A method for preparing r-mandelic acid by a two-step microbial transformation method
A technology for microbial transformation and mandelic acid, applied in the direction of microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of large pollution, low utilization rate of raw materials, high cost, etc., achieve high molar conversion rate, easy operation, The effect of increasing productivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
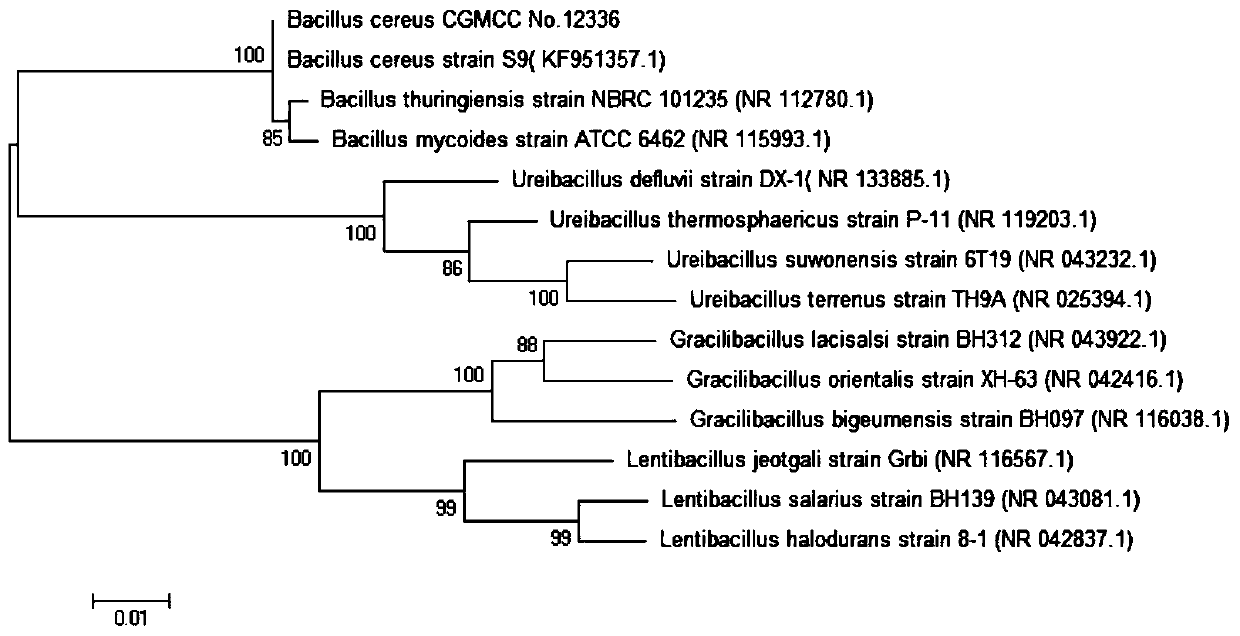
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] (1) Slant culture: Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No.3361 was inoculated into the slant medium, and cultured at 30° C. for 3 days. The composition of the slant medium: wort juice 10g / L, yeast powder 3g / L, peptone 5g / L, glucose 10g / L, agar 20g / L, solvent is water, pH is natural; After cooling, make a slope.
[0028] (2) Seed culture: use an inoculation needle to take an inoculation loop of bacteria from the slant culture medium and inoculate it into 4 bottles of 250ml Erlenmeyer flasks containing 100ml of seed culture medium, and cultivate at 30°C and 180rpm for 24 hours to obtain seed liquid. Seed medium composition: glucose 30g / L, yeast powder 3g / L, ammonium sulfate 5g / L, KH 2 PO 4 1g / L, K 2 HPO 4 ·3H 2 O 1g / L, MgSO 4 0.25g / L, the solvent is water, the pH is natural, and sterilized at 120°C for 20min.
[0029] (3) Fermentation culture: Inoculate the seed liquid in 8 bottles of 1000ml Erlenmeyer flasks containing 500ml fermentation medium with an inoculum size ...
Embodiment 2
[0037] In the Erlenmeyer flask containing the phosphate buffer of 7.0 with 20ml pH, add embodiment 1 method gained wet thallus to 0.04, 0.06, 0.08, 0.10, 0.12, 0.14 and 0.16g / ml (dry weight), add respectively final concentration 0.11 mol / L ethyl benzoylformate, respectively placed in a shaker at 30°C and 180rpm for 48 hours. After the reaction, the transformation liquid was centrifuged, and the supernatant was extracted with ethyl acetate to detect the transformation. The ratio and the enantiomeric excess value of ethyl mandelate are shown in Table 2. Separation and purification are the same as in Example 1.
[0038] The results show that the conversion rate tends to increase with the increase of the bacterial concentration, and the increase of the bacterial mass indicates that the amount of carbonyl reductase as a biological reaction catalyst increases. For the microbial conversion reaction accompanied by coenzyme regeneration, the bacterial The increase in the amount not on...
Embodiment 3
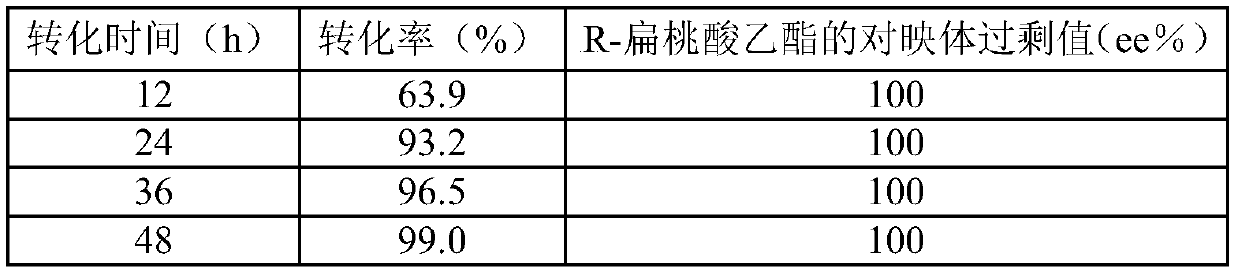
[0042] In the Erlenmeyer flask containing the phosphate buffer of 7.0 with 20ml pH, add embodiment 1 method gained wet thallus to 0.10g / ml (dry weight), add 0.11mol / L ethyl benzoylformate respectively, place respectively at 30 ℃, 180rpm shaker for 12, 24, 36, 48 and 60h. After the reaction, the conversion solution was centrifuged, and the supernatant was extracted with ethyl acetate to extract the substrate and product, and the conversion rate and R-mandelic acid were detected by gas chromatography. Ethyl ester enantiomeric excess value, the results are shown in Table 3. Separation and purification are the same as in Example 1.
[0043] The results showed that the conversion rate tended to increase with the increase of the conversion time, and the conversion rate basically reached the maximum value when the reaction time was 48 hours. Saccharomyces cerevisiae CGMCC No.3361 reduction substrate ethyl benzoylformate can obtain highly optically pure R-mandelic acid ethyl ester, a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com