Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
58results about How to "Excellent cuttability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
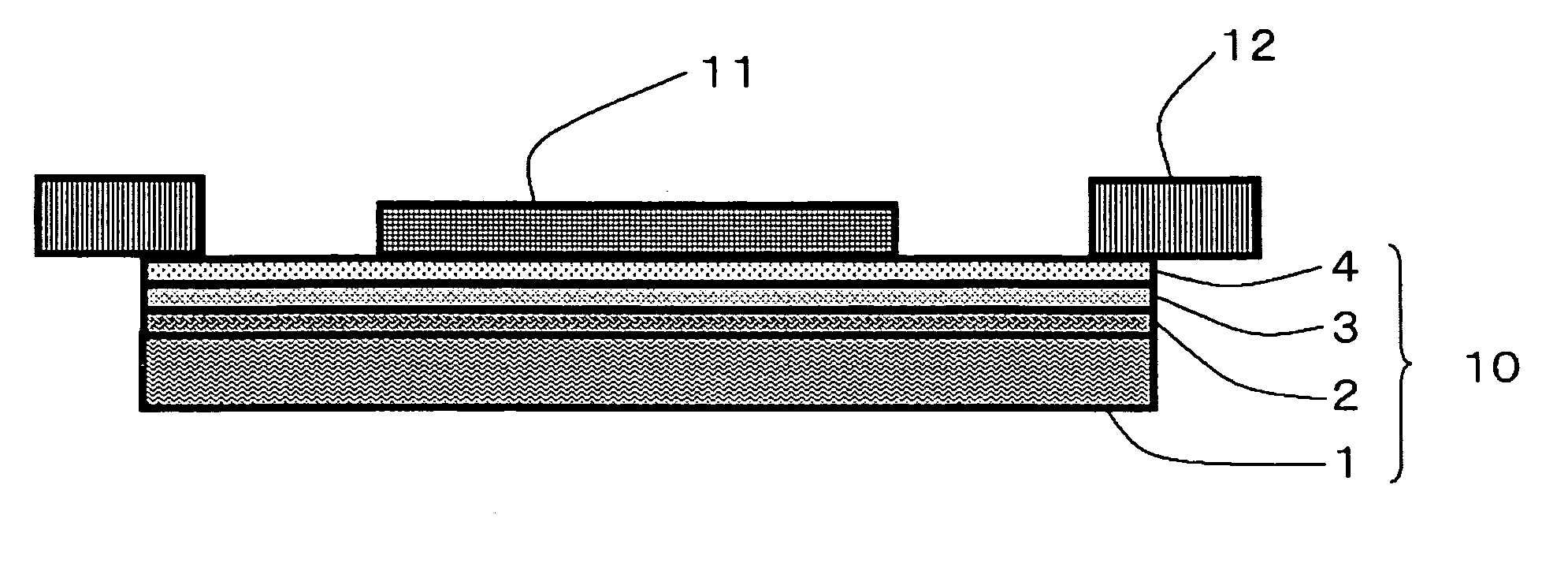
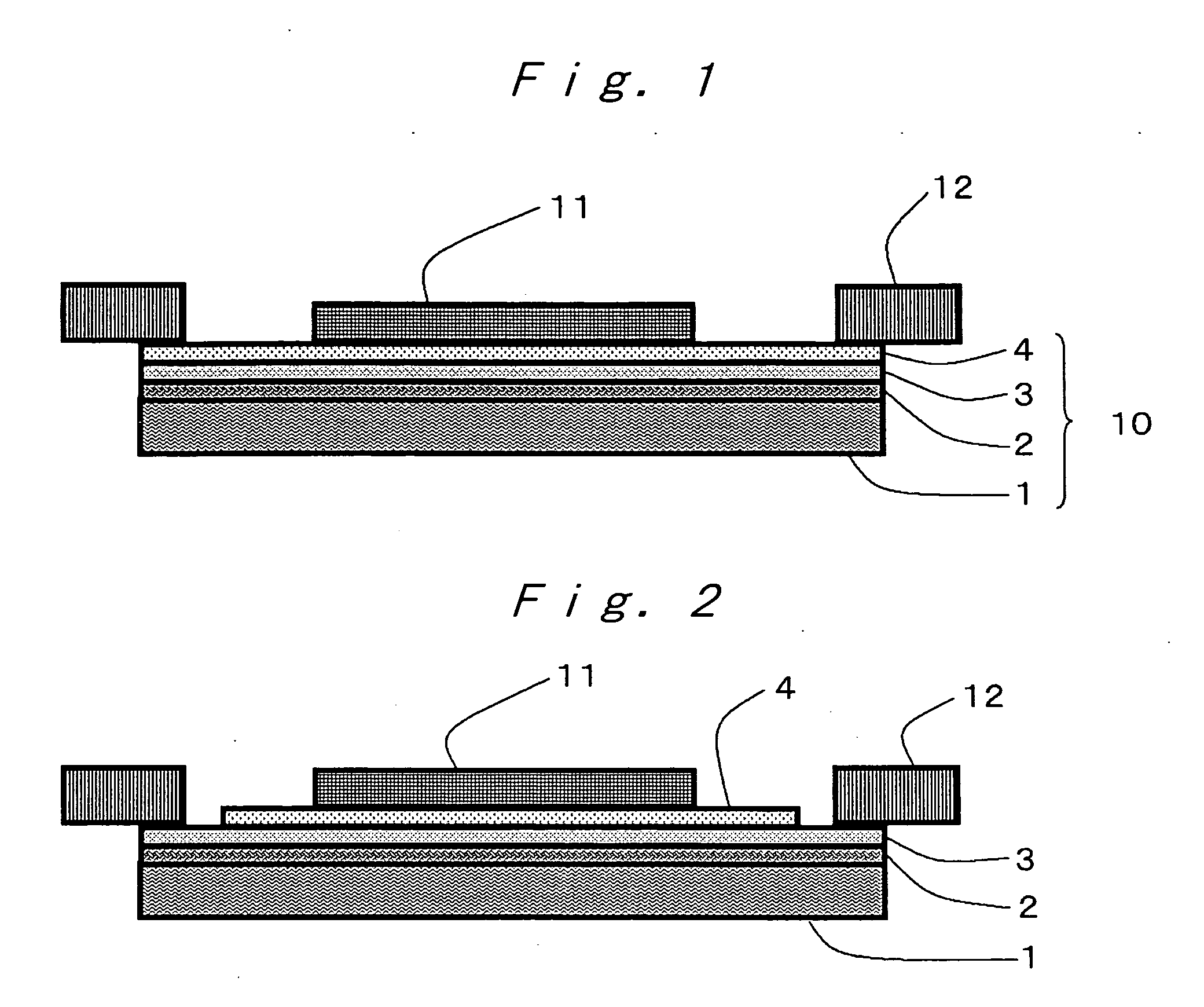
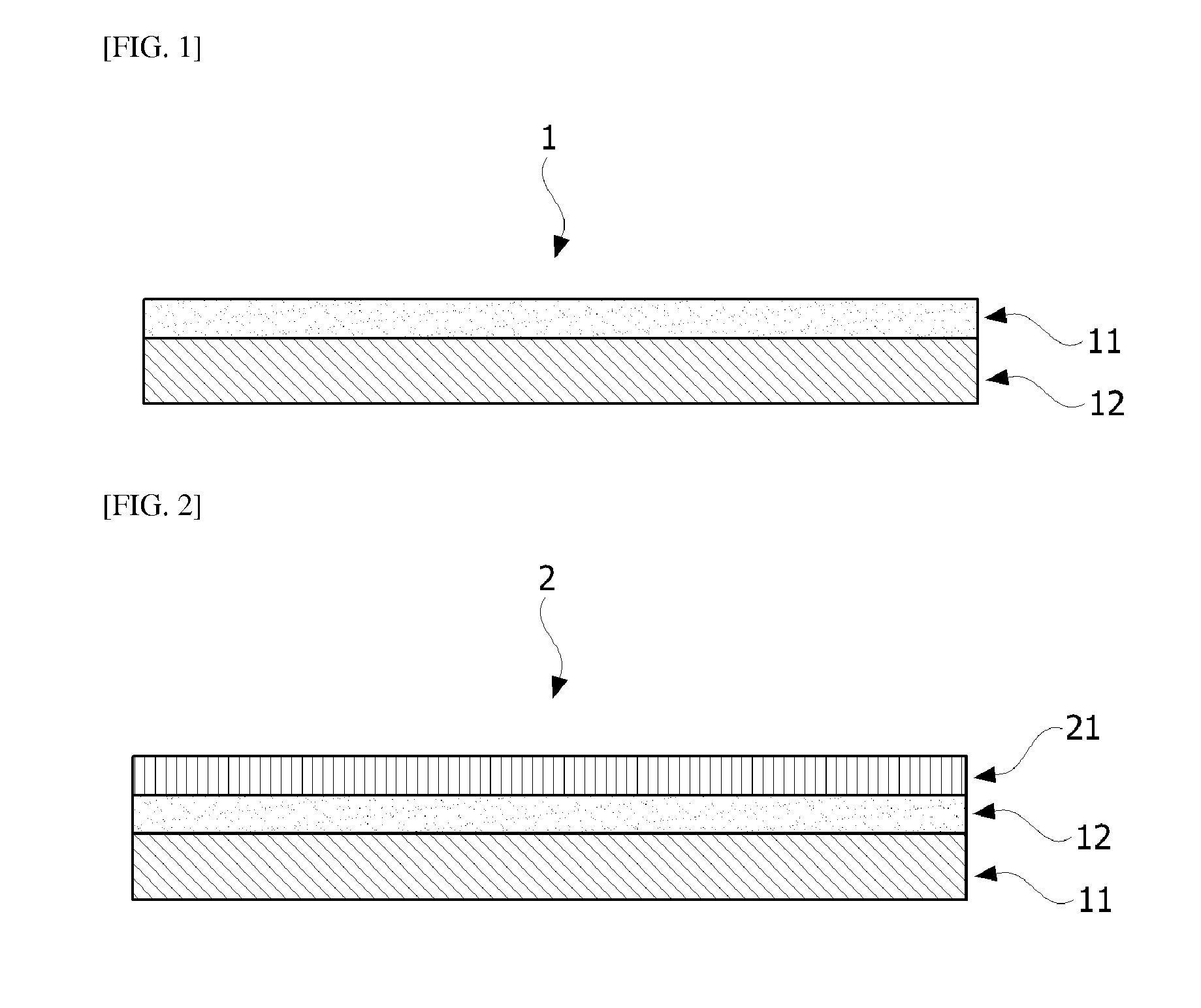
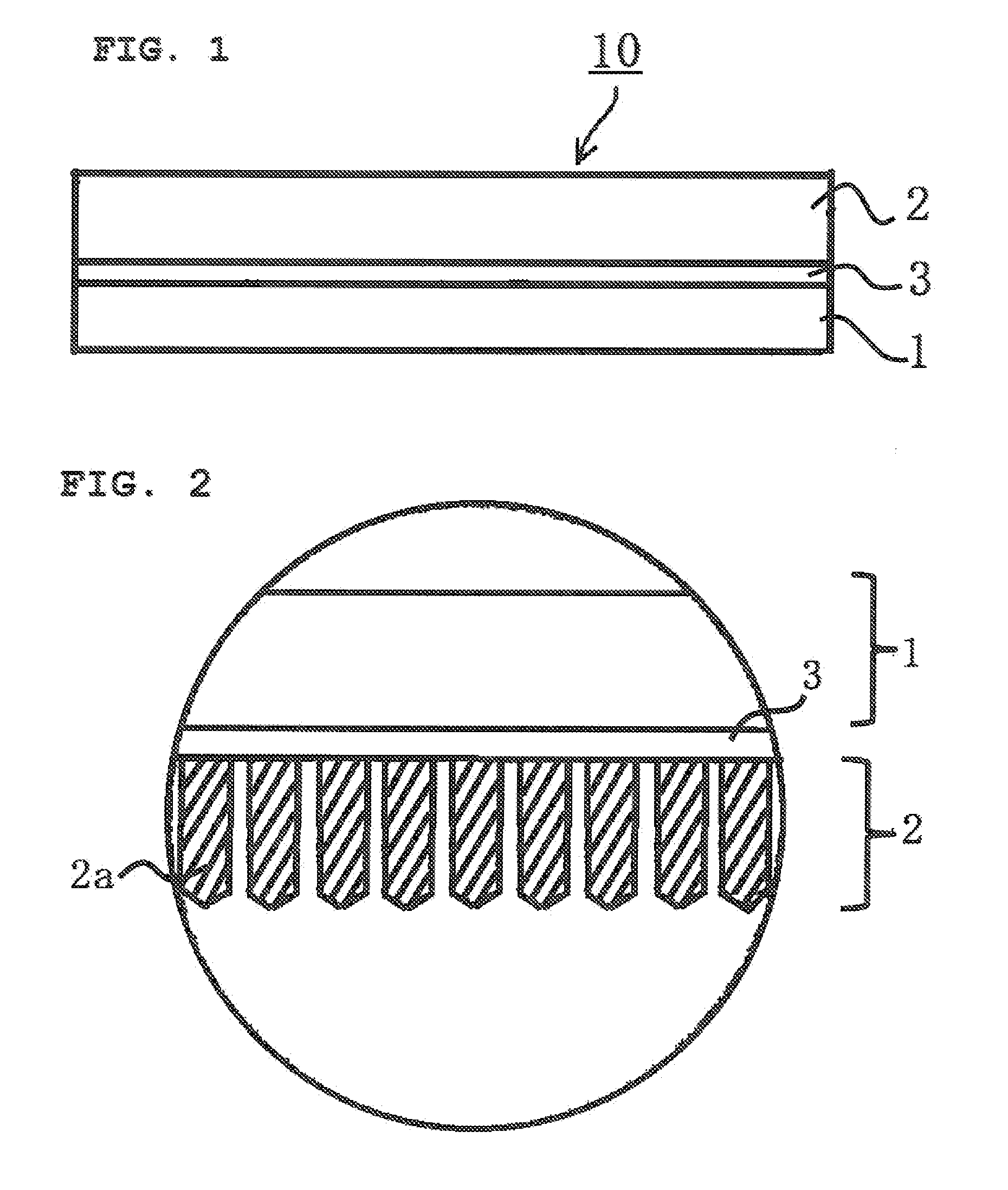
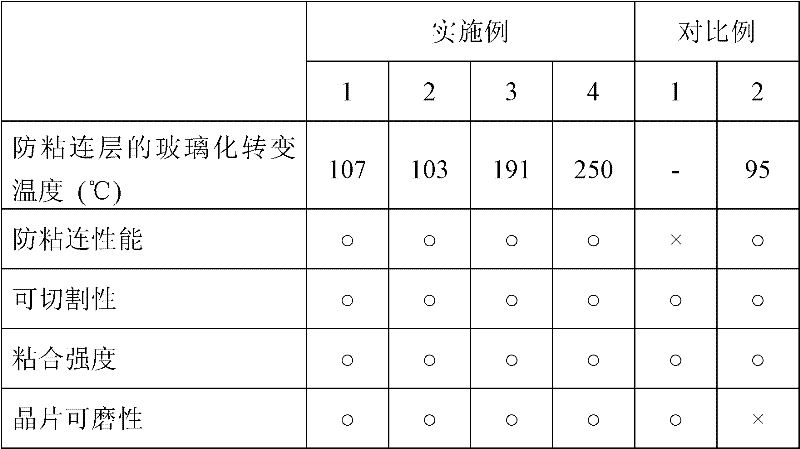
Wafer-processing tape
InactiveUS20060204749A1Easy to peelReduce whisker-like scrapsFilm/foil adhesivesSolid-state devicesElastic modulusChemistry
A wafer-processing tape (10), having an intermediate resin layer (2), a removable adhesive layer (3), and, if necessary, an adhesive layer (4), which are laminated in this order on a substrate film (1), wherein a storage elastic modulus at 80° C. of the intermediate resin layer is larger than a storage elastic modulus at 80° C. of the removable adhesive layer.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
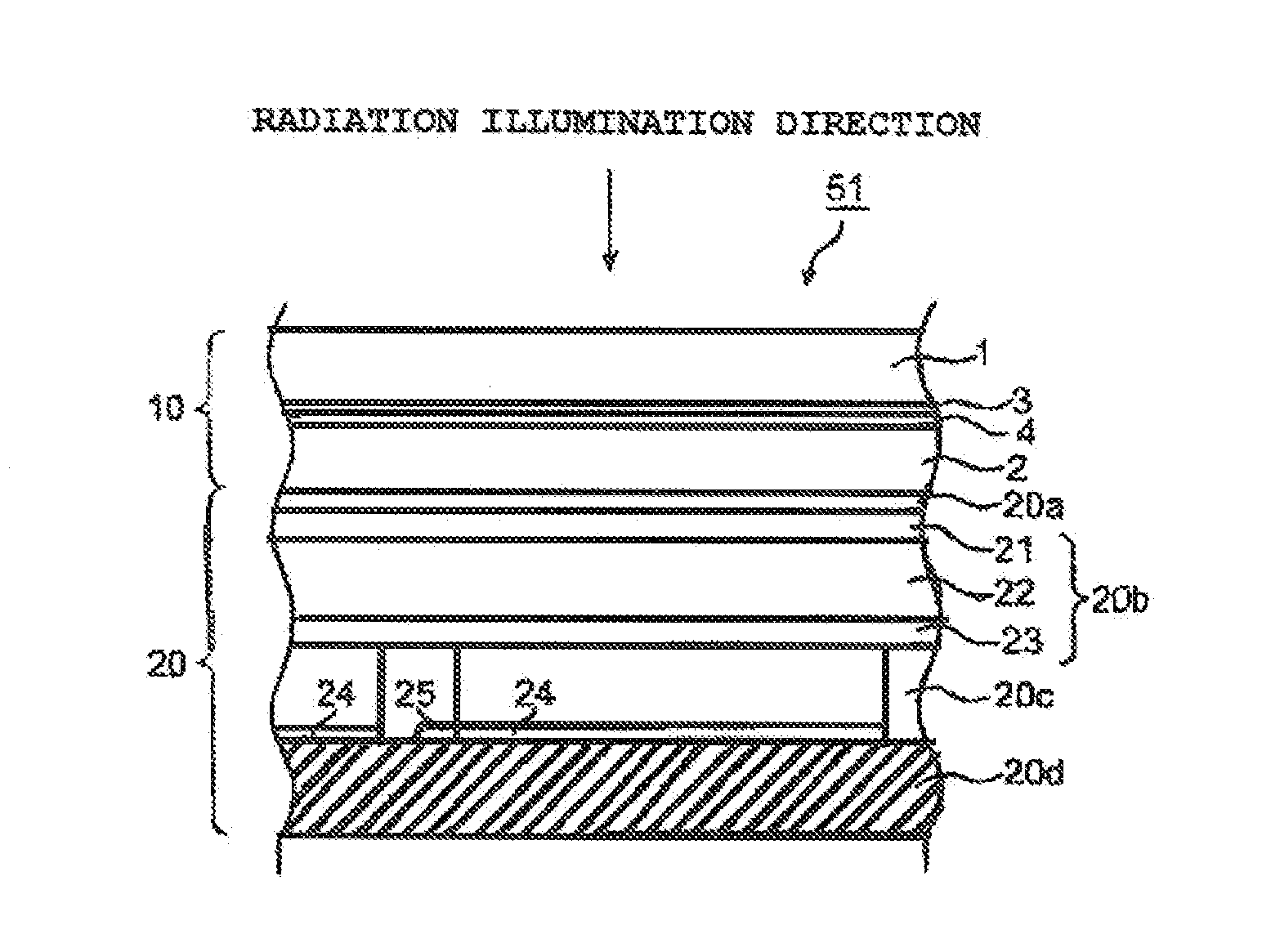
Deposition substrate and scintillator panel
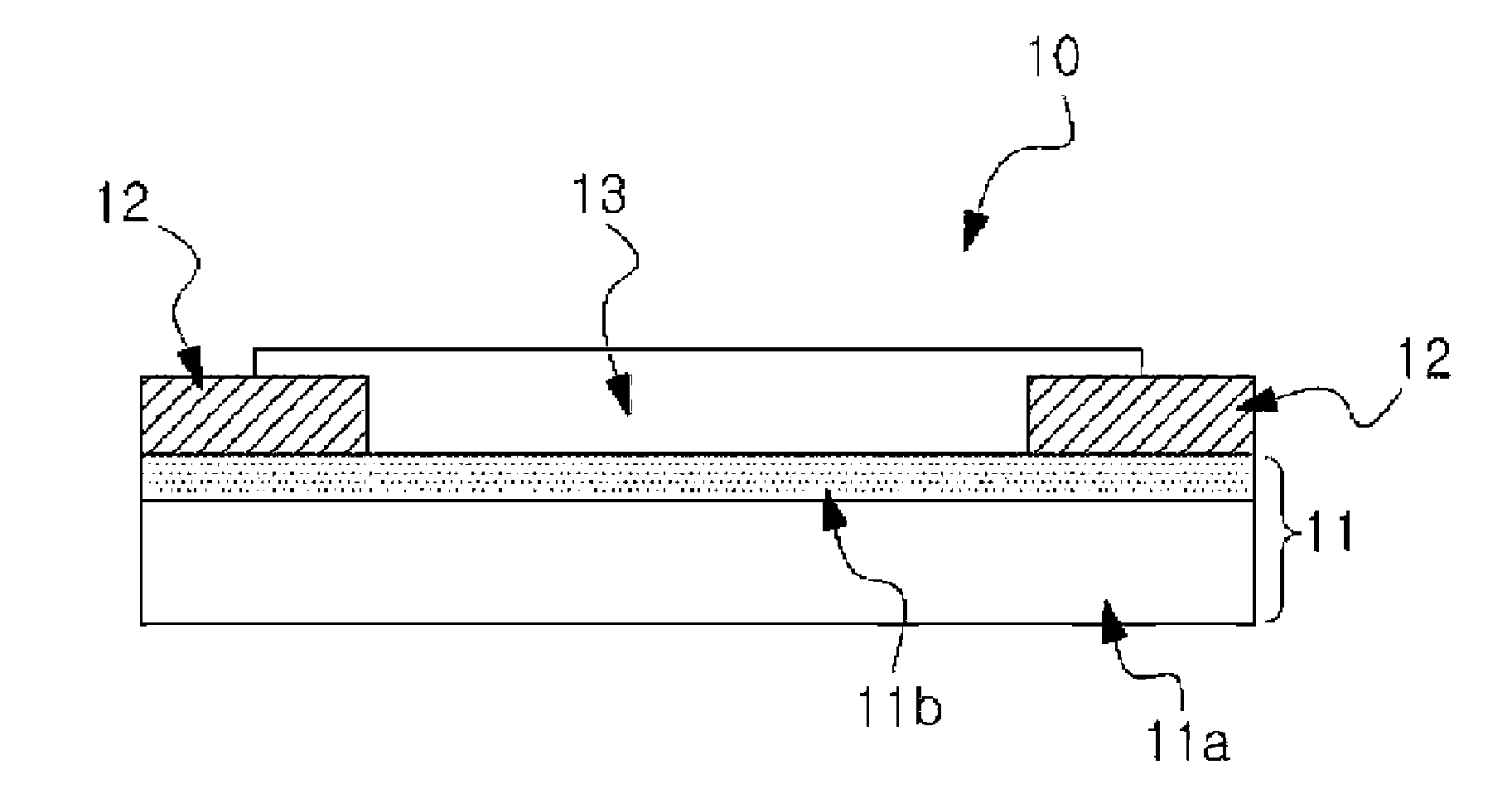
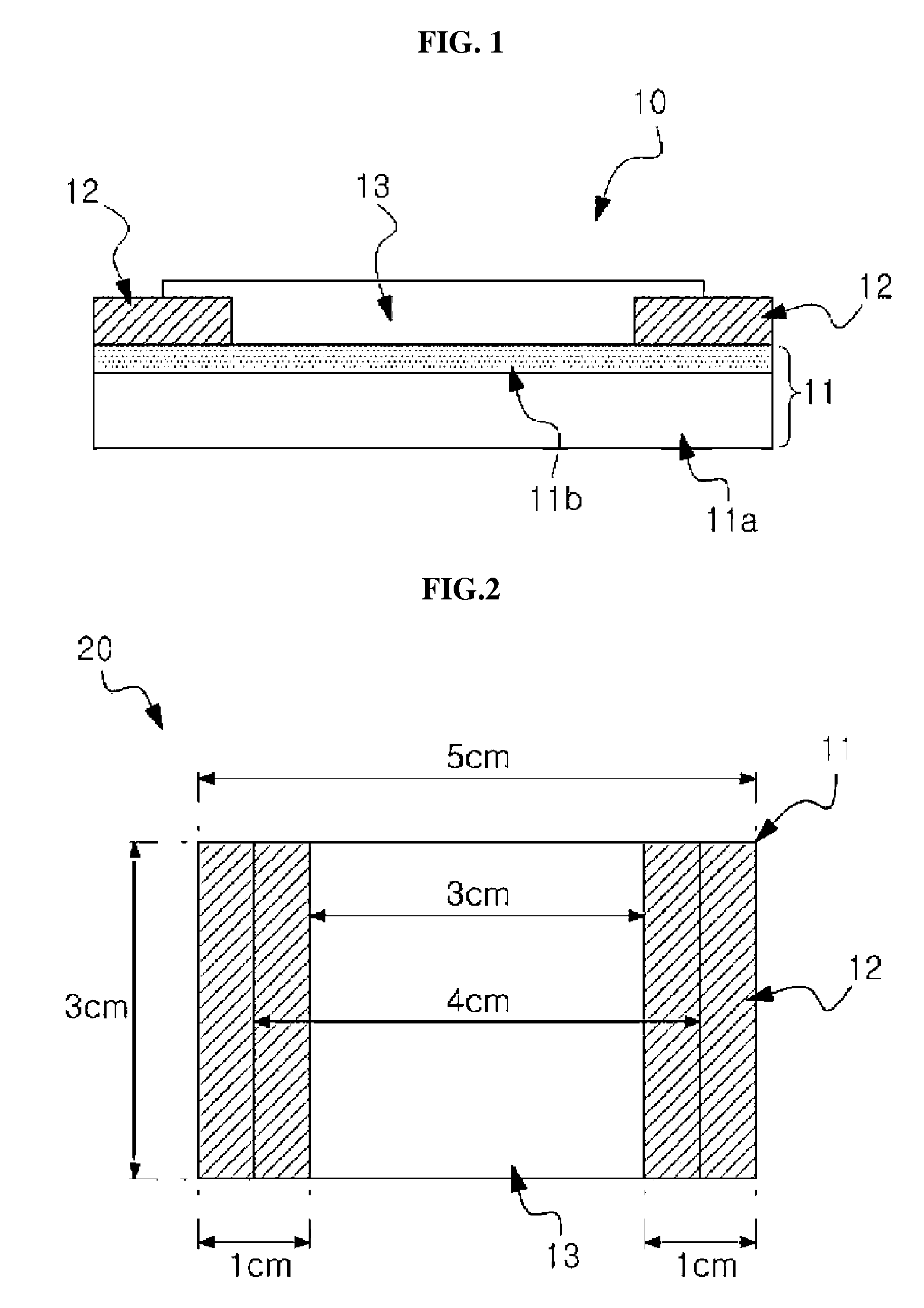
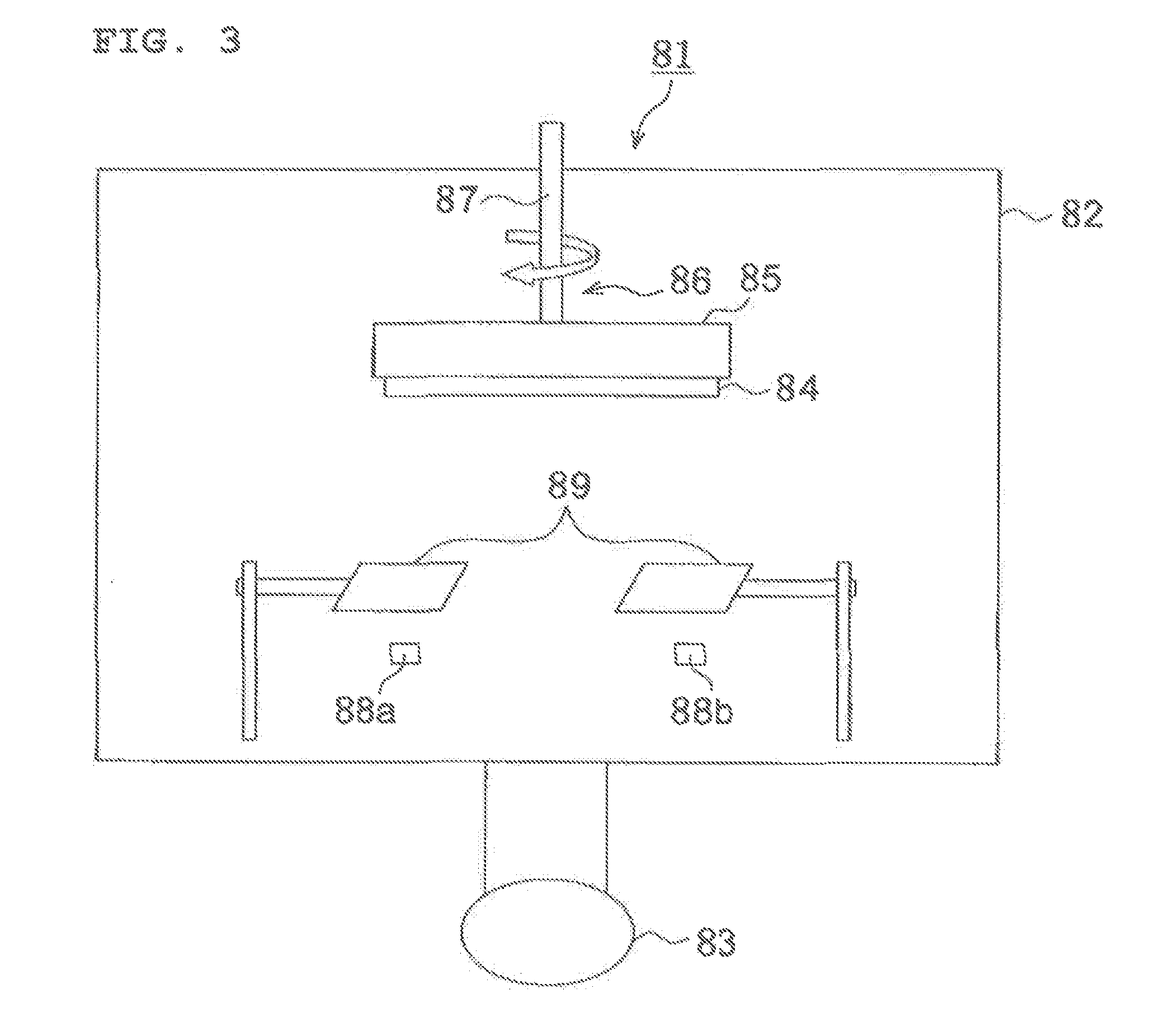
ActiveUS20140239196A1Excellent cuttabilityUniform Image QualityDiffusing elementsPhotometryIn planeFlat panel detector
An object of the invention is to provide scintillator panels which can give radiographic images such as X-ray images with excellent sharpness and excellent uniformity of sharpness, which realize devices such as flat panel detectors having uniform image quality characteristics in the light-receiving plane, and which exhibit excellent cuttability, excellent sharpness and excellent in-plane uniformity of sharpness. A scintillator panel of the invention includes a support, a reflective layer on the support, and a scintillator layer formed on the reflective layer by deposition. The reflective layer includes light-scattering particles and a binder resin. A specific region of the reflective layer is defined by a resin or includes light-scattering particles having a specific area average particle diameter, or the reflective layer has a specific arithmetic average roughness.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
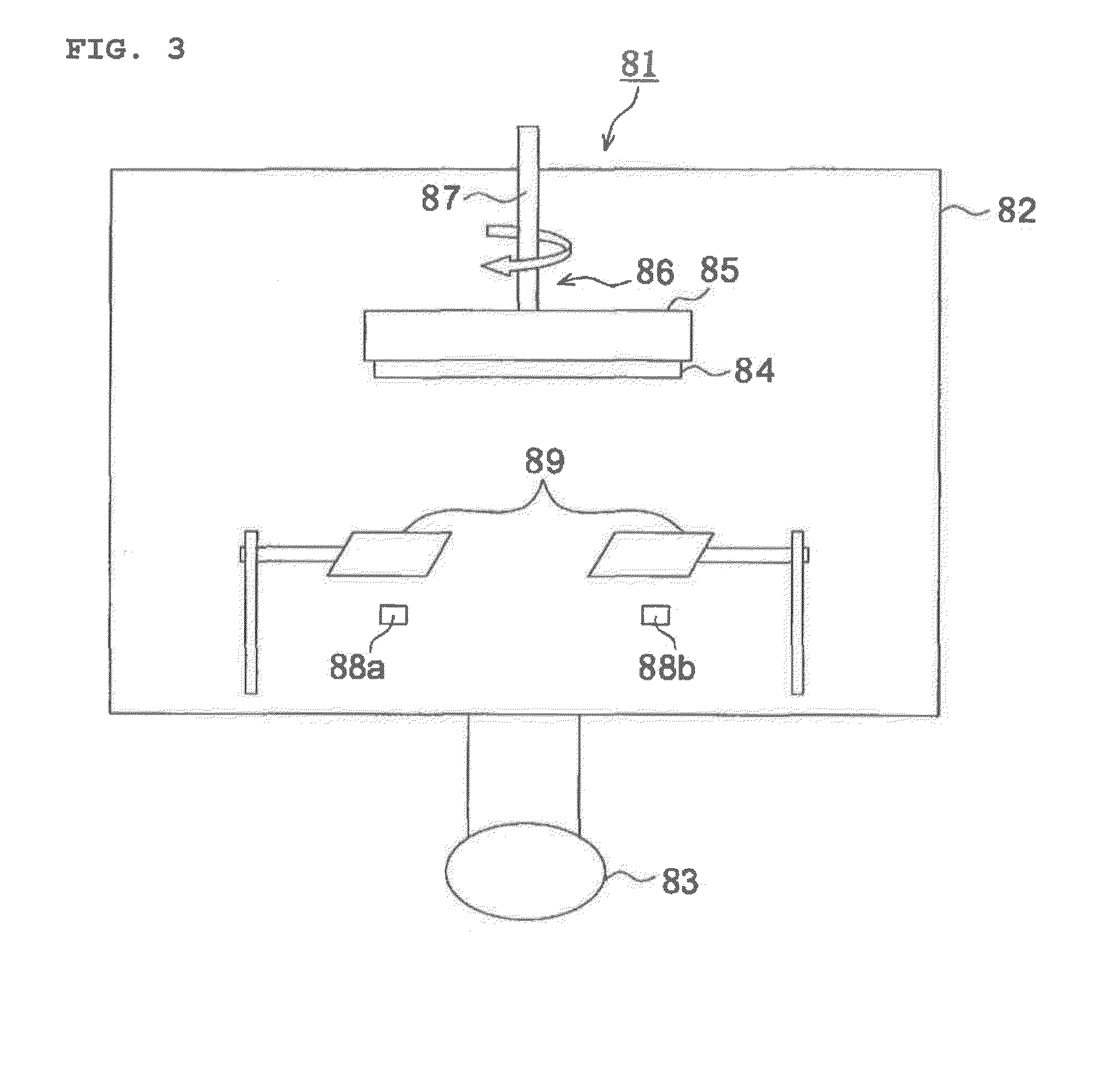
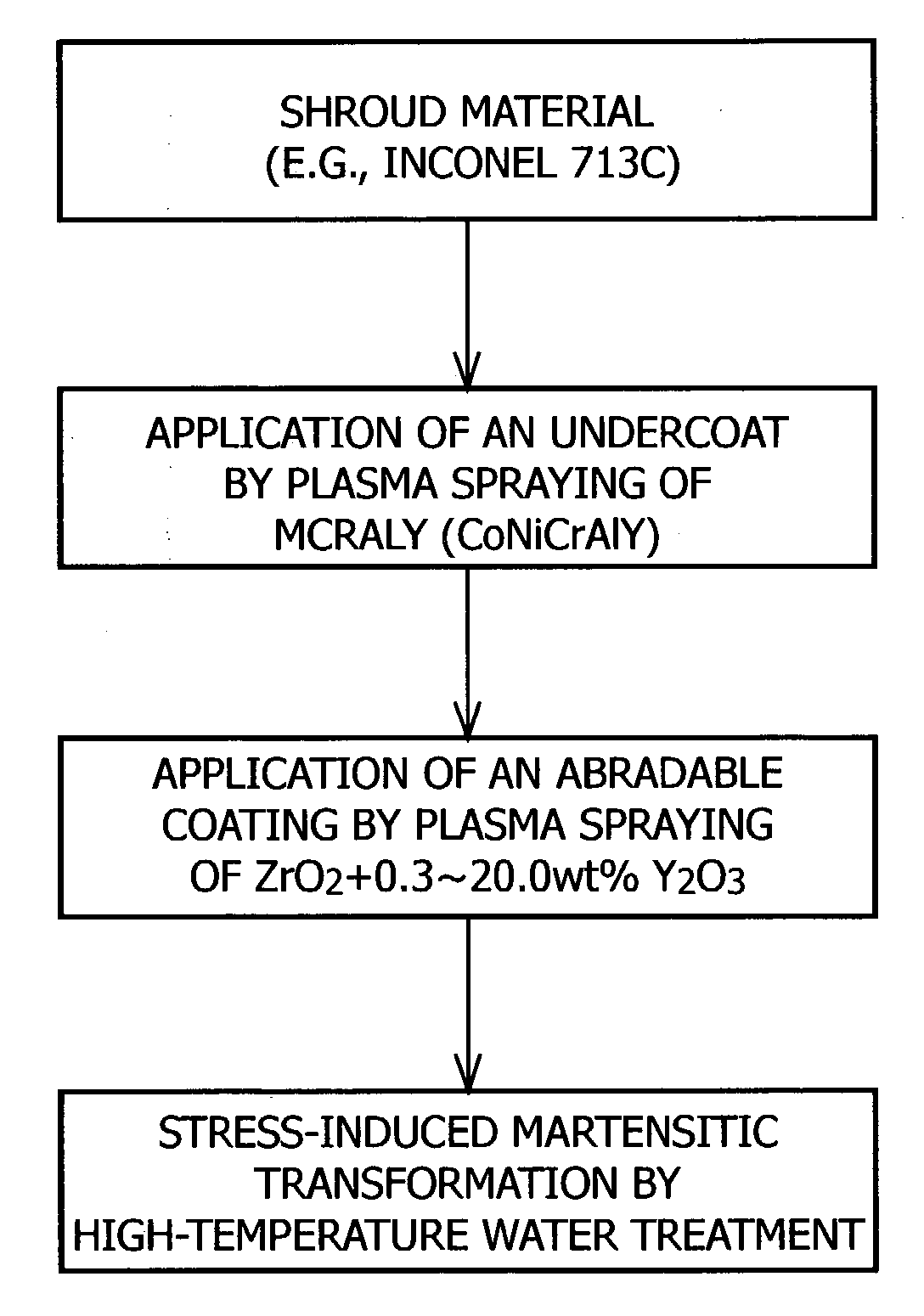
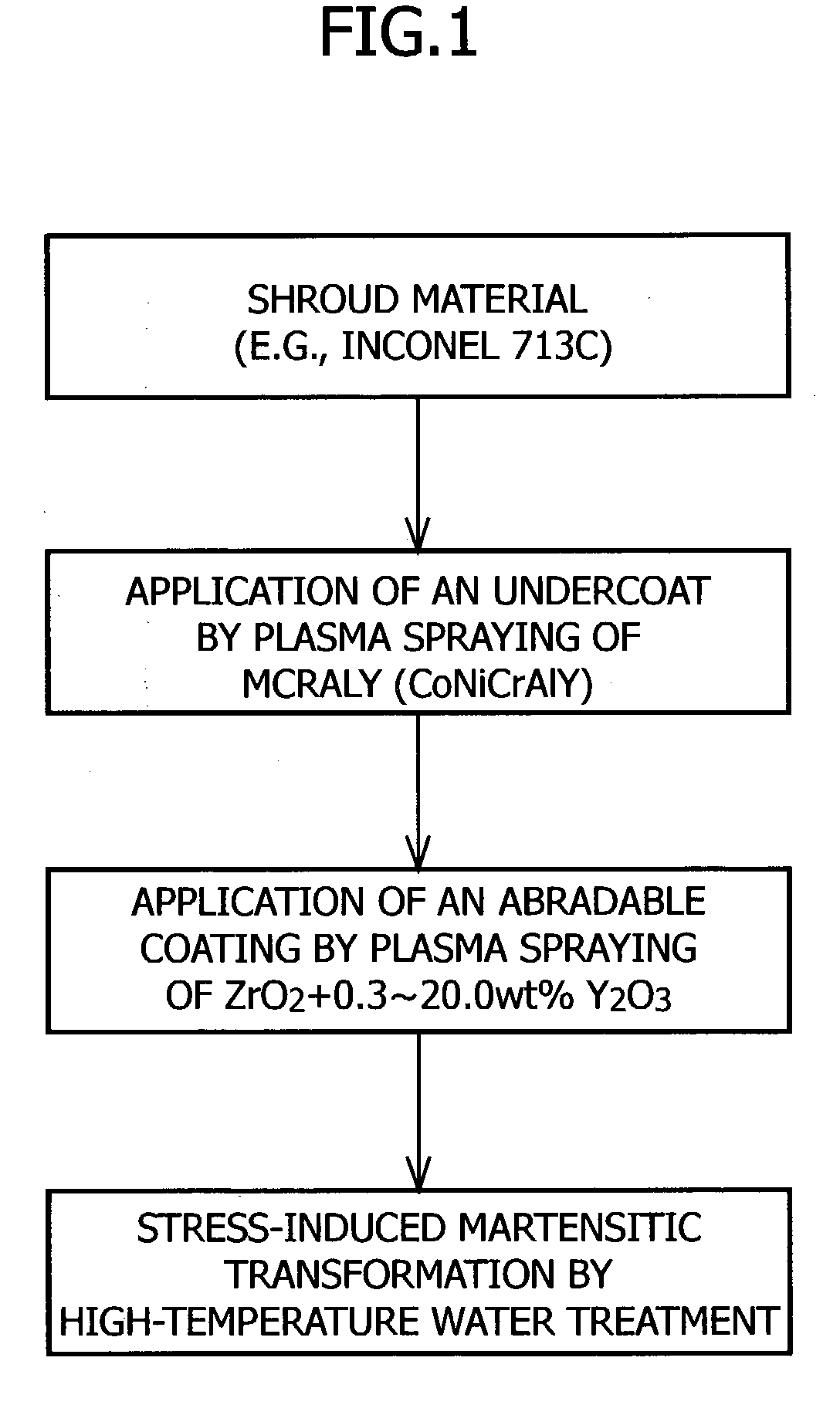
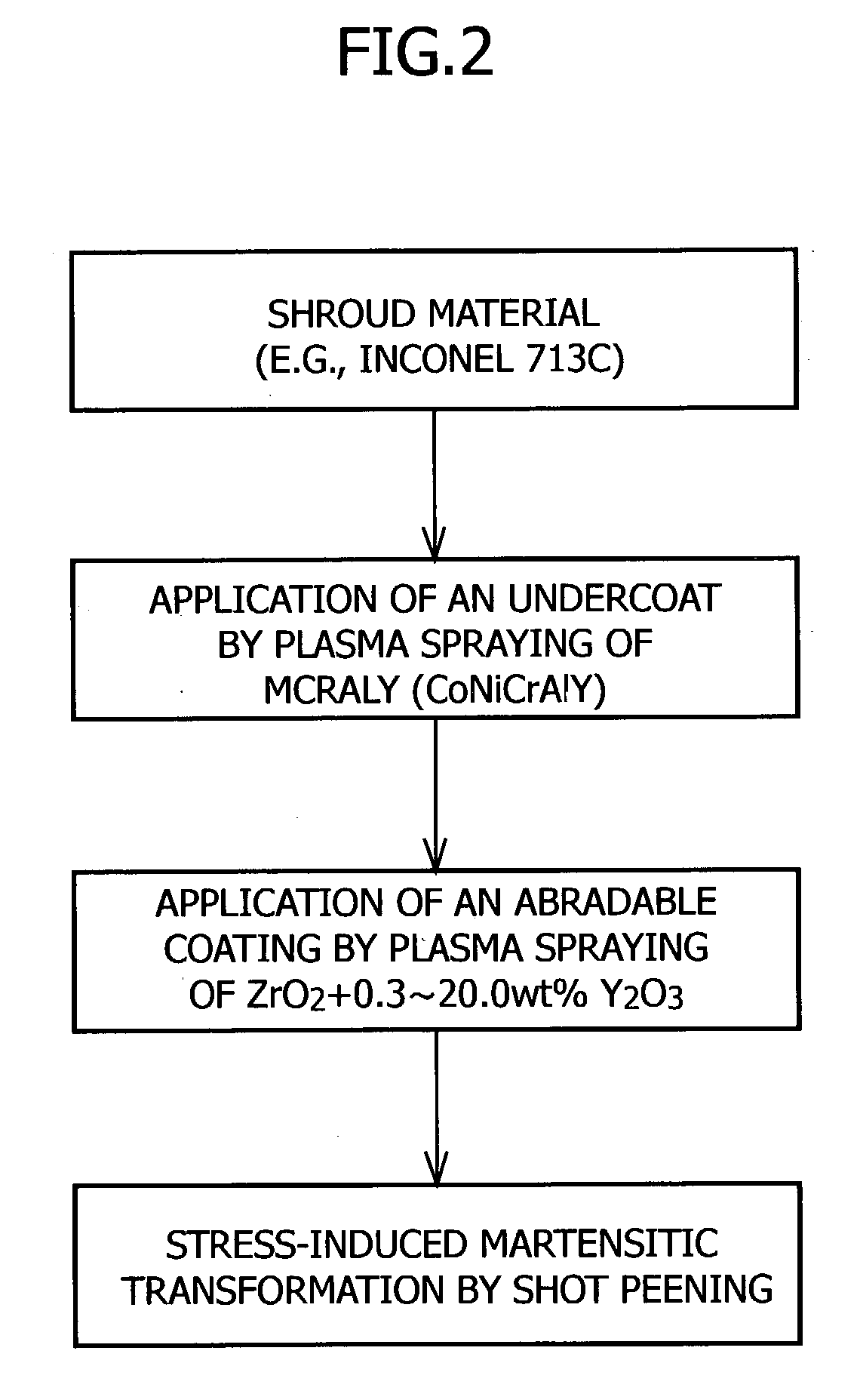
Abradable coating and method for forming same
InactiveUS20040022949A1Excellent cuttabilityImprove performanceMolten spray coatingPretreated surfacesMetallurgyCrystal structure
The present invention provides an abradable coating which is applied to the surfaces of stationary parts in rotary machinery such as gas turbines and does not cause damage or other trouble to the blades, as well as a method for forming the same. This method for forming an abradable coating comprises the steps of coating a shroud material with a partially stabilized zirconia ceramic material to form a zirconia ceramic layer having a cubic or tetragonal crystal structure on the surface of the shroud material; and subjecting the shroud material having the zirconia ceramic layer formed thereon to high-temperature water treatment at a temperature of 100 to 450° C. for 1 to 300 hours and thereby transforming the crystal structure of the zirconia ceramic layer into a monoclinic crystal structure. Alternatively, shot peening may be employed in place of the high-temperature water treatment.
Owner:HASEZAKI KAZUHIRO +2
Adhesive film and touch panel
ActiveUS20120231245A1Excellent characteristicsExcellent cuttabilityDigital data processing detailsSynthetic resin layered productsHeat resistanceTouchpad
The present invention relates to an adhesive film and to a touch panel. According to the present invention, even when the adhesive film is applied to a touch panel, for example, a capacitive touch panel, and directly attached to a conductive layer, the adhesive film effectively prevents the resistance of the conductive layer from being raised and exhibits good heat resistance. In addition, according to the present invention, an adhesive film having superior durability, optical characteristics, cuttability, workability, wettability and resistance to warping is provided.
Owner:KOZA NOVEL MATERIALS KOREA CO LTD
Cubic Boron Nitride Compact
InactiveUS20080302023A1Poor EDM-cuttabilityImprove conductivityPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesBorideAluminium carbide
A polycrystalline cubic boron nitride compact which comprises greater than 75 volume % and not greater than 90 volume % cubic boron nitride particles, the cubic boron nitride particles comprising particles of at least two average particle sizes, and a binder phase constituting the balance of the compact and comprising at least one titanium compound selected from titanium boride, titanium nitride, titanium carbide and titanium carbonitride and at least one aluminium compound selected from aluminium oxide, aluminium boride, aluminium nitride, aluminium carbide and aluminium carbonitride.
Owner:GOUDEMOND IAIN PATRICK +2
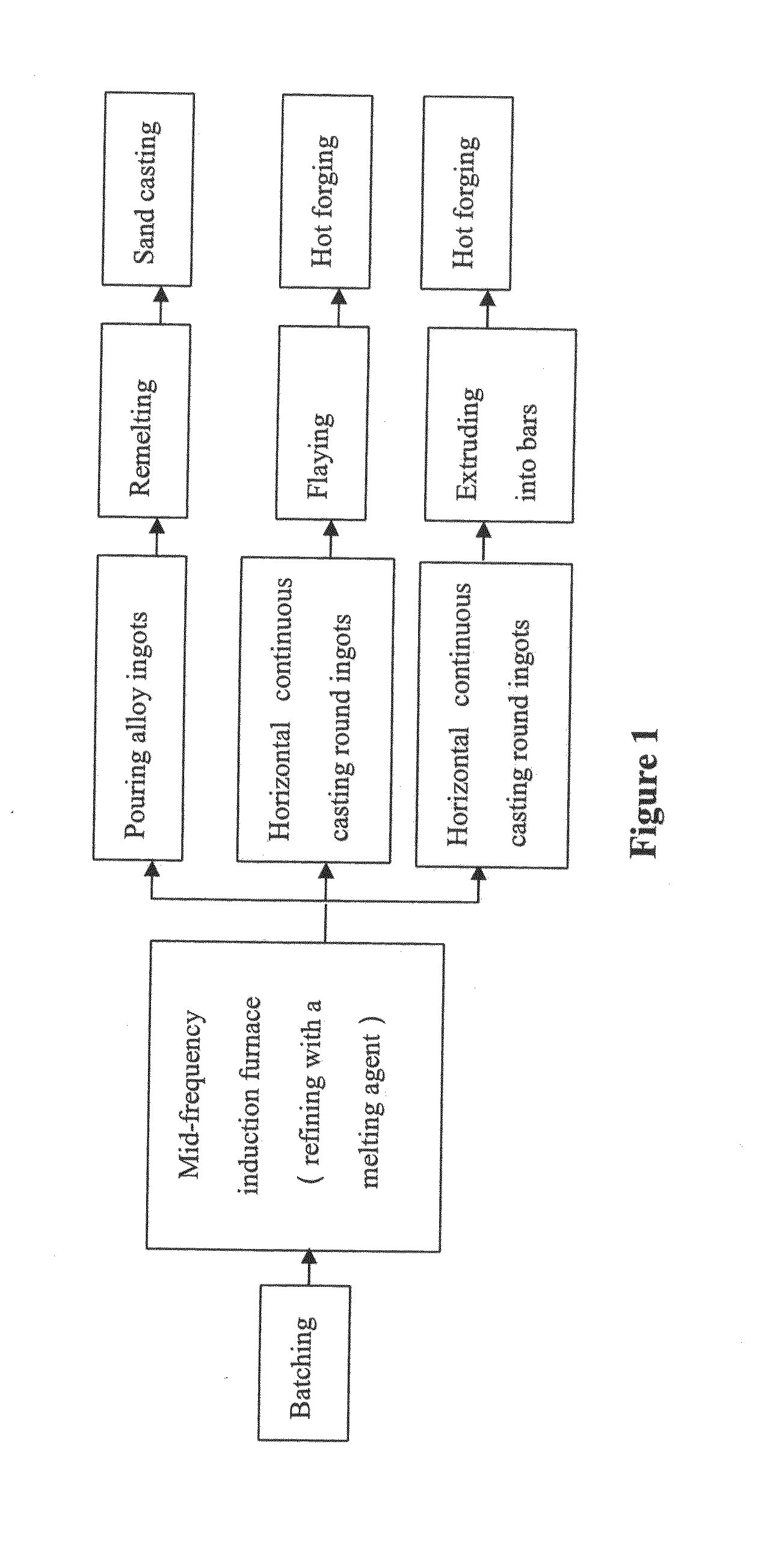
Lead-free free-cutting aluminum brass alloy and its manufacturing method
ActiveUS7776163B2Improve dezincification corrosion resistance of alloyDecrease castabilityRare-earth elementMetallic materials
Owner:XIAMEN LOTA INT CO LTD
Substrate film and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20140045319A1Increase thermal resistanceGood dimensional stabilityFilm/foil adhesivesPolyureas/polyurethane adhesivesHeat resistanceStress relaxation
Provided are a substrate film and a method of manufacturing the substrate film. The substrate film may have excellent thermal resistance and dimensional stability, has excellent stress relaxation to prevent damage of a wafer caused by remaining stress, inhibits damage to or flying-off of the wafer caused by application of a non-uniform pressure during the processing of the wafer, and has excellent cuttability. Accordingly, the substrate film of the present invention can be effectively used as a processing sheet in a process of processing various kinds of wafers including dicing, back-grinding or picking-up.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Lead-Free, Bismuth-Free Free-Cutting Phosphorous Brass Alloy And Its Manufacturing Method
The present invention relates to a lead-free, bismuth-free free-cutting phosphorous brass alloy and its method of manufacture. The alloy comprises: Cu; Zn; 0.59 to 1.6 wt % P; and other elements in the amount of 0.005 to 0.6 wt %, which comprise at least two elements selected from the group consisting of Al, Si, Sb, Sn, Rare earth element (RE), Ti and B, and the balance being unavoidable impurities. The phosphorous brass alloy contains a combined wt % of Cu and Zn of between 97.0 wt % and 99.5 wt %, within which the content of Zn is above 40 wt %. Considering the solid solubility of P in the matrix of copper will be decreased rapidly with the temperature decrease and form the brittle intermetallic compounds Cu3P with Cu, the present invention relies upon P to ensure excellent cuttability of the invented alloy. The invented alloy is reasonably priced, and has excellent cuttability, castability, hot and cold workability, dezincification corrosion resistance, mechanical properties and weldability. The phosphorous brass alloy is a useful alloy for spare parts, forging and castings that require cutting, and particularly in forging and castings for low pressure die casting that requires cutting, grinding, welding and electroplating. The phosphorous brass alloy may also be used for faucets, valves and bushings of water supply systems, and for bar and wire materials that require high corrosion resistance and compactness.
Owner:XIAMEN LAVIDA HI TECH MATERIAL CO LTD
Rapidly curing compound having good adhesive properties
InactiveUS20130317169A1Fast curingQuick implementationNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesPolymer chemistrySilane
Owner:TREMCO ILLBRUCK PRODN
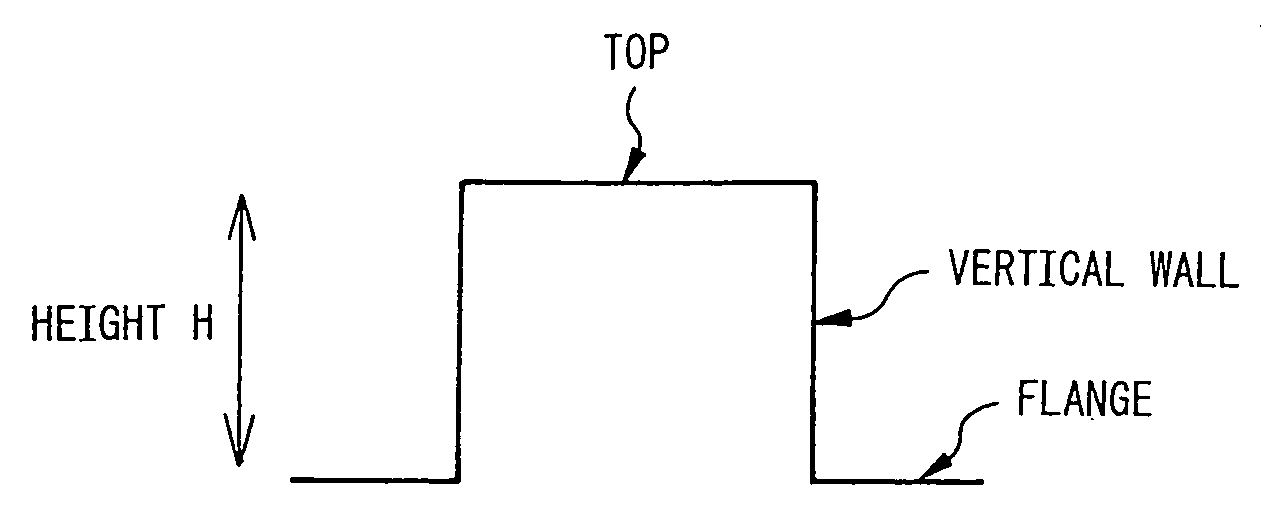
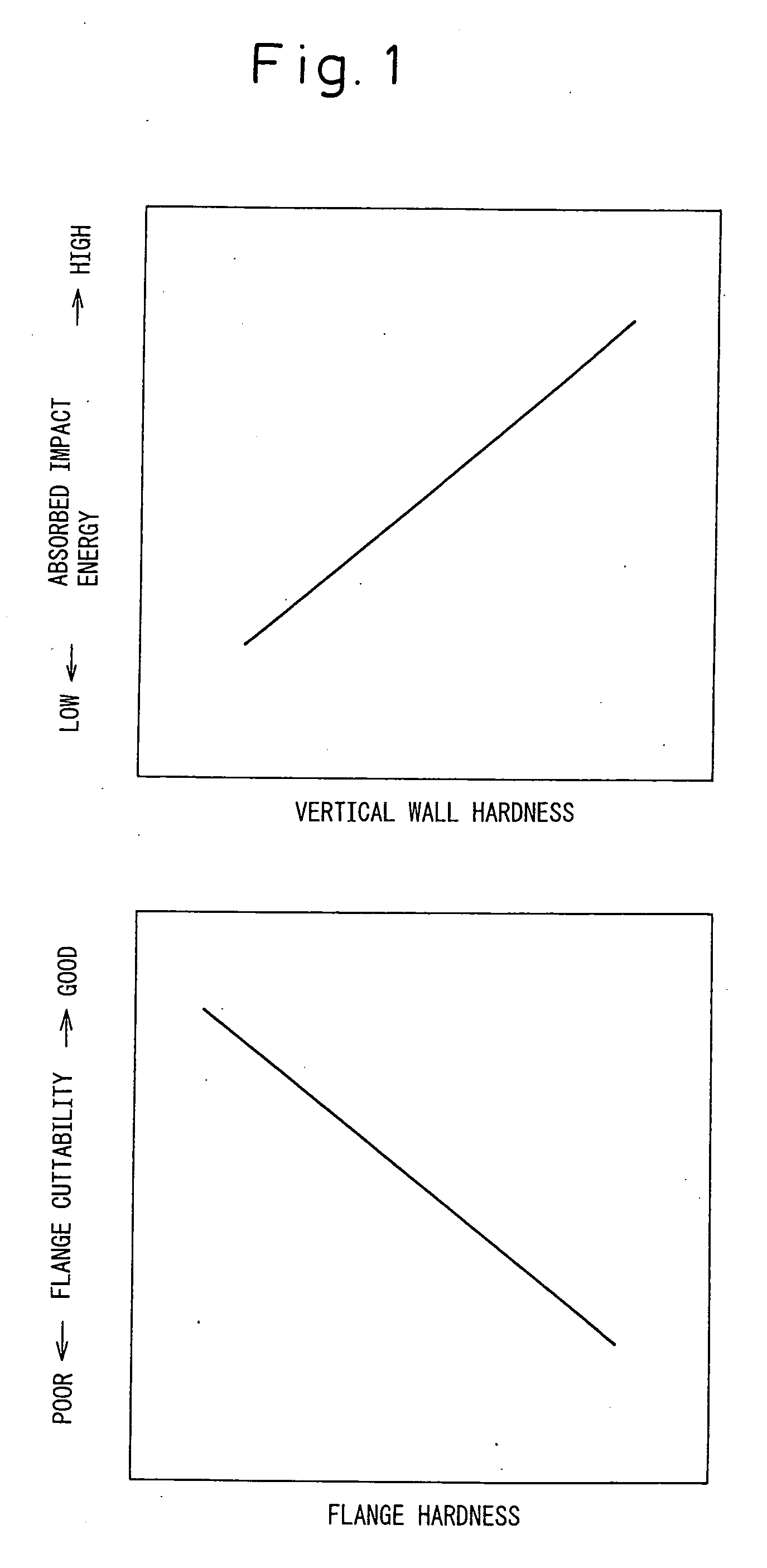
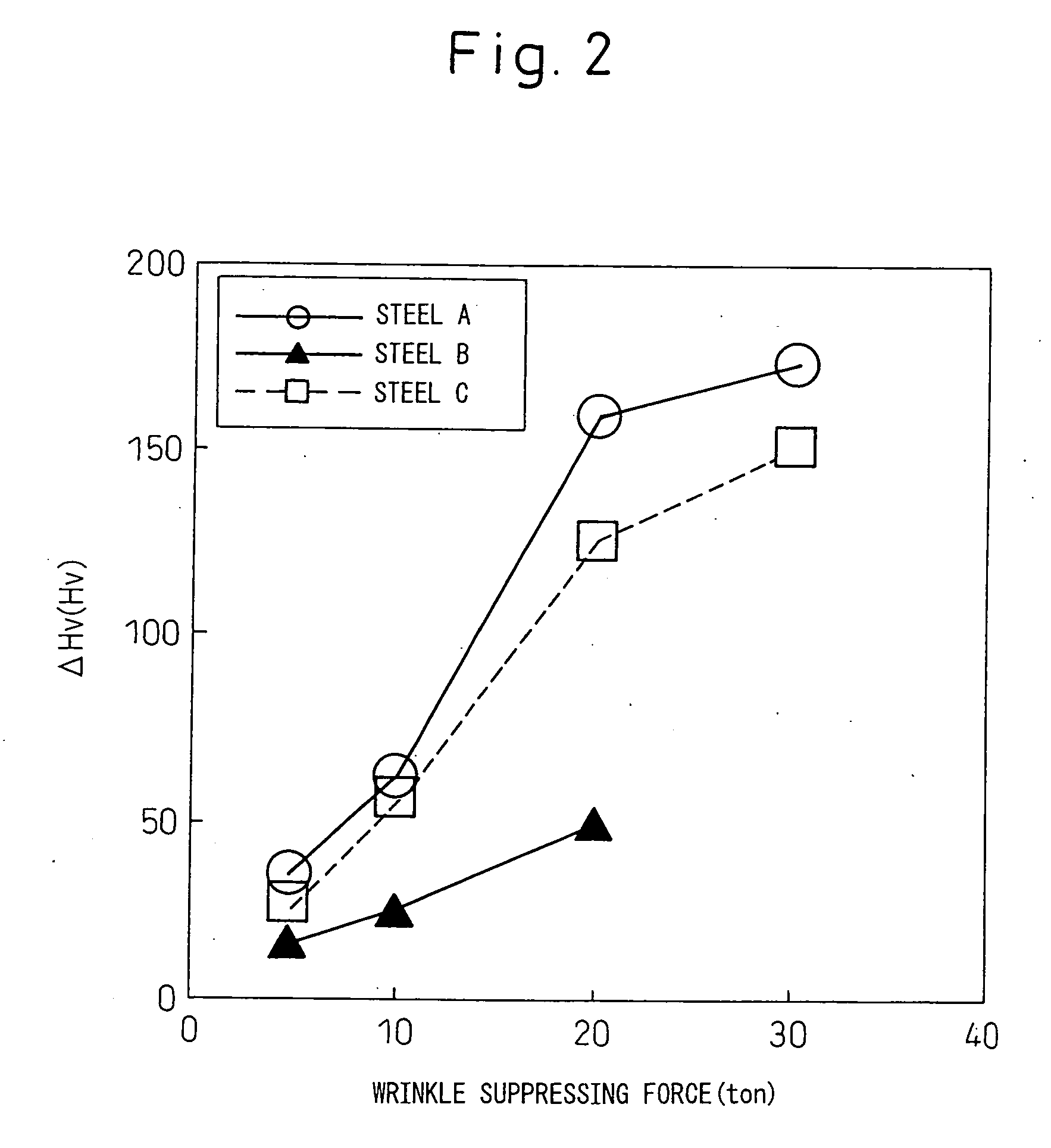
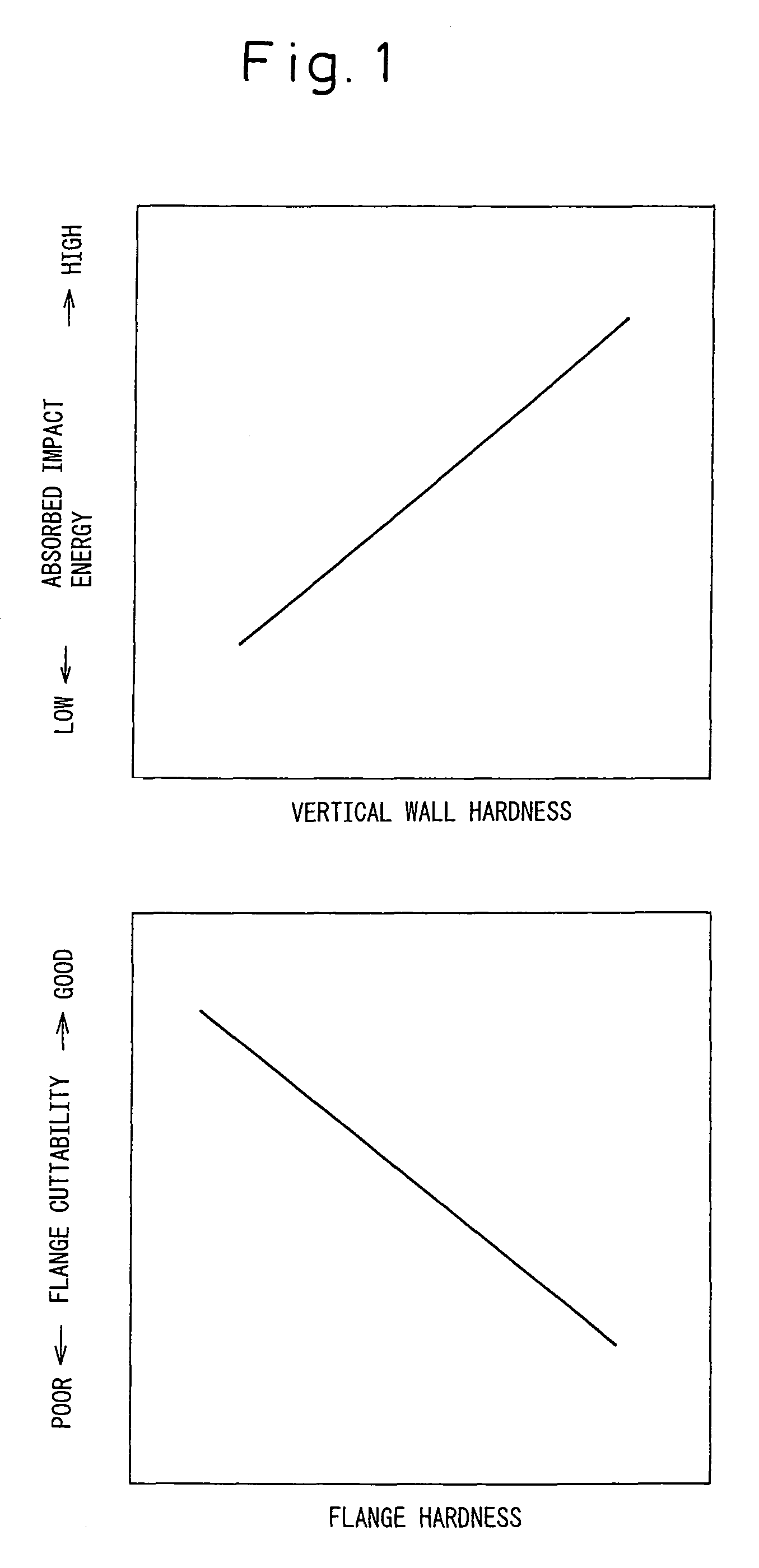
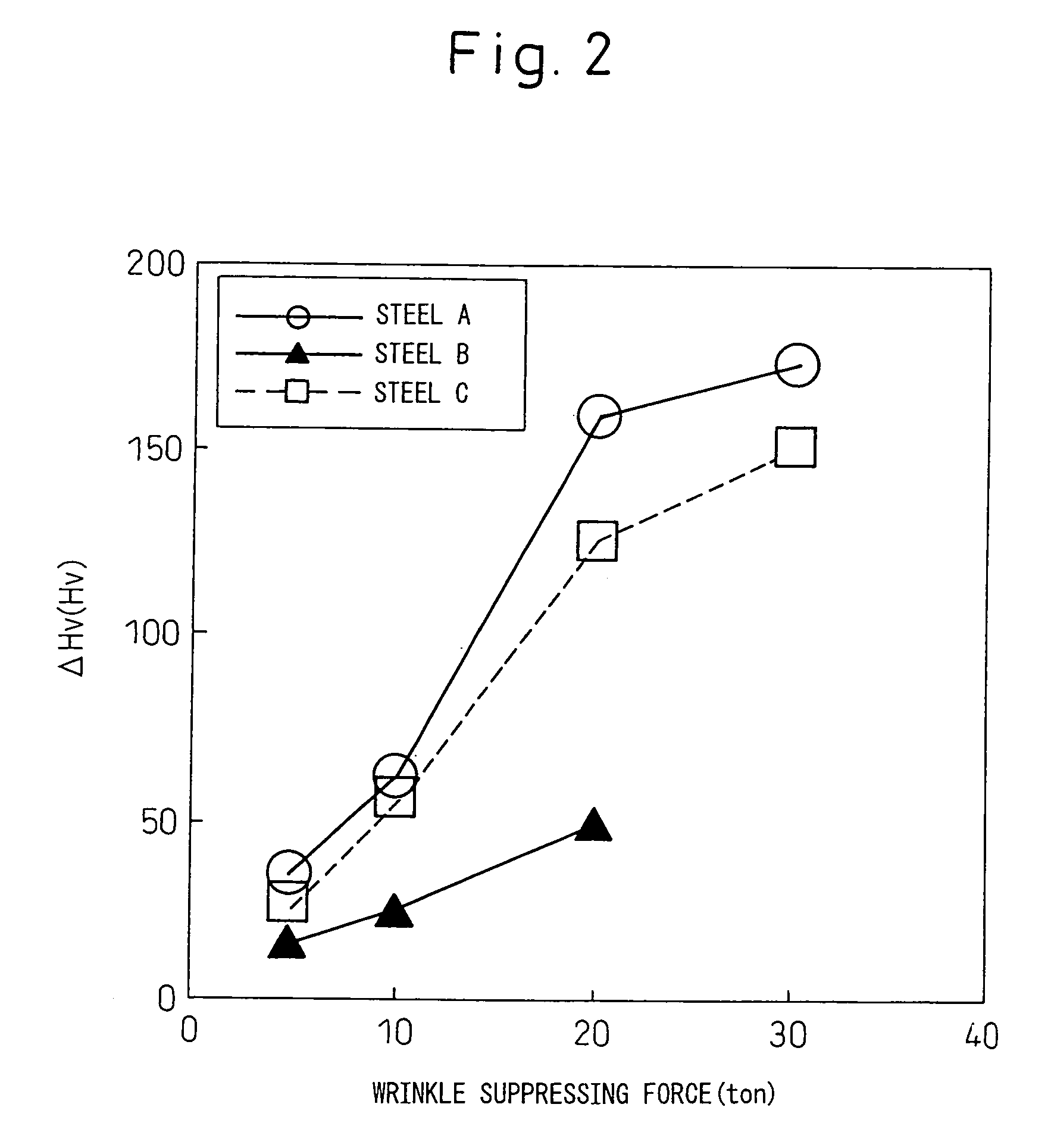
Structural component for automobile, two-wheeled vehicle or railcar excellent in impact-absorption property, shape fixability and flange cuttability, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090160217A1Promote absorptionInferior in cuttabilityVehicle seatsPig casting plantsEngineeringHardness
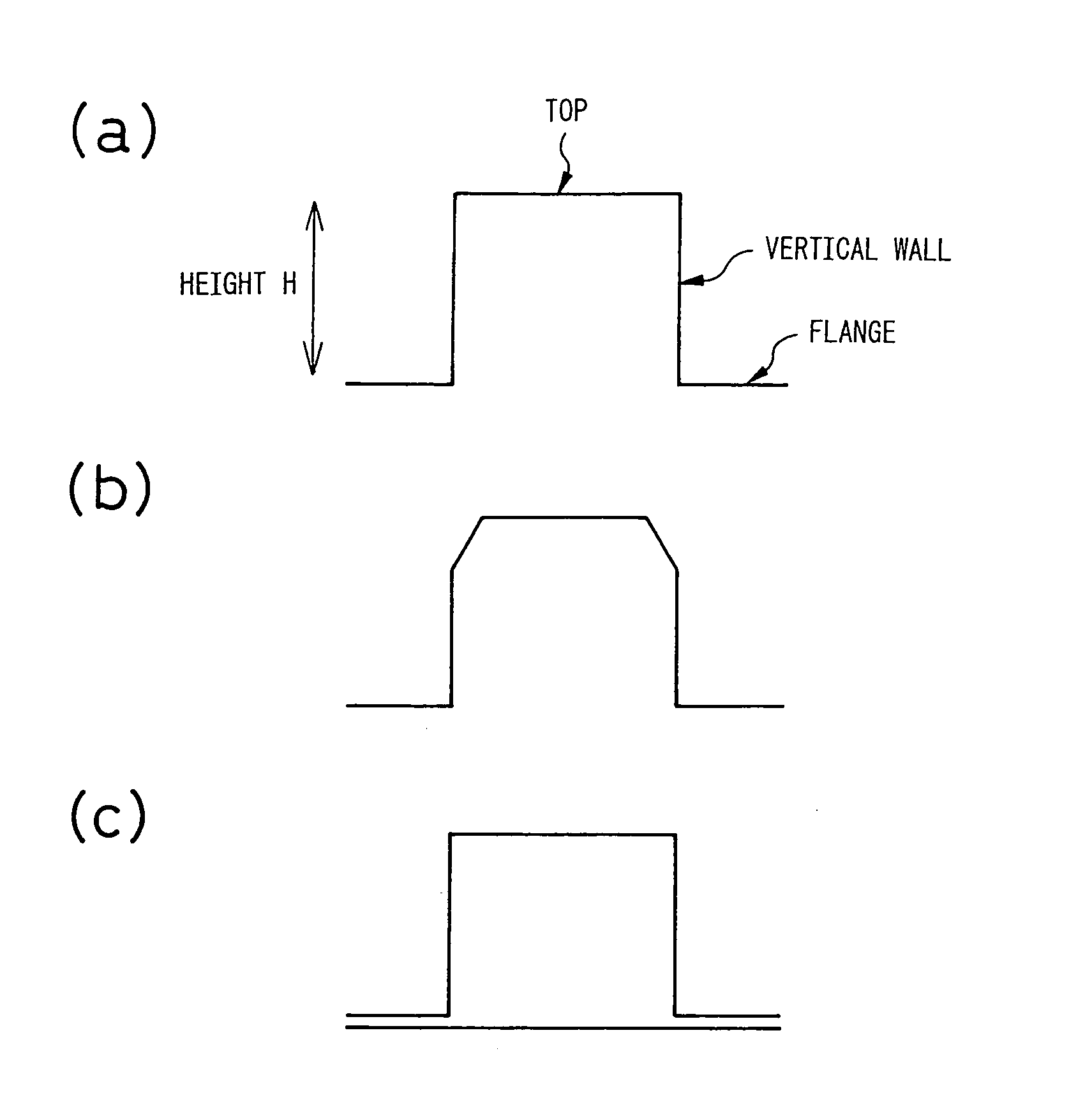
The invention provides structural component for an automobile, two-wheeled vehicle or railcar excellent in impact-absorption property, shape fixability and flange cuttability, and method for producing the same, which structural component has a hat-like shape including vertical walls and flanges, wherein distal ends of the flanges contain 20 vol % or greater of austenite phase and have a cross-section hardness expressed as Vickers harness of 150˜350, and a center regions of the vertical walls have, in a common cross-section with the flanges, a content of deformation-induced martensite phase exceeding that of the distal ends of the flanges by 10 vol % or greater and a cross-section hardness expressed as Vickers hardness that exceeds that of the distal ends of the flanges by 50 or greater.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMIKIN STAINLESS STEEL CORP
Deposition substrate and scintillator panel
ActiveUS20140239195A1Excellent cuttabilityHigh sensitivityPhotometryBleaching apparatusX-rayReflective layer
An object of the invention is to provide a scintillator panel which exhibits excellent cuttability and can be cut without the occurrence of problems such as the separation of a scintillator layer and which can give radiographic images such as X-ray images with excellent sensitivity and sharpness. The scintillator panel of the invention includes a reflective layer and a scintillator layer formed by deposition on a support, and the reflective layer includes light-scattering particles and a specific binder resin and has a specific thickness.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
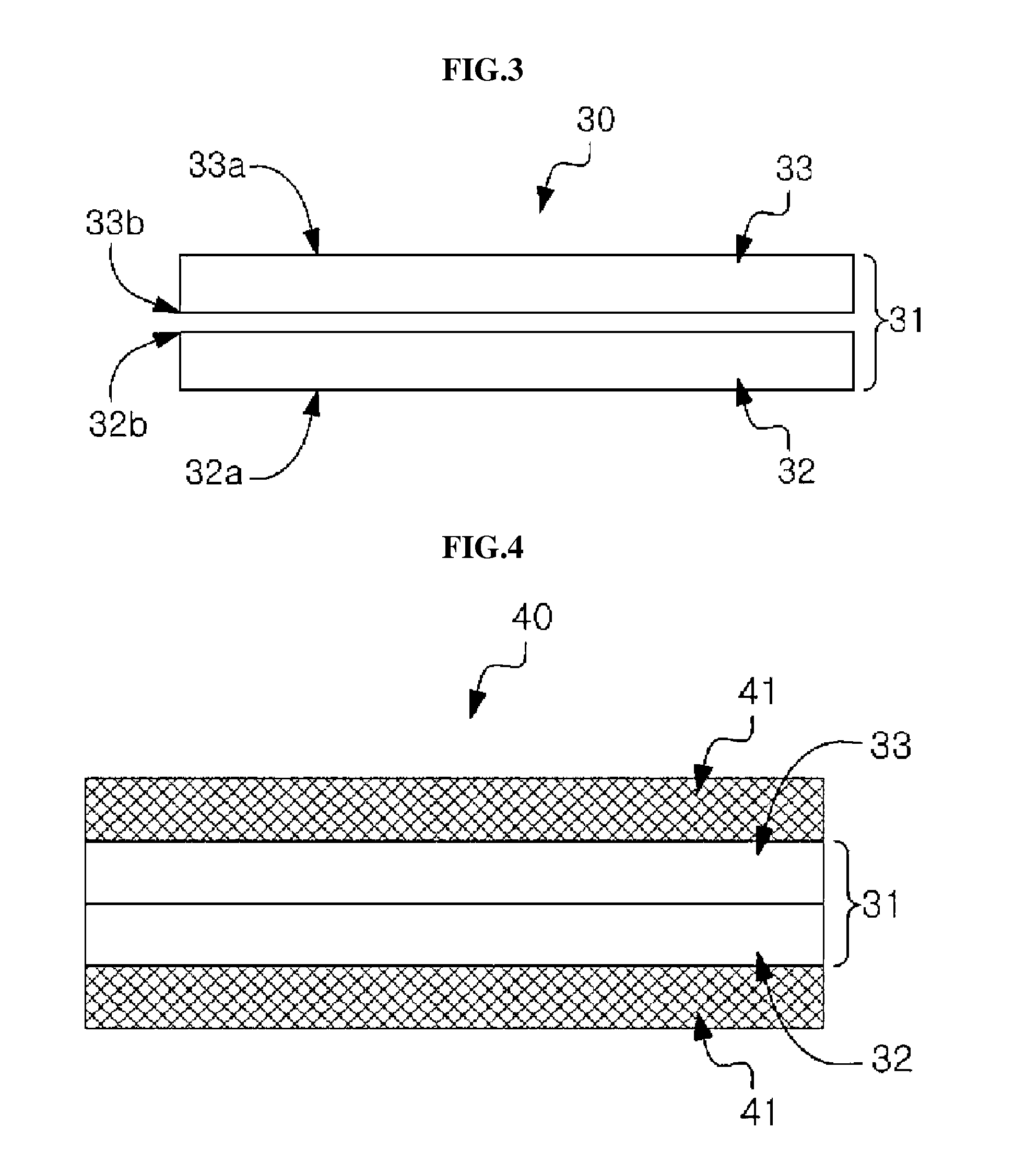
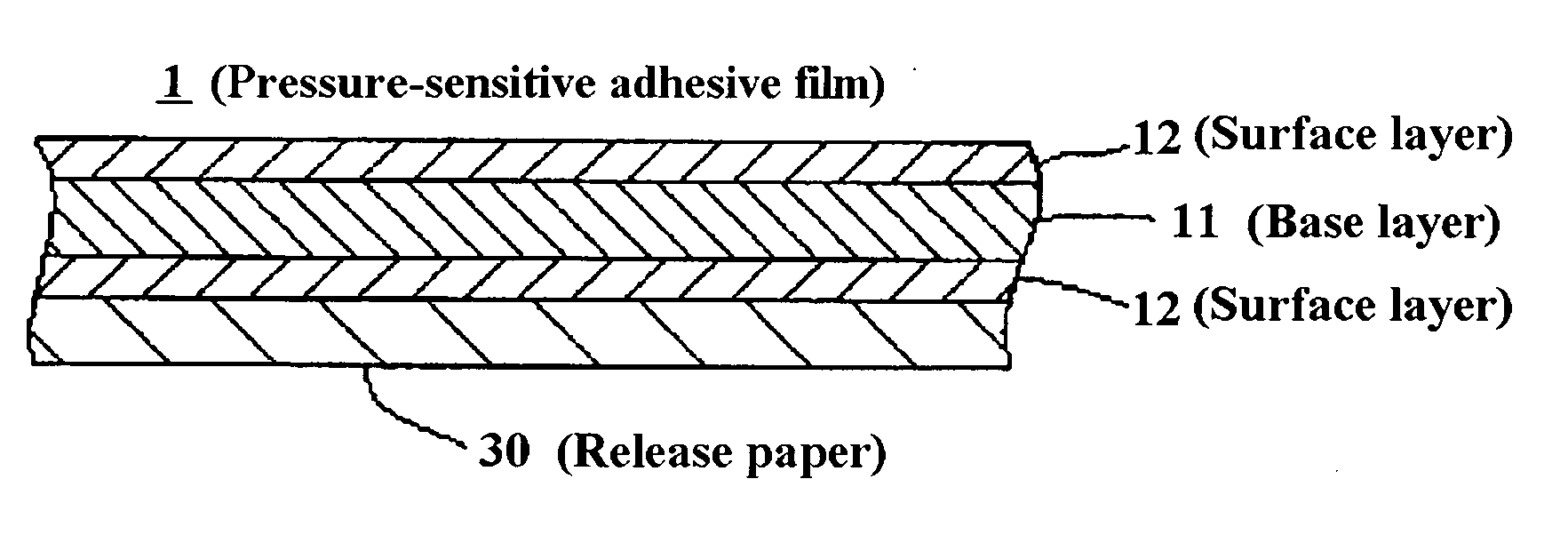
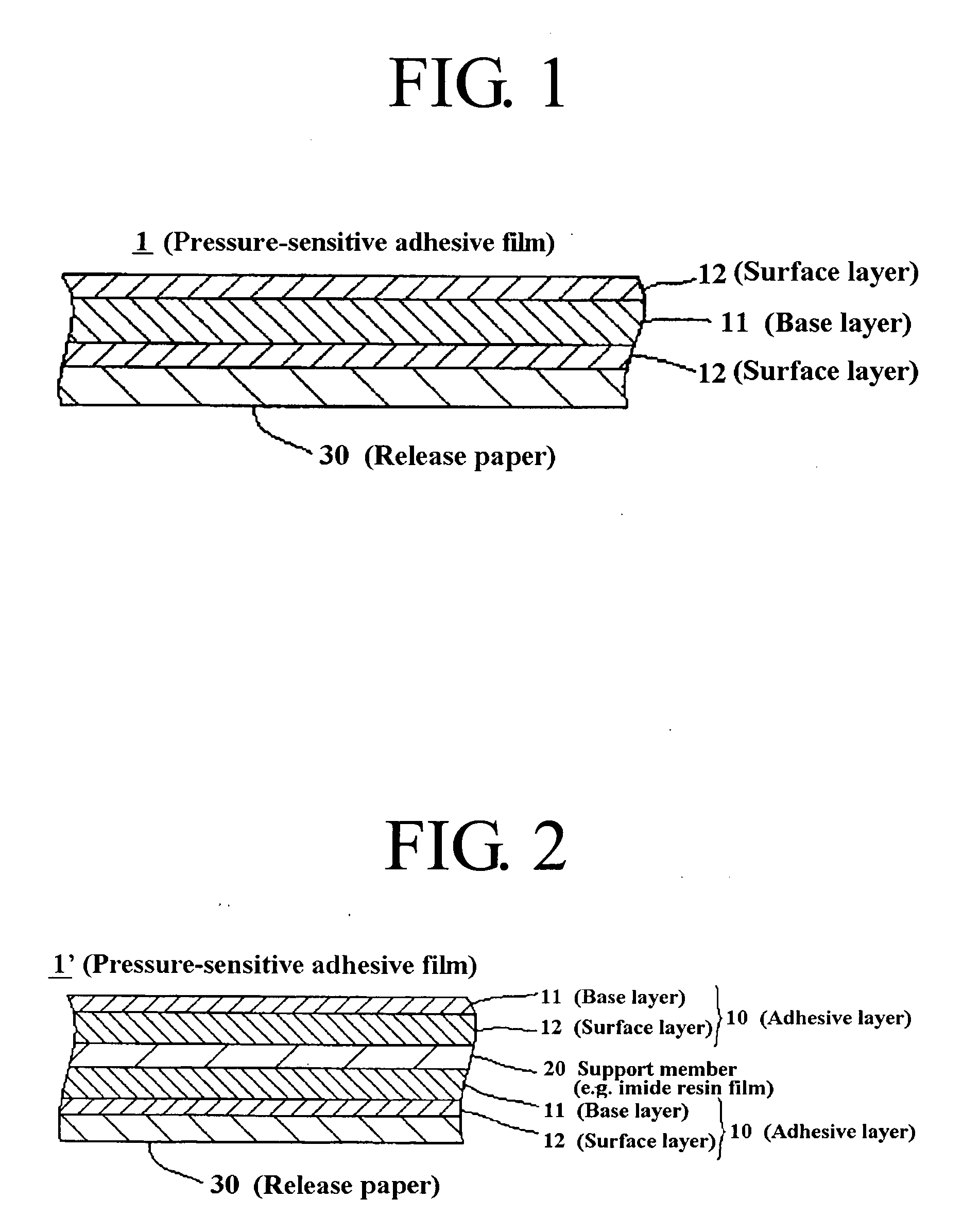
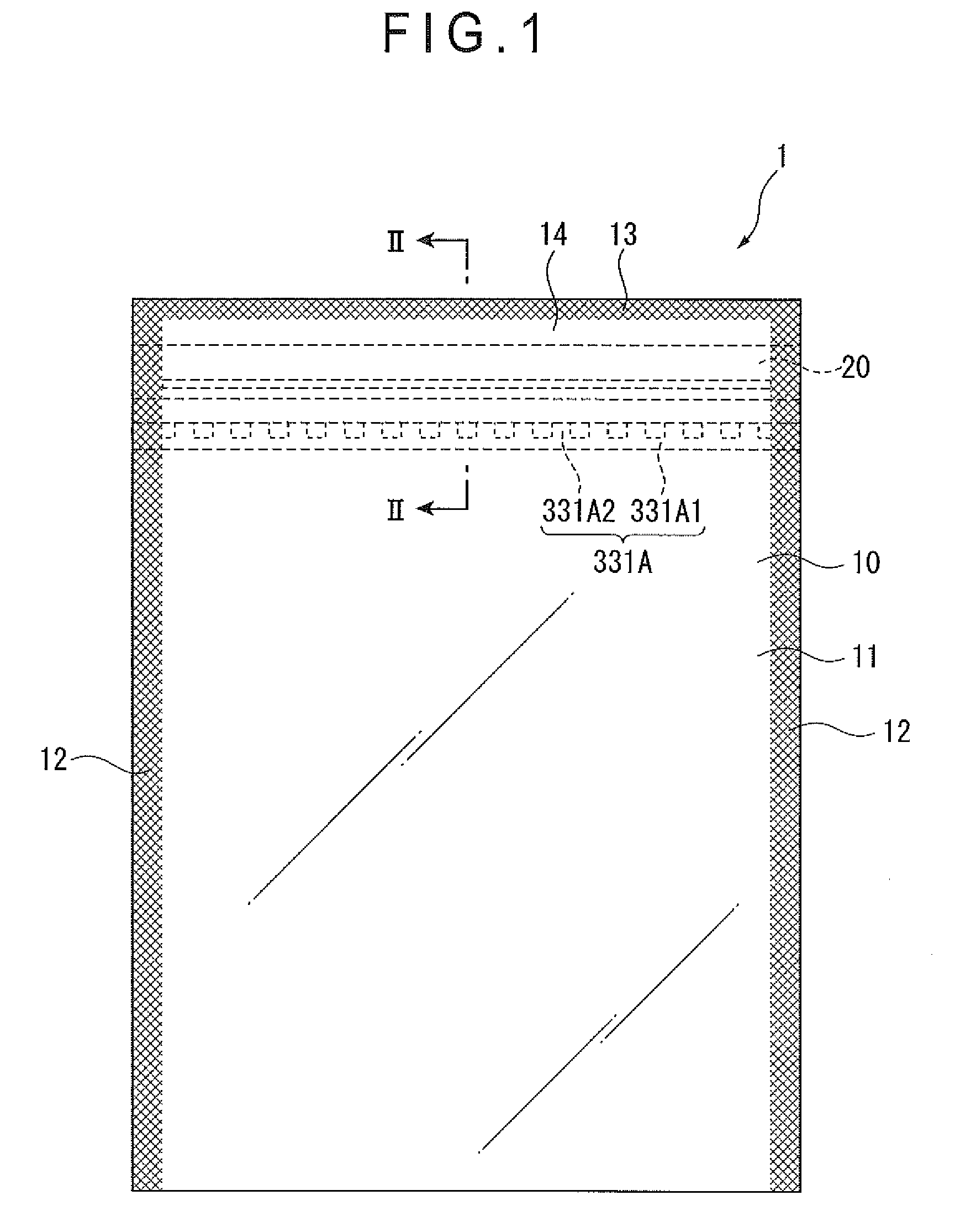
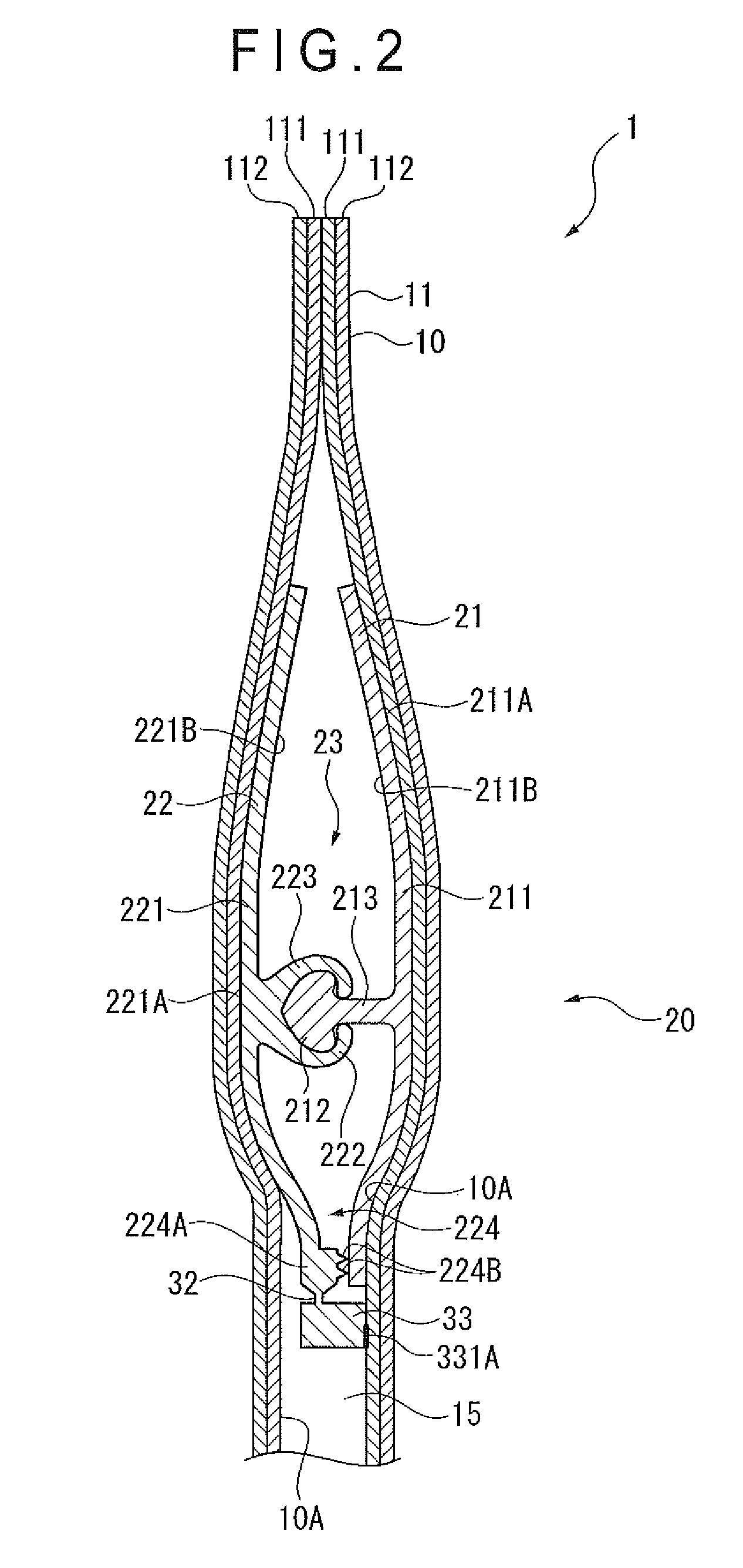
Adhesive Film
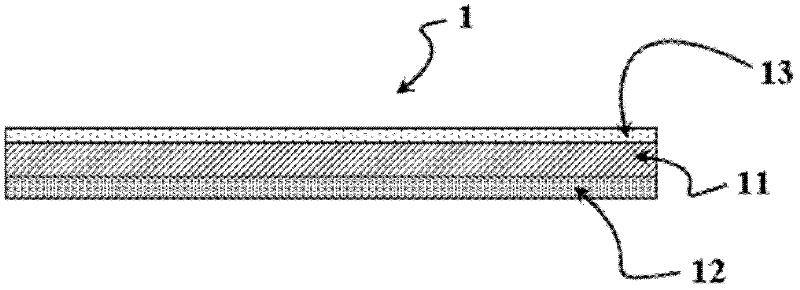
ActiveUS20090286073A1Improve machinabilityExcellent cuttabilityAdhesive articlesSynthetic resin layered productsPunchingUltimate tensile strength
To provide a hardenable pressure-sensitive adhesive film which is excellent in cuttability and permits excellent shearing such as punching or perforating without adhesive spew.[Means for Solving Problems] A hardenable pressure-sensitive adhesive film (1), characterized by being produced by laminating an isotropic support sheet (11) made of a resin which exhibits lengthwise and widthwise shear strengths of 2 to 2000 g [200 mm / min 25 mm width], preferably 5 to 1000 g, still preferably 10 to 500 g in the thickness range of 2 to 60 [mu]m with a face sheet (12) made of a resin-base pressure-sensitive adhesive. In the film (1), the face sheet(s) (12) may be present on either or both sides of the support sheet (11).
Owner:KYODO GIKEN CHEM
Adhesive composition, adhesive film, method for preparing the adhesive film and display part
ActiveCN102952505ASuppresses resistance changesBroaden applicationNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesFilm/foil adhesivesMeth-Morpholine
Owner:CHEIL IND INC
Adhesive film for semiconductor
ActiveUS20170233610A1Easily bury unevennessIncrease resistanceNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesAdhesive articlesSemiconductor chipSemiconductor package
The present invention relates to an adhesive film for a semiconductor that can more easily bury unevenness such as through wires of a semiconductor substrate or a wire attached to a semiconductor chip and the like, and yet can be applied to various cutting methods without specific limitations to realize excellent cuttability, thus improving reliability and efficiency of a semiconductor packaging process.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Aramid cord treatment
ActiveUS20060147711A1Improve penetrationFew treatmentFibre typesPretreated surfacesAdductBisphenol F
A composition and method for treating an aramid cord include a bisphenol-A-based- and / or a bisphenol-F-based-liquid epoxy resin, a reactive diluent, and a curing agent. The composition and method also may include an elastomer-modified epoxy-functional adduct and / or an elastomer-modified epoxy-resin adduct.
Owner:CONTITECH USA INC
Transmission belts comprising a cord with at least two fused yarns
InactiveUS6921572B2Improve cohesionImprove adhesionV-beltsPedestrian/occupant safety arrangementYarnDecomposition
A transmission belt is made of a cord, a rubber or thermoplastic matrix, and an adhesion material which is able to adhere the cord to the rubber or thermoplastic matrix. The cord is made of at least two yarns, such that a first yarn has a melting or decomposition point T1 and a second yarn has a melting point T2, wherein T1>T2. A ratio of a linear density of the first yarn to a linear density of the second yarn is between 1,000:1 and 1:1, wherein the second yarn is fused to the first yarn. A method of making such cords includes intertwining the first and the second yarn and then heating to a temperature between T1 and T2, with the heating step being integrated with or followed by a step wherein the cord is subjected to a dipping treatment with a rubber adhesion material.
Owner:TWARON PROD GMBH +1
Rapidly curing compound having good adhesive properties
InactiveUS8865817B2Fast curingQuick implementationNon-macromolecular adhesive additivesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsPolymer chemistryPolymer
A curable compound is provided, which can be obtained as a mixture of at least two components to be stored separately, of which one component includes a silane-modified polymer and the component of a second component includes an acid or basic salt containing water of crystallization. An aminic adhesion promoter is contained in one or both components or a further component, with the stipulation that no component contains all three substances. Additionally, a method is provided for accelerating the curing of a silane-modified polymer, in which an acid or basic salt containing water of crystallization is added to the silane-modified polymer.
Owner:TREMCO ILLBRUCK PRODN
Adhesive composition having high flexibility
InactiveUS20150140249A1Eliminate stepsIncrease flexibilityLayered productsEster polymer adhesivesCarbon numberPolymer science
The present invention relates to an adhesive composition comprising: an alkyl acrylic acid ester monomer having an alkyl carbon number of 2 to 14; an acrylic acid ester monomer containing a hydroxyl group; and a copolymer obtained by copolymerizing an acrylic acid ester monomer. The present invention also provides the adhesive composition and an adhesive film using the same, a touch panel, and an electronic device. The adhesive composition of the present invention has characteristics of high flexibility and good cutting properties, durability, transparency, etc.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Brass alloys having superior stress corrosion resistance and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS20110132569A1Improve stress corrosion resistanceGood castabilityFoundry mouldsFoundry coresAlloyImpurity
The present invention relates to a brass alloy having superior stress corrosion comprising: 59.0-64.0 wt % Cu, 0.6-1.2 wt % Fe, 0.6-1.0 wt % Mn, 0.4-1.0 wt % Bi, 0.6-1.4 wt % Sn, at least one element selected from Al, Cr and B, the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities, wherein the content of Al is 0.1-0.8 wt %, the content of Cr is 0.01-0.1 wt %, the content of B is 0.001-0.02 wt %. The alloy according to the present invention does not contain toxic elements such as lead and antimony, has superior corrosion resistance and good cuttingability and is suitable for the accessories in the potable water supply systems produced by casting, forging and extruding.
Owner:XIAMEN LOTA INT CO LTD
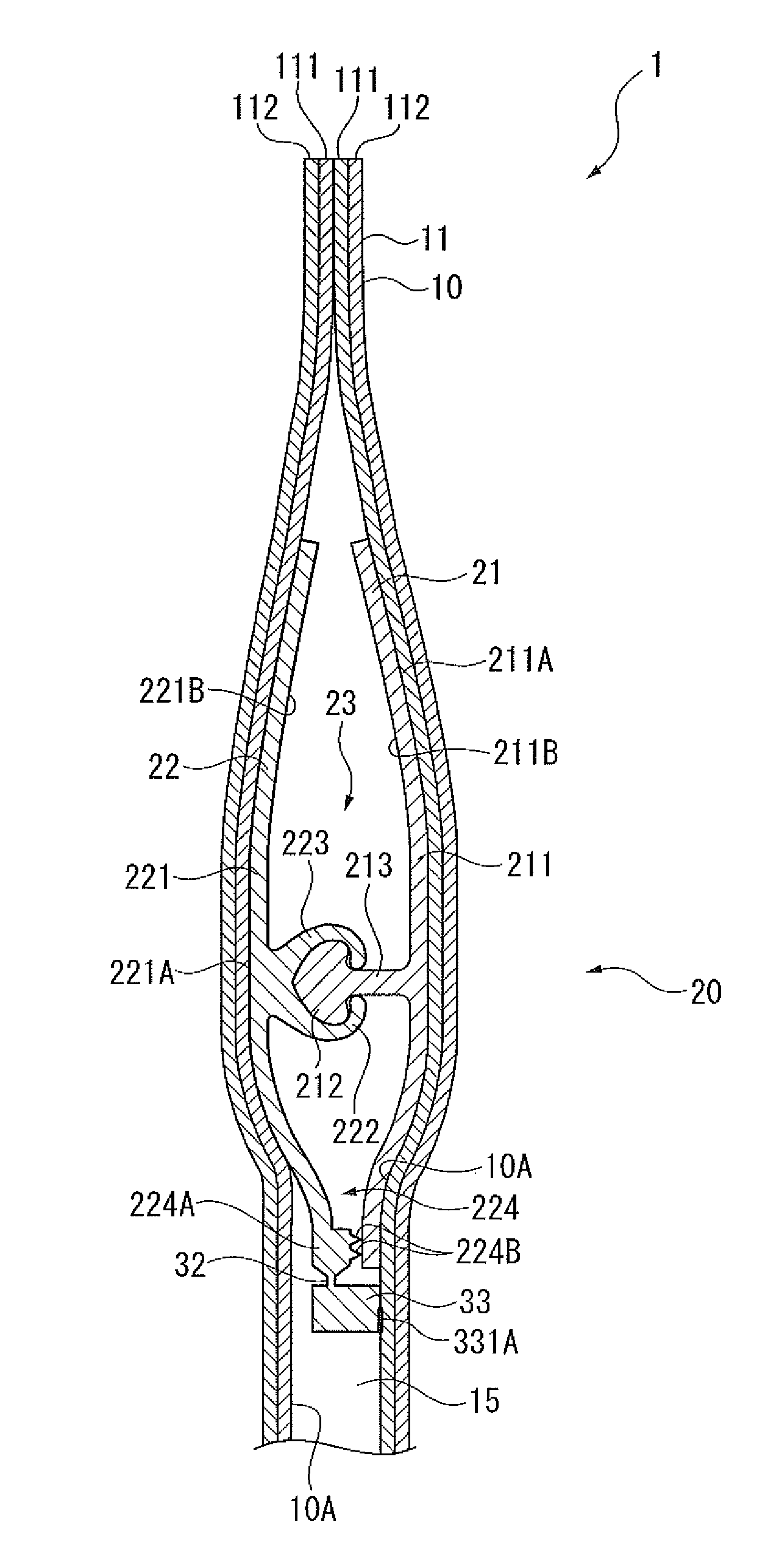
Zipper tape and packaging bag with zipper tape
InactiveUS8646972B2Excellent cuttabilityEasy to openSnap fastenersFlexible coversEngineeringMechanical engineering
A seal base, which is thicker than a thick portion and is bondable to an inner surface of a bag body, is continuously connected to one of belt-like bases of a zipper tape via a belt-like cutting portion that is thinner than the thick portion and separates a containing space from an outside. A first linking portion having a first corner (a) is defined by a cutting outer surface of the cutting portion and a seal outer continuous surface of the seal base. A second linking portion having a second corner (b) is defined by a contained cutting surface of the cutting portion and a contained seal continuous surface of the seal base.
Owner:IDEMITSU UNITECH CO LTD
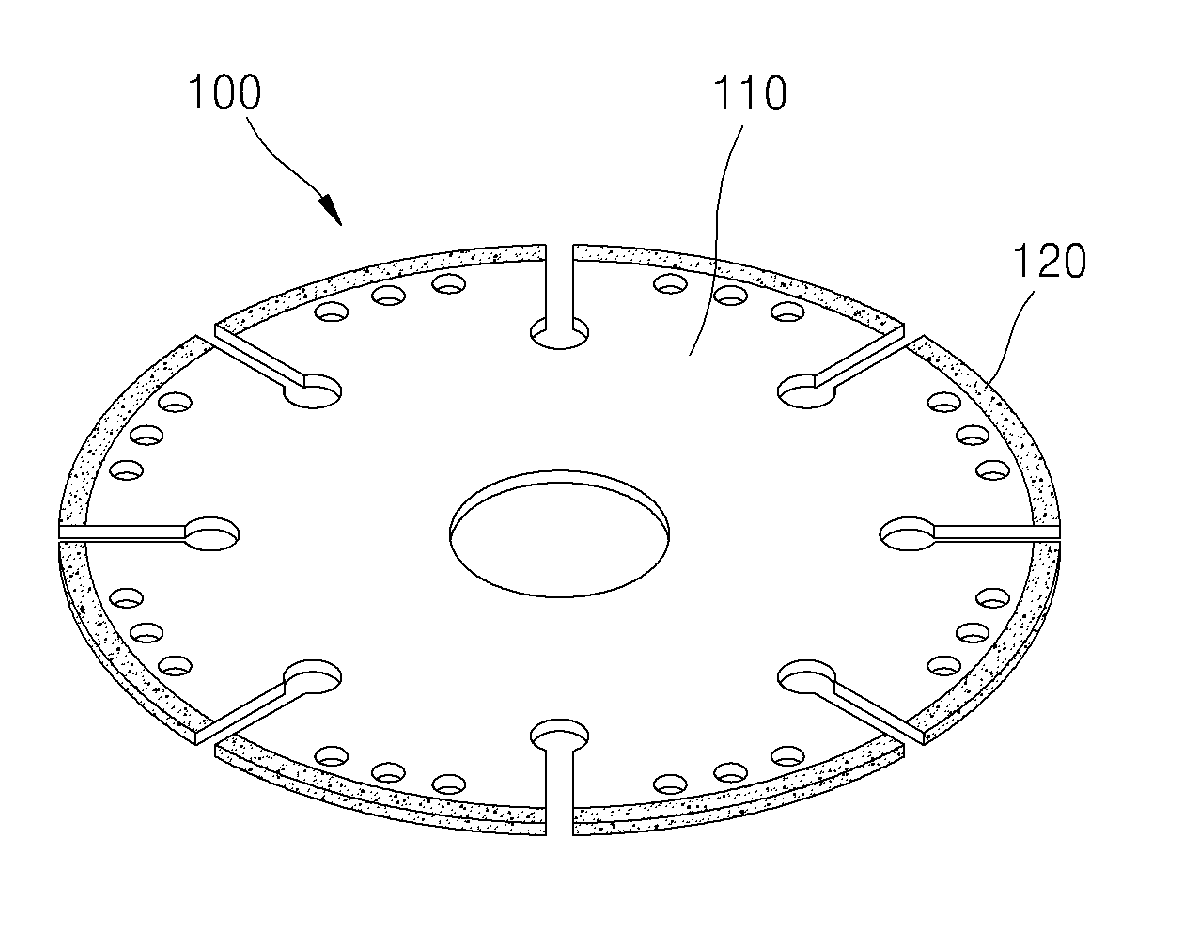
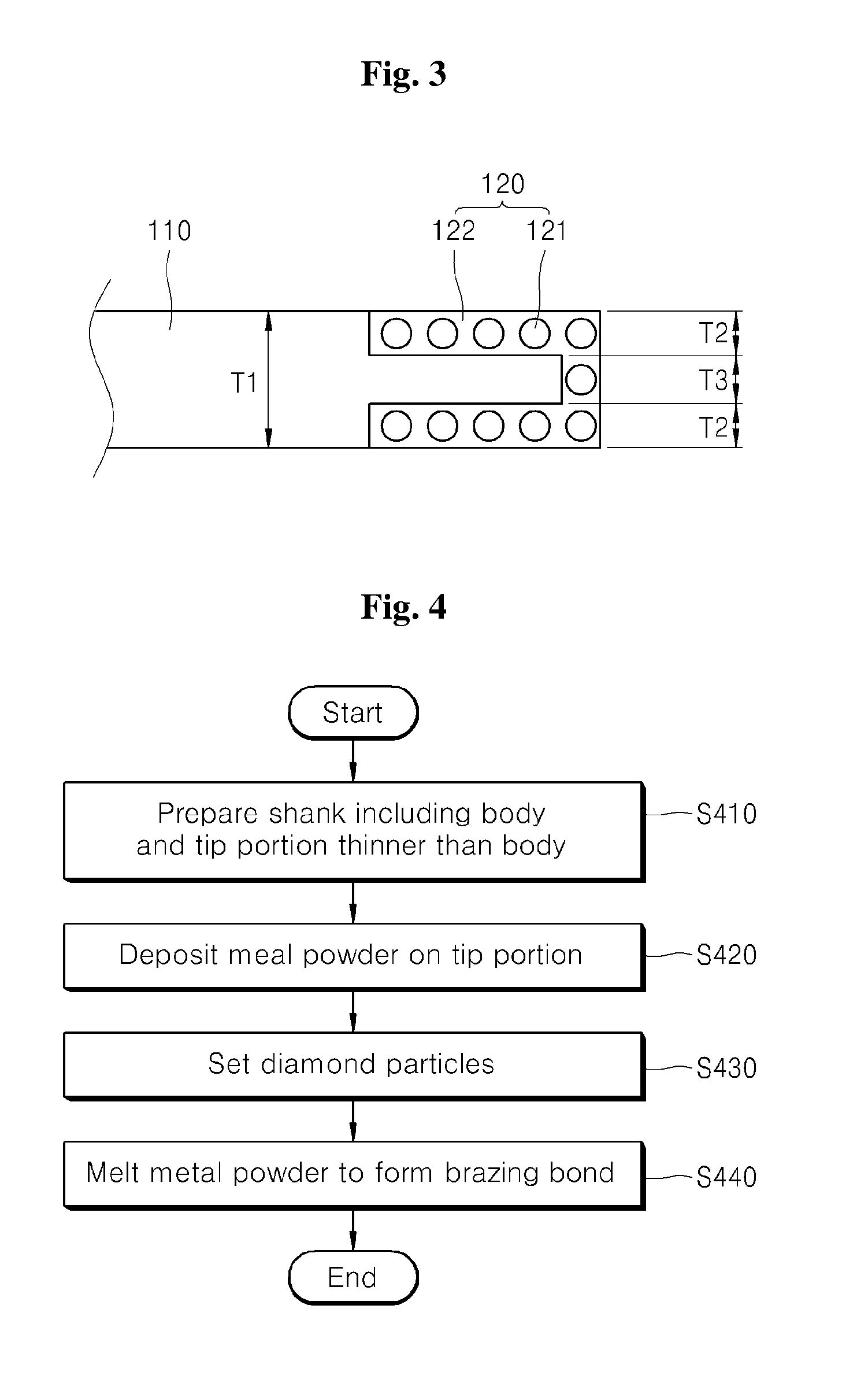
Brazing bond type diamond tool with excellent cuttability and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20130059510A1Cuttability is improvedIncrease speedPigmenting treatmentRevolution surface grinding machinesDiamond toolDiamond
The present disclosure provides a brazing bond type diamond tool having excellent cuttability and a method of manufacturing the same. The diamond tool includes a shank having a body and a tip portion formed along an edge of the body, and a brazing bond layer formed on the tip portion of the shank to secure diamond particles with a brazing bond. The tip portion is thinner than the body and is integrally formed with the body.
Owner:NIWA DAIYAMONDO INDS
Lead-free free-cutting corrosion-resistant silicon-bismuth brass alloy
A lead-free free-cutting corrosion-resistant silicon-bismuth brass alloy, including the following: between 60.0 and 65.0 wt % of Cu, between 0.6 and 1.8 wt % of Si, between 0.2 and 1.5 wt % of Bi, between 0.02 and 0.5 wt % of Al, less than 1.5 wt % of Ni+Mn+Sn, between 0.01 and 0.5 wt % of La—Ce alloy, between 0.002 and 0.02 wt % of B, with the remainder being Zn and inevitable impurities, wherein the total amount of impurities are no more than 0.5 wt %.
Owner:NINGBO XINGAODA ADVANCED METALLIC MATERIALS +1
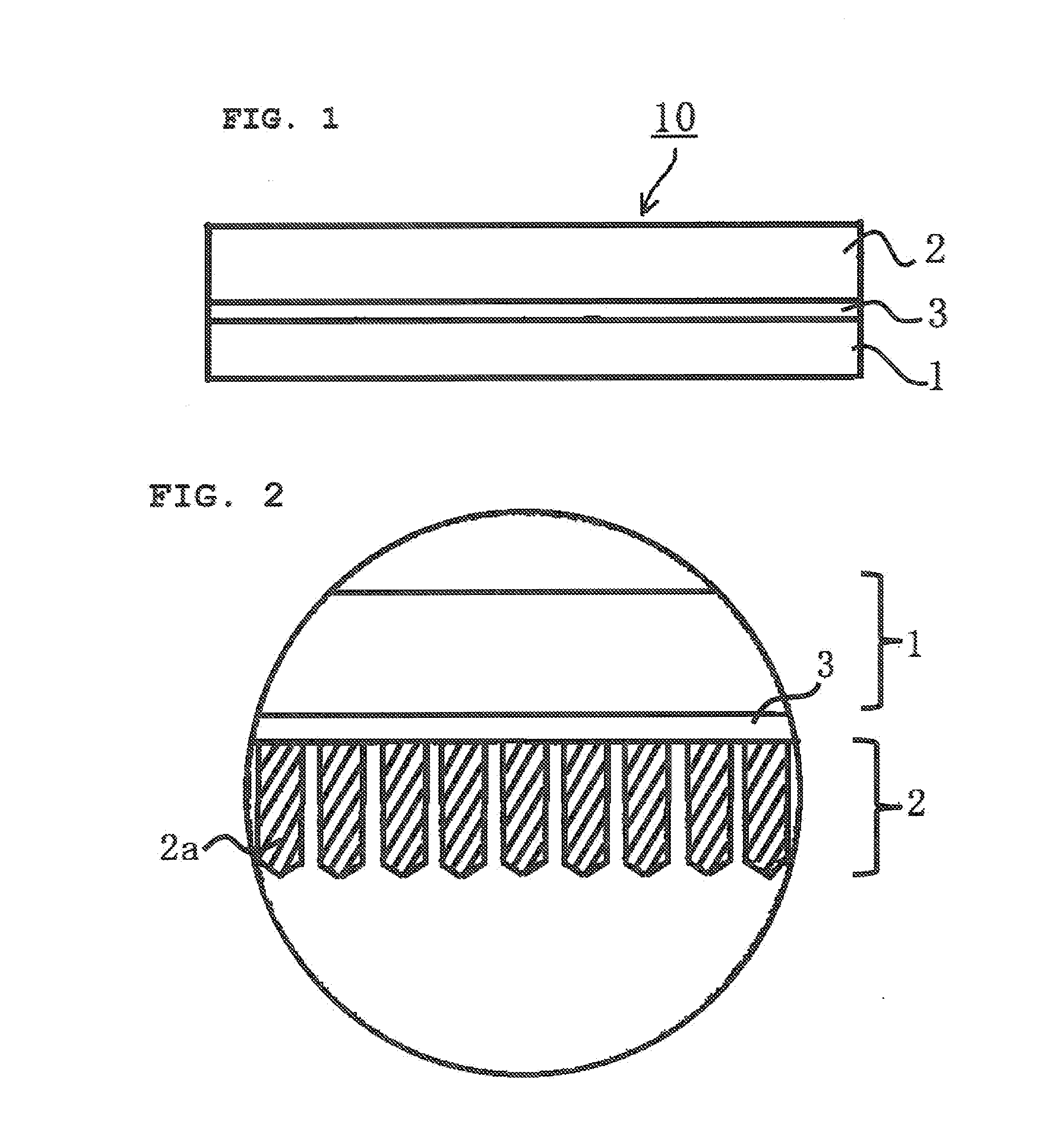
Wafer processing sheet
ActiveUS20120202337A1Efficient processingIncrease crosslink densitySynthetic resin layered productsSolid-state devicesHeat resistanceStress relaxation
Provided is a sheet for processing a wafer. The sheet can exhibit excellent heat resistance and dimensional stability, prevent breakage of a wafer in response to residual stress due to excellent stress relaxation properties, inhibit damage to or dispersion of the wafer due to application of a non-uniform pressure, and also exhibit excellent cuttability. The sheet can effectively prevent a blocking phenomenon from occurring during wafer processing. For these reasons, the sheet can be useful for processing a wafer in various wafer preparation processes such as dicing, back-grinding and picking-up.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Lead-free, bismuth-free free-cutting phosphorous brass alloy
The present invention relates to a lead-free, bismuth-free free-cutting phosphorous brass alloy and its method of manufacture. The alloy comprises: Cu; Zn; 0.59 to 1.6 wt % P; and other elements in the amount of 0.005 to 0.6 wt %, which comprise at least two elements selected from the group consisting of Al, Si, Sb, Sn, Rare earth element (RE), Ti and B, and the balance being unavoidable impurities. The phosphorous brass alloy contains a combined wt % of Cu and Zn of between 97.0 wt % and 99.5 wt %, within which the content of Zn is above 40 wt %. Considering the solid solubility of P in the matrix of copper will be decreased rapidly with the temperature decrease and form the brittle intermetallic compounds Cu3P with Cu, the present invention relies upon P to ensure excellent cuttability of the invented alloy. The invented alloy is reasonably priced, and has excellent cuttability, castability, hot and cold workability, dezincification corrosion resistance, mechanical properties and weldability. The phosphorous brass alloy is a useful alloy for spare parts, forging and castings that require cutting, and particularly in forging and castings for low pressure die casting that requires cutting, grinding, welding and electroplating. The phosphorous brass alloy may also be used for faucets, valves and bushings of water supply systems, and for bar and wire materials that require high corrosion resistance and compactness.
Owner:XIAMEN LAVIDA HI TECH MATERIAL CO LTD
Wafer processing sheet
ActiveCN102460655AAvoid breakingAvoid damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHeat resistanceStress relaxation
The present invention relates to a wafer processing sheet. The present invention provides a wafer processing sheet which is excellent in heat resistance and dimensional stability, and which has superior stress relaxation property to prevent a wafer from being damaged or delimited by residual stresses or a non-uniform pressure, and which has superior cutting property. In addition, the present invention provides a sheet which can effectively suppress a blocking phenomenon during a wafer processing process or the like. Consequently, a base of the present invention can be valuably used as a processing sheet in a variety of wafer processing processes including dicing, back grinding, picking-up and so on.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Lead-Free Free-Cutting Aluminum Brass Alloy And Its Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20100158748A1Improve dezincification corrosion resistance of alloyDecrease castabilityRare-earth elementImpurity
The present invention provides a lead-free free-cutting aluminum brass alloy and its manufacturing method. The alloy comprises: 57.0˜63.0 wt % Cu, 0.3˜0.7 wt % Al, 0.1˜0.5 wt % Bi, 0.2˜0.4 wt % Sn, 0.1˜0.5 wt % Si, 0.01˜0.15 wt % P, at least two elements selected from the group of 0.01-0.15 wt % Mg, 0.0016-0.0020 wt % B, and 0.001-0.05 wt % rare earth elements and the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities. The inventive alloy has excellent castability, weldability, cuttability and corrosion resistance. It is suitable for low pressure die casting, gravity casting, horizontal continuous casting, forging and extrusion. Its metal material cost is lower than bismuth brass. It is particularly applicable for components used in drinking water supply systems and other structural components. It is a new environmentally-friendly free-cutting aluminum brass alloy.
Owner:XIAMEN LOTA INT CO LTD
Substrate for lithium ion battery separators and lithium ion battery separator
ActiveUS20210288382A1Excellent in tensile strength and cuttabilityHigh adhesionLayered productsSecondary cellsLithium electrodeFiber
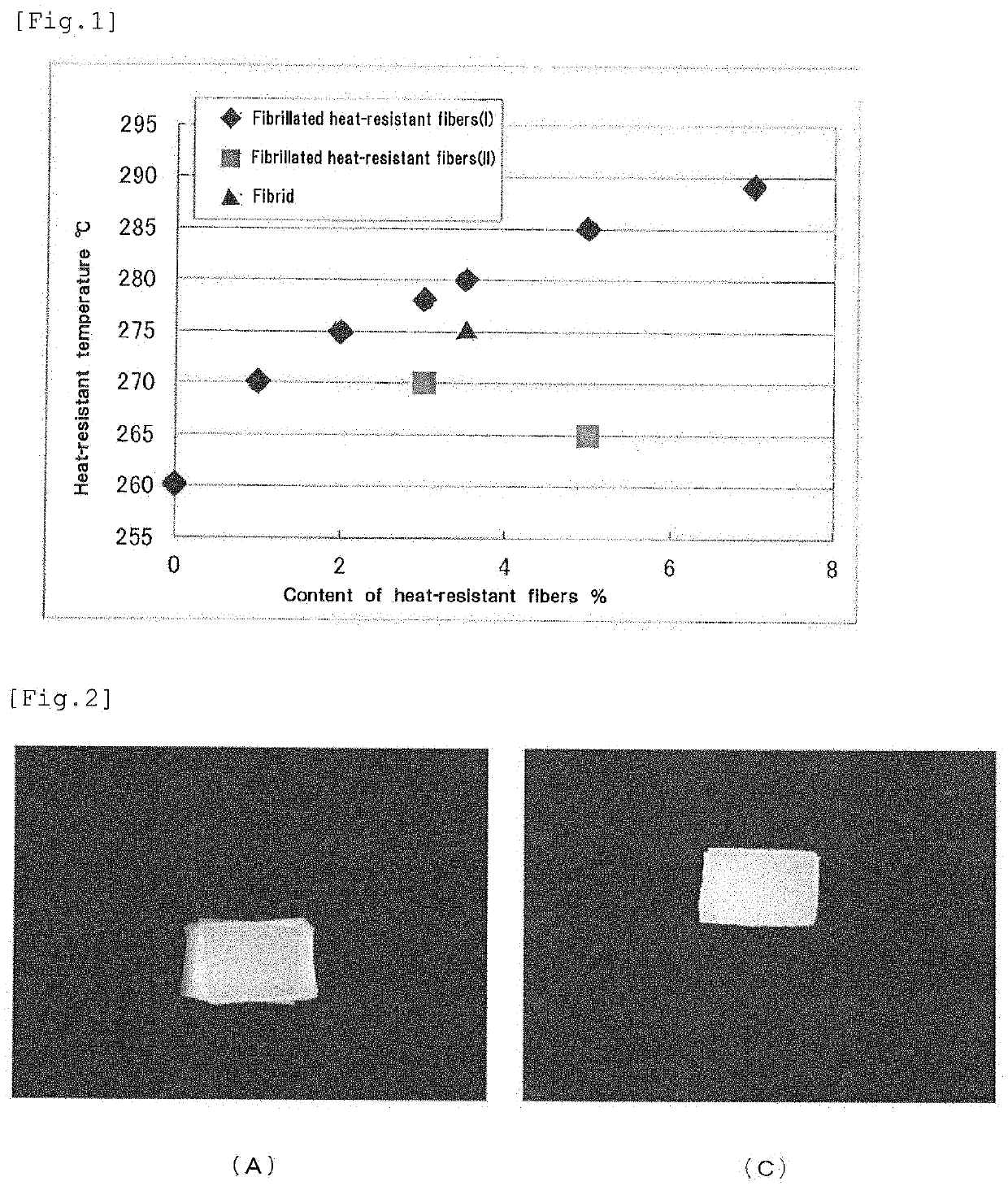
It is an object of the present invention to provide a substrate for lithium ion battery separators which has high adhesion to an inorganic particle layer, can be made thin and is excellent in tensile strength and cuttability and a lithium ion battery separator including the substrate for lithium ion battery separators. The substrate for lithium ion battery separators which contains heat-resistant fibers and synthetic resin short fibers contains fibrillated heat-resistant fibers having a modified freeness of not more than 300 ml as the heat-resistant fibers and has a content of the fibrillated heat-resistant fibers having a modified freeness of not more than 300 ml of not less than 1.0 mass % to less than 5.0 mass % based on the total of all the fiber components contained in the substrate. The modified freeness is a value measured in accordance with JIS P8121-2:2012 except that an 80-mesh wire net having a wire diameter of 0.14 mm and an opening of 0.18 mm is used as a screening plate and the concentration of a sample is 0.1%.
Owner:MITSUBISHI PAPER MILLS LTD
Structural component for automobile, two-wheeled vehicle or railcar excellent in impact-absorption property, shape fixability and flange cuttability, and method for producing the same
ActiveUS8129035B2Promote absorptionInferior in cuttabilityVehicle seatsPig casting plantsEngineeringHardness
The invention provides structural component for an automobile, two-wheeled vehicle or railcar excellent in impact-absorption property, shape fixability and flange cuttability, and method for producing the same, which structural component has a hat-like shape including vertical walls and flanges, wherein distal ends of the flanges contain 20 vol % or greater of austenite phase and have a cross-section hardness expressed as Vickers harness of 150˜350, and a center regions of the vertical walls have, in a common cross-section with the flanges, a content of deformation-induced martensite phase exceeding that of the distal ends of the flanges by 10 vol % or greater and a cross-section hardness expressed as Vickers hardness that exceeds that of the distal ends of the flanges by 50 or greater.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL & SUMIKIN STAINLESS STEEL CORP
Flexible foam with improved insulation properties
InactiveUS20180258245A1Stable and tolerant and robust manufacturing processHigh strengthElastomerSulfur
An expanded polymeric material which consists of at least 200 phr, preferably at least 300 phr, but less than 1000 phr, preferably less than 700 phr ingredients in total, comprising 100 phr of at least one polymer, of which at least one is a sulphur and / or metal oxide crosslinkable elastomer and at least 40 phr, preferably at least 55 phr of at least one polymeric flame retardant, preferably a brominated polymeric flame retardant.
Owner:ARMACELL ENTERPRISE GMBH & CO KG
Lead-free free-cutting magnesium brass alloy and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20090311127A1Excellent cuttabilityReduce consumptionFoundry mouldsFoundry coresCastabilityMechanical property
A lead-free free-cutting magnesium brass alloy comprises 56.0 to 64.0 wt % Cu, 0.6 to 2.5 wt % Mg, 0.15 to 0.4 wt % P and other elements 0.002 to 0.9 wt % which comprise at least two elements selected from the group consisting of Al, Si, Sb, Sn, Re, Ti and B and the balance being Zn and unavoidable impurities. The process for producing such alloy is also proposed. The invented alloy is excellent in cuttability, castability, hot and cold workability, corrosion resistance, mechanical properties and weldability and particularly applicable in spare parts, forging and castings which need cutting, grinding and electroplating process. The cost of necessary metal materials of the invented alloy is lower than lead-free free-cutting bismuth and antimony brass alloy and is equivalent to lead-contained brass alloy.
Owner:XU CHUANKAI +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com