Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
83 results about "Rate limiting enzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Rate-limiting enzyme. A rate-limiting enzyme is a key enzyme of which the activity determines the overall rate of a metabolic pathway. Previous definition.
Kit for Treatment of Cancer
InactiveUS20080287541A1Effective treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRate limiting enzymeAdduct
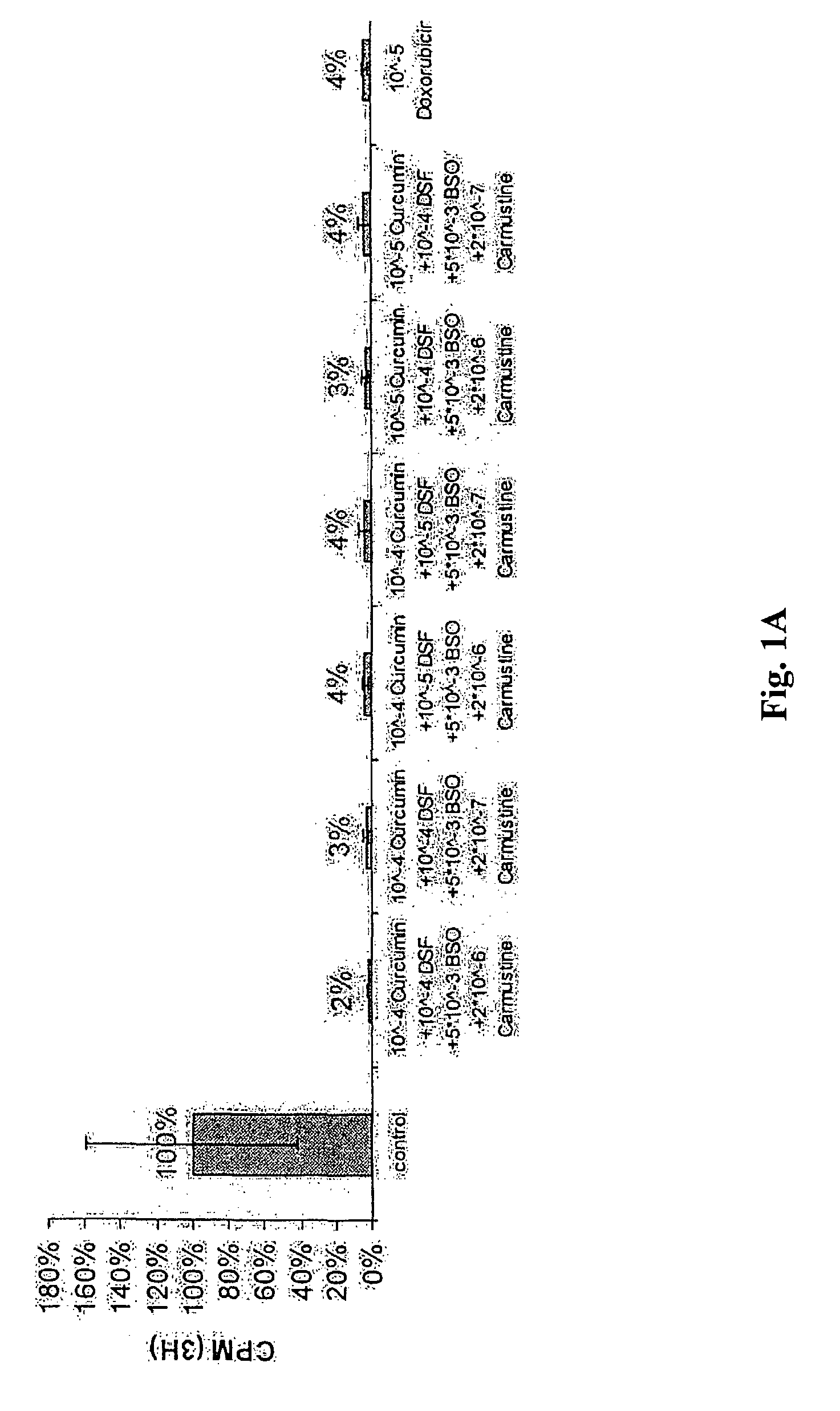
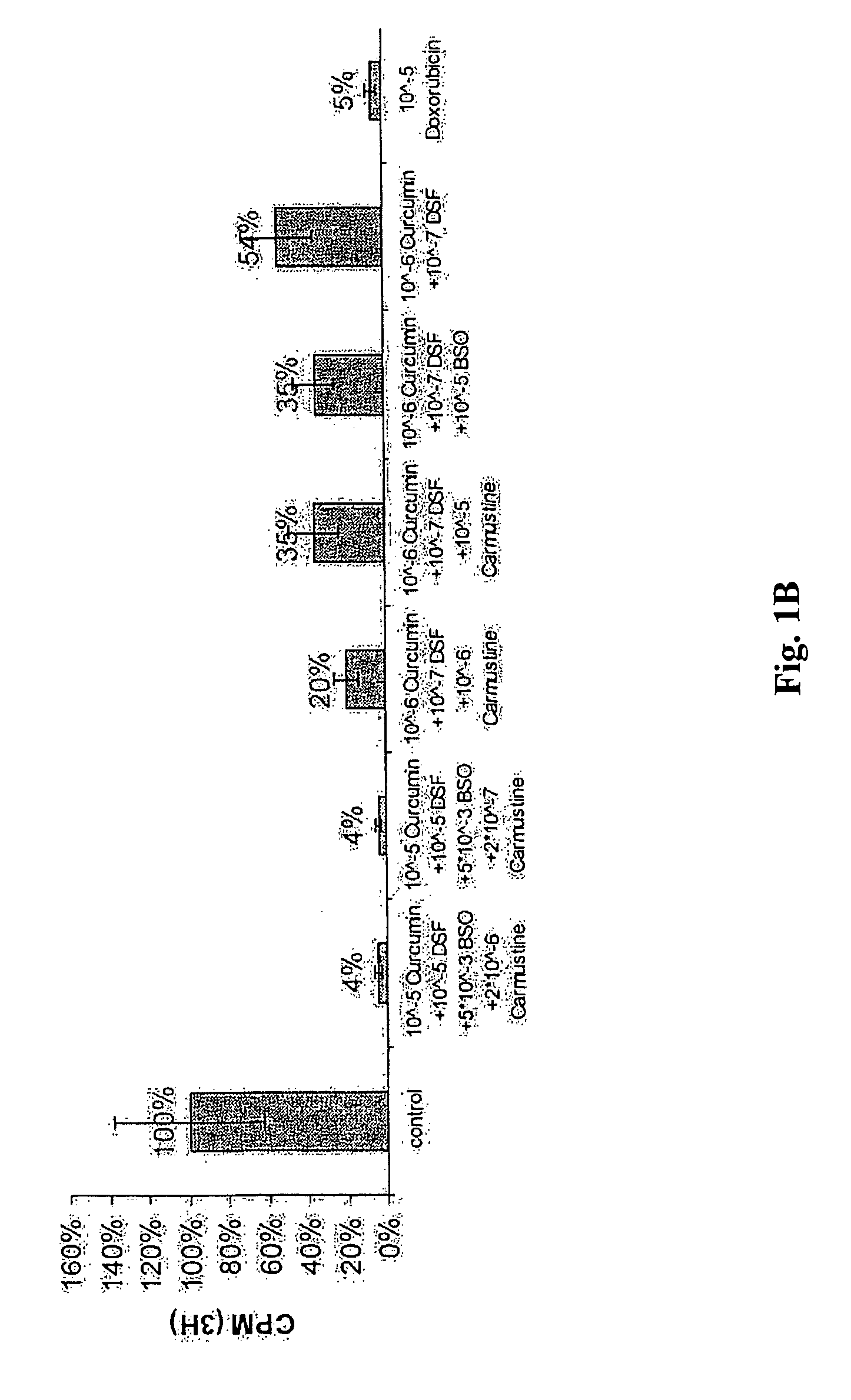
The present invention relates to a kit for the treatment of cancer comprising (a) a container for containing a first compound (i) or a precursor thereof, said first compound or precursor being a compound that oxidizes glutathione (GSH); (b) a container for containing a second compound (ii) or a precursor thereof, said second compound or precursor being a compound that forms an adduct or conjugate with GSH; (c) a container for containing a third compound (iii) or a precursor thereof, said third compound or precursor being a compound that inhibits the rate-limiting enzyme of GSH biosynthesis, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS); and (d) a container for containing a fourth compound (iv) or a precursor thereof, said fourth compound or precursor being a compound that inhibits the enzyme responsible for the conversion of GSSG to GSH, glutathione reductase (GR).
Owner:REDOXIA ISRAEL
Composition for whitening skin
ActiveCN103040692AGood ability to scavenge aerobic free radicalsReduce outputCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCrocus sativus flower extractCrocus
The invention discloses a composition for whitening skin, which comprises whitening functional components including persimmon leaf extractive, ginkgo leaf extractive, lotus extractive, crocus sativus flower extractivea pomegranate fruit extractive, dogwood fruit extractive, licoflavone, nicotinamide and ascorbyl glucoside. According to the invention, the whitening functional components can act before generating melanin, in the process of generating melanin, and after generating melanin; the purpose of whitening skin is achieved in multiple aspects of inhibiting gene expression of related rate-limiting enzyme synthesized by melanin, inhibiting enzymatic activity of the related rate-limiting enzyme synthesized by melanin, eliminating oxygen free radicals, reducing generated melanin, limiting melanin to transfer towards horn cells and the like; therefore, the composition for whitening skin disclosed by the invention is safe and effective.
Owner:BEIJING INDAL TECH RES INST
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and production method
PendingCN114480240AGrow fastImprove expression levelBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCell factory
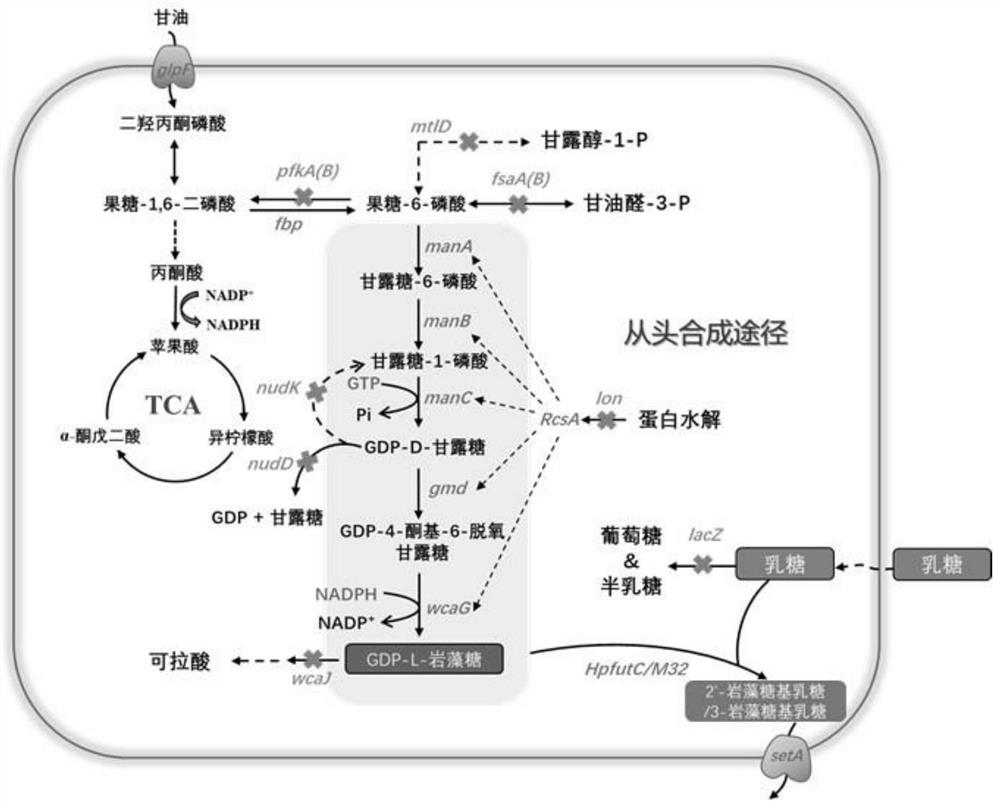
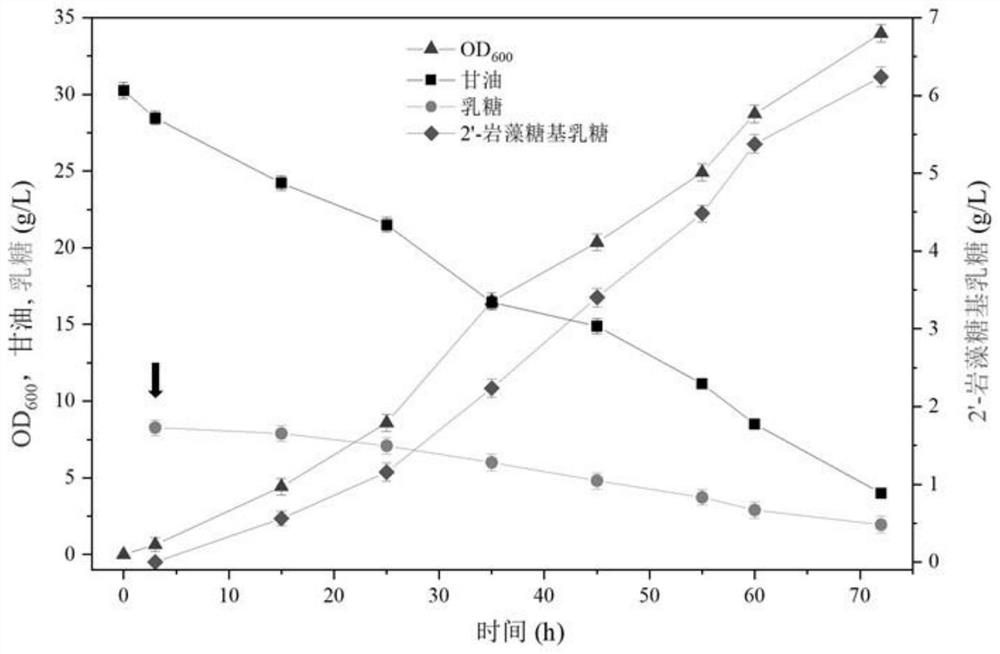
The invention relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing fucosyllactose and a production method of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to metabolic engineering and food fermentation technologies. According to the invention, a synthetic biological means is utilized, an escherichia coli cell factory of fucosyllactose is constructed based on a de novo synthetic route, bypass related genes lacZ, wcaJ, nudD, pfkA and lon in host cells are knocked out by adopting a CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing technology, and genes manB, manC, gmd and wcaG are assembled through a multi-plasmid expression system, so that the fucosyllactose is obtained. Constructing expression vectors with different copy numbers to increase the expression level of key genes; fucosyltransferase from different sources is screened, so that the activity of rate-limiting enzyme is improved. The constructed recombinant escherichia coli can be used for synthesizing 2 '-fucosyllactose and 3-fucosyllactose by utilizing glycerol, is stable in heredity and high in expression level, and has obvious industrial production potential.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Composition and method of preventing and treating redox diseases
ActiveUS8226992B1Avoid disruptionReduce and preventFood ingredient as antioxidantBiocideCafestolS glutathiolation
Methods and compositions useful for preventing the disruption of thiol (sulfur) signaling which affects degenerative / age related disease and other disease states related to thiol redox signaling, such as S-glutathiolation. The compositions are capable of increasing the DNA transcription of Gamma-Glutamyl-cysteine synthase which is the rate limiting enzyme for the production of the thiol regulating enzyme Glutathione. The acid-stable compositions disclosed herein contain esterfied and free form cafestol and kahweol, and may be formed using ground roasted or unroasted coffee beans. The beans in combination with water are exposed to cavatonic energy sonic or mechanical. C&K typically increase cholesterol and damage the liver. The compositions disclosed are absorbed before or after the distal portion of the small intestines, eliminating liver toxicity and increases in cholesterol. Additional materials may be added to the compositions, such as additional hydrophobic compounds hydrophilic compounds, and may be added to the film or embedded in the compositions by the cavitation process. The process is also adapted for use in all standard methods of brewing coffee, causing the coffee to possess the disclosed compositions.
Owner:OKERLIN III JOHN R
Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacteria and construction method and application thereof
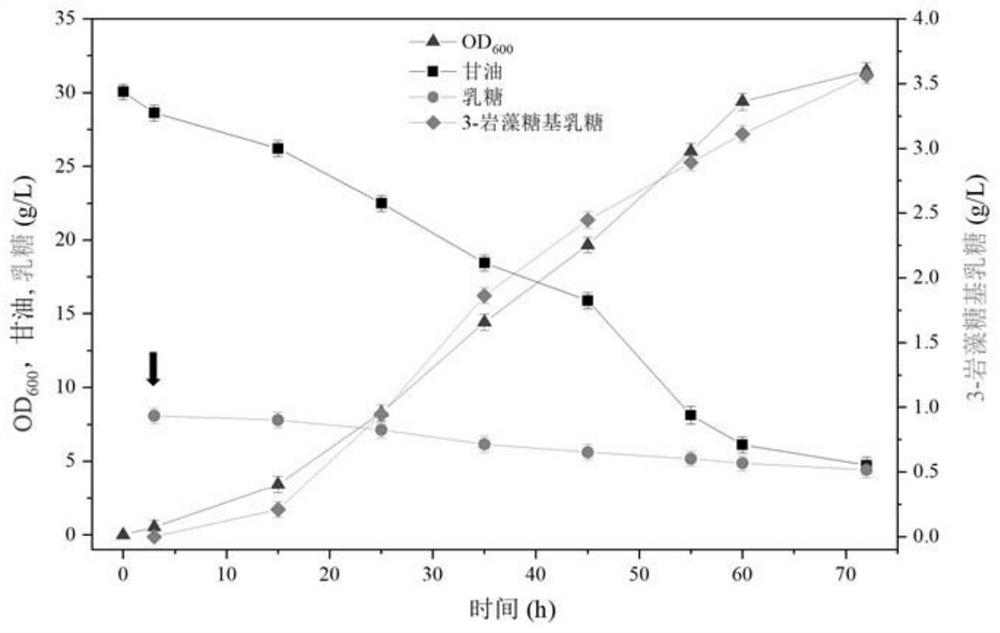
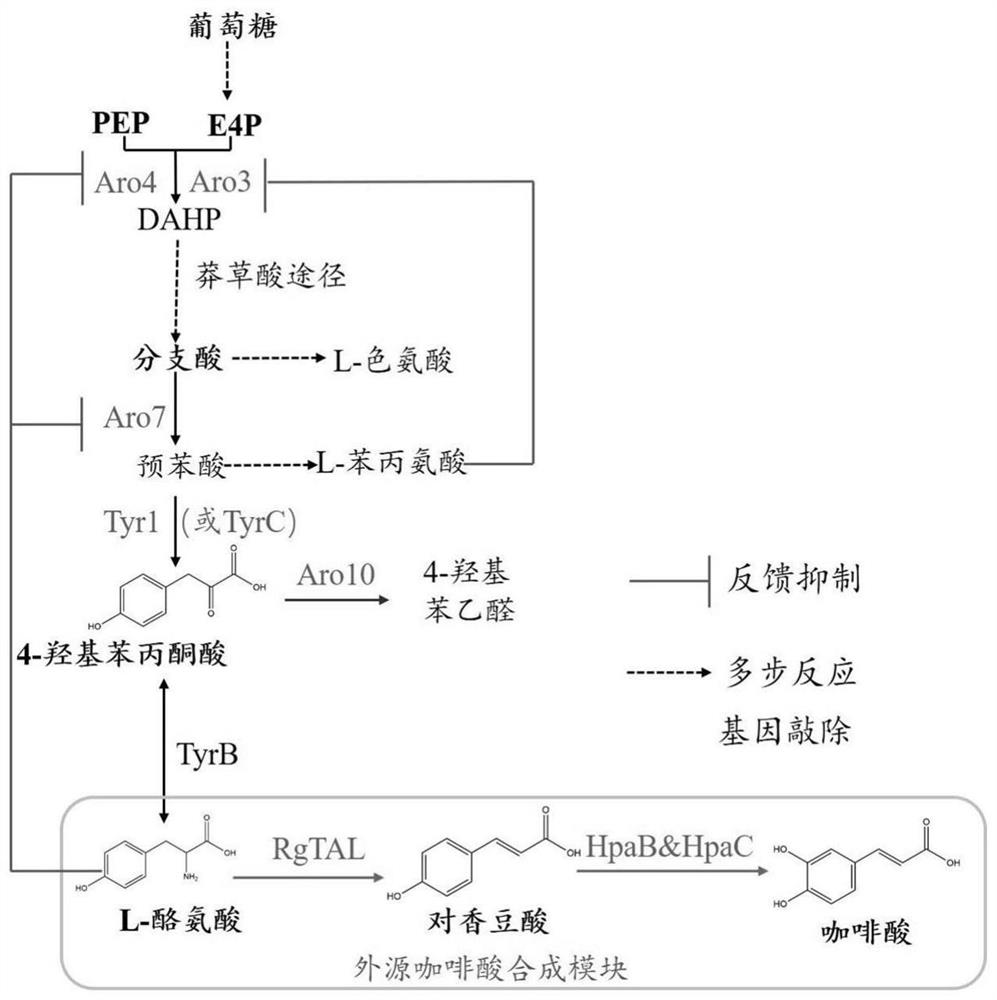
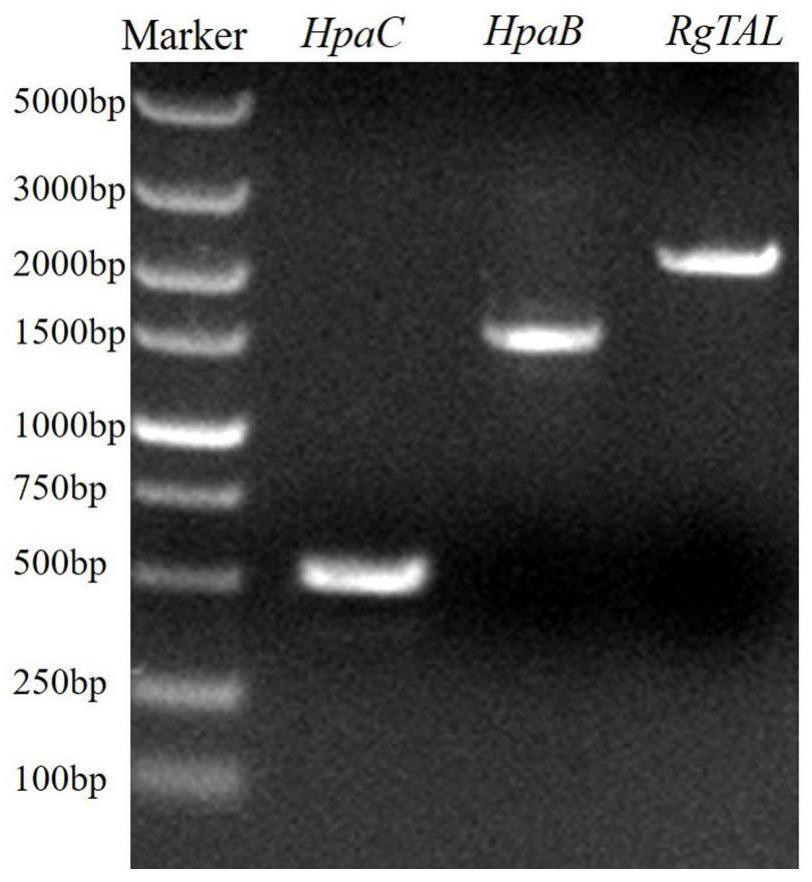
ActiveCN111849794AOne-step synthesisFull synthesisCarbon-nitrogen lyasesFungiCaffeic acidRate limiting enzyme
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium. According to the saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacterium, an RgTAL gene, an HpaB gene and an HpaC gene are integrated in a genome. The invention further discloses a construction method and application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant bacteria. The invention finally discloses a production method of caffeic acid. According to the invention, three exogenous genes required by caffeic acid synthesis are integrated into saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosomes; total synthesis from glucose to caffeic acid is achieved through knockout of competitive pathway genes, elimination of feedback inhibition steps and overexpression of rate-limiting enzymes, the shake flask yield reaches about 760 mg / L, the shake flaskyield is the highest level of the yeast yield reported at present, and a new method is provided for industrial production of caffeic acid.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Preparation of wild cactus polysaccharide extract and high-efficient serum cholesterol-reducing function
InactiveCN101474235AImprove developmentImprove utilizationMetabolism disorderPlant ingredientsCoenzyme A biosynthesisIn vivo
The invention relates to the preparation of a wild cactus polyoses extract and the highly effective function thereof for reducing serum cholesterase. The extract is a polyoses extracted from the natural wild cactus polyoses, and can reduce the total cholesterol content in the hypercholesterolemia and obviously improve the lipid metabolic disturbance by improving the activity of in vivo lipid metabolic key enzyme lecithin cholesterin acylase and reducing the activity of synthetical rate-limiting enzyme 3-hydroxy-3-methyl pentane diacid coenzyme A reductase of liver cholesterin; the invention has no obviouse adverse reaction and can be used for preparing medicines used for lowering the cholesterin.
Owner:ZHANJIANG NORMAL UNIV
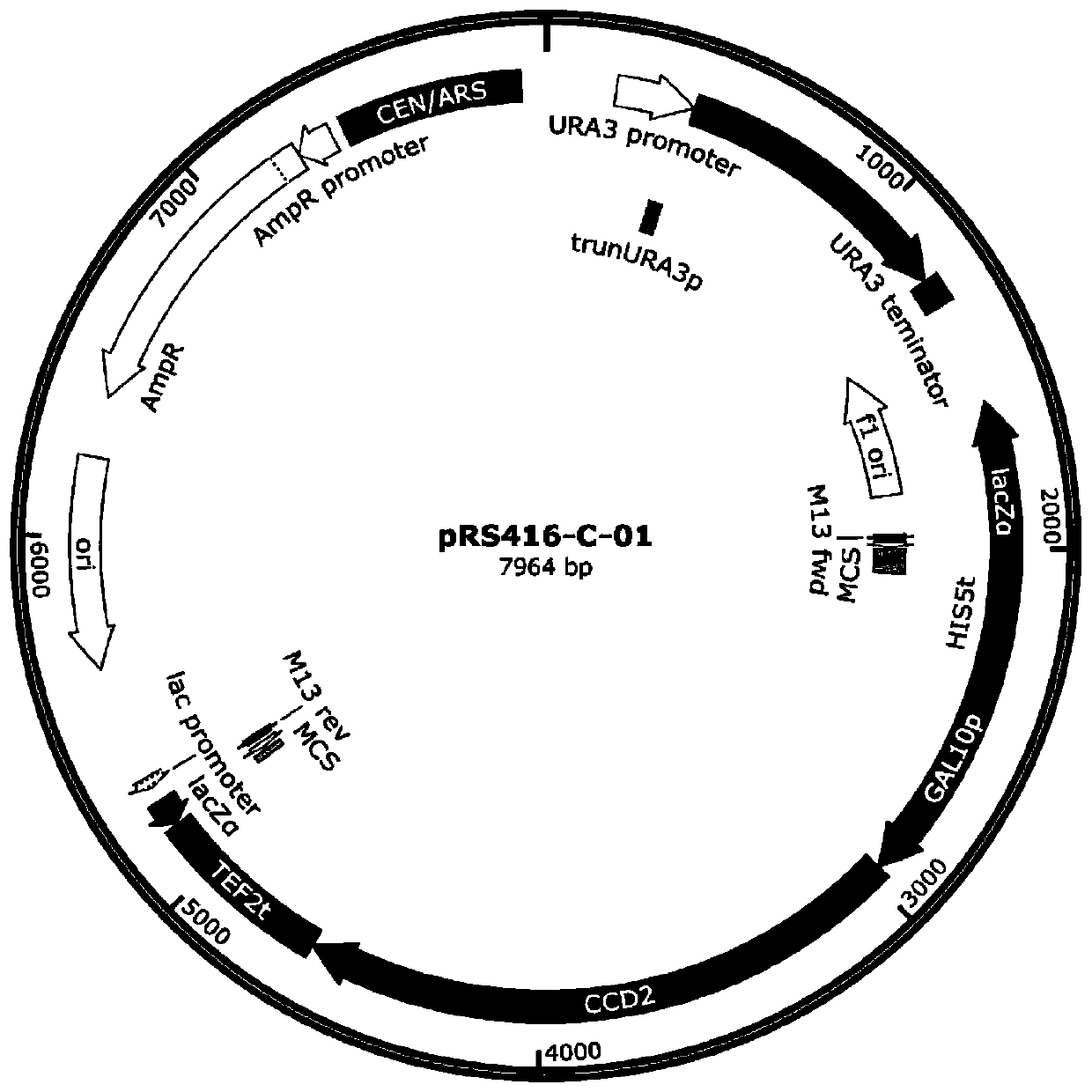
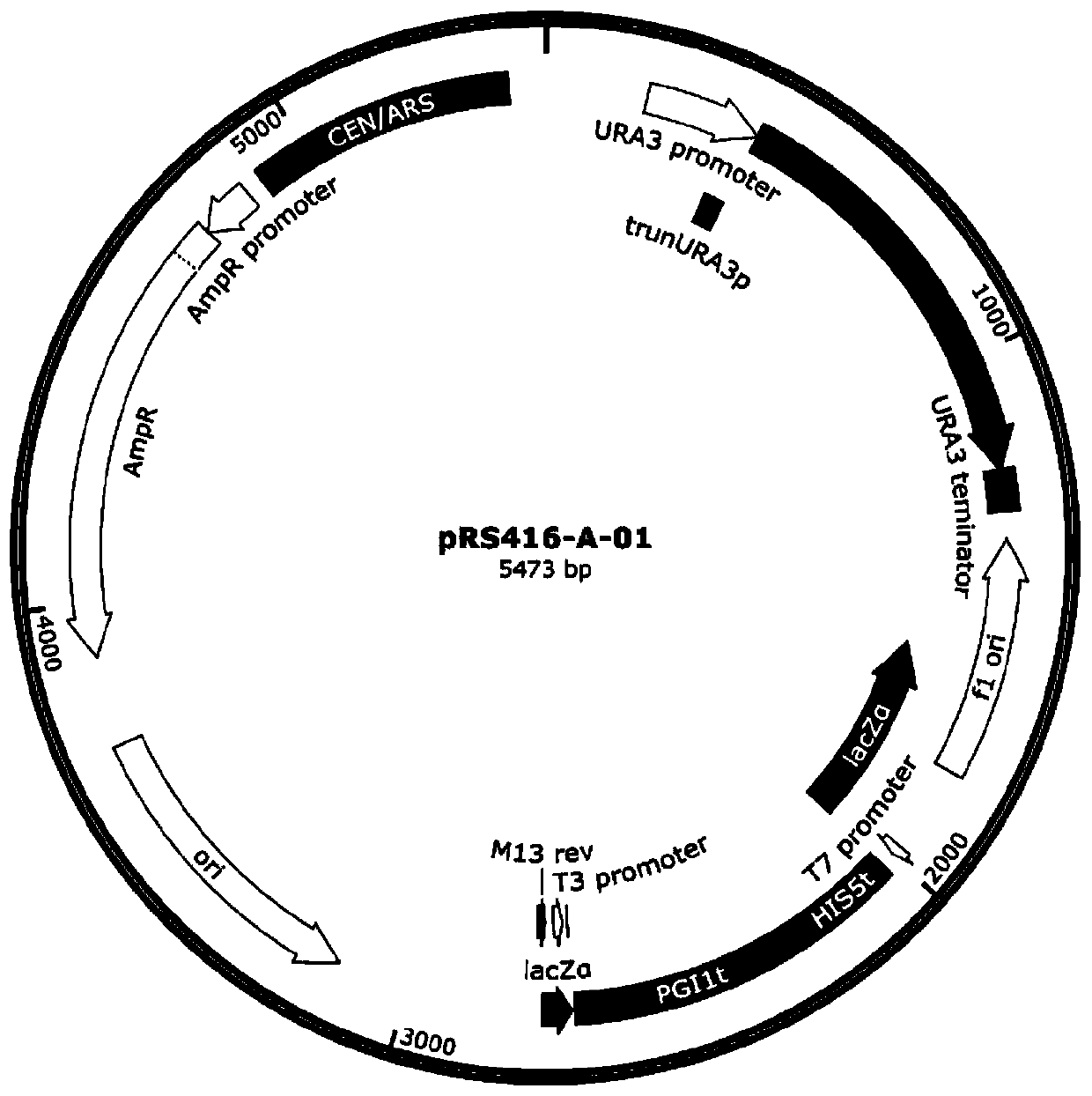
Gene engineering strain streptomyces tsukubaensis L20 and application thereof
ActiveCN105154382AHigh expressionIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention provides a gene engineering strain streptomyces tsukubaensis L20 and application thereof. The gene engineering strain streptomyces tsukubaensis L20 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center; the preservation date is August 19, 2015; the preservation number is CGMCC No. 11252. The gene engineering strain streptomyces tsukubaensis L20 is relatively stable in inheritable character and fermentation unit, the culture and fermentation conditions are suitable for industrialized production, and the fermentation unit reaches a high level; the gene engineering strain streptomyces tsukubaensis L20 is utilized for improving the expression amount of a rate-limiting enzyme in a tacrolimus biosynthetic pathway through gene engineering, and serves as the rate-limiting enzyme during gene engineering of the tacrolimus biosynthetic pathway to improve the yield of tacrolimus, so that the cost of an industrialized production process can be reduced, and the fermentation unit of tacrolimus can be improved by 30%.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
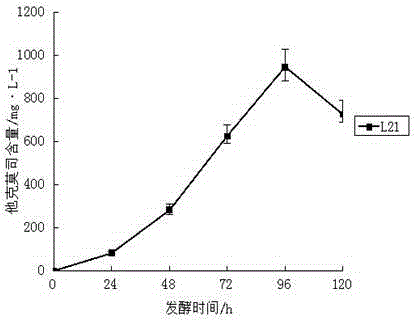
Genetic engineering strain Streptomyces tsukubaensis L21 and application thereof
ActiveCN105176904AHigh copy numberIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGenetic engineering
The invention provides genetic engineering strain Streptomyces tsukubaensis L21. The fungus preservation unit is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center), the preservation date is August 19, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No. 11253. According to the genetic engineering strain Streptomyces tsukubaensis L21, the strain genetic character and the fermentation unit are stable, culture and fermentation conditions are suitable for industrial production, and the fermentation unit is high. The copy number of specific controlling genes in the Tacrolimus creature biosynthetic pathway is increased through genetic engineering, and the genes improve rate-limiting enzyme in the Tacrolimus creature biosynthetic pathway so as to increase the Tacrolimus yield, reduce the cost in the industrial production process and improves the Tacrolimus fermentation unit to 945 mg / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
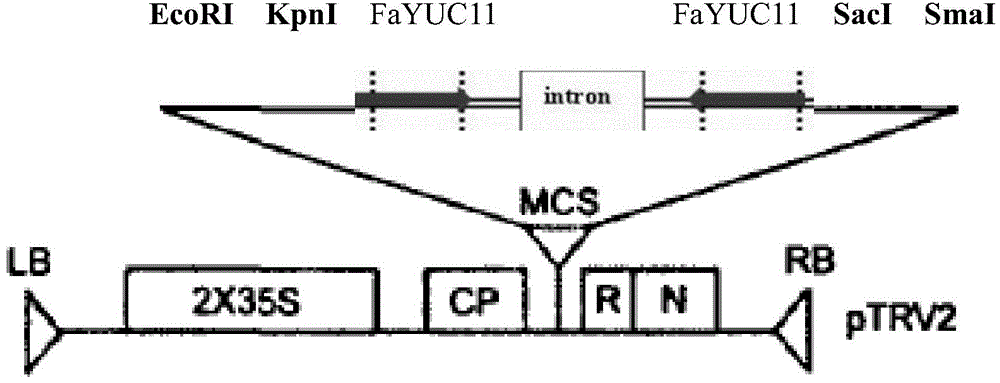
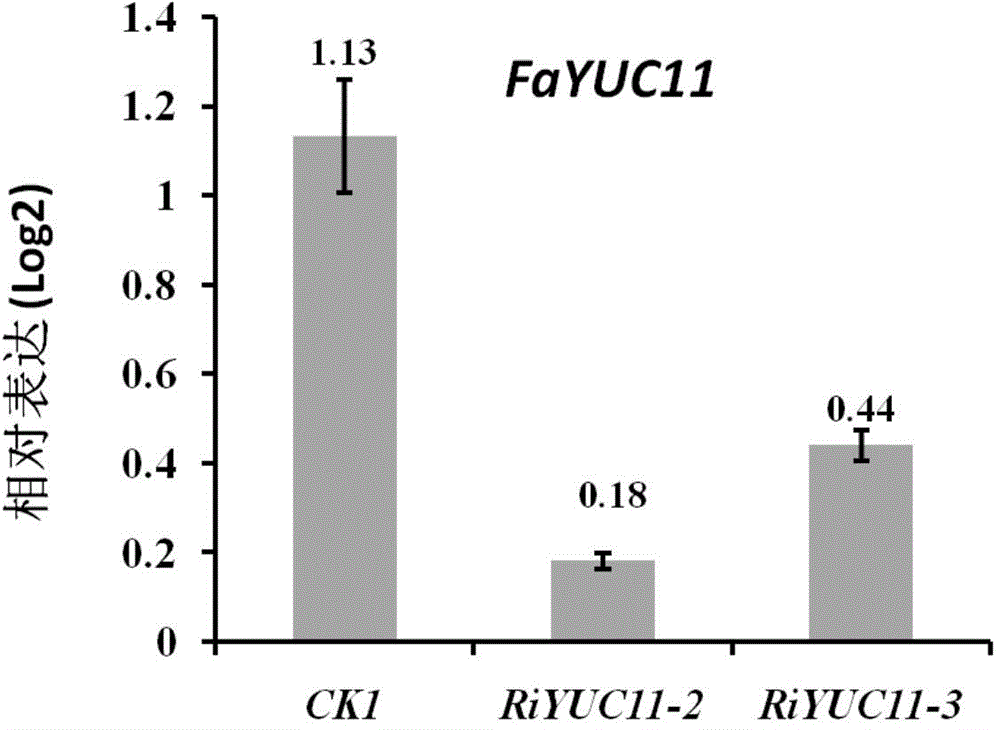
Strawberry auxin synthetic rate-limiting enzyme gene FaYUC11 and application
The invention relates to an agricultural biotechnology, discloses a strawberry auxin synthetic rate-limiting enzyme gene FaYUC11 and application in adjustment of fruit sizes, and provides a nucleotide sequence and a protein sequence of the gene. A method for using the FaYUC11 to adjust the fruit sizes comprises the following steps of: constructing a virus induction silent vector of the FaYUC11 gene; and transferring the silent vector in agrobacterium, infecting young green fruits of strawberries by using a micro-injection method, and establishing a transgenosis strawberry strain silenced by the virus induction FaYUC11 gene. The content of free auxin in achenes (seeds) can be reduced through gene silencing; the growth rate of fruits in vertical and horizontal diameters is reduced; simultaneously, the hardness of fruits and the content of soluble solids are influenced; and thus, the gene disclosed by the invention has good application prospect in the aspect of adjusting and controlling the fruit sizes of strawberries, and has important significance on development of functional SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) molecular markers and breeding of high-quality large strawberries.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
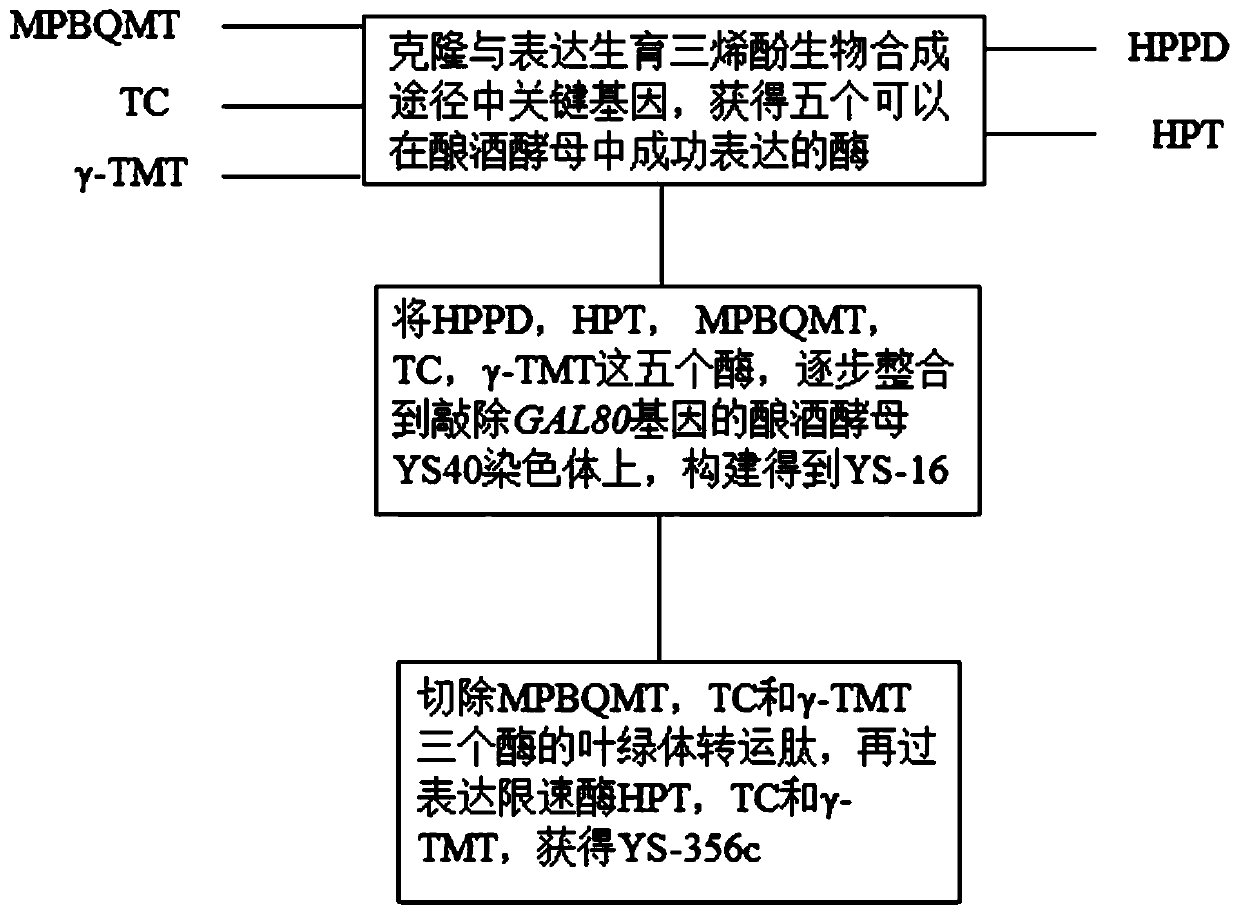
Enzymes expressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae, genetically engineered bacterium highly producing alpha- and gamma-tocotrienols as well as construction method of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN110423732AAchieve productionIncrease productionFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyGamma-Tocotrienol
The invention discloses key enzymes expressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae, genetically engineered bacterium highly producing alpha- and gamma-tocotrienols as well as a construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium. Five enzymes capable of being expressed in the saccharomyces cerevisiae including HPPD, HPT, MPBQMT, TC and gamma-TMT respectively, are obtained through gene cloning and codon optimization; the five enzymes are integrated in saccharomyces cerevisiae genomes step by step, and the genetically engineered saccharomycete strain highly producing alpha- and gamma-tocotrienolsis constructed by further excising chloroplast transit peptides and over-expression rate-limiting enzyme, named YS-356c and has the collection number of CCTCC NO:M2019572. The tocotrienol yield reaches 2.09 mg / g dry cell weight. The engineered bacterium can be cultured by fermentation, alpha- and gamma-tocotrienols can be obtained directly from the bacterium, and the engineered bacterium has goodmarket prospects and application values.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Cancer-targeting recombinant oncolytic gene-adenovirus and construction method and application thereof
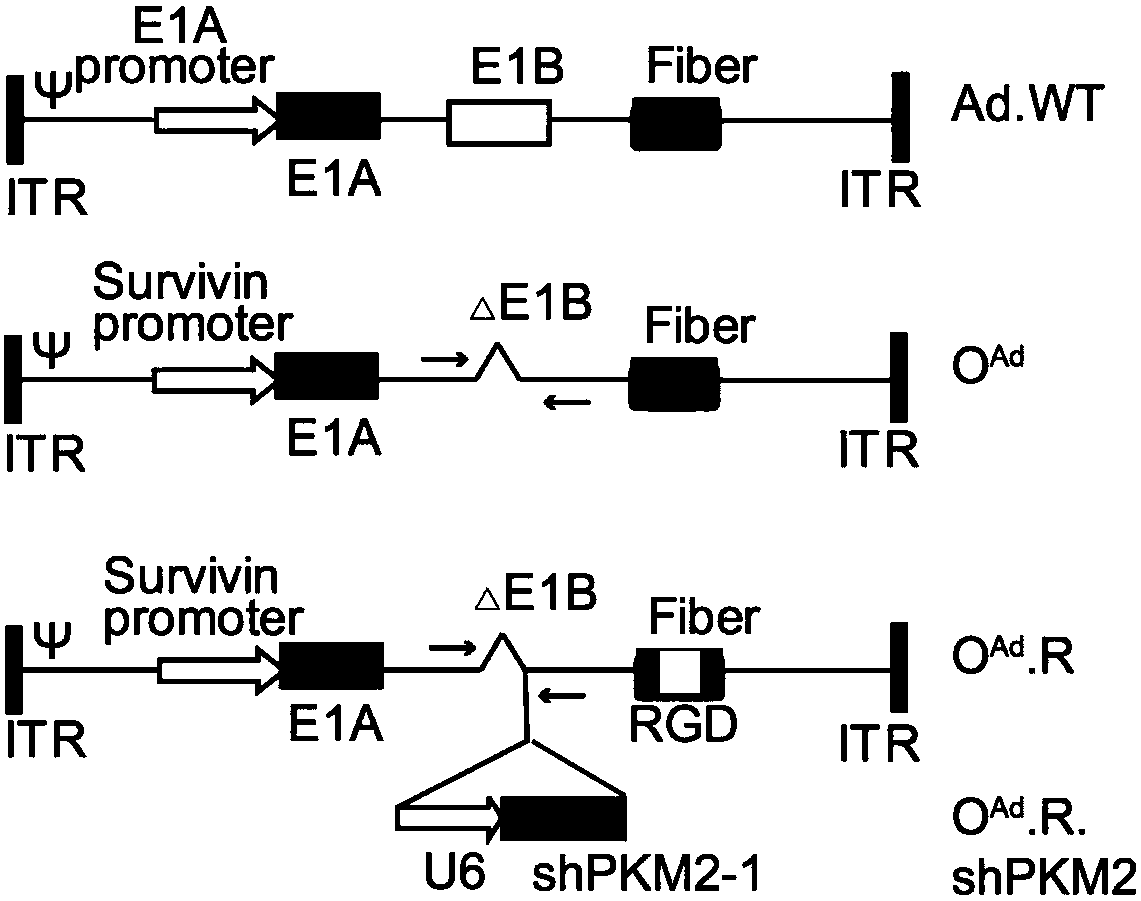
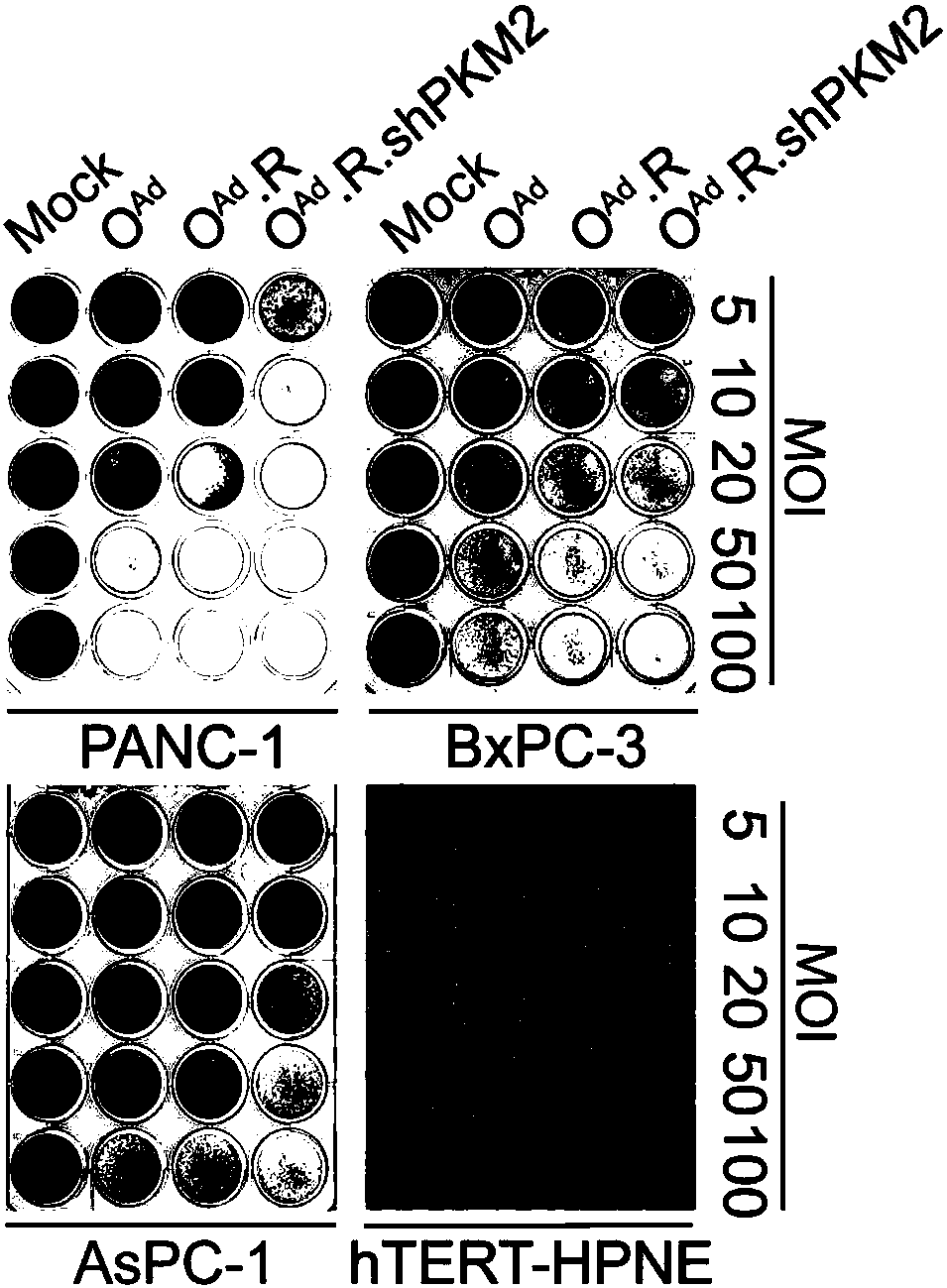
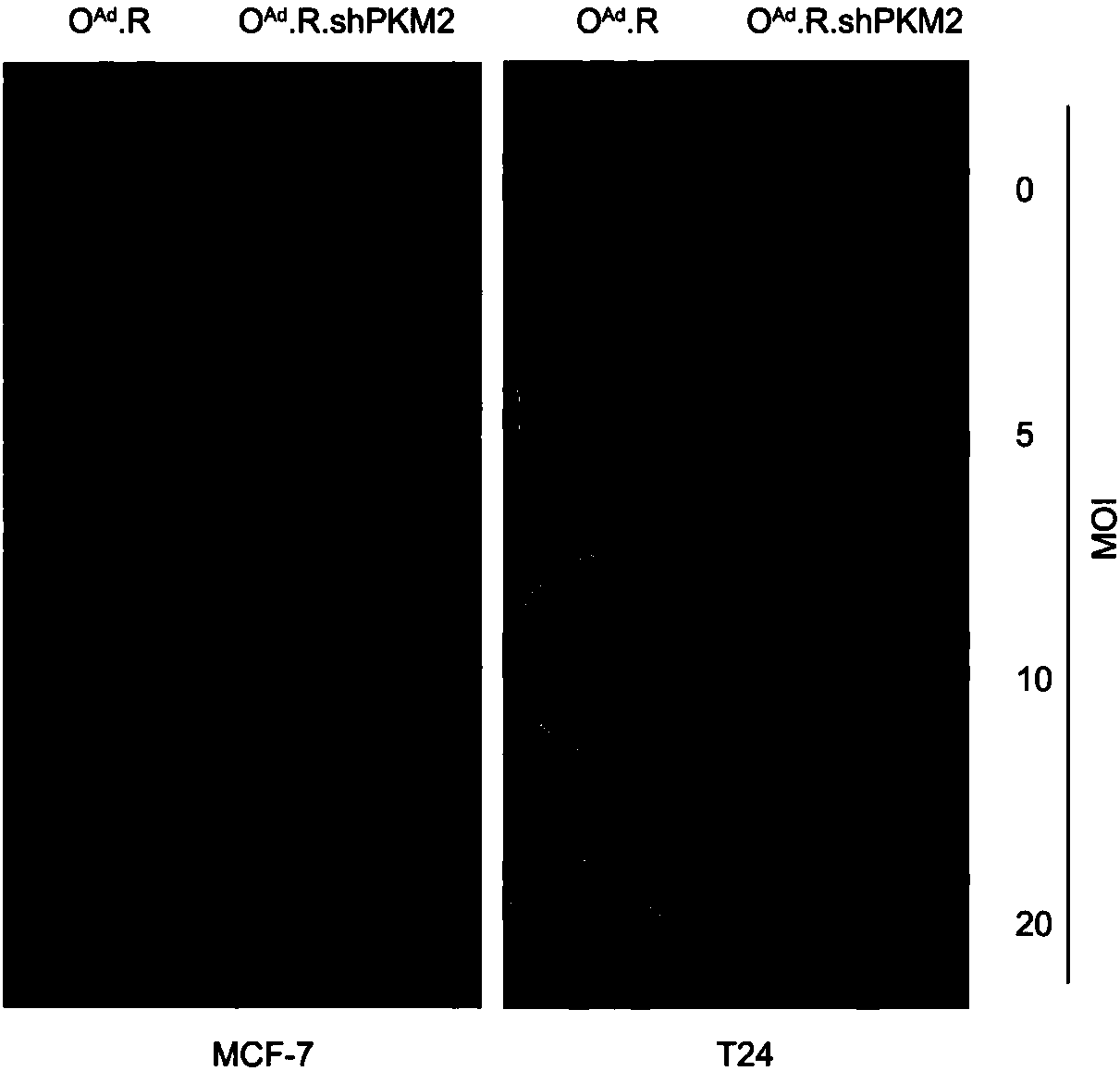
ActiveCN108342366AAchieve successful interferenceLow toxicityMicroorganism based processesFermentationCancer targetingRate limiting enzyme
The present invention discloses a group of cancer-targeting recombinant oncolytic gene-adenovirus, comprising OncoAd, OncoAd. RGD, and OncoAd. RGD. shPKM2. The invention also discloses a constructionmethod and application of the recombinant oncolytic gene-adenovirus OncoAd. RGD. shPKM2 in preparing of a medicine for treating pancreatic cancer. The recombinant oncolytic gene-adenovirus OncoAd. RGD. shPKM2 can achieves silencing of expression of rate-limiting enzyme gene PKM2 by means of replication of an adenoviral vector, and can play an effective pancreatic cancer killing effect.
Owner:SHANGHAI YUANSONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10
The present invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria and application thereof in production of coenzyme Q10. The genetically engineered bacteria comprises coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria and desired genes transferred into the coenzyme Q10 producing bacteria, and the desired genes are a demethylnaphthoquinone methyltransferase gene, a 2-octo isoprene-3-methyl-6-methoxy-1,4-hydroquinone hydroxylase gene and a 3-demethyl ubiquinone-93-methyl transferase gene. Rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF in a coenzyme Q10 synthetic route are transferred into rhodobacter sphaeroides, and by in-series over-expression of the three rate-limiting enzyme genes UbiE, UbiG and UbiF, coenzyme Q10 synthesizing capability of the rate-limiting enzyme genes can be strengthened; and compared with the rhodobacter sphaeroides with no desired gene being transformed, by use of the genetically engineered bacteria for coenzyme Q10 producing, the yield of the coenzyme Q10 is increased by more than 20%.
Owner:SHANGYU NHU BIOCHEM IND
Increased Bacterial CoA and Acetyl-CoA Pools
InactiveUS20090186398A1Enhanced intracellular levelImprove throughputBacteriaTransferasesBacteroidesBiotechnology
Methods of increasing the cellular pool of A-CoA and thus driving the metabolic pathways in the direction of A-CoA containing metabolites by overexpressing rate limiting enzymes in A-CoA synthesis. Methods of increasing intracellular levels of CoA and A-CoA through genetic engineering of bacterial strains in conjunction with supplementation with precursor molecules.
Owner:RICE UNIV
3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene RKHMGR and application thereof
ActiveCN110747206AHigh expressionIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses a 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene RKHMGR and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, an amino acid sequence encoded by thegene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, the gene is a key enzyme gene of carotenoid synthesis in YM25235 of Rhodosporidium Kratochvilovae, is the first rate limiting enzyme in an MVA pathway, and can regulate the YM25235 of the Rhodosporidium Kratochvilovae to generate the carotenoid. According to the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene RKHMGR and the application thereof, microorganismis transformed by means of genetic engineering, the yield of the carotenoid in the microorganism is improved, and a foundation is laid for large-scale commercial production of the carotenoid.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
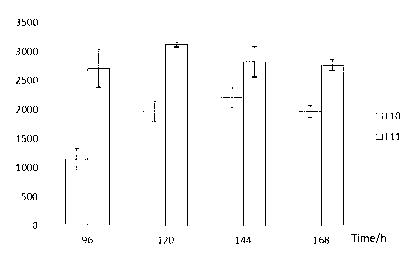
Gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis L11 construction and culture method
InactiveCN103131662ARaise the fermentation unitStable genetic traitsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyStreptomyces chattanoogensis
The invention provides a gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis. The preservation registration number of the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis is CGMCC No.7182, the nucleotide sequence of the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis is represented by SEQ ID NO.1, and the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis is obtained through the genetic construction of a rate-limiting enzyme in the biosynthetic way of natamycin. Compared with gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis L10, the gene engineering strain Streptomyces chattanoogensis L11 has the advantages of more stable hereditary characters, improvement of the natamycin fermentation unit to 3.12g / L from 2.21g / L, shortening of the natamycin fermentation period to 120h from 144h, improvement of the natamycin output by 40%, shortening the fermentation period by 24h, and reduction of the industrialized production process, and can be applied to the generation of natamycin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Increased bacterial CoA and acetyl-CoA pools
Methods of increasing the cellular pool of A-CoA and thus driving the metabolic pathways in the direction of A-CoA containing metabolites by overexpressing rate limiting enzymes in A-CoA synthesis. Methods of increasing intracellular levels of CoA and A-CoA through genetic engineering of bacterial strains in conjunction with supplementation with precursor molecules.
Owner:RICE UNIV
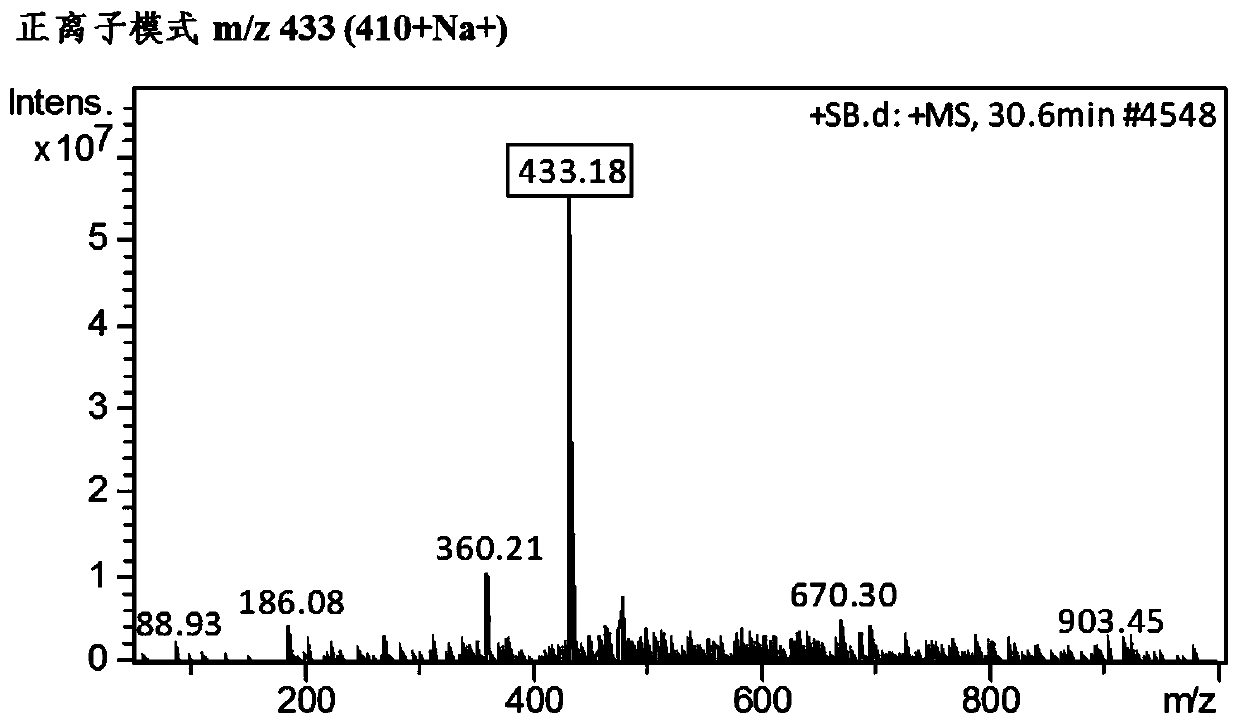
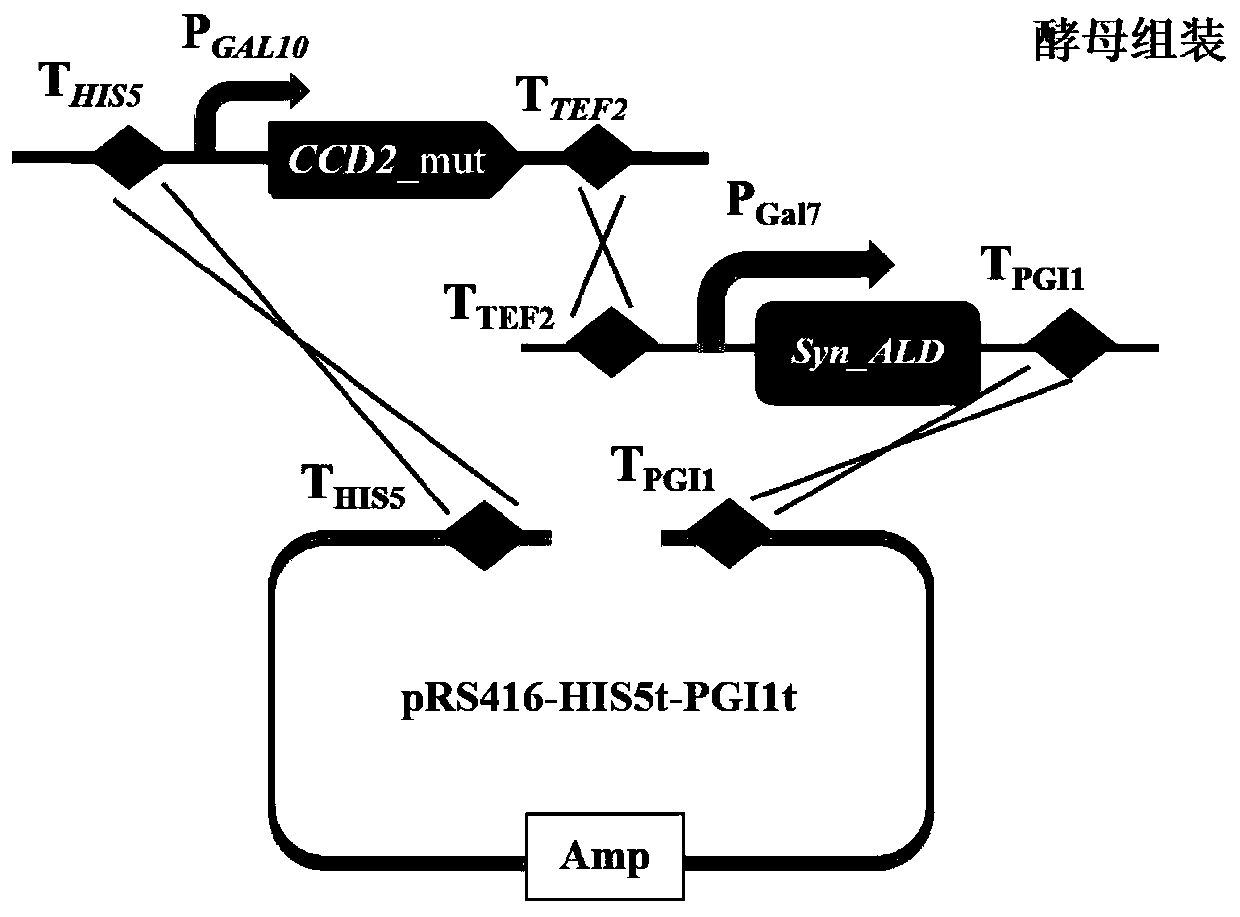
Saffron crocus sourced CCD2 mutant, coding sequence and application thereof, as well as recombinant yeast strain for producing crocetin
ActiveCN109810958AShort synthesis pathHigh catalytic efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyZeaxanthin synthesis
The invention relates to the technical field of genetic engineering, and discloses a saffron crocus sourced CCD2 mutant, a coding sequence and application thereof, as well as a recombinant yeast strain for producing crocetin. The CCD2 mutant is provided with one or two or above of V120F, Y190K / A, R192V / F, E211A, E212A, T290V, K320A and S323F / A / T locus mutations. A rate-limiting enzyme CCD2 in thesynthesis route of the crocetin is transformed, the crocetin is directly synthesized from beta-carotene by widening the substrate spectrum of the CCD2, and the existing synthesis route of the crocetinis simplified and reconstructed, so that the problem that the total yield of multiple reactions is generally low is solved; and meanwhile, the efficiency of the CCD2 catalyzing an original substratezeaxanthin to synthesize the crocetin is improved, and the yeast strain of the high-yield crocetin is further obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
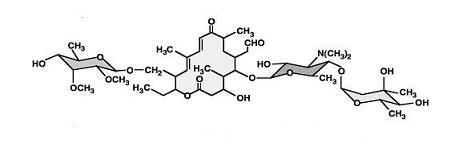
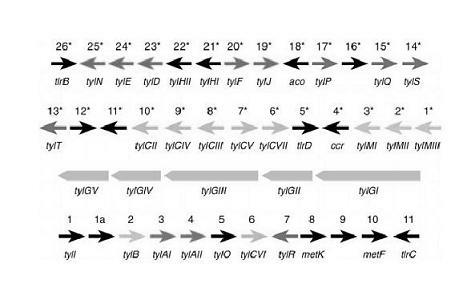
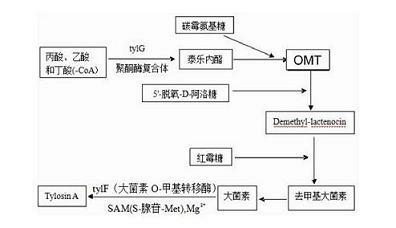
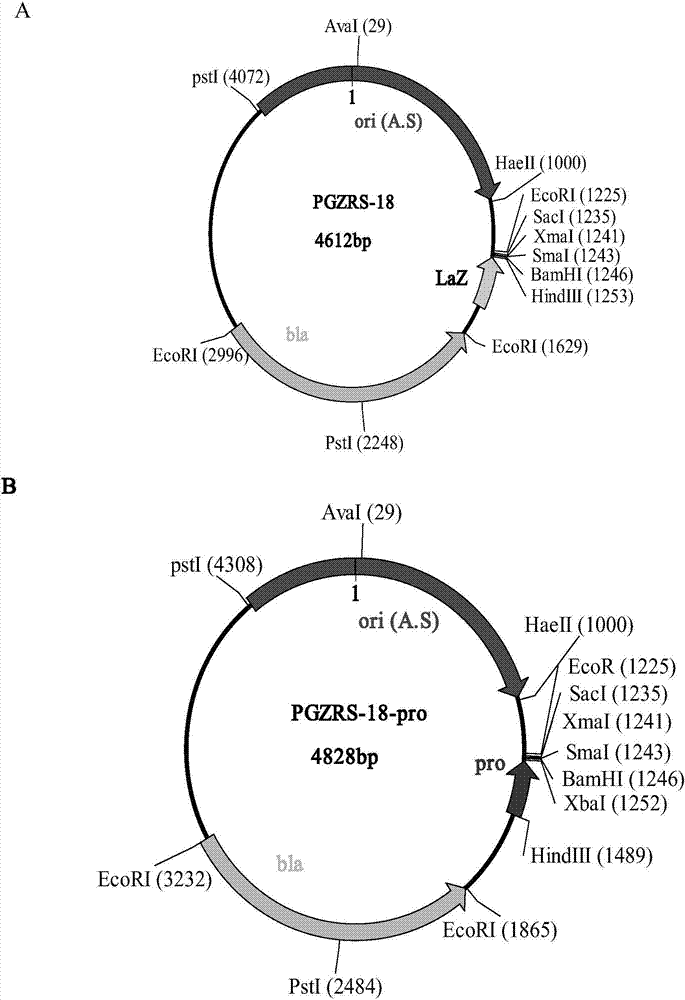
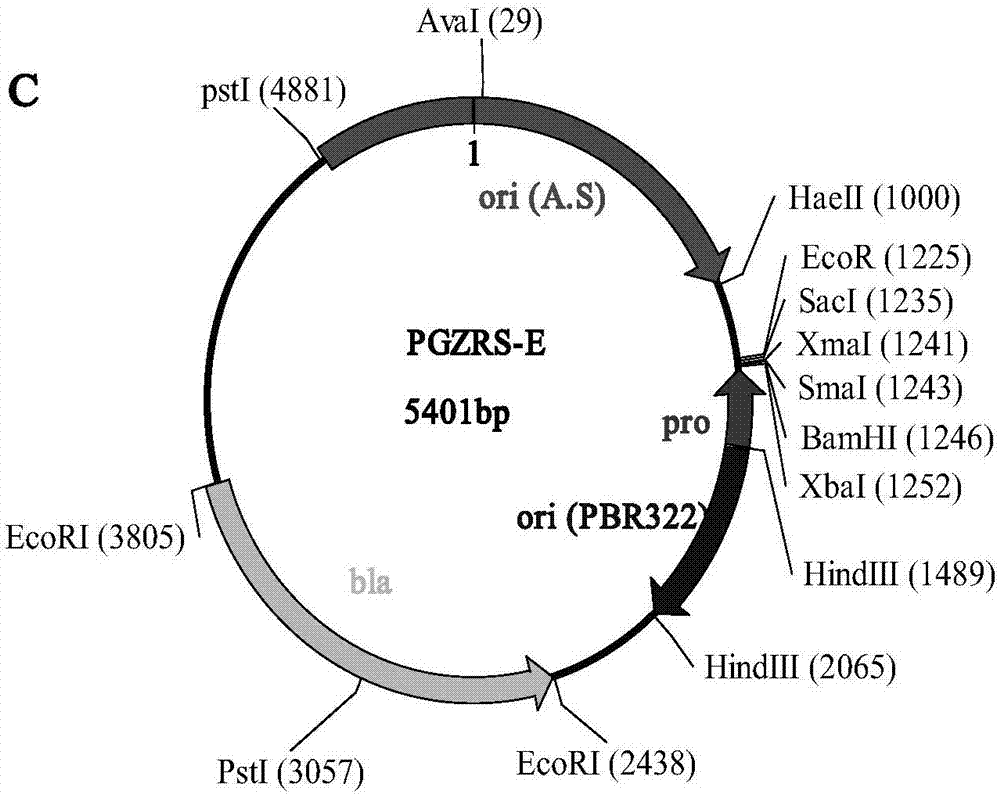
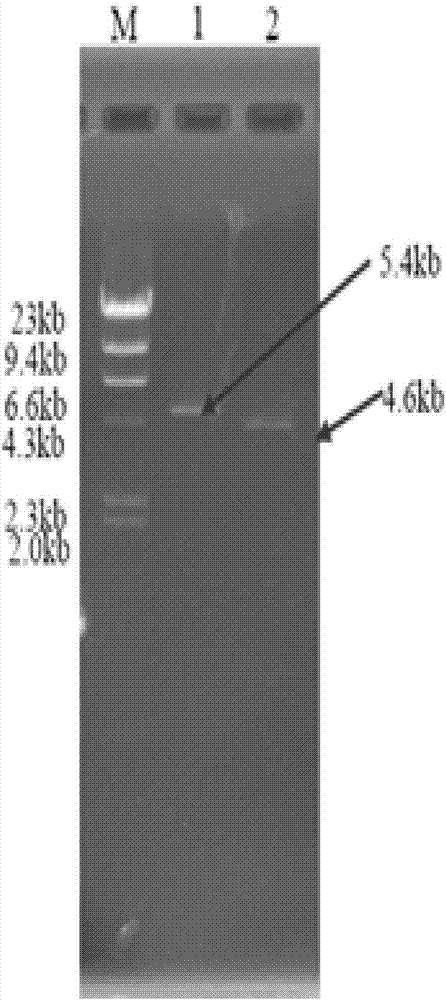
Tylosin gene engineering strain and application thereof
InactiveCN102690775AIncrease productionIncrease contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShuttle vectorEnzyme Gene
The invention relates to a tylosin gene engineering strain. The construction method for the tylosin gene engineering strain comprises the following steps: cloning tylosin through polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to synthesize crucial rate-limiting enzyme gene TylF and Vitreoscilla hemoglobin VHb gene, constructing a recombinant plasmid by using an E. coli-streptomyces shuttle vector, importing the recombinant plasmid into Escherichia coli ET12567 / pUZ8002, performing conjugal transfer culture on the Escherichia coli ET12567 / pUZ8002 and streptomyces fradiae spores, converting streptomyces, screening a converter through apramycin resistance, further confirming the converter by using PCR, and finally obtaining the gene engineering strain. The tylosin gene engineering strain can be directly used in the industrial production of tylosin; and compared with the tylosin gene engineering strain used in the conventional industrial production, the tylosin gene engineering strain has the advantages that the yield of the tylosin can be obviously improved to be 17,000-18,000u / ml and the content of a component A in the tylosin is effectively improved to be 94-95 percent.
Owner:宁夏泰瑞制药股份有限公司
Actinobacillus succinogenes PZ improving yield of succinic acid, and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106995794AIncrease productionHigh activityBacteriaTransferasesMicrobiologyRate limiting enzyme
The invention provides an actinobacillus succinogenes PZ improving yield of succinic acid, and a construction method thereof. The construction method comprises the steps of constructing an expression carrier, constructing recombinant plasmid and constructing the actinobacillus succinogenes PZ. The actinobacillus succinogenes starting strain is connected in series with and expressed excessively by gene pepck of a key rate-limiting enzyme, PEPCK, for generating succinic acid by using the actinobacillus succinogenes, and gene zwf of G6PDH improving the restoring force level in a body, so as to acquire the actinobacillus succinogenes PZ. The actinobacillus succinogenes PZ can improve the yield of succinic acid, and has the potential of industrial production application.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
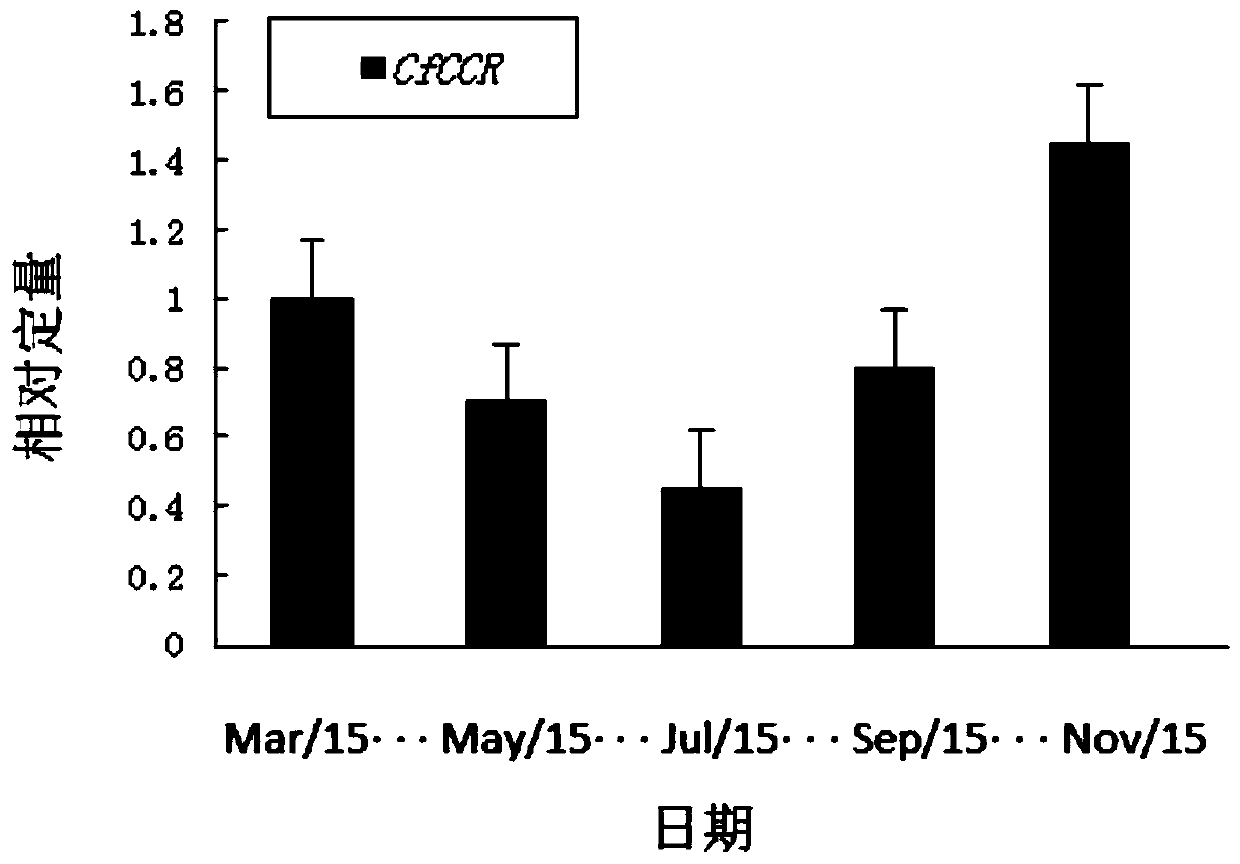
Cryptomeria fortunei CfCCR gene and application thereof
ActiveCN111139253AImprove stress resistanceImprove qualityBacteriaOxidoreductasesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a cryptomeria fortunei CfCCR gene and an application thereof, belonging to the technical fields of plant molecular biology and gene engineering. The cryptomeria fortunei ligninsynthesis regulation CfCCR gene provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1, and the amino acid sequence of an expression protein of the cryptomeria fortunei lignin synthesis regulation CfCCR gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO. 2. The CfCCR gene is a key rate-limiting enzyme of a lignin synthesis specific pathway, regulates the expression of related genes for synthesizing lignin in plants through encoding protein, and plays an important role in biosynthesis and stress resistance of lignin. The tobacco transformed with the CfCCR gene is increased in lignin expression and developed in cell walls. Thus, the thickness of xylem cell walls in plant stems like cryptomeria fortunei can be changed by expressing the CfCCR gene, so the wood density is increased, and the wood quality and plant stress resistance are improved.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Metabonomics technology-based persistent organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism research method
InactiveCN107643390ARich varietyGood quantitative effectComponent separationBiological testingStatistical analysisCytotoxicity
The present invention discloses a metabonomics technology-based persistent organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism research method. According to the method, HepG2 cells are exposed to organicpollutants, the intracellular and extracellular culture liquid metabolites can be effectively analyzed by using UHPLC / Q-Trap MS, the influence of the organic pollutants on the cell metabolism pathwaycan be intuitively reflected by combining statistical analysis and metabolic pathway analysis, and by using a biological detection method, the activity of rate-limiting enzyme related to the metabolicpathway is further rapidly analyzed. According to the present invention, the organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism is clarified according to the intracellular metabolite content change andthe activity change of the rate-limiting enzyme in the metabolic pathway, and the pollutant toxicity action mechanism evaluation method is constructed based on molecular biology, and the metabonomicstechnology-based persistent organic pollutant cytotoxicity action mechanism research method has advantages of easy operation, rapid detection, high sensitivity, strong selectivity, good repeatability,comprehensive information acquisition and the like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineered yeast for fermentation production of alpha-santalene and application of engineered yeast
PendingCN114507613AEfficient productionImprove metabolic fluxFungiTransferasesBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a yeast engineering bacterium for fermentation production of alpha-santalene and application of the yeast engineering bacterium, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Yeast is used as an original strain, and the yeast engineering bacterium for fermentation production of alpha-santalene is obtained through gene introduction construction. The engineered yeast strain can efficiently produce alpha-santalene, the shake flask fermentation yield of the engineered yeast strain is nearly 3.0 g / L, and the fermentation yield of a 1L fermentation tank can reach 15 g / L. The metabolic flux in the alpha-santalene biosynthesis pathway is improved through high expression of key rate-limiting enzyme in the metabolic pathway, enhancement of precursor supply and a multi-copy strategy, the alpha-santalene is efficiently generated by using the pichia pastoris, and the method has the characteristics of short period, environmental protection and resource saving. The engineered yeast strain for producing alpha-santalene at high yield has a wide application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV HANGZHOU GLOBAL SCI & TECH INNOVATION CENT
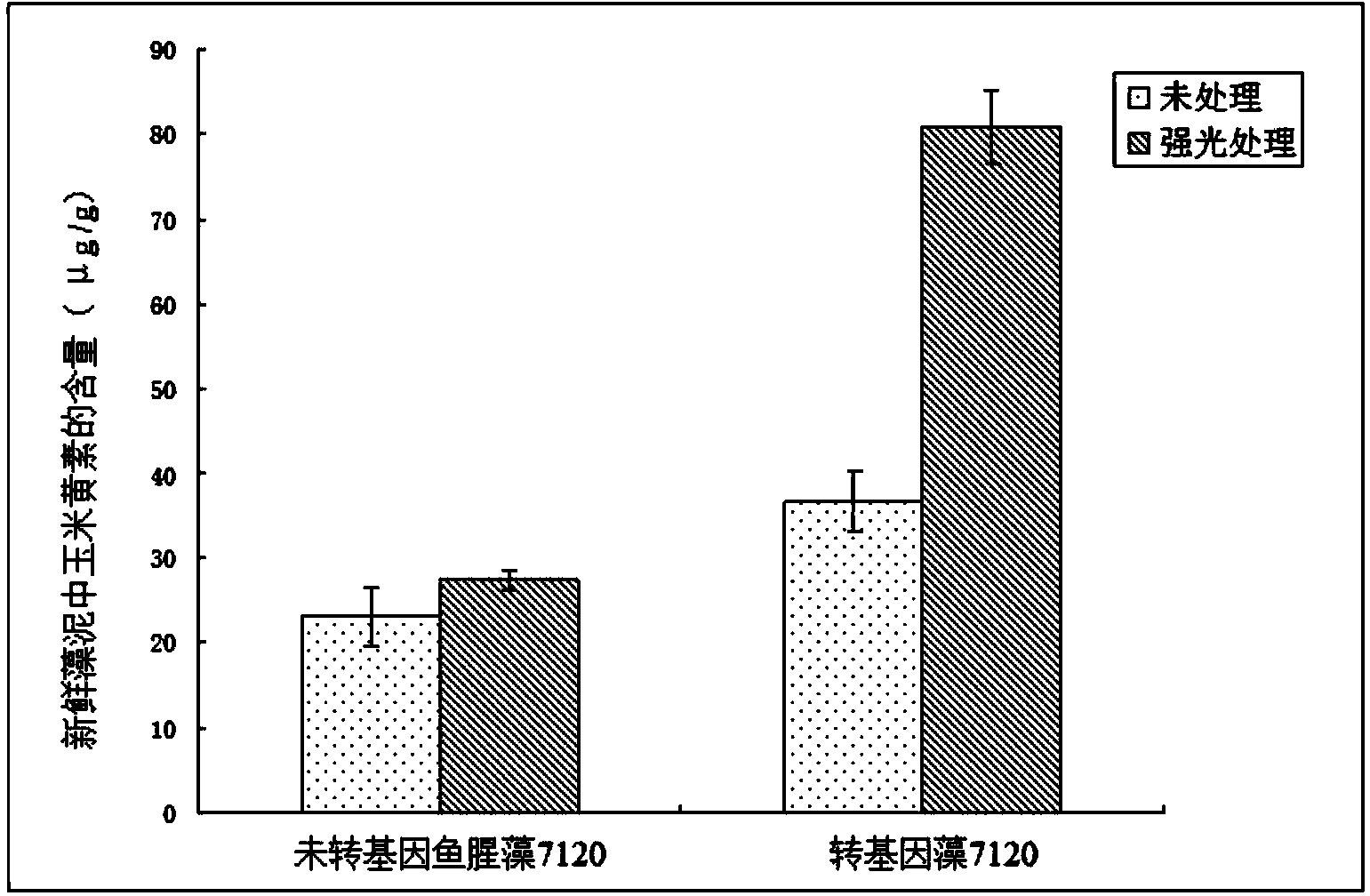
Method for increasing content of zeaxanthin in anabaena
InactiveCN103882048AIncrease contentBacteriaMicroorganism based processesZeaxanthin synthesisEnzyme Gene
The invention discloses a method for increasing content of zeaxanthin in anabaena. The method is characterized by comprising the following specific steps: cloning critical rate-limiting enzyme gene beta-carotene hydroxylase gene for synthesis of zeaxanthin from dunaliella salina teodoresce, constructing the gene into a shuttle expression vector pRL25C, and transferred into anabaena by a triparetal conjugation method, genetically modified anabaena is obtained by resistance screening, and after 16000Lx high-light treatment, the method has the advantage that the content of zeaxanthin in genetically modified anabaena is increased greatly compared with wild type anabaena, and can be increased by 3.8 times to the greatest extent.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
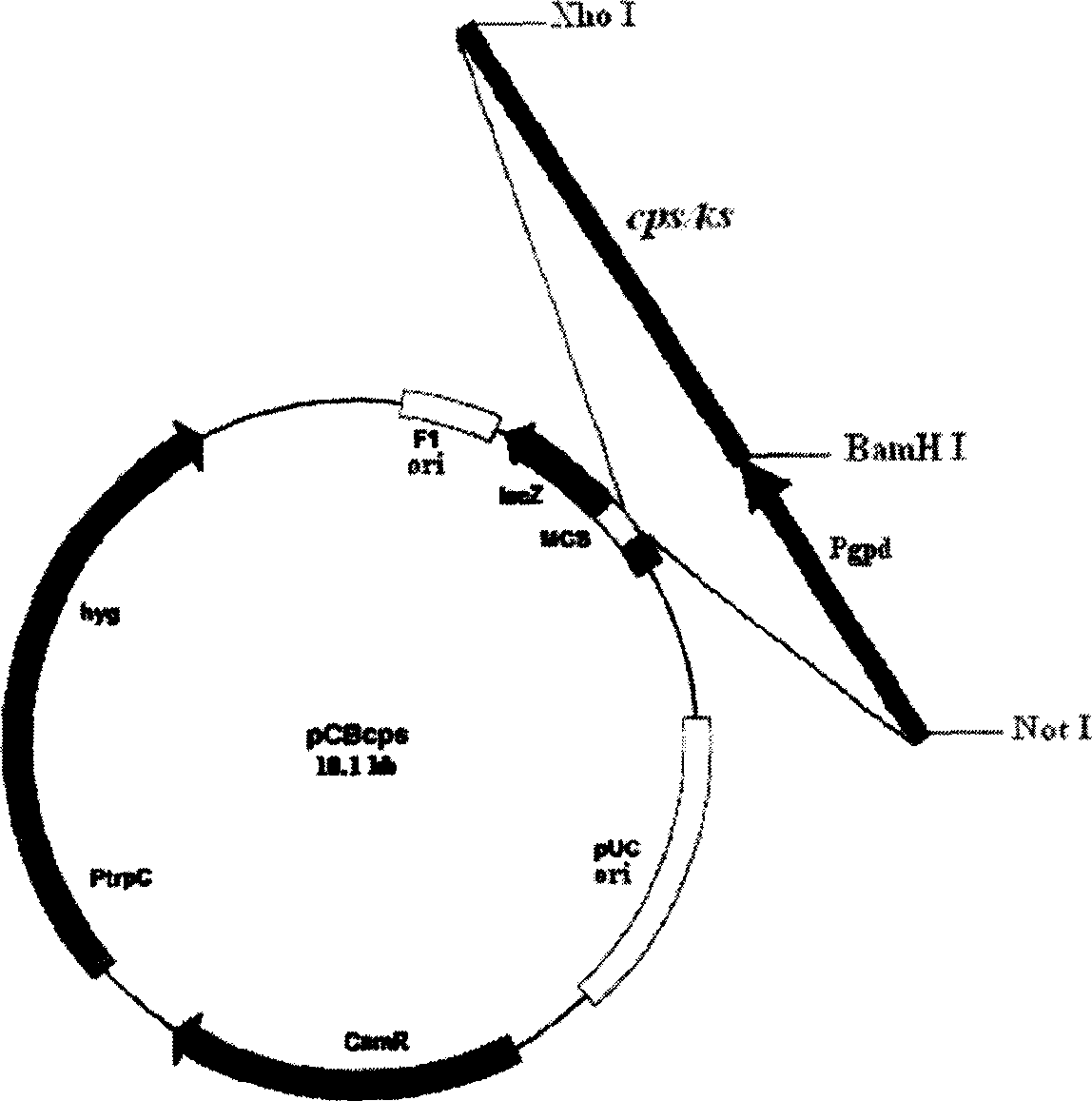
Gibberella gene engineering bacterium and its preparation and application
InactiveCN1654630AStrong ability to synthesize gibberellinsBreeding goals are clearFungiFermentationBiotechnologyGene vector
The present invention provides one kind of genetically engineered bakanae fungus. The genetically engineered bakanae fungus is prepared through the process of: PCR amplification of rate-limiting enzyme gene cps / ks synthesized with gibberellin and powerful promoter Pgpd or PtrpC, cloning them to corresponding sites of the target plasmid capable of expressing in mycelial fungus to obtain super-expressing cps / ks gene vector with driving powerful promoter, transforming the super-expressing cps / ks gene vector into bakanae fungus to obtain the genetically engineered bakanae fungus. The present invention improves bakanae fungus by means of genetic engineering technology, and has determined fungus culturing target and high efficiency. The obtained engineered bakanae fungus has powerful gibberellin synthesizing ability, 40 % raised from the initial bakanae fungus strain.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for breeding high-yield enramycin strain
InactiveCN107630028AOvercome blindnessOvercome workloadMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesHigh resistanceOpen reading frame
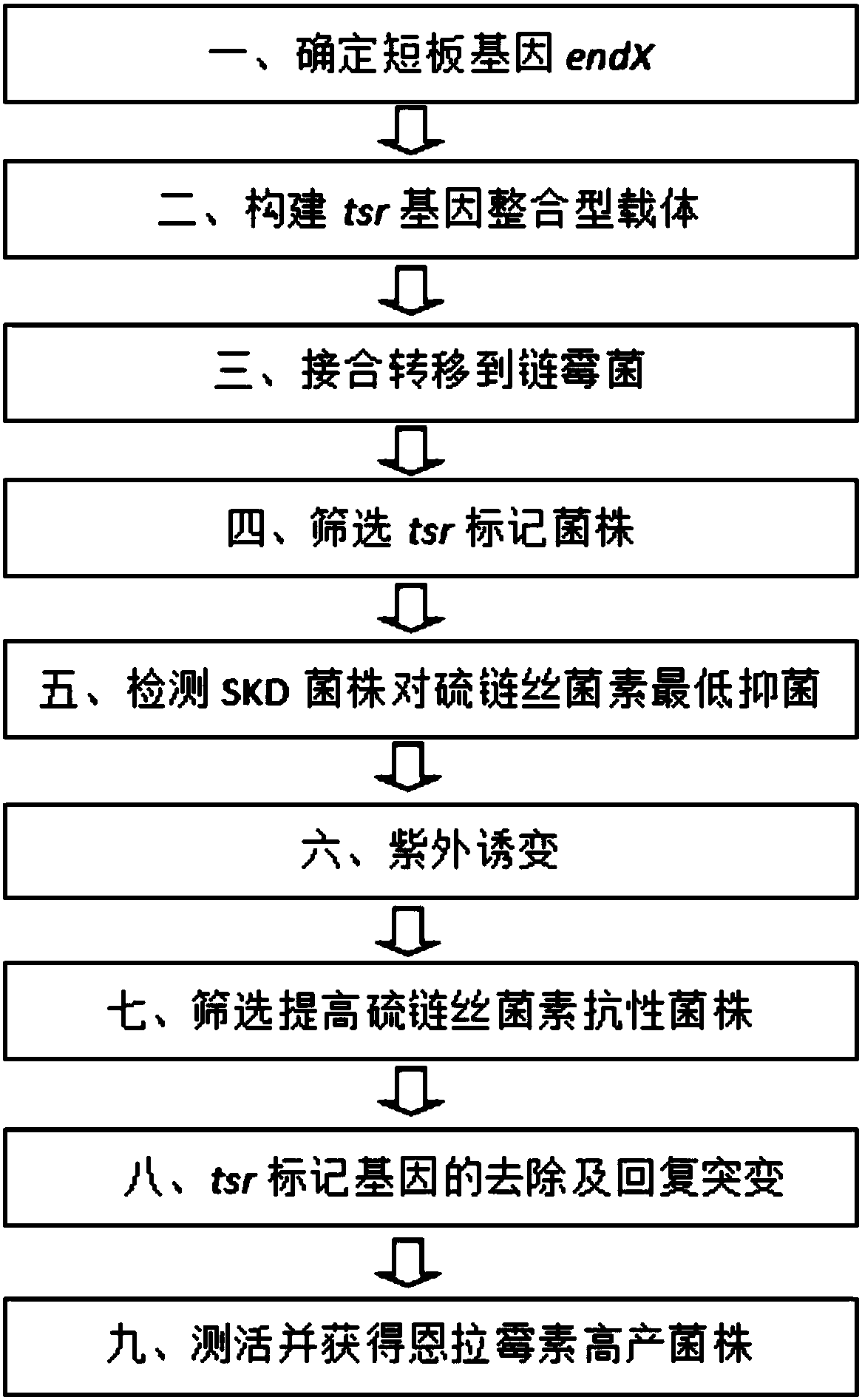
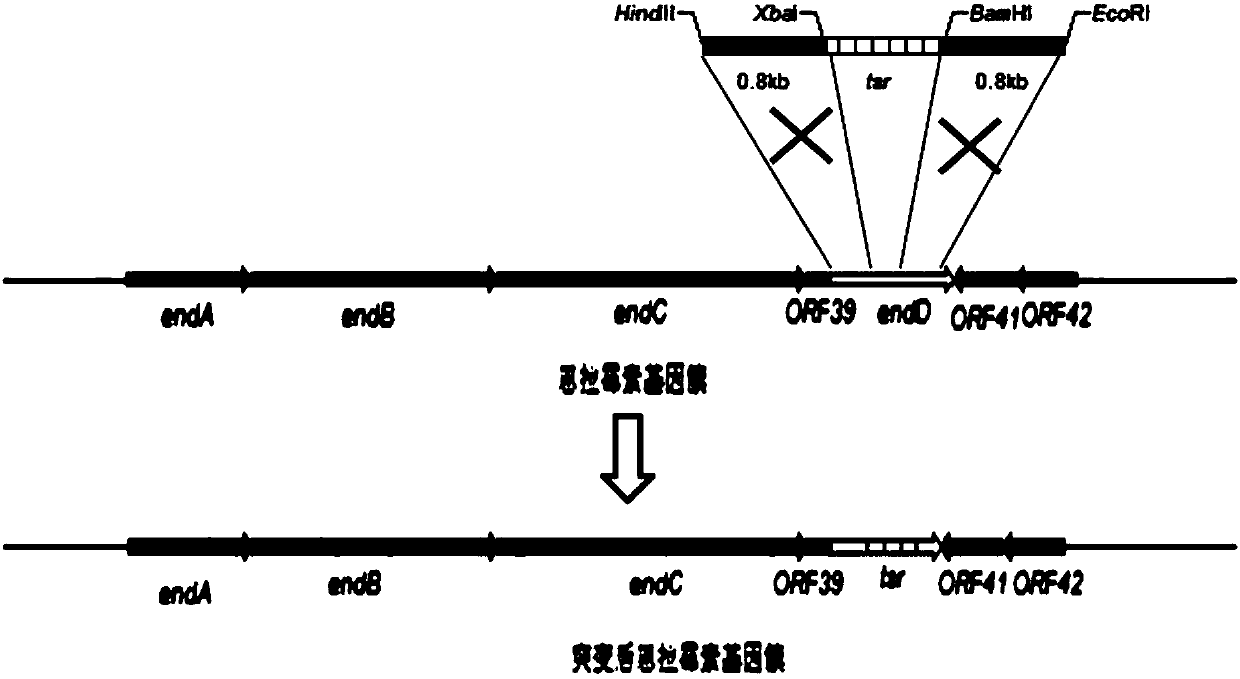
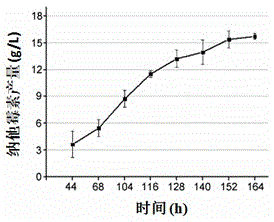
The invention relates to a method for breeding a high-yield enramycin strain. The method comprises the following steps: determining the short gene of a rate-limiting enzyme coding gene in the enramycin biological synthesizing process; constructing a thiostrepton resistance gene integrating vector; mutagenizing the modified strains, and screening a thiostrepton high-resistance strain from the modified strains; and carrying out genetic manipulation on the screened high-resistance strain, and restoring the tsr open reading frame to the original endX gene to obtain the strain which is an enramycinhigh-yield mutant strain. The method combines advantages of a traditional mutation breeding technology and a modern molecular biological method to realize quick and efficient screening of the enramycin high-yield strain. The method is applicable to screening of other antibiotic high-yield strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Construction method for efficient biosynthesis of streptomycete drugs
ActiveCN105018514AOvercoming difficult preparationOvercoming purchasing problemsMicroorganism based processesFermentationPharmaceutical SubstancesRate limiting enzyme
The present invention provides a construction method for efficient biosynthesis of streptomycete drugs. The construction method comprises: based on an inducible promoter O[R]O[lac] and a strong promoter ermEp<*>, firstly constructing a gradient induction expression system in streptomycete; controlling the expression level of target gene through the gradient induction, and carrying out coupled analysis on the relationship between the expression level of the target gene and the yield of the target drug so as to reveal the rate-limiting reaction in the drug biosynthesis path and the suitability of the rate-limiting enzyme; and through a constitutive promoter ermEp<*>, rationally carrying out series coupling on the encoding genes highly expressing the relevant rate-limiting enzyme so as to obtain a strain of the high-yield S Chattanoogensis producing strain L12, and transporting the strain to the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center to preserve, wherein the preservation number is CGMCC No.10157. According to the present invention, the shake flask fermentation results show that the Natamycin yield in the S Chattanoogensis L12 is 3.3 times the yield in the S Chattanoogensis L10, and the 50 L fermentation tank small test results show that the highest yield achieves 15.7 g / L; and the method of the present invention has characteristics of efficiency, accuracy and simple operation, and is generally suitable for other streptomycetes.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for acquiring transgenic hevea plant by virtue of laticifer specific promoter
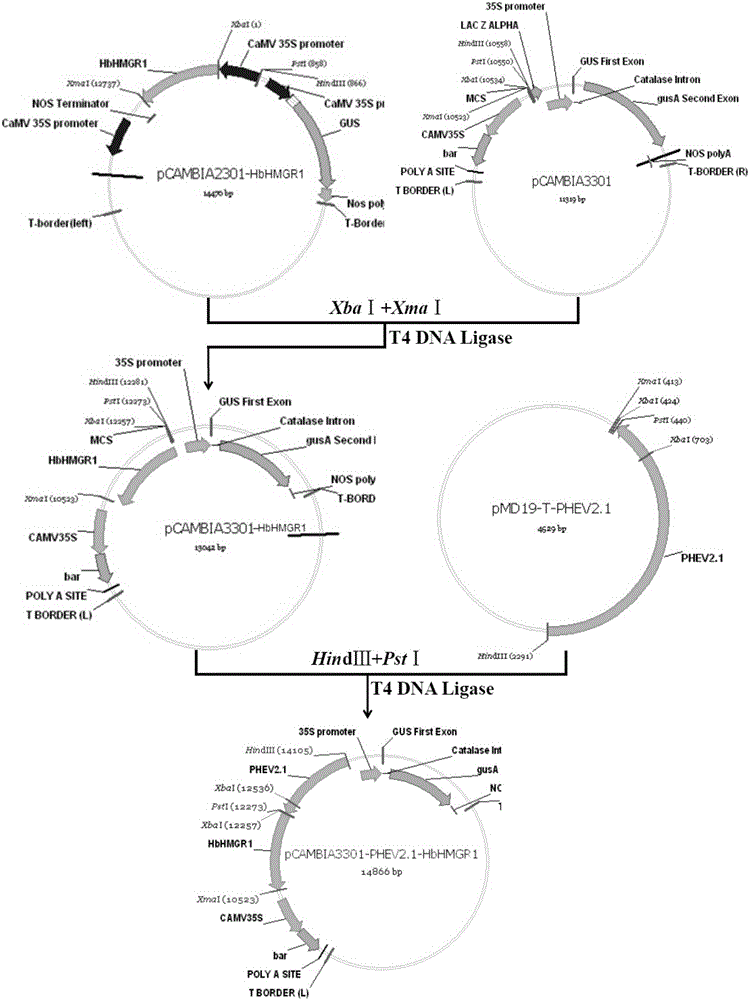
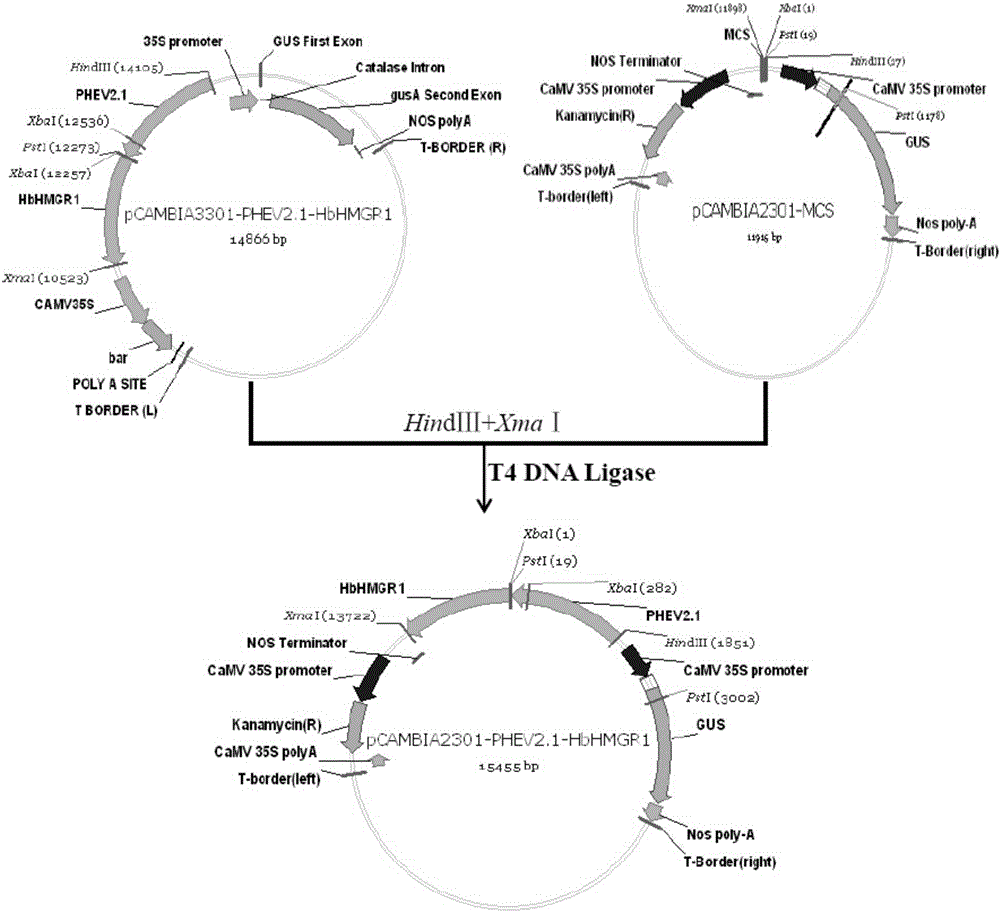
The invention discloses a method for acquiring a transgenic plant by cloning a hevea laticifer specific strong promoter PHEV2.1, linking the promoter to a key rate-limiting enzyme HbHMGR1 gene of a natural rubber biosynthesis route so as to construct a plant expression vector, and transforming hevea fragile embryogenic calluses. According to the method disclosed by the invention, PHEV2.1 and HbHMGR1 genes are cloned from a good hevea variety material, the laticifer specific plant expression vector pCAMBIA2301-PHEV2.1-HbHMGR1 is constructed, and the hevea fragile embryogenic calluses are transformed, so that a transgenic hevea embryoid and the transgenic plant are obtained; through GUS staining, PCR and reverse PCR, it is proved that the transgenic plant is acquired, and by detecting through a fluorescent quantitative PCR technology, it is proved that the expression quantities of the HbHMGR1 gene in the transgenic hevea embryoid and in the transgenic plant are significantly improved; therefore, the method lays a foundation for the improvement of a rubber yield by virtue of a genetic engineering method.
Owner:RUBBER RES INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
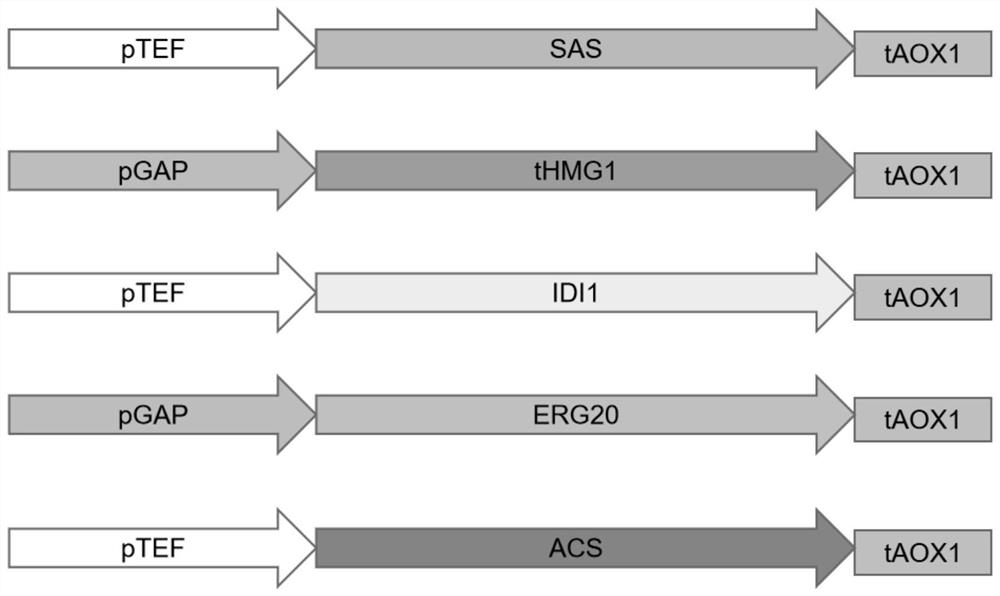
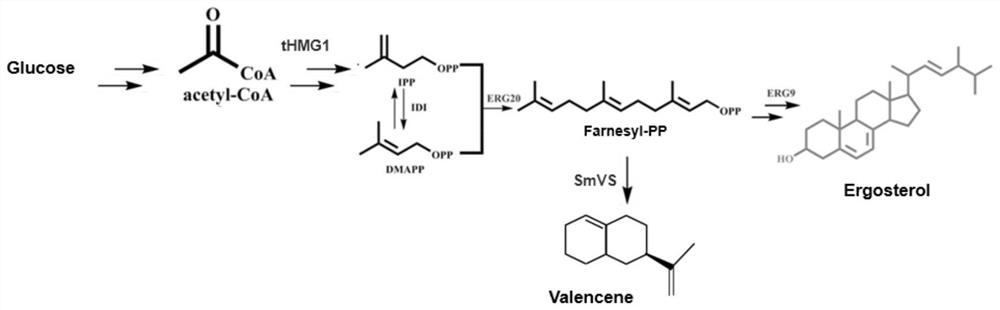
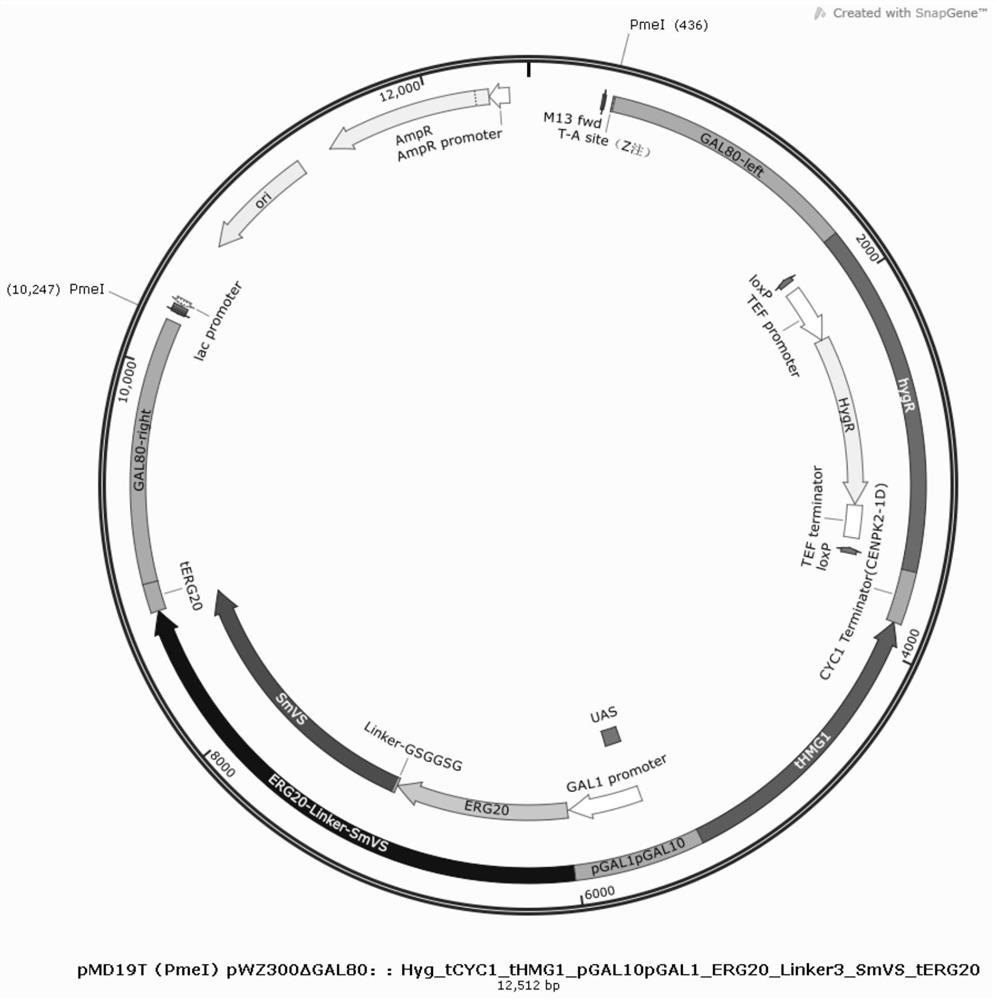
Genetically engineered bacterium with high yield of valarene as well as construction method and application of genetically engineered bacterium
PendingCN114107078AEnhance metabolic pathway metabolic strengthHigh expressionFungiTransferasesFPP SynthaseMicrobiology
The invention provides a construction method of a high-yield valarene gene engineering bacterium, which comprises the following steps: integrating and expressing an MVA pathway rate-limiting enzyme-truncated HMG-CoA reductase coding gene (tHMG1) and integrating and fusing and expressing an FPP synthase coding gene (ERG20) and a valarene synthase coding gene (SmVS) in saccharomyces cerevisiae in a homologous recombination manner, so as to enhance the metabolic intensity of an MVA pathway; and the expression of the varrenene is enhanced. Meanwhile, a squalene synthase encoding gene ERG9 promoter is replaced with a copper ion induced promoter pCUP1, the ergosterol competitive pathway is reduced, and the yield of the valarene is increased; and finally, obtaining the gene engineering strain with high yield of the varrenene. The shake flask fermentation yield of the valarene of the genetically engineered bacterium can reach about 117mg / L, the fermentation tank yield can reach about 8g / L, and the genetically engineered bacterium completely has a commercial production level and has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:湖北冠众通科技有限公司
Methods for indentifying compounds that modulate gluconeogenesis through the binding of CREB to the PGC-1 promoter
InactiveUS6974671B1Restored glucose homeostasisRescued expressionElectrolysis componentsGenetic material ingredientsDiabetes mellitusGlucocorticoid
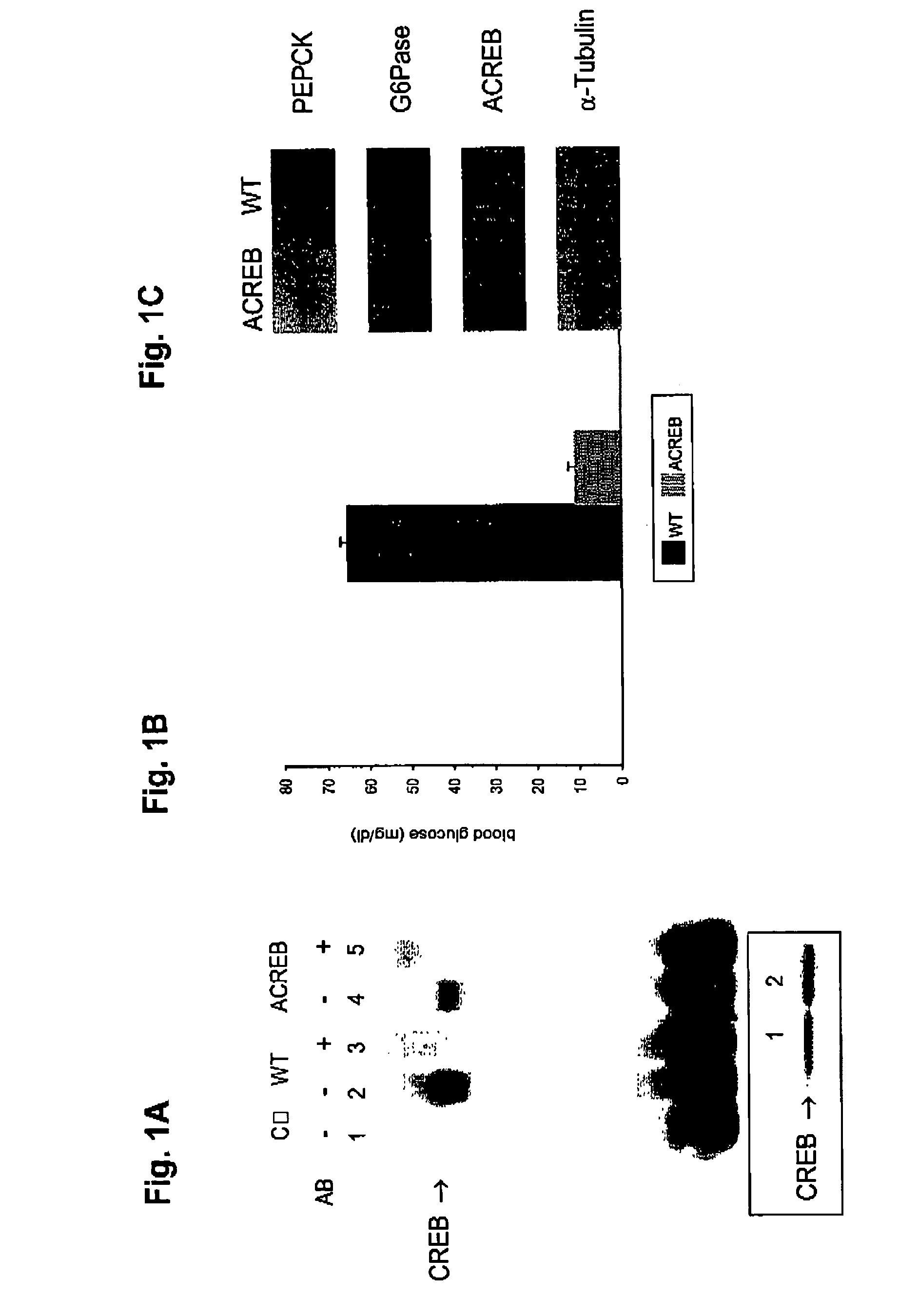
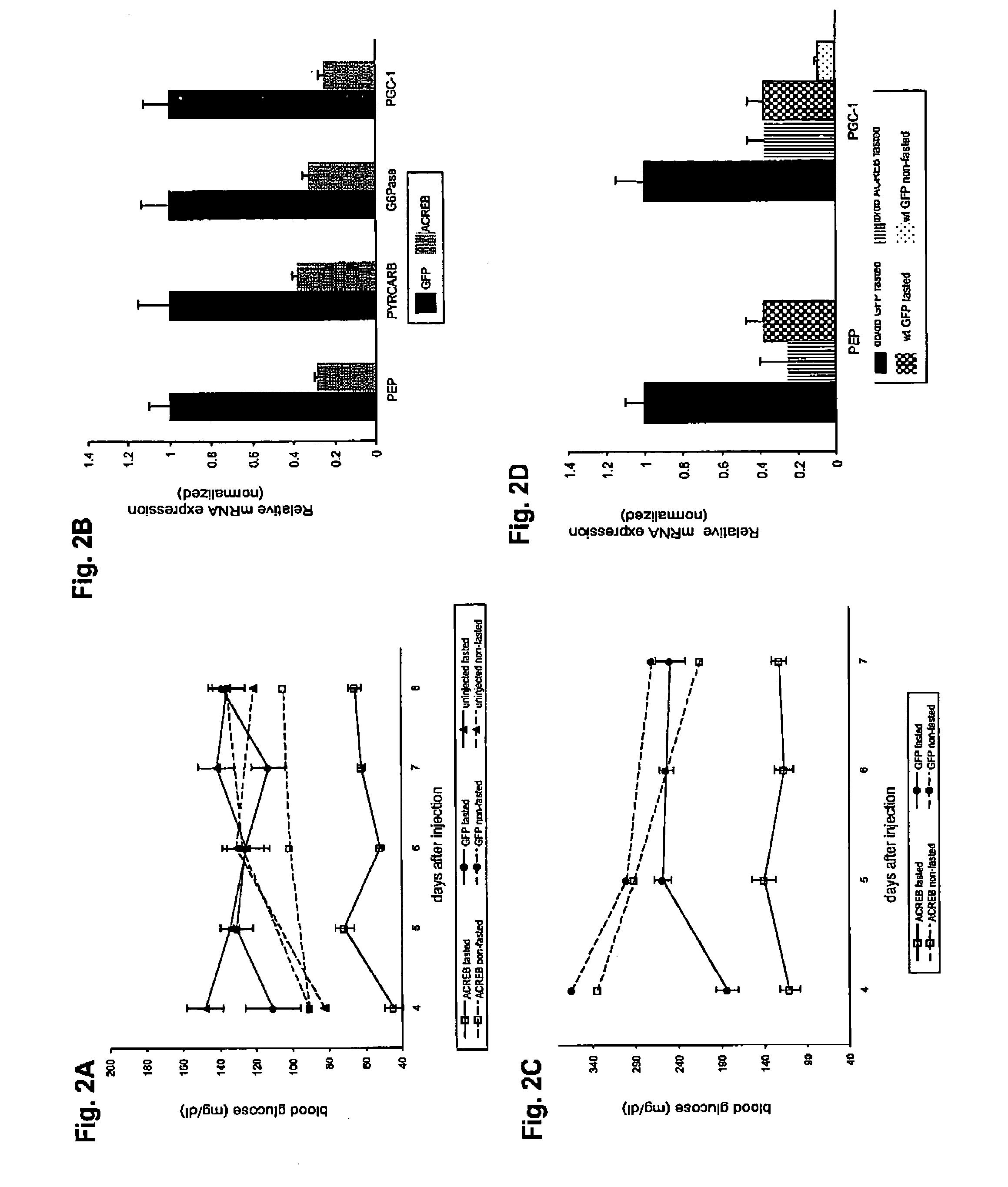
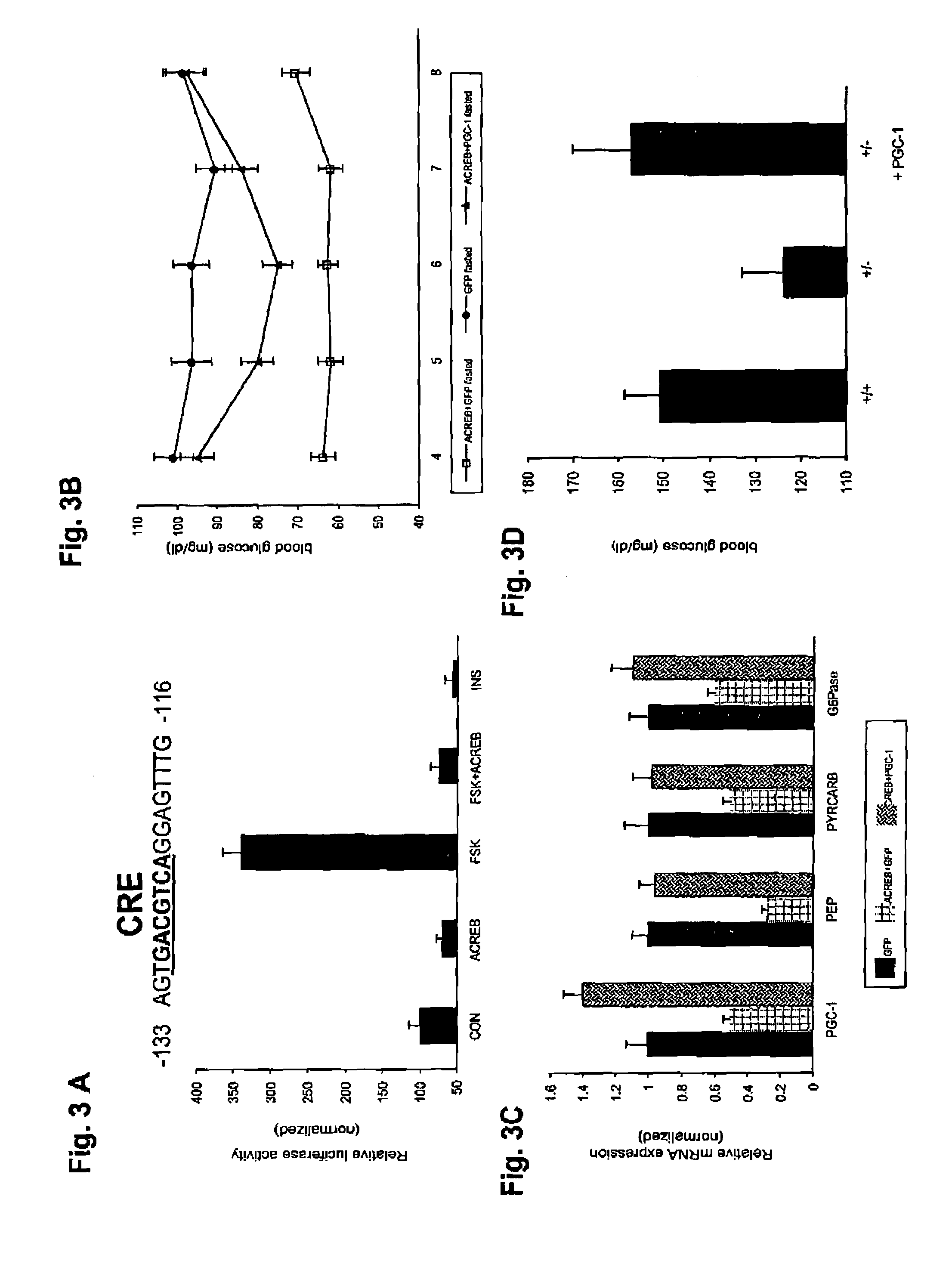
In accordance with the present invention, it has been discovered that CREB regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis via the co-activator, PGC-1. PGC-1 potentiated glucocorticoid induction of the gene for PEPCK, the rate limiting enzyme in gluconeogenesis, via the glucocorticoid response unit in the promoter, indicating that activation of PGC-1 by CREB in liver contributes to the pathogenesis of diabetes mellitus. In accordance with the above discoveries, the present invention provides a method of identifying a compound that modulates gluconeogenesis. The invention method comprises contacting CREB and a nucleic acid comprising a PGC-1 promoter with a test compound, and determining if the test compound modulates binding between CREB and the PGC-1 promoter.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
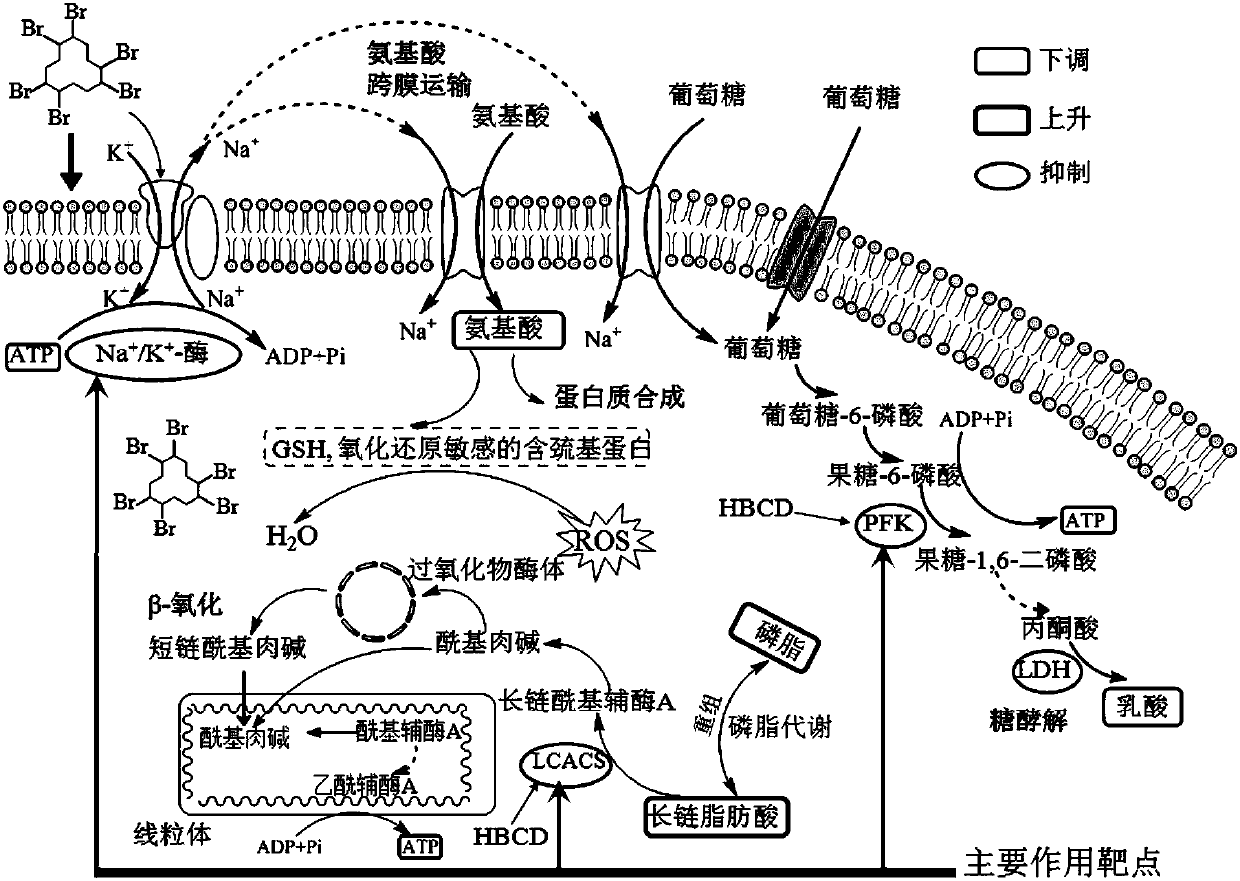
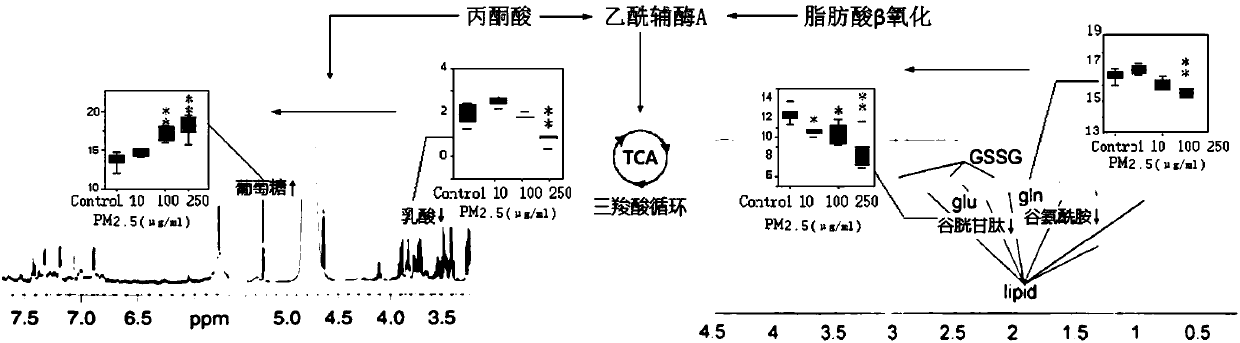
Method for evaluating effect of PM2.5 particles on free radical metabolic pathways in human lung cells
InactiveCN109839498AReflect the real situationIntuitive informationBiological testingMetaboliteOxygen
The invention discloses a method for evaluating an effect of PM2.5 full chemical component particles on free radical metabolic pathways in human lung cells. The method is characterized in that human lung-bronchial epithelial cells are exposed by means of the PM2.5 full chemical component particles, a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC- MS) can be used for effectively analyzing micromolecular metabolites in cells, enzymatic activity is quickly analyzed by combining with a biological detection method, and changes of the micromolecular metabolites related associated with intracellular free radical metabolism and activity changes of a rate-limiting enzyme that plays a key role in energy metabolism are integrated, in summary, a set of new methods for evaluating the interference on intracellular oxygen free radical metabolism after cells are exposed to toxic effect of exogenous pollution are constructed based on molecular biology. The method can analyze the influence of contaminantson the free radical metabolic pathways in the cells intuitively, and has the advantages of simple preprocessing method, rapid detection, good repeatability, comprehensive information acquisition andthe like.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com