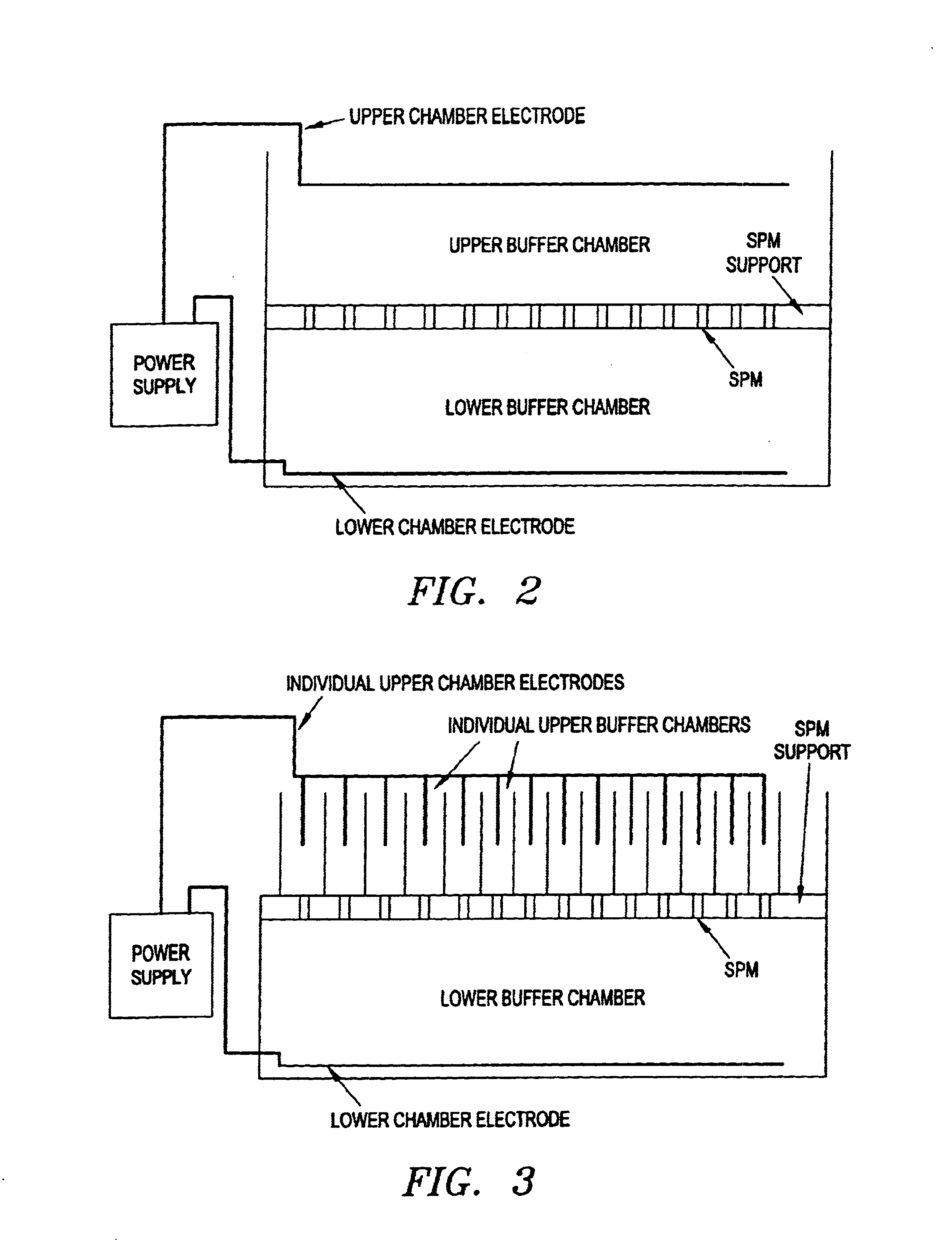
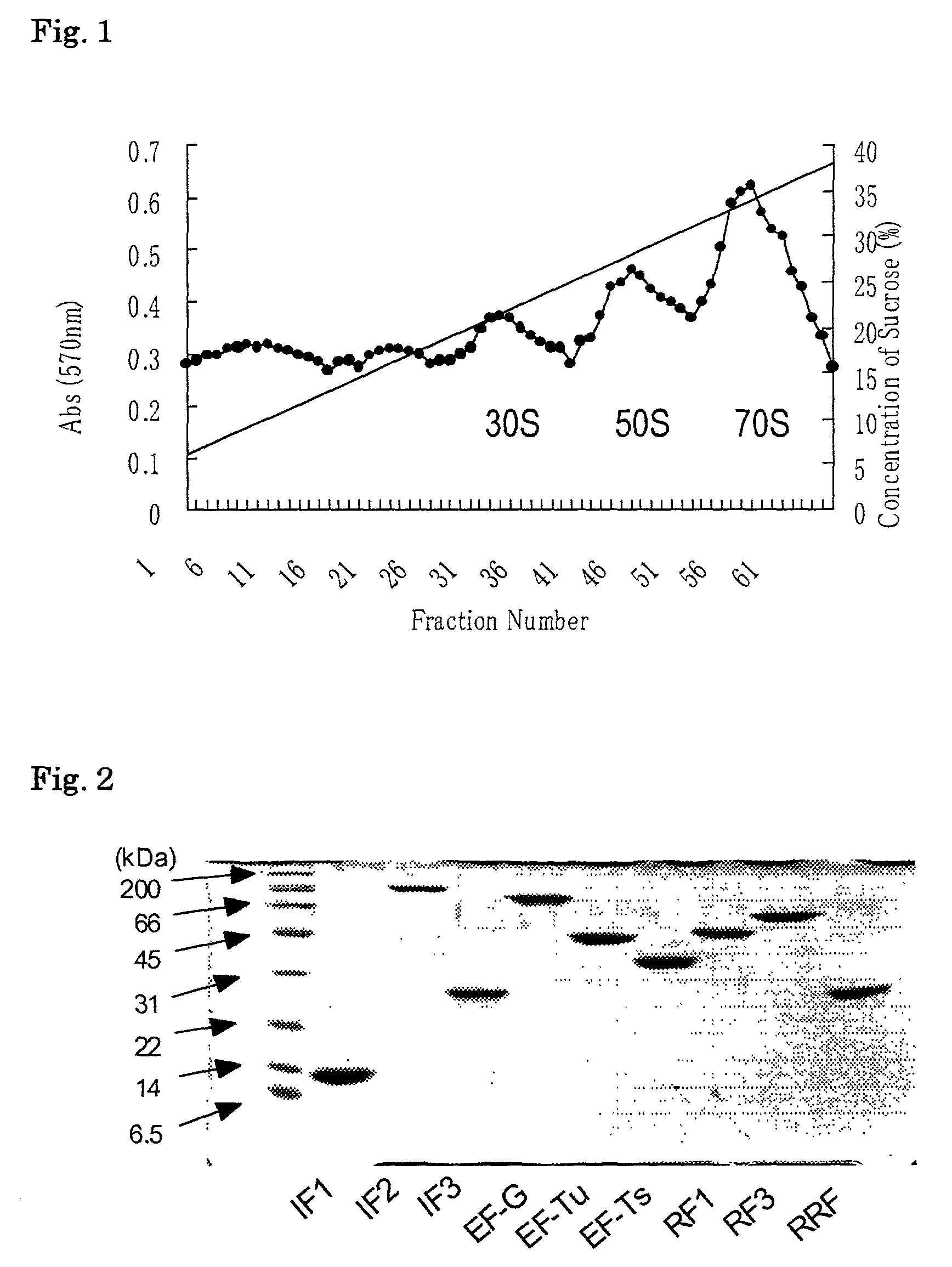
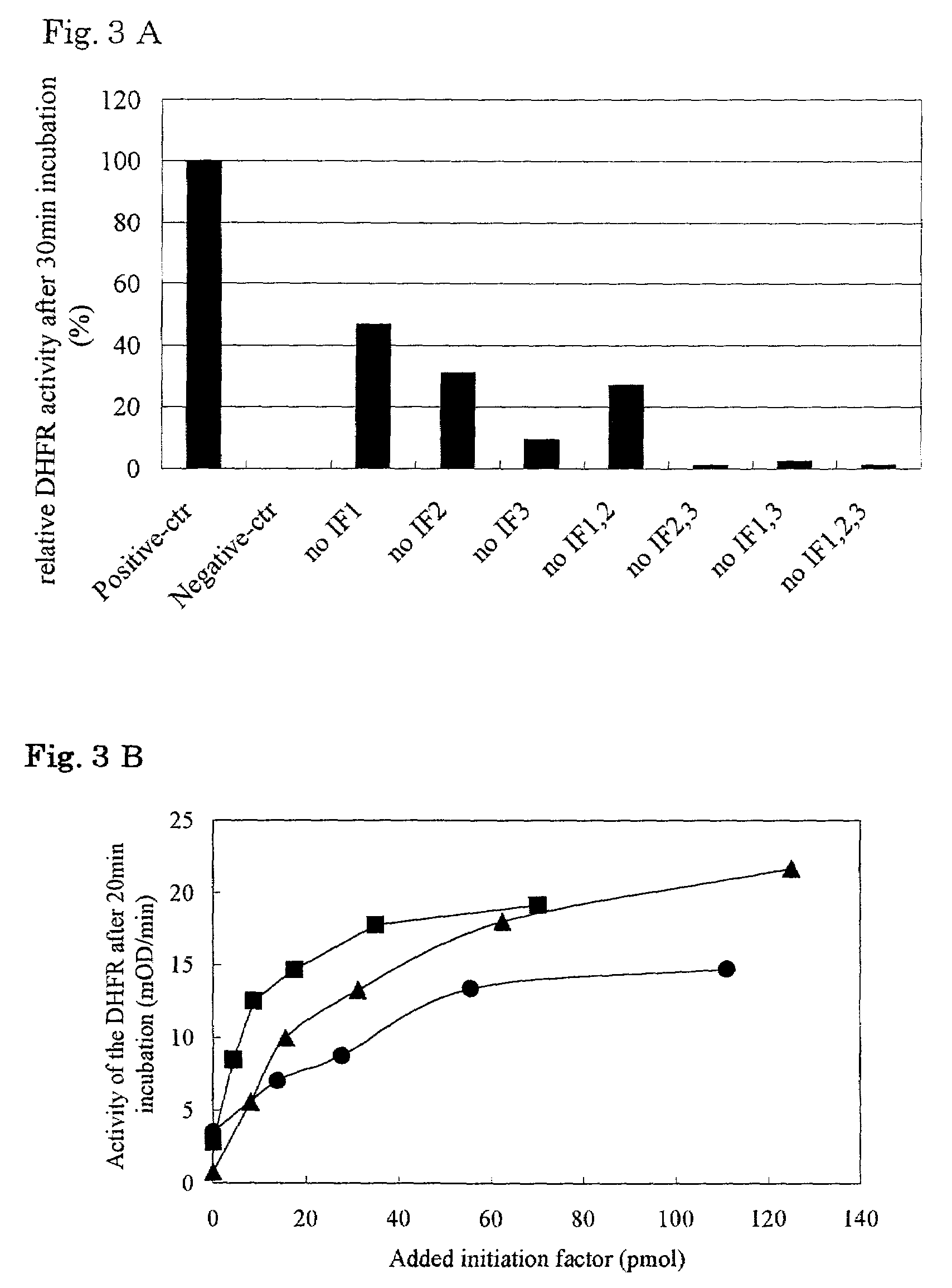
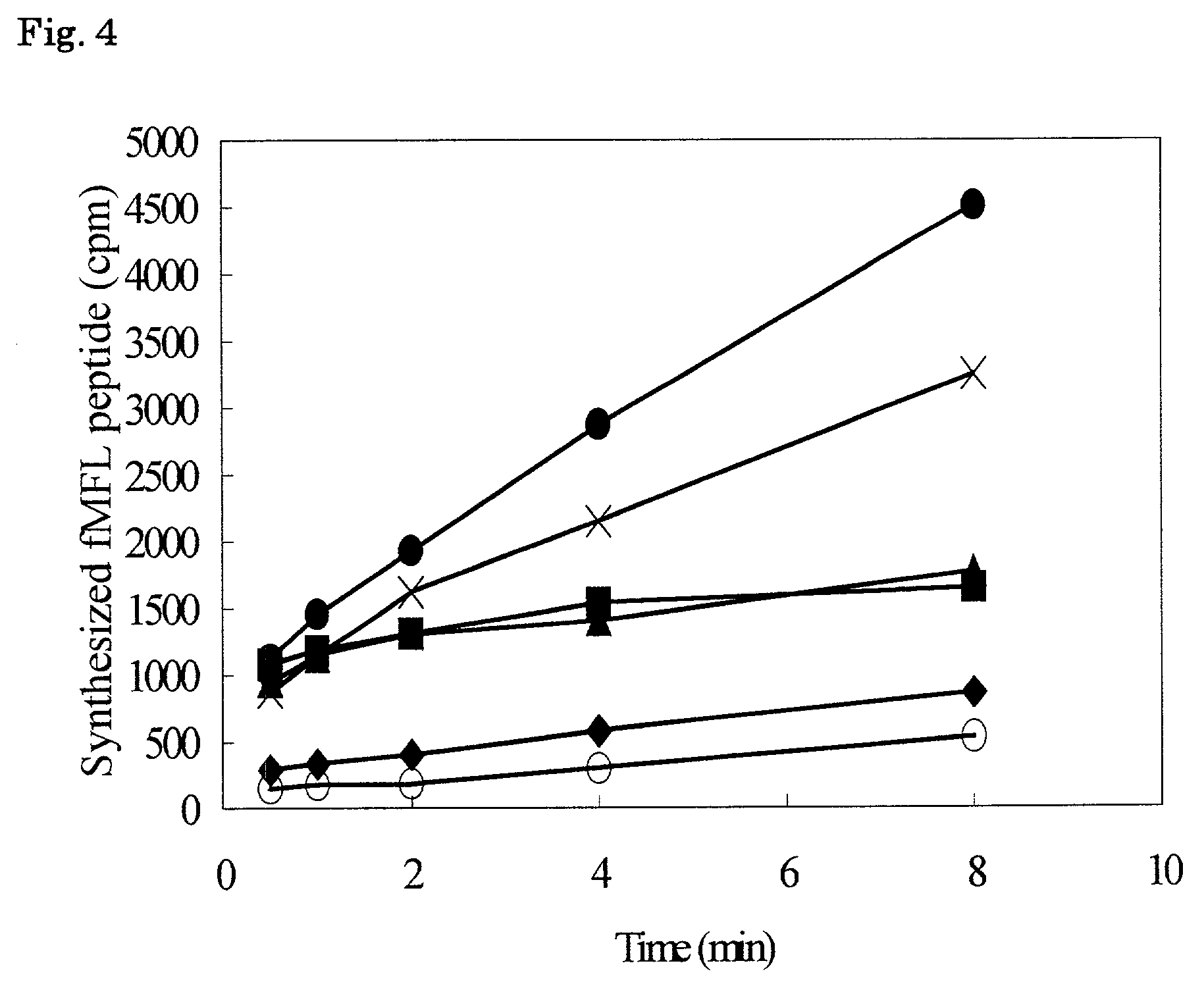
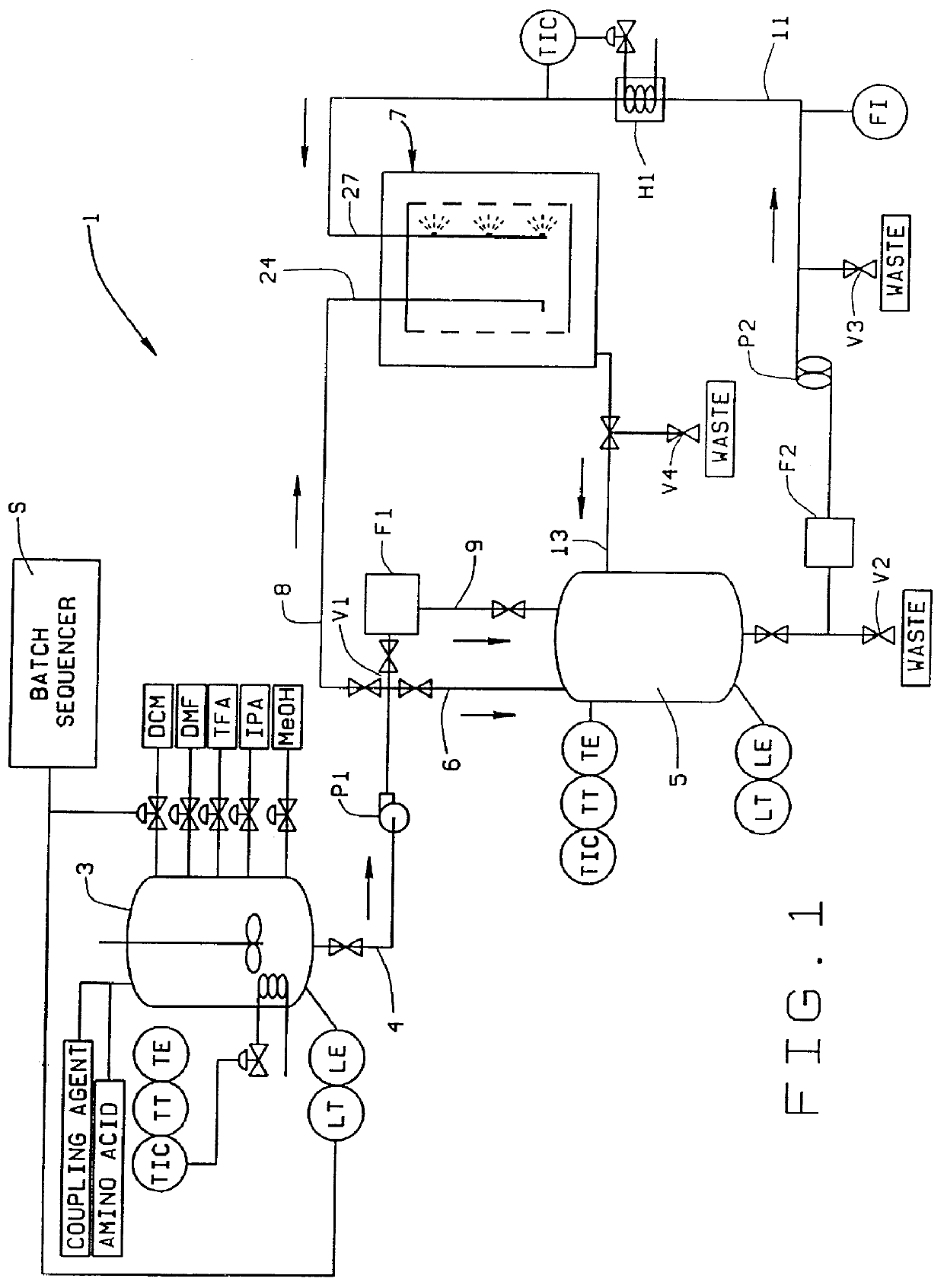
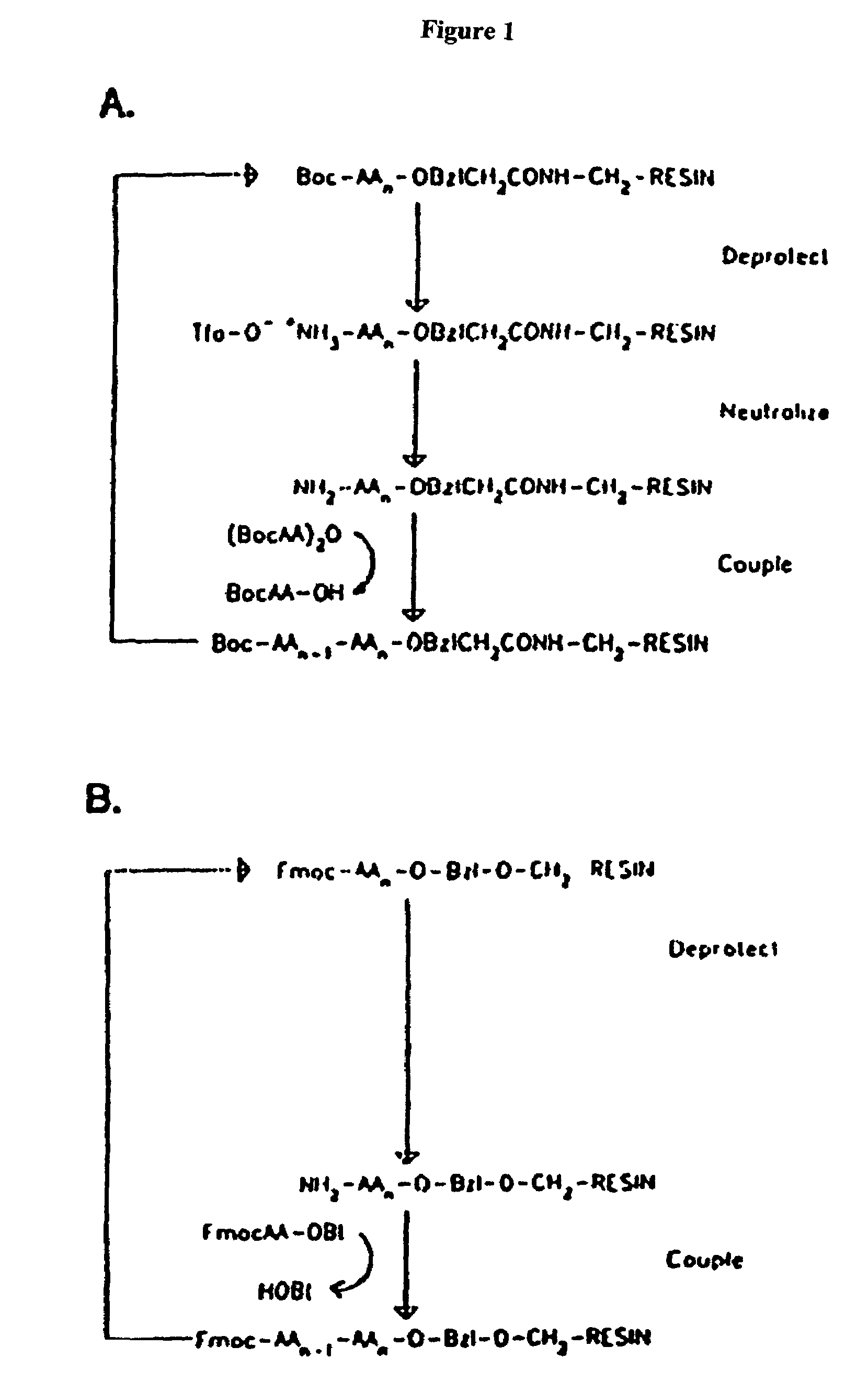
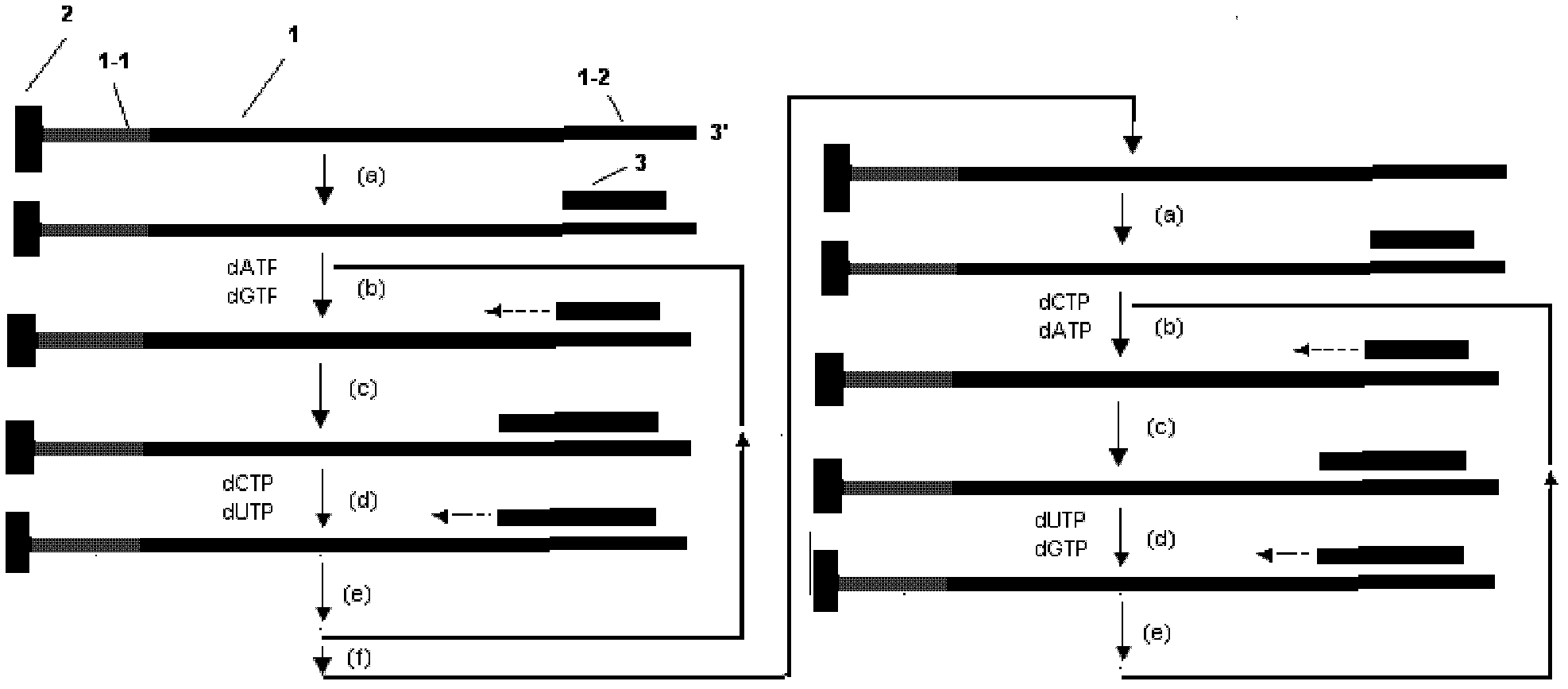
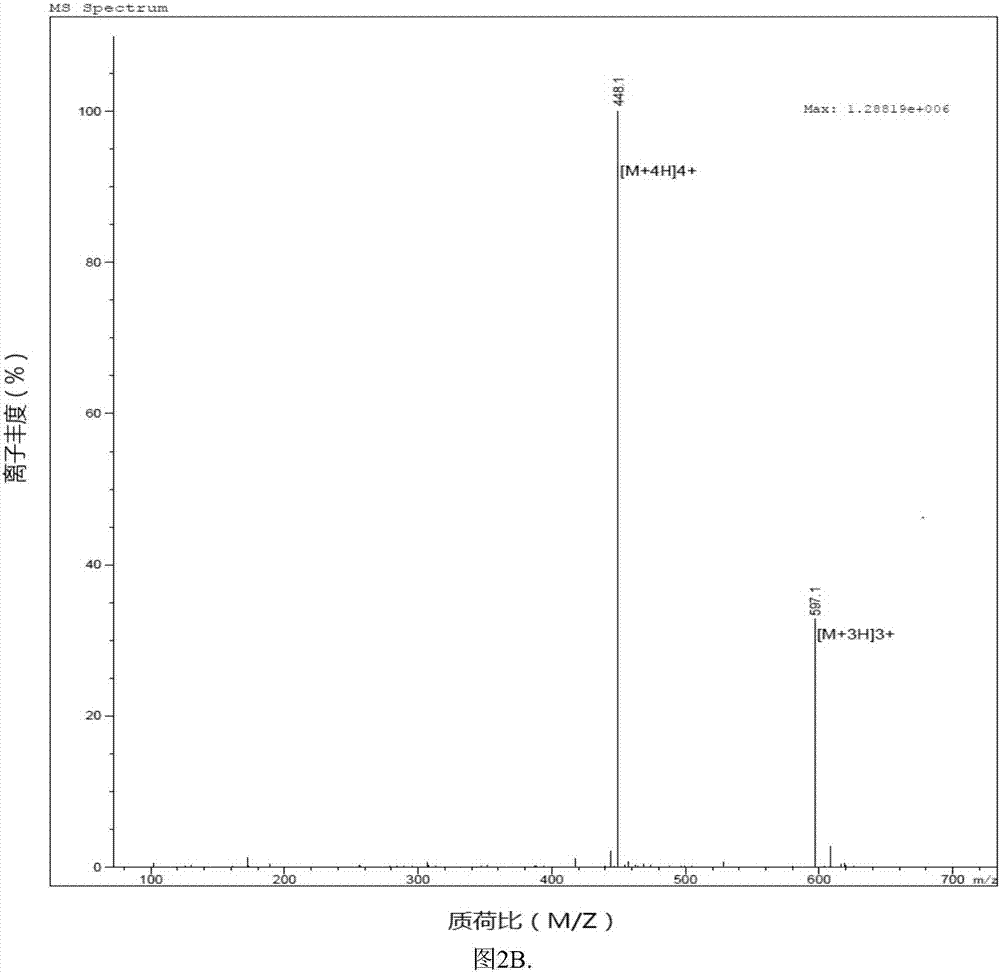
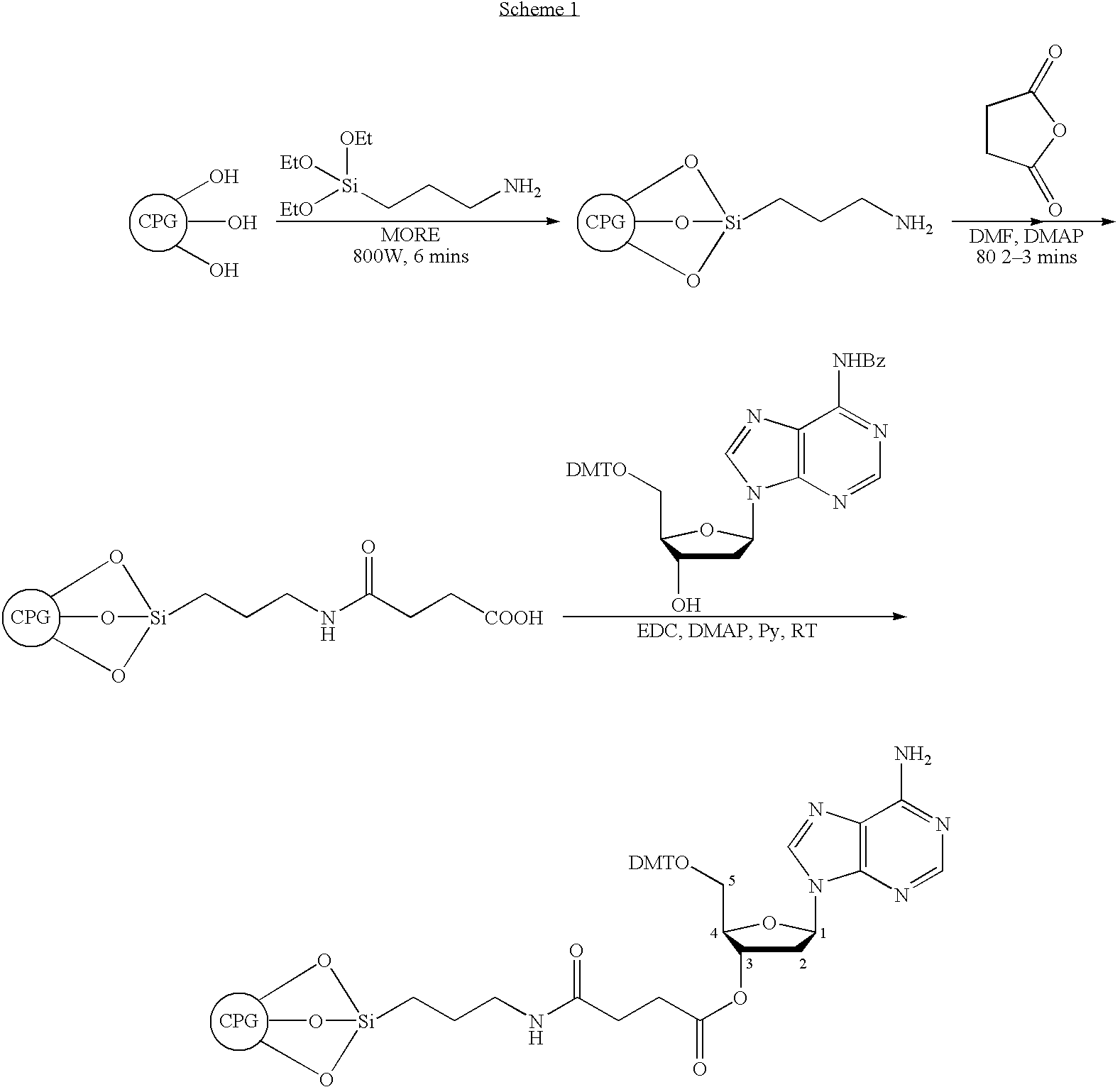
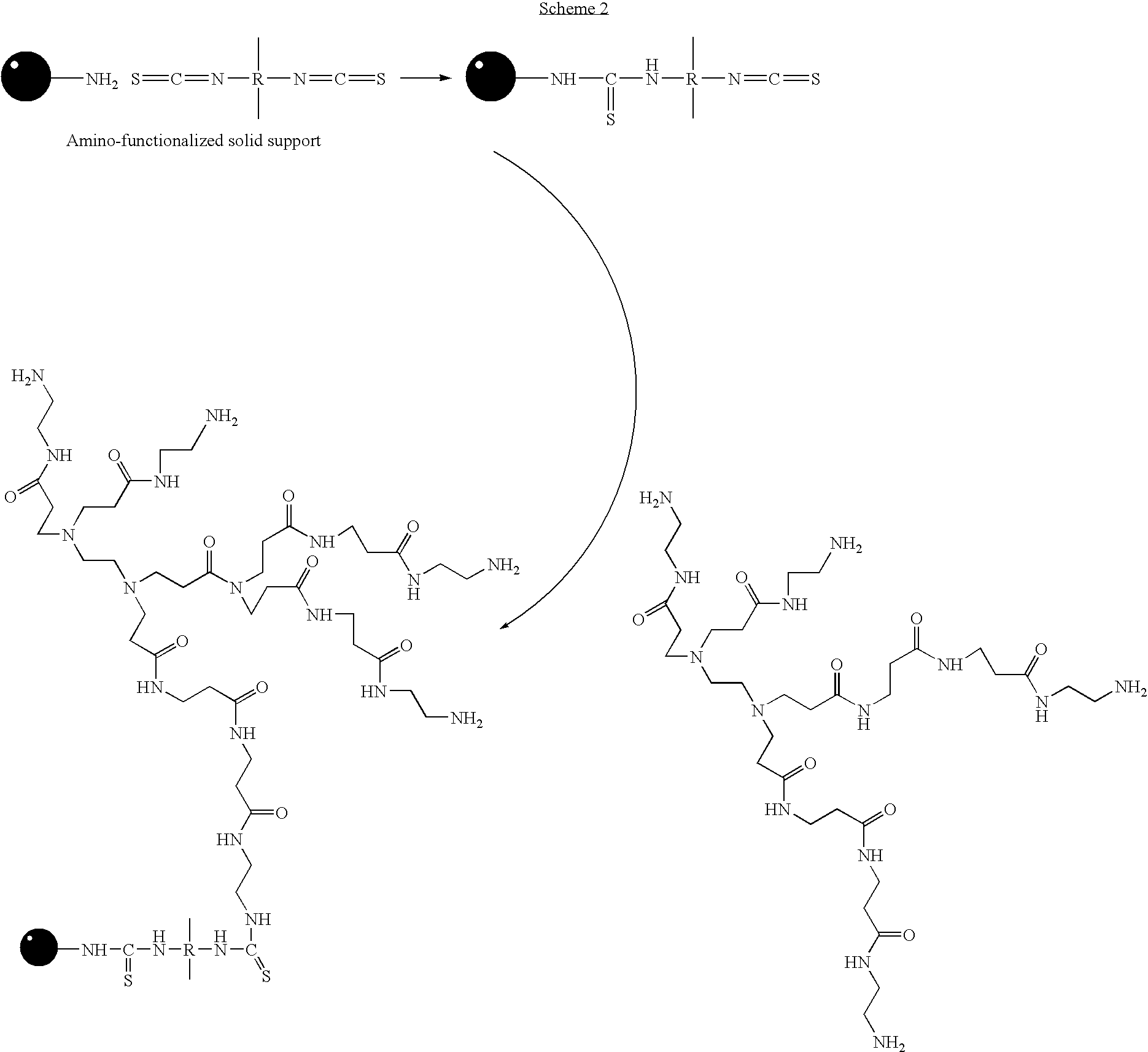
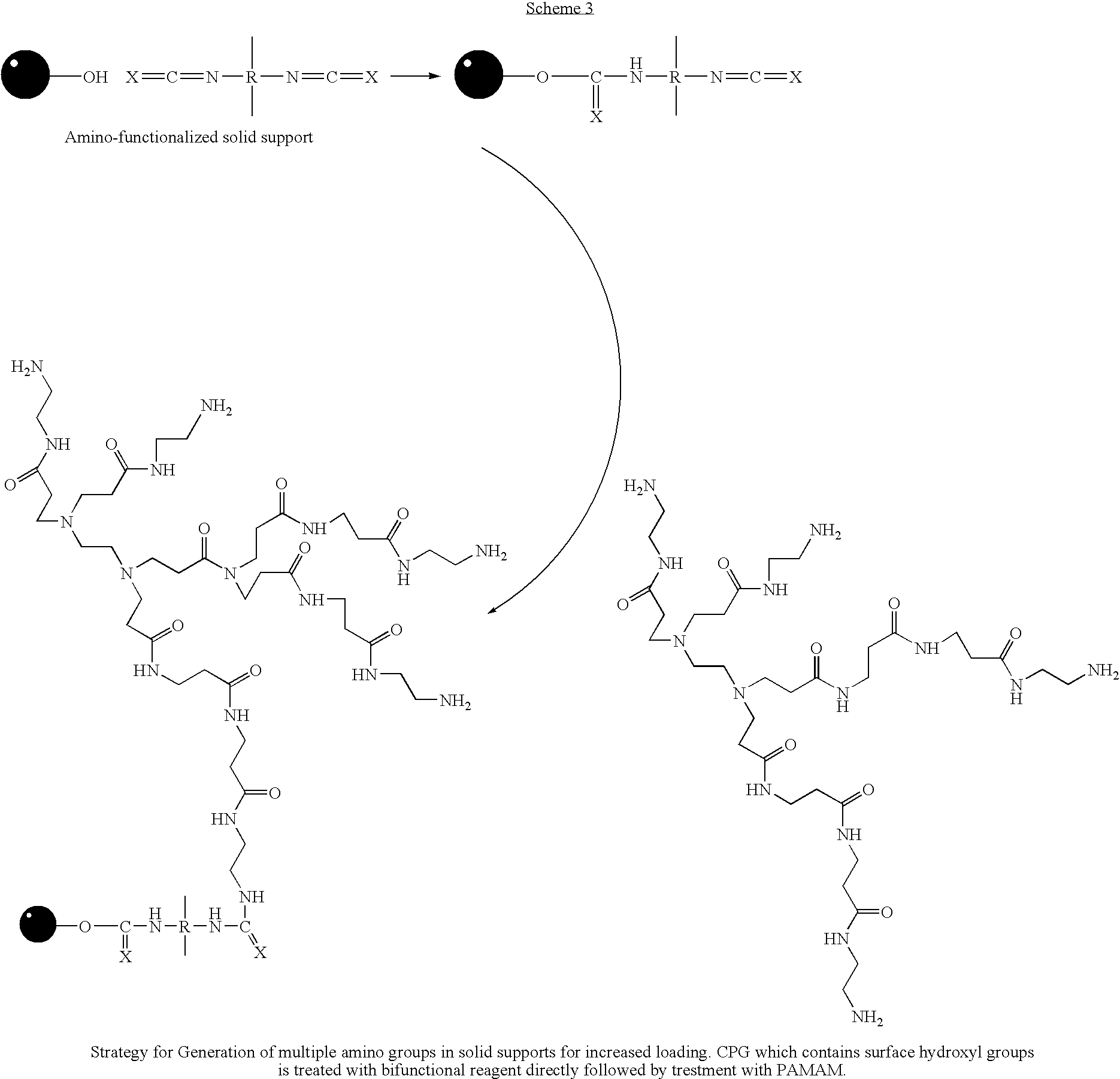
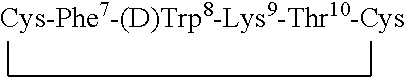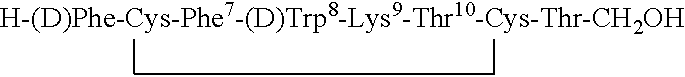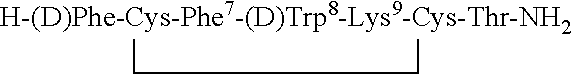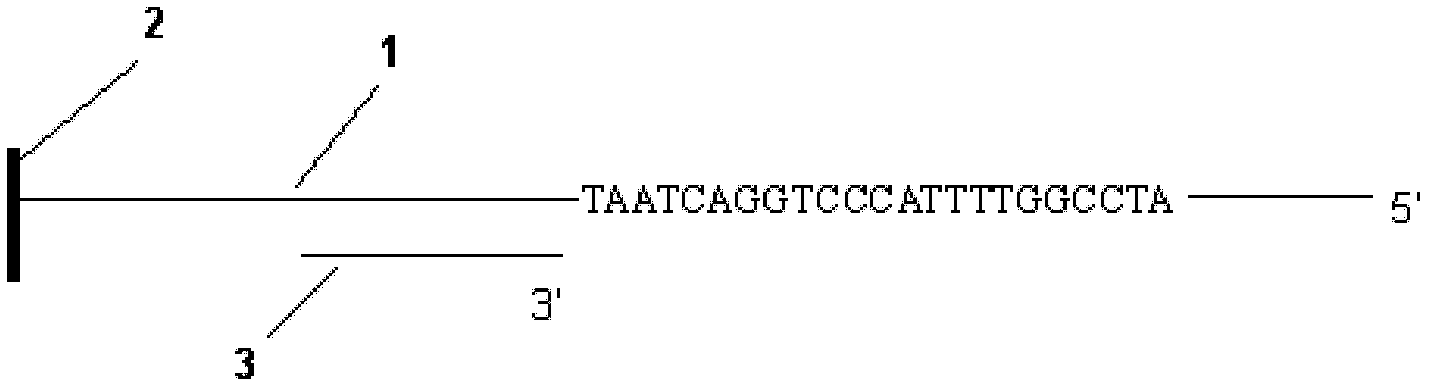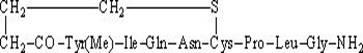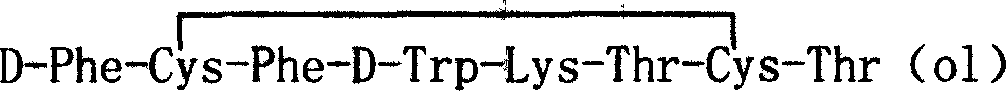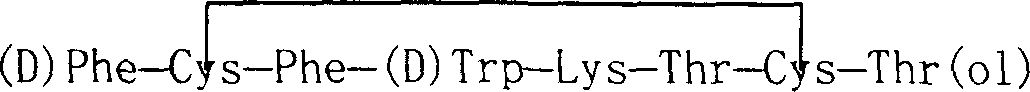Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
664 results about "Peptide synthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
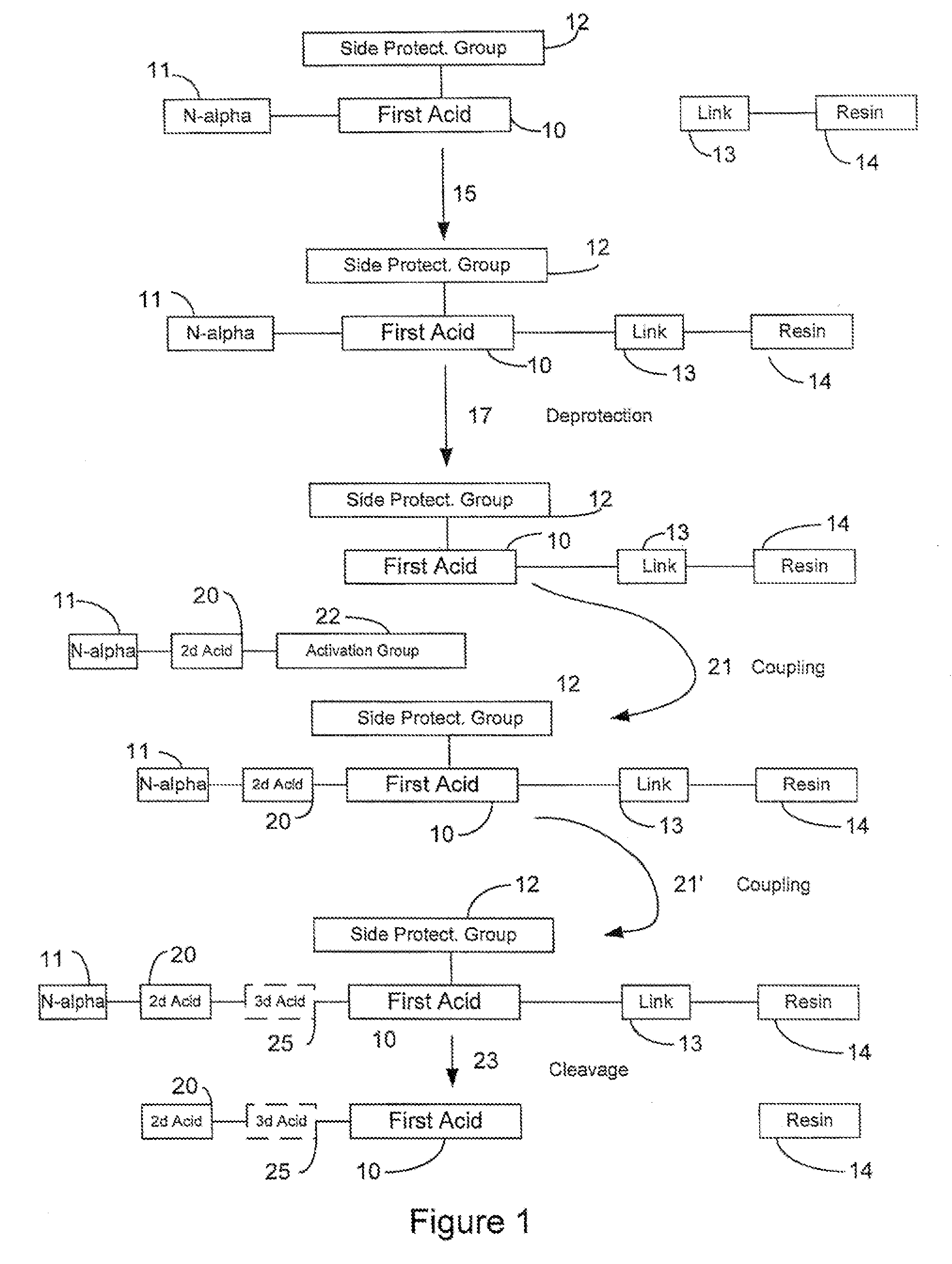
In organic chemistry, peptide synthesis is the production of peptides, compounds where multiple amino acids are linked via amide bonds, also known as peptide bonds. Peptides are chemically synthesized by the condensation reaction of the carboxyl group of one amino acid to the amino group of another. Protecting group strategies are usually necessary to prevent undesirable side reactions with the various amino acid side chains. Chemical peptide synthesis most commonly starts at the carboxyl end of the peptide (C-terminus), and proceeds toward the amino-terminus (N-terminus). Protein biosynthesis (long peptides) in living organisms occurs in the opposite direction.
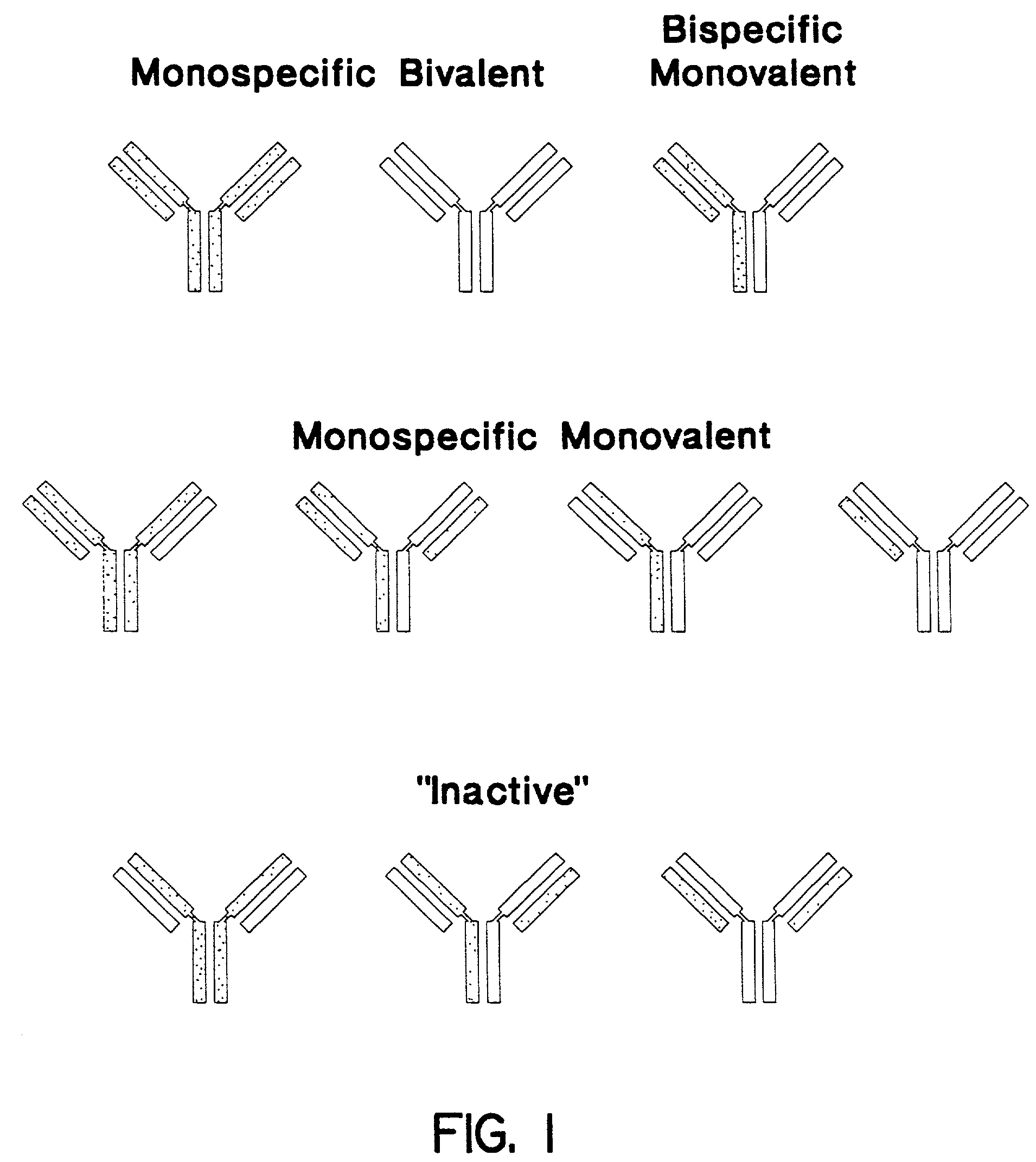
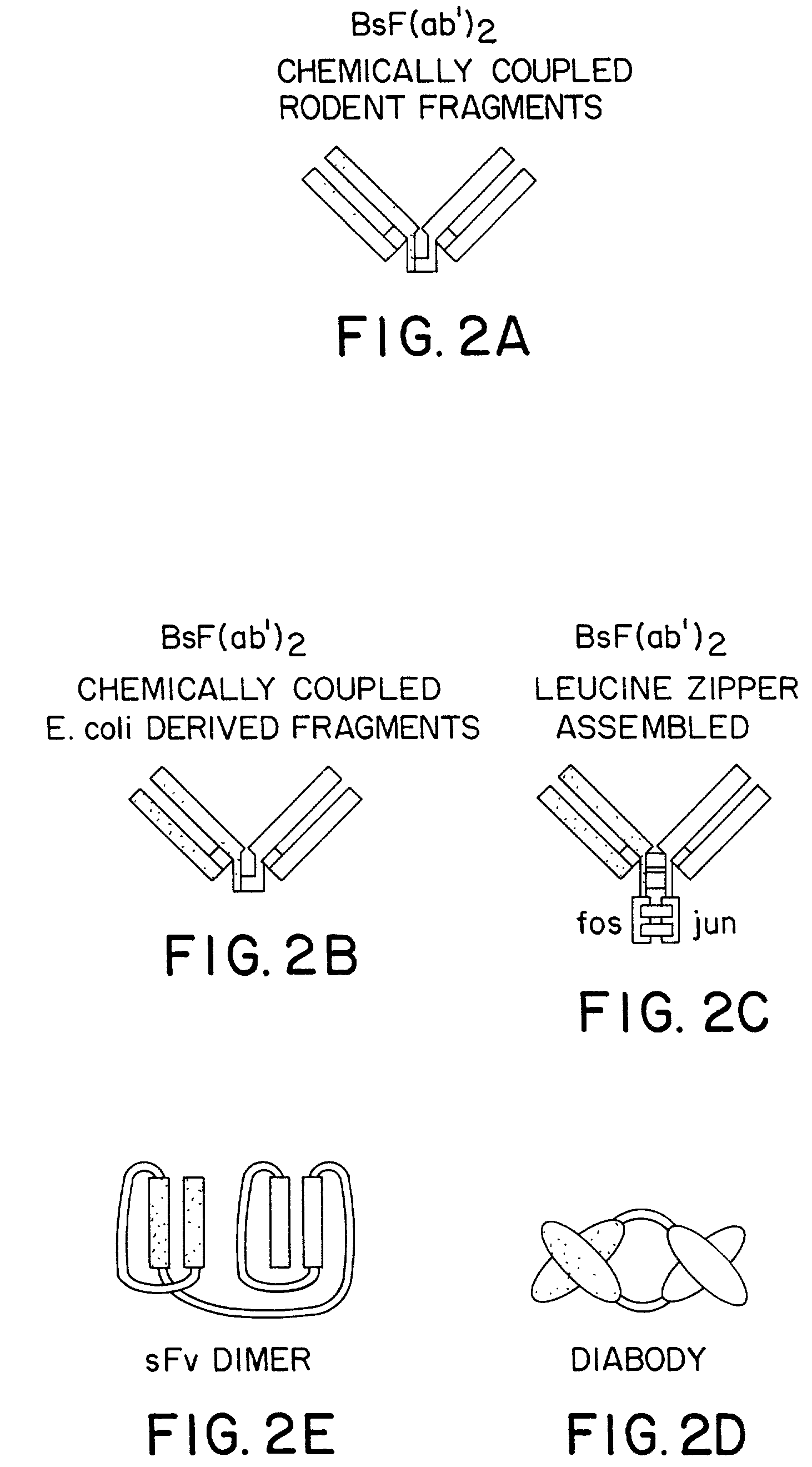
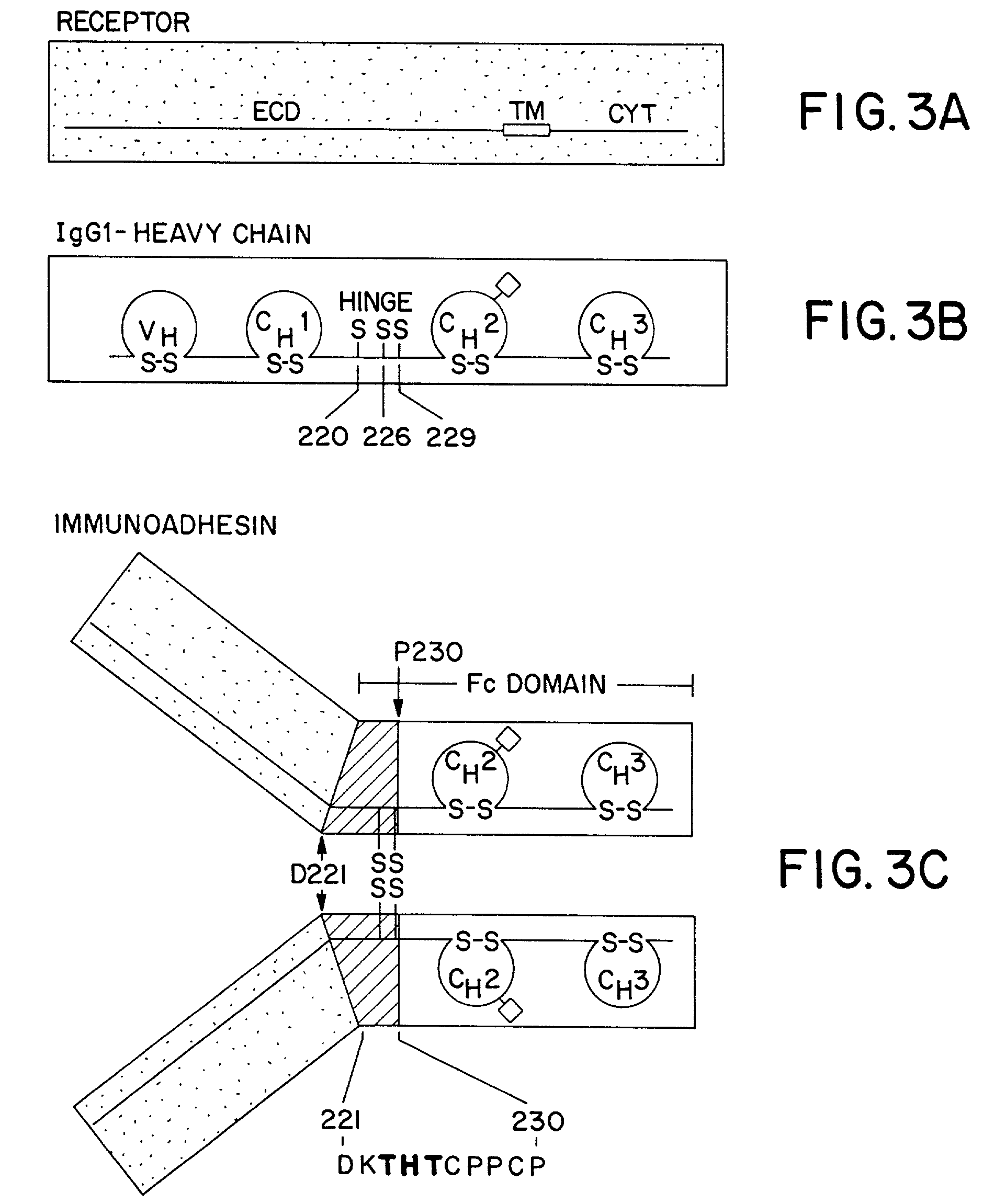
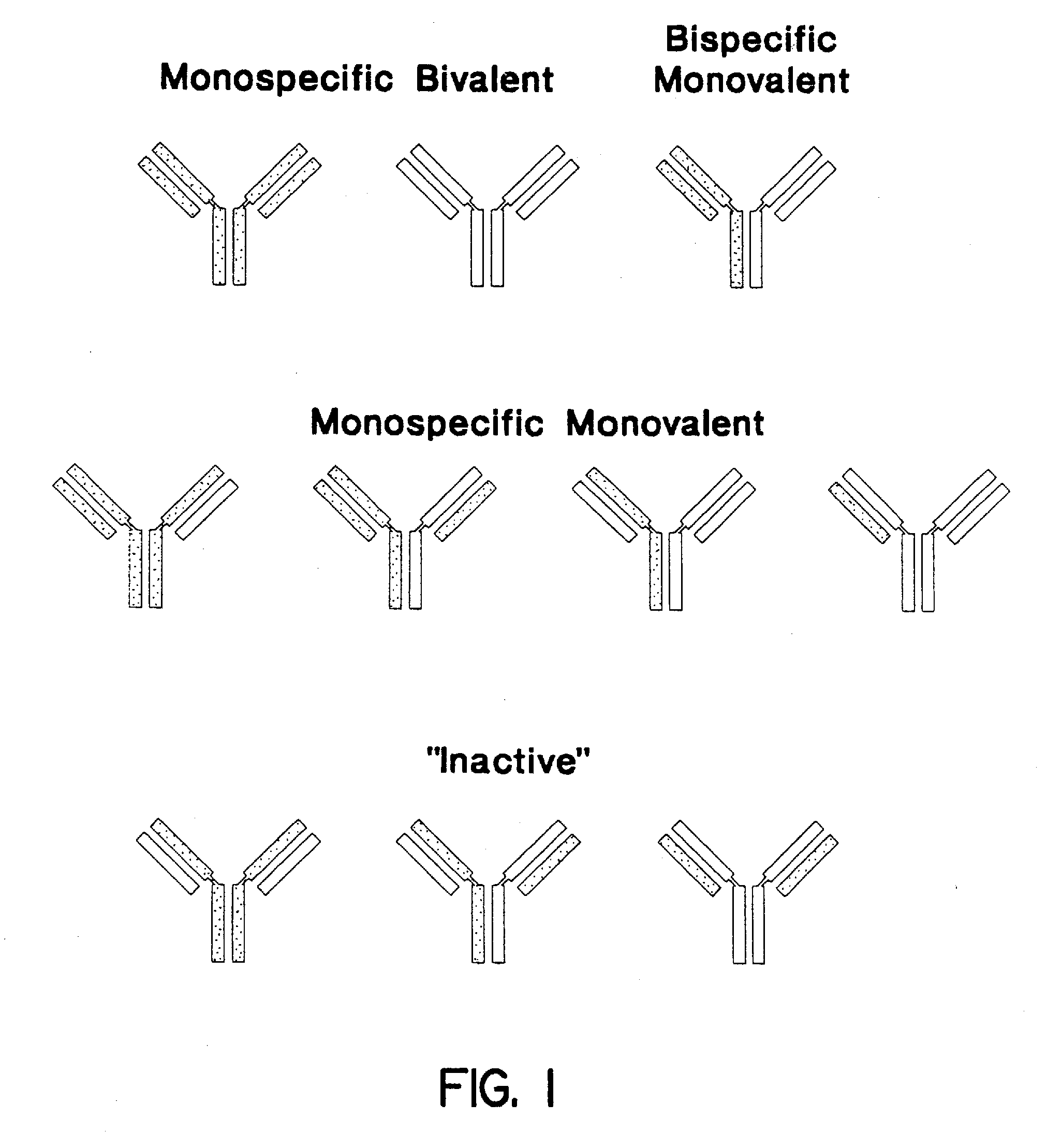
Method for making heteromultimeric polypeptides
InactiveUS7642228B2Increase productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAmino acid side chain
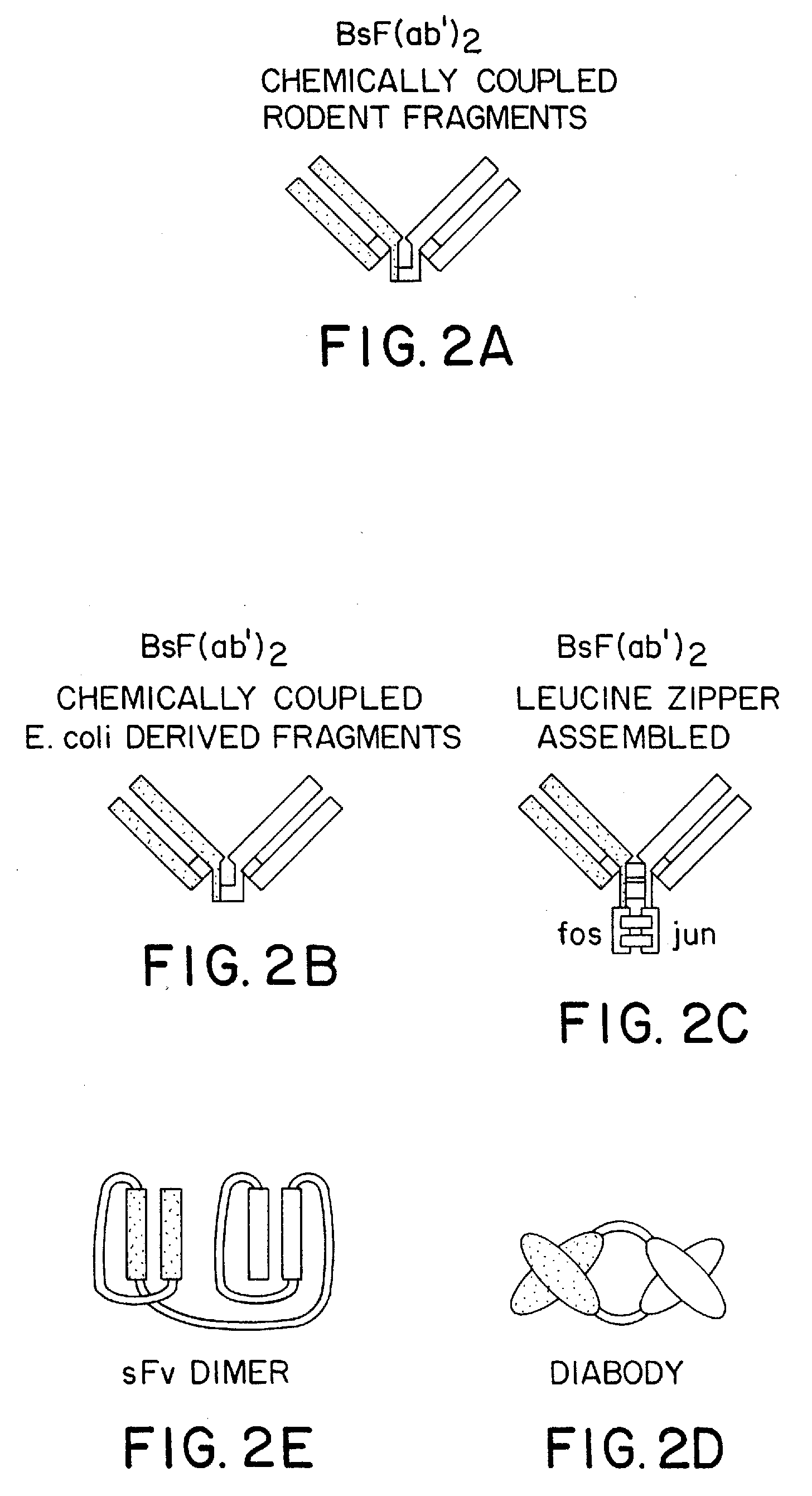
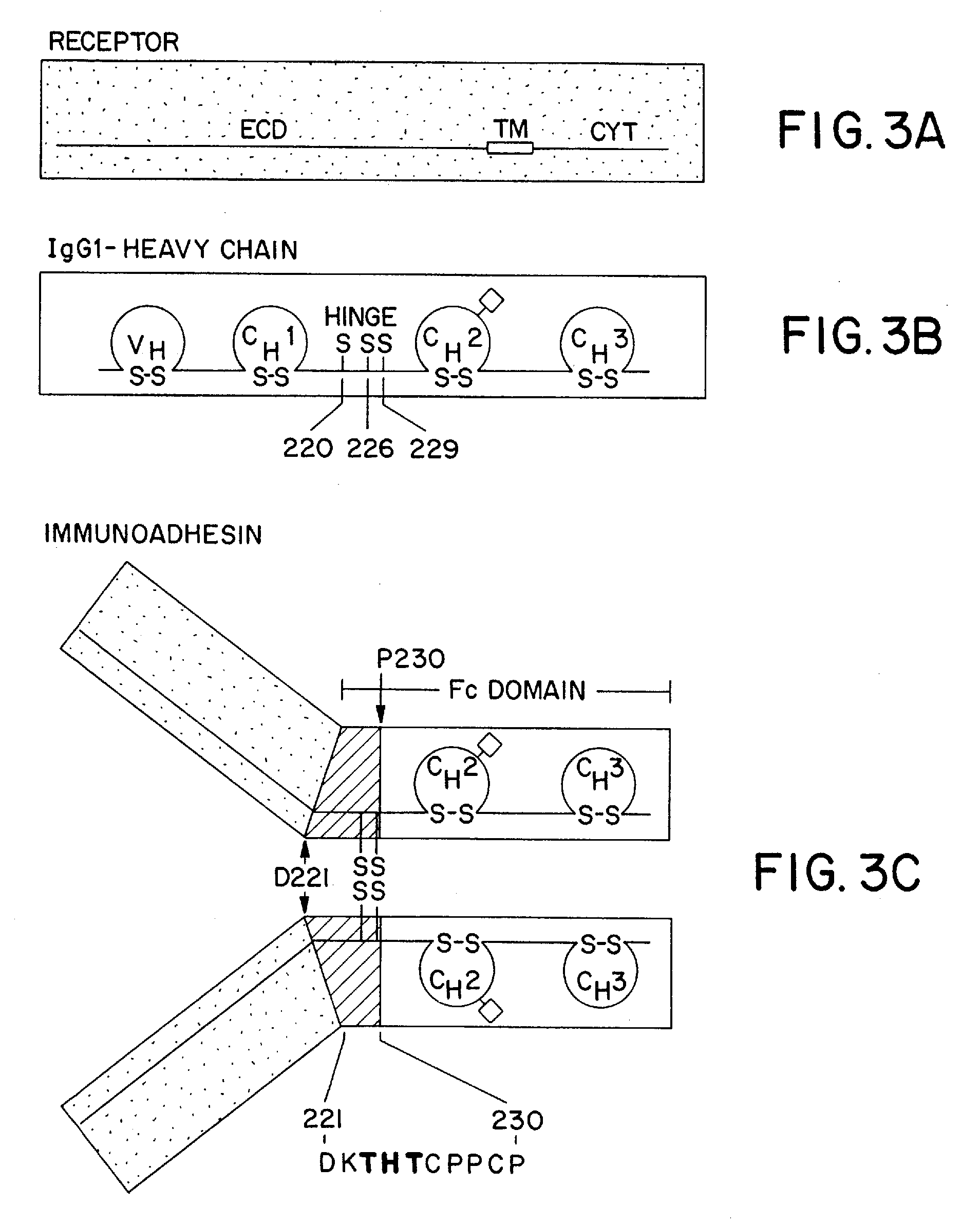
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method involves introducing a protuberance at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding cavity in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that the protuberance can be positioned in the cavity so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation. “Protuberances” are constructed by replacing small amino acid side chains from the interface of the first polypeptide with larger side chains (e.g. tyrosine or tryptophan). Compensatory “cavities” of identical or similar size to the protuberances are created in the interface of the second polypeptide by replacing large amino acid side chains with smaller ones (e.g. alanine or threonine). The protuberance and cavity can be made by synthetic means such as altering the nucleic acid encoding the polypeptides or by peptide synthesis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Method for making heteromultimeric polypeptides
InactiveUS20070014794A1Increase productionAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCrystallographyAmino acid side chain
The invention relates to a method of preparing heteromultimeric polypeptides such as bispecific antibodies, bispecific immunoadhesins and antibody-immunoadhesin chimeras. The invention also relates to the heteromultimers prepared using the method. Generally, the method involves introducing a protuberance at the interface of a first polypeptide and a corresponding cavity in the interface of a second polypeptide, such that the protuberance can be positioned in the cavity so as to promote heteromultimer formation and hinder homomultimer formation. “Protuberances” are constructed by replacing small amino acid side chains from the interface of the first polypeptide with larger side chains (e.g. tyrosine or tryptophan). Compensatory “cavities” of identical or similar size to the protuberances are created in the interface of the second polypeptide by replacing large amino acid side chains with smaller ones (e.g. alanine or threonine). The protuberance and cavity can be made by synthetic means such as altering the nucleic acid encoding the polypeptides or by peptide synthesis.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
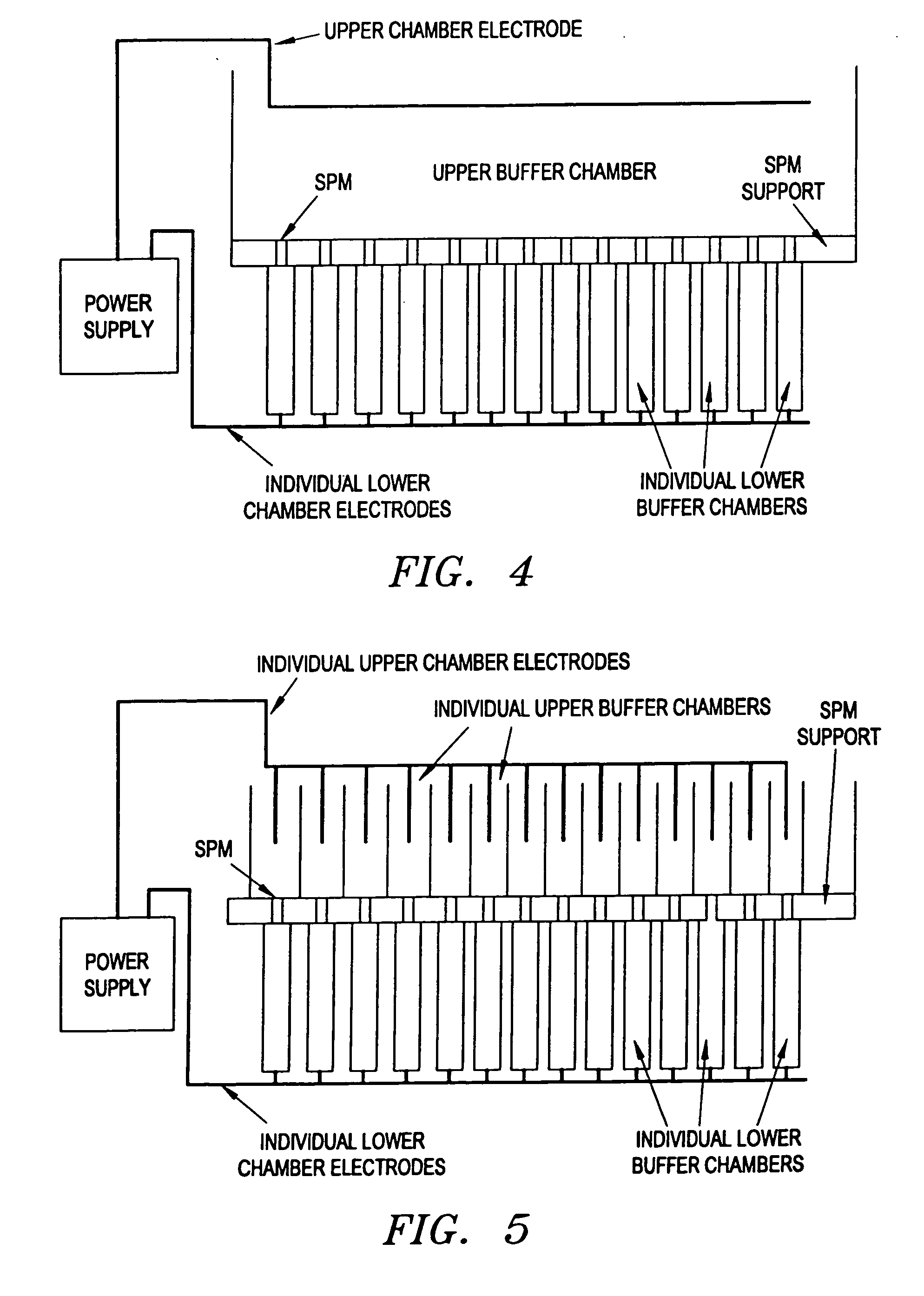
Electronic systems and component devices for macroscopic and microscopic molecular biological reactions, analyses and diagnostics
InactiveUS6780584B1Favorable zoneImprove responseMaterial nanotechnologySequential/parallel process reactionsAntigenElectronic systems
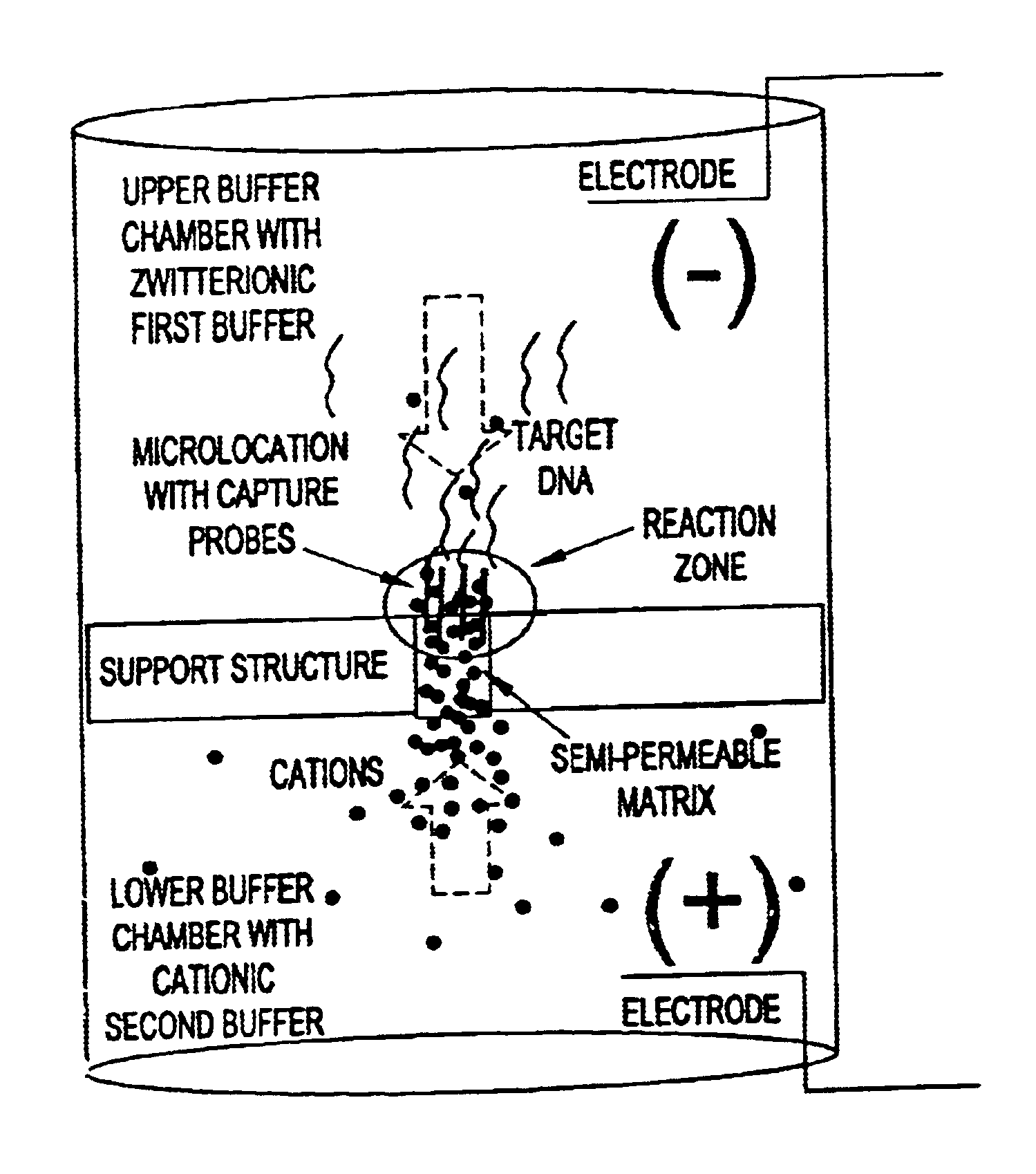
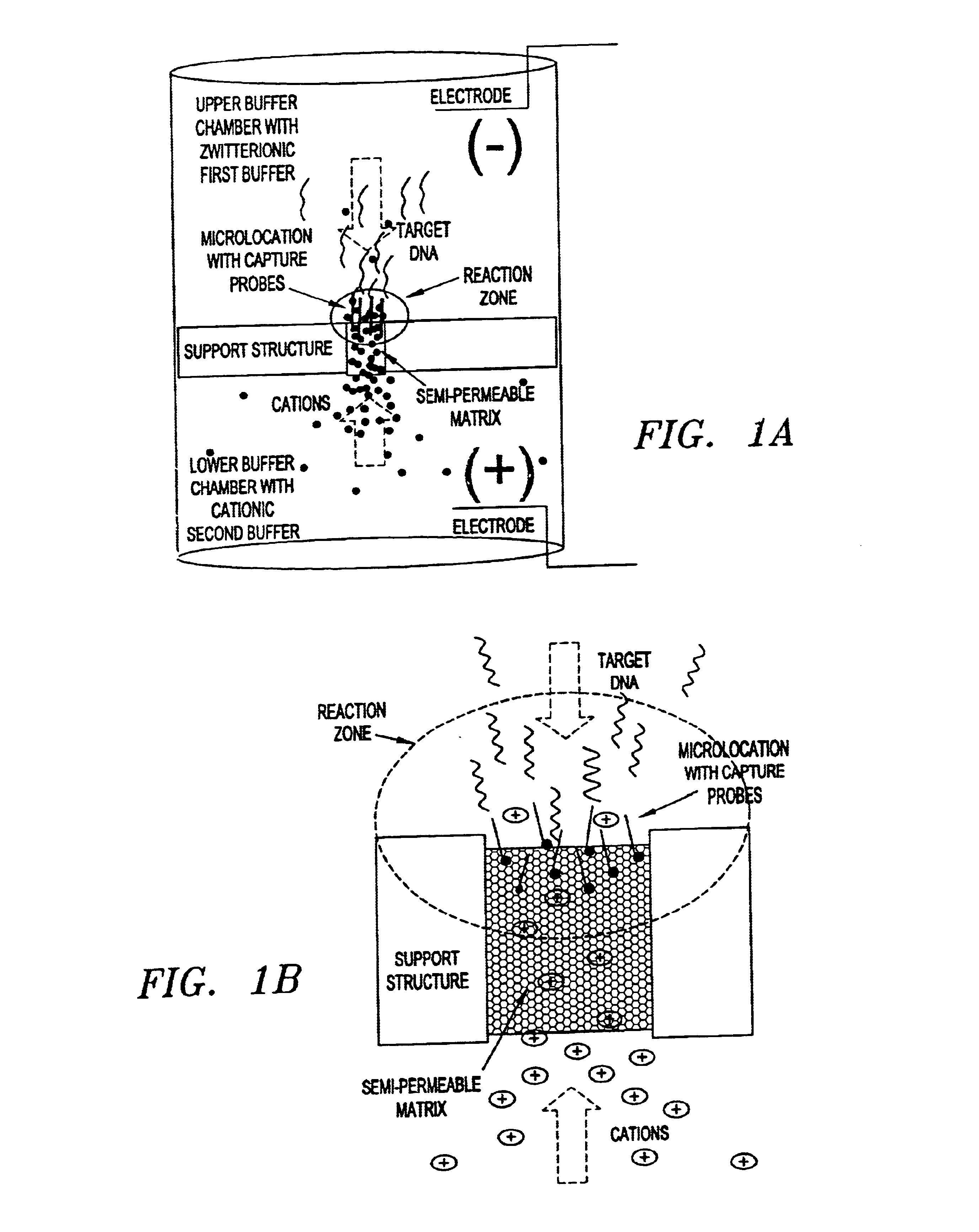
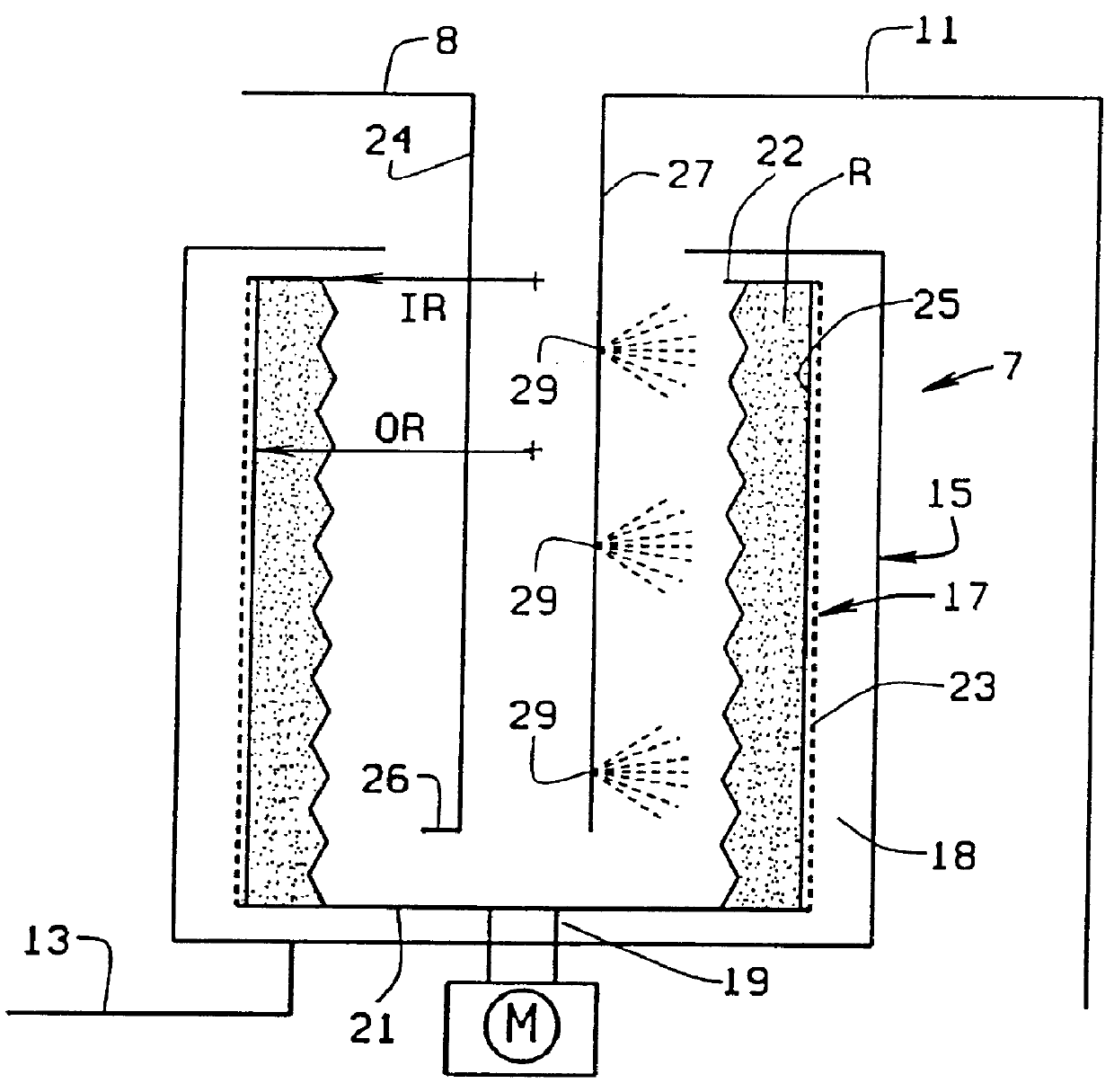
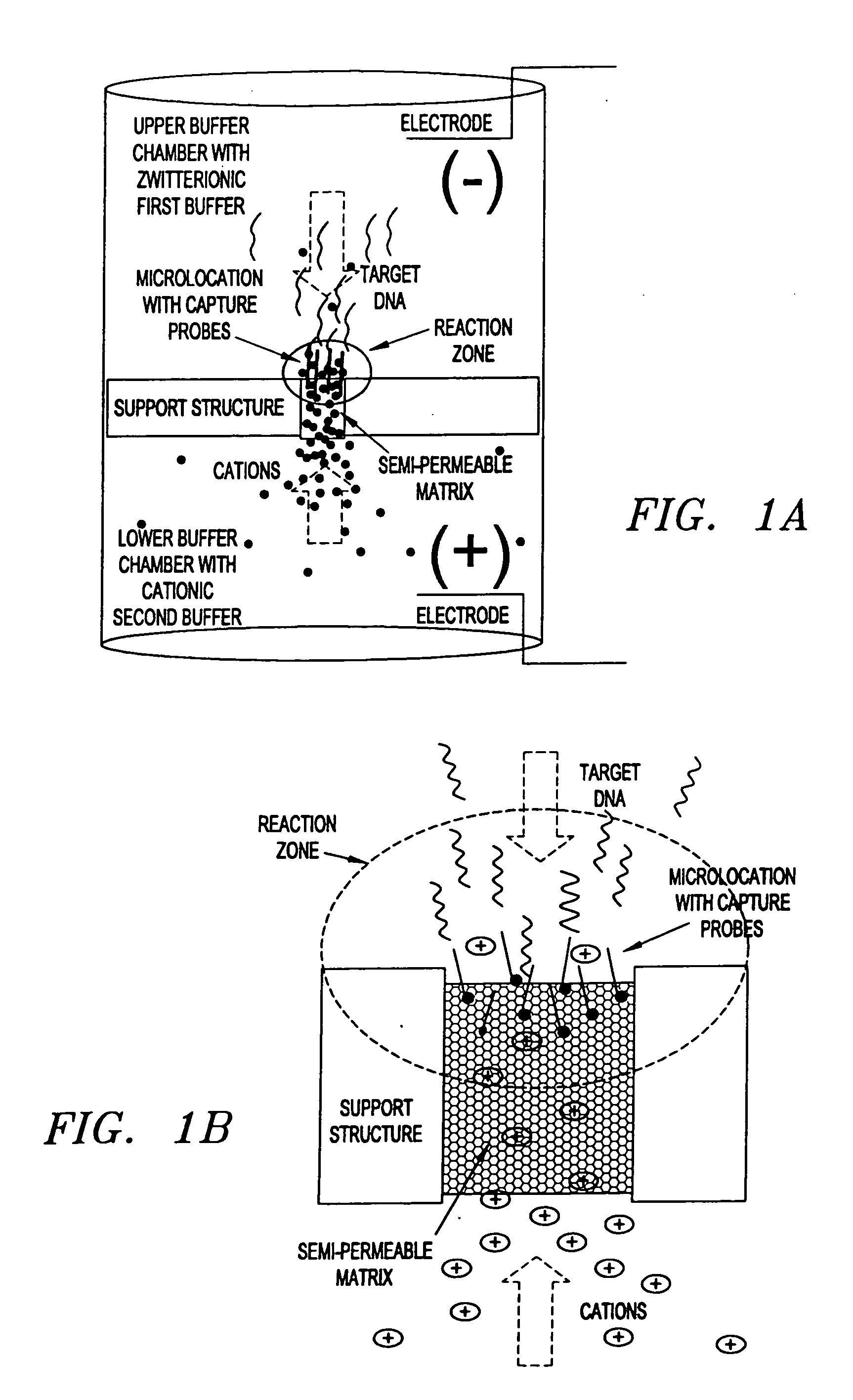
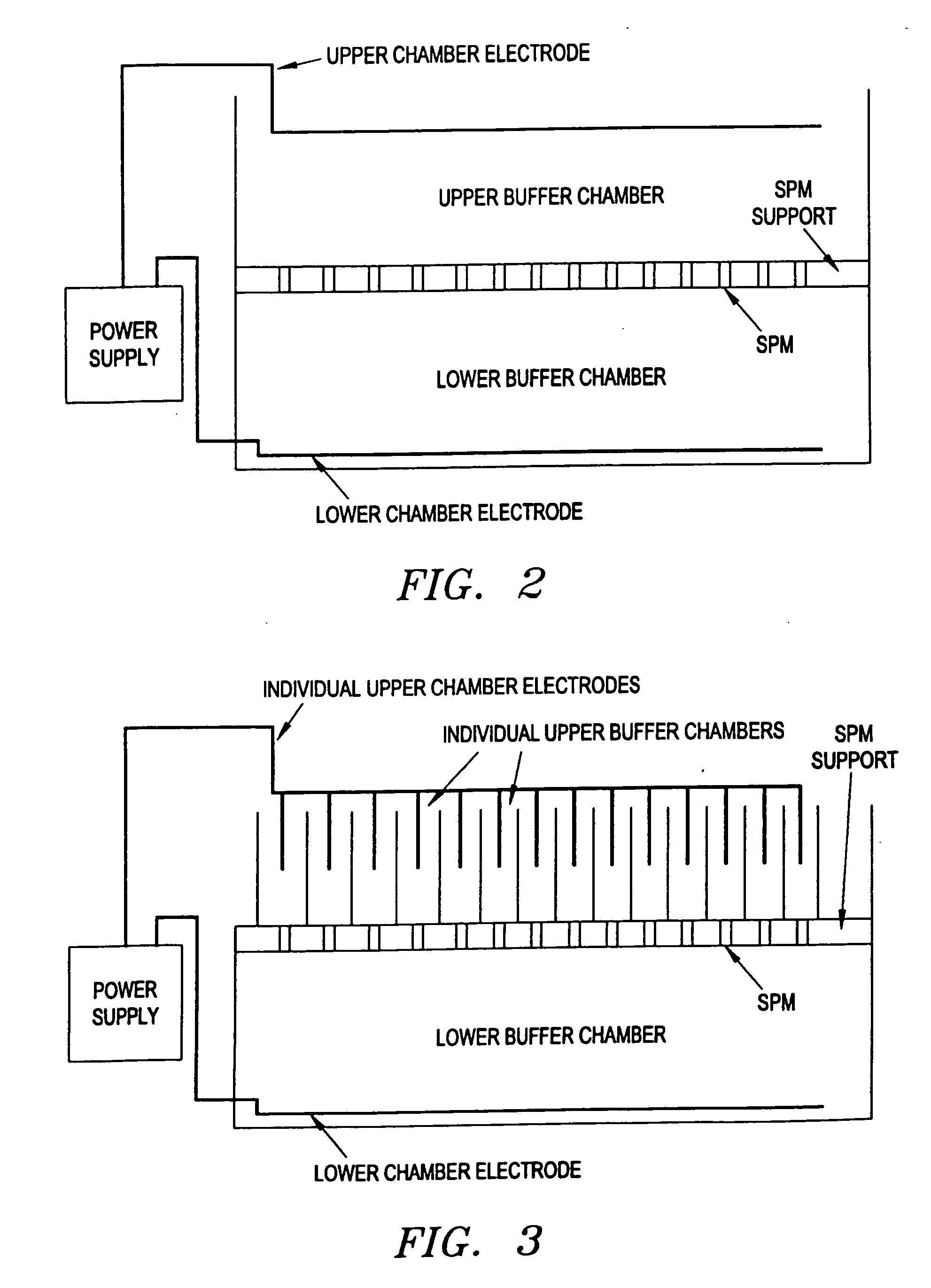
This invention pertains to the design, fabrication, and uses of an electronic system which can actively carry out and control multi-step and multiplex reactions in macroscopic or microscopic formats. In particular, these reactions include molecular biological reactions, such as nucleic acid hybridizations, nucleic acid amplification, sample preparation, antibody / antigen reactions, clinical diagnostics, combinatorial chemistry and selection, drug screening, oligonucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis, peptide synthesis, biopolymer synthesis and catalytic reactions. A key feature of the present invention is the ability to control the localized concentration of two or more reaction-dependant molecules and their reaction environment in order to greatly enhance the rate and specificity of the molecular biological reaction.
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL +1
Process for producing peptides by using in vitro transcription/translation system
The present invention relates to a reaction system whereby a peptide produced in an in vitro peptide synthesis system can be efficiently isolated at a high purity from the reaction system. Thus the present invention is a process for producing a peptide or a peptide derivative by using a reaction system of transcribing a DNA into an RNA and then translating the RNA produced or a reaction system of translating an RNA in vitro wherein at least one protein component of the reaction system is labeled with a first substance which adheres to a second substance, and said second substance is used as an adsorbent for capturing said labeled protein components after translating.
Owner:BIOCOMBER
Conformationally constrained backbone cyclized peptide analogs
Novel backbone cyclized peptide analogs are formed by means of bridging groups attached via the alpha nitrogens of amino acid derivatives to provide novel non-peptidic linkages. Novel building units disclosed are Nα(ω-functionalized) amino acids constructed to include a spacer and a terminal functional group. One or more of these Nα(ω-functionalized) amino acids are incorporated into a peptide sequence, preferably during solid phase peptide synthesis. The reactive terminal functional groups are protected by specific protecting groups that can be selectively removed to effect either backbone-to-backbone or backbone-to-side chain cyclizations. The invention is specifically exemplified by backbone cyclized bradykinin antagonists having biological activity. Further embodiments of the invention are somatostatin analogs having one or two ring structures involving backbone cyclization.
Owner:DEVELOGEN ISRAEL
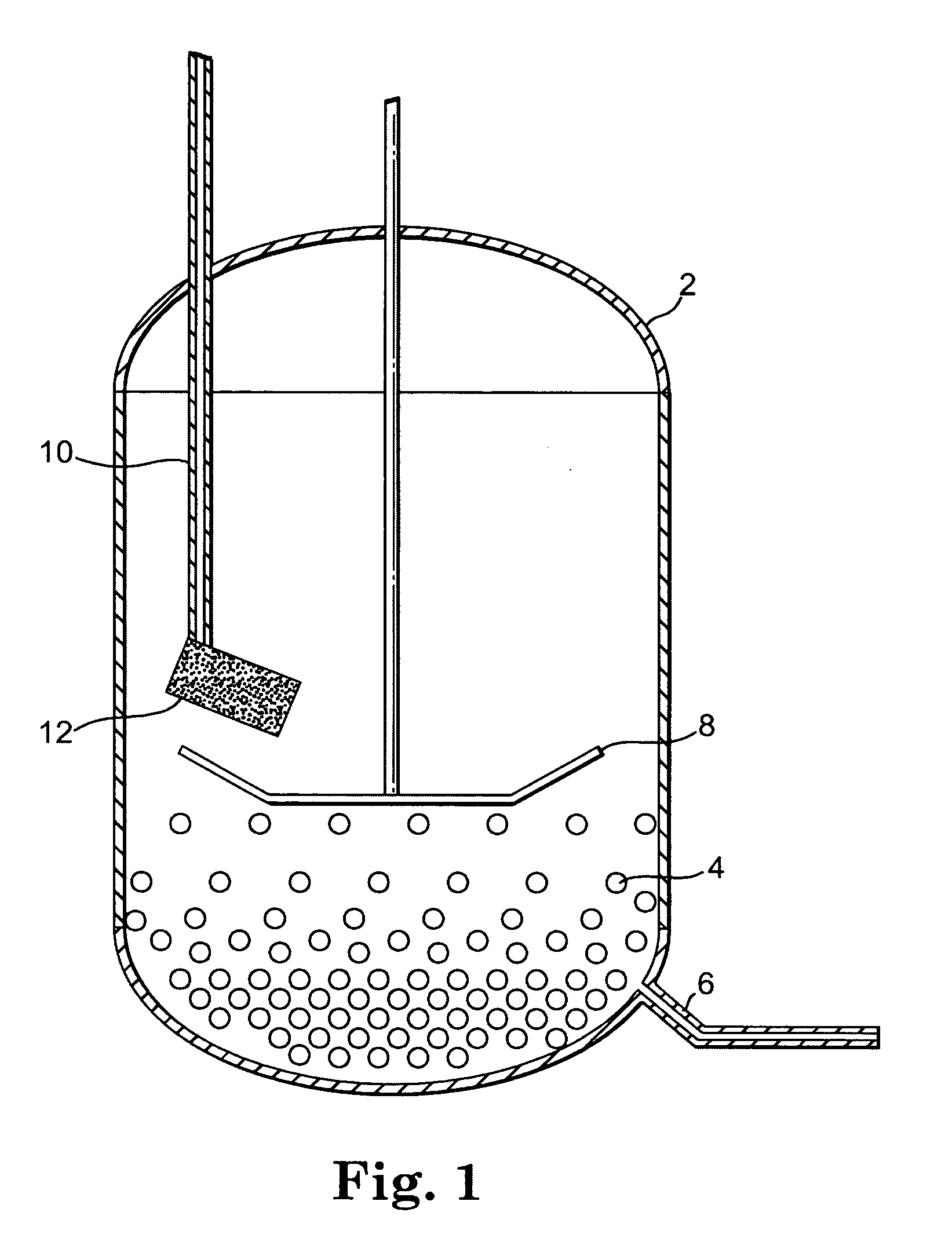
Reactor and method for solid phase peptide synthesis
InactiveUS6028172AIncrease productionHigh yieldPeptide librariesSequential/parallel process reactionsReactor systemEngineering
PCT No. PCT / US98 / 02634 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 9, 1999 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 9, 1999 PCT Filed Feb. 10, 1998 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 34633 PCT Pub. Date Aug. 13, 1998A solid phase peptide synthesis reactor system and method of operating the reactor are provided. The reactor system includes a basket rotatable about an axis within a housing and a receiver which delivers fluid to, and collects fluid from, the housing. The basket has a perforate side wall against which a resin cake for the peptide synthesis is formed. The reactor and receiver form a loop or circuit through which solutions are circulated. The circulation of the solutions prevents the reactor from flooding so that the basket will not be submerged in solution and allows for the use of less liquid. Thus greater amino acid concentrations may be used. The method includes forming a resin cake of uniform depth on the wall of the spinning basket and spraying the solutions against the resin cake while spinning the basket. The solutions will pass through the resin cake and drain to the receiver to be circulated or recycled through the system or discharged from the system. Before a subsequent solution is introduced into the reactor system, the prior solution is purged from the system to help control exposure time of the peptide to the solutions.
Owner:MALLINCKRODT INC
Electronic systems and component devices for macroscopic and microscopic molecular biological reaction, analyses, and diagnostics
InactiveUS20050026202A1Favorable zoneImprove responseBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMaterial nanotechnologyMultiplexBiopolymer
This invention pertains to the design, fabrication, and uses of an electronic system which can actively carry out and control multi-step and multiplex reactions in macroscopic or microscopic formats. In particular, these reactions include molecular biological reactions, such as nucleic acid hybridizations, nucleic acid amplification, sample preparation, antibody / antigen reactions, clinical diagnostics, combinatorial chemistry and selection, drug screening, oligonucleotide and nucleic acid synthesis, peptide synthesis, biopolymer synthesis, and catalytic reactions. A key feature of the present invention is the ability to control the localized concentration of two or more reaction-dependant molecules and their reaction environment in order to greatly enhance the rate and specificity of the molecular biological reaction
Owner:ADOR DIAGNOSTICS SRL
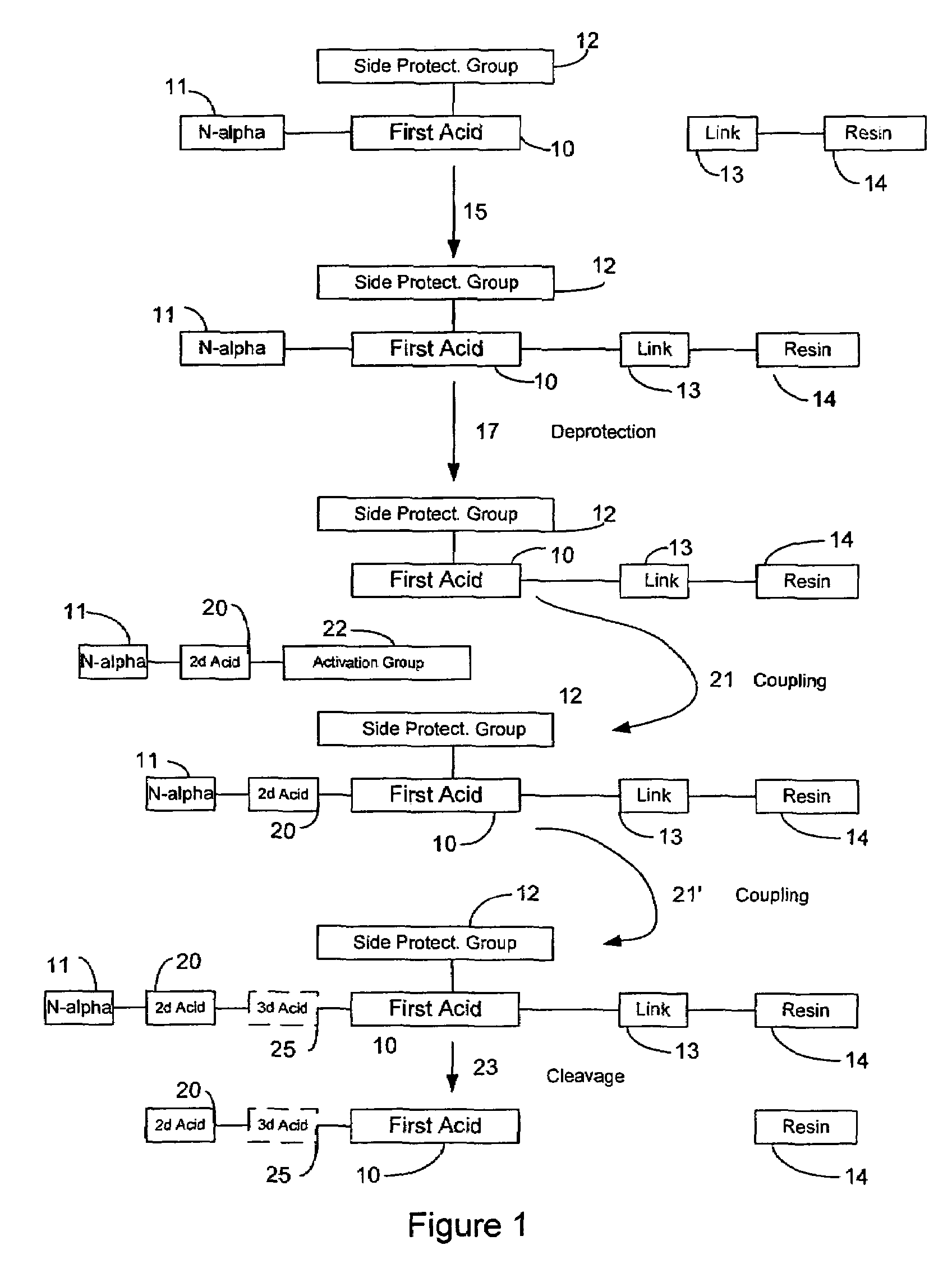
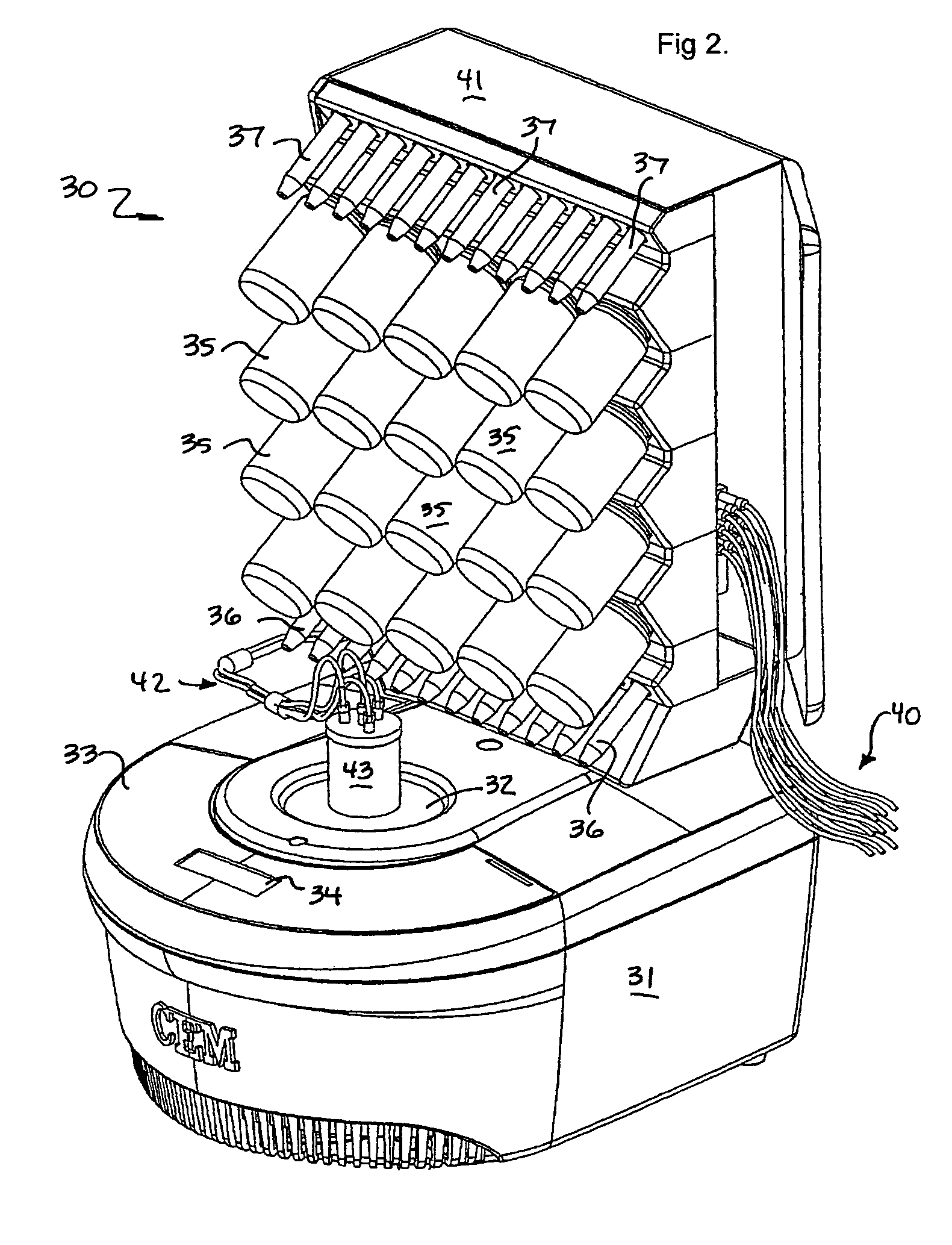
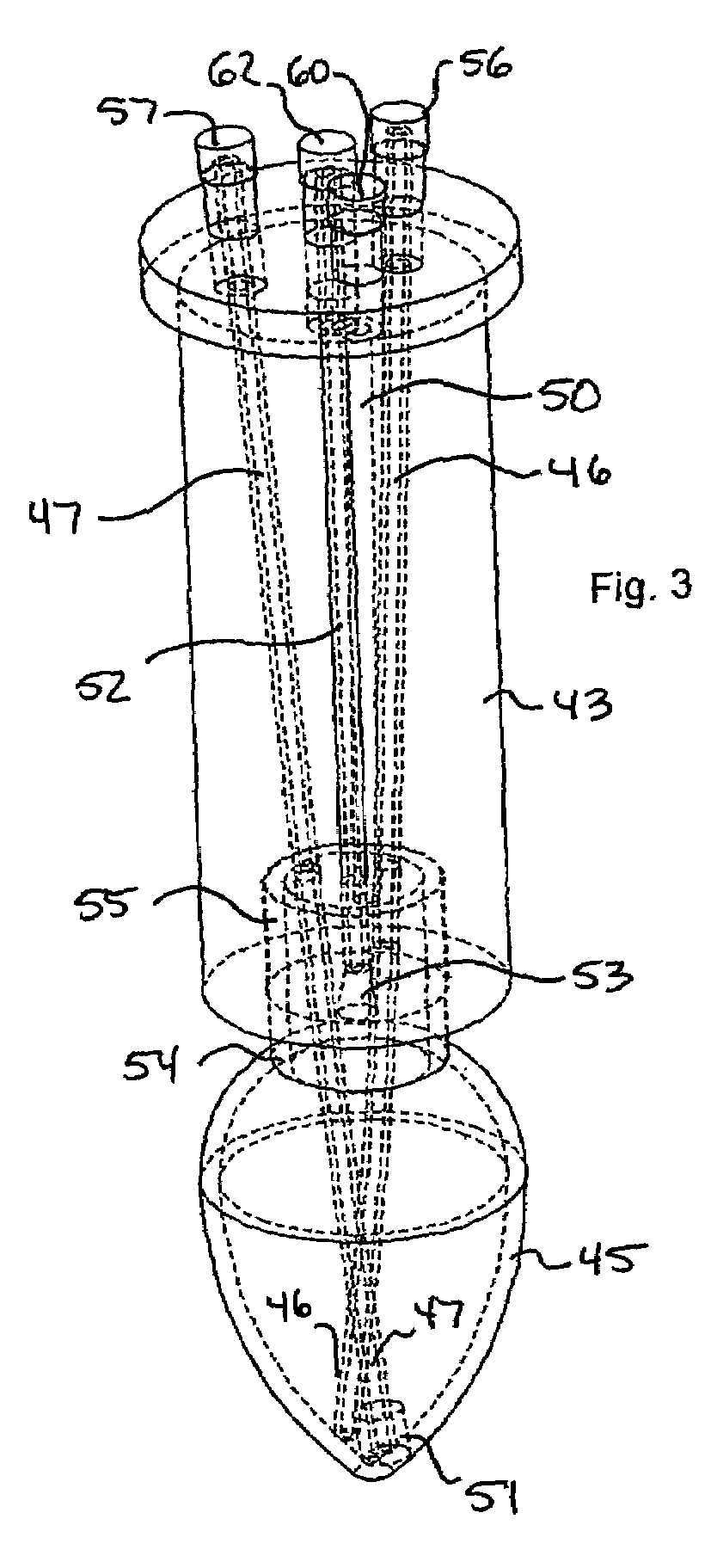
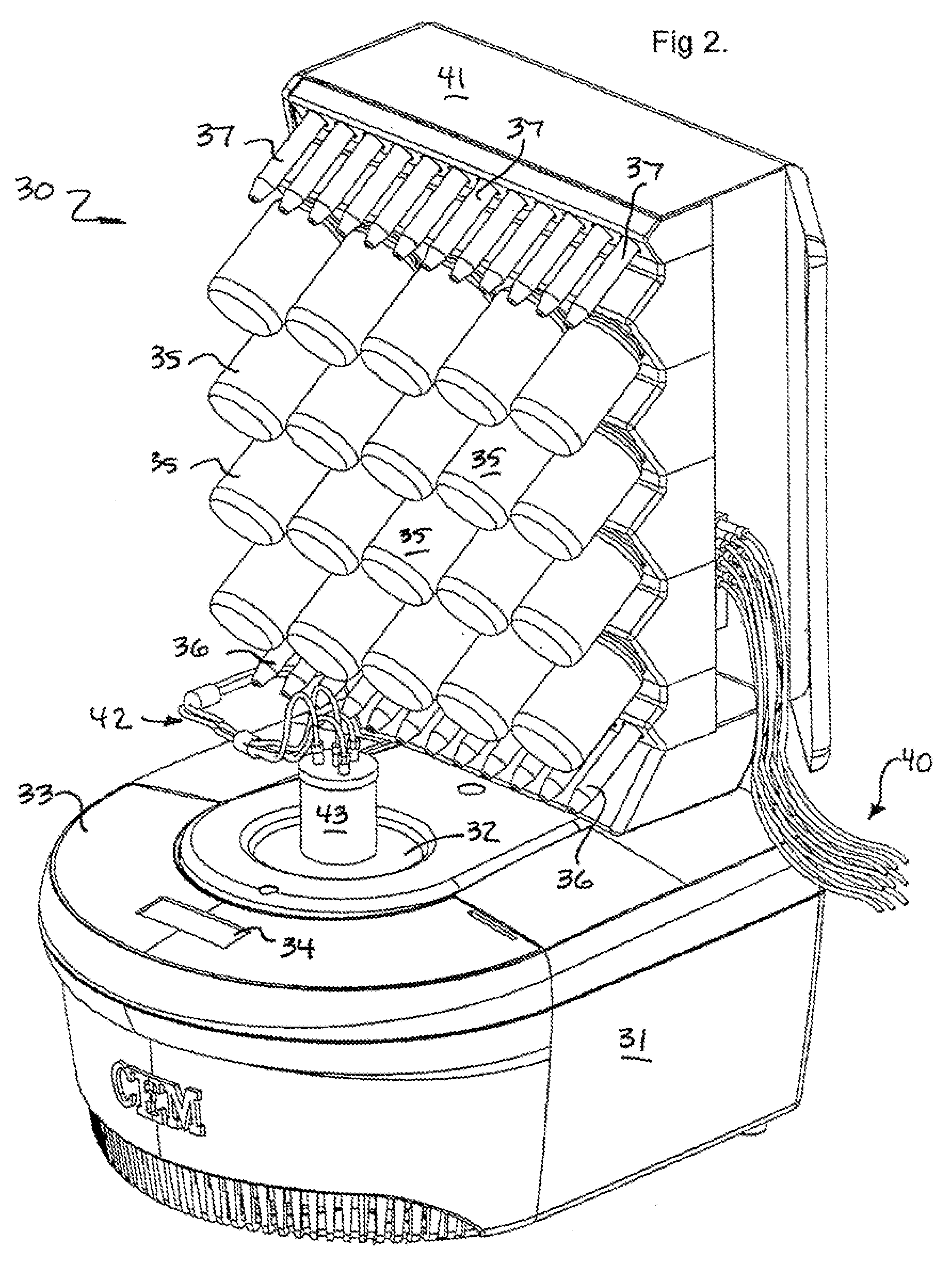
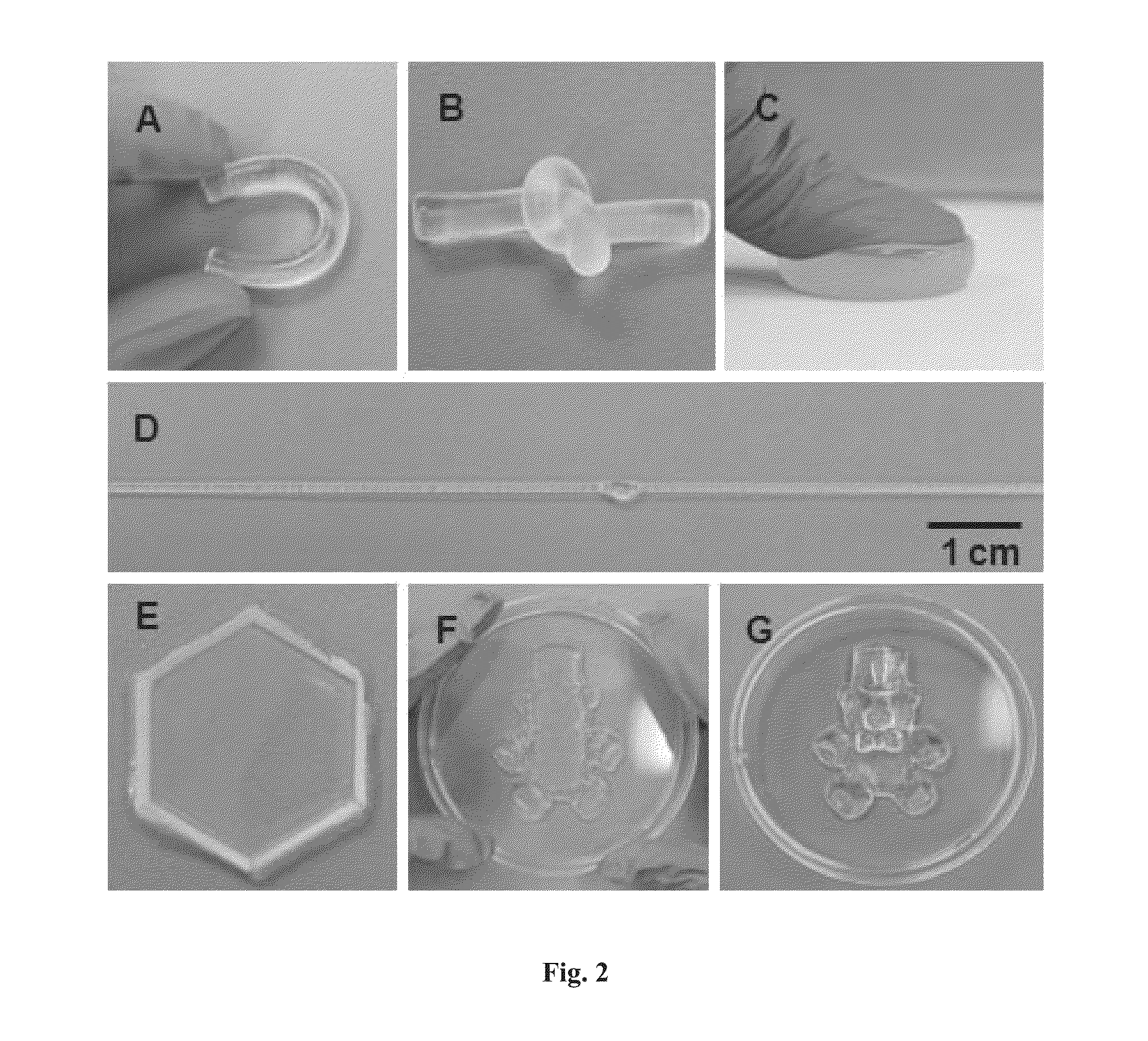
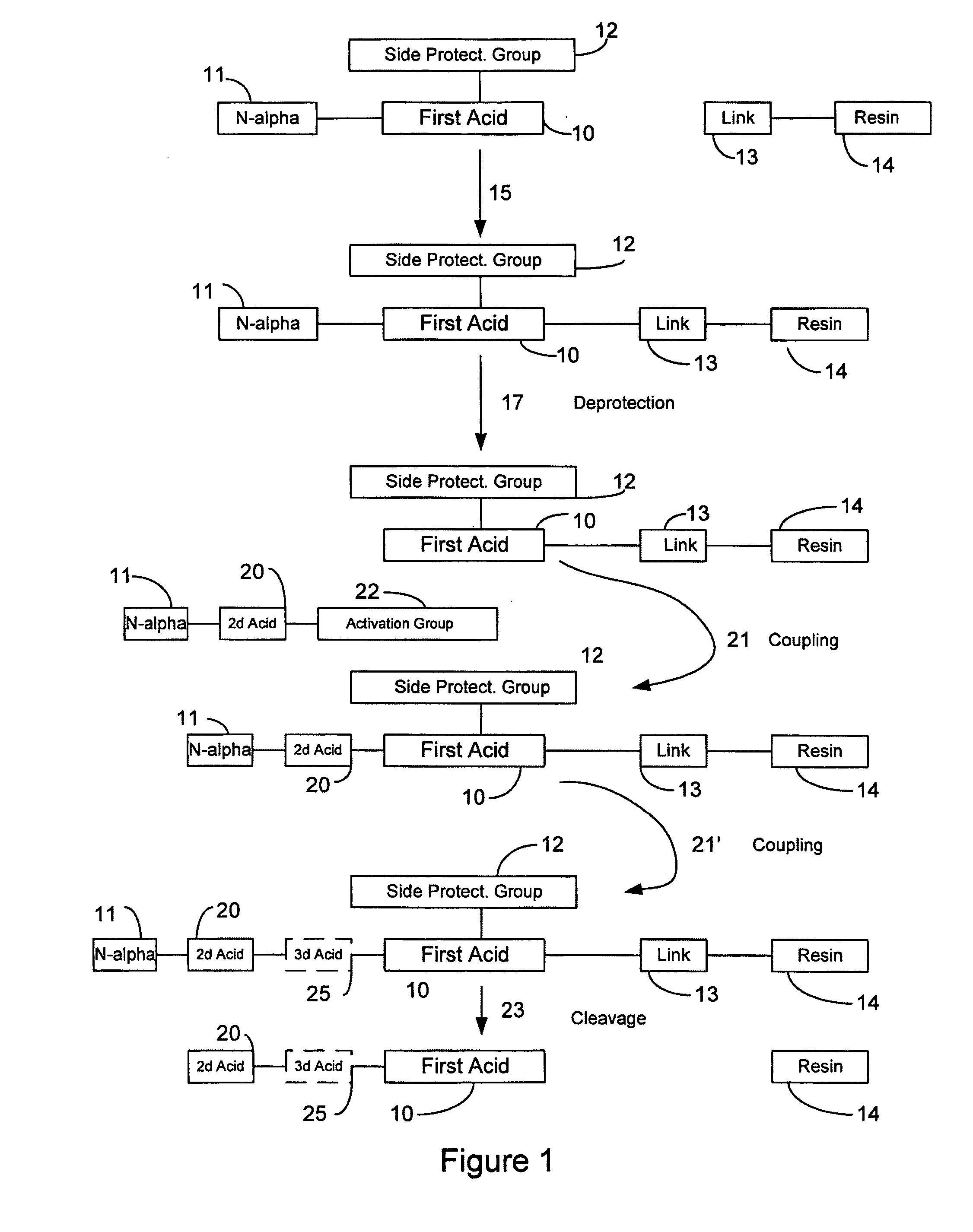
Microwave-assisted peptide synthesis
ActiveUS7393920B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsCombinatorial chemistrySolid-phase synthesis
An instrument and process for accelerating the solid phase synthesis of peptides is disclosed. The method includes the steps of deprotecting a protected first amino acid linked to a solid phase resin by admixing the protected linked acid with a deprotecting solution in a microwave transparent vessel while irradiating the admixed acid and solution with microwaves, then activating a second amino acid by adding the second acid and an activating solution to the same vessel while irradiating the vessel with microwaves, then coupling the second amino acid to the first acid while irradiating the composition in the same vessel with microwaves, and cleaving the linked peptide from the solid phase resin by admixing the linked peptide with a cleaving composition in the same vessel while irradiating the composition with microwaves.
Owner:CEM CORP
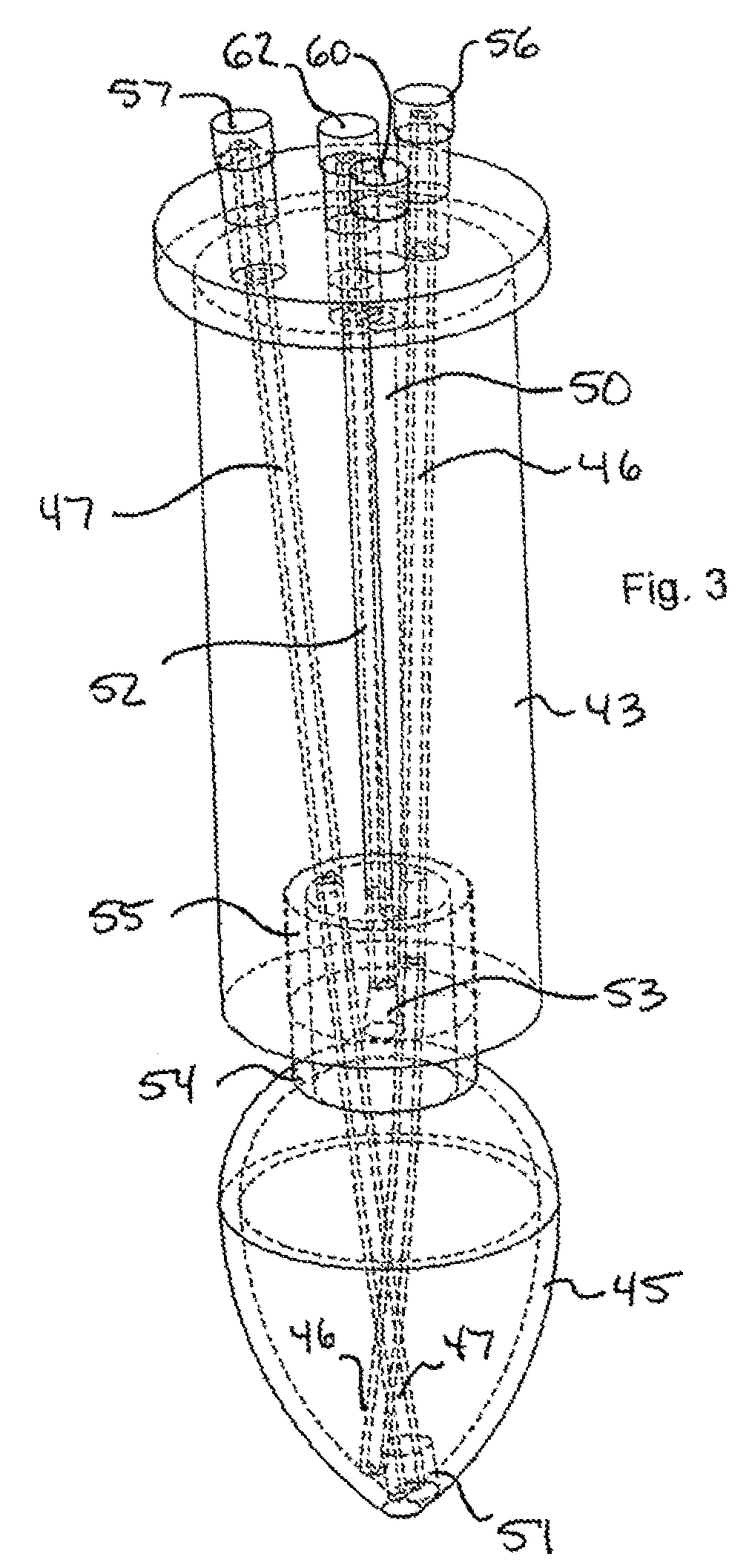
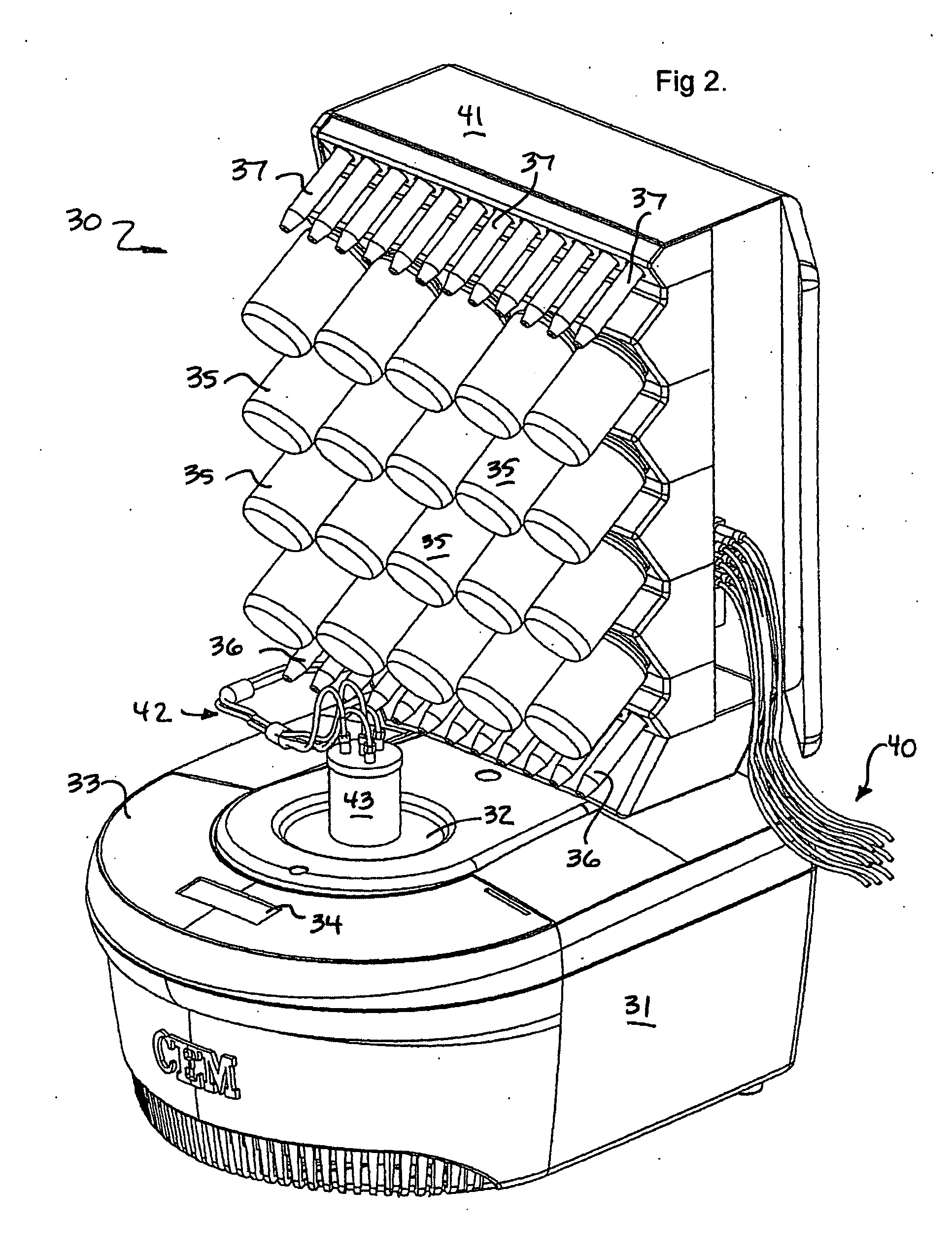
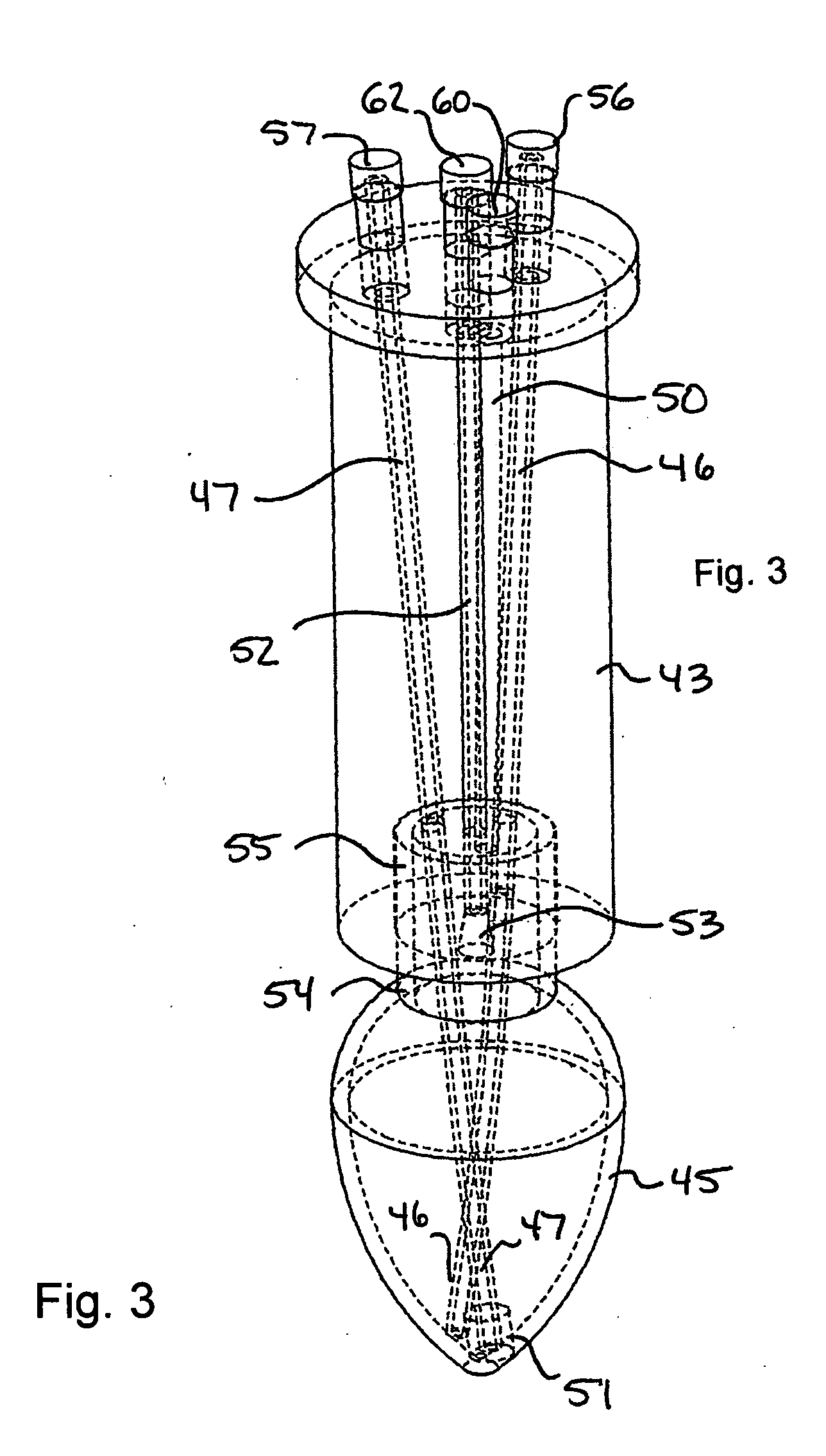
Microwave-assisted peptide synthesis
InactiveUS7902488B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsMicrowave cavityCombinatorial chemistry
An instrument and associated method are disclosed for the accelerated synthesis of peptides by the solid phase method. The instrument includes a microwave cavity, a microwave source in communication with the cavity, a column in the cavity formed of a material that is transparent to microwave radiation, a solid phase peptide support resin in the column, respective filters for maintaining the solid phase support resin in the column, a first passageway for adding starting compositions to the column, a second passageway for removing compositions from the column, and a third passageway for circulating compositions from the column into the third passageway and back to the column.
Owner:CEM CORP
Peptide synthesis and deprotection using a cosolvent
InactiveUS20050165215A1Speed up the processMinimize impactPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesOrganic solventCombinatorial chemistry
The invention provides methods for synthesizing peptides, which include taking an organic solvent having non-resin bound protected peptide and performing a deprotection reaction on the non-resin bound protected peptide. In these methods it is not required that the peptide is dried immediately before providing to the deprotection reaction. Also provided are methods of synthesizing peptides, wherein a protected peptide is formed in a solution phase reaction, dissolved into an organic solvent, and then introduced into a deprotection reaction. Also provided are methods of synthesizing peptides, wherein a non-resin bound protected peptide is concentrated in an organic solvent prior to being subject to a deprotection reaction.
Owner:BIGELOW ROGER +2
Solid-phase peptide synthesis and agent for use in such synthesis
InactiveUS7348404B2Peptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsCombinatorial chemistrySolid-phase synthesis
The present invention relates to an improved process for the production of peptides by solid-phase synthesis. The invention also relates to agents which are useful in solid-phase peptide synthesis.
Owner:ZEALAND PHARM AS
Decoding and sequencing method by real-time synthesis of two nucleotides into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
InactiveCN102634586AIncrease the lengthLower Sequencing CostsMicrobiological testing/measurementSynthetic nucleotideDeoxycytidine triphosphate
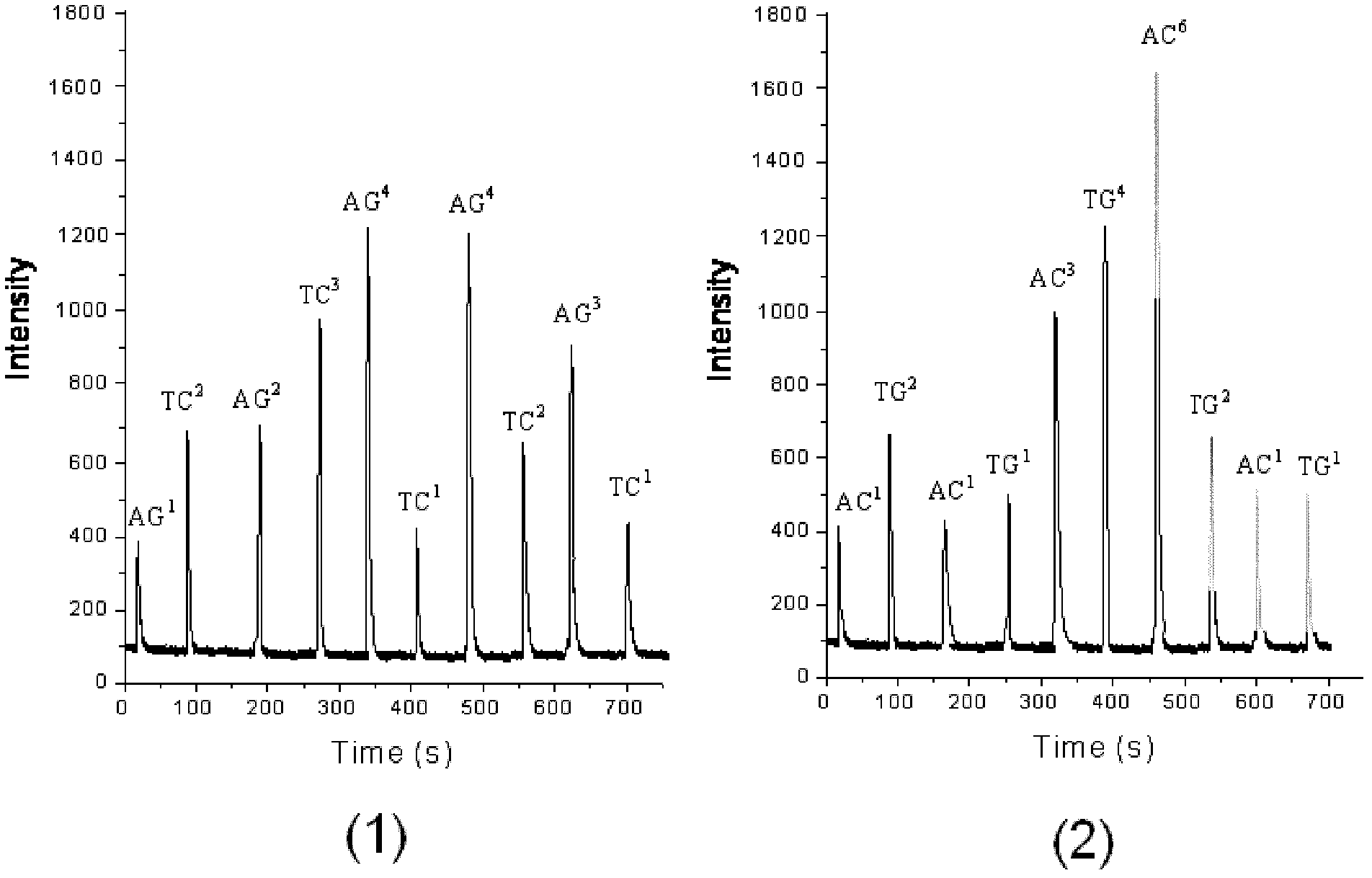
The invention discloses a decoding and sequencing method by real-time synthesis of two nucleotides into deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Single-sequencing reactions are performed on two different nucleotides of X and Y simultaneously and a base sequence fragment code of XYn is obtained according to the quantitative relation between the number of synthesizing nucleotides and the number of the detected molecules which are generated in real time. The sequencing comprises two sets of sequencing reactions on the same template; and in either set of sequencing, a cycle that two different nucleotides synthesize the sequencing reaction simultaneously is performed on deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP), deoxycytidine triphosphate (dCTP), deoxyguanosine triphosphate (dGTP) and deoxy-thymidine triphosphate (dTTP) containing four nucleotides in the mode that each nucleotide is used once in a cycle. After a plurality of sequencing reactions, information of a plurality of XYn ranked according to a sequencing order by the first set is obtained. When the set of sequencing reactions is completed, denaturation is performed to eliminate the extended strand of a sequencing primer and the sequencing primer is re-crossed to perform the second set of sequencing reactions; information of a plurality of XYn ranked by the second sequencing reaction is obtained; the specific base sequence of nucleic acid fragment to be detected is assembled by decoding the information of a plurality of XYn ranked according to a sequence order by the two sets.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for synthesizing triptorelin from solid phase polypeptide
ActiveCN101357936AConvenient sourceReduce usagePeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionSide chainFreeze-drying
The invention discloses a preparation method of solid phase peptide synthesis triptorelin, which includes the following steps: with Rink Amide AM resins or Rink Amide MBHA resins as starting materials, amino acids with protective groups are sequentially connected according to solid phase synthesis, so as to obtain protective decapeptide resins, and meanwhile crude products are obtained by sequentially removing Fmoc-protective groups and synchronously removing side-chain protective groups and cutting peptides, and triptorelin elaborate products are prepared after the crude products are separated and purified by C18 (or C8 ) column and freeze-dried. The preparation method is stable in technology, convenient in raw and auxiliary material sources, short in production cycle, high in yield, stable in quality, low in production cost and high in transpeptidase yield. Besides, as the preparation method avoids using poisonous reagents, such as hydrogen fluoride, and the like, the pollution of three wastes is low, purification yield is over 25 percent and each step of transpeptidase yield is above 98 percent; the yield after cutting peptides is 78.8 percent and the total yield is 25.4 percent.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA
Process for solid-phase microwave synthesis of polypeptide
InactiveCN1699404AIncrease reaction rateLower activation energyPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionCombinatorial chemistrySolvent
Disclosed is a process for solid-phase microwave synthesis of polypeptide comprising, (1) preparing amino acid and resin compound, (2) removing amino protecting group through microwave radiation, (3) condensating amino acid through microwave radiation, (4) replacing amino acids, repeating step (2) and (3) to synthesize the needed polypeptides, (5) preparing the polypeptides crude product.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
One-pot synthesis of highly mechanical and recoverable double-network hydrogels
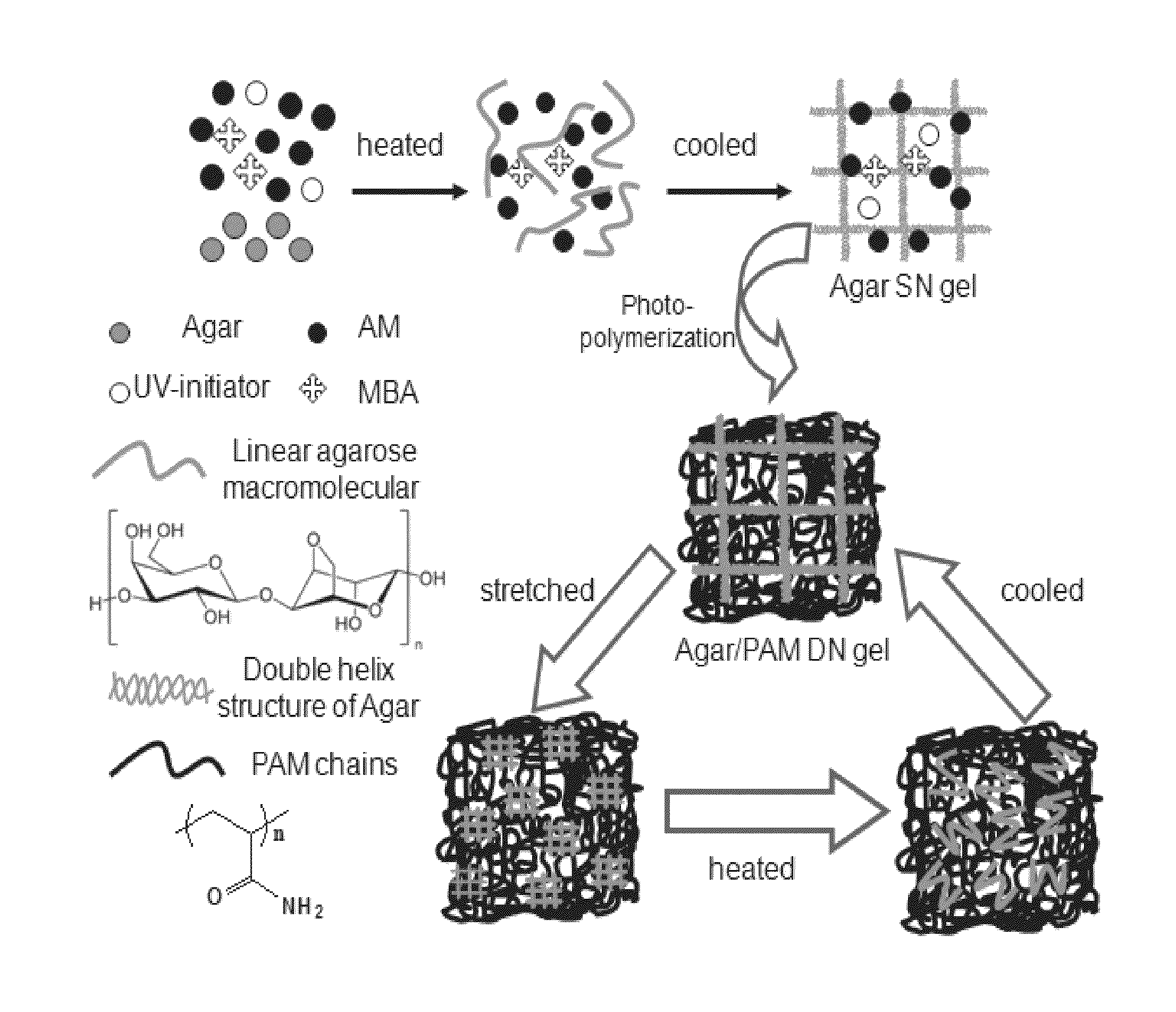
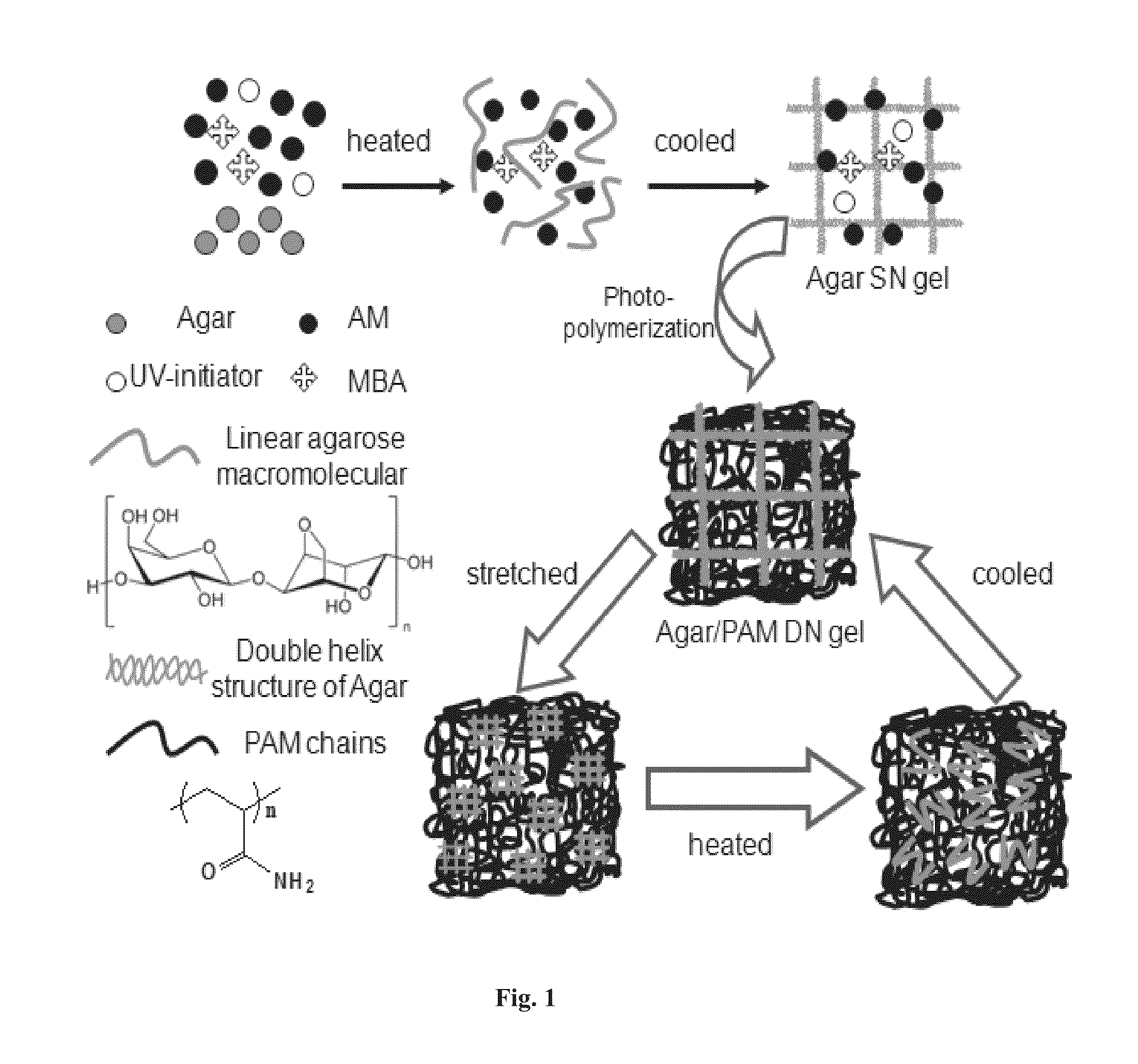
A method of forming a hybrid physically and chemically cross-linked double-network hydrogel with highly recoverable and mechanical properties in a single-pot synthesis is provided. The method comprises the steps of combining the hydrogel precursor reactants into a single pot. The hydrogel precursor reactants include water; a polysaccharide; a methacrylate monomer; an ultraviolet initiator; and a chemical crosslinker. Next the hydrogel precursor reactants are heated to a temperature higher than the melting point of the polysaccharide and this temperature is retained until the polysaccharide is in a sol state. Then the single-pot is cooled to a temperature lower than the gelation point of the polysaccharide and this temperature is retained to form a first network. Thereafter, photo-initiated polymerization of the methacrylate monomer occurs via the ultraviolet initiator to form the second network.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
Microwave-assisted peptide synthesis
InactiveUS20060025567A1Enhanced couplingAnalysis using chemical indicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsCombinatorial chemistrySolid-phase synthesis
An instrument and process for accelerating the solid phase synthesis of peptides is disclosed. The method includes the steps of deprotecting a protected first amino acid linked to a solid phase resin by admixing the protected linked acid with a deprotecting solution in a microwave transparent vessel while irradiating the admixed acid and solution with microwaves, then activating a second amino acid by adding the second acid and an activating solution to the same vessel while irradiating the vessel with microwaves, then coupling the second amino acid to the first acid while irradiating the composition in the same vessel with microwaves, and cleaving the linked peptide from the solid phase resin by admixing the linked peptide with a cleaving composition in the same vessel while irradiating the composition with microwaves.
Owner:CEM CORP
Semeglutide synthesis method
ActiveCN109369798AReduce generationHigh purityPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionSide chainSynthesis methods
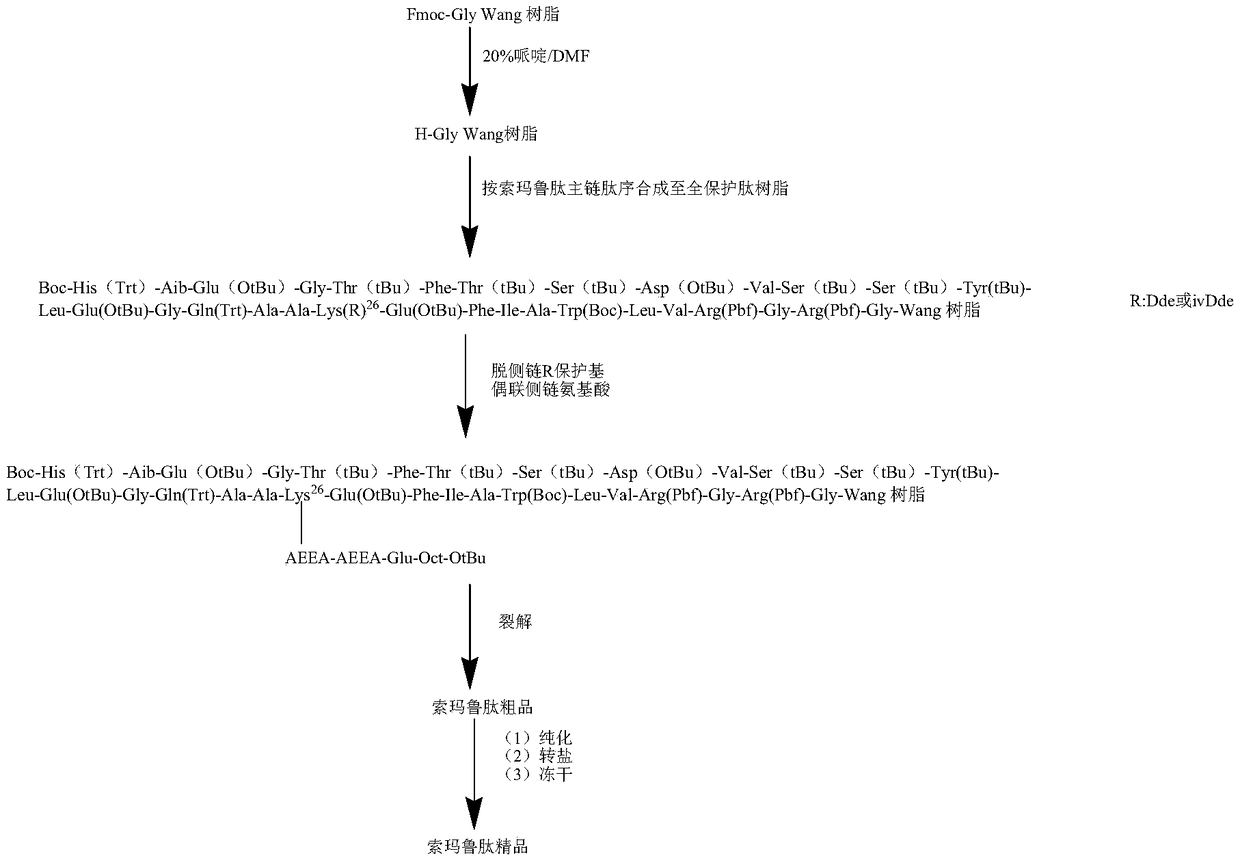
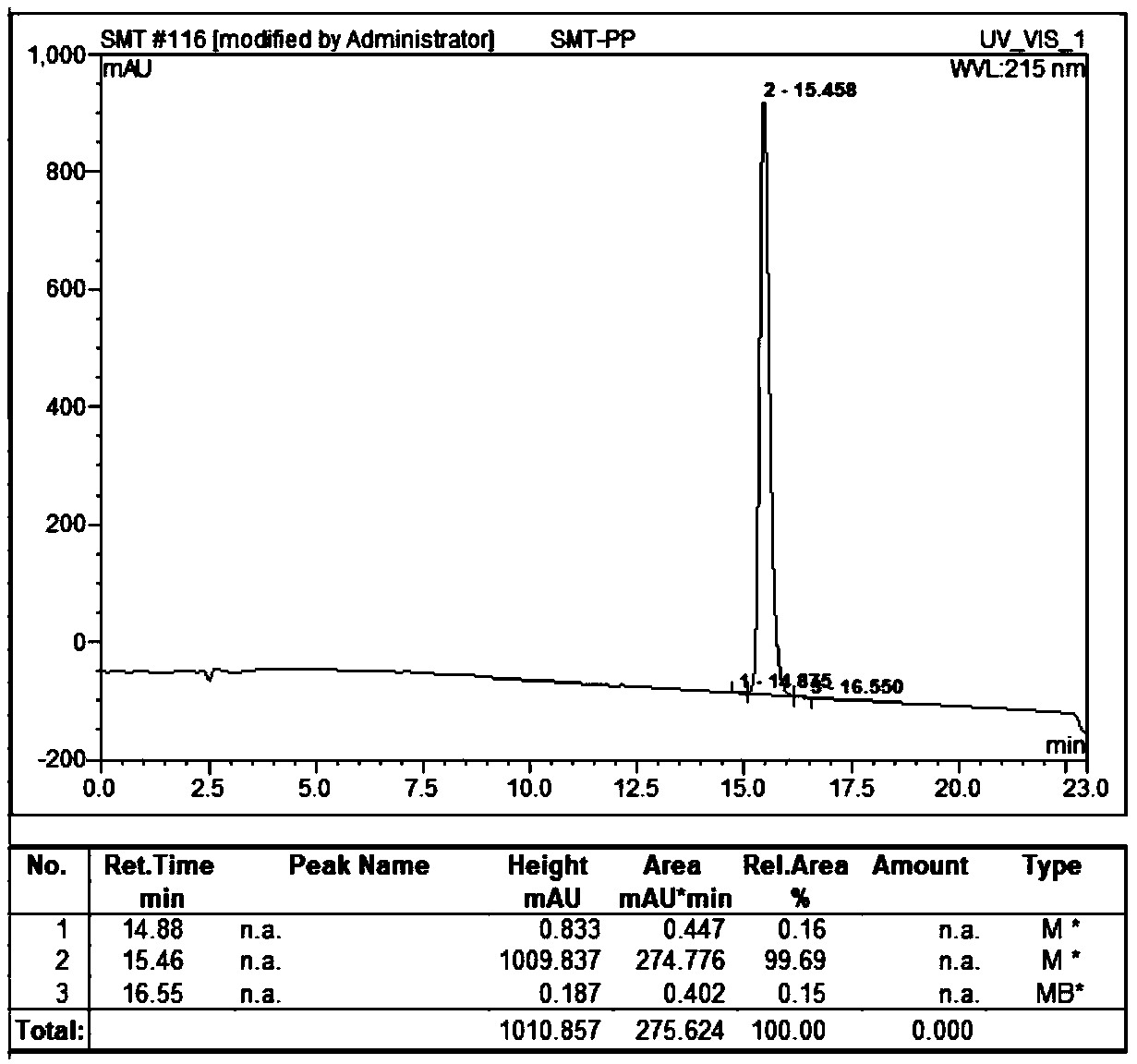
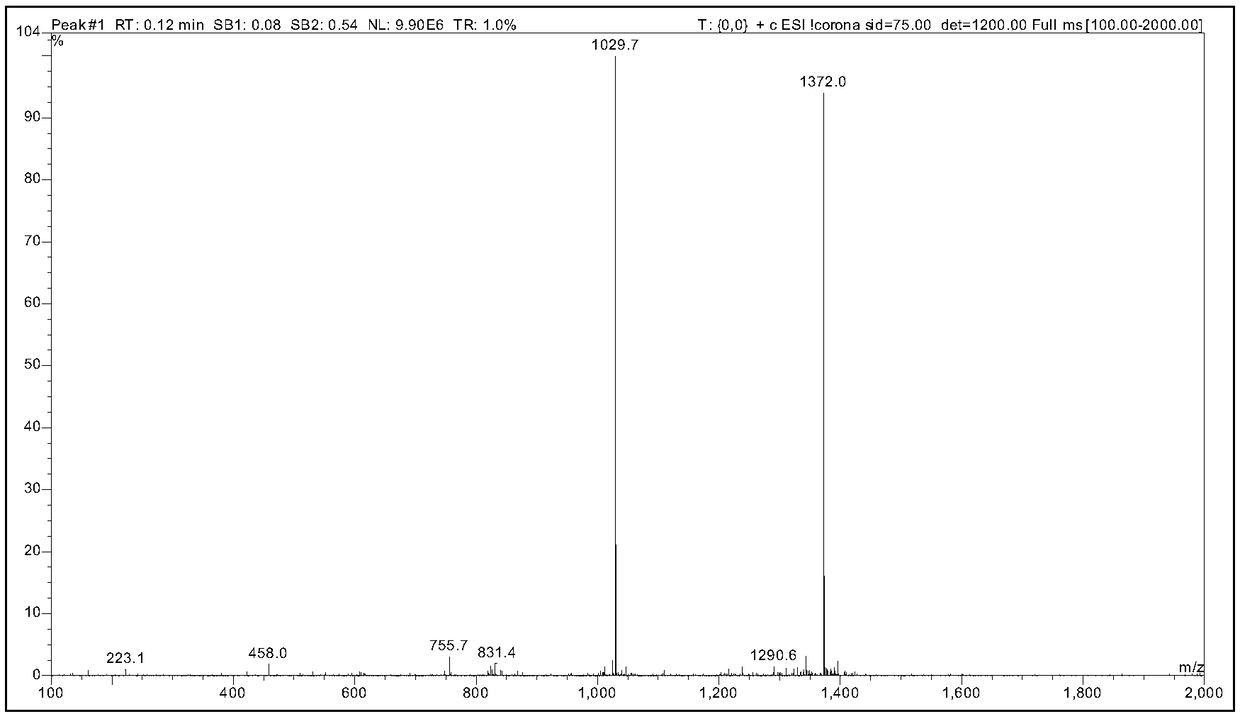
The invention discloses a semeglutide synthesis method and belongs to the technical field of polypeptide synthesis. The method comprises the steps as follows: an initial carrier is synthesized with Fmoc-Gly Wang resin as a solid phase, 30 amino acids on a main chain of semeglutide are activated and coupled with a novel condensing agent T3P (1-propanephosphonic anhydride), then, a Lys26side chain protection group of the main chain is removed, Fmoc-AEEA-AEEA, Fmoc-Glu-OtBu and Oct-Otbu are sequentially activated and coupled through the condensing agent T3P for condensing, all-protection peptideof semeglutide is obtained, and semeglutide is obtained through cracking and precipitation. By means of the method, the amino acid coupling efficiency is improved, the recemization peptide and deletion peptide impurities produced in the semeglutide synthesis process are greatly reduced, particularly, deletion impurities (Lys26 side chain AEEA deletion) with properties very similar to those of theproduct are effectively inhibited or reduced, the purity of a crude product is increased, the purification difficulty is reduced, and industrial enlarged production is facilitated.
Owner:苏州天马医药集团天吉生物制药有限公司
Preparation method of polypeptide synthesis carbetocin
ActiveCN102167723AConvenient sourceHigh peptide yieldPeptide preparation methodsCarbetocinDiethyl ether
The invention discloses a preparation method of polypeptide synthesis carbetocin. The technical scheme of the method comprises the steps of taking Rink Amide MBHA (methylbenzene hydrogen amine) resin as an initial raw material; taking Fmoc-protected amino acid as a monomer; sequentially connecting amino acid, wherein Cys adopts Fmoc-Cys (CH2CH2CH2COOR)-OH, and the last amino acid uses Fmoc-Tyr (Me)-OH, and obtaining protected nonapeptide resin; removing the Fmoc azyl protected group of Tyr; cutting straight chain peptide from the resin by peptide cutting reagents such as FTA (fault tree analysis) and the like; precipitating a straight chain peptide rough product by adding diethyl ether; performing ring formation reaction by adding BOP (butyl octyl phthalate) / HOBt (oxhydryl benzotriazole) / DMF (dimethyl formamide); and purifying the preparation type HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography) in a separating way to obtain a target product. After the method is used, the each-step peptide connecting yield is more than 99%, the peptide cutting yield is 96.2%, and the gross yield is as high as more than 35%. The preparation method is convenient to industrial implementation, and has a higher industrial prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA
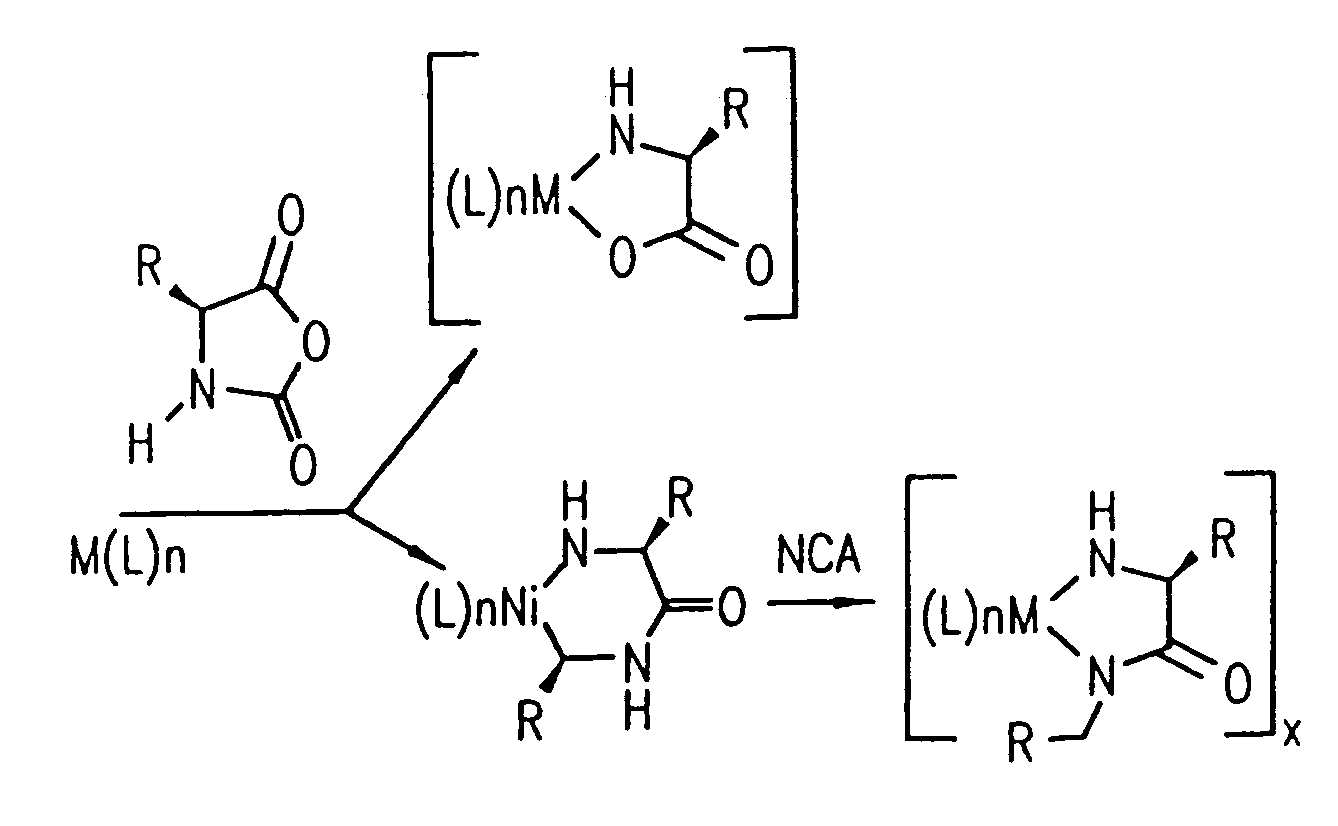
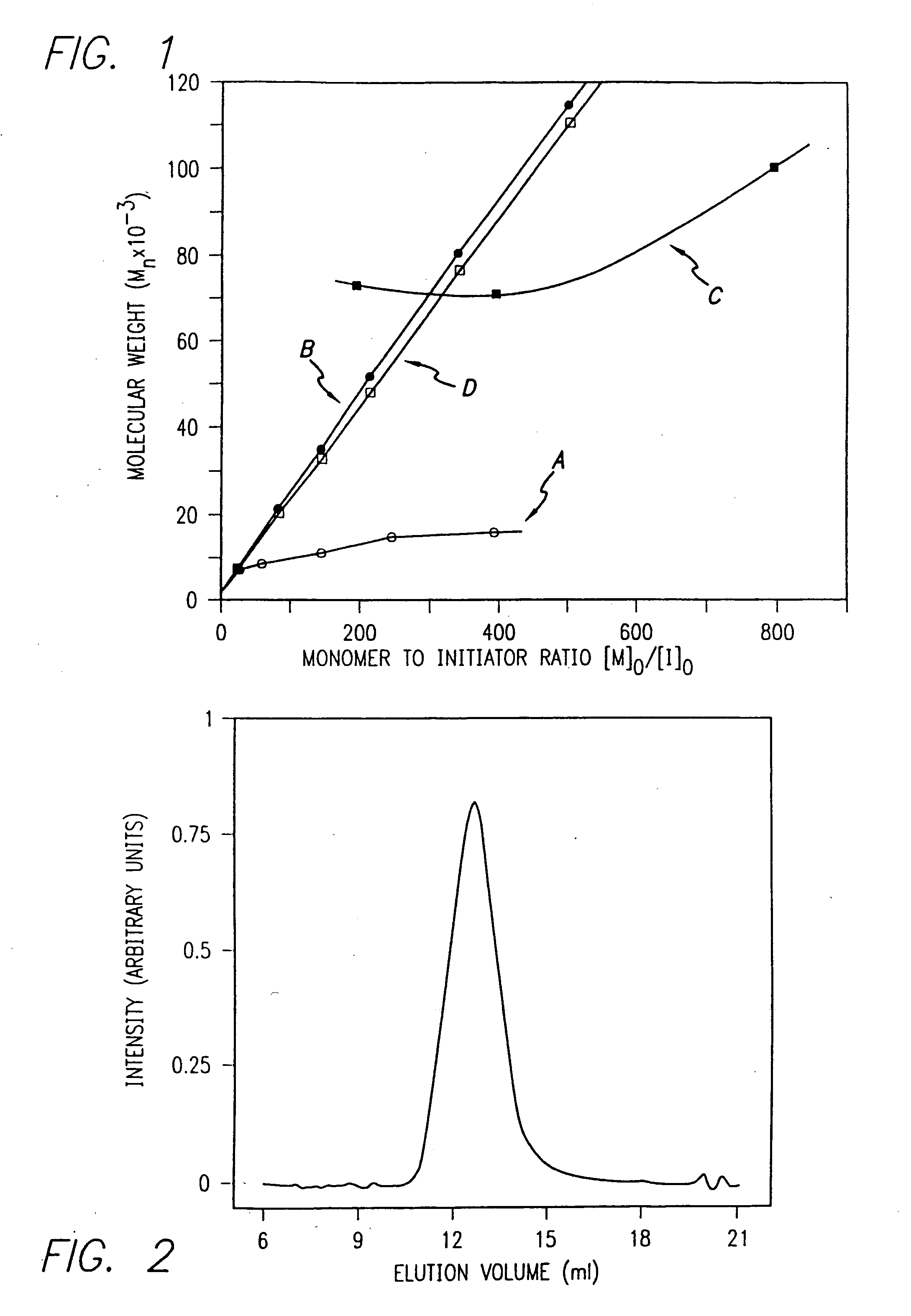
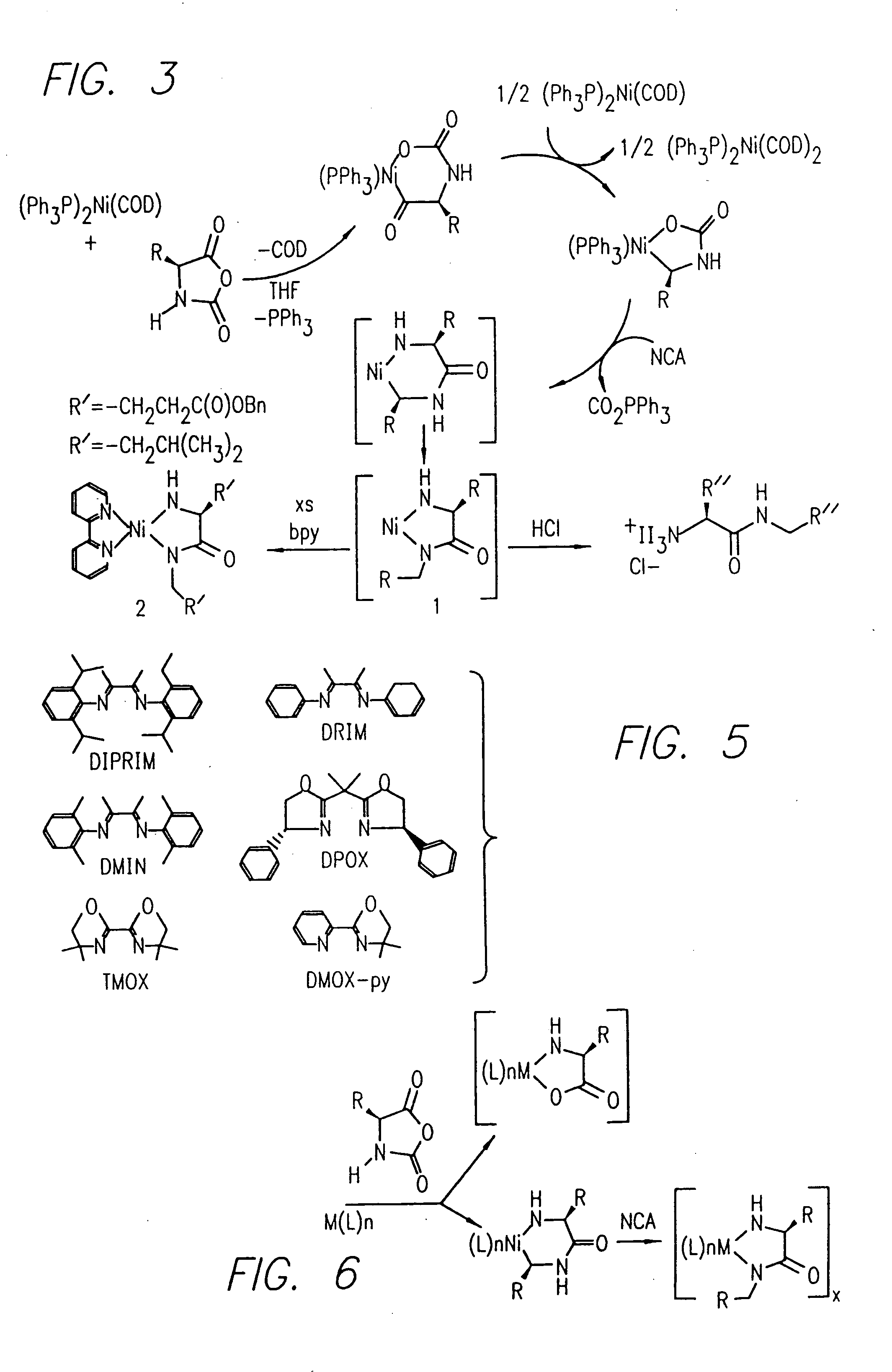
Methods and compositions for controlled polypeptide synthesis
InactiveUS20080125581A1Elimination reactionEasy to controlPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsSynthesis methodsEnd-group
Methods and compositions for the generation of polypeptides having varied material properties are disclosed herein. Methods include means for initiating the polymerization of aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydride (NCA) monomer by combining the monomer with an amido-containing metallacycle, for making self assembling amphiphilic block copolypeptides and related protocols for adding oligo(ethyleneglycol) functionalized aminoacid-N-carboxyanhydrides (NCAs) to polyaminoacid chains. Additional methods include means of adding an end group to the carboxy terminus of a polyaminoacid chain by reacting an alloc-protected amino acid amide with a transition metal-donor ligand complex to forming an amido-amidate metallacycle for use in further polymerization reactions. Novel compositions for use in peptide synthesis and design including five and six membered amido-containing metallacycles and block copolypeptides are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Solid-phase synthesis process of octreotide acetate
ActiveCN1569890AIncrease reaction rateRapid responsePowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsAutoxidationOctreotide acetate
The invention discloses the solid-phase synthesis process of octreotide acetate which consists of, bonding acetal product with macromolecular resin, merging the bonded products with protection amino acid residue in sequence to obtain octapeptide resin, cutting the octapeptide from the resin to obtain aqueous solution, carrying out naturally oxidation in air to obtain Octreotide, charging glacial acetic acid into Octreotide aqueous solution, and freeze-drying.
Owner:SINOPHARM A THINK PHARMA
Method for preparing bivalirudin through solid-liquid combination
ActiveCN104031127ASolve difficult coupling problemsReduce contentPeptide preparation methodsFluid phaseEngineering
The invention belongs to the field of polypeptide synthesis and relates to a method for preparing bivalirudin through solid-liquid combination. The bivalirudin is prepared by adopting a method for combining a liquid phase and a solid phase, impurity peptides can be well avoided, the purity of crude peptides is improved, and the production cost is reduced. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a fragmental hexapeptide Fmoc-Arg(pbf)-Pro-Gly-Gly-Gly-Gly-OH by adopting a liquid phase method, and connecting peptides onto the solid phase. By utilizing the method, impurity peptides Biv+ / -Gly and Biv+ / -2Gly can be avoided, and the problem that the peptides are difficultly completely coupled during solid phase Arg connection is avoided. By utilizing the synthesis process, the purity of the crude peptides can be over 90 percent, and the purification difficulty is reduced, so that the purity of the final product exceeds 99.5 percent, and the production cost is further reduced. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is simple in operation and low in synthesis cost, and is conductive to large-scale industrial production.
Owner:JINAN KANGHE MEDICAL TECH
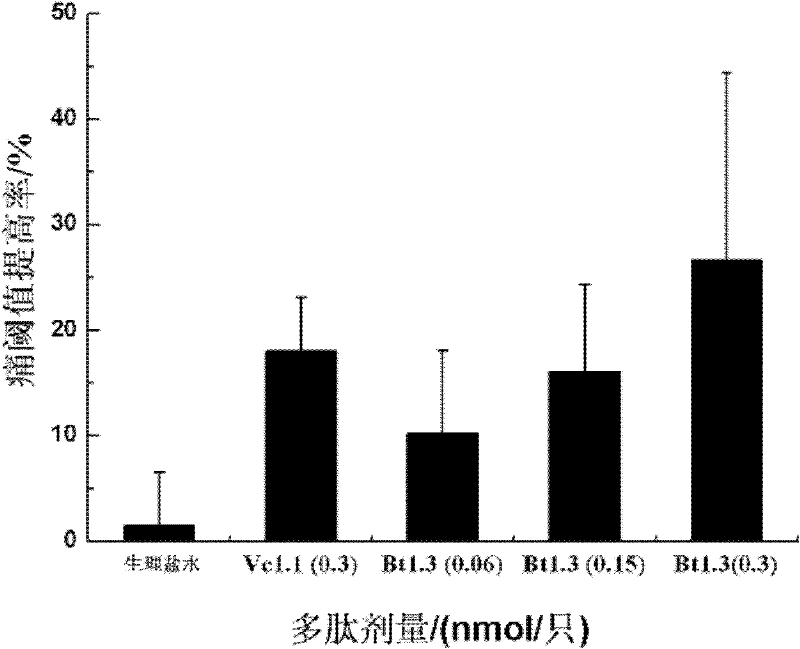
Barrel-shaped alpha conantokin Bt1.3 and application thereof
The invention discloses barrel-shaped alpha conantokin Bt1.3 and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the barrel-shaped alpha conantokin Bt1.3 is a sequence 2 in a sequence table; and the nucleotide sequence of a coding gene of the conatokin is a sequence 1 in the sequence table. The connection modes of a disulfide bond of the conantokin are Cys1-Cys3 and Cys2-Cys4; and Cys starting from the amino terminal of the conantokin is respectively marked as Cys1, Cys2, Cys3 and Cys4 in sequence. Experiments prove that: Bt1.3 linear peptide (RKCCSNPACNRYNPAIC) is synthesized by an Fmoc-solid-phase peptide synthesis method, and is folded by one step in buffer solution of NH4HCO3 to form the Bi1.3 conantokin; and analgesic experiments prove that the alpha conantokin has high analgesic activity in rat sciatic nerve hemisection models.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Preparation method of synthesizing octriotide from solid phase polypeptide
ActiveCN1923849AConvenient sourceReduce usagePeptidesBulk chemical productionHydrogen fluorideSide chain
The invention discloses an aoqu-peptide preparing method of solid-phase polypeptide, which comprises the following steps: adopting 2-chloride-trityl resin, 4-methyl trityl resin or 4-methoxyl trityl resin as raw material; connecting amino acid with protective group according to solid-phase synthetic method; obtaining protected octapeptide resin; removing Fmoc-protective group sequently; stripping side-chain protective group; cutting peptide to obtain reduced aoqu-peptide; oxidizing through air under pH 7-11 condition; separating and purifying rought product through C18 (C8) column to produce exquisite.
Owner:SHANGHAI SOHO YIMING PHARMA
Synthetic method for semaglutide
PendingCN109456402ADestroy secondary structureTroubleshoot compositingPeptide preparation methodsBulk chemical productionSide chainCombinatorial chemistry
The invention discloses a synthetic method for semaglutide and belongs to the field of polypeptide synthesis. In the method, amino acids at 1-30 positions of a main sequence of the semaglutide is obtained by adopting solid phase synthesis, Val at 10 position and Ser at 11 position adopt Fmoc-Val10-Ser11 (Psi(Me, Me) pro)-OH; and an Lys side chain at 20 position adopts Fmoc-Lys(X)-OH. The method comprises the following steps of performing cracking precipitation to obtain a semaglutide crude peptide; and performing purification to obtain the semaglutide. In the method, by introducing the Fmoc-Val10-Ser11 (Psi(Me, Me) pro)-OH to solve the problem of difficult sequence synthesis of the semaglutide, difficult sequence synthesis becomes simple and easy; and meanwhile, the yield is greatly increased, the purity of the crude peptide is greatly improved, the production cost is greatly lowered, and industrial amplification production is facilitated.
Owner:SINOPEP ALLSINO BIOPHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Process and systems for peptide synthesis
ActiveUS7439222B2Reduce in quantityReduce the amount requiredBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsCouplingCombinatorial chemistry
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Synthesis of photolabile 2-(2-nitrophenyl)propyloxycarbonyl protected amino acids
InactiveUS20050101763A1Carbamic acid derivatives preparationPeptide/protein ingredientsCombinatorial chemistryProtecting group
The 2-(2-nitrophenyl)propyloxycarbonyl (NPPOC) group has been introduced as a photolabile amino protecting group for amino acids to be used as building blocks in photolithographic solid-phase peptide synthesis. NPPOC-protected amino acids were found to be cleaved in the presence of UV light about twice as fast as the corresponding o-nitroveratryloxycarbonyl (NVOC)-protected amino acids. The protected amino acids are of particular use in the synthesis of peptide arrays.
Owner:TRUSTEES OF BOSTON UNIV
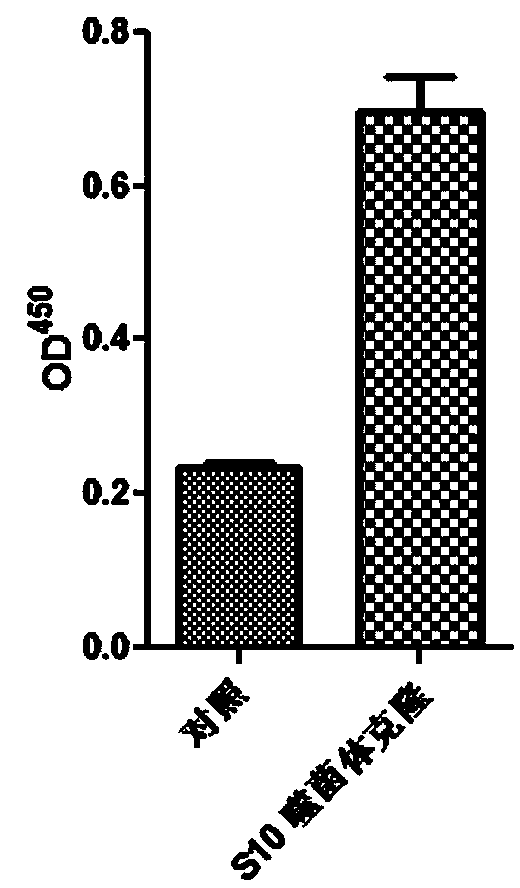
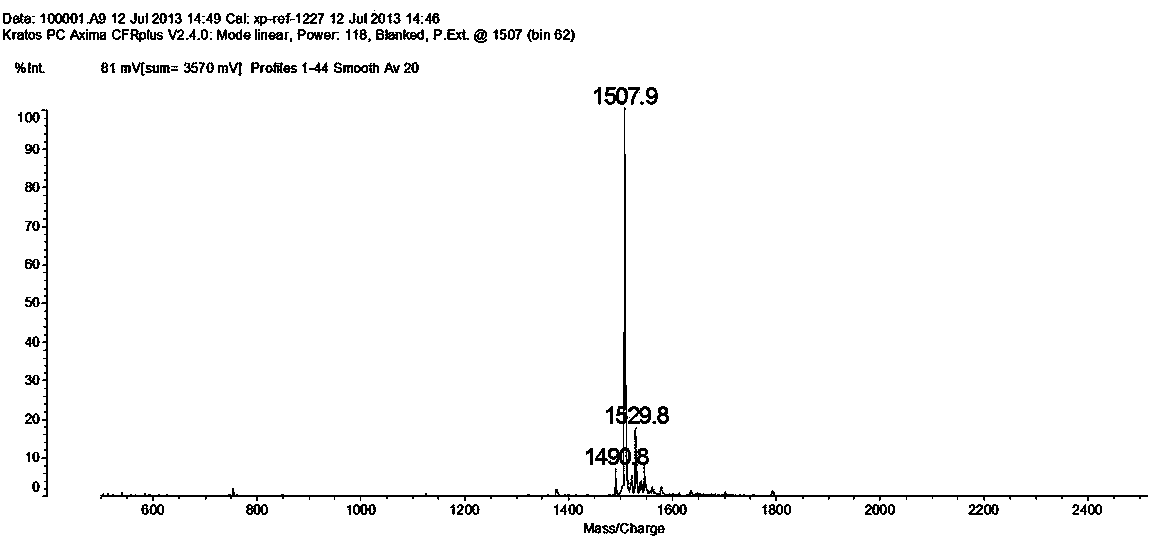
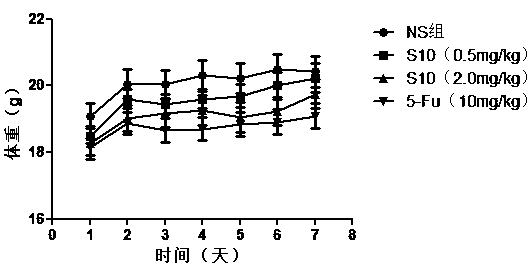
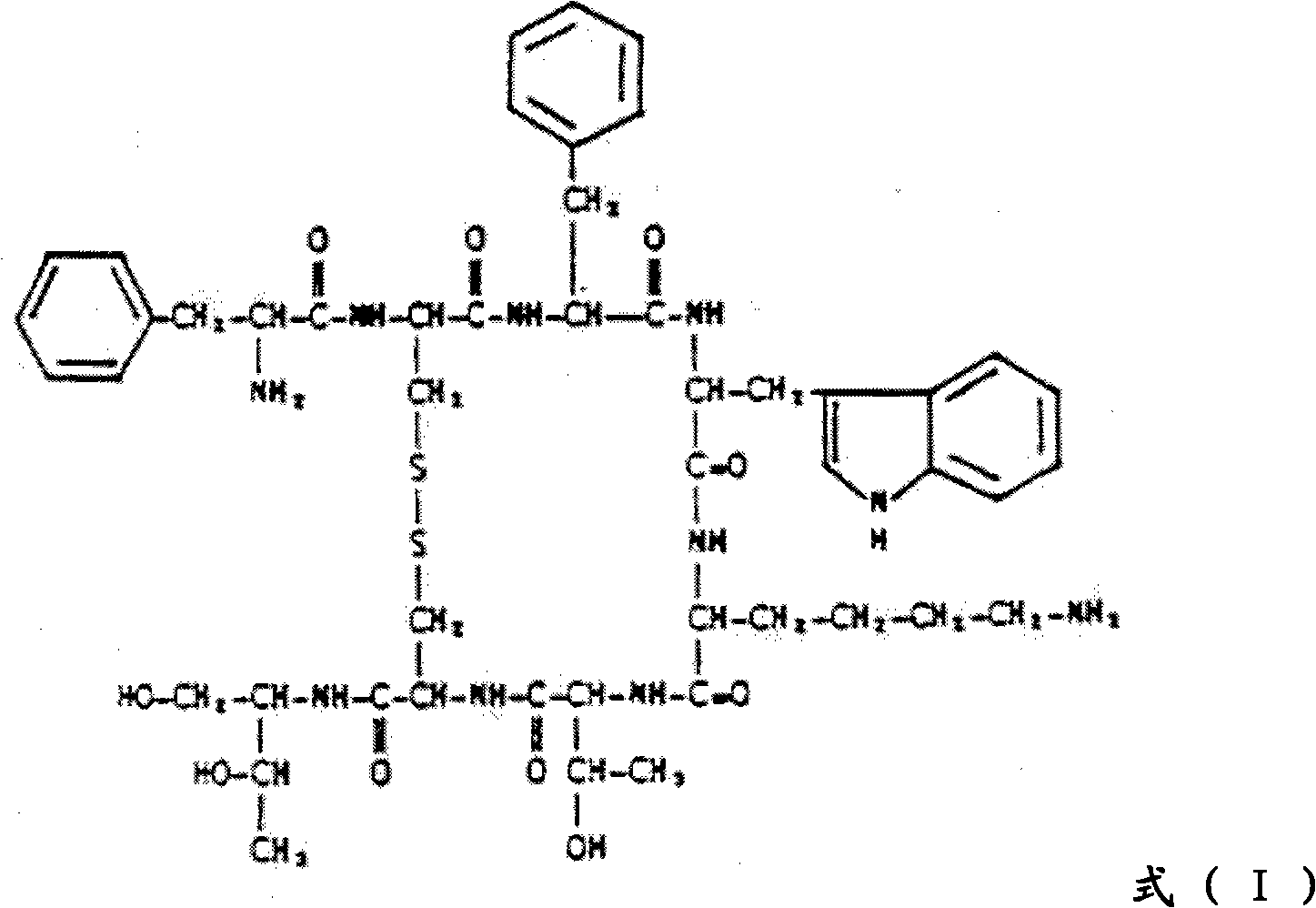
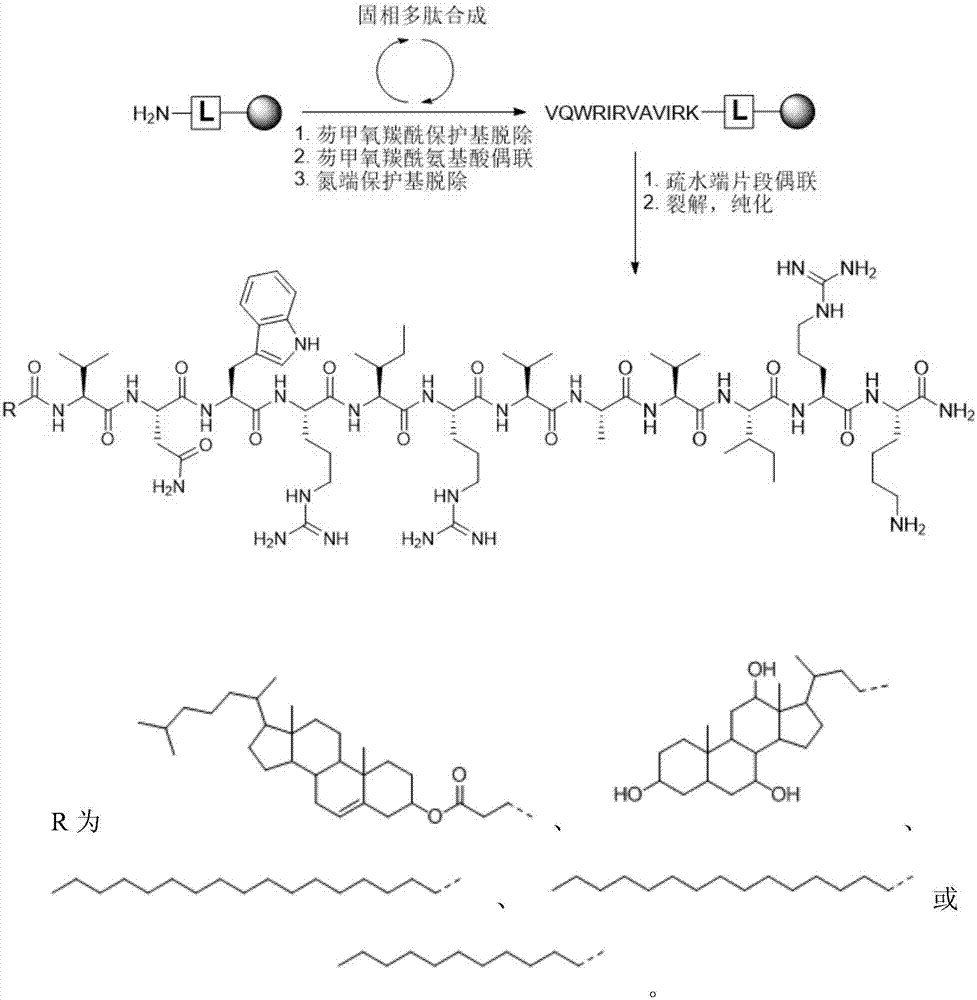
PD-L1 IgV affinity peptide S10 with antitumor activity
ActiveCN104086627AGood antitumor activityInhibit growthPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsPharmacyColon carcinoma
The invention belongs to the technical field of biological pharmacy, and concretely relates to a PD-L1 IgV affinity peptide S10 product with antitumor activity, and preparation and application thereof. The affinity peptide S10 is specifically bond at PD-l1 IgV region, has the amino acid sequence of WSHGGHQHFIRF, and has the molecular weight of 1507.7. The affinity peptide S10 is prepared through a Fomc solid-phase peptide synthesis method, and plays a role as a main active composition for preparing anti-colorectal carcinoma medicines. The provided affinity peptide S10 is obtained by utilizing a phage-display peptide-library screening technology and taking PD-L1 IgV as a target for performing high-flux screening. Experiments of bearing a cancer in a mouse prove that affinity peptide S10 has relatively good antitumor activity, is capable of obviously inhibiting growth of tumor in a mouse, and provides new thinking and theoretical base for research and exploitation of medicines based on PD-L1.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Preparation method of octreotide
InactiveCN101863961AHigh yieldSuitable for mass productionPeptide preparation methodsOctreotideSolid phases
The invention relates to a preparation method of octreotide, which comprises the steps of preparing crude linear peptide by an Fmoc / tBu solid-phase peptide synthesis method and preparing octreotide from the crude linear peptide through oxidizing reaction, wherein the oxidizing reaction is carried out under the pH of 7.0-7.5 and in the presence of hydrogen peroxide, and the charging molar ratio of the hydrogen peroxide and the crude linear peptide is 7-9 / 1. The invention adopts the hydrogen peroxide to oxidize the crude linear peptide so as to obtain the octreotide, the oxidizing reaction can be finished only within 1-3h, compared with the traditional air oxidizing method, the reaction time is greatly shortened, the octreotide product yield is tremendously improved, and the method is suitable for mass production of the octreotide and salts thereof.
Owner:苏州中科天马肽工程中心有限公司
Antibacterial peptide derivate and application thereof
ActiveCN107446019ASmall molecular weightGood monodispersityAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsNucleic acid transportChemical synthesis
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines, mainly relates to an antibacterial peptide derivate and the application thereof, in particular to a hydrophobic modified antibacterial peptide DP7 derivate and the application thereof. The hydrophobic modified antibacterial peptide is characterized in that a hydrophobic fragment is coupled to nitrogen terminal of the antibacterial peptide to realize the hydrophobic modification. The invention also provides a micelle which is prepared through the hydrophobic modified antibacterial peptide, and the application of the hydrophobic modified antibacterial peptide and the micelle in preparation of antibacterial medicines, preparation of a nucleic acid transporter and the preparation of an immunologic adjuvant. The antibacterial peptide is small in molecular weight and can be conveniently synthesized through an Fmoc solid-phase multi-peptide synthesis method; the hydrophobic fragment based chemical synthesizing coupling method is simple and easy to carry out.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Methods and processes for attaching compounds to matrices
InactiveUS20050239112A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsChemical MoietyEngineering
The present invention describes extremely rapid and efficient methods for the attachment of chemical moieties to matrices by the use of microwave technology. The methods of the invention can be applied in a variety of ways for the preparation of different types of matrices for a variety of applications including but not limited to the functionalization of various solid supports, and matrices in the form of powder, beads, sheets, and other suitable surfaces for use in applications including but not limited to oligonucleotide synthesis, peptide synthesis, environmental clean up (removal of toxic materials), immunoassays, affinity chromatography, combinatorial chemistry, microarrays, proteomics and medical diagnostics.
Owner:SPRING BANK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com