Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering bacterium for highly yielding medium-chain fatty acid ethyl ester as well as construction method thereof
A fatty acid ethyl ester and yeast engineering technology, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problem of low ester production capacity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0033] Example 1: Construction of a genetically engineered strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae with high yield of ethyl caproate
[0034] (1) Construction of genetically engineered strains
[0035] 1) Construction of pUC-APEKB plasmid
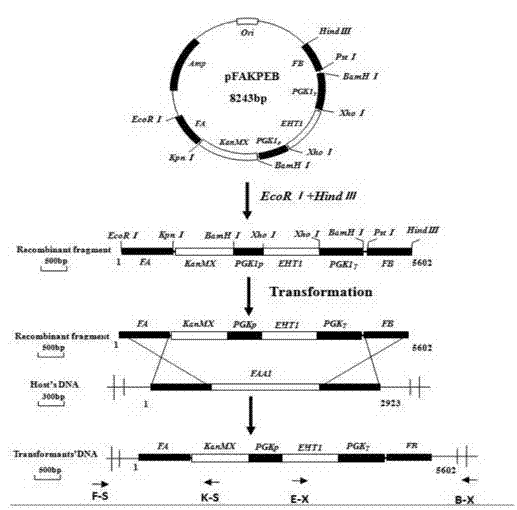
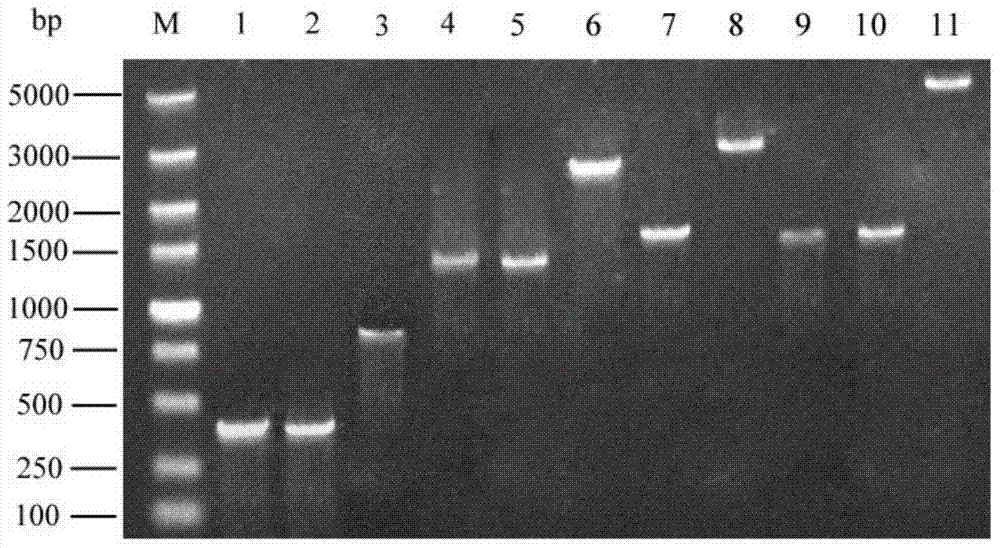
[0036] The homologous recombination plasmid pUC-APEKB is constructed with pUC-19 as the basic plasmid, and the construction process is as follows figure 1 As shown, using the haploid a8 or α5 of AY15 as a template, PCR amplification yields a 411 bp upstream homology arm FA and a 409 bp downstream homology arm FB, respectively, through EcoRI / KpnI and PstI / HindIII Double enzyme digestion and ligation into pUC-19 to obtain plasmid pUC-FAB. Using the haploid a8 or α5 of AY15 as the template, the 1356bp alcohol hexanoyltransferase gene EHT1 was obtained by PCR amplification, which was inserted into the promoter PGK1p and terminator PGK1 on the pPGK1 plasmid by XhoI single enzyme digestion T In between, the plasmid pPGK1-E was obtained; using the pPGK1-E ...
Embodiment 2
[0057] Example 2: Simulated corn raw material liquid liquor fermentation experiment
[0058] 1) Fermentation process route:
[0059] Corn flour → soaking → liquefaction → saccharification → cooling → inoculation → fermentation → steaming wine → measurement index
[0060] 2) Process conditions: soaking conditions: 60~70℃, immersion for 20min; liquefaction conditions: 85~90℃, adding high temperature resistant α-amylase, liquefaction for 90min; saccharification conditions: 55~60℃, adding glucoamylase, saccharification for 20min fermentation Conditions: 30°C, 15 days. When steaming wine, take 100mL mash, add 100mL water, and steam 100mL wine sample.
[0061] 3) Ingredients: corn flour: 60g; add water 180mL; high temperature resistant α-amylase: 30μL; glucoamylase: 90μL; acid protease: 1.2mL; nutrient salt: 1mL; inoculation amount: 7.5%;
[0062] According to the above-mentioned simulation process, the fermentation experiment of corn raw material liquid liquor was carried out on the engine...
Embodiment 3
[0070] Example 3: Solid-state Daqu liquor fermentation experiment
[0071] 1) Fermentation process route:
[0072] Sorghum → soaking → steaming → spreading → mixing koji → culture and saccharification for 24 hours → inoculation → fermentation → distillation
[0073] 2) Process conditions: soaking conditions: 95~98℃, fully absorbing water without hard cores; cooking conditions: steaming at normal pressure for about 30 minutes, uniform particles and no white cores. Fermentation conditions: 30°C, 15 days. Steaming conditions: 100g distillers grains, add 100mL water, steam 100mL wine sample.
[0074] 3) Ingredients: 50g sorghum; 5g Daqu; inoculation amount: 5%;
[0075] Perform solid-state Daqu liquor fermentation experiments on Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineering strains a8-1, α5-1, EY15 and starting strains a8, α5, and AY15 according to the above-mentioned simulation process; shake and weigh every 12 hours during the fermentation, and record the weight loss; after the fermentation is o...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com