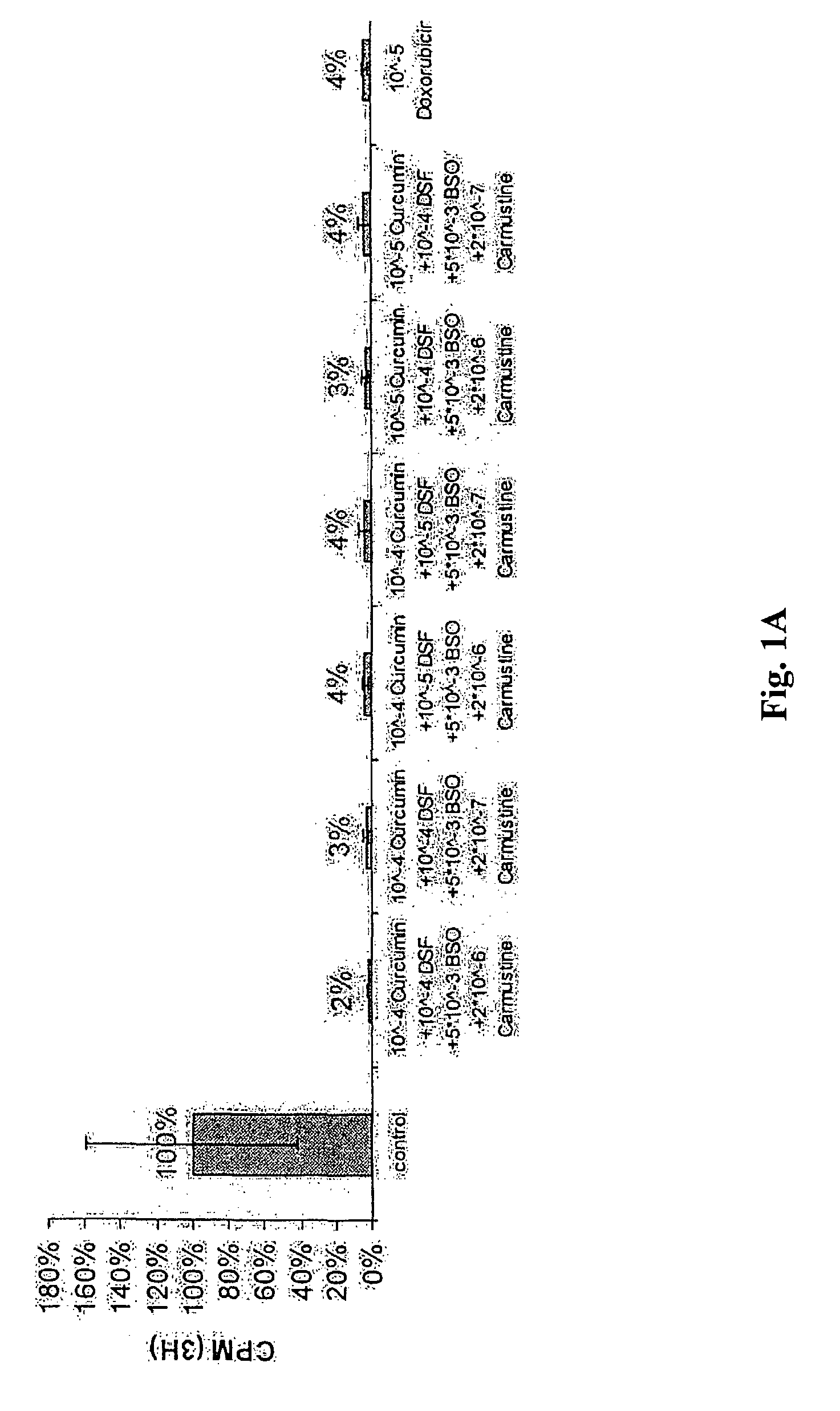
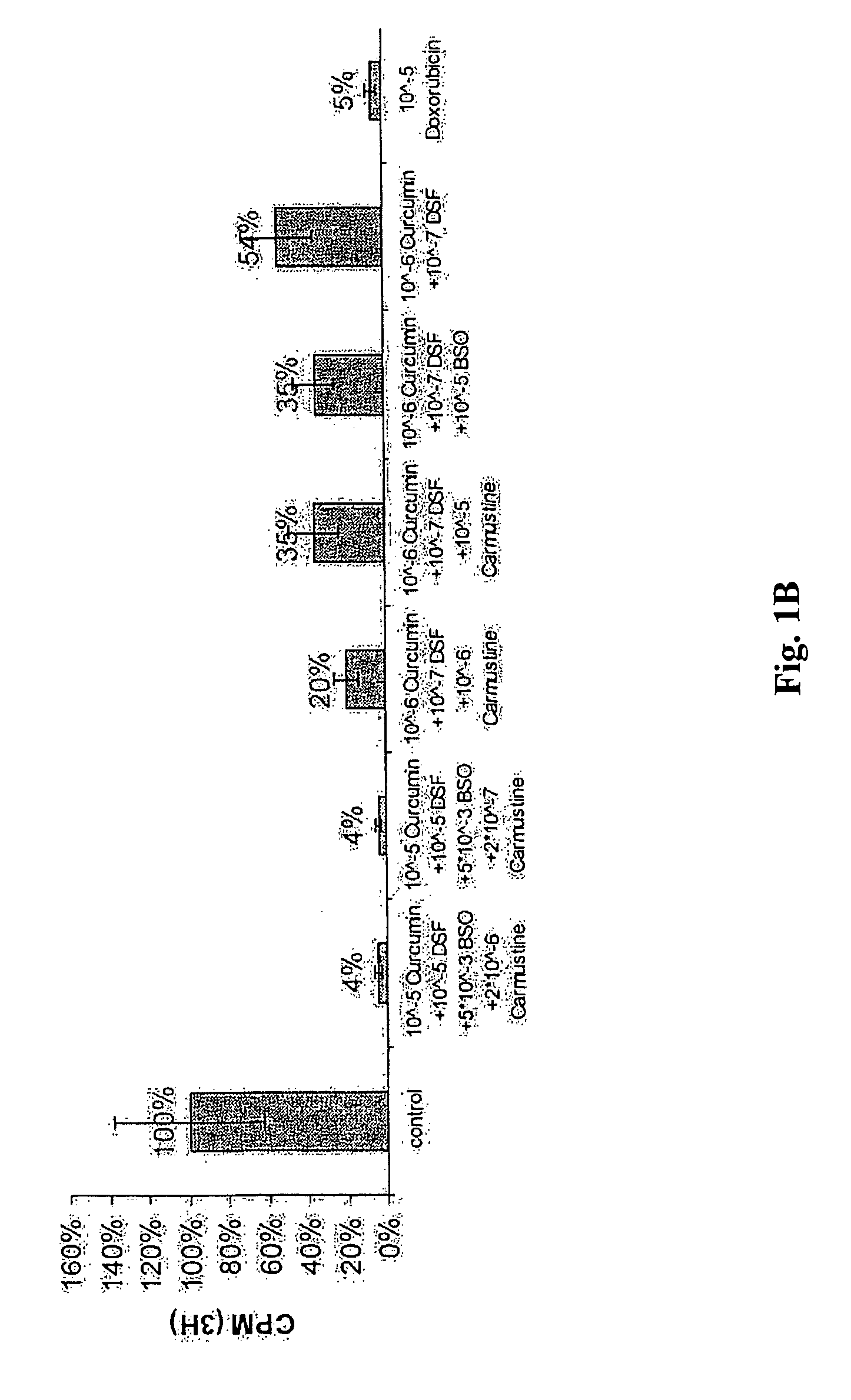
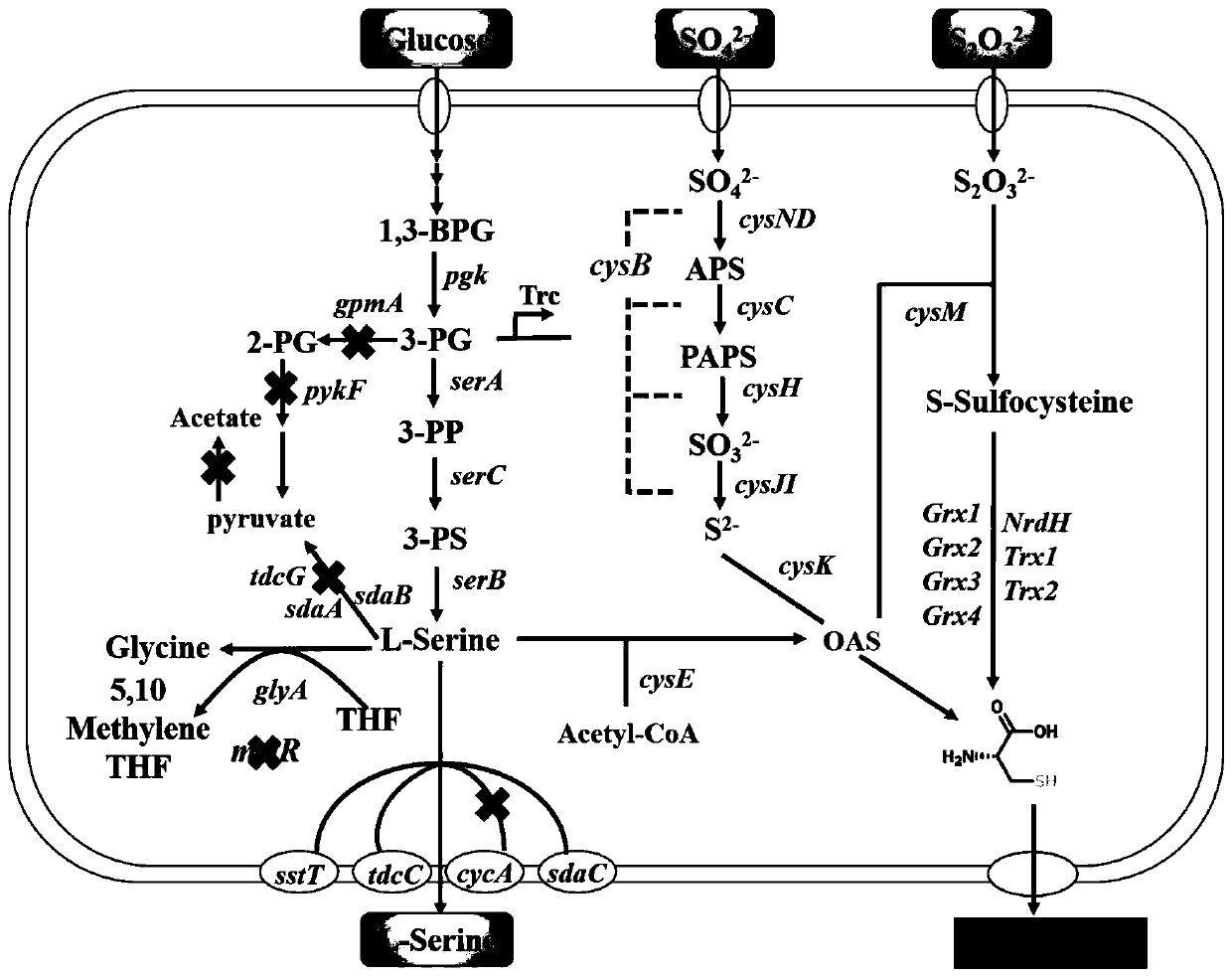
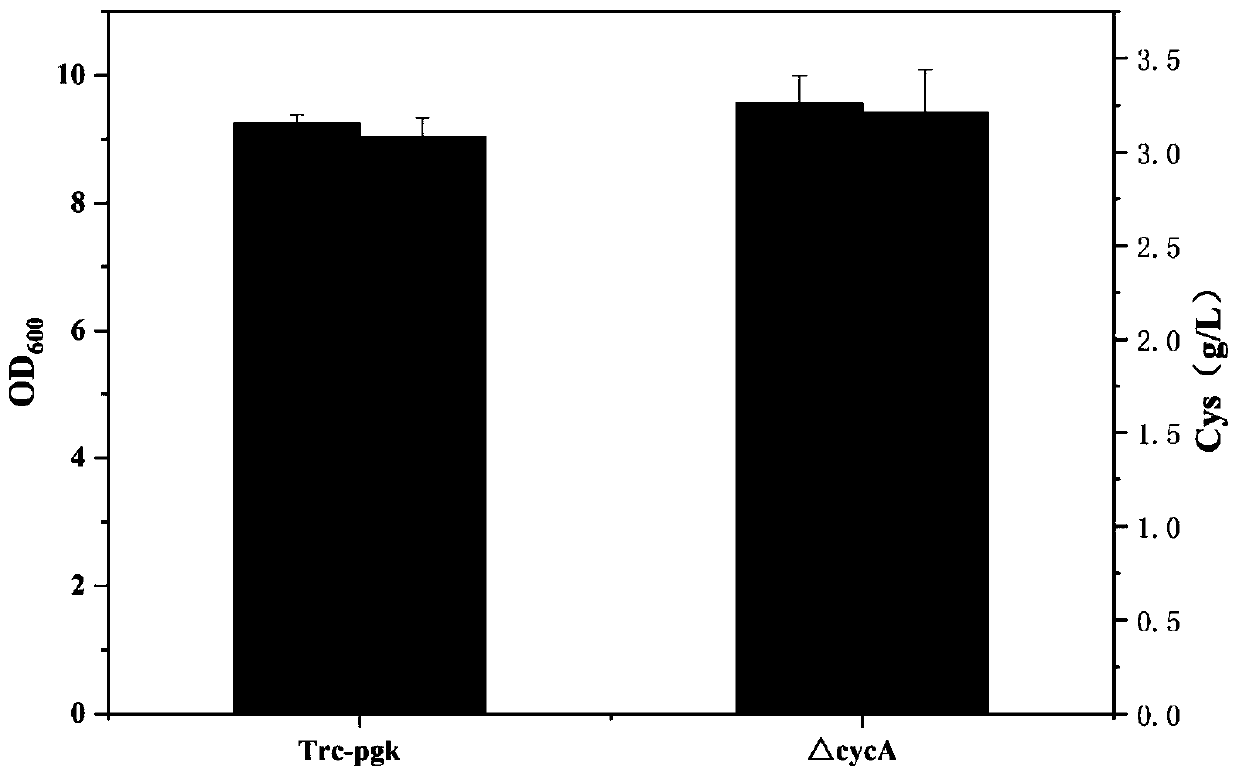
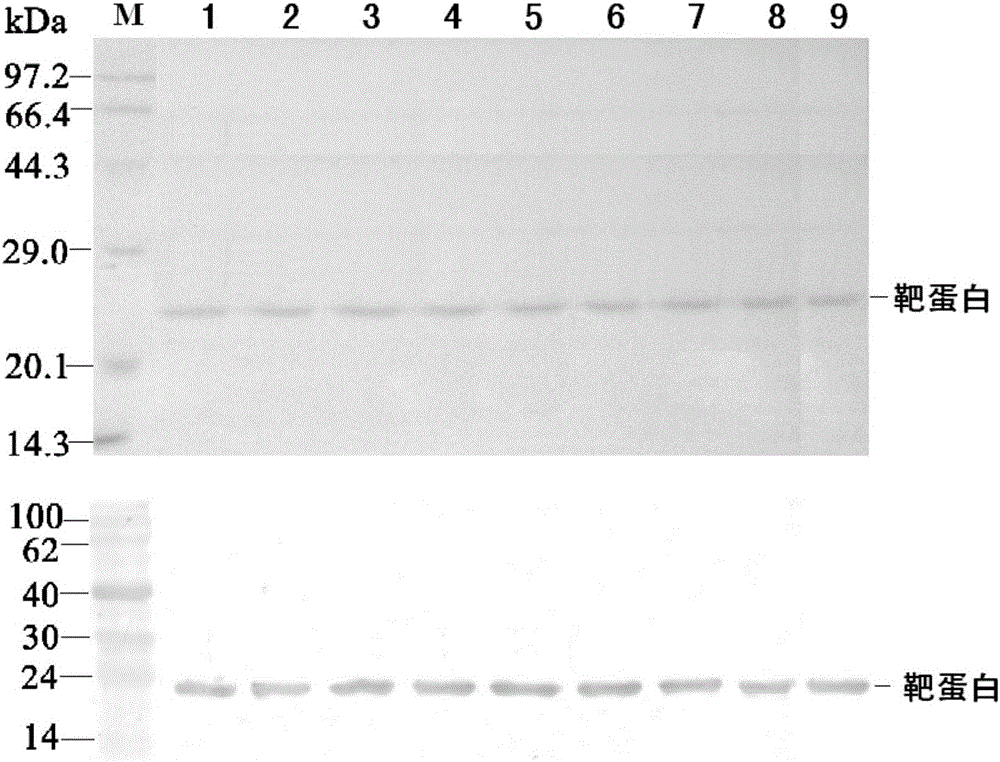
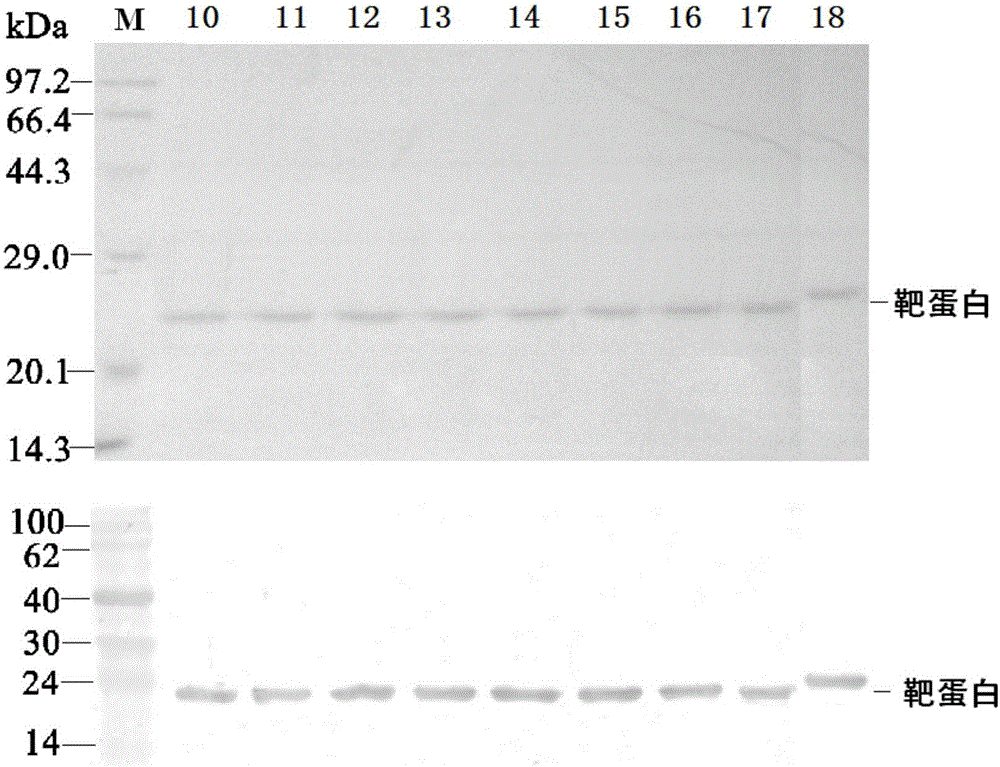
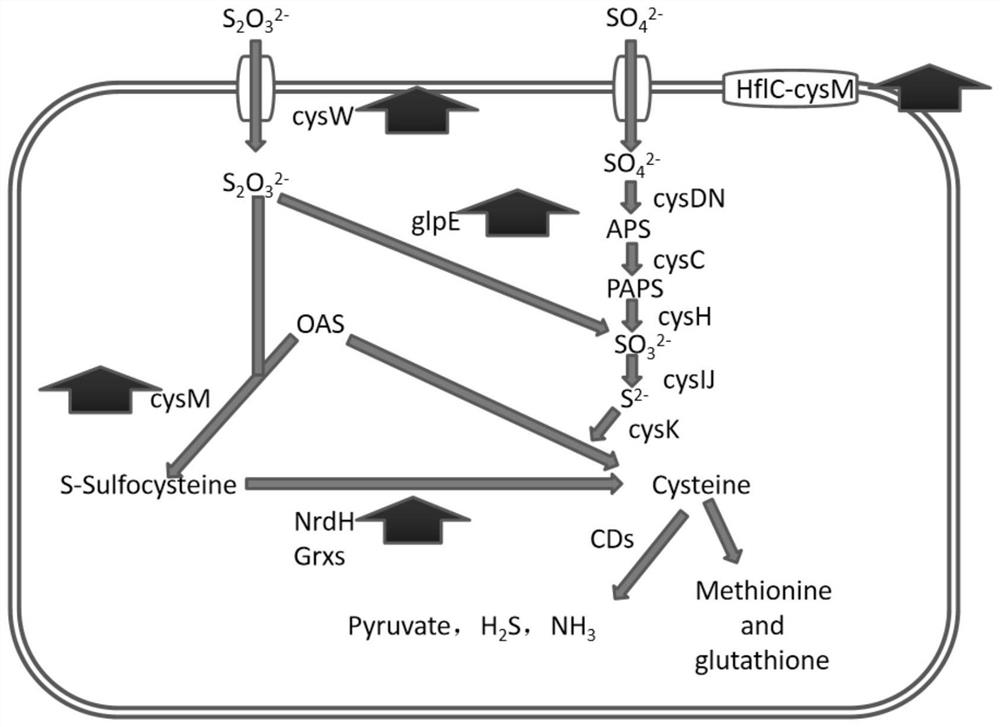
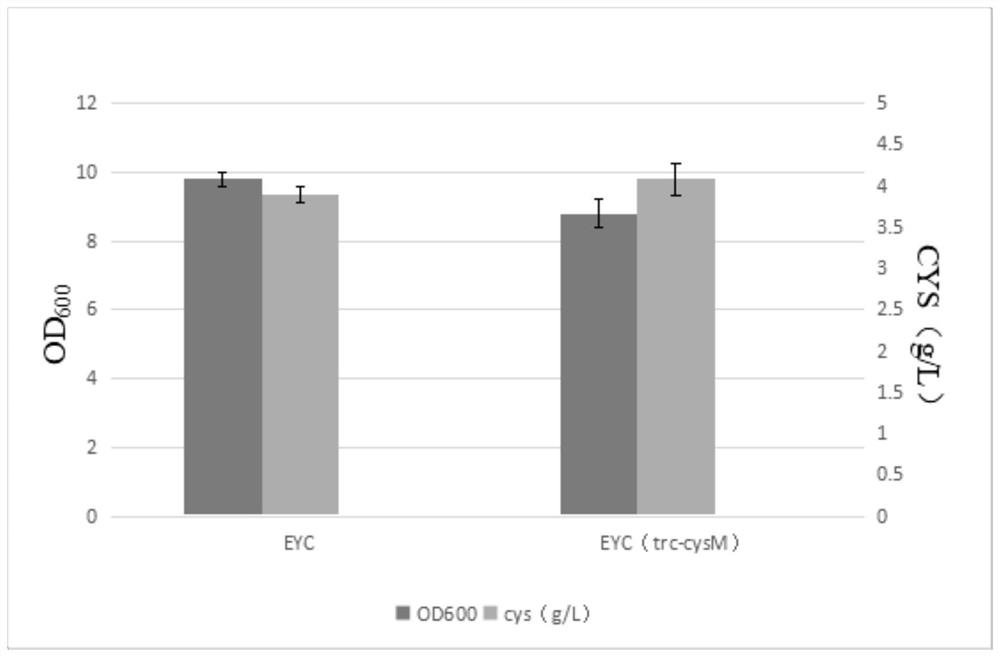
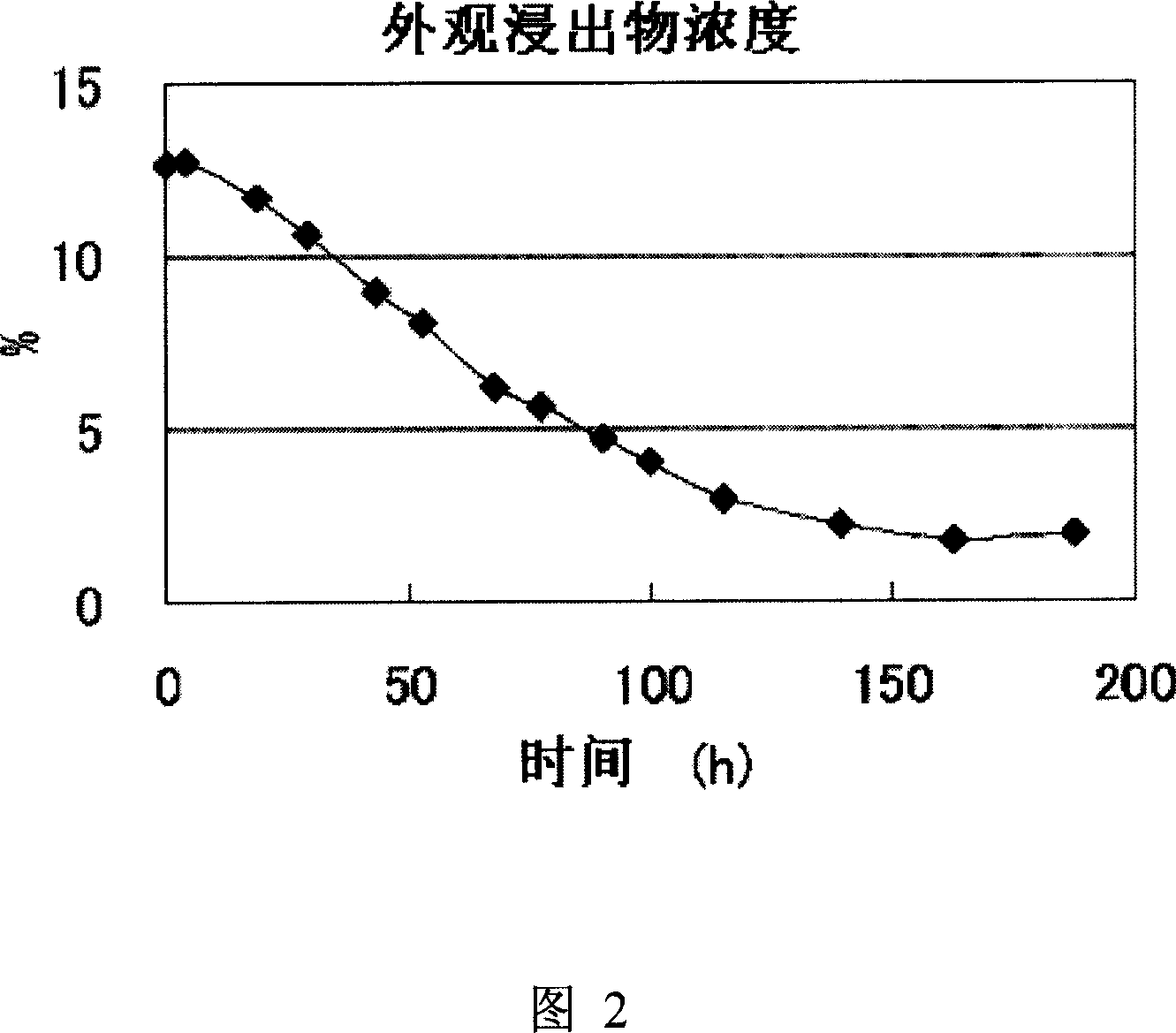
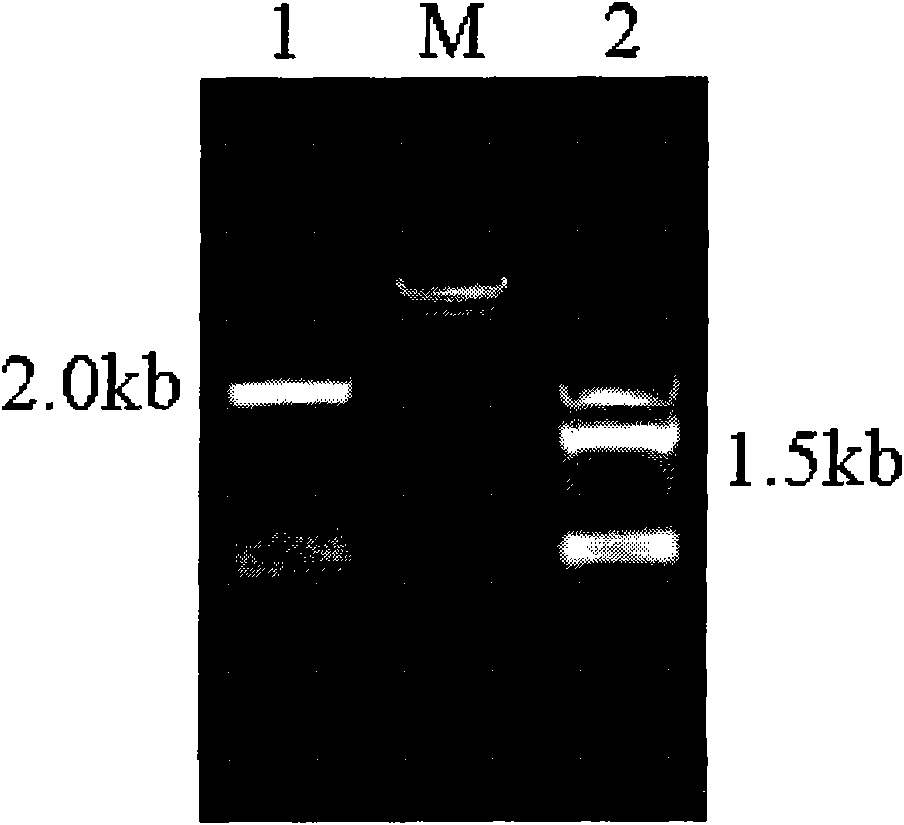
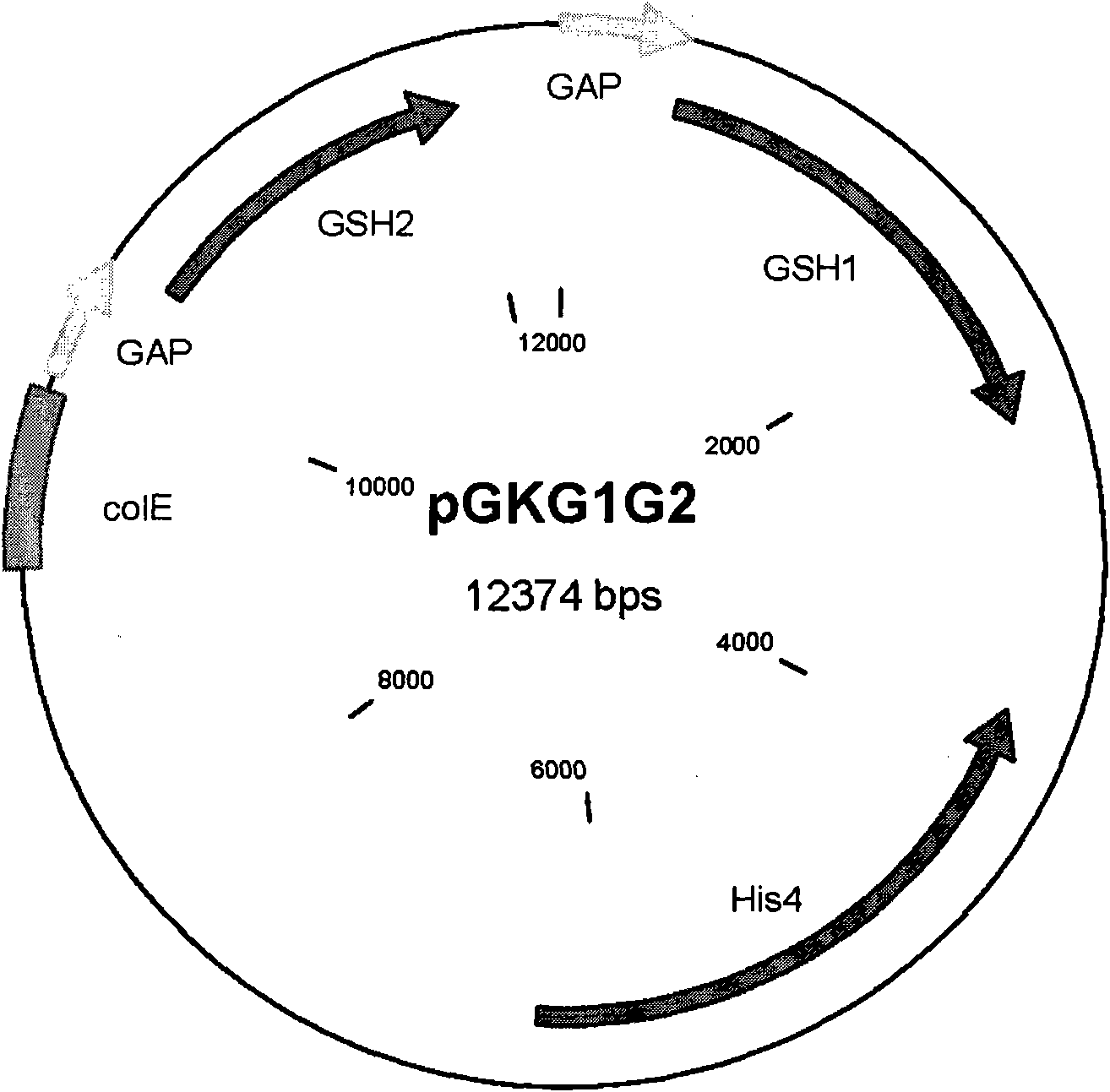
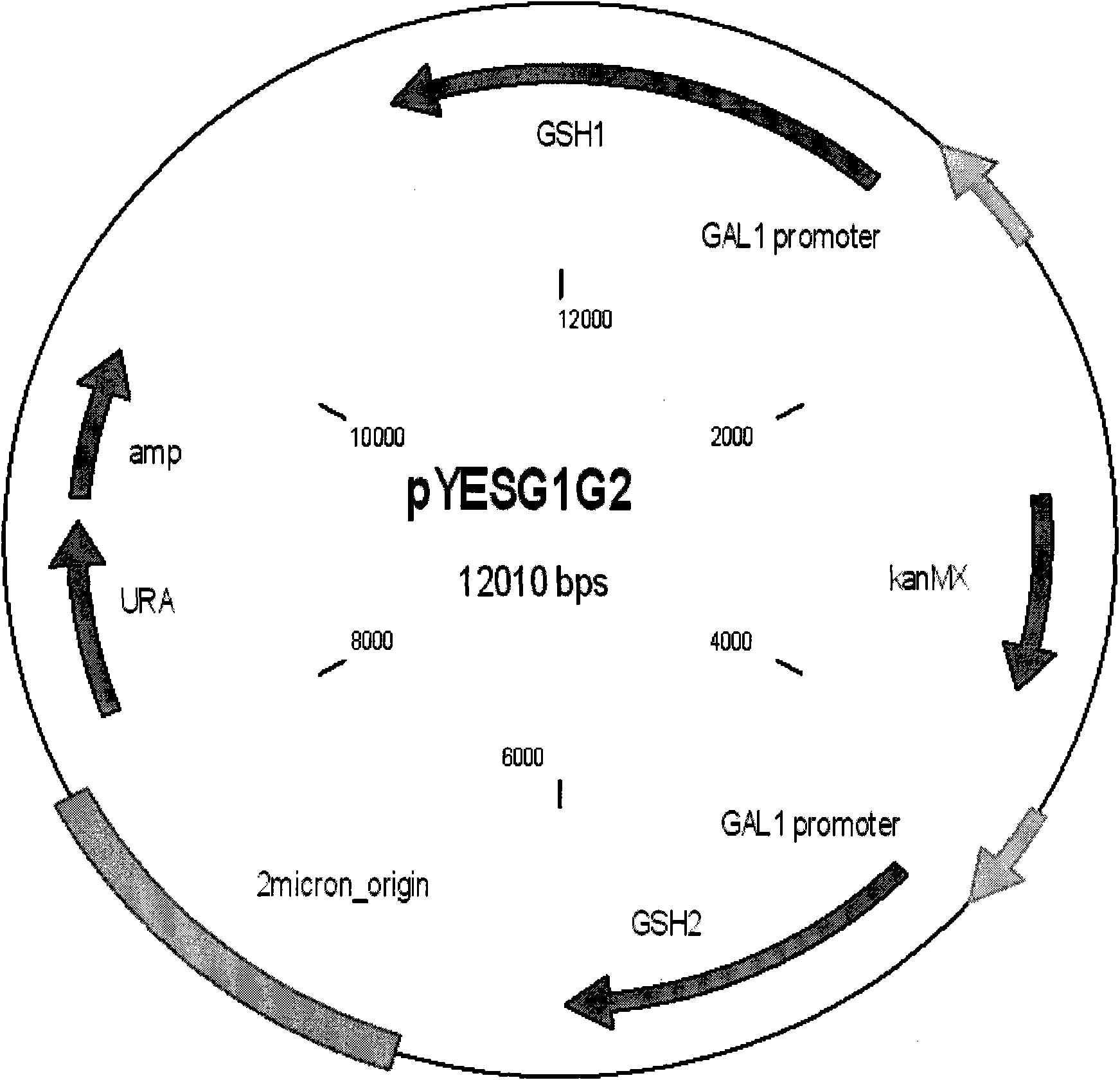
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Cysteine synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cysteine is a thiol-containing non-essential amino acid that is oxidized to form CYSTINE. Cysteine is a non-essential sulfur-containing amino acid in humans, related to cystine, Cysteine is important for protein synthesis, detoxification, and diverse metabolic functions.
Kit for Treatment of Cancer
InactiveUS20080287541A1Effective treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsRate limiting enzymeAdduct
The present invention relates to a kit for the treatment of cancer comprising (a) a container for containing a first compound (i) or a precursor thereof, said first compound or precursor being a compound that oxidizes glutathione (GSH); (b) a container for containing a second compound (ii) or a precursor thereof, said second compound or precursor being a compound that forms an adduct or conjugate with GSH; (c) a container for containing a third compound (iii) or a precursor thereof, said third compound or precursor being a compound that inhibits the rate-limiting enzyme of GSH biosynthesis, gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GCS); and (d) a container for containing a fourth compound (iv) or a precursor thereof, said fourth compound or precursor being a compound that inhibits the enzyme responsible for the conversion of GSSG to GSH, glutathione reductase (GR).
Owner:REDOXIA ISRAEL
Method for high-yield production of L-cysteine by metabolic engineering modification of corynebacterium glutamicum
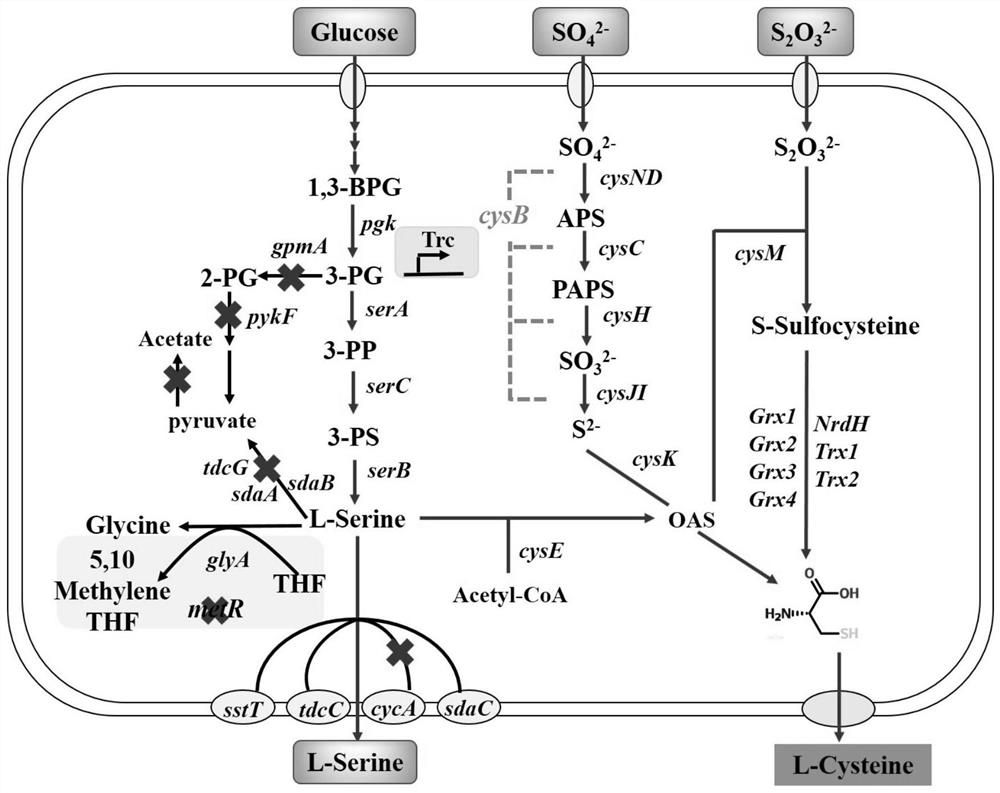
The invention provides a method for high-yield production of L-cysteine by metabolic engineering modification of corynebacterium glutamicum. The method comprises the following steps: knocking out an L-cysteine desulfhydrase gene aecD while overexpressing a serine acetyltransferase gene cysE to obtain an L-cysteine accumulation strain; respectively overexpressing the serine acetyltransferase genescysE of escherichia coli and arabidopsis thaliana, and obtaining EcysE(M201R) most beneficial to L-cysteine synthesis after activity comparison; respectively overexpressing L-cysteine transporter proteins from escherichia coli and pantoea ananatis, and comparing the influences of different transporter proteins on the yield of L-cysteine to obtain a transporter protein Bcr most beneficial to L-cysteine secretion; promoting the synthesis of L-cysteine by improving the level of a precursor L-serine; and finally fermenting for 3-4 days by using 50-60 g / L glucose as a substrate, wherein the contentof L-cysteine reaches 800-1000 mg / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Genetically engineered bacterium for high yield of L-cysteine, construction method and application
ActiveCN111019877AReduce the effect of synthesisImprove utilizationBacteriaStable introduction of DNAHeterologousMicrobacterium
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium of L-cysteine, a construction method of the genetically engineered bacterium and application of the genetically engineered bacterium in preparation of L-cysteine through microbial fermentation. The construction method comprises the following steps: (1) strengthening a serine module of an escherichia coli L-cysteine synthetic route, so thatthe serine utilization capability of escherichia coli is enhanced; (2) weakening the transfer of serine, so that the influence of byproducts on the L-cysteine synthesis is weakened; (3) increasing the expression of a sulfur module synthesis gene; and (4) heterologously expressing serC gene of Cornebacterium glutarum on a plasmid to obtain an escherichia coli genetically engineered bacterial strain with high L-cysteine yield, wherein the L-cysteine yield is increased from 2.7 g / L to 3.83 g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Hybridized tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) and application thereof to glutathione peroxidase preparation
ActiveCN105018482AEasy to prepareIncrease vitalityEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses hybridized tRNA (transfer ribonucleic acid) and application thereof to glutathione peroxidase preparation and belongs to the field of biotechnology. The hybridized tRNA relates to sequences SEQ ID No: 1-16, consists of 90 basic groups, and not only can serve as substrate tRNA for selenocysteine synthesis, but also can be recognized by autologous elongation factor EF-Tu of escherichia coli. A hybridized tRNA gene is obtained by a gene synthesis method, then a GPX (glutathione peroxidase) gene is synthetized or amplified, the hybridized tRNA gene and the GPX gene are assembled on a secretory prokaryotic expression vector capable of expressing the hybridized tRNA, a TAG engineering strain is transformed and subjected to induced expression in presence of sodium selenite, and a catalytic group Sec of the GPX is introduced into a substrate binding site of protein in a way that conventional amino acids enter a peptide chain, so that the protein is given with high GPX activity. The hybridized tRNA and application thereof to glutathione peroxidase preparation have the advantages that the method is simple, and zymoprotein is high in activity, yield and stability, so that the problems that natural GPX is limited in source and instable in property are solved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Genetic engineering strain capable of high yielding L-cysteine and construction and application of genetic engineering strain
The invention relates to a genetic engineering strain capable of high yielding L-cysteine, a construction method for the genetic engineering strain and application of the genetic engineering strain in microbial-fermentation preparation of the L-cysteine. According to the method, the Escherichia coli genetic engineering strain capable of high yielding the L-cysteine is obtained through (1) strengthening the efficiency of conversion of the L-cysteine from S-Sulfocysteine in an Escherichia coli L-cysteine synthesis way and (2) strengthening the utilization ratio of thiosulfate radicals in the Escherichia coli L-cysteine synthesis way, and the yield of the L-cysteine is increased to 4.88g / L from 3.90g / L.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Homocysteine synthase inhibitor
InactiveCN102056894AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticNervous disorderOrganic chemistryHomocysteine synthesisOSB-CoA synthetase
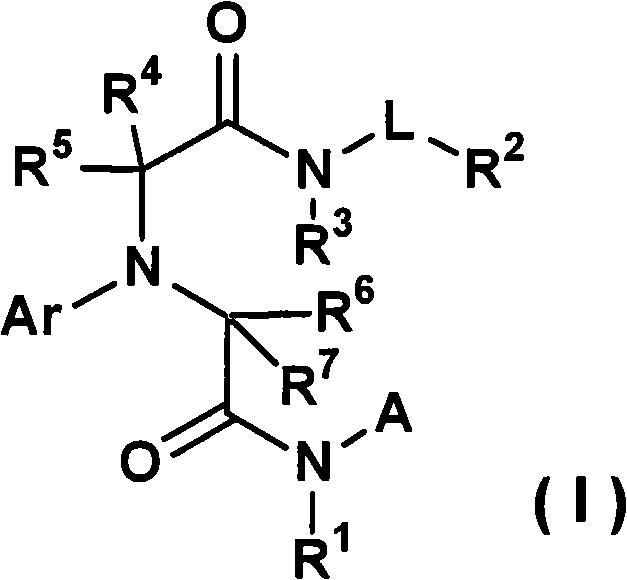
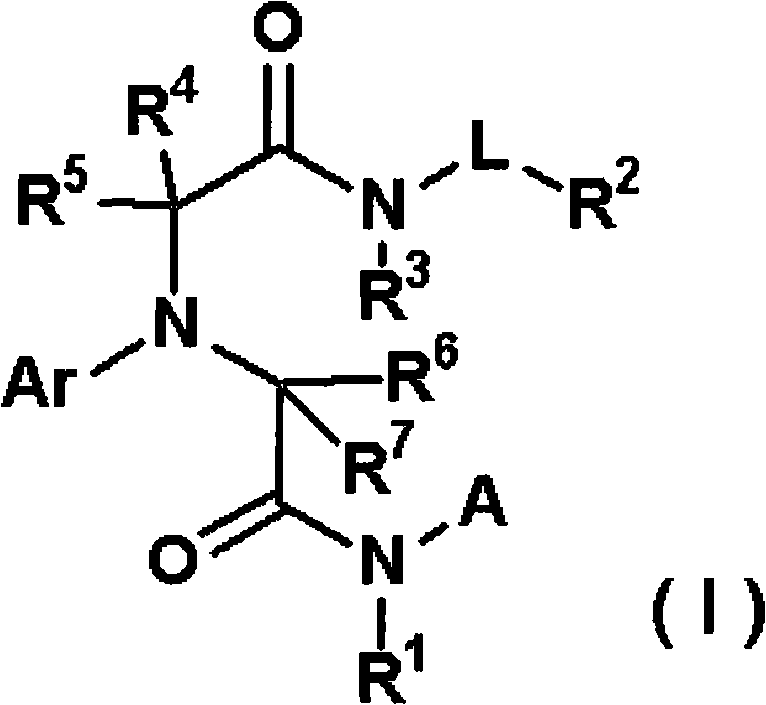
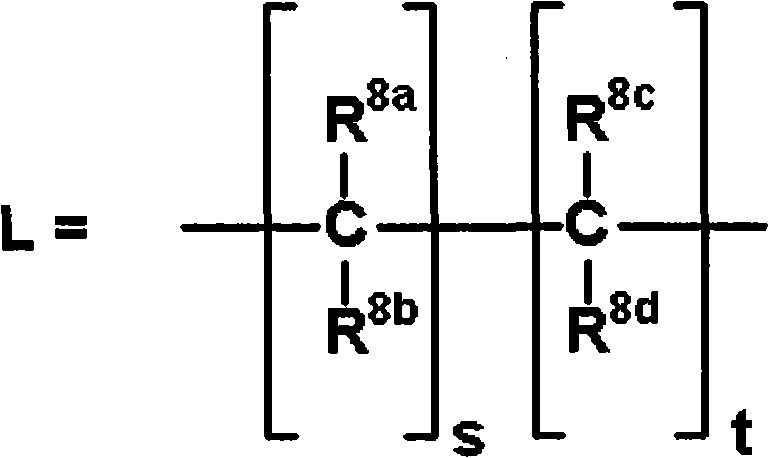
Disclosed is a homocysteine synthase inhibitor which is useful for the prevention or treatment of a disease associated with homocysteine synthase. Specifically disclosed is a compound represented by general formula (I) [wherein each symbol is as defined in the description], a pharmacologically acceptable salt of the compound, or a solvate of the compound or the pharmacologically acceptable salt, which can be used as the homocysteine synthase inhibitor.
Owner:MITSUBISHI TANABE PHARMA CORP
Engineered escherichia coli for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
ActiveCN106497858ASynthesis efficiently utilizes the C4 pathway to promoteEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPUC19Escherichia coli
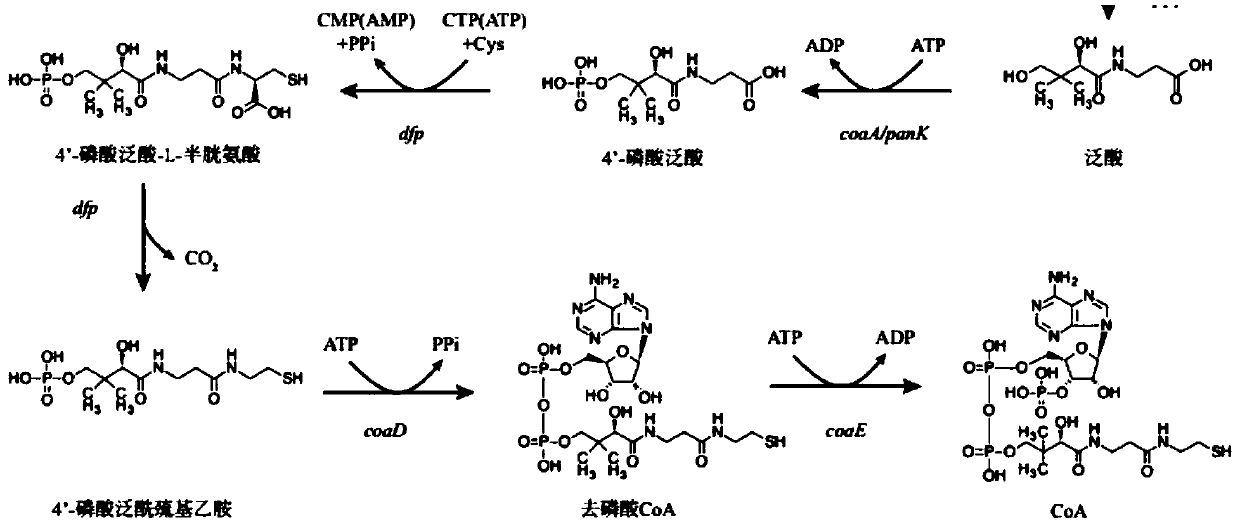
The invention discloses engineered escherichia coli for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering and microbial fermentation. The engineered escherichia coli is characterized by carrying out co-expression of a gene coaA for coding pantothenate kinase, a gene dfp for coding phosphoric acid pantothenylcysteine synthetase and decarboxylase and a gene coaD for coding phosphoric acid CoA pyrophosphorylase from an escherichia coli CoA synthetic pathway by using pUC19 and pETDuet-1 vectors on the basis of excess expression of 5-aminolevulinate synthase hemA which is used as a key enzyme in a synthetic pathway of 5-aminolevulinic acid C4 by using a vector pRSFDuet-1-hemA to build recombination strains. Shake-flask culture proves that the yield of recombinant bacteria ALA for co-expression of CoA pathway genes is obviously improved; the maximum yield reaches 700mg / L and is increased by about 46% in comparison with contrast.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process For Preparing Serine-Rich Protein Employing Cysteine Synthase (CYSK) Gene
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a serine-rich foreign protein comprising culturing a bacterium containing the cysteine synthase (cysK) gene and a gene encoding the serine-rich foreign protein. The present invention comprises the steps of culturing a bacterium transformed with an expression vector containing a gene encoding a serine-rich foreign protein and an expression vector containing the cysK gene, or a bacterium transformed with an expression vector containing the cysK gene and a gene encoding a serine-rich foreign protein and isolating the foreign protein therefrom. The present invention is expected to be widely used to increase the production yield of a serine-rich foreign protein.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Wolfberry glutamyl cysteine synthetase and encoding gene and application
InactiveCN105734024AHigh resistance to cadmium ionsImprove salt toleranceLigasesVector-based foreign material introductionSalt resistanceGMO Plants
The invention discloses wolfberry glutamyl cysteine synthetase and an encoding gene and application.The amino acid sequence of wolfberry glutamyl cysteine synthetase is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1.The encoding gene of the wolfberry glutamyl cysteine synthetase is transferred into a target plant, and a transgenic plant high in cadmium ion resistance and high in salt resistance is obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Construction method and application of piggyBac transposon vector for producing transgenic goat
InactiveCN102181467AIncrease productionQuality improvementVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryAgricultural scienceGreen fluorescent protein
The invention discloses a construction method of a piggyBac transposon vector for producing a transgenic goat. The construction method mainly comprises the steps of: (1) synthesizing a section of base sequence comprising a PB5' end and a PB3' end necessary for transposition of a piggyBac transposon, reserving multiple cloning sites in the middle of the PB5' end and the PB3' end during synthesis, and then cloning the sequence into a pBluSKm vector to construct a pBluSKm-PB vector; and then cloning a rumen-specific expression promoter PRD-SPRR II, cysteine synthesis genes cysE and cysM which are subjected to codon preferred optimization, a Neomycin resistant gene and a green fluorescent protein gene to the pBluSKm-PB vector to finally construct a pBluSKm-PB-PRD-cysEM-NEO-EGFP transposon vector. The transposon vector obtained by the invention can meet the requirements of cell screening, micromanipulation under an inverted fluorescence microscope, production of the transgenic goat and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Cr (VI) stress resistant petroleum contaminated soil immobilized bioremediation technology
ActiveCN113042521AContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesBioremediationPetroleum oil
The invention discloses a Cr (VI) stress resistant petroleum contaminated soil immobilized bioremediation technology. The method comprises the following steps of: by taking tartary buckwheat shells as a raw material, carrying out hydrothermal carbonization in an ethylenediamine aqueous solution and a ascorbic acid solution, carrying out rotary heating in formic acid and loading nano zero-valent aluminum, so as to gradually improve the reducibility of biochar, thereby realizing the reduction of Cr (VI); and loading glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthetase to enhance the detoxification capability of microorganisms. The method is very effective for bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soil stressed by heavy metal Cr (VI), and the heavy metal Cr (VI) in the soil is partially removed while petroleum is removed.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GEOLOGY & MINERAL RESOURCES +1
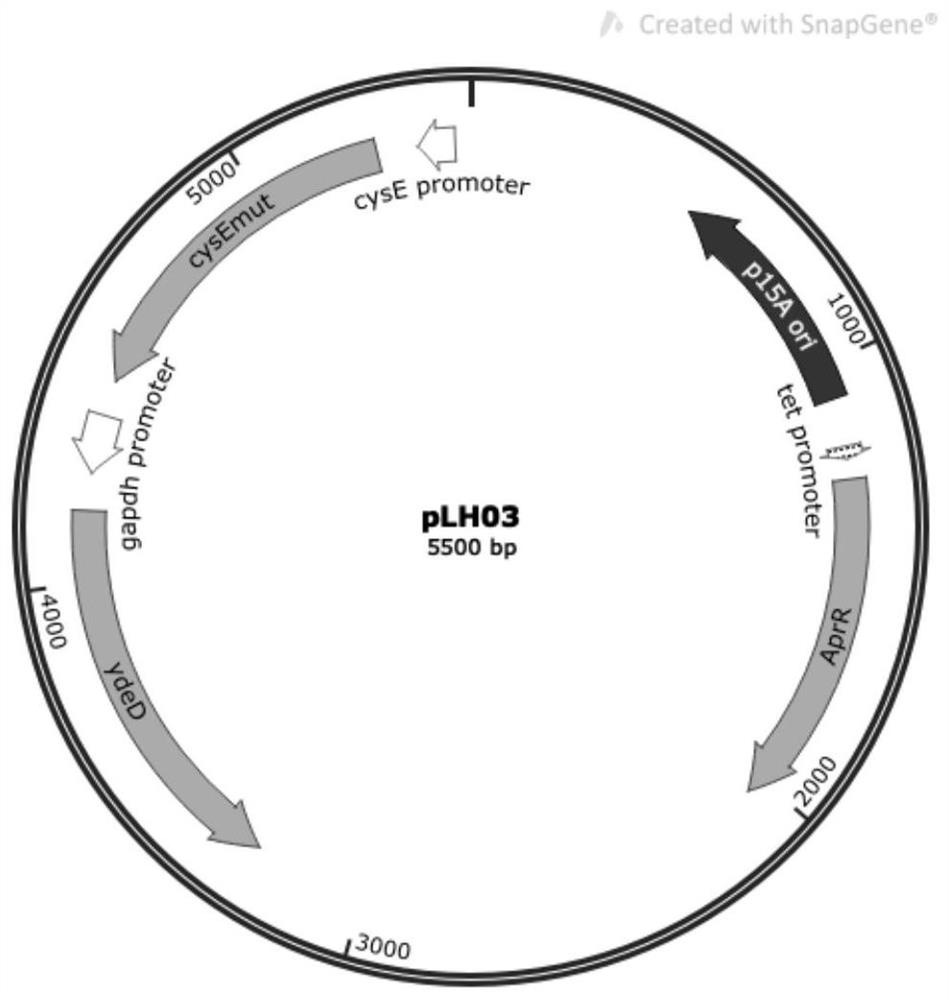
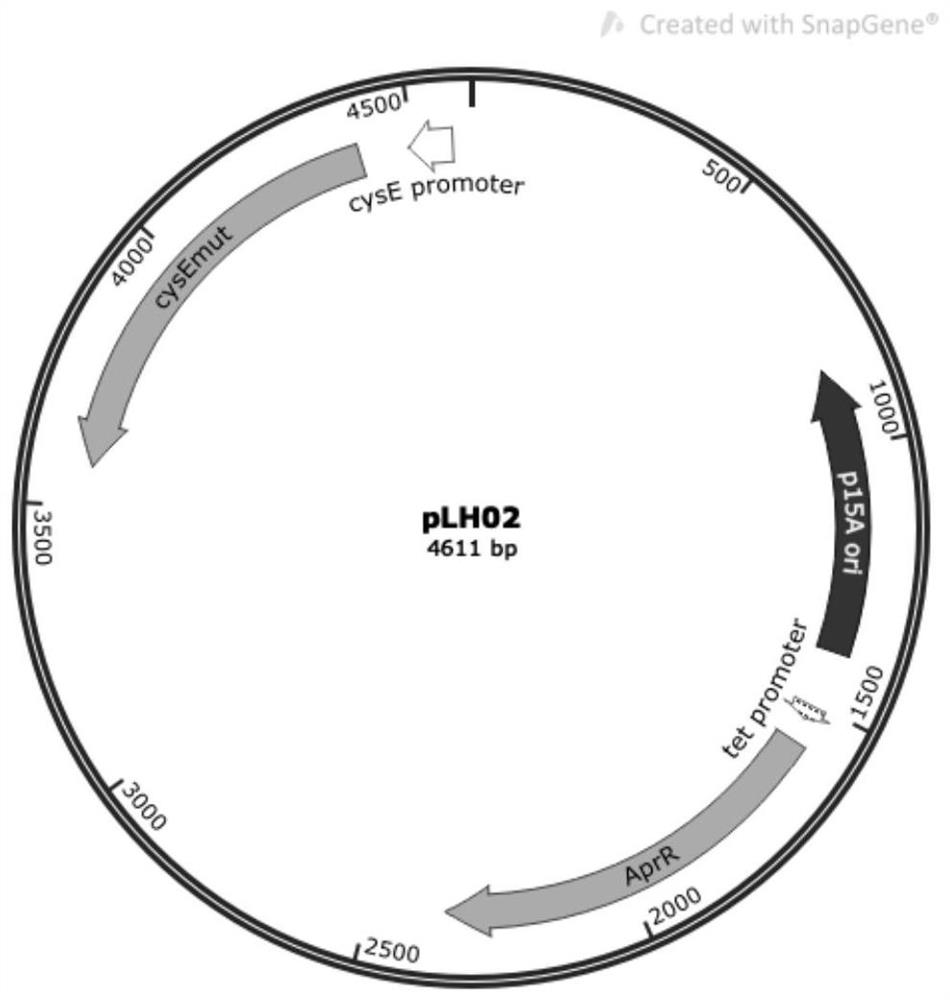
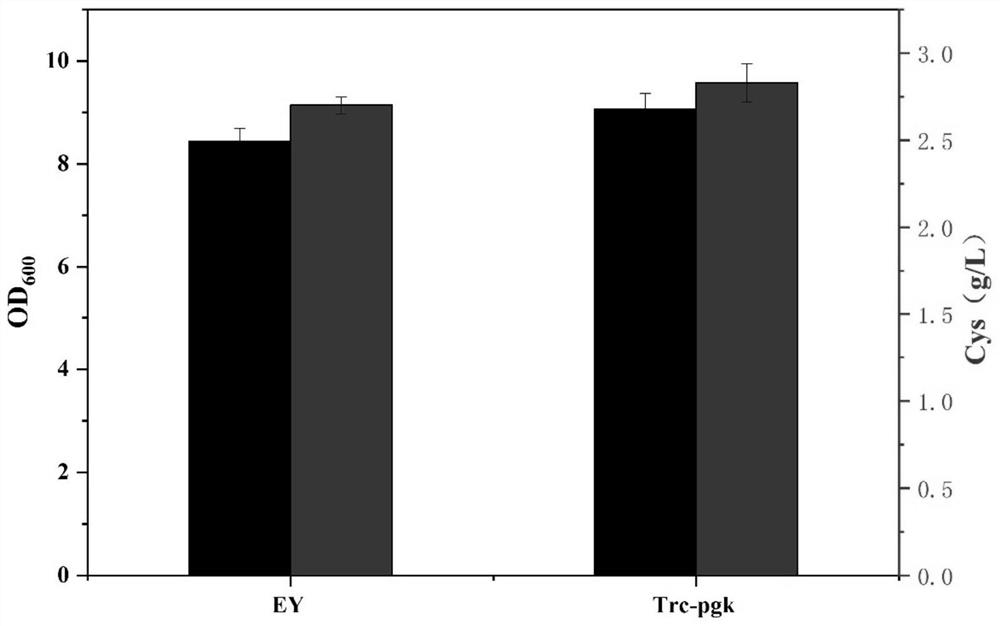
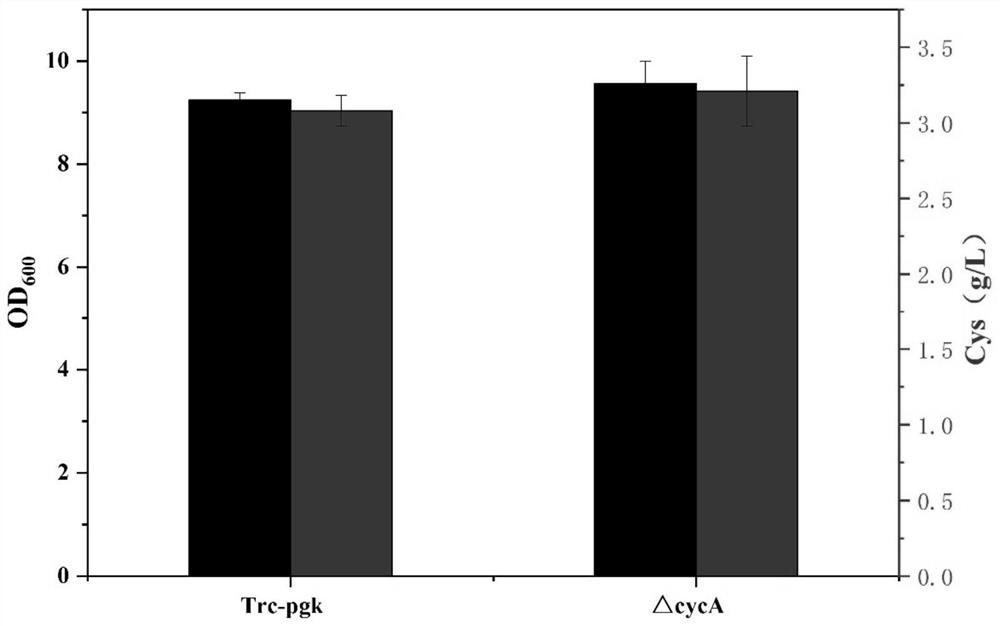
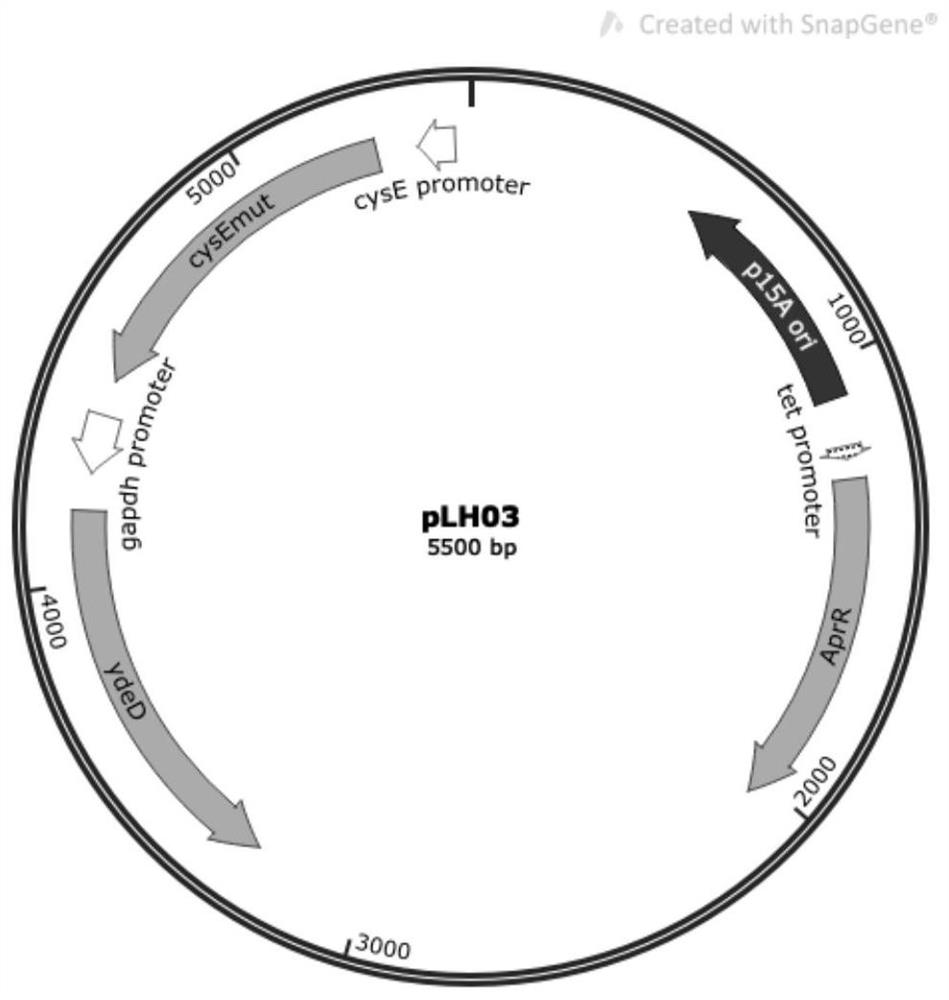
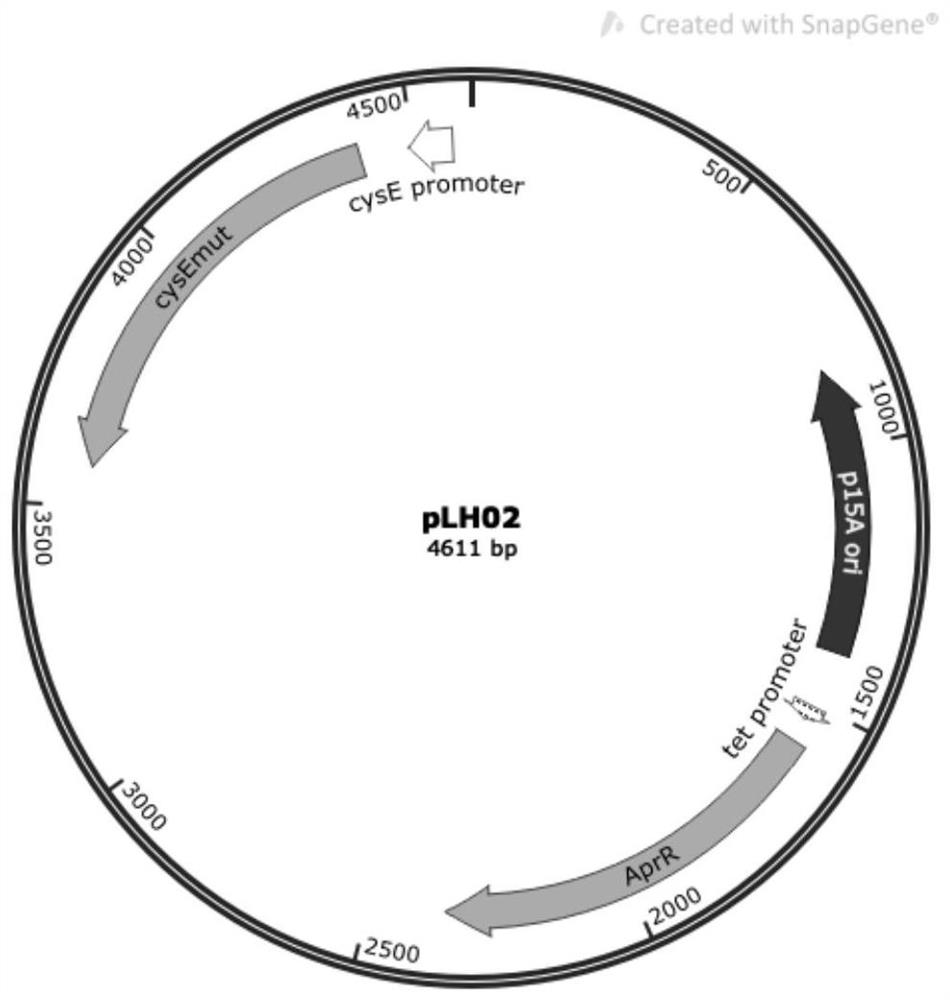
Construction method and application of recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing L-cysteine
ActiveCN113388630ALess genetic modificationGood production application valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention provides a construction method and application of recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing L-cysteine. The construction method comprises the following transformation ways: (1) adapting an L-cysteine expression plasmid pLH03 and an escherichia coli chassis cell, wherein the chassis cell is a K-12 series strain; (2) performing individual and / or combined expression on the L-cysteine synthetic pathway gene by using constitutive promoters with different intensities; and (3) knocking out an L-cysteine decomposition pathway gene and a precursor L-serine decomposition pathway gene of the L-cysteine decomposition pathway gene independently and / or in combination. The recombinant strain constructed by the invention is relatively less in gene modification, has high yield of L-cysteine, and has relatively high production and application values.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Application of gallic acid in reversing drug resistance of streptococcus suis to antibiotics
ActiveCN111249264AAddressing drug resistanceGood reversal effectAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyGallic acid ester
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Construction method of recombinant plasmids for glutathione biosynthesis
ActiveCN112662700AThe steps of the construction method are simpleFast growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationSynexpressionCysteine synthesis
The invention discloses a construction method of recombinant plasmids for glutathione biosynthesis, and relates to the technical field of bioengineering, the recombinant plasmids constructed by the method are saccharomyces cerevisiae double-gene co-expression plasmids, an OAS anabolism pathway of cysteine is introduced into saccharomyces cerevisiae cells through overexpression of serine O-acetyltransferase (SATase), synthesis of endogenous cysteine of saccharomyces cerevisiae can be promoted, the glutathione synthesis capacity of the saccharomyces cerevisiae in combination with overexpression of gamma-glutamylcysteine synthetase (GSH I) can be improved, and the growth speed of the saccharomyces cerevisiae in the logarithmic phase can be accelerated while the yield of the saccharomyces cerevisiae glutathione can be effectively improved.
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
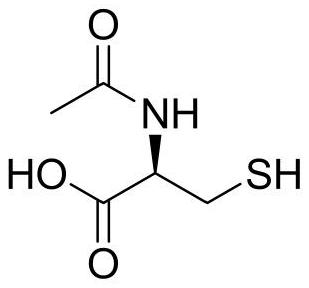
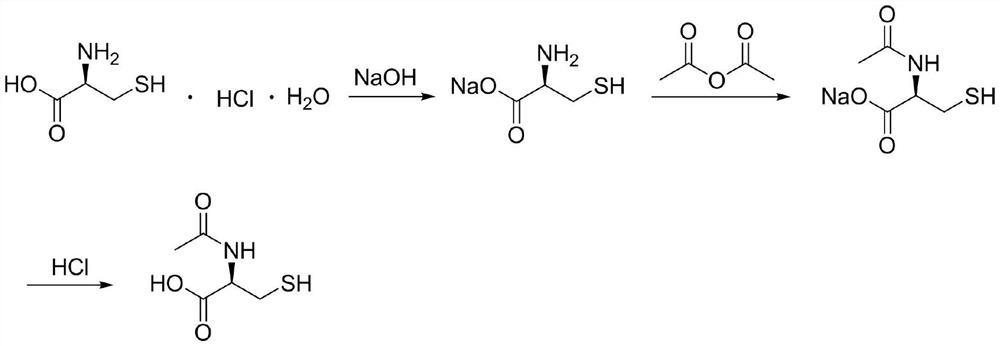
Synthesis method of N-acetyl-L-cysteine
ActiveCN113461580AReduce generationLower BThiol preparationAcetic anhydrideCYSTEINE HYDROCHLORIDE MONOHYDRATE
The invention discloses a synthesis method of N-acetyl-L-cysteine, which belongs to the field of amino acid manufacture, and comprises the following steps of: dissociating commercially available industrial L-cysteine hydrochloride monohydrate serving as a starting material by using sodium hydroxide to obtain L-cysteine sodium salt, acylating with acetic anhydride to obtain N-acetyl-L-cysteine sodium salt, and finally, adjusting the acid with hydrochloric acid to obtain an N-acetyl-L-cysteine crude product, and refining the crude product with pure water to obtain an N-acetyl-L-cysteine finished product. According to the synthesis method disclosed by the invention, the material ratio and reaction conditions are optimized, on the basis of reducing the cost of the raw materials, the conversion rate is increased to 97% or above, the generation of related impurities is greatly reduced, the post-treatment operation steps are optimized, the efficiency is improved, and the reaction molar yield is increased to 80% or above under the condition that the product quality is not influenced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG JINHUA CONBA BIO PHARM CO LTD
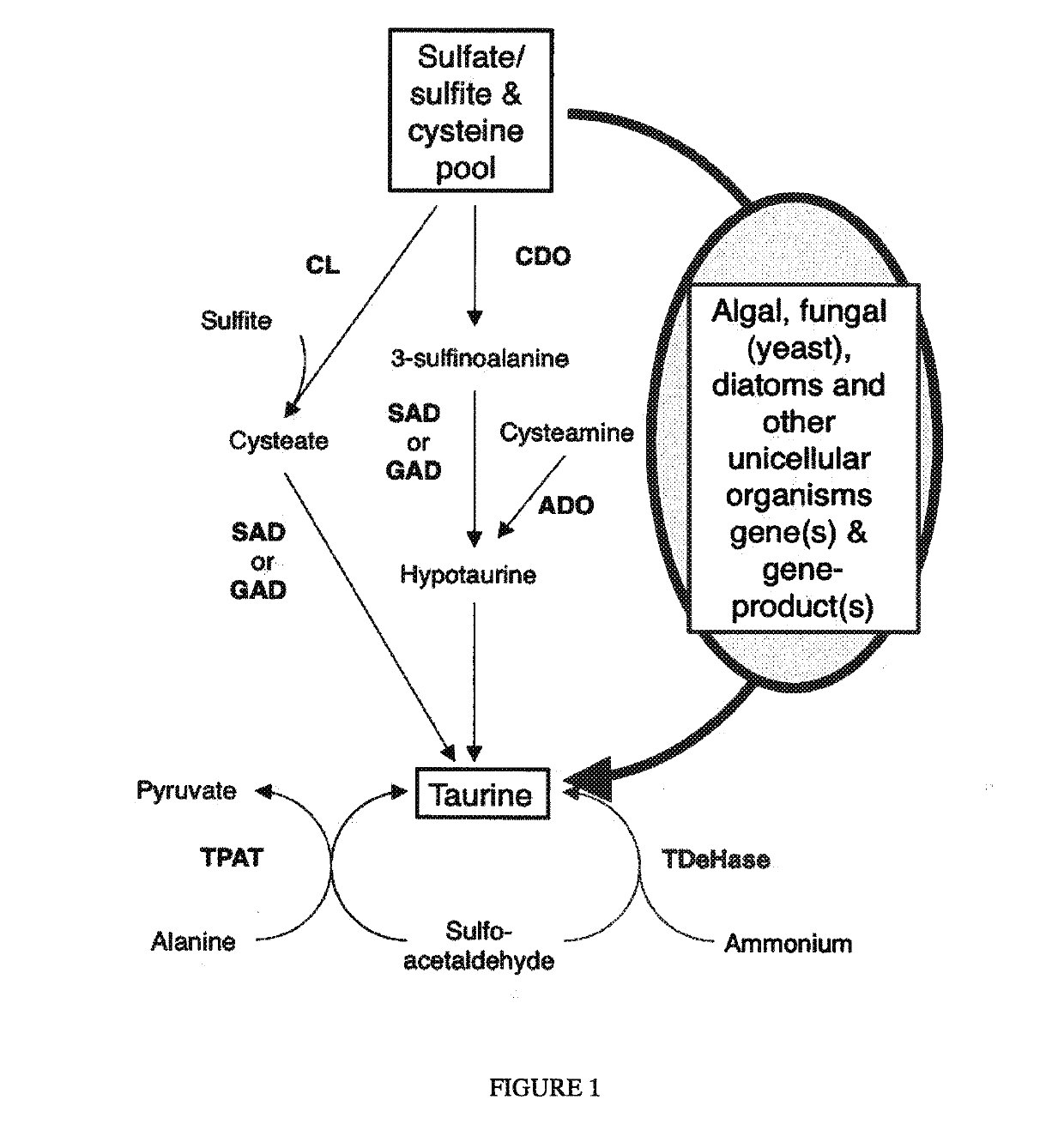
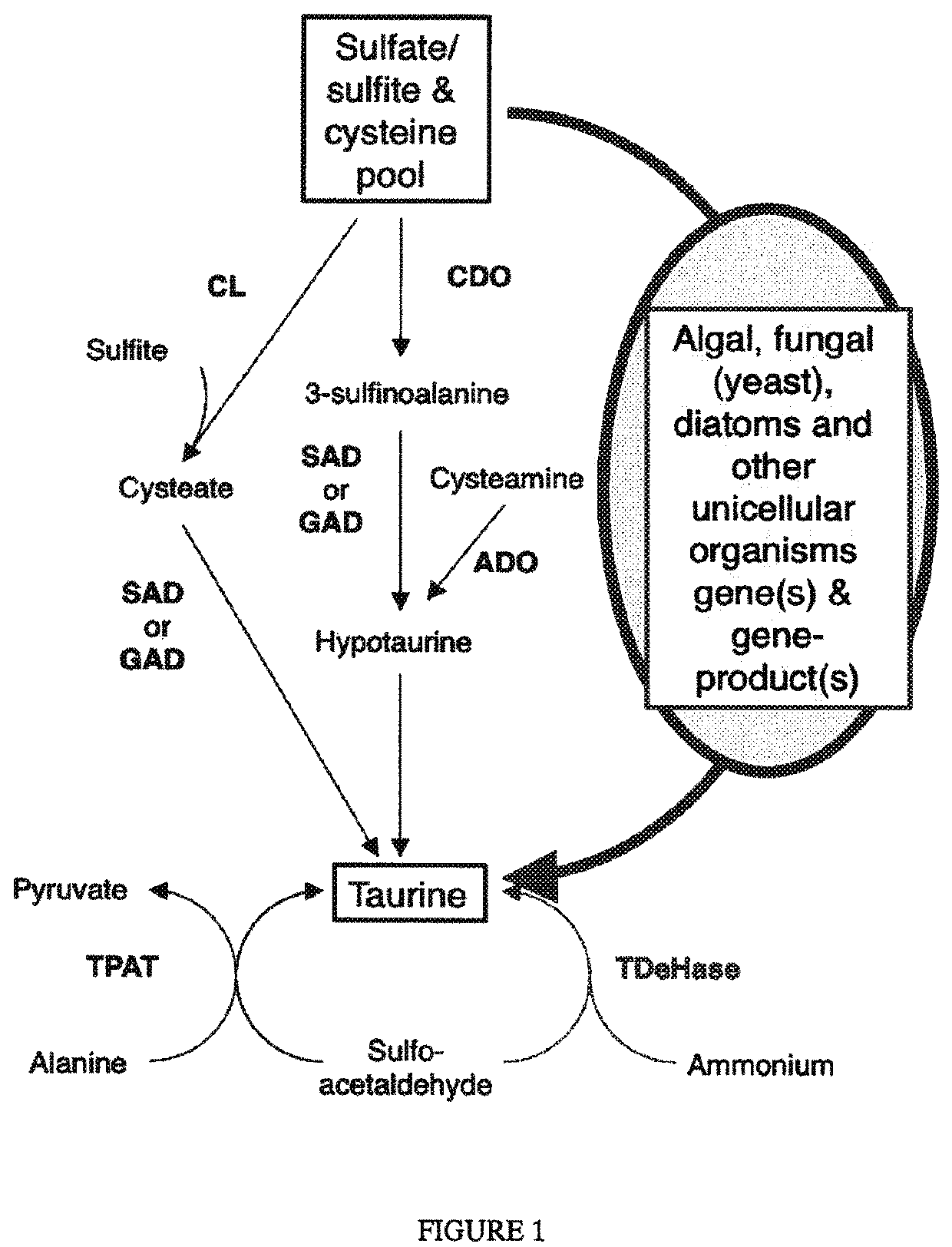
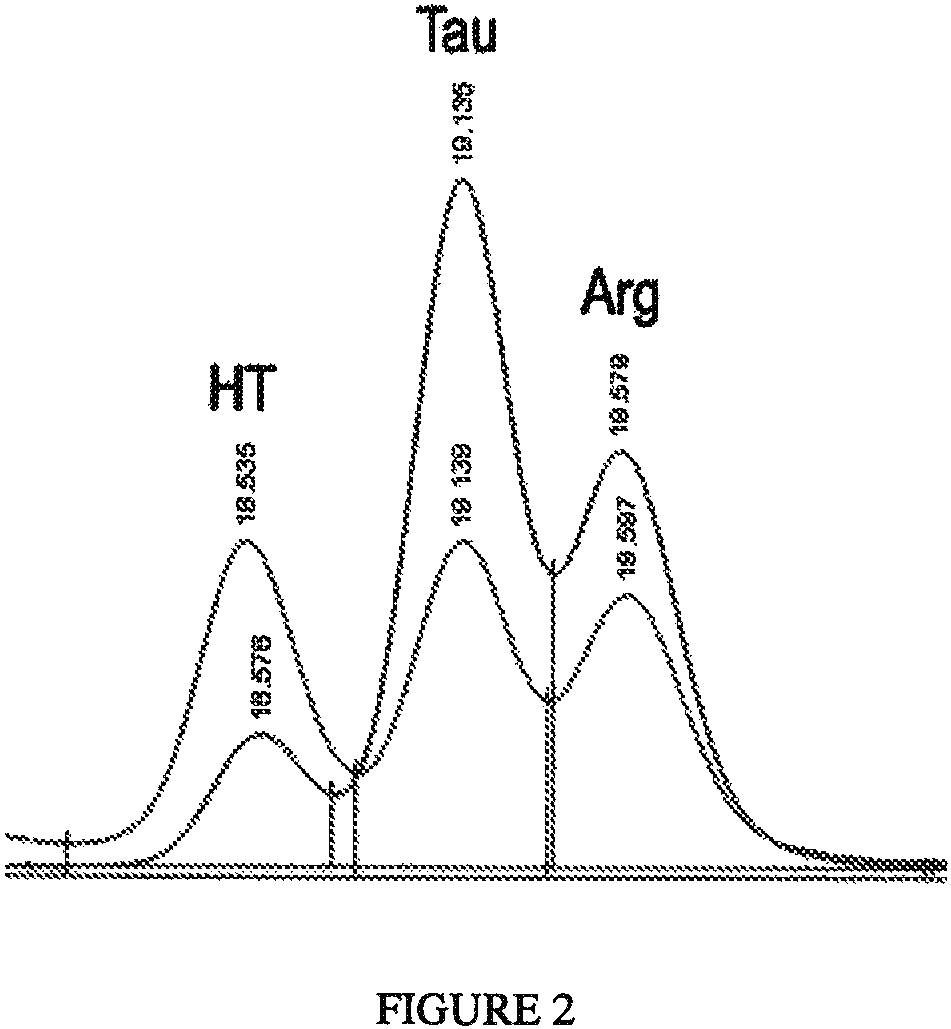
Algal and fungal genes and their uses for taurine biosynthesis in cells
The present invention describes an approach to produce taurine or increase hypotaurine or taurine production in prokaryotes or eukaryotes. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic transformation of organisms with algal, microalgal or fungal genes that encode proteins that pool catalyze the conversion of sulfur-containing compounds such as sulfate or cysteine to taurine. The invention describes methods for the use of polynucleotides for cysteine dioxygenase-like (CDOL), sulfmoalanine decarboxylase-like (SADL), cysteine sulfate / decarboxylase or a portion of the cysteine synthetase / PLP decarboxylase (partCS / PLP-DC) polypeptide in bacteria, alga, yeast, or plants to produce taurine or increase hypotaurine or taurine. The preferred embodiment of the invention is in plants but other organisms may be used. Taurine production or increased levels of hypoataurine or taurine in plants could be used as nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, or therapeutic compounds or as a supplement in animal feed or for animal feed or as an enhancer for plant growth or yield
Owner:PLANT SENSORY SYST
Reed gamma-glutamyl cysteine synthetase gene PcGCS and its application
InactiveCN101067136AImprove abilitiesEnzymesVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceGlutamylcysteine Synthetase
The present invention discloses one kind of reed gamma-gluamyl-cysteine synthetase gene PcGCS and its plant expression vector. The present invention discloses also the application of gene PcGCS in culturing heavy metal resisting plant, especially Agrostis stolonifera. Experiment shows that the transgenic plant of the present invention has greatly raised heavy metal enriching capacity.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cysteine synthase gene and use thereof
The present invention relates to a cysteine synthase gene and use thereof, especially a brewery yeast having controlled hydrogen sulfide-producing capability, a process for producing alcoholic beverages with controlled hydrogen sulfide amount. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast whose hydrogen sulfide-producing capability that increases the product flavor is controlled by enhancing the expression level of YGR012W gene encoding brewery yeast cysteine synthase Ygr012wp, particularly non-ScYGR012W gene specific to lager brewing yeast, and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Preparation method of immobilized enzyme used for synthesizing gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine
InactiveCN110964712AEfficient removalEfficient adhesionThiol preparationOrganic compound preparationBenzyl groupGlutamine
The invention discloses a preparation method of an immobilized enzyme used for synthesizing gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine, belonging to the technical field of biosynthesis. According to the invention, full contact between gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase and raw materials including L-glutamine and S-benzyl-L-cysteine is promoted in virtue of preparation of the immobilized enzyme, so effective exertionof catalytic activity is ensured. A synthesis method of gamma-L-glutamyl-L-cysteine has the advantages of usage of easily available raw materials, mild reaction conditions, simple and convenient reaction and post-treatment operation, high product yield and purity and low cost, and is suitable for industrial production.
Owner:MUDANJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
A kind of genetic engineering bacterium producing L-cysteine, construction method and application
ActiveCN111019877BEasy to synthesizeIncrease productionBacteriaStable introduction of DNAHeterologousMicrobacterium
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for simultaneously producing glutathione and S-adenosyl methionine at high yield
ActiveCN101676384AIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesS-Adenosyl methionineS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
The invention provides a recombined strain capable of simultaneously compressing glutathione synthetase system and adenosyl methionine synthetase and a method for simultaneously producing glutathione and S-adenosyl methionine at high yield. The recombined strain comprises: fragment capable of exogenously expressing gama-glutamyl cysteine synthetase or glutathione synthetase and fragment capable of exogenously expressing adenosyl methionine synthetase and the strain is capable of expressing glutathione synthetase system and / or adenosyl methionine synthetase, thereby fermenting glutathione and adenosyl methionine. The recombined strain is capable of simultaneously producing glutathione and adenosyl methionine by fermentation at high yield and independently producing glutathione or adenosyl methionine by fermentation.
Owner:浙江拜克生物科技有限公司
Method for extracting glutathione
InactiveCN106282280ANothing producedHigh yieldPeptide preparation methodsFermentationHigh concentrationReverse osmosis
The invention discloses a method for extracting glutathione. The method includes adding water, adenosine triphosphate, Y--glutamic acid and cysteine synthase GSH I into L-glutamic acid, L-cysteine and glycine which are used as substrates, carrying out catalysis, adding glutathione synthase GSH II into the substrates, carrying out catalysis, carrying out two-step reaction to obtain mixed solution with glutathione, the Y--glutamic acid and cysteine synthase and the glutathione synthase, separating the glutathione, the Y--glutamic acid and cysteine synthase and the glutathione synthase from one another to obtain low-concentration glutathione aqueous solution, the Y--glutamic acid and cysteine synthase and the glutathione synthase and allowing the Y--glutamic acid and cysteine synthase and the glutathione synthase to return systems to be reuse; carrying out low-pressure reverse osmosis concentration and high-pressure reverse osmosis concentration on the obtained low-concentration glutathione aqueous solution, then adding absolute ethyl alcohol into the glutathione aqueous solution, carrying out alcohol-precipitation crystallization on the glutathione aqueous solution to ultimately obtain glutathione products and recycling and reusing ethyl alcohol solution. The method has the advantages that high-concentration glutathione solution can be obtained by the aid of the method, the usage of the absolute ethyl alcohol can be reduced during alcohol-precipitation crystallization, energy consumption and the production cost can be decreased, the yield can be increased, the productivity can be improved, wastewater and waste gas can be prevented in production procedures, and accordingly the method is an environment-friendly, green and efficient production process.
Owner:河北美邦工程科技股份有限公司
Construction method and application of recombinant Escherichia coli for synthesizing l-cysteine
ActiveCN113388630BLess genetic modificationGood production application valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The present invention provides a construction method and application of recombinant Escherichia coli for synthesizing L-cysteine, and the construction method includes the following transformation approaches: (1) adapting L-cysteine expression plasmid pLH03 to Escherichia coli chassis cells, the Chassis cells are K-12 series strains; (2) L-cysteine synthesis pathway genes are expressed individually and / or in combination using constitutive promoters of different strengths; (3) L-Cysteine synthesis pathway genes are individually and / or in combination knocked out Cysteine catabolism pathway gene and its precursor L-serine catabolism pathway gene. The recombinant strain constructed by the invention has less genetic modification, high L-cysteine production and good production and application value.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Algal and fungal genes and their uses for taurine biosynthesis in cells
ActiveUS11078547B2Improve the level ofImprove featuresFodderTransferasesProkaryote organismsFungal gene
The present invention describes an approach to produce taurine or increase hypotaurine or taurine production in prokaryotes or eukaryotes. More particularly, the invention relates to genetic transformation of organisms with algal, microalgal or fungal genes that encode proteins that pool catalyze the conversion of sulfur-containing compounds such as sulfate or cysteine to taurine. The invention describes methods for the use of polynucleotides for cysteine dioxygenase-like (CDOL), sulfinoalanine decarboxylase-like (SADL), cysteine sulfate / decarboxylase or a portion of the cysteine synthetase / PLP decarboxylase (partCS / PLP-DC) polypeptide in bacteria, alga, yeast, or plants to produce taurine or increase hypotaurine or taurine. The preferred embodiment of the invention is in plants but other organisms may be used. Taurine production or increased levels of hypoataurine or taurine in plants could be used as nutraceutical, pharmaceutical, or therapeutic compounds or as a supplement in animal feed or for animal feed or as an enhancer for plant growth or yield.
Owner:PLANT SENSORY SYST
Preparation method for synthesizing diaryl thioether compound based on L-cysteine
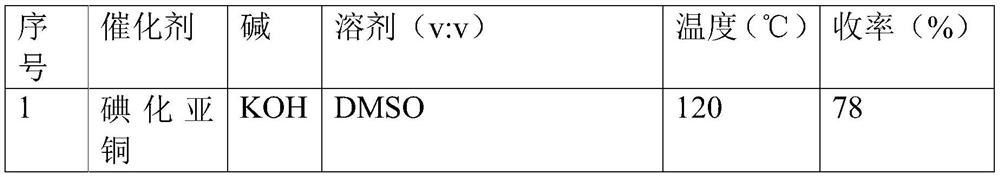
PendingCN113999149AImprove compatibilityMild reaction conditionsSulfide preparationChemical synthesisPtru catalyst
The invention belongs to the intermediate field of pharmaceutical chemical industry, and relates to a preparation method for synthesizing a diaryl thioether compound based on L-cysteine. The method comprises the following steps: under the protection of inert gas, adding substituted iodobenzene and L-cysteine into an aprotic polar solvent, then adding a copper salt catalyst and alkali, and reacting at 100-150 DEG C for 6-24 hours to obtain the diaryl thioether compound. The method has the advantages of simple and mild reaction conditions, safety, no toxicity, low price, simplicity and convenience in operation, good functional group compatibility, efficient reaction system, small environmental pollution and the like; diaryl thioether is an important pharmaceutical and chemical synthesis intermediate and chiral ligand, and has very wide application in the fields of biological medicine, organic synthesis, chemistry and chemical engineering and the like, so that the method has relatively high use value and social and economic benefits.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
A bioremediation method for immobilized petroleum-contaminated soil against cr(ⅵ) stress
ActiveCN113042521BInnovative Immobilized Bioremediation MethodContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganism based processesCarbonizationBioremediation
The invention discloses a method for immobilized bioremediation of oil polluted soil against Cr(VI) stress. Using tartary buckwheat shells as raw materials, the reducibility of biochar was gradually improved by hydrothermal carbonization in ethylenediamine aqueous solution and ascorbic acid solution, rotating heating in formic acid, and loading nano-sized zero-valent aluminum, in order to achieve the reduction of Cr(Ⅵ). ; Enhance the detoxification ability of microorganisms by loading glutamylcysteine synthetase and glutathione synthase; At the same time, the heavy metal Cr(Ⅵ) in the soil was partially removed.
Owner:CHONGQING INST OF GEOLOGY & MINERAL RESOURCES +1
Process for preparing serine-rich protein employing cysteine synthase (cysk) gene
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a foreign protein comprising culturing a bacterium containing the cysteine synthase (cysK) gene and a gene encoding the foreign protein. The present invention comprises the steps of culturing a bacterium transformed with an expression vector containing a gene encoding a serine-rich foreign protein and an expression vector containing the cysK gene, or a bacterium transformed with an expression vector containing the cysK gene and a gene encoding a serine-rich foreign protein and isolating the foreign protein therefrom. The present invention is expected to be widely used to increase the production yield of a serine-rich foreign protein.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
A kind of Escherichia coli engineering bacteria producing 5-aminolevulinic acid
ActiveCN106497858BSynthesis efficiently utilizes the C4 pathway to promoteEasy to synthesizeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses engineered escherichia coli for producing 5-aminolevulinic acid and belongs to the fields of metabolic engineering and microbial fermentation. The engineered escherichia coli is characterized by carrying out co-expression of a gene coaA for coding pantothenate kinase, a gene dfp for coding phosphoric acid pantothenylcysteine synthetase and decarboxylase and a gene coaD for coding phosphoric acid CoA pyrophosphorylase from an escherichia coli CoA synthetic pathway by using pUC19 and pETDuet-1 vectors on the basis of excess expression of 5-aminolevulinate synthase hemA which is used as a key enzyme in a synthetic pathway of 5-aminolevulinic acid C4 by using a vector pRSFDuet-1-hemA to build recombination strains. Shake-flask culture proves that the yield of recombinant bacteria ALA for co-expression of CoA pathway genes is obviously improved; the maximum yield reaches 700mg / L and is increased by about 46% in comparison with contrast.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for preparing serine-rich protein employing cysteine synthase (cysk) gene
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a foreign protein comprising culturing a bacterium containing the cysteine synthase (cysK) gene and a gene encoding the foreign protein. The present invention comprises the steps of culturing a bacterium transformed with an expression vector containing a gene encoding a serine-rich foreign protein and an expression vector containing the cysK gene, or a bacterium transformed with an expression vector containing the cysK gene and a gene encoding a serine-rich foreign protein and isolating the foreign protein therefrom. The present invention is expected to be widely used to increase the production yield of a serine-rich foreign protein.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
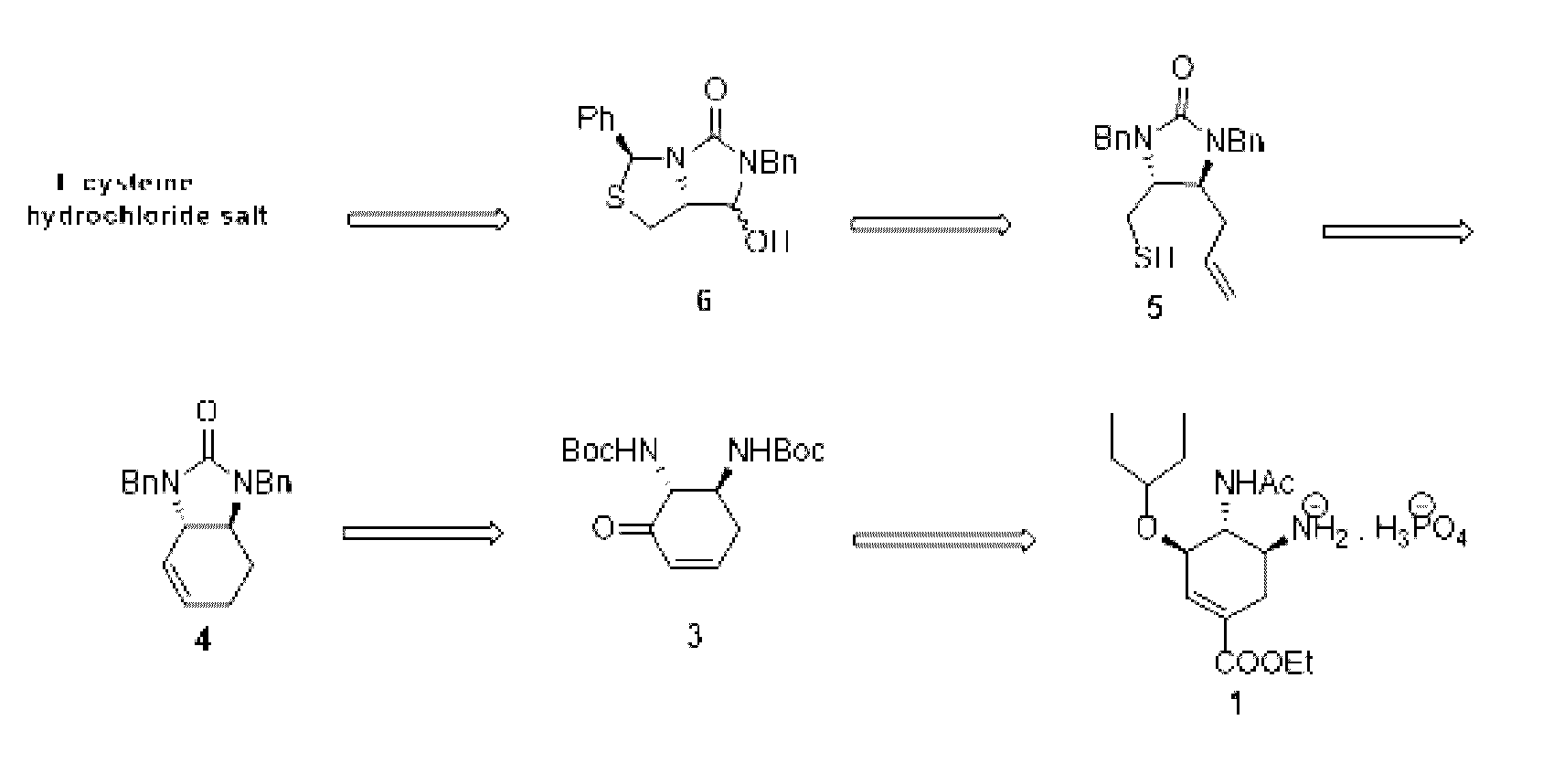
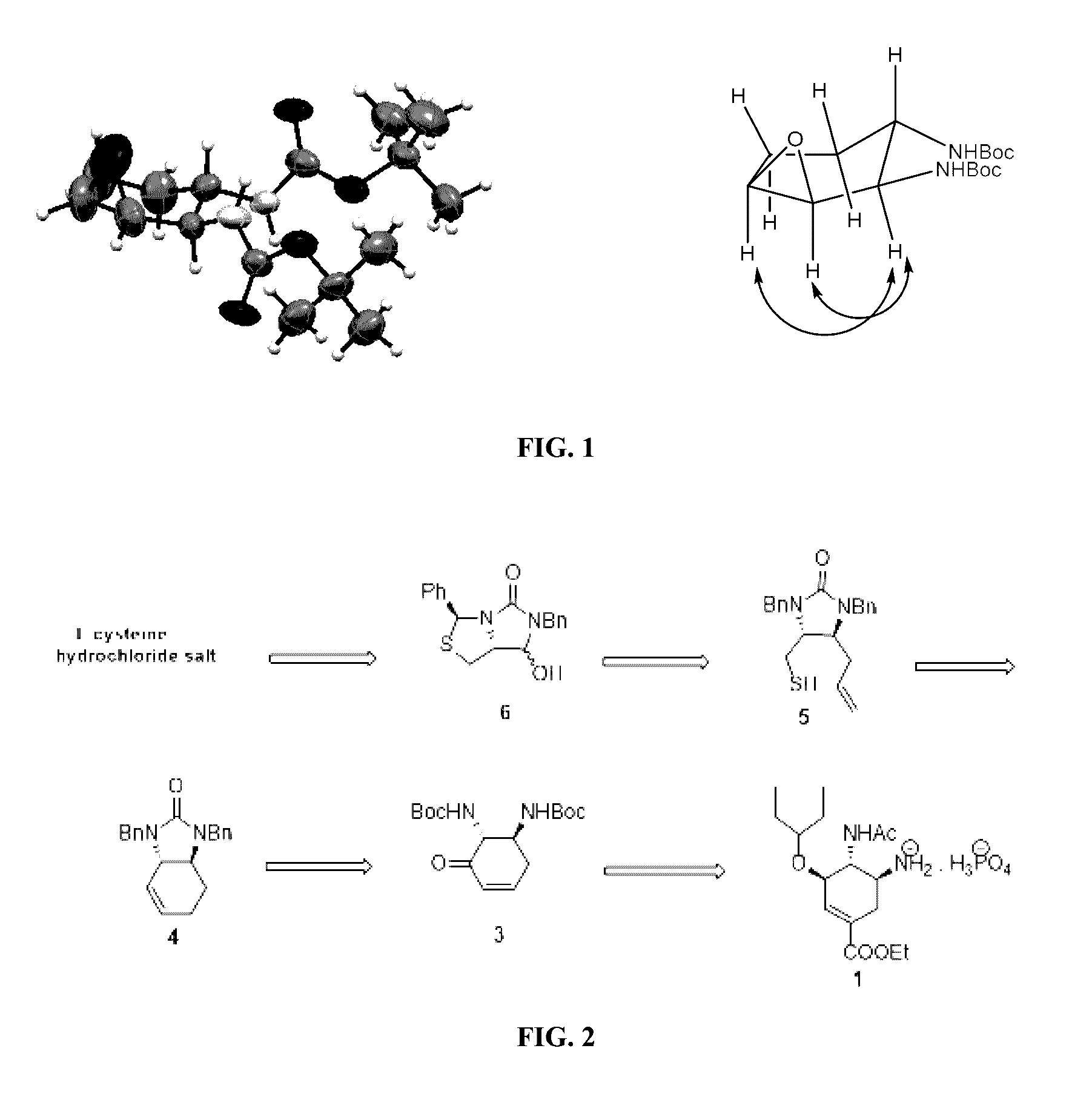
Process for the preparation of intermediate for the preparation of oseltamivir phosphate
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com