Motor control device, motor control system, motor control module and refrigerating unit
A technology of motor control and control system, applied in the fields of motor control system, motor control module, refrigeration device, and motor control device, can solve the problem of complicated device, inability to adjust the error between the motor rotor shaft and the control shaft, and the undocumented load torque estimation method and other problems to achieve the effect of reducing the impact of switching
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
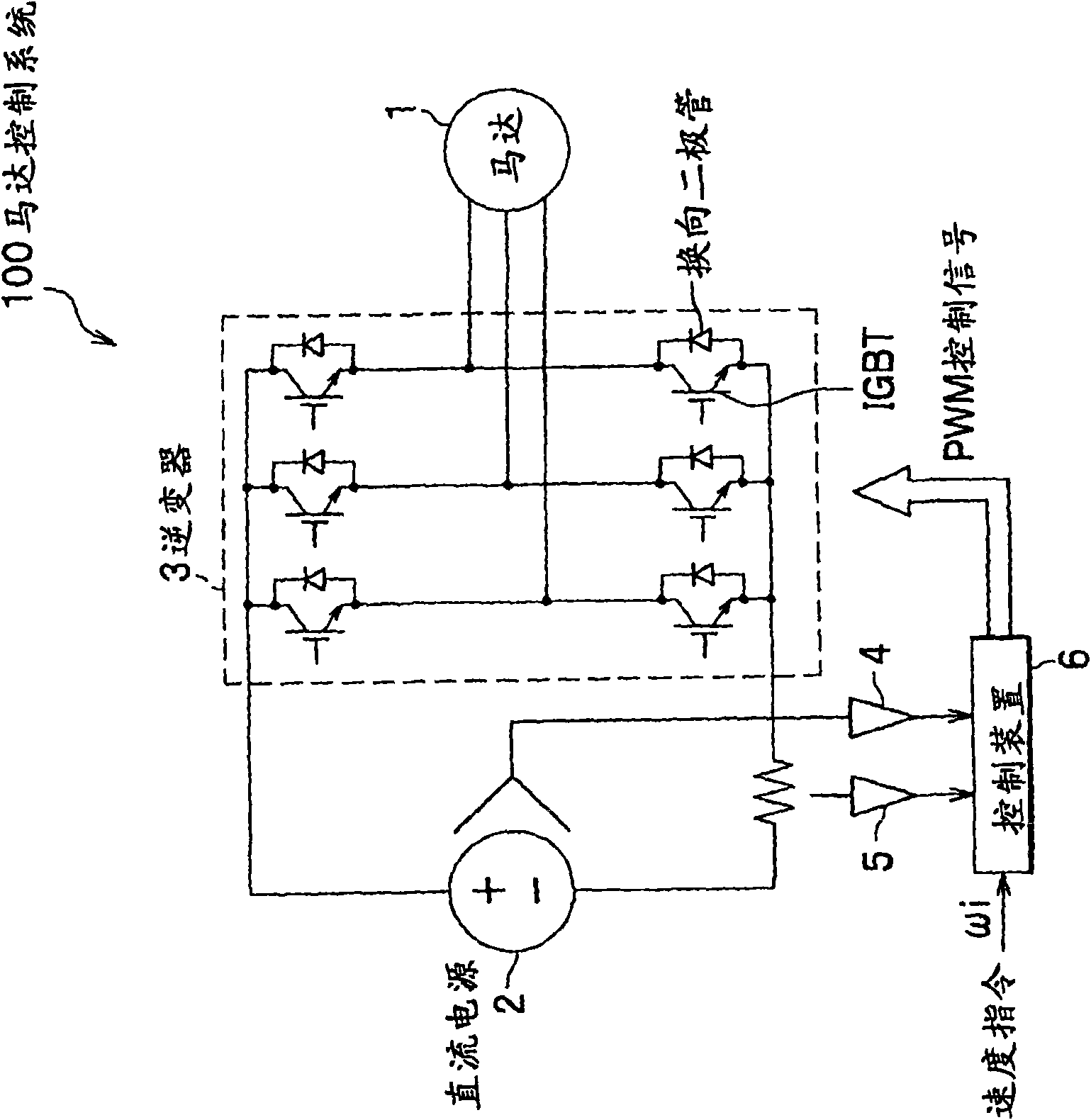
[0031] figure 1 It is a configuration diagram of the motor control system according to the first to third embodiments of the present invention.
[0032] The motor control system 100 includes: a permanent magnet synchronous motor 1; a DC power supply 2; an inverter 3 that converts DC power to AC power; a DC voltage detector 4 that detects the voltage of the DC power supply 2; A DC current detector 5 that detects the current on the DC side; and a control device 6.
[0033] Motor 1 is a permanent magnet synchronous motor.
[0034] The DC power supply 2 is a converter (rectifier) or a battery that converts AC power supplied from a commercial power supply into DC power, and supplies power to the DC side of the inverter 3.
[0035] The inverter 3 includes: six IGBTs (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistors); and a commutation diode connected to the collector and emitter of each IGBT.
[0036] In addition, the control device 6 processes the detection signals of the DC voltage detector 4 and the...
no. 2 approach
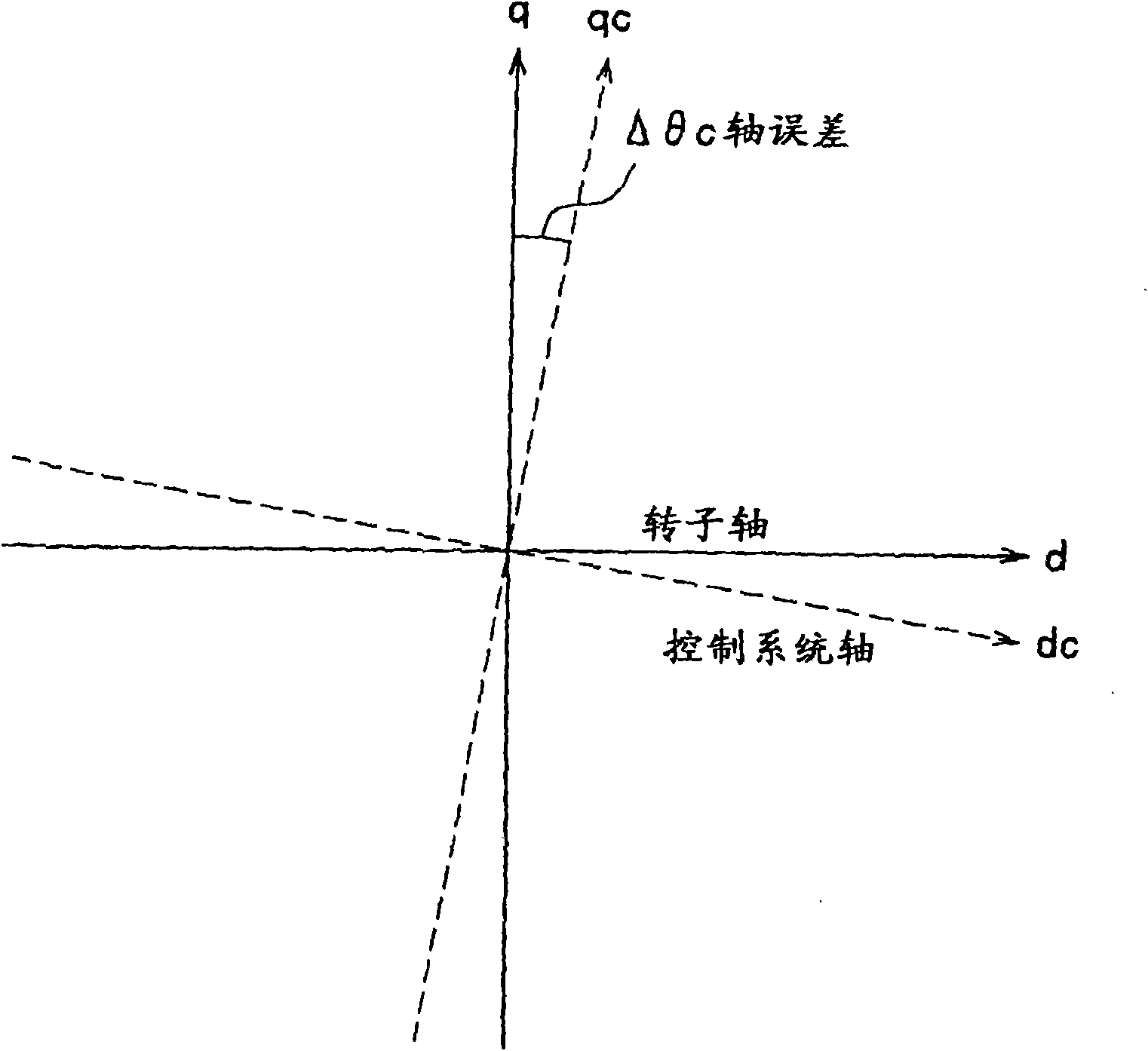
[0087] Picture 12 It is a detailed functional block configuration diagram of the voltage command controller 12 (12b) as the motor control device of the second embodiment of the present invention. versus Figure 4 The difference is that, as shown in equation (6), the voltage command value calculation is changed to the sum of the output of the vector calculator 42 and the output of the current controllers 39 and 40. The current reproduction calculation and phase estimation processing are the same as in the first embodiment.
[0088] V dc * = r * I dc * - ω 1 * Lq * I qc * + ΔV dc V qc * = r * I qc * + ω 1 * Ld * I dc * + ω 1 * Ke * + ΔV qc . . . ( 6 )
[0089] Here, ΔVdc and ΔVqc are the outputs of the current controllers 39 and 40.
[0090] In addition, the start sequence, the current vector phase adjustment in the synchrono...
no. 3 approach
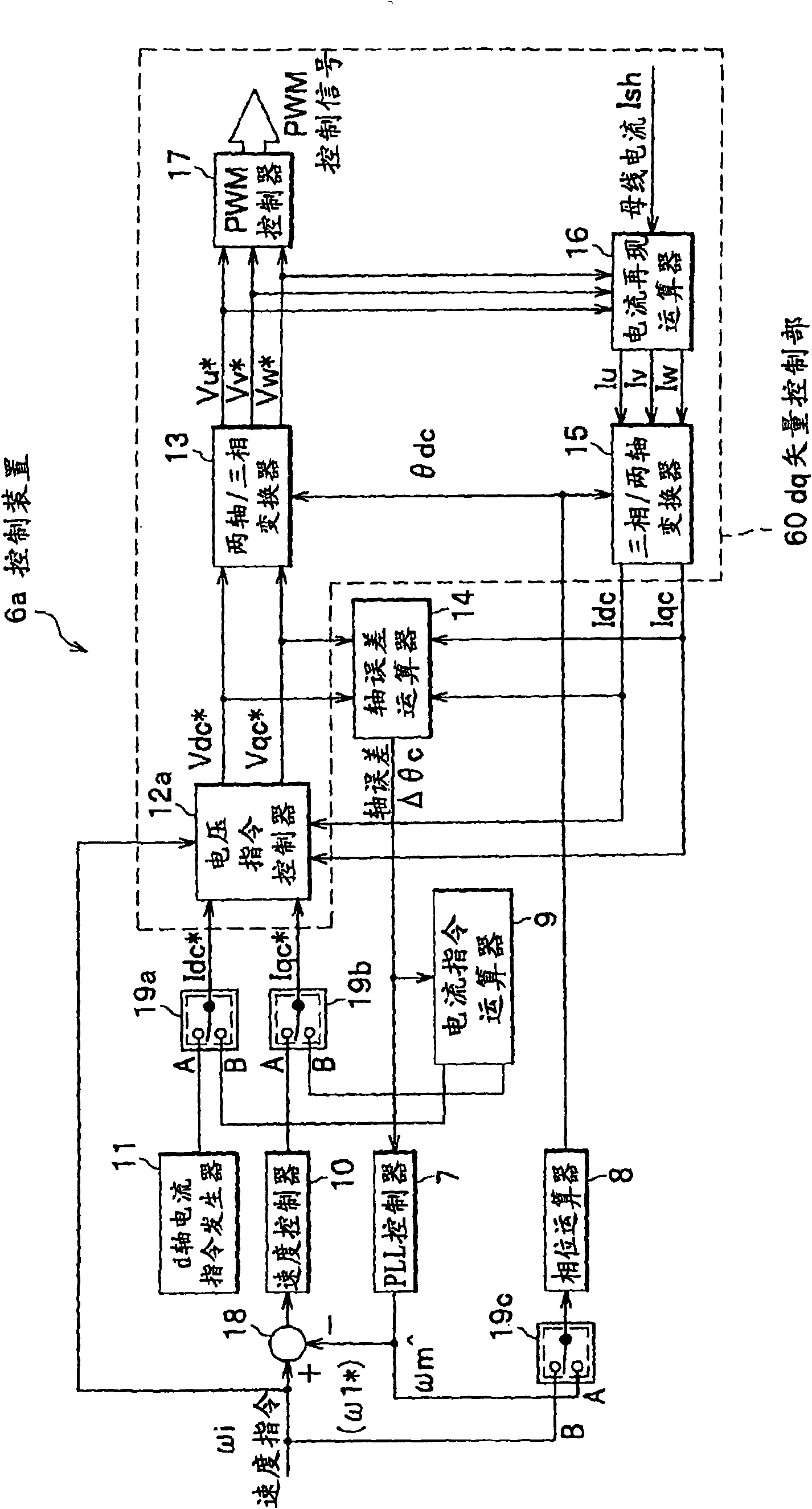
[0092] The structural elements of the motor control device of the third embodiment of the present invention are the same as figure 1 The parts shown are the same, but the vector control method inside the control device 6 is different.
[0093] (The overall structure of control)
[0094] Figure 13 It is a functional block configuration diagram of the control device 6 (6b) as the third embodiment of the present invention. In addition, with figure 2 The parts with the same number perform the same actions.
[0095] versus figure 2 The different part is: the qc-axis current command value Iqc in the sensorless mode is calculated from the low-pass filter 52 * ; And the PLL controller 7 that performs estimation processing of the rotation speed ωm of the motor 1 ( figure 2 ) Is changed to a speed error calculator 50 for calculating a speed error and an adder 51 for calculating the sum of the speed error and the speed command.
[0096] That is, the speed error calculator 50 performs a prop...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com