Method for rapidly and nondestructively detecting astaxanthin in C.zofingiensis cells
A non-destructive testing, chlorella technology, applied in the direction of material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve the problems of long time required, reduce work efficiency, increase the process required for testing, etc., to simplify testing steps and sample pretreatment. The effect of simplicity and shortened inspection time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] In the process of developing the technical solution of the present invention, the inventors of the present application studied the variation trend of the intracellular astaxanthin content of the chlorella C. zofingiensis.
[0048] 1.1 Strain activation and seed liquid preparation
[0049] The strains of Chlorella zofingiensis preserved in the laboratory were transferred to the slant equipped with modified Basal medium for cultivation, the cultivation temperature was 28°C, and the light was 10 μmol m -2 the s -1 , and observe the growth of Chlorella.
[0050] Use an inoculation loop to inoculate the Chlorella algae lawn into the modified Basal liquid medium, at a temperature of 28 °C and a light of 10 μmol m -2 the s -1 Cultivate under certain conditions for 3 to 5 days as seed liquid.
[0051] The composition of the improved Basal medium (pH6.1) described therein is shown in Table 1 below (in mg / L):
[0052] Table 1
[0053]
[0054]
[0055] 1.2 Chlorel...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2 Correlation between the intracellular astaxanthin content of Chlorella and the average fluorescence intensity of Chlorella cells
[0069] During the cultivation of Chlorella C. zofingiensis in Example 1, the inventors of the present application found that the cells of Chlorella changed from green to orange-red, which was mainly due to the chlorophyll and primary carotenoids in the cells under high light, low nitrogen, etc. Under stress conditions, it can induce the accumulation of secondary carotenoids, mainly astaxanthin and other carotenoids. The cell morphology of Chlorella cells under the optical microscope at the beginning, during and at the end of the culture are as follows: figure 2 Shown in A, B, and C diagrams.
[0070] Astaxanthin can exhibit the maximum emission wavelength after being excited by a specific wavelength, which is related to its content in the cell. In this example, a BD Accuri C6 flow cytometer was used to measure the average fluore...
Embodiment 3
[0078] Example 3 The linear regression analysis of the astaxanthin content measured by the average fluorescence intensity of chlorella cells and the HPLC method
[0079] In order to realize the rapid and accurate analysis of the astaxanthin content in the cells of Chlorella, the average fluorescence intensity of the cells was measured by flow cytometry in this experiment, and linear regression analysis was performed with the astaxanthin content in the cells of Chlorella to determine the Flow cytometry is a fast and accurate non-destructive detection method.
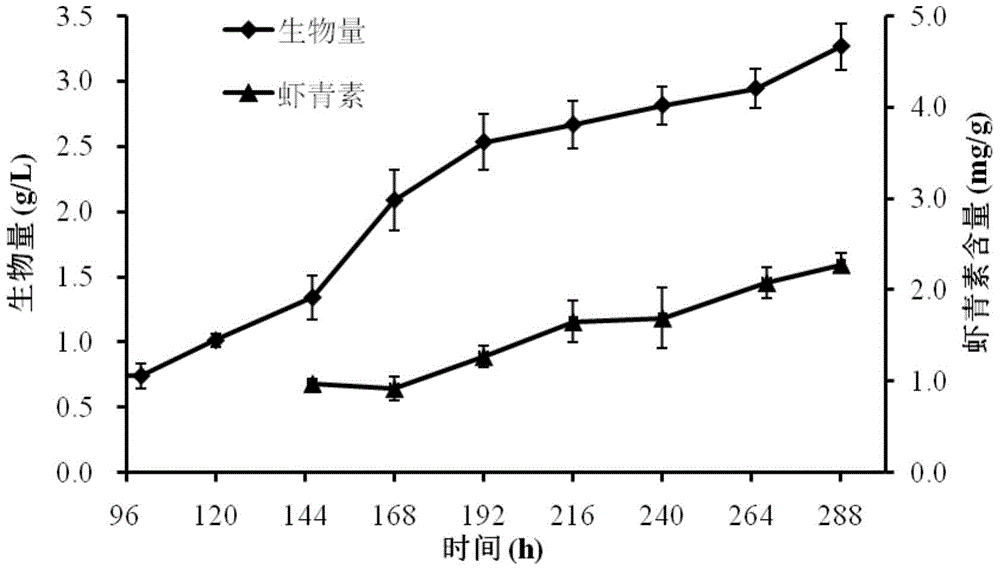
[0080] In Example 1, the chlorella intracellular astaxanthin content of the chlorella samples cultivated to the 146h, 168h, 192h, 216h, 240h, 264h, and 288h was measured by HPLC assay, and the results are as follows figure 1 shown. The common logarithm of the measured values of these astaxanthin contents (in μg / g, representing the content of astaxanthin per gram of dry algal powder) is taken as the ordinate to the base...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com