Controller of permanent magnet synchronous motor
A technology for synchronous motors and control devices, which can be used in motor generator control, AC motor control, electronic commutation motor control, etc., and can solve problems such as d-axis current command value error, inability to fully weaken magnetic field control, and inability to install
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
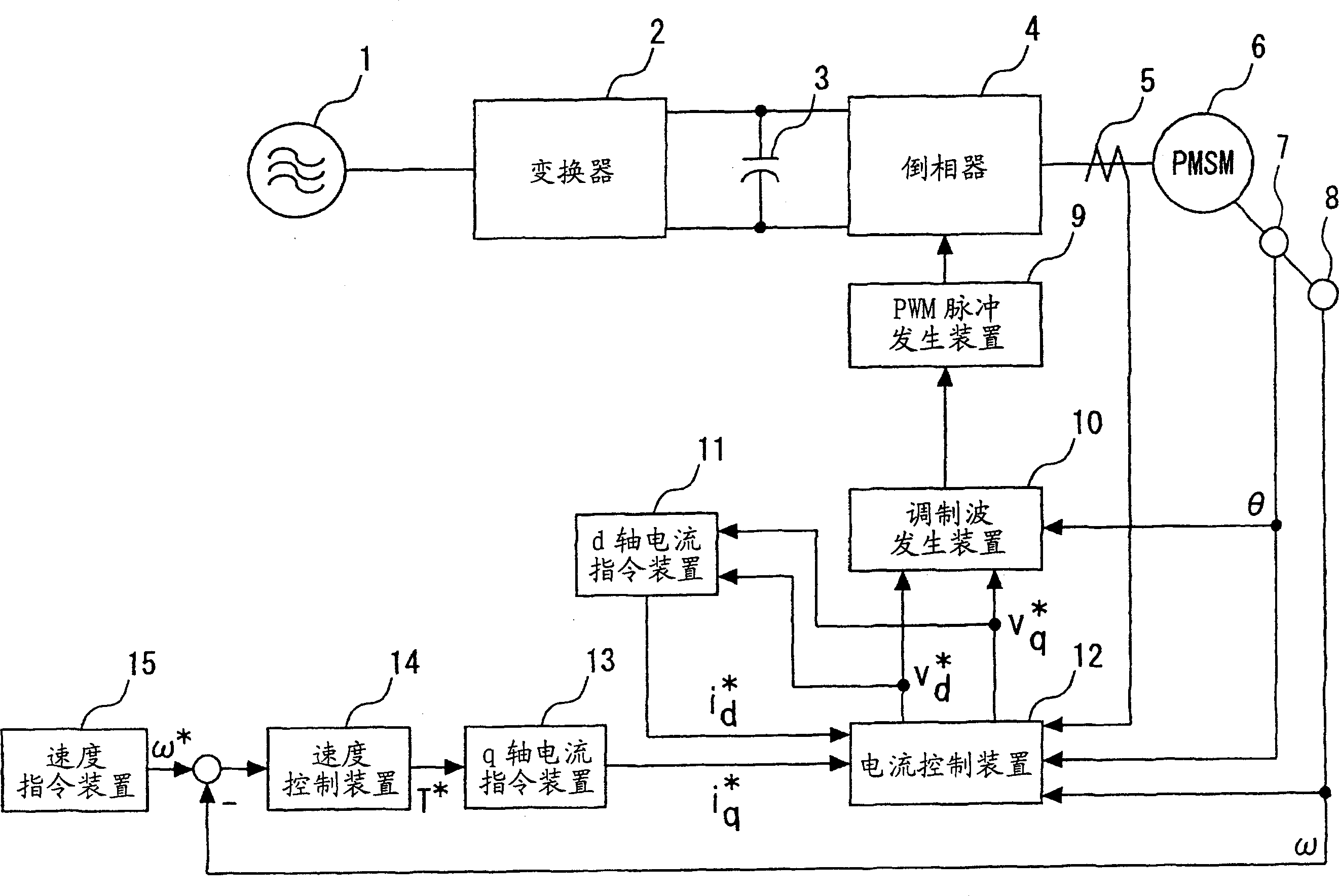
[0016] figure 1 It is a block diagram showing the control device of the permanent magnet type synchronous motor in Embodiment 1 of the present invention. In the figure, the control device of permanent magnet synchronous motor consists of AC power supply 1, converter 2, smoothing capacitor 3, inverter 4, current detector 5, permanent magnet synchronous motor 6, motor position detector 7, motor speed Detector 8 , PWM pulse generating device 9 , modulated wave generating device 10 , current control device 12 , q-axis current command device 13 , speed control device 14 and speed command device 15 constitute. AC power 1 is input into converter 2 . Converter 2 outputs a DC voltage, which is smoothed by smoothing capacitor 3 and input to inverter 4 . The inverter 4 is switched by the PWM pulse generator 9 to output a variable voltage and a variable frequency AC voltage to drive the permanent magnet synchronous motor 6 .
[0017] The motor position detector 7 and the motor speed de...
Embodiment approach 2
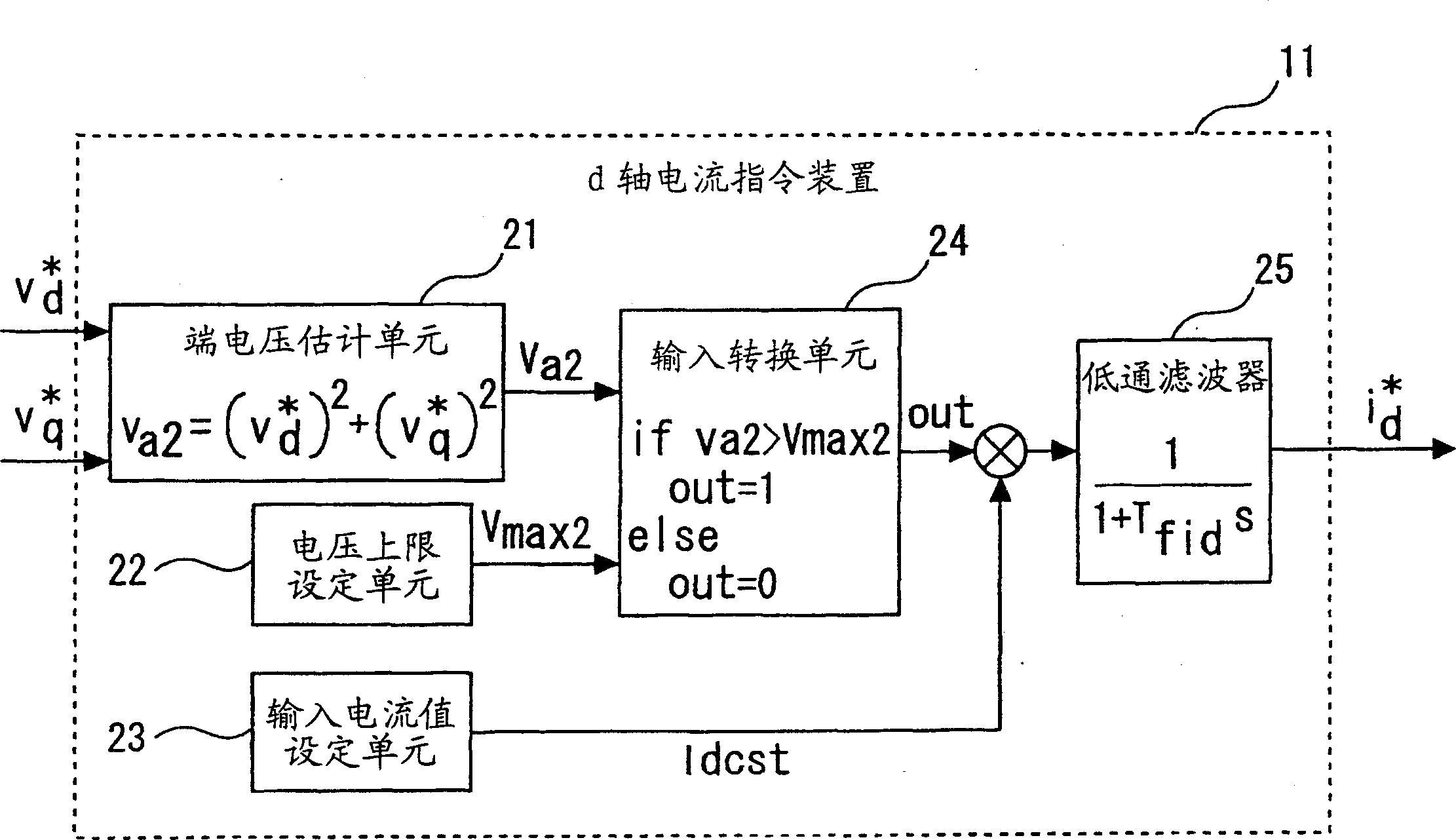
[0045] In the above Embodiment 1, as figure 2 The d-axis current command device 11 is constituted as such, but it may also be as Figure 5 With such a structure, the same operation can also be performed by such a structure.
[0046] Figure 5 It is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the d-axis current command device used in the control device of the permanent magnet type synchronous motor in Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0047] In Embodiment 2, instead of the input switching unit 24 for field weakening control, a current limiter 26 , an integral operation unit 27 , and an input conversion unit 28 for field weakening control having different processing contents are newly provided. again, in Figure 5 in, use with figure 2 Components denoted by the same symbols perform the same operations as those in the first embodiment.
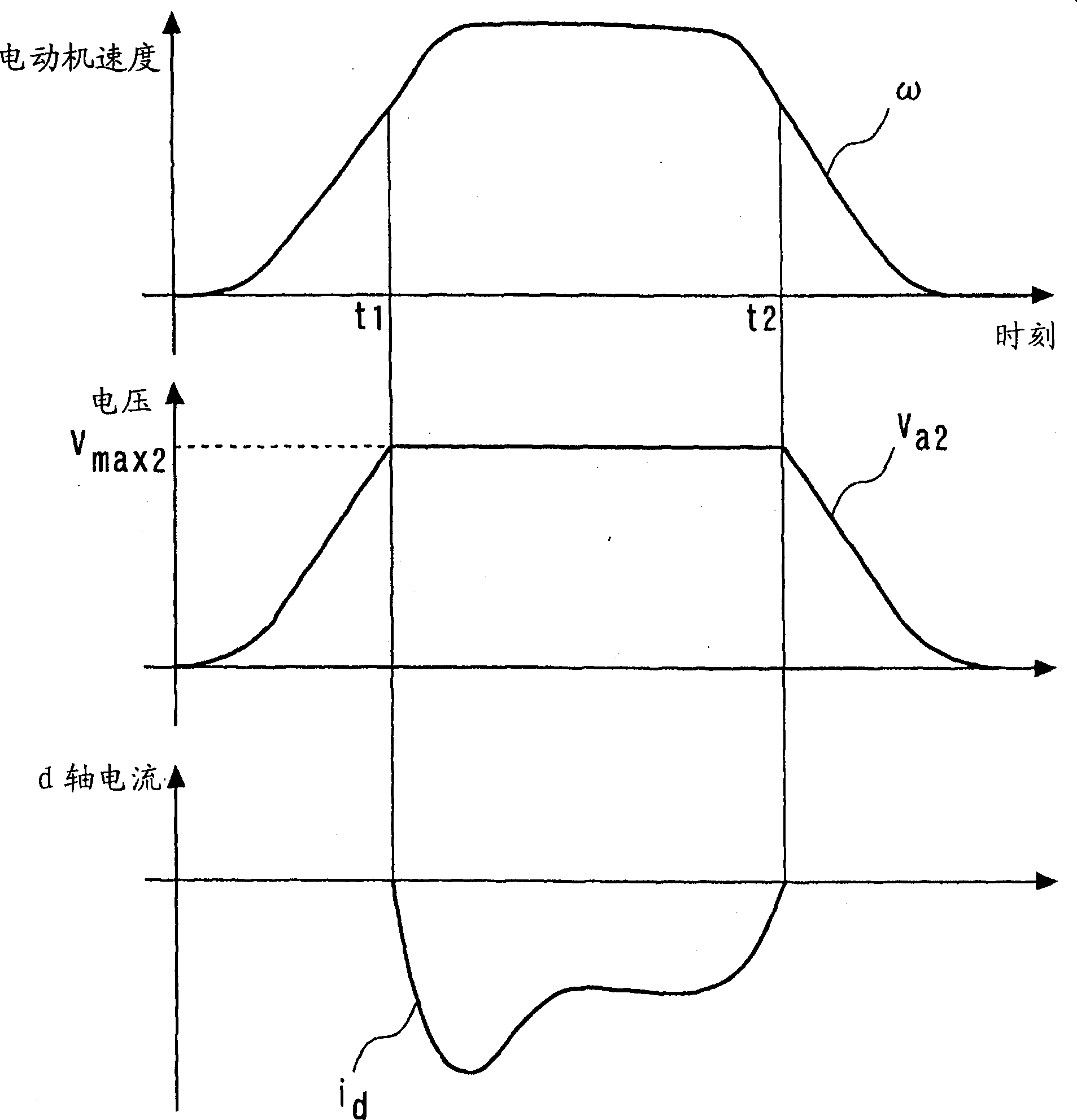
[0048] The input switching unit 28 performing different field weakening controls compares the terminal voltage va2 estimate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com