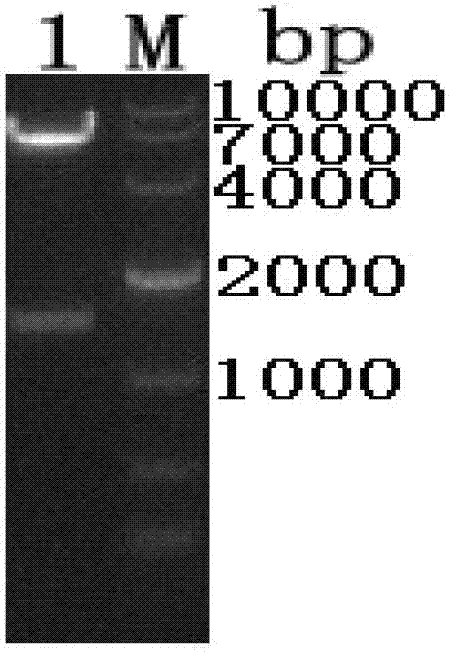Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33 results about "Phosphoglycerate kinase 1" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
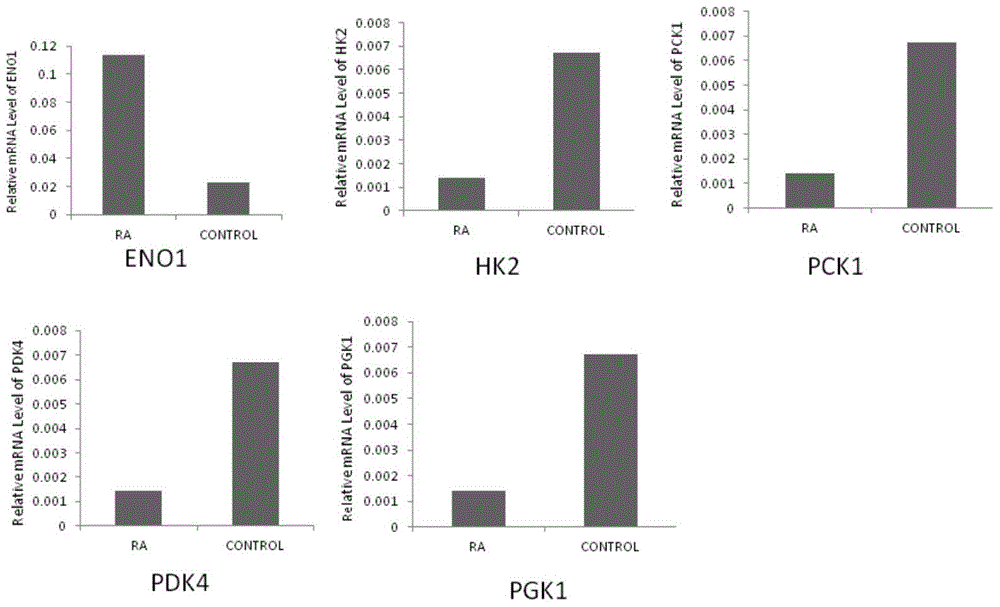
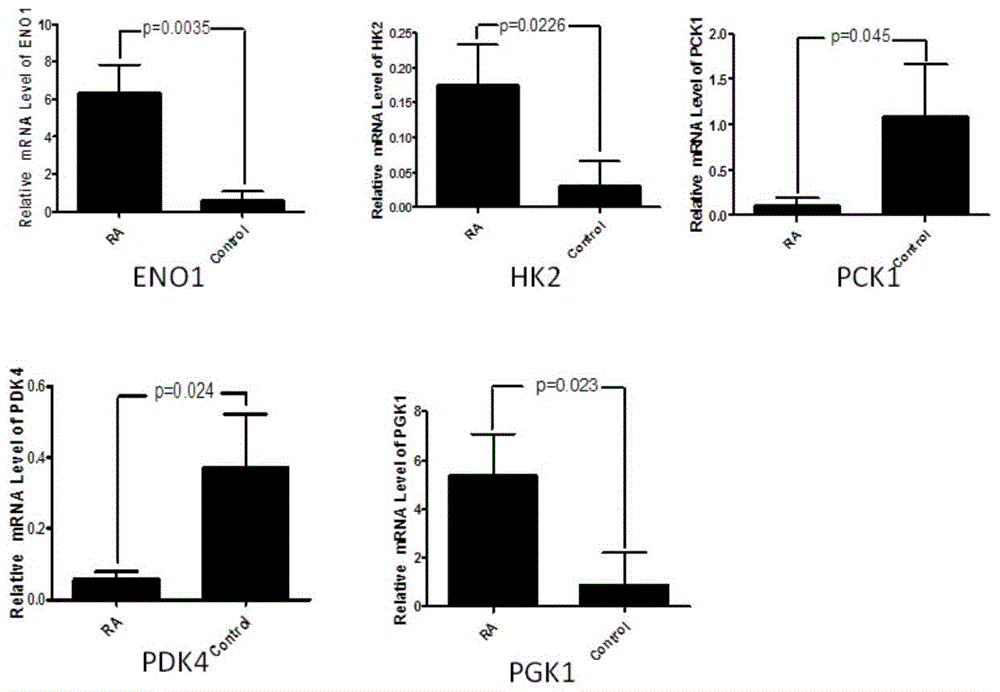
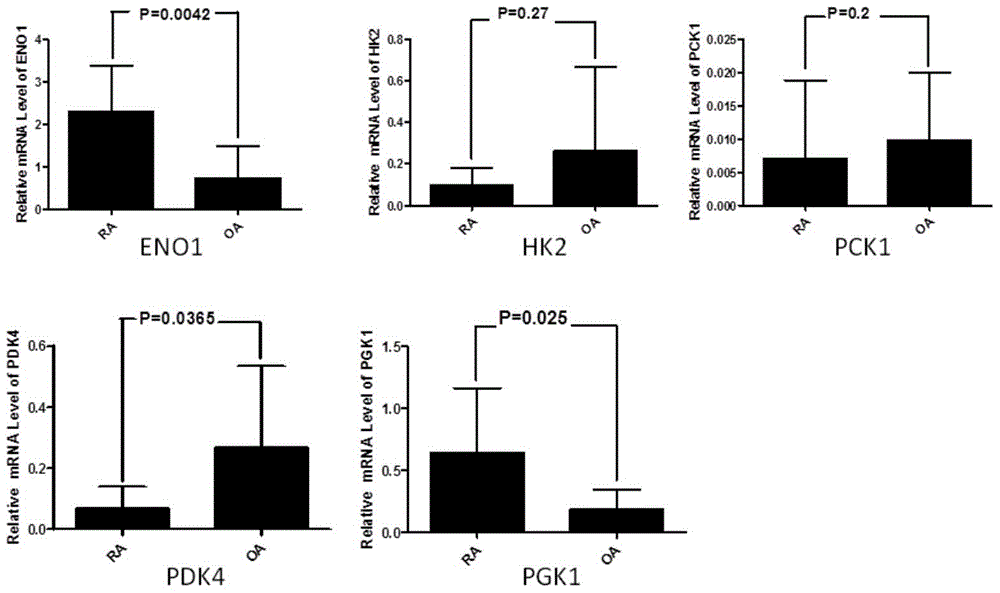
Phosphoglycerate kinase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PGK1 gene.
Nucleic acid construct for endogenously expressing RNA polymerase in cells
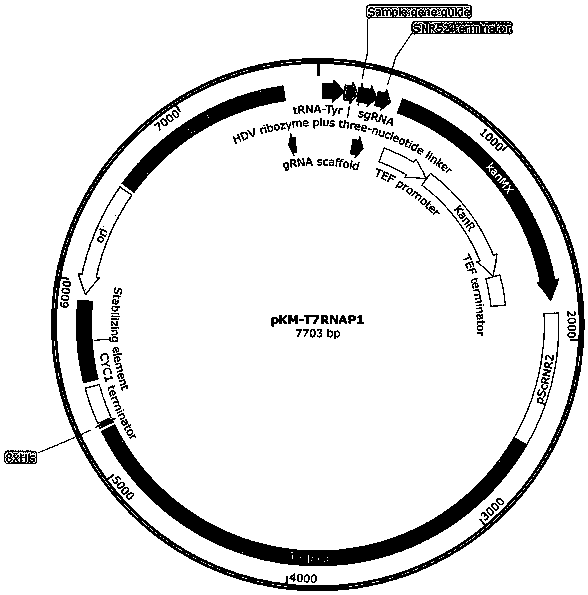
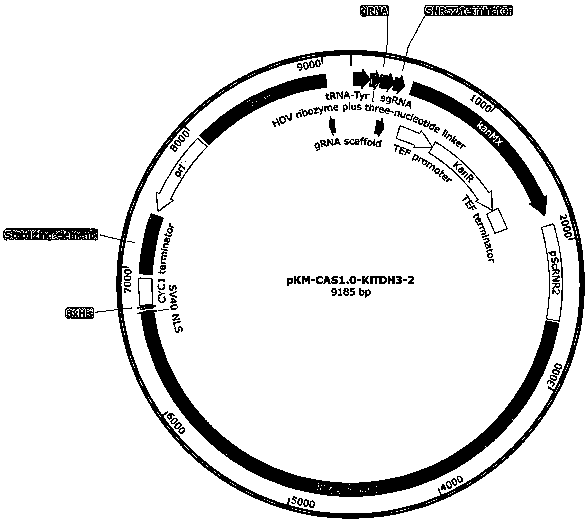
The invention provides a nucleic acid construct for endogenously expressing RNA polymerase in cells, and particularly discovers a novel nucleic acid construct capable of greatly enhancing protein translation efficiency. The nucleic acid construct consists of a promoter with specific promotion intensity (such as RNR2, ADH1, GAPDH, TEF1, PGK1 and SED1) and coding sequences of proteins of RNAP (suchas T7RNAP, T3RNAP, T4RNAP and T5RNAP), if the nucleic acid construct of the invention is applied into a yeast extracorporeal protein synthesis system, the activity of synthesized luciferase is quite high relative to light unit value (RLU), and the effect can be the same as the effect of T7RNAP added exogenously. The effect can reach up to 6.6* 107.
Owner:KANGMA SHANGHAI BIOTECH LTD
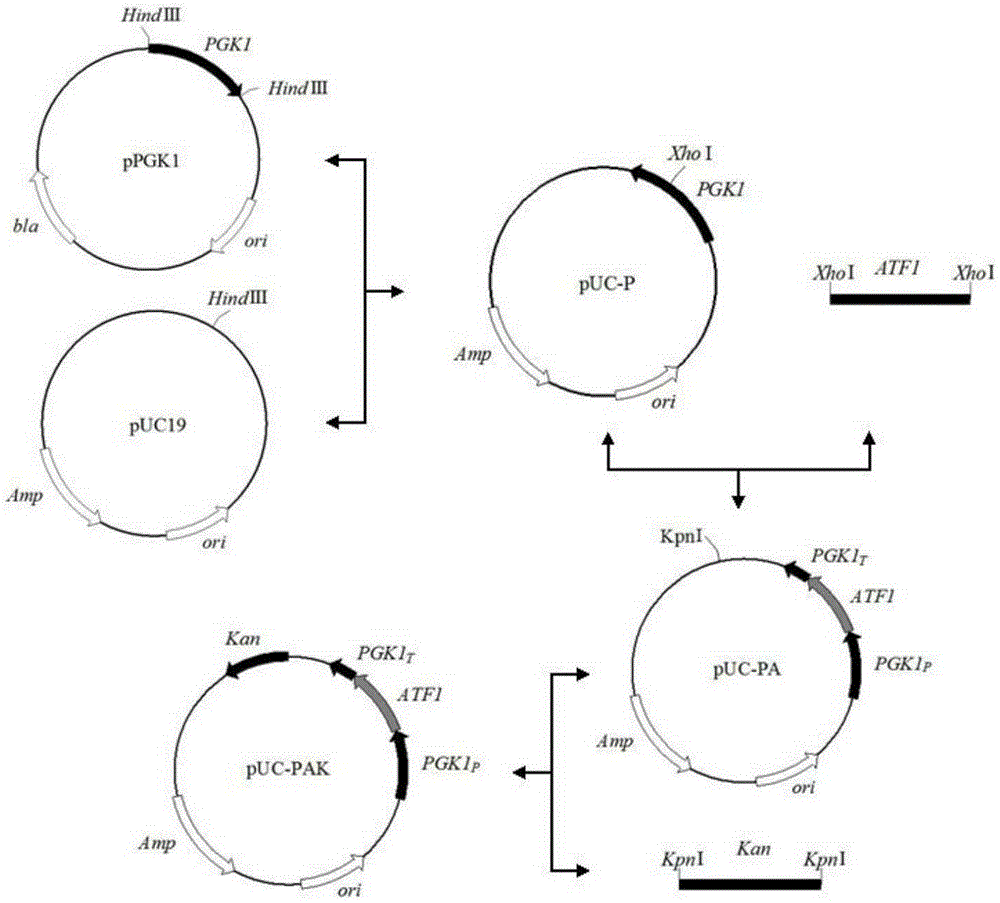
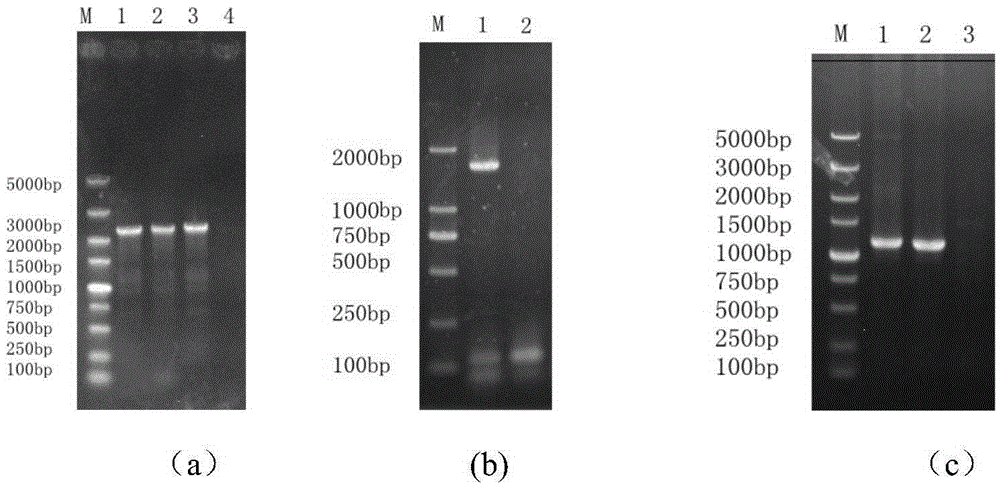
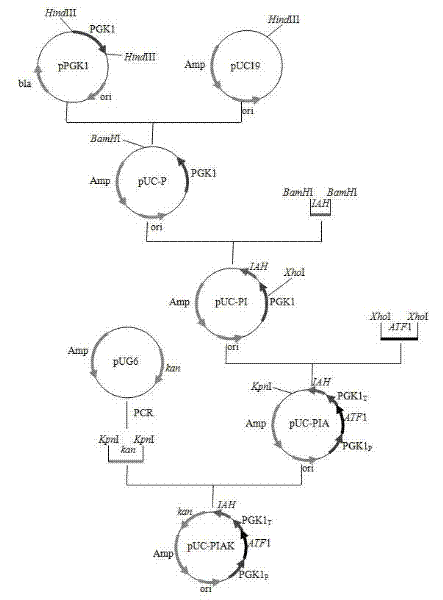
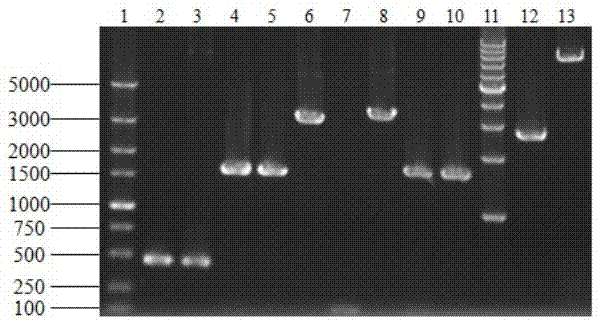
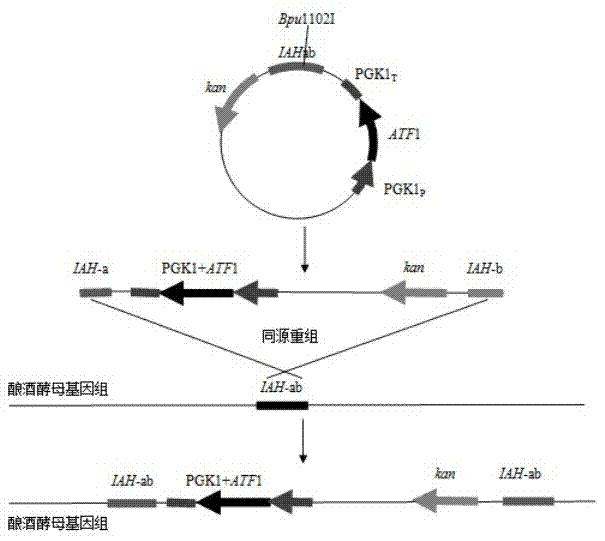
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as building and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
PendingCN105385615AReduce outputOvercome flavor incongruityFungiHydrolasesEster hydrolaseBio engineering
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol as well as a building method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. According to the building method provided by the invention, through completely knocking out an amino acid transaminase gene BAT2 and an ester hydrolase gene IAH1 in an original strain, and selecting a strong promoter PGK1 over-expression alcohol acetyltransferase I gene ATF1 at the same time, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of ester and low yield of higher alcohol is obtained. Compared with a parent strain, other fermentation performances of built recombinant bacteria are not affected, the total quantity of acetic acid ester is obviously increased and reaches 1303.6mg / L, wherein the content of ethyl acetate is 52 times that of the original strain, isoamyl acetate is increased to 73.7mg / L, the content of main higher alcohol is 151.8mg / L and is reduced by 61.4 percent in comparison with that of the original strain. By using the saccharomyces cerevisiae, ester yield is significantly increased while the higher alcohol yield is reduced, the higher requirements of white spirit related fields on yeast are met and the application prospect is wide.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield and construction method thereof
ActiveCN102199556AReduce contentIncrease contentFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationEster hydrolaseGenetic engineering
The invention discloses Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with high ester yield. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria EY-13 were collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 17, 2010, the collection number is CGMCC NO.4350, and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria are recommended to be named Saccharomyces cerevisiae. PGK1 derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae is selected as a promoter; and the construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria with the high esteryield comprises a step of knocking-out an IAH1 gene for encoding ester hydrolase in a Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome when an ATF1 gene which is derived from the Saccharomyces cerevisiae and is used for encoding alcohol acetyltransferase is overexpressed. Compared with initial recipient bacteria, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genetic engineering bacteria have the advantages that: after rice wine fermentation is simulated, the content of isoamylol is about one half, the content of ethyl acetate is improved by 20 times, the content of isoamyl acetate is 100mg / L, and the content of isobutyl acetate is 5 to 7mg / L; and after liquor fermentation is simulated, the content of total esters is improved by 4 times and the content of the ethyl acetate is improved by 35 times, so an excellent strain is provided for the production of brewing industry.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN102796675AImprove the lubrication effectImprove securityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLipid formation
The invention relates to a rhodotorula glutinis oil genetic engineering strain and a construction method and an application thereof. The construction method of the genetic engineering strain is mainly as follows: utilizing rDNA (recombinant deoxyribonucleic acid) of rhodotorula glutinis as a target sequence for homologous integration, using strong promoter genes PGK1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae and malate dehydrogenase genes ME of chaetomium cochloides to construct an expression vector to be introduced into rhodotorula glutinis, and enabling ME genes to obtain high-efficient expression in a rhodotorula glutinis body, wherein the content of lipid in a transformant is improved by 2.5 times in comparison with a wild strain. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, key enzyme genes and a strong promoter for anabolism of the lipid are introduced on the basis that the anabolism of microbial oil is known, so that the lipid metabolism is regulated and controlled, and the yield of oil is improved. The genetic engineering strain can be applied to production of the microbial oil and development of functional oil related products, such as medicaments, health care products and the like.
Owner:广州溯原生物科技股份有限公司
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of flavor ethyl ester and construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
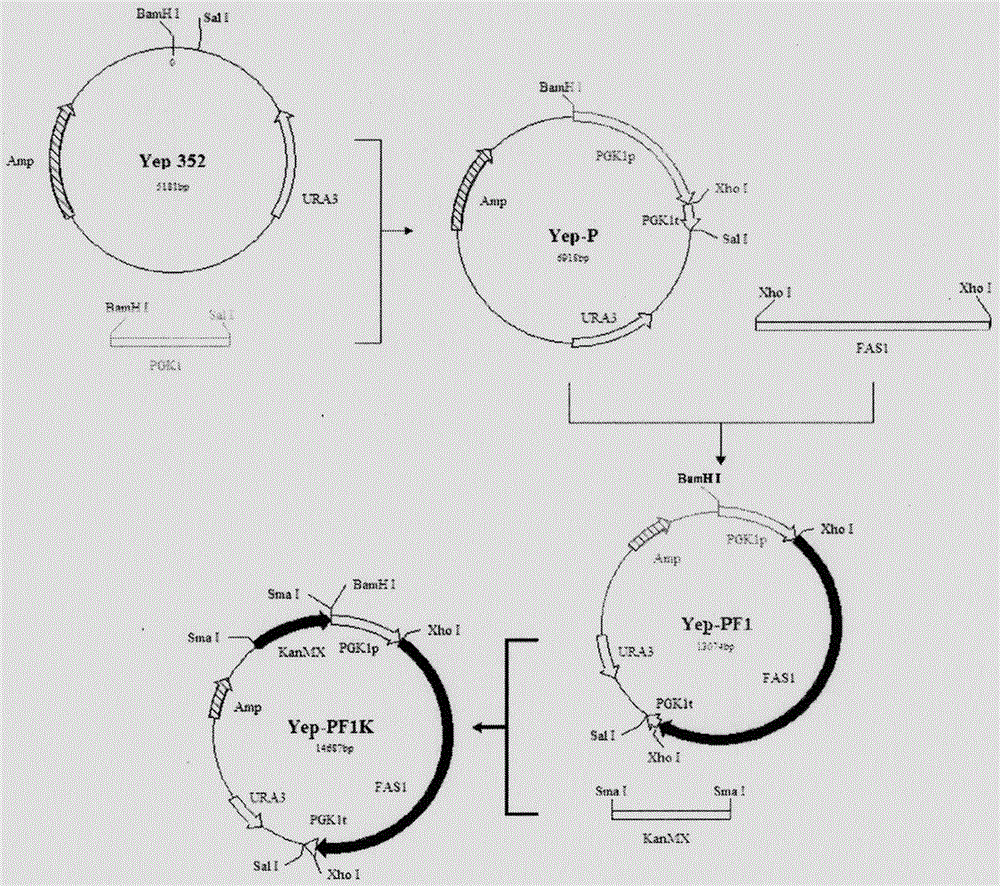
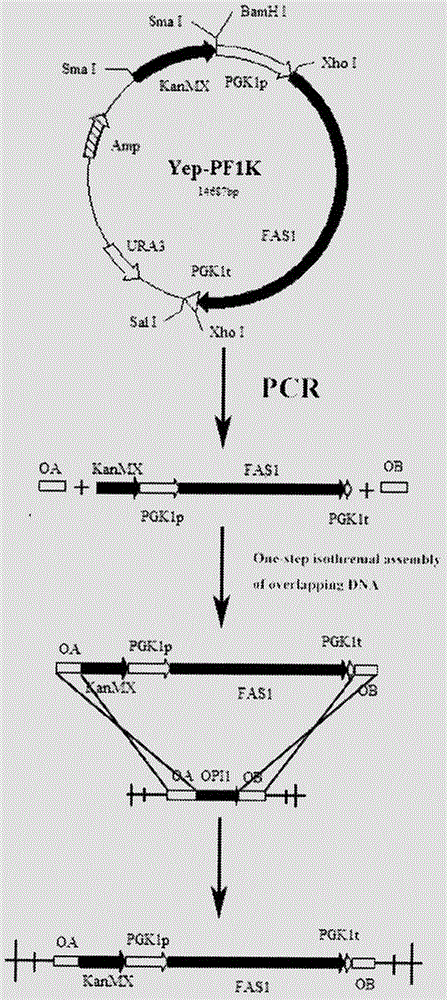
The invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of flavor ethyl ester and a construction method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. An encoding gene FAS1 of a strong promoter PGK1 over-expressed fatty acid synthetase beta subunit is selected, an inositol-mediated controlling gene OPI1 is knocked out, and the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain with high yield of flavor ethyl ester is obtained. Compared with original strains, the strain has the following advantages under the condition that other fermentation performance of the strain is basically not affected: the content of ethyl acetate reaches 52.49 mg / L and is increased by 2.61 times than that of the original strains after 5 days of simulated liquid-state liquor fermentation of a corn material; the content of medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester ethyl caproate, the content of ethyl caprylate, the content of ethyl caprate and the content of ethyl laurate are increased by 1.21 times, 2.66 times, 2.53 times and 1.27 times respectively than those of the original strains; the content of long-chain fatty acid ethyl ester ethyl myristate and the content of ethyl palmitate are increased by 1 time and 56.7% respectively.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Freezing-resistant yeast strain for bread fermentation and breeding method thereof
ActiveCN103497903AImprove synthesis abilityEnsure safetyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTrehalose-6-phosphate synthase
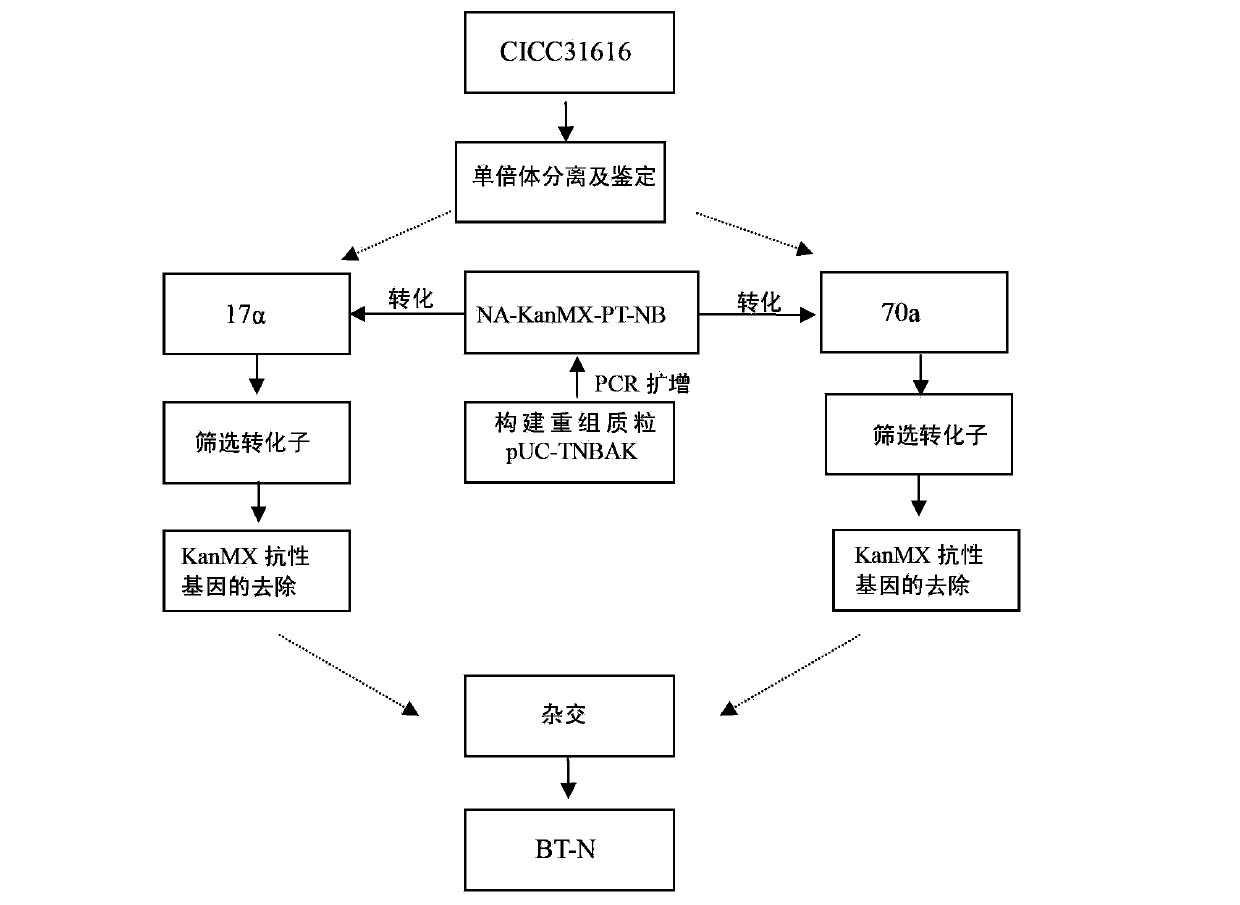
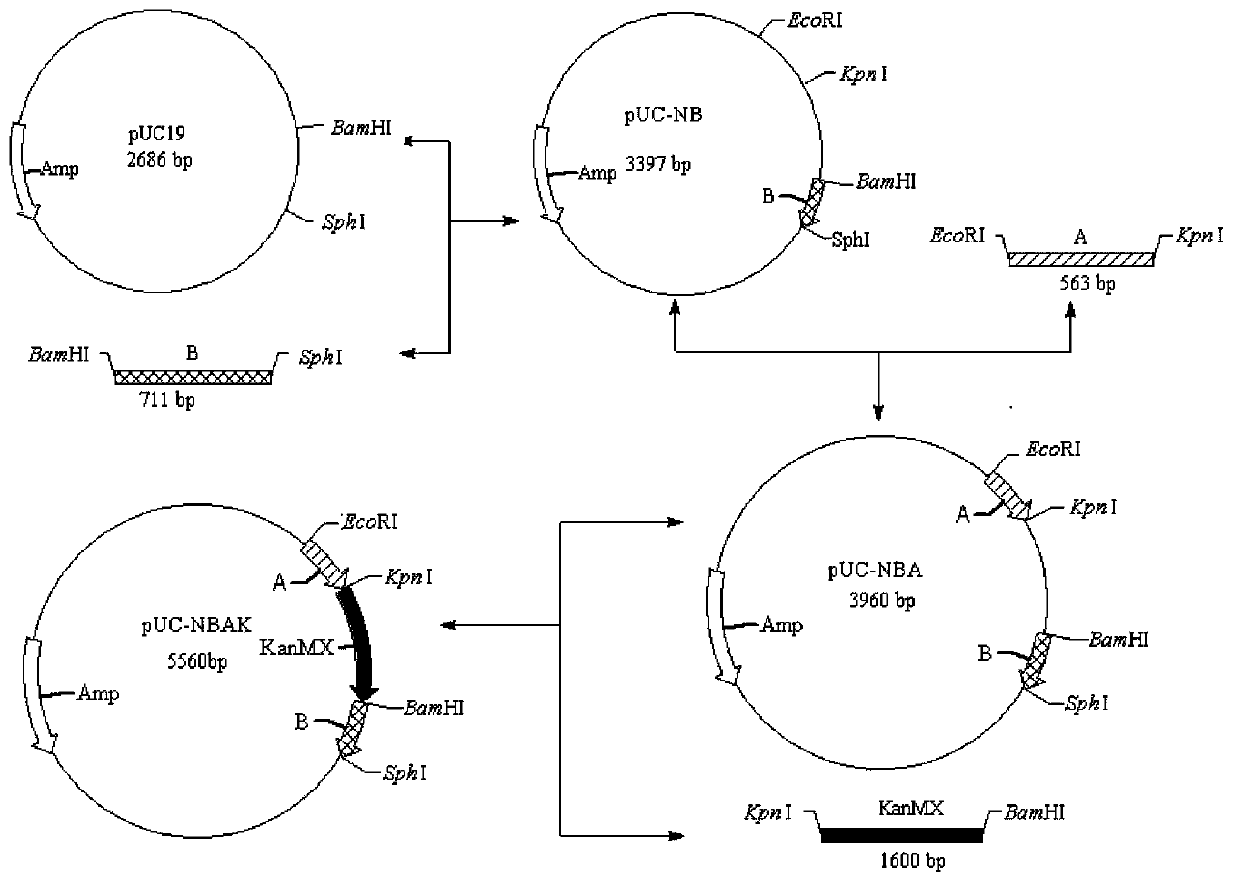
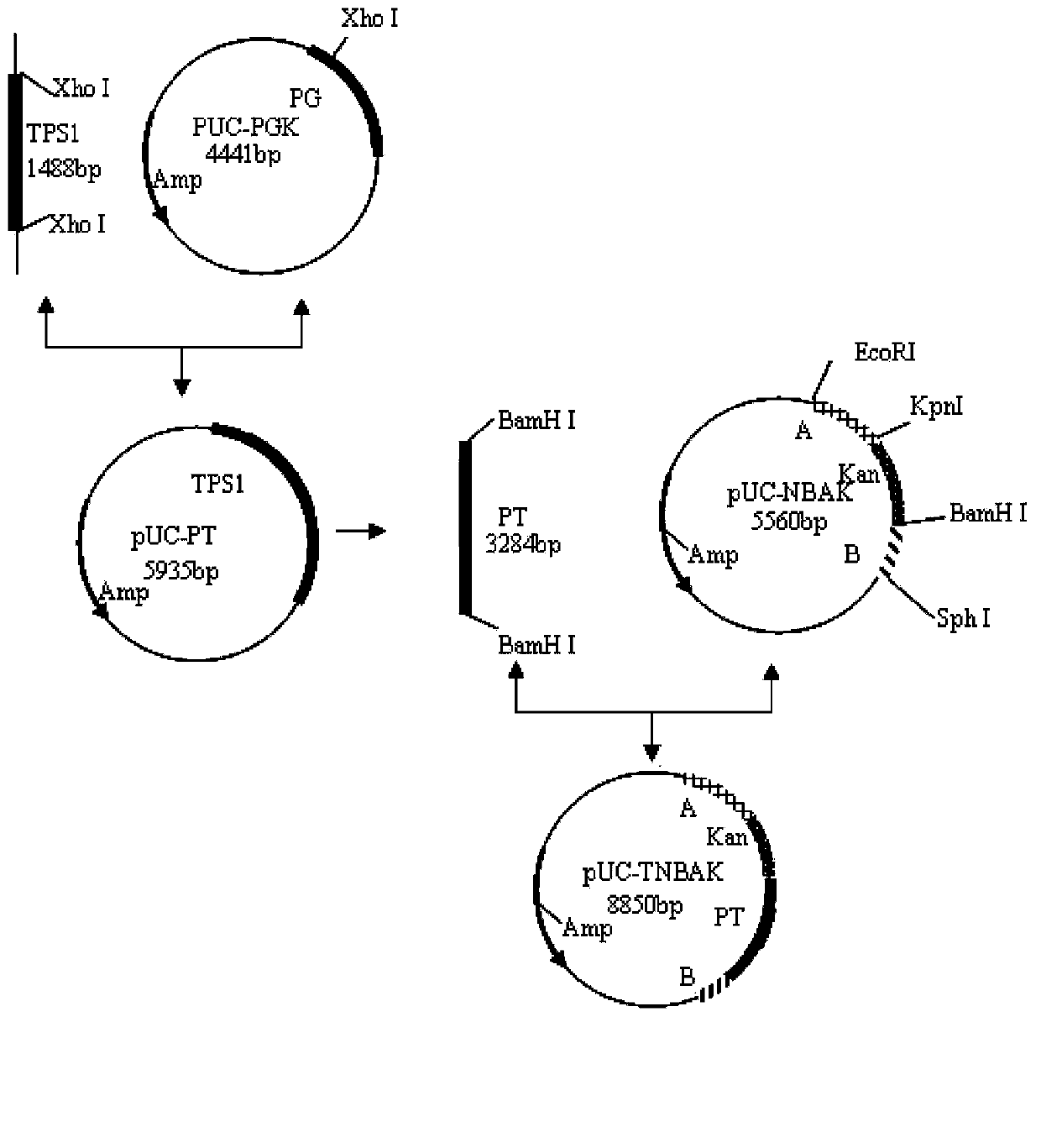
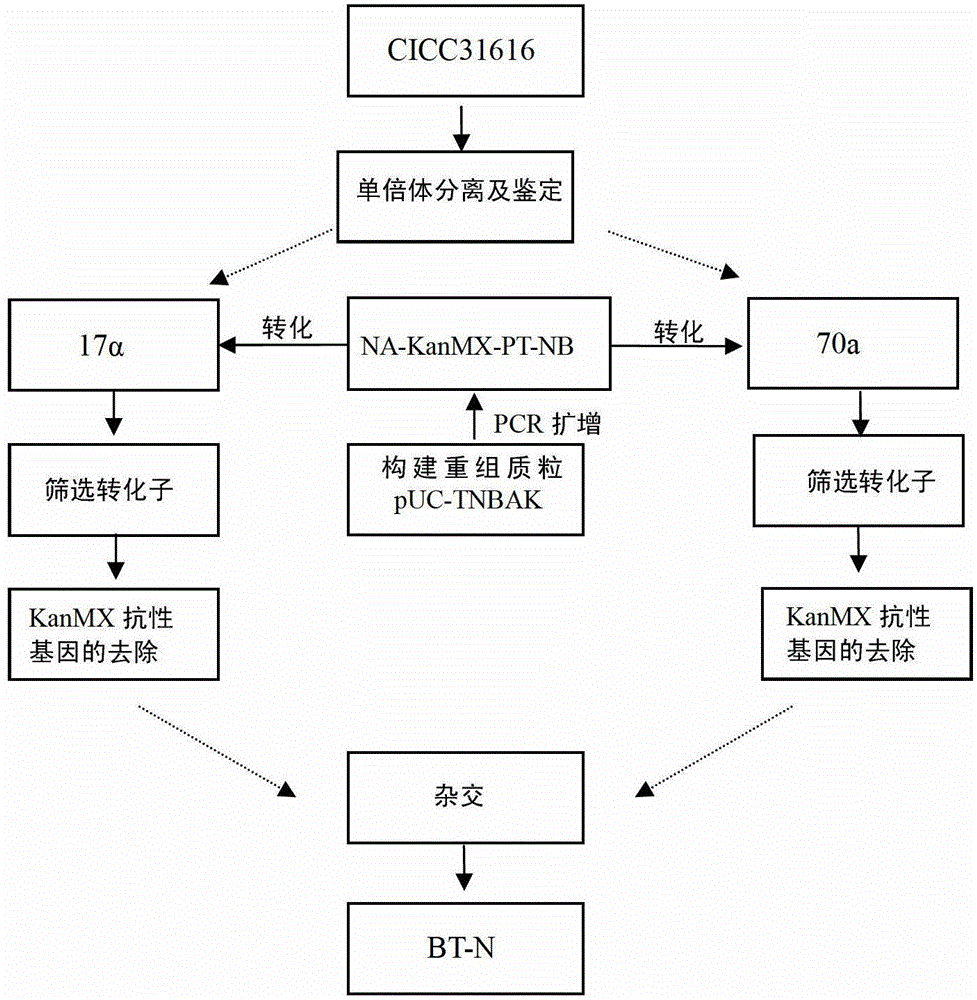
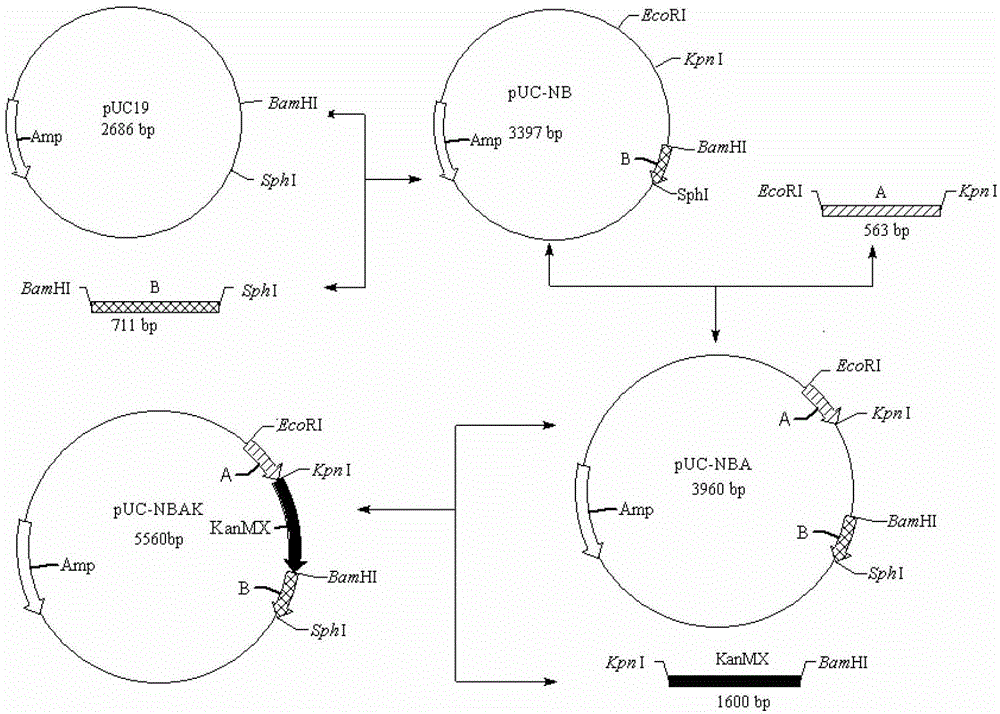
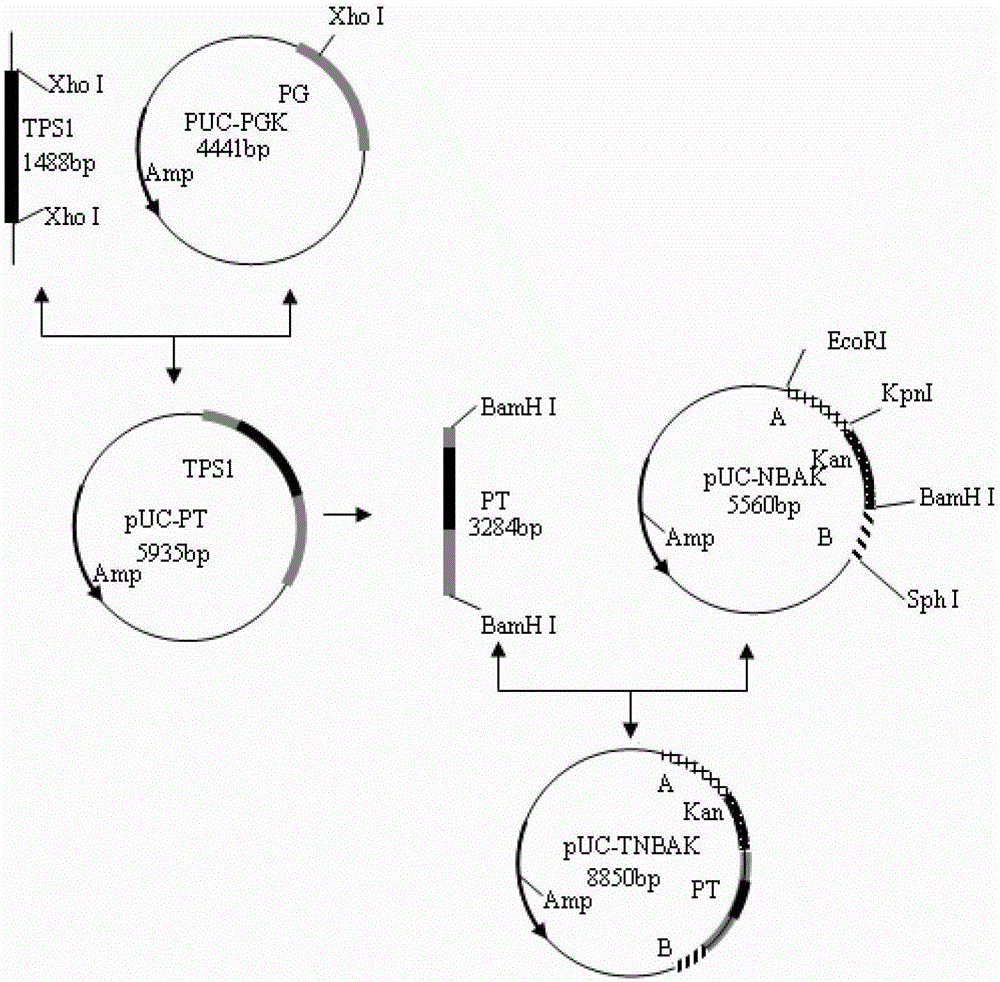
A freezing-resistant yeast strain for bread fermentation and a breeding method thereof. The yeast strain provided by the invention is saccharomyces cerevisiae BT-N with an accession number of CGMCC No.7151. When other fermentation performance is not influenced, the strain has a cell freezing survival rate of 92.75% after being frozen at -20 DEG C for 21 days and has a relative fermentation capacity of 53.24%, which are increased by 57.39% and 24.78% respectively when compared with parent strains (who have a freezing survival rate is 35.36% and have a relative fermentation capacity of 28.46%). The strain is realized by knocking out of the neutral trehalase coding gene NTH1 of saccharomyces cerevisiae CICC31616, and overexpression of the trehalose-6-phosphate synthase coding gene TPS1 by selecting a strong promoter PGK1. The bred yeast strain has no special requirements for fermentation equipment or conditions, can be used by equipment and under conditions of common factories, and has wide application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for highly yielding medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester as well as construction method thereof
ActiveCN103571764AIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesFatty acid activating enzymeBacterial strain
The invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for highly yielding medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester. The saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium is realized by selecting a strong promoter PGK1 (Phosphoglycerate kinase 1) for overexpression coding of an EHT1 (Ethanol Hexanoyl Transferase 1) gene of alcohol acyltransferase and knocking out a gene FFA1 (Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1) of an exogenous fatty acid activating enzyme. The preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7937. Under the condition that other fermenting properties are not affected, compared with a parent bacterial strain, the content of ethyl hexanoate can be improved to 2.23mg / L after simulating fermentation of corn raw material liquid white spirit for 15 days, wherein the content is 2.75 times the original bacteria. The contents of ethyl caprylate and ethyl caprate are respectively improved by 52% and 62%. After fermentation for 30 days, the contents of ethyl hexanoate, ethyl caprylate and ethyl caprate are respectively improved by 120%, 16.2% and 16.7%. After simulating fermentation of corn raw material liquid white spirit for 15 days, the content of ethyl hexanoate can be improved to 2.83mg / L which is 2.8 times the original bacteria, and the contents of ethyl caprylate and ethyl caprate are respectively improved by 43.3% and 40.9%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Quinazoline derivative as pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1) activator
ActiveCN102526057APrevent sepsisAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsAcute hyperglycaemiaCerebral thrombosis
The invention relates to a quinazoline derivative as a pgk1 (phosphoglycerate kinase 1) activator. Specially, the invention relates to application of the compound shown in formula I or pharmaceutically-acceptable salts, solvates, esters and prodrugs thereof in preparing medicines as pgk1 activators, or in preparing medicines for treating and / or preventing hyperglycemia, cerebral thrombosis and complications thereof, wherein the substituents are indicated as in the specification.
Owner:北京安塞迩生物科技有限公司
Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene engineering bacterium capable of utilizing xylose and glucose jointly as well as construction method and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae gene engineering bacterium
ActiveCN106282040AIncrease consumption rateSolve the problem of low consumption rateFungiBiofuelsBiotechnologyC. tropicalis
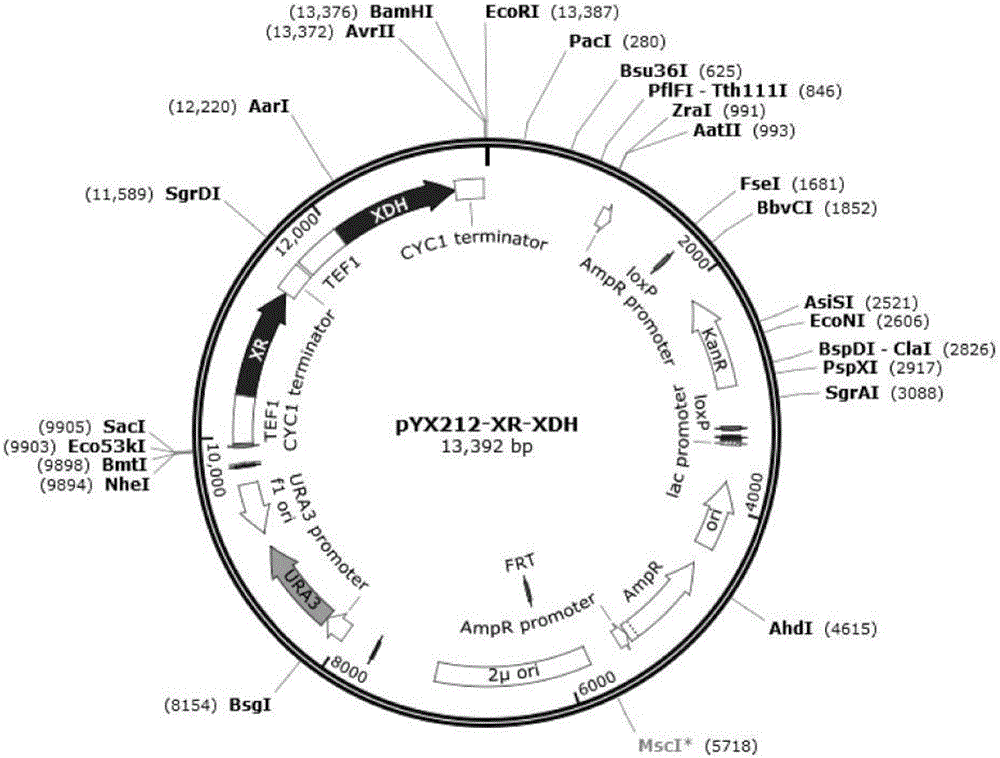
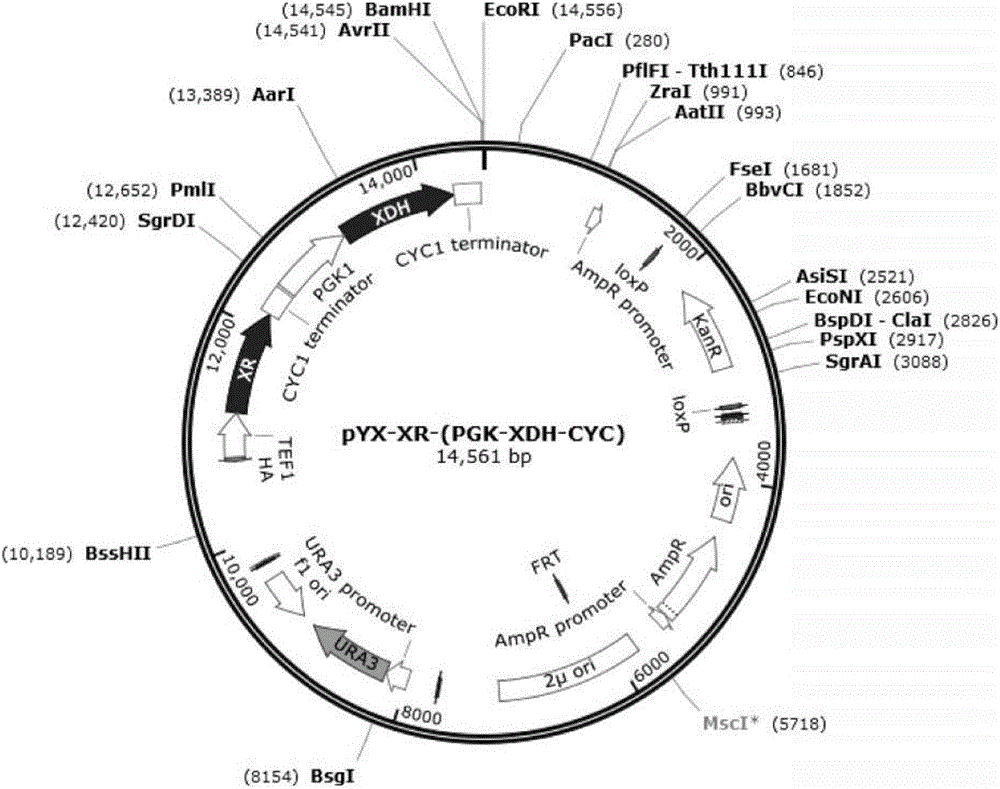
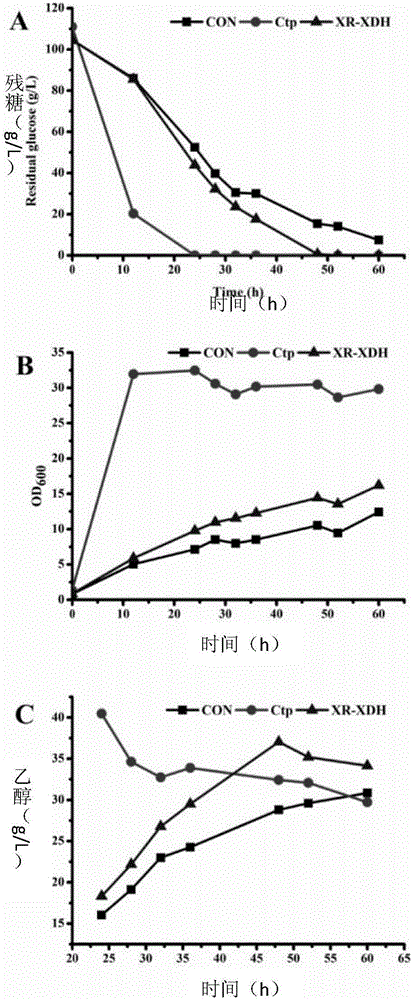
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms and molecular biology and in particular relates to a strain, a construction method thereof and fermentation application thereof. By taking a high-copy free type plasmid pYX212 as a carrier, xylose reductase (XR) and xylitol dehydrogenase (XDH) from candida pseudotropicalis are over-expressed in a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and the enzyme activity of the XDH is regulated through saccharomyces cerevisiae endogenous promoters TEF1 and PGK1, so that a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of improving the consumption speed of xylose in joint utilization of the xylose and glucose can be obtained. According to the strain, the construction method thereof and the fermentation application thereof, molecular manipulation is simple and the joint utilization of the xylose and the glucose can be primarily realized without the need of a site-directed mutation or long-period evolution process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Fast-fermenting bread yeast strain and construction method thereof
ActiveCN104073449AMeeting the needs of "fast" yeastHigh starting capacityFungiPre-baking dough treatmentBiotechnologyComplete sequence
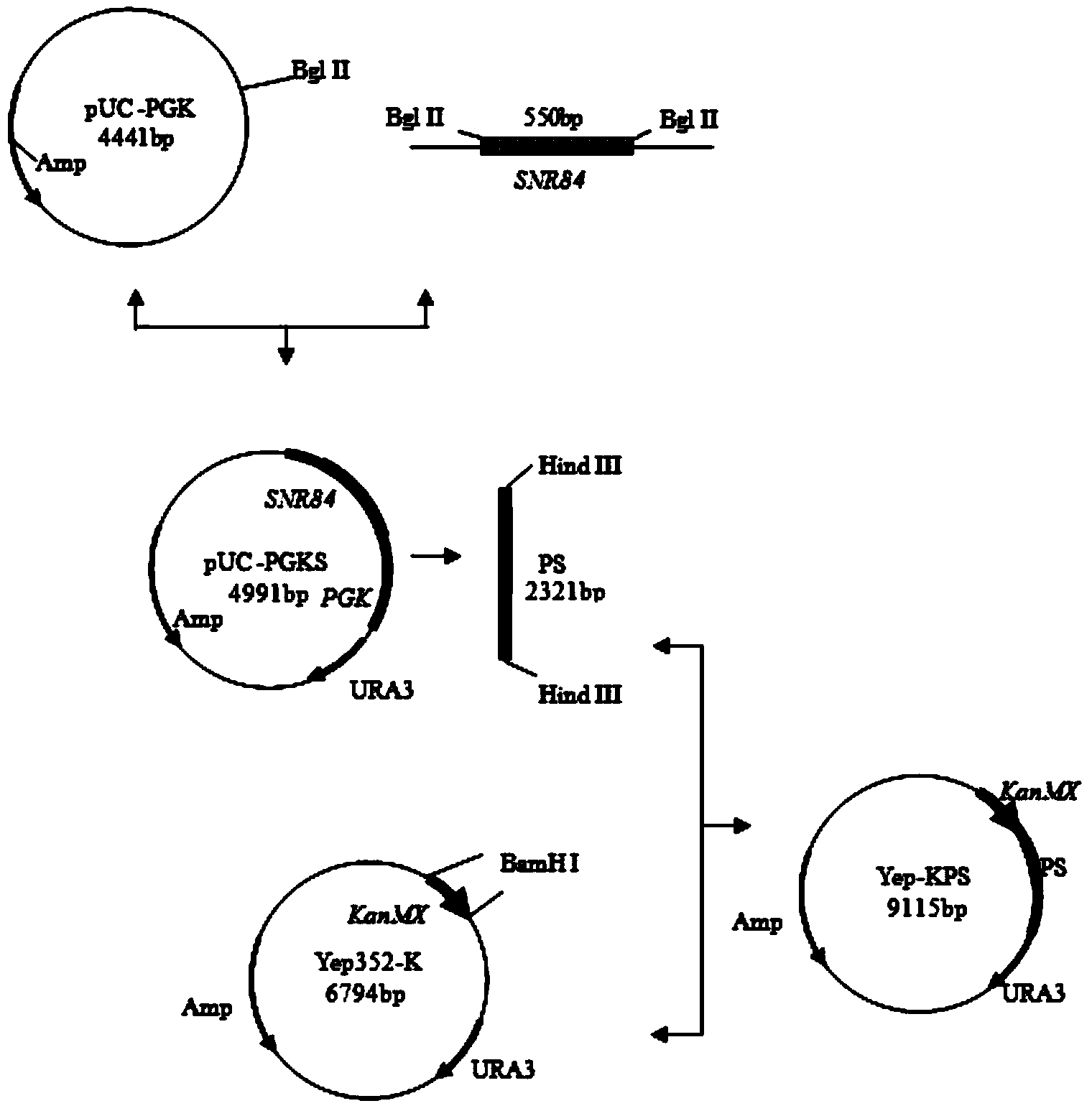
The invention discloses a fast-fermenting bread yeast strain and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of a bioengineering technology. The construction method comprises the following steps: knocking out phosphoglucomutase genes PGM2 completely in the parent bread yeast strain; meanwhile, choosing a strong promoter PGK1 to over-express the complete sequence of H / ACA small nucleolus RNA (SNR84) to acquire the fast-fermenting yeast strain. The CO2 gas production of the fast-fermenting bread yeast strain in a non-sugaring paste for 1 hour reaches to 818mL; compared with the parent strain, the CO2 gas production is improved by 21.2% (the CO2 gas production of the parent strain fermenting in the non-sugaring paste for 1 hour reaches to 675mL); meanwhile, the fermenting time is shortened by 18.0%. The bread yeast strain has a good fermentability during fermenting in the non-sugaring paste, so that the requirement for the 'fast' yeast in a cooked wheaten food processing market is met. Therefore, the bread yeast strain has an extensive application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Yeast strain for displaying metallothionein on cell surface and application of same in heavy metal adsorption
InactiveCN104774865AAvoid damageAvoid direct bindingFungiOther chemical processesBiotechnologyReduction rate
The invention discloses a yeast strain for displaying metallothionein on a cell surface and application of the same in heavy metal adsorption. The yeast strain for displaying metallothionein on the cell surface is obtained by integrating a box gene for displaying metallothionein on the cell surface and a constitutive promoter P<PGK1> gene into the chromosome of a host stain via an integrative vector; and the yeast strain can continuously and stably express metallothionein on the cell surface. The recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain provided by the invention has good adsorption capability and tolerance to a plurality of heavy metals like Cd<2+>, Cu<2+> and Cr<6+>; e.g., the strain needs 12 h for complete reduction of Cr<6+> with a concentration of 50 mg / L, 6 h faster compared with an original strain, and has a reduction rate 1.5 times of the reduction rate of the original strain; the removal rates of the strain to Cu<2+>, total Cr and Cd<2+> are increased by 13.35%, 10.13% and 19.39% respectively compared with the original strain; so the strain has great application potential in the field of treatment of heavy metals.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Application of a set of tumor-associated antigens in early screening kit for esophageal cancer and kit thereof
The invention belongs to the field of tumor molecular biology, and particularly relates to application of a set of tumor-associated antigens in an early screening kit for esophageal cancer and a kit thereof. The kit provided by the invention comprises a solid phase carrier and esophageal cancer tumor-associated antigens coated on the solid phase carrier, wherein the esophageal cancer tumor-associated antigens consists of a CP96 gene expression, a CRP78 gene expression, an MMP-10 gene expression, a cav-1 gene expression, a CDC25B gene expression, a PGK1 gene expression and an HSP105 gene expression; and the kit further comprises a phycoerythrin-conjugated secondary antibody. The detection specificity and sensitivity of the kit provided by the invention for esophageal cancer are as high as 96.1% and 95.1%, respectively. Compared with the tissue biopsy, the kit provided by the invention only needs to collect the blood of the person to be examined to screen the risk of esophagus cancer with small trauma and side effects, and is easy to use and provided with good clinical application prospects.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ZHENGZHOU UNIV
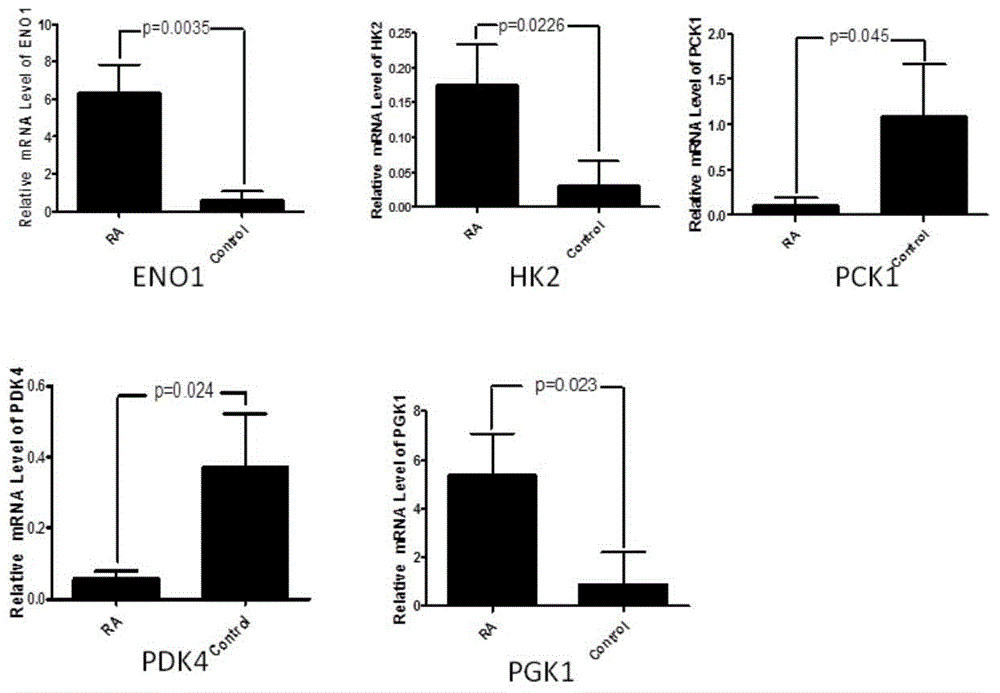
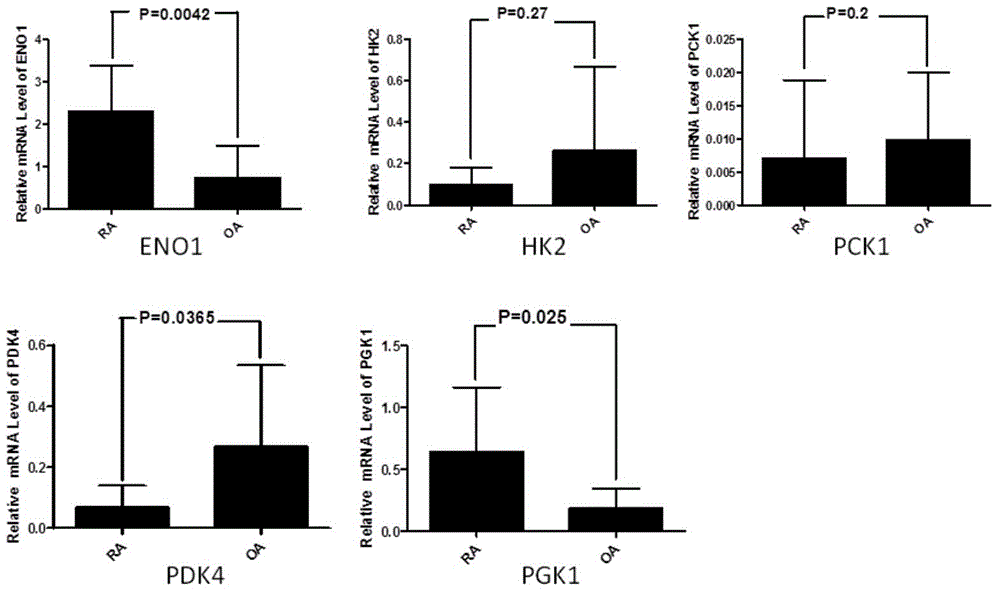
Application of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 to preparation of rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis reagent
InactiveCN104698194AImprove expression levelUnderstanding PathogenesisDisease diagnosisBiological testingPhosphoglycerate mutaseRheumatoide arthritis
The invention discloses a blood marker-PGK1 for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis, and discloses a reagent for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis. The reagent comprises a PGK1 antibody, an HRP-IgG antibody and a conventional reagent in a blood diagnosis reagent. The conventional reagent in the blood diagnosis reagent comprises a carbonate buffer solution, PBST washing liquor, confining liquid, a developing solution and a stop solution. The prepared detection reagent has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, high in specificity and the like and is capable of being widely applied to preliminary survey and health examination of clinical rheumatoid arthritis and providing a reliable basis for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:常晓天
High-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria
ActiveCN102604848AIncrease contentExcellent strainFungiMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainMicrobiological culture
The invention relates to high-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria; a method for preparing the brewing yeast bacteria provided by The invention comprises the following steps: selecting strong promoters PGK1 so as to overexpress ATF2 gene coding alcohol acetyl transferase, thereby obtaining high-yield acetate brewing yeast engineering bacteria SaccharomycescerevisiaeEY-14, wherein a preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.5635. According to The invention, on a condition that other fermenting performance is not influenced, transformant bacterial strains are compared with parent strains (SaccharomycescerevisiaeCGMCC No 2.1525); after simulation of semi-solid fermentation, the content of ethyl acetate is increased by 3.6 times; thecontent of isoamyl acetate is increased to 55.2mg / L; the content of isobutyl acetate is increased to 33.8mg / L; the sifted engineering bacteria has no specific demand for fermentation equipment and conditions; the equipment and conditions of normal white sprits factories can be used; therefore, the engineering bacteria has wide application propose and brings marked economic benefit to industrial production of the white sprits factories.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
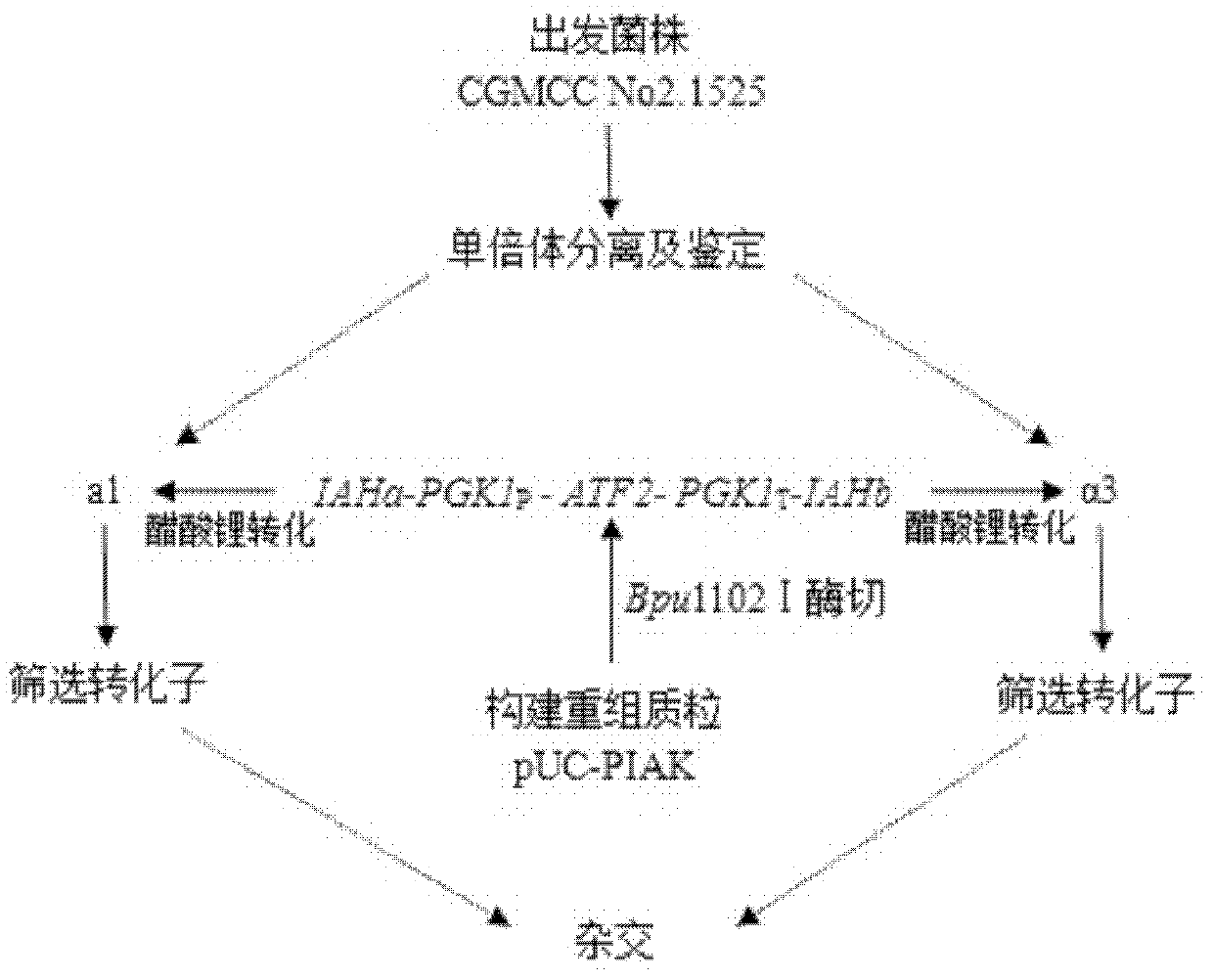
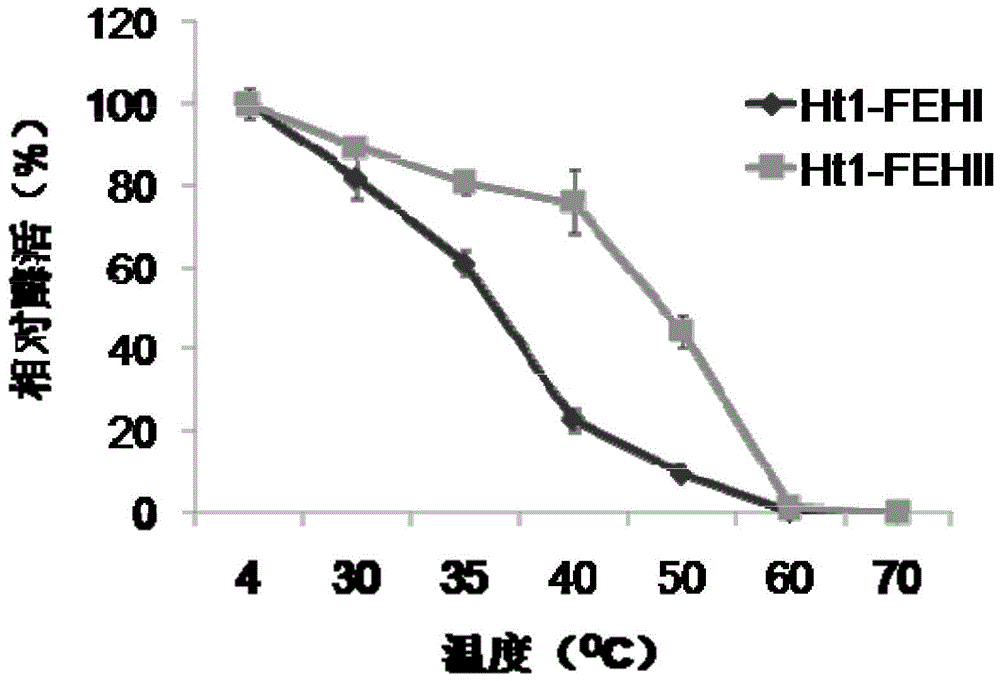
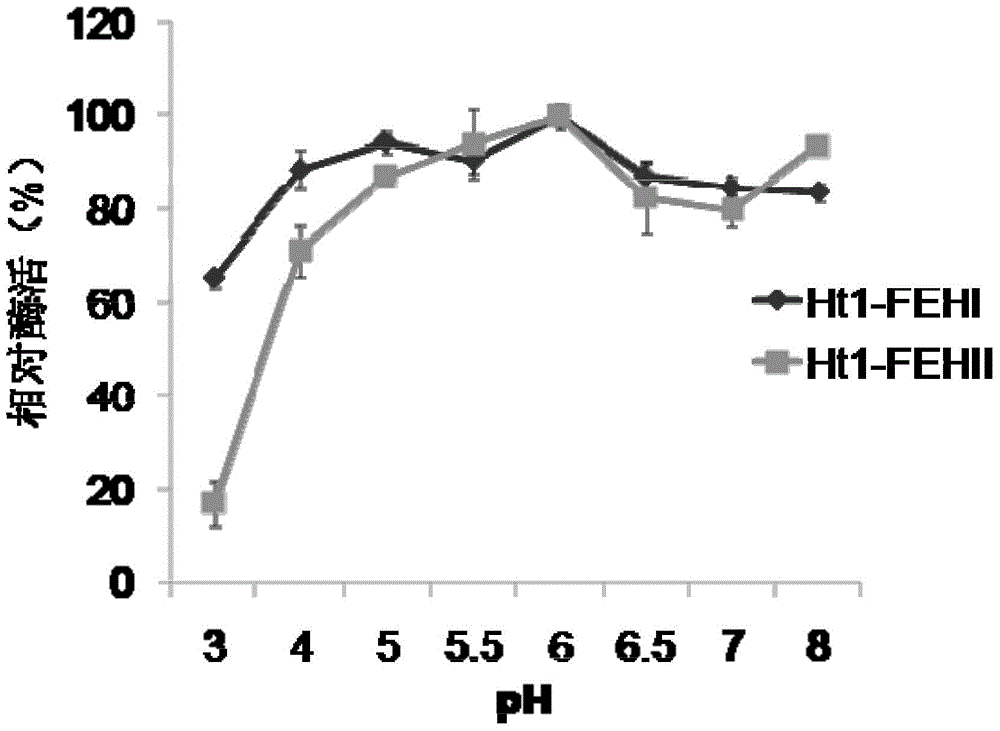
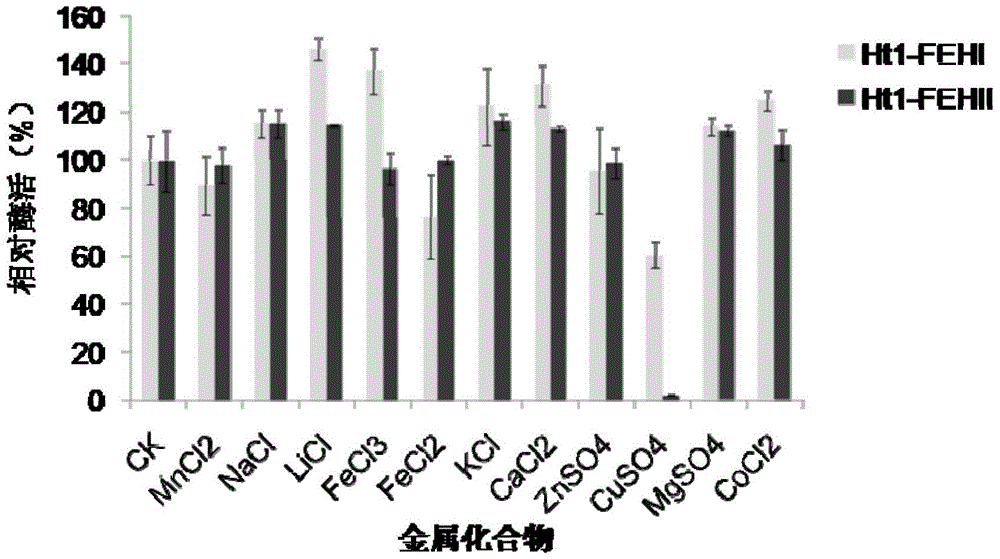
Recombinant vector containing Jerusalem artichoke fructan 1-exohydrolase gene and application thereof in producing alcohol by fermentation
The invention discloses a recombinant vector containing Jerusalem artichoke fructan 1-exohydrolase gene and application thereof in producing alcohol by fermentation. The recombinant plasmid is prepared by the following steps: inserting a Saccharomyces cerevisiae 3-phosphoglyceric kinase gene PGK1 promoter between EcoRV and SpeI enzyme digestion sites of an expression vector pUG6, inserting a CYC1-terminator-fused Jerusalem artichoke fructan 1-exohydrolase gene Ht 1-FEHs between SpeI and HpaI enzyme digestion sites of the expression vector pUG6, and inserting an 18SrDNA sequence segment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome between XbaI and BstEII enzyme digestion sites of the expression vector pUG6. The invention also discloses application of the recombinant plasmid in producing alcohol by fermentation. The Jerusalem artichoke inulase genes Ht-FEHI and Ht-FEHII can promote fermentation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce alcohol, thereby providing a new method for enhancing the alcohol yield of Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
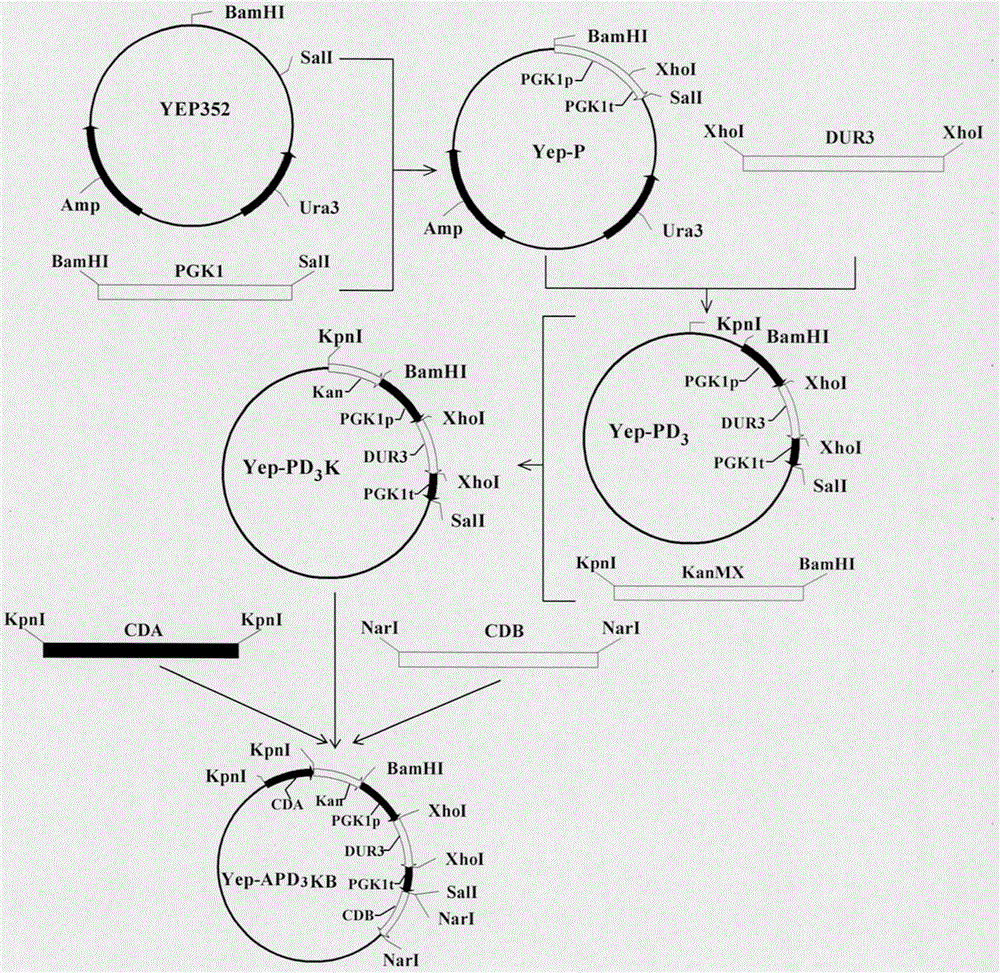
Ethyl carbamate (EC) low-yield saccharomyces cerevisiae strain obtained by knocking-out CAR1 and over-expressing DUR3 and construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
InactiveCN106119142AReduce the content of ECOvercome the effects of high cancer riskFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyEthyl ester
The invention discloses an ethyl carbamate (EC) low-yield saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a construction method thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering technology. The ethyl carbamate low-yield saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is obtained by knocking-out a copy arginase gene CAR1 in a parent saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and by over-expressing a gene DUR3 of urea transporter Dur3p by virtue of a strong promoter PGK1. In a wine brewing experiment, the constructed saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, compared with the parent strain, can avoid other fermenting performances and flavor substances from being affected, and can significantly reduce the contents of urea and EC, wherein the content of the urea is reduced by 45.51% and the content of the EC is reduced by 36.92%. The saccharomyces cerevisiae strain can meet the relatively high requirements of wine related fields on yeast; and the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain has a broad application prospect.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A new way of high-yielding ethyl lactate produced by Saccharomyces cerevisiae and its application
ActiveCN108642095BLow ability to form ethyl lactateReduce outputFungiMicroorganism based processesHeterologousLactate dehydrogenase
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly discloses a new method for producing high-yield ethyl lactate by using a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application of the strain. High-yield ethyl lactate is produced through the simultaneous heterologous expression of lactate dehydrogenase, propionyl-CoA transferase and alcohol acyltransferase in saccharomycescerevisiae. Pyruvate decarboxylase is completely knocked out from an original strain, and lactate dehydrogenase is overexpressed to obtain the yeast strain with a certain capability of generating L-lactic acid; a strong promoter TEF1 is selected and adopted for overexpressing propionyl-CoA transferase, a strong promoter PGK1 is selected and adopted for overexpressing alcohol acyltransferase, witha homothallic gene HO as an integration site, a copy number of propionyl-CoA transferase is increased, the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain capable of significantly increasing the yield of ethyl lactate is obtained, and the yield of ethyl lactate obtained by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain reaches 353.1 mg / L; compared with the original strain, the yield of isoamyl alcohol is decreased by49.9%, the yield of phenylethyl alcohol is decreased by 59.2%, and the new method meets the higher requirements of yeast in the related field of liquor and has broad application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Marker for the diagnosis of cancer
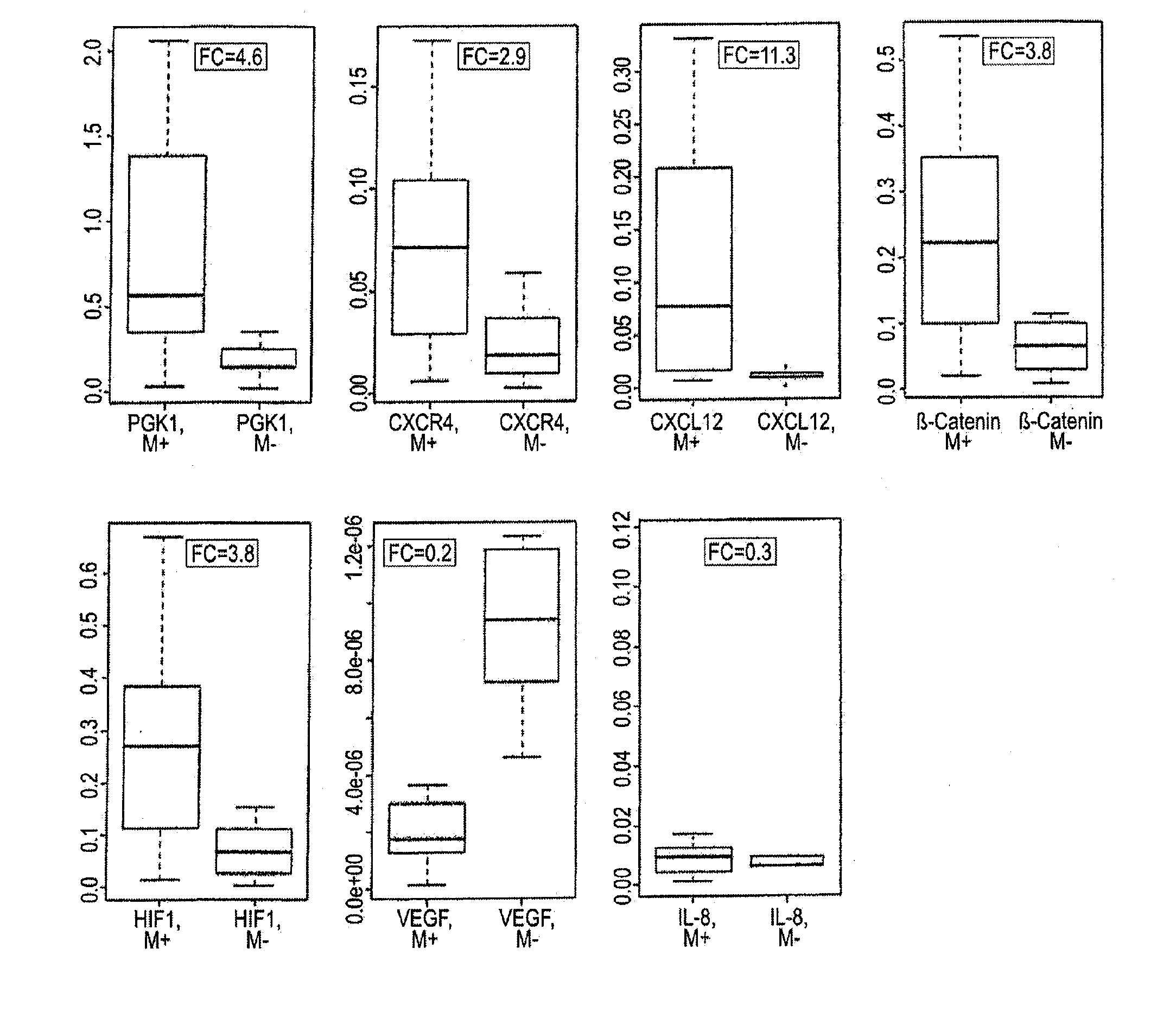
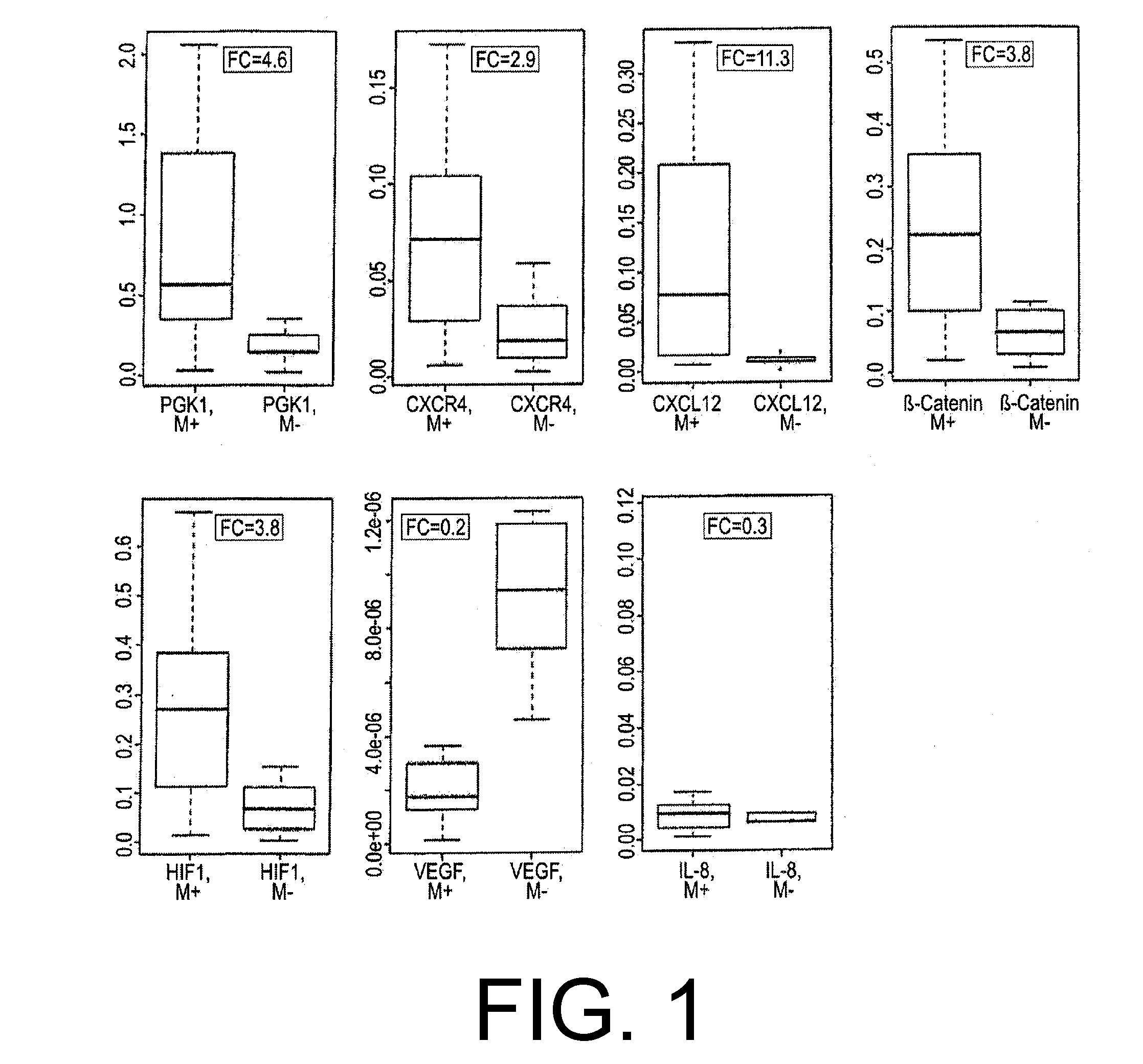
ActiveUS20100247432A1Easy to modifyReserved functionOrganic active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary tumorLymphatic Spread
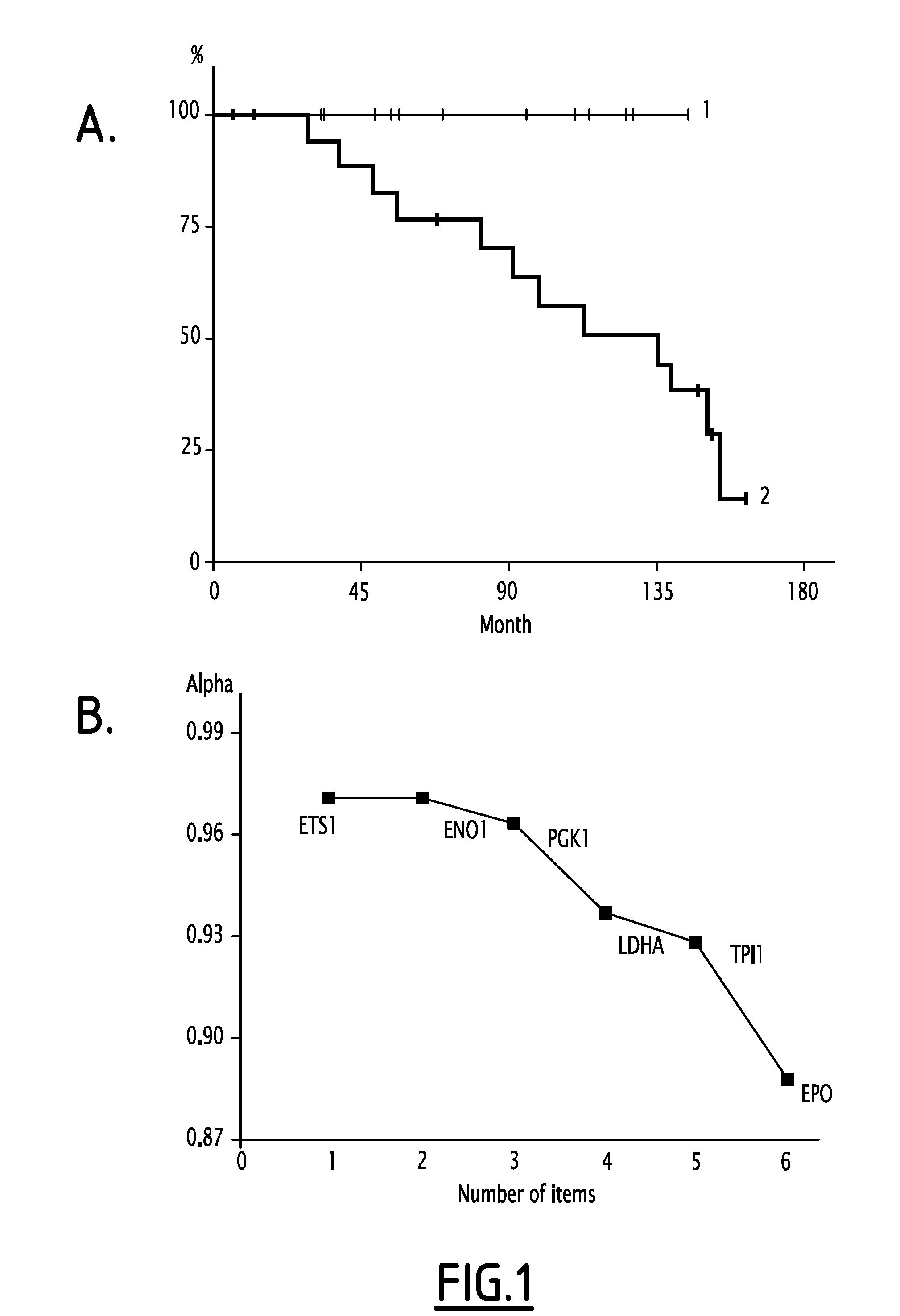
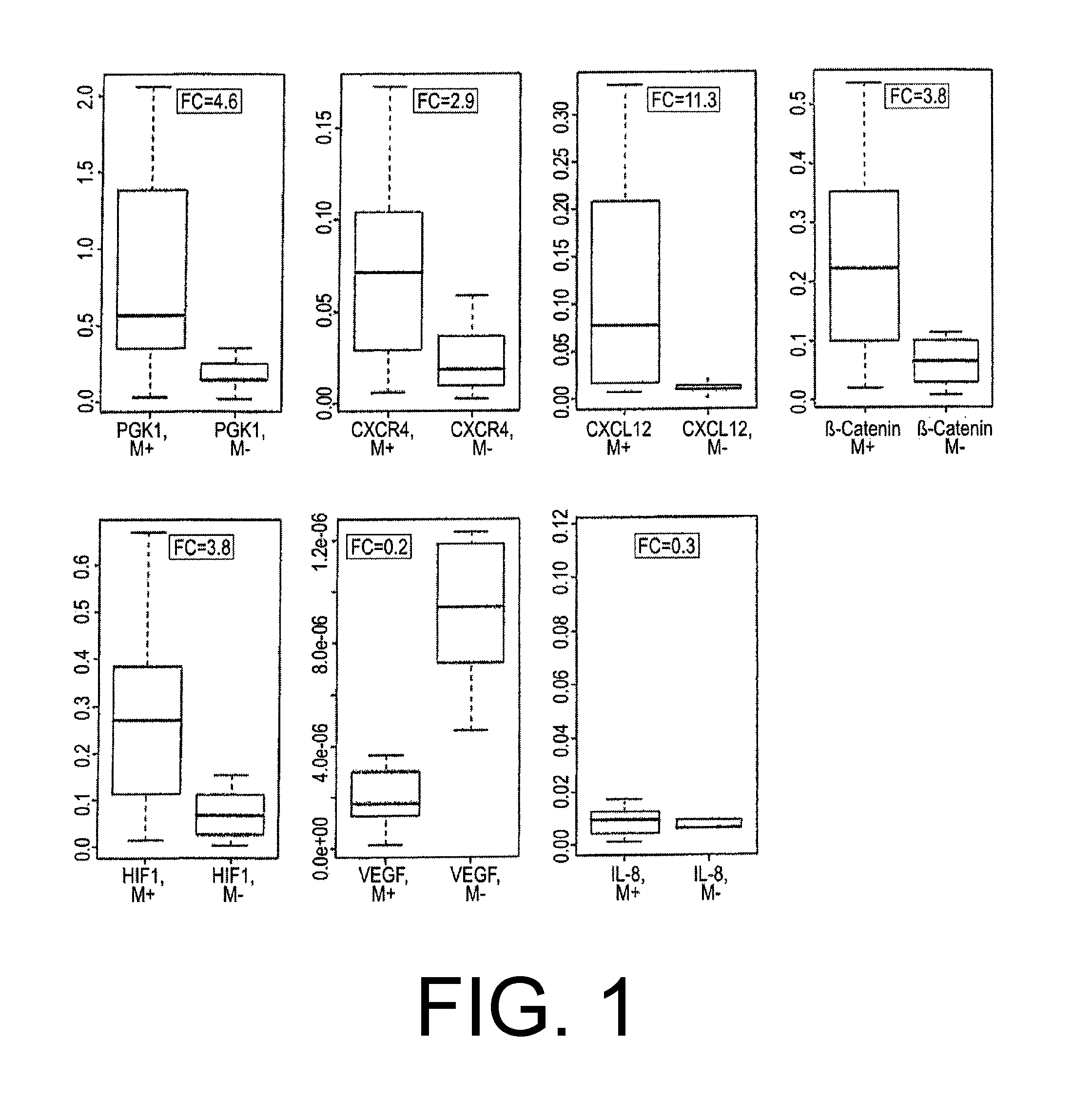
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing peritoneal carcinoses or metastatic primary tumors in a subject, as well as to a method for providing a prognosis to a subject diagnosed with a primary tumor to develop metastases, in particular peritoneal carcinosis, comprising the step of determining the level of expression of at least phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) gene. Further, the invention relates to a diagnostic kit, comprising at least one substance for detection of the activity and / or expression of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) and / or β-catenin, either alone or in combination with the detection of CXCR4 and / or CXCL12, for the diagnosis or prognosis of peritoneal carcinoses and / or metastatic primary tumors. Also, a method for the preventive treatment of peritoneal carcinoses and / or metastatic primary tumors in a subject in need thereof is disclosed, wherein the method comprises the step of administering to the subject at least a pharmaceutically effective amount of a substance inhibiting the activity and / or expression of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1).
Owner:CAPNOPHARM GMBH
Methods for predicting outcome of breast cancer, and/or risk of relapse, response or survival of a patient suffering therefrom
InactiveUS20130143753A1High riskNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementCTGFLower risk
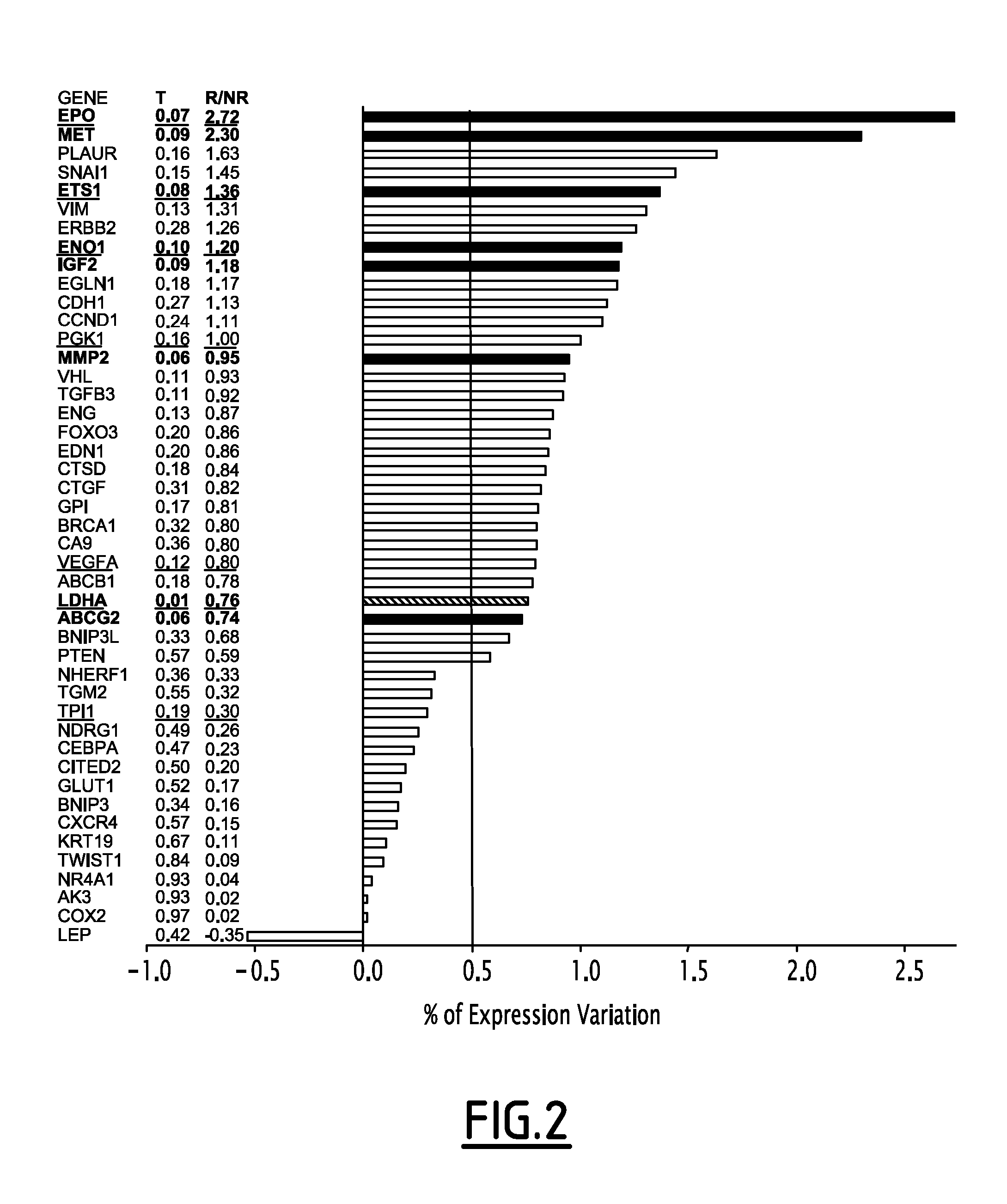
The present invention relates to biomarkers allowing predicting breast tumor and solid tumor outcome using hypoxia related genes. More specifically, the present invention relates to a method for predicting the survival of a patient suffering from cancer, said method comprising the steps of (a) measuring the expression of at least five genes selected from the group consisting of GLUT1, PGK1, LDHA, ENO1, CAIX, NHERF1, TPI, AMF / GPI, VEGFA, TGFB3, ENG, LEP, EDN1, MDR1, AK3, MXR1, TGM2, CDH1, MMP2, CK1 9, VIM, CXCR4, UPAR, CATHD, CTGF, C0X2, MET, IGF-2, CCND1, EPO, NDRG1, BNIP3, NIX, ETS1, PHD2, TWIST1, DEC1, SNAH, CEBPA, CITED2, F0X03A, NUR77, BRCA1, PTEN, VHL and ERBB2 in a biological sample of said patient, and (b) analyzing the expression values to generate a risk score of relapse, wherein a risk score superior or equal to three is indicative of high risk of relapse and a risk score inferior or equal to two is indicative of a low risk of relapse. In particular the following genes: EPO, ETS1, ENO1, PGK1, LDHA, TPI and optionally VEGFA were significantly over-expressed in patients with relapse.
Owner:ADELBIO +2
Marker for the diagnosis of cancer
ActiveUS9075067B2Easy to modifyReserved functionOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsLymphatic SpreadBeta-catenin
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing peritoneal carcinoses or metastatic primary tumors in a subject, as well as to a method for providing a prognosis to a subject diagnosed with a primary tumor to develop metastases, in particular peritoneal carcinosis, comprising the step of determining the level of expression of at least phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) gene. Further, the invention relates to a diagnostic kit, comprising at least one substance for detection of the activity and / or expression of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) and / or β-catenin, either alone or in combination with the detection of CXCR4 and / or CXCL12, for the diagnosis or prognosis of peritoneal carcinoses and / or metastatic primary tumors. Also, a method for the preventive treatment of peritoneal carcinoses and / or metastatic primary tumors in a subject in need thereof is disclosed, wherein the method comprises the step of administering to the subject at least a pharmaceutically effective amount of a substance inhibiting the activity and / or expression of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1).
Owner:CAPNOPHARM GMBH
A highly tolerant yeast strain and its construction method
ActiveCN104017742BHigh activityImprove antifreeze effectFungiPre-baking dough treatmentHigh resistanceAgricultural science
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Saccharomyces boulardii surface display system and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103031329AImprove adsorption capacityGood probiotic propertiesFungiMicroorganism based processesSurface displayHeterologous
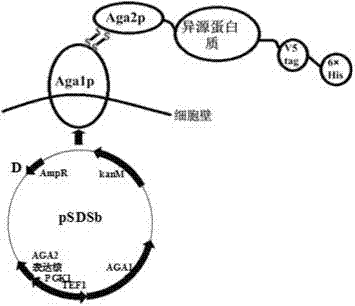
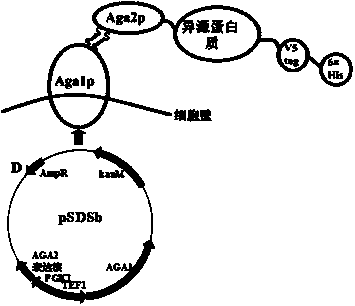
The invention relates to a protein surface display system and specifically provides a surface display system taking saccharomyces boulardii as an expression heterologous protein of the surface display system. The saccharomyces boulardii of the system is purchased from Laboratoires Biocodex in France, the registration certificate number of an imported drug is s20040038, an AGA1 gene and an AGA2 gene are obtained by amplification in a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) group, a pPIC9AGA2 plasmid is taken as a template for amplification of an AGA2 gene expression core, and the AGA2 gene of the saccharomyces boulardii is used for replacing the AGA2 gene in the AGA2 gene expression core. The obtained AGA1 gene and the AGA2 gene expression core after replacement are connected onto a basic plasmid pSP and respectively controlled by over-expression promoters TEF1 and PGK1, and then a general surface display expression plasmid pSDSb which can express on the surface of the saccharomyces boulardii can be further obtained. The system disclosed by the invention can continuously express the heterologous protein which is fused with Aga2p, be displayed on the surface of the saccharomyces boulardii, further realize the over-expression of the certain heterologous protein, take the heterologous protein as a pathogen live vaccine carrier, further research the interaction between the proteins and realize the actions which can not be replaced by other microorganism carriers.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for screening phosphoglycerate kinase and substrate binding mode
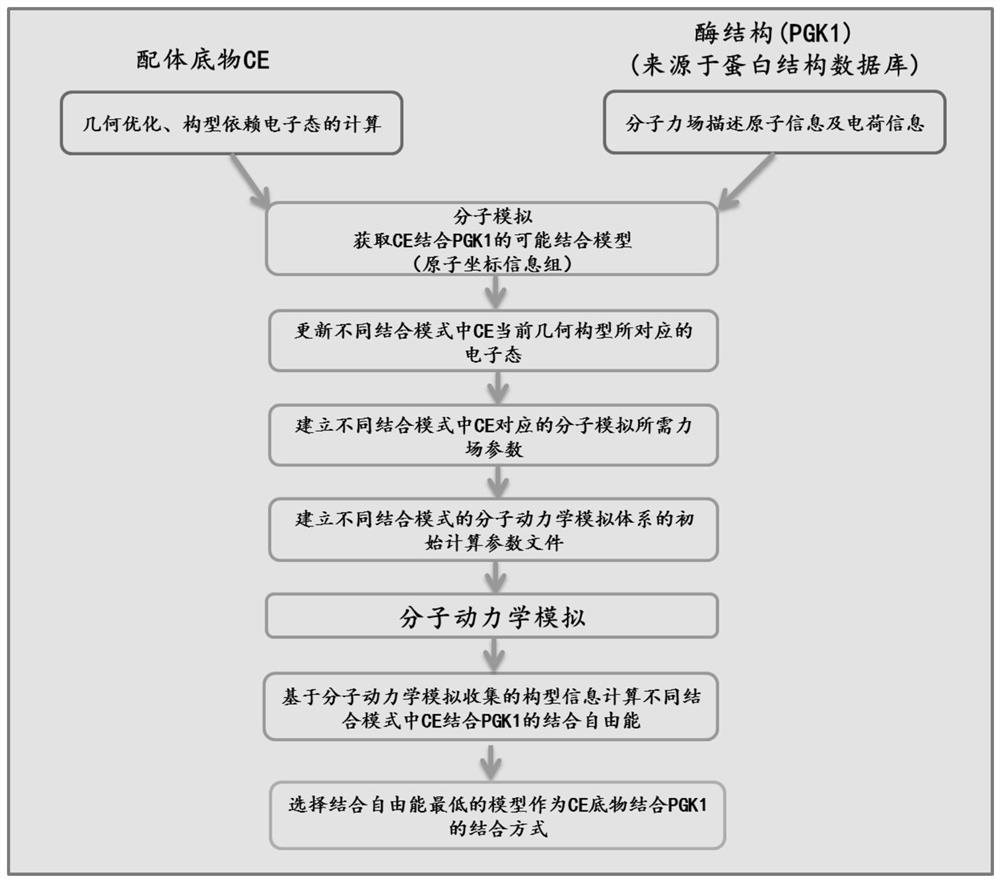
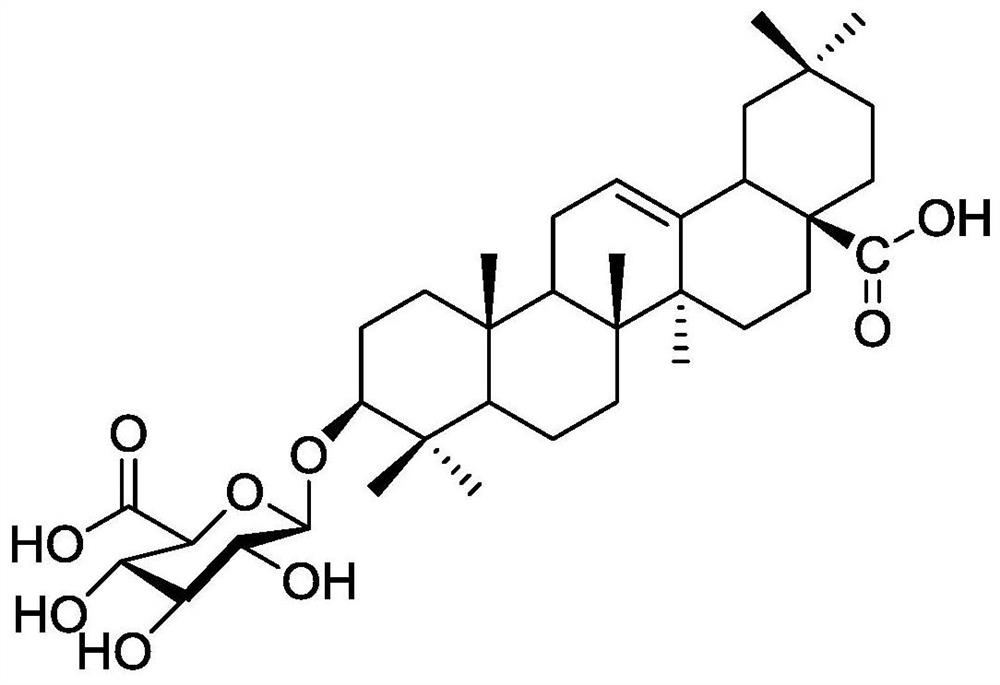
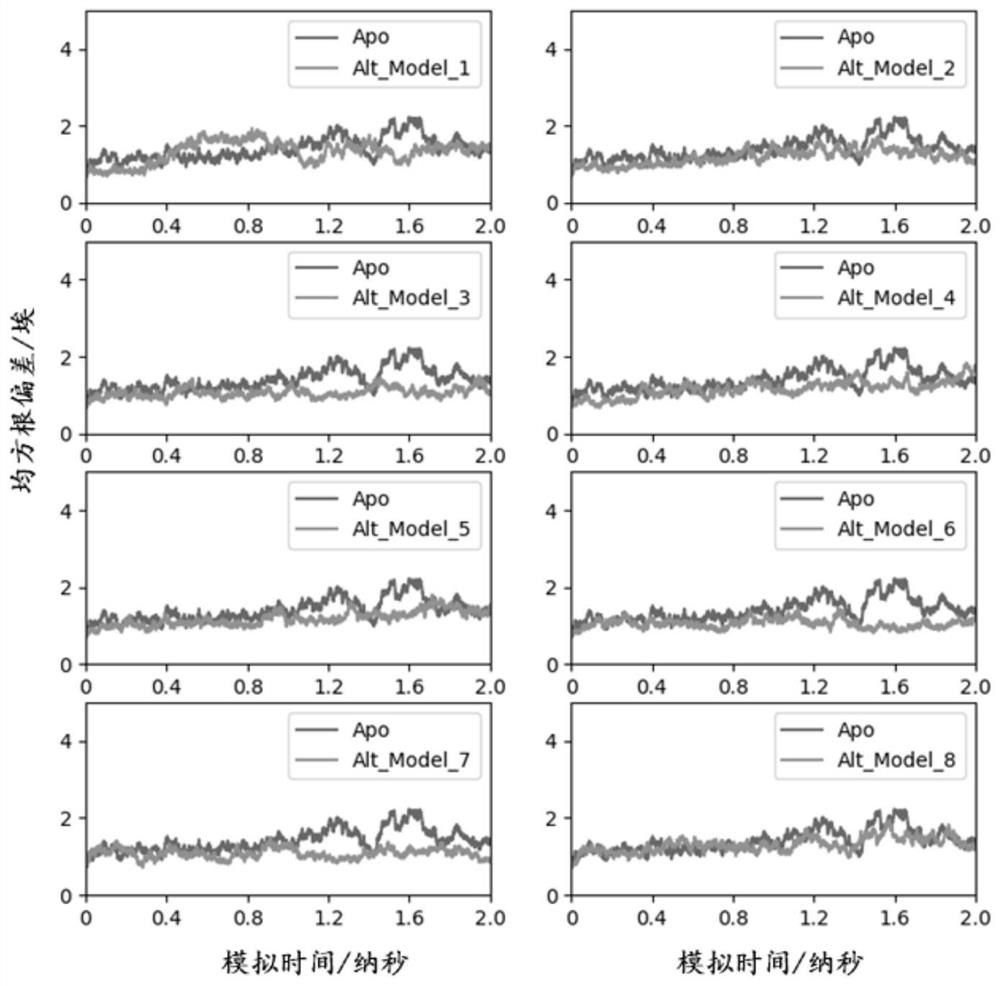
PendingCN112669904AImprove accuracyAccurate screening and judgmentHybridisationInstrumentsSubstrate InteractionPhosphoglycerate kinase
The invention discloses a method for screening a phosphoglycerate kinase and substrate binding mode, and relates to a method for calculating and screening the phosphoglycerate kinase and substrate binding mode. The invention provides a method for exploring the interaction mode of phosphoglycerate kinase and a substrate. By combining quantum chemistry calculation, molecular simulation, molecular dynamics conformation collection and conformation-based combination free energy calculation, the combination mode of phosphoglycerate kinase and a substrate is accurately screened, and a good effect is achieved on prediction of the combination mode of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 (PGK1) and a potential calendula officinalis glycoside substrate (CE).
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 in the preparation of diagnostic reagents for rheumatoid arthritis
InactiveCN104698194BStrong specificityIncreased sensitivityDisease diagnosisBiological testingPhosphoglycerate mutaseEarly rheumatoid arthritis
The invention discloses a blood marker-PGK1 for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis, and discloses a reagent for rheumatoid arthritis clinical diagnosis. The reagent comprises a PGK1 antibody, an HRP-IgG antibody and a conventional reagent in a blood diagnosis reagent. The conventional reagent in the blood diagnosis reagent comprises a carbonate buffer solution, PBST washing liquor, confining liquid, a developing solution and a stop solution. The prepared detection reagent has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, high in specificity and the like and is capable of being widely applied to preliminary survey and health examination of clinical rheumatoid arthritis and providing a reliable basis for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:常晓天
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium capable of utilizing whey efficiently to produce ethyl alcohol and construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium
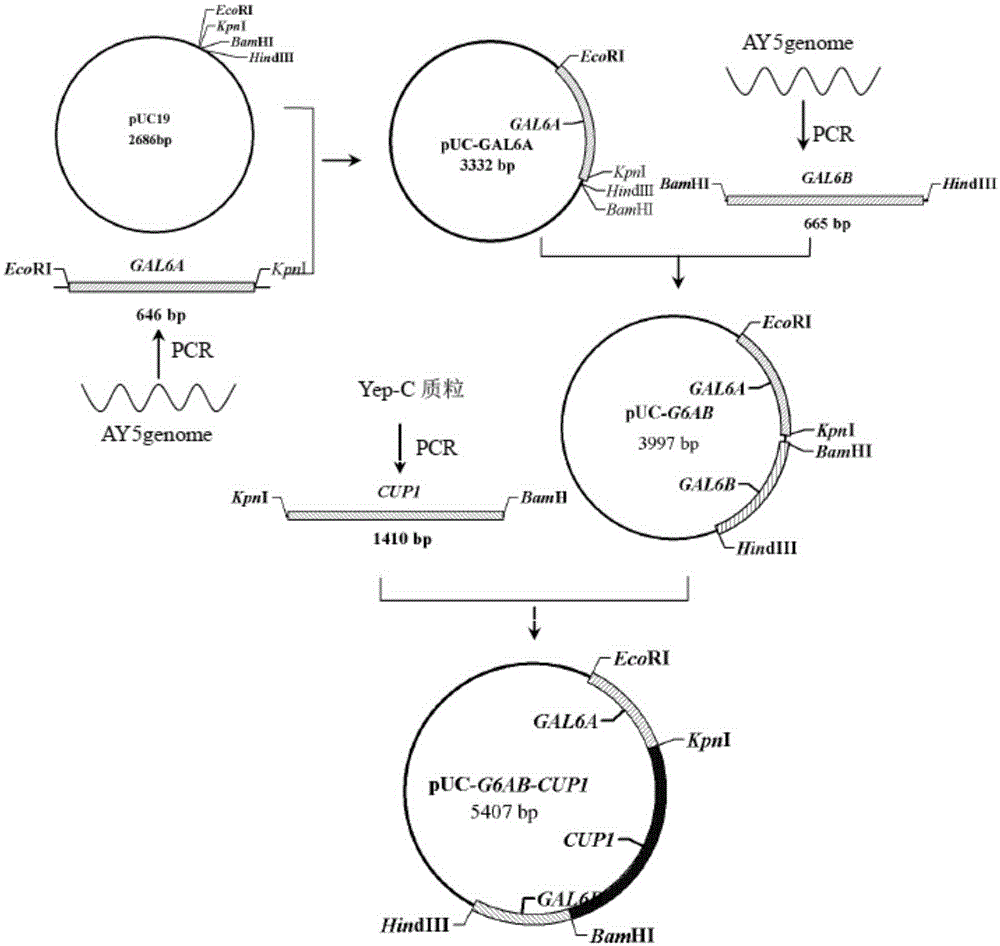
Disclosed is a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium capable of utilizing whey efficiently to produce ethyl alcohol. A strong promoter PGK1 is selected to express a lactose lytic enzyme gene LAC4 and a lactose permease gene LAC12 respectively, MIG1, NTH1 and GAL6 genes are knocked out, and semi-lactose metabolism regulation of saccharomyces cerevisiae is eliminated during relief of glucose repression to obtain the high-durability saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium AY5MG capable of utilizing the whey efficiently to produce the ethyl alcohol, wherein the collection number is CGMCC No.11223. The bacterium can grow and ferment to generate the ethyl alcohol in a culture medium with the whey concentration of 120g / L (the lactose content being 53.1g / L) without influences on fermenting property, the fermentation cycle is 54 hours, utilization rate of lactose in the whey is 98.7%, and the yield of the absolute ethyl alcohol to the lactose is 49.7% (equivalent to 92.3% of theoretical yield); glucose repression on semi-lactose is relieved, and accordingly, glucose and the semi-lactose are utilized at the same time; normal fermentation can be realized when the content of the ethyl alcohol is 19%(v / v) or the fermentation temperature is 39 DEG C.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
A strain of baker's yeast suitable for fermentation of dough without adding sugar and its breeding method
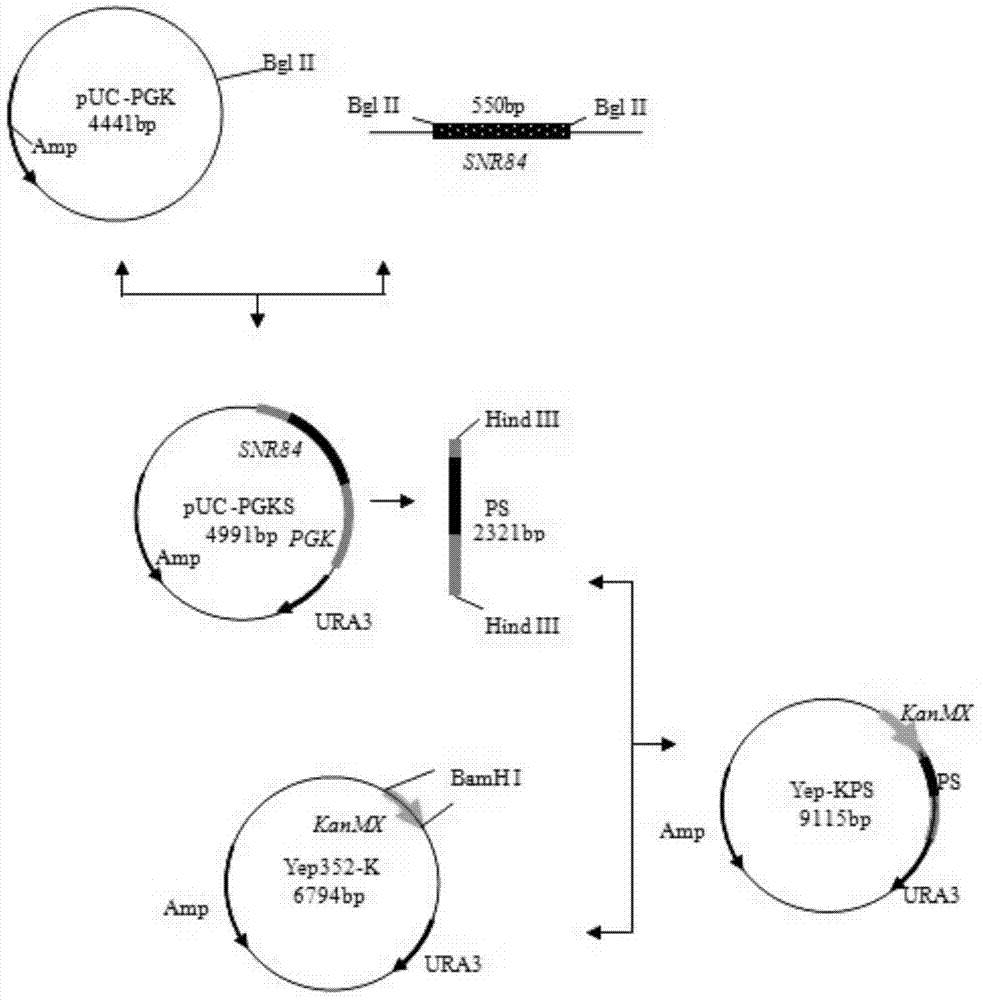
ActiveCN104073449BMeeting the needs of "fast" yeastHigh starting capacityFungiPre-baking dough treatmentBiotechnologySmall nucleolar RNA
The invention discloses a baker's yeast strain suitable for dough fermentation without adding sugar and a breeding method thereof, belonging to the technical field of bioengineering. The present invention obtains the fast-fermenting baker's yeast strain by completely knocking out the glucose phosphomutase gene PGM2 in the parental baker's yeast strain, and selecting the strong promoter PGK1 to overexpress the whole sequence of H / ACA small nucleolar RNA (SNR84) . The fast-fermenting baker's yeast strain was subjected to 1h CO in unsweetened dough fermentation 2 Gas production reached 818mL, which was 21.2% higher than that of the parental strain (the parental strain was fermented without sugar for 1h CO 2 Gas production is 675mL), and the fermentation time is shortened by 18.0%. The baker's yeast has strong fermentation ability in dough without adding sugar and has wide application prospects.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Saccharomyces boulardii surface display system and construction method thereof
InactiveCN103031329BImprove adsorption capacityGood probiotic propertiesFungiMicroorganism based processesSurface displayHeterologous
The invention relates to a protein surface display system and specifically provides a surface display system taking saccharomyces boulardii as an expression heterologous protein of the surface display system. The saccharomyces boulardii of the system is purchased from Laboratoires Biocodex in France, the registration certificate number of an imported drug is s20040038, an AGA1 gene and an AGA2 gene are obtained by amplification in a DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) group, a pPIC9AGA2 plasmid is taken as a template for amplification of an AGA2 gene expression core, and the AGA2 gene of the saccharomyces boulardii is used for replacing the AGA2 gene in the AGA2 gene expression core. The obtained AGA1 gene and the AGA2 gene expression core after replacement are connected onto a basic plasmid pSP and respectively controlled by over-expression promoters TEF1 and PGK1, and then a general surface display expression plasmid pSDSb which can express on the surface of the saccharomyces boulardii can be further obtained. The system disclosed by the invention can continuously express the heterologous protein which is fused with Aga2p, be displayed on the surface of the saccharomyces boulardii, further realize the over-expression of the certain heterologous protein, take the heterologous protein as a pathogen live vaccine carrier, further research the interaction between the proteins and realize the actions which can not be replaced by other microorganism carriers.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for highly yielding medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester as well as construction method thereof
ActiveCN103571764BIncrease contentFungiMicroorganism based processesFatty acid activating enzymeBacterial strain
The invention provides a saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for highly yielding medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester. The saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium is realized by selecting a strong promoter PGK1 (Phosphoglycerate kinase 1) for overexpression coding of an EHT1 (Ethanol Hexanoyl Transferase 1) gene of alcohol acyltransferase and knocking out a gene FFA1 (Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1) of an exogenous fatty acid activating enzyme. The preservation number is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7937. Under the condition that other fermenting properties are not affected, compared with a parent bacterial strain, the content of ethyl hexanoate can be improved to 2.23mg / L after simulating fermentation of corn raw material liquid white spirit for 15 days, wherein the content is 2.75 times the original bacteria. The contents of ethyl caprylate and ethyl caprate are respectively improved by 52% and 62%. After fermentation for 30 days, the contents of ethyl hexanoate, ethyl caprylate and ethyl caprate are respectively improved by 120%, 16.2% and 16.7%. After simulating fermentation of corn raw material liquid white spirit for 15 days, the content of ethyl hexanoate can be improved to 2.83mg / L which is 2.8 times the original bacteria, and the contents of ethyl caprylate and ethyl caprate are respectively improved by 43.3% and 40.9%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A freeze-resistant yeast strain for bread fermentation and its breeding method
ActiveCN103497903BImprove synthesis abilityEnsure safetyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTrehalose-6-phosphate synthase
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
The protein kinase activity of phosphoglycerate kinase 1 as a target for cancer treatment and diagnosis
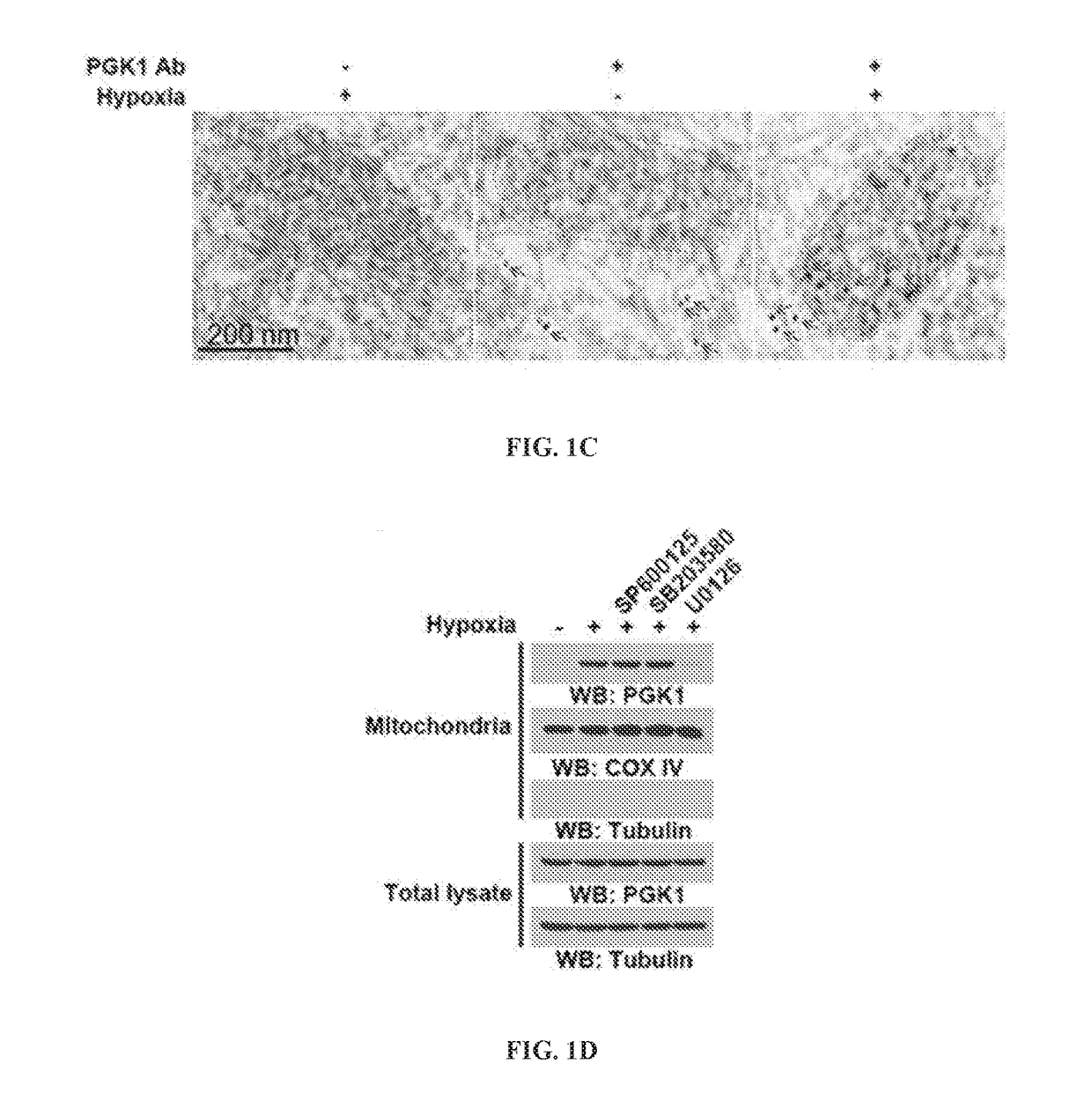
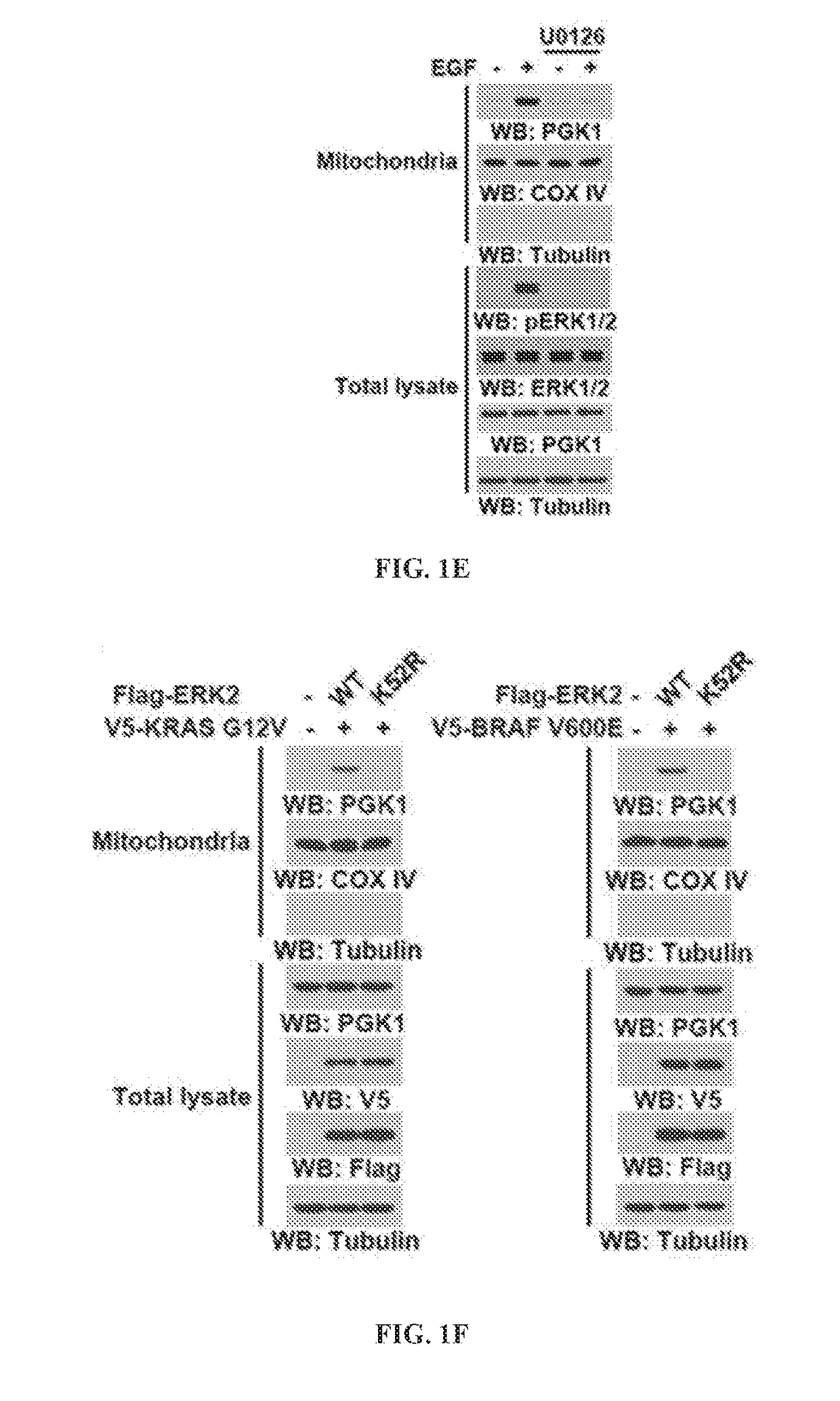
InactiveUS20180011102A1Enhances glycolysisEnhances glutaminolysis-driven lipid synthesisCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer cellPhosphoglyceric acid
Compositions and methods for characterizing cancer cells by determining a marker of PGK1 activity. For example, methods are provided for predicting a patient response to a PGK1 inhibitor, a MEK / ERK inhibitor, an EGFR inhibitor, or a PIN1 inhibitor therapy. Methods for treating patients with such therapies are likewise provided.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com