Novel pharmaceutical agents containing carbohydrate moieties and methods of their preparation and use
a technology of carbohydrate moieties and pharmaceutical agents, which is applied in the direction of drug compositions, biocides, metabolic disorders, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the access of many classes of known and potentially useful pharmaceutical agents, unable to achieve proper delivery of therapy across the blood brain barrier into affected nigrostriatal tissues, and unable to achieve the effect of good aqueous solubility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
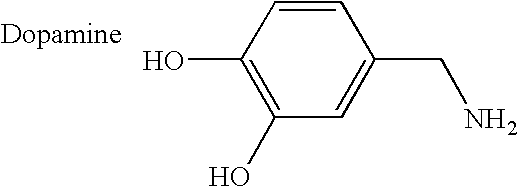
Preparation of Dopamine Gluconamide and Dopamine Gluconamine
[0148] Representative compounds for use according to the instant methods were synthesized as disclosed in co-pending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 09 / 547,506 (now U.S. Pat. No. 6,548,484 B1), incorporated herein by reference in its entirety. Briefly, gluconolactone and 3-hydroxytryamine were reacted slowly in methanol to form a white solid dopamine gluconamide precipitant. The product was collected by filtration, washing and drying in vacuo (i.e., dopamine gluconamide, Compound #1, below).
example 1-1
Preparation of Dopamine Gluconamide
[0149]
[0150] Gluconolactone (1.9 gm, 10.5 mmol) and triethylamine (TEA; 1.1 gm, 10.5 mmol) were added to methanol (25 mL) in a 100 mL round bottom flask with stirring. The gluconolactone was allowed to dissolve. When the solid was dissolved, the solution was stirred for an additional 10 minutes and then 3-hydroxytyramine (2.0 gm, 10.5 mmol) was added slowly, i.e., allowing it to dissolve. The reaction mixture was stirred in the dark for about 2 hrs. during which time a white solid precipitant appeared. The white solid precipitant was collected by filtration, washed with methanol (5 mL) and dried in vacuo for 6 hrs. to give dopamine gluconamide (1.69 gm, 5.10 mmol, 48.6% yield). Melting point of the synthesis product was 154-155° C. Predicted: C14H21N1 (331.32): C, 50.75%, H, 6.39%, N, 4.23%; analysis results of synthetic product: C, 50.65; H, 6.63; N, 4.444.
example 1-2
Protection of Aromatic Dopamine Hydroxyl Residues
[0151]
[0152] Dopamine gluconamide (EXAMPLE 1, supra; 0.75 gm, 2.26 mmol) was added to acetone (40 mL) in a 100 mL round bottom flask with stirring. Then, the reaction mixture was refluxed for 2 hrs., after which time it was allowed to cool to room temperature (about 22-25° C.). The resultant white solid was removed by filtration and dried in vacuo for 7 hrs. yielding the isopropylidine protected dopamine gluconamide (0.68 gm, 1.83 mmol, 81.0% yield). Melting point of the synthesis product was 170° C.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com