Protein C-terminal peptide enrichment method based on Edman degradation
A protein and enrichment technology, applied in the preparation of test samples, etc., can solve the problems of low reaction efficiency and low recovery rate of terminal peptide enrichment, achieve high enrichment selectivity, and improve the effect of enrichment selectivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
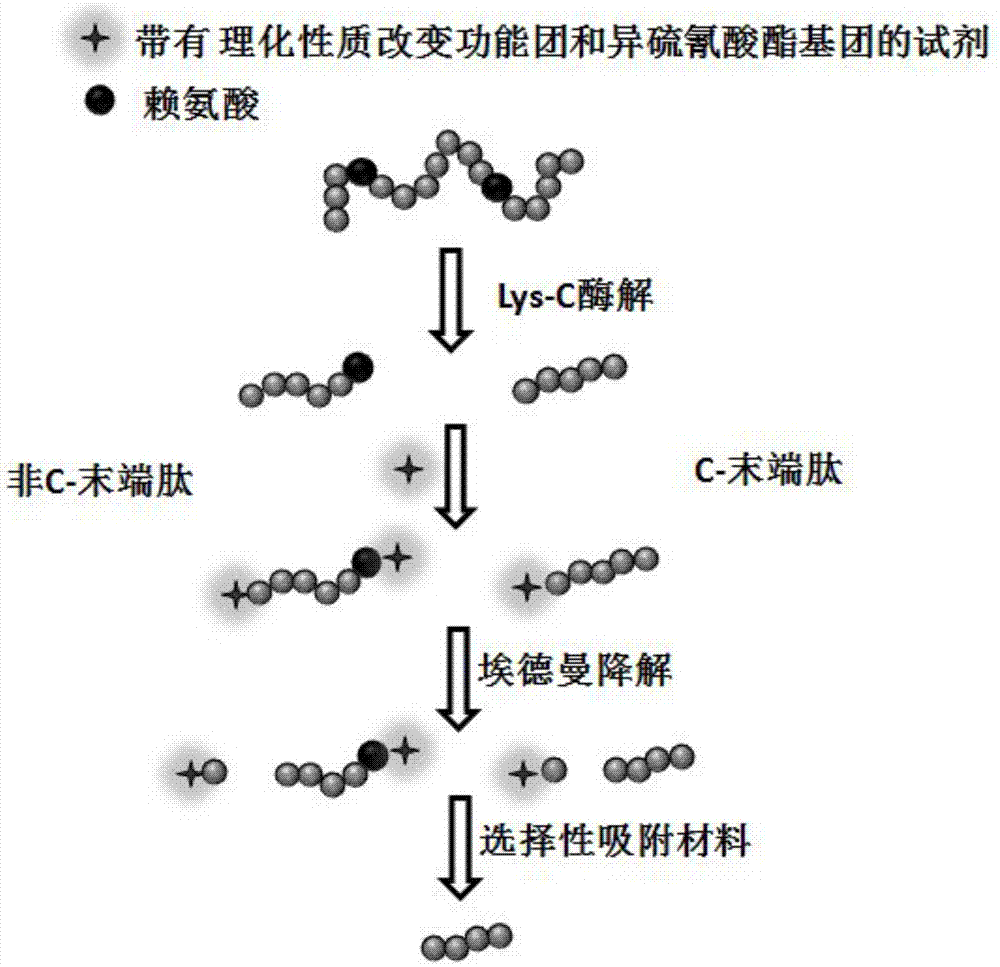
[0018] Such as figure 1 As indicated, protein C-terminal peptide enrichment was carried out as follows:
[0019] 1) Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein: The two extracted plasma proteins were dissolved in 50mM NaHCO3 (pH7.5), then heat denatured at 90°C for 20min, cooled to room temperature and then reduced (10mM DTT, 56°C, 2h) to alkane Kylation (25mM IAA, protected from light at room temperature, 40min), followed by adding Lys-C at an enzyme / protein ratio of 1:25 for enzymatic hydrolysis and reacting in a 37°C water bath for 16h.
[0020] 2) Edman degradation of protein enzymatic peptides: under alkaline conditions (pH = 8.0), 45 ° C React with the protein enzymatic peptide, the reaction time is 30 minutes. After the reaction mixed solution was lyophilized, 10 microliters to 1 milliliter of anhydrous trifluoroacetic acid was added and reacted at 45° C. for 10 minutes to cleave the N-terminal amino acid of the peptide from the peptide.
[0021] 3) Enrichment of protein C-term...
Embodiment 2
[0023] Such as figure 1 As indicated, protein C-terminal peptide enrichment was carried out as follows:
[0024] 1) Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein: The two extracted plasma proteins were dissolved in 50mM NaHCO3 (pH7.5), then heat denatured at 90°C for 20min, cooled to room temperature and then reduced (10mM DTT, 56°C, 2h) to alkane Kylation (25mM IAA, protected from light at room temperature, 40min), followed by adding Lys-C at an enzyme / protein ratio of 1:25 for enzymatic hydrolysis and reacting in a 37°C water bath for 16h.
[0025] 2) Edman degradation of protein enzymatic peptides: under alkaline conditions (pH = 8.0), 45 ° C React with the protein enzymatic peptide, the reaction time is 30 minutes. After the reaction mixed solution was lyophilized, 10 microliters to 1 milliliter of anhydrous trifluoroacetic acid was added and reacted at 45° C. for 10 minutes to cleave the N-terminal amino acid of the peptide from the peptide.
[0026] 3) Enrichment of protein C-term...
Embodiment 3
[0028] Such as figure 1 As indicated, protein C-terminal peptide enrichment was carried out as follows:
[0029] 1) Enzymatic hydrolysis of protein: The two extracted plasma proteins were dissolved in 50mM NaHCO3 (pH7.5), then heat denatured at 90°C for 20min, cooled to room temperature and then reduced (10mM DTT, 56°C, 2h) to alkane Kylation (25mM IAA, protected from light at room temperature, 40min), followed by adding Lys-C at an enzyme / protein ratio of 1:25 for enzymatic hydrolysis and reacting in a 37°C water bath for 16h.
[0030] 2) Edman degradation of protein enzymatic peptides: under alkaline conditions (pH = 8.0), 45 ° C React with the protein enzymatic peptide, the reaction time is 30 minutes. After the reaction mixed solution was lyophilized, 10 microliters to 1 milliliter of anhydrous trifluoroacetic acid was added and reacted at 45° C. for 10 minutes to cleave the N-terminal amino acid of the peptide from the peptide.
[0031] 3) Enrichment of protein C-term...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com