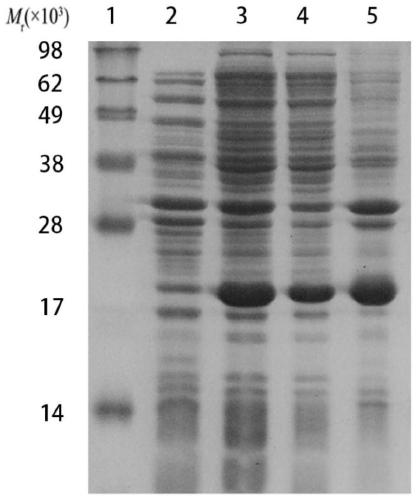
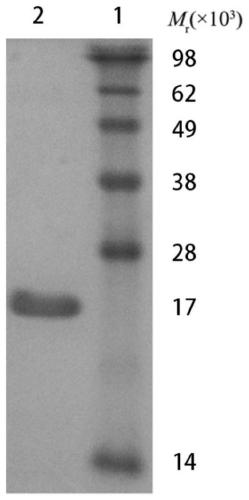
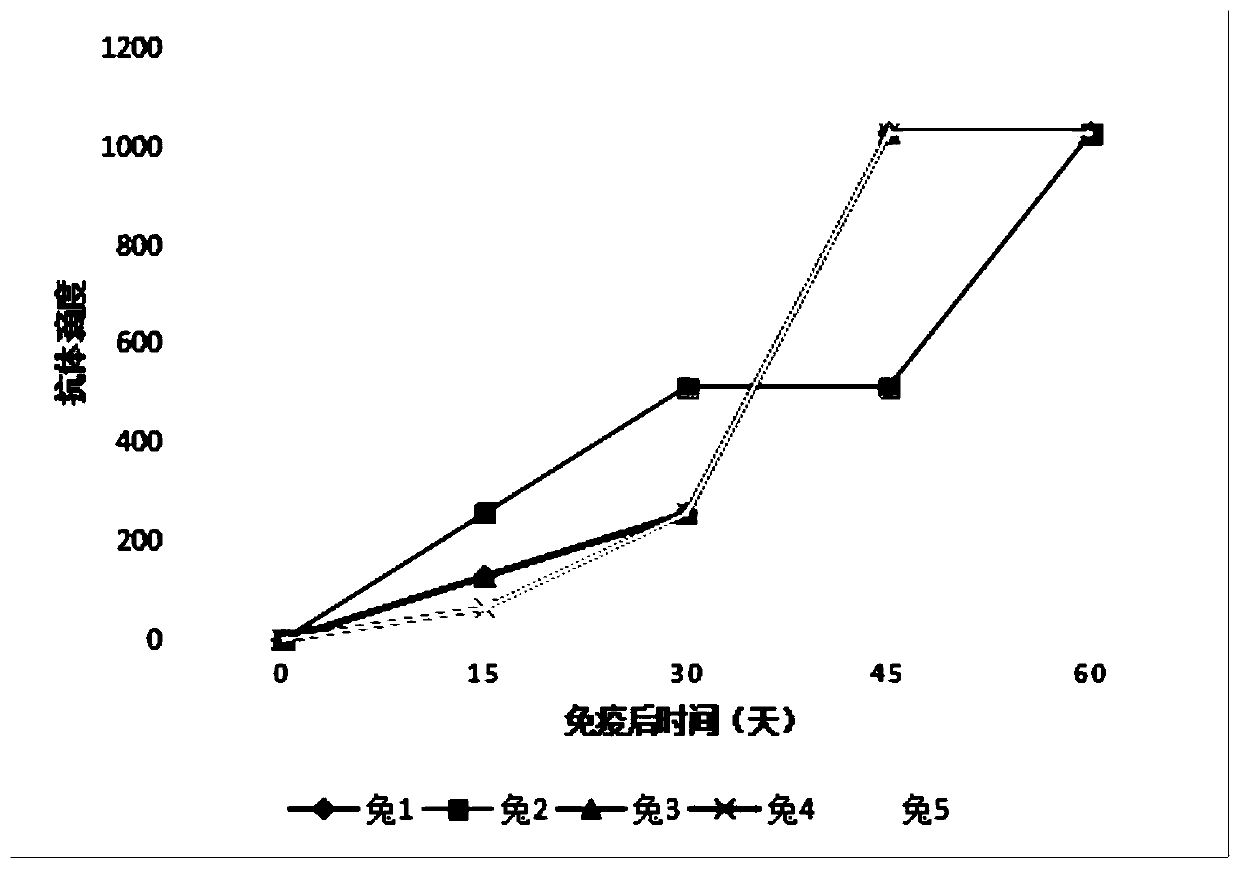
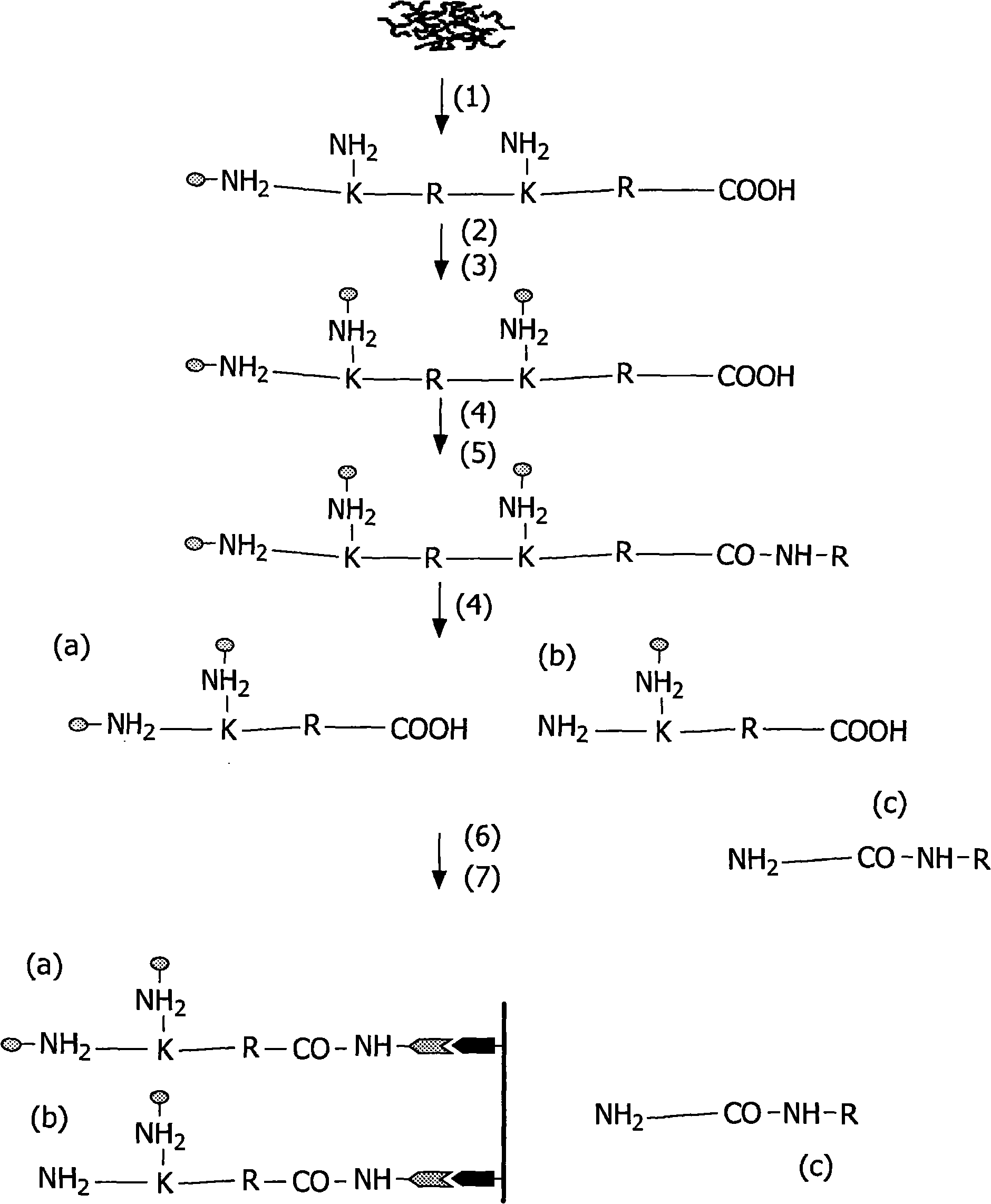
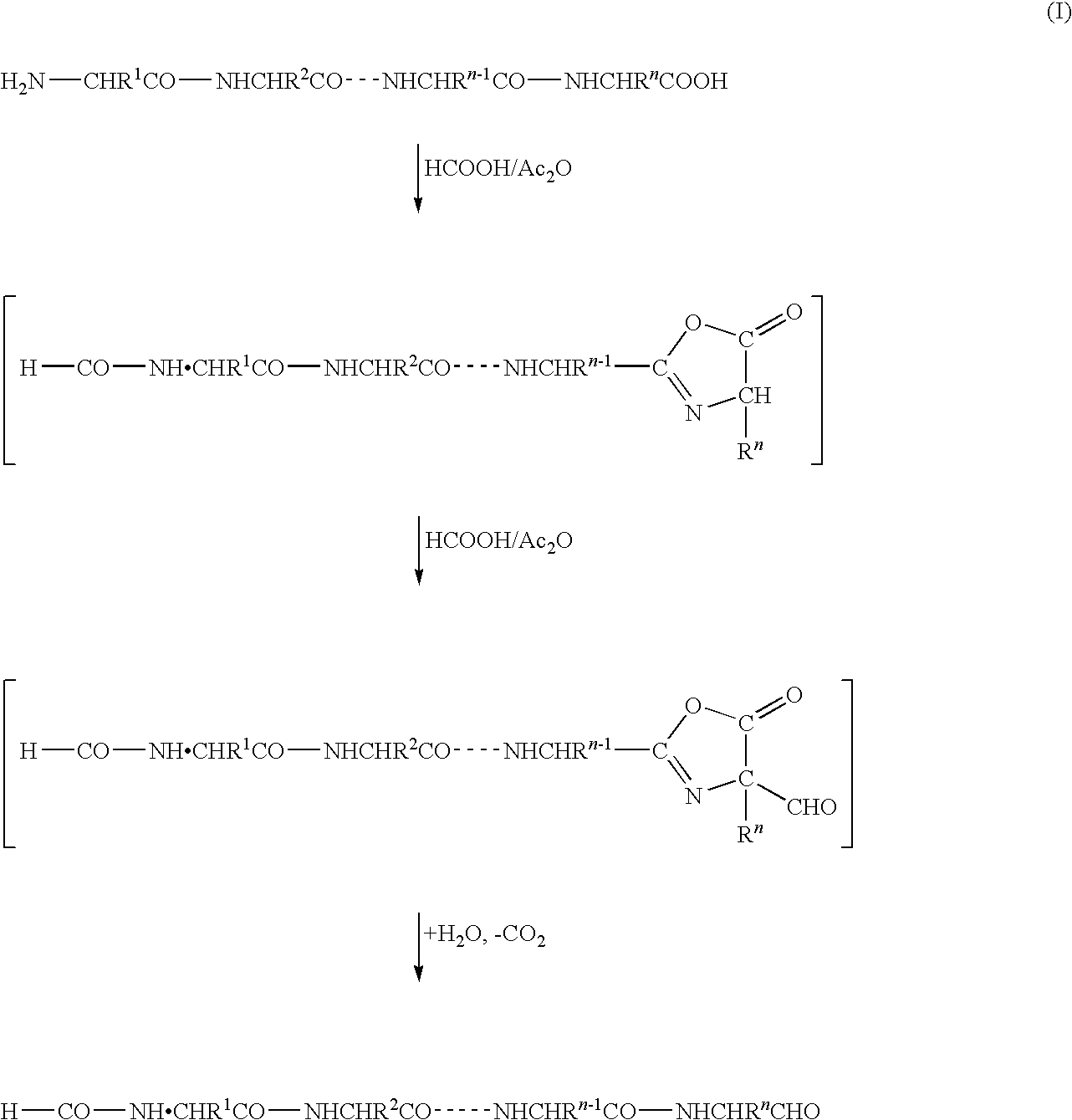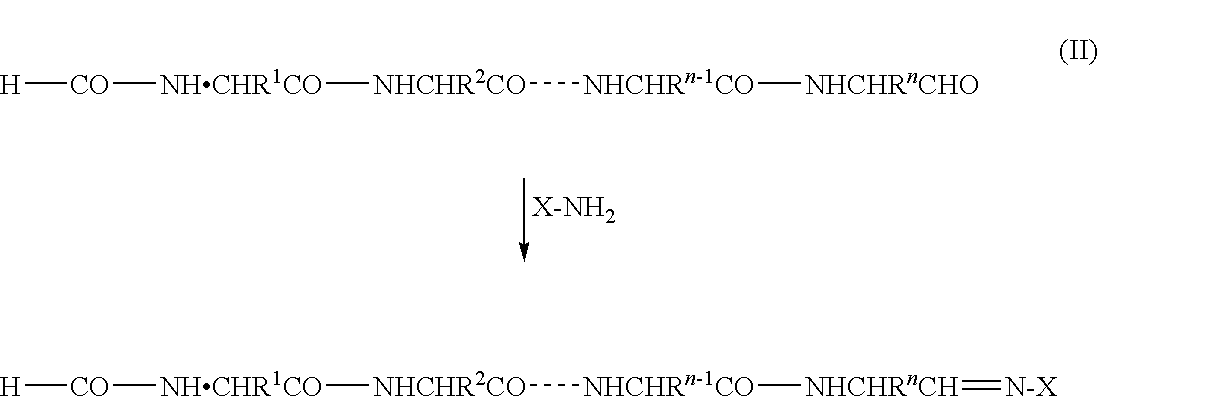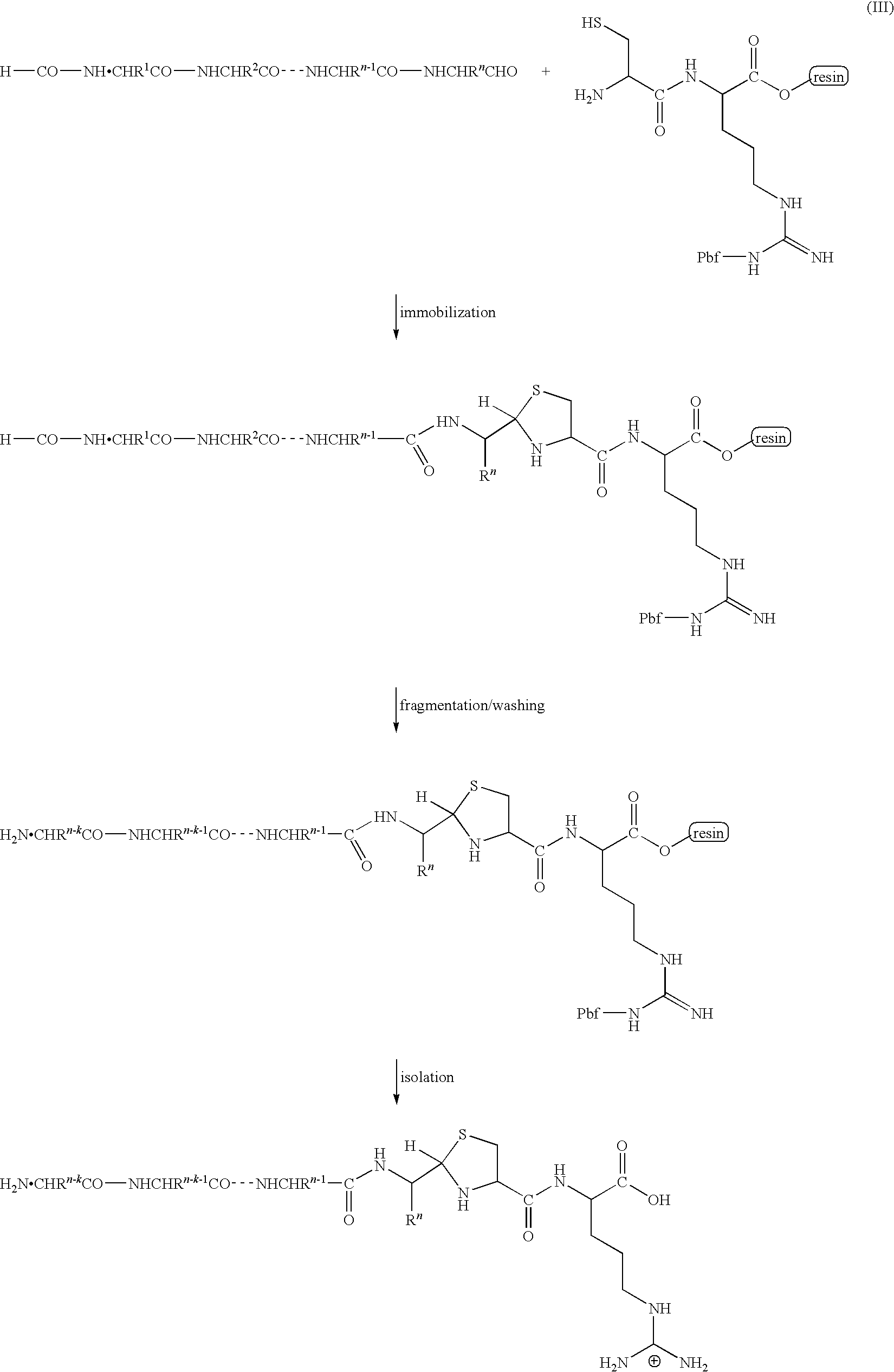Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
35 results about "C terminal peptide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
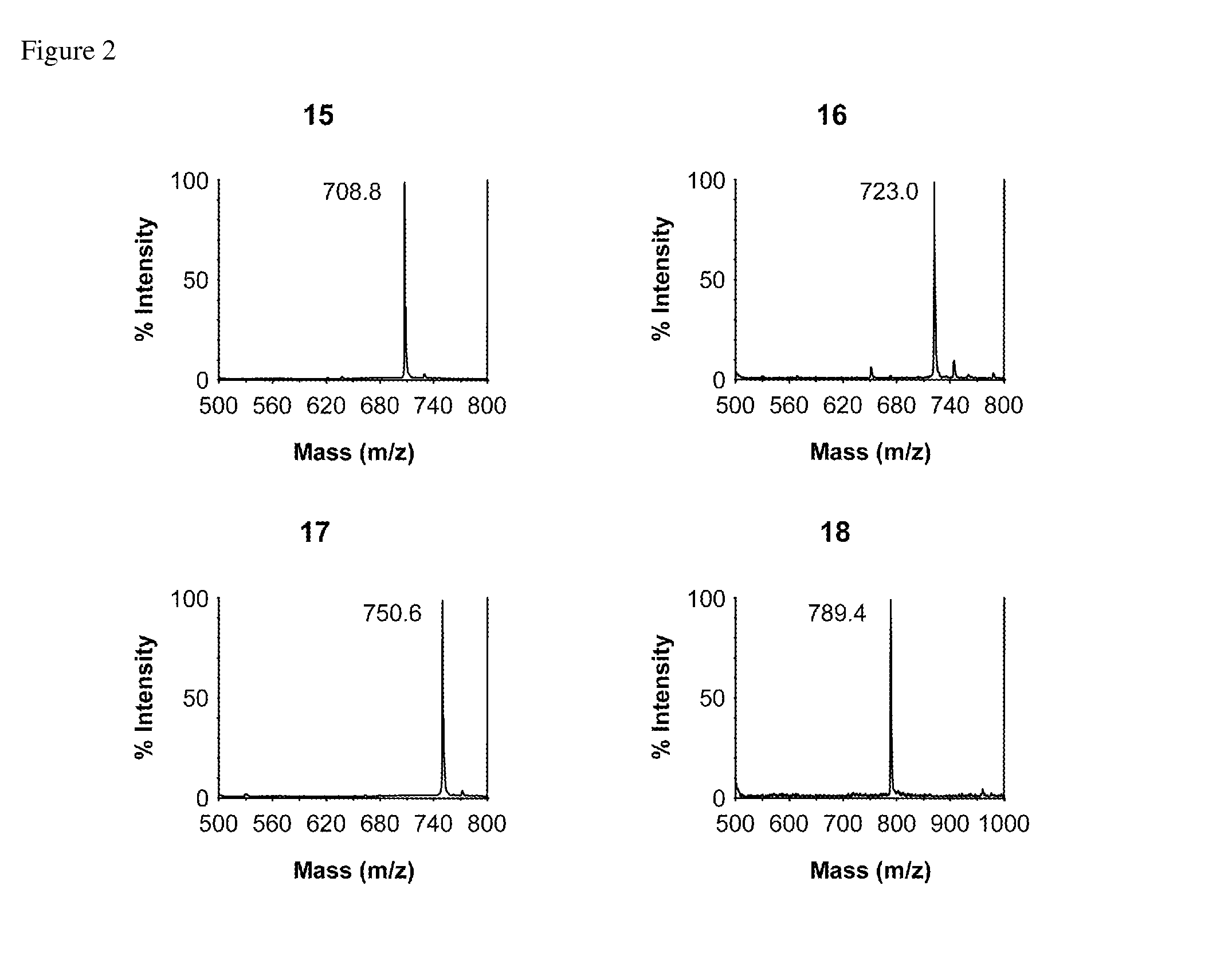
The C-terminal of the peptide is synthesized as an amide to neutralize negative charge created by the C-terminal COOH. This modification is added to prevent enzyme degradation, to mimic native proteins, and in some cases to remove hydrogen bonding at the C-terminal of the peptides which may interfere with the assays.
Protein complexes having Factor VIII:C activity and production thereof
InactiveUS6060447AImprove stabilityHigh yieldPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFactor iiADAMTS Proteins
Recombinant protein complexes having human Factor VIII:C activity are expressed in a eukaryotic host cell by transforming the host cell with first and second expression cassettes encoding a first polypeptide substantially homologous to human Factor VIII:C A domain and a second polypeptide substantially homologous to human Factor VIII:C C domain, respectively. In the present invention, the first polypeptide may be extended having at its C-terminal a human Factor VIII:C B domain N-terminal peptide, a polypeptide spacer of 3-40 amino acids, and a human Factor VIII:C B domain C-terminal peptide. Expression of the second polypeptide is improved by employing an .alpha..sub.1 -antitrypsin signal sequence.
Owner:NOVARTIS VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS INC
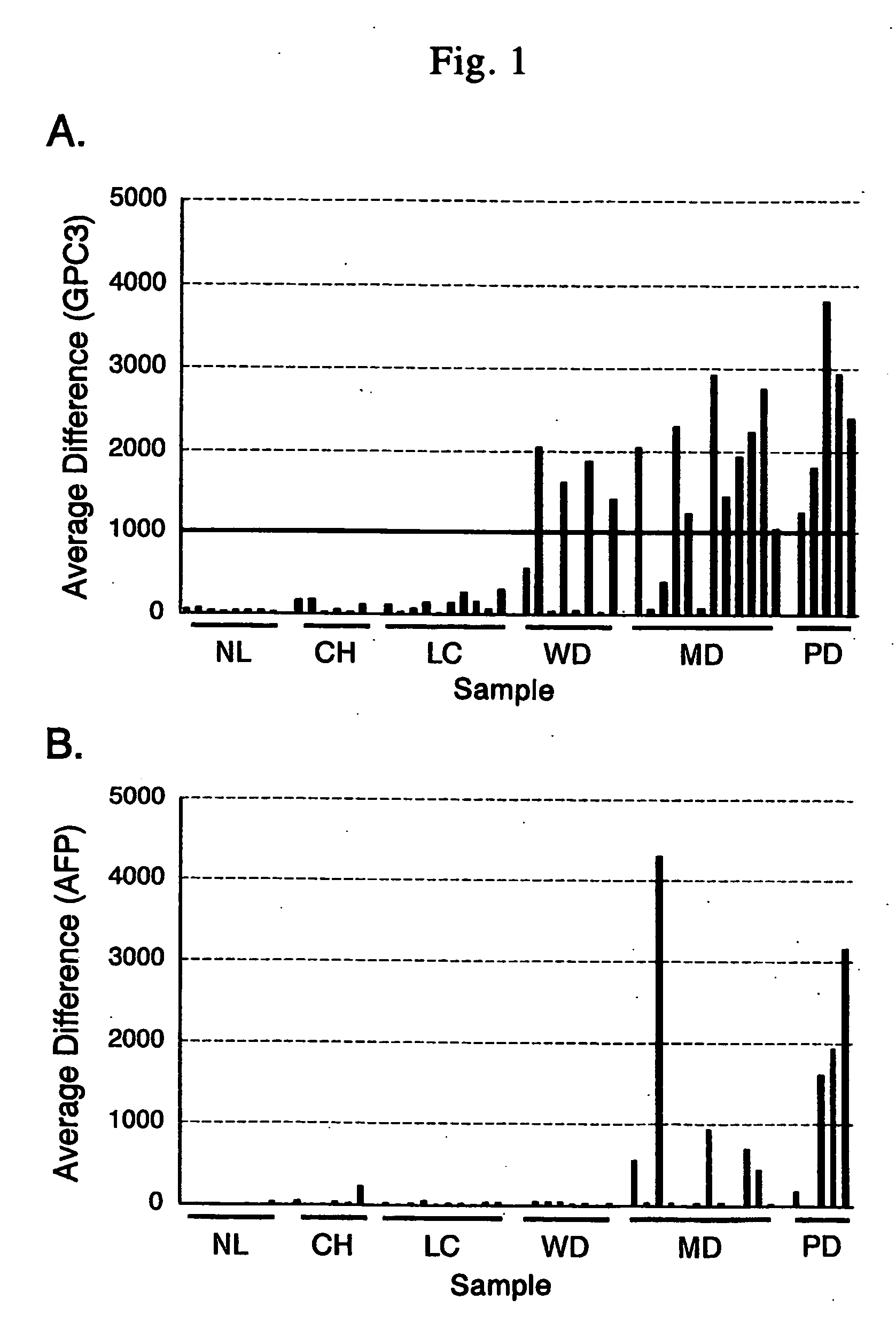
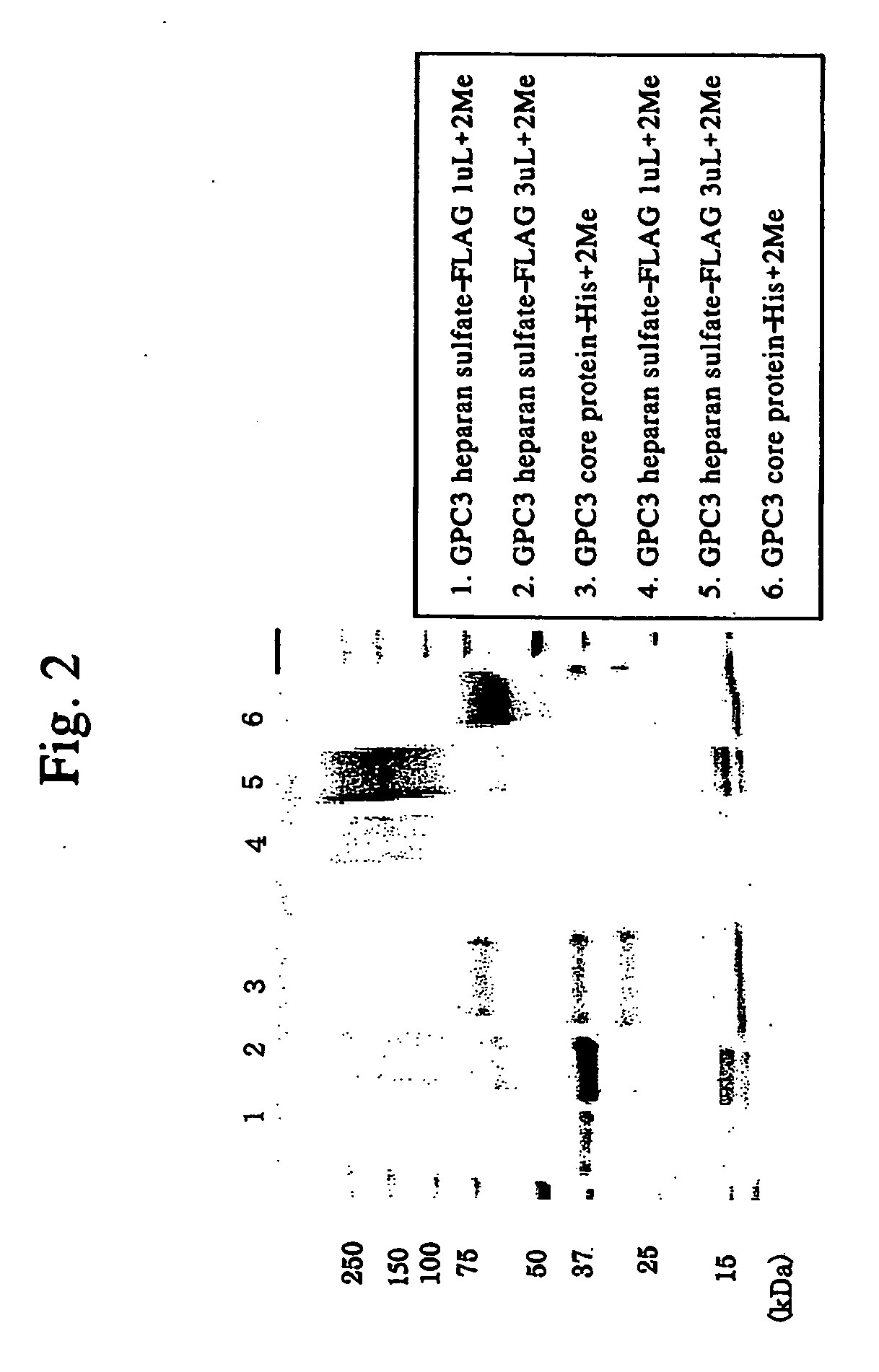
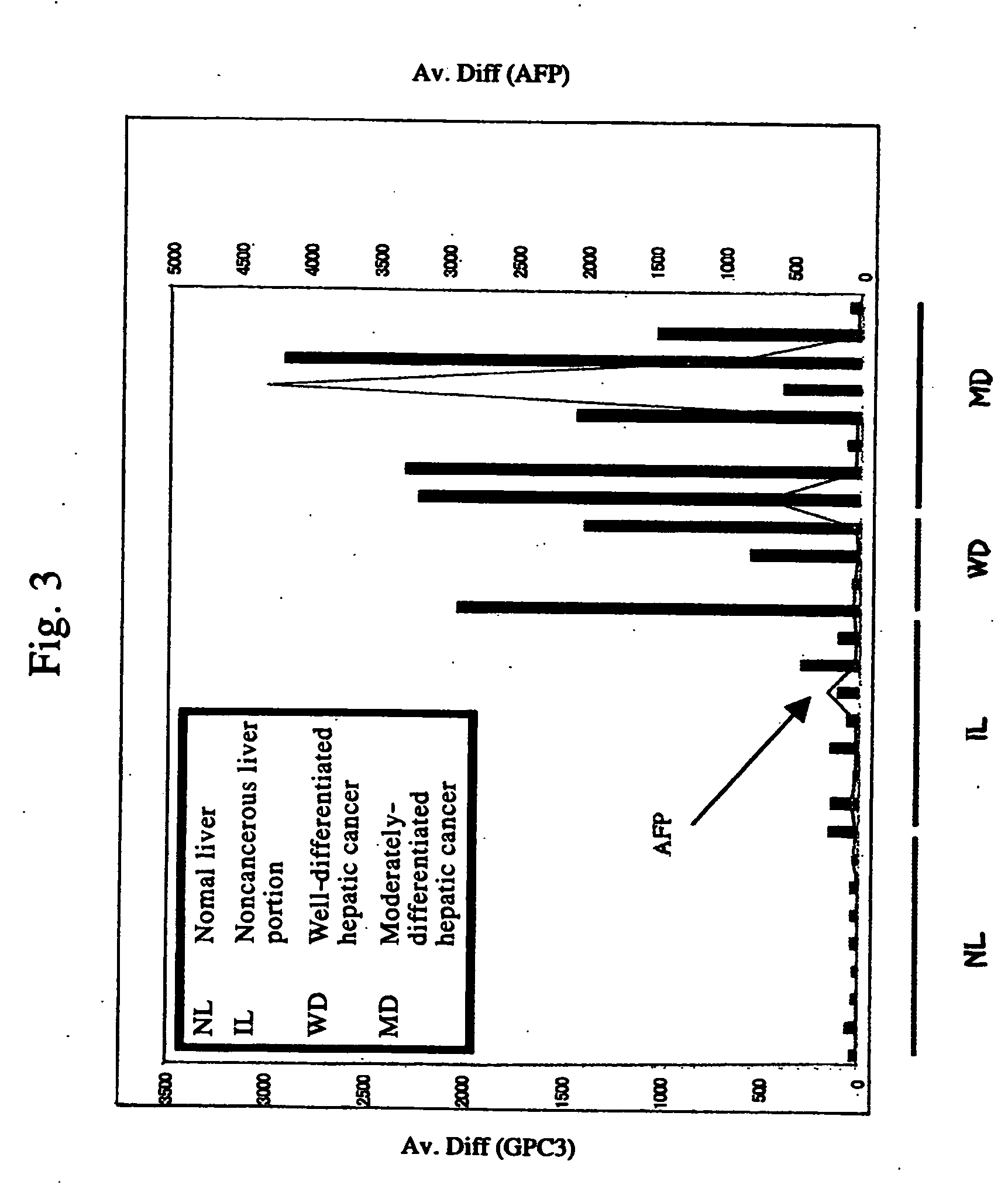
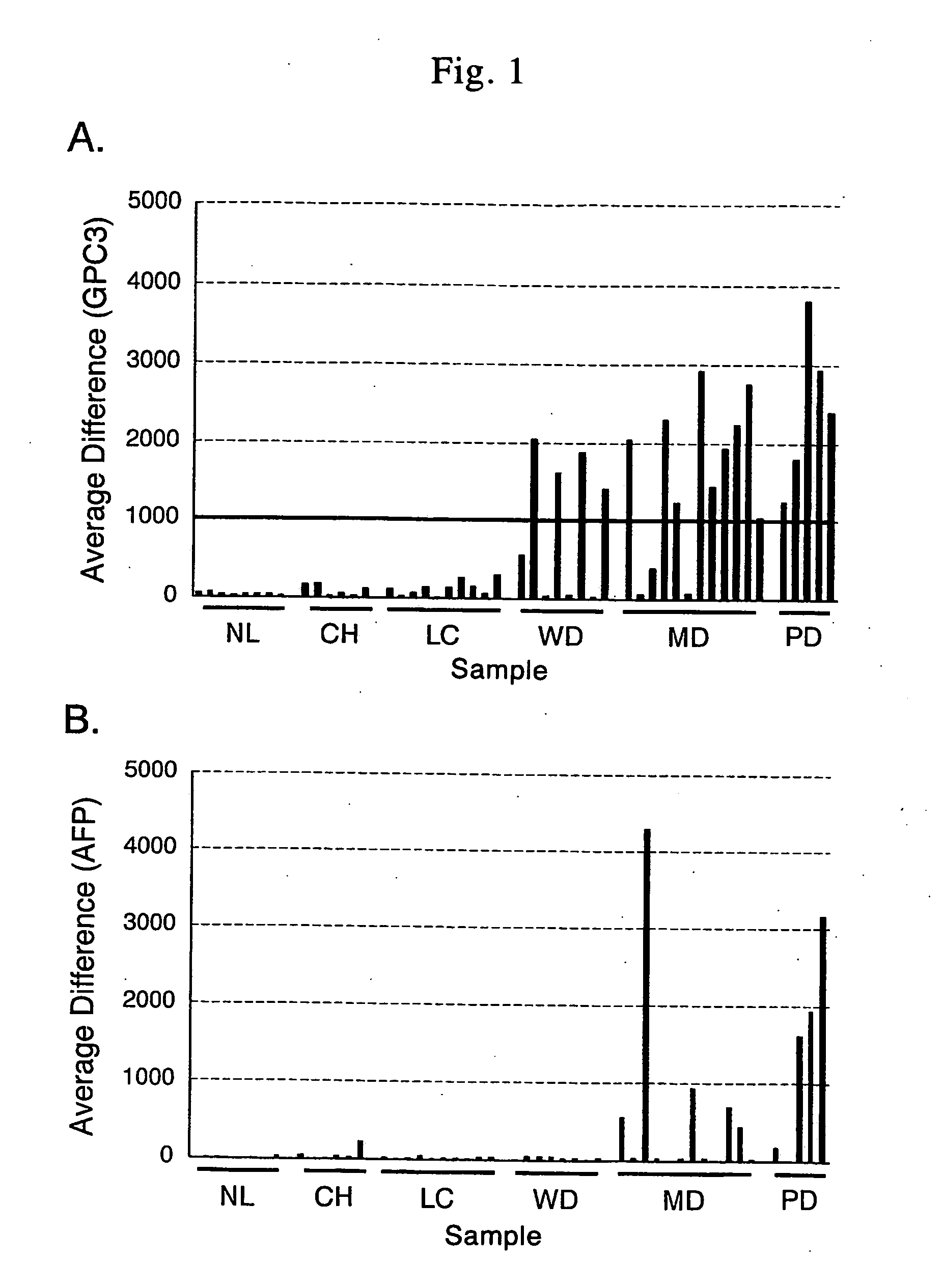
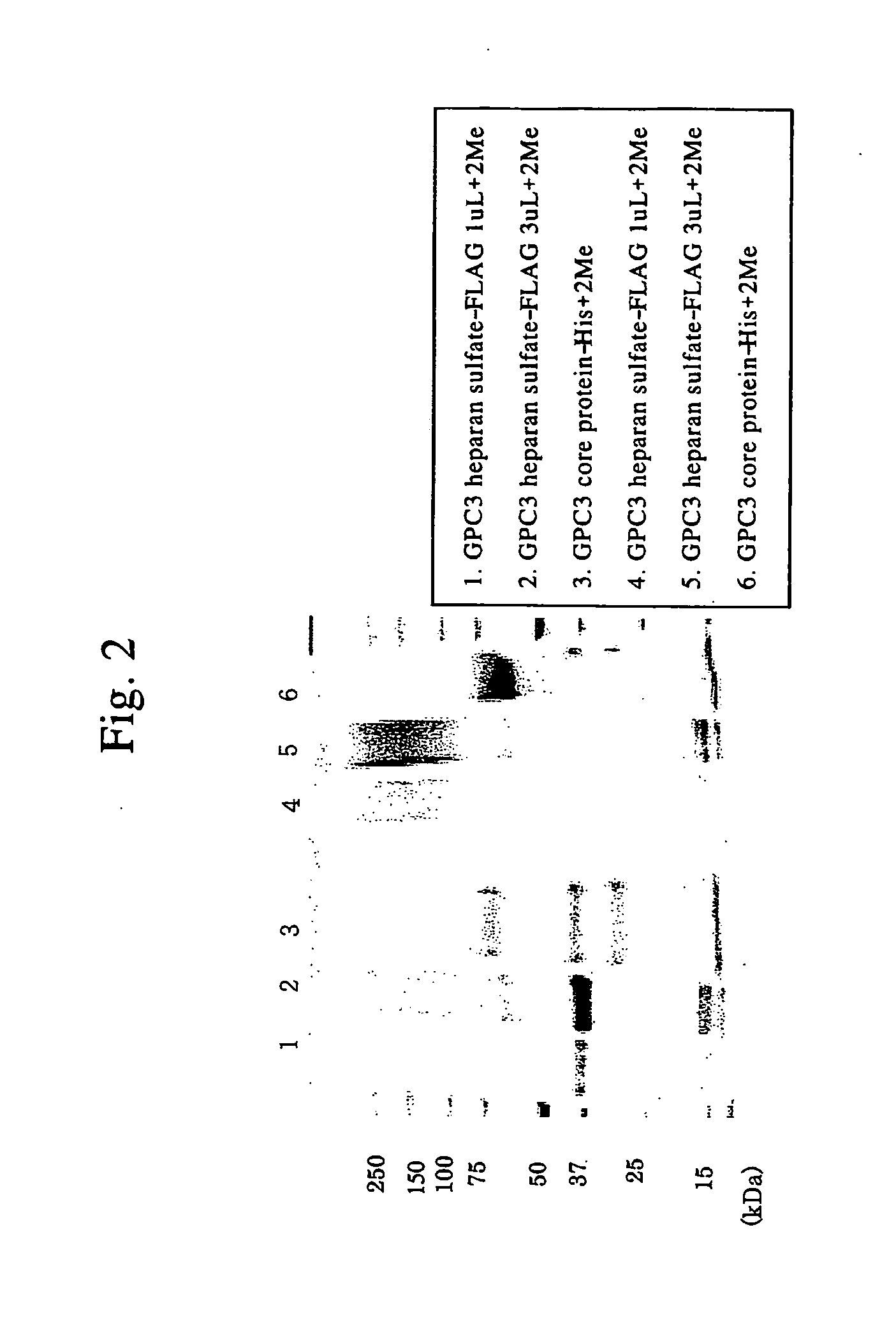
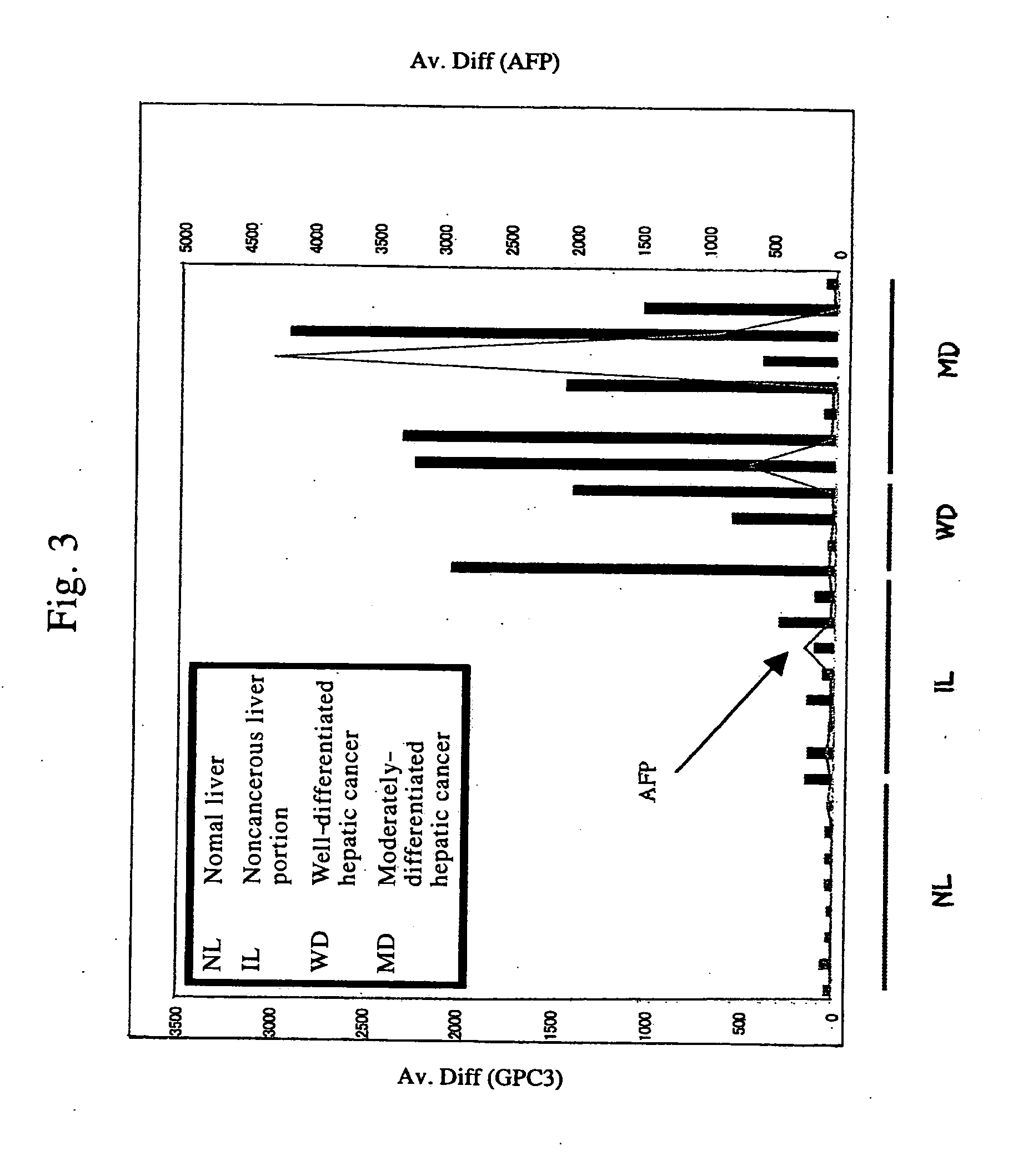
Antibody against n-terminal peptide or c-terminal peptide of gpc3 solubilized in blood
InactiveUS20060167232A1Useful in therapyImprove fusion efficiencyImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellAnticarcinogen
Disclosed is an antibody against a secreted form of GPC3 capable of detecting a secreted form of glypican 3 (GPC3) in a test sample. It is possible to determine whether a subject suffers from cancer, in particular hepatoma. Also disclosed is an antibody against GPC as well as a cell disrupting agent and an anti-cancer agent comprising the same, which can disrupt cells, in particular cancer cells.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibody against secreted N-terminal peptide of GPC3 present in blood or C-terminal peptide of GPC3
InactiveUS20060188510A1Improve fusion efficiencyImprove stabilityImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsCancer cellAnticarcinogen
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Protein complexes having factor VIII:C activity and production thereof
InactiveUS20060122376A1Improve stabilityHigh yieldFactor VIISugar derivativesProtein-protein complexA domain
Recombinant protein complexes having human Factor VIII:C activity are expressed in a eukaryotic host cell by transforming the host cell with first and second expression cassettes encoding a first polypeptide substantially homologous to human Factor VIII:C A domain and a second polypeptide substantially homologous to human Factor VIII:C C domain, respectively. In the present invention, the first polypeptide may be extended having at its C-terminal a human Factor VIII:C B domain N-terminal peptide, a polypeptide spacer of 3-40 amino acids, and a human Factor VIII:C B domain C-terminal peptide. Expression of the second polypeptide is improved by employing an .alpha.sub.1-antitrypsin signal sequence.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Method of identifying peptides in a proteomic sample
ActiveUS7422865B2Reduce complexityReduce stepsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative determinationImproved method
The present invention provides a new and improved method for reducing the complexity of a proteomic sample, and preferably also for allowing identification of proteins in the sample. In one aspect, the invention provides a highly efficient method for identifying proteins in a proteomic sample by characterizing a single N-terminal peptide per protein. In another aspect, the invention provides a method for identifying proteins in a proteomic sample by characterizing a single C-terminal peptide per protein. In another aspect, the present invention provides a method for quantitative determination of differential protein expression and / or modification in different samples. In another aspect, the invention relates to kits useful for conveniently performing a method in accordance with the invention.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
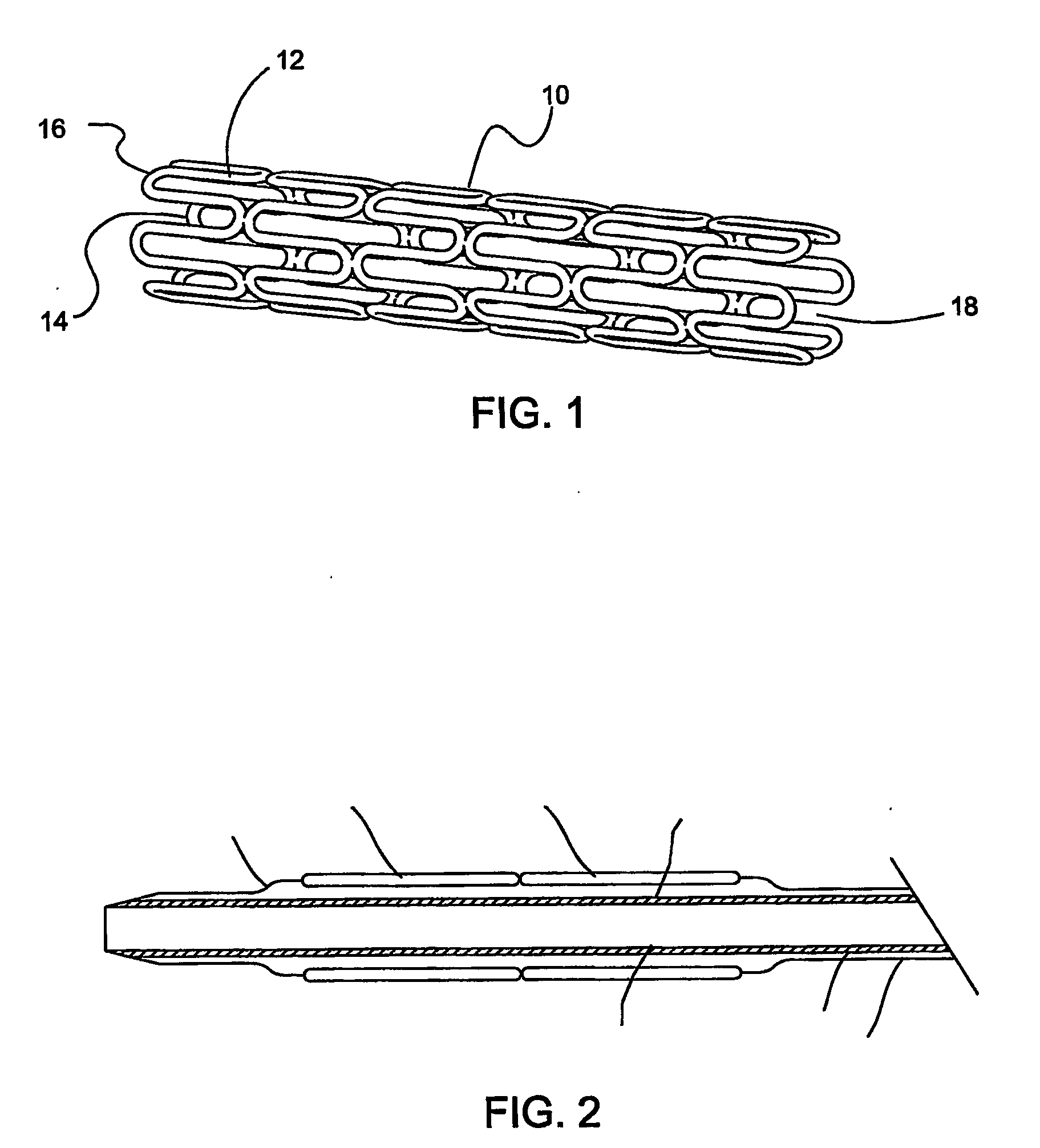
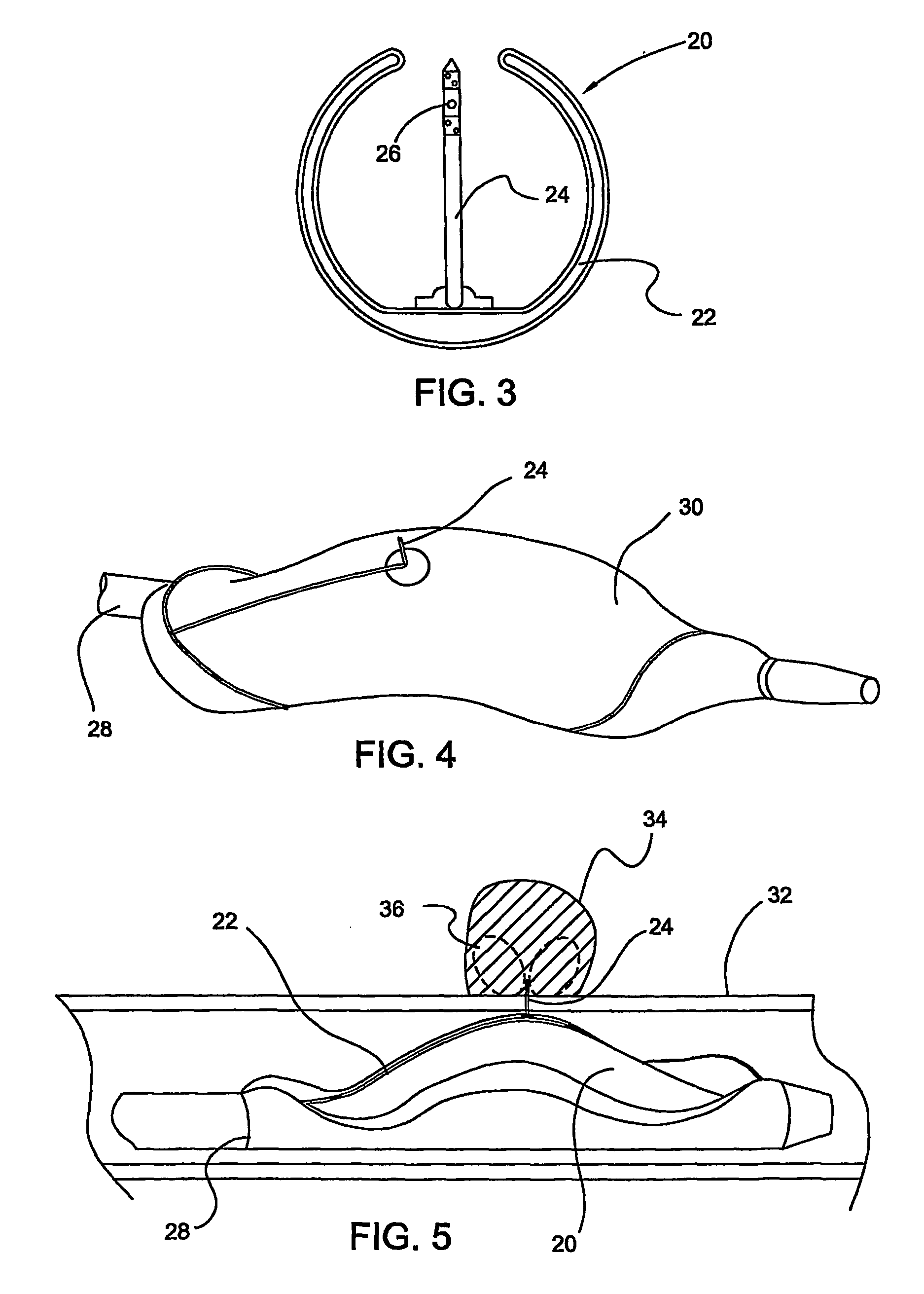
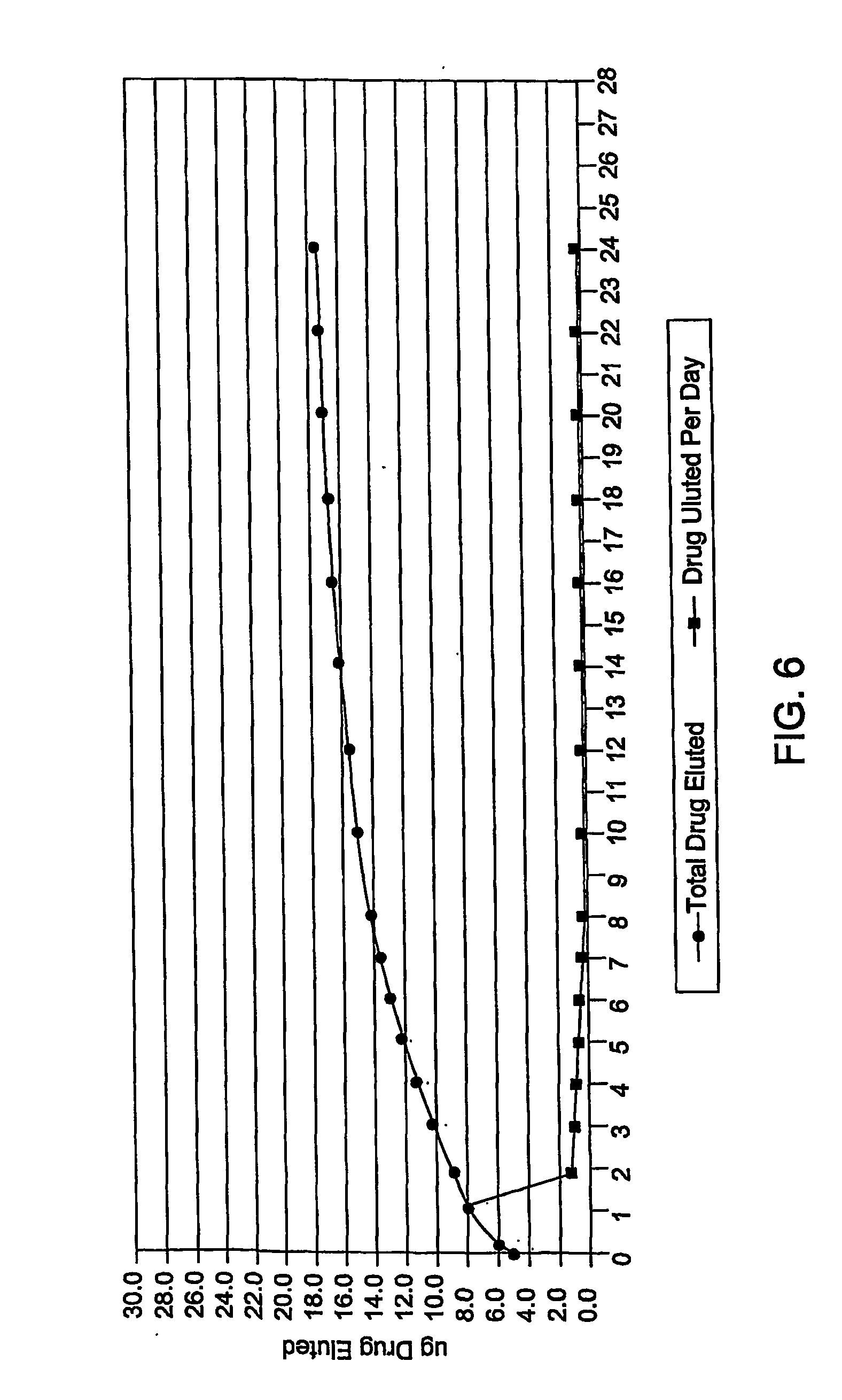
Medical devices with proteasome inhibitors for the treatment of restenosis
Methods, compositions and devices for inhibiting restenosis are provided. Specifically, proteasome inhibitor compositions and medical devices useful for the site specific delivery of proteasome inhibitors are disclosed. In one embodiment the medical device is a vascular stent coated with a proteasome inhibitor selected from the group consisting of a boronic acid, a C-terminal peptide aldehyde and derivatives and analogues thereof. In another embodiment an injection catheter for delivery an anti-restenotic effective amount of proteasome inhibitor to the adventitia is provided.
Owner:MEDTRONIC VASCULAR INC
Characterising polypeptides
InactiveUS20050042713A1High selectivityImprove completenessPeptide/protein ingredientsComponent separationPeptide fragmentReactive agent
Provided is a method for characterising a polypeptide or a population of polypeptides, which method comprises the steps of: (a) optionally reducing disulphide linkages in the polypeptides, if they are present and capping free thiols in the polypeptides, if they are present; (b) contacting a sample comprising one or more polypeptides with a cleavage reagent which cleaves one or more polypeptides on the C-terminal side of a lysine residue to produce peptide fragments; (c) optionally deactivating the cleavage reagent; (d) contacting the sample with a lysine reactive agent to cap ε-amino groups; (e) removing those peptides having capped ε-amino groups; and (f) recovering the C-terminal peptides.
Owner:ELECTROPHORETICS LTD
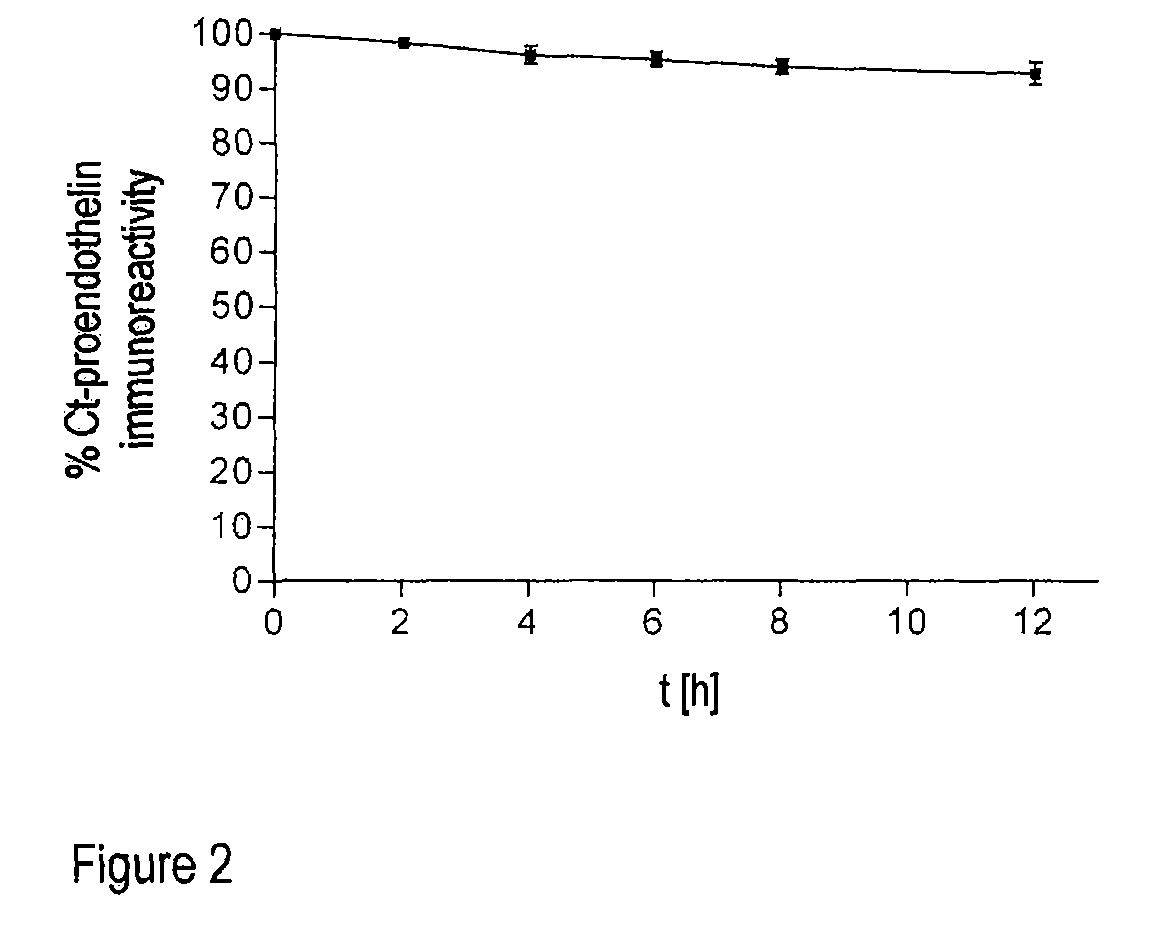
Method for the determination of the formation of endothelins for medical diagnostic purposes, and antibodies and kits for carrying out such a method
ActiveUS8124366B2Peptide/protein ingredientsBiological material analysisMedical diagnosisBlood plasma
The invention relates to an in vitro method for detecting the formation of endothelins during serious illnesses, especially cardiovascular diseases, inflammations, sepsis and cancer, in whole blood, plasma or serum of a human patient for medical diagnosis. Using this method, relatively long-lasting peptide fragments, especially a C-terminal peptide fragment, of the processed primary prepro- or proendothelins that contain neither the actual biologically active endothelin nor its direct precursor, big endothelin, can be detected.
Owner:BRAHMS GMBH
Synthesis of peptide alpha-thioesters
InactiveUS7414106B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsThioester synthesisCyclic peptide
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
N-or C-terminal peptide selection method for proteomics
ActiveUS20060134723A1Reduce complexityReduce stepsAnalysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementQuantitative determinationMass spectrometry
The present invention provides a new and improved method for quantitative determination and / or identification of proteins in a sample. In one aspect, the invention provides a mass spectroscopic method for comparing protein levels in two or more samples by differentially isotopically labeling each sample's proteins' N- or C-termini. In another aspect, the invention provides a mass-spectroscopic method for identifying a sample as source for a protein from a mixture of two or more samples by differentially isotopically labeling each sample's proteins' N- or C-termini.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
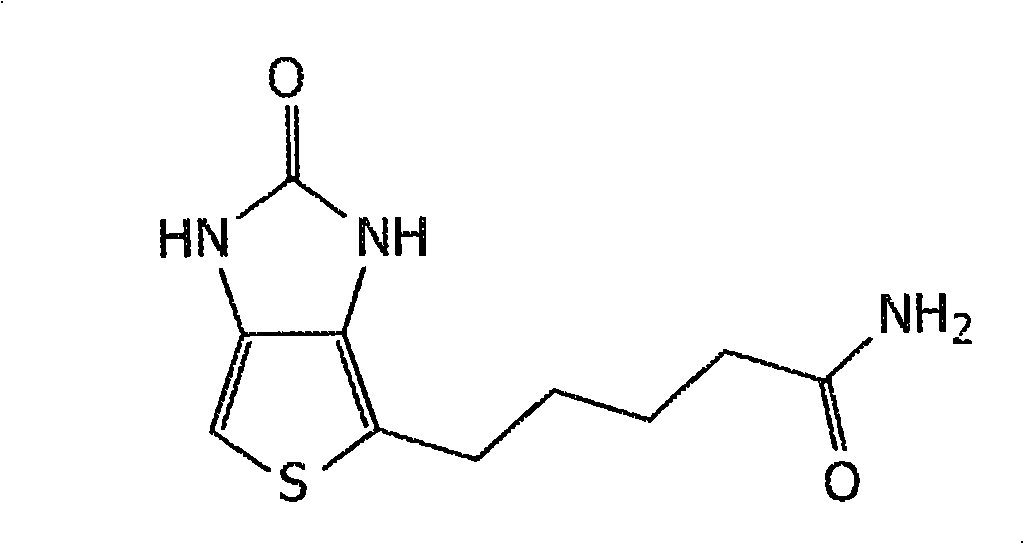
A kind of preparation method of plicanatide
ActiveCN104628827BDifficult to separate and purifyEase of industrial productionPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionSide chainCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of pulikanatide, comprising the following steps: 1) Fmoc-Leu-resin carrier adopts Fmoc solid-phase synthesis method according to the polypeptide sequence sequence of pulikanatide from carbon end to nitrogen end Coupling one by one to obtain peptide resins protected by side chain groups; 2) Peptide resins are sequentially deprotected according to Cys4‑Cys12 and Cys7‑Cys15 respectively, and then oriented to form a ring to obtain fully protected pulikanatide peptide resins; 3) Cleavage The reagent cleaves the peptide resin protected by the side chain group, and 4) after desalting, it is purified and freeze-dried to obtain plicanatide. The preparation process of pulikanatide adopted in the present invention has practical industrial application prospects and considerable economic and practical value.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
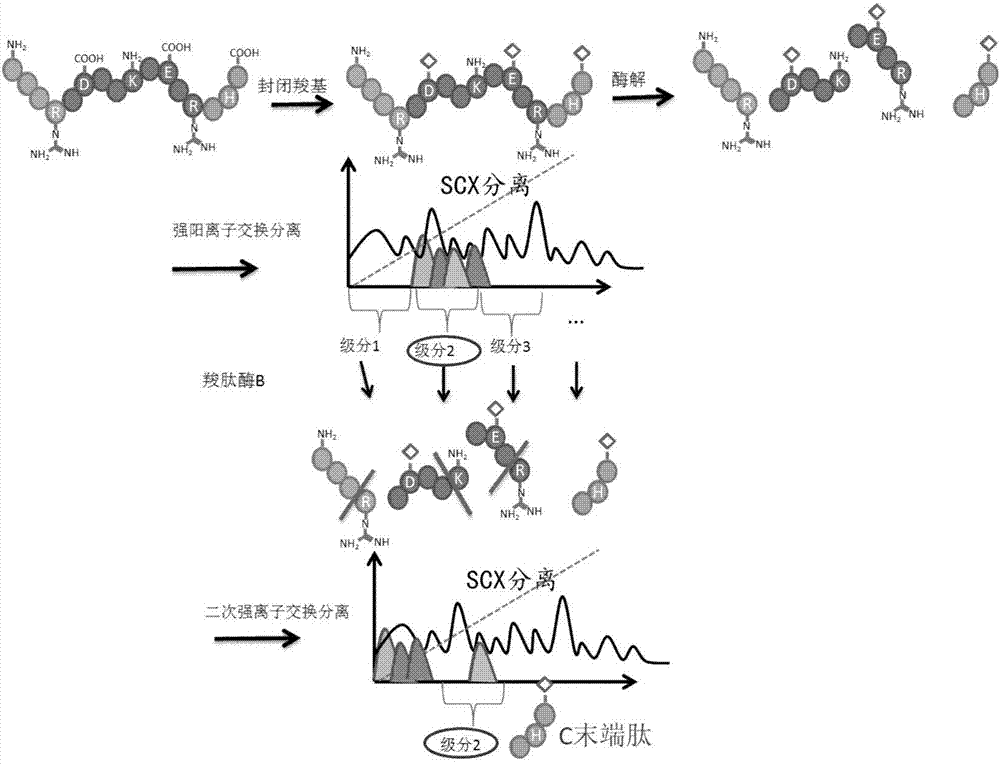
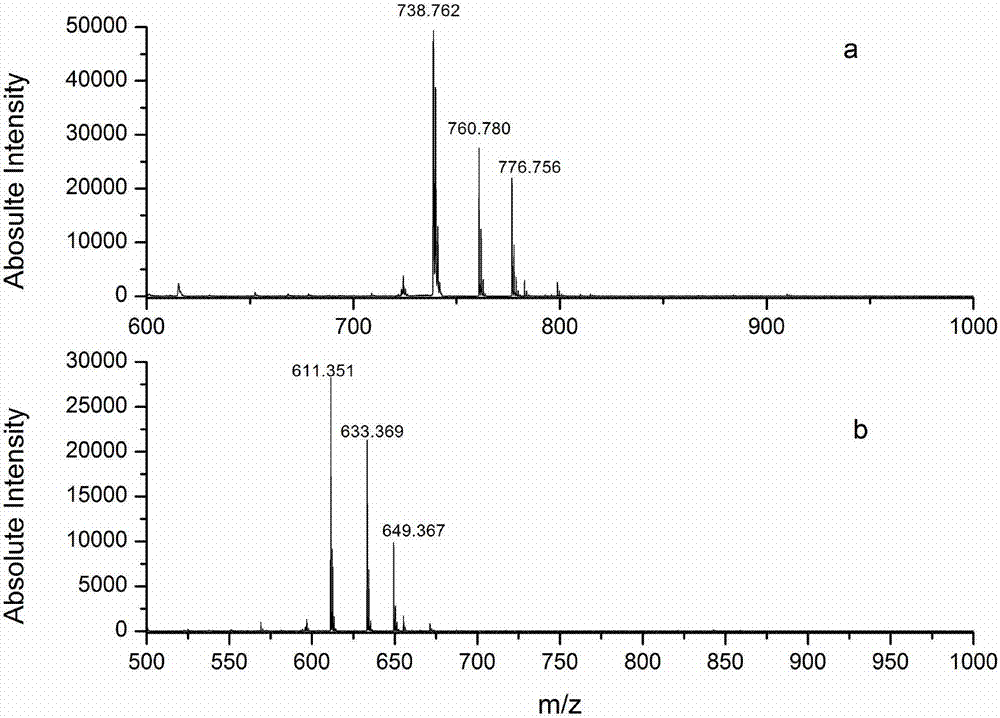
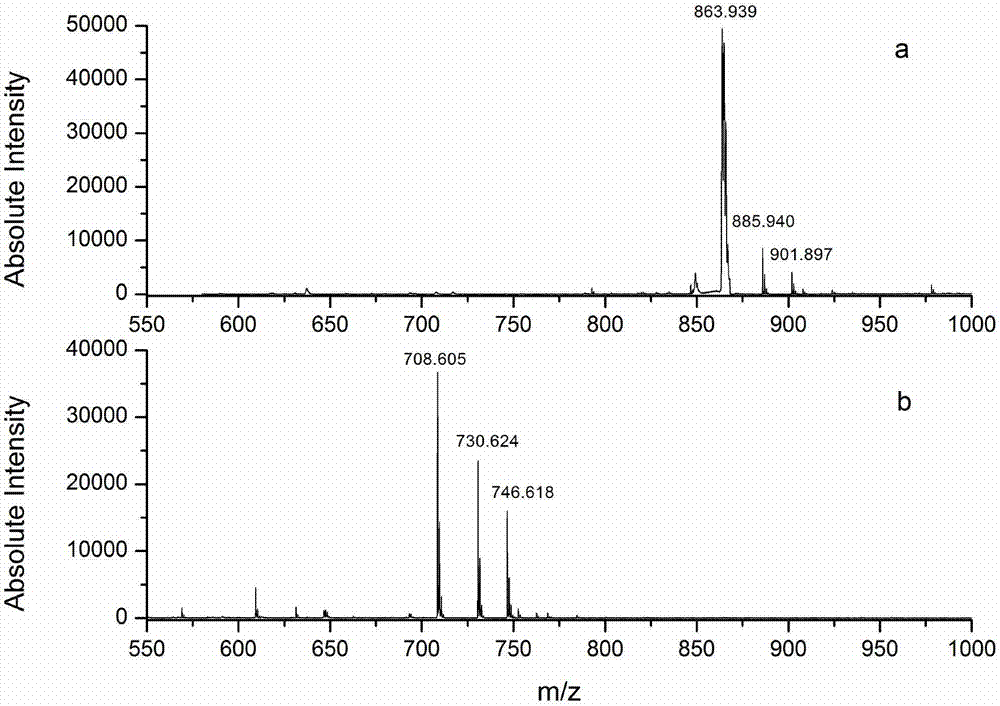
Protein C-terminal enriching method based on carboxypeptidase and strong cation exchange chromatography
InactiveCN107384998AImprove reaction efficiencyHigh selectivityPeptide preparation methodsFermentationChromatographic separationEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to a protein C-terminal enriching method based on a carboxypeptidase and strong cation exchange chromatography. The protein C-terminal enriching method comprises the steps of closing of the protein free carboxyl, enzyme digestion of protein alkaline loci, separation by adopting the ion exchange chromatography and cutting of peptide fragmental carboxyl terminal alkaline amino acid. A protein sample closes the free carboxyl at the tail end and a side chain of C at a protein level firstly, then enzyme digestion is conducted on the protein alkaline loci so as to generate a middle peptide fragment, and the carboxyl terminal is the alkaline amino acid; grading is conducted on an enzyme-digested product by adopting the ion exchange chromatography to obtain a plurality of fractions; and finally cutting is conducted on the alkaline amino acid of the carboxyl terminal of the middle peptide fragment, secondary ion exchange chromatographic separation is conducted on each friction so as to exclude the middle peptide fragment which shifts in the retention time, and thus the C terminal peptide fragment of the protein is obtained. The protein C-terminal enriching method has the advantages that the enzyme digestion efficiency, the removal efficiency and the enriching efficiency are high, multiple enzymes can be adopted to conduct enzyme digestion, and the coverage degree of identification of the C terminal is improved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
C-terminus modification method, c-terminus immobilization method and analysis method for protein or peptide
InactiveUS20090325227A1Easily and reliably isolating C-terminalRapidly accurately reliably determiningPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsC-terminusMass spectrometric
The present invention provides a method for inexpensively, easily and efficiently modifying the C-terminus of a protein or peptide; a method for easily and reliably isolating a C-terminal peptide fragment of a protein or peptide; and a method for rapidly, accurately and reliably determining an amino acid sequence of a protein or peptide by using a mass spectroscope. A method comprising the step of adding a formylation reagent and a catalyst to a protein or peptide to convert a carboxyl group into an aldehyde group. A method comprising the step of reacting a nucleophilic reagent with the aldehyde group to modify the C-terminus of the protein or peptide. A method comprising the step of reacting a support having a nucleophilic group to immobilize the protein or peptide. A method comprising the step of fragmenting the immobilized protein or peptide, washing the support, and isolating the C-terminal peptide fragment from the support. A method comprising the step of subjecting the isolated C-terminal peptide fragment to mass spectrometry and determining an amino acid sequence.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +2
Protein production method, fusion protein, and antiserum
InactiveUS20110223686A1Improve isolationPromote recoveryImmunoglobulins against bacteriaPeptide preparation methodsMicroorganismSerum ige
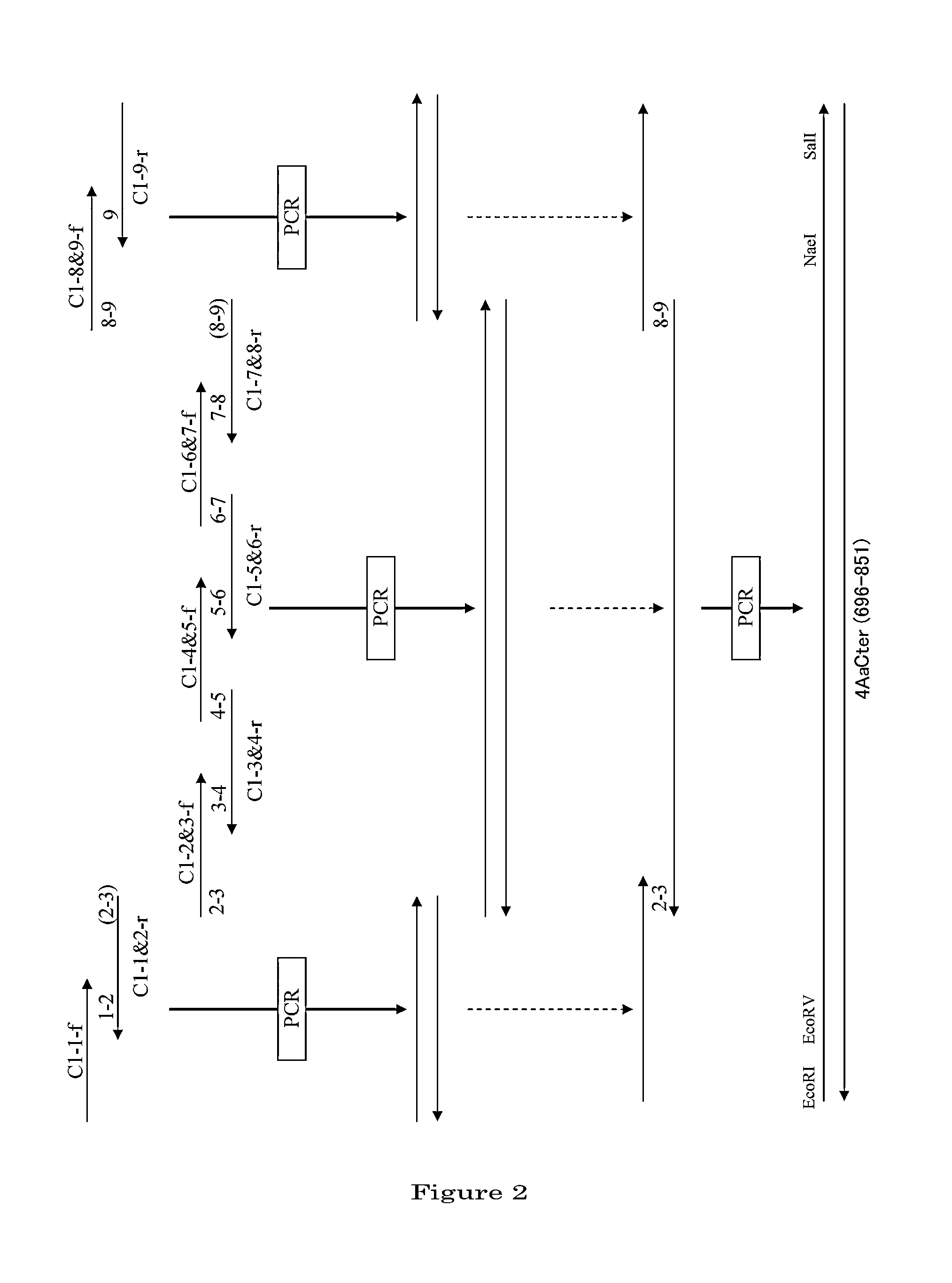
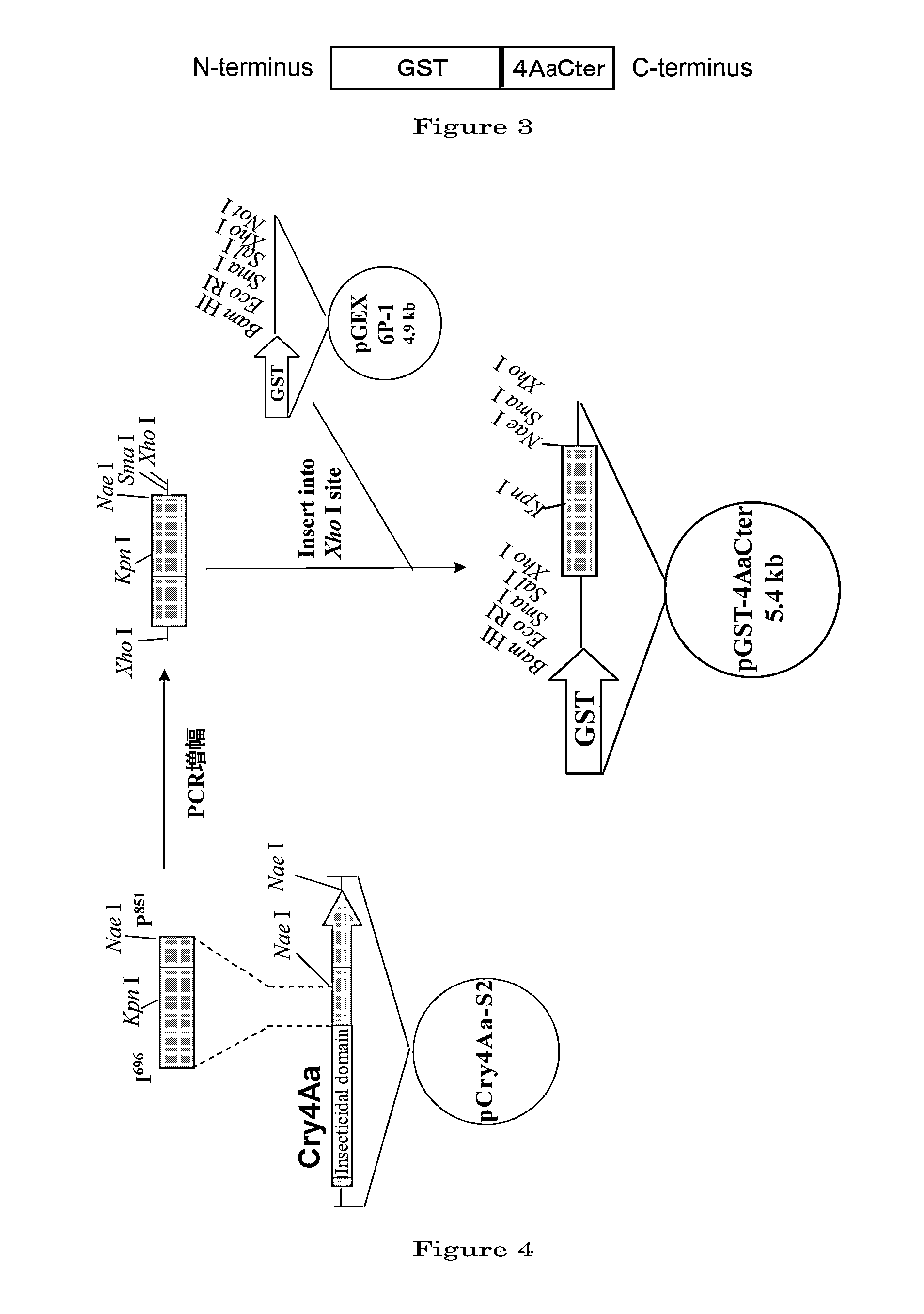
Disclosed are a highly efficient method for production of heterologous proteins performed by utilizing microorganisms, as well as fusion proteins, and an antiserum. The method includes a method for production of a protein (A) in the form of a fusion protein, comprising the steps of (a) preparing a DNA which codes for a fusion protein comprising the peptide chain forming the protein (A) and the C-terminal peptide or its fragment (B) of the Cry proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis, and (b) introducing the DNA into a host bacterium to transform the same, and (c) allowing the fusion protein to be expressed in the transformed host bacterium, as well as a method for production of the protein (A) itself comprising a further step of removing the peptide chain (B) from the fusion protein obtained.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
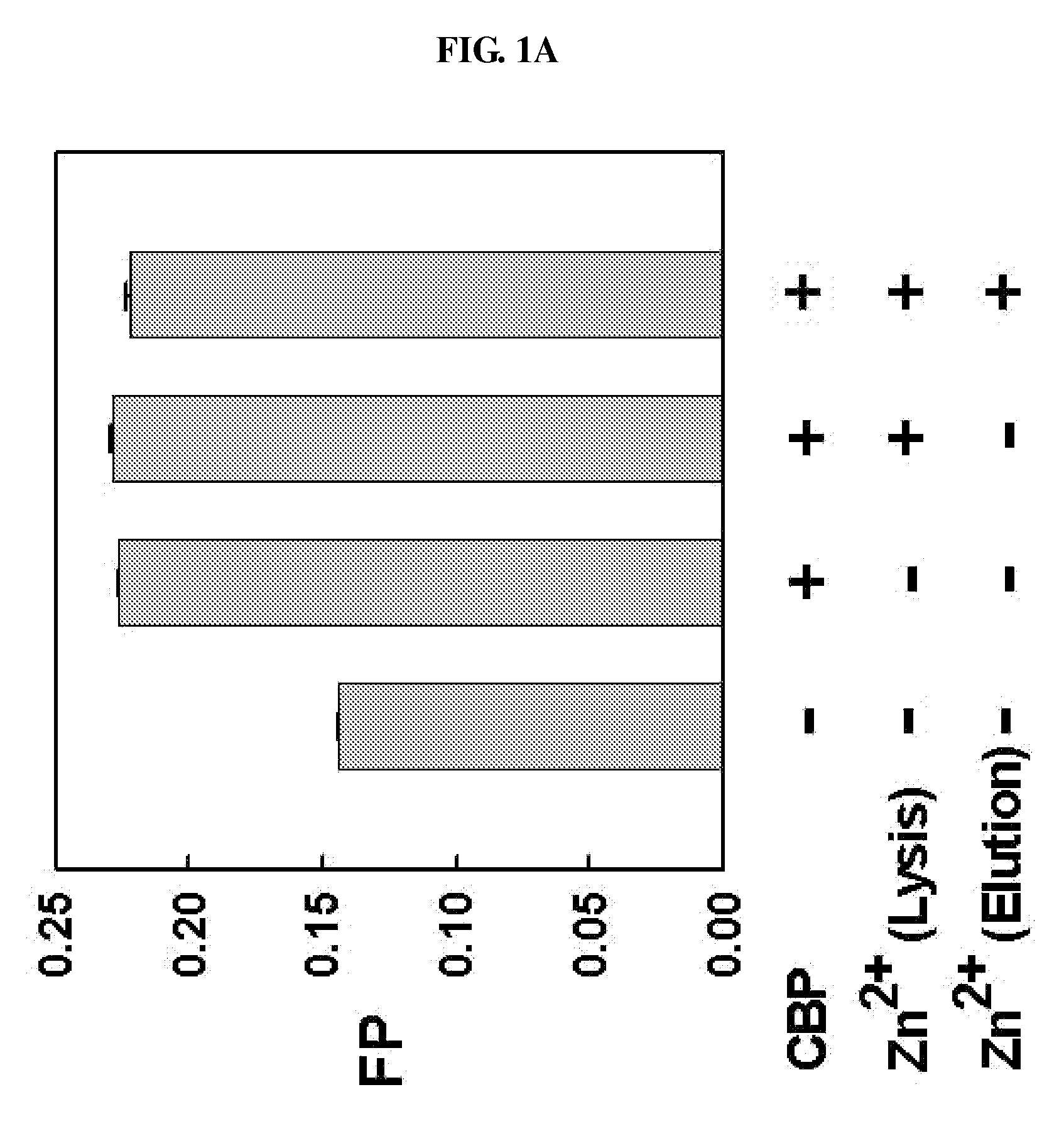
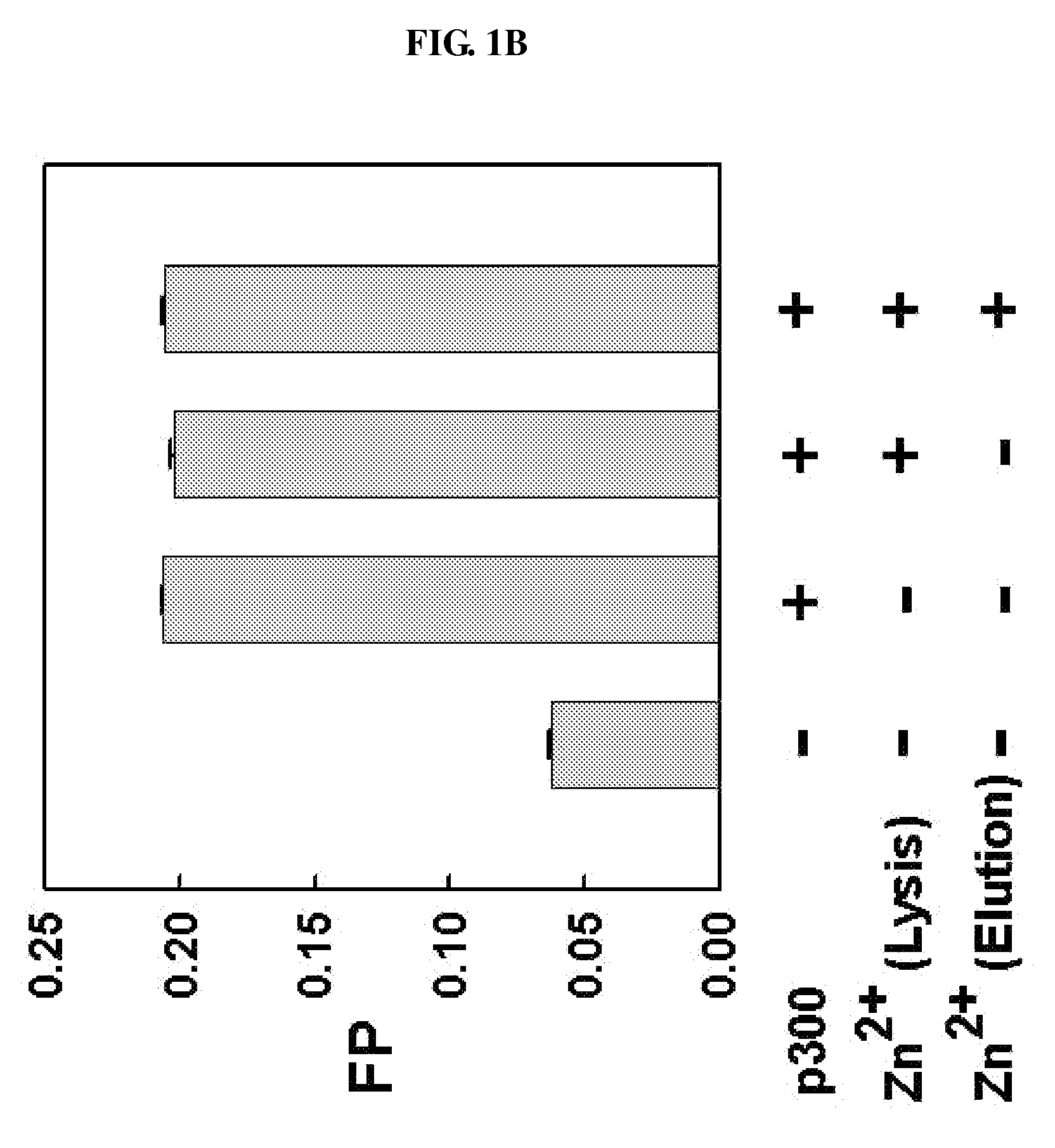
METHOD FOR QUANTITATIVE ANALYSIS OF INTERACTIONS BETWEEN HIF-1ALPHA C-TERMINAL PEPTIDES AND CBP OR p300 PROTEINS AND METHOD OF SCREENING INHIBITORS USING THE SAME
InactiveUS20090029390A1Simple methodCompound screeningApoptosis detectionS-NitrosylationPhosphorylation
The present invention relates to a method for quantitative analysis of interactions between fluorescein-labeled HIF-1α (alpha) C-terminal peptides and cAMP-responsive element binding protein (CBP) or p300 proteins, and a method of screening inhibitors against the formation of HIF-1α-p300 or HIF-1α-CBP protein complexes using the above method.Therefore, the fluorescence polarization (FP) measurement method of the present invention is useful for systemically evaluating the HIF-1α-CBP or HIF-1α-p300 interactions, and examining the effects of posttranslational modifications (hydroxylation, S-nitrosylation, and phosphorylation) of the C-TAD peptide of HIF-1α on the recruitment of p300.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
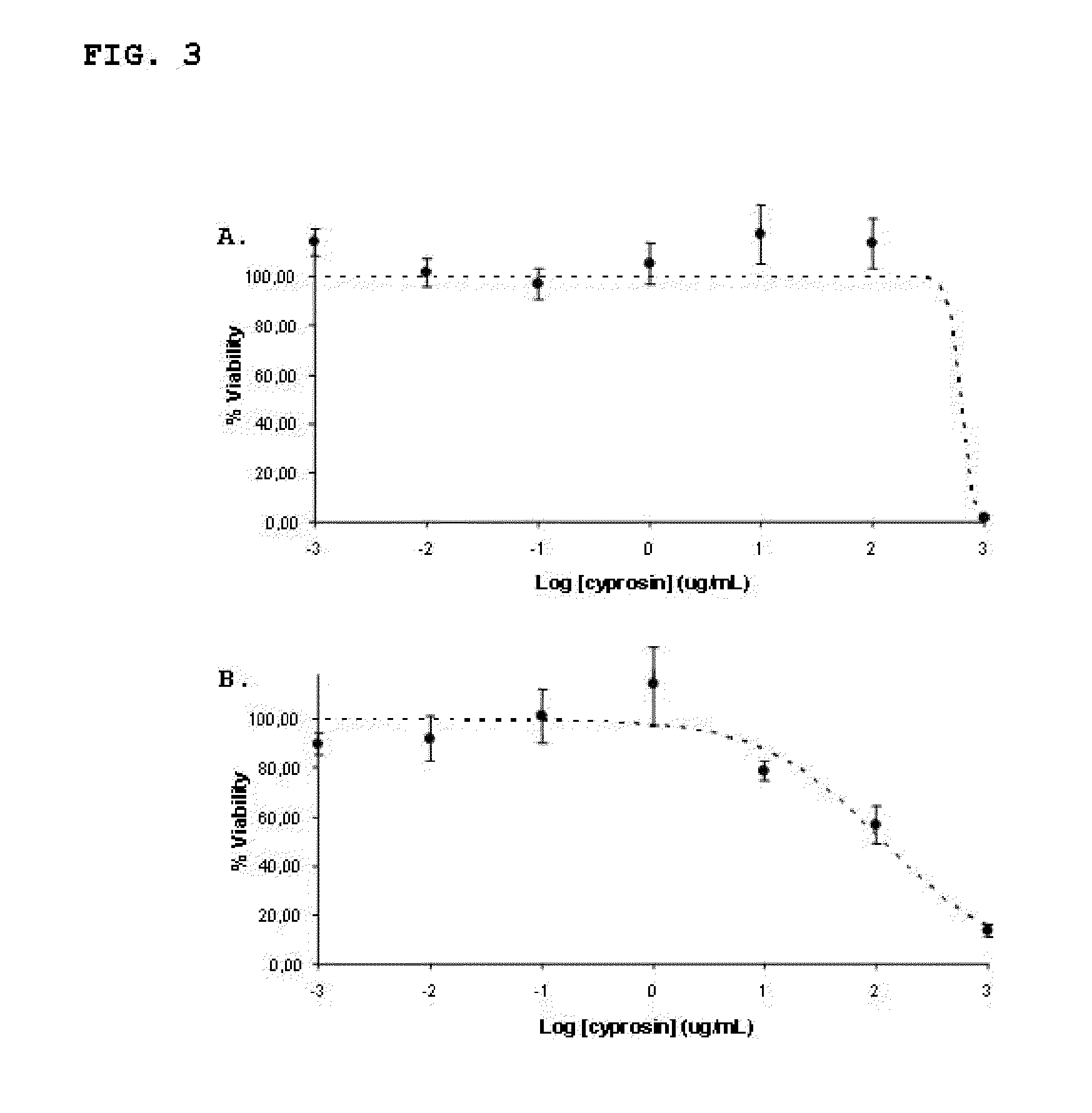
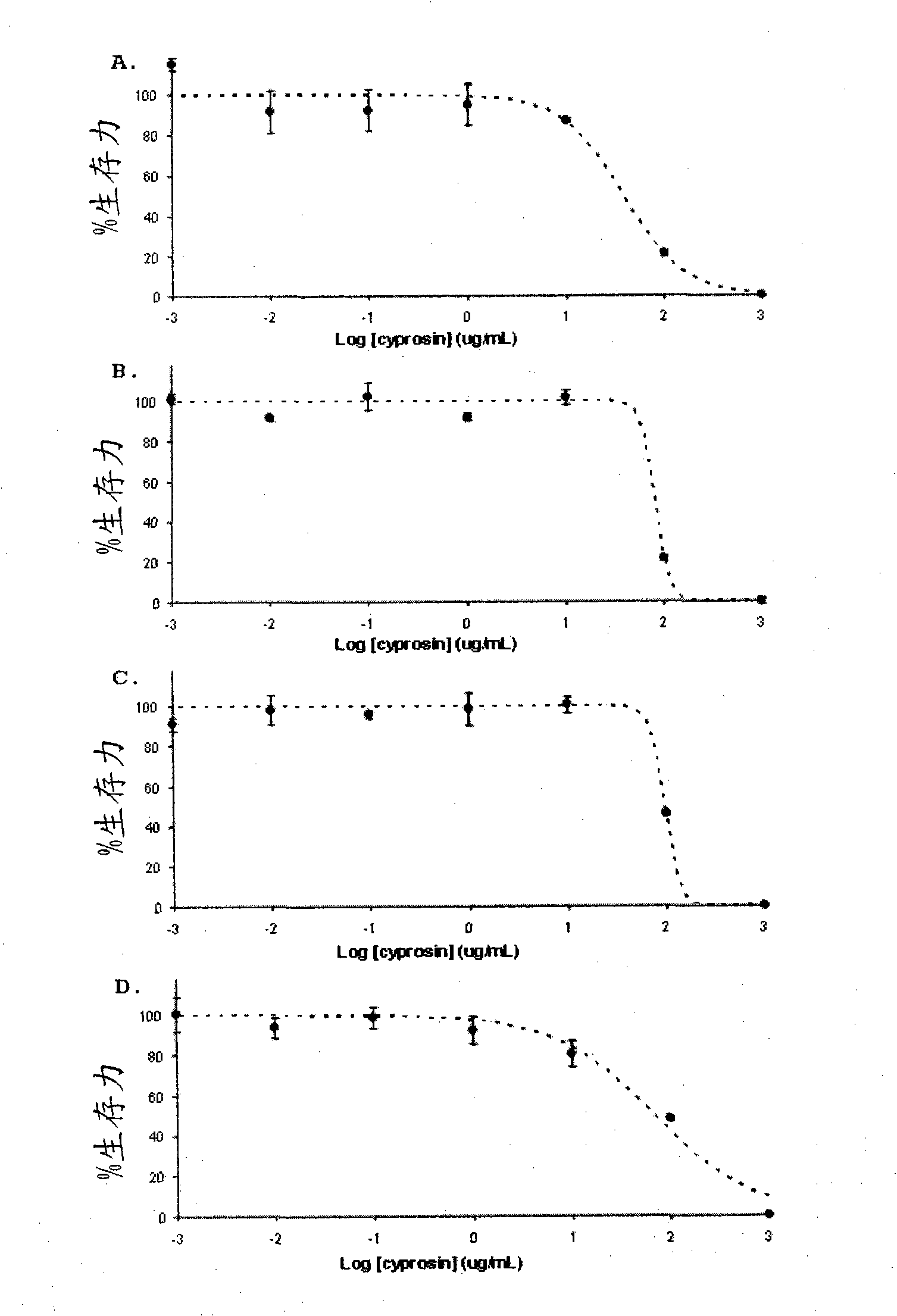
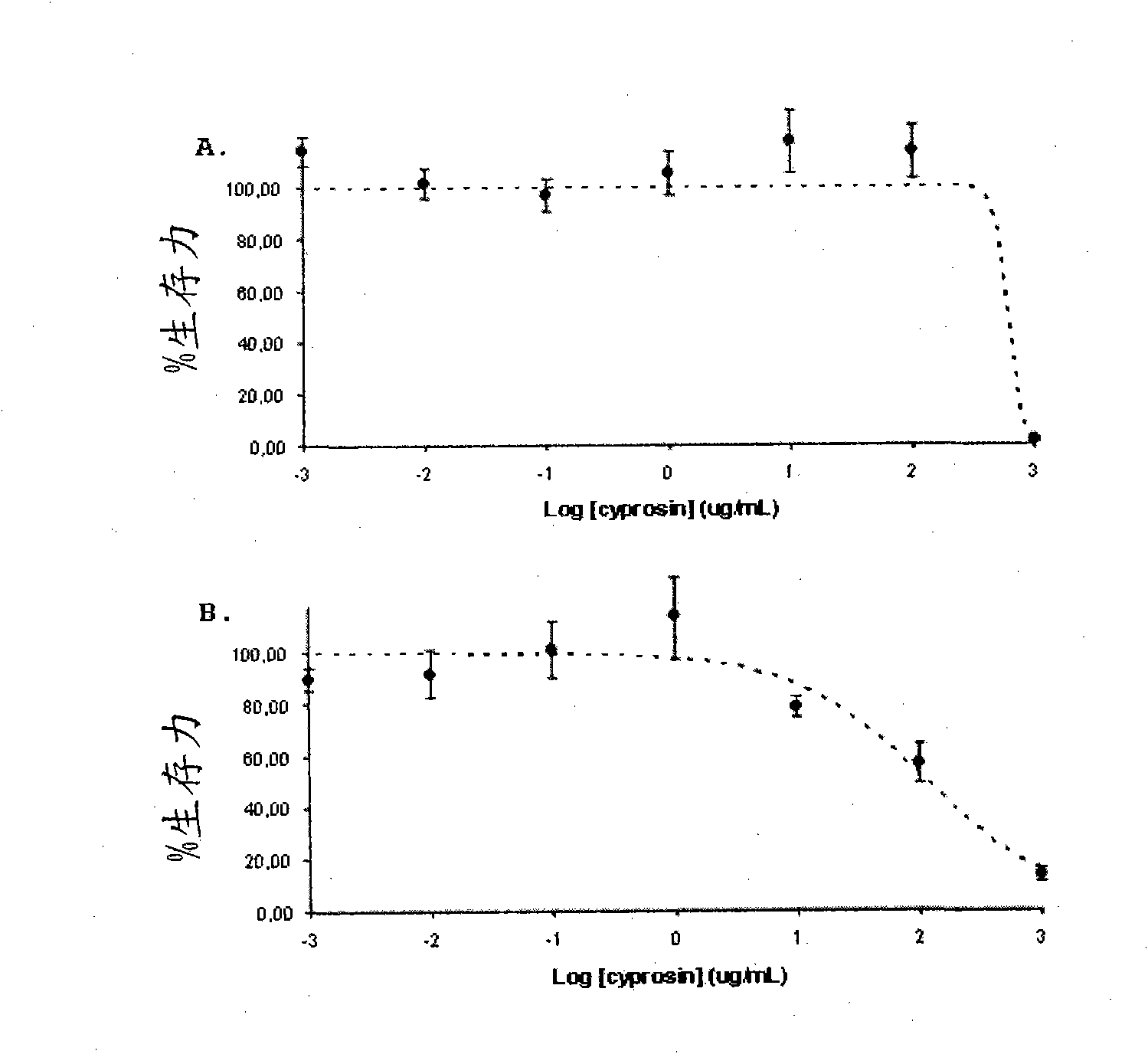
Pharmaceutical compositions containing the enzyme cyprosin, an aspartic peptidase from cynara cardunculus and its inclusion in antitumour formulations
InactiveUS20110104286A1Inhibit cell proliferationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsHeterologousMyokine
An aspect of the present invention is the use of a preparation containing a phytepsin, more specifically a cyprosin, containing the heterodimer, its N-terminal pro-peptide, the mature N-terminal peptide, and mature C-terminal peptide, as well as other precursor species, processing products, and aggregate species, either isolated or in any combinations of the former, native, extracted and partially purified from flowers of Cynara cardunculus, or recombinant, extracted from the supernatant from a culture of Saccharomyces cereviseae genetically modified for the heterologous production of cyprosin, for therapeutic applications more precisely for its use as an antitumor agent.
Owner:ECBIO INVESTIGACAO E DESENVOLVIMENTO EM BIOTECHA
Inhibitors of fusion between viral and cell membranes as well as compositions and methods of using them
ActiveUS20170216448A1Improve efficacyEfficiently in vitroOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCell membraneViral membrane
The present application relates to an inhibitor of fusion between a viral membrane from an enveloped virus and a cell membrane, where the viral membrane comprises a fusion mediating protein including a C-terminal peptide. The inhibitor comprises the C-terminal peptide of the fusion mediating protein from an enveloped virus and tocopherol or a derivative or pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof attached to the C-terminal peptide. Also disclosed is a pharmaceutical composition including the inhibitor as well as methods of inhibiting viral fusion, blocking viral spread, and preventing or treating viral infection, with the inhibitor or pharmaceutical composition.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
Fusion proteins for the treatment of allergic diseases
InactiveUS9005630B2Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFibrinogenBioinformaticsDisease cause
The present invention relates to a fusion protein comprising a first peptide and a second peptide linked together with a linker, wherein the first peptide is an allergen and the second peptide is a targeting unit and the second targeting unit peptide is a FGL-2 C-terminal peptide according to SEQ ID no 1. Provided herein are also uses of said fusion protein as a vaccine for treating shrimp allergy, as well as a vaccine composition and methods of its production.
Owner:VETERINRINSTTET
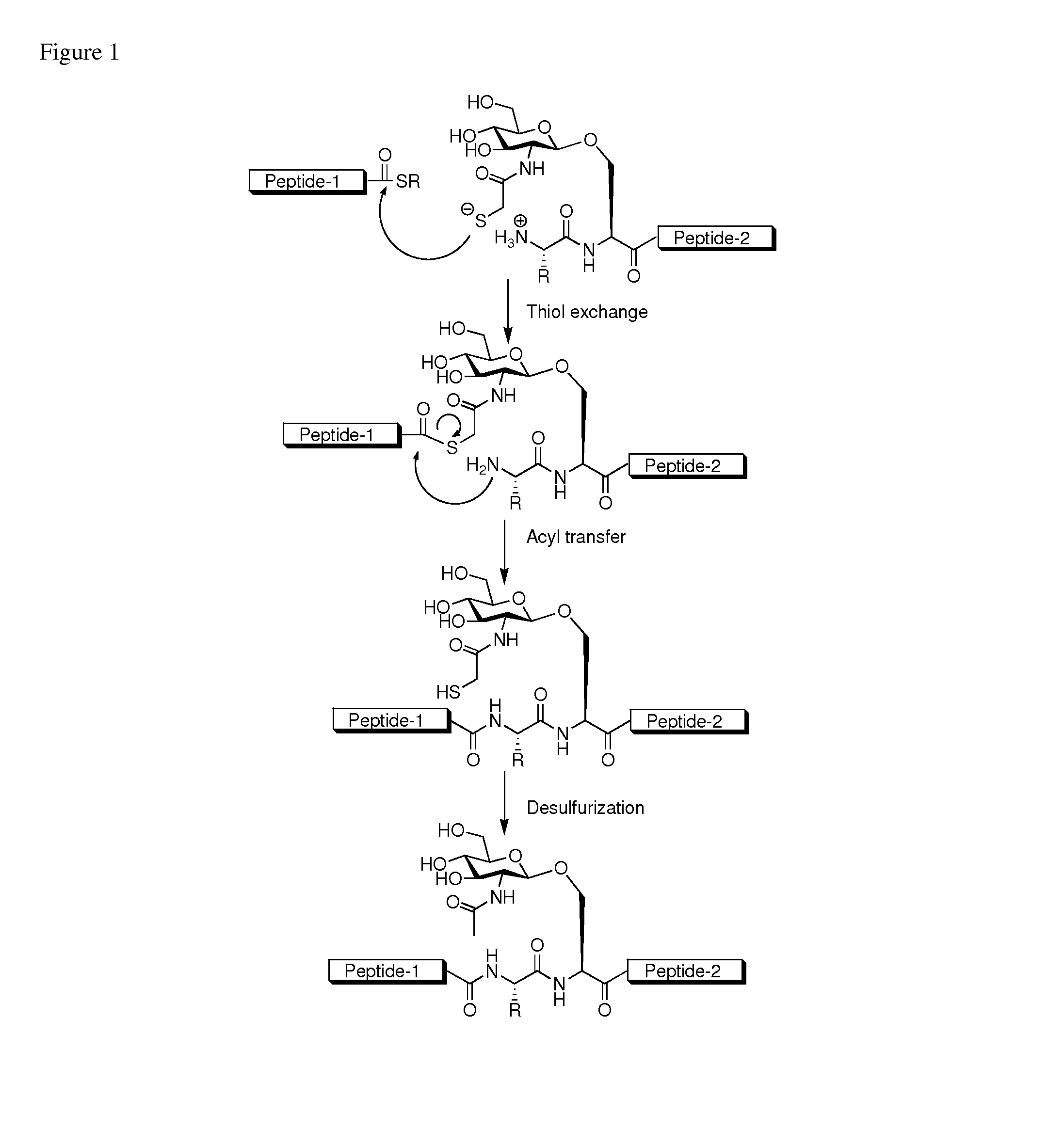
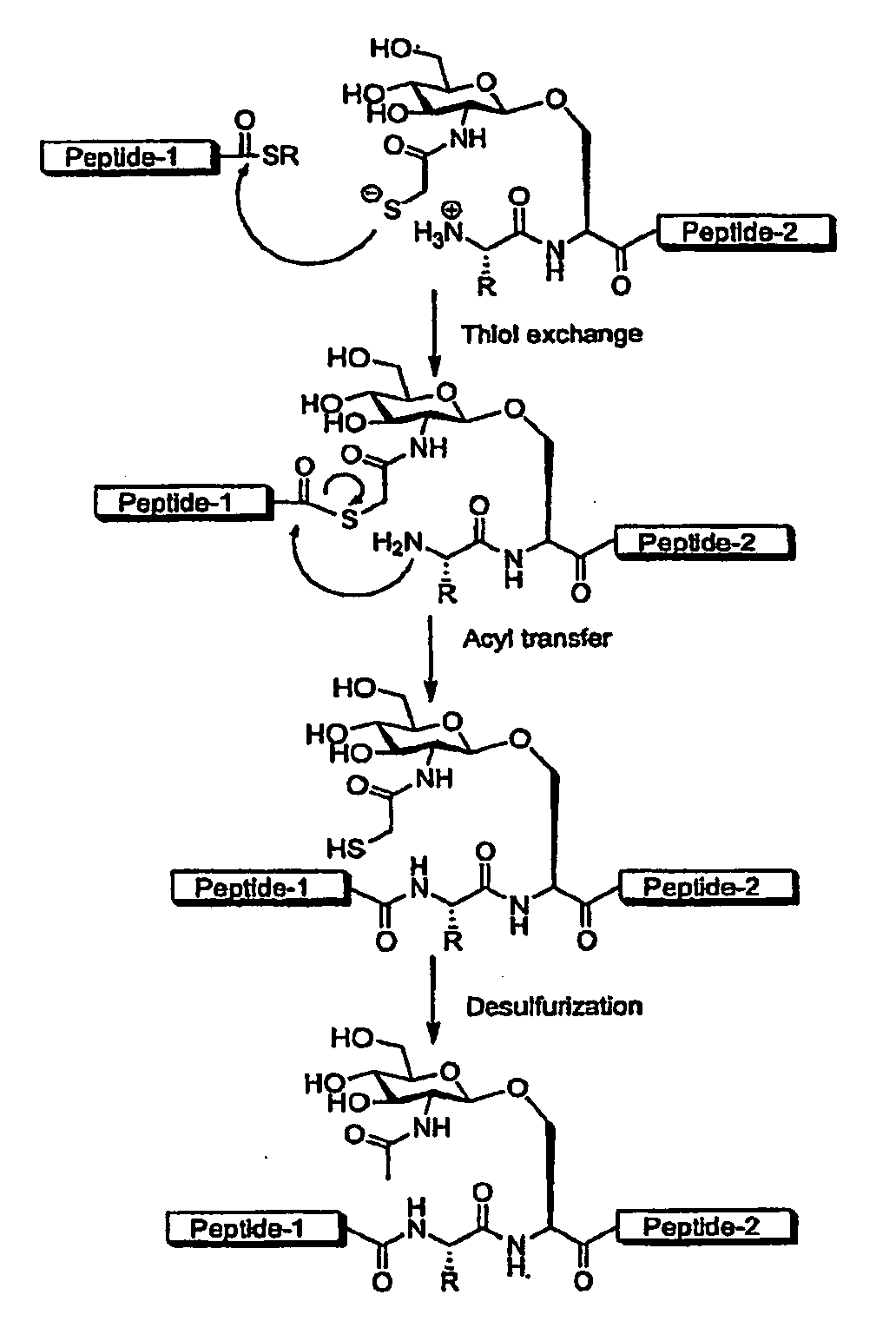
Method of preparing glycopeptides
ActiveUS8816050B2Difficult to prepareHigh yieldSaccharide peptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsGlycopeptideCarbohydrate moiety
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Pharmaceutical compositions containing the enzyme cyprosin, an aspartic peptidase from cynara cardunculus and its inclusion in antitumour formulations
The object of the present invention is the use of a preparation containing a phytepsin, more specifically a cyprosin, containing the heterodimer, its N-terminal pro-peptide, the mature N-terminal peptide, and mature C-terminal peptide, as well as other precursor species, processing products, and aggregate species, either isolated or in any combinations of the former, native, extracted and partially purified from flowers of Cynara cardunculus, or recombinant, extracted from the supernatant from a culture of Saccharomyces cereviseae genetically modified for the heterologous production of cyprosin, for therapeutic applications more precisely for its use as an antitumor agent.
Owner:ECBIO INVESTIGACAO E DESENVOLVIMENTO EM BIOTECHA SA
Anti-obese immunogenic hybrid polypeptides and Anti-obese vaccine composition comprising the same
InactiveUS20110002955A1Process stabilityStable anti-obesityPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulinsNucleotideHepatitis B virus surface Antigen
Disclosed is an immunogenic hybrid polypeptide for the prevention and treatment of obesity, in which a mimetic peptide of a B cell epitope of apolipoprotein B-IOO; a rabies virus helper T cell epitope or hepatitis B virus surface antigen helper T cell epitope and a C-terminal peptide fragment of mouse apolipoprotein Cu or a mimetic peptide of a B cell epitope of apolipoprotein B-100 are fused to each other in that order in the direction from the N terminus to the C terminus thereof. Also, a vaccine composition for the prevention and treatment of obesity, comprising the immunogenic hybrid polypeptide is disclosed, along with a polynucleotide encoding the immunogenic hybrid polypeptide, a recombinant expression vector carrying the polynucleotide, a host cell anchoring the recombinant expression vector, and a method for producing the immunogenic hybrid polypeptide by culturing the host cell transformed with the recombinant expression vector.
Owner:SJ BIOMEDIC INC
Synthesis of peptide alpha-thioesters
InactiveUS20070129537A1Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsThioester synthesisCyclic peptide
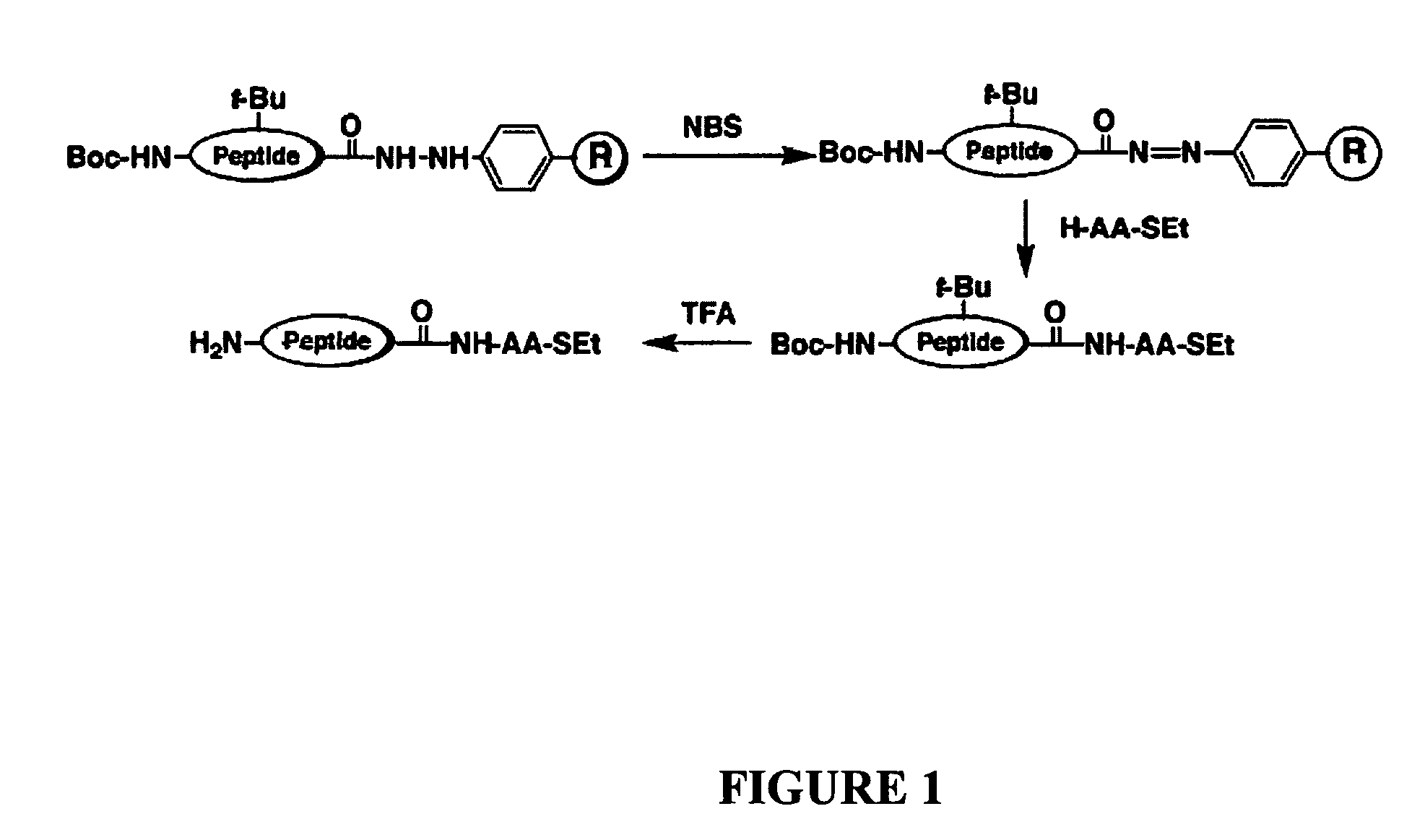
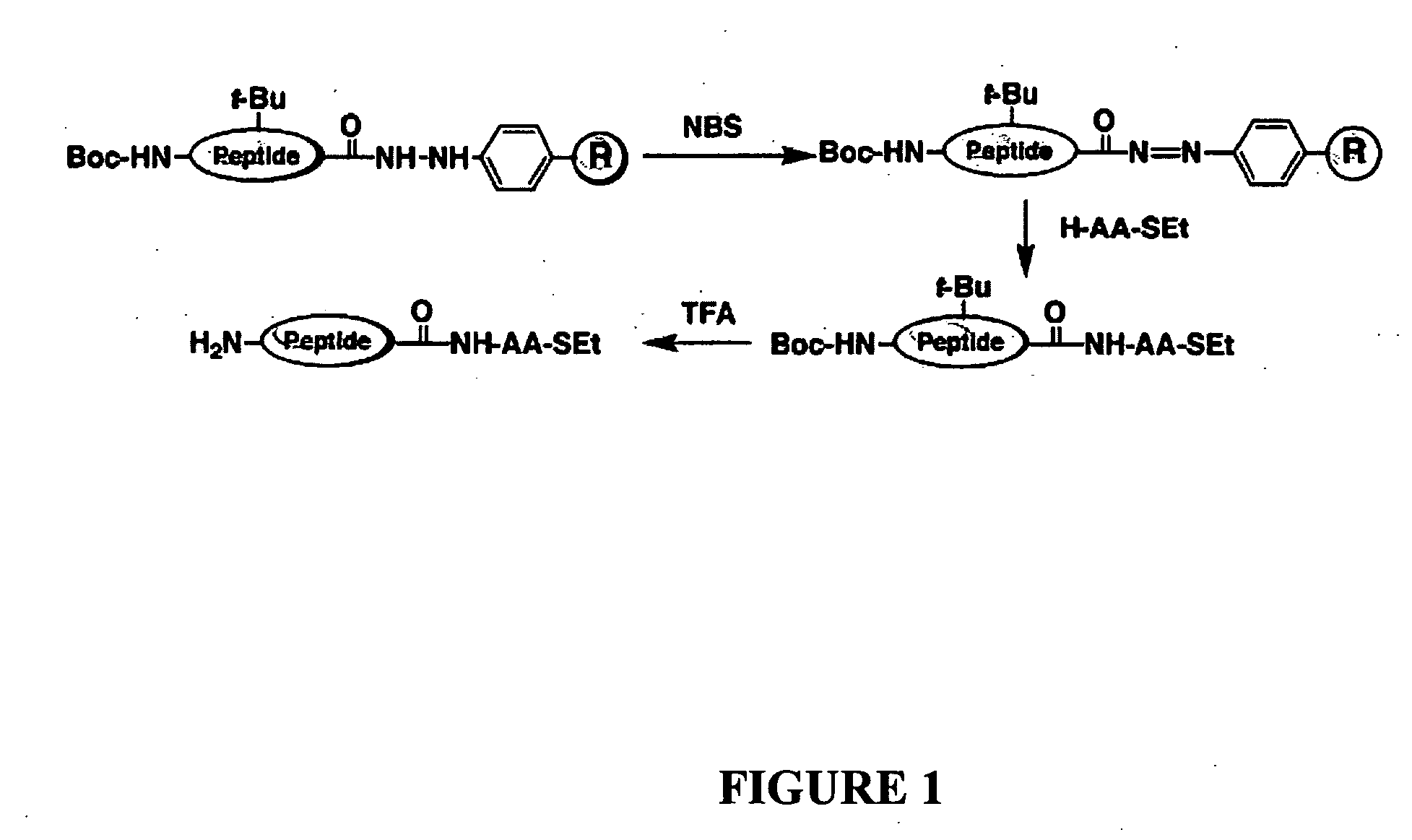
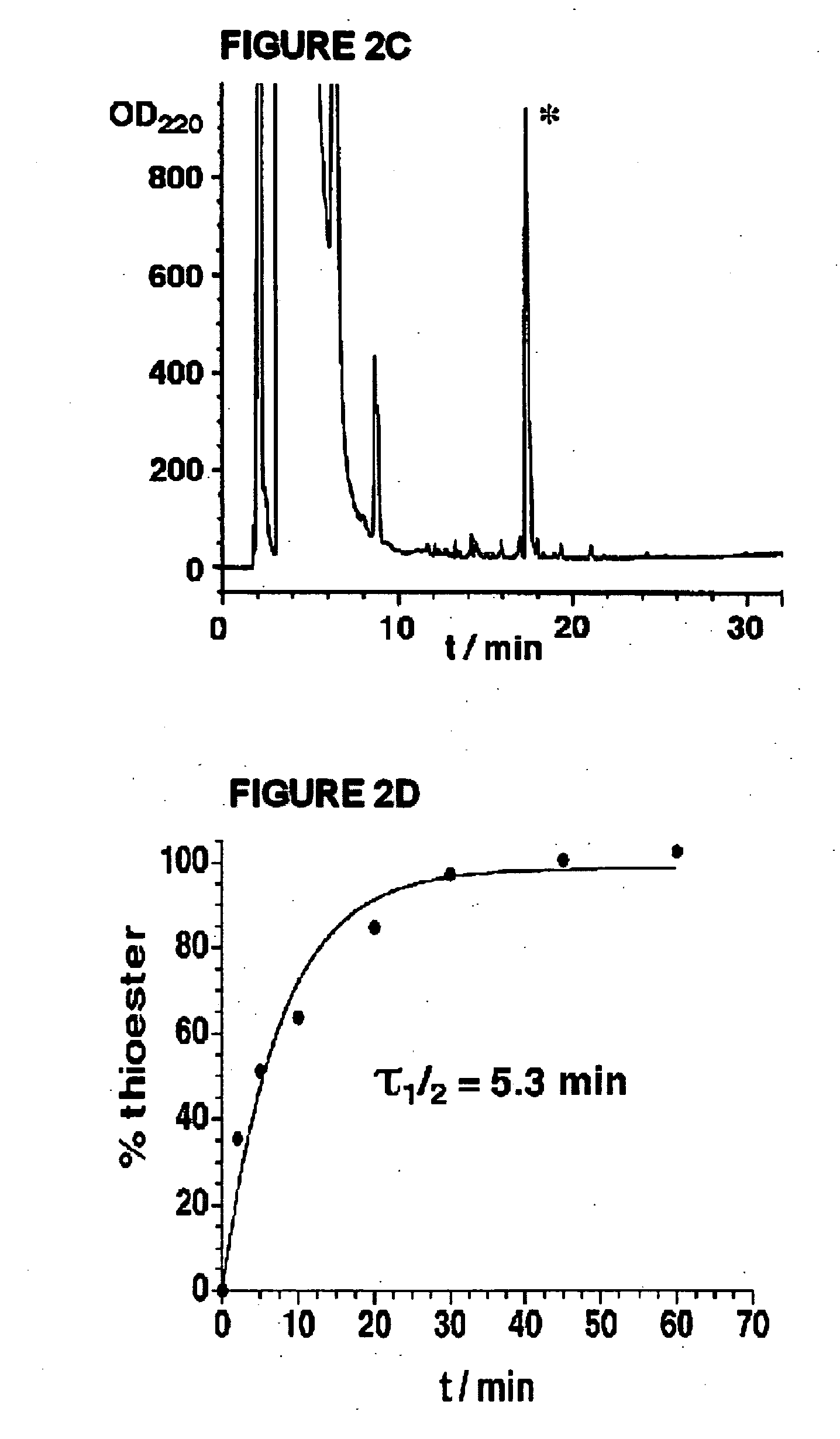
Disclosed herein is a new method for the solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) of C-terminal peptide α thioesters using Fmoc / t-Bu chemistry. This method is based on the use of an aryl hydrazine linker, which is totally stable to conditions required for Fmoc-SPPS. When the peptide synthesis has been completed, activation of the linker is achieved by mild oxidation. The oxidation step converts the acyl-hydrazine group into a highly reactive acyl-diazene intermediate which reacts with an α-amino acid alkylthioester (H-AA-SR) to yield the corresponding peptide α-thioester in good yield. A variety of peptide thioesters, cyclic peptides and a fully functional Src homology 3 (SH3) protein domain have been successfully prepared.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Borrelia garinii OspA protein C-terminal peptide fragment and application thereof
ActiveCN110483624AGood immune protectionNo adverse side effectsAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsSide effectBorrelia garinii
The invention provides a Borrelia garinii OspA protein C-terminal peptide fragment and an application thereof. The OspA peptide fragment (126-274aa), containing the His label, of the Borrelia gariniiprovided by the invention has good immune protection on rabbits, and does not generate adverse side effects on organisms. The invention provides an effective means for treating or preventing Borreliaburgdorferi infection.
Owner:ICDC CHINA CDC
Methods for analysing protein samples based on the identification of c-terminal peptides
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Diketopiperazine forming dipeptidyl linker
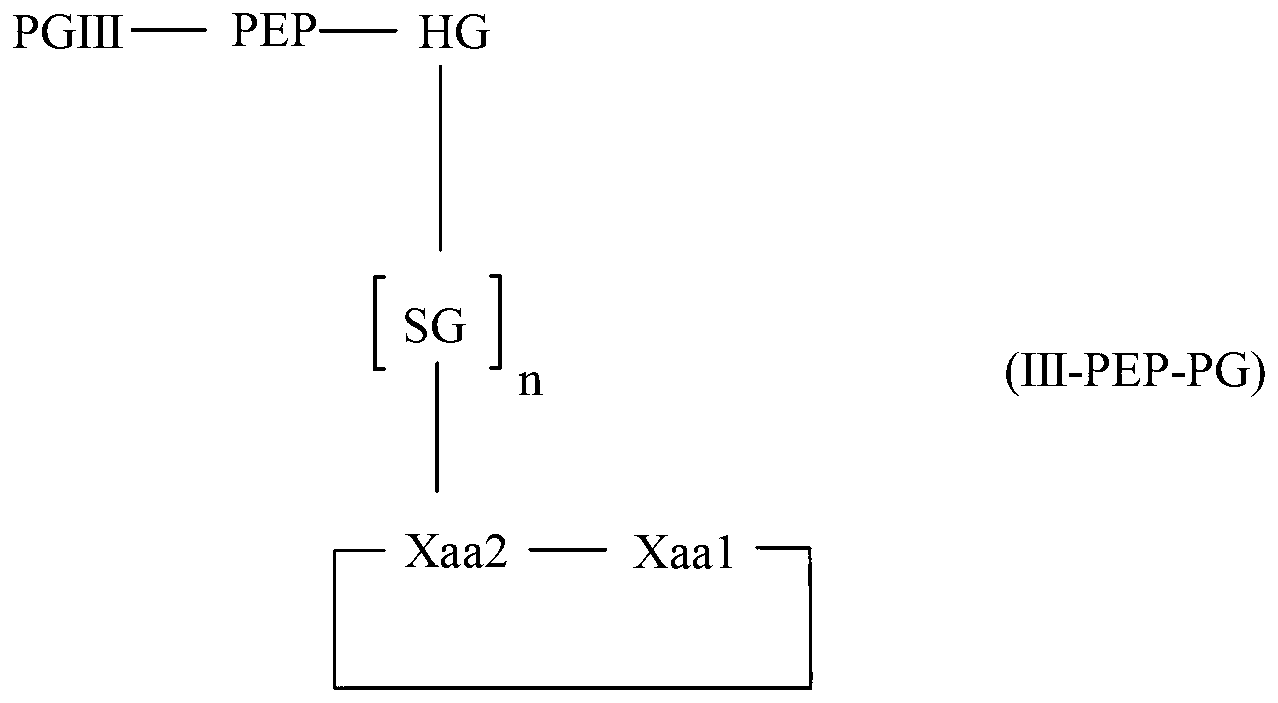
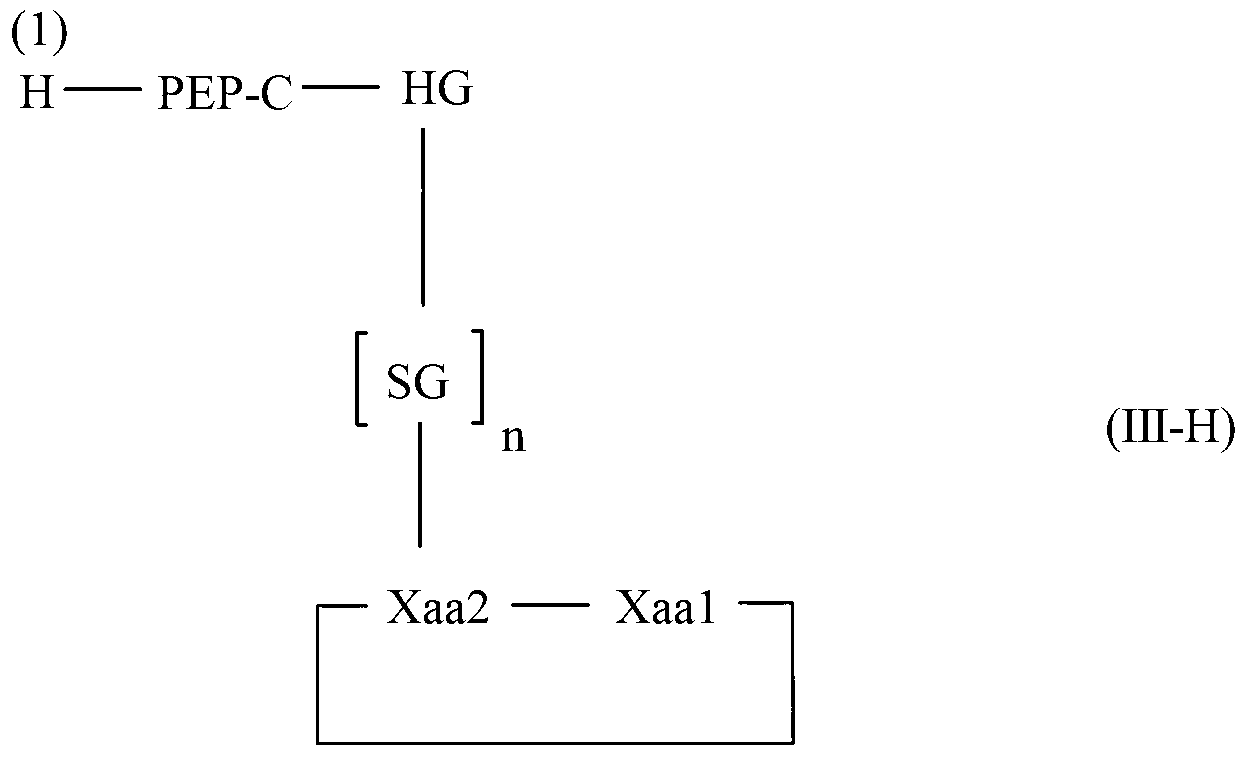
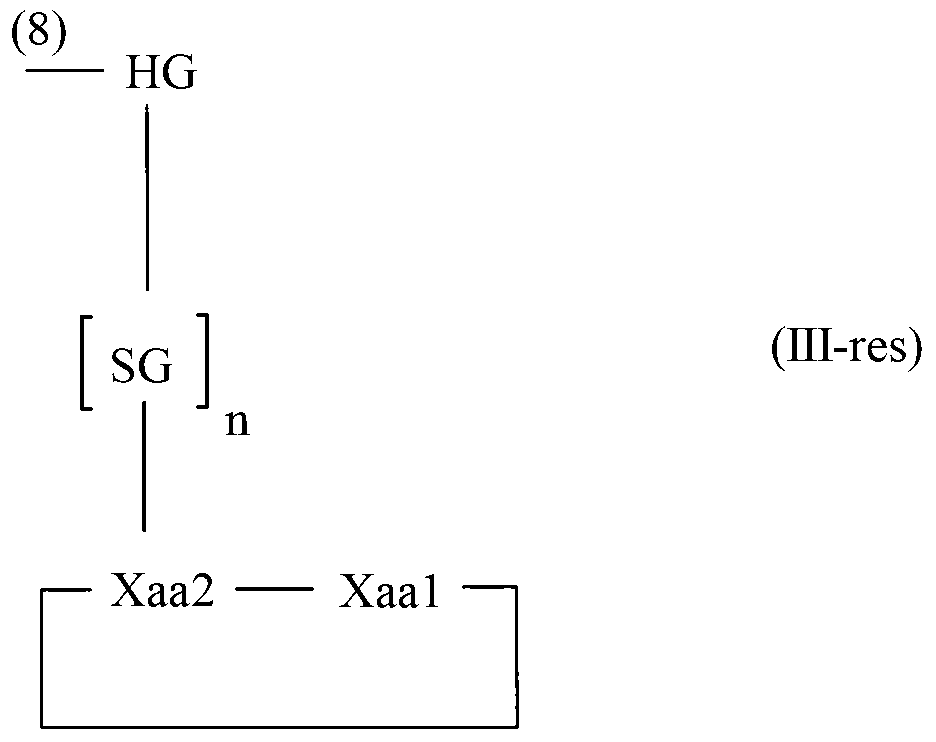
The invention relates to a method for homogeneous solution phase peptide synthesis (HSPPS) of a N-terminal peptide fragment PEP-N and a C-terminal peptide fragment C-PEP, with C- PEP carrying a specific diketopiperazine (DKP) comprising C-terminal protecting group, which contains a handle group HG, with HG being connected to the C-terminus of the peptide fragment; thereby this specific DKP comprising C-terminal protecting group can be selectively cleaved from the peptide as a conventionally used C-terminal protecting group. By the use of this DKP and HG comprising C-terminal protecting group, certain process steps in convergent peptide synthesis based on a combination of HSPPS and solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS) can be avoided. The invention relates further to a method for the preparation of such specifically protected fragment C-PEP by SPPS by using a linker comprising a specific dipeptide and HG for connecting the growing peptide chain to the resin, which linker forms said DKP group, when the peptide fragment C-PEP is cleaved from the supporting resin; and further to the intermediates of the preparation method.
Owner:LONZA LTD
Application of a polypeptide in the preparation of drugs for intravenous, intraperitoneal or nasal administration
ActiveCN108992661BGood analgesic effectLittle side effectsNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNasal cavitySide effect
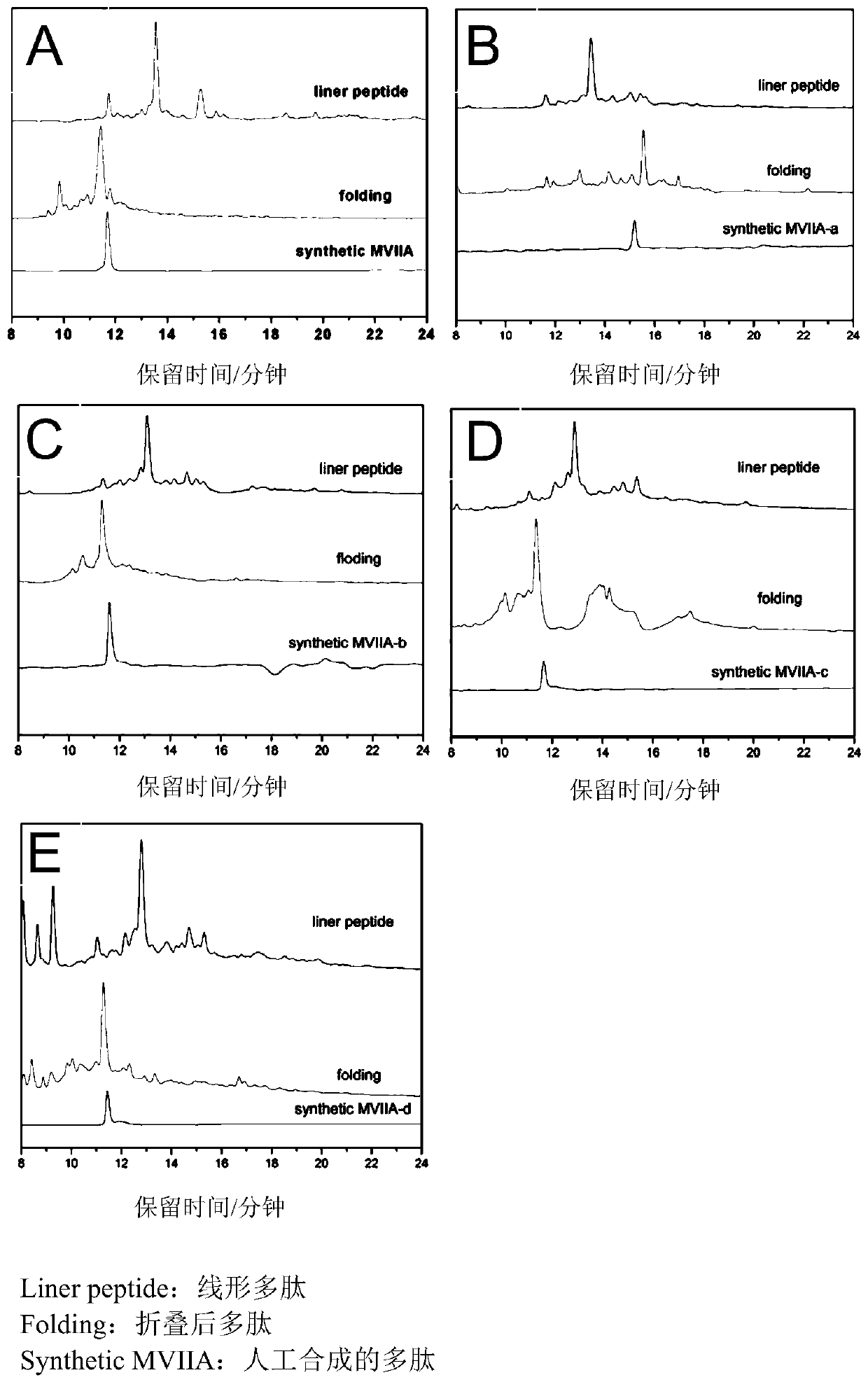
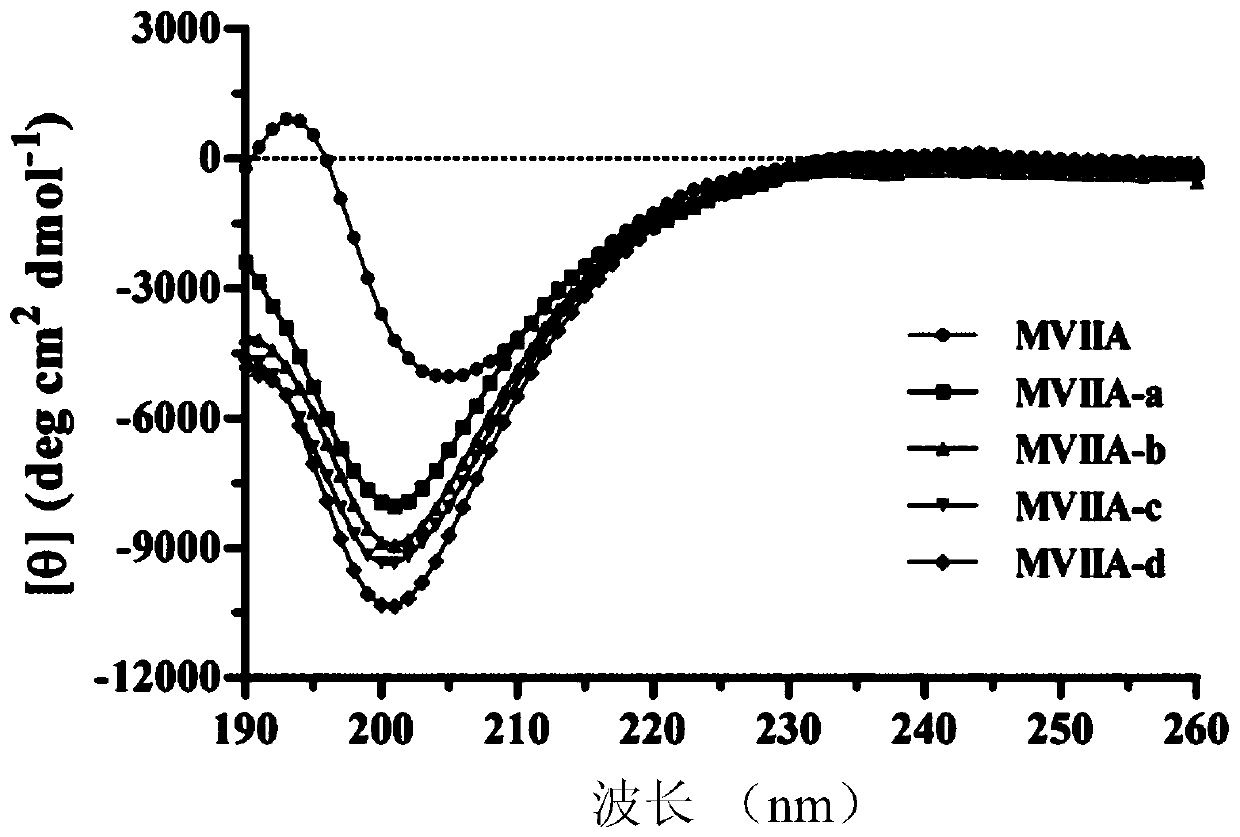
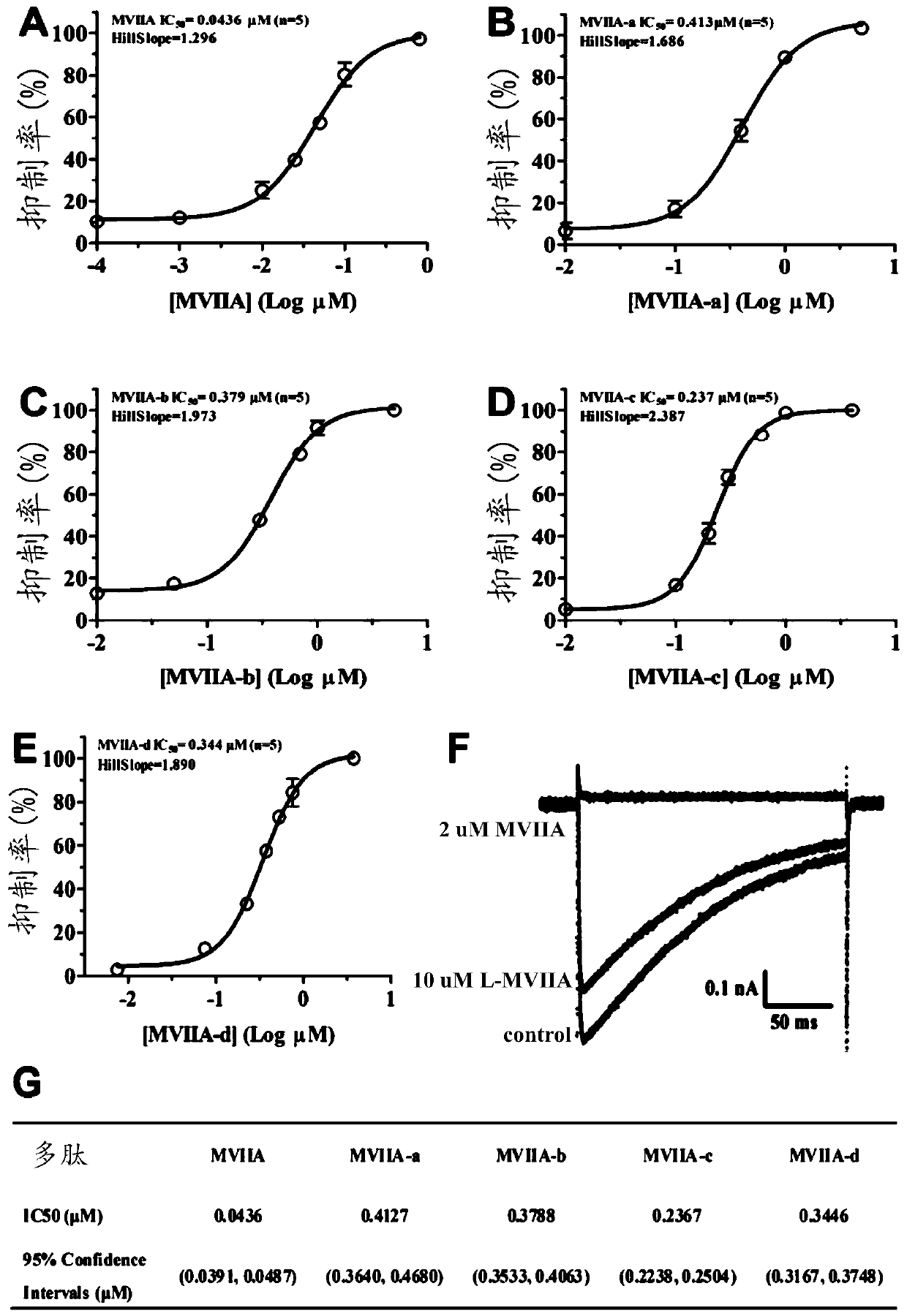
The invention relates to the application of a polypeptide in the preparation of drugs for intravenous, abdominal or nasal administration. In the present invention, the C-terminus of ziconotide is connected with the N-terminus of the cell membrane penetrating peptide through three glycines to obtain a polypeptide that can pass through the blood-brain barrier. The polypeptide of the present invention is suitable for intravenous, intraperitoneal or nasal administration, with convenient operation and low clinical risk. Its drug effect in the body lasts for a long time, has excellent analgesic effect, and has small side effects. for large-scale clinical application. The preparation of the polypeptide of the invention is simple, the preparation process and the quality of the preparation process are controllable, and it is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:SHENZHEN RUIJIAN BIOSCI TECH LTD
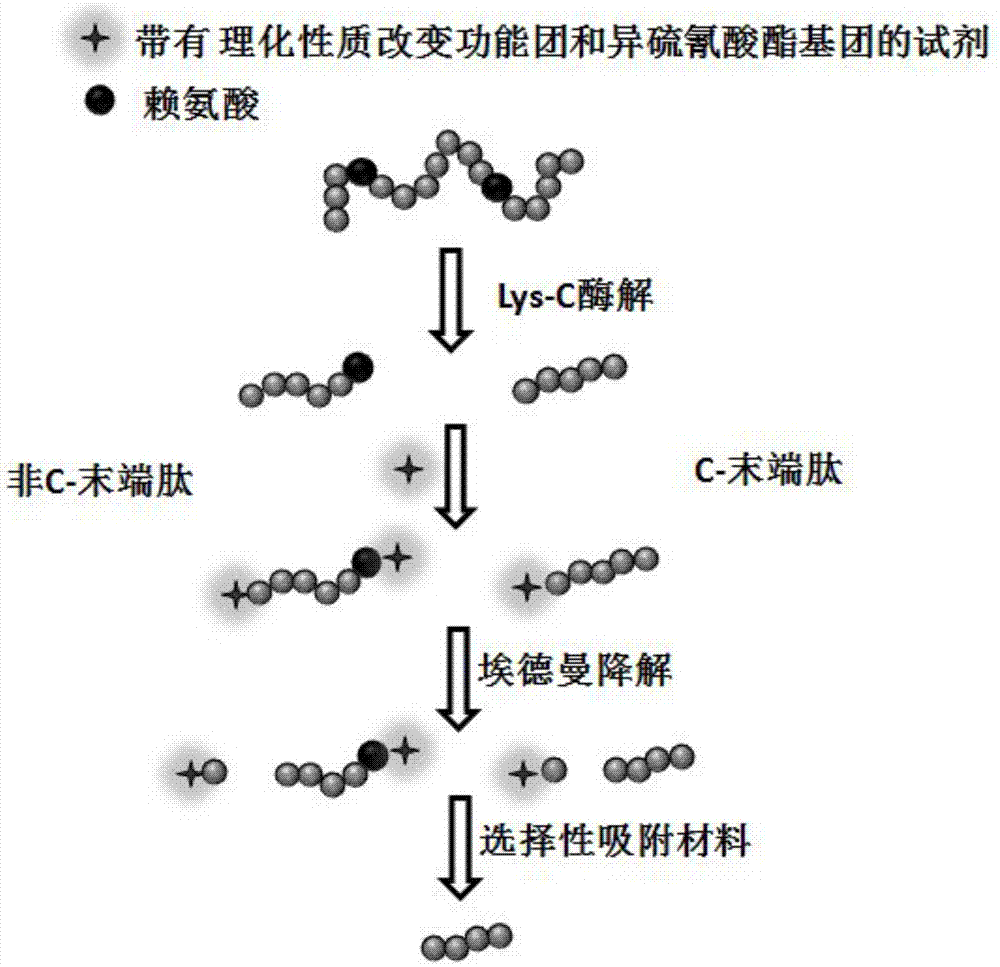
Protein C-terminal peptide enrichment method based on Edman degradation
InactiveCN106855477AFacilitates selective adsorptionHigh enrichment selectivityPreparing sample for investigationEnzyme digestionSide chain
The invention relates to a protein C-terminal peptide enrichment method based on Edman degradation. According to the protein C-terminal peptide enrichment method based on Edman degradation, a protease used for enzyme digestion of peptide chains after lysine is used for enzymatic hydrolysis of a protein sample so as to provide the C terminal of an obtained protein non-C-terminal peptide with a lysine, wherein the protein C-terminal peptide generally contains no lysine; the peptide segments obtained via enzymatic hydrolysis is labeled with an amino reaction reagent with physicochemical property improving functional groups and isorhodanate functional groups; after labeling, Edman degradation is carried out under strong acidic conditions so as to cut the N-terminal first amino acid of the peptide segments off from the peptide segments; the C terminal lysine side chain amino groups of the protein non-C-terminal peptide are labeled with the physicochemical property improving functional groups, so that the physicochemical properties of the protein non-C-terminal peptide are obviously different from that of protein C-terminal peptide; selective absorption of the protein non-C-terminal peptide is carried out based on the different of the physicochemical properties of the protein non-C-terminal peptide and that of the protein C-terminal peptide so as to obtain the protein C-terminal peptide via enrichment.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of preparing glycopeptides
ActiveUS20110060121A1High yieldHigh puritySaccharide peptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsThioester synthesisGlycopeptide
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Therapeutic application of S. pyogenes C-terminal peptide
ActiveUS9289485B2Bacterial antigen ingredientsWhole-cell/virus/DNA/RNA ingredientsMedicineImmunogenicity
A method for treating rheumatic heart disease comprising administering an immunogenic composition against group A beta hemolytic streptococcus.
Owner:GUGLIELMI LUIZA GUILHERME +1
Protein production method, fusion protein, and antiserum
InactiveUS8865428B2Improve isolationPromote recoveryBacterial antigen ingredientsDepsipeptidesAureobasidium sp.Bacillus thuringiensis
Disclosed are a highly efficient method for production of heterologous proteins performed by utilizing microorganisms, as well as fusion proteins, and an antiserum. The method includes a method for production of a protein (A) in the form of a fusion protein, comprising the steps of (a) preparing a DNA which codes for a fusion protein comprising the peptide chain forming the protein (A) and the C-terminal peptide or its fragment (B) of the Cry proteins produced by Bacillus thuringiensis, and (b) introducing the DNA into a host bacterium to transform the same, and (c) allowing the fusion protein to be expressed in the transformed host bacterium, as well as a method for production of the protein (A) itself comprising a further step of removing the peptide chain (B) from the fusion protein obtained.
Owner:UNIV OKAYAMA +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com