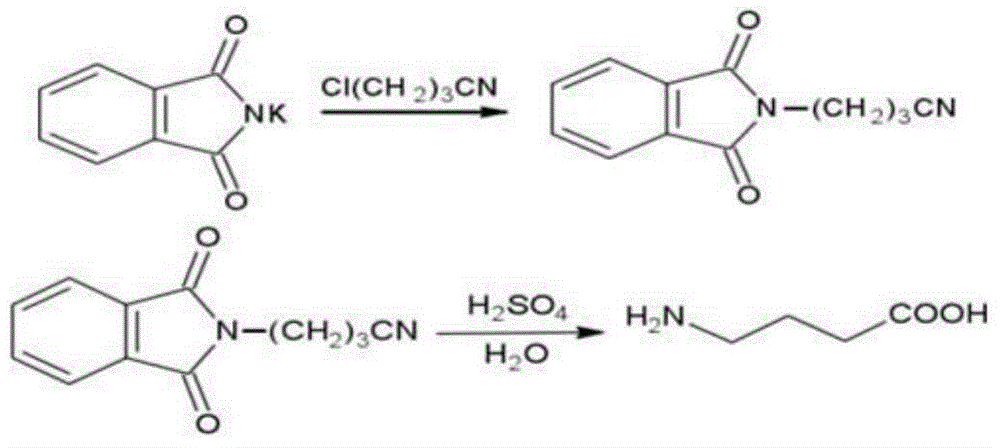
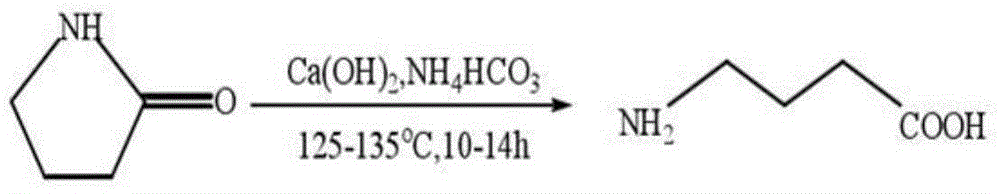
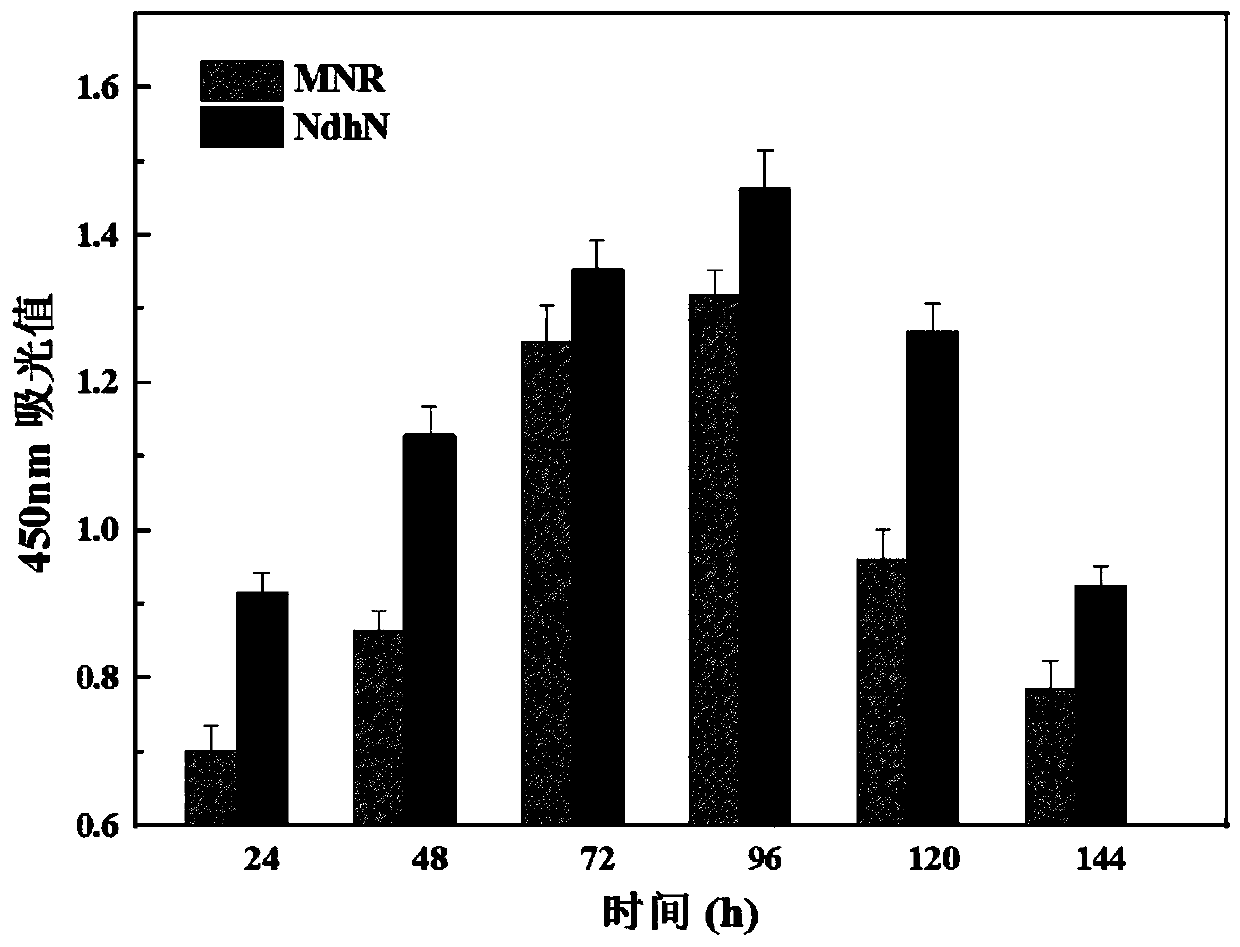
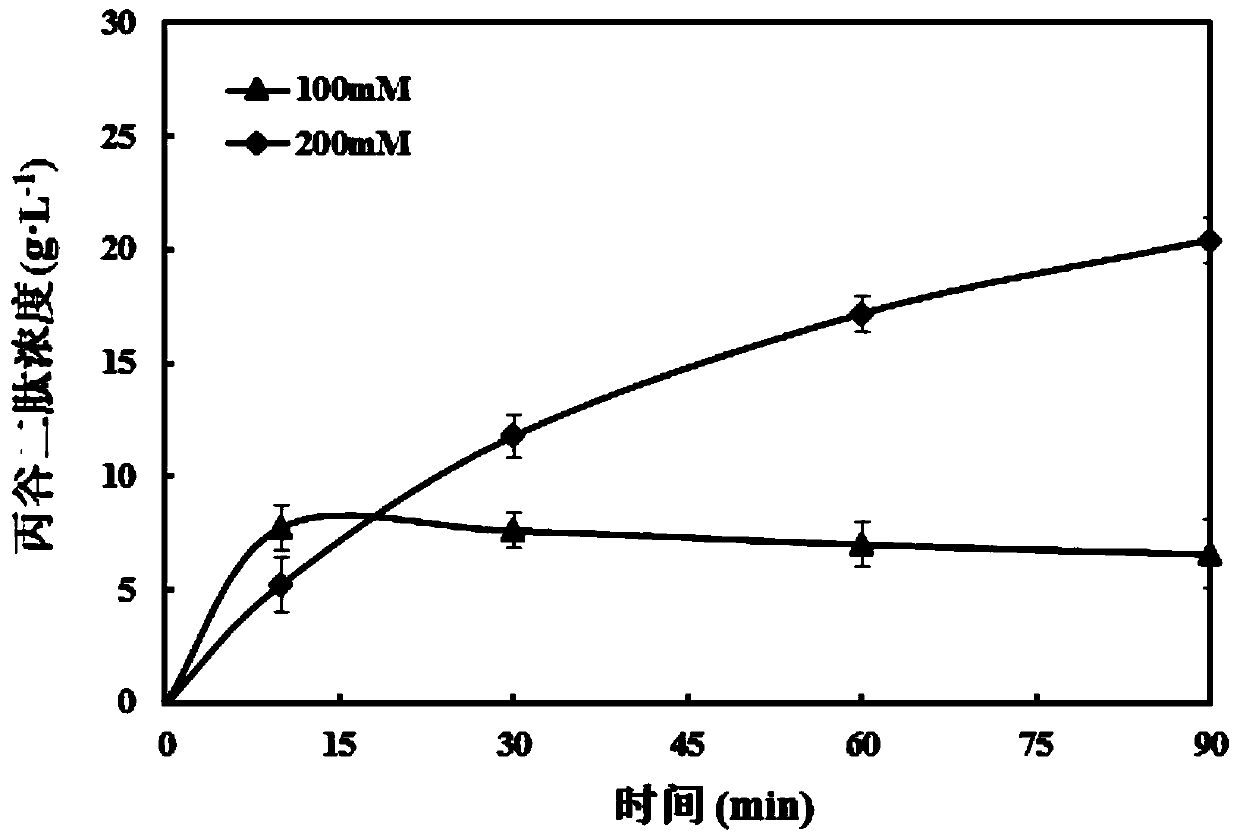
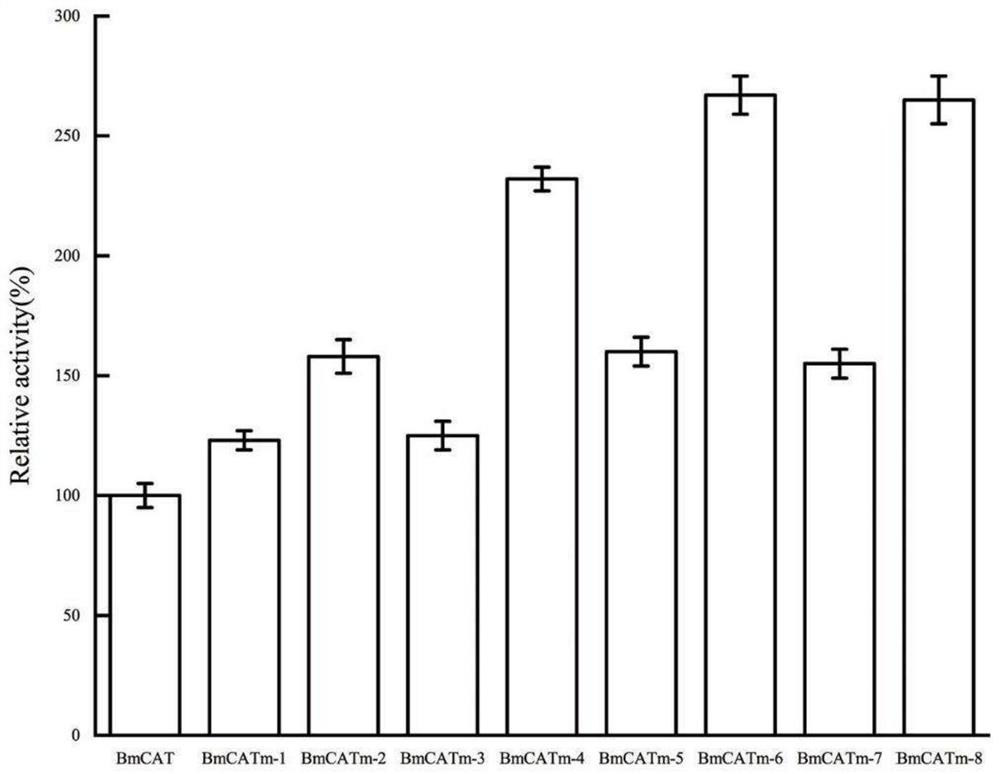
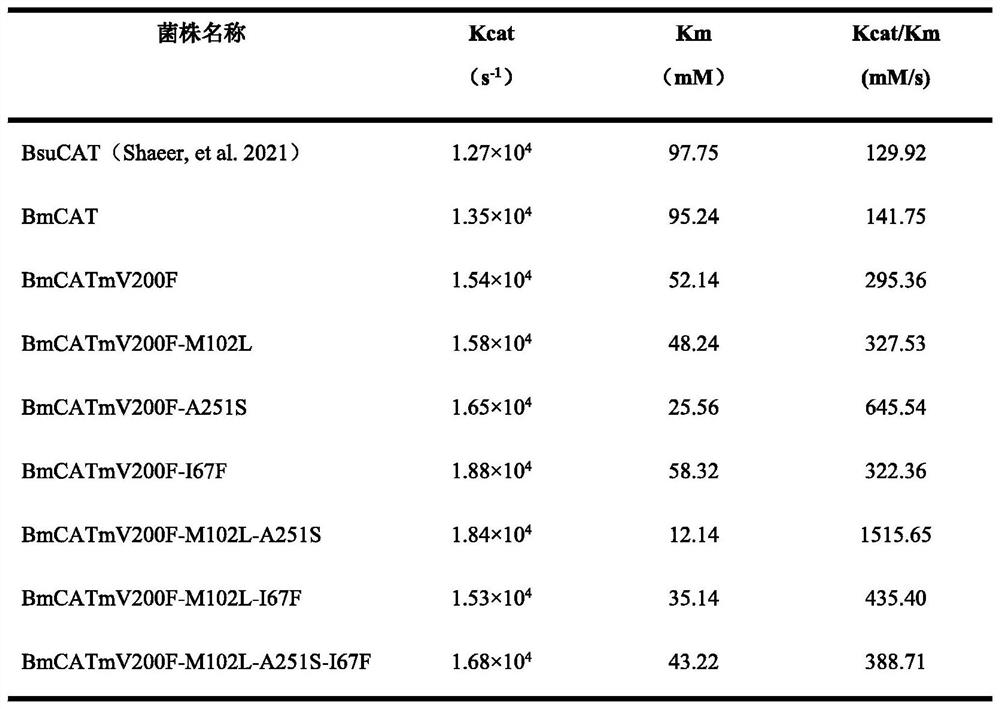
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
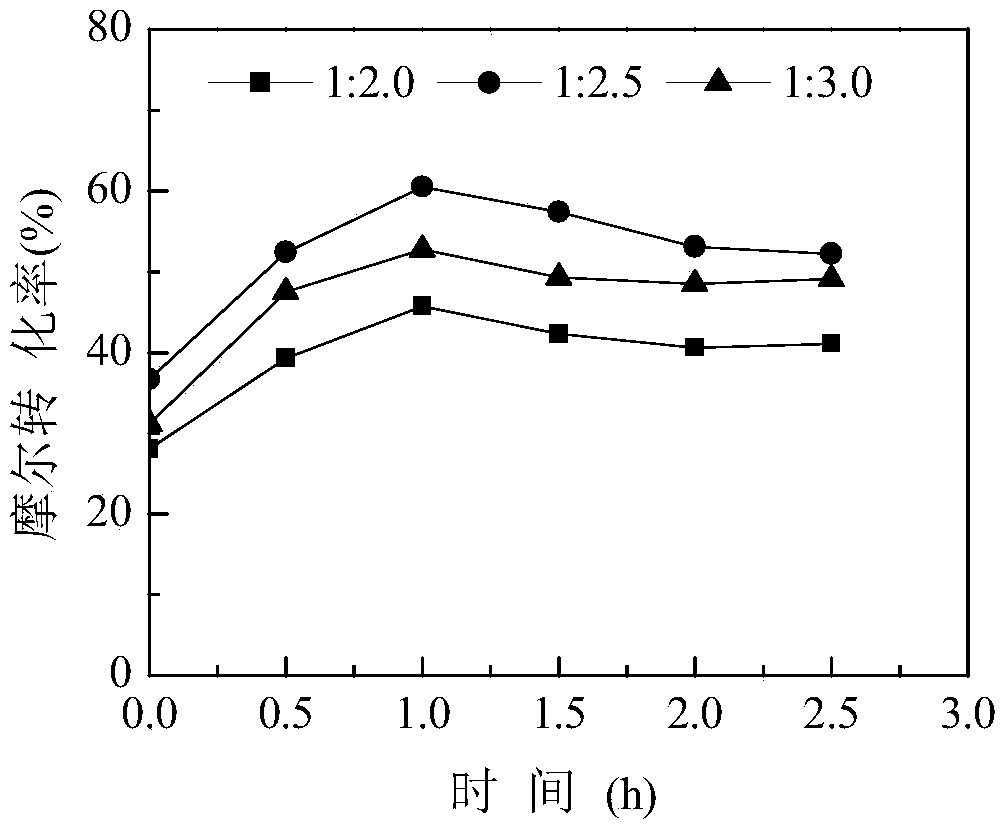
43results about How to "High molar conversion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for preparing GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) by using biotransformation method
ActiveCN105087699AShort productionIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiological activationDrug biotransformation
The invention discloses a method for preparing GABA (gamma-aminobutyric acid) by using a biotransformation method, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of GABA. The method comprises the following steps: adopting lactobacillus brevis CGMCC NO.3414 as an original strain; carrying out enrichment culture and thallus collection; resuspending the thallus in a scientifically compounded buffer solution of a mixture of L-sodium glutamate and glutamic acid; adding Na2B4O7.10H2O or MgSO4 having relatively strong activation for the endoenzyme generated by the strain, so as to enable the activity of endoenzyme to be maximally given into play; catalyzing and converting the mixture of L-sodium glutamate and glutamic acid into GABA, wherein the content of GABA in the conversion solution is 45.74-202.18 g / L, the molar conversion rate of the substrate is 95.92-99.75%, and the thallus can be repeatedly used for 8 times. According to the method, the product quality and yield are improved, the environment is protected, the method is relatively good in economic and social benefits and applicable to scale production, and industrial popularization is facilitated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Catalyst for preparing o-fluoroaniline from o-fluoronitrobenzene by hydrogenation and preparation method of catalyst
ActiveCN104117353AImprove stabilitySolution to short lifeOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationO-fluoronitrobenzeneMetal
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing o-fluoroaniline from o-fluoronitrobenzene by hydrogenation. The catalyst contains an Al2O3 supporter and the following components in percentage by mass: 0.05%-1% of Pt supported on the Al2O3 supporter, 0.05%-3% of metal M1 and 0.01%-3% of metal M2, wherein the metal M1 is Pd, Sn or Zn; the metal M2 is K, Co, Ga, In, Mn, Ag or Ce. Besides, the invention also provides a preparation method of the catalyst. When the catalyst prepared by the preparation method is used for catalyzing o-fluoronitrobenzene hydrogenation, the mole conversion rate of o-fluoronitrobenzene is up to 100%, the mole percentage of a defluorination product is smaller than 0.1%, the amount of o-fluoronitrobenzene treated by the catalyst of unit mass is large, the use amount of the catalyst is small, and the catalyst can be reused after being regenerated.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof to glutamine dipeptide synthesis
ActiveCN106754447AEliminate separation and purificationEfficient productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyDipeptide
The invention discloses a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof to glutamine dipeptide synthesis. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae contains an exogenous gene with the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses a recombinant vector containing the gene, the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and a method for glutamine dipeptide synthesis through biotransformation by using the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae. The condition that saccharomyces cells still have high catalytic activity after the multi-time circulation utilization is discovered; the obvious industrial advantages are realized. The method and the application provided by the invention have the advantages that the raw materials are cheap and can be easily obtained; the operation is simple and convenient and can be easily controlled; the synthesis path is green and efficient; the biosecurity is high; the reaction speed is high; the conversion rate is high, and the like; The foundation is laid for the industrial production of the glutamine dipeptide.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
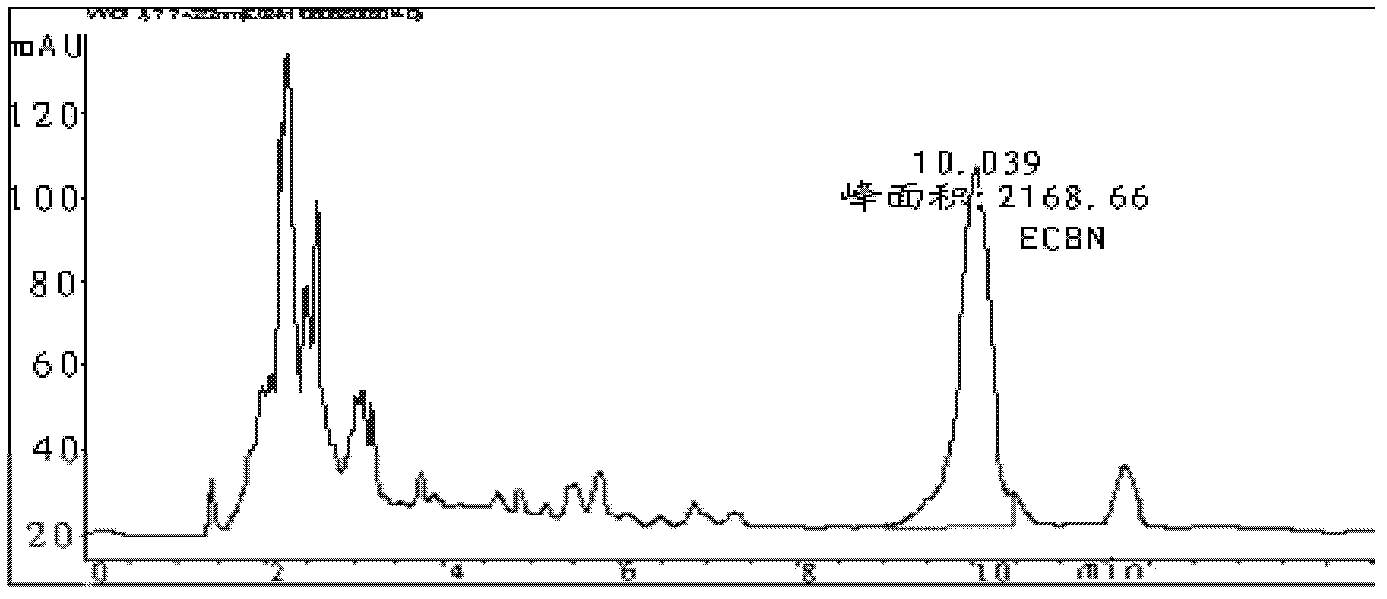
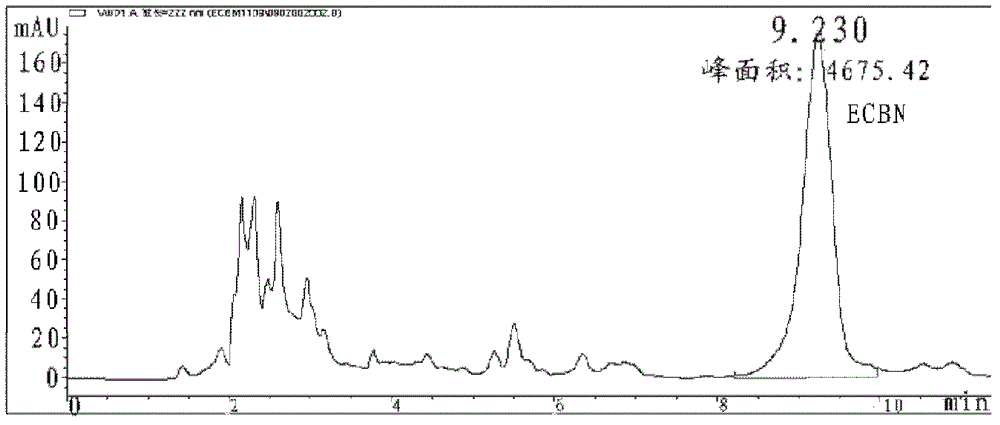
Method for converting echinocandin B by using microbial enzyme
ActiveCN103074403AEasy to separate and purifyHigh molar conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic solventPhosphate
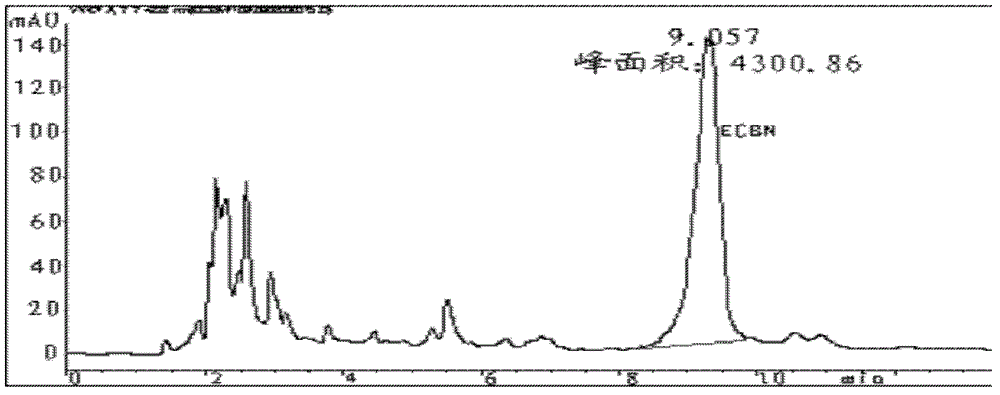
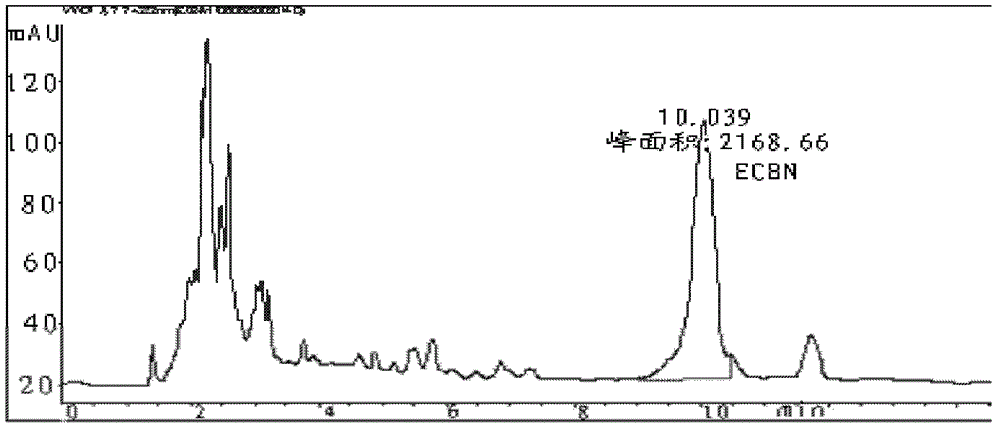
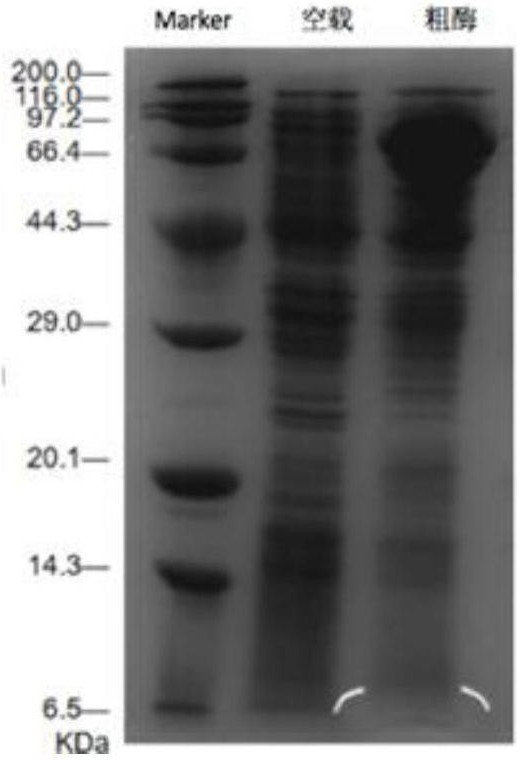
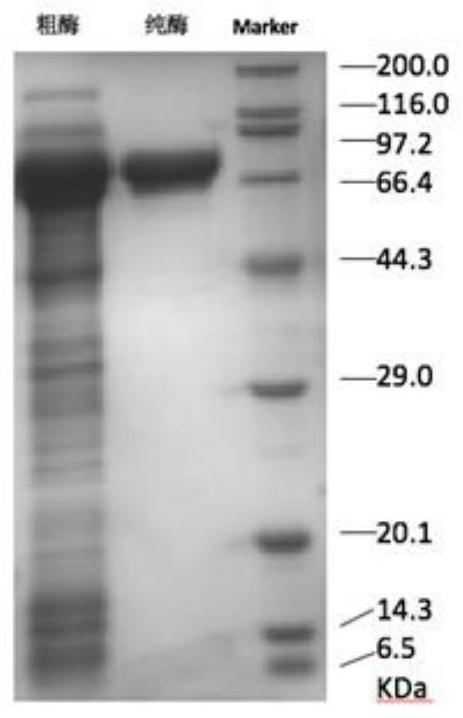
The invention provides a method for converting echinocandin B (ECB) by using microbial enzyme. The method comprises the steps that: (1) microbes are fermented, such that echinocandin B deacylase is obtained; (2) when fermentation is finished, phosphate is added into the fermentation broth; ultrasonic processing is carried out; and supernatant is obtained by centrifugation, and the supernatant is echinocandin B deacylase crude enzyme solution; (3) the crude enzyme solution is purified, such that echinocandin B deacylase enzyme solution is obtained; (4) echinocandin B is dissolved in ethanol, and is mixed with the deacylase enzyme solution; mixing and stirring are carried out, such that the material is converted into echinocandins B nucleus; when conversion is finished, filtering is carried out; and the filtrate is obtained; and (5) the filtrate is processed by using macroporous adsorption resin; echinocandins B nucleus is absorbed on resin; and echinocandins B nucleus is eluted by using an organic solvent. According to the invention, a molar conversion rate is high, a conversion time is short, an obtained product is easy to separate and to purify, and ECB deacylase can be repeatedly used.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Biosynthesis method of beta-alanine
InactiveCN108048500AOvercome transmembrane resistanceImprove stabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyReaction rate
The invention discloses a biosynthesis method of beta-alanine, which includes reaction of transforming and compounding beta-alanine by recombined brewing yeast full cell catalyzed L- asparaginic acid,wherein the recombined brewing yeast contains exogenous L- aspartic acid-alpha- decarboxylase encoding gene. The method and application have advantages of low-priced and easy-acquired raw materials,simple and easy-controlled operation, green and high-efficient synthetic route, good in biological safety, quick in reaction rate, high in converting rate, and others; the method and application alsolay a foundation of the industrialization of beta-alanine.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
Method for efficiently producing steroid medicine precursor by fermentation
ActiveCN109706107AIncrease productivityEnhance cell viabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyBiological organism
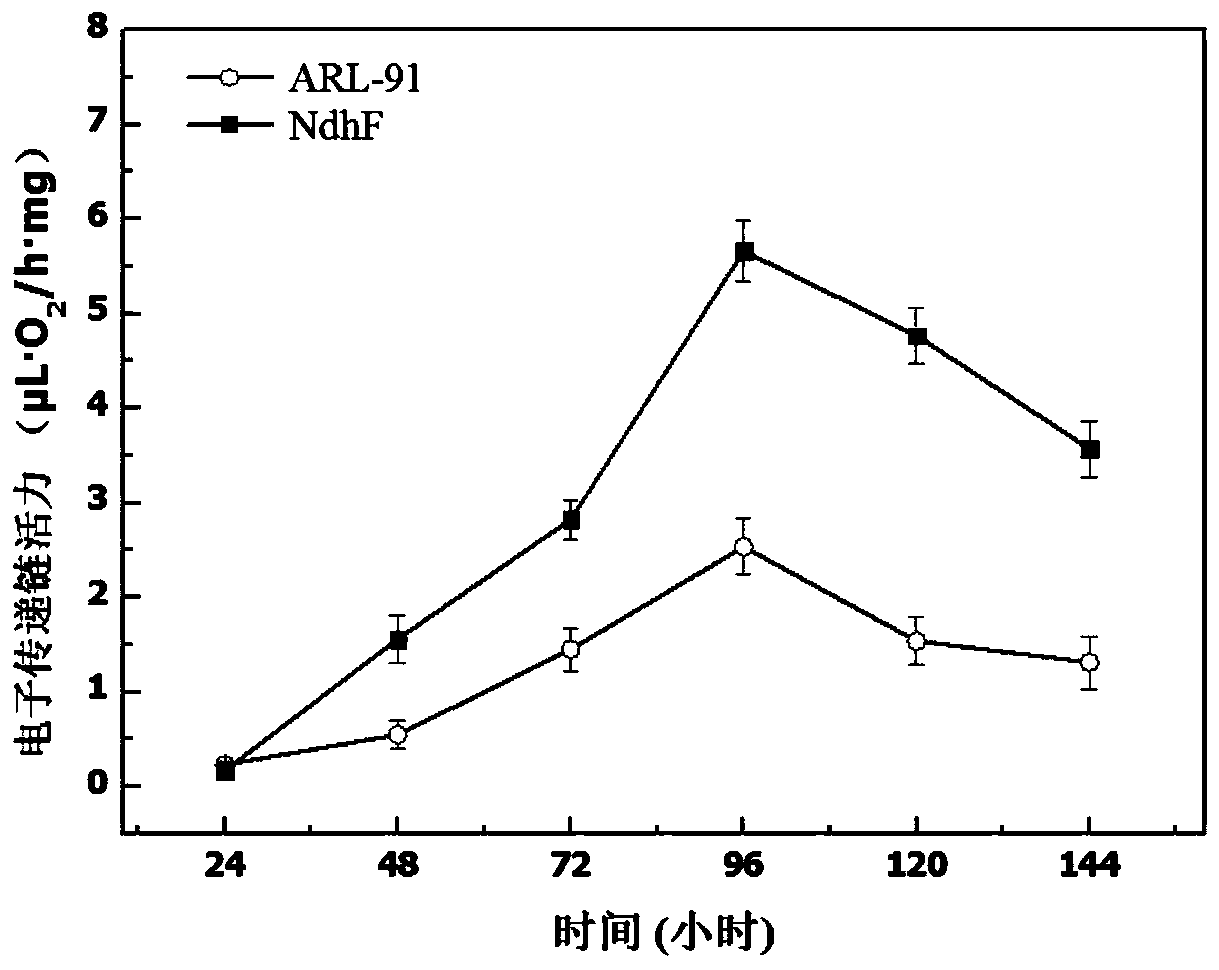
The invention belongs to the technical field of biocatalysis, and particularly relates to a method for improving steroid medicine production strain vitality to efficiently produce a steroid medicine precursor by fermentation. The method improves steroid medicine production strain vitality to efficiently produce a steroid medicine precursor by fermentation through the overexpression of type II NADHdehydrogenase gene, and solves the problems of long fermentation cycle and low production efficiency during the steroid medicine precursor production by a microbiological method. A new method for reducing production cost of steroid medicine precursor is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for enhancing steroid medicine precursor production by strengthening NADH dehydrogenation
ActiveCN109706108AReduce contentRaise the ratioBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobial transformation
The invention belongs to the technical field of biocatalysis, and particularly relates to a method for enhancing the steroid medicine precursor production by strengthening the intracellular NADH dehydrogenation of a steroid medicine production strain. The method introduces NADH dehydrogenase-NDH2 which has no proton-pump function and exists insteroid medicine production strain microorganisms, constructs a NDH2-enhanced steroid medicine precursor production strain to strengthen the dehydrogenation of NADH in the steroid medicine precursor production strain, solves a problems of long fermentation cycle and low production efficiency caused by excessive accumulation of NADH in the process of microbial transformation production of the steroid medicine precursor, and can help reduce energy consumption and save production cost in the production process of the steroid medicine precursor. The method can be effectively used for strengthening the intracellular NADH dehydrogenation of other industrial production strains, and has wide application value. A new method for reducing the production cost of steroid medicine precursor is provided.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method for preparing (S)-(+)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran by transforming engineering strains
InactiveCN107904269AIncrease concentrationImprove toleranceOrganic chemistry methodsMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliCalcium alginate
The invention provides a method for preparing (S)-(+)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran by transforming engineering strains. The method is characterized in that the (S)-(+)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran is preparedby taking 3-ketotetrahydrofuran as a substrate, immobilizing thallus cells, which are obtained by fermenting genetically engineered bacteria escherichia coli LC001 and can provide an enzyme continuously, through calcium alginate into a biological catalyst, and carrying out catalytic reaction. The method for preparing the (S)-(+)-3-hydroxytetrahydrofuran by transforming the engineering strains, provided by the invention, has the advantages of convenience for operation, high yield, moderate reaction conditions, environment friendliness, high catalysis specificity, high catalysis efficiency, high substrate and product tolerance and low cost, and has potential value in industrialized production.
Owner:安徽联创生物医药股份有限公司
Preparation method for salvianolic acid A
ActiveCN102531901AProcess stabilityQuality is easy to controlCarboxylic acid esters separation/purificationMedicineEngineering
The invention provides a preparation method for a salvianolic acid A conversion solution, more specifically, a preparation method for obtaining salvianolic acid A by means of macroporous resin column chromatography, extraction and a silicagel column. The salvianolic acid A obtained by the method can be industrially produced, and moreover, the purity of the salvianolic acid A is high, so that the medication safety is guaranteed. The invention provides a simple, convenient and high-efficiency method for the preparation of the salvianolic acid A. When the method provided by the invention is used for preparing the salvianolic acid A, the process is stable, the quality can be controlled, the conversion rate is high, the total yield of the salvianolic acid A as main product is high, and the cost is low; and in combination with the separation and purification technique, the method can industrially prepare the high-purity salvianolic acid A in large batches.
Owner:SUZHOU LEINA PHARMA RES DEV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing 5alpha-androstanedione and application thereof
ActiveCN111484961AHigh molar conversionLow priceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChemistrySpirochaete
The invention belongs to the technical field of biocatalysis, and particularly relates to construction and application of genetically engineered bacteria for one-step conversion from cheap substrate phytosterol (PS) as a raw material to 5alpha-androstanedione (5alpha-AD). The 5alpha-reductase gene from treponema pallidum is heterologously expressed into mycobacteria mainly producing androstenedione (AD), and one-step biotransformation from phytosterol to 5alpha-AD is realized, so that green and efficient production of 5 alpha-AD is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Construction of co-enzyme regeneration system and application of co-enzyme regeneration system in high-efficiency catalysis of 5 alpha-AD
ActiveCN110643557ASolve the limiting problem of low catalytic activityIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesHeterologousEngineered genetic
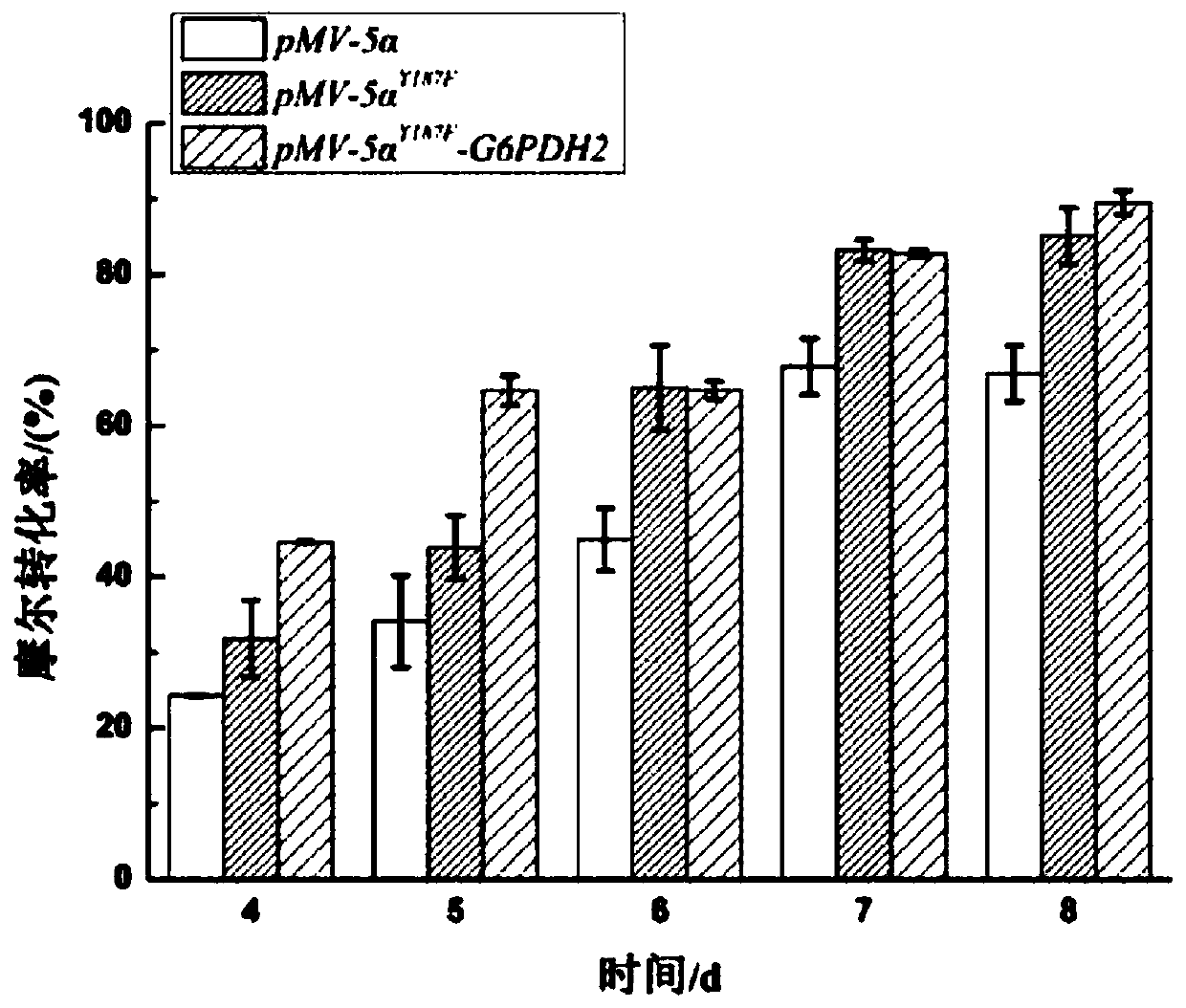
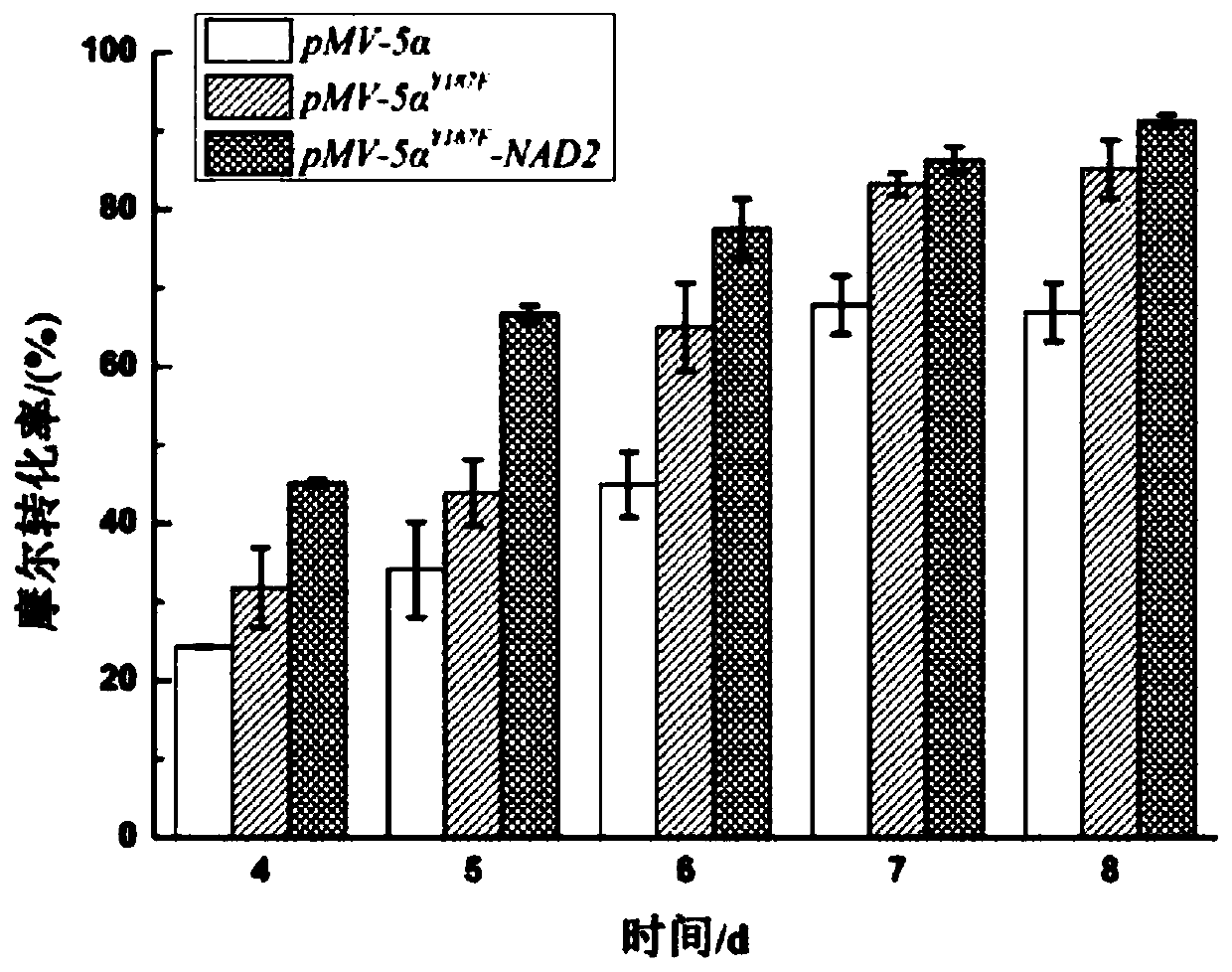
The invention provides a co-enzyme regeneration system and particularly relates to a genetically engineered bacterium of 5 alpha-reductase constructed by tandem of glucose-6-phosphate-dehydrogenase (G6PDH) and 5alpha<Y187F>-reductase recombinant and tandem of NAD kinase and 5alpha<Y187F>-reductase recombinant and application of the 5 alpha<Y187F>-reductase in high-efficiency catalysis of 5 alpha-AD production. The 5 alpha<Y187F>-reductase is electrotransformed into a mycobacterium respectively with mycobacterium-derived G6PDH and NAD kinase recombinant plasmids to subject to heterologous expression, detection on production efficiency of the 5 alpha<Y187F>reductase discovers that the co-expressed genetically engineered bacterium MNR M3 / 261-5 alpha<Y187F>-G6PDH2 on production of the 5 alpha-AD is increased from previous 67.8 percent to 89.5 percent, the co-expressed strain MNR M3 / 261-5 alpha<Y187F>-NAD2 on production of the 5 alpha-AD is increased from previous 67.8 percent to 92.6 percent, the limitation problem of low catalytic activity of the 5 alpha-reductase is effectively solved, and a new thought is provided to molecular improvement of the 5 alpha-reductase.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
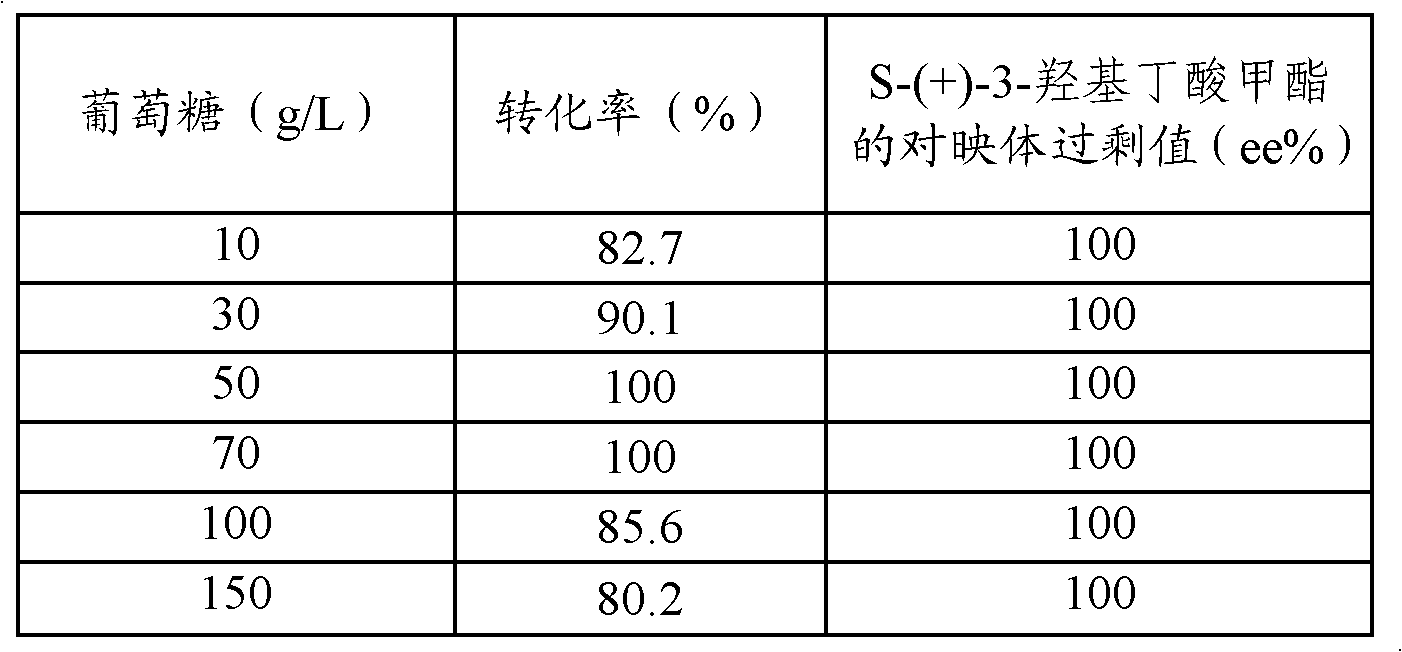
Method for preparing S-(+)-3-methyl hydroxybutyrate through microbial transformation
InactiveCN102071227AHigh molar conversionHigh enantiomeric excessMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydroxybutyric acidAcetic acid
The invention provides a method for preparing S-(+)-3-methyl hydroxybutyrate through microbial transformation, which comprises the following steps that: in phosphate buffer solution with the pH value being 5.0 to 8.0, methyl acetoacetate is used as substrates, enzyme-containing strains obtained through fermenting saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No. 2266 are used as microbial catalysts, conversion region is carried out for 8 to 40h at 25 to 45 DEG C, after the reaction is completed, and conversion liquid is prepared into the S-(+)-3-methyl hydroxybutyrate through separation and purification. The method provided by the invention has the main beneficial effects that 1. produced strains are safe and innoxious and are easy to be cultured in a large scale; 2. a large number of biological catalysts can be obtained, and the cost is low; 3. the reaction conditions are mild, and the environmental-friendly effect is realized; 4. the operation is simple and convenient, and the addition of coenzymes with a high price is not needed in the reaction process; and 5. the large-scale industrialized production is easy to realize, and the mol conversion rate is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
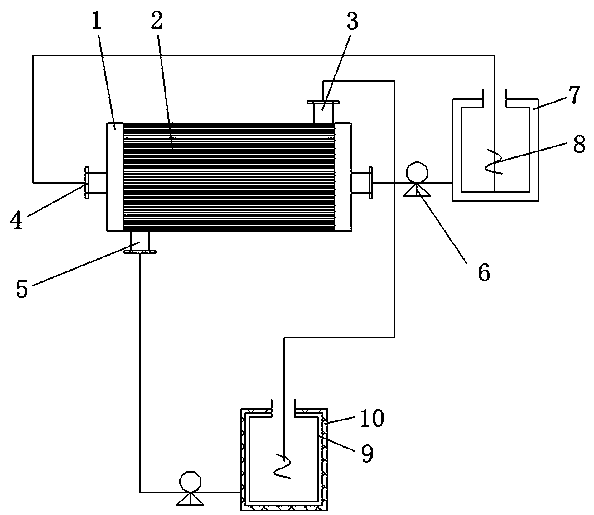
Method for preparing r-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate by utilizing coupling extraction of enzyme membrane reactor
ActiveCN109943482ADisinhibitionDetoxifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsOrganic solventCoupling
The invention relates to a method for preparing r-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutanoate by utilizing coupling extraction of an enzyme membrane reactor. The method adopts the enzyme membrane reactor, an organicsolvent charging barrel and a substrate charging barrel, wherein filter membranes are distributed inside the enzyme membrane reactor, one side of the upper end of the enzyme membrane reactor is connected with a feed liquid outlet, one side of the enzyme membrane reactor is provided with an organic solvent outlet, one side of the lower end of the enzyme membrane reactor is connected with a feed liquid inlet, and the other side of the enzyme membrane reactor is provided with an organic solution inlet. The method is simple in process, the emulsification phenomenon in the reaction and extraction processes is decreased, the yield is improved, the loss of an organic solvent is reduced, multiple times of extraction are not needed, the operation is simple and convenient, the large-scale industrialproduction is facilitated, a product can be continuously collected, the inhibition of the product to enzyme or the toxicity of the product to cells is relieved, the molar conversion rate is improved,and thus the industrial production is facilitated.
Owner:江苏惠利生物科技有限公司
Method for converting echinocandin B by using microbial enzyme
ActiveCN103074403BEasy to separate and purifyHigh molar conversionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismOrganic solvent
The invention provides a method for converting echinocandin B (ECB) by using microbial enzyme. The method comprises the steps that: (1) microbes are fermented, such that echinocandin B deacylase is obtained; (2) when fermentation is finished, phosphate is added into the fermentation broth; ultrasonic processing is carried out; and supernatant is obtained by centrifugation, and the supernatant is echinocandin B deacylase crude enzyme solution; (3) the crude enzyme solution is purified, such that echinocandin B deacylase enzyme solution is obtained; (4) echinocandin B is dissolved in ethanol, and is mixed with the deacylase enzyme solution; mixing and stirring are carried out, such that the material is converted into echinocandins B nucleus; when conversion is finished, filtering is carried out; and the filtrate is obtained; and (5) the filtrate is processed by using macroporous adsorption resin; echinocandins B nucleus is absorbed on resin; and echinocandins B nucleus is eluted by using an organic solvent. According to the invention, a molar conversion rate is high, a conversion time is short, an obtained product is easy to separate and to purify, and ECB deacylase can be repeatedly used.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF PHARMA IND CO LTD +1
Method for producing 1, 4-butanediamine by using recombinant escherichia coli
ActiveCN112921022AReduce manufacturing costIncreased specific enzyme activityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliArginine
The invention discloses a method for producing 1, 4-butanediamine by using recombinant escherichia coli, which belongs to the genetic engineering technology, and is characterized in that an arginine decarboxylase mutant and agmatine enzyme are successfully expressed by using a high-copy plasmid pXMJ19 to construct recombinant bacteria. Whole-cell transformation results show that the original bacteria do not have the capability of excessively accumulating 1, 4-butanediamine, and the recombinant bacteria can realize excessive accumulation of 1, 4-butanediamine; and meanwhile, based on the characteristic that the genetically engineered strain can excessively accumulate 1, 4-butanediamine, enzymatic conversion is successfully adopted to produce 1, 4-butanediamine by taking arginine as a substrate. IPTG (isopropyl-beta-d-thiogalactoside) is added in a cell culture process to induce enzyme expression, and magnesium ions and coenzyme pyridoxal phosphate are added in a transformation system according to enzymatic properties of the arginine decarboxylase. Finally, 72.6 g.L <-1 > 1, 4-butanediamine can be accumulated through 24-hour conversion, and the yield of agmatine serving as an intermediate product is 0.14 g / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for preparing duloxetine chiral intermediate through microbial conversion
ActiveCN102643879AAchieving large-scale cultivationEasy to grow on a large scaleMicroorganism based processesFermentationDuloxetineMicrobial transformation
The invention provides a method for preparing duloxetine chiral intermediate (S)-3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thineyl) propanenitrile through microbial conversion. The method comprises the following step of: converting 3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thineyl) propanenitrile into the (S)-3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thineyl) propanenitrile under the catalysis of enzyme-containing thallus cells obtained by fermentation of saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No. 2266. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easiness and convenience for operation, low cost, high product yield, high purity and suitability for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
Method for transforming echinocandin b into echinocandin b nucleus by microbial fermentation
ActiveCN103374593BHigh molar conversionEasy to operateMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismEchinocandin B
The invention discloses a method for converting echinocandin B into an echinocandin B parent nucleus through microbial fermentation. The method is characterized by comprising the following step of: adding an echinocandin B substrate in a fermentation process to carry out conversion, wherein the echinocandin B substrate is added in batches or added in a flowing manner.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ZHENYUAN PHARMA CO LTD +1
Esterification conversion method of gulonic acid
PendingCN110746388AReduce moistureShorten the high temperature reaction timeOrganic chemistrySodium bicarbonateSodium ascorbate
The invention relates to an esterification conversion method of gulonic acid. The method comprises: uniformly mixing industrial methanol and concentrated sulfuric acid, adding a gulonic acid dry product in a stirring state, carrying out a methyl esterification reaction in a staged temperature changing manner, sequentially adding sodium bicarbonate and deionized water, heating, carrying out a conversion reaction, cooling after the reaction is finished, and carrying out centrifugal separation to obtain the sodium ascorbate. According to the invention, the gulonic acid esterification conversion method is simple in process, easy to operate, low in cost, capable of greatly increasing the molar conversion rate from gulonic acid to VC sodium (increased by 1.5-3.2% compared with the prior art) andsuitable for large-scale production.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
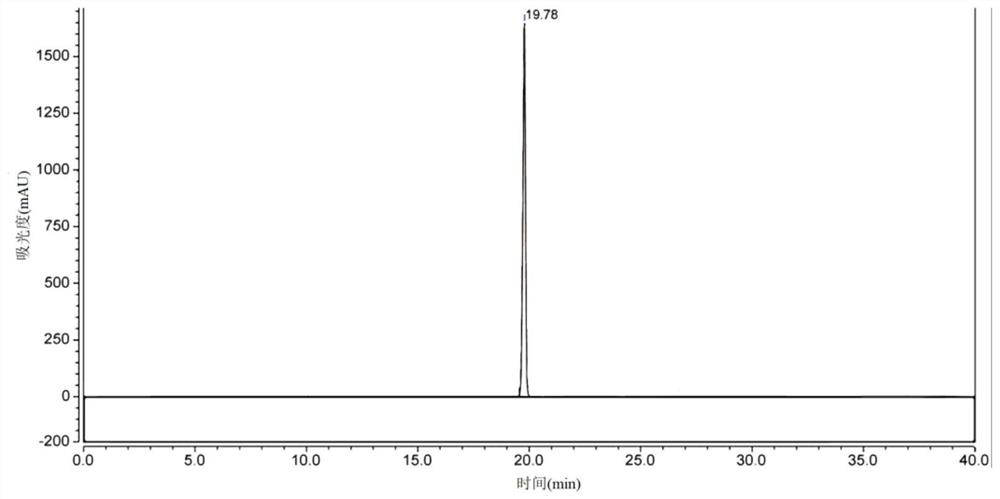
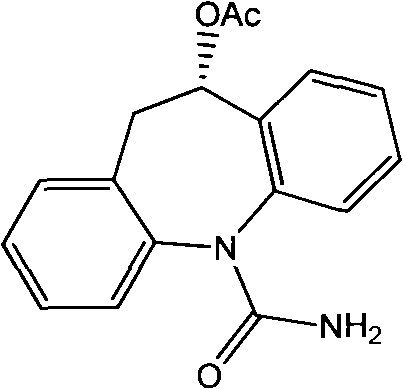
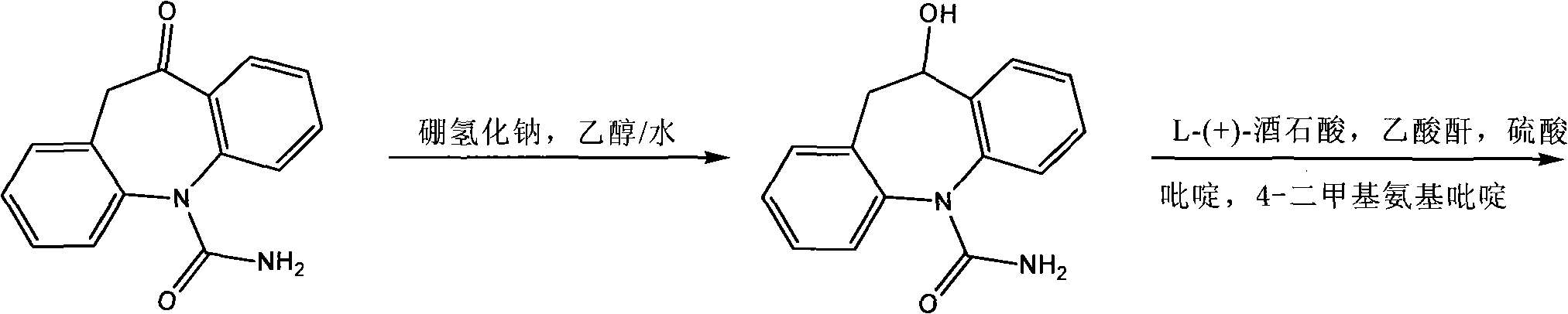
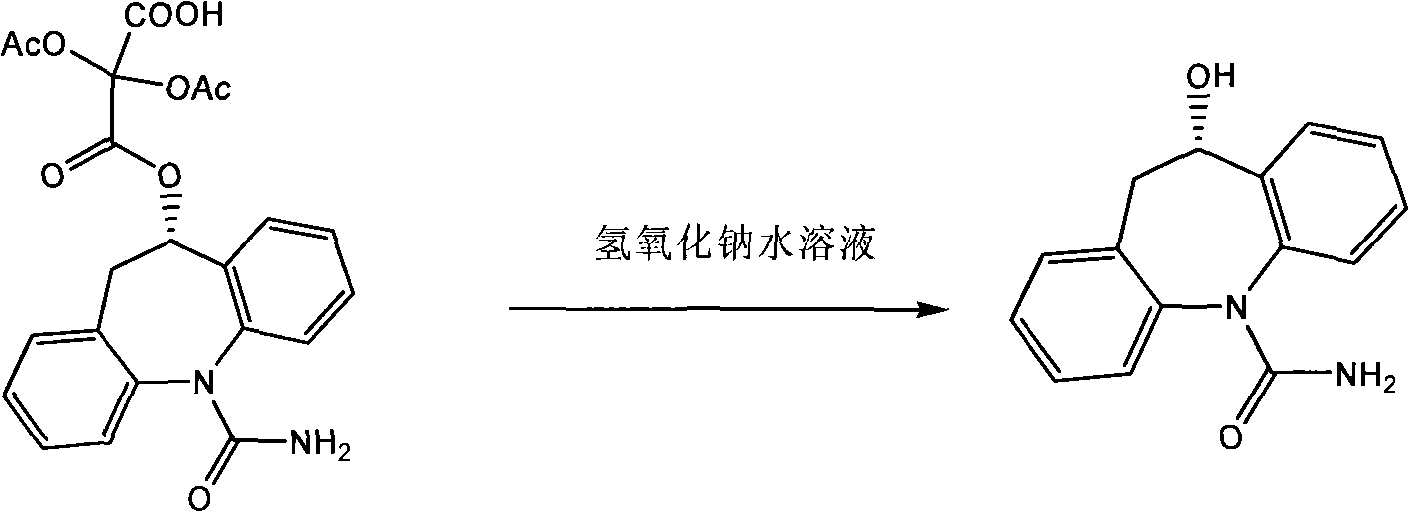
Synthesis process for preparing eslicarbazepine with microbial method
ActiveCN102465159BEasy to grow on a large scaleLow costFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismSynthesis methods
The invention relates to the technical fields of heterocyclic chemistry and microorganisms, in particular to a synthesis process for preparing eslicarbazepine with a microbial method. In view of the defects of high toxicity of all reagents, more reaction steps, difficulty in splitting, low raw material conversion rate and the like in the prior art, the invention provides a novel synthesis process for preparing eslicarbazepine acetate, wherein the eslicarbazepine is prepared through biotransformation reaction by taking oxcarbazepine as a substrate and an enzyme-containing thalli cell, obtained through fermenting saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No.2230, as a biocatalyst.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
A method for enzymatically synthesizing Danshensu
ActiveCN108424937BOriginalHigh molar conversionCarbon-nitrogen lyasesBacteriaChemical synthesisDihydroxyphenylalanine
The invention discloses a novel method for synthesizing danshensu. The method uses tyrosine ammonia lyase, phenylpyruvate reductase and glucose dehydrogenase to catalyze levodopa to produce danshensu. Specifically, 0.5-1.5mol of levodopa (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine), 10-30g / L of wet bacterium of tyrosine ammonia lyase, and 10-30g of wet bacterium of phenylpyruvate reductase / L, 10-30g / L of wet cells of glucose dehydrogenase were placed in a reactor and mixed evenly, the pH value was adjusted to 7.0, the temperature was 30°C, and the catalytic reaction was carried out for 16-20h to obtain Danshensu. For the first time, the method uses tyrosine ammonia lyase, phenylpyruvate reductase and glucose dehydrogenase to produce danshensu enzymatically with levodopa as a substrate, saving raw materials and avoiding the pollution of chemical synthesis.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
Catalyst and preparation method for preparing o-fluoroaniline by hydrogenation of o-fluoronitrobenzene
ActiveCN104117353BImprove stabilitySolution to short lifeOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationO-fluoronitrobenzeneMetal
The invention discloses a catalyst for preparing o-fluoroaniline from o-fluoronitrobenzene by hydrogenation. The catalyst contains an Al2O3 supporter and the following components in percentage by mass: 0.05%-1% of Pt supported on the Al2O3 supporter, 0.05%-3% of metal M1 and 0.01%-3% of metal M2, wherein the metal M1 is Pd, Sn or Zn; the metal M2 is K, Co, Ga, In, Mn, Ag or Ce. Besides, the invention also provides a preparation method of the catalyst. When the catalyst prepared by the preparation method is used for catalyzing o-fluoronitrobenzene hydrogenation, the mole conversion rate of o-fluoronitrobenzene is up to 100%, the mole percentage of a defluorination product is smaller than 0.1%, the amount of o-fluoronitrobenzene treated by the catalyst of unit mass is large, the use amount of the catalyst is small, and the catalyst can be reused after being regenerated.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method for preparing duloxetine chiral intermediate through microbial conversion
ActiveCN102643879BAchieving large-scale cultivationEasy to grow on a large scaleMicroorganism based processesFermentationDuloxetineMicrobial transformation
The invention provides a method for preparing duloxetine chiral intermediate (S)-3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thineyl) propanenitrile through microbial conversion. The method comprises the following step of: converting 3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thineyl) propanenitrile into the (S)-3-hydroxyl-3-(2-thineyl) propanenitrile under the catalysis of enzyme-containing thallus cells obtained by fermentation of saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No. 2266. The method has the advantages of mild reaction conditions, easiness and convenience for operation, low cost, high product yield, high purity and suitability for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:瑞博(杭州)医药科技有限公司
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application in synthesizing dipeptide
ActiveCN106754447BEliminate separation and purificationEfficient productionFungiMicroorganism based processesDipeptideNucleotide
The invention discloses a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and application thereof to glutamine dipeptide synthesis. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae contains an exogenous gene with the nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses a recombinant vector containing the gene, the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae and a method for glutamine dipeptide synthesis through biotransformation by using the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae. The condition that saccharomyces cells still have high catalytic activity after the multi-time circulation utilization is discovered; the obvious industrial advantages are realized. The method and the application provided by the invention have the advantages that the raw materials are cheap and can be easily obtained; the operation is simple and convenient and can be easily controlled; the synthesis path is green and efficient; the biosecurity is high; the reaction speed is high; the conversion rate is high, and the like; The foundation is laid for the industrial production of the glutamine dipeptide.
Owner:INNOBIO CORP LTD
Catalase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN114752576AHigh industrializationGood application prospectBacteriaBiofuelsLactate oxidaseH2O2 - Hydrogen peroxide
The invention discloses a catalase mutant and application thereof. The mutant is mutated at least at one of the following positions of an initial catalase amino acid sequence: 67th isoleucine is mutated into phenylalanine, 102nd methionine is mutated into leucine, 200th valine is mutated into phenylalanine, and 251st alanine is mutated into serine, and the initial catalase amino acid sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the mutant. Compared with initial catalase BmCAT, the amino acid sequence of the catalase mutant is replaced, and the formed mutant remarkably improves the capability of catalyzing hydrogen peroxide. In the process of biosynthesizing pyruvic acid by using lactate oxidase, hydrogen peroxide generated in the reaction process is eliminated by using whole-cell catalysis for expressing the catalase mutant, the use amount of enzyme is small, the elimination rate of hydrogen peroxide is remarkably improved, the maximum molar conversion rate of the product pyruvic acid is 99.7%, and the method has a very high industrial application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG YANGCHENG BIOLOGY TECH CO LTD
A kind of recombinant Escherichia coli producing 5-methylpyrazine-2 carboxylic acid
ActiveCN110684705BImprove conversion efficiencyShort cycleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
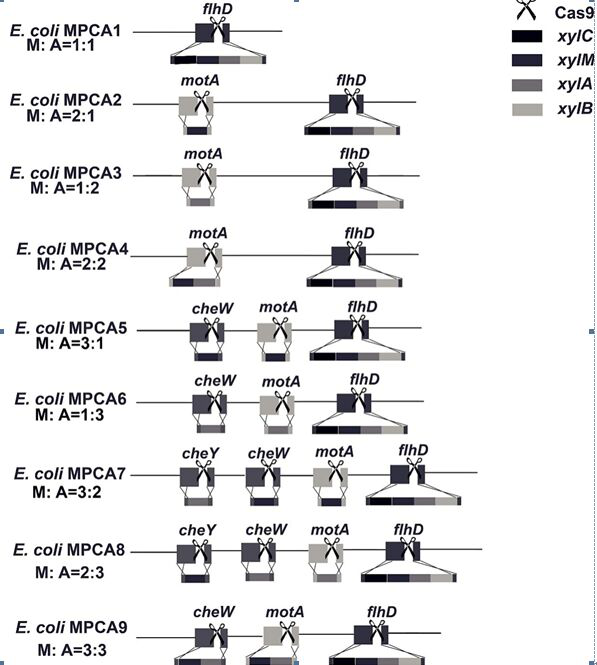
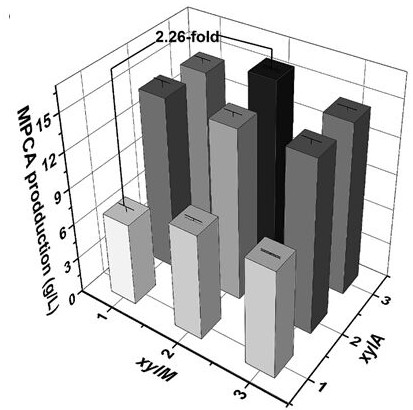
The present invention relates to a recombinant Escherichia coli producing 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid, in particular to a method for adjusting the ratio of xylene monooxygenase disubunits to increase 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid . Said adjustment of xylene monooxygenase disubunit ratio refers to Escherichia coli ( E. coli BL21(DE3)) was used as a starting strain to construct 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid by integrating the genes of xylene monooxygenase, benzyl alcohol dehydrogenase and benzaldehyde dehydrogenase by using CRISPR / cas9 homologous recombination Synthetic pathway. The bacterial strain of the present invention can increase the yield of 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid in recombinant Escherichia coli to 15.6 g / L, laying a foundation for the industrial production of 5-methylpyrazine-2-carboxylic acid.
Owner:迪嘉药业集团股份有限公司
A method for producing glycyrrhetinic acid by microbial transformation and its culture medium
ActiveCN104805169BHigh molar conversionSuitable for industrial productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismAspergillus japonicus
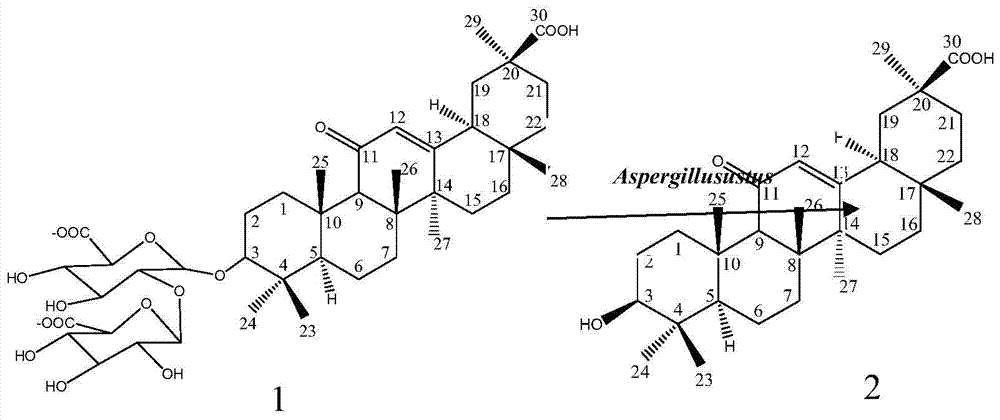
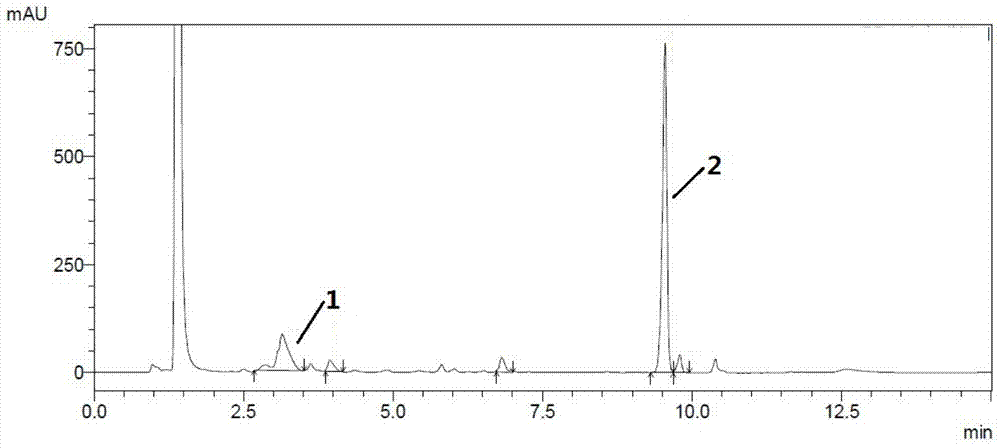
The invention discloses a method for microbial transformation and production of glycyrrhetinic acid and a culture medium thereof. The method comprises the following steps: insert the seed solution of Aspergillus ustus into the transformation medium according to the inoculation amount of 3%-20% by volume, and cultivate it at 25°C-37°C for 48 hours-240 hours, wherein the transformation culture The base includes the following components: glycyrrhizic acid 1-15 g / L, NaNO3 1-10 g / L, pH 3-7. The method uses Aspergillus pyrorrhizinum to convert glycyrrhetinic acid for the first time, the final conversion product is single, and the molar conversion rate of glycyrrhetinic acid is as high as 96.5%, which is suitable for industrial production of glycyrrhetinic acid.
Owner:国药集团健康产业研究院有限公司
A method for preparing r-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyric acid ethyl ester by coupling extraction with enzyme membrane reactor
ActiveCN109943482BDisinhibitionDetoxifyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHydroxybutyric acidOrganic solvent
The invention relates to a method for preparing r-4-chloro-3-hydroxybutyrate ethyl by coupling extraction with an enzyme-membrane reactor, comprising an enzyme-membrane reactor, an organic solvent barrel and a substrate barrel, the enzyme-membrane reactor The interior of the enzyme membrane reactor is distributed with a filter membrane, and the upper end of the enzyme membrane reactor is connected to a feed liquid outlet, one side of the enzyme membrane reactor is provided with an organic solvent outlet, and the lower end of the enzyme membrane reactor is connected to a feed liquid inlet, An organic solution inlet is installed on the other side of the enzyme membrane reactor. The method is simple in process, reduces the emulsification phenomenon in the reaction and extraction process, improves the yield, reduces the loss of the organic solvent, does not need to extract multiple times, is simple and convenient to operate, is conducive to large-scale industrial production, and can continuously collect products. The inhibition of the product to the enzyme or the toxicity to the cell is removed, and the molar conversion rate is improved, which is more conducive to industrial production.
Owner:江苏惠利生物科技有限公司
A method for preparing r-mandelic acid by a two-step microbial transformation method
ActiveCN106086090BHigh enantiomeric excessEasy to grow on a large scaleMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrobial transformationBacillus cereus
The invention discloses a method for preparing R-mandelic acid by the aid of two-step microbial transformation processes. The method includes carrying out transformation reaction on ethyl benzoylformate, first thalli and buffer solution with a pH (potential of hydrogen) value of 6-8 under conditions of the temperature of 20-45 DEG C and the speed of 100-200 rpm to obtain R-ethyl mandelate; carrying out reaction on the R-ethyl mandelate, second thalli, organic solvents and buffer solution with a pH value of 7-9 under conditions of the temperature of 20-40 DEG C and the speed of 100-200 rpm to obtain the R-mandelic acid. The ethyl benzoylformate is used as a substrate during the transformation reaction, the first thalli are obtained by means of fermentation cultivation by the aid of saccharomyces cerevisiae and are used as catalysts during the transformation reaction, and the buffer solution with the pH value of 6-8 is used as a reaction medium during the transformation reaction. The R-ethyl mandelate is used as a substrate during the reaction, the second thalli are obtained by means of fermentation cultivation by the aid of bacillus cereus and are used as catalysts during the reaction, the organic solvents are used as complex solubilizers during the reaction, and the buffer solution with the pH value of 7-9 is used as a reaction medium during the reaction. The method has the advantages that the method is low in cost and is environmentally friendly, and the reaction conditions are mild; the R-mandelic acid is easy to industrially produce on a large scale; the method is easy and convenient to implement and high in molar transformation rate; the yield can be increased and can reach 99.8%, and the ee value can be increased and can reach 100%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
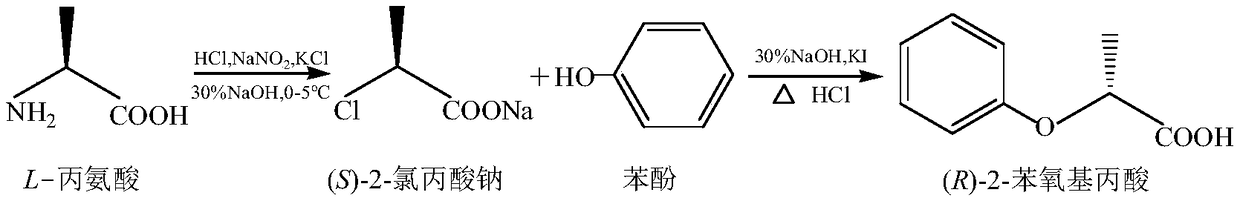
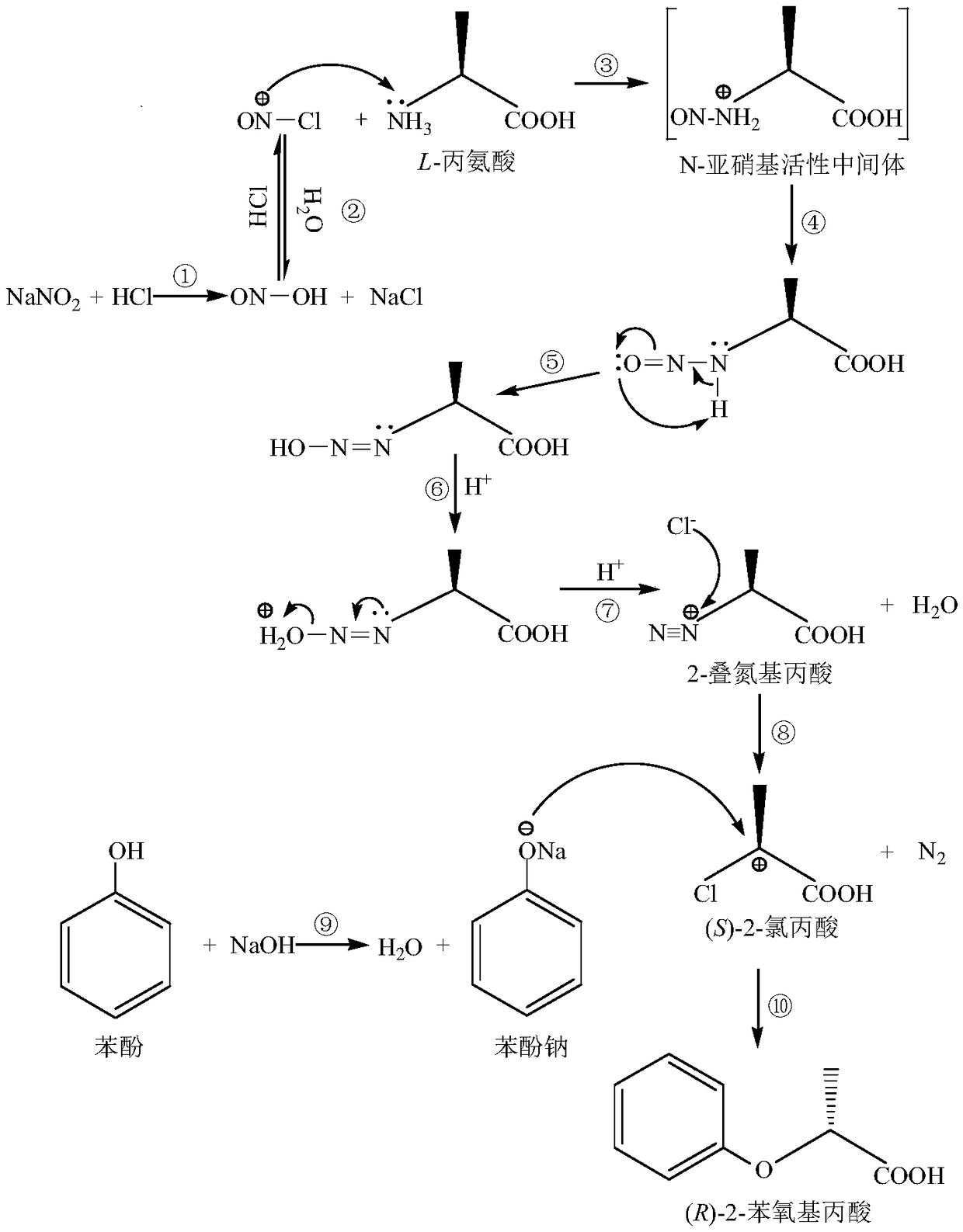
Chemical synthesis method of (R)-2-phenoxypropionic acid
InactiveCN109111355AHigh molar conversionHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid salt preparationChemical synthesis2-Chloropropionic acid
The invention discloses a chemical synthesis method of (R)-2-phenoxypropionic acid. The chemical synthesis method comprises the following steps: performing diazotization and chlorination on L-alanineserving as a starting material to obtain (S)-2-chloropropionic acid; then carrying out an etherification reaction to obtain (R)-2-phenoxypropionic acid ((R)-PPA). According to the method, diazotization and chlorination are performed on L-alanine serving as the starting material to obtain (S)-2-chloropropionic acid, and then the etherification reaction is carried out to obtain the (R)-PPA, whereinthe molar conversion rate of (R)-2-phenoxypropionic acid is up to 92.45 percent. The chemical synthesis method of the (R)-PPA is proposed for the first time, and has the advantages of cheapness and easy availability of raw materials, simple process and higher product purity and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
A kind of method for high-efficiency fermentation to produce steroid drug precursor
ActiveCN109706107BIncrease productivityEnhance cell viabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention belongs to the technical field of biocatalysis, and in particular relates to a method for improving the activity of a steroid drug-producing strain and efficiently fermenting and producing a steroid drug precursor. The present invention improves the activity of the steroid drug production strain by overexpressing the type II NADH dehydrogenase gene and efficiently ferments the steroid drug precursor to solve the problems of long fermentation period and low production efficiency in the production of the steroid drug precursor by microbial method. The reduction in the cost of production of steroid precursors provides new methods.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com