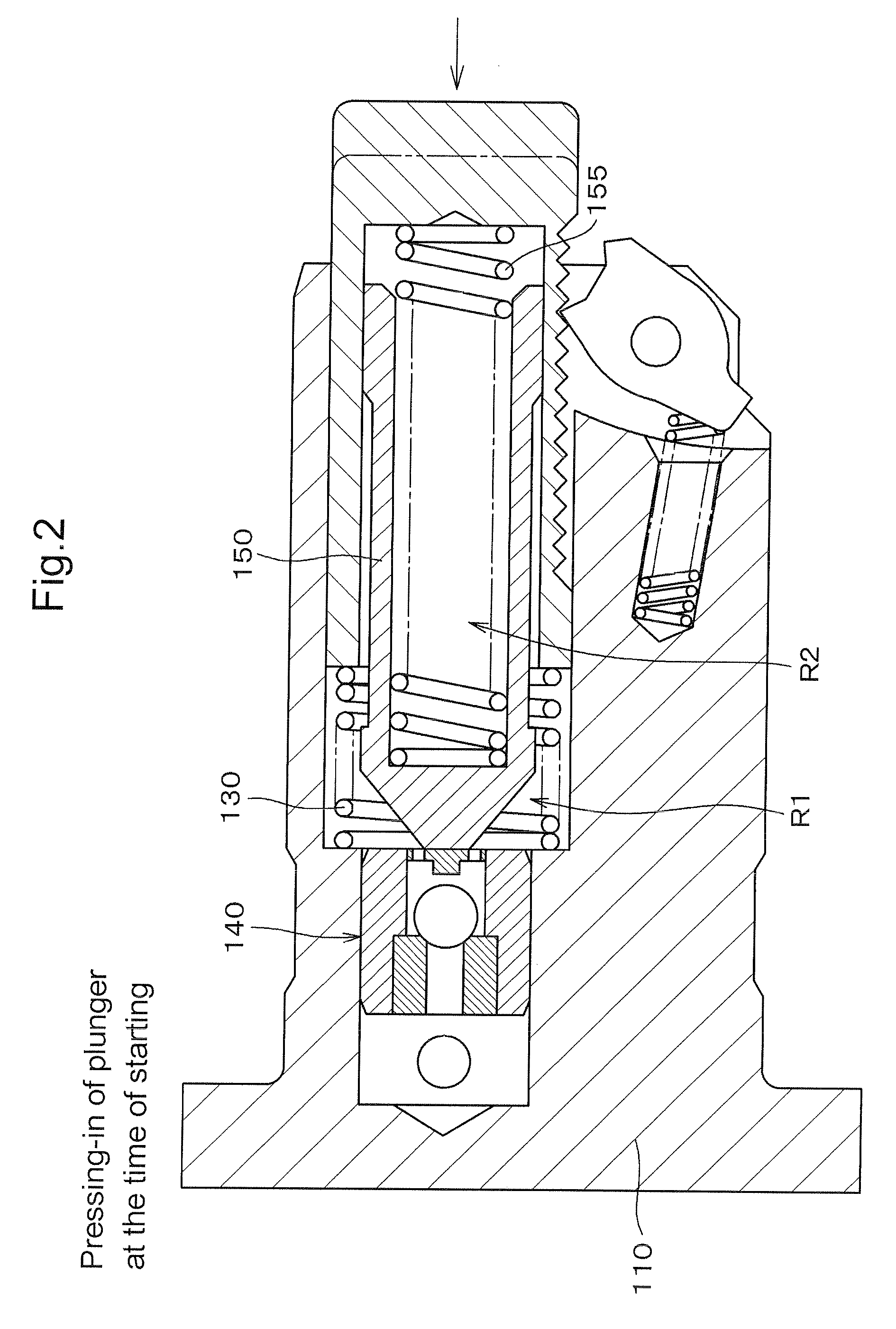
Hydraulic tensioner
InactiveUS20090209378A1Appropriate pressing forceSame damping performanceGearingEngineeringHigh pressure
The hollow plunger of a hydraulic tensioner, slidably receives a sleeve that divides the high pressure oil chamber into two parts. The first part is formed by the plunger and a plunger-accommodating hole of the tensioner housing. The second part is formed by the plunger and the sleeve. Two springs, one being in the first part, and the other being in the second part, urge the plunger in the protruding direction. When the second part is filled with oil during ordinary engine operation, a negative pressure in the second part exerts a force opposing protruding movement of the plunger. Therefore, the springs can be made strong enough to prevent excessive chain vibration and noise during engine start-up when the parts of the high pressure oil chamber are not filled with oil, without causing the tensioner to exert excessive force on the chain during ordinary engine operation.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
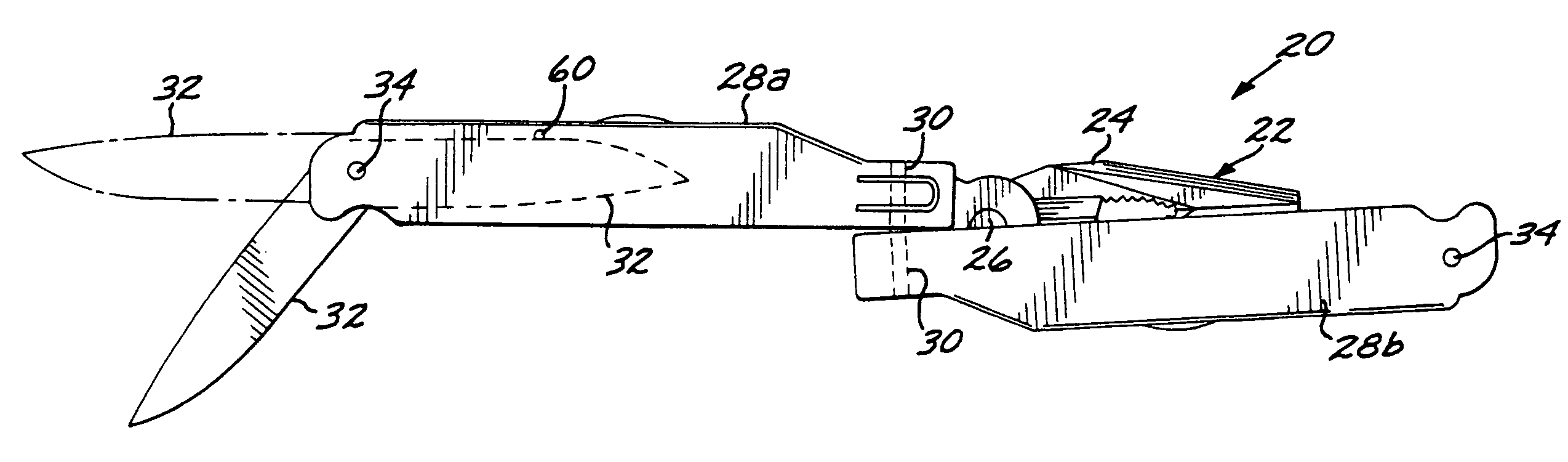
Hand tool with multiple locking blades controlled by a single locking mechanism and release
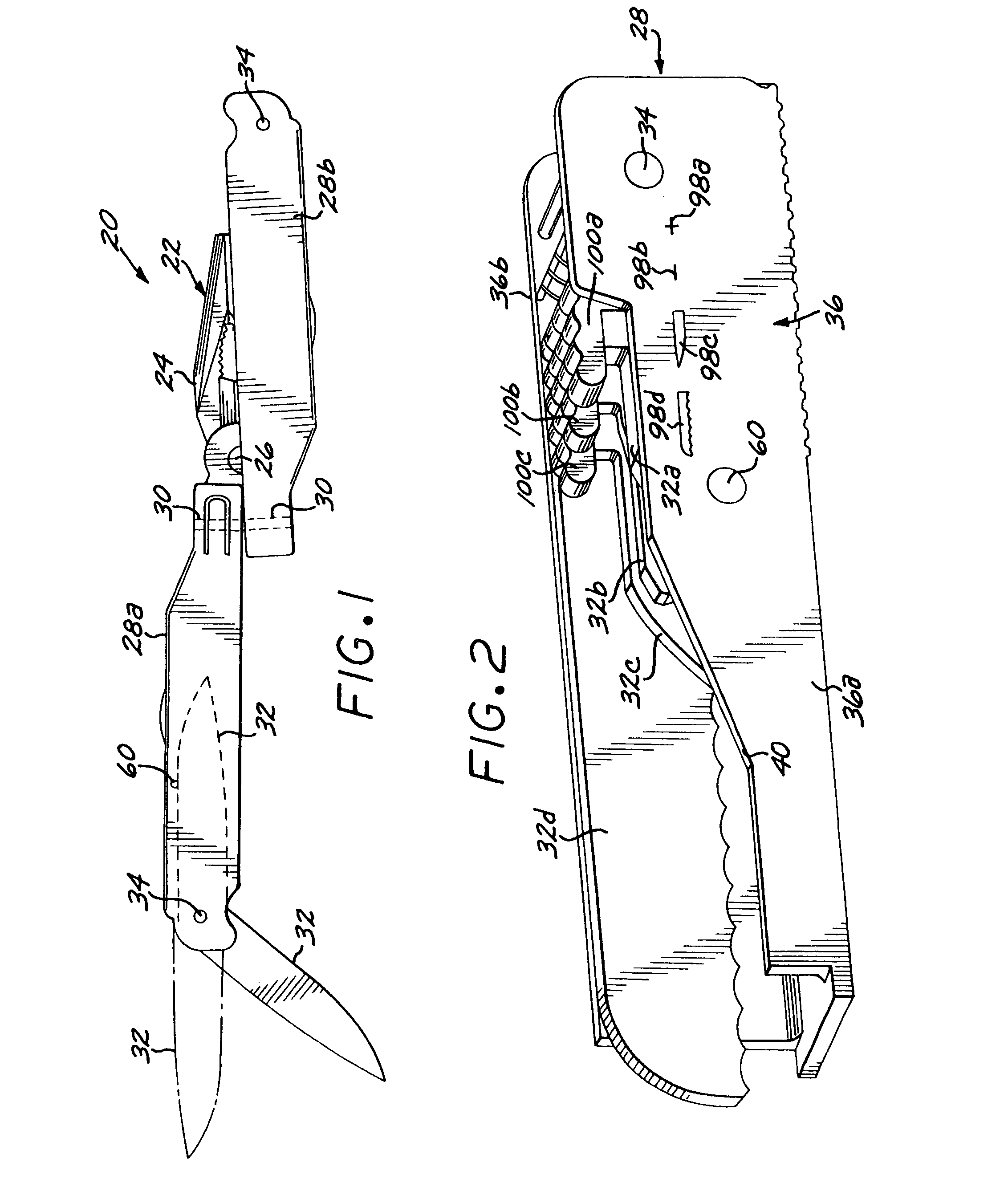
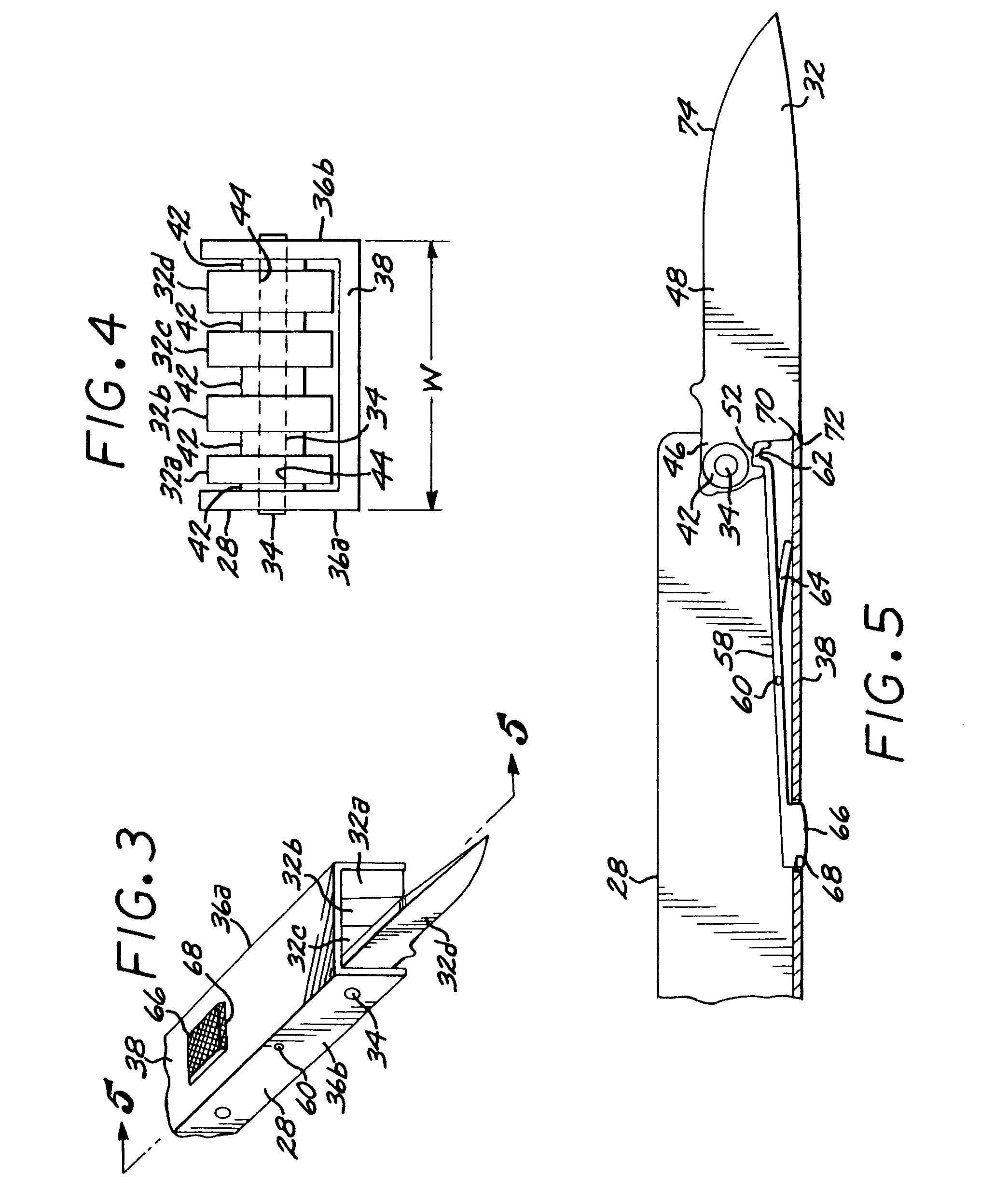
InactiveUS7080423B2Keep the same performanceSame resultPliersThrusting weaponsLocking mechanismEngineering
A hand tool such as a knife or a combination tool includes multiple blades, each independently rotatable on a common axle between a closed position within a handle of the tool and an open position extending from the handle. Each blade is positively but releasably locked into its open position. Those blades which remain closed are biased toward the closed position when the opened blade is locked into position and also as it is opened and closed. A single locking, releasing, and biasing mechanism serves all of the blades in one handle.
Owner:LEATHERMAN TOOL GROUP
Drain pump
ActiveUS20110008153A1Reduce operation soundReduce vibration and noisePump componentsCombination enginesImpellerAir bubble
A drain pump that maintains pump performance and reduces noise and vibration accompanying water scooping of a rotary impeller includes a large-diameter blade divided into an inner blade and an outer blade. A radius of an impeller scooping up water is the sum of the lengths of the inner and outer blades in a radial direction. The large-diameter blade is divided at a position where the amount of generated air bubbles is large, and the inner and outer blades are alternately disposed. Accordingly, air bubbles are escaped to a downstream side in a rotational direction, so that the intensity of the collision between the blades and air bubbles is decreased reducing noise caused by the burst of air bubbles and vibration caused by a collision load of the flow of a gas-liquid mixture.
Owner:FUJIKOKI CORP
Phased shifted oscilator and antenna
ActiveUS20100103043A1Wider coverage rangeReduce electromagnetic interferencePulse automatic controlOscillations generatorsPhase shiftedPhase-shift oscillator
This invention describes new and improved phased shifted injection oscillator, a phased shifted injection locked push-push oscillator and a phased array antennas (PAA). The PAAs in accordance with an exemplary embodiment of the present invention are low cost, and therefore can be used in various commercial applications, such as wireless communication or satellite mobile television.
Owner:BEAM NETWORKS
Nucleic acid extraction method
InactiveUS20100063268A1Easy to separateImprove washing efficiencySugar derivativesAminosugarsBiological materialsHydroxymethyl
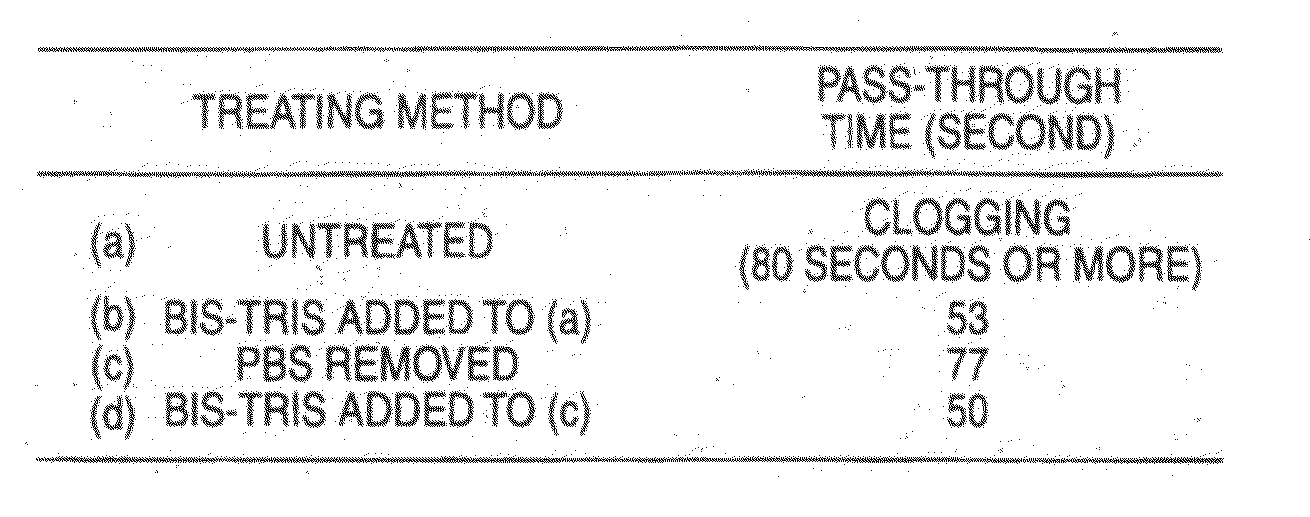
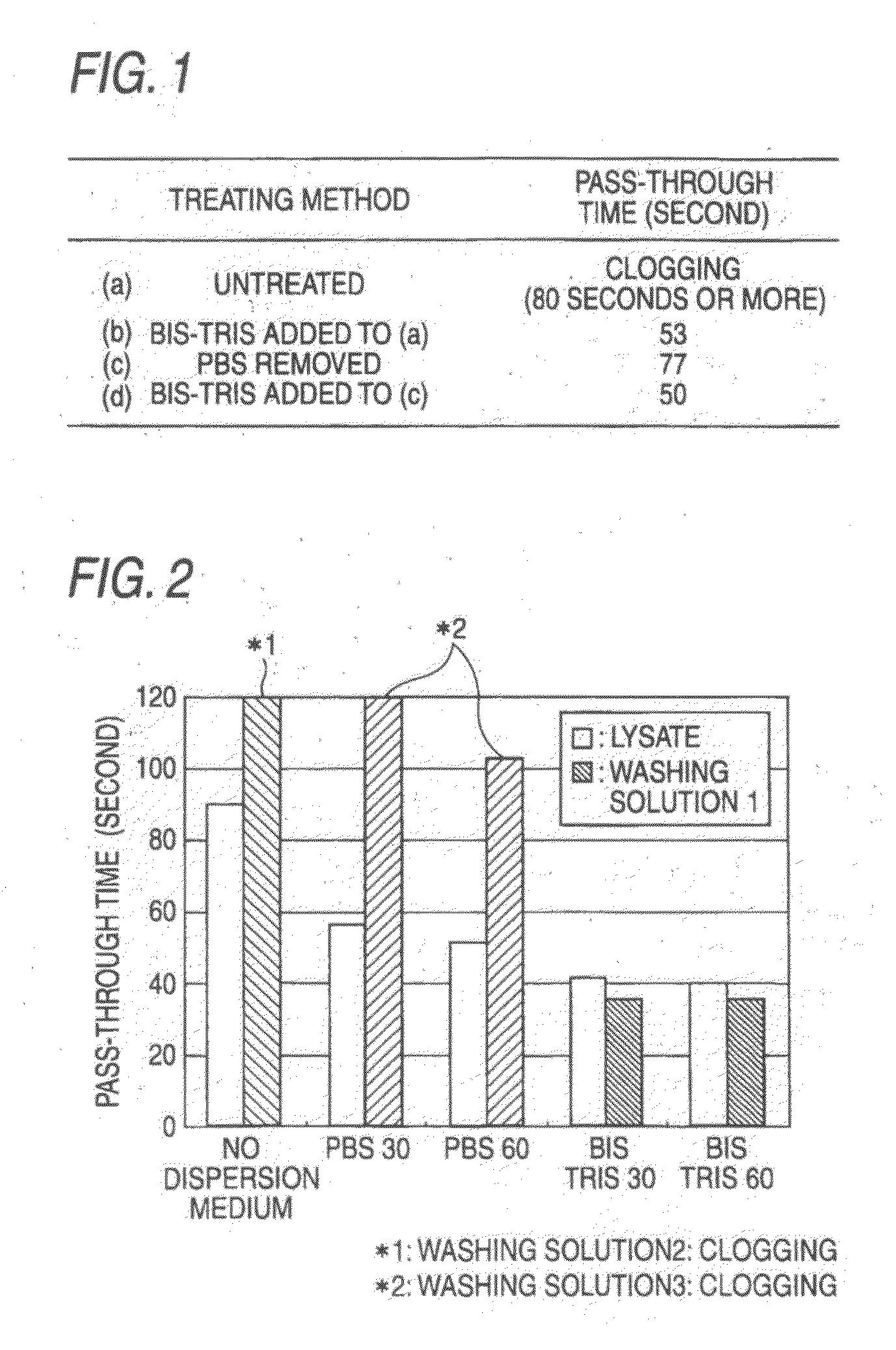
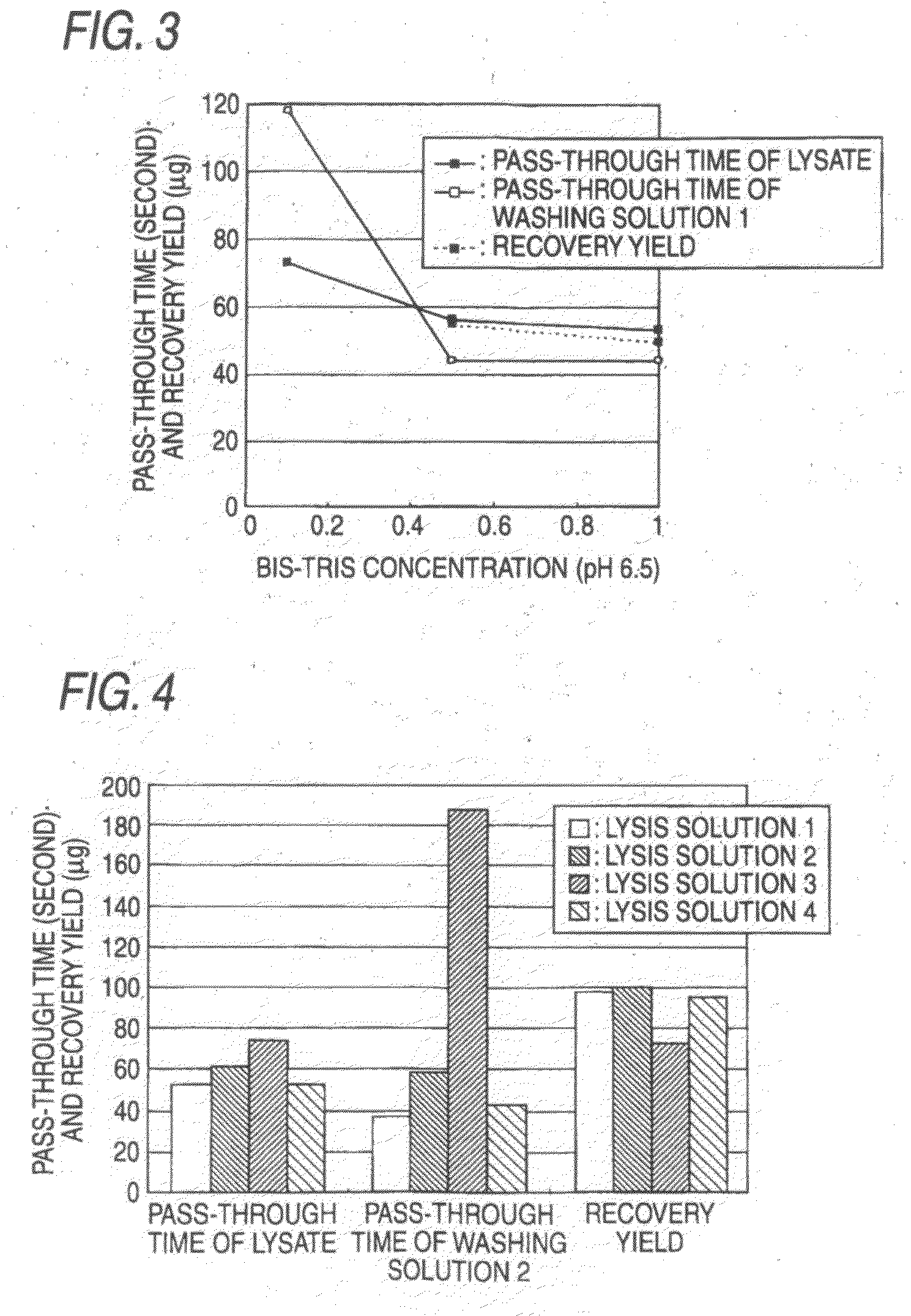
A method for extracting a nucleic acid, which comprises: (a) preparing a biomaterial containing a solution by a following step (i) or (ii): (i) a step in which a biomaterial containing a phosphate buffer solution or a Bis-Tris (N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)iminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane) buffer solution is prepared; or (ii) a step in which a buffer solution contained in a biomaterial is replaced with a Bis-Tris buffer solution; (b) dissolving the biomaterial with a lysis solution, and eluting a nucleic acid contained in the biomaterial; (c) preparing a lysate solution by adding a water-soluble organic solvent to the nucleic acid-eluted solution obtained in the step (b); (d) allowing the nucleic acid contained in the lysate solution to be adsorbed by a solid material; (e) washing impurities remaining in the solid material and the lysis solution; and (f) desorbing the absorbed nucleic acid from the solid material by a recovering solution.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
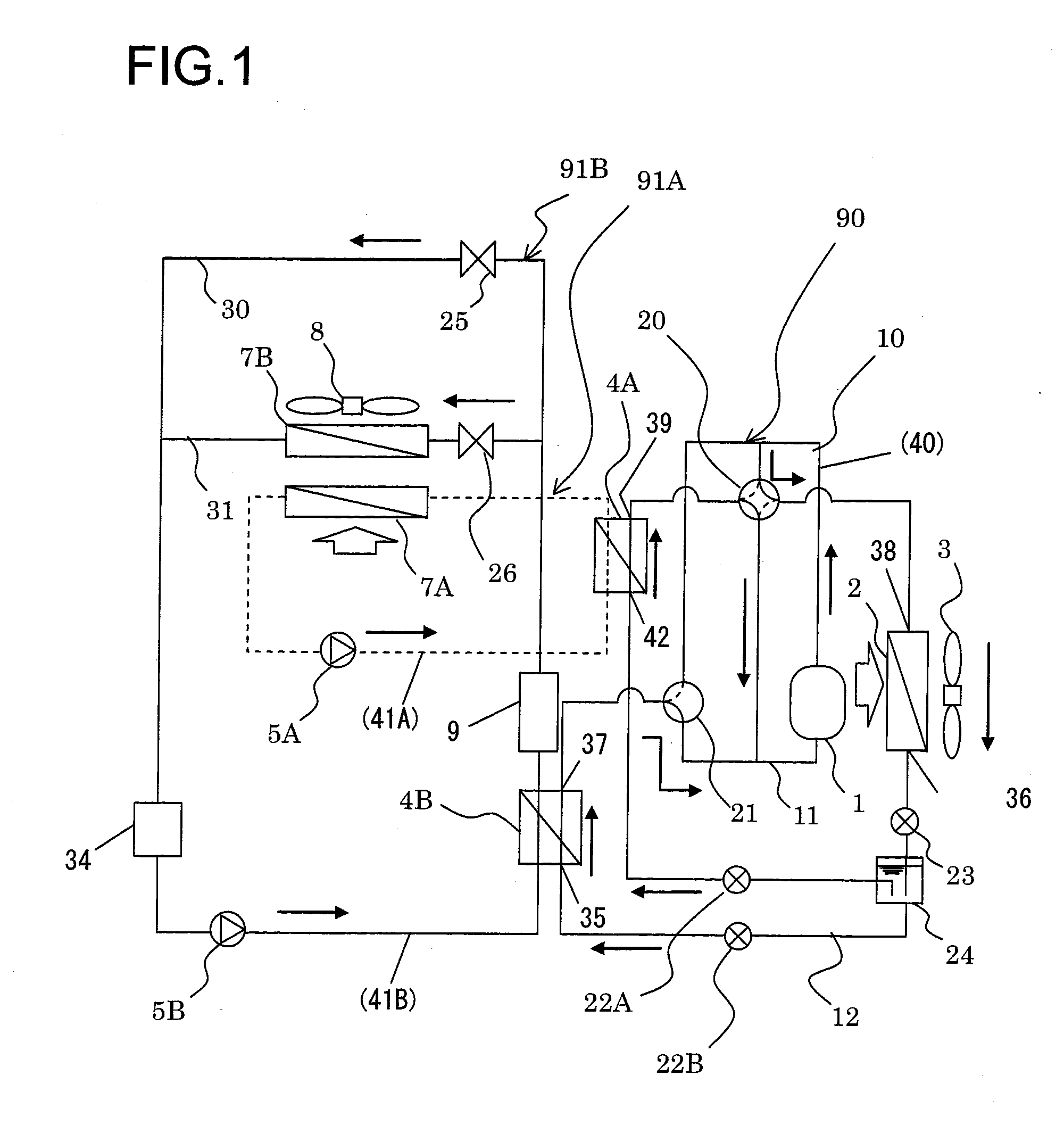
Vehicle air-conditioning apparatus
ActiveUS8733126B2Increased power consumptionKeep the same performancePower to auxillary motorsPower to electric heating circuitsIn vehicleEngineering
A vehicle air-conditioning apparatus, including: a refrigerant circulation channel that flows a refrigerant, the refrigerant circulation channel provided in a refrigeration cycle system including, as connected in a cyclic pattern, a compressor for the refrigerant, an outdoor heat-exchanger exchanging heat between the refrigerant and an outdoor air, an expansion valve reducing pressure of the refrigerant, and an air-conditioning heat-exchange circuit exchanging heat between the refrigerant and air to be introduced into a vehicle interior; and an equipment heat-exchange circuit connected in parallel to the circuit and exchanging heat between the refrigerant and in-vehicle equipment. The circuit includes a cooling heat-transfer medium circulation channel that circulates a heat-transfer medium for cooling. The cooling channel has a cooling heat-exchanger exchanging heat between the refrigerant in the channel and a cooling heat-transfer medium for cooling the in-vehicle equipment and a cooling circulation pump for circulating the cooling heat-transfer medium.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
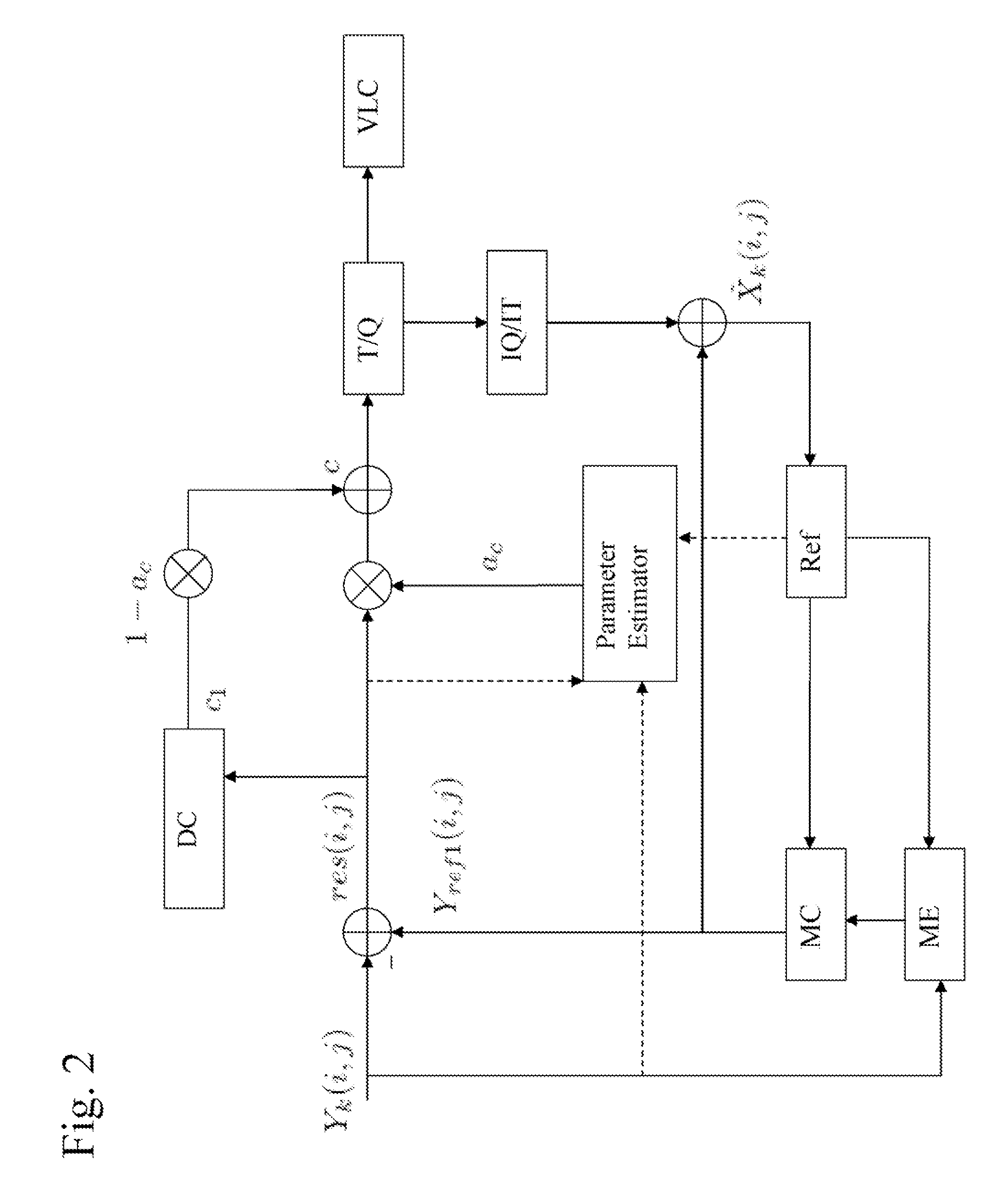
Optimal Denoising for Video Coding
ActiveUS20070291842A1Same and good performanceSimple methodColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionVideo encoding
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Swelling tape comprising polyurethane film and method for manufacturing same
ActiveUS20160376472A1Uniform thicknessLow costDomestic sealsLamination ancillary operationsPolymer scienceCarbamate
A swelling tape is disclosed comprising a polyurethane film and a method for manufacturing the same. The swelling tape comprises: a base layer including a polyurethane film that is composed of a chain of monomers joined by urethane links as a result of a reaction between a liquid polyol and a crosslinker; and an adhesive layer formed on a first surface of the base layer in a direction horizontal to a lengthwise direction of the base layer. When made with the liquid polyol and the crosslinker, a resulting polyurethane film exhibits appearance and performance similar to polyurethane film prepared through extrusion. The resulting polyurethane film has a uniform thickness and the advantage of being produced at a low cost.
Owner:SEIL HITEC CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com