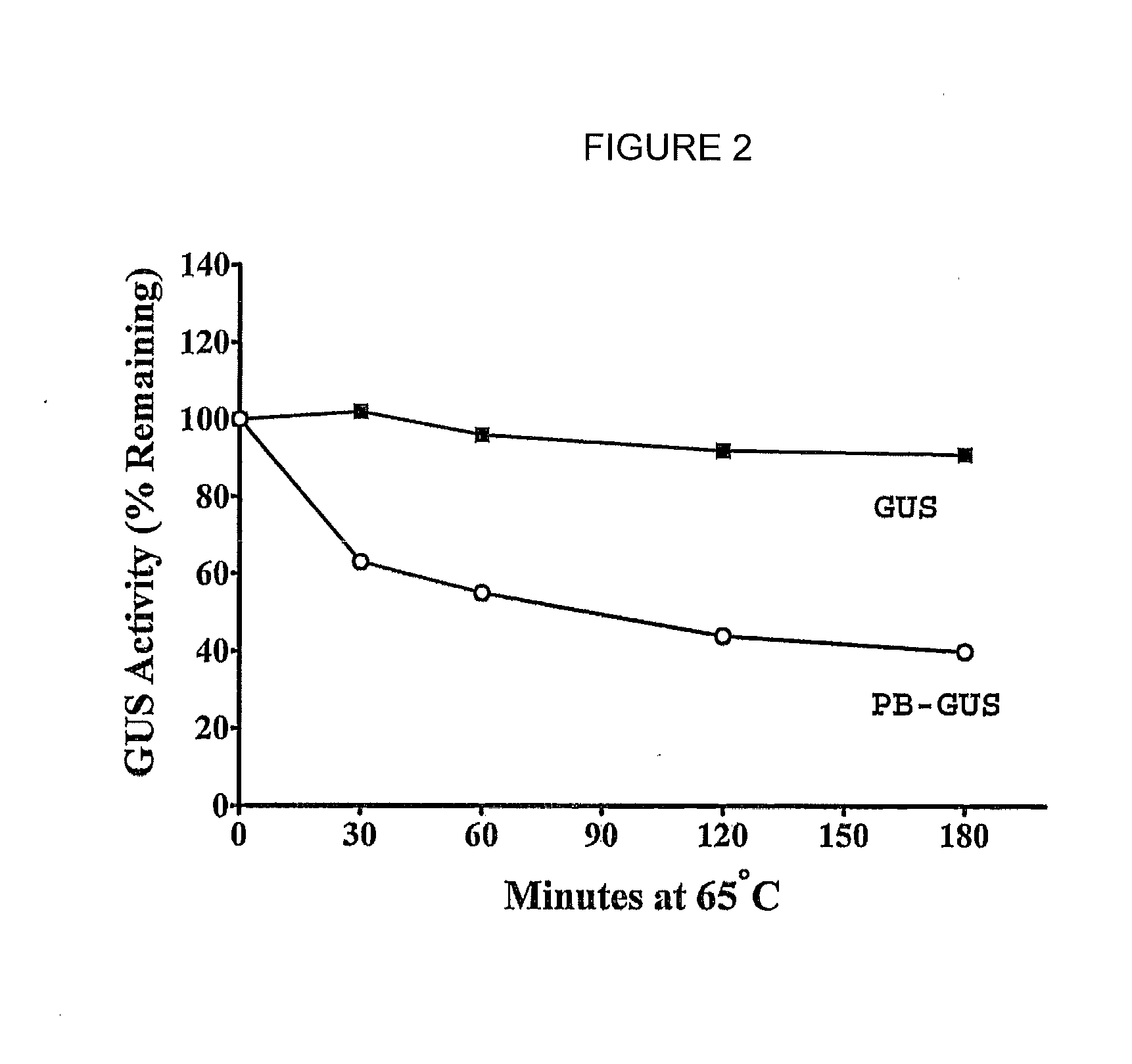
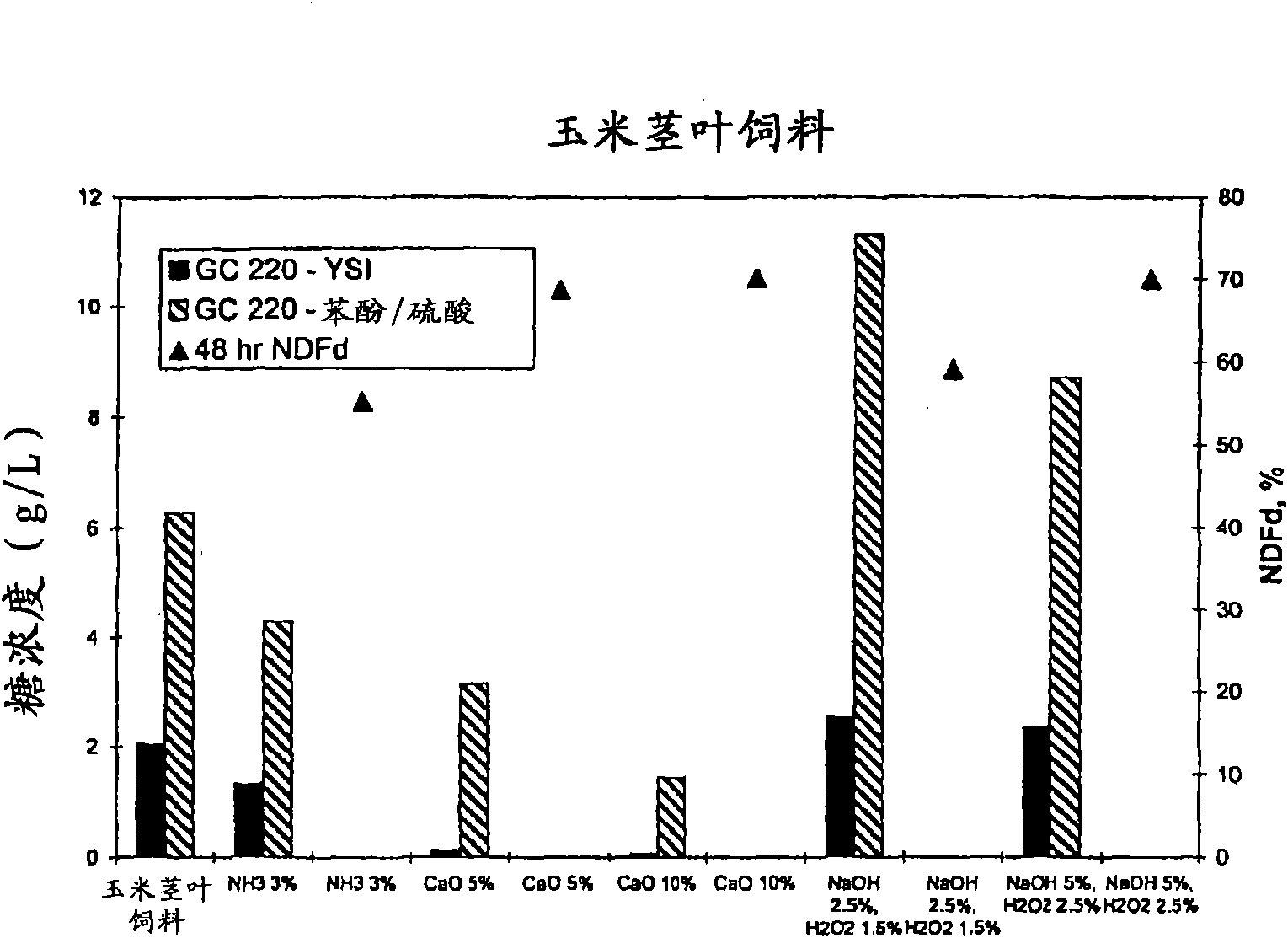
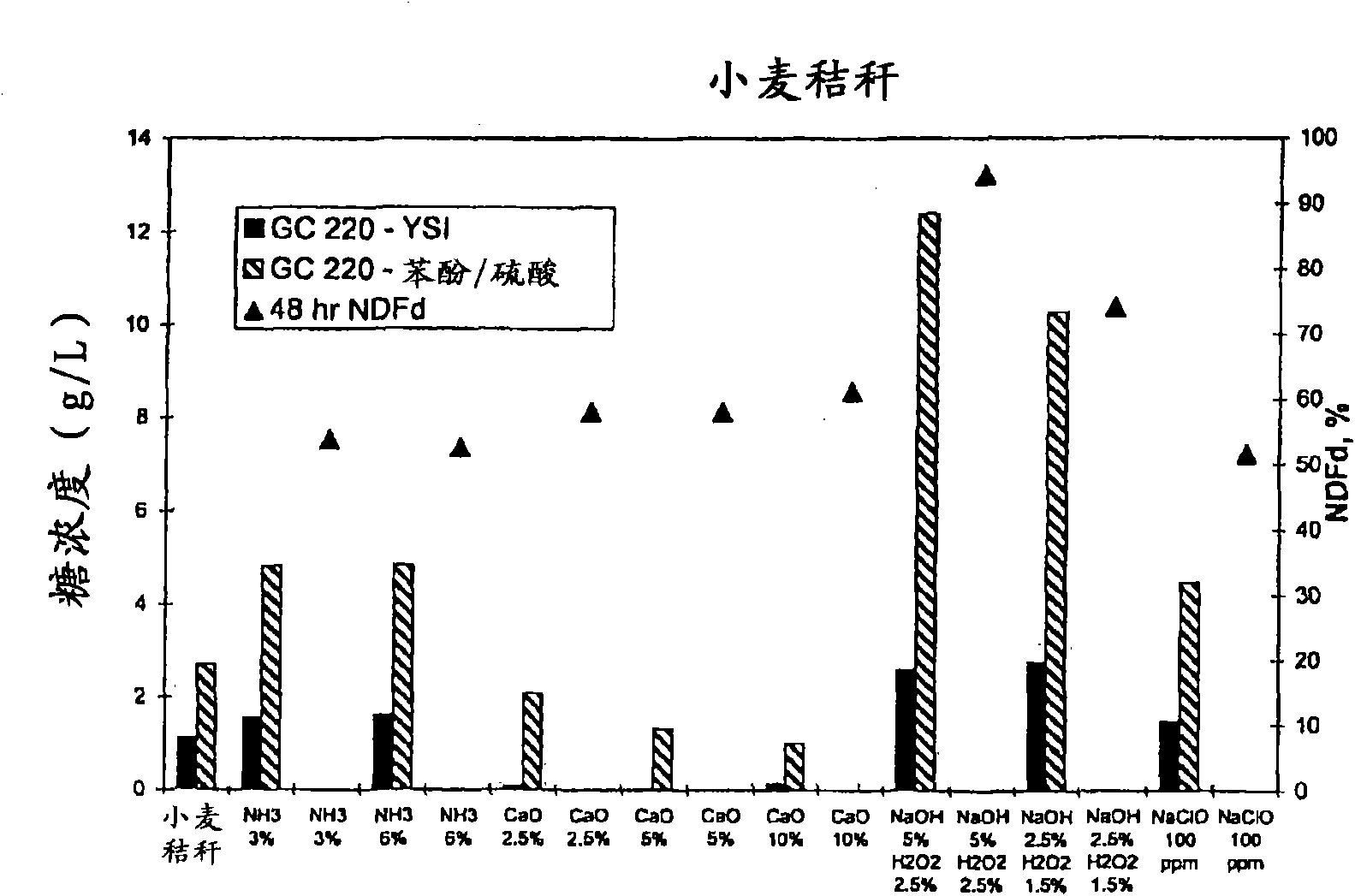
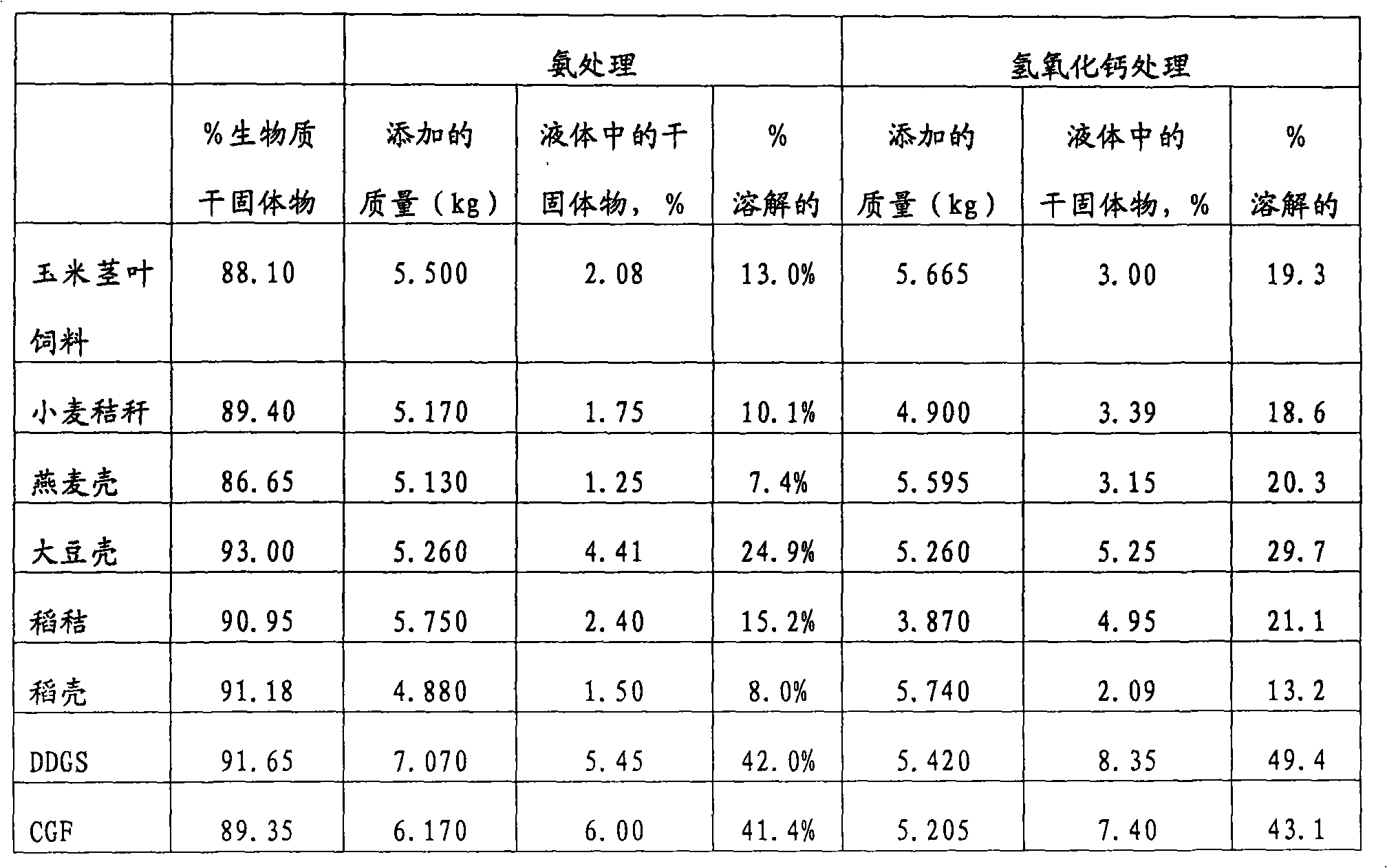
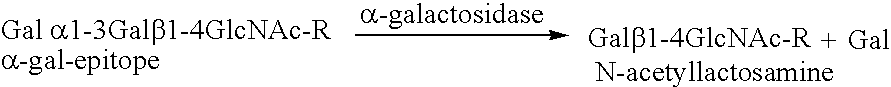Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
102 results about "Carbohydrate moiety" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
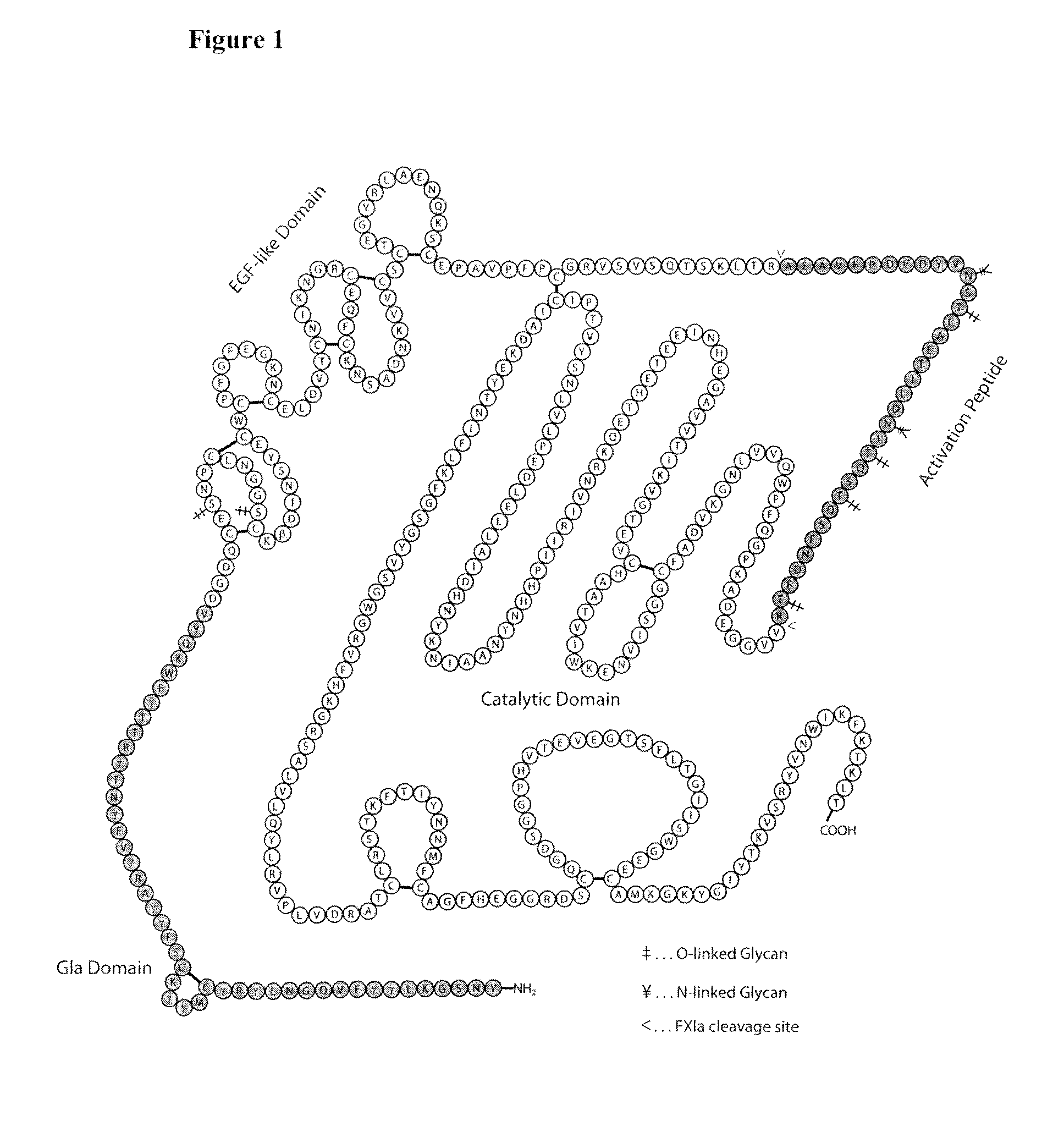
The carbohydrate moiety on an antibody is located at the hinge region of the Fc domain, with a sufficient distant from the variable region that regulates antigen interaction.
Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20080145441A1Reliably modulatedAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsMoietyCarbohydrate moiety
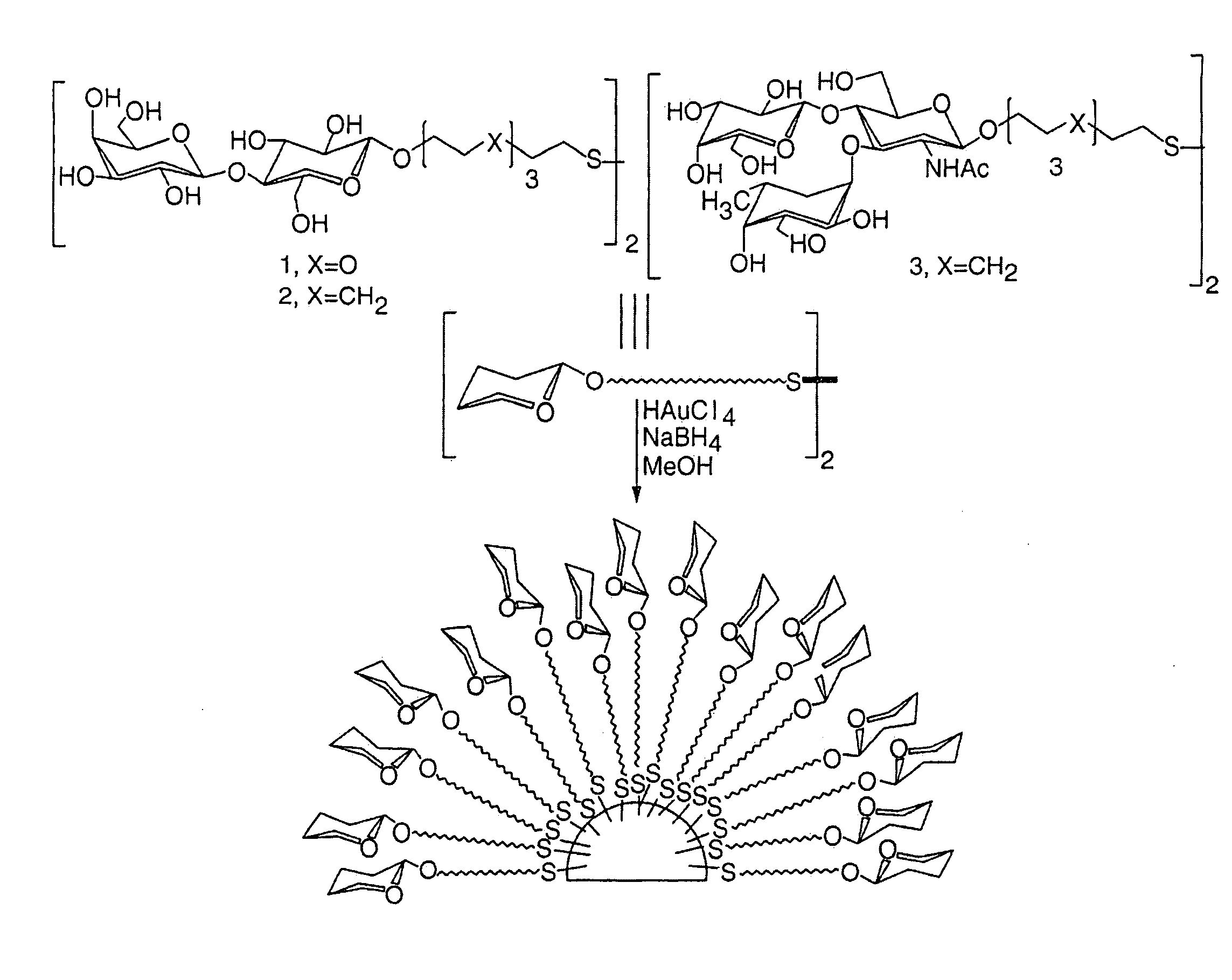
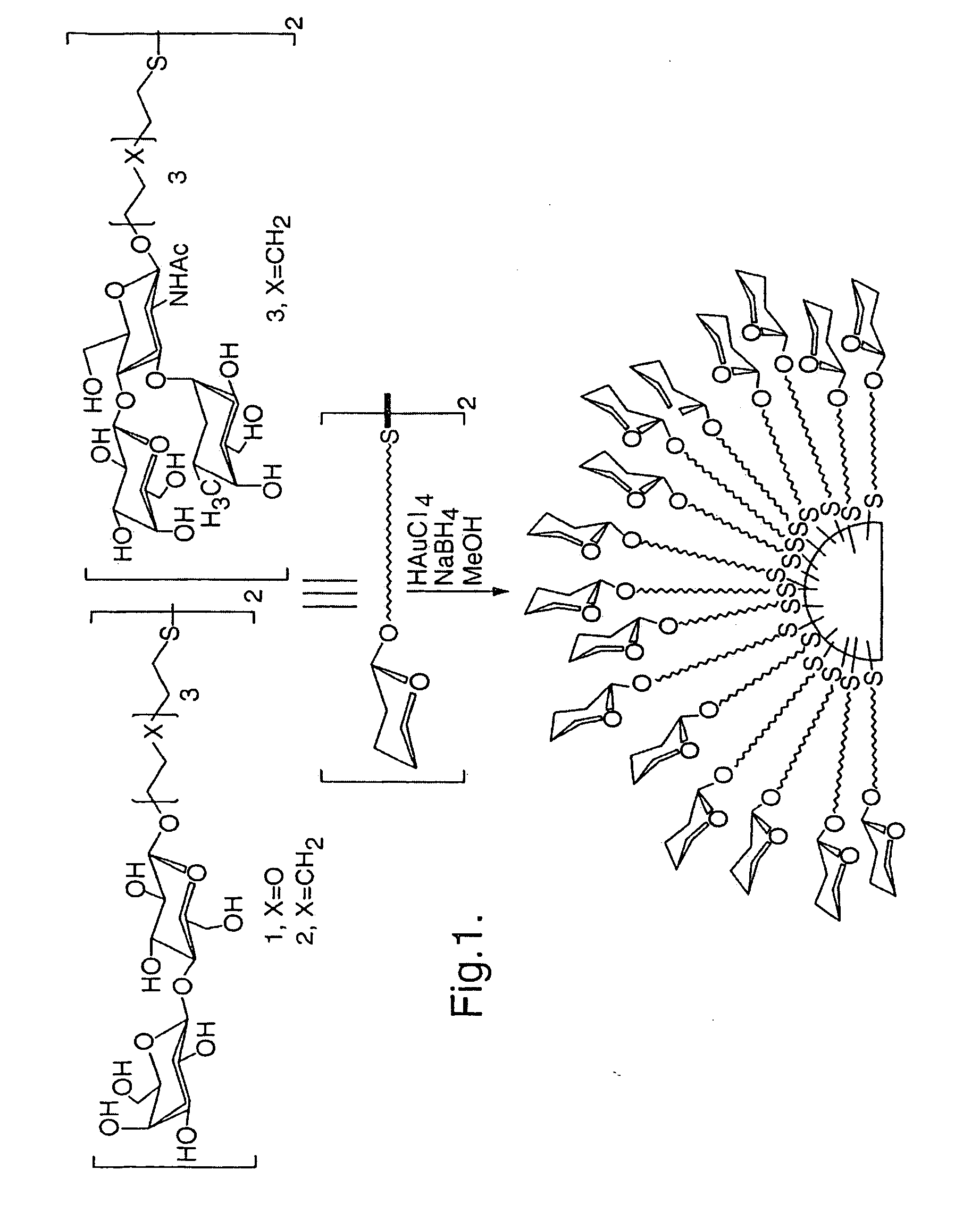
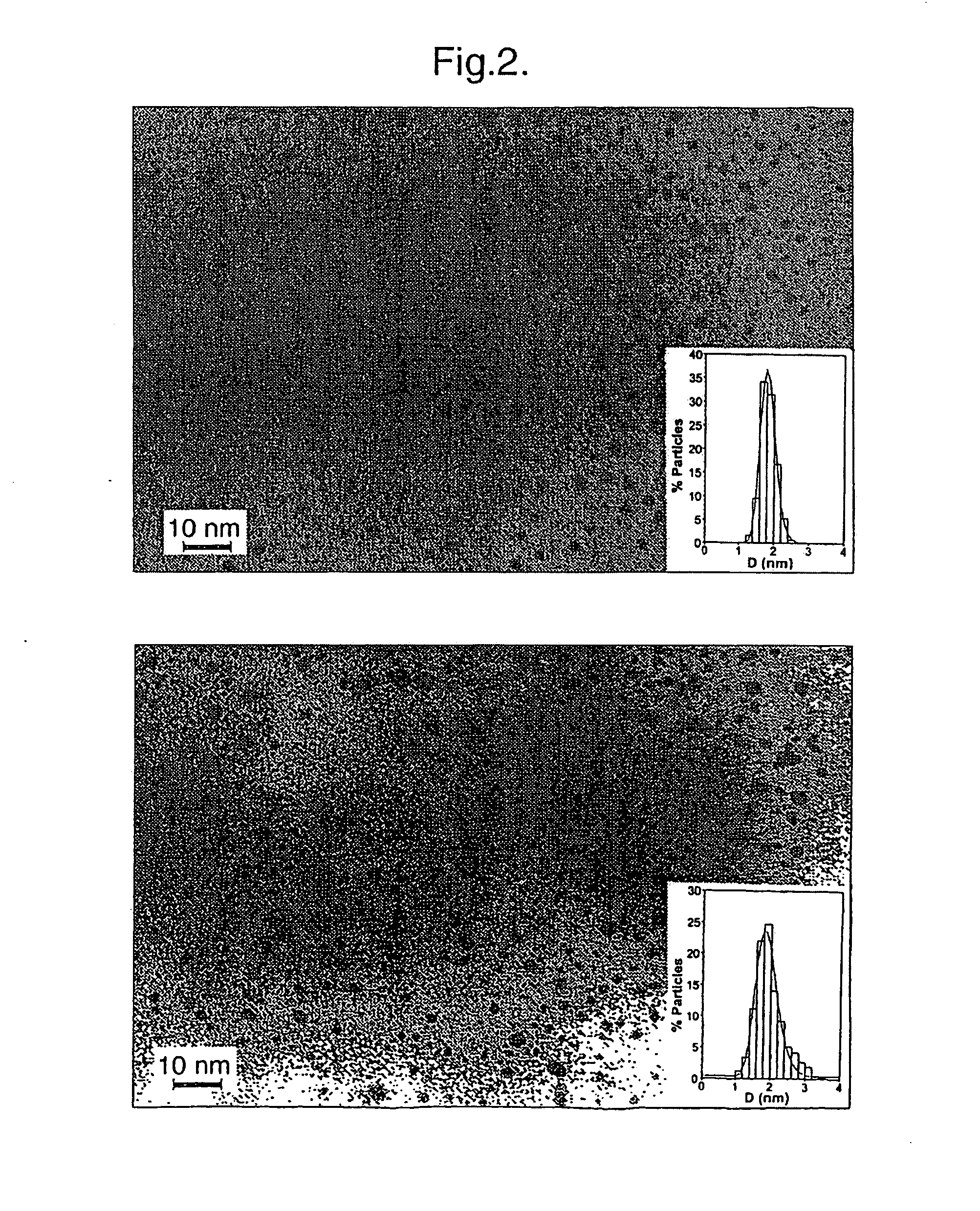
Materials and methods for studying and modulating the interaction of carbohydrate-containing moieties with other species are described, in particular, small particles, e.g. clusters of metal or semiconductor atoms, which can be employed as a substrate for immobilising a plurality of ligands comprising carbohydrate groups. These “nanoparticles” can then be used to study carbohydrate mediated interactions, e.g. with other carbohydrates or proteins, and as therapeutics and diagnostic reagents.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Chemical modification of DNA using peptide nucleic acid conjugates
InactiveUS6165720AReduce deliveryHigh transfection efficiencyFungiBacteriaEukaryotic plasmidsBiological activation
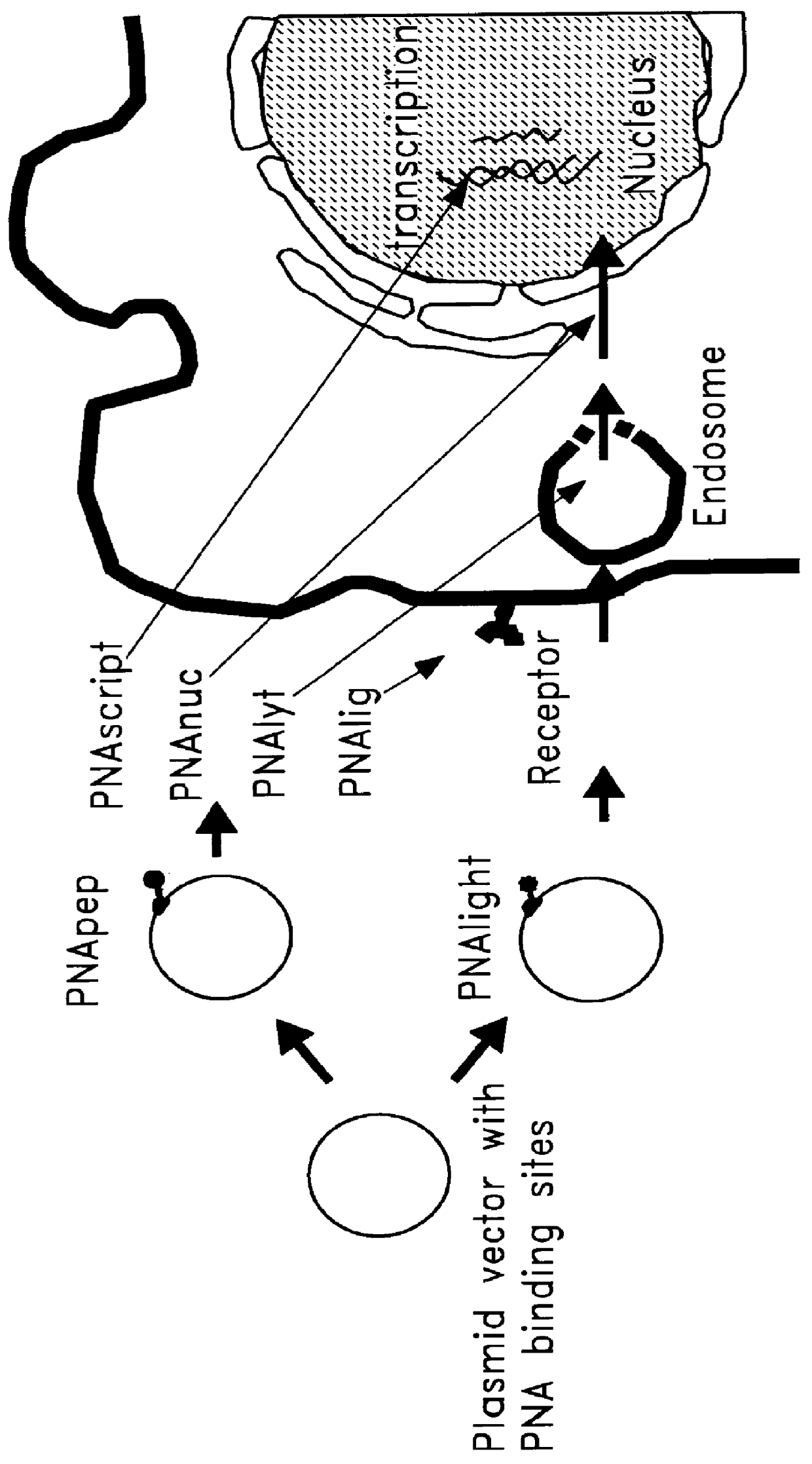
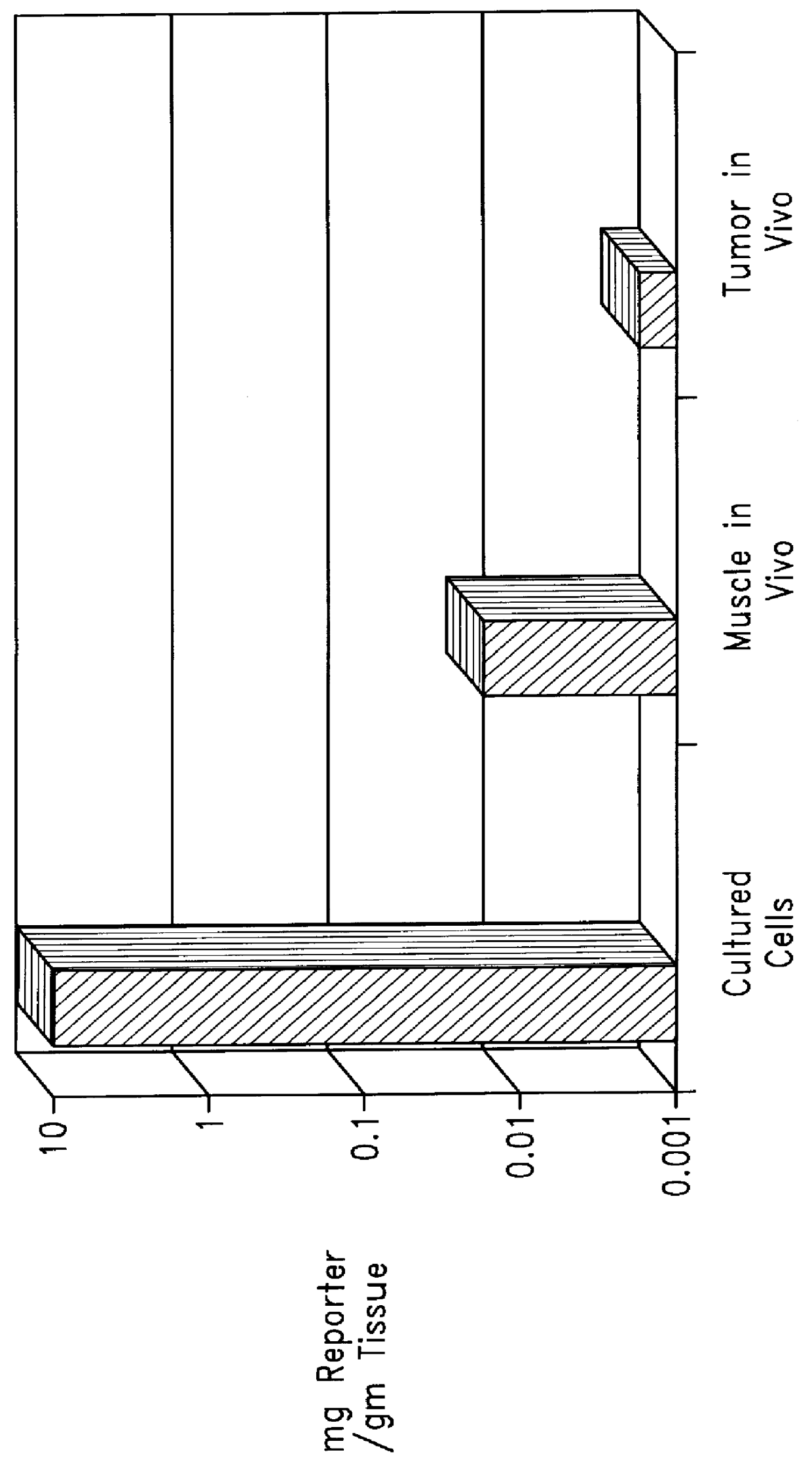
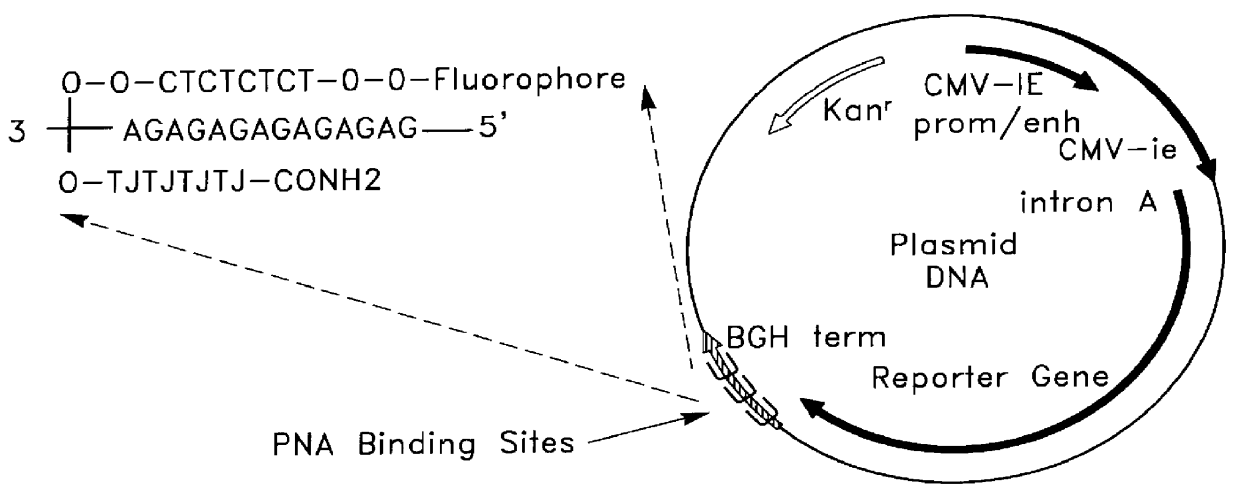
Complexes comprising a nucleic acid molecule and a conjugated peptide nucleic acid (PNA). The PNA may be labeled or conjugated to a protein, peptide, carbohydrate moiety or receptor ligand. These complexes are used to transfect cells to monitoring plasmid biodistribution, promote nuclear localization, induce transcriptional activation, lyse the endosomal compartment and facilitate transfection. These complexes increase the efficiency of expression of a particular gene.
Owner:GENE THERAPY SYST +1
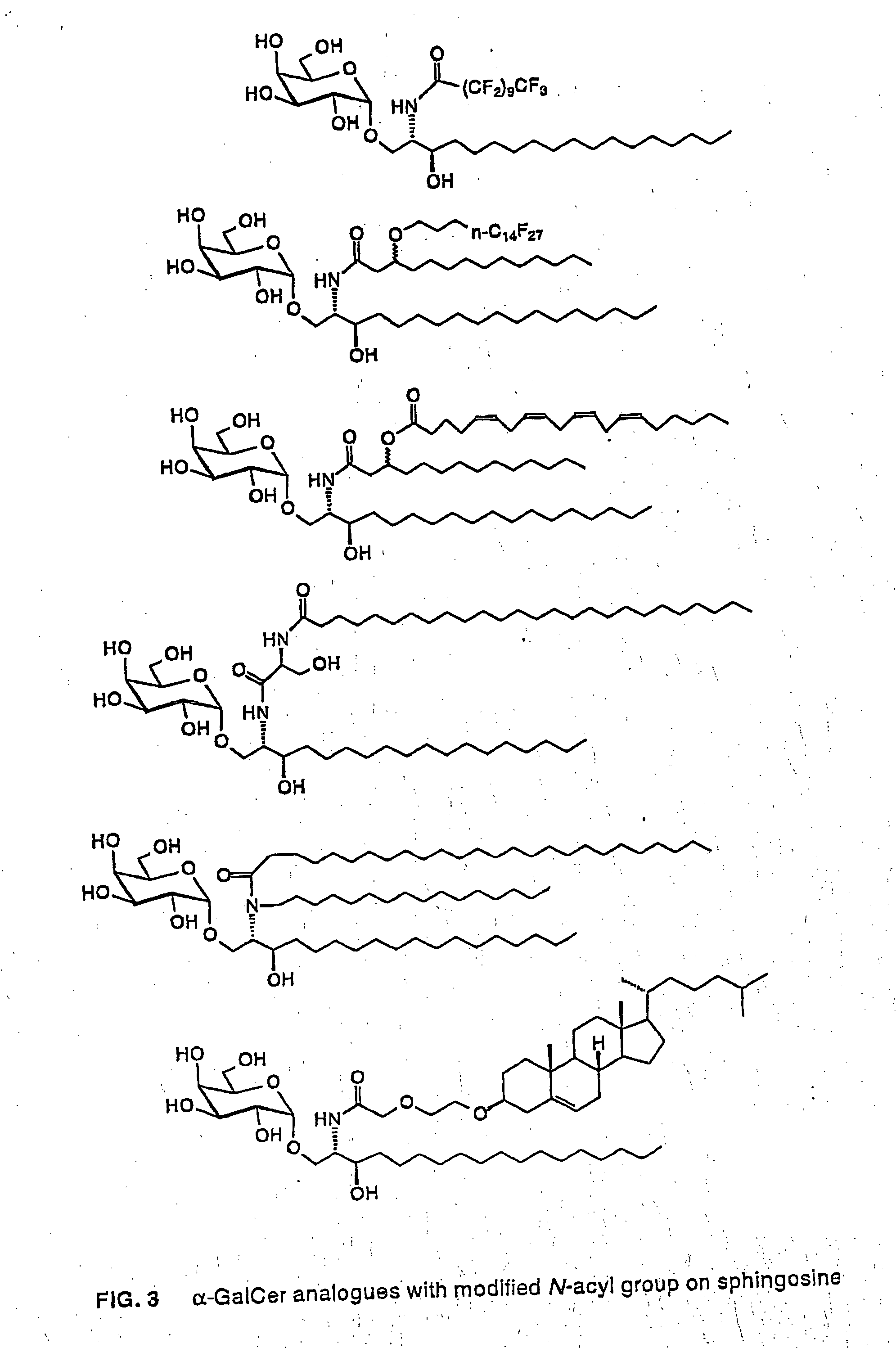
Glycosylceramide analogues
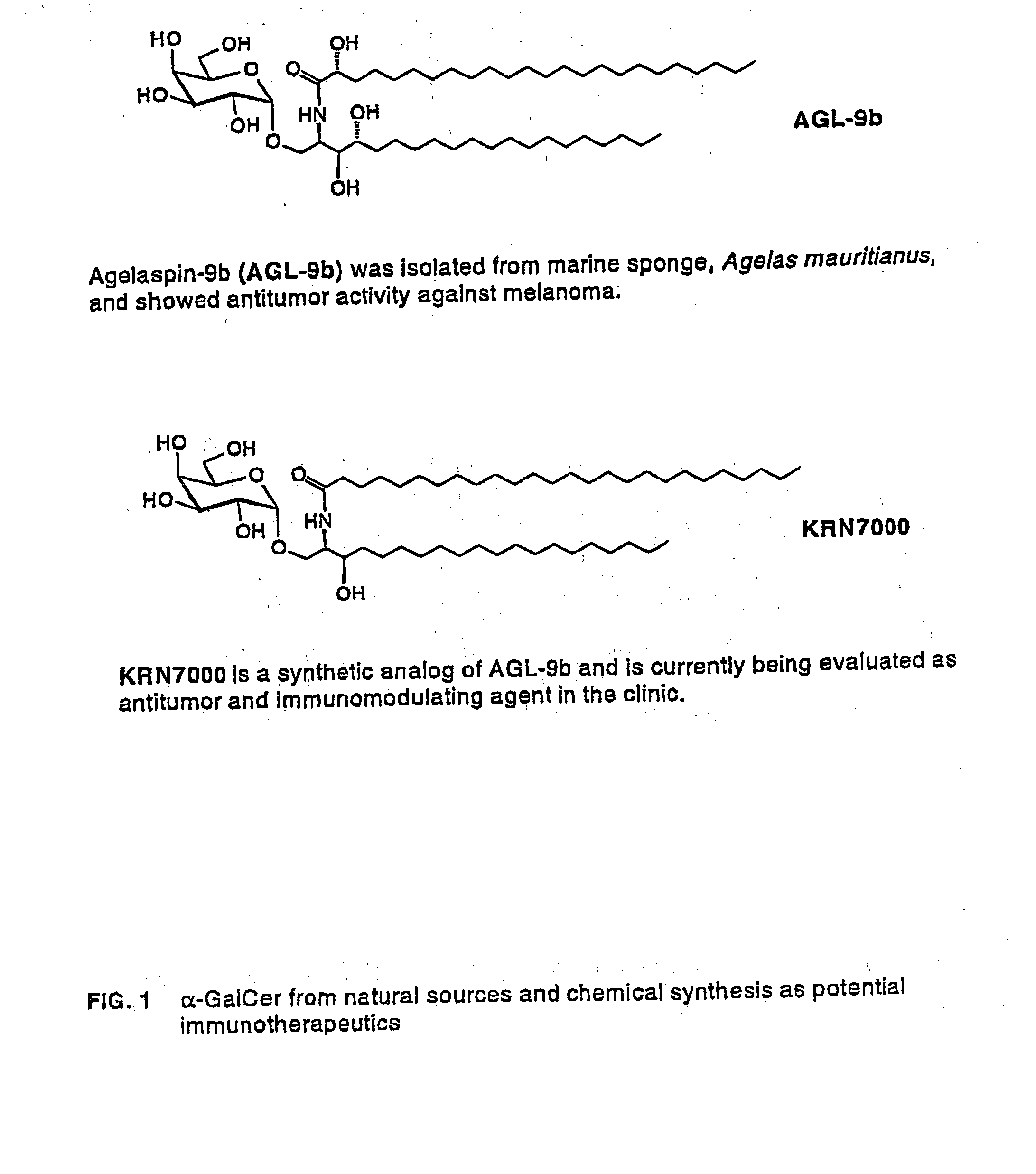
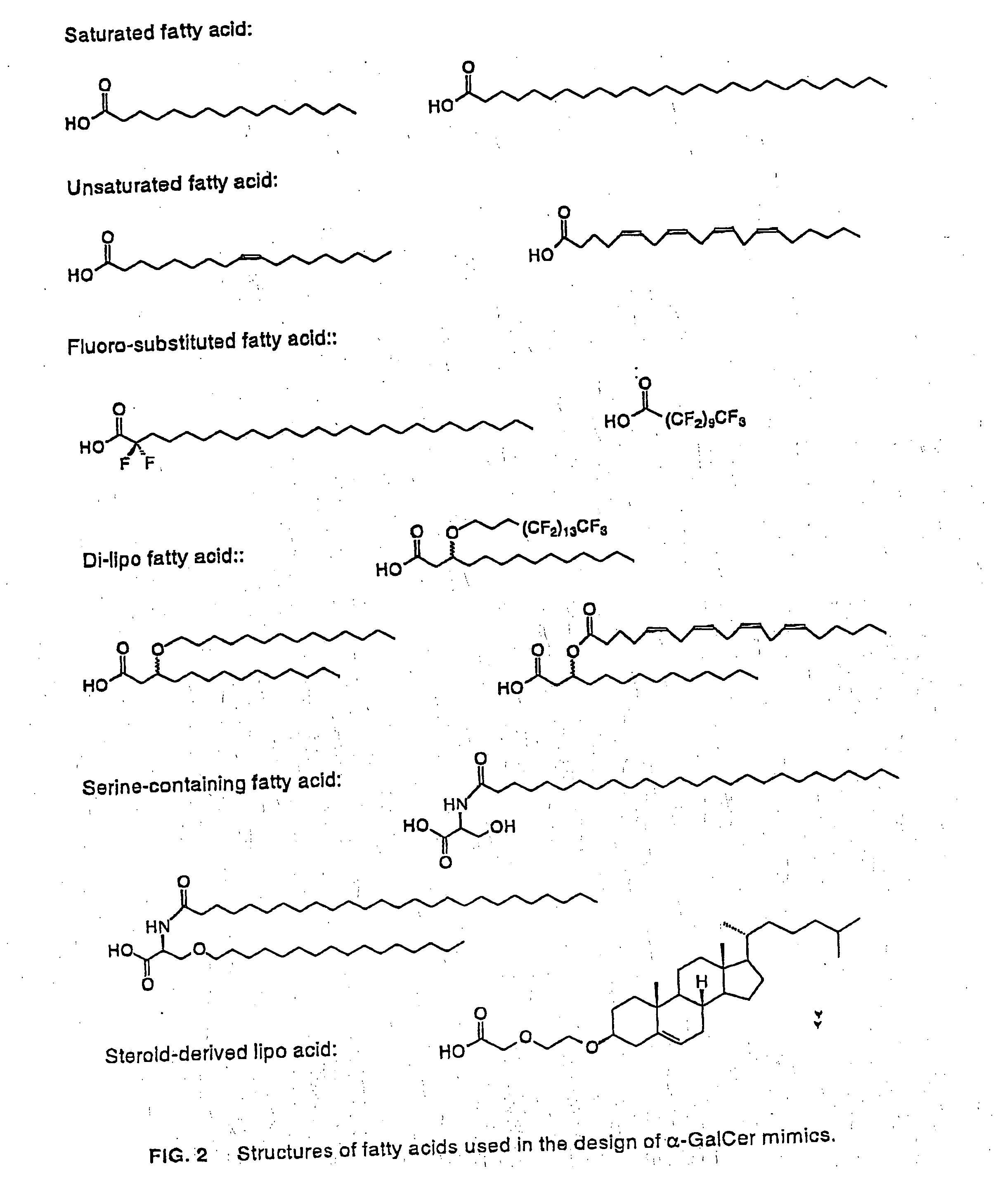
Glycosylceramide analogues are disclosed in which the ceramide moiety and optionally the carbohydrate moiety are modified or replaced. These analogues are useful as immunomodulators, antitumor agents, and as other pharmaceutical agents.
Owner:ONCOTHYREON +1
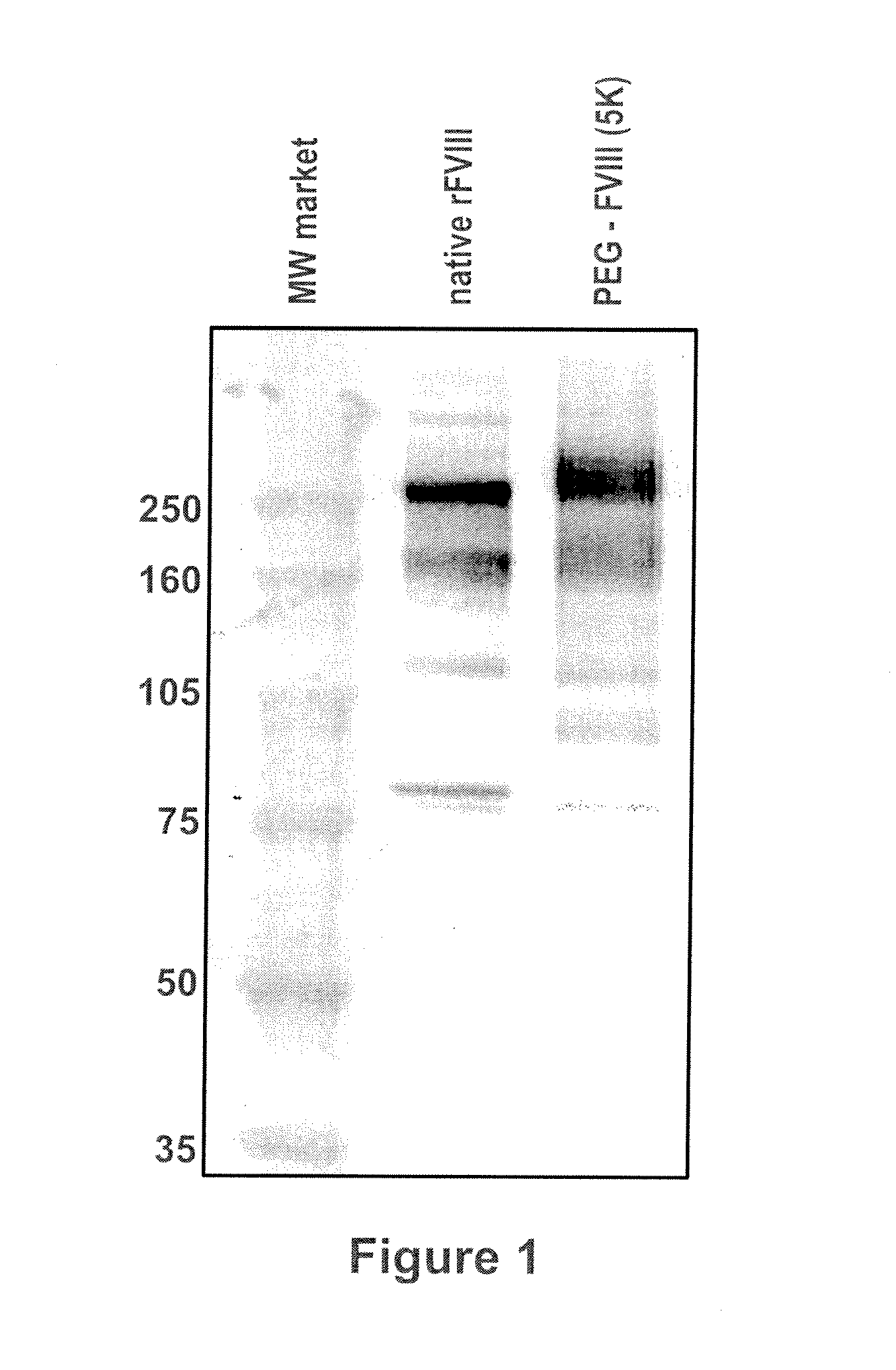
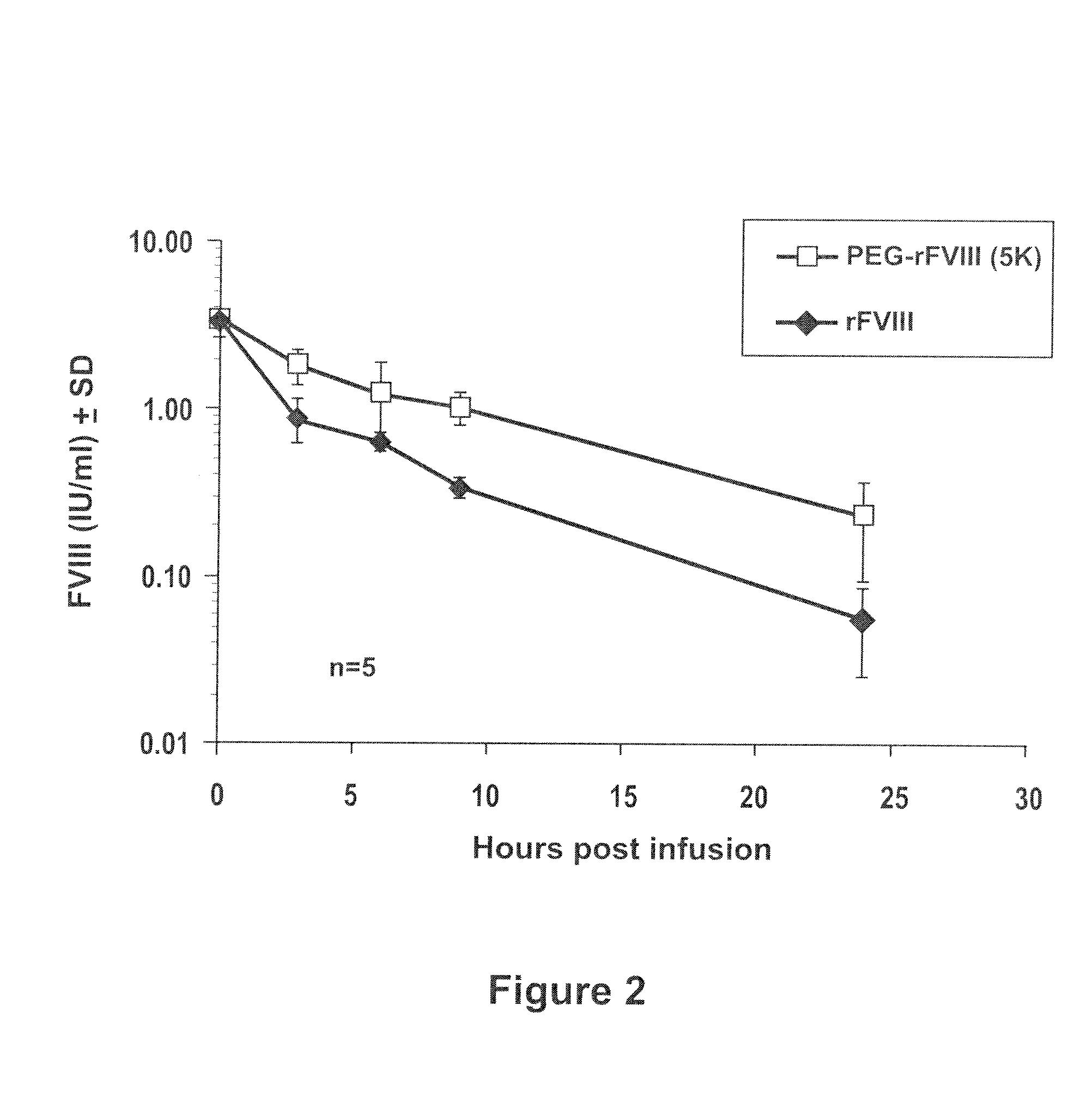
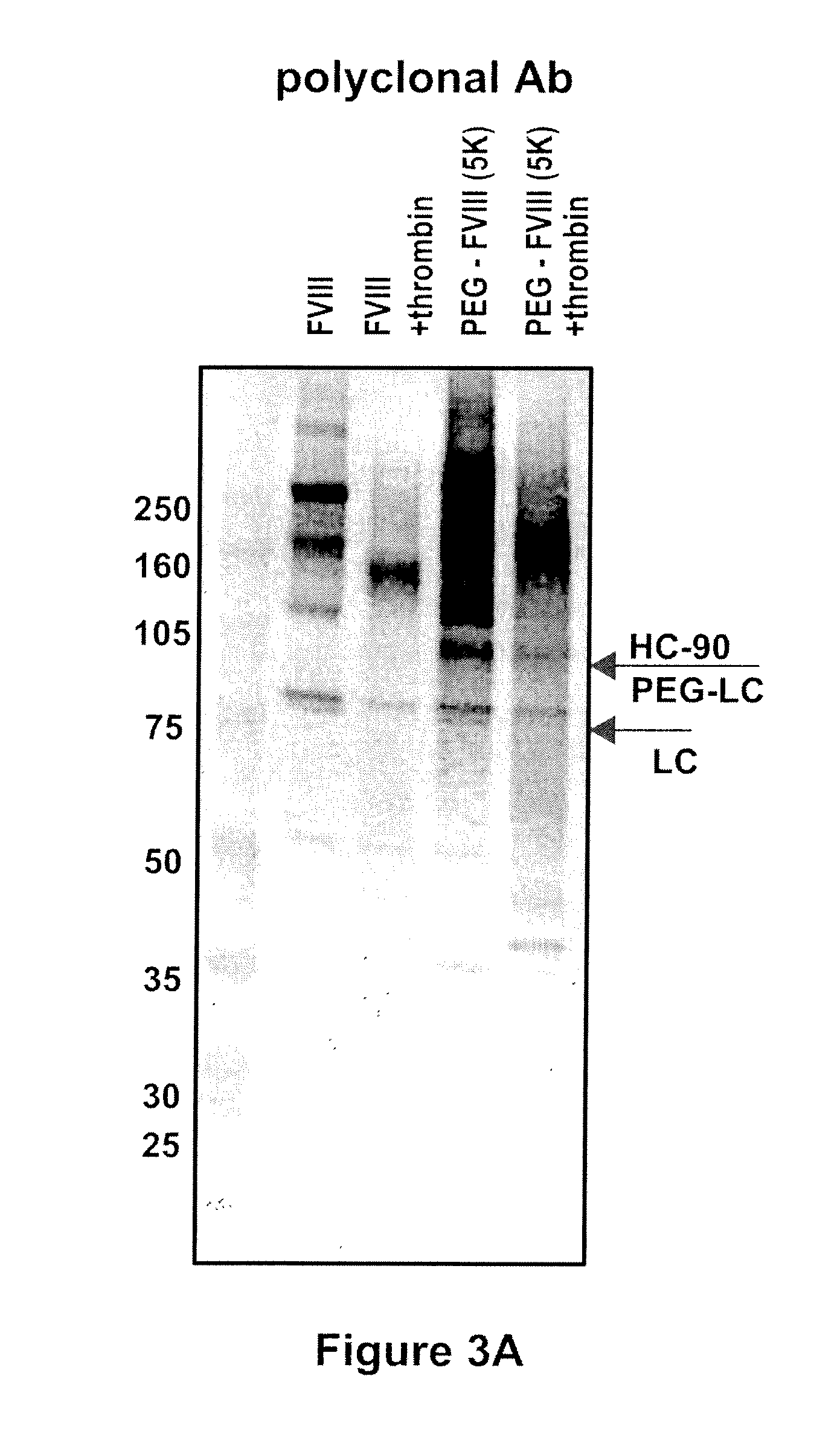
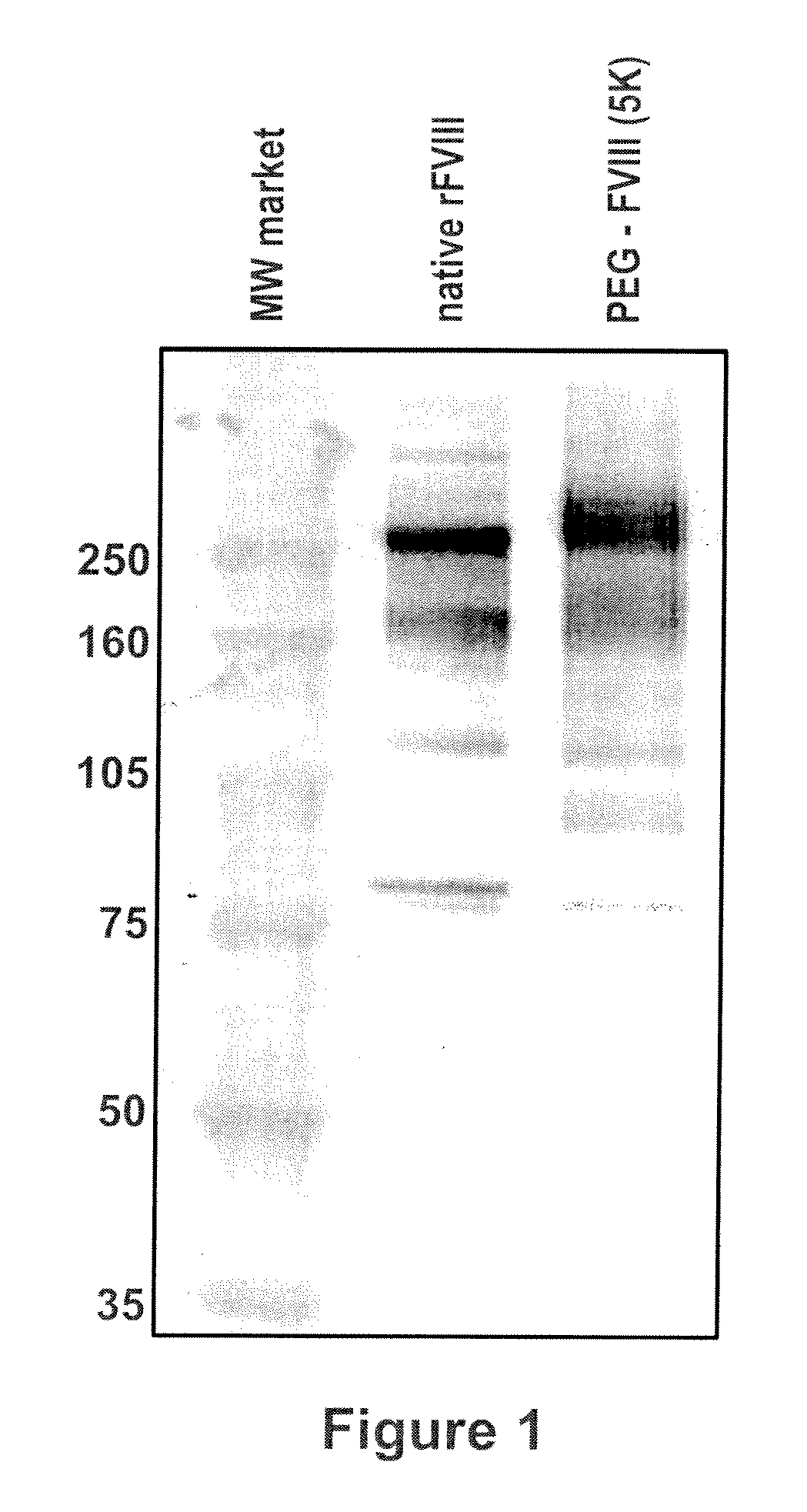
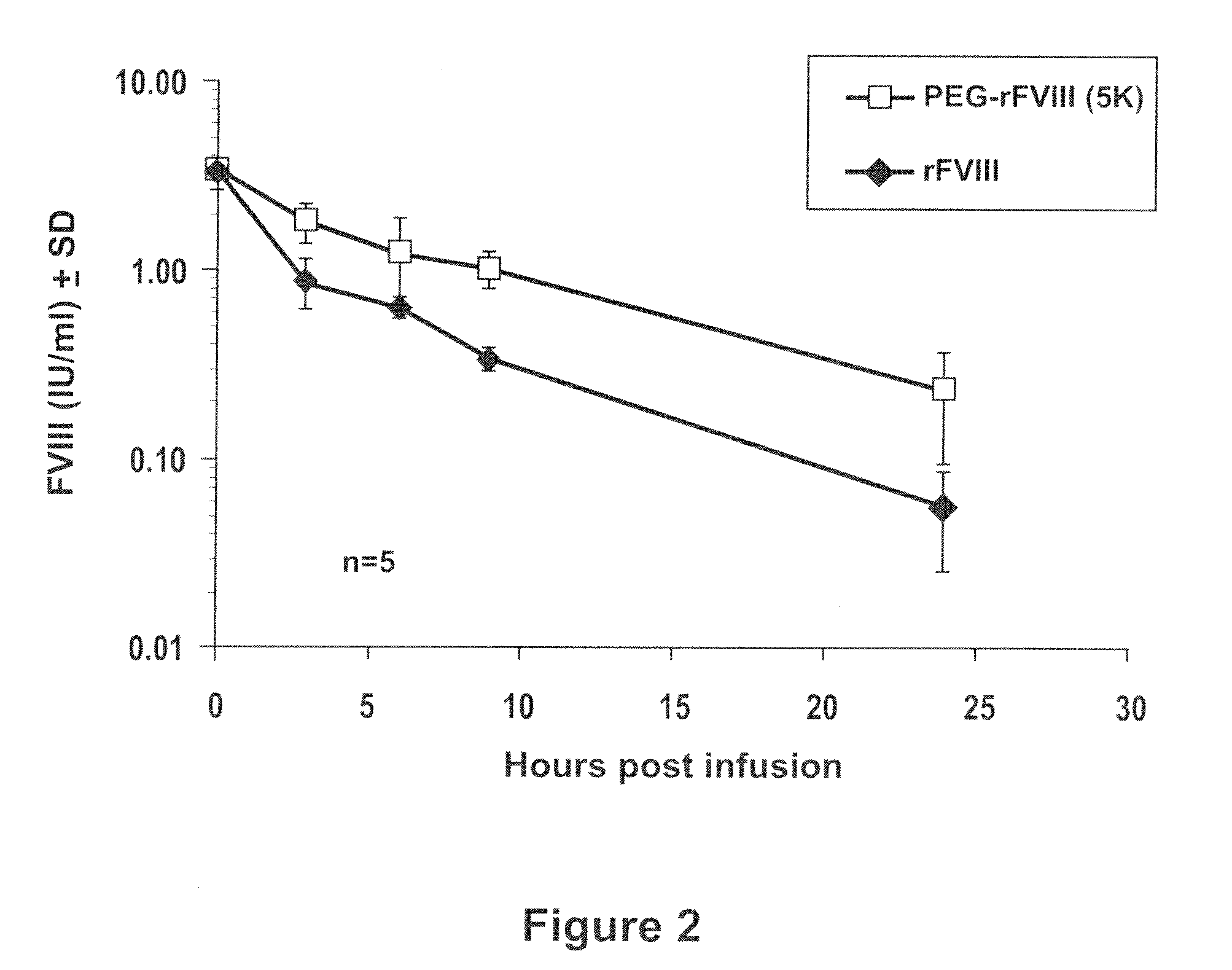
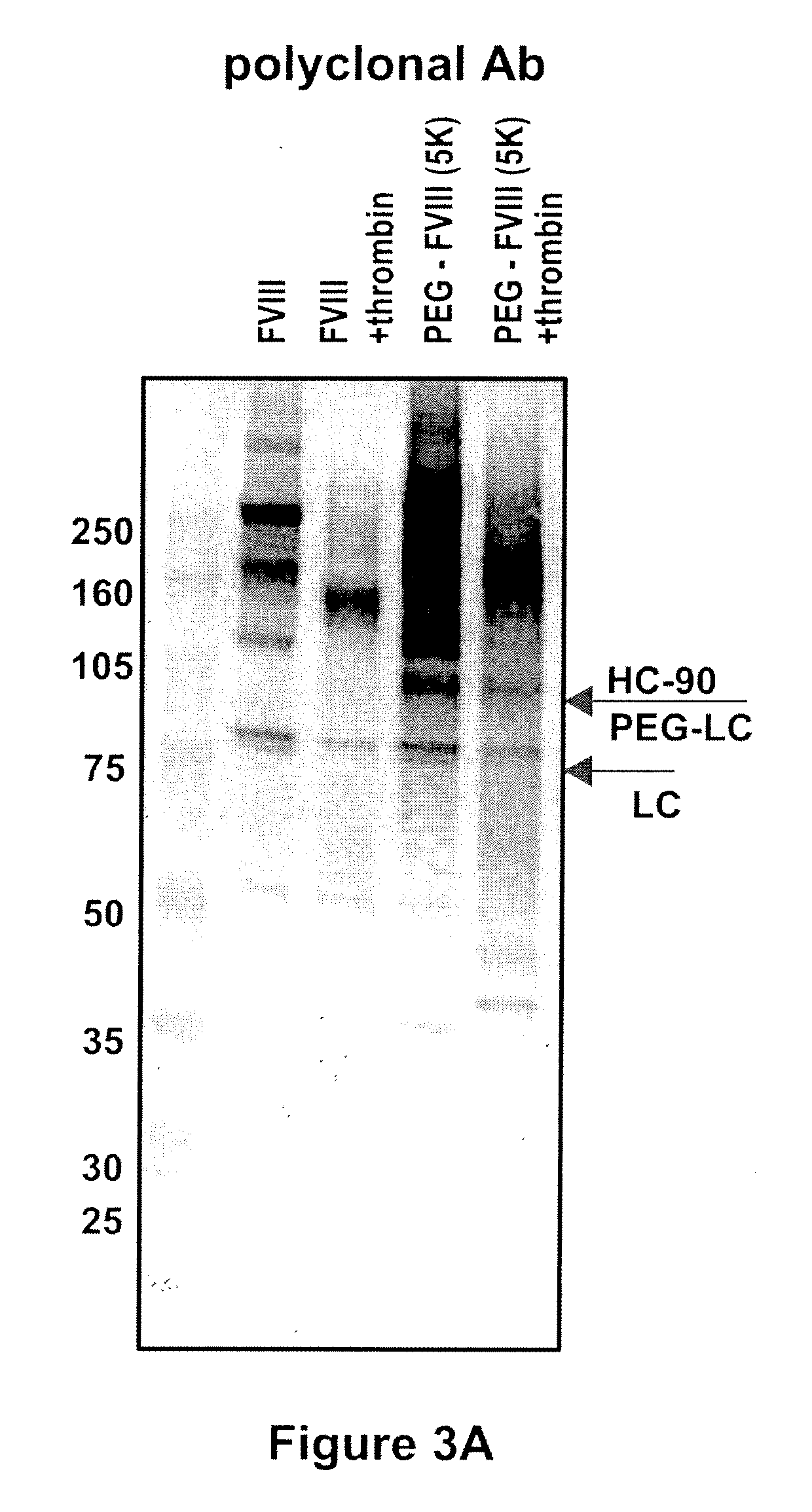
Factor VIII polymer conjugates
The invention is a proteinaceous construct comprising a Factor VIII molecule which is conjugated to a water-soluble polymer via carbohydrate moieties of Factor VIII, and methods of preparing same.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Long chain glycolipids useful to avoid perishing or microbial contamination of materials
InactiveUS20140178444A1Cost-effective processReduce the overall heightAntibacterial agentsBiocideMicroorganismCompound (substance)
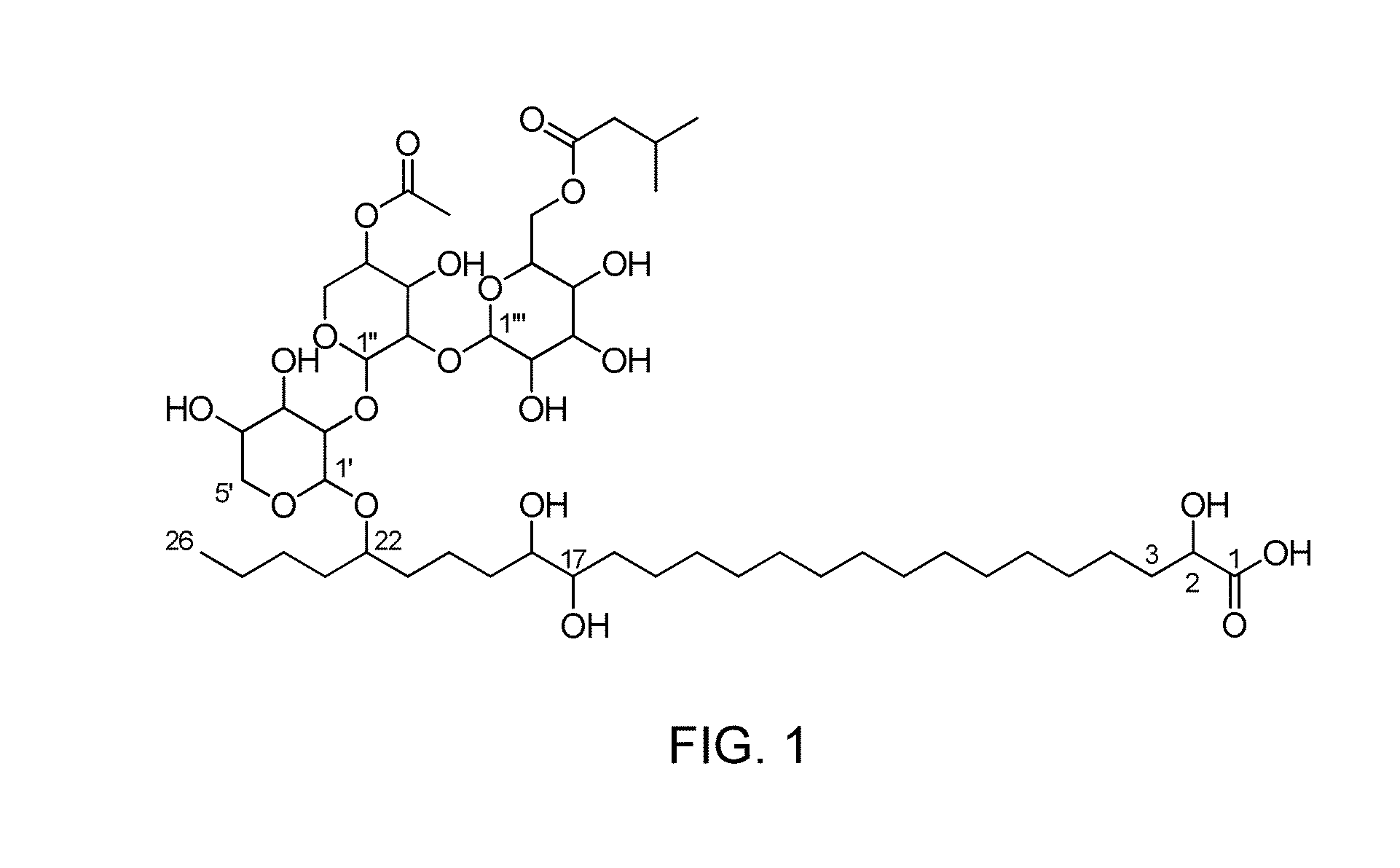
The invention relates to the use of, and methods of use employing, certain glycolipid compounds as defined in detail below and having preservative or antimicrobial properties, novel compounds of the glycolipid class, and related invention embodiments.The compounds have the formula Iwherein m is 3 to 5, n is 2 to 5, o is 0 or 1 and p is 3 to 17, with the proviso that the sum m+n+o+p is not less than 14; andR is a carbohydrate moiety bound via one of its carbon atoms to the binding oxygen,and / or a physiologically, especially pharmaceutically or nutraceutically or cosmetically, acceptable salt thereof, or an ester thereof,as such or in the form of a composition,where the compound may be present in open chain form and / or in the form of a lactone (FIG. 1).
Owner:IMD NATURAL SOLUTIONS GMBH
Method of Preparing More Digestible Animal Feed
InactiveUS20080220125A1Improve nutritional qualityImprove practicalityConfectioneryAnimal feeding stuffAdditive ingredientCarbohydrate moiety
Disclosed herein are methods of treating an edible fiber source to make an animal feed with increased digestible energy. An exemplary method includes hydrolyzing the edible fiber source with an inorganic fiber hydrolyzing agent in a twin screw mixer that shears the edible fiber to a size of between 0.5 to 25 mm. The hydrolysis in the mixer occurs at pressure of about 14 psig or higher with a temperature about 100° C. to 110° C. The inorganic hydrolysis liberates a first portion of soluble carbohydrates from the edible fiber source. The inorganically hydrolyzed material is also treated (before or after) with a fiber degrading enzyme to solubilize a second portion of carbohydrates. The dually hydrolyzed material is dried to form an animal feed or feed ingredient having a soluble and insoluble carbohydrate fraction with the amount of soluble carbohydrate being at least 45% wt / wt of the total carbohydrates obtained from the edible fiber source.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
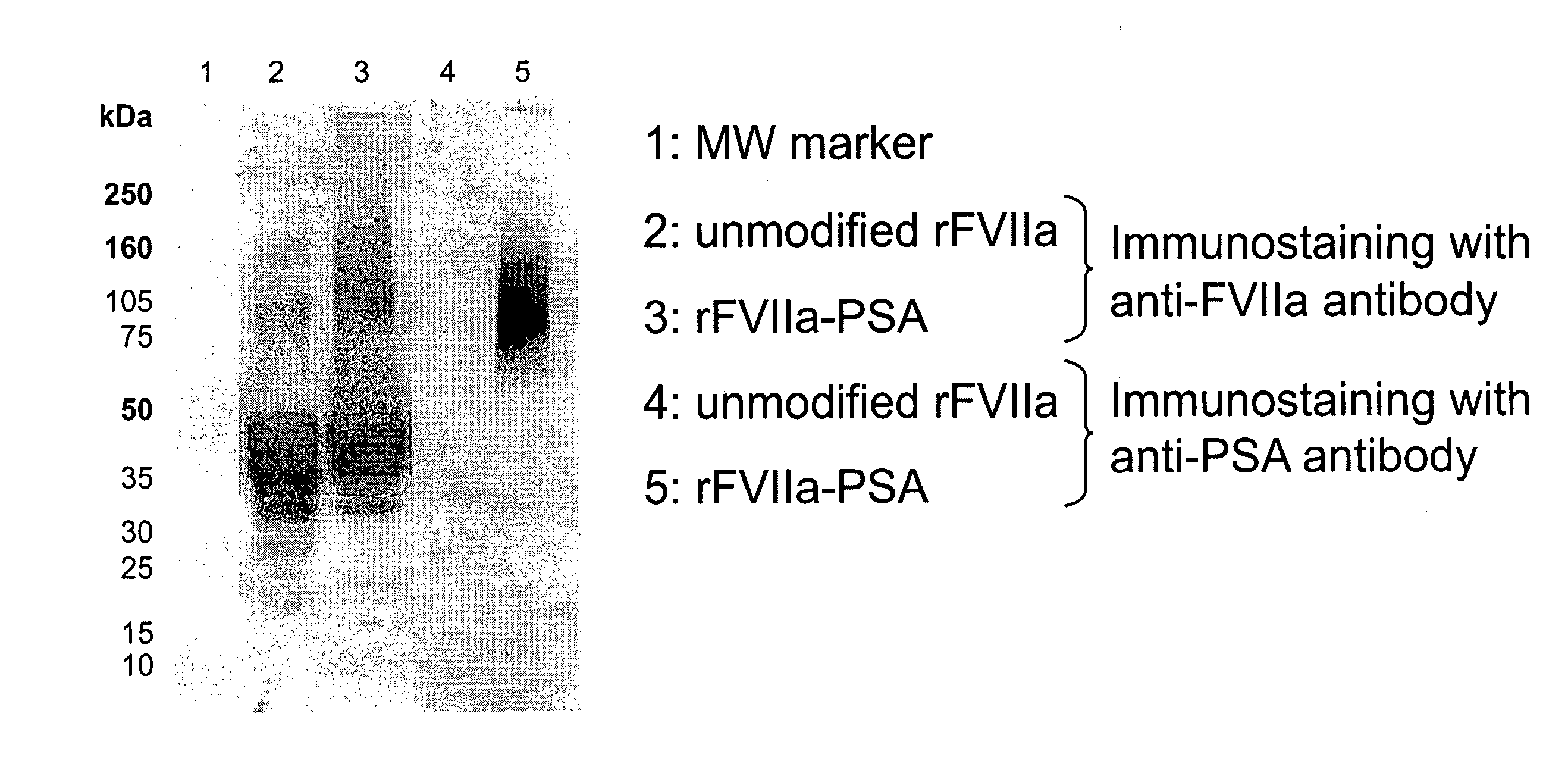
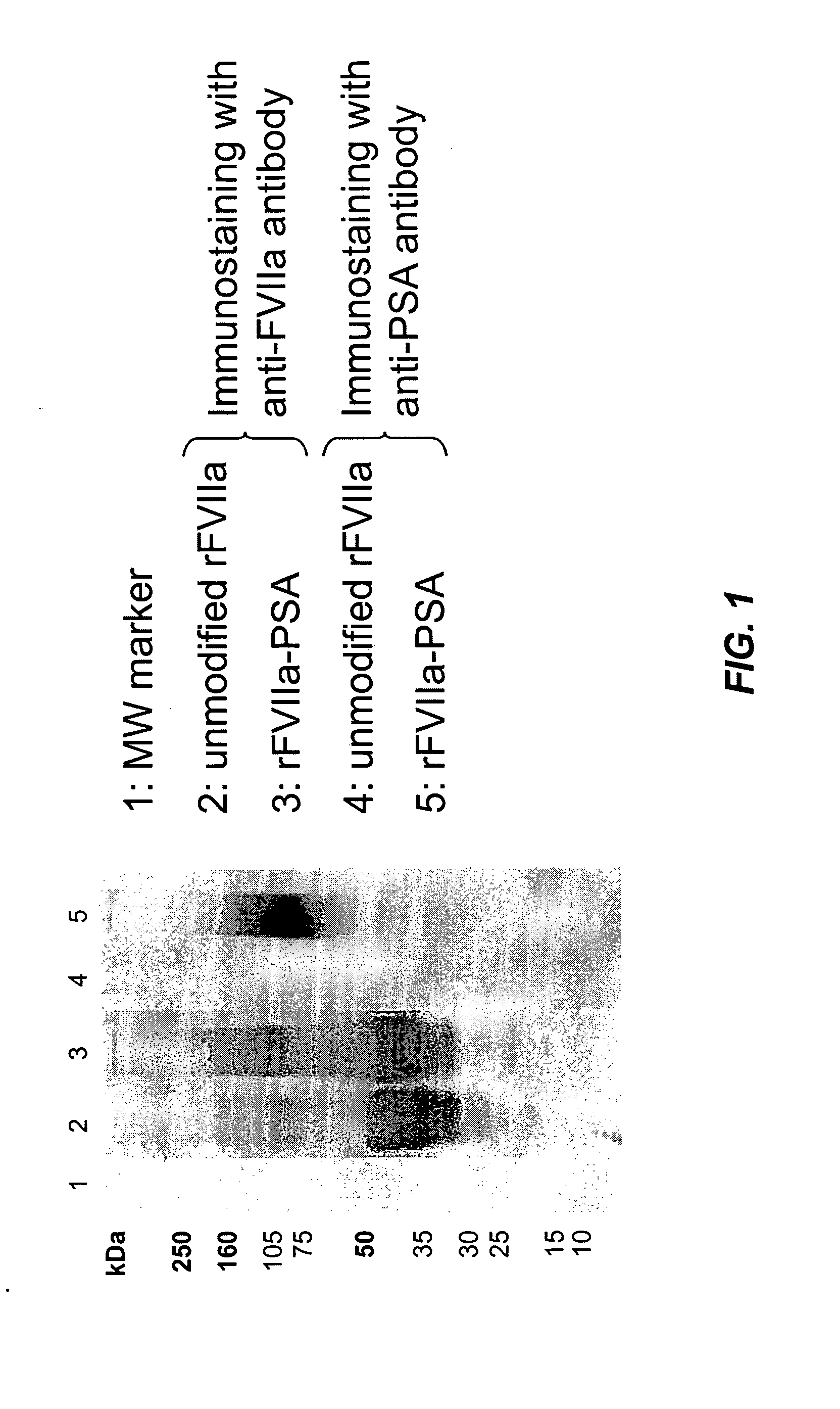
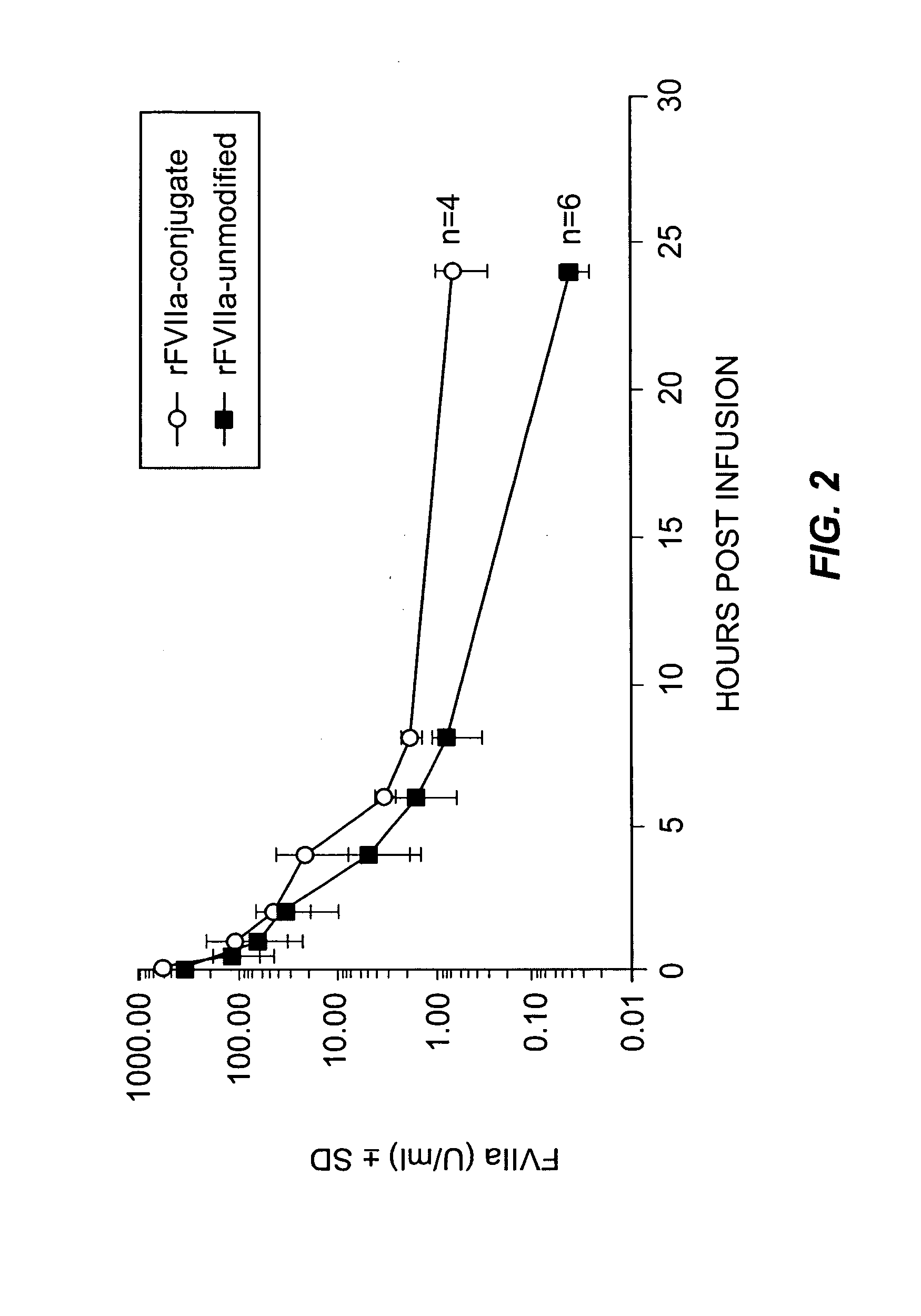
Factor VIIa-Polysialic Acid Conjugate Having Prolonged In Vivo Half-Life
ActiveUS20080221032A1Control bleedingProlong half-life in vivoPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsFactor VIIaHalf-life
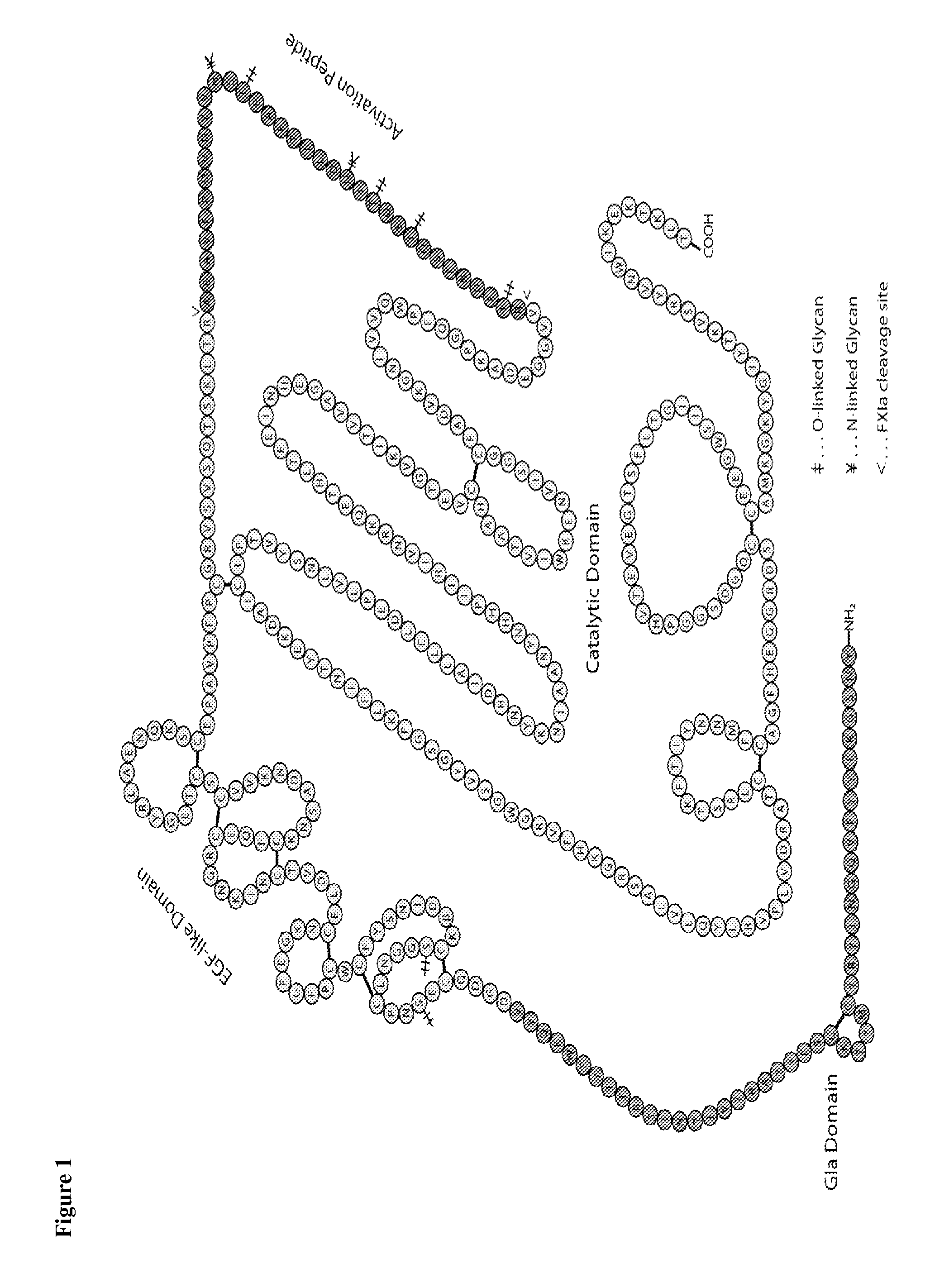
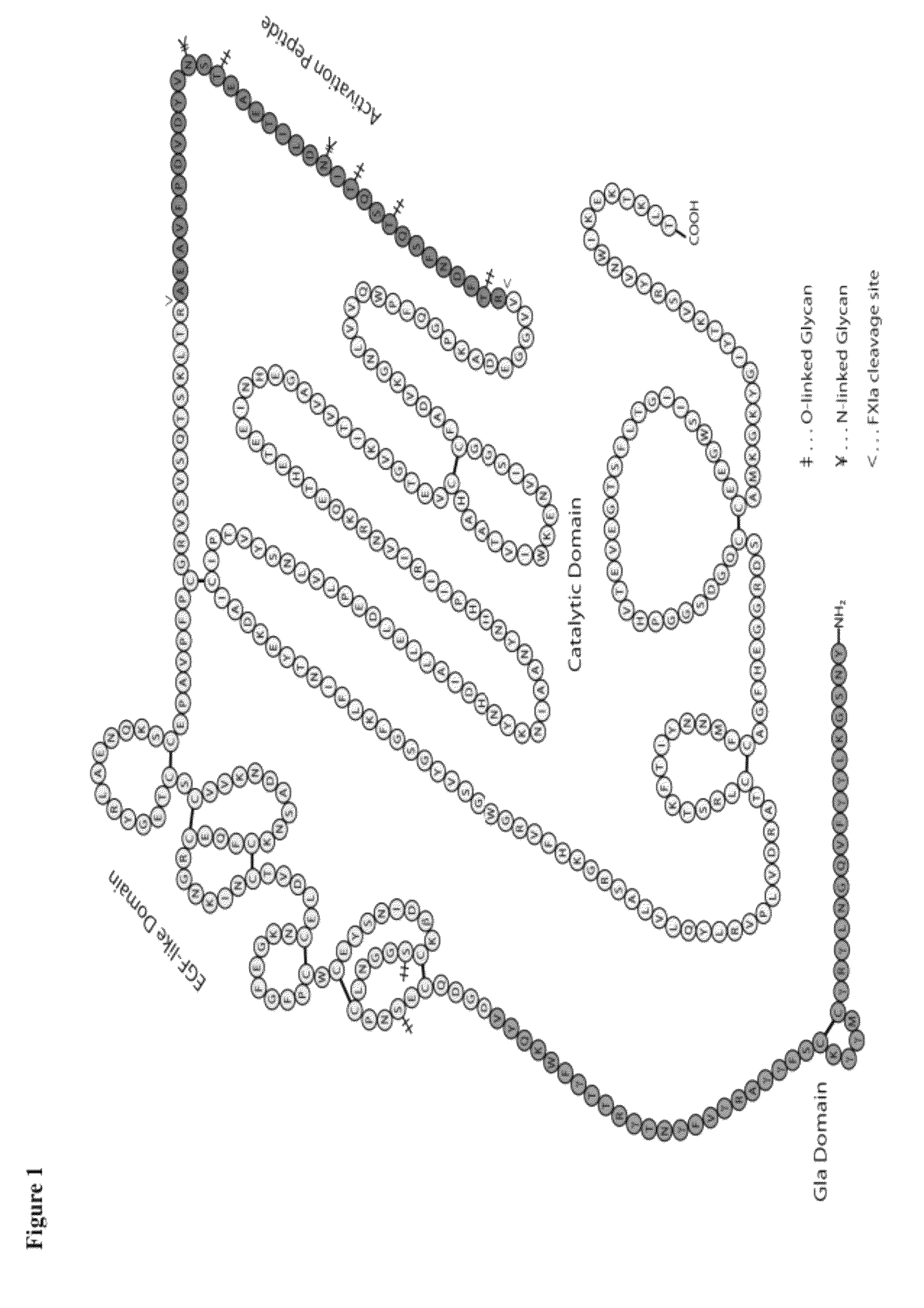
The present invention relates to a proteinaceous construct comprising plasmatic or recombinant factor VIIa (FVIIa) or biologically active derivatives thereof, which are bound to a carbohydrate moiety comprising 1-4 sialic acid units, wherein the in vivo half-life of the proteinaceous construct is substantially prolonged in the blood of a mammal, as compared to the in vivo half-life of a FVIIa molecule not bound to a carbohydrate moiety. The invention also provides a method for controlling bleeding in a mammal having a bleeding disorder due to functional defects or deficiencies of FVIIa, FVIII, or FIX. The invention also provides a method for controlling bleeding in a mammal during surgery or trauma.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Synthetic hyperglycosylated, and hyperglycosylated protease-resistant polypeptide variants, oral formulations and methods of using the same
ActiveUS20060204473A1Increased protease resistanceNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsHybrid typeInterferon receptor
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites, as well as erythropoietin and darbepoetin alfa, each of which are linked to a penetrating peptide that facilitates translocation of a substance across a biological barrier as well as pharmaceutical compositions, including oral formulations, of the same. The present invention further provides oral formulations of hyperglycosylated or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:ALIOS BIOPHARMA INC +1
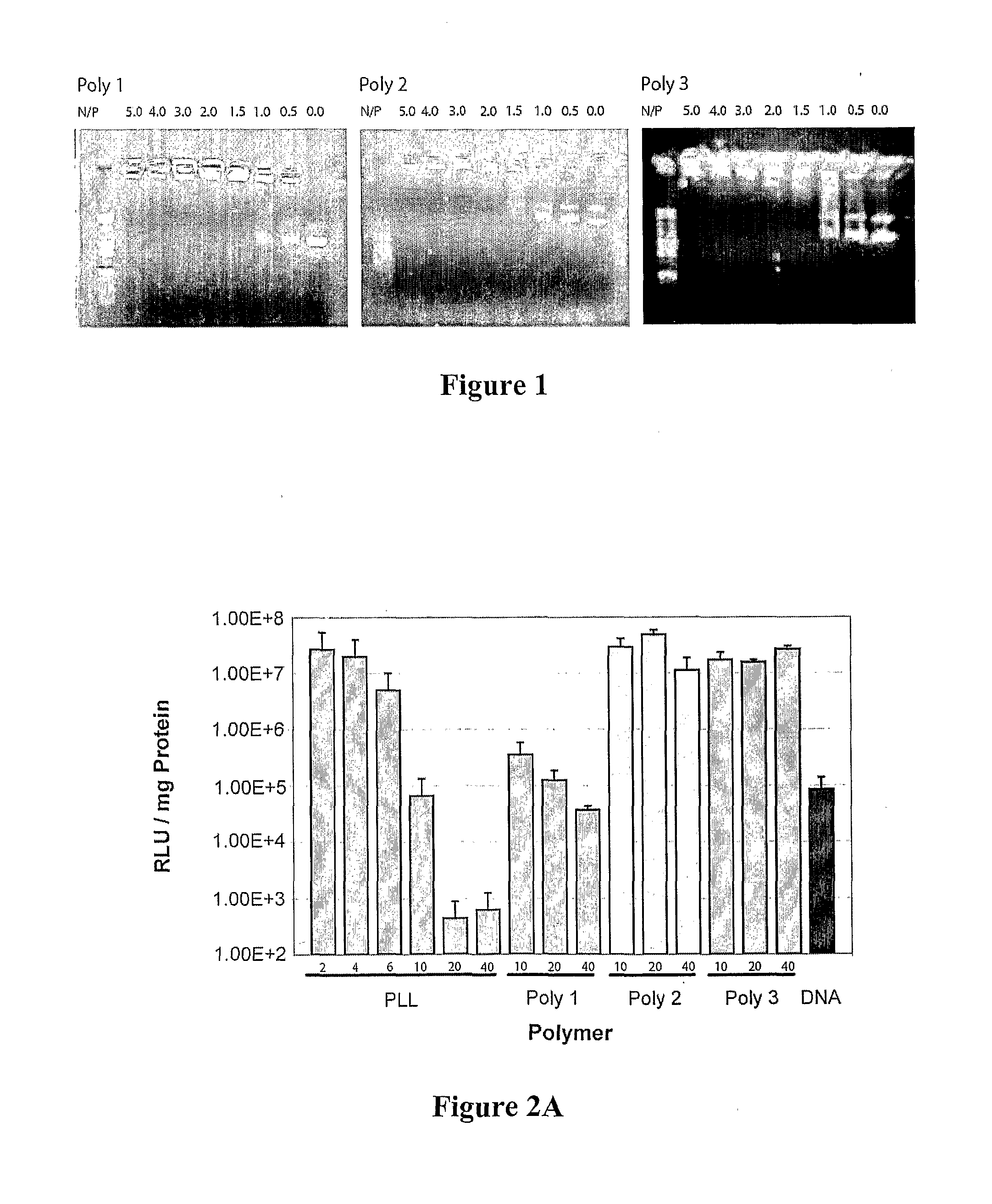
Polymeric Materials and Methods
Chimeric polymer compositions and methods are provided in which a plurality of carbohydrate moieties and amino acids form the backbone of a polymer. Most preferably, the polymer includes alternating saccharide and peptide portions to form the chimeric polymer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
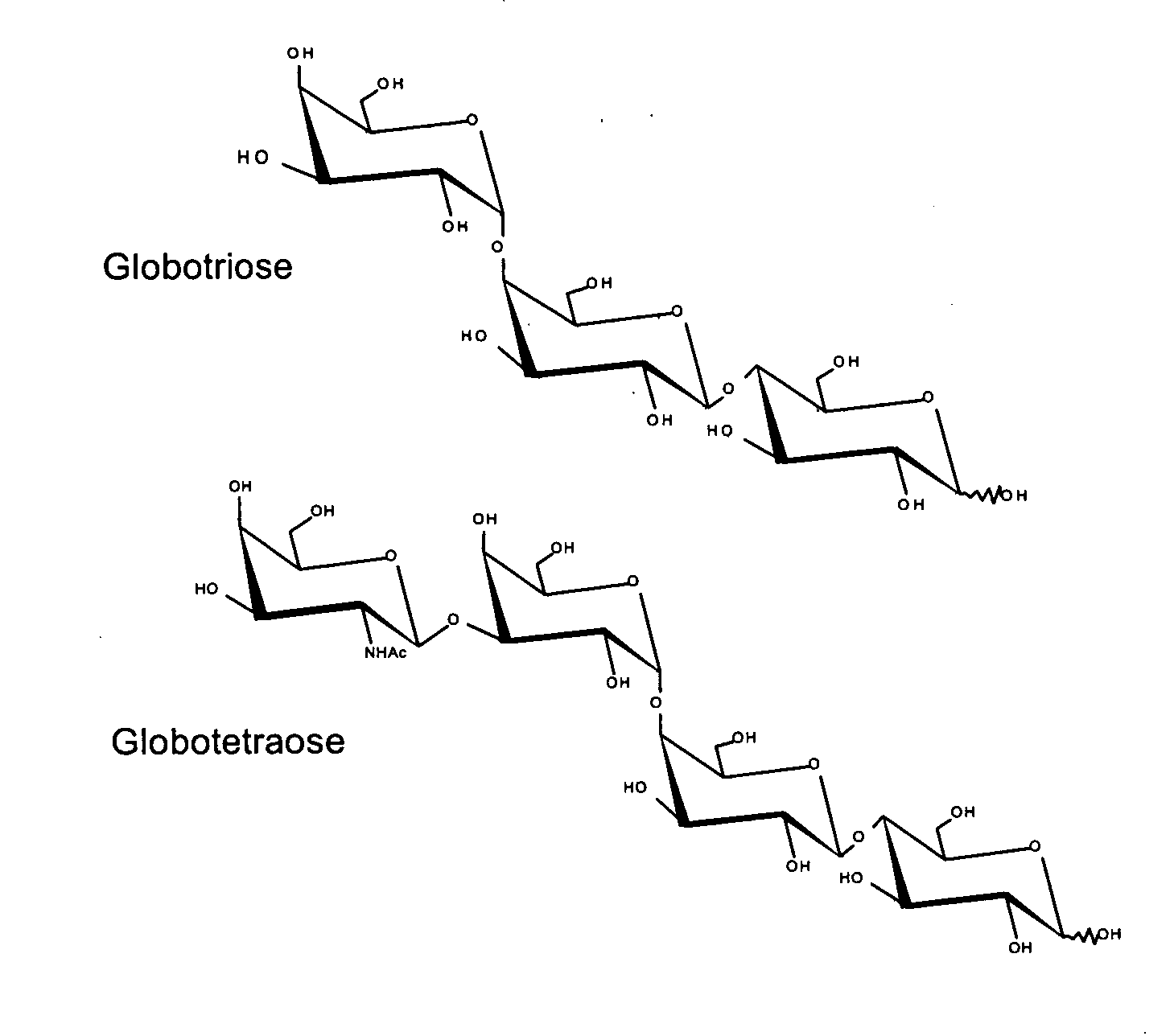
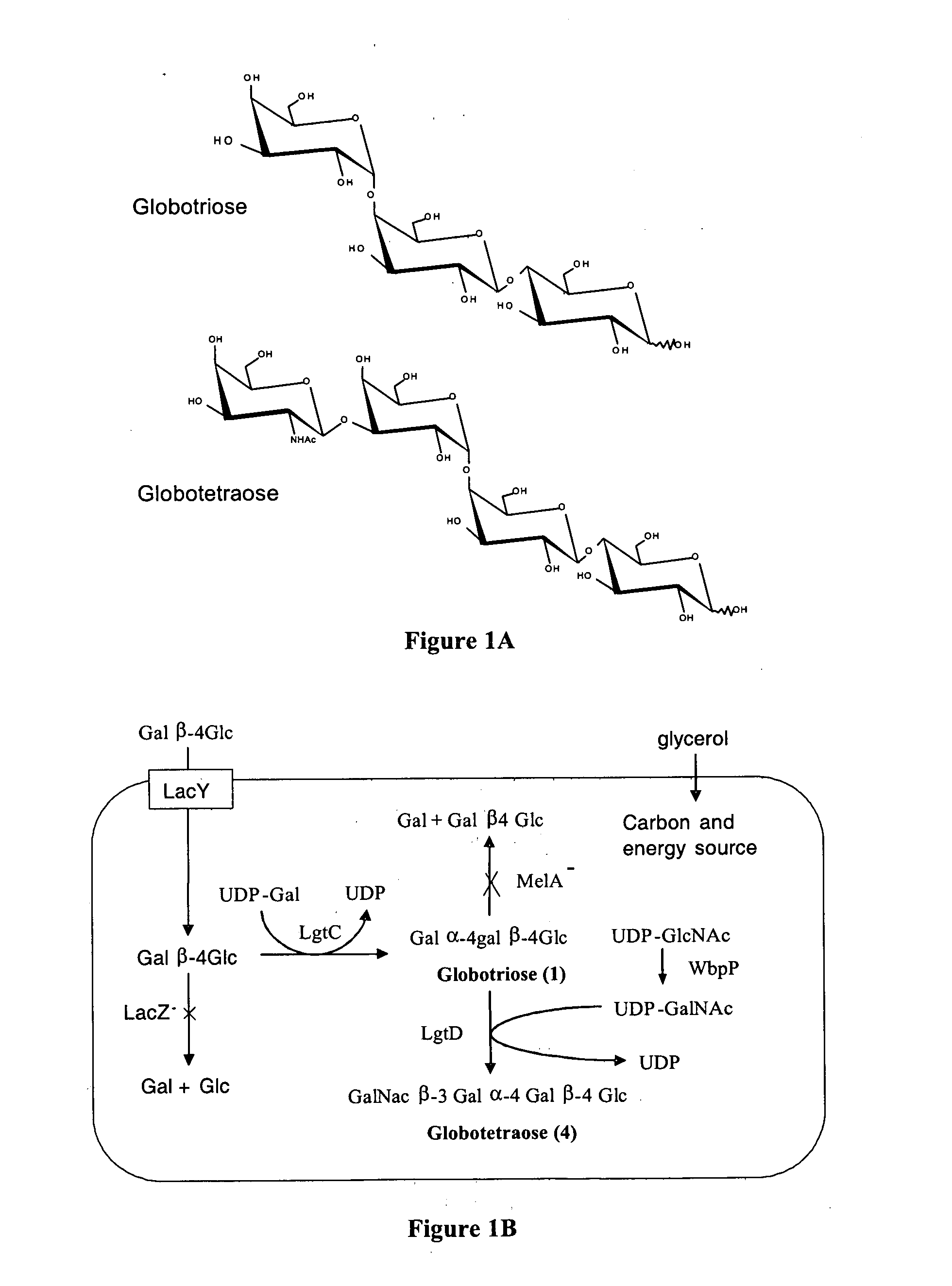
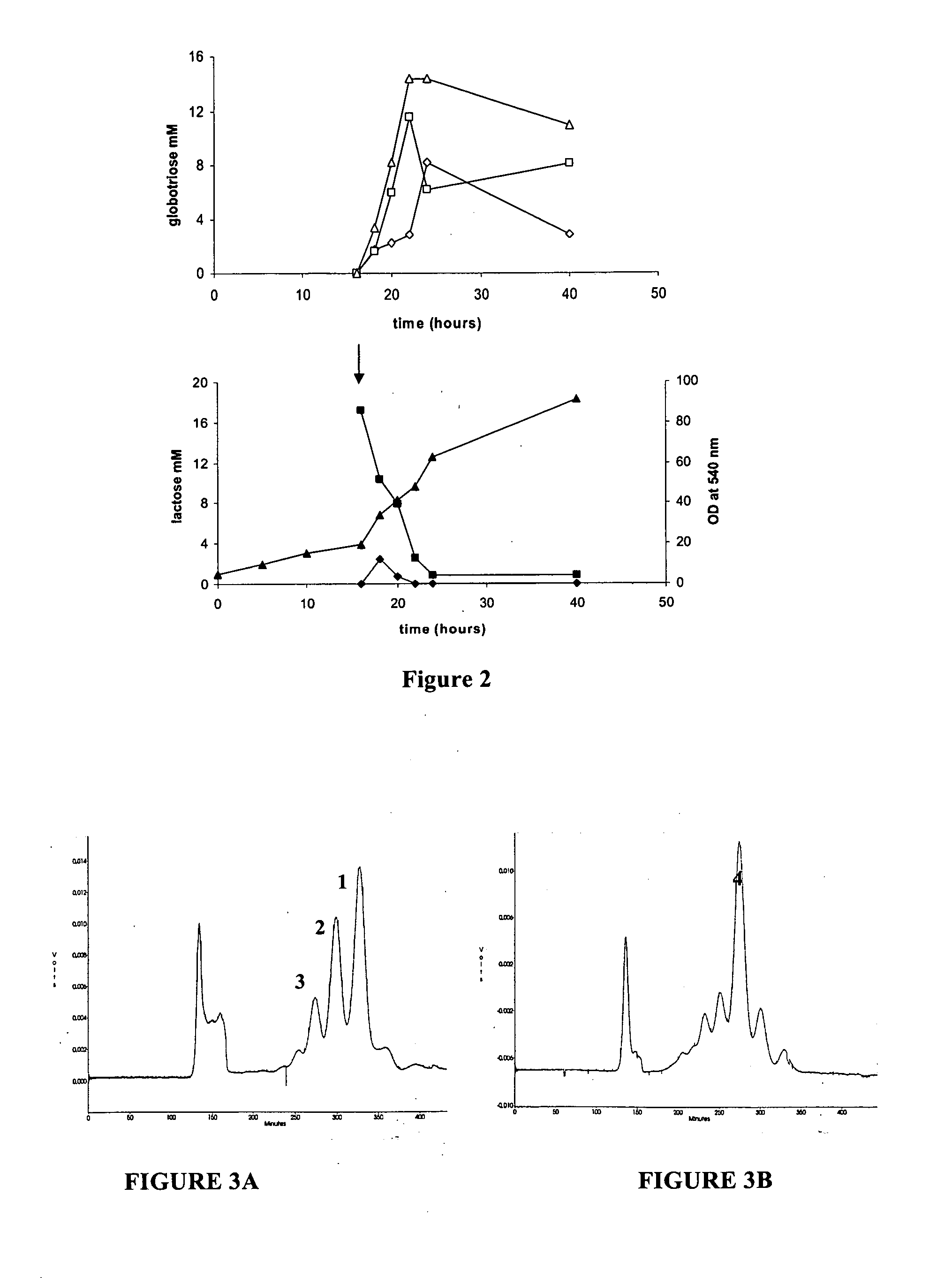
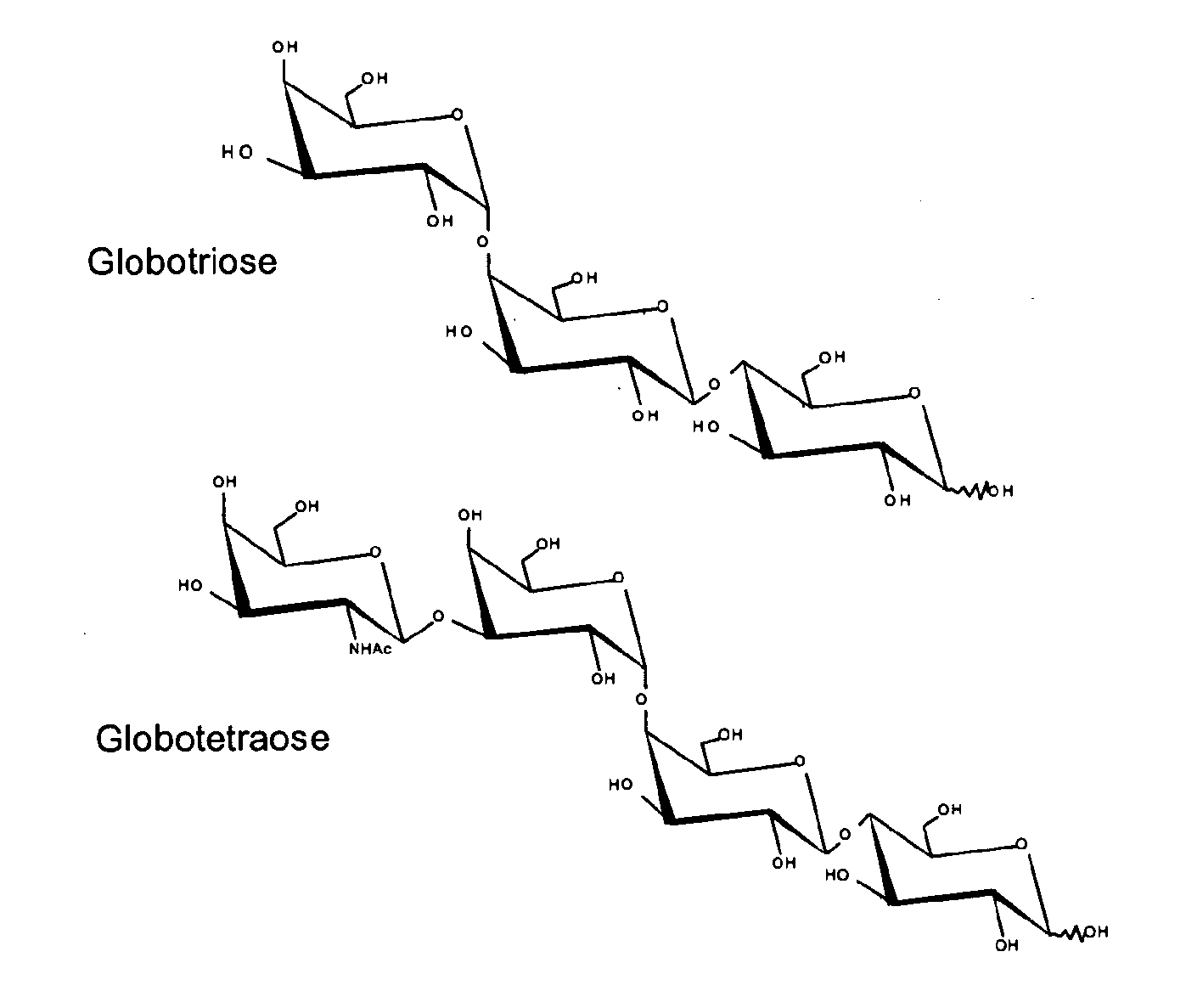
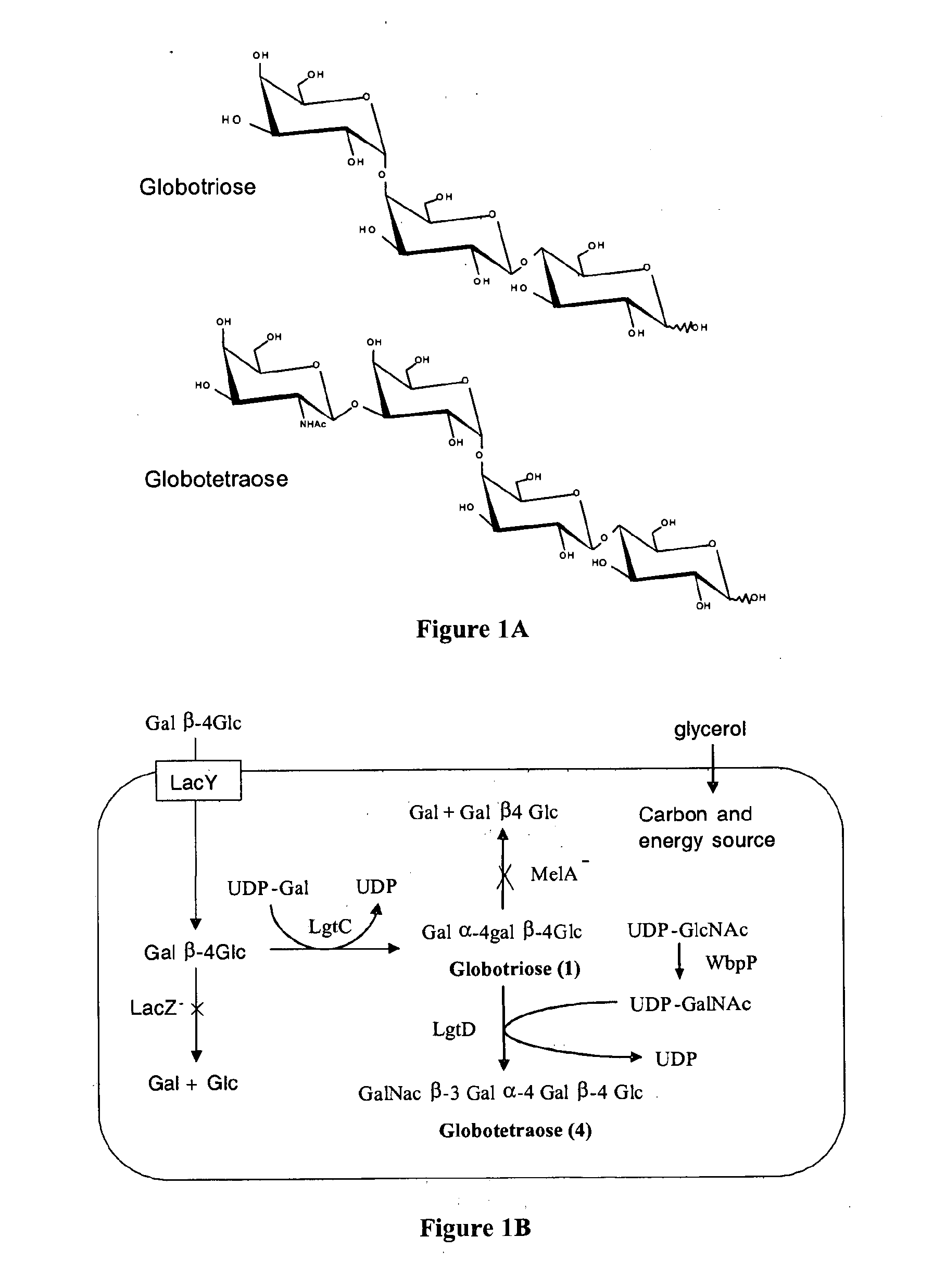
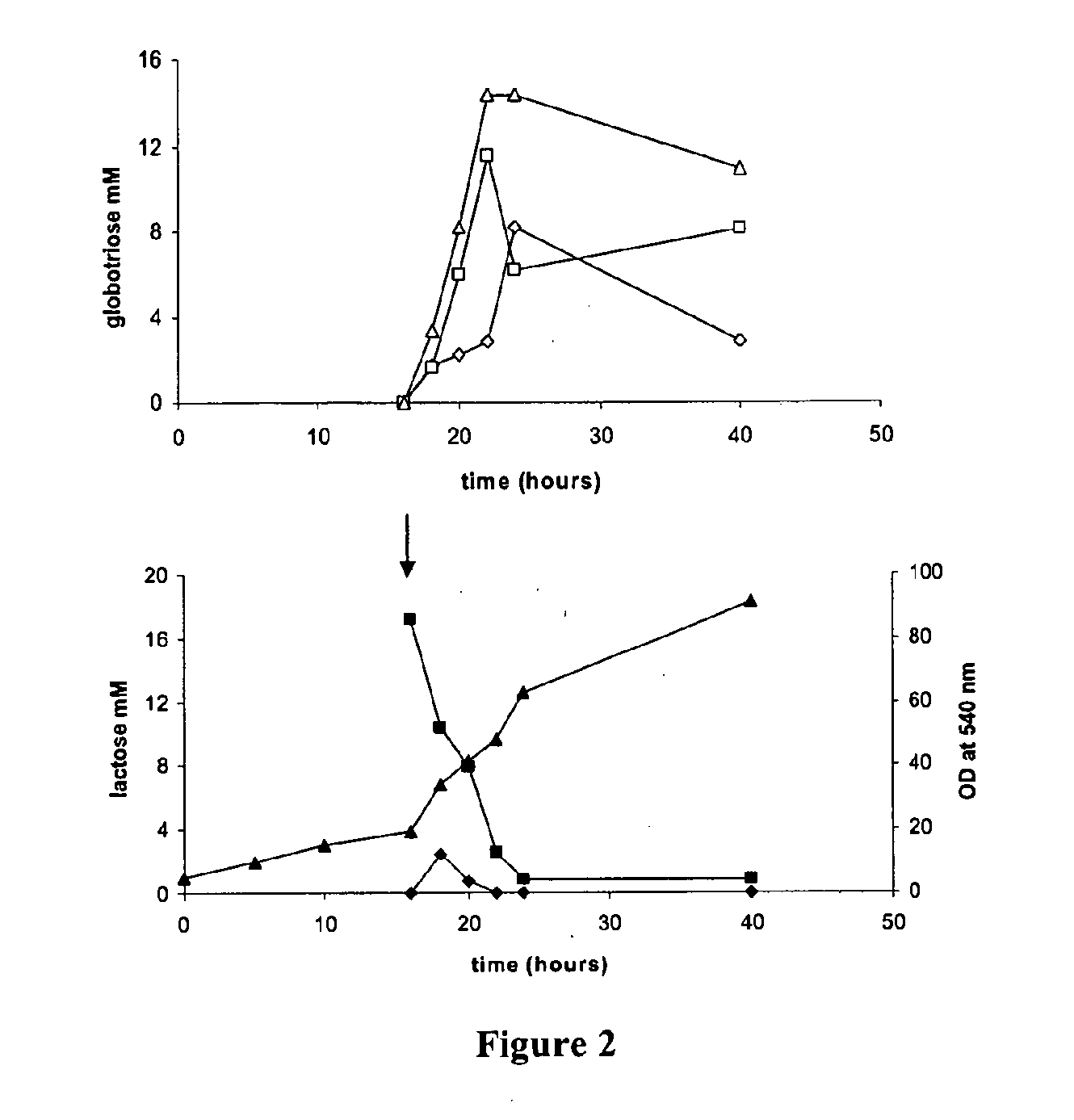
Production of globosides oligosaccharides using metabolically engineered microorganisms
The present invention relates to the large scale in vivo synthesis of globosides oligosaccharides; especially globotriose, globotetraose and globopentaose, which are the carbohydrate portions of globotriosylceramide (Gb3Cer), globotetraosylceramide (Gb4Cer) and globopentaosylceramide (Gb5Cer) respectively. It also relates to high yield production of potential anticancer vaccines of the globo-series glycosphingolipids, including the Globo-H. It also relates to the use of the glycosyltransferase encoded by the lgtD gene from Haemophilus influenzae as a beta1,3 galactosyl transferase to catalyze the transfer of a galactose moiety from UDP-Gal to an acceptor bearing the terminal non reducing structure GalNAcbeta-3-R to form the Galbeta-3GalNAcbeta-3-R structure
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
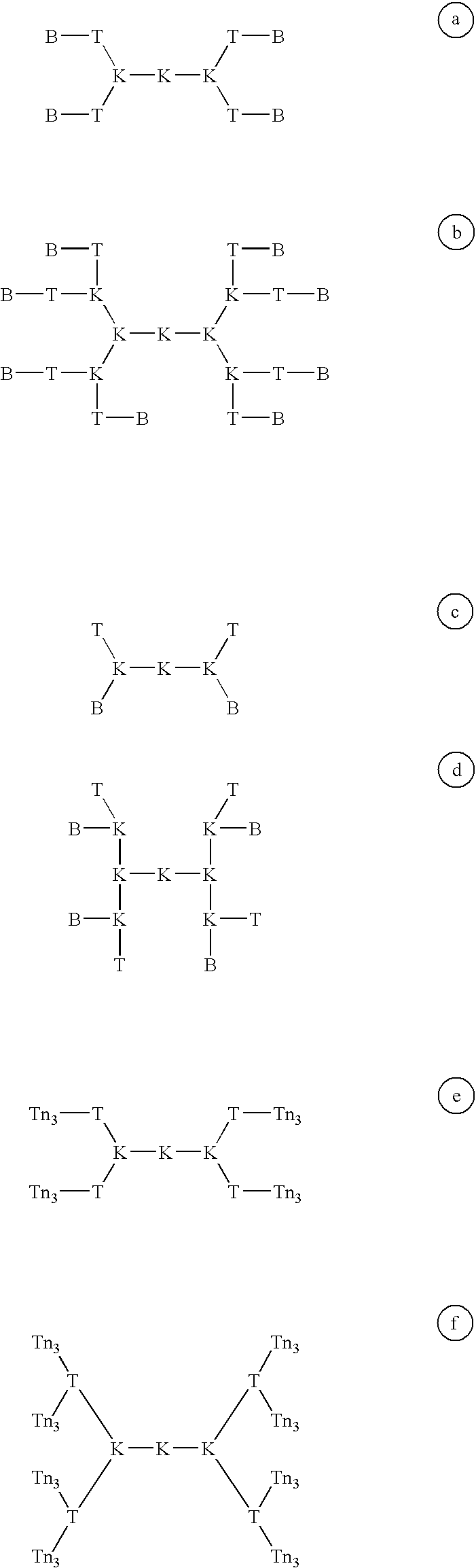
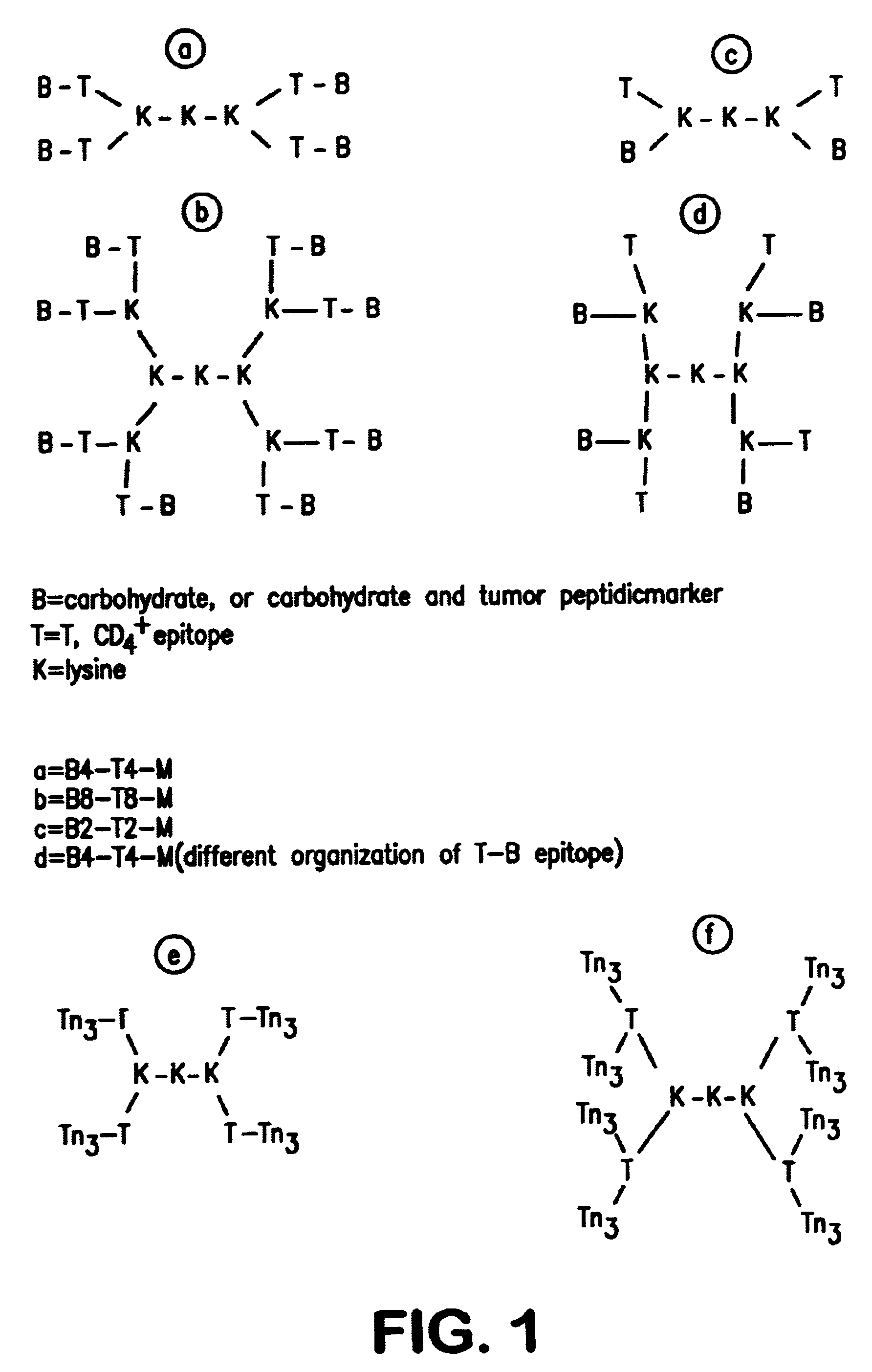
Multiple antigen glycopeptide carbohydrate vaccine comprising the same and use thereof
InactiveUS6676946B2Enhance antibody responseEfficient T cell helpPeptide/protein ingredientsBacteria peptidesT epitopeGlycopeptide
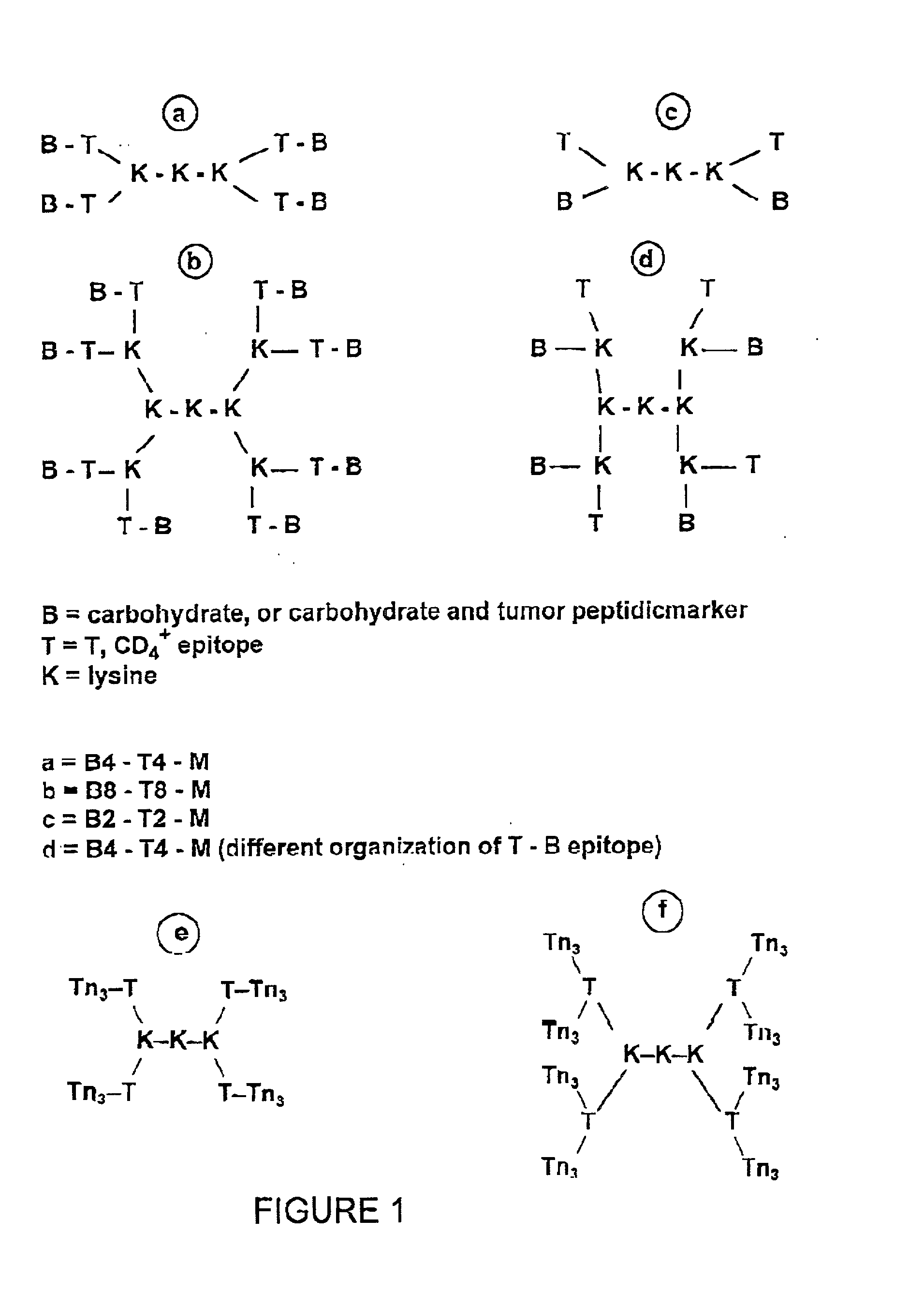
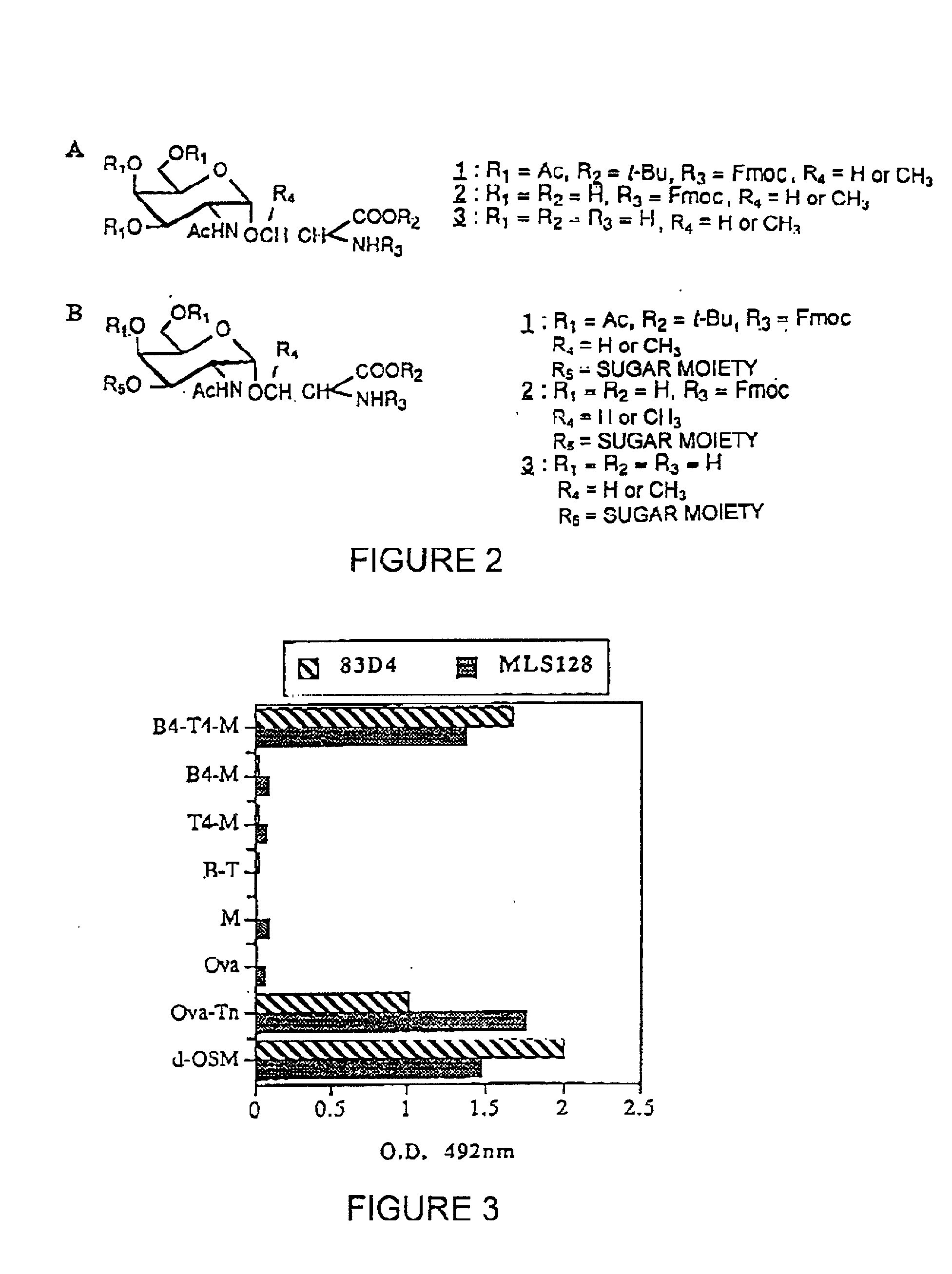
A carbohydrate peptide conjugate containing:(i) a carrier containing a dendrimeric poly-lysine enabling multiple epitopes to be covalently attached thereto,(ii) at least one peptide containing one T epitope or several identical or different T-epitopes,(iii) at least one carbohydrate moiety which is tumor antigen, or a derivative thereof, containing a B epitope, provided it is not a sialoside, or several identical or different epitopes, wherein said conjugate containing at least 3-lysines and up to 15 lysine covalently linked to one another, and wherein:(a) to the NH2 and of at least two lysine residues is bound at least one carbohydrate residue being not a sialoside, optionally substituted and containing an epitope and wherein the peptide containing one T epitope is covalently bound to the end of said carbohydrate which induces immune responses.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
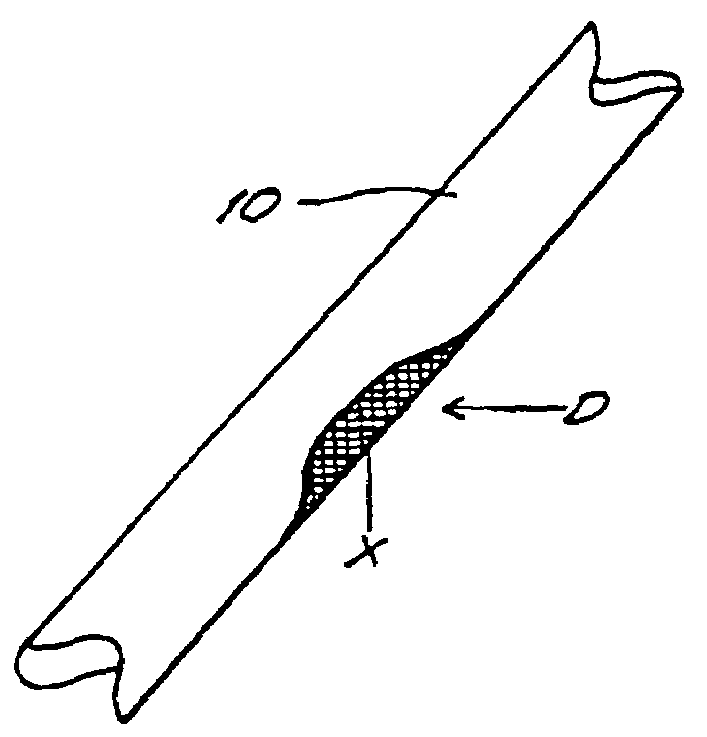
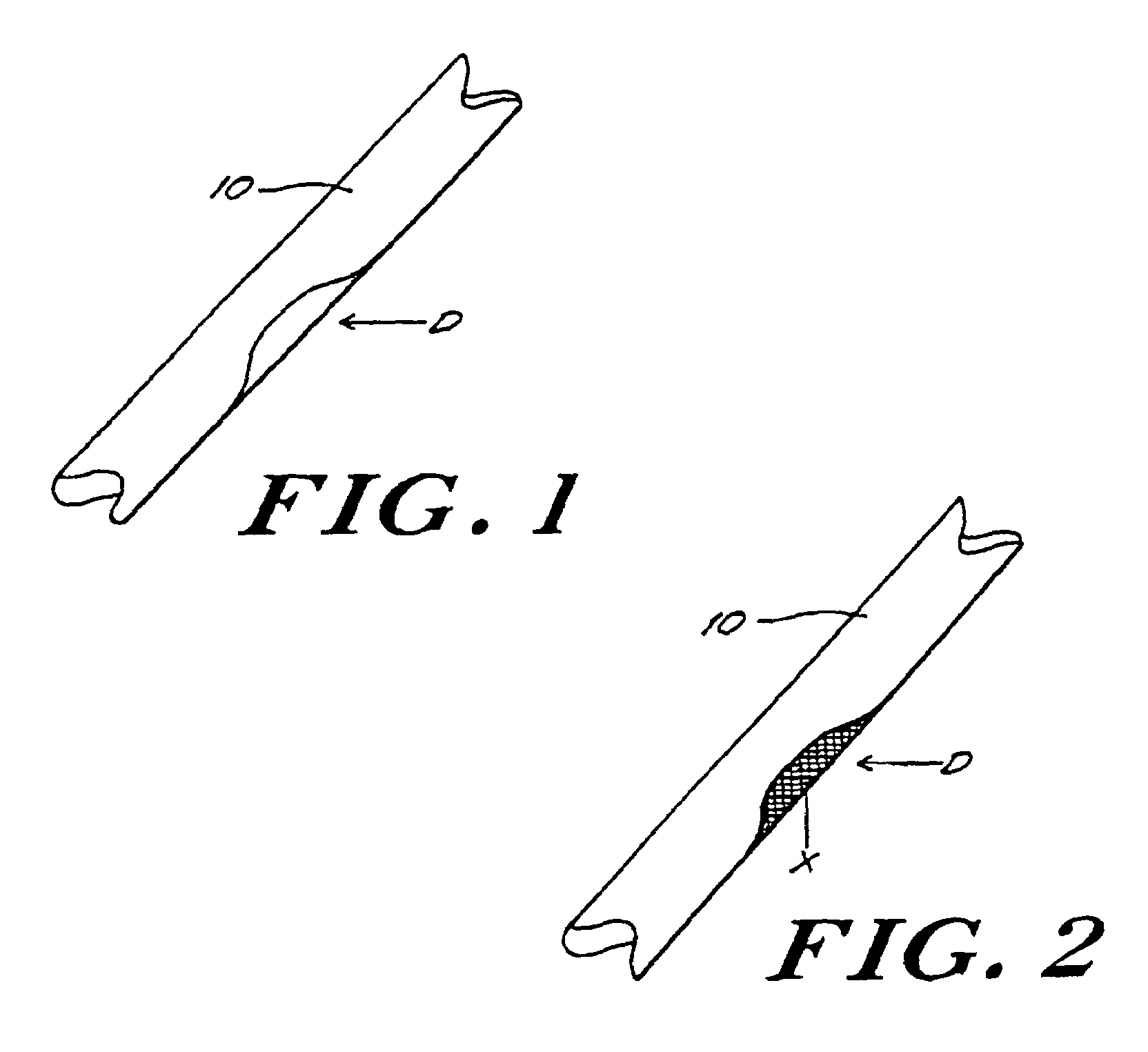
Bone xenografts
The invention provides an article of manufacture comprising a substantially non-immunogenic bone xenograft for implantation into humans. The invention further provides a method for preparing a bone xenograft by removing at least a portion of a bone from a non-human animal to provide a xenograft (X); washing the xenograft in saline and alcohol; subjecting the xenograft to a cellular disruption treatment; and treating the xenograft with a glycosidase to remove surface carbohydrate moieties. The invention also provides an article of manufacture produced by the above identified method of invention. The invention further provides a bone xenograft for implantation into a human including a portion (10) of a bone from a nonhuman animal, wherein the portion has substantially no surface carbohydrate moieties which are susceptible to glycosidase digestion. Each xenograft of the invention has substantially the same mechanical properties as a corresponding native bone.
Owner:APERION BIOLOGICS
Multiple antigen glycopeptide carbohydrate vaccine comprising the same and use thereof
InactiveUS20030157115A1Enhance antibody responseEfficient T cell helpPeptide/protein ingredientsVirus peptidesT epitopeGlycopeptide
A carbohydrate peptide conjugate comprising: a carrier comprising a dendrimeric poly-Lysine enabling multiple epitopes to be covalently attached thereto, at least one peptide comprising one T epitope or several identical or different T epitopes, at least one carbohydrate moiety, or a derivative thereof, containing B epitope, provided it is not a sialoside, or several identical or different epitopes. Use of this conjugate for inducing immune response.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Factor viii polymer conjugates
ActiveUS20100113364A1Quality improvementFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsCarbohydrate moietySoluble polymer
The invention is a proteinaceous construct comprising a Factor VIII molecule which is conjugated to a water-soluble polymer via carbohydrate moieties of Factor VIII, and methods of preparing same.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Deicing solution
InactiveUS7045076B2Optimize their synergismEliminate foamOther chemical processesChloride saltCarbohydrate moiety
A deicing formulation which includes at least one carefully selected and further processed agricultural by-product selected from BCS, DCS and CCSL, a chloride salt and water. The formulation has a viscosity of 100 to 140 centipoises at 0° C. (32° F.), and a liquid adhesion rating of at least 4. Each of BCS, DCS and CCSL contain a low molecular carbohydrate fraction in an amount sufficient to lower the freezing point threshold value of the formulation.
Owner:SEARS ECOLOGICAL APPL CO
Synthetic hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variants, oral formulations and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20060182716A1Skeletal disorderSaccharide peptide ingredientsInterferon receptorCarbohydrate moiety
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention further provides oral formulations of protease-resistant or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, the protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, the protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, a protease-resistant polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:LAWRENCE M BLATT +1
Production of globosides oligosaccharieds using metabolically engineered microorganisms
The present invention relates to the large scale in vivo synthesis of globosides oligosaccharides; especially globotriose, globotetraose and globopentaose, which are the carbohydrate portions of globotriosylceramide (Gb3Cer), globotetraosylceramide (Gb4Cer) and globopentaosylceramide (Gb5Cer) respectively. It also relates to high yield production of potential anticancer vaccines of the globo-series glycosphingo lipids, including the Globo-H. It also relates to the use of the glycosyltransferase encoded by the lgtD gene from Haemophilus influenzae as a β1,3 galactosyl transferase to catalyze the transfer of a galactose moiety from UDP-Gal to an acceptor bearing the terminal non reducing structure GalNAcβ-3-R to form the Galβ-3GalNAcβ-3-R structure
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Carbohydrate fraction and use thereof for a flat postprandial glucose response
The invention relates to a combination of heat-treated nutritional composition having a carbohydrate fraction comprising a) 5-30 wt % of one or more monosaccharides selected from galactose, ribose and mannose; b) carbohydrates capable of providing b1) sustained release glucose and b2) rapidly available glucose; c) optionally fructose; d) glucose-containing disaccharides other than maltose and sucrose; and e) optionally sugar polyols. The invention also pertains to the use of such a heat-treated nutritional composition for controlling glucose levels in blood and / or tissue, especially for preventing and / or treating diabetics, insulin-resistance, obesity, postprandial glucose response, metabolic syndrome, syndrome X, hyperglycemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyperinsulinemia, dyslipidemia, dysfibrinolysis and / or disorders associated with major surgery or trauma.
Owner:NV NUTRICIA
Hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants and methods of use
The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites. The present invention provides synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists comprising consensus or hybrid Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonists, containing one or more native or non-native glycosylation sites, as well as erythropoietin and darbepoetin alfa, each of which are linked to a penetrating peptide that facilitates translocation of a substance across a biological barrier as well as pharmaceutical compositions, including oral formulations, of the same. The present invention further provides oral formulations of hyperglycosylated or protease-resistant, hyperglycosylated polypeptide variants, which polypeptide variants lack at least one protease cleavage site found in a parent polypeptide, and thus exhibit increased protease resistance compared to the parent polypeptide, which polypeptide variants further include (1) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one non-native glycosylation site not found in the parent protein therapeutic or (2) a carbohydrate moiety covalently linked to at least one native glycosylation site found but not glycosylated in the parent protein therapeutic. The present invention further provides compositions, including oral pharmaceutical compositions, comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides containers, devices, and kits comprising the synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, the hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or the hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant. The present invention further provides therapeutic methods involving administering an effective amount of an oral pharmaceutical composition comprising a synthetic Type I interferon receptor polypeptide agonist, a hyperglycosylated polypeptide variant, or a hyperglycosylated, protease-resistant polypeptide variant to an individual in need thereof.
Owner:ALIOS BIOPHARMA INC +1
Nanoparticle-peptide compositions
The present invention provides nanoparticles and compositions comprising such nanoparticles, as well as methods for intracellular delivery of peptides, and methods of producing nanoparticles and related products. The nanoparticles comprise a core comprising a metal and / or a semiconductor atom; and a corona comprising a plurality of ligands covalently linked to the core, wherein at least a first ligand of said plurality comprises a carbohydrate moiety that is covalently linked to the core via a first linker, and wherein at least a second ligand of said plurality comprises a peptide of choice that is covalently linked to the core via a second linker. The second linker comprises a peptide portion and a non-peptide portion, wherein said peptide portion of said second linker comprises the sequence X1X2Z1, wherein: X1 is an amino acid selected from A and G; X2 is an amino acid selected from A and G; and Z1 is an amino acid selected from Y and F.
Owner:MIDATECH LTD
Biocatalytic synthesis of aminodeoxy purine N9-beta-D-nucleosides containing 3-amino-3-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose, 3-amino-2,3-dideoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose, and 2-amino-2-deoxy-beta-D-ribofuranose as sugar moieties
Purine N9-β-D-nucleosides containing 3-amino-3-deoxy-β-D-ribofaranose, 3-amino-2,3-dideoxy-β-D-ribofuranose, and 2-amino-2-deoxy-β-D-ribofuranose as sugar moieties are synthesized by biocatalytic transglycosylation of purine bases and the respective 3′-amino-3′-deoxyuridine, 3′-amino-3′-deoxythymidine and 2′-amino-2′-deoxyuridine as donors of the carbohydrate moiety, and the cells of Escherichia coli as a biocatalyst or glutaraldehyde (GA) treated cells of Escherichia coli as a biocatalyst or a mixture of thymidine (uridine) phosphorylase and purine nucleoside phosphorylase.
Owner:METKINEN
Fitness and exercise-enhancing tablet containing protein isolate
InactiveUS20090226542A1Easy to carryBoost energy levelsBiocideSugar food ingredientsVitamin CProtein isolate
An exercise-enhancing food tablet, preferably a hard or chewable candy or mint, is disclosed for enhancing exercise and physical fitness when ingested before, during, and / or after exercise. The edible tablet includes a mixture of carbohydrate and protein, the protein portion being between 20% and 40% of the mixture by weight, and preferably between 25% and 33% of the mixture by weight. The protein portion is preferably whey protein, but can be any combination of whey protein, soy protein, and pea protein. The carbohydrate portion of the mixture is preferably 85% dextrose and 15% fructose, but can be any combination of dextrose, maltodextrin, fructose, and sucrose. In preferred embodiments, sodium, potassium, magnesium, vitamin C, and / or caffeine are also included. The tablets can also include a flavoring, such as spearmint, peppermint, or fruit flavoring. In preferred embodiments the tablets weigh substantially 2 grams, and an adult serving is eight tablets.
Owner:CRESTA ANDREA K
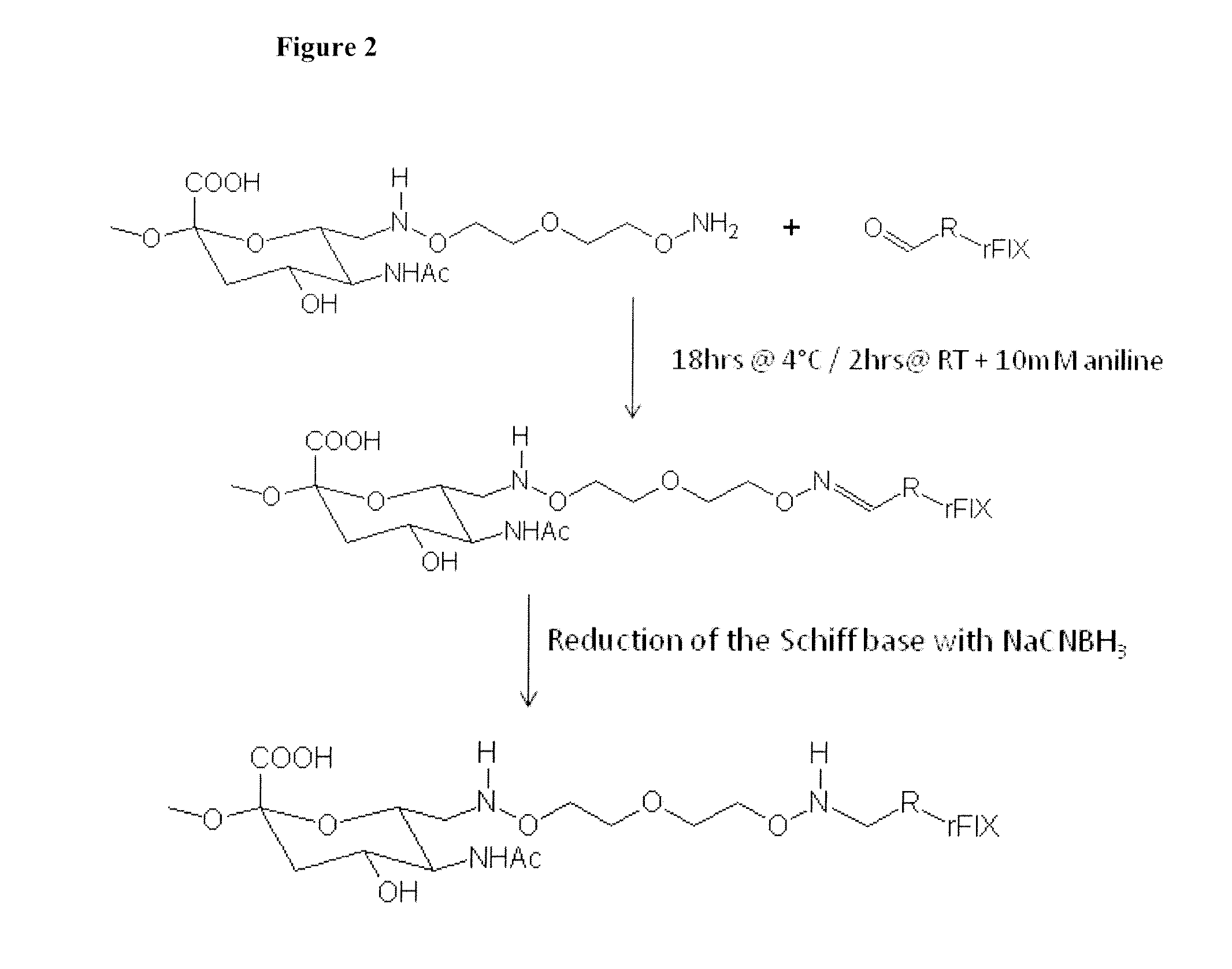
Nucleophilic catalysts for oxime linkage
ActiveUS20120035344A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesLow costFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrazoneTherapeutic protein
The invention relates to materials and methods of conjugating a water soluble polymer to an oxidized carbohydrate moiety of a therapeutic protein comprising contacting the oxidized carbohydrate moiety with an activated water soluble polymer under conditions that allow conjugation. More specifically, the present invention relates to the aforementioned materials and methods wherein the water soluble polymer contains an active aminooxy group and wherein an oxime or hydrazone linkage is formed between the oxidized carbohydrate moiety and the active aminooxy group on the water soluble polymer, and wherein the conjugation is carried out in the presence of a nucleophilic catalyst.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
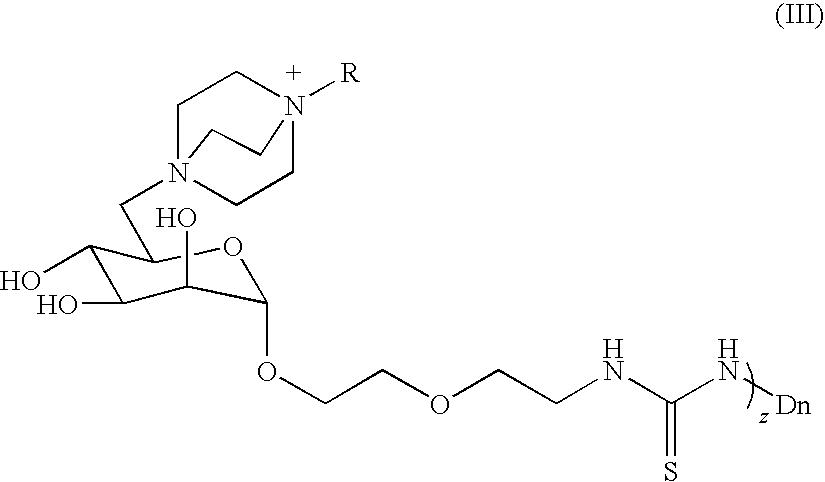
Quaternary ammonium functionalized glycodendrimers, methods for the production and use thereof
The present invention provides novel antimicrobial agents that are quaternary ammonium functionalized glycodendrimers. In one embodiment, the quaternary ammonium functionalized glycodendrimers are compounds of Formula (I): (Q+−-S-L)z-DnX− wherein: D is a dendrimer; n is the generation number of the functionalized dendrimer; z is an integer less than or equal to 2(n+2); L is a linking group; Q+ represents a quaternary ammonium moiety; and S represents a carbohydrate moiety. The present invention further provides formulations containing the antimicrobial agents of the invention, methods of making the agents and formulations of the invention, and methods of using the same as effective and / or broad spectrum antimicrobial agents. The agents and formulations of the invention find use in medicine, for the treatment of various inflammatory conditions or diseases, for example, and have numerous industrial applications.(Q+−-S-L)z-DnX− (I)
Owner:MONTANA STATE UNIVERSITY +1
Nucleophilic catalysts for oxime linkage
ActiveUS8642737B2Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesLow costFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrazoneTherapeutic protein
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Modified enzyme treatment method
InactiveUS20130011381A1Extended half-lifeConvenient treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsDrug compositionsLysosomal enzyme defectCarbohydrate moiety
Disclosed is a method for the treatment of lysosomal storage disease in mammals wherein the mammal is administered a therapeutically effective amount of an isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase whereby said storage diseased disease is relieved in the brain and visceral organs of the mammal. There is also disclosed an isolated, modified recombinant β-glucuronidase wherein the modification is having its carbohydrate moieties chemically modified so as to reduce its activity with respect to mannose and mannose 6-phosphate cellular delivery system while retaining enzymatic activity. Also disclosed are other lysosomal enzymes within the scope of the invention.
Owner:SAINT LOUIS UNIVERSITY
Method of preparing more digestible animal feed
ActiveCN101674733AAnimal feeding stuffPulping with inorganic basesAdditive ingredientCarbohydrate moiety
Disclosed herein are methods of treating an edible fiber source to make an animal feed with increased digestible energy. An exemplary method includes hydrolyzing the edible fiber source with an inorganic fiber hydrolyzing agent in a twin screw mixer that shears the edible fiber to a size of between 0.5 to 25 mm. The hydrolysis in the mixer occurs at pressure of about 14 psig or higher with a temperature about 1000C to 110 DEG C. The inorganic hydrolysis liberates a first portion of soluble carbohydrates from the edible fiber source. The inorganically hydrolyzed material is also treated (before or after) with a fiber degrading enzyme to solubilize a second portion of carbohydrates. The dually hydrolyzed material is dried to form an animal feed or feed ingredient having a soluble and insoluble carbohydrate fraction with the amount of soluble carbohydrate being at least 45% wt / wt of the total carbohydrates obtained from the edible fiber source.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
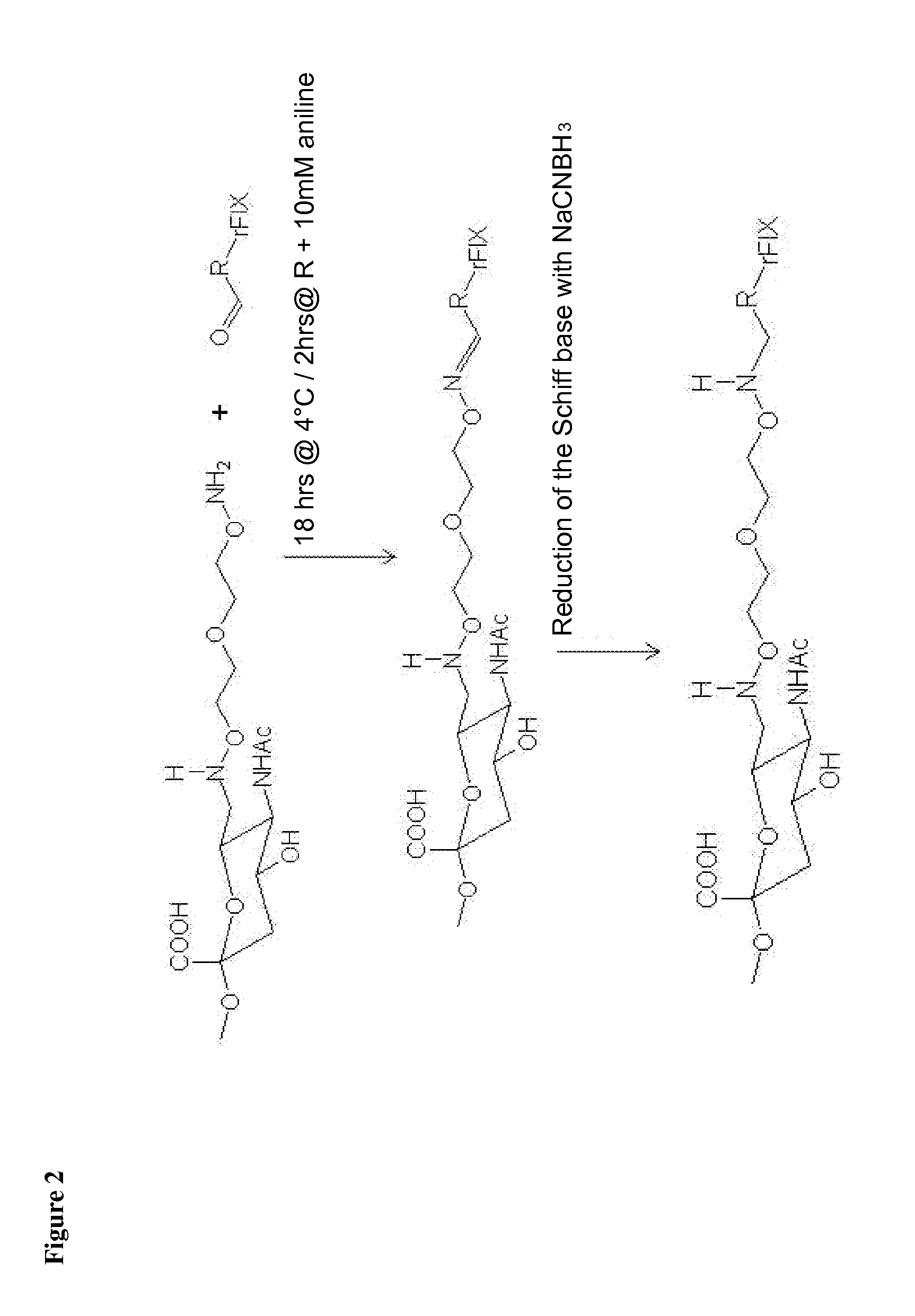
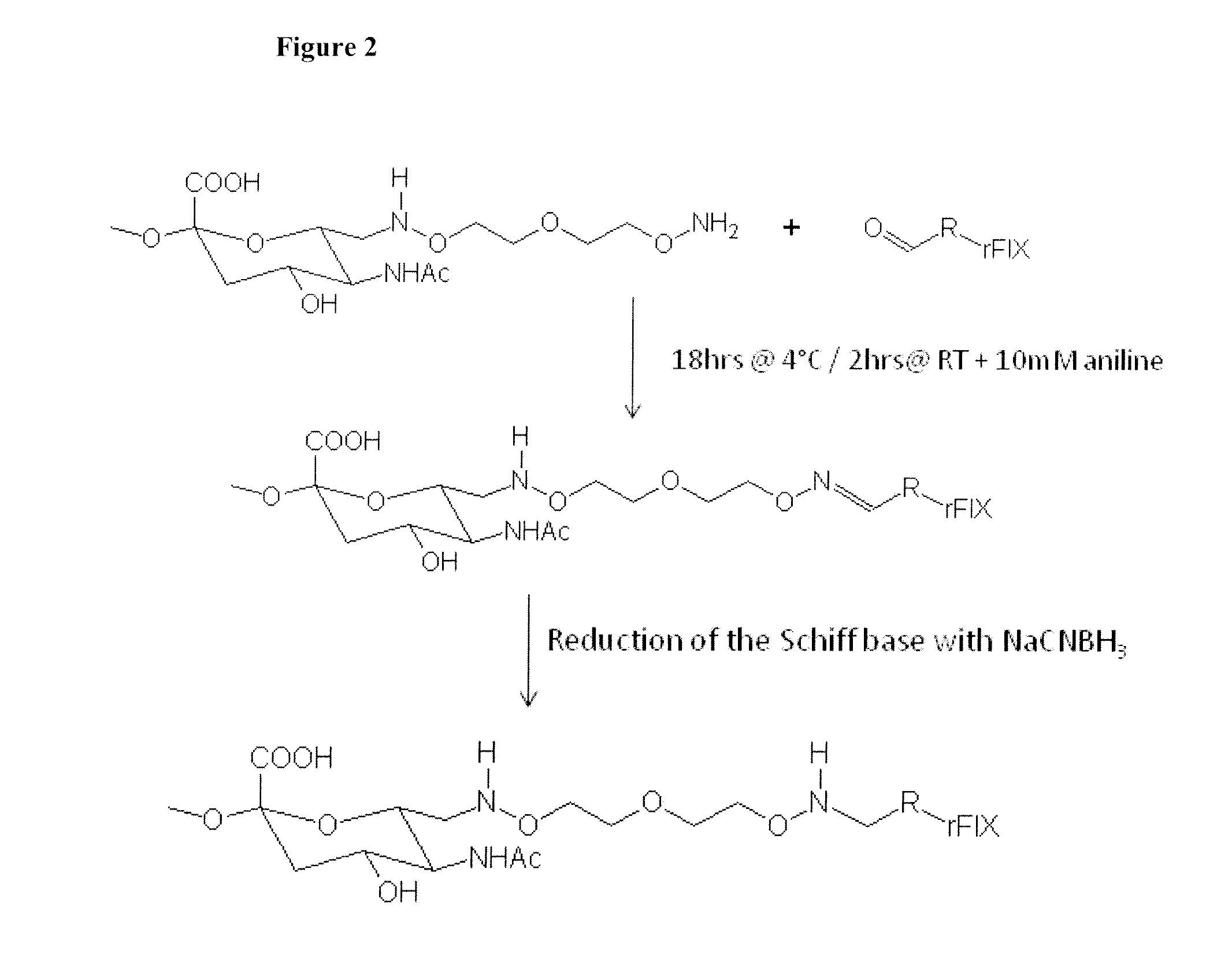
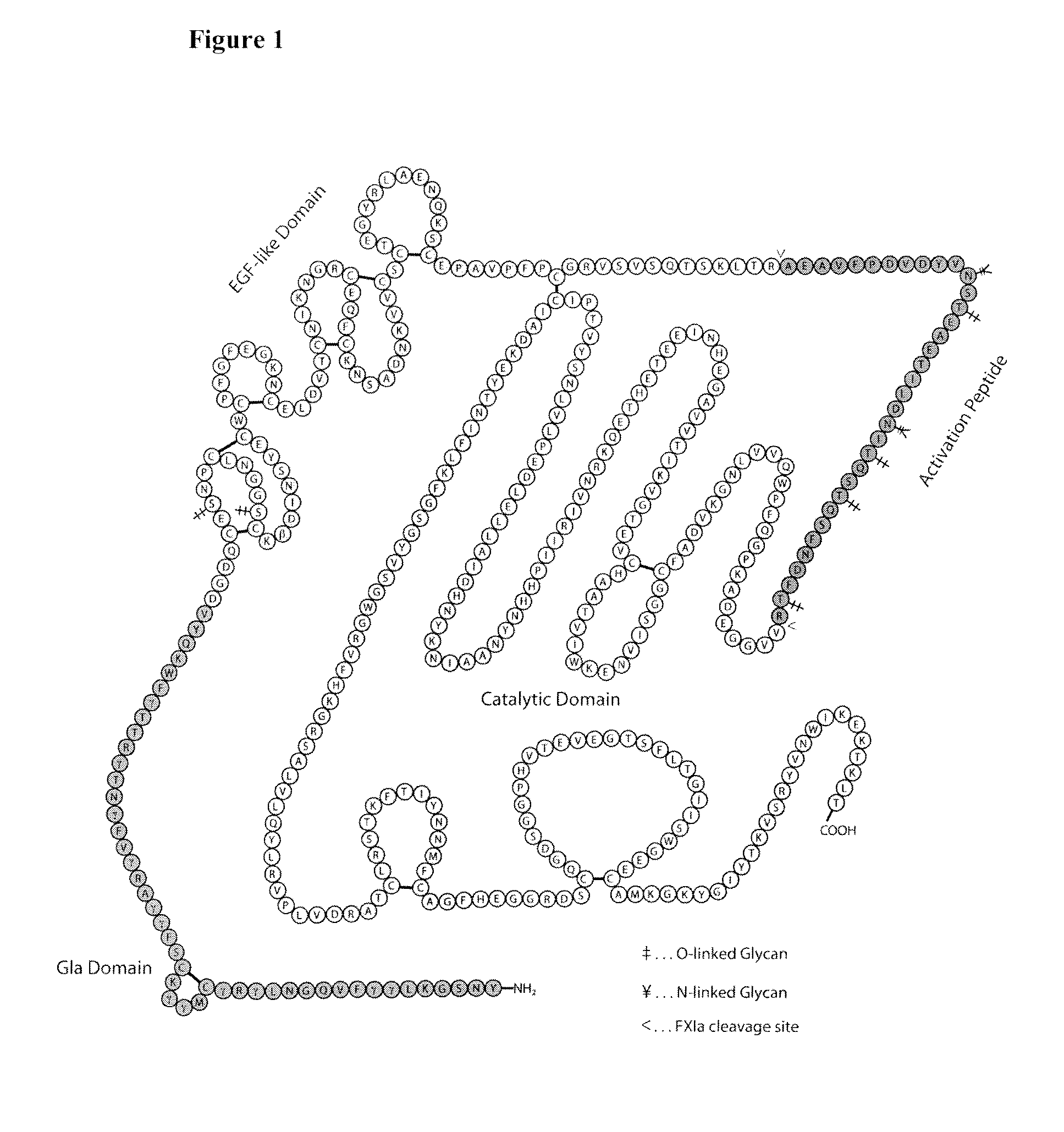
Blood coagulation protein conjugates
ActiveUS20110028693A1Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesLow costFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsWater solubleAniline
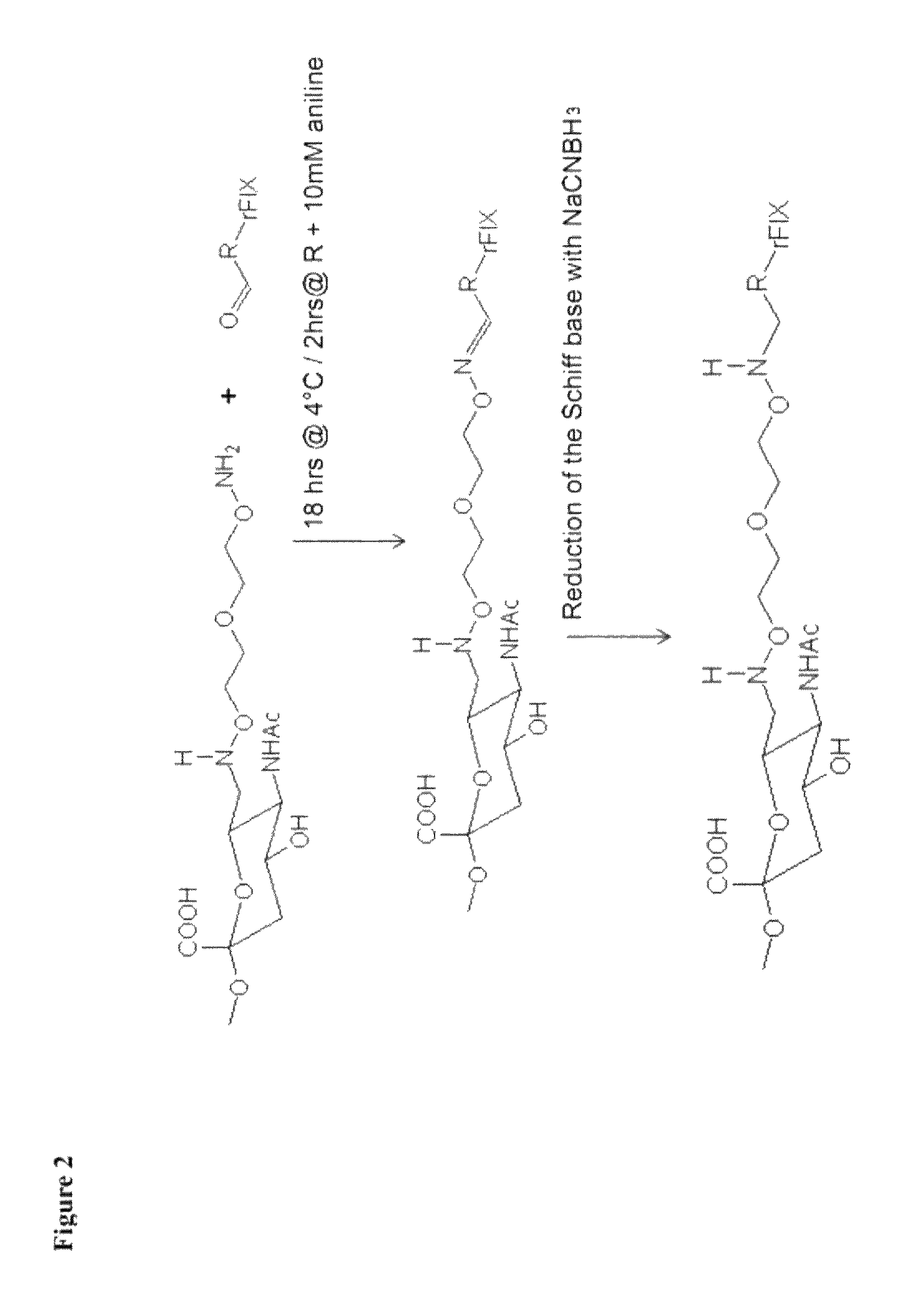
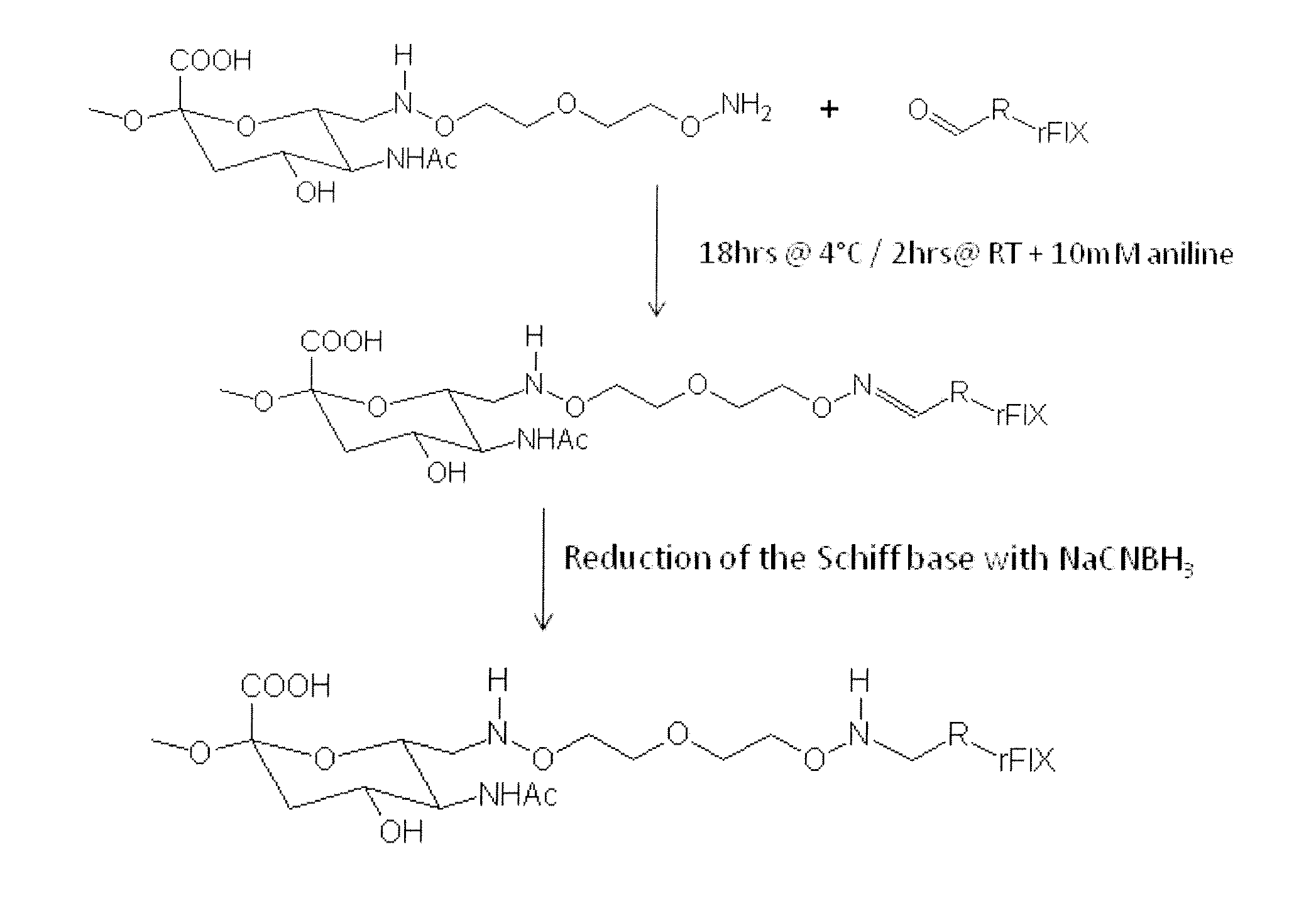
The invention relates to materials and methods of conjugating a water soluble polymer to an oxidized carbohydrate moiety of a blood coagulation protein comprising contacting the oxidized carbohydrate moiety with an activated water soluble polymer under conditions that allow conjugation. More specifically, the present invention relates to the aforementioned materials and methods wherein the water soluble polymer contains an active aminooxy group and wherein an oxime linkage is formed between the oxidized carbohydrate moiety and the active aminooxy group on the water soluble polymer. In one embodiment of the invention the conjugation is carried out in the presence of the nucleophilic catalyst aniline. In addition the generated oxime linkage can be stabilized by reduction with NaCNBH3 to form an alkoxyamine linkage.
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Novel pharmaceutical agents containing carbohydrate moieties and methods of their preparation and use
Hydrophilic N-linked pharmaceutical compositions, methods of their preparation and use in neuraxial drug delivery comprising a glycosyl CNS acting prodrug compound covalently N-linked with a saccharide through an amide or an amine bond and a formulary consisting of an additive, a stabilizer, a carrier, a binder, a buffer, an excipient, an emollient, a disintegrant, a lubricating agent, an antimicrobial agent or a preservative, with the proviso that the saccharide moiety is not a cyclodextrin or a glucuronide.
Owner:CHRISTIAN SAMUEL T
Blood coagulation protein conjugates
ActiveUS8637640B2Improved pharmacokinetic propertiesLow costFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsWater solubleAniline
Owner:TAKEDA PHARMA CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com