Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application in synthesizing dipeptide
A technology for recombining Saccharomyces cerevisiae and glutamate dipeptide, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of long reaction time, high cost of enzyme separation and purification, low production efficiency, etc., to avoid the use of antibiotics, solve the difficulty of enzyme recovery, and reduce production costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0025] The amino acid mixture mentioned in the preparation of the above seeds and induction medium contains the following components: Arginine 0.2g / L, Aspartic acid 1.0g / L, Glutamic acid 1.0g / L, Isoleucine Acid 0.3g / L, Lysine 0.3g / L, Valine 1.5g / L, Methionine 0.2g / L, Phenylalanine 0.5g / L, Serine 3.75g / L, Tyrosine 0.3g / L And adenine 0.4g / L.
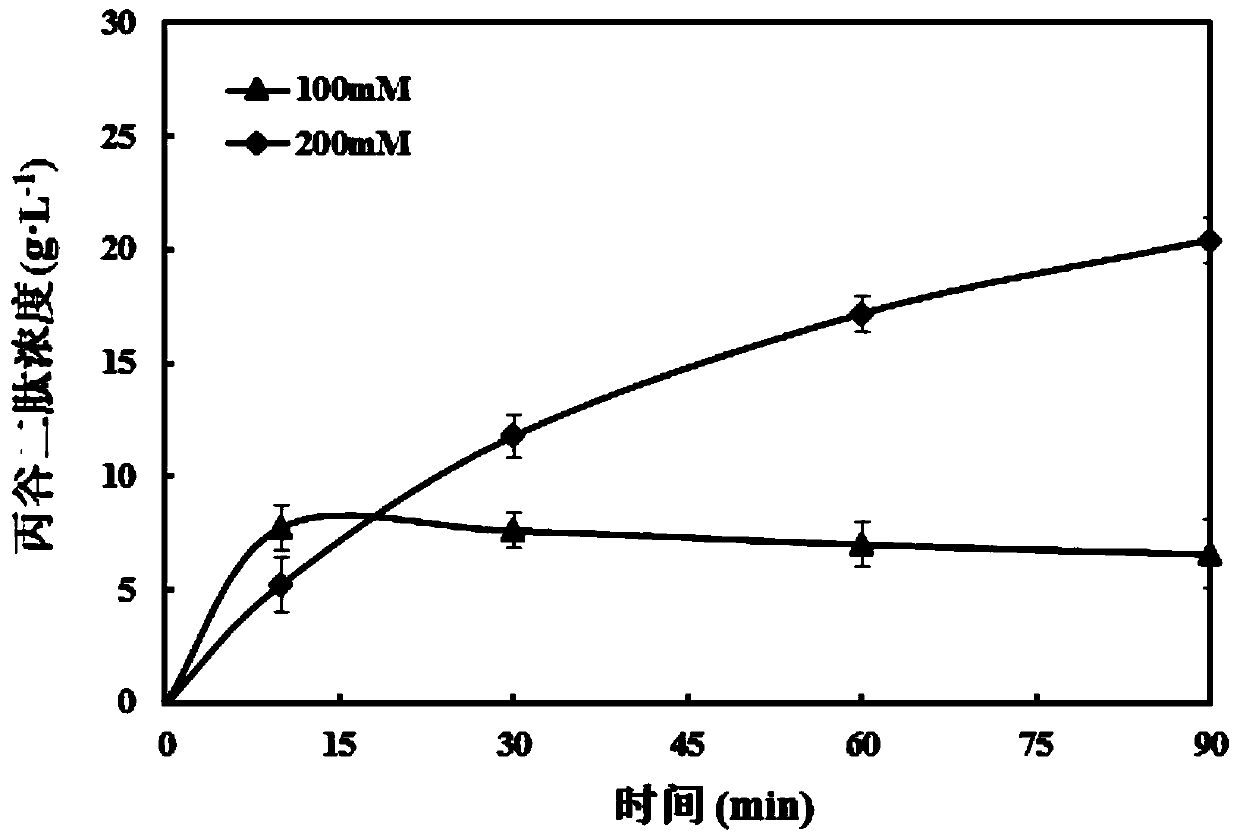
[0026] On this basis, the present invention further provides a biosynthetic method of glucodipeptide, which consists in the step of using the transformation reaction of the above-mentioned recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the present invention to the substrate.
[0027] The biosynthesis of CG dipeptide is a relatively mature technology, and its substrate can be described as a substrate comprising a carboxyl component and an amine component according to the prior art. In the present invention, the carboxyl component is selected from amino acid esters and amino acid Amide, most preferably L-alanine methyl ester hydrochloride; said am...
Embodiment 1
[0052] Construction of recombinant yeast cells:
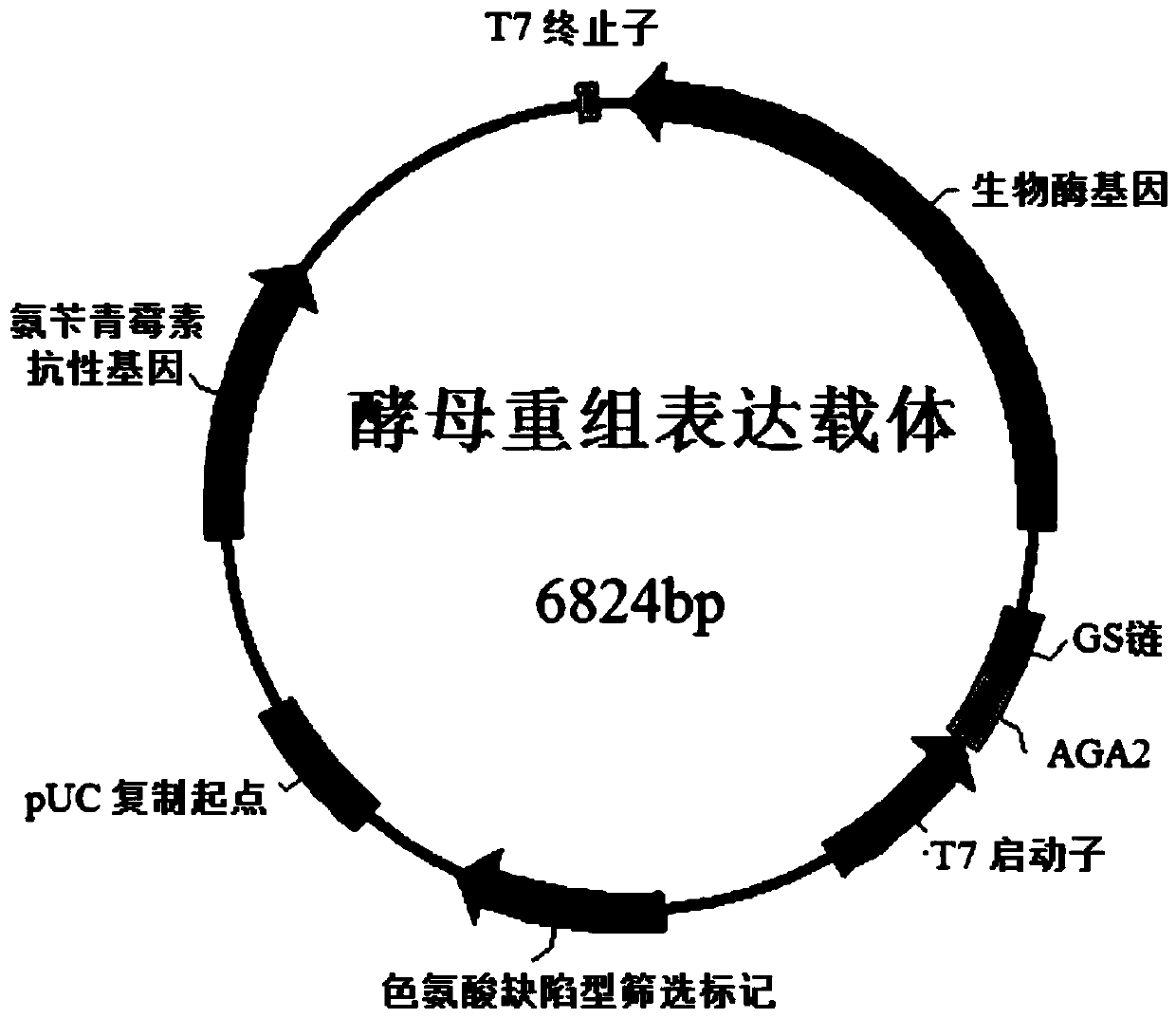
[0053] According to the known nucleotide sequence (SEQ ID NO.5), the upstream and downstream primers SEQ ID NO.3 / 4 were designed to be derived from the genus Sphingobacterium sp. The genome of the strain Sphingobacterium siyangensis (CGMCC strain number: 1.6855) was used as a template to amplify the biological enzyme gene (SEQ ID NO.1).
[0054] Among them, the PCR reaction system (50μL):
[0055]
[0056] PCR reaction conditions:
[0057]
[0058] After the PCR reaction, 2 μL of the PCR product was taken for agarose gel electrophoresis detection, and the amplified PCR product was purified using a PCR product purification kit (OMEGA, USA) and stored in a -20°C refrigerator for later use.
[0059] The PCR product and the expression vector pYD1 were digested and purified and ligated overnight, and the ligated product was transformed into E.coli DH5α competent cells, and the transformants were screened on the plate of LB-r...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Fermentation culture of recombinant yeast cells:
[0062] The recombinant yeast cells were inoculated into the seed medium, and the cells were activated at 30°C and 180rpm. Then transfer to the seed medium for expansion culture, 30°C, 180rpm shaking culture. After growing to a suitable biomass, they were inoculated into 1.0L induction medium and cultured at 20°C with 150rpm aeration. After 16 to 24 hours, put into the tank and collect the cells by centrifugation. It is the recombinant yeast cell used in the present invention.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com