Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium capable of utilizing whey efficiently to produce ethyl alcohol and construction method of saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium
A technology of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and construction method, which is applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as releasing the regulation of galactose metabolism, and achieve the effect of wide application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Genetically Engineered Bacteria to Remove Galactose Metabolism Regulation
[0034] (1) Construction of genetic engineering strains
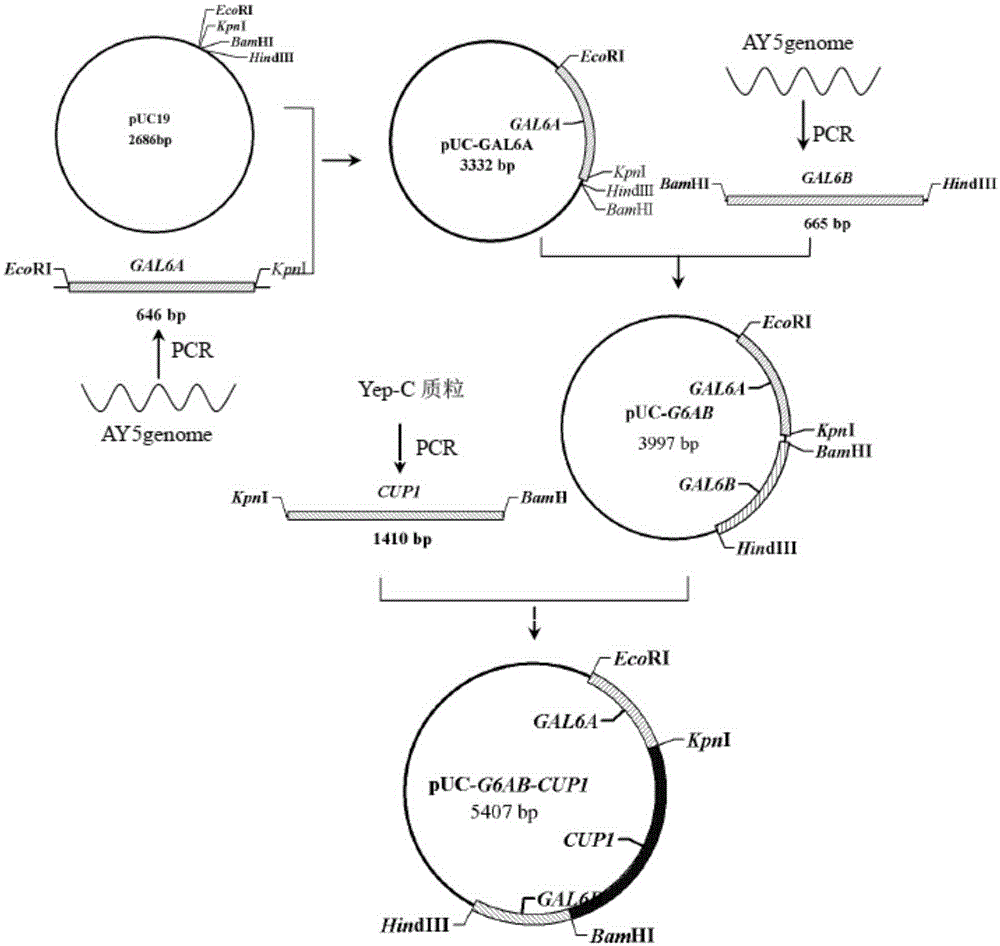
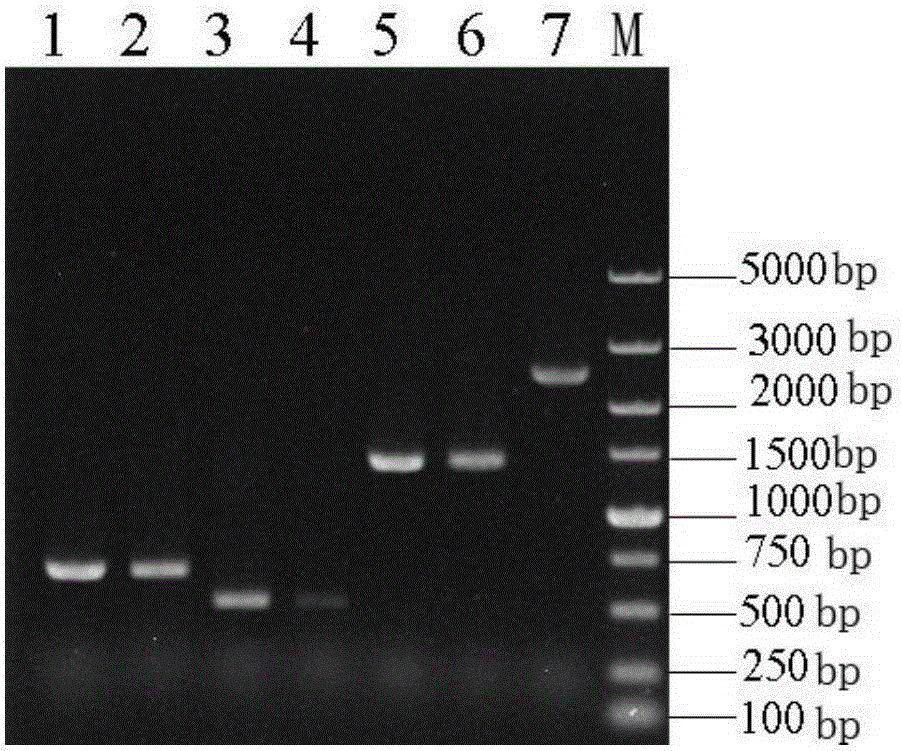
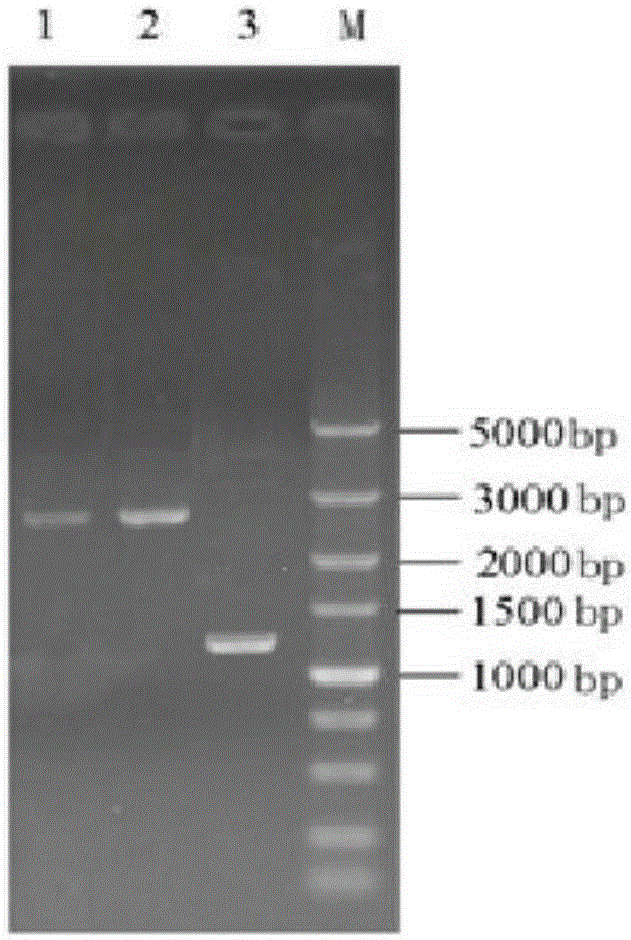
[0035] 1) Using the genome of Saccharomyces cerevisiae AY5 (SaccharomycescerevisiaeCGMCCNo2.1364) as a template, using G6A-U and G6A-D as primers, PCR was used to amplify the fragment GAL6A with a length of 646bp upstream of the full sequence of the GAL6 gene, and similarly use G6B- U and GB6-D were used as primers to amplify the 665bp fragment GAL6B downstream of the full sequence of the GAL6 gene (see Table 1 for primer sequences and restriction sites), and then connect GAL6A and GAL6B to the pUC19 plasmid to obtain the plasmid pUC- G6AB;
[0036] 2) Using the Yep-C plasmid as a template and using Cup-U, Cup-D1, and Cup-D2 as primers, a 1410bp copper resistance gene CUP1 was amplified and connected to the plasmid pUC-G6AB to obtain the plasmid pUC-G6AB-CUP1 (see the build process fig...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Research on Fermentation Performance of Engineering Bacteria Using Whey to Produce Fuel Ethanol
[0051] Inoculate AY5MG and its parent AY-510B24M into 20mL glucose culture medium, and culture overnight at 30°C for 12 hours; after centrifugation and washing, transfer all the bacterial liquid to 200mL whey medium, and culture and ferment at 30°C. Whey medium (g / L): whey powder 120 (lactose content is 53.1g / L), (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 5. MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O1, make up to 1L with water. During the fermentation period, the samples were shaken every 24 hours, and the weight loss was recorded; after the fermentation, the culture was stopped and weighed;
[0052] Table 2 Fermentation performance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae receptor strain and engineered strain in whey
[0053]
[0054] Note: The data shown are the average of the results of three parallel experiments.
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3: Study on glucose repression of whey decomposition products of whey-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacteria and starting strains
[0056] The engineering bacteria and the recipient bacteria were respectively inserted into 5mL YEPD culture medium, and cultured overnight at 30°C for 12h; all the bacterial liquids were transferred to 20mL galactose culture medium, and cultured at 30°C for 24h. Prepare simulated whey breakdown product medium: glucose 3g, galactose 3g, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 0.5g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O0.1g, yeast powder 0.2g, peptone 0.1g, KH 2 PO 4 0.3g, distilled water 100mL. Inoculate according to 10% inoculum amount, and culture statically at 30°C. Shake samples at regular intervals during fermentation, measure different sugar concentrations, and see the results Figure 5 . Lactose in whey is first decomposed into glucose and galactose in the engineered strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and then enters their respective metabolic pat...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com