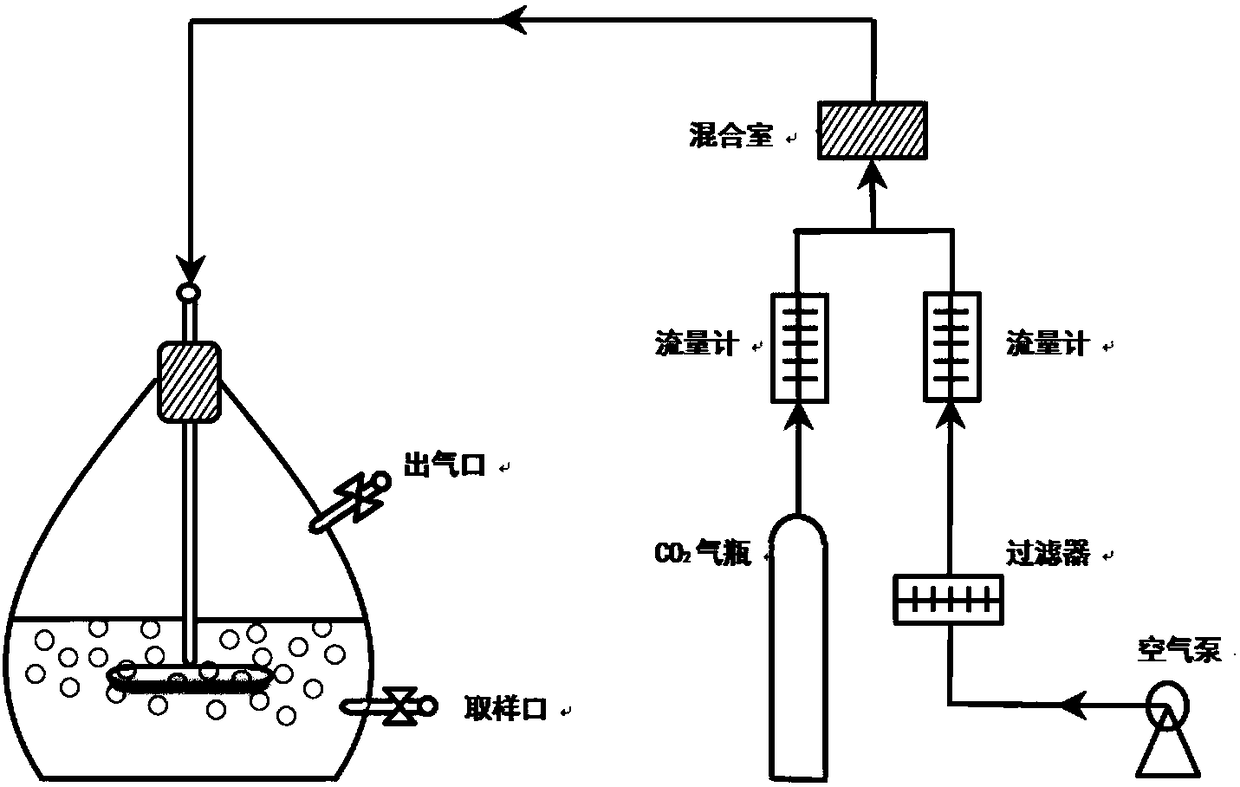
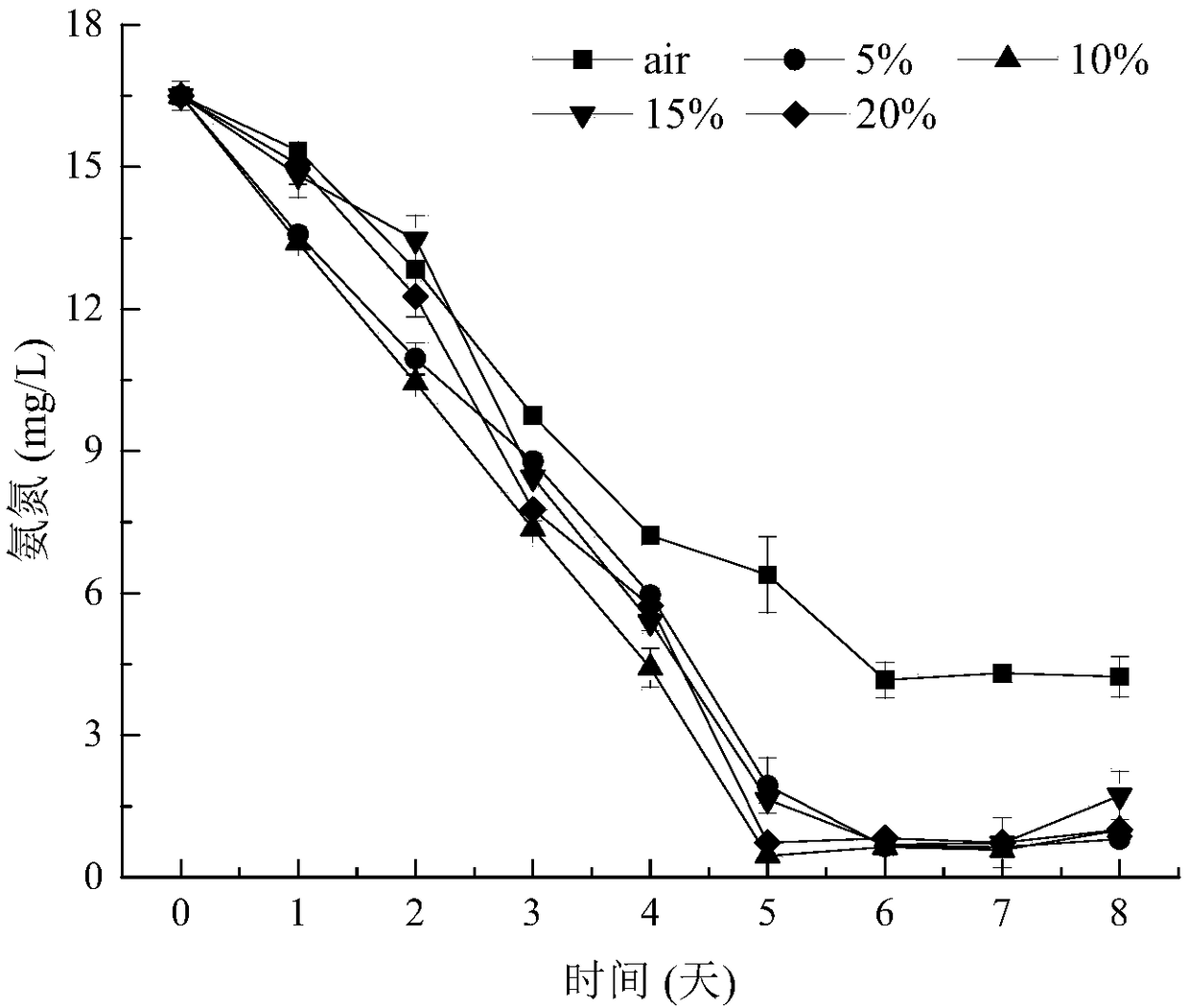
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
295 results about "Chlorella vulgaris" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chlorella vulgaris is the scientific name for a single-celled algae that lives in bodies of fresh water. It is also known as sun chlorella or green algae. Its name comes from the Greek word for green, chloros, and ella, which means small, and vulgaris means common or ordinary.
Method for extracting and purifying xanthophyl from chlorella algae powder
InactiveCN101130513AEfficient extractionOrganic chemistryAlgae medical ingredientsLuteinAqueous sodium hydroxide
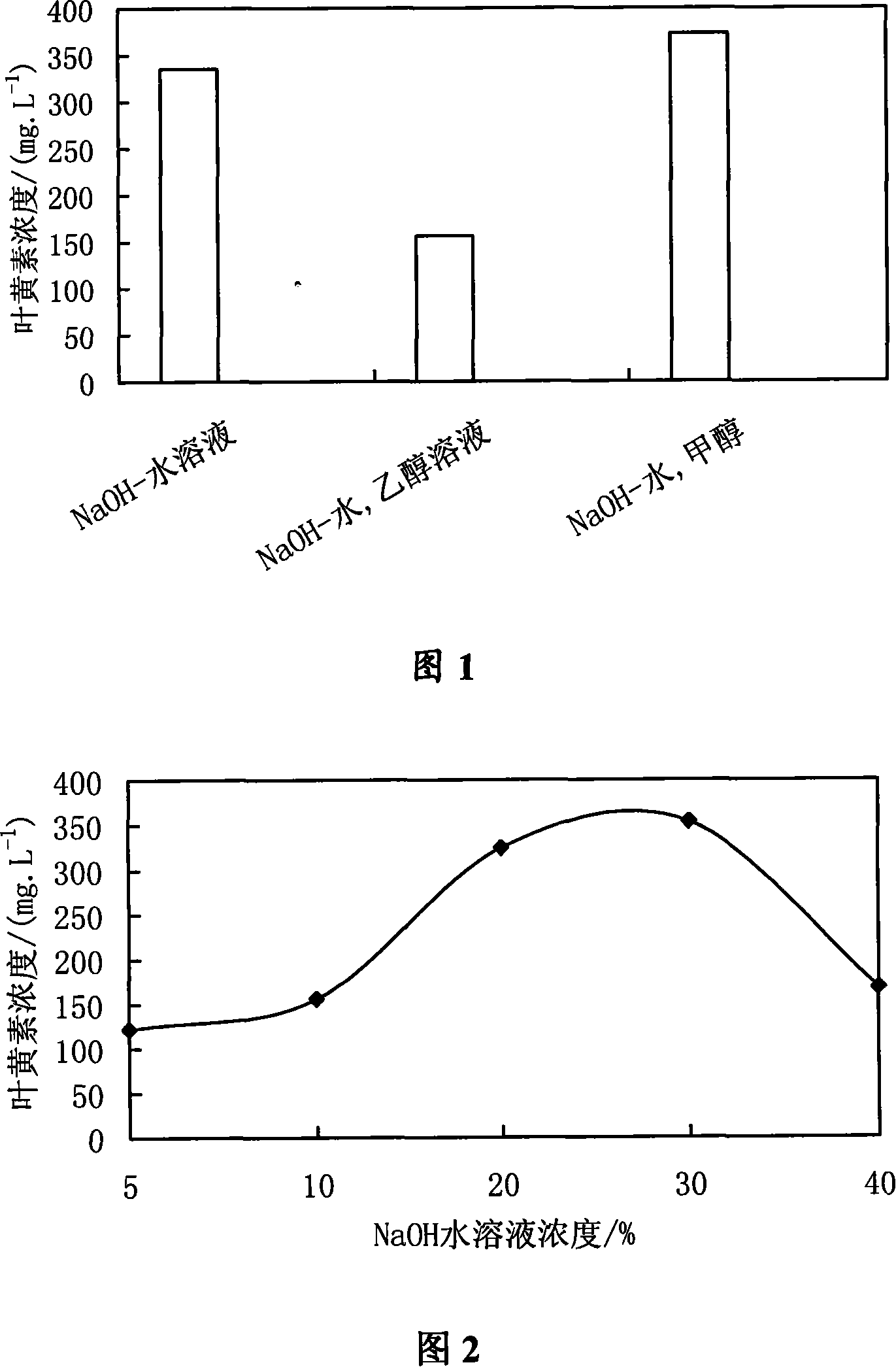
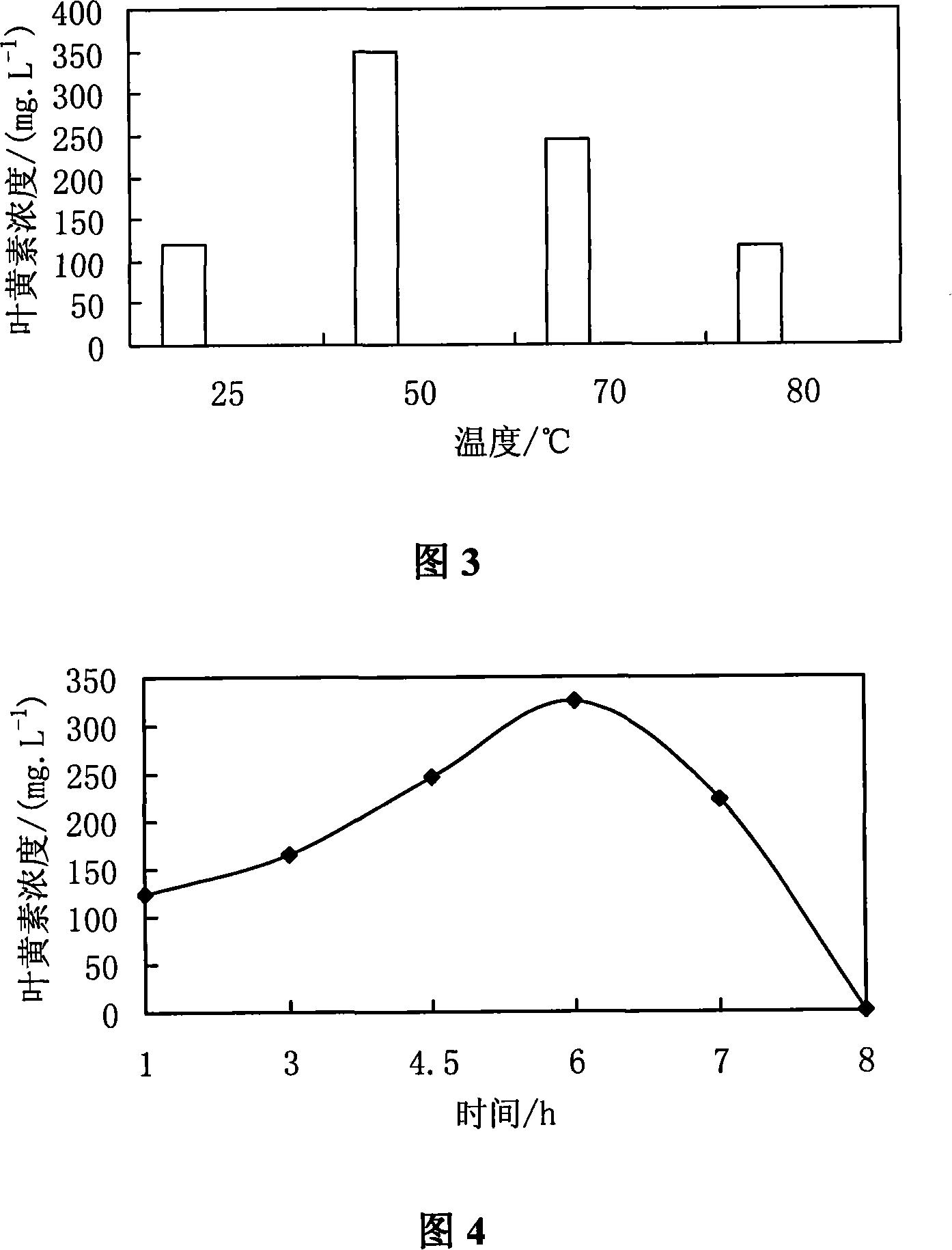
The invention discloses an extracting and purifying method of lutein from pellet algae in the biological technical domain, which comprises the following steps: extracting lutein and ester through composite agent; using 5-20% sodium hydroxide to saponify; rotating; evaporating; washing; crystallizing; obtaining high-purity lutein crystal; weighing 0. 2-2g algae powder to place in the 50-500ml centrifuge tube; adding 8. 0-80. 0ml composite liquid solvent to extract under 10-40 deg. c for 0. 5-2h; adding 10-100ml 5%-30% sodium hydroxide solution into the test tube with hybrid extractant; saponifying at 30-70 deg. c for 3-8h; centrifuging under low temperature for 5-10 min; extracting the product from organic phase. The invention ensures the optimum saponifying technique, which is extracted from pellet algae cell effectively.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING +1
Preparation method for chlorella anti-oxidative peptide
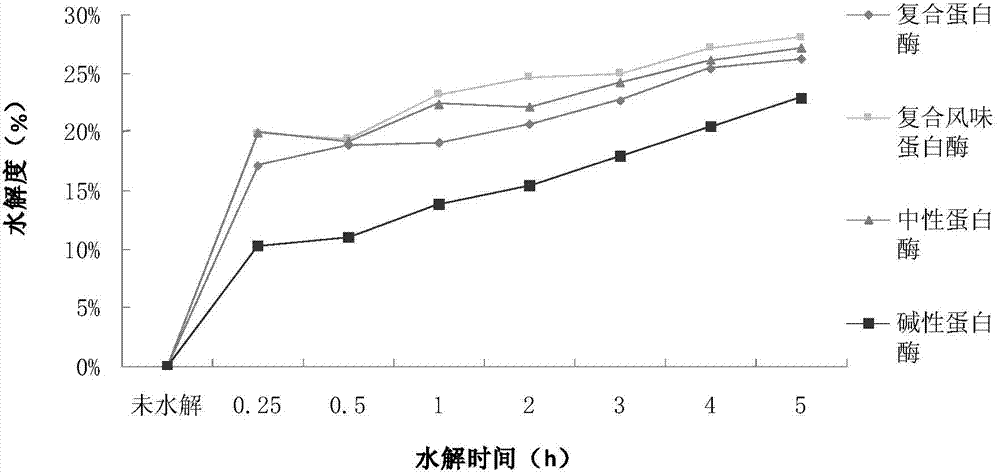
ActiveCN104120160APromote fragmentationAvoid adverse effects such as nutrient lossMicroorganism based processesFermentationHydrolysateWater soluble
The invention discloses a preparation method for a chlorella anti-oxidative peptide. The preparation method is as follows: by taking chlorella as material, carrying out wall-breaking treatment on the chlorella to obtain soluble protein by utilizing a dilute alkali swelling-combined ultrasonic-wave process; and hydrolyzing the chlorella protein by a biological enzyme method to obtain the chlorella anti-oxidative peptide with remarkable anti-oxidative effect. The invention further discloses a treatment process combining ultralow temperature treatment, high pressure treatment with dilute alkali swelling and ultrasonic waves, which can improve yield of the water-soluble protein and can further improve anti-oxidative ability of hydrolysate. A product obtained by virtue of the preparation method disclosed by the invention is high in purity and strong in anti-oxidative activity.
Owner:安徽汉芳生物科技有限公司
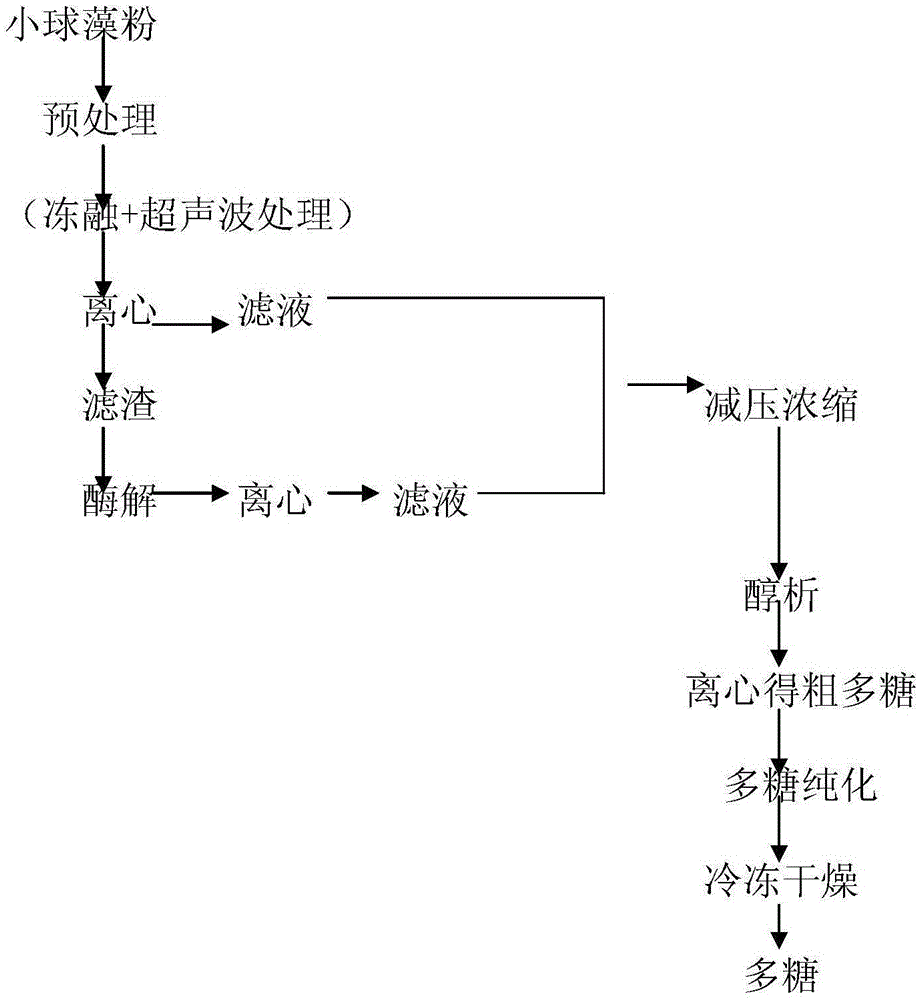
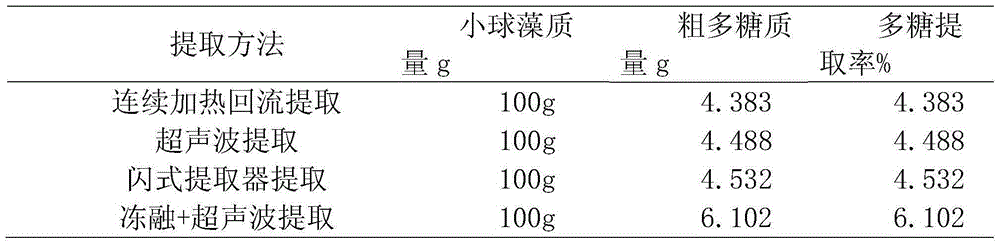
Chlorella polysaccharide extraction method
The invention discloses a chlorella polysaccharide extraction method, and relates to the technical field of marine organisms. Cell walls are completely broken through alternate freezing and thawing; meanwhile, the bad influences that nutrition of raw materials is lost and effective components of the raw materials are seriously destroyed due to high temperature are avoided by combining an ultrasonic-assistant extraction method, and polysaccharides in chlorella cells can be promoted to be quickly dissolved out. Compared with a traditional polysaccharide extraction method, the chlorella polysaccharide extraction method has the advantages of being low in energy consumption, high in polysaccharide extraction rate and recovery rate and low in production cost. According to the method of combining alternate freezing and thawing with ultrasonic extraction, the chlorella polysaccharide extraction rate is 1.34-1.39 times of that of the traditional extraction method, and the recovery rate is 1.1-1.58 times of that of the traditional extraction method.
Owner:都宝君
Special penaeus orientalis functional biological feed in the thickness marking period
The present invention discloses a special penaeus orientalis functional biological feed in the thickness marking period and the functional biological feed consists of the following components: import fish meal, shrimp meal, fermented peanut meal, fermented soybean meal, yeast lysates, cuttlefish powder, high gluten flour, calcium dihydrogen phosphate, soybean lecithin, fish oil, vitamin-mineral premixes, probiotics and functional additives; wherein the probiotics consist of Bacillus subtilis subsp., Candida utilis yeast and Bifidobacterium longum; the functional additives are made of natural astaxanthin, linolenic acid, fermented chlorella and fermented spirulina. The functional biological feed aims at the physical characteristics of high density, high nutrition and fast growth of penaeus orientalis seedlings in the thickness marking period, uses high-quality animal protein, contains high levels of unsaturated fatty acids and bio-fermentation raw materials, is rich in lecithin, has a reasonable balance ratio of calcium and phosphorus, and fortified vitamin nutrition, adds immunoenhancers, living beneficial bacteria and digestive enzymes, promotes the rapid growth, enhances disease resistance and improves survival rate of penaeus orientalis seedlings which have strong body constitution and tidy specifications, and lay a solid foundation for subsequent successful breeding.
Owner:YANTAI DALE FEED CO LTD
Skin firming and lifting compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS20080292651A1Improve skin appearanceReducing and preventing sign of agingBiocideCosmetic preparationsPolygonum fagopyrumBambusa vulgaris
Disclosed is a composition comprising a combination of: Polygonum fagopyrum seed extract, Chlorella vulgaris extract, palmitoyl wheat protein hydrolysate, algae extract, and tripeptide. The composition may further comprise one or more of the following: Citrus unshiu peel extract, Sphacelaria scoparia extract, Bambusa vulgaris extract, Pisum sativum (pea) extract, Evodia rutaecarpa fruit extract, and dipalmitoylhydroxy proline. Such compositions are useful in methods for aiding in improving skin firmness, lifting the skin, preventing or decreasing skin sagging, and preventing or decreasing visible signs of aging resulting from internal and external causes such as environmental stresses.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Chlorella and application thereof
InactiveCN101824386AImprove fixation efficiencyIncrease productionUnicellular algaeDispersed particle separationBiodieselMicrobiology
The invention discloses a strain of chlorella, which is classified to be named as chlorella vulgaris and is preserved in China Centre for Type Culture Collection, and the preservation number is CCTCC NO.: M 209256. The invention also discloses the application of the chlorella in producing microalgae oil and fixing CO2. The chlorella can endure 24.5% of CO2 concentration, the content of grease can reach 17-31%, and the invention has higher CO2 fixing efficiency than ordinary seawater algae, and can obtain high-yield microalgae oil by selecting appropriate culture conditions, so the culture cost of the microalgae can be greatly reduced, and a good production strain is provided for preparing biodiesel by the microalgae oil.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105559064APromote absorptionEnhance immune functionFood ingredient functionsImmunologic functionCancer cell proliferation
The invention provides five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets and a preparation method thereof. The five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets are prepared from the following raw materials in parts by mass: 10-20 parts of chlorella vulgaris, 1-10 parts of dunaliella salina, 1-10 parts of euglena, 1-10 parts of red algae, 10-20 parts of spirulina and 10-20 parts of probiotic powder. The five-alga probiotic enzyme tablets provided by the invention adopt the chlorella, dunaliella salina, red algae, spirulina and euglena for complementation in nutrition, and obtain trace elements easier to absorb by a human body through probiotic fermentation, thereby helping to reinforce the immunologic function of the human body, resist virus infection and proliferation, inhibit cancer cell proliferation, repair the damage of an organism quickly, remove vivotoxin, suppress blood pressure and blood sugar rise, reduce the serum cholesterol content, and thus improve the comprehensive conditioning of the human body.
Owner:于蜀豪 +1
Method for synthesizing astaxanthin by inducing chlorella vulgaris by using plant hormones and iron ions
ActiveCN103045709ASynthesis fastEfficient accumulationMicroorganism based processesFermentationPlant hormoneAstaxanthin
The invention belongs to the field of microalgae biotechnologies, and particularly relates to a method for synthesizing astaxanthin by inducing chlorella vulgaris by using plant hormones and iron ions. The method specifically comprises the steps of: activating and culturing the chlorella vulgaris in a liquid culture medium to obtain a synchronously growing chlorella vulgaris solution for later use; and taking the chlorella vulgaris solution growing to an exponential growth phase, adding the plant hormones and the iron ions in the chlorella vulgaris solution, replenishing a carbon source and a nitrogen source for culturing, ending the culturing until the accumulation of the astaxanthin in chlorella vulgaris cells is maximum (the accumulation of the astaxanthin is determined by adopting a liquid chromatography during sampling), and harvesting cell disruption and extracting the astaxanthin. The method is simple and easy to operate and low in cost, and is capable of remarkably increasing the yield of the astaxanthin, thereby greatly increasing the efficiency of producing the astaxanthin by the chlorella vulgaris.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Production method of high-quality microalgae biodiesel
ActiveCN103451101AImprove qualityQuality adjustmentUnicellular algaeBiofuelsBiodieselPhotobioreactor
The invention relates to a production method of high-quality microalgae biodiesel. The method includes: inoculating Chlorella vulgaris (CCTCC: M209256) seeds into a photobioreactor loaded with a fermentation medium, at a first fermentation stage, controlling the illumination intensity at 8-10Klux, the initial pH at 6.0-7.5, the ventilation intensity at 0.4-0.7VVM, the concentration of CO2 at 0.5-2.0%, and the temperature at 24-26DEG C; at a second fermentation stage, keeping the illumination intensity at 30-70Klux, the ventilation intensity at 0.4-0.7VVM, the concentration of CO2 at 0.5-2.0%, and the temperature at 27-30DEG C, and finishing fermentation when the algal liquid turns into light yellow or the chlorophyll in the algae declines substantially. The algal cells obtained by the method have an oil content of over 35%, a stable CN value of more than 50, and a ratio of unsaturated fatty acid to saturated fatty acid at 1.5-2.4.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Chlorella autotrophic-heterotrophic mixed culture method
InactiveCN104357330AImprove qualityUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesQuality cultureHigh density
The invention discloses a Chlorella autotrophic-heterotrophic mixed culture method, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps: heterotrophic culture of Chlorella in mechanical-stirring fermentation tank, Chlorella solution dilution, and optical autotrophic culture of Chlorella. By using the method, the Chlorella can achieve high-density culture level in a short culture period, and the quality of Chlorella is greatly enhanced as compared with that of the Chlorella subjected to heterotrophic culture, thereby achieving the optical autotrophic culture level and implementing high-density high-quality culture of Chlorella.
Owner:GANSU DEFU BIOTECH
Method for cultivating chlorella by heterotrophic nutrition fermentation
InactiveCN101481656AGrowth inhibitionRealize efficient heterotrophic fermentation cultureUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesPotassium nitrateThree stage
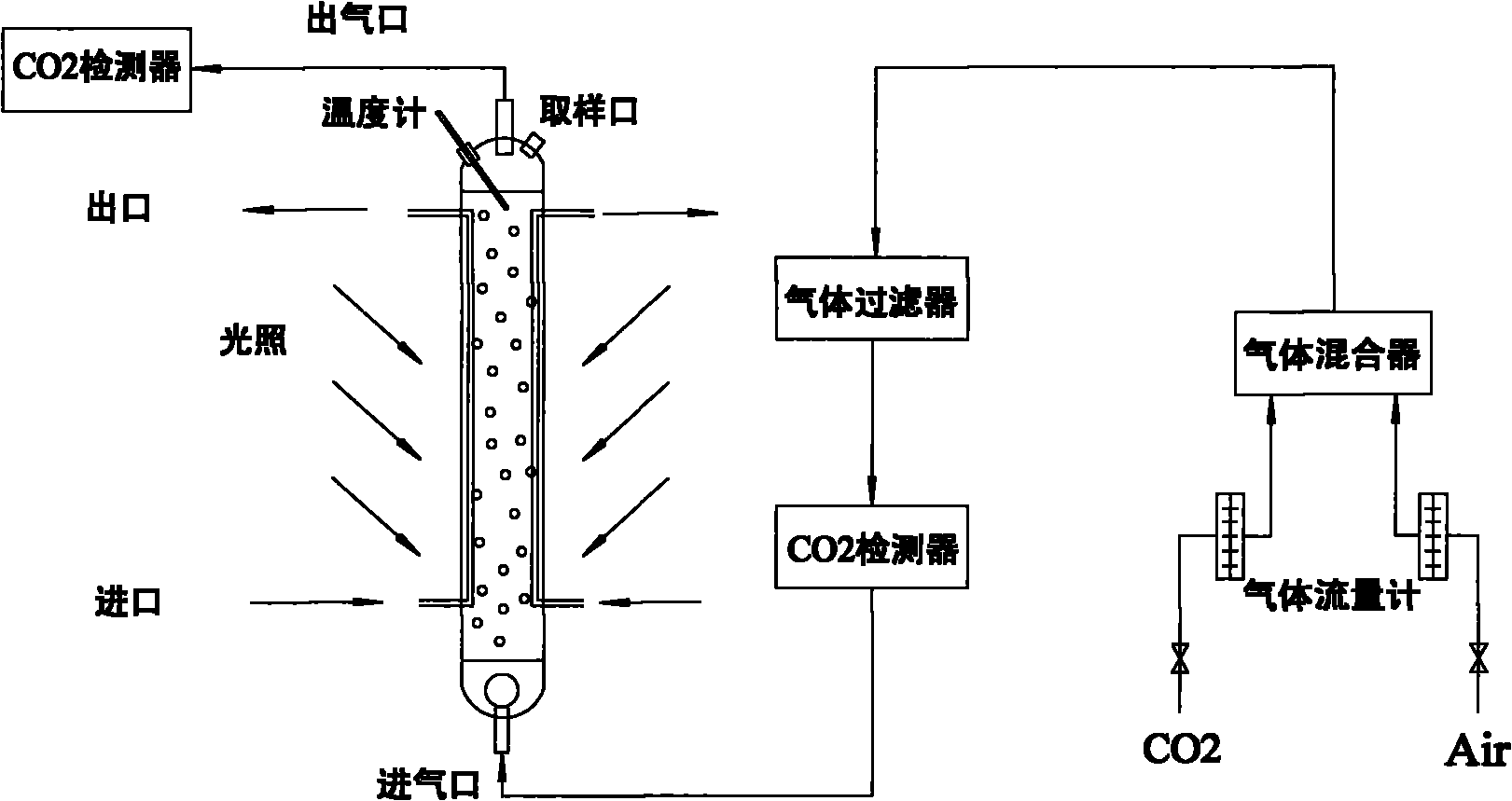
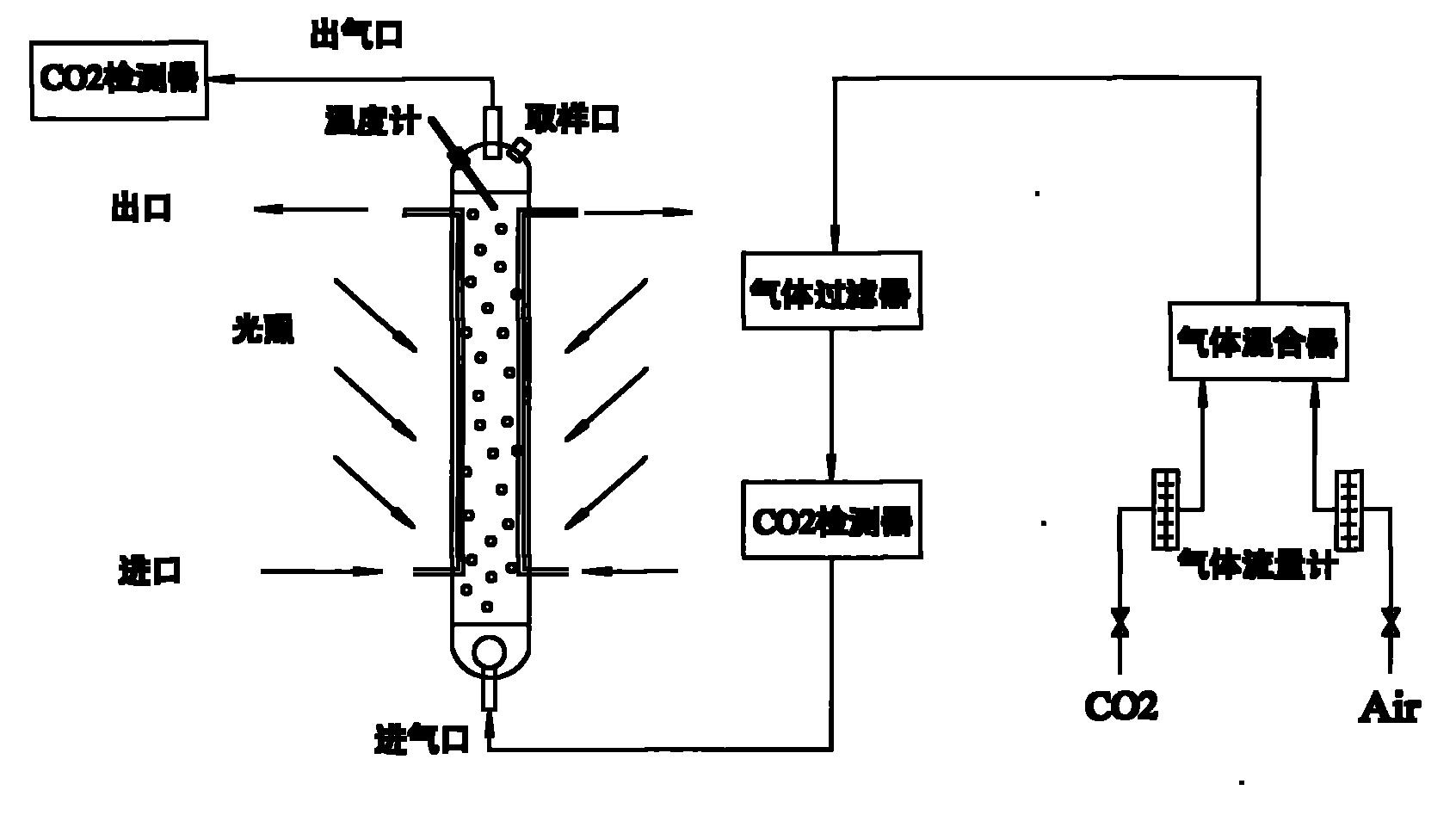
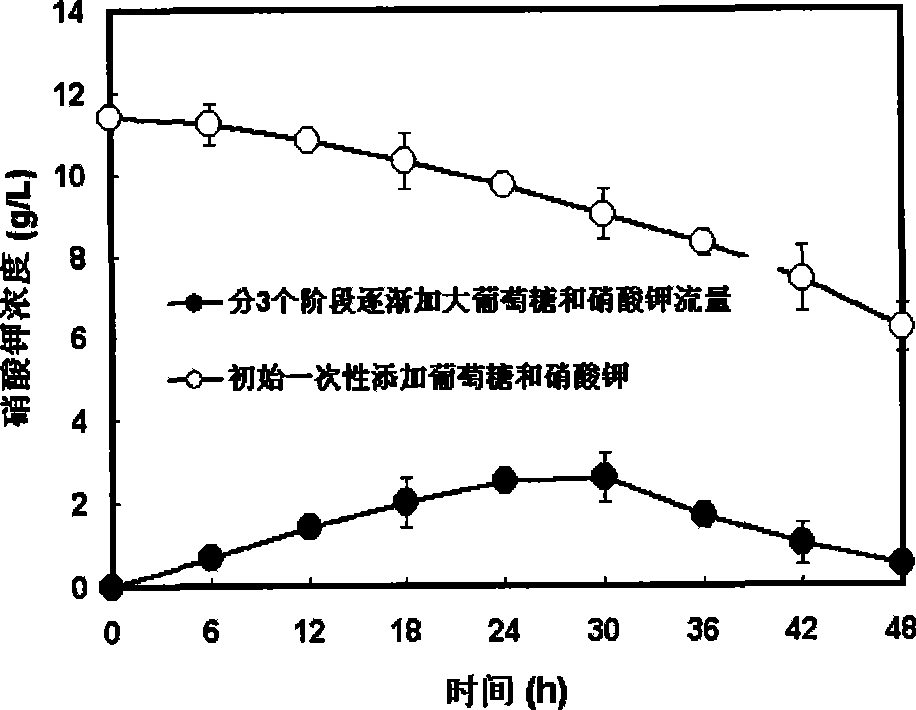
A method of heterotrophic culture of chlorella in fermentor belongs to the biotechnology field. The method adopts chlorella USTB-01 (culture collection number: CGMCC No. 1448, and collection date: Aug. 25, 2005) which is obtained after being screened. In the process of heterotrophic culture of chlorella USTB-01 in fermentor, the flow amounts of glucose and potassium nitrate are increasingly raised at three stages according to the different growing periods of chlorella USTB-01, so as to ensure the quick growth of chlorella USTB-01. After 2 days of culture, over 45g / L of chlorella biomass can be obtained. Therefore, the method lays a foundation for the efficient industrial heterotrophic culture of the chlorella in fermentor.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
A kind of co-cultivation method of freshwater rotifers and chlorella
ActiveCN102273431AGuaranteed normal reproductionAvoid breedingUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesFresh water organismSafety control
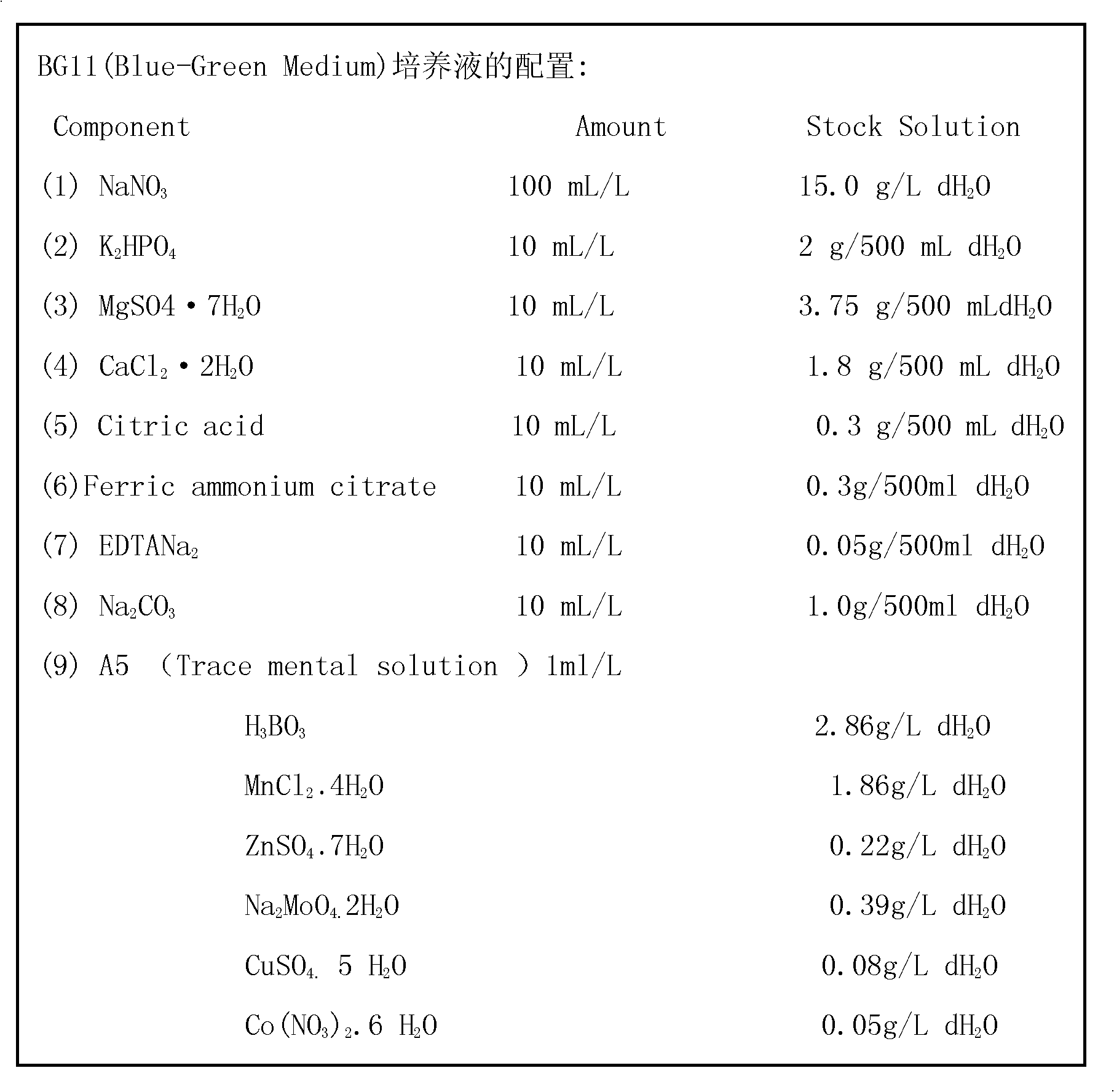
The invention discloses a method for separating dominant rotifers and co-culturing the dominant rotifer and chlorella vulgaris in an O3 / BAC (biological activated carbon) advanced treatment process, which comprises the following steps of: a. determining the rotifers in the O3 / BAC advanced treatment process: researching population structures of planktonic animals in various process flows of waterplant ozone activated carbon advanced wastewater treatment, sampling and respectively quantitatively and qualitatively analyzing; b. separating the dominant rotifers in the O3 / BAC advanced treatment process: acclimating in dark at room temperature over night, picking up health and lively adults by using a dropper for further culturing; c. culturing the chlorella vulgaris: grafting purified single chlorella vulgaris in a Blue-Green Medium culture solution; d. carrying out adaptability on the rotifers: directly grafting the rotifers with the initial grafting density of 10-30 / L in the cultured chlorella vulgaris solution; e. co-culturing: co-culturing according to the initial grafting density of the rotifers; and f. subcultring: if the rotifers in a culturing system is dead, transiting the rotifers for subcultring. Co-culturing the dominant rotifers indoors for a longer time in the O3 / BAC advanced treatment process is realized, and the density of the rotifers is maintained at 400-600 ind / ml. Particularly, experimental material is provided for safety control and risk assessment research of the rotifers in life drinking water.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Common chlorella as well as culturing method and application thereof
ActiveCN102586116ALow costStrong toleranceUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesSpecial designOil production
The invention provides a common chlorella, which is chlorella C9-JN2010 with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M2010373; and the invention further provides a culturing method of the common chlorella. The culturing method comprises the following steps: using secondary outlet water, which is obtained by treating municipal sewage and / or industrial sewage in a sewage treatment plant, as a culture medium; and culturing the chlorella after the chlorella is inoculated, wherein the initial inoculating density is 1.0 multiplied by 107 cfu / ml-6.0 multiplied by 107 cfu / ml, and the culturing conditionis that the light cycle is 10h:14h-16h:8h, the light intensity is 5000-15000 lux, the culturing temperature is 20-30 DEG C, the pH value is 6.5-8.5, the CO2 gas throughput is 0.01-0.2 VVm, and the CO2 concentration is 15.0%-30.0% (v / v). The invention further provides an application of the common chlorella in sewage treatment and oil production. The common chlorella provided by the invention has the advantages of strong CO2 tolerance and high production strength; through the adoption of the culturing method provided by the invention, the sewage treatment and the production of the biological energy are combined with other side products (such as proteins, cosmetic raw materials, and animal feeds), so that the production cost is reduced, the waste resources are comprehensively utilized as well as the energy-saving and emission reducing green production is realized; and the culturing method provided by the invention has the advantages of skillful and special design as well as suitability for being popularized and applied on a large scale.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Skin firming and lifting compositions and methods of use
ActiveUS7700110B2Improve skin firmnessLifting skinBiocideCosmetic preparationsPolygonum fagopyrumBambusa vulgaris
Disclosed is a composition comprising a combination of: Polygonum fagopyrum seed extract, Chlorella vulgaris extract, palmitoyl wheat protein hydrolysate, algae extract, and tripeptide. The composition may further comprise one or more of the following: Citrus unshiu peel extract, Sphacelaria scoparia extract, Bambusa vulgaris extract, Pisum sativum (pea) extract, Evodia rutaecarpa fruit extract, and dipalmitoylhydroxy proline. Such compositions are useful in methods for aiding in improving skin firmness, lifting the skin, preventing or decreasing skin sagging, and preventing or decreasing visible signs of aging resulting from internal and external causes such as environmental stresses.
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Chlorella preservation method
ActiveCN105779293AAvoid transportation inconvenienceGuaranteed reliabilityMicroorganism based processesMicroorganism preservationSterile waterGlycerol
The invention provides a chlorella preservation method. The preservation method comprises the following steps of: at normal temperature, mixing chlorella concentrated solution with sterile water in a volume ratio of (1-3):1, and then adding glycerol, tea extract and potassium sorbate for preservation, wherein the mass final concentration of glycerol is 1-4%, the mass final concentration of tea extract is 1-4%, and the mass final concentration of the potassium sorbate is 0.04-0.08%. The chlorella preservation method has the advantages that a preservation technology is simple, enlarged production can be easily realized, aiming at solving the problems that chlorella can be easily polluted due to misoperation in a preservation process and important indexes such as biomass, chlorophyll and active polysaccharide of chlorella after resurrection decline quickly, a safe and efficient protective agent is screened and compounded, and storage and transportation can be carried out at normal temperature, so that low temperature energy consumption and transportation inconvenience are avoided.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Use of chlorella in food
InactiveCN102246964AIncrease nutritionHigh protein contentDough treatmentFood preparationVitamin CPotassium
The invention relates to the use of chlorella in food. The food component disclosed by the invention comprises wall-broken chlorella concentration or wall-broken chlorella dry powder, wherein the wall-broken chlorella concentration or wall-broken chlorella dry powder accounts for 0.4 to 0.8 percent of the total weight of the food component; and active carbon accounts for 0.05 to 0.08 percent of the weight of the wall-broken chlorella concentration or wall-broken chlorella dry powder. The food component comprises wheat flour which accounts for 85 to 98 percent of the total weight of the food component. In the invention, the wall-broken chlorella concentration or wall-broken chlorella dry powder is used to process biscuits, moon cakes, noodles, candies and other foods. The chlorella has the following food nutritional characteristics: 1, the protein content is higher than 50 percent; and 2, the vitamin content and mineral content are high, and the content of vitamin C, vitamin A, vitamin B and minerals such as calcium, potassium, iodine, iron and the like is 80 times higher than that in common food, and when the chlorella is added into food, enough nutrients required by human bodies are supplied.
Owner:张炳泉
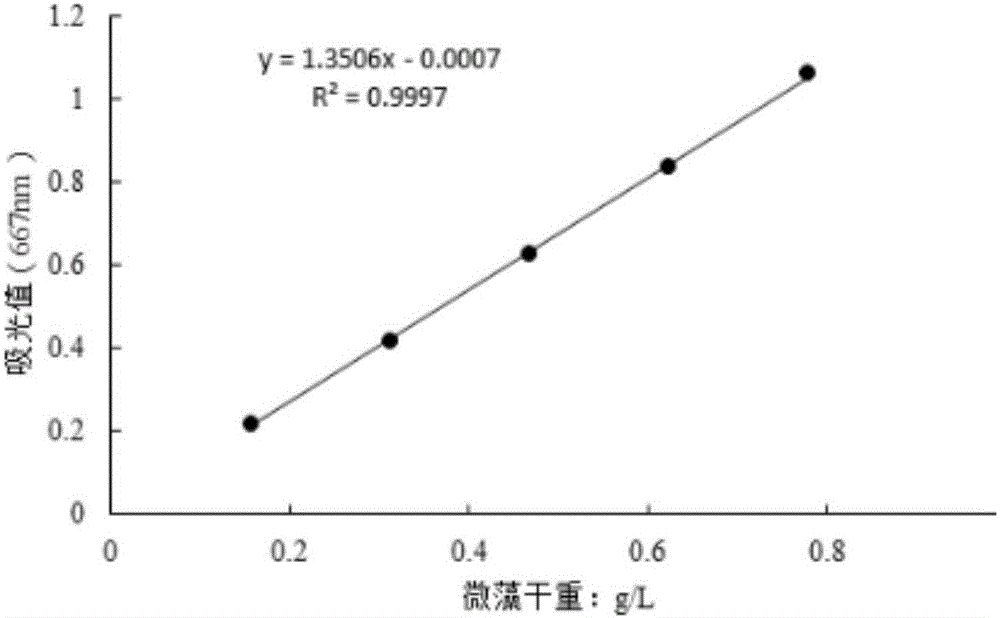
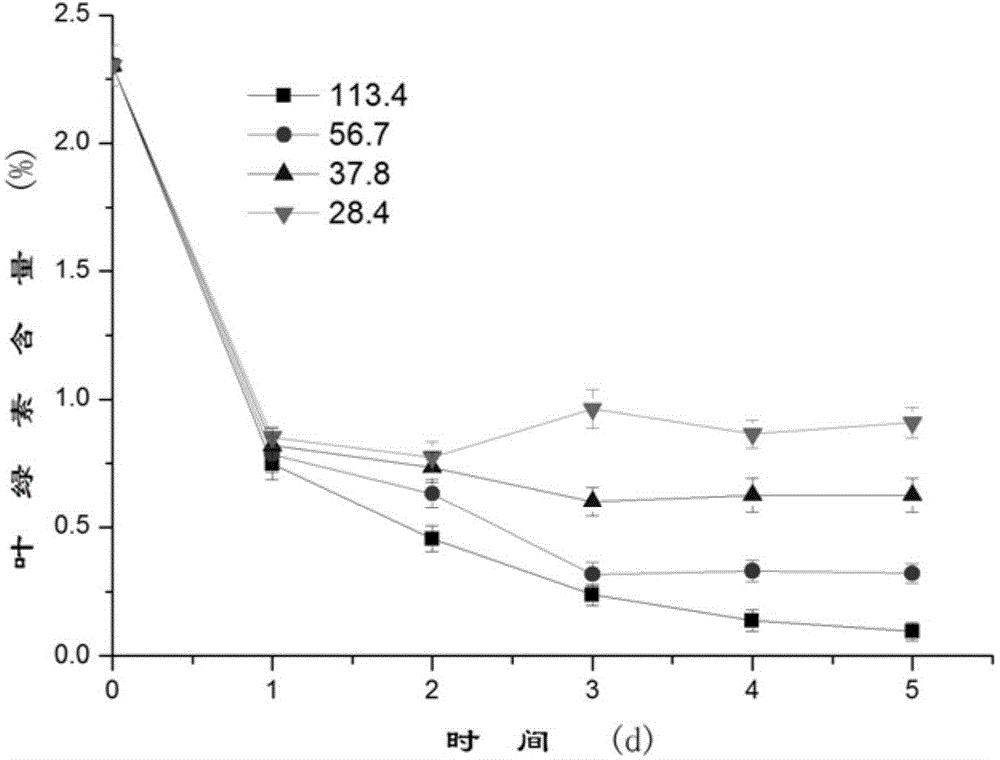
High-density culture method for improving chlorophyll and protein content of chlorella at same time
InactiveCN104152357AHigh density stateEfficient accumulationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesHigh densityMicrobiology
The invention provides a high-density culture method. The high-density culture method comprises the following steps: (1) activated chlorella is cultured with successive illumination to enable the chlorella to be in logarithmic phase; (2) the culture solution of the chlorella which is in the logarithmic phase in the step (1) is used as a seed solution and collected in a heterotrophic fermentation container for heterotrophic culture in darkness with the culture temperature of 28-35 DEG C and the culture time of 3-5 days, the carbon nitrogen ratio of a culture medium used in the heterotrophic fermentation container is 28.4-113.4; (3) the culture solution of the chlorella is diluted until the cell density of the chlorella reaches 10-20 g / L, a nitrogen source is added into the culture solution of the chlorella to enable the culture solution of the chlorella to contain 14.7-88.2 mol / L of nitrogen, the chlorella is conducted with photoinduction culture with the culture temperature of 20-35 DEG C and the culture time of 1-3 days. According to the invention, the culture method can improve the chlorophyll and protein content of the chlorella at the same time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Horticultural crop composite biological nutrient medium and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102503666AHas antibacterial activityDoes not affect absorptionFertilizer mixturesCellulosePolyacrylamide
The invention relates to a horticultural crop composite biological nutrient medium which comprises a substrate, and microalgae and a culture fluid thereof. The horticultural crop composite biological nutrient medium is characterized by comprising the following components in percentage by mass: 1.5-5.5% of sodium alginate, 0.5-3.5% of chitosan, 0.5-5.5% of polyacrylamide, 1-5% of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose, 5-20% of shell powder and 60.5-91.5% of clay. The microalgae are fresh water Chlorella which can be autotrophic, heterotrophic or mixedly cultured after being cultured to later exponential growth phase, the concentration is greater than or equal to 3.0*10<6>cell / ml, and the addition amount is preferably sufficient in the substrate without flowing. The invention has the effects of moisture retention, nutrient slow release and soil improvement; most materials are aquiculture byproducts, thereby changing wastes into valuable substances and having obvious environmental protection effect; and the nutrient medium can be completely degraded within 3-5 years, and can not have permanent damage on soil. The microalgae reserved in the soil can have an active effect on the soil, increase the soil fertility and improve the physical and chemical properties of the soil.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Loach fry breeding method
InactiveCN103548731ASolve the problem of survival rateAvoid influenceClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaFisheryPond loach
The invention discloses a loach fry breeding method which includes the steps: sunning a V-shaped breeding pond until cracks and white coverings are formed at the bottom of the V-shaped breeding pond, and then injecting non-pollution water into the V-shaped breeding pond; placing chlorella into the pond to cultivate the water two days before feeding water spots into the pond, and adding the chlorella into the breeding pond every three days; adding tubificidae into the breeding pond after 7 days, performing pest control by fish insecticides with traditional Chinese medicine materials within 7-9 days; stopping use of the chlorella and mainly using the tubificidae and fish mash feed with 32 proteins after 14-16 days; stopping use of the tubificidae and completely using the feed for breeding after 22-24 days. The dosage of the fish insecticides is 0.4 gram per cubic meter of water, the usage amount of the feed is 80 grams per 10,000 loach fries every day, and finished inched fries are obtained after 28-30 days. The loach fry breeding method has the advantage that the survival rate of loach fry production is high.
Owner:GUIZHOU QIUXING AQUATIC PROD
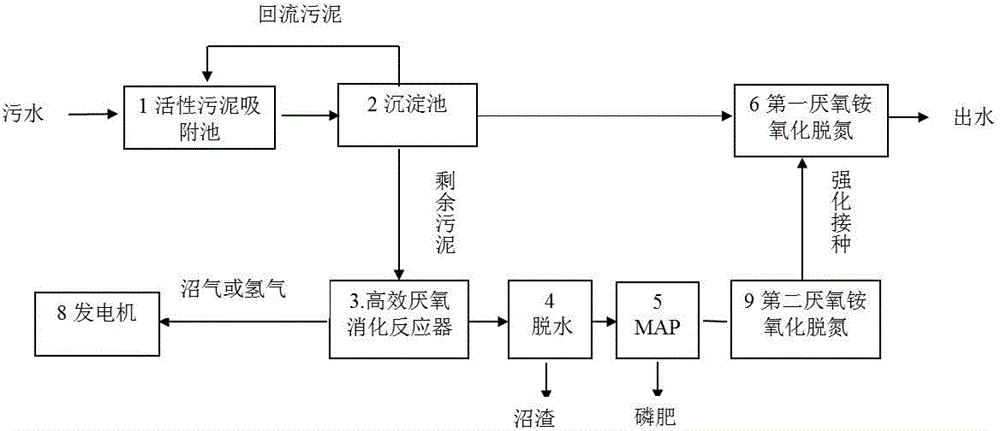
Efficient, energy-saving and consumption-reducing sewage treatment method for resource recovery
ActiveCN104609660AAvoid churnSolve the mud age contradictionWaste based fuelTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesActivated sludgeMagnesium ammonium phosphate
The invention relates to an efficient, energy-saving and consumption-reducing sewage treatment method for resource recovery. Inflow sewage and return sludge are sufficiently mixed in an activated sludge adsorption tank, most carbon and a small part of nitrogen in the sewage are transferred to the return sludge, effluent enters a settling pond for solid-liquid separation, clear water and residual sludge are drained, the residual sludge enters an efficient anaerobic digestion reactor, hydrogen or biogas and digested sludge are obtained, biogas slurry produced after dewatering of the digested sludge is conveyed into a fluidized bed reactor provided with a settling zone through MAP (magnesium ammonium phosphate), and part of residual biogas slurry obtained with an MAP method and clear water drained from the settling pond enter an anaerobic ammonium oxidation, denitrification and oxidation system respectively for denitrification; or, the clear water drained from the settling pond and the biogas slurry are merged, and denitrification treatment is performed through dominant algae and nitrogen-fixing bacteria; dominant algae adopt chlorella; finally, water is discharged. Carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus elements in sewage can be comprehensively utilized, and the method has the advantages of energy outward transportation, phosphorus recovery, low nitrogen transformation energy consumption or nitrogen recovery, greatly shortening of the reaction time and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Methods of treating impaired glucose metabolism via administration of algal biomass
InactiveUS20120027724A1Lower mean plasma glucose concentrationDecreasing concentration of plasma glucoseOrganic active ingredientsBiocideDry weightIntestinal microorganisms
The invention is directed to methods of using Chlorella protothecoides microalgal biomass in the treatment of individuals having impaired glucose metabolism. In some cases, the patient has impaired fasting glucose, impaired glucose tolerance, or diabetes. In some methods, algal biomass is used to reduce blood glucose and / or body fat in a subject, or to increase the relative abundance of beneficial gut microflora in a subject. In preferred embodiments, the biomass is derived from Chlorella protothecoides cultures grown heterotrophically in which the algal cells comprise at least 15% algal oil by dry weight.
Owner:CORBION BIOTECH INC +1
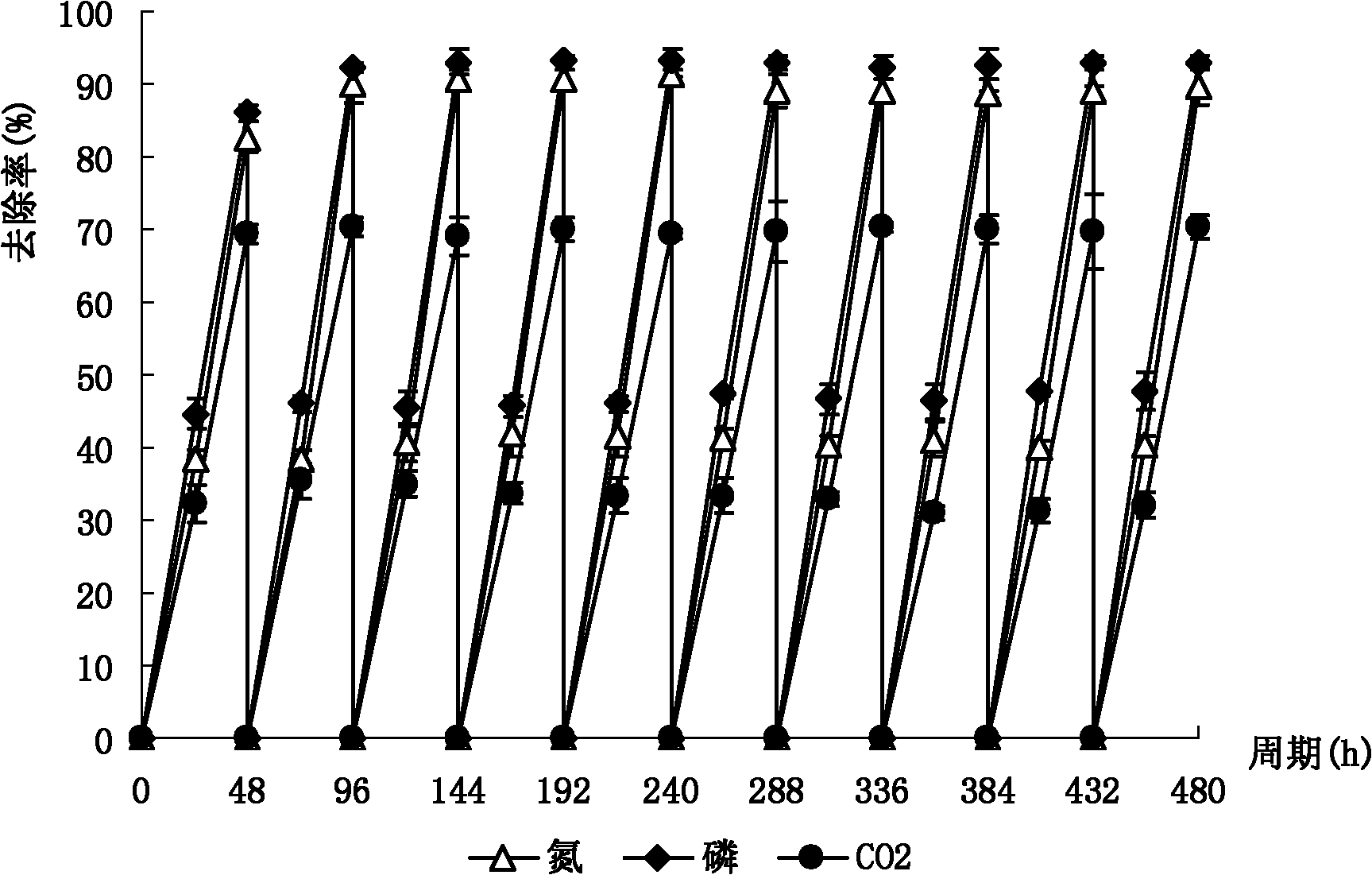
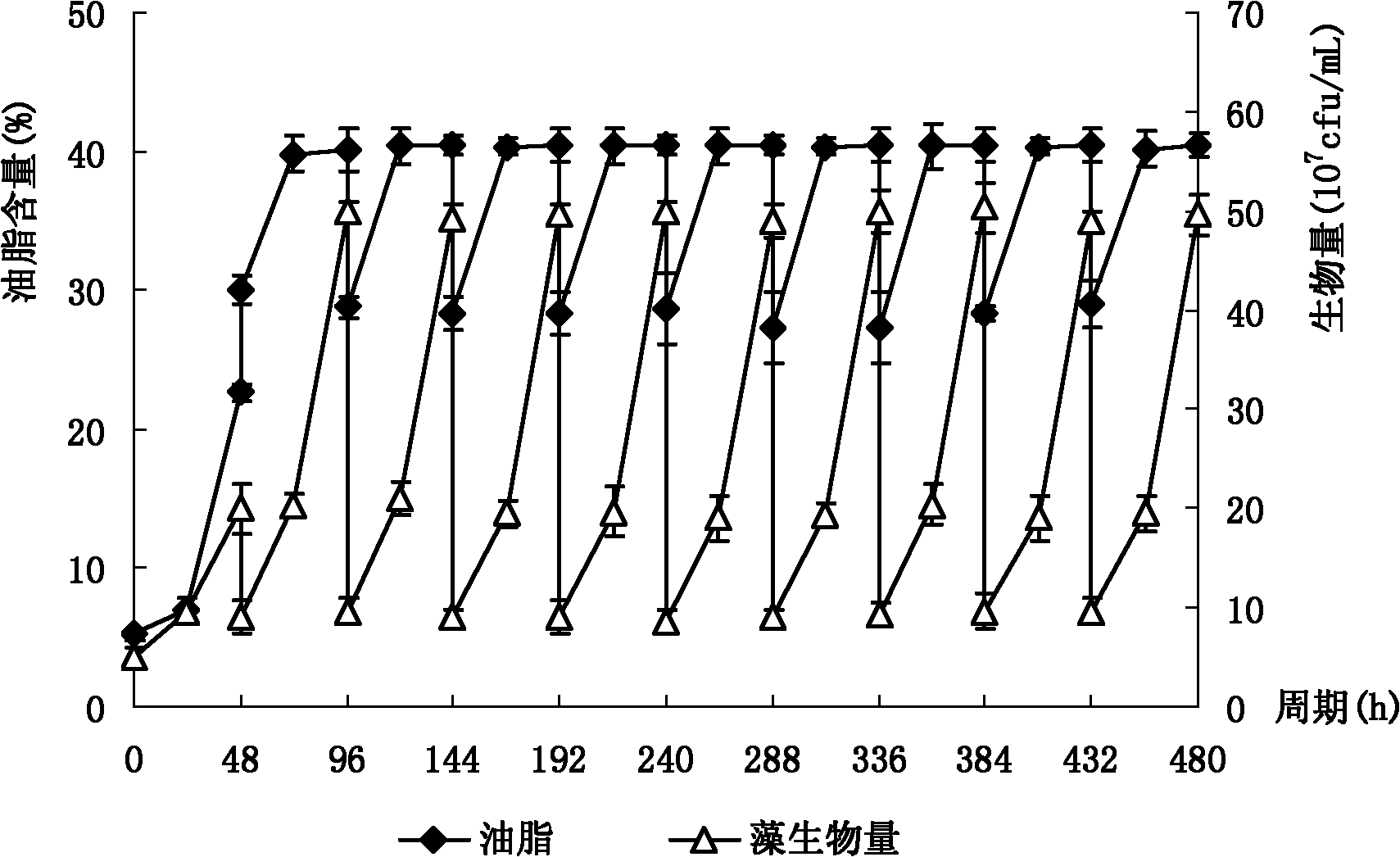
Chlorella vulgaris used for combined treatment of wastewater and waste gas while synchronously realizing solid carbon denitrification
ActiveCN106399109AStrong anti-pollutionEfficient removalGas treatmentUnicellular algaeSolid carbonBiodiesel
The invention relates to the field of wastewater and waste gas pollution control and microalgae biodiesel production, and particularly relates to chlorella vulgaris used for combined treatment of wastewater and waste gas while synchronously realizing solid carbon denitrification, in particular to chlorella vulgaris DH2 used for treating municipal sewage and thermal power plant flue gas while synchronously realizing grease accumulation. An algae species is provided for using microalgae technology for wastewater and waste gas treatment while coproducing biodiesel. Chlorella vulgaris is named as DH2, collected at the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on 28th, Sep. 2016 and registered under the number of CGMCC13056. Chlorella vulgaris has high anti-pollution capability, can grow, propagate and accumulate grease in actual sewage, can effectively remove pollutants like nitrogen and phosphorus in high-nitrogen-content municipal sewage and can realize wastewater and waste gas resource transformation.
Owner:LIAONING DONGKE ELECTRIC POWER
Defensin mNP-1 and applications thereof in preparing anti-influenza virus drugs
The invention relates to defensin mNP-1 which utilizes chlorella to express modified rabbit defensin NP-1(Mnp-1), the defensin expressed in the chlorella has strong inhibition or skilling effect on bird flu virus H5N1 and H9N2. The result of the invention can be applied for preparing anti-influenza virus drugs.
Owner:北京中加保罗生物科技有限公司
Separation method of chlorella species for high production of polysaccharide
ActiveCN105713837AHigh in polysaccharidesIncrease osmotic pressureUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesVitamin CGlycerol
The invention relates to economic microalgae research and development application, and aims at providing a separation method of a chlorella species for high production of polysaccharide. The method comprises the following steps: adding glycerol, rhamnose and vitamin C to a Basal culture solution, so that a culture solution HPSC-M of the chlorella species for high production of the polysaccharide is obtained; and separating epiphytic algae from stems of wild dendrobium officinale, and conducting pressure screening in a high-temperature dry environment, so that the chlorella for high production of the polysaccharide is obtained. The method disclosed by the invention, compared with a conventional breeding method, has the characteristics of being simple and convenient to operate, low in cost, free from special requirements on the professional skills of operators, strong in applicability and the like; and a necessary technical method is provided for chlorella breeding.
Owner:汪凡越
Alexin and application thereof to preparation of antibacterial medicament
The invention expresses a refitted rabbit defensin NP-1 (mNP-1) by using chlorella. The defensin expressed in chlorella has a very strong inhibiting or killing effect on Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-positive bacteria and the like, and can be used for killing medicament-resistant bacteria. A result of the invention can be applied to preparation of a medicament which is resistant to the Gram-negative bacteria and the Gram-positive bacteria, and can be applied to preparation of medicament which is resistant to super bacteria.
Owner:北京中加保罗生物科技有限公司
Functional compound feed special for turbot
InactiveCN104543463AGrow fastPrevention and treatment of red mouth diseaseAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyJuvenile fish
The invention discloses a functional compound feed special for turbot. The functional compound feed consists of the following components: Peru fish meal, shrimp shell meal, a beer yeast, corn protein, fermented peanut meal powder, bread powder, calcium dihydrogen phosphate, premixed materials for fish, probiotics, imported fish oil, wheat germs, whey powder and xanthan gum, wherein the probiotics consist of freeze-dried powder of saccharomycetes, bacillus subtilis, tea polysaccharide, dunaliella salina powder, sargassum thunbergii powder and chlorella vulgaris powder in proportions. According to the turbot fed by the feed disclosed by the invention, main delicate flavor materials in muscles can be significantly increased, and the total contents of amino acids, total contents of essential amino-acids, total contents of unsaturated fatty acids and the like are improved to different extents; all indexes such as muscle strength, freshness, fishy smell and taste can be significantly improved; and the immunities of juvenile fish and adult fish can be significantly improved, so that red mouth diseases and albinism of the turbot can be effectively prevented and treated. The feed disclosed by the invention is environmentally-friendly and pollution-free in raw material, and is suitable for large-scale cultivation of the turbot.
Owner:QINGDAO RENHAI AQUATIC PROD FEED TECH
Nutritional meal replacement powder containing spirulina components, and production method thereof
InactiveCN105724917APhysiological balanceTo promote metabolismFood preparationBiotechnologyVegetable oil
The invention discloses a nutritional meal replacement powder containing spirulina components, and a production method thereof. The nutritional meal replacement powder mainly comprise spirulina powder, chlorella pyrenoidosa powder, dunaliella salina powder, euglena powder, soybean protein isolate powder, microencapsulated soybean plant oil powder and edible salt. The nutritional meal replacement powder is produced through the steps of crushing, mixing, split packaging and packaging. The nutritional meal replacement powder is produced through compounding the spirulina powder, the chlorella pyrenoidosa powder, the dunaliella salina powder and the euglena powder according to a scientific ratio, and purifying the above mixture, and can be digested and absorbed by human bodies to realize physiologic balance, promote metabolism and enhance immunity. The nutritional meal replacement powder is a comprehensive nutrition set meal containing abundant proteins, chlorophylls, vitamins, mineral matters, calcium, iron, zinc and selenium. The nutritional meal replacement powder is convenient to carry and eat.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG JOHNSUN BIOLOGICAL ENG CO LTD
Method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting astaxanthin in C.zofingiensis cells
ActiveCN104964957AEasy to handleSimplify detection stepsFluorescence/phosphorescenceAstaxanthinLinear regression
The invention provides a method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting astaxanthin in C.zofingiensis cells. The method comprises the following steps of (1) re-suspending algal cells collected from a known C.zofingiensis suspension sample to regulate the known C.zofingiensis suspension sample into heavy suspension with cell density of 6*10(5) to 2*10<6>CFU / mL by virtue of de-ionized water or a phosphate buffer solution, detecting the average fluorescence intensity of the heavy suspension in an FL1 channel or an FL2 channel by virtue of a flow cytometer, and performing linear regression on a log value of the content of astaxanthin in the known C.zofingiensis suspension sample and a log value of the corresponding measured average fluorescence intensity in the FL1 or FL2 channel to obtain a standard curve; (2) preparing a sample to be detected: re-suspending algal cells collected from C.zofingiensis suspension to be detected to regulate the C.zofingiensis suspension to be detected into algal cell heavy suspension to be detected with cell density of 6*10(5) to 2*10<6>CFU / mL by virtue of de-ionized water or a phosphate buffer solution; (3) detecting the average fluorescence intensity of the sample to be detected in the FL1 channel or the FL2 channel by virtue of the flow cytometer, and calculating the content of astaxanthin in the sample to be detected according to the standard curve obtained in step (1). The method has the characteristic of high detection efficiency.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Environment-friendly microalgae cultivating method
InactiveCN108546648ALow costReduce fixed processing costsBacteriaUnicellular algaeSludgeEconomic benefits
The invention discloses an environment-friendly microalgae cultivating method, and belongs to the field of environmental engineering and microalgae biotechnologies. The method is capable of using CO2in different concentrations as a carbon source of chlorella growth, adding the CO2 to sludge dehydrated liquid, and improving a biomass of chlorella. The method has the advantages of using a flue gasCO2 as the carbon source which is added into the sludge dehydrated liquid for cultivating the chlorella, generating a biomass energy and recycling nitrogen and phosphorus in sewage at the same time, and reducing the cost of sewage treatment. The environmental benefit and the economic benefit are realized simultaneously. In addition, the chlorella absorbs and uses the CO2, the setting treatment cost of the CO2 is reduced, and other nitrogen-phosphorus and carbon sources cannot be added in a cultivation process so as to obtain the considerable biomass.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for screening high-lipid content mutant microalgae strain
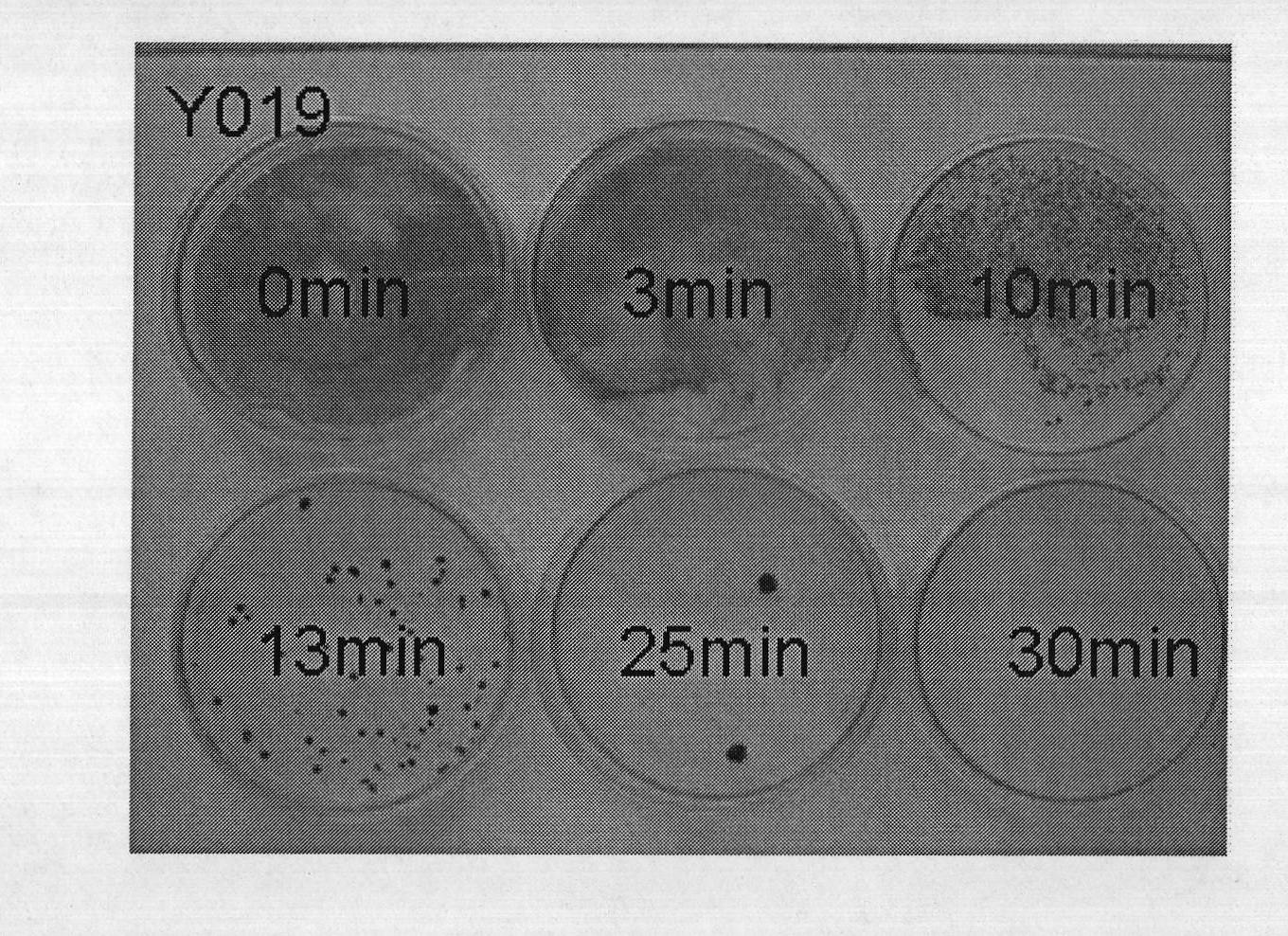
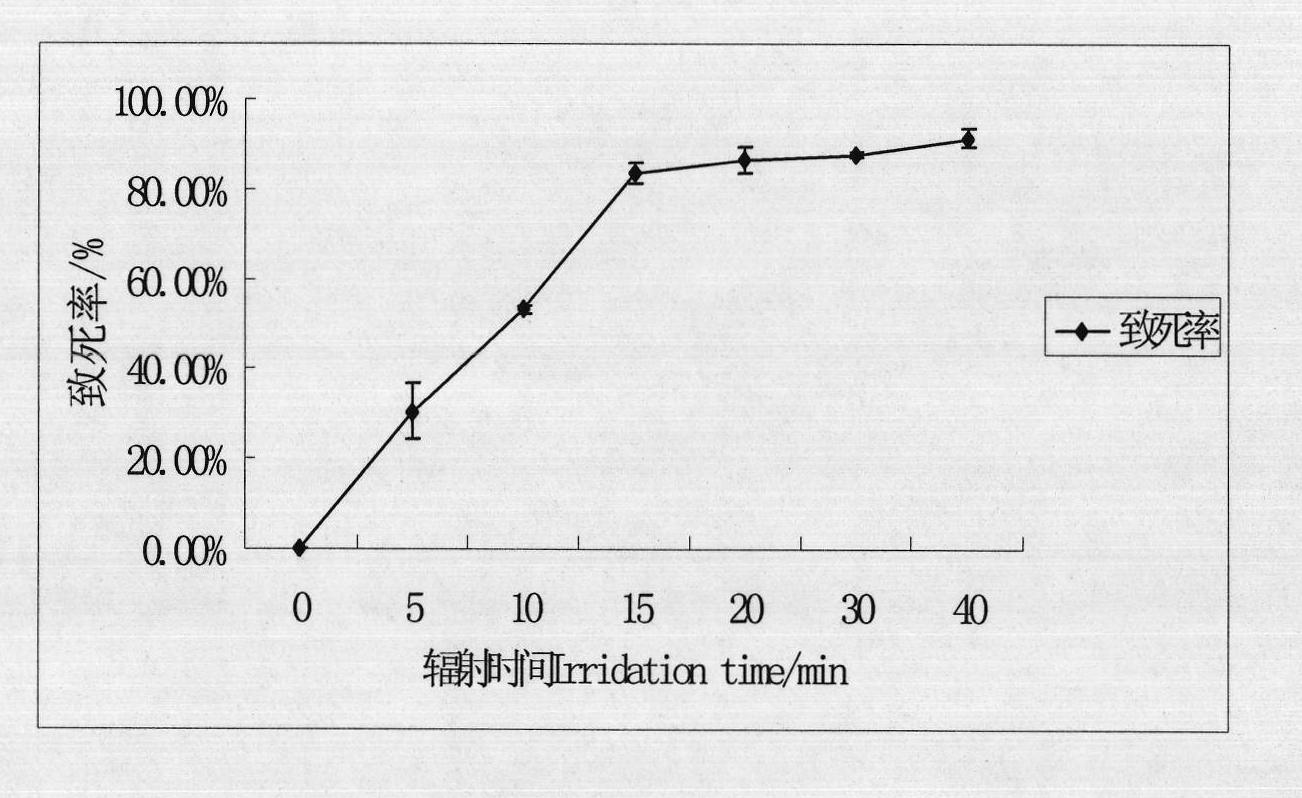
InactiveCN101988035APromote growthHigh oil contentUnicellular algaeMutant preparationBiodieselLipid content
The invention relates to a method for screening a high-lipid content mutant microalgae strain, which comprises the following steps of: performing irradiation treatment on the diluted algae solution of chlorella vulgaris Y019; performing dark culture on mutagenic algae solution, coating the cultured algae solution onto a solid high salt medium (HSM) for culture, sequentially inoculating the cultured algae solution onto a new solid HSM, performing numbering and testing OD490; adding a Nile red dye and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) into the algae solution, and testing the lipid content of the mutant microalgae strain; and when the ratio C of a unit OD490 neutral lipid absorption value B1 of the mutant strain to the unit OD490 neutral lipid absorption value B2 of the chlorella vulgaris Y019 is over 110 percent, determining the mutant strain as the high-lipid content mutant strain which is named Y019-M37 and preserved at the China center for type culture collection with the collection number of CCTCC NO.M2010170. The method is simple to screen and detection and consumes less time; and the obtained mutant strain has a high growth rate and high lipid content, is a useful source for the preparation of biodiesel and has vast biodiesel development prospect.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com