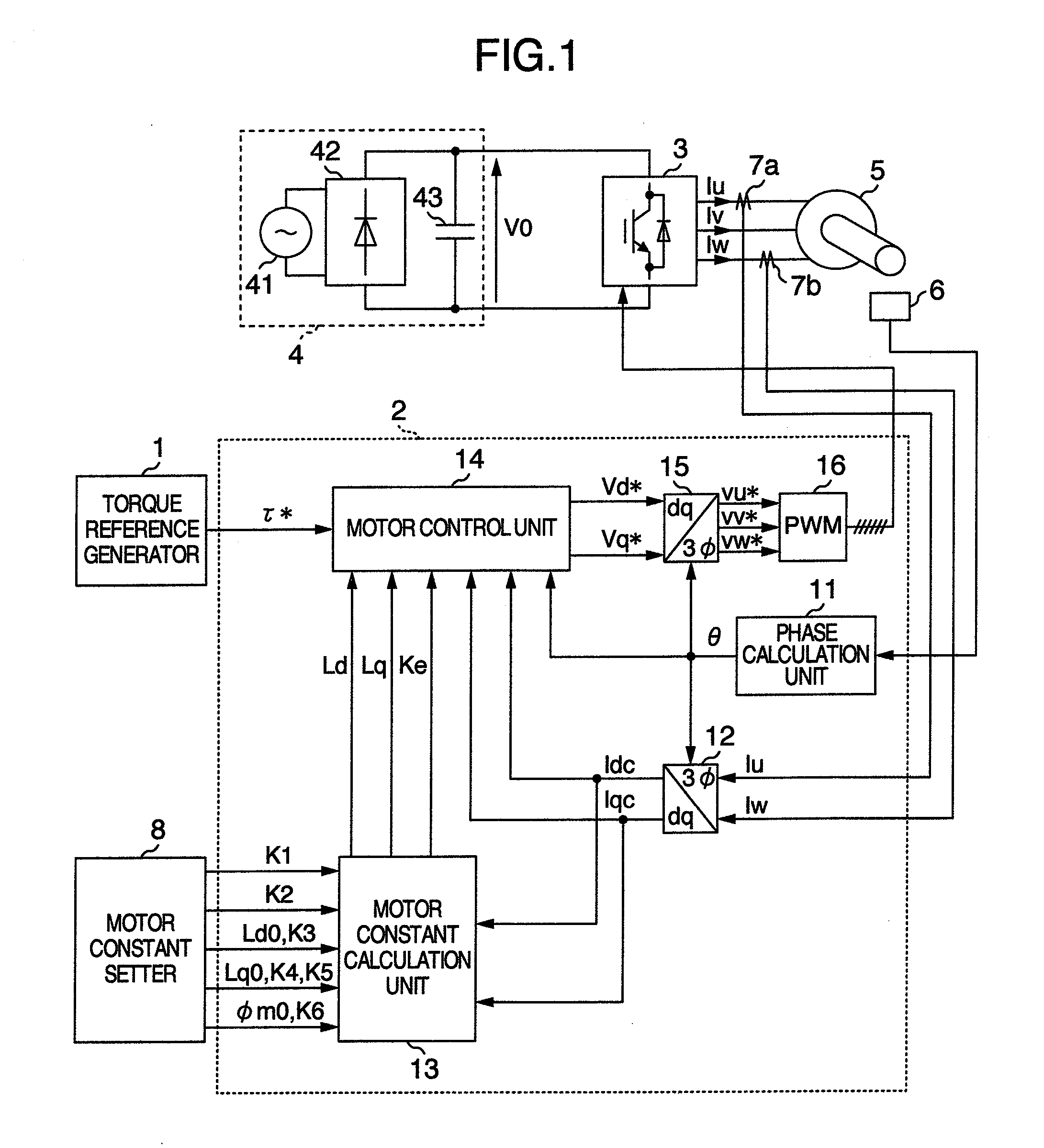
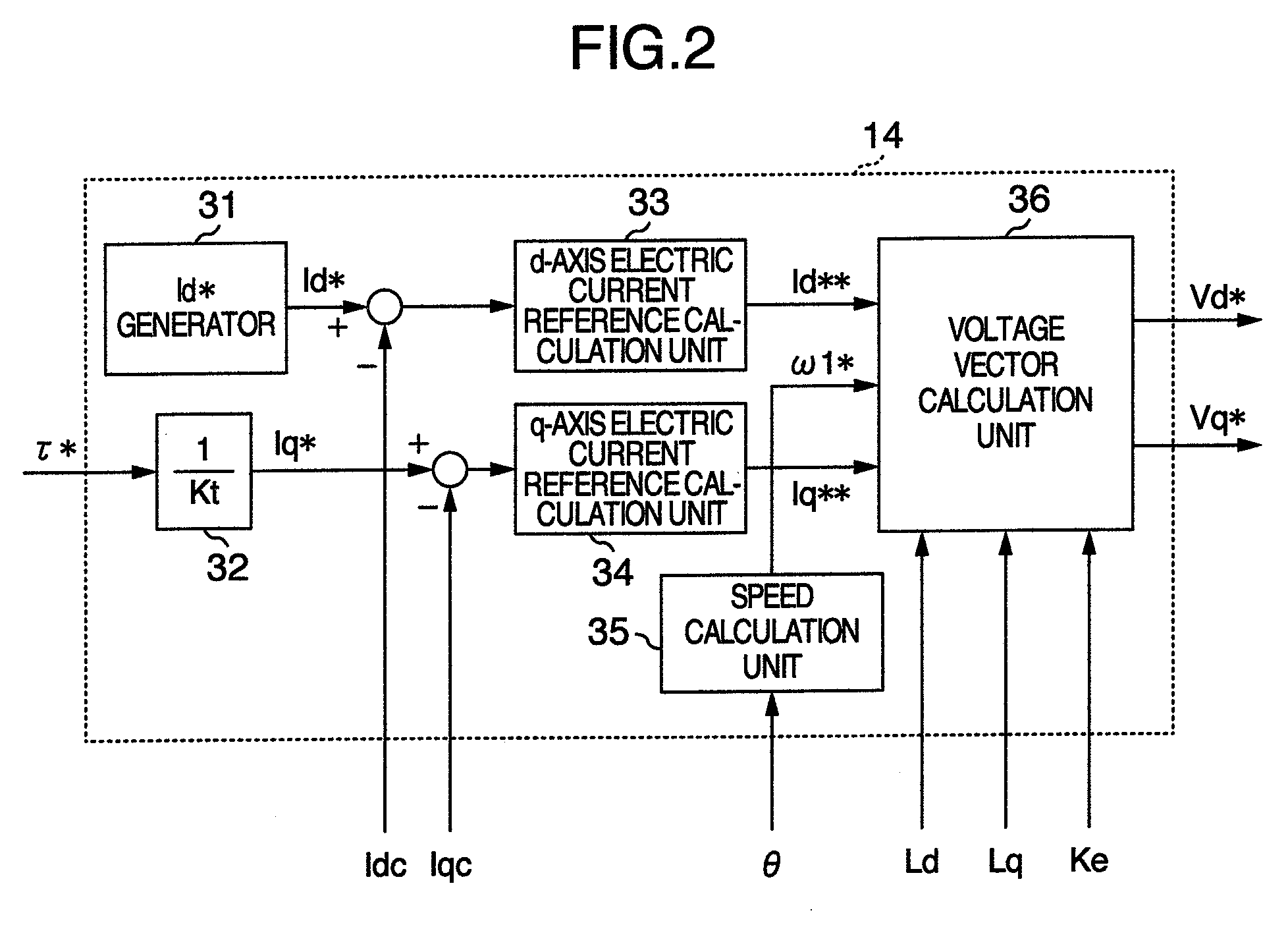
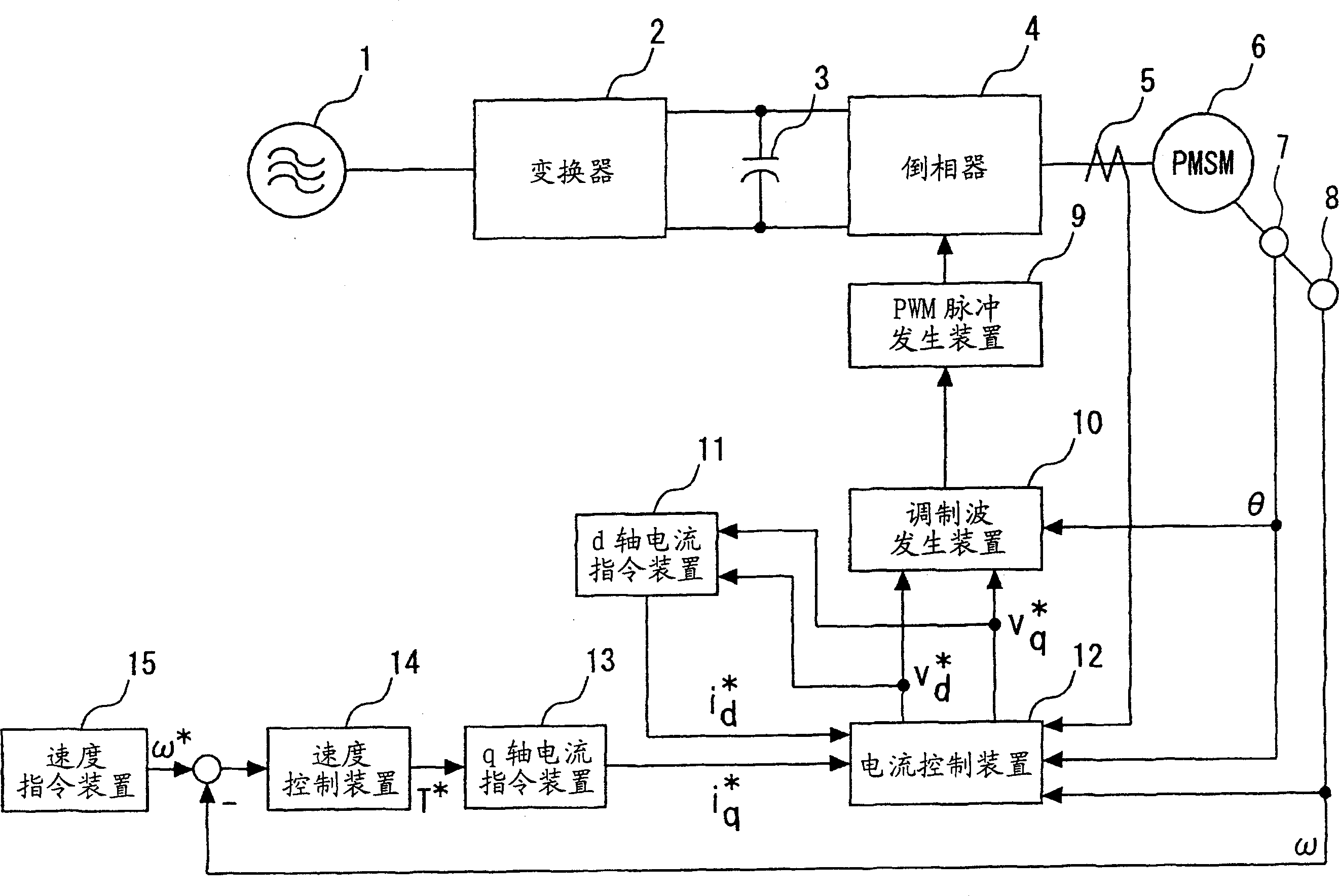
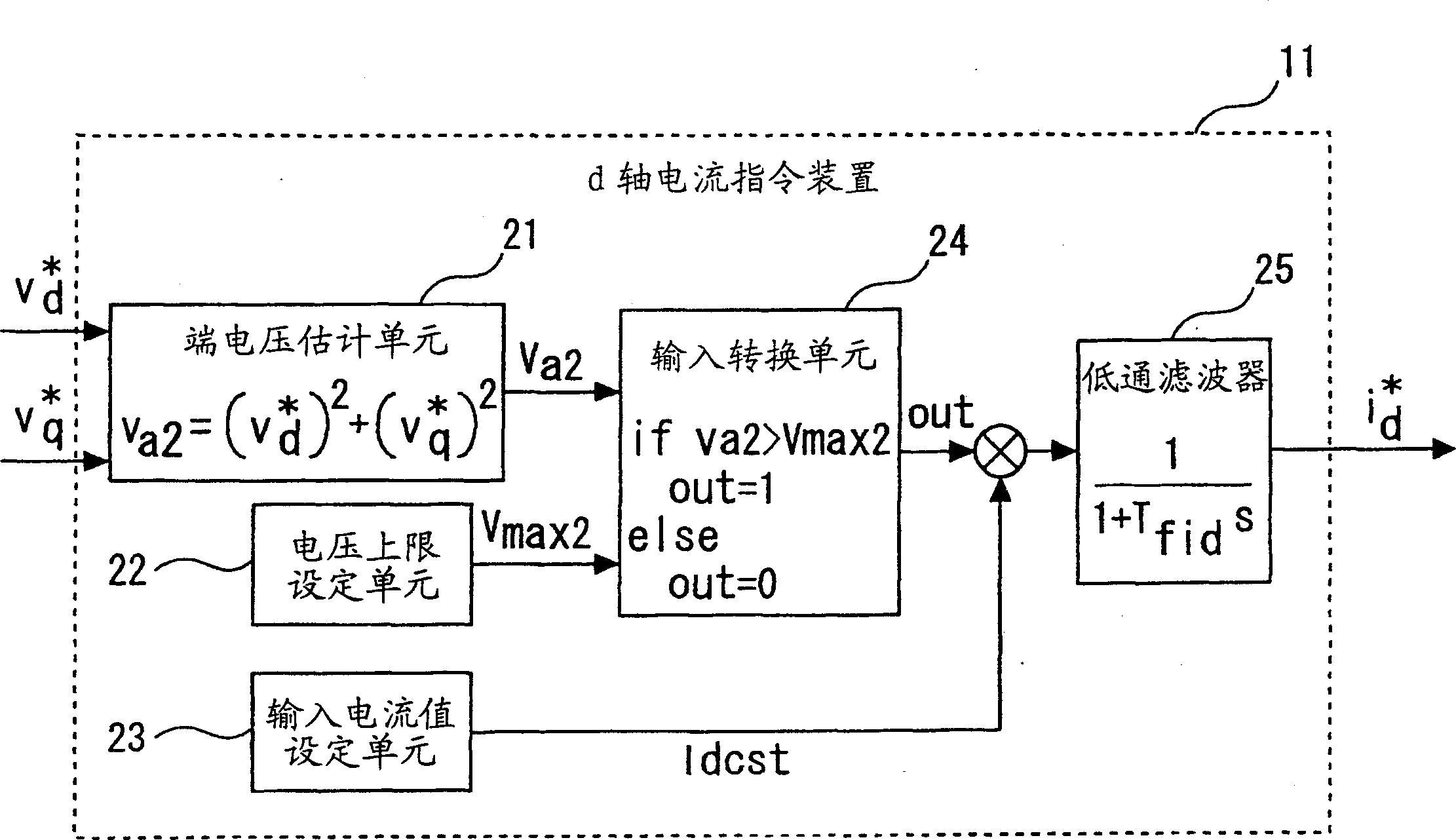
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
121 results about "Motor constants" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The motor size constant (KM) and motor velocity constant (Kᵥ, alternatively called the back EMF constant) are values used to describe characteristics of electrical motors.
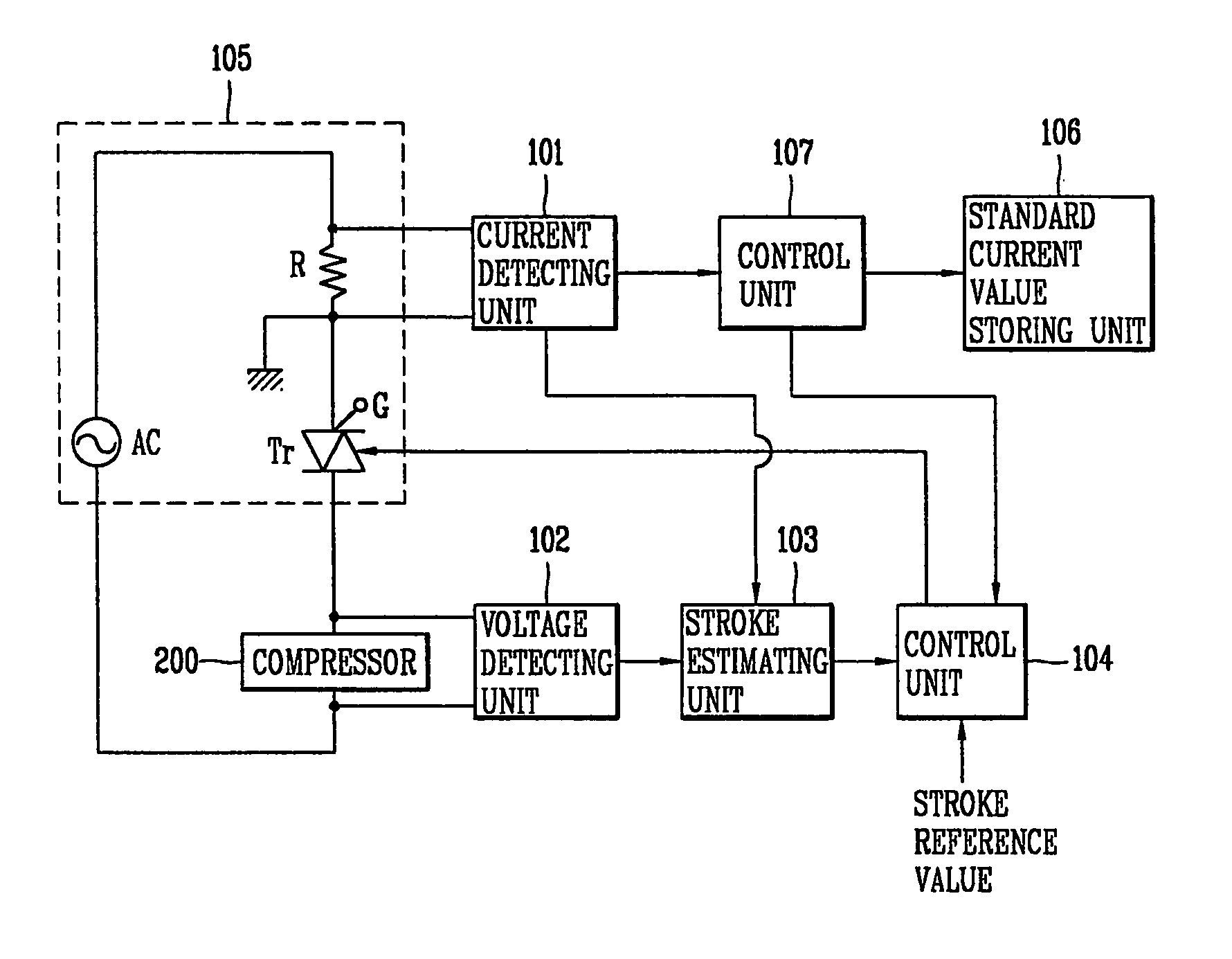
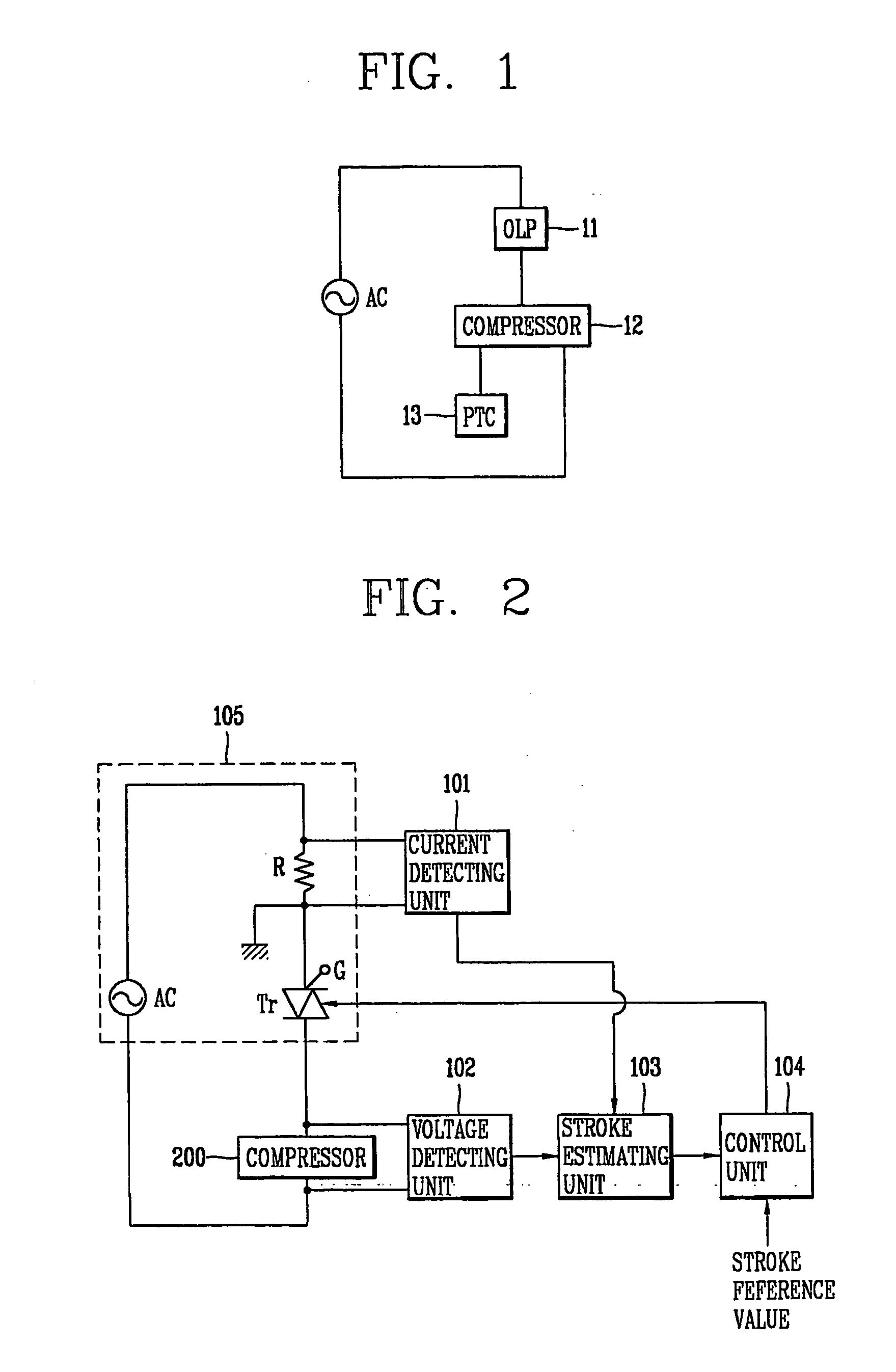
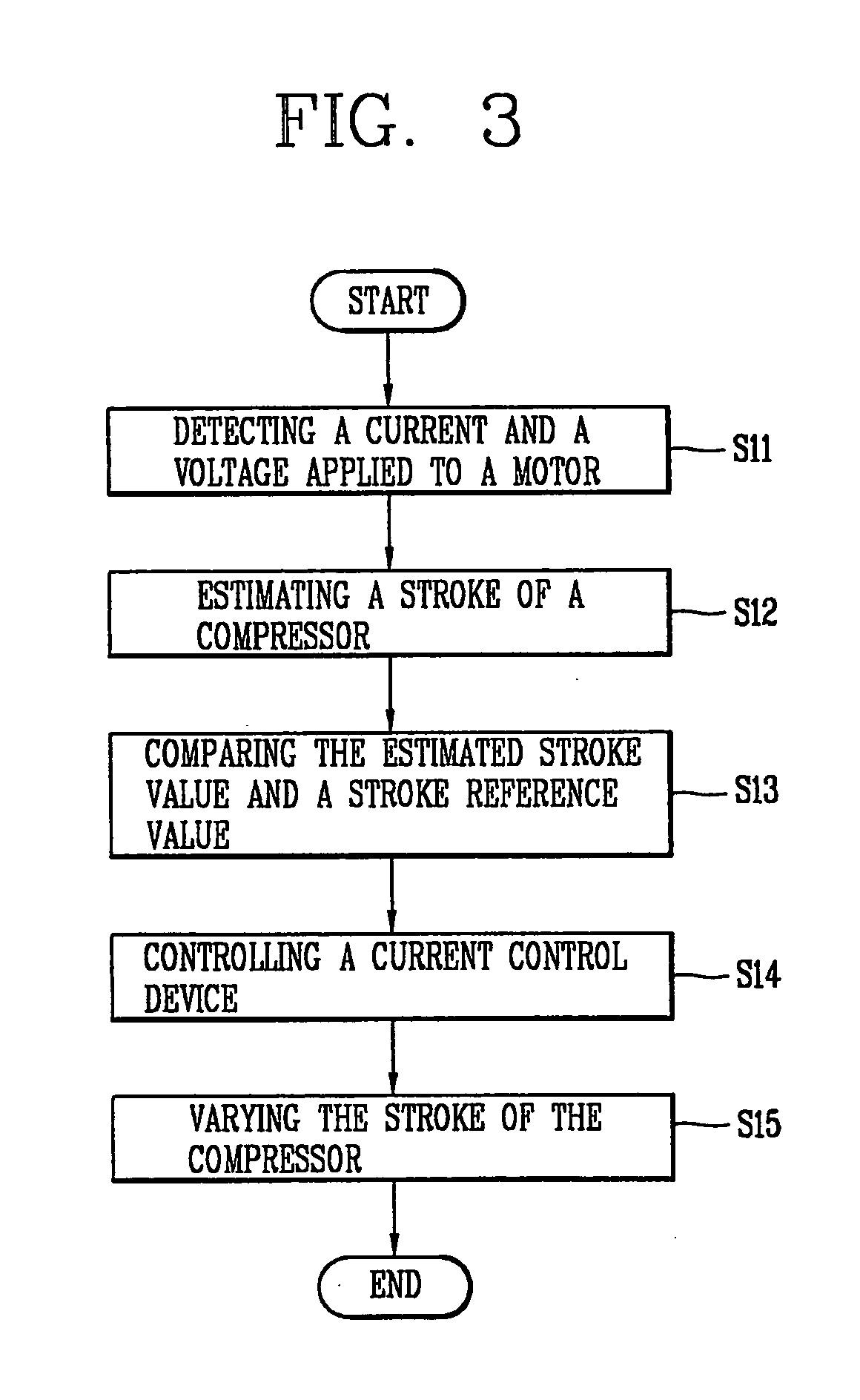
Operation control apparatus for compressor and method thereof
InactiveUS20060048530A1Low production costDomestic cooling apparatusCompression machines with non-reversible cycleElectrical resistance and conductanceControl signal
In an operation control apparatus and a method thereof, the compressor can be protected from overloading through a current control device instead of an OLP (Over Load Protector) and a PTC thermistor (Positive Temperature Coefficient thermistor). The operation control apparatus includes: a stroke estimated unit for estimating a stroke of the compressor on the basis of a current and a voltage applied to an interior motor of the compressor and a motor constant of the interior motor; a control unit for generating a control signal for varying a stroke of the compressor on the basis of the estimated stroke value and a preset stroke reference value; and a current control means being turned on / off so as to vary a stroke voltage applied to the interior motor of the compressor.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
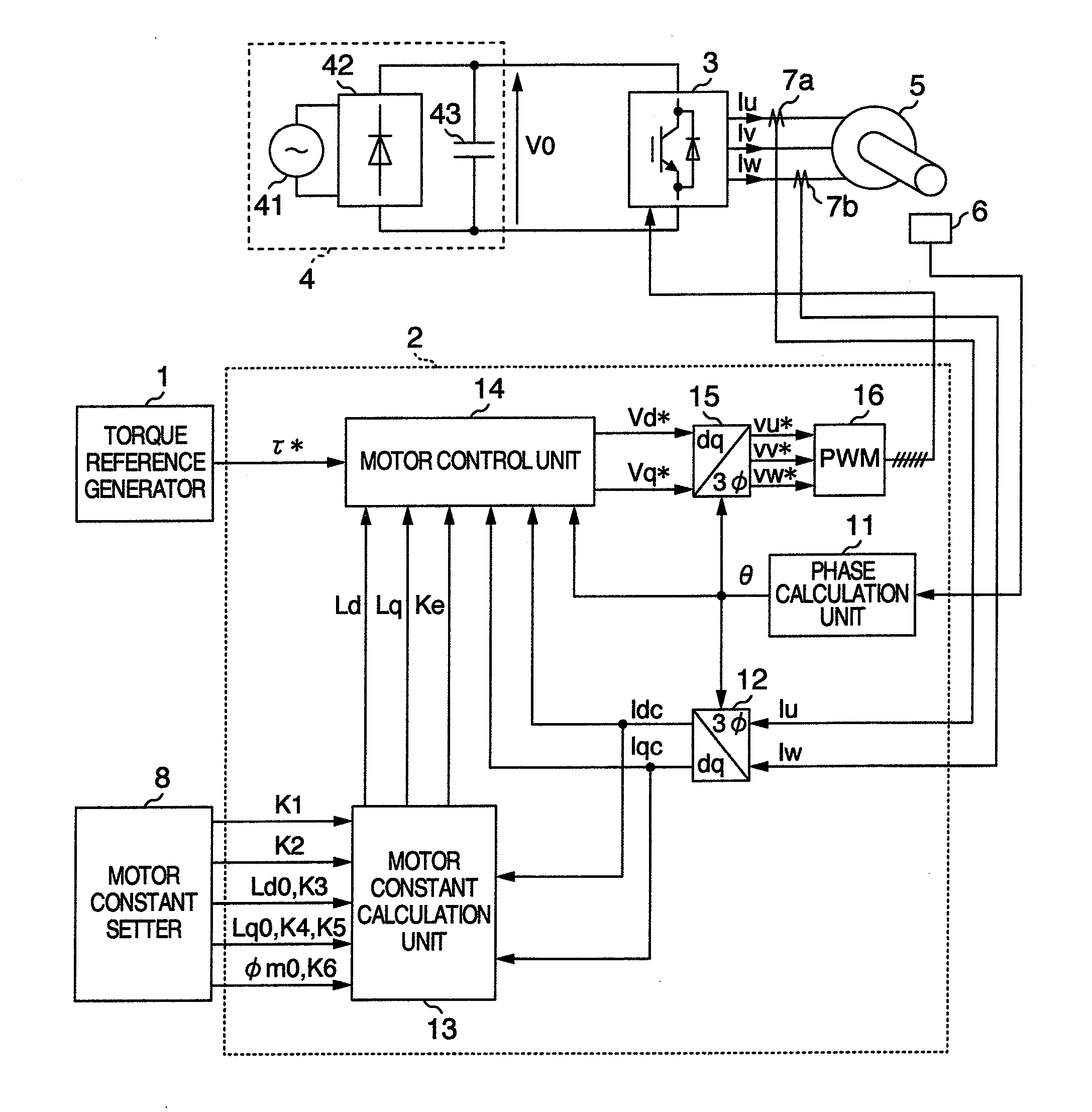
Control apparatus for ac motor
ActiveUS20090140674A1High-precision torque controlImprove responseSynchronous motors startersVector control systemsState variableOrthogonal basis
It is attained by being provided with a motor constant calculation unit for calculating electric constants of a motor, and by correcting setting values of electric constants defined on one of the axes of two orthogonal axes, by a functional expression using a state variable defined on the same axis, and by correcting them by a functional expression using a state variable defined on the other axis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Controller of permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveCN1784824AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsSynchronous motorTerminal voltage
A controller of a permanent magnet synchronous motor in which terminal voltage of the motor can be controlled with high accuracy even for a variation in motor constant through a simple arrangement without requiring square root or complex calculation expressions. Terminal voltage of the motor is controlled by feeding a negative current to d-axis such that the maximum output voltage of an inverter does not exceed the terminal voltage of the permanent magnet synchronous motor. Magnitude of the d-axis current component is regulated by comparing a voltage command value being inputted to the inverter with a terminal voltage upper limit (threshold value) being set based on the maximum output voltage of the inverter, switching the d-axis current component in the negatively increasing direction when the voltage command value exceeds the terminal voltage upper limit, and switching the d-axis current component in the negatively decreasing direction when the voltage command value does not exceed the terminal voltage. The motor is controlled such that the terminal voltage thereof does not exceed the maximum output voltage of the inverter.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
Engaging control method and engaging control device for clutch of hybrid automobile
ActiveCN102991495AReduce shockImprove driving comfort performanceHybrid vehiclesClutchMotor constants
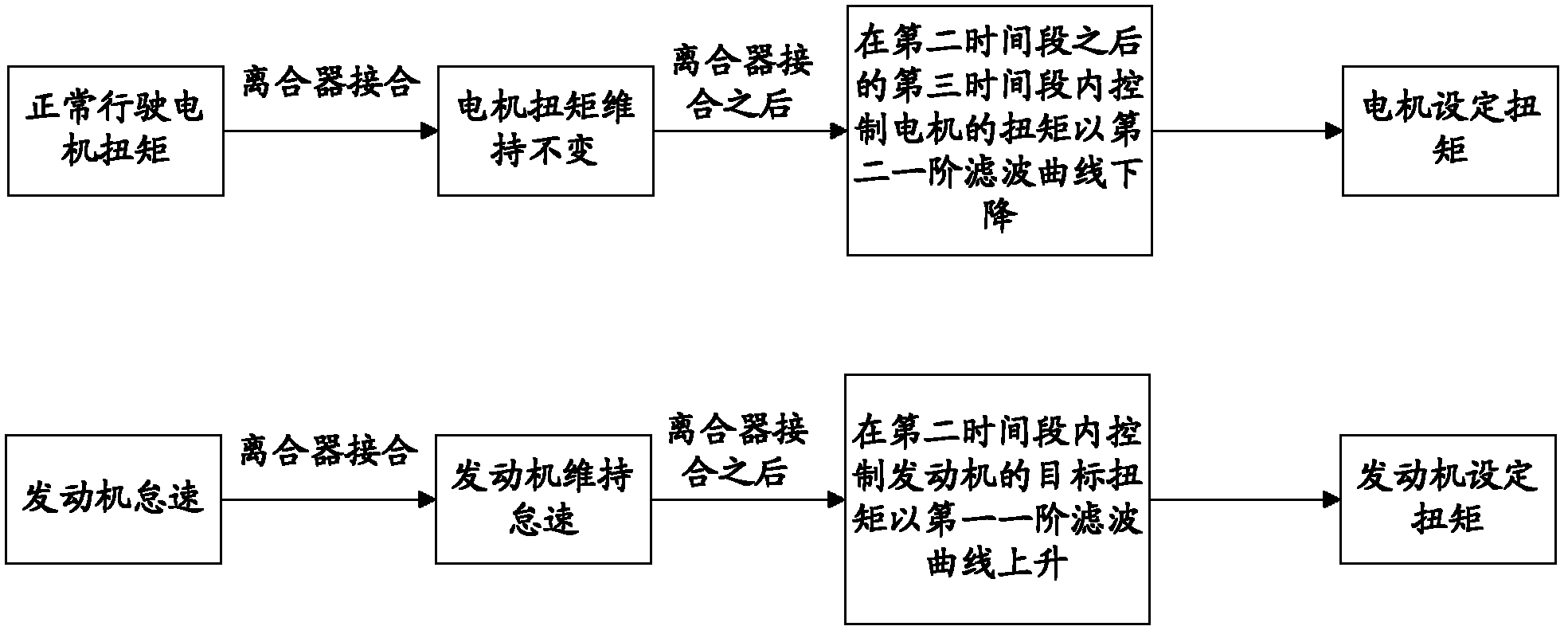
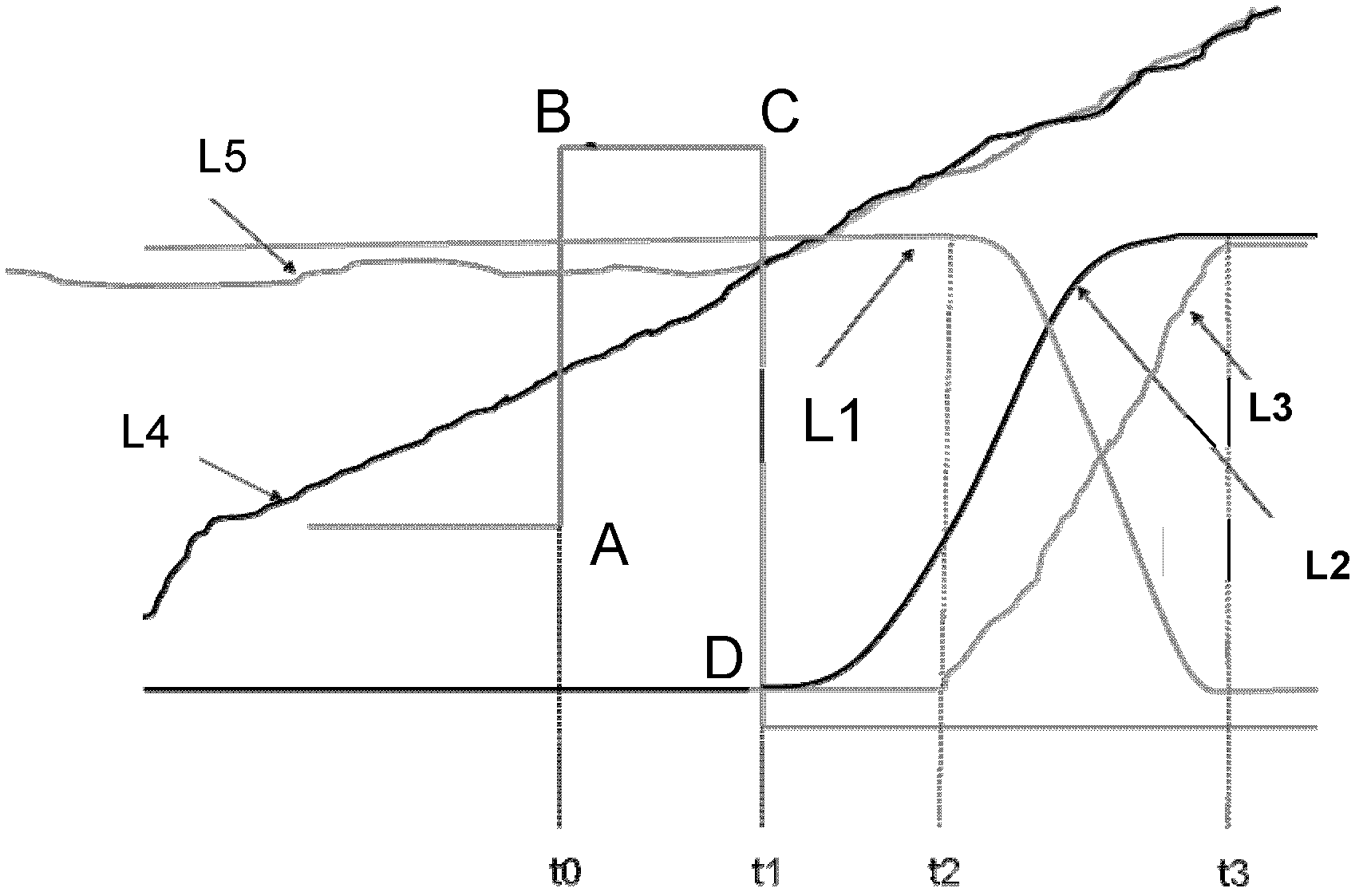
The invention provides an engaging control method and an engaging control device for a clutch of a hybrid automobile. The method comprises the following steps of: receiving a clutch engaging control instruction; in the clutch engaging process of the first time period, controlling the torque of a motor constant; simultaneously controlling an engine to maintain an idle speed operating condition; after clutch engaging is finished, controlling the target torque of the engine to increase in a first first-order filtration curve within the second time period, and simultaneously controlling the torque of the motor constant; and controlling the torque of the motor to decrease in a second first-order filtration curve within the third time period after the second time period. By utilizing the engaging control method and the engaging control device, the power output of vehicles can be smoothly switched from a state that the motor serves as main power to a state that the engine serves as main power, so that vehicle impact during the model clutch engaging process is reduced, and the driving comfort can be improved.
Owner:BEIQI FOTON MOTOR CO LTD
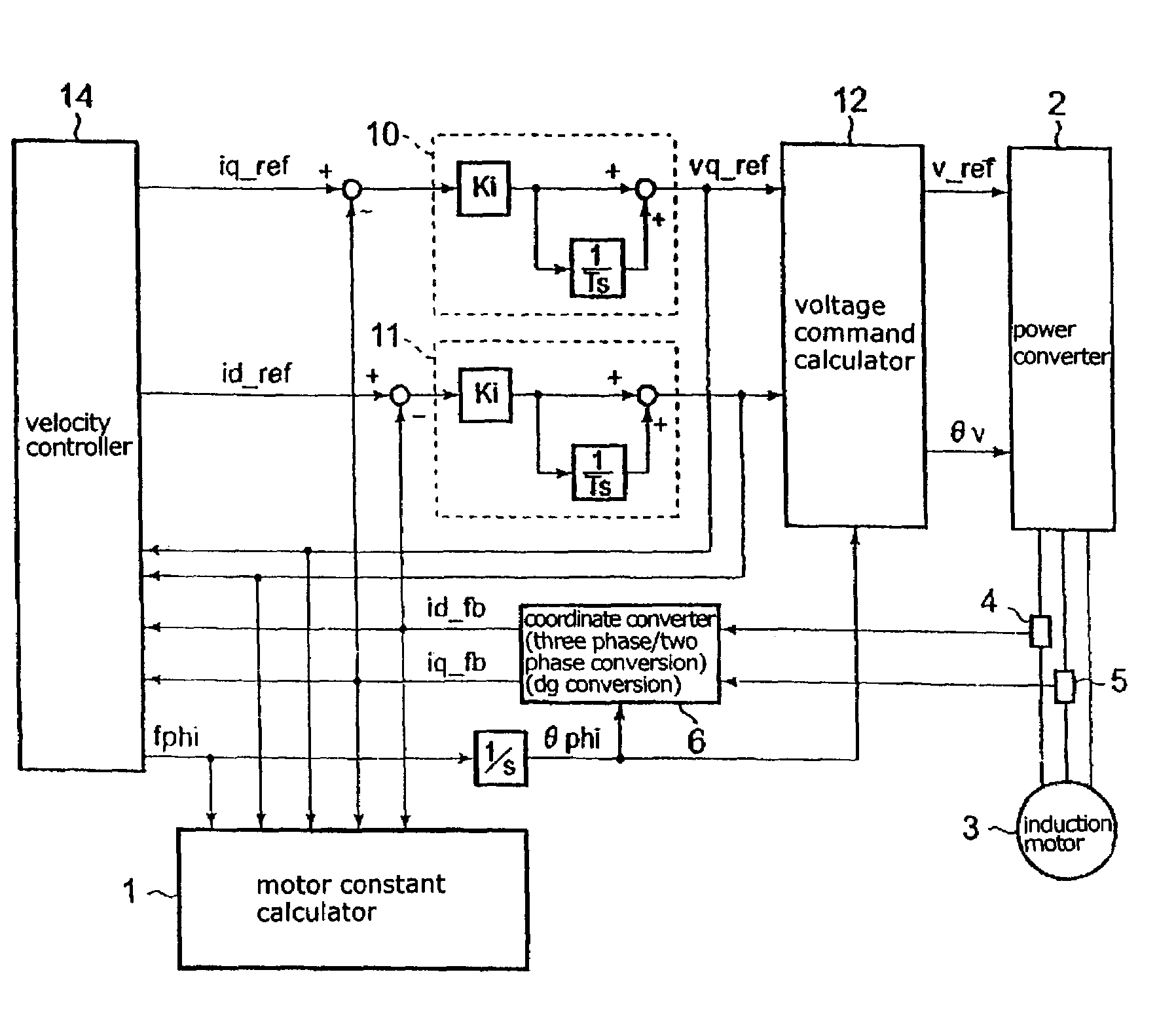
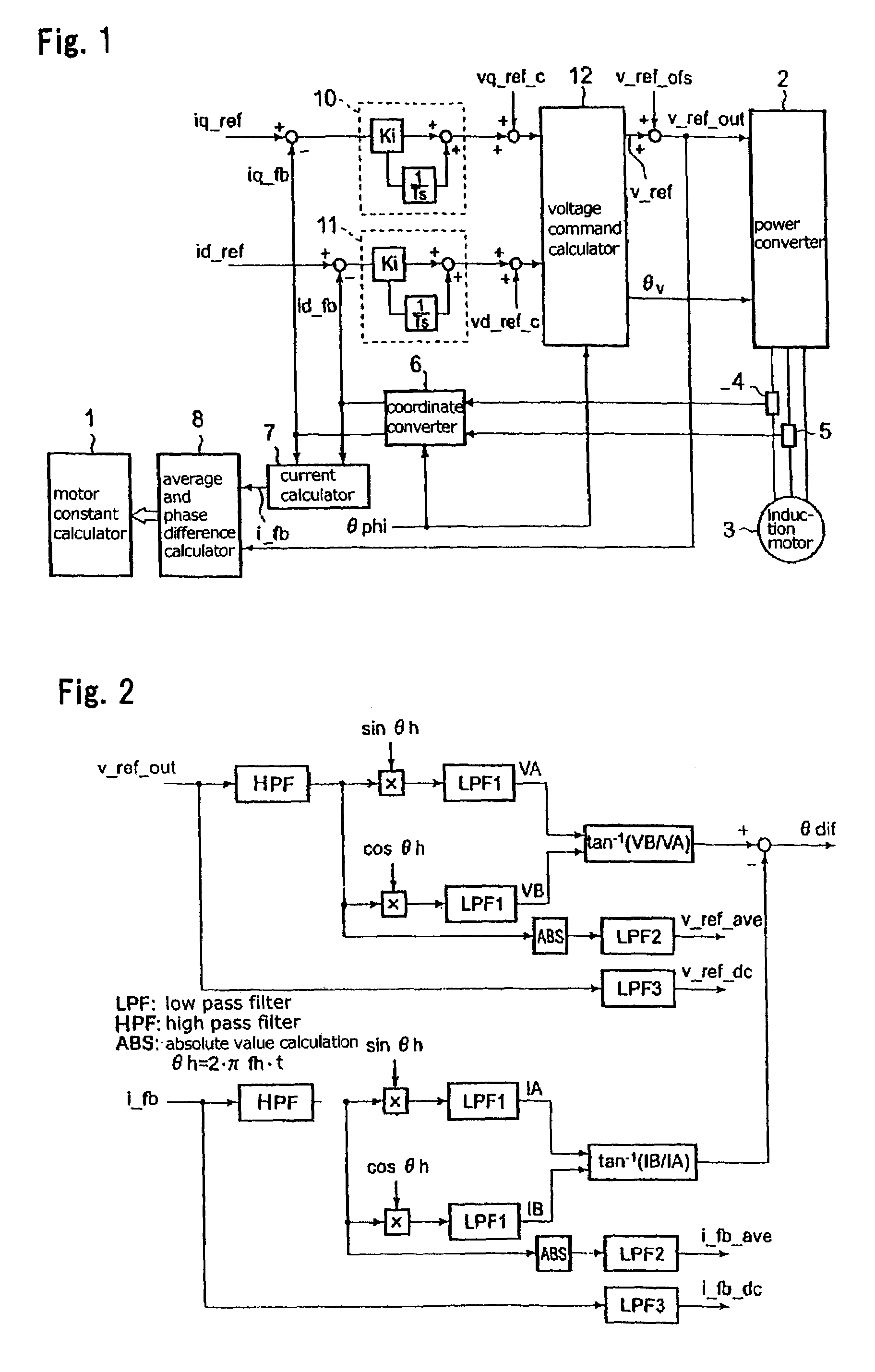
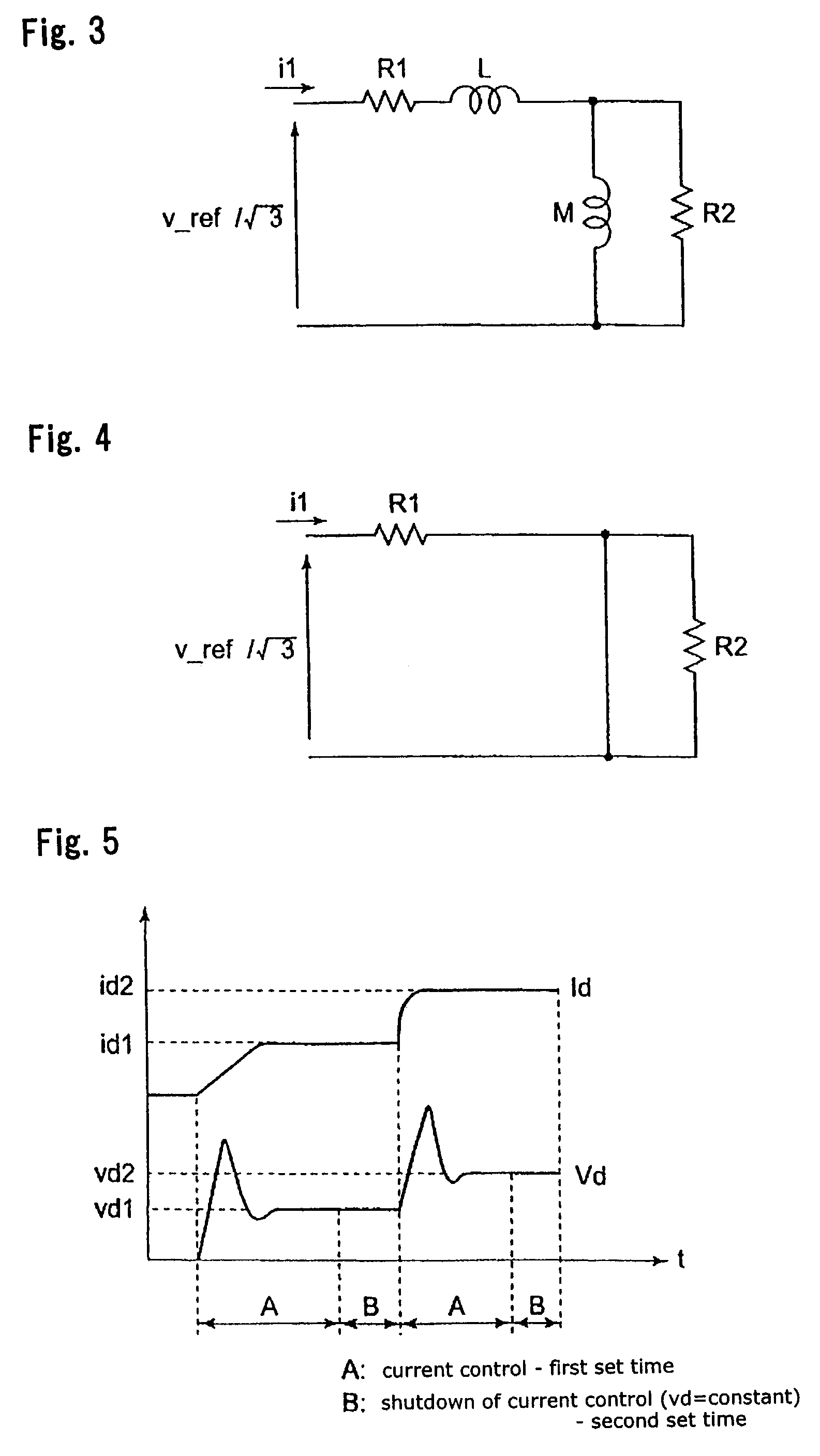
Method of measuring motor constant for induction motor
InactiveUS7039542B2Accurate resistanceEasy to controlVehicle testingSingle-phase induction motor startersElectrical resistance and conductanceLine resistance
A method of measuring a motor constant is provided in a vector control apparatus for an induction motor. A voltage output phase θv is set at a previously set arbitrary phase. Prior to applying a current, a current command is fed to operate the vector control apparatus with a proportional-plus-integral controller being set operative. After conduction for a predetermined time, the gain of the proportional-plus-integral controller is set to zero to maintain an integrated value constant and accordingly fix a voltage command value. In this state, a current command value and a detected current value are measured. This measurement is performed at two levels of current, and a primary resistance value (or a line-to-line resistance value) is derived from the slope.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Control apparatus for AC motor
ActiveUS8044618B2Enabling useSet more correctly and more simply and convenientlySynchronous motors startersVector control systemsState variableOrthogonal basis
It is attained by being provided with a motor constant calculation unit for calculating electric constants of a motor, and by correcting setting values of electric constants defined on one of the axes of two orthogonal axes, by a functional expression using a state variable defined on the same axis, and by correcting them by a functional expression using a state variable defined on the other axis.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Single-phase position sensorless permanent magnet motor control apparatus
InactiveUS20080018289A1Reduce vibrationReduce noiseMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersLow noiseTerminal voltage
A single-phase permanent magnet motor control apparatus, in particular, a low price, flat output torque, low vibration, low noise single-phase permanent magnet motor control apparatus, and a fan and pump using such a single-phase permanent magnet motor control apparatus are provided. In a single-phase permanent magnet motor control apparatus for driving a single-phase permanent magnet motor by using a DC power supply, a converter for converting DC to AC, and a control circuit for controlling the converter, a motor current measuring unit, a terminal voltage measuring unit, a correction unit for correcting an impedance drop in motor constants, and a calculation unit for finding an induced voltage to be obtained by control are included, and a polarity of a terminal voltage is determined on the basis of a value of the found induced voltage.
Owner:JAPAN SERVO CO LTD
Motor speed control method and control system
ActiveCN111245332AImprove travel satisfactionMeet load torque requirementsAC motor accelaration/decelaration controlMotor parameters estimation/adaptationMotor speedLoad torque
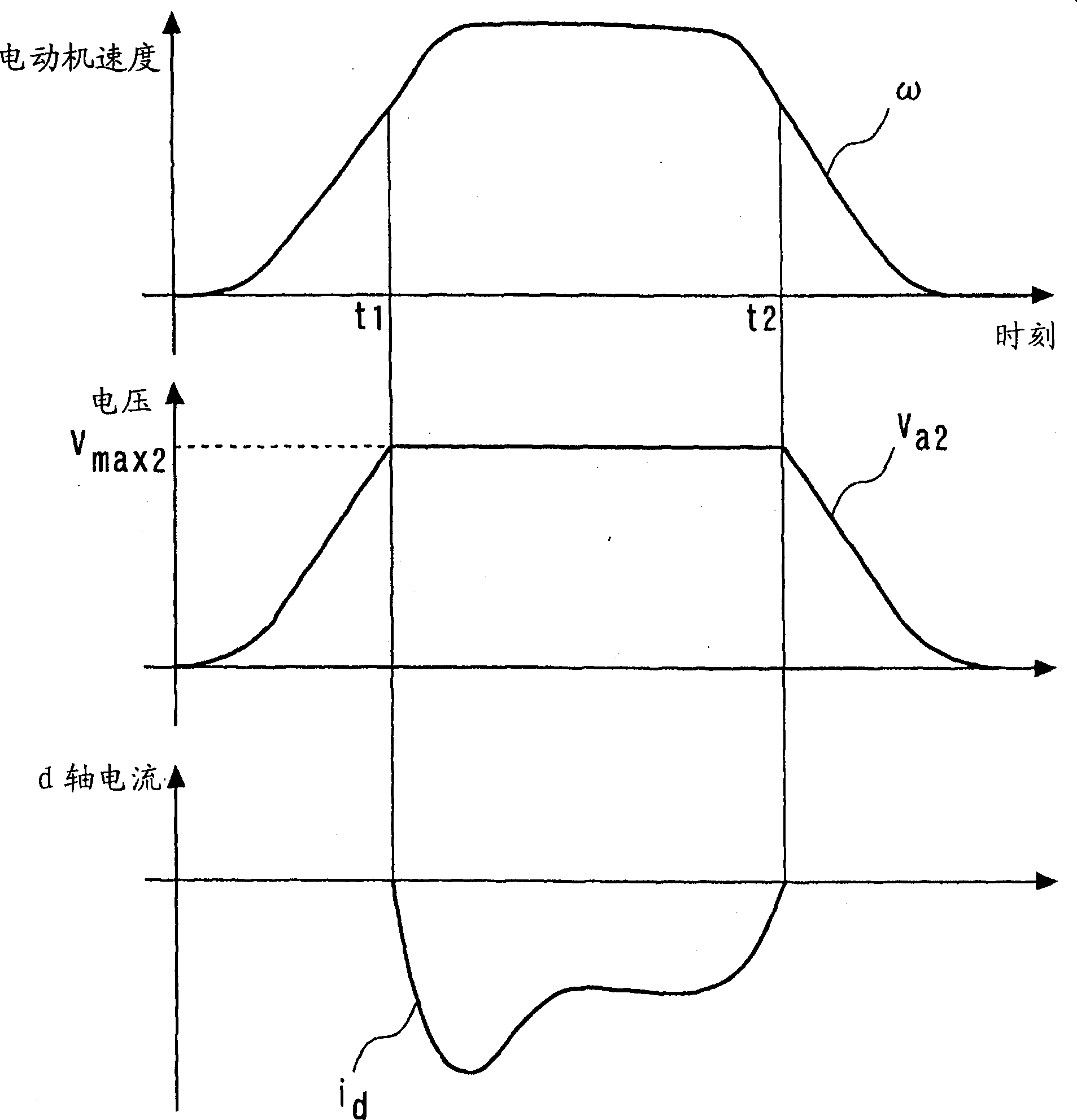
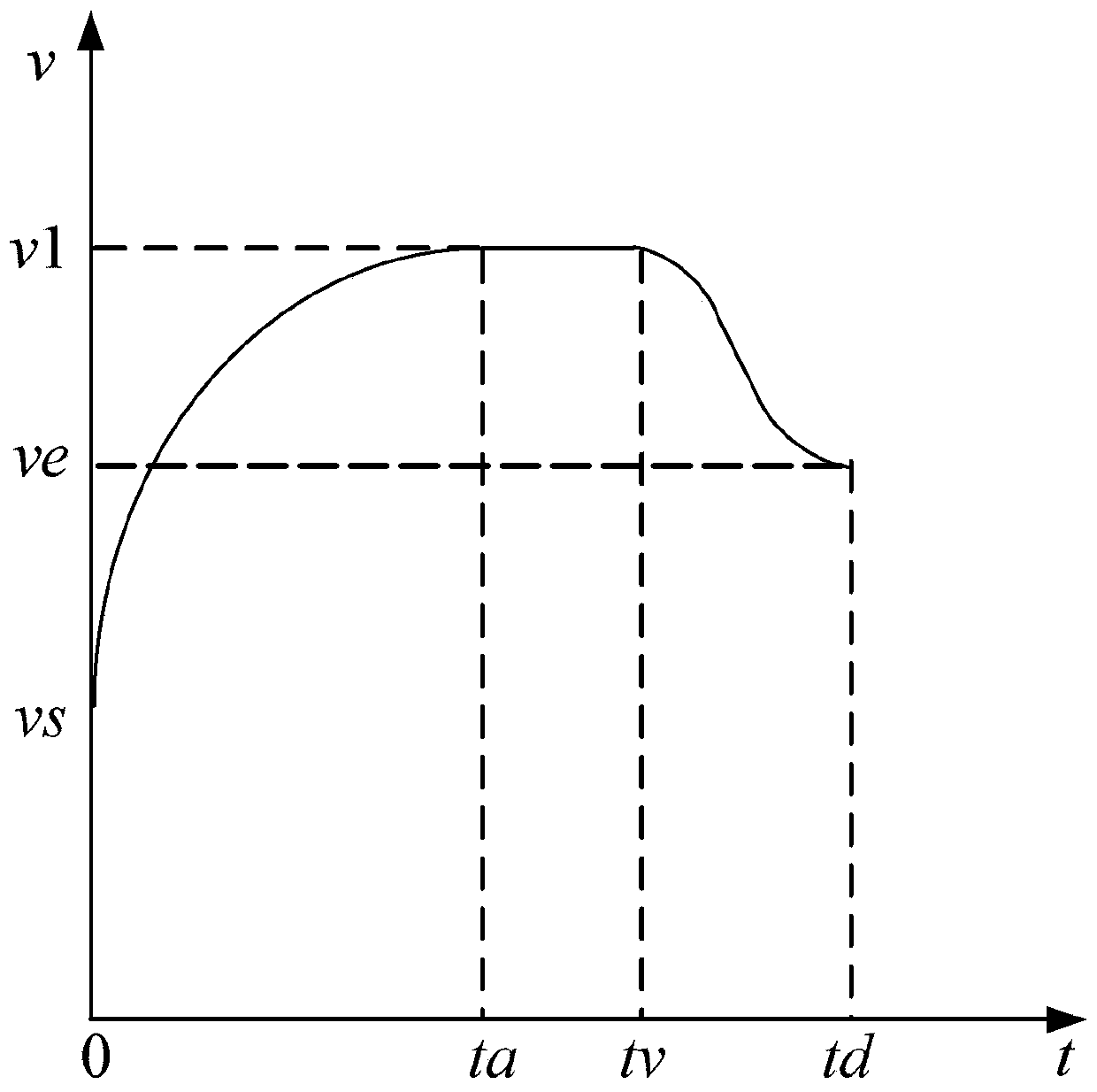
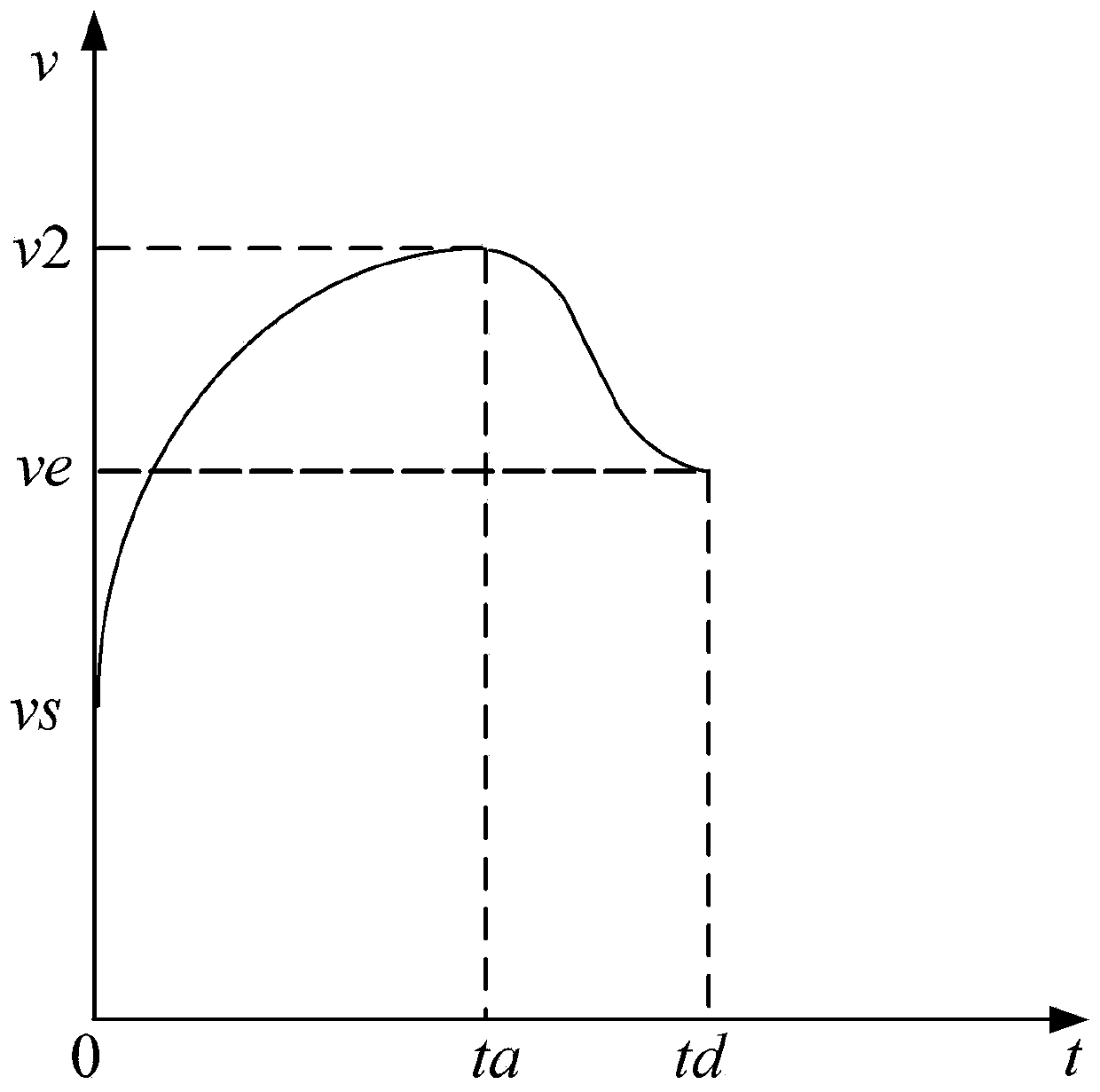
The invention provides a motor speed control method and control system, and the speed control method employs an asymmetric S-shaped speed curve, and comprises: determining an acceleration curve equation through calculation according to a preset parabola curve equation at an acceleration stage of a motor, and controlling acceleration operation of the motor through the acceleration curve equation; in the motor constant-speed stage, controlling the motor to operate at a constant speed according to the speed corresponding to the acceleration termination moment in the acceleration stage; and in themotor deceleration stage, adopting a preset S-shaped speed curve with constant jerk, and controlling the motor to decelerate according to the S-shaped speed curve with the constant jerk. According tothe invention, an acceleration curve of a quadratic parabola with a downward opening is designed, the motor torque in the acceleration stage meets the load torque requirement, the running stroke of the motor is greatly improved within the same acceleration time, then the acceleration efficiency is improved, and in addition, by conducting reasonable trajectory planning on the whole movement process, connection between all movement stages is smooth and free of impact.
Owner:南京岸鸣智能科技有限公司
Method for controlling interior permanent magnet synchronous motor
ActiveUS20130328508A1Improved fuel ratioHigh outputHybrid vehiclesElectronic commutation motor controlMotor speedPermanent magnet synchronous motor
Disclosed is a method for controlling a permanent magnet synchronous motor to maximize use of voltages of a battery by voltage phase control within weak magnetic flux area and to achieve compensation for a torque error through a torque compensator when driving the permanent magnet synchronous motor for hybrid vehicles. In particular, the method controls a permanent magnet synchronous motor so that voltage use can be maximized in a weak magnetic flux area by using voltage near maximum voltage through voltage phase control utilizing magnetic flux-based map data receiving a torque command and motor speed / batter output voltage as inputs and torque error can be compensated using a torque compensation filter when a motor constant is changed in the weak magnetic flux by a circumstance parameter, when the permanent magnet synchronous motor mounted in a hybrid vehicle and an electric vehicle is driven.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +2
Method for measuring motor constant of induction motor
InactiveCN1441908AElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsLine resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A method of measuring a motor constant is provided in a vector control apparatus for an induction motor. A voltage output phase [theta]v is set at an previously set arbitrary phase. Prior to applying a current, a current command is fed to operate the vector control apparatus with a proportional-plus-integral controller being set operative. After conduction for a predetermined time, the gain of the proportional-plus-integral controller is set to zero to maintain an integrated value constant and accordingly fix a voltage command value. In this state, a current command value and a detected current value are measured. k is measured at two levels of current, and a primary resistance value (or a line-to-line resistance value) is derived from the slope.
Owner:YASKAWA DENKI KK
Method and apparatus for motor lock or stall detection
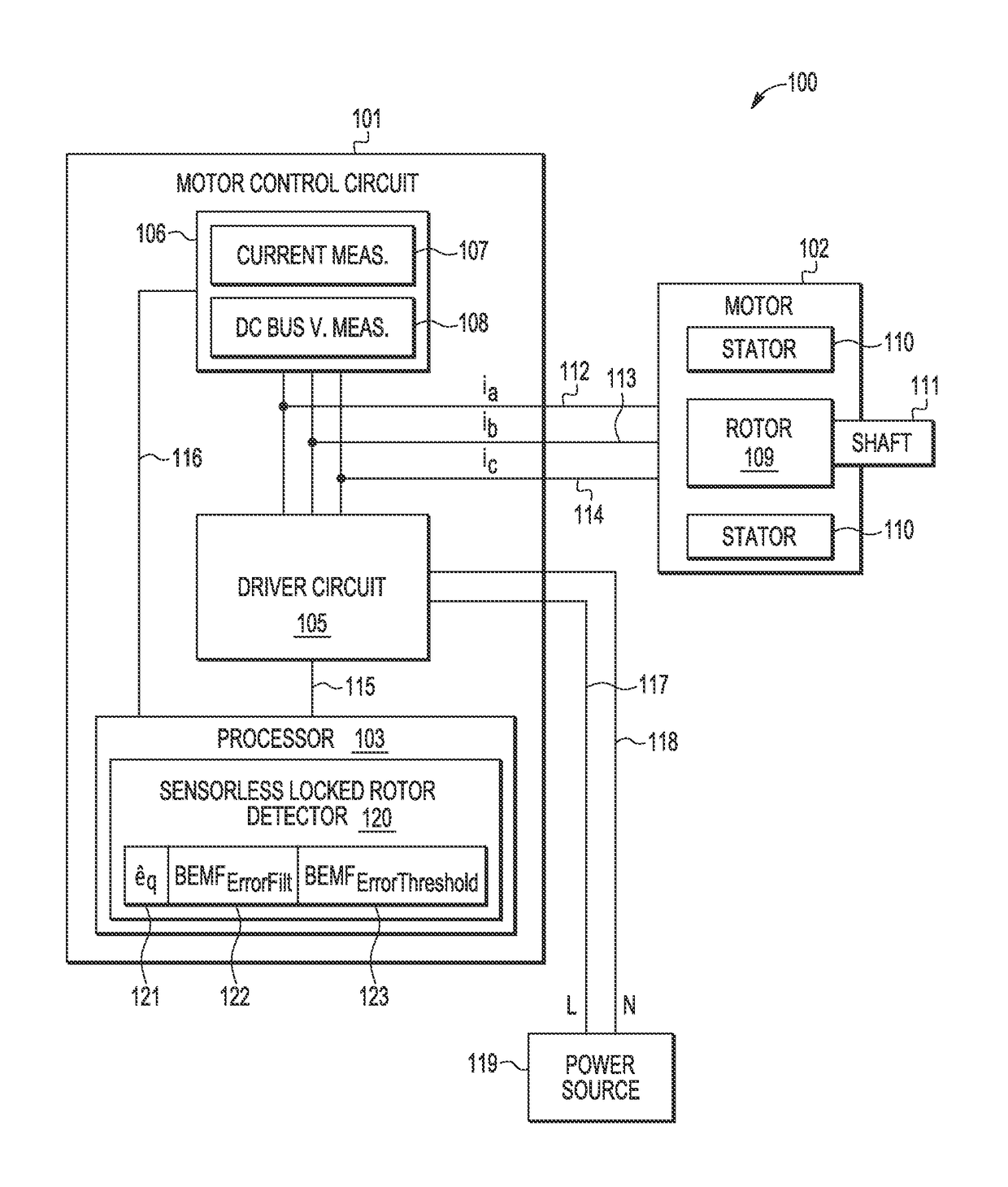
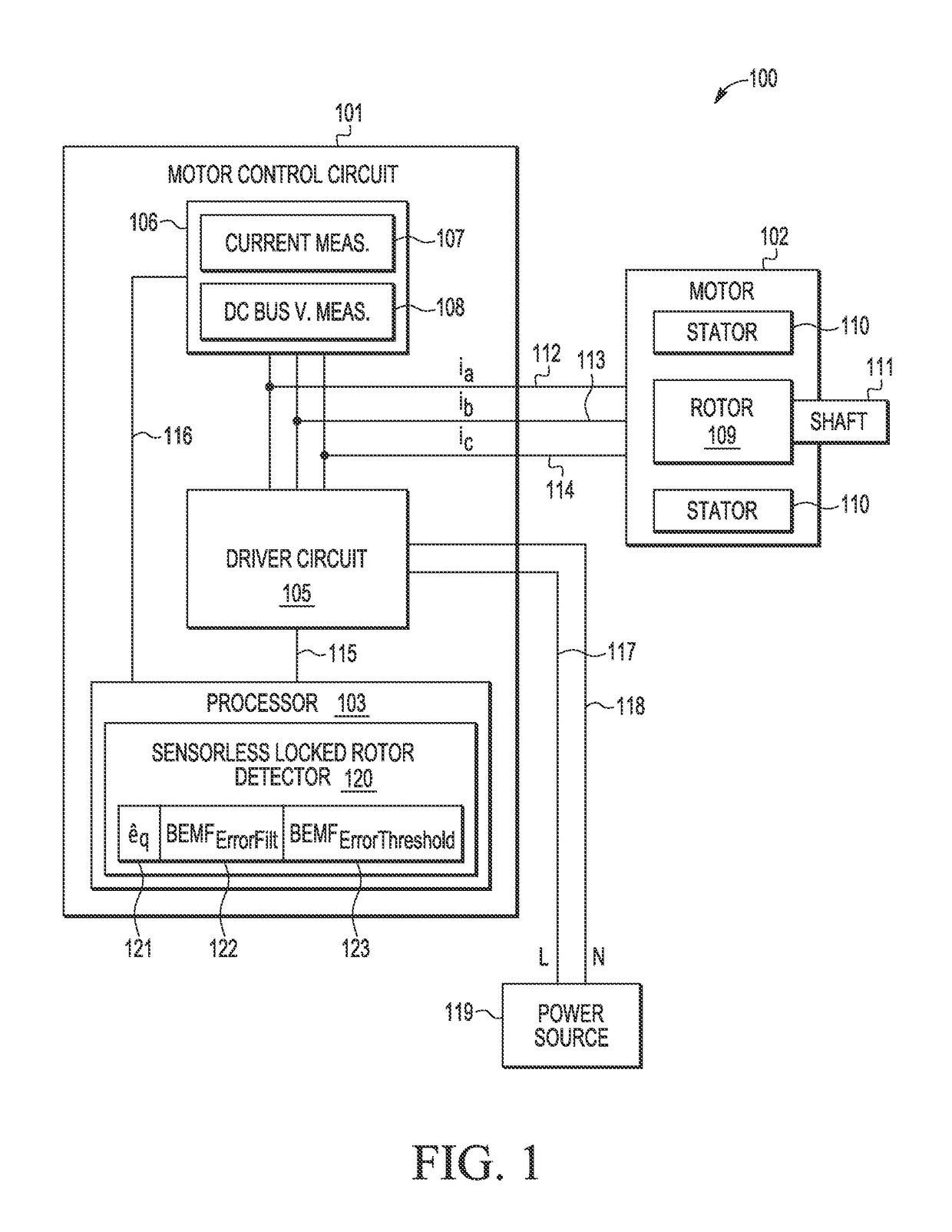
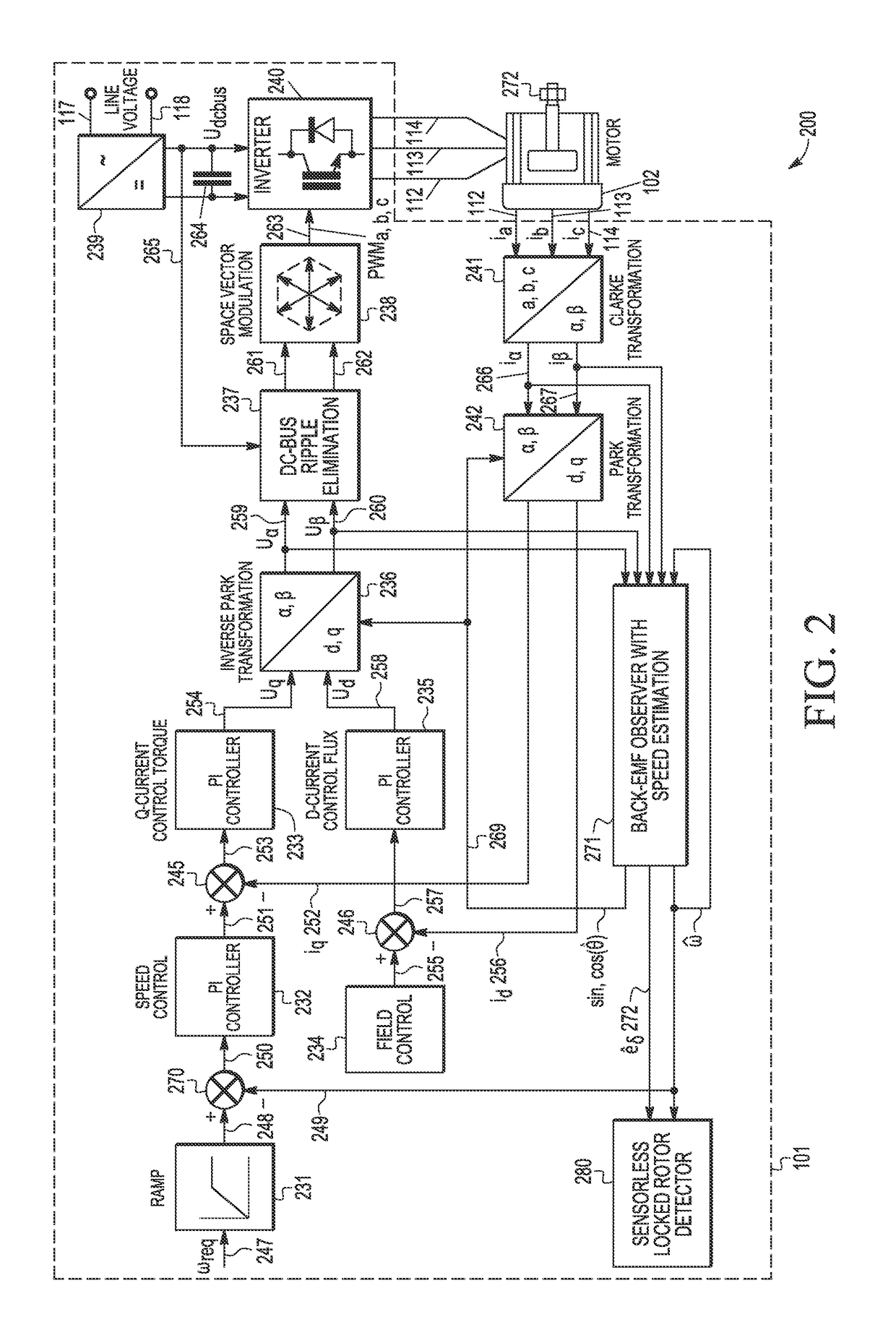
ActiveUS10075107B2Commutation monitoringElectric motor controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorCircumflex
A method and apparatus are provided for detecting a rotor lock condition in a sensorless permanent magnet synchronous motor. A BEMF observer determines an estimated rotor speed {circumflex over (ω)} and a first BEMF voltage value in an estimated rotor-related γ,δ reference frame. In addition, a second estimated BEMF voltage value is calculated in a rotor-related d,q reference frame based on at least a first motor constant and an estimated rotor speed {circumflex over (ω)}. After generating a BEMF error filter value from the first and second estimated BEMF voltage values and calculating a BEMF error threshold value as a function of the estimated rotor speed {circumflex over (ω)} that is subject to a minimum threshold BEMF value, a rotor lock condition is detected based on at least the BEMF error filter value and the BEMF error threshold value.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Motor control device, motor drive system, washing machine, air conditioner and method of changing magnetization amount of permanent magnet motor
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
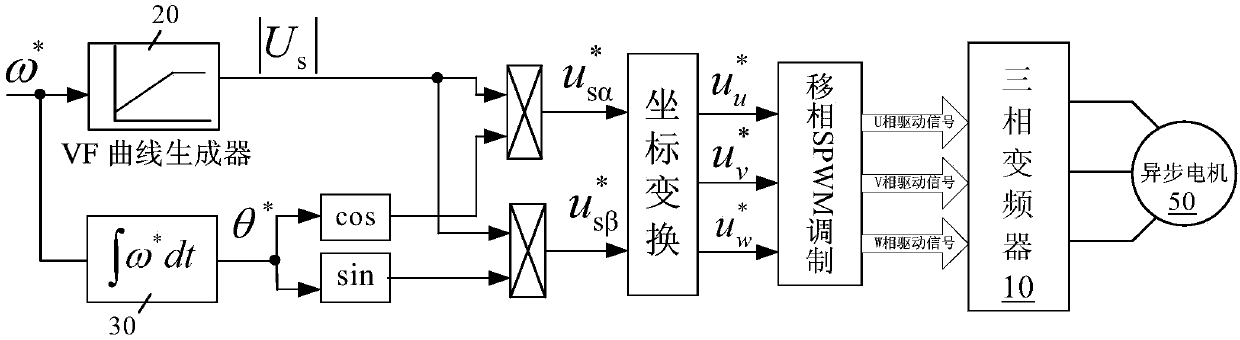
Asynchronous motor constant voltage frequency ratio control method used for three-phase frequency converter
ActiveCN106549622AImprove start-up performance under loadImprove low frequency carrying capacityAC motor controlFrequency ratioEngineering
The invention discloses an asynchronous motor constant voltage frequency ratio control method used for a three-phase frequency converter. The asynchronous motor constant voltage frequency ratio control method comprises a main control step, and additionally a feedback compensation step is added onto the main control step; and the feedback compensation step comprises a stator resistance voltage drop compensation step, a stator voltage amplitude compensation step and a slip frequency compensation step. According to the method, the load starting performance, low-frequency load capacity and speed accuracy of an asynchronous motor are improved, the load starting torque can reach 115% of rated load, and the asynchronous motor can stably operate in a full-load mode at the low frequency of 1 Hz, and the revolving speed error can be controlled within 0.1 Hz, so that the asynchronous motor can stably operate in the frequency band of 0 to 50 Hz, the oscillation of the asynchronous motor is well inhibited, the system stability is effectively improved, and the method is applicable to being widely spread and applied.
Owner:BEIJING LEADER & HARVEST ELECTRIC TECH
Spindle motor and disk drive apparatus
ActiveUS8599517B1Sufficient torqueReduce startup timeRecord information storageRecording on magnetic disksRotor magnetsElectric machine
A spindle motor of a disk drive apparatus includes a base unit, a stator, a covered cylindrical rotor hub, a rotor magnet, and a bearing mechanism. The rotor magnet is an Nd—Fe—B bond magnet. The thickness of the rotor magnet in the radial direction is about 0.7 mm or more and about 1.0 mm or less. The distance between the rotor magnet and the stator core in the radial direction is about 0.15 mm or more and about 0.20 mm or less. A torque constant Kt of torque generated between the stator and the rotor magnet is about 4 mN·m / A or more and about 6 mN·m / A or less. A motor constant Km is about 2 mN·m / (A·√Ω) or more and about 4 mN·m / (A·√Ω) or less.
Owner:NIPPON DENSAN CORP
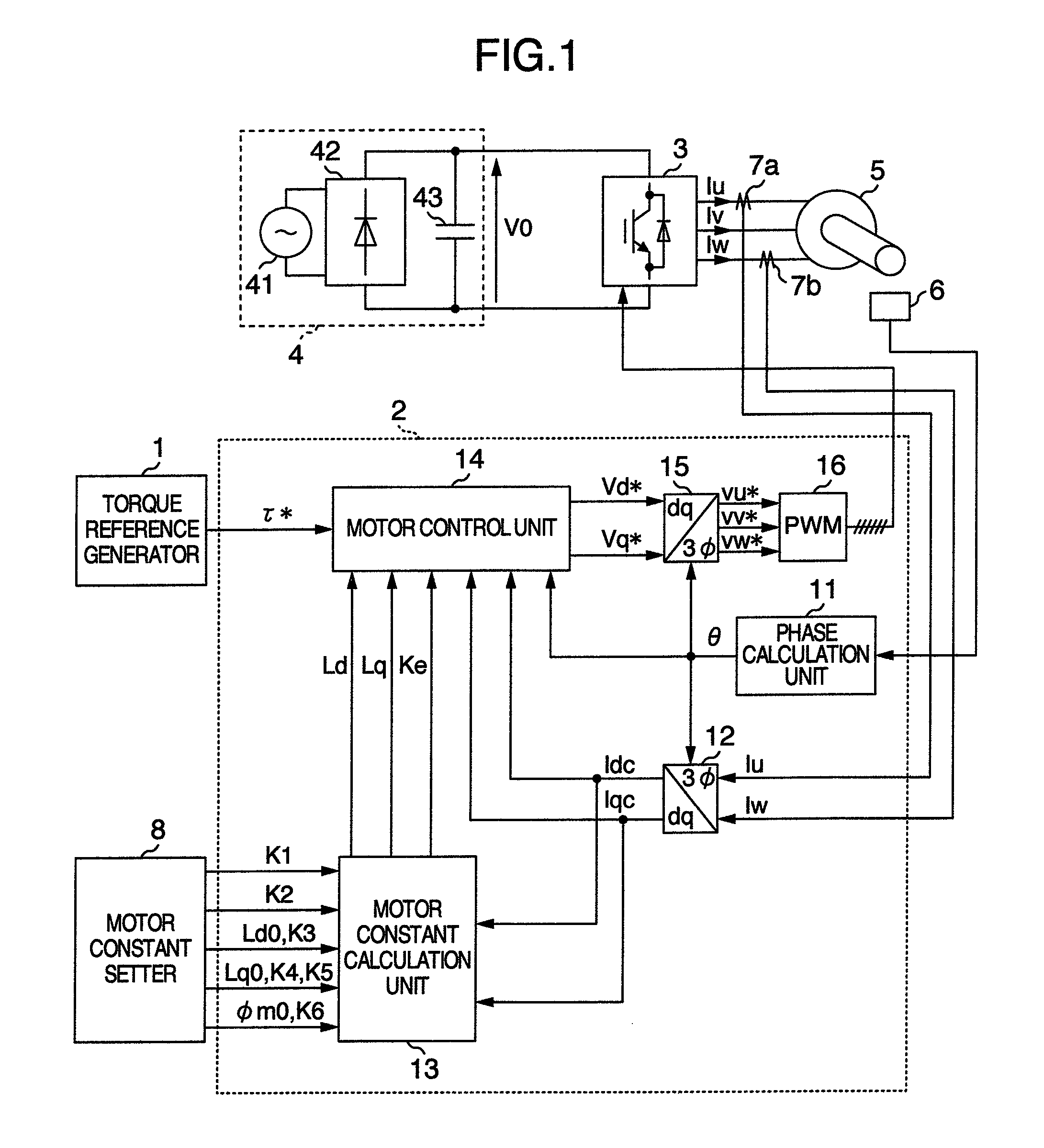
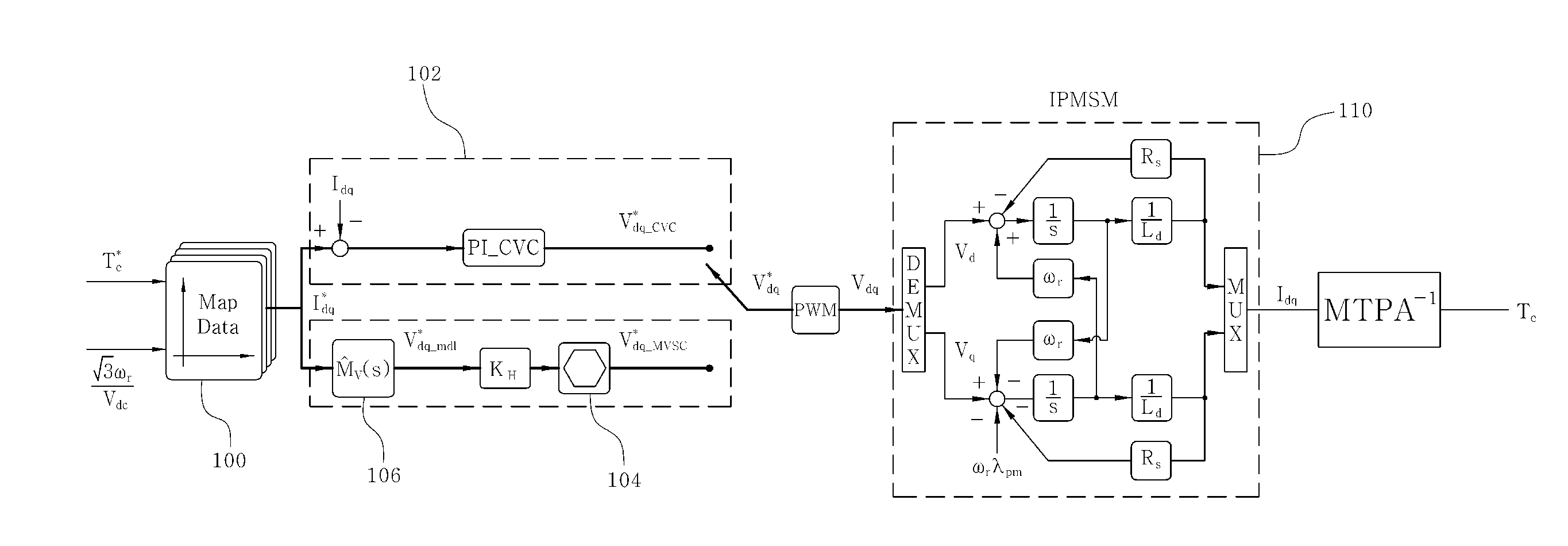
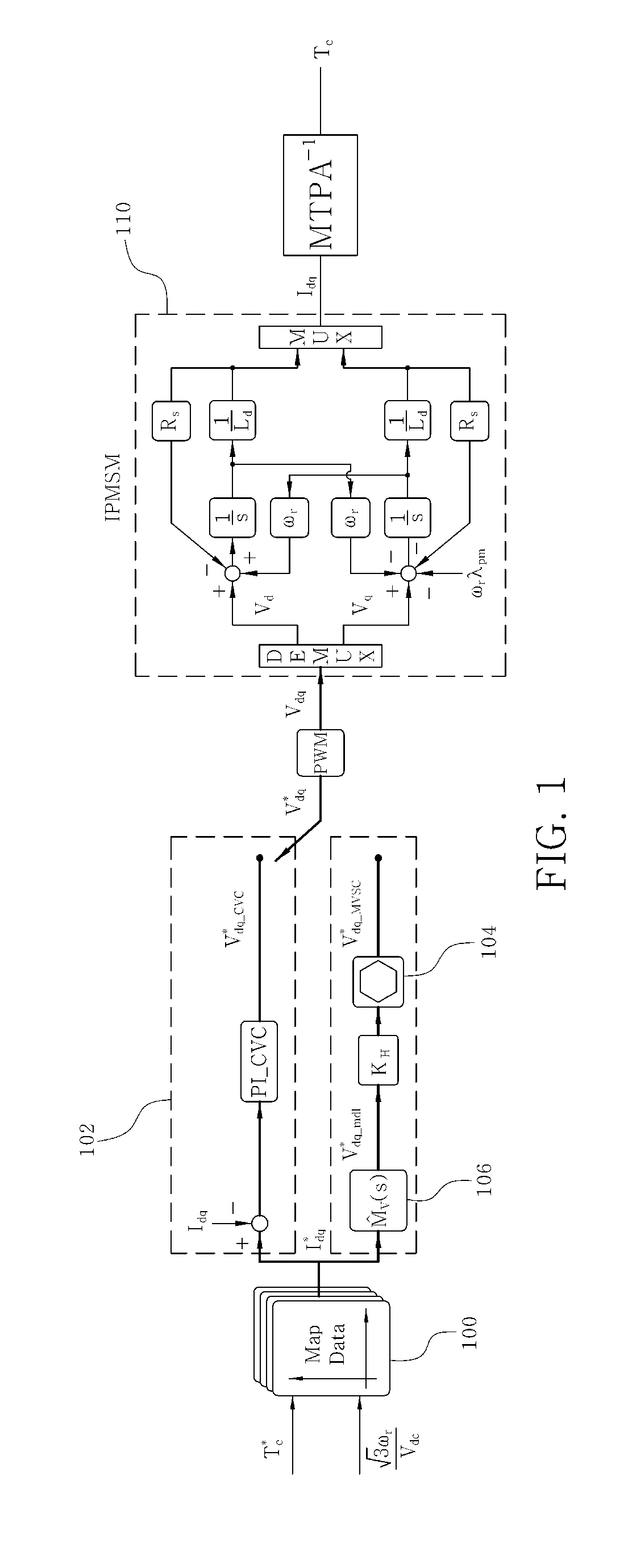
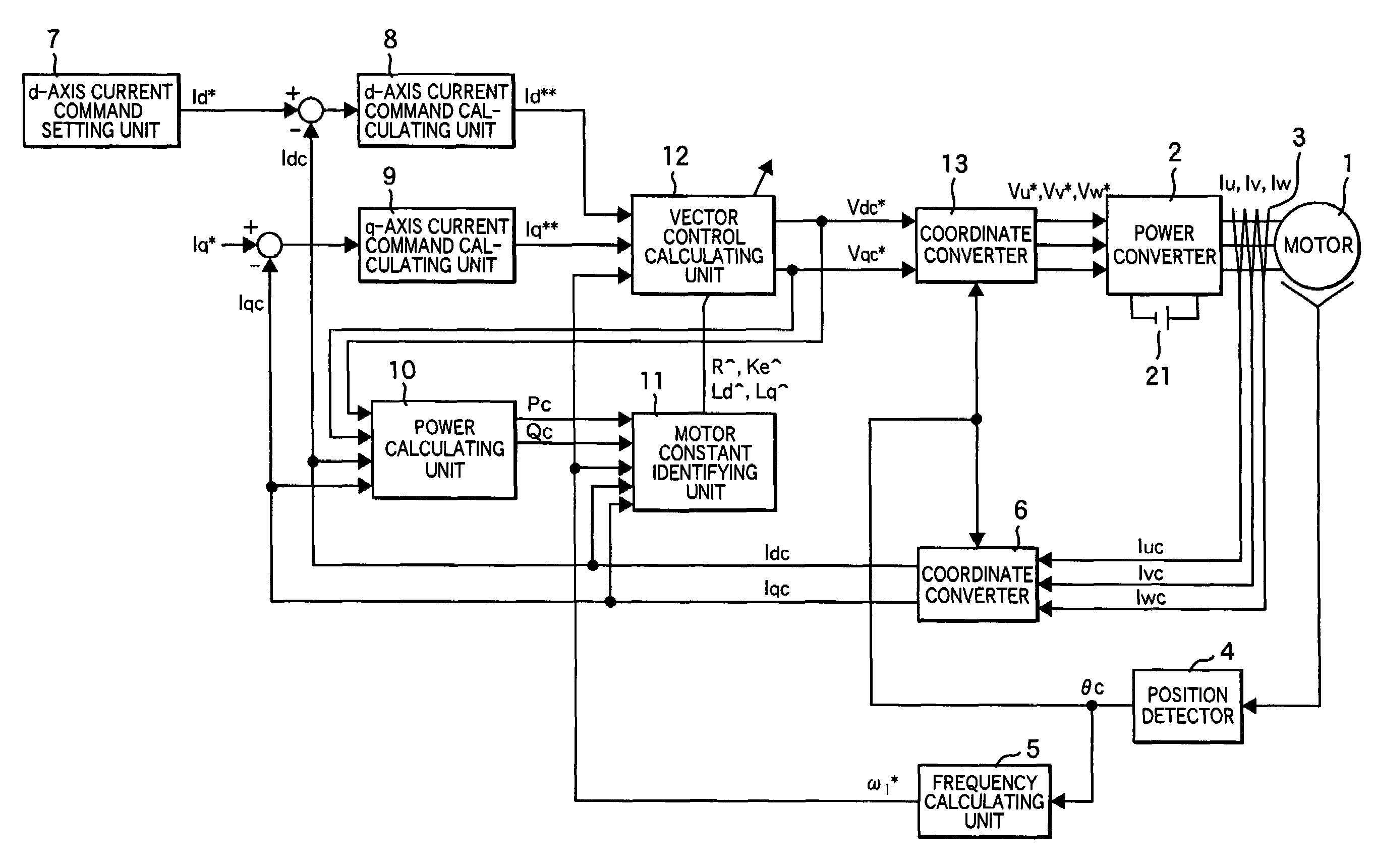
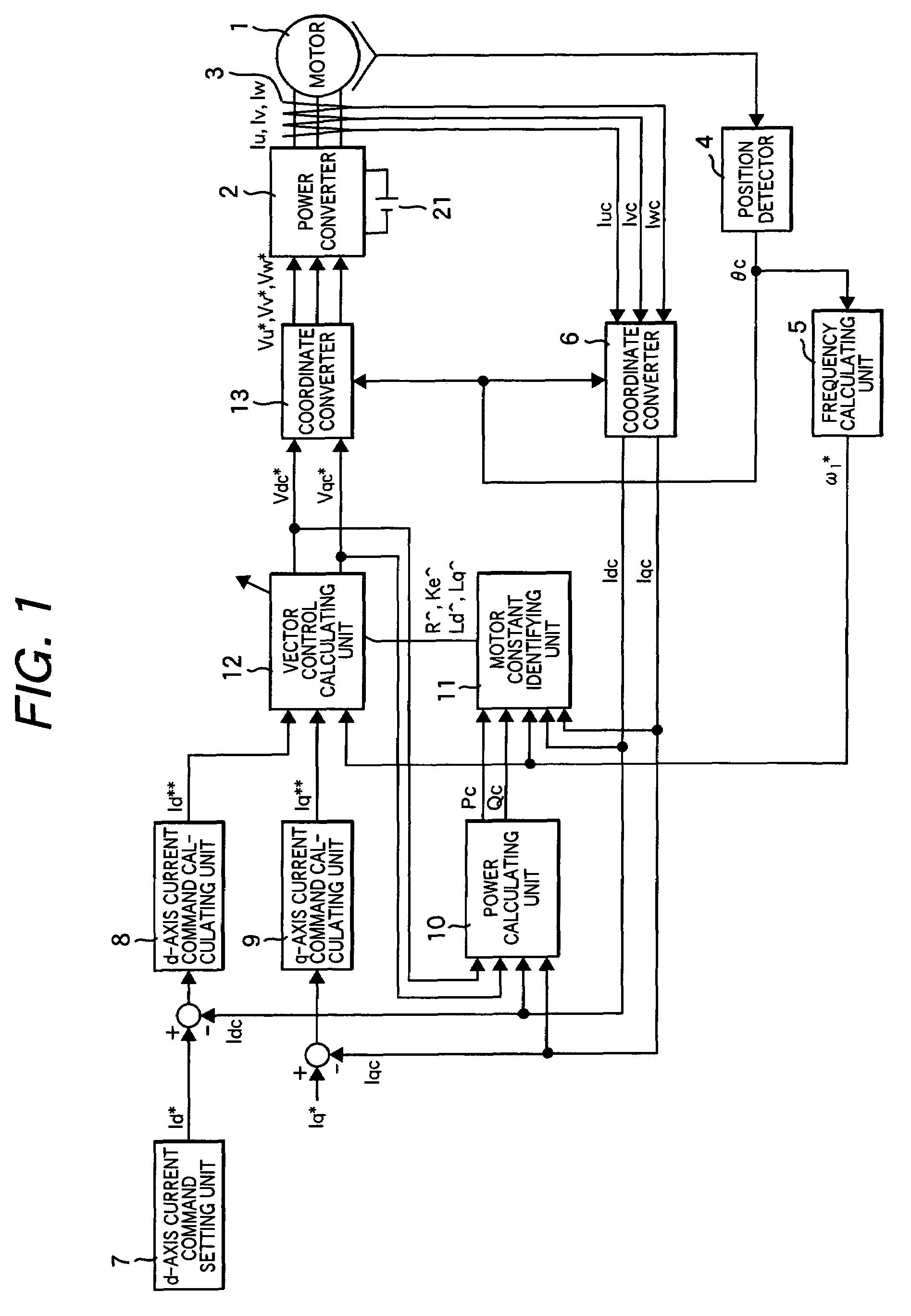
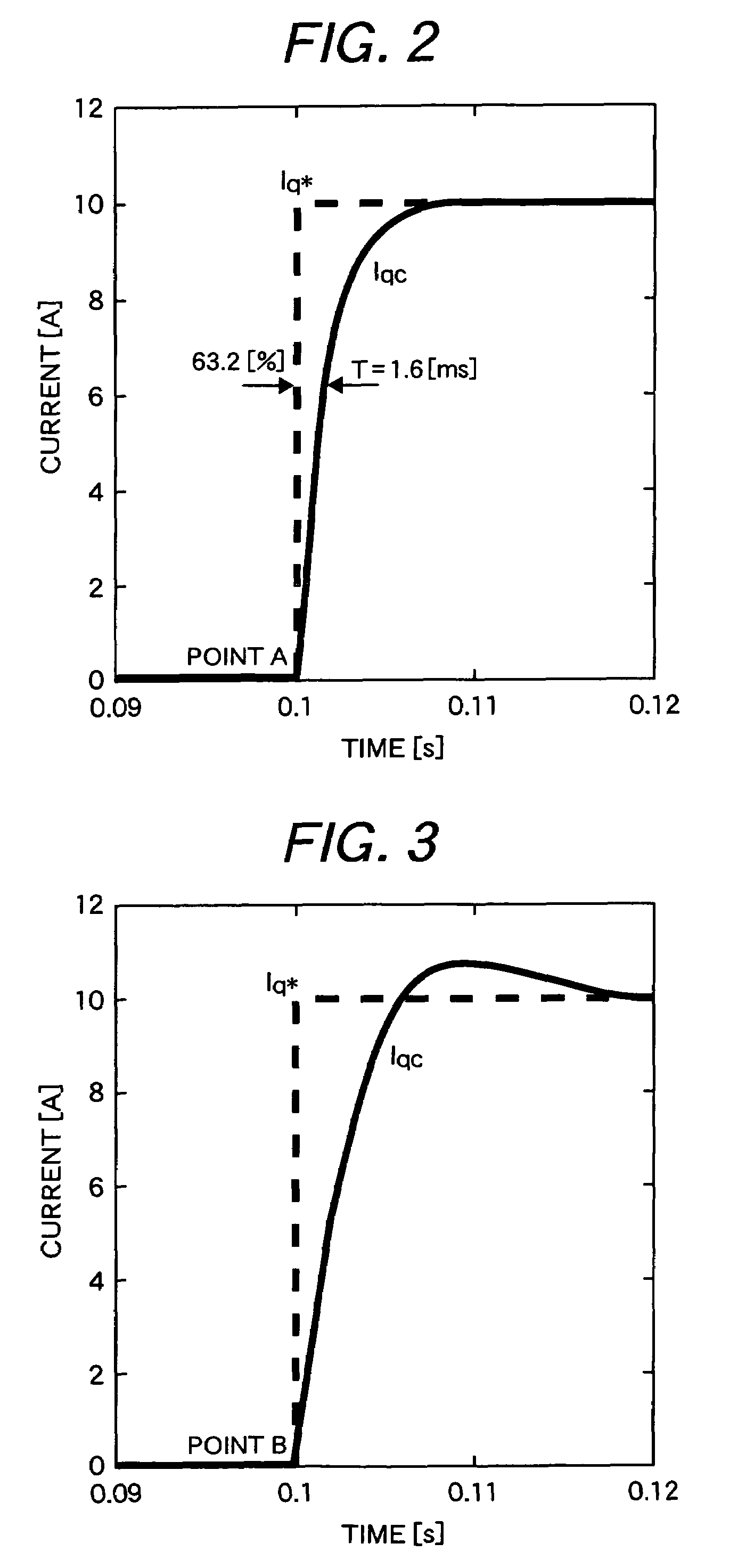
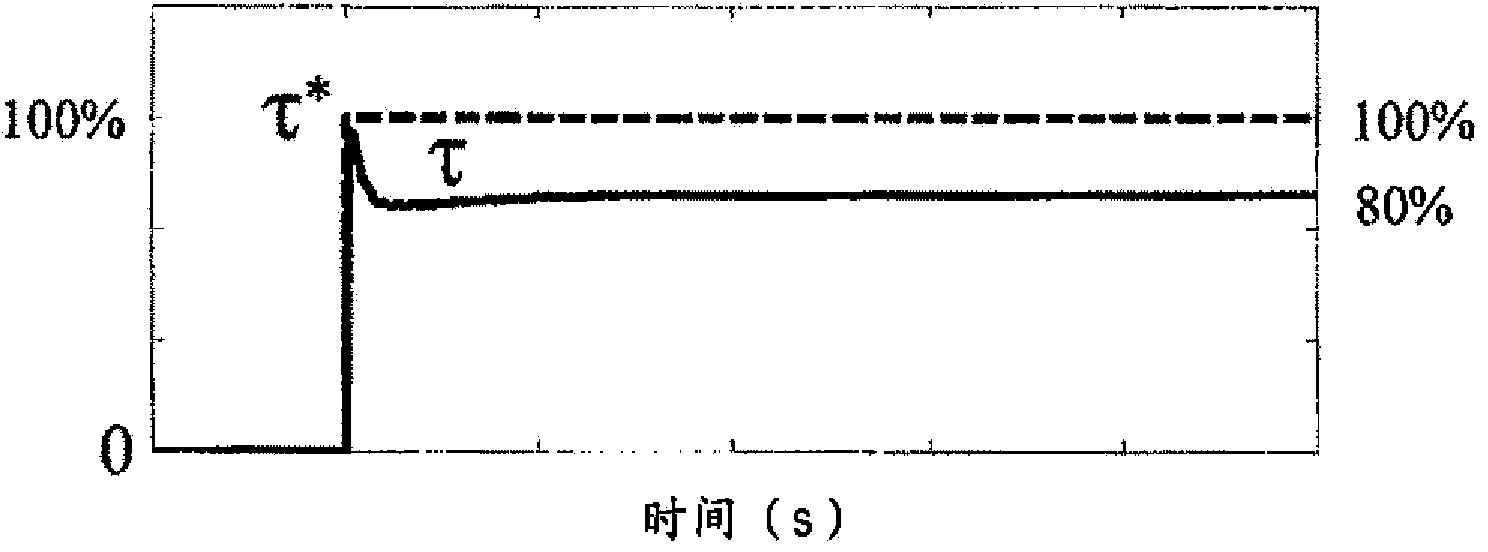
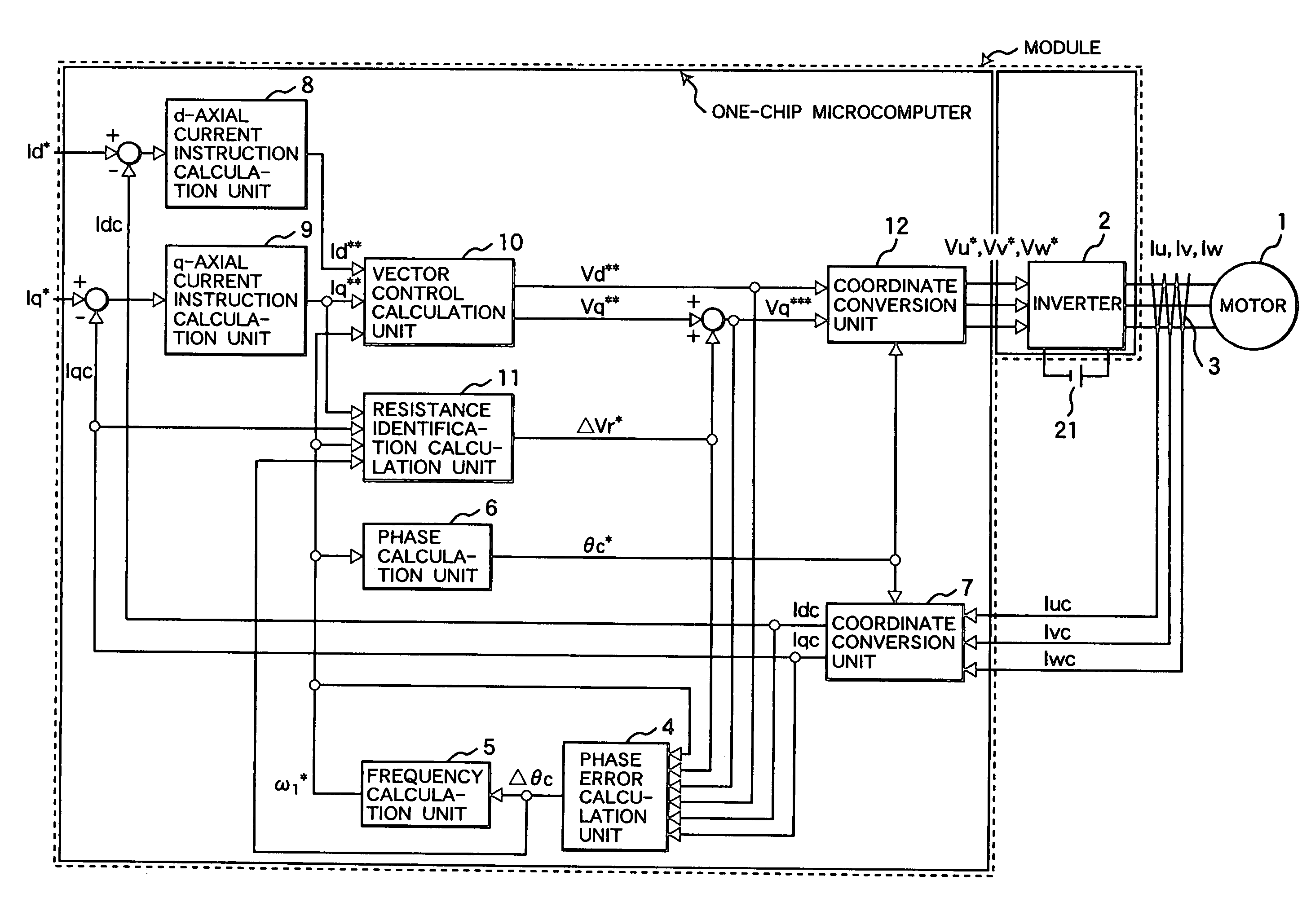
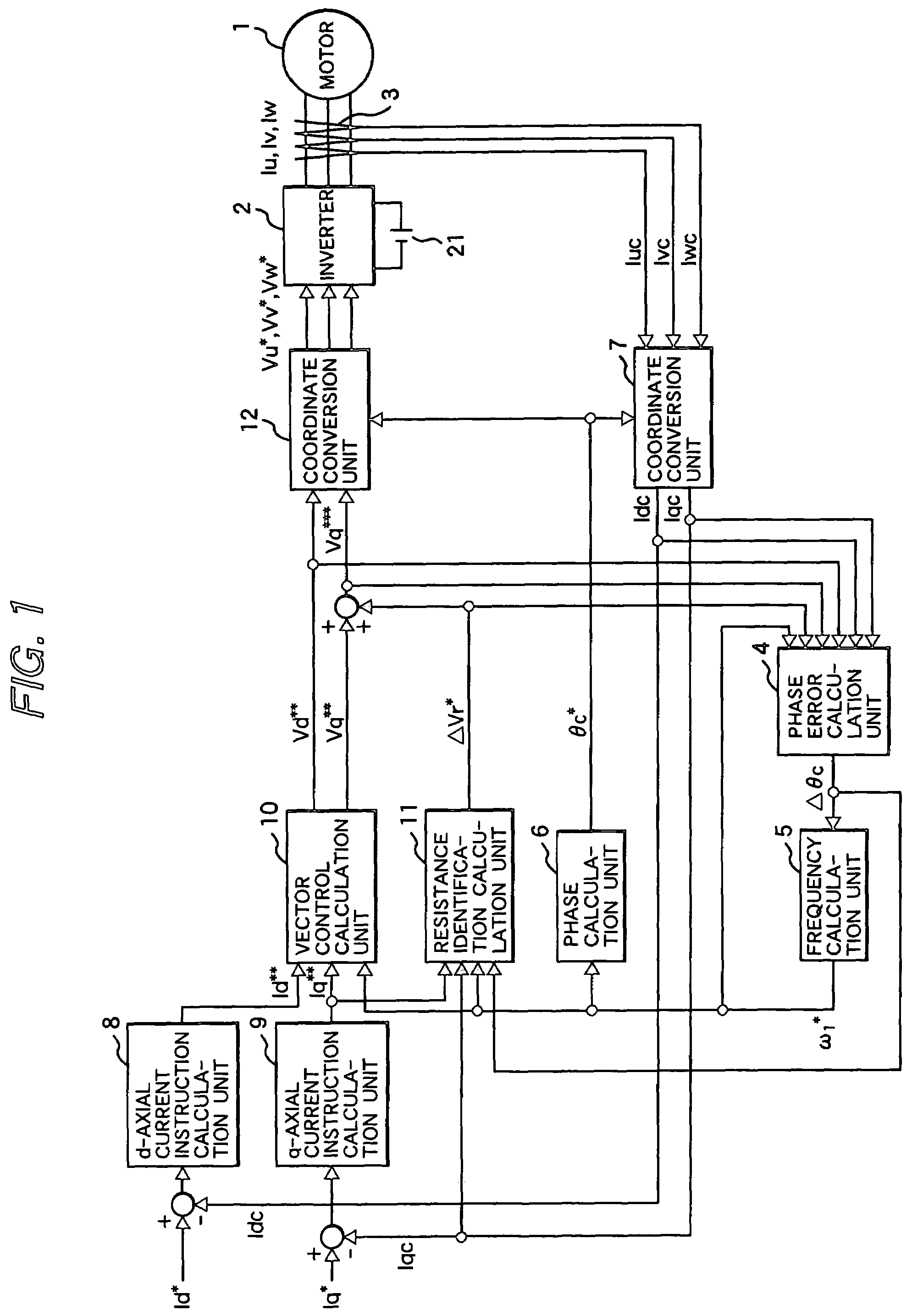
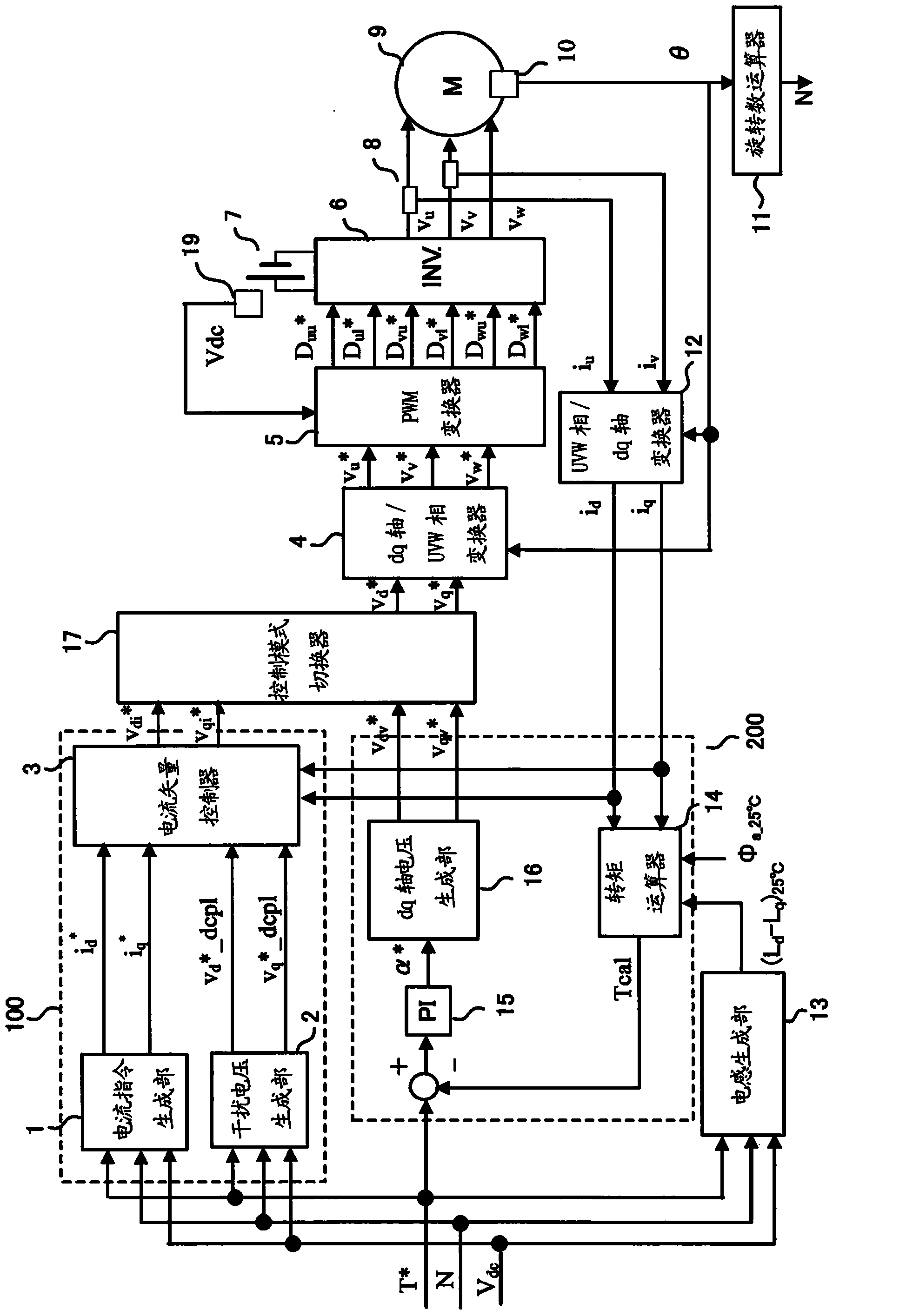
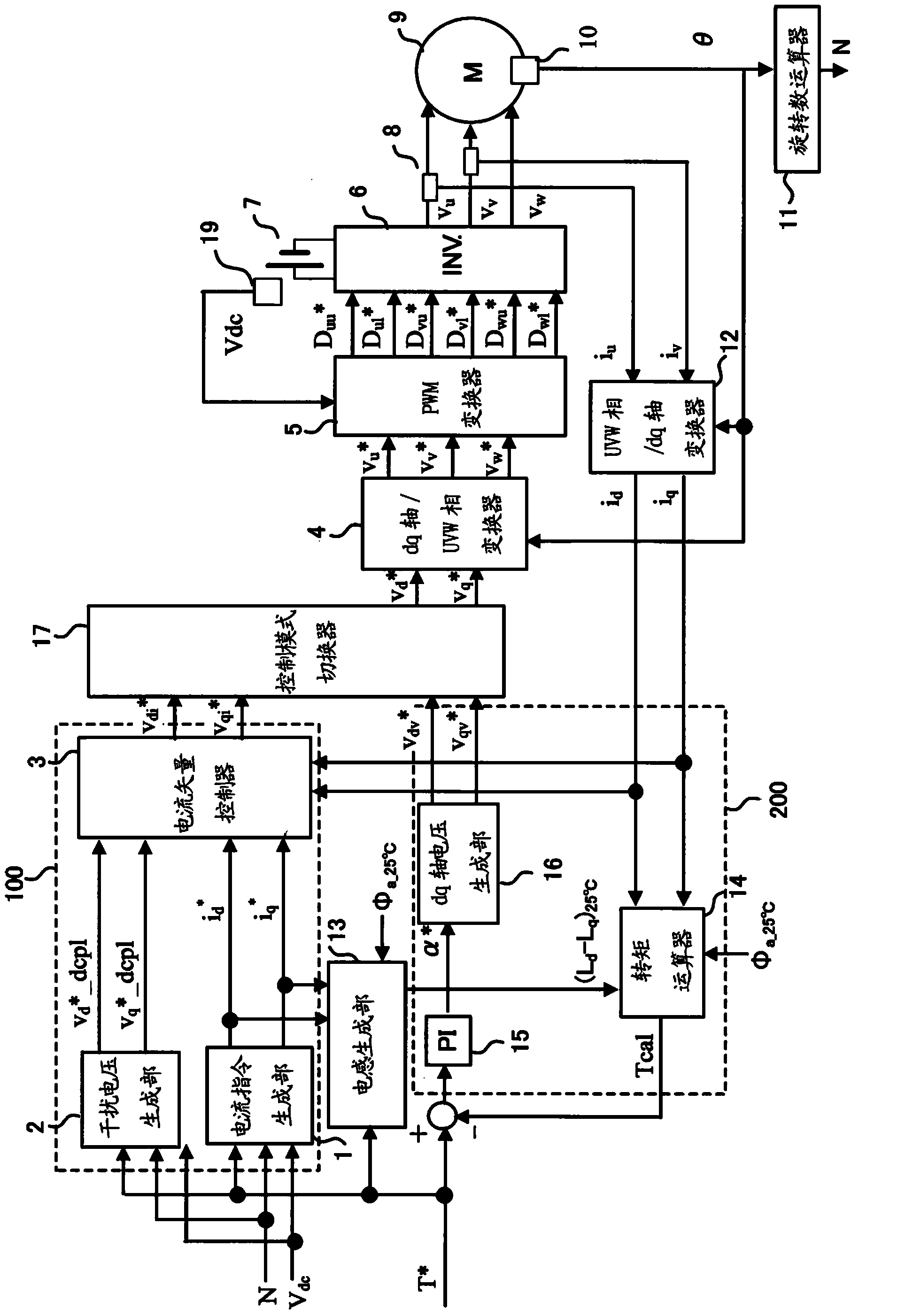
Vector controller for a permanent magnet synchronous motor, inverter module, and permanent magnet synchronous motor constant display system
InactiveUS7521887B2Highly precise and highly responsive torque controlHighly precise and highly torque controlSynchronous motors startersDC motor speed/torque controlPermanent magnet synchronous motorPermanent magnet synchronous generator
A vector controller for a permanent magnet synchronous motor uses current command values and detected currents of the d-axis and q-axis, a calculated frequency, and motor constant settings to control the output voltage of a power converter; the motor constants are identified by use of active or reactive power obtained from the output voltage and detected current of the power converter, the calculated frequency, and the detected current immediately before or during an actual operation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Motor control device and work machine using same
InactiveCN103858332AHigh precision torque controlAC motor controlVector control systemsElectric machineEngineering
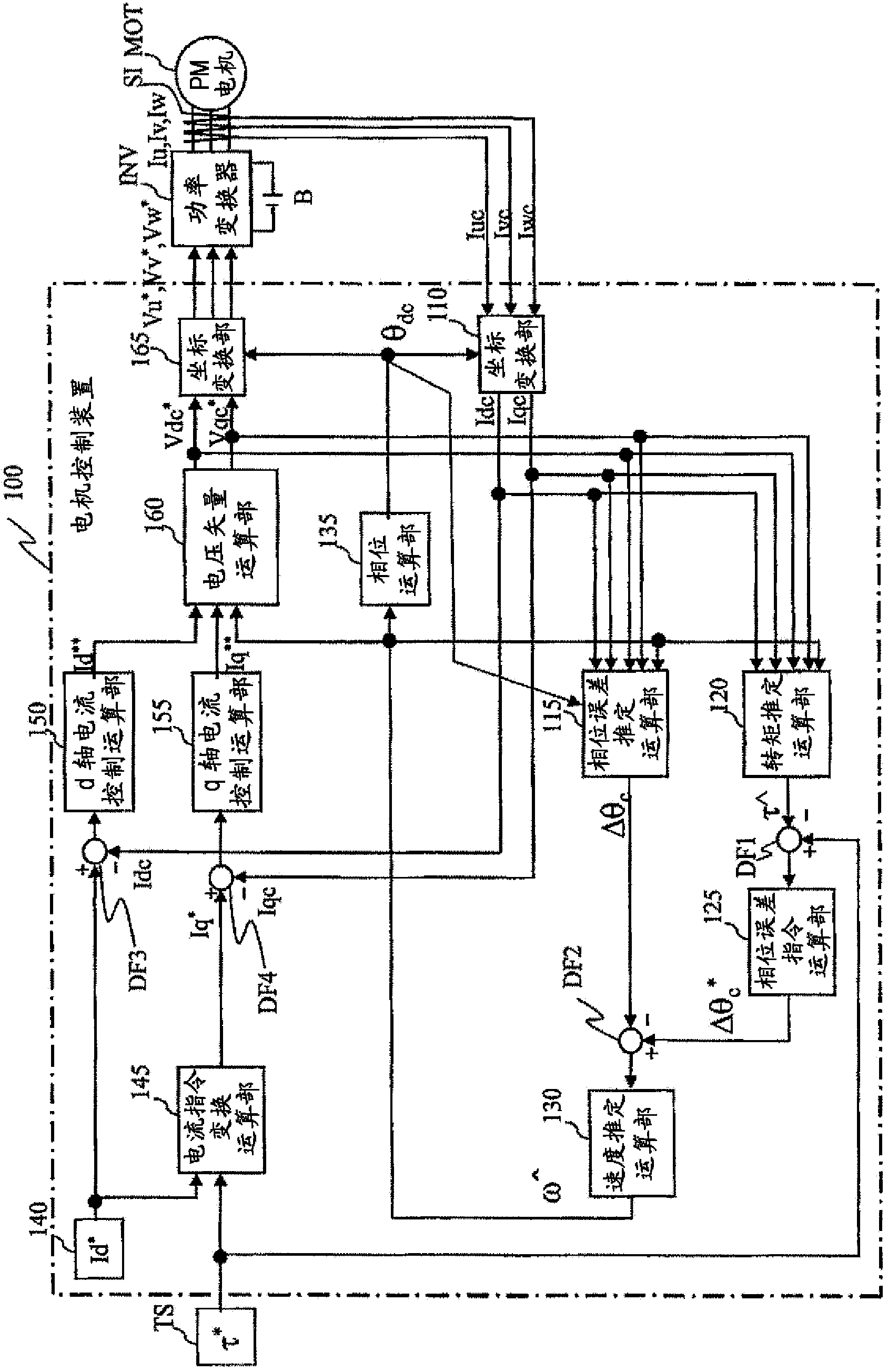
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a motor control device that can compensate even for errors in motor constant settings and that is capable of high-precision torque control. A motor control device (100) comprises a control unit that controls the current supplied to a motor so that a current command value determined on the basis of a torque command value for a motor (MOT) matches a detected current value for current supplied to the motor (MOT) by way of a power converter (INV). The control unit estimates the torque output by the motor and controls the current supplied to the motor so that the estimated value for the torque of the motor matches the torque command value. A torque estimation computation unit (120) estimates the torque output by the motor. A phase error command computation unit (125) calculates a command value for phase error on the basis of the deviation between the estimated torque value and the torque command value. A speed estimation computation unit (130) outputs an estimated speed value so that an estimated phase error value matches the command value for phase error.
Owner:NIHON KENKI CO LTD
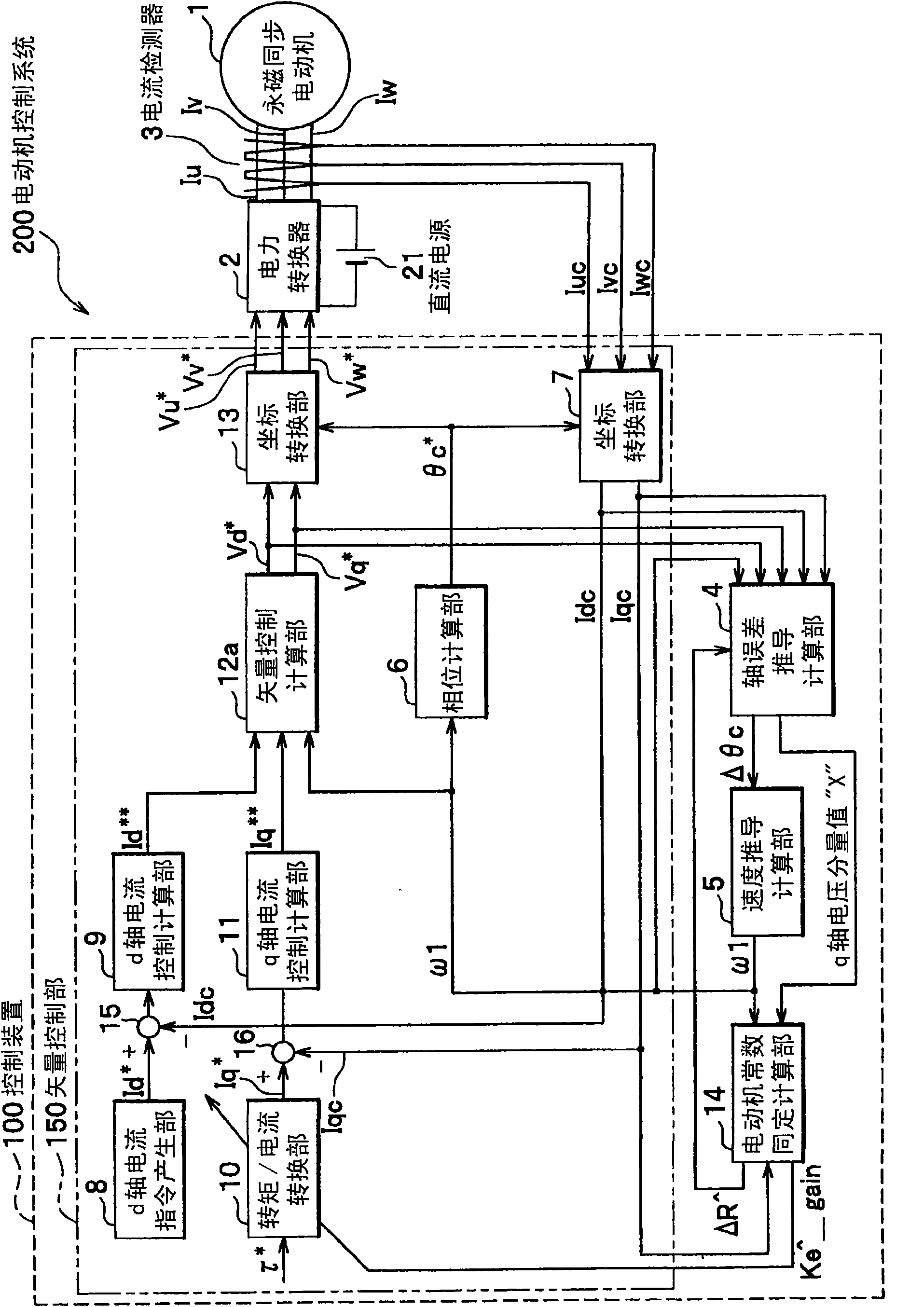
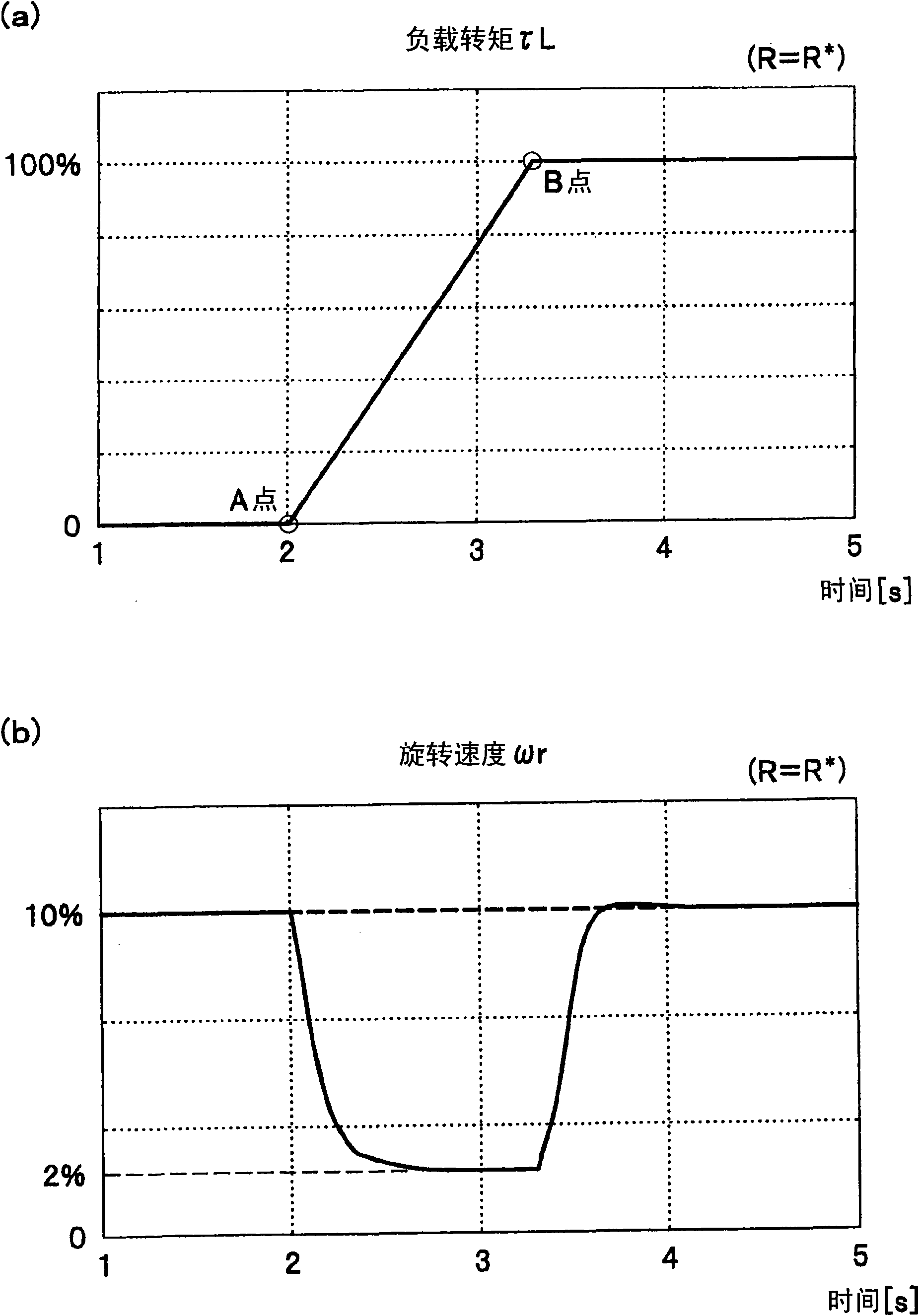
Control system for permanent magnet synchronous motor and module
ActiveUS7388341B2Synchronous motors startersVector control systemsControl vectorPermanent magnet synchronous motor
A vector control system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor, using a current control equivalent output value, a frequency instruction value, a current detection value, an inference phase error value, and a motor constant, identifies a motor resistance equivalent or a resistance setting error equivalent. Next, the vector control unit, using the identified value, corrects a set value R* equivalent of a voltage instruction calculation unit and a n inference phase error calculation unit.Thereby, a vector control system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor can realize a robust control characteristic for changing of a resistance constant of a motor in a low rotation speed area under position sensor-less control. Further, a vector control system for a permanent magnet synchronous motor can be applied in common in a system performing inexpensive current detection.
Owner:HITACHI POWER SEMICON DEVICE
Motor controlling device, motor drive system, method of motor control, semiconductor device and electronic device
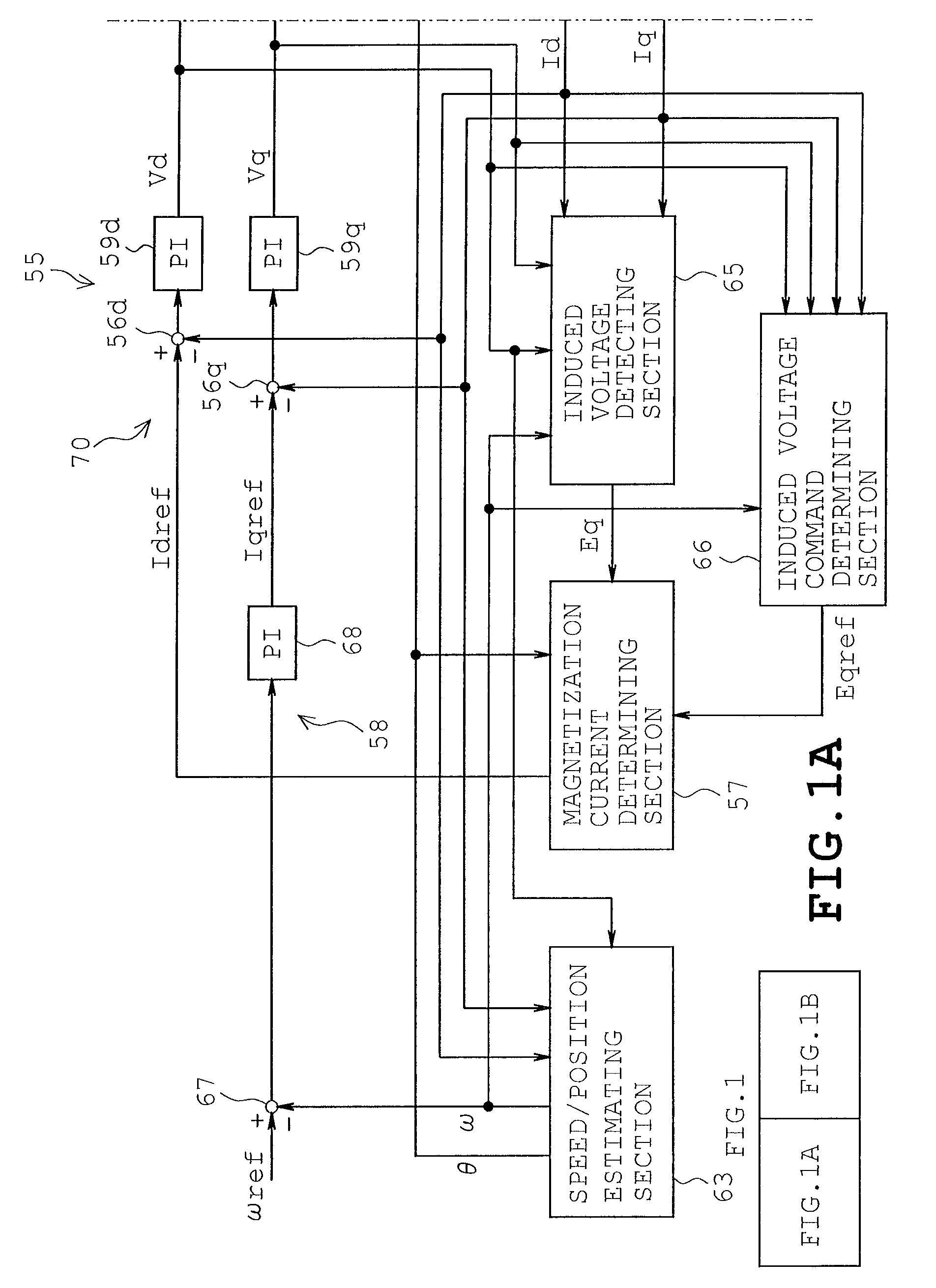
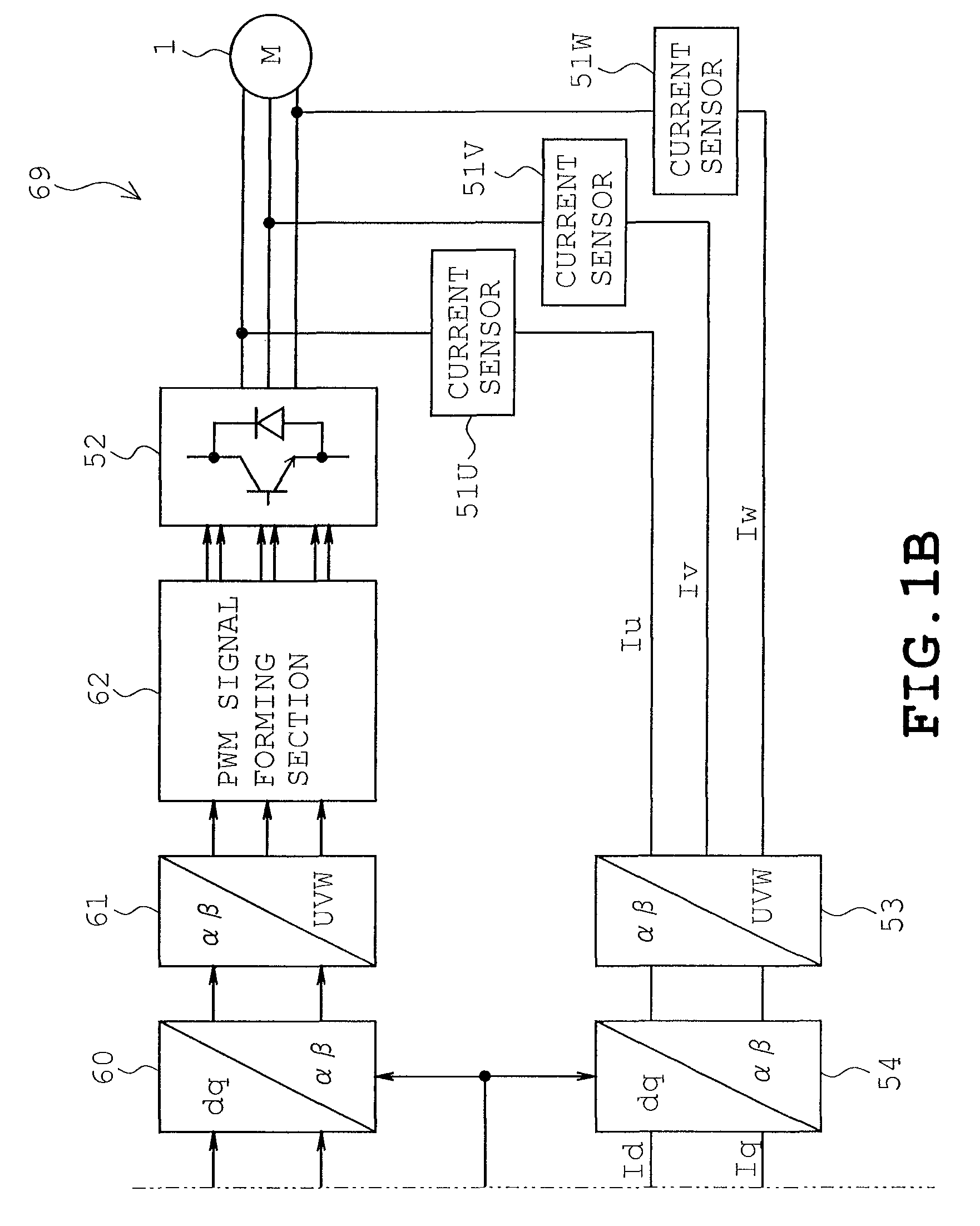
InactiveUS7977899B2Low costFast processingMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersPhase currentsComputation process
A motor control device is disclosed which is arranged so as to perform a PWM control for a permanent magnet motor including a rotor having a permanent magnet and a stator with a multiphase winding. The motor control device includes a position detection unit which executes an analog computation process for induced voltages of respective phases of the motor based on a phase voltage equation having, as operation terms, respective phase voltages, respective phase currents, winding inductance, winding resistance and a neutral point voltage, the winding inductance and the winding resistance being motor constants of the motor, thereby generating and delivering a rotational position signal of the rotor based on a phase relation of the induced voltages, and a digital processing unit which has a function of generating and delivering a sinusoidal PWM signal based on the rotational position signal, thereby controlling the motor.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Method and Device for Operating a Braking Device, Braking Device
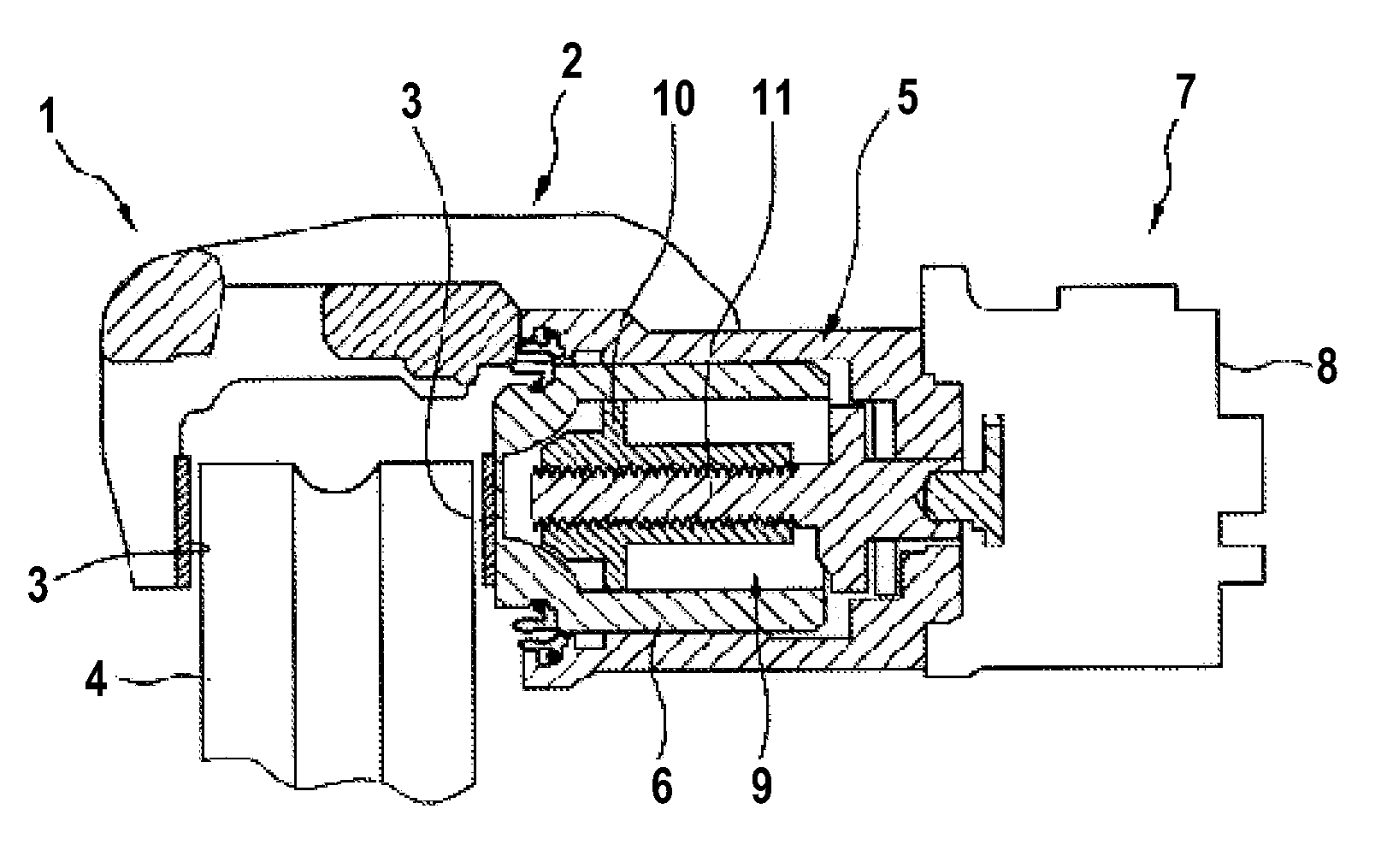
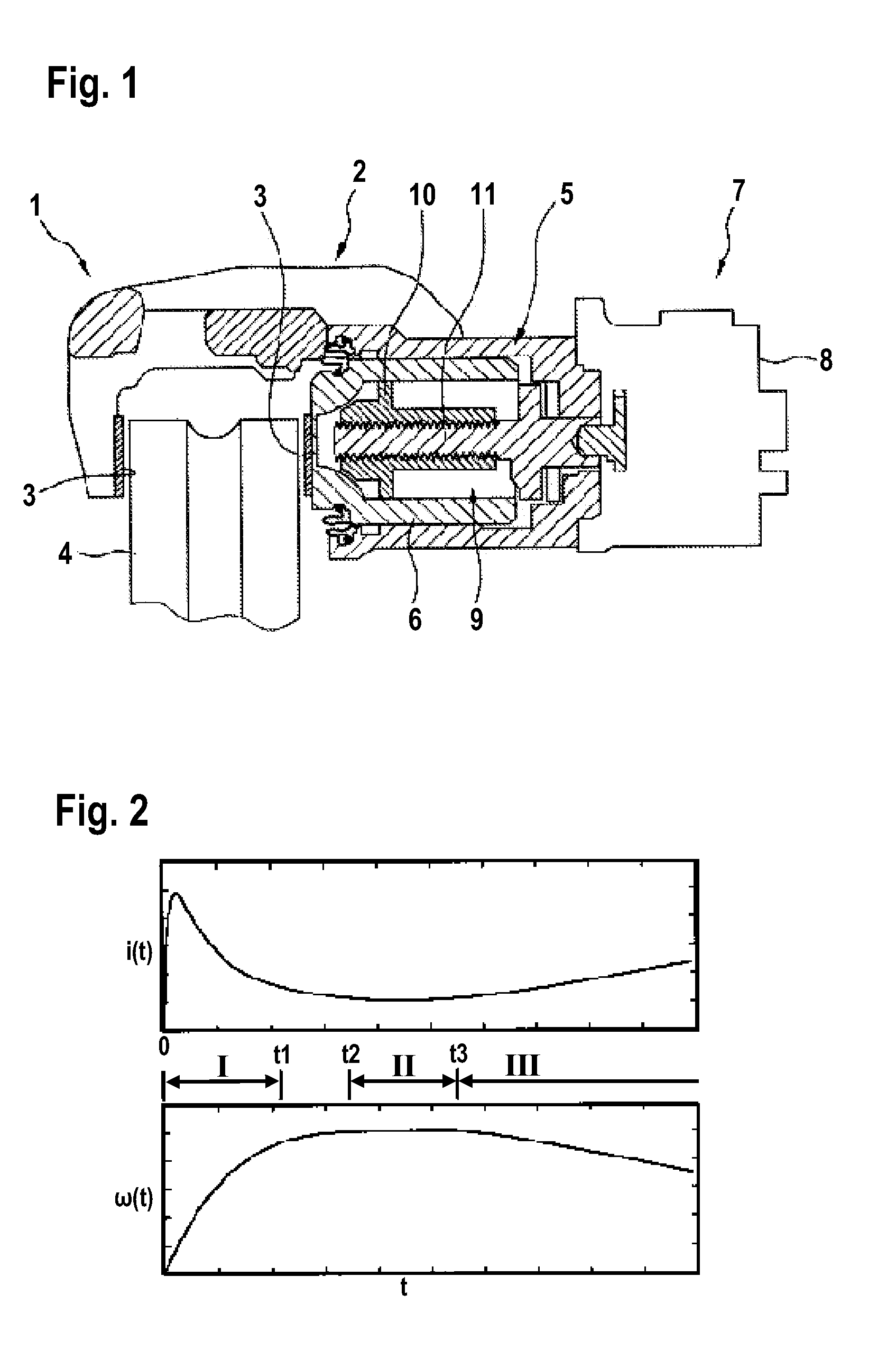
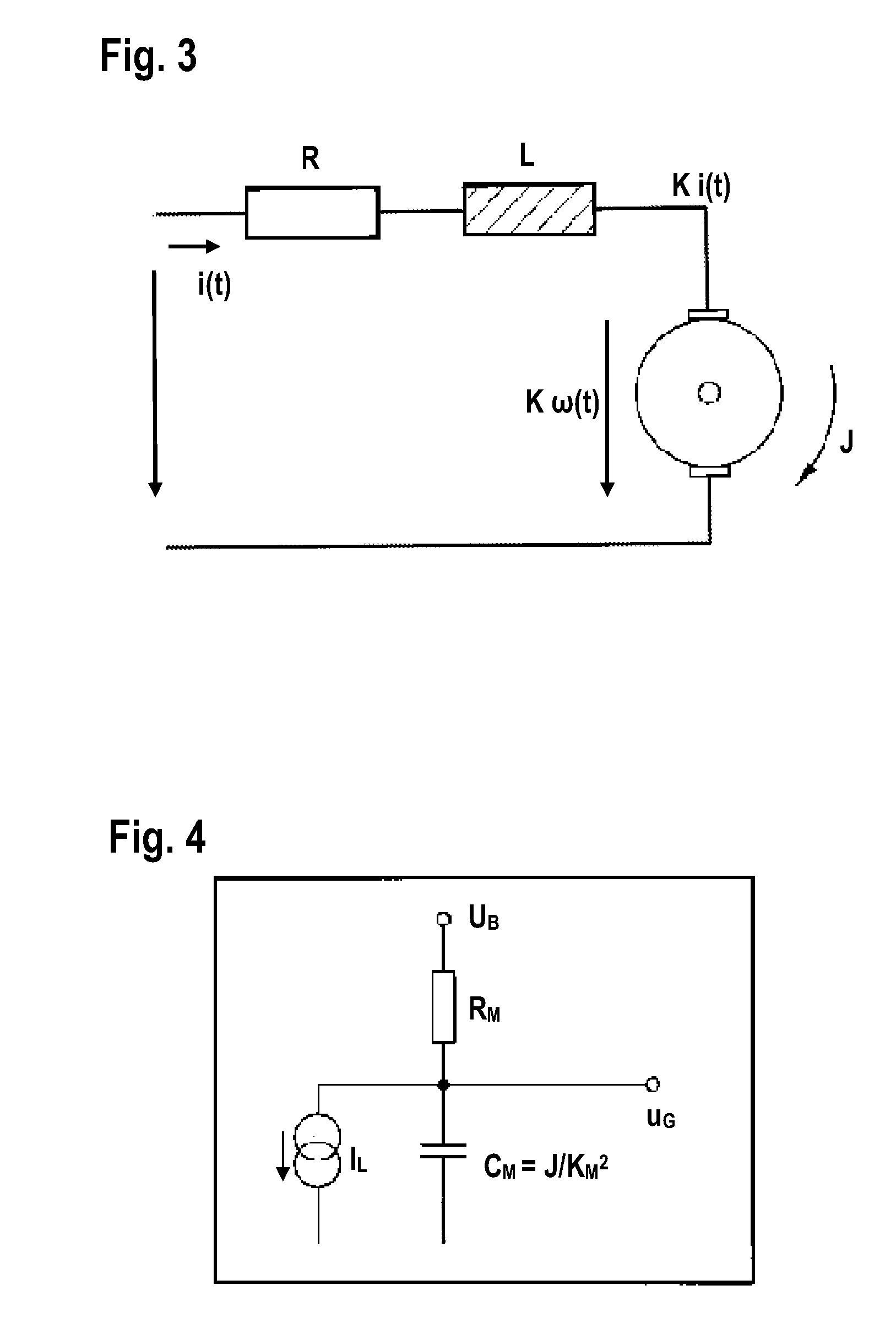
ActiveUS20160103430A1Simple calculationRapid and resource-savingMotor/generator/converter stoppersDC motor speed/torque controlPower flowMotor constants
The disclosure relates to a method for operating a braking device, in particular a parking brake device, which comprises an actuator having an electric motor that displaces an actuator element as desired into a brake application position or into a brake release position, wherein the electric motor is controlled in dependence upon a motor constant and an electrical resistance of the electric motor, characterized in that as the actuator element is displaced a prevailing motor input voltage and a prevailing motor current are ascertained, and that the motor constant and the electrical resistance are determined in dependence upon the ascertained motor input voltage and the ascertained motor current.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
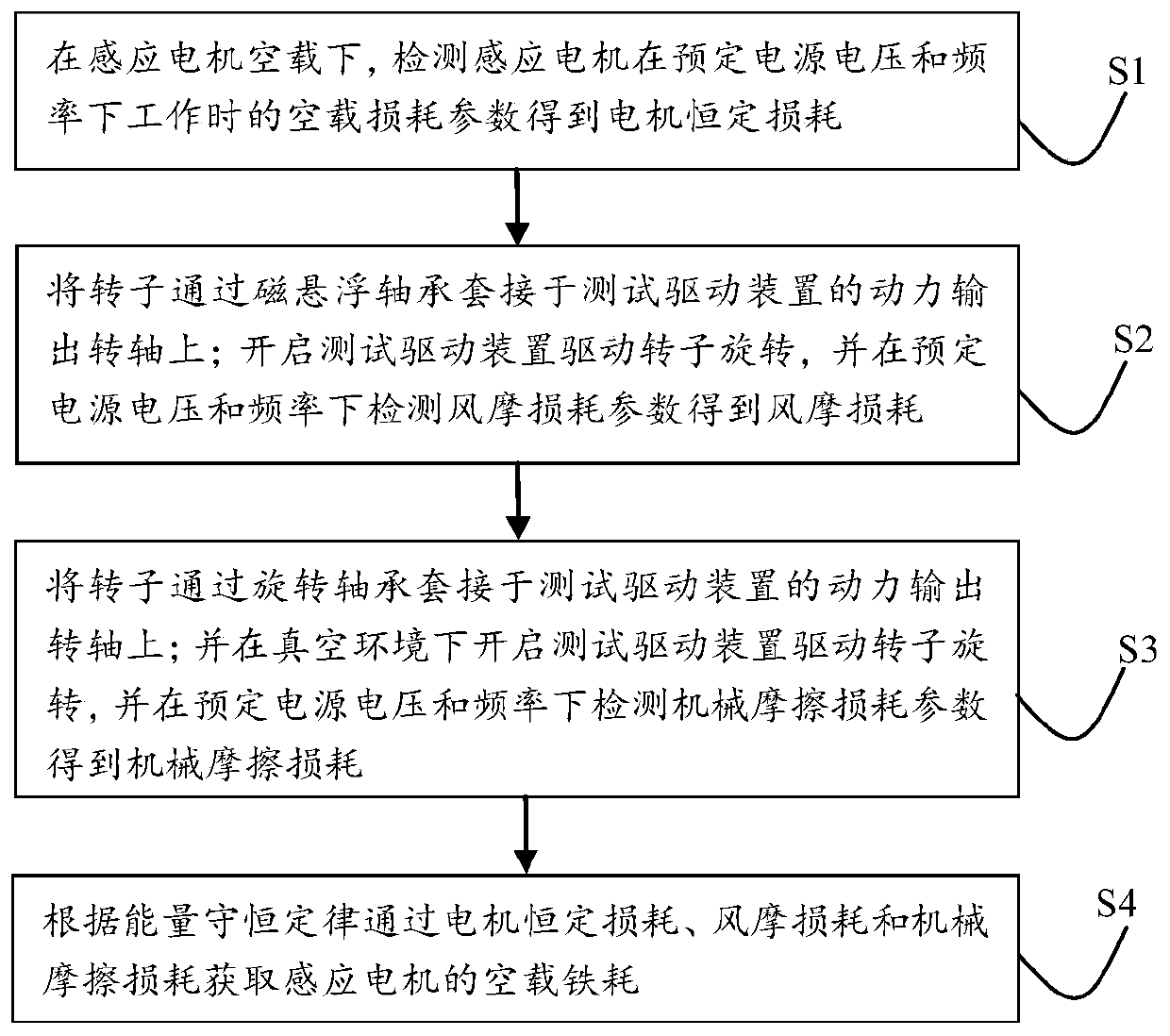
No-load iron loss test method for induction motor
ActiveCN109901068AEffectively measure the lossGet no-load iron consumptionResistance/reactance/impedenceDynamo-electric machine testingElectric machineFriction loss
The invention relates to a no-load iron loss test method for an induction motor. The method includes the following steps that: under the no-load condition of the induction motor, the no-load loss parameters of the induction motor working under a predetermined input voltage and frequency are obtained, so that motor constant loss is obtained; a rotor sleeves the power output shaft of a test drivingdevice through a magnetic suspension bearing; the test driving device is started so as to drive the rotor to rotate, and the wind friction loss parameters are detected under the predetermined input voltage and frequency, so that wind friction loss can be obtained; the rotor sleeves the power output shaft of the test driving device through a rotary bearing; the test driving device is started undera vacuum environment so as to drive the rotor to rotate, and mechanical friction loss parameters are detected under the predetermined input voltage and frequency, so that mechanical friction loss is obtained; and the no-load iron loss of the induction motor is obtained on the basis of the motor constant loss, the wind friction loss and the mechanical friction loss. With the no-load iron loss testmethod for the induction motor adopted, the wind friction loss and mechanical friction loss inside the motor can be effectively measured, and the no-load iron loss of the induction motor can be accurately obtained.
Owner:BEIDOU AEROSPACE AUTOMOBILE BEIJING CO LTD
Driving apparatus for electric motor
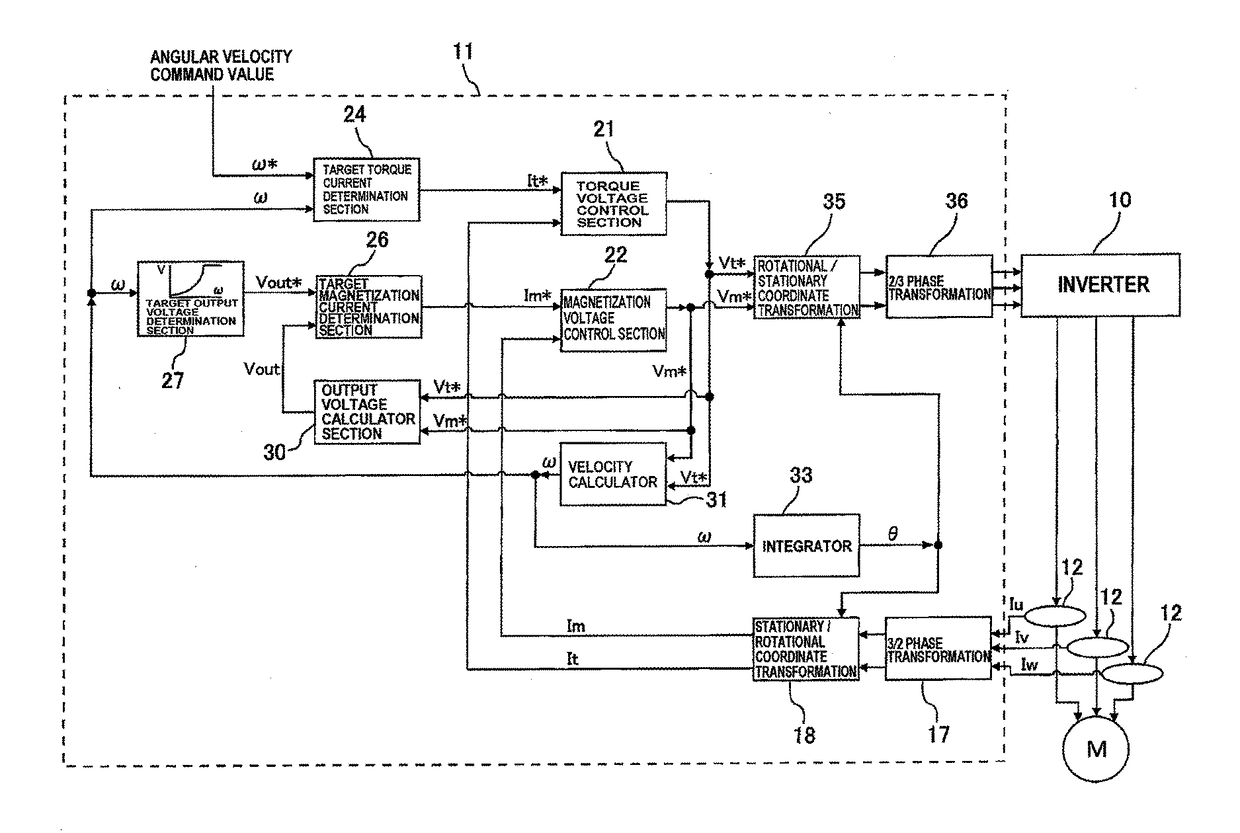
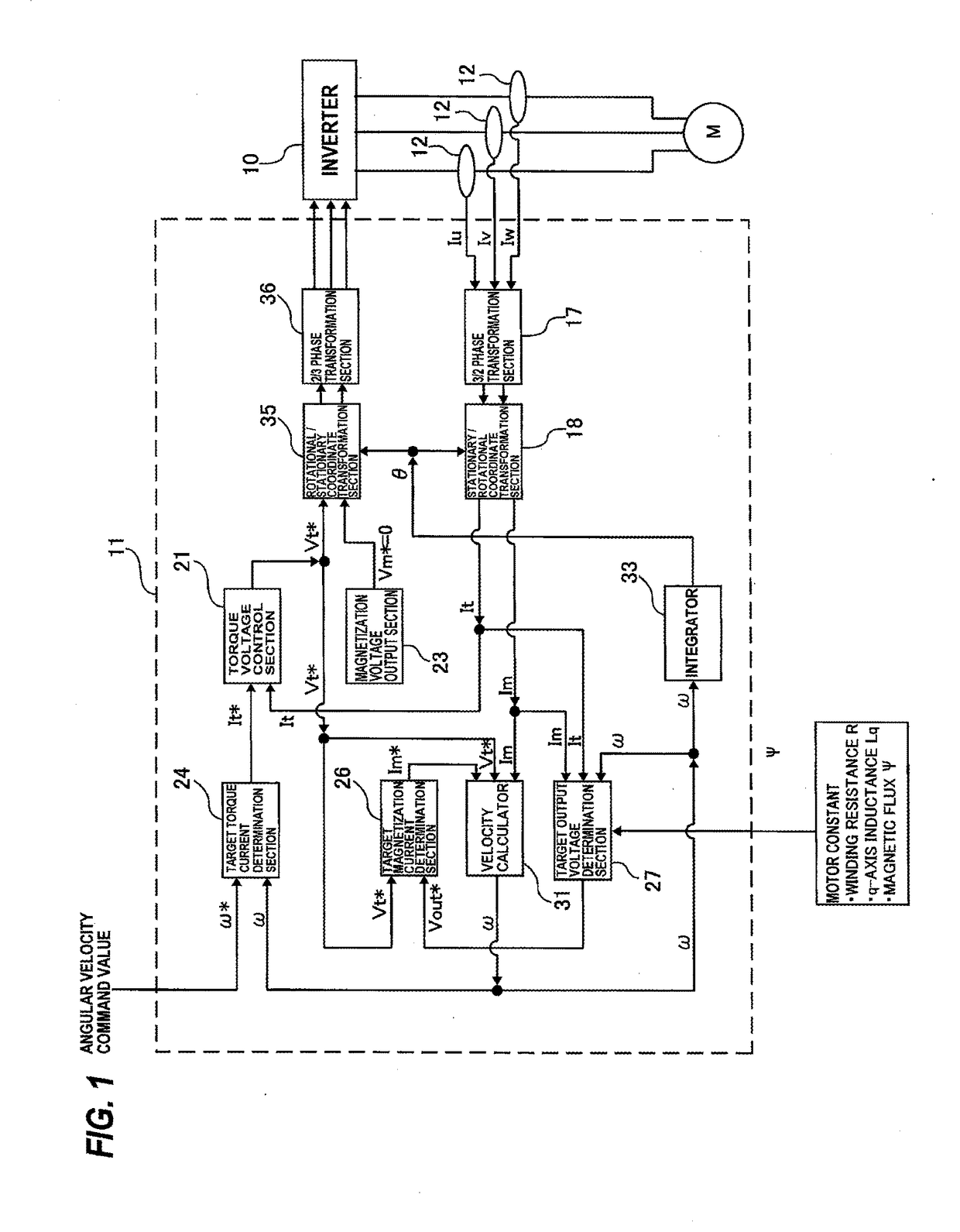
ActiveUS20170070171A1Efficient driveAC motor controlVector control systemsPower inverterControl vector
A driving apparatus for driving an electric motor, such as a synchronous motor or an induction motor, and more particularly to a driving apparatus which performs a vector control based on an output current of an inverter. The driving apparatus of the present invention includes an inverter, a current detector configured to detect an output current of the inverter, and a vector controller configured to transform the output current, detected by the current detector, into a torque current and a magnetization current and to control the torque current and the magnetization current. The vector controller includes a target-output-voltage determination section configured to determine a target output voltage from the torque current, the magnetization current, an angular velocity of the rotor, and motor constants, and a target-magnetization-current determination section configured to determine a magnetization-current command value based on a deviation between the torque-voltage command value and the target output voltage.
Owner:EBARA CORP
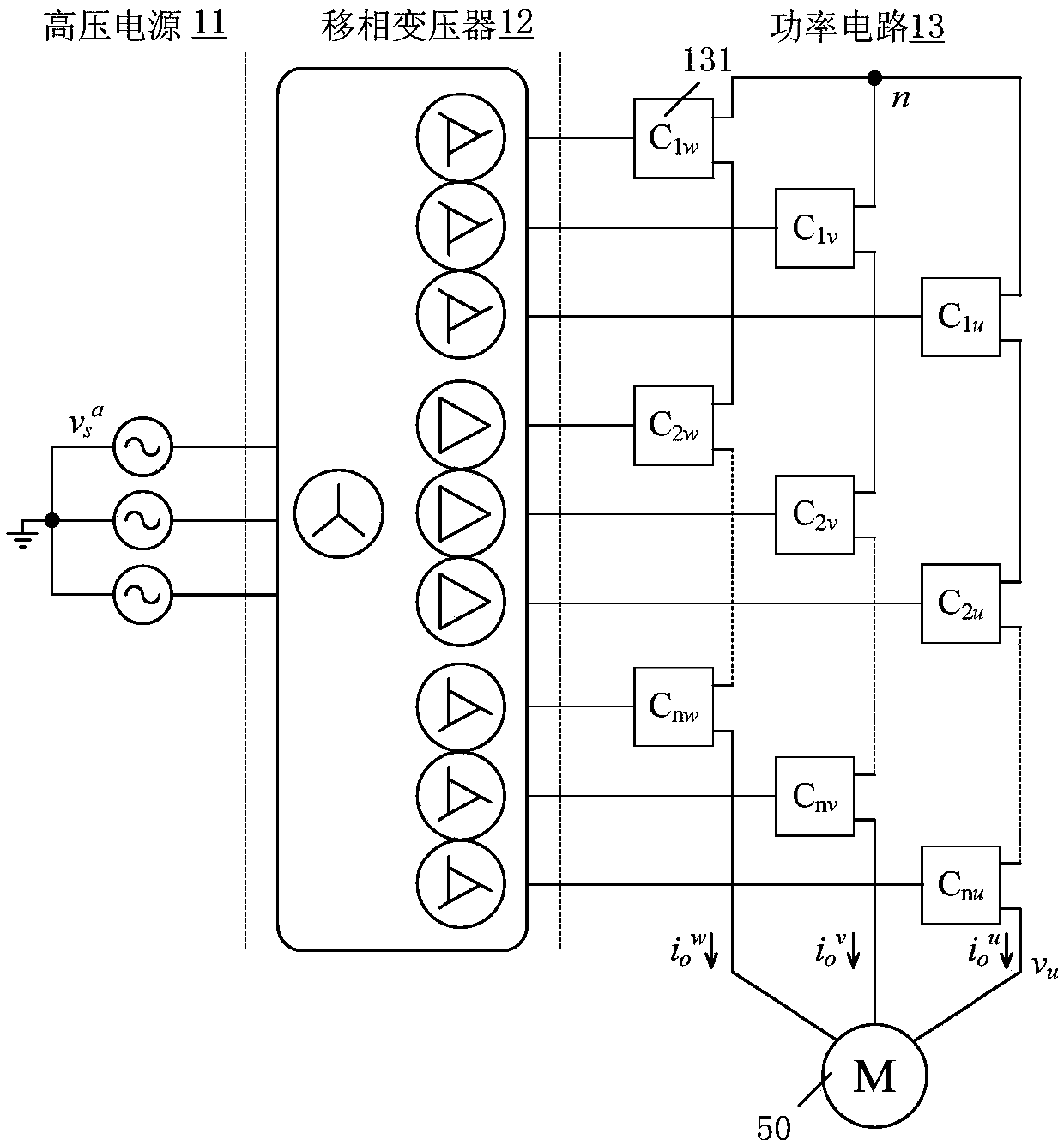
Double-motor constant power synchronous control system free of rigid shaft connection
ActiveCN105529960AConstant Power SynchronizationImprove work efficiencyAC motor controlMultiple dynamo-electric motors speed regulationFrequency changerConstant power
The invention discloses a double-motor constant power synchronous control system free of rigid shaft connection. Two motors free of rigid shaft connection are controlled by two frequency changers, so that constant power synchronization of the two motors is guaranteed. Host position control of a main frequency changer is combined with a slave maximum load torque breaking unit of a slave frequency changer, so that the two motors free of rigid shaft connection can realize constant power control, namely the maximum speeds of the two motors are determined according to the motor with the maximum load, and output shaft position synchronization of the two motors is guaranteed in the whole operational process. According to the system, the two motors free of rigid shaft connection can realize constant power control, namely the maximum speeds of the two motors are determined according to the motor with the maximum load, and the output shaft position synchronization of the two motors is guaranteed in the whole operational process, so that the work efficiency of the system is improved.
Owner:WUHAN GUIDE ELECTRIC DRIVE TECH CO LTD +1
Device for controlling electric motor and method for controlling electric motor
ActiveCN104335476ADegradation of control performance cannot be avoidedIncrease computing loadElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlEngineeringPhase control
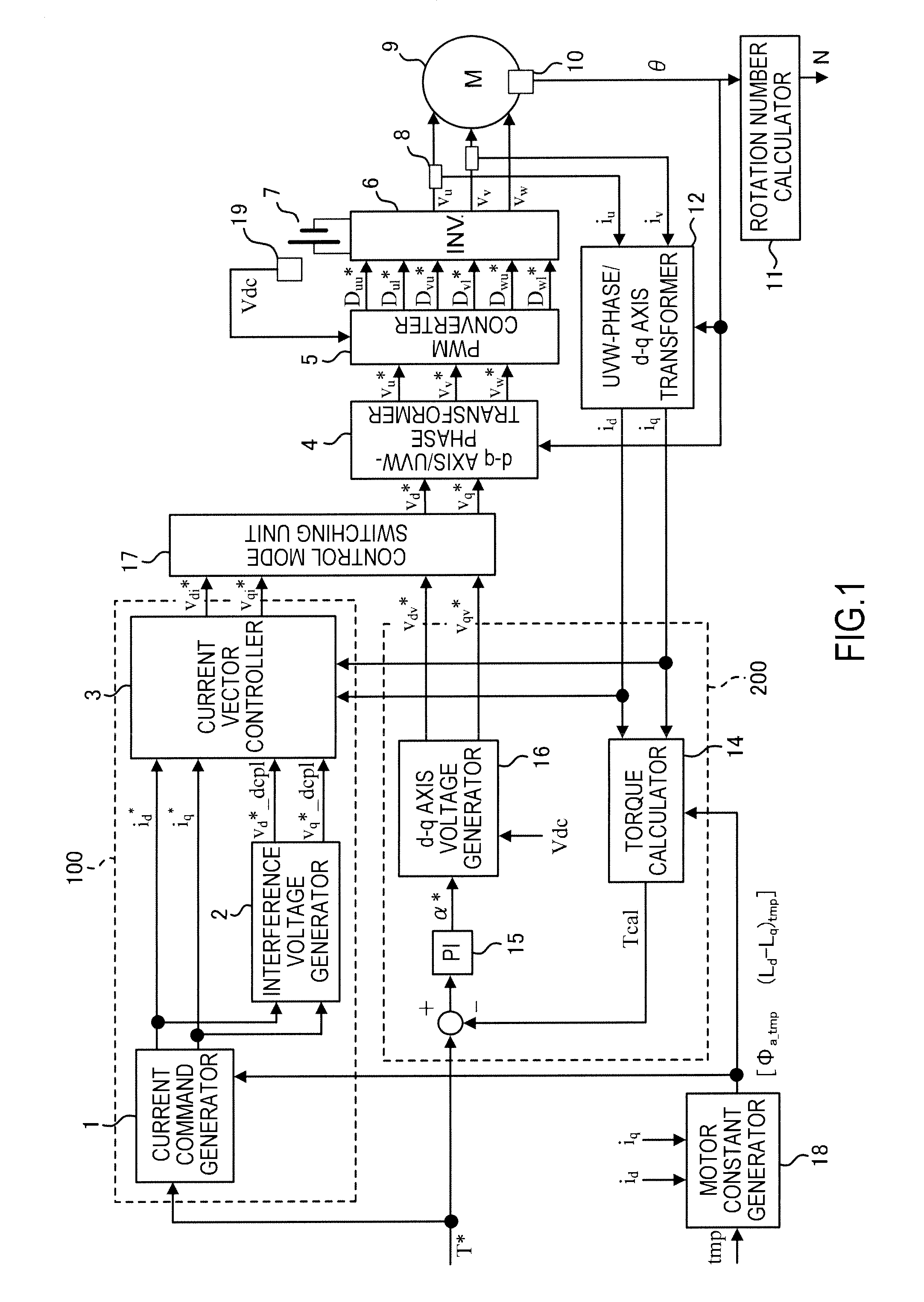
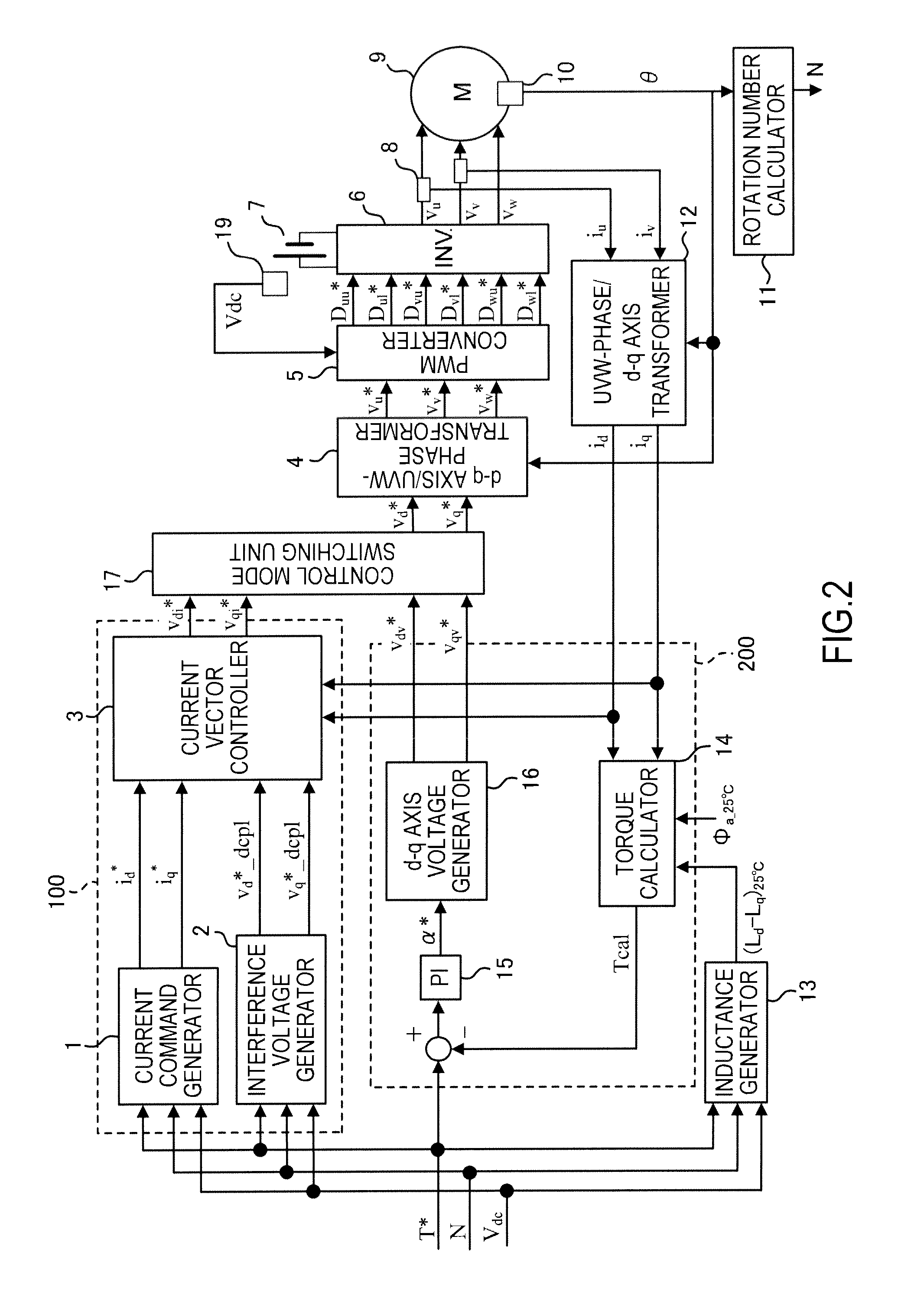
An electric motor control device includes: a motor constant generator configured to generate a motor constant by using a temperature as a parameter; a current control unit configured to generate a current command value to an electric motor based on the motor constant and a torque command value and execute a current control mode in which a voltage applied to the electric motor is controlled to match the current command value; a voltage phase control unit configured to calculate a torque estimation value of the electric motor and execute a voltage phase control mode in which a feedback operation is performed for a voltage phase based on the difference between the torque estimation value and the torque command value; and a control mode switching unit configured to switch to the voltage phase control mode in a high rotation area where a flux weakening control is performed. The torque estimation value is calculated using the motor constant common to generation of the current command value in the current control mode.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Motor control device and electrical equipment with motor controlled thereby
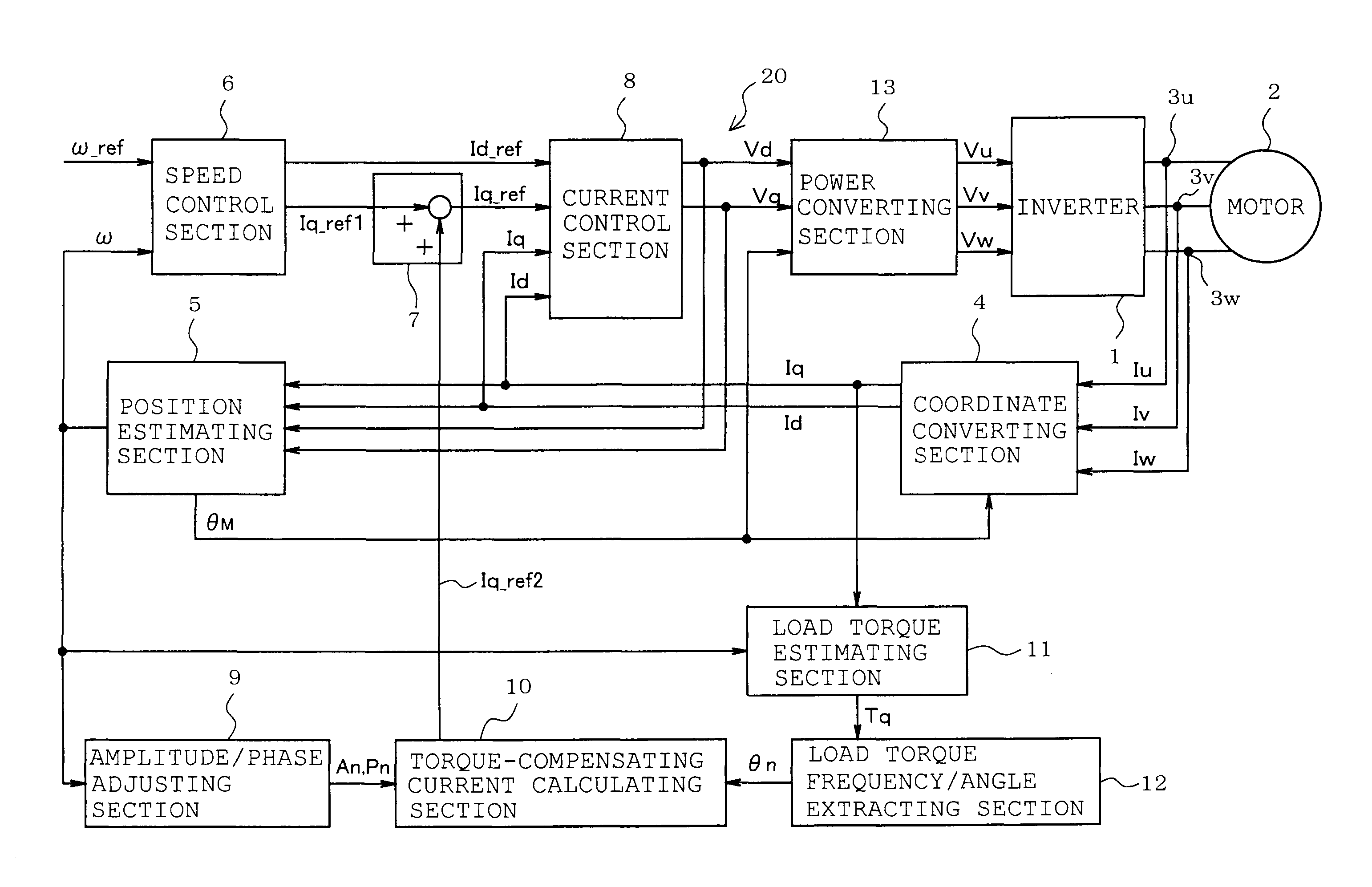
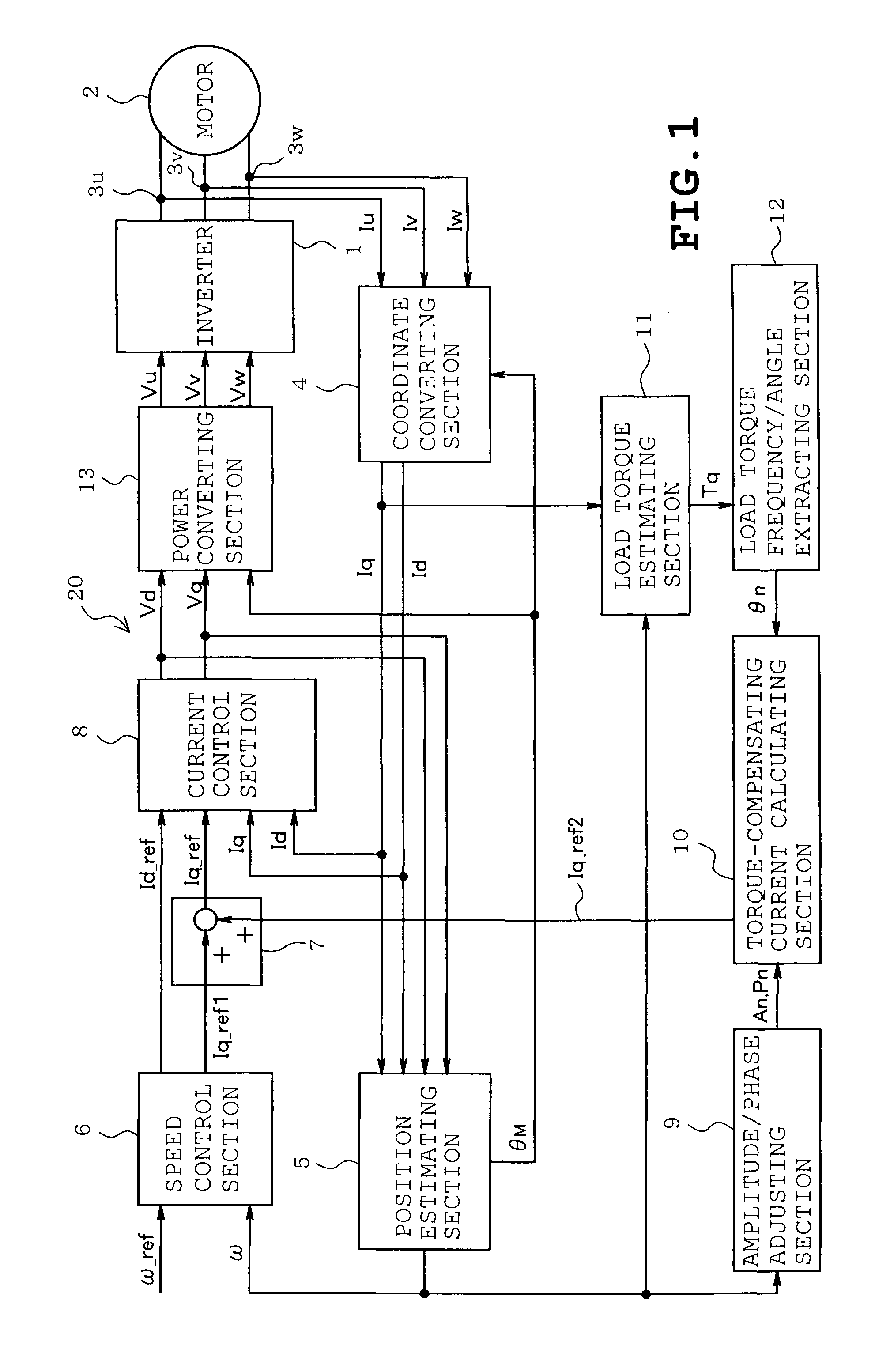
ActiveUS8536812B2Precise torque controlSuppress fluctuationsTorque ripple controlCommutation monitoringElectricityLoad torque
A motor control device includes a current detecting unit detecting current flowing into a motor winding, a speed / electrical angle estimating unit estimating a rotational speed and an electrical angle of the motor, based on the current, a load torque estimating unit estimating load torque to be developed by a load, from a torque current obtained based on the current and the electrical angle, a motor constant and inertia moment of the motor inclusive of the load, a load torque phase calculating unit calculating a phase of periodic fluctuation indicated by the load torque, a torque-compensating current determining unit determining a sinusoidal torque-compensating current, based on the load torque phase, and an amplitude / phase adjusting unit detecting speed fluctuation of the motor to adjust amplitude and phase of the torque compensating current by increasing or decreasing the amplitude and the phase so that the speed fluctuation is reduced.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Motor constant-speed forward/reverse rotation control circuit
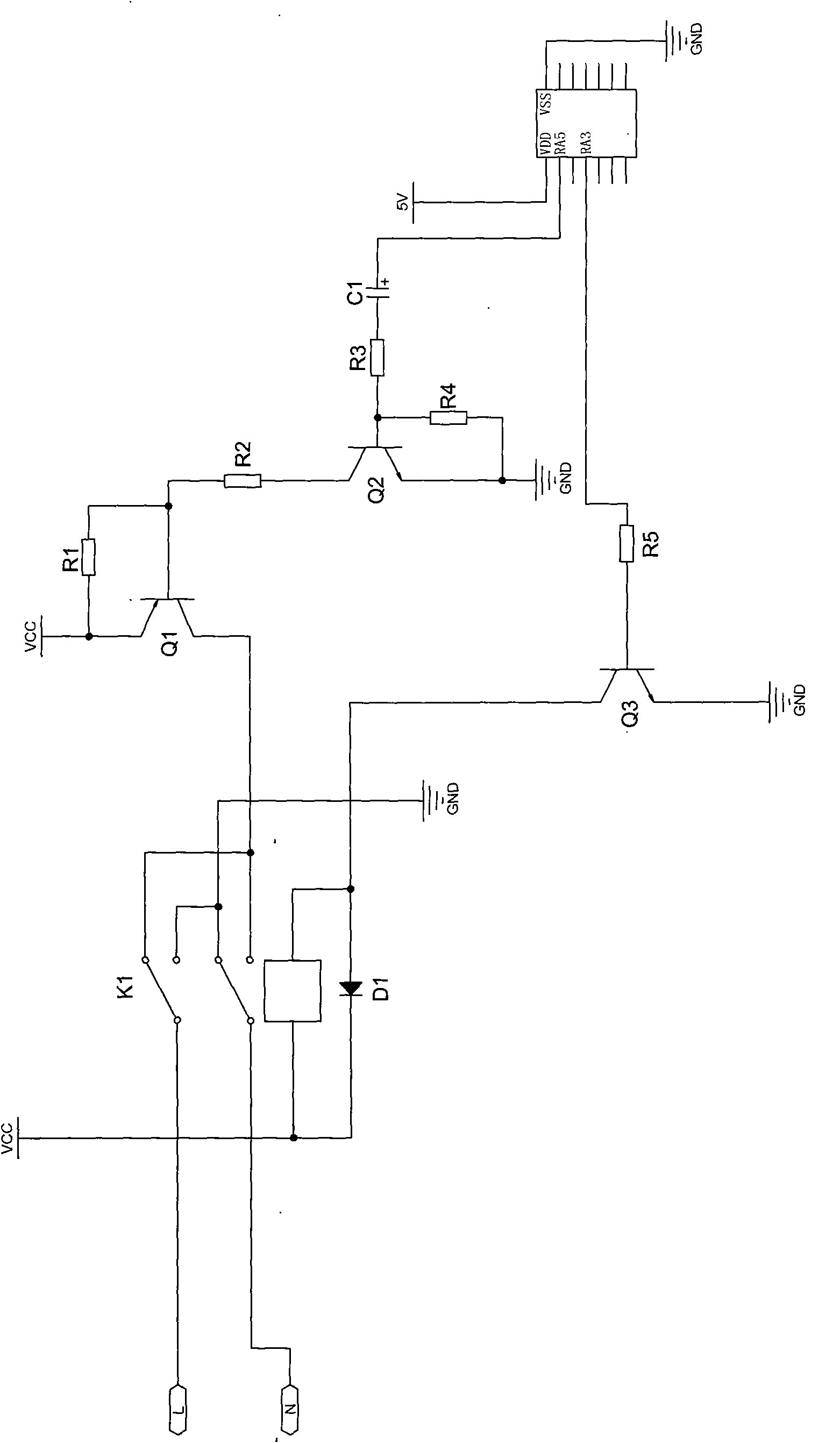
ActiveCN101997468AImprove stabilityLow failure rateField or armature current controlDc motor startersFailure rateControl signal
The invention discloses a motor constant-speed forward / reverse rotation control circuit. A control signal output pin of a master chip outputs motor forward / reverse rotation control signals to the base electrode of a third crystal triode, the collector electrode of the third crystal triode is connected with a power source by an electromagnetic relay, and the electromagnetic relay is provided with at least a first moving contact and a second moving contact which are correspondingly communicated with the positive pole and the negative pole of the motor; the normally closed contact of the electromagnetic relay corresponding to the first moving contact is connected with the collector electrode of a first crystal triode, and the corresponding normally open contact is earthed; the normally closed contact of the electromagnetic relay corresponding to the second moving contact is earthed, and the corresponding normally open contact is connected with the collector electrode of the first crystal triode; and the base electrode of the first crystal triode is connected with the collector electrode of a second crystal triode, and a modulation signal output pin of the master chip outputs PWM signals to the base electrode of the second crystal triode. By controlling the electromagnetic relay based on the motor forward / reverse rotation control signals to realize the forward / reverse rotation of the motor and determining the rotation speed of the motor based on PWM signals, the invention has the advantages of high stability and low failure rate.
Owner:SAKURA BATH & KITCHEN PRODS CHINA
Electric motor control device and electric motor control method
ActiveUS20150061557A1Improve performanceIncrease loadCommutation monitoringMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase controlMotor constants
An electric motor control device includes: a motor constant generator configured to generate a motor constant by using a temperature; a current control unit configured to generate a current command value to an electric motor based on the motor constant and a torque command value and execute a current control mode; a voltage phase control unit configured to calculate a torque estimation value of the electric motor and execute a voltage phase control mode in which a feedback operation is performed for a voltage phase based on the difference between the torque estimation value and the torque command value; and a control mode switching unit configured to switch to the voltage phase control mode in a high rotation area where a flux weakening control is performed. The torque estimation value is calculated using the motor constant common to generation of the current command value in the current control mode.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Motor constant-speed forward/reverse rotation control circuit
ActiveCN101997468BImprove stabilityLow failure rateField or armature current controlDc motor startersFailure rateControl signal
The invention discloses a motor constant-speed forward / reverse rotation control circuit. A control signal output pin of a master chip outputs motor forward / reverse rotation control signals to the base electrode of a third crystal triode, the collector electrode of the third crystal triode is connected with a power source by an electromagnetic relay, and the electromagnetic relay is provided with at least a first moving contact and a second moving contact which are correspondingly communicated with the positive pole and the negative pole of the motor; the normally closed contact of the electromagnetic relay corresponding to the first moving contact is connected with the collector electrode of a first crystal triode, and the corresponding normally open contact is earthed; the normally closed contact of the electromagnetic relay corresponding to the second moving contact is earthed, and the corresponding normally open contact is connected with the collector electrode of the first crystal triode; and the base electrode of the first crystal triode is connected with the collector electrode of a second crystal triode, and a modulation signal output pin of the master chip outputs PWM signals to the base electrode of the second crystal triode. By controlling the electromagnetic relay based on the motor forward / reverse rotation control signals to realize the forward / reverse rotation of the motor and determining the rotation speed of the motor based on PWM signals, the invention has the advantages of high stability and low failure rate.
Owner:SAKURA BATH & KITCHEN PRODS CHINA
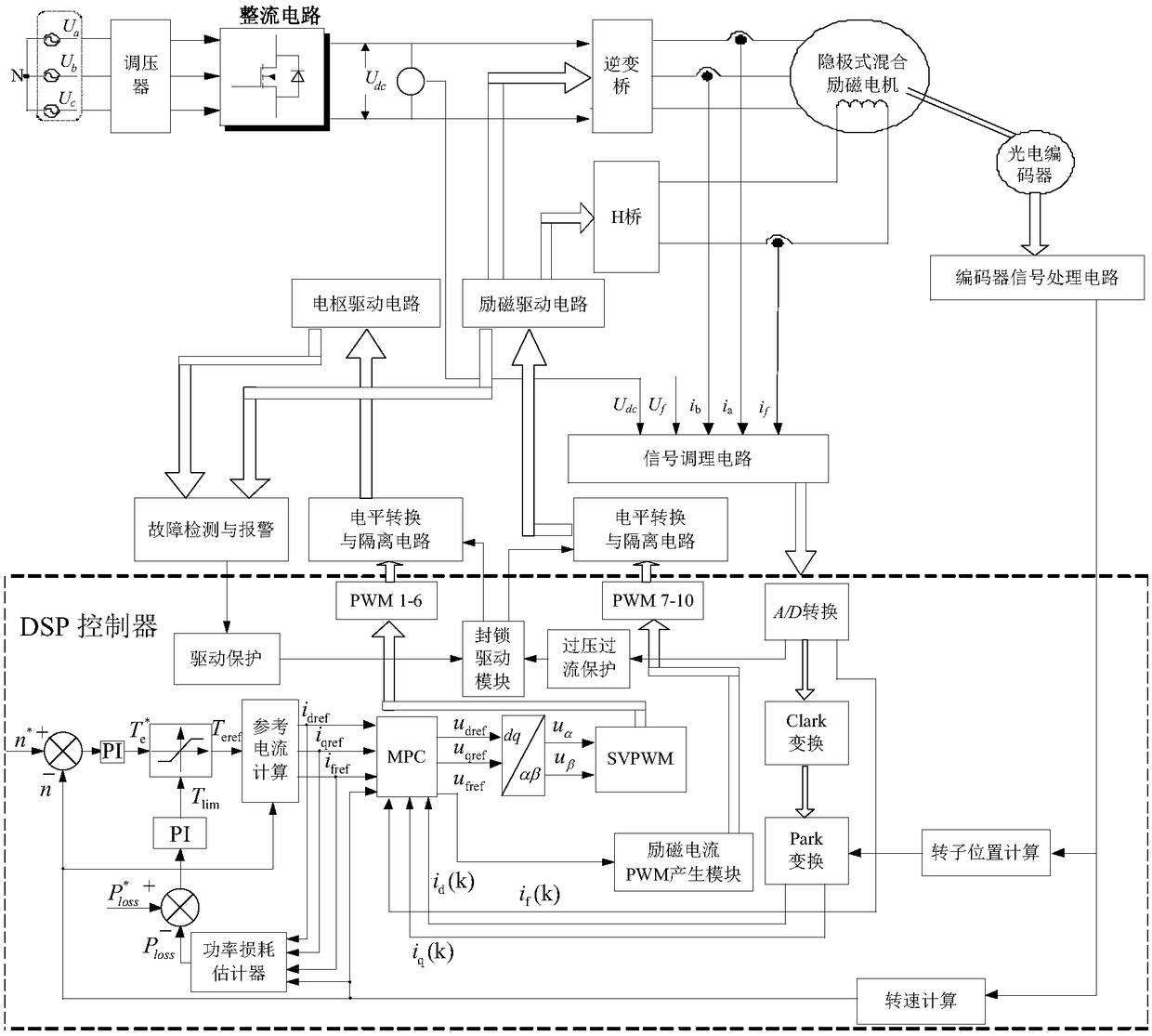
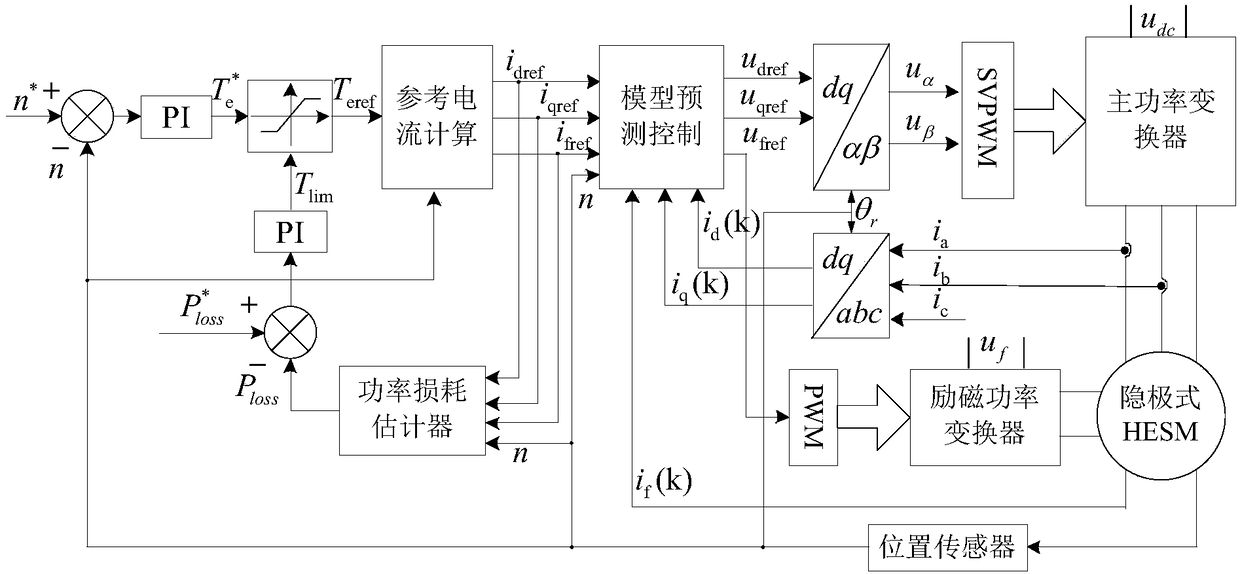
Non-salient pole type hybrid excitation motor constant-power loss model prediction control method
ActiveCN108418485AGuaranteed thermal stabilityGive full play to the output abilityElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsInterference resistanceSynchronous motor
The invention disclose a non-salient pole type hybrid excitation motor constant-power loss model prediction control method, and realizes quick and stable operation of a hybrid excitation synchronous motor while constant power loss is maintained. By comparison of given power loss and actual power loss and by combination of a constant power loss control strategy, a d-axis reference current i<dref>,a q-axis reference current i<qref>, and an excitation reference current i<fref> are calculated; and model prediction control is performed based on a voltage prediction model, a reference current and an actual current feedback value, and non-salient pole type hybrid excitation synchronous motor constant-power loss model prediction control is realized finally. By virtue of the control method provided by the invention, the output capability of the motor and an inverter is given into full play; the maximum output torque is improved in a wide speed range, the speed regulation range is expanded, andsystem efficiency is improved; high dynamic response, low torque fluctuation, and high interference resistance and robustness are realized; and in addition, the control method is simple and can be realized easily, and real-time environment application can be facilitated.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Controller for permanent magnet synchronous motor and motor control system
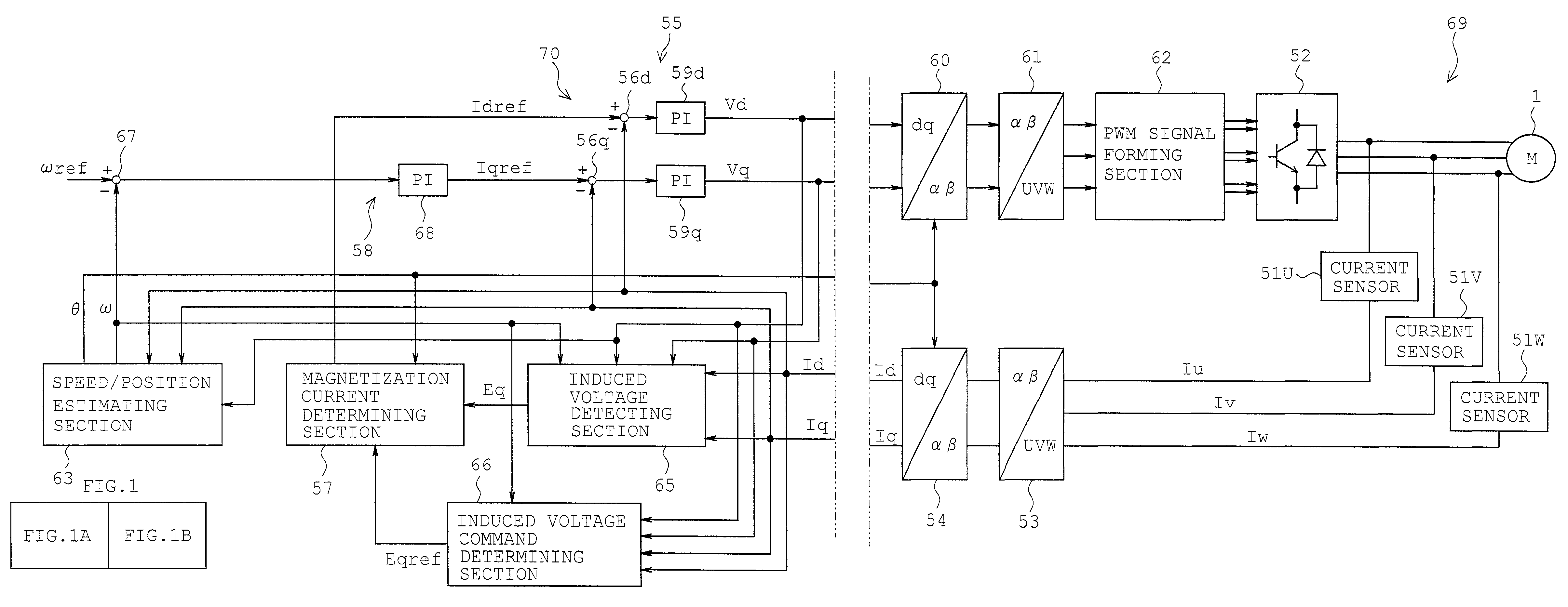
InactiveCN101615883AHigh precisionInhibitory dysregulationElectronic commutation motor controlElectric motor controlLow speedControl signal
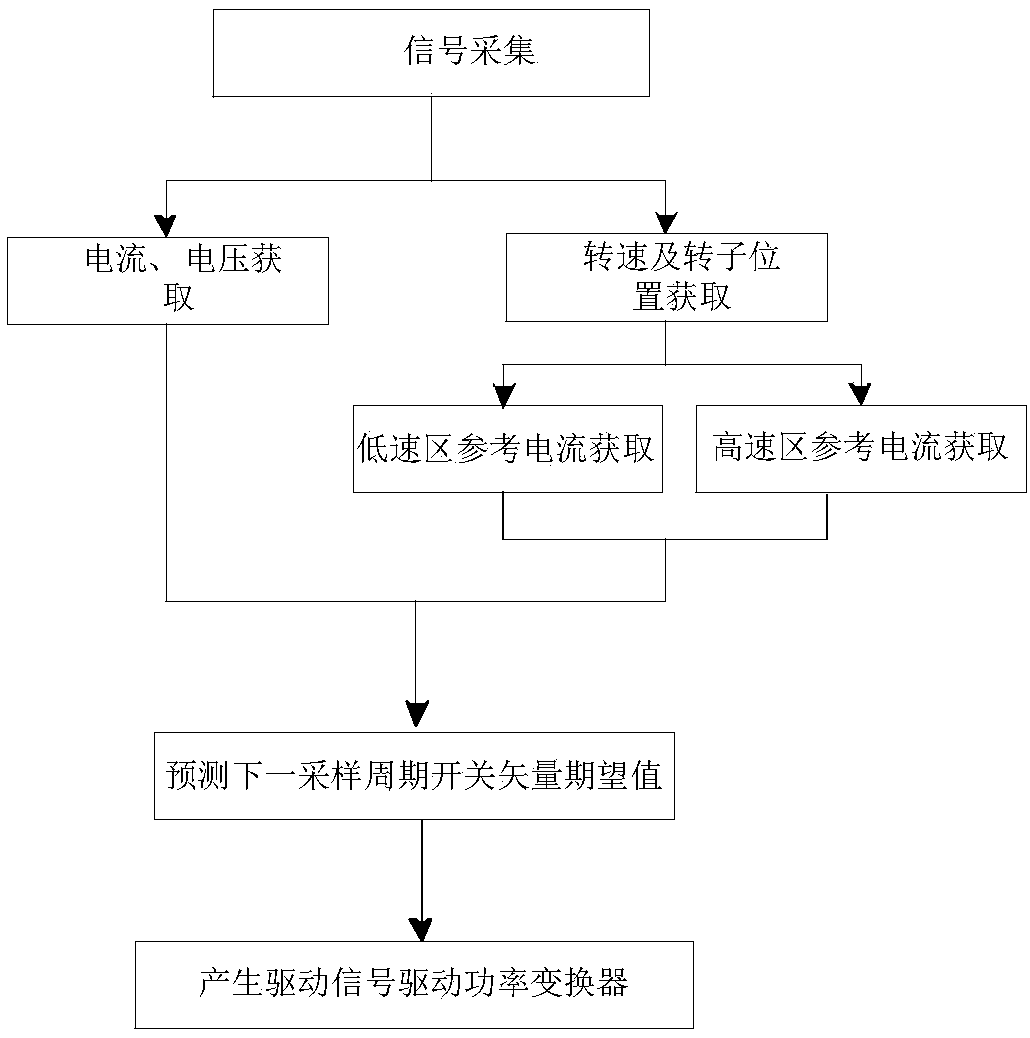
The invention provides a controller for permanent magnet synchronous motor and a motor control system. Two motor constants in the two zones such as a low-speed zone and a high-speed zone are defined. A motor control system includes: a permanent magnet synchronous motor; a power converter connected to the motor, a current detector configured to detect a current flowing through the permanent magnet synchronous motor, a controller generating a control signal for controlling the power converter; the controller comprising: a vector controller configured to generate the control signal on the basis of the detected current; an axial error estimating computing unit configured to estimate an axial error information which is a difference between a phase value of the motor and the phase estimation value obtained by integrating a rotational speed estimation value of the motor; a speed estimating computing unit, which is characterized in that: a motor constant identification computing unit configured to identify a motor constant of the permanent magnet synchronous motor with the q-axis voltage component and the rotational estimation value or a rotational speed command and reflects the identified motor constant in generating the control signal by the vector controller.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Motor control apparatus and motor control method
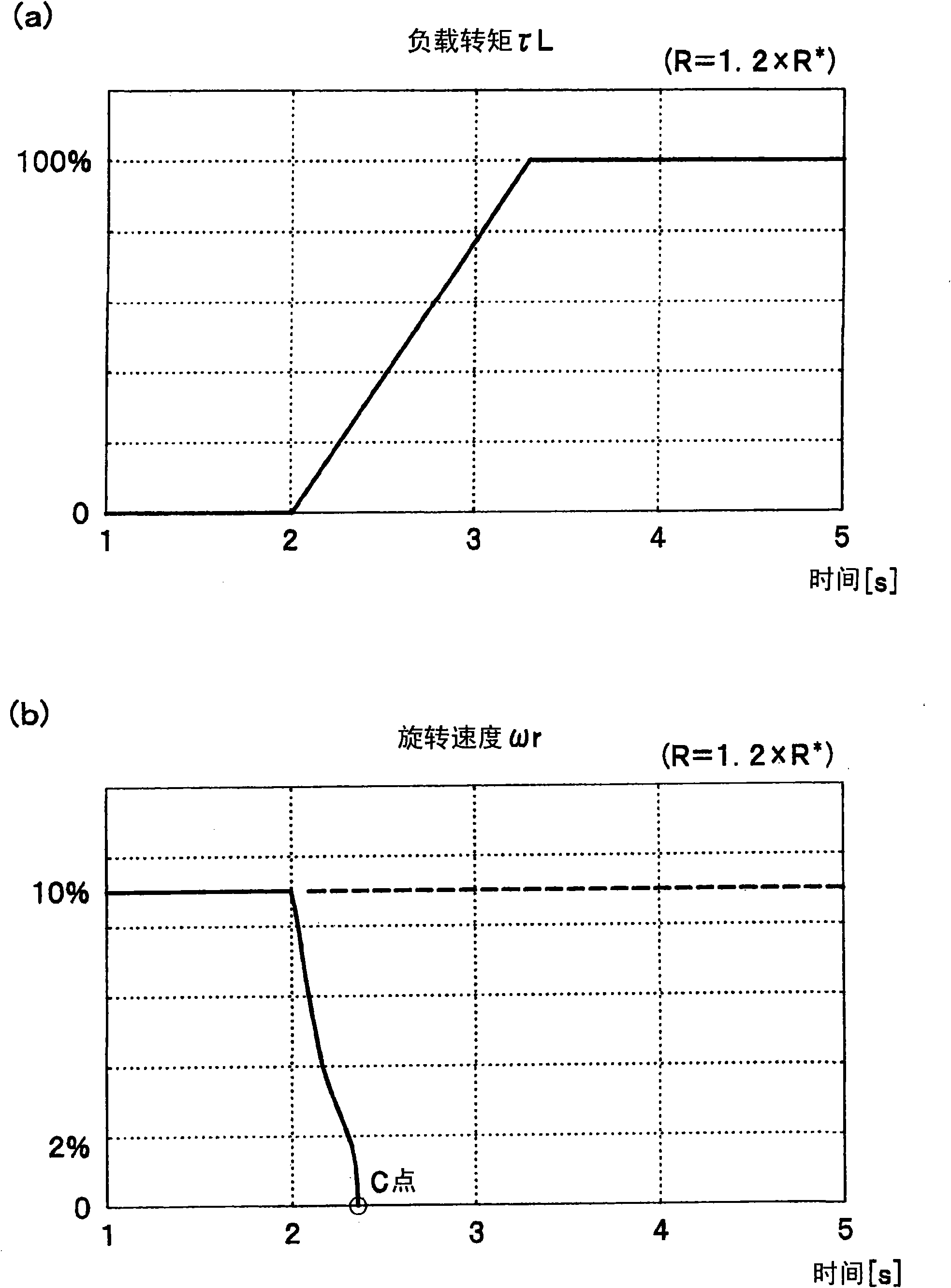
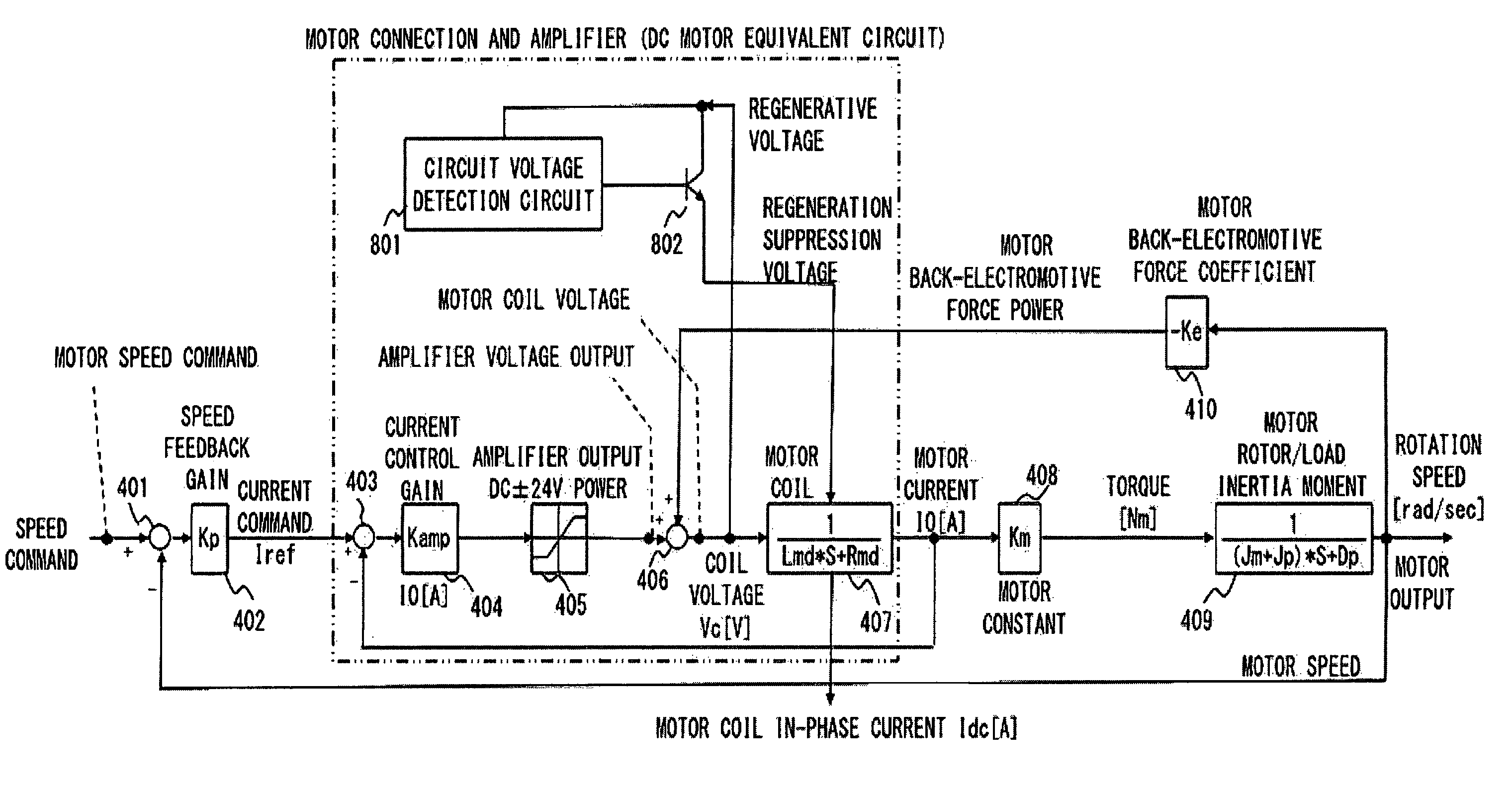
InactiveUS7821219B2Generated regenerative powerEliminate useElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersPhase currentsMotor drive
Size and weight reduction of a motor-driven vehicle, robot or the like is achieved. A current command Iref from a speed feedback gain is supplied to each of circuits with coefficients of sin(θm), sin(θm+2π / 3) and sin(θm−2π / 3) to generate three-phase signals. The three-phase signals are respectively supplied to current control gains through adder-subtracters. Further, signals from motor constants are added together by an adder to produce motor torque. Furthermore, coil voltages output from adders pass through diodes and are then added together by an adder, and the signal is supplied to a regenerative voltage determiner. When a regenerative voltage becomes excessive, in-phase current Idc is supplied through a regeneration control gain to adder-subtracters.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com