Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
63 results about "Autosomal dominant transmission" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Autosomal-dominant inheritance, a pattern of inheritance in which the transmission of a dominant allele on an autosome causes a trait to be expressed. Males and females are usually affected with equal frequency.
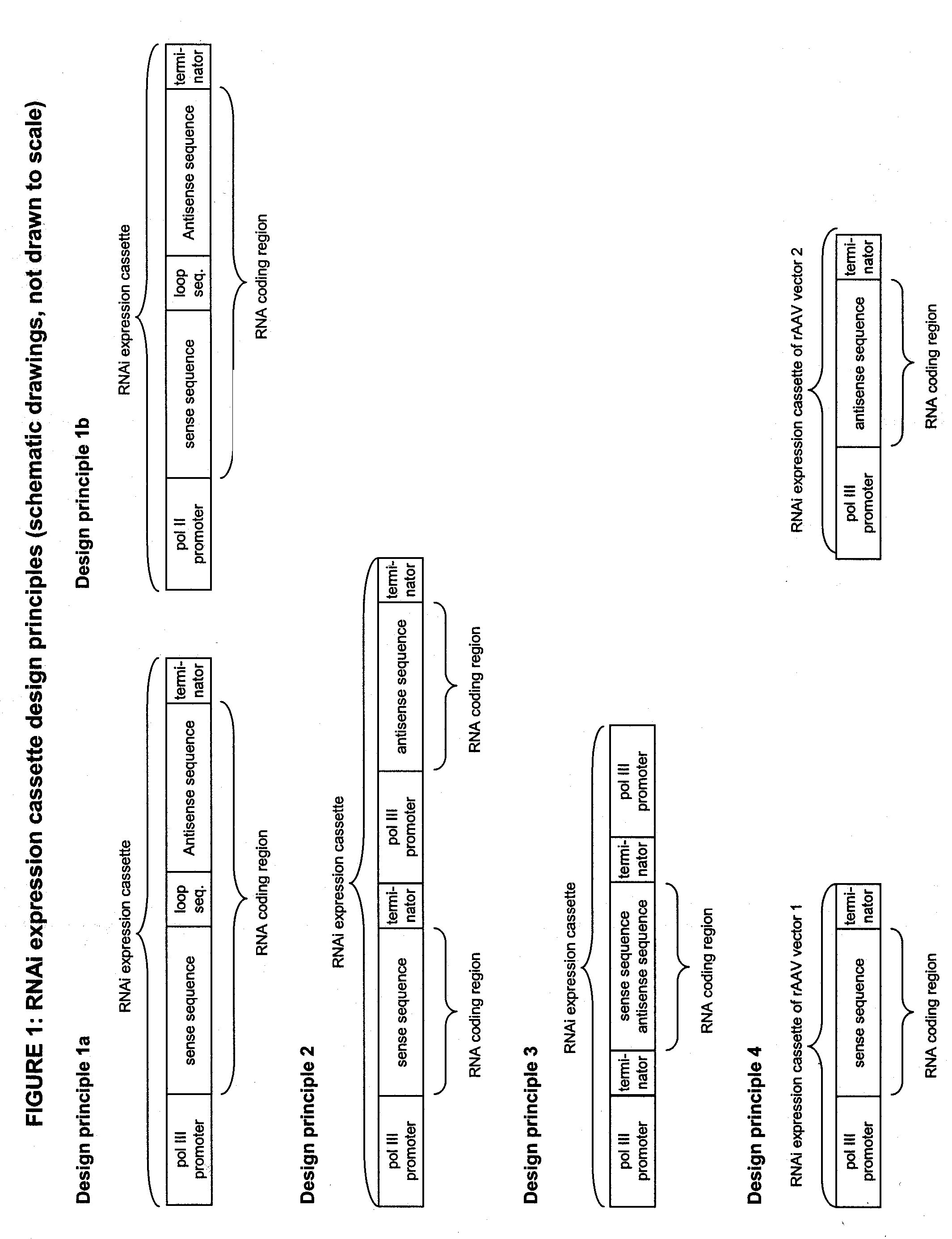
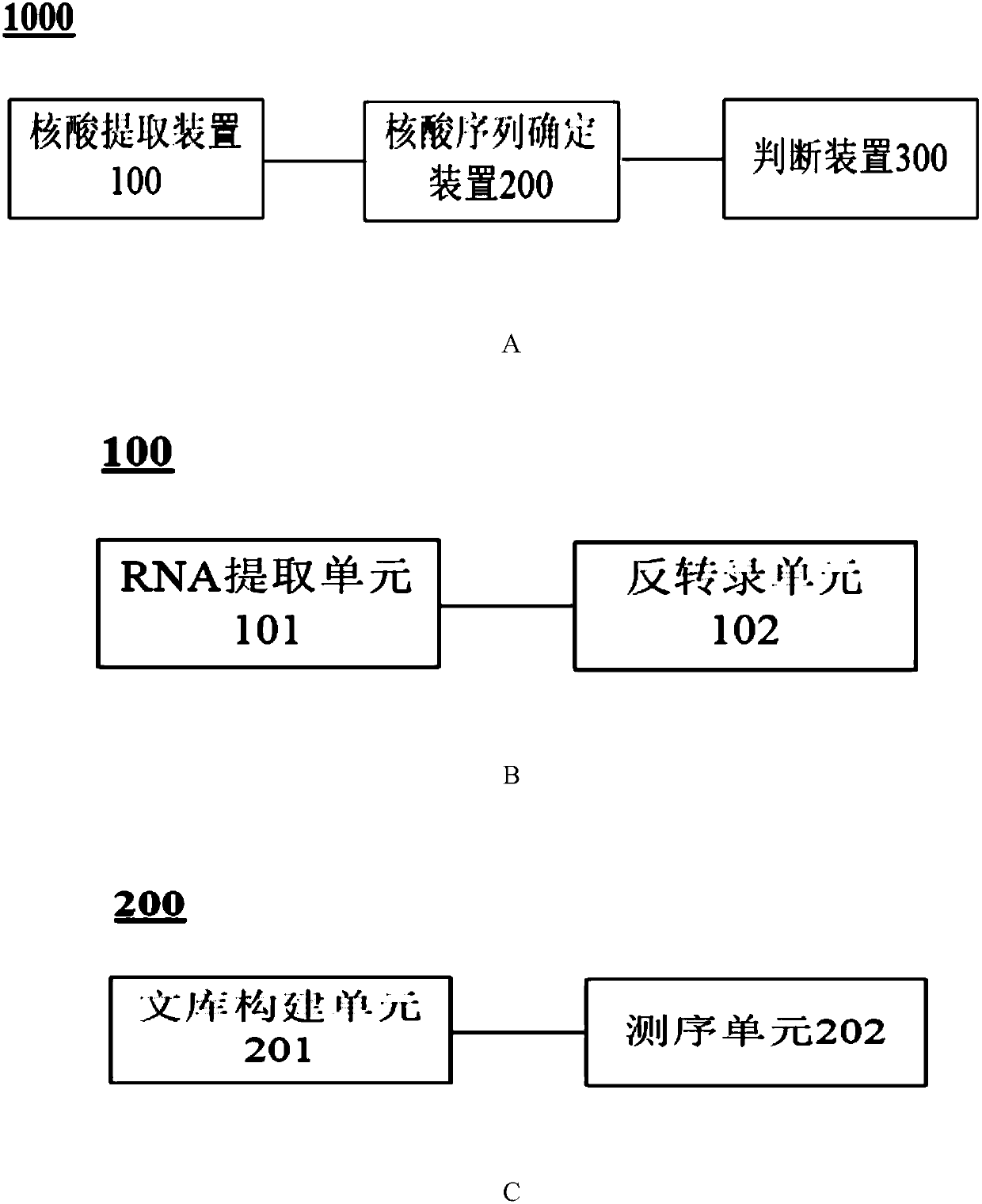
DECREASING GENE EXPRESSION IN A MAMMALIAN SUBJECT IN VIVO VIA AAV-MEDIATED RNAi EXPRESSION CASSETTE TRANSFER
InactiveUS20050019927A1High efficacyStrong specificityVectorsPeptide/protein ingredientsDecreased ConcentrationIn vivo
Decreasing the expression of genes in a mammalian subject has multiple applications ranging from cancer therapy to anti-infective therapy or treatment of autosomal dominant genetic disorders. Yet, there is still a lack of efficient technologies to achieve that goal in mammalian subjects in vivo. The present invention relates to methods for decreasing gene expression by administering to a mammalian subject a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector in vivo with said vector comprising an RNA interference (RNAi) expression cassette whose RNA expression products directly or indirectly lead to a decrease in expression of the corresponding RNAi target gene. Upon successful transduction with the recombinant adeno-associated viral vector, the RNA expression products of the RNAi expression cassette will decrease the cellular concentration of the mRNA transcripts of the RNAi target gene, thus resulting in decreased concentration of the protein encoded by the RNAi target gene.
Owner:HILDINGER MARKUS +1
New application of ginkgolide B
InactiveCN102018702APromote apoptosisPromote growthOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderCanine kidneyCytotoxicity
The invention discloses application of ginkgolide B to preparation of medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A madin-darby canine kidney (MDCK) vesicle model is used for screening to find that the ginkgolide B inhibits formation and growth of vesicles. An experimental result shows that: the ginkgolide B has an obvious inhibiting effect on the formation and growth of MDCK vesicles and the effect of the ginkgolide B is in dose response relationship; the ginkgolide B has no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the ginkgolide B is independent of the cytotoxicity; the ginkgolide B does not obviously induce MDCK cell apoptosis, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the ginkgolide B is independent of cell apoptosis promotion of the ginkgolide B; the ginkgolide B can promote the MDCK cells or vesicles to form tubular structures; and the effect is in dose response relationship; and the ginkgolide B has an inhibiting effect on the growth of the embryonic kidney vesicles. The ginkgolide B provides experimental data for development of a specific medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
PKD1 gene mutation detection kit and detection method
ActiveCN104531883AComprehensive detection rangeLow mismatch rateMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisNephrosisPKD1
The invention provides a primer set, a kit and a detection reaction system for detecting PKD1 gene mutation through the long fragment PCR and high-throughput sequencing technology, a non-diagnosis-purpose method for external PKD1 gene mutation detection, a non-diagnosis-purpose method for external PKD1 gene analysis and a method for detecting new mutation sites on the PKD1 gene. According to the method, the primer set is used for carrying out long fragment PCR amplification on the PKD1 gene of a sample, and detecting or analyzing is carried out through high-throughput sequencing. The autosomal dominant genetic polycystic nephrosis (adult polycystic nephrosis) can be diagnosed through the assistance of a detection result, previous unknown new mutation on a plurality of PKD1 real genes can be obtained and supplied to doctors or researchers so that the relevance between the mutation and the adult polycystic nephrosis can be studied.
Owner:北京圣谷智汇医学检验所有限公司
Biological information analysis method for human single-gene genetic disease detection
InactiveCN110931081AAnalyze content clearlyEasy to analyzeProteomicsGenomicsCandidate Gene Association StudyGenotype
The invention provides a biological information analysis method for human single-gene genetic disease detection. The method comprises the following steps: S1, screening mutation harmful sites; S2, screening the sample relationship of human single-gene genetic disease detection; S3, performing gene function screening. According to the method, harmful mutation sites can be quickly and clearly screened from human exon sequencing data; the annotation analysis on the detected SNP, InDel and other genomic variations and an external database is carried out to determine the genomic position, variationfrequency, protein harmfulness, genotype heterozygosity, functional pathways and other information of the variations; the candidate genes are screened by using an autosomal invisible genetic model, an autosomal dominant genetic model, new mutation screening and common mutation gene screening, so the candidate genes are determined, GO and KEGG enrichment analysis is performed on the candidate genes, and powerful evidences are provided for determining the candidate genes related to diseases.
Owner:GUANGZHOU GENE DENOVO BIOTECH
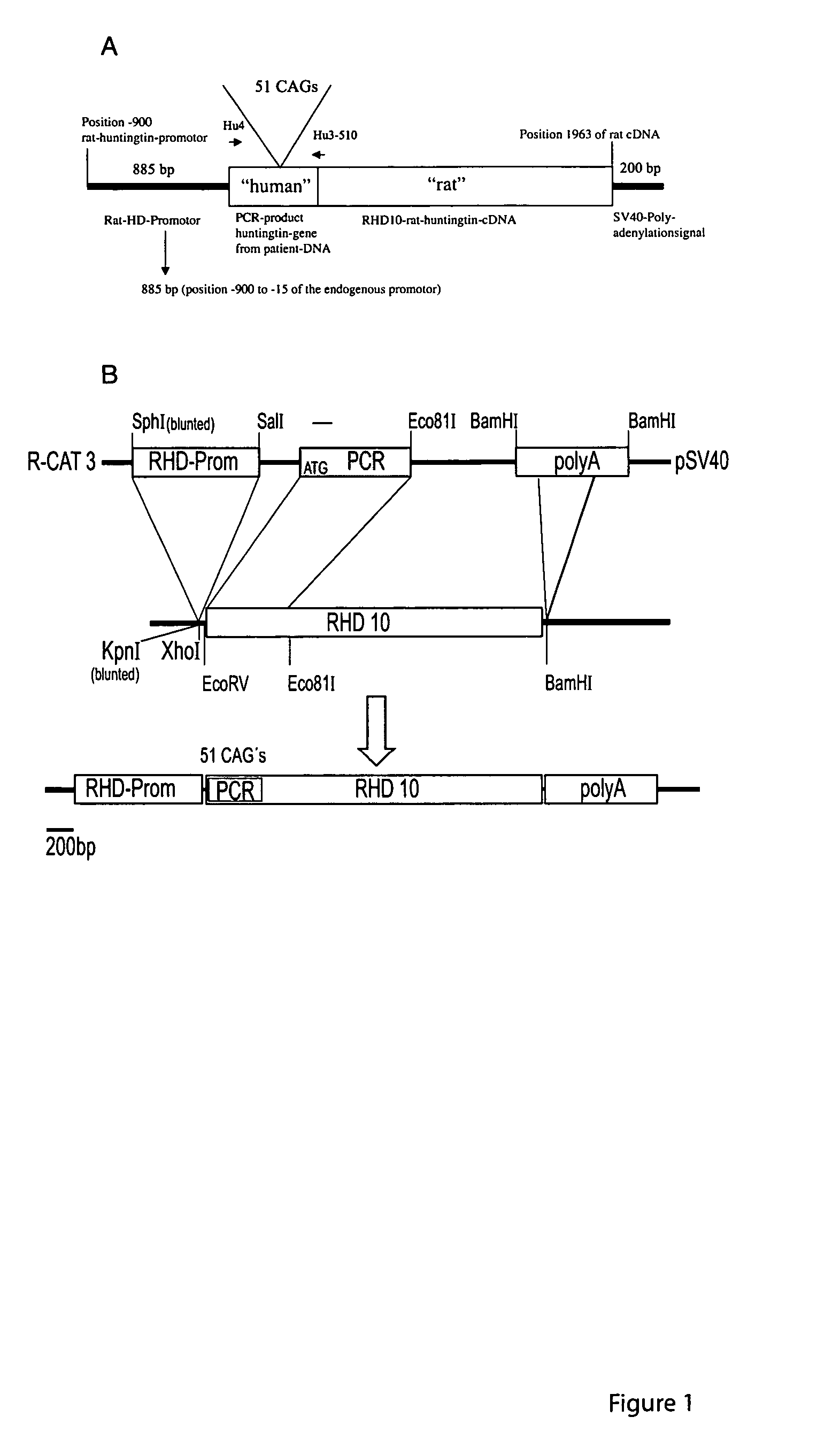
Transgenic rat as animal model for human huntingdon's disease
InactiveUS20070044162A1Lower metabolismReduced CMRGGlcBiocideGenetic material ingredientsHuntingtons choreaTherapeutic effect
Huntington's Disease (HD) is an autosomal-dominant inherited progressive neurodegenerative disease from the group of CAG repeat / polyglutamine diseases and is characterized by a triad of psychiatric alterations, dementia and motor dysfunction. On a sub-cellular level, a mutation with extended CAG tri-nucleotide repeats has been identified as the cause of HD. The therapeutic effects of certain substances can be tested on neurotoxically-induced or transgenic animal models with expanded CAG-repeats. In the present invention, transgenic rats were generated and characterized for human HD. Said rat model for human HD and other diseases of the CNS carries 51 CAG repeats under the control of a rat promoter and has a slow progressive neurological phenotype, closely reflecting human HD syndrome. The comparability of the rat model in relation to human HD is characterized by neuropathological, neuroradiological and neurochemical modifications accompanied by typical behavioral symptoms.
Owner:RIESS OLAF +1
Human polycystic albumen -1 quantitative determination kit
The invention relates to a reagent box to quantitatively detect multivesicular protein-1 content in human body fluid, using anti-human multivesicular protein-1 N-end monoclonal antibody and anti-human mulitvesicular protein-1 N-end polyclonal antibody, adopting immunologic technique to establish a double-antibody filled enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) method of quantitatively detecting body fluid and multivesicular protein-1 content in tissue cracking liquid. Comparing the difference in multivesicular protein-1 content in body fluid, judge if the patient has autosomal dominant hereditary nephropathy and has an important reference value in clinic diagnosis of this disease and provides an effective route to prevent and cure this disease as soon as possible.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
New application of curcumin
InactiveCN102018689ADoes not induce apoptosisPromote apoptosisKetone active ingredientsUrinary disorderCanine kidneyCytotoxicity
The invention discloses application of curcumin to preparation of medicaments for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A madin-darby canine kidney (MDCK) vesicle model is used for screening to obtain the curcumin which inhibits formation and growth of vesicles. An experimental result shows that: the curcumin has an obvious inhibiting effect on the formation and growth of MDCK vesicles and the effect of the curcumin is in dose response relationship; the curcumin has no cytotoxicity to MDCK cells, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the curcumin is independent of the cytotoxicity; the curcumin does not obviously induce MDCK cell apoptosis, so that the vesicle inhibiting effect of the curcumin is independent of cell apoptosis promotion of the curcumin; the curcumin can promote the MDCK cells or vesicles to form tubular structures; and the effect is in dose response relationship; and the curcumin has an inhibiting effect on the growth of the embryonic kidney vesicles. The curcumin is expected to be developed into a specific medicament for preventing and / or treating autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
An animal model and a method for producing an animal model
The present invention discloses a non-human animal model for a hereditary autosomal dominant disease. The non-human animal model expresses at least one phenotype associated with the disease and is obtained by a genetic determinant. The invention also relates to sperm cells and embryos comprising the genetic determinant for an autosomal dominant disease. Furthermore, methods for producing the non-human animal model, sperm cell, and embryos are disclosed.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
Leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK2) drosophila model for parkinson's disease: wildtype1 (WT1) and G2019S mutant flies
InactiveUS20100175140A1Effective preventionEffective treatmentCompounds screening/testingGenetic engineeringNeuronal degenerationWild type
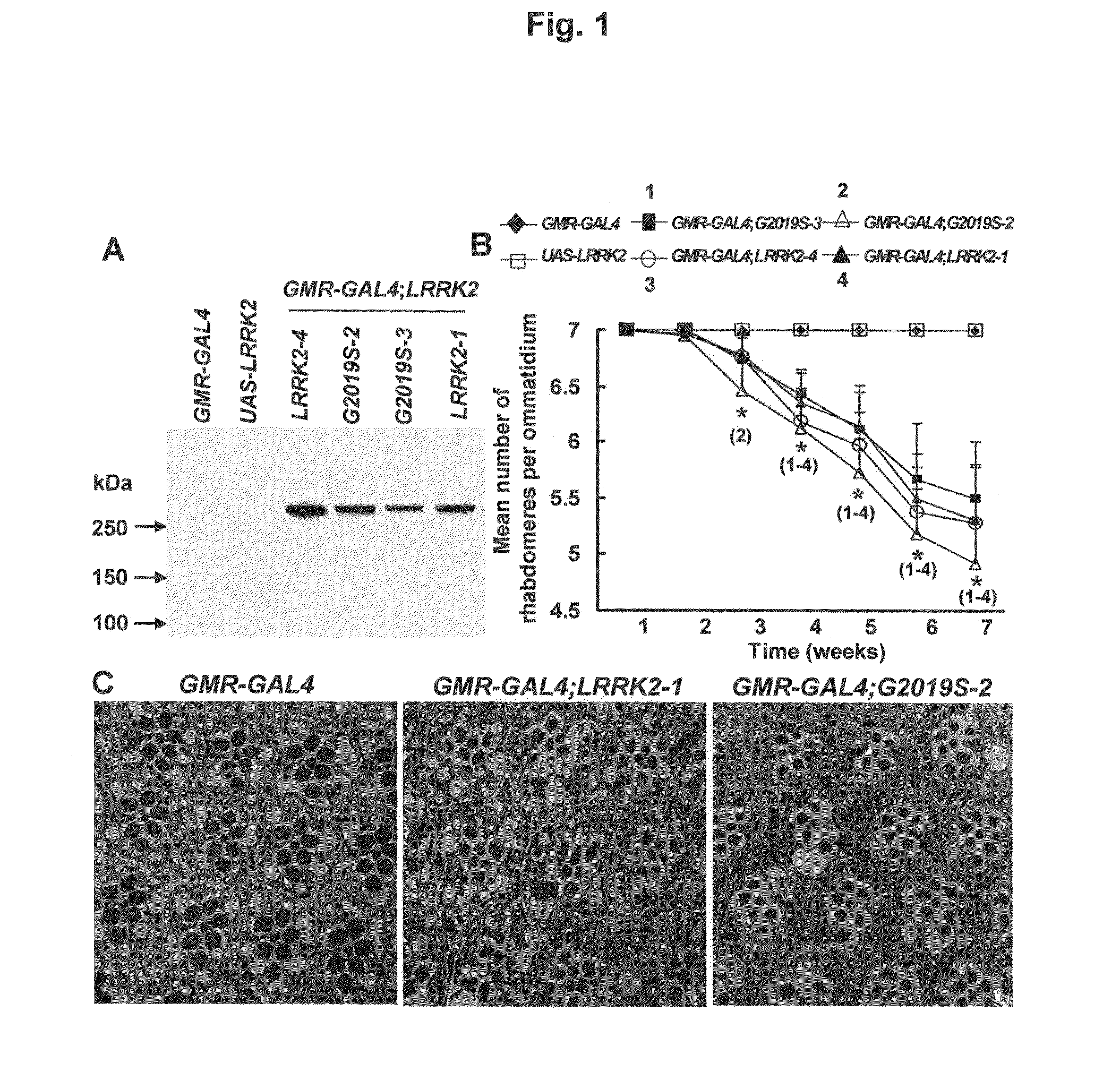
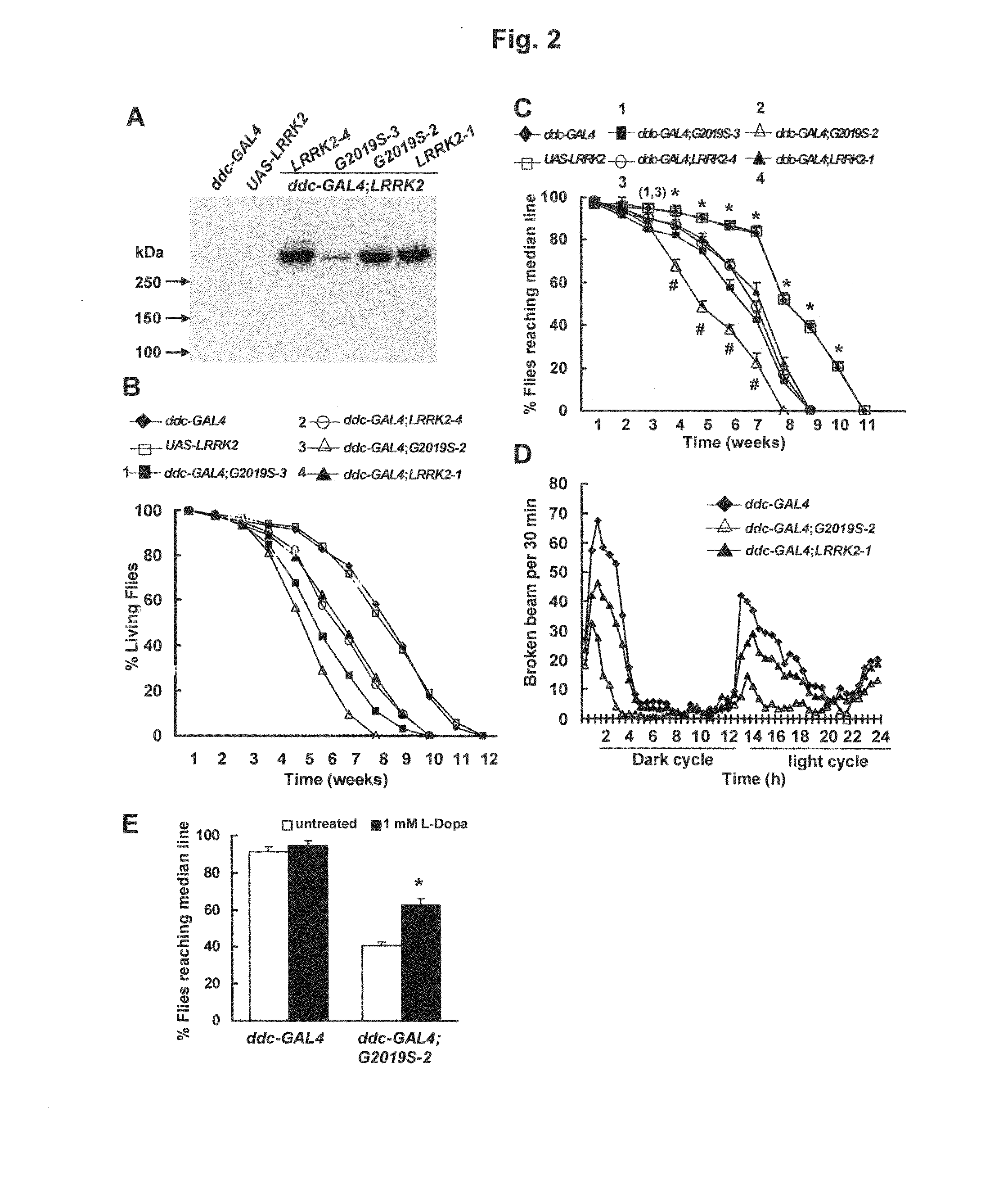
Mutations in the leucine-rich repeat kinase (LRRK2) gene cause late-onset autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease (PD) with pleiomorphic pathology. Previously, we and others found that expression of mutant LRRK2 causes neuronal degeneration in cell culture. Here we used the GAL4 / UAS system to generate transgenic Drosophila expressing either wild-type (WT1) human LRRK2 or LRRK2-G2019S, the most common mutation associated with PD. Expression of either WT1 human LRRK2 or LRRK2-G2019S in the photoreceptor cells caused retinal degeneration. Expression of WT1 LRRK2 or LRRK2-G2019S in neurons produced adult-onset selective loss of dopaminergic neurons, locomotor dysfunction, and early mortality. Expression of mutant G2019S-LRRK2 caused a more severe parkinsonism-like phenotype than expression of equivalent levels of WT1 LRRK2. Treatment with L-DOPA improved mutant LRRK2-induced locomotor impairment but did not prevent the loss of tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)-positive neurons. To our knowledge, this is the first in vivo “gain-of-function” model which recapitulates several key features of LRRK2-linked human parkinsonism. These flies may provide a useful model for studying LRRK2-linked pathogenesis and for future therapeutic screens for PD intervention.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
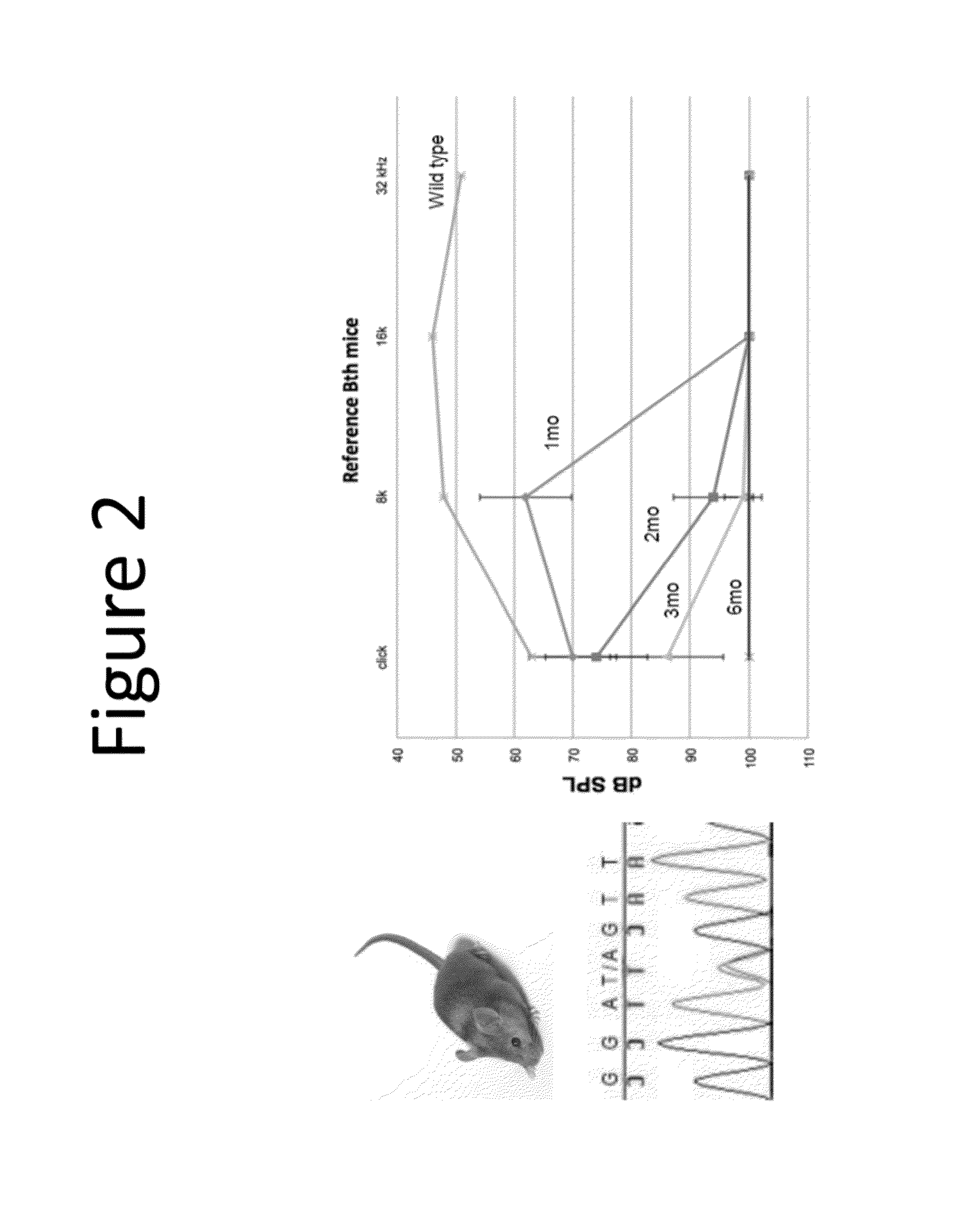
Methods to prevent and treat autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss
ActiveUS20160090597A1Organic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsAutosomal dominant traitMedicine
The present invention provides in certain embodiments a method of treating autosomal dominant non-syndromic hearing loss (ADNSHL) in a patient in need thereof comprising: (a) identifying a mutation in an ADNSHL-causing gene, (b) preparing a ADNSHL therapeutic miRNA, and (c) administering to the patient a pharmaceutical composition comprising the ADNSHL therapeutic miRNA and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier.
Owner:UNIV OF IOWA RES FOUND
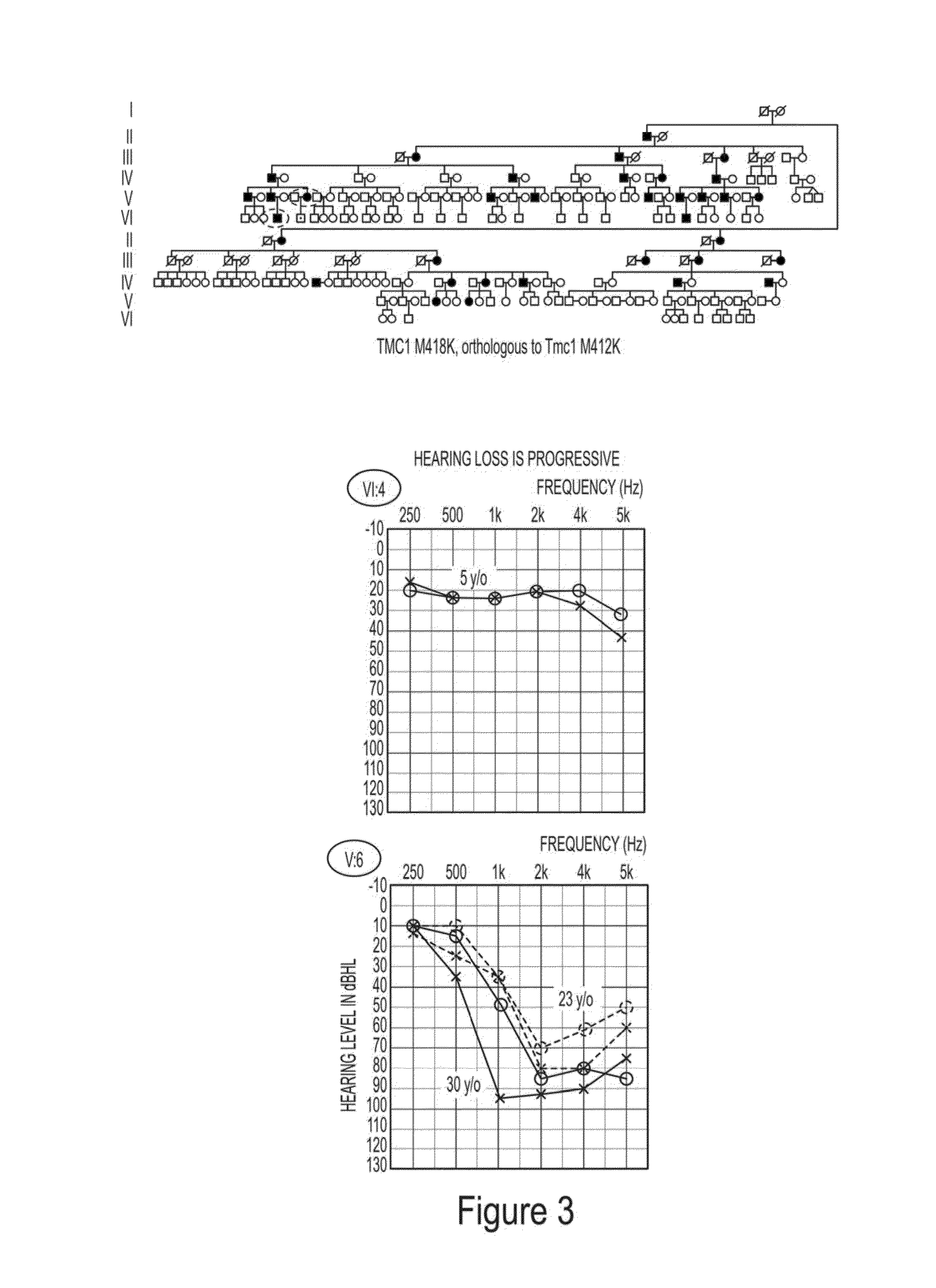
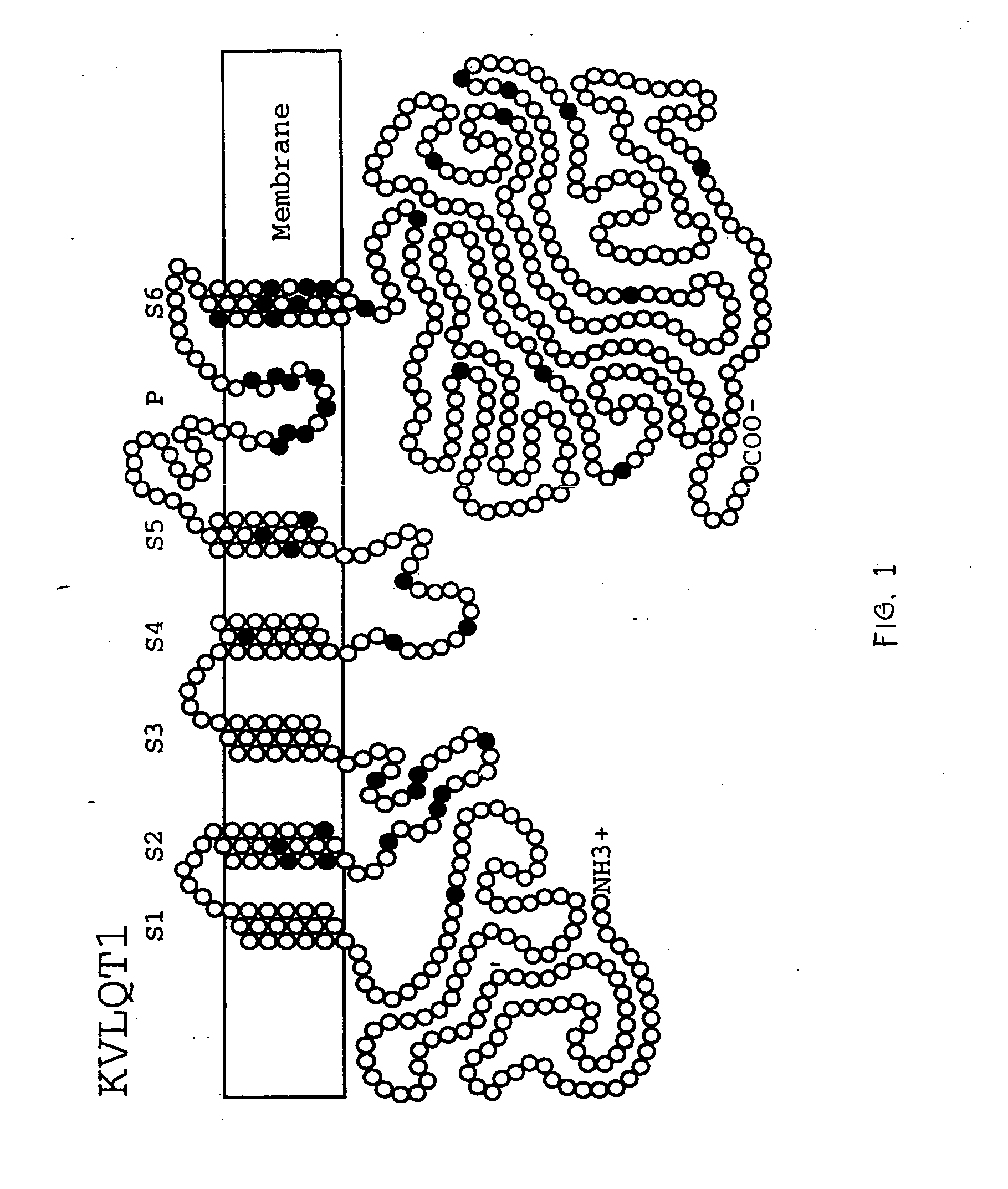
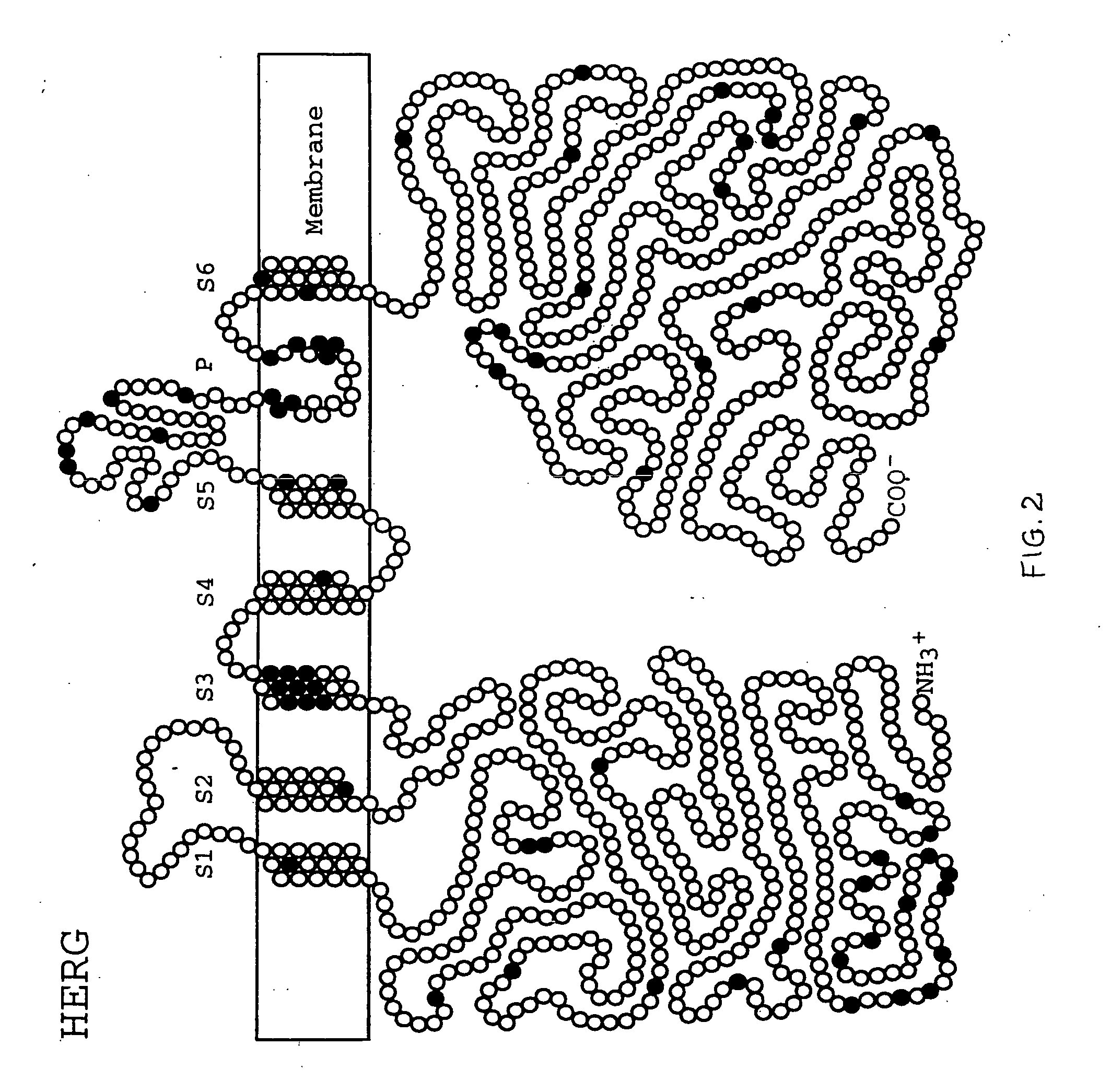
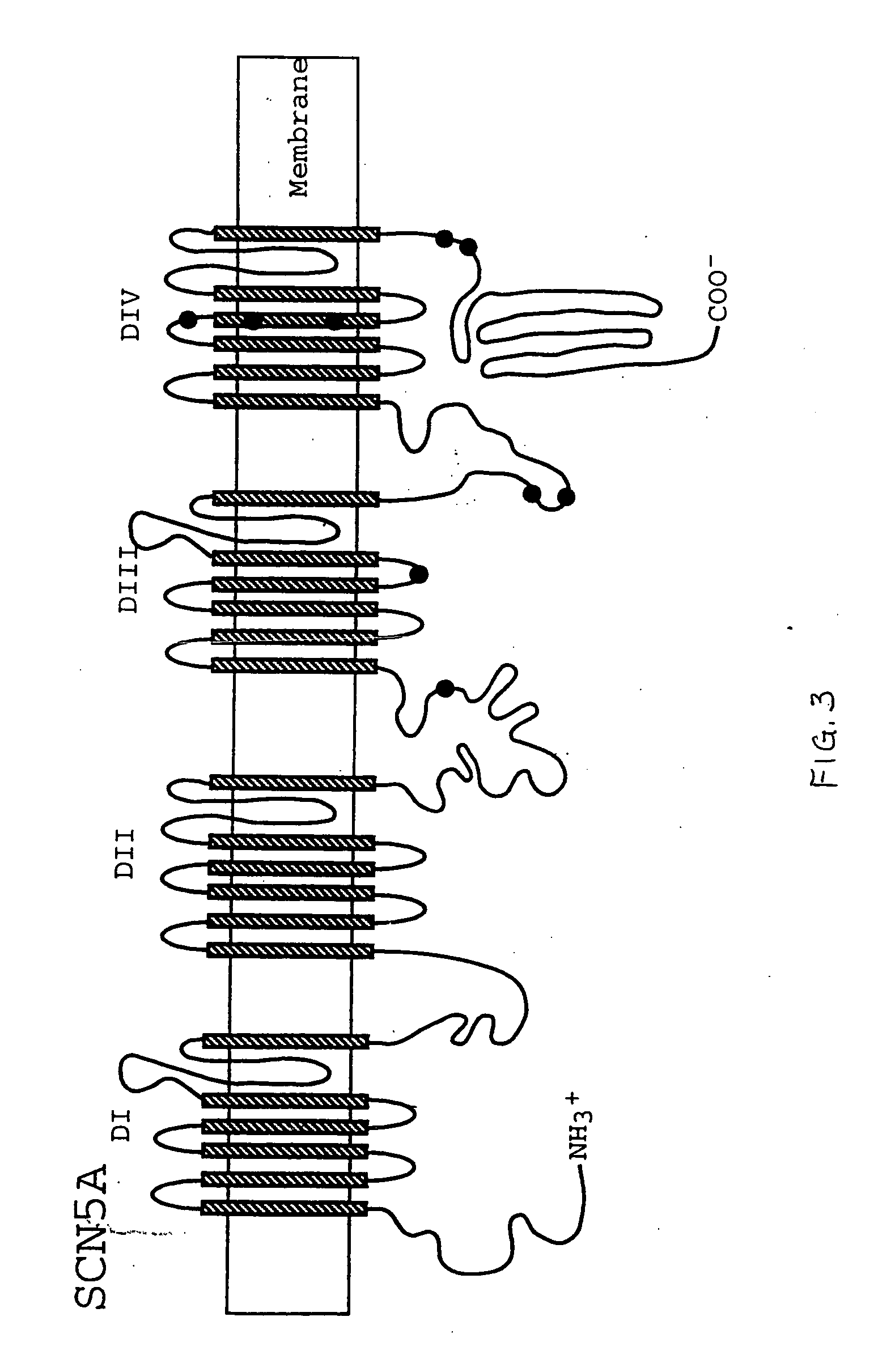
Alterations in the long QT syndrome genes KVLQT1 and SCN5A and methods for detecting same
Long QT Syndrome (LQTS) is a cardiovascular disorder characterized by prolongation of the QT interval on electrocardiogram and presence of syncope, seizures and sudden death. Five genes have been implicated in Romano-Ward syndrome, the autosomal dominant form of LQTS. These genes are KVLQT1, HERG, SCN5A, KCNE1 and KCNE2. Mutations in KVLQT1 and KCNE1 also cause the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome, a form of LQTS associated with deafness, a phenotypic abnormality inherited in an autosomal recessive fashion. Mutational analyses were used to screen 262 unrelated individuals with LQTS for mutations in the five defined genes. A total of 134 mutations were observed of which eighty were novel.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Transgenic pig model for a hereditary neurodegenerative autosomal dominant disease
The present invention discloses a non-human animal model for a hereditary autosomal dominant disease. The non-human animal model expresses at least one phenotype associated with the disease and is obtained by a genetic determinant. The invention also relates to sperm cells and embryos comprising the genetic determinant for an autosomal dominant disease. Furthermore, methods for producing the non-human animal model, sperm cell, and embryos are disclosed.
Owner:AARHUS UNIV
N-end polyclonal antibody PAPC1 of anti-human multicapsular protein-1
InactiveCN1526733AStrong specificityImprove stabilityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysisEscherichia coliFhit gene
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
FGFR inhibitor for use in the treatment of hypophosphatemic disorders
InactiveUS20150072019A1Increasing cortical bone volumeIncreasing the thicknessOrganic active ingredientsBiocideOSTEOGLOPHONIC DYSPLASIAAutosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets
The present invention relates generally to 3-(2,6-Dichloro-3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-1-{6-[4-(4-ethyl-piperazin-1-yl)-phenylamino]-pyrimid-4-yl}-1-methyl-urea or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof or a pharmaceutical composition comprising 3-(2,6-Dichloro-3,5-dimethoxy-phenyl)-1-{6-[4-(4-ethyl-piperazin-1-yl)-phenylamino]-pyrimid-4-yl)-1-methyl-urea or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof for use in the treatment of X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets (XLH), autosomal dominant hypophosphatemia rickets (ADHR), autosomal recessive hypophosphatemic rickets (ARHR), tumor-induced osteomalacia, post-renal transplant hypophosphatemia, epidermal nevus syndrome, osteoglophonic dysplasia or McCune-Albright syndrome.
Owner:NOVARTIS AG
Separated encoded IFNLR1 mutant nucleic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN109943569AEfficient screeningEasy to detectFermentationGenetic engineeringWild typeGene Mutant
The invention relates to a gene mutant and application thereof, in particular to application of a reagent for detecting a mutation site for preparing and screening out a biological sample easily infected with nonsyndromic autosomal dominant hereditary hearing loss, separated encoded IFNLR1 mutant nucleic acid, separated polypeptide, a system for screening out the biological sample easily infectedwith nonsyndromic autosomal dominant hereditary hearing loss, and a reagent kit, a construction body and reconstitution cells for screening out the biological sample with the nonsyndromic autosomal dominant hereditary hearing loss. Compared with a wild IFNLR1 gene, the separated encoded IFNLR1 mutant nucleic acid has c.296G>A mutation. By detecting whether or not the novel mutant exists in the biological sample, whether or not the biological sample is easily infected with the ADNSHL syndrome can be effectively detected.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF PLA +1
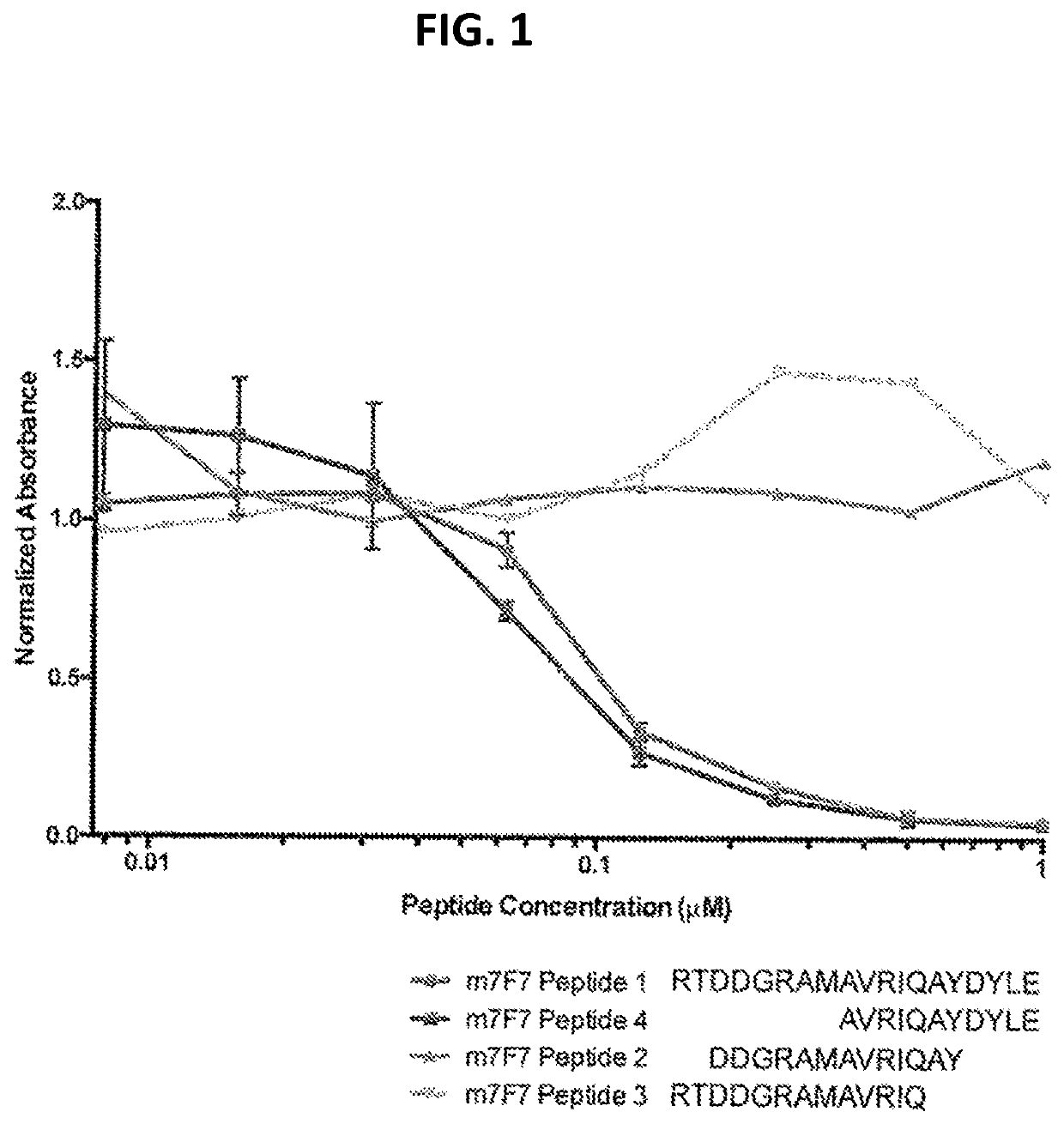
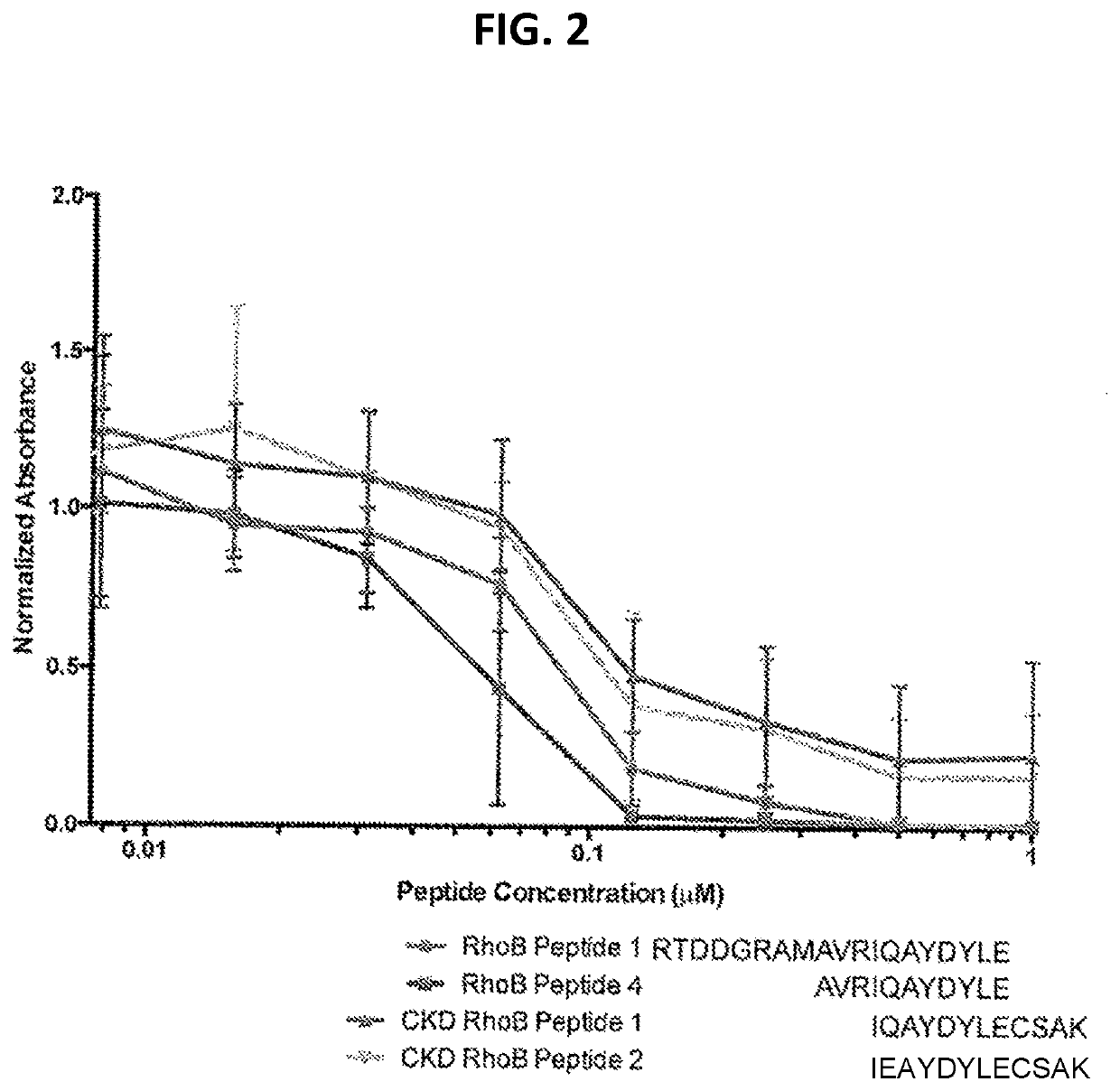
Compositions comprising ligands to rhob protein and the uses thereof
PendingUS20200200760A1Immunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisProtein profilingDisease
Methods and compositions are provided for diagnosing of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), chronic kidney diseases, kidney dysfunction, and preeclampsia in a subject, preferably in a urine sample of a human subject. The methods and compositions enable the detection or measurement in the sample or from a protein profile generated from the sample, of RhoB protein or peptide fragments thereof. Comparing the protein level(s) of the RhoB protein or peptide fragments thereof in the subject's sample with the level of the same protein or peptide(s) in a reference standard, permits the determination of a diagnosis of ADPKD and other said diseases, or the identification of a risk of developing ADPKD and other said diseases, or enables the monitoring of the status of progression or remission of ADPKD and other said diseases in the subject.
Owner:LANKENAU INST FOR MEDICAL RES
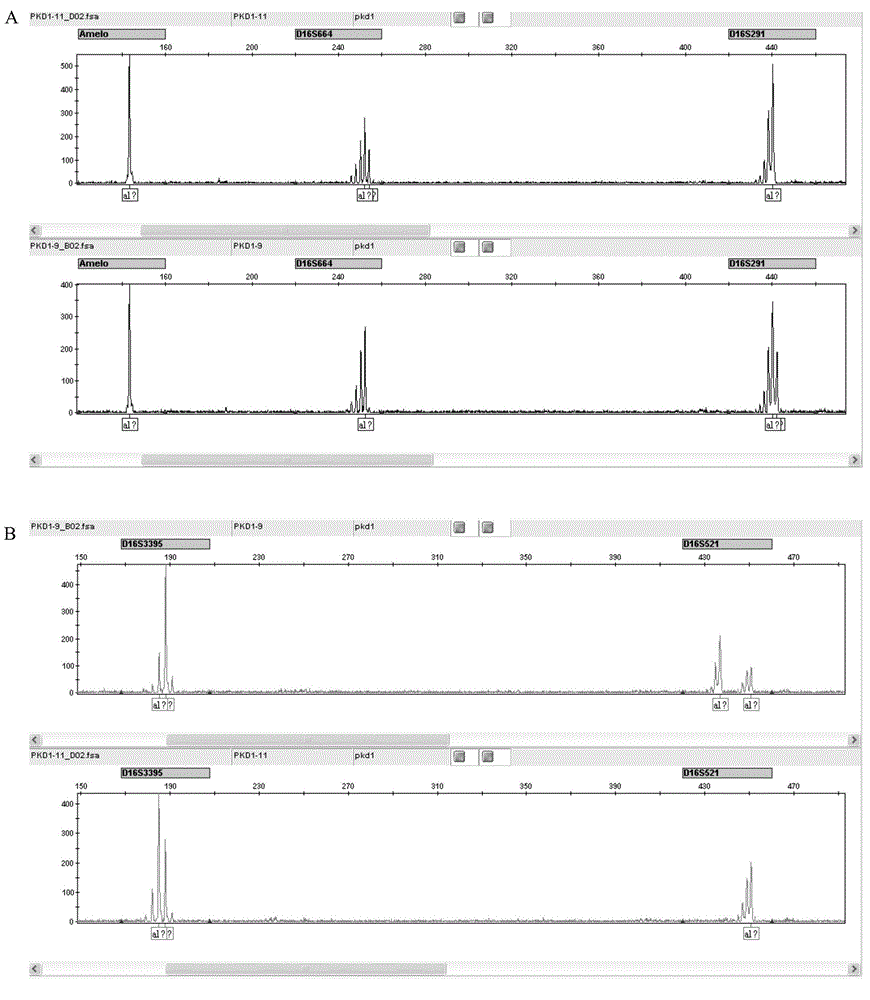
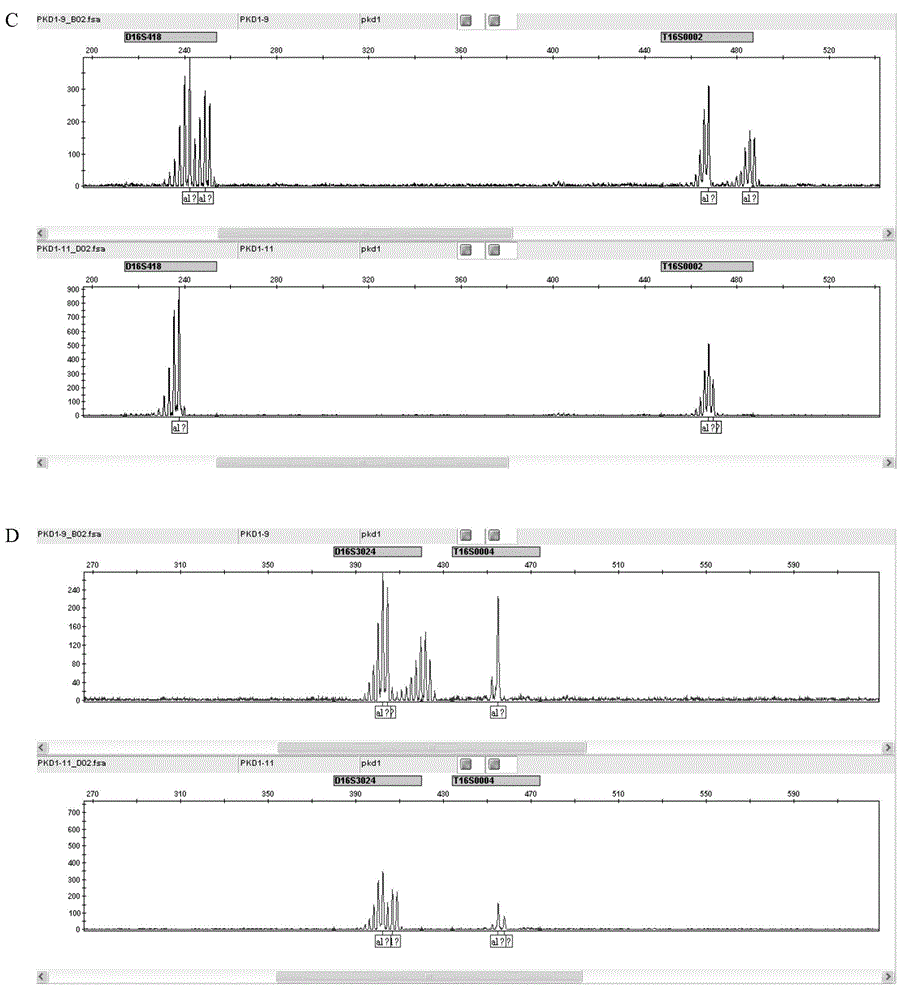
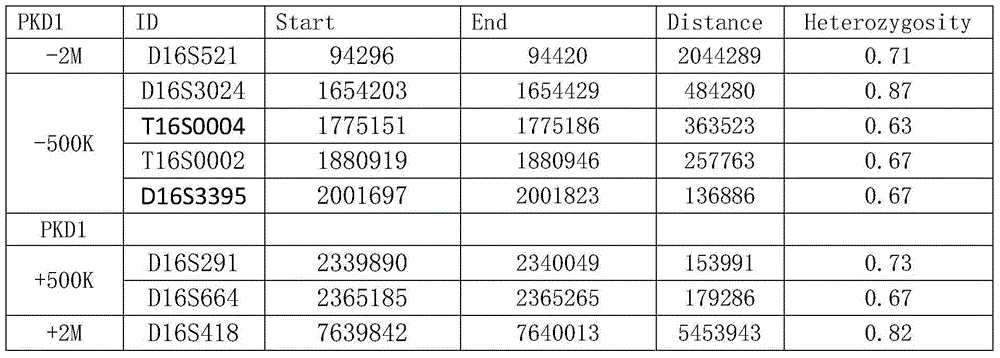
STR locus of PKD1 gene and application thereof
ActiveCN106282172AImprove compatibilityWide range of choicesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationPrenatal diagnosisNucleic acid sequencing
The invention discloses an STR locus of a PKD1 gene. The STR locus has a nucleic acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also discloses an application of the STR locus of the PKD1 gene, wherein the STR locus is applied to the preplantation genetile diagnosis or prenatal diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney. With higher resolution, the STR locus of the PKD1 gene disclosed by the invention is applied to the linkage heredity analysis of the PKD1 gene, can be used for remarkably improving the typing recognition efficiency and accuracy, and provides a basis for clinical preplantation genetile diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney.
Owner:THE INT PEACE MATERNITY & CHILD HEALTH HOSPITAL OF CHINA WELFARE INST
Detection kit for autosomal dominant inheritance polycystic kidney disease
InactiveCN1434130AIncrease the number ofAvoid mistakesMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAutosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney DiseaseHigh pressure
The present invention relates to the field of detection technology in medical molecular physiology, it is a kit for detecting autosomal dominant inheritance polycystic kidney disease. According to the structure property of pathogenic gene type A and type B of patient said invention can synthesize correspondent primer, adopt molecular physiological techonlogy and combine it with single-strand conformation polymorphism analysis method or high-pressure liquid-phase chromatography analysis method to make detection, and can directly detect out the mutant site and mutation type of pathogenic gene of the autosomal recessive inheritance polycystic kidney disease for preventing and curing said disease.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Application of berberine to preparing drug for preventing and treating familial adenomatous polyp
InactiveCN102058590AGood control effectNo obvious side effectsOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemApoptosisBiological activation
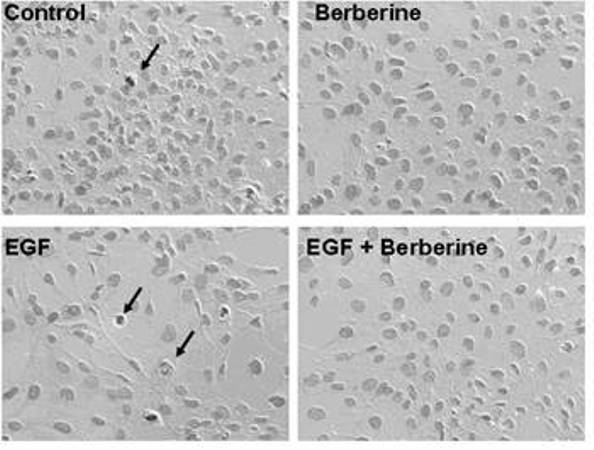
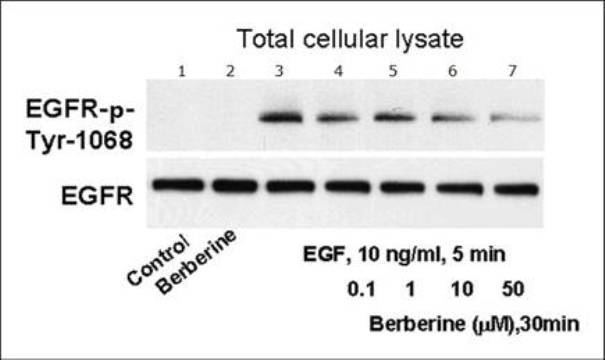
The invention relates to novel application of berberine, in particular to application of the berberine to preparing a drug for preventing and treating familial adenomatous polyp (FAP). The FAP is an autosomal dominant hereditary disease which is characterized by multiple adenomatous polyps in the digestive tract, mainly comprises CFAP (Classical Familial Adenomatous Polyp) and AFAP (Attenuated Familial Adenomatous Polyp) and is not rare in clinic; and early intervention is significant. In the invention, the applied berberine can bring inhibitory action to the cell growth of colon cancer cells and FAP cell line (IMCE), wherein the mechanism includes inhibiting cell proliferation, promoting apoptosis, down regulating expression of COX-2 and AP-1, inhibiting synthesis of PGE2 (Prostaglandin E2) and activation of EGFR (Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor) and Akt and brings out well effect when applied to FAP patients in a long term. The invention provides a novel safe, effective, and economic method for preventing and treating the FAP.
Owner:GENERAL HOSPITAL OF TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
Pig SOX10 mutant gene causing inner ear hypoplasia and application of pig SOX10 mutant gene
The invention relates to a pig SOX10 mutant gene causing inner ear hypoplasia and an application of the pig SOX10 mutant gene. The pig SOX10 mutant gene is characterized in that the 321st basic groupcytosine C of an SOX10 gene coding region is subjected to replication (SOX10 c.321 dupC), the mutation can cause infertility of the inner ear and is autosomal dominant inheritance, and can be used forpathogenesis, prevention, diagnosis and treatment research of infertility of the inner ear of a human body. The pig SOX10 mutant gene can be used for preparation of a disease animal model with incomplete development of the inner ear. The model can be used for research on pathogenesis, prevention, diagnosis and treatment on human inner ear hypoplasia, and is of great significance to research on inner ear hypoplasia.
Owner:ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
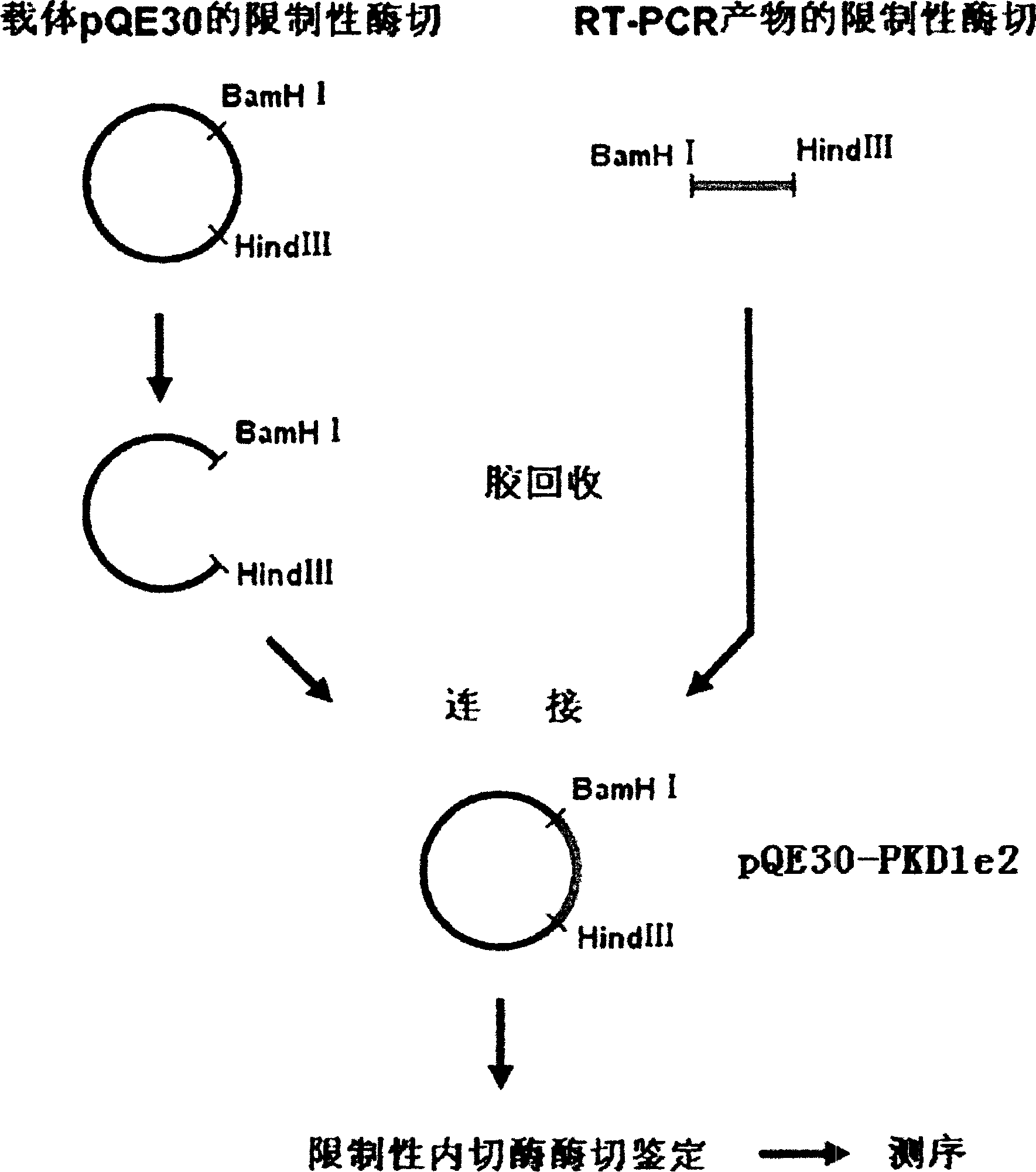
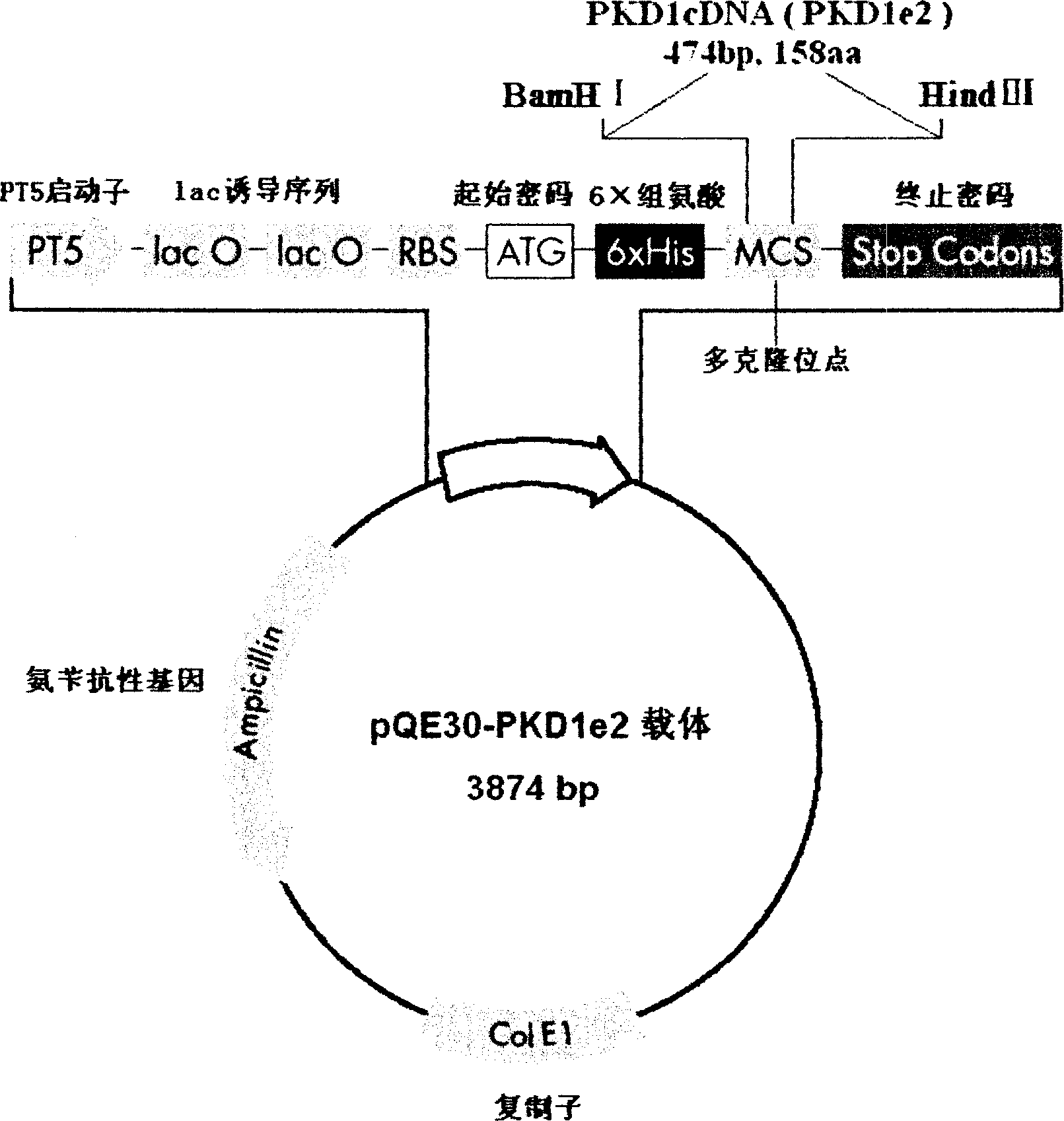
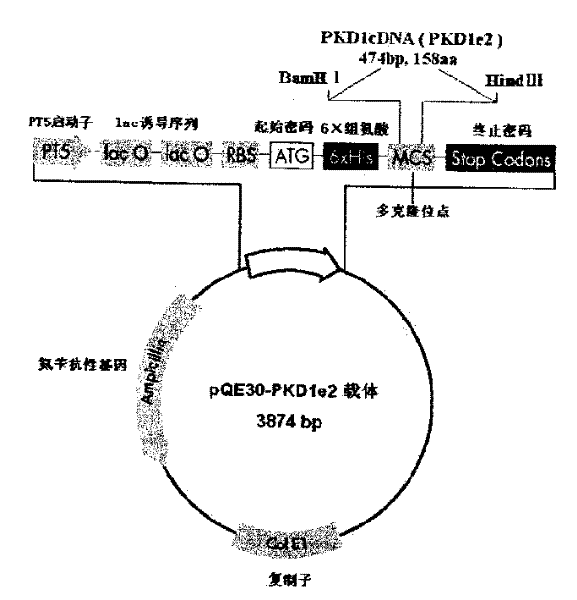
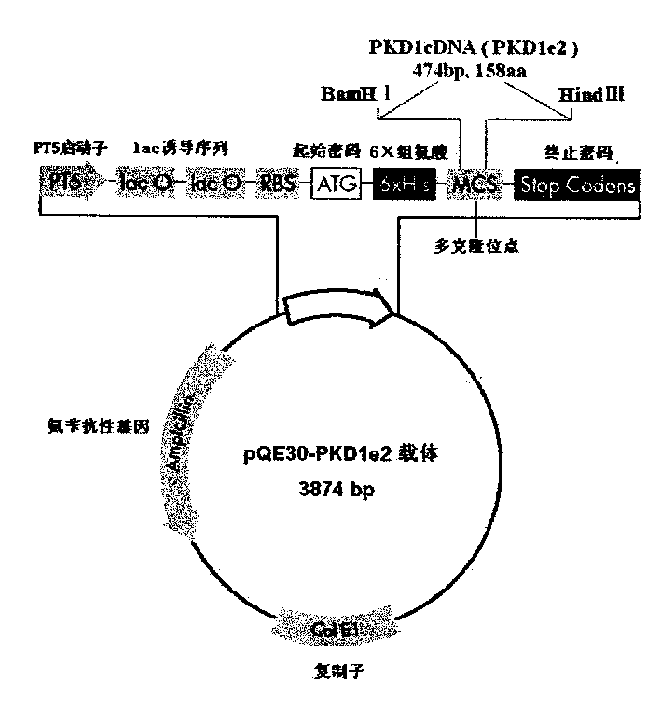
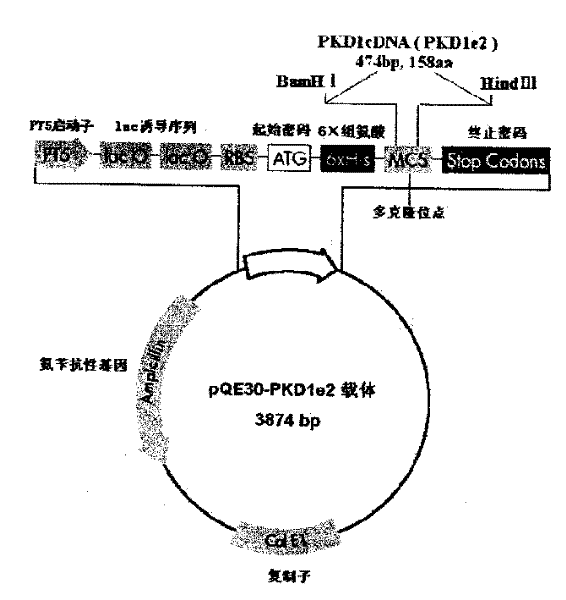
N-end fusion protein PC-1-e2 of human multicapsular protein-1
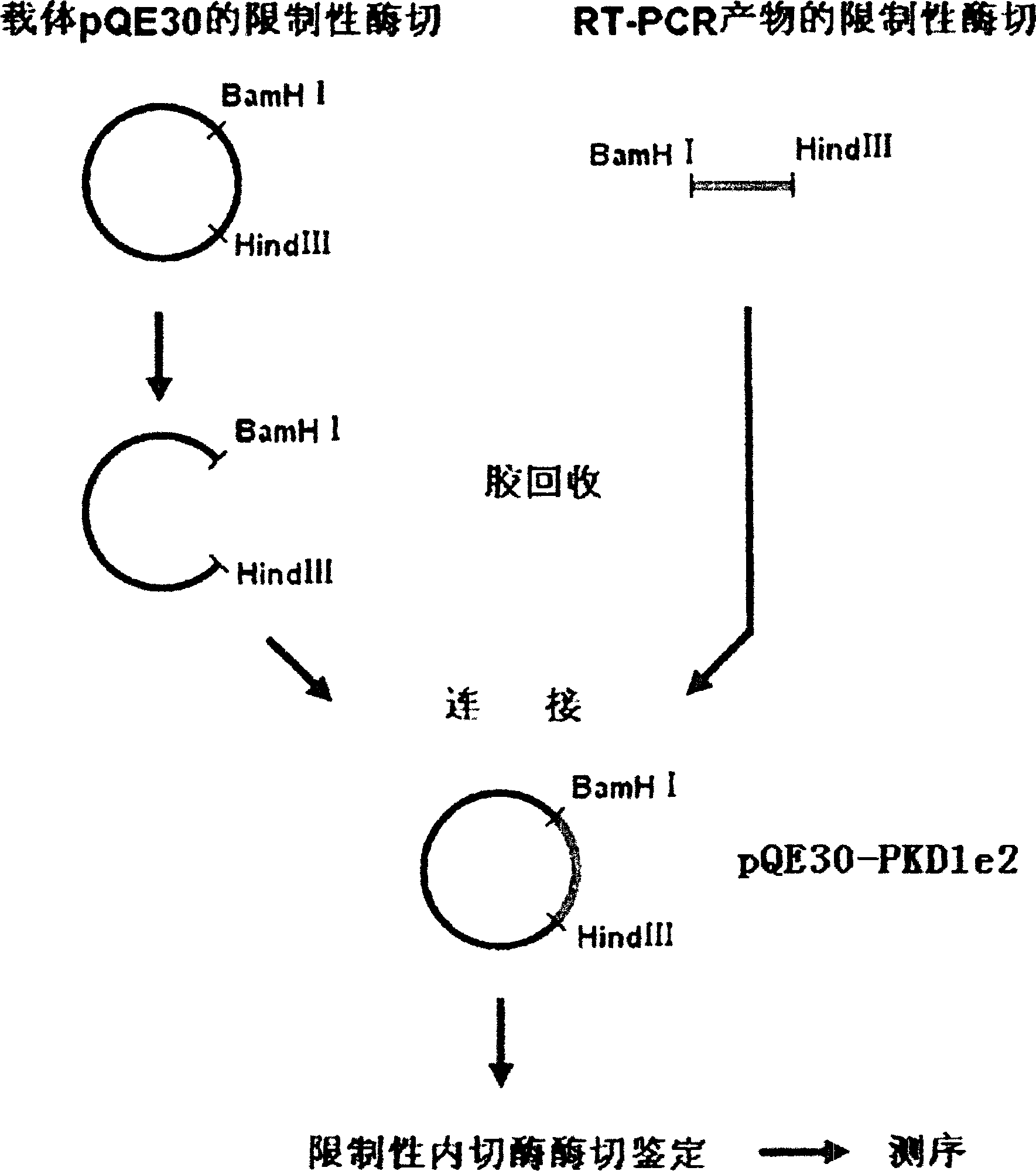
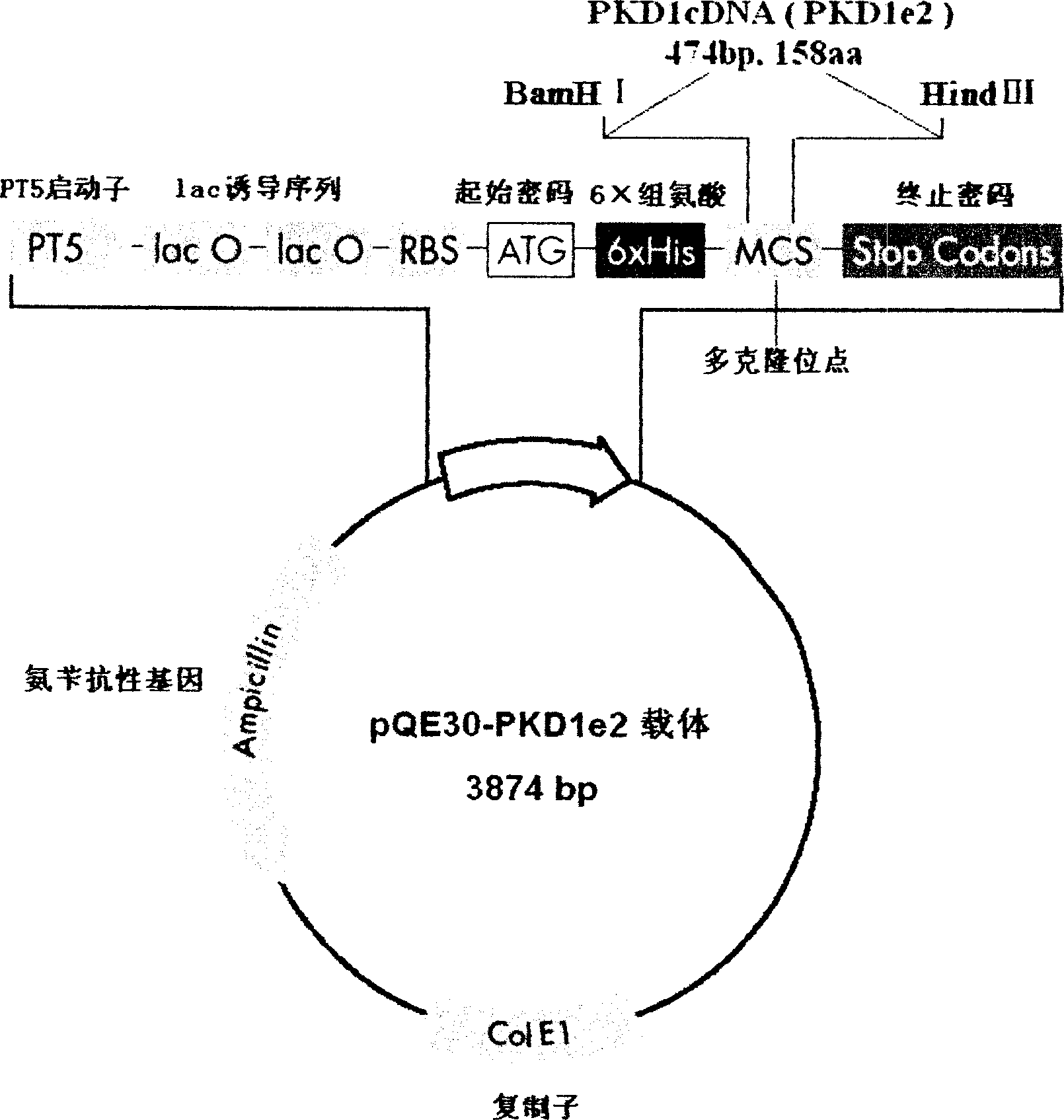
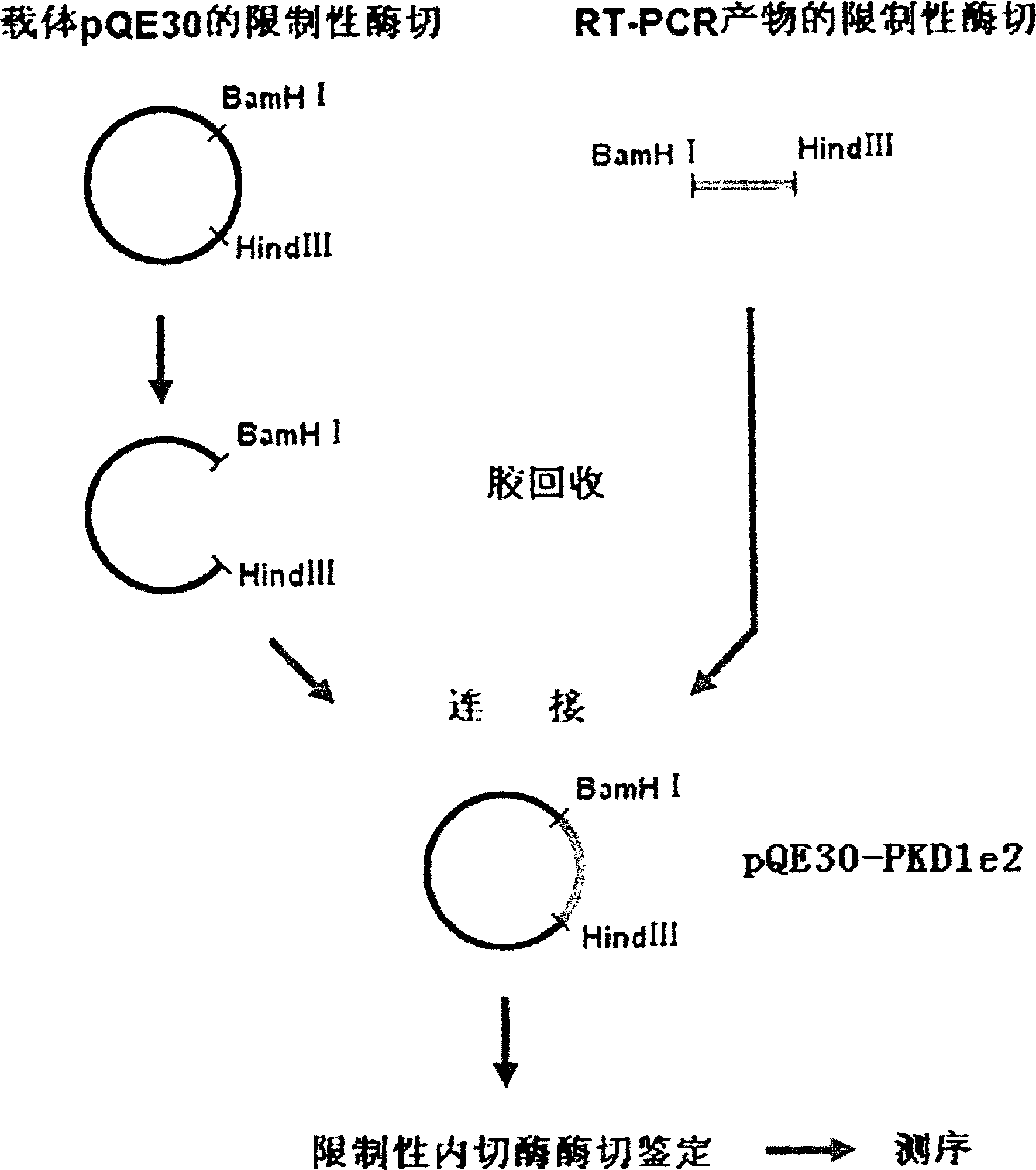
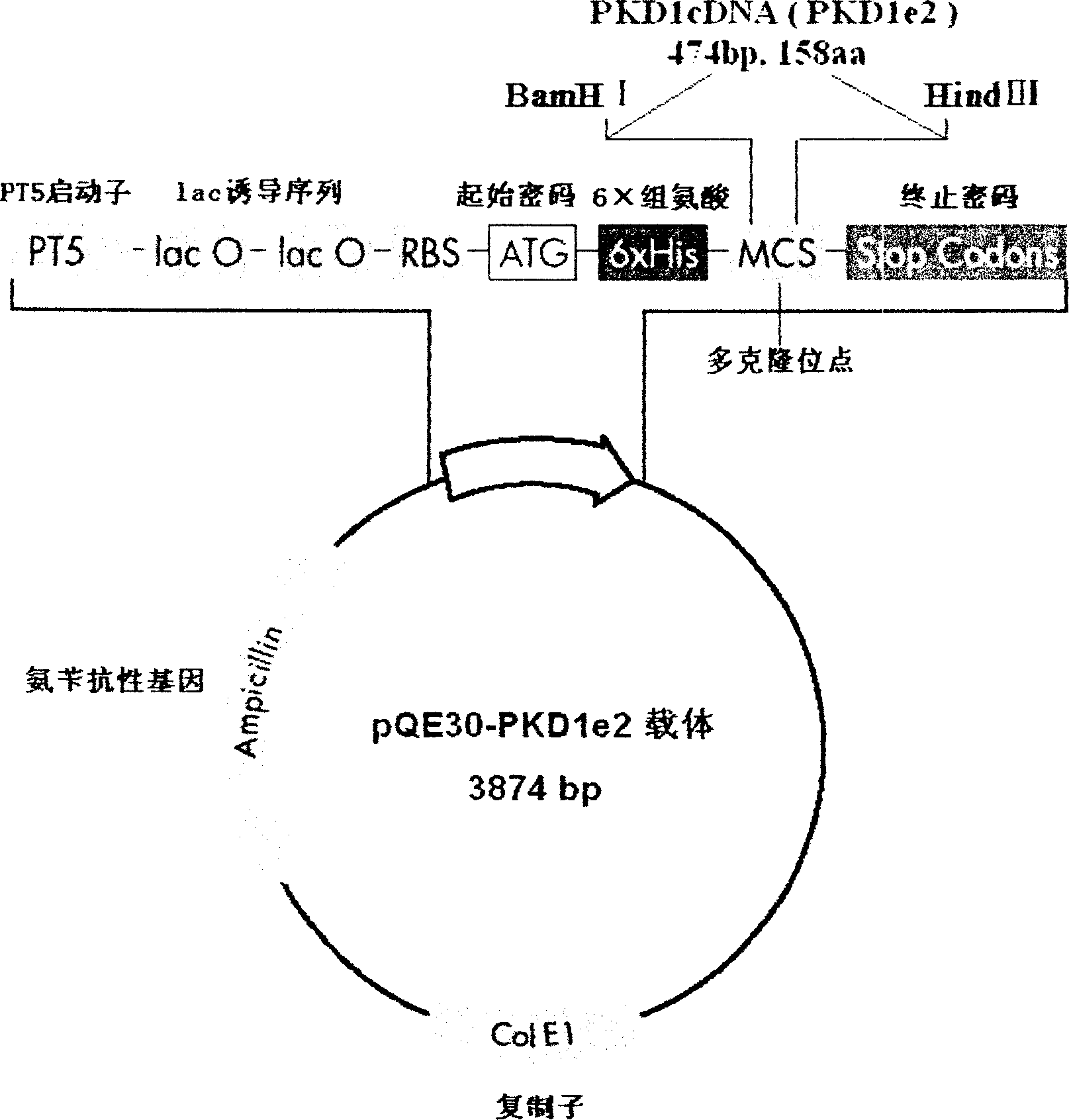
InactiveCN1526736ALow costNo obvious side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansEscherichia coliRenal Tubular Epithelial Cells
The present invention relates to medicine molecular biology engineering technology, and is one kind of 1N-end fusion protein PC-1-e2 of human polycystic protein-1. According to cDNA sequence of human polycystic kidney disease-1 gene and the molecular structure of its encoded product, polycystic protein-1 (PC-1), the gene is cloned to cDNA-PKD1e2 in the N end of the protein and its prokaryotic expression carrier pQE30-PKD1e2 is constituted by means of molecular biology engineering technology. N-end fusion protein PC-1-e2 of PC-1 is induced in colibacillus. Cytobiology experiment shows that the fusion protein has obvious inhibition to the proliferation of the epidermis cell line of in vitro cultured human polycystic kidney cyst lining and the epidermis cell strain of far end renal tubule in dog kidney, so that it may be used in preparing medicine for treating autosomal dominant hereditary polycystic kidney disease, the reagent for the mechanism research of the disease, and anti-PC-1 antibody.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
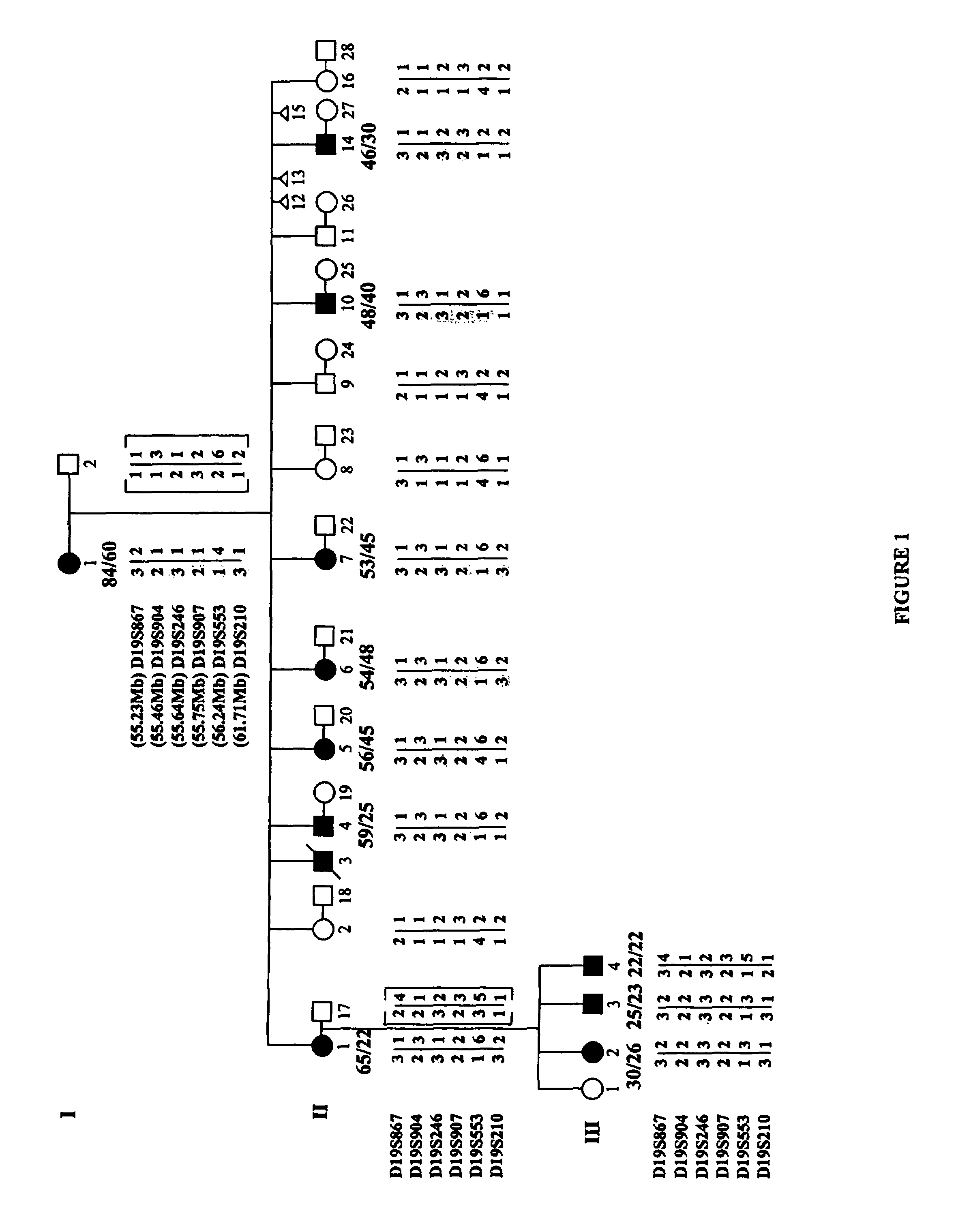
Compositions and methods for spinocerebellar ataxia
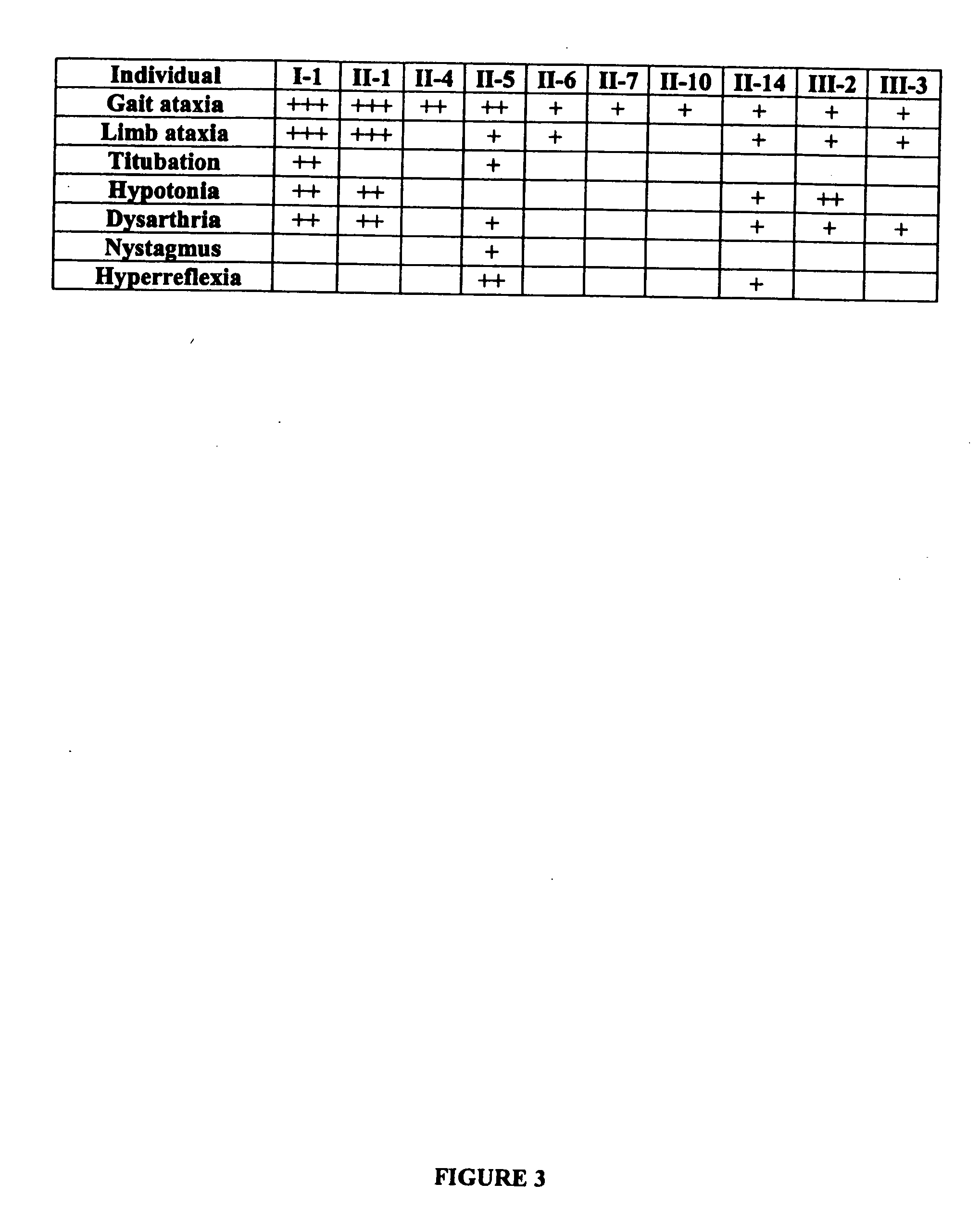
ActiveUS20060292604A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyAutosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia
The autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs) represent a growing and heterogeneous clinical phenotype with ongoing discovery of causative etiologies. Methods: The authors collected DNA and clinically characterized a three-generation Filipino family segregating a dominant ataxia. Following elimination of several known SCA loci, a genome-wide linkage study was undertaken with additional fine mapping of 19q13. Results: Clinical characterization of affected family members revealed cerebellar signs including gait ataxia, limb ataxia / dysmetria, titubation, hypotonia, dysarthria, and nystagmus. Linkage was found in a ˜4 cM region of 19q13 bounded by markers D19S867 and D19S553, with a maximum LOD score of 3.89 at markers D19S904, D19S246, and D19S907. This region overlaps with, though markedly reduces the previously described SCA13 locus. Conclusion: An autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia clinically distinguishable from SCA13 overlaps with the SCA13 locus on chromosome 19q13.3.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Primer and kit for detecting dominant hereditary cerebral artery disease related gene and application
InactiveCN106148504AGood for clinical diagnosisReduce typesMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationForward primerDisease
The invention provides a primer pair, a primer and kit for detecting a dominant hereditary cerebral artery disease related gene and application. The primer pair consists of a forward primer provided with a sequence shown by SEQIDNo.1 or its sequence and a reverse primer provided with a sequence shown in SEQIDNo.2 or its homologous sequence. The primer is applicable to detection of autosomal dominant genetic disease cerebral arteries (CADASIL) related genes of subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy and judgment whether the p.C201Y loci of a NOTCH3 gene mutates or not, and a reference is provided for clinical diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI NINTH PEOPLES HOSPITAL SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
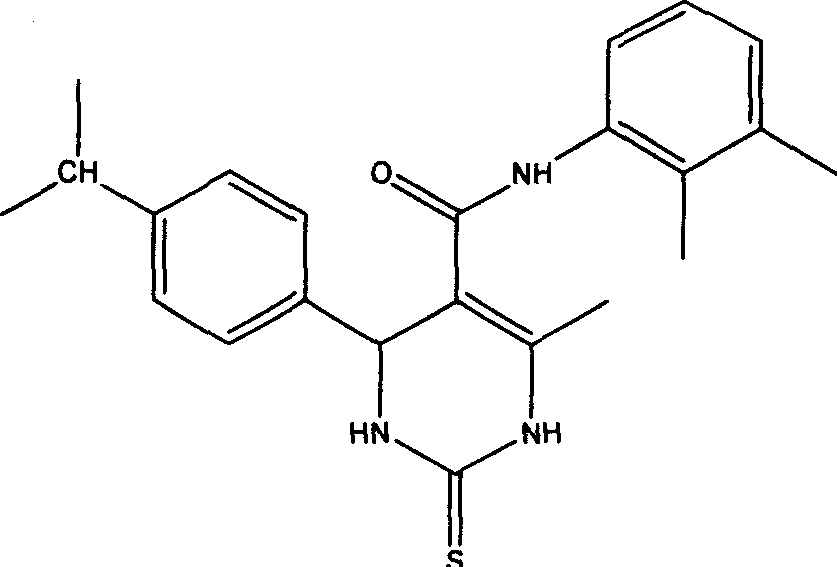
Application of pyrimidone compounds in preparing medicine
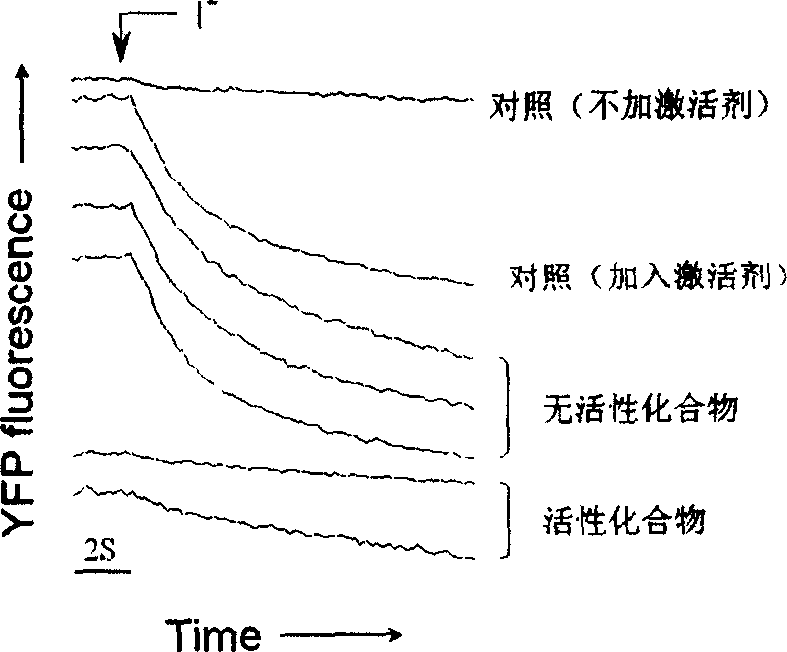
InactiveCN1739521AAct quicklyObvious in vivo toxic effectsOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemDiarrheaPolycystic kidney
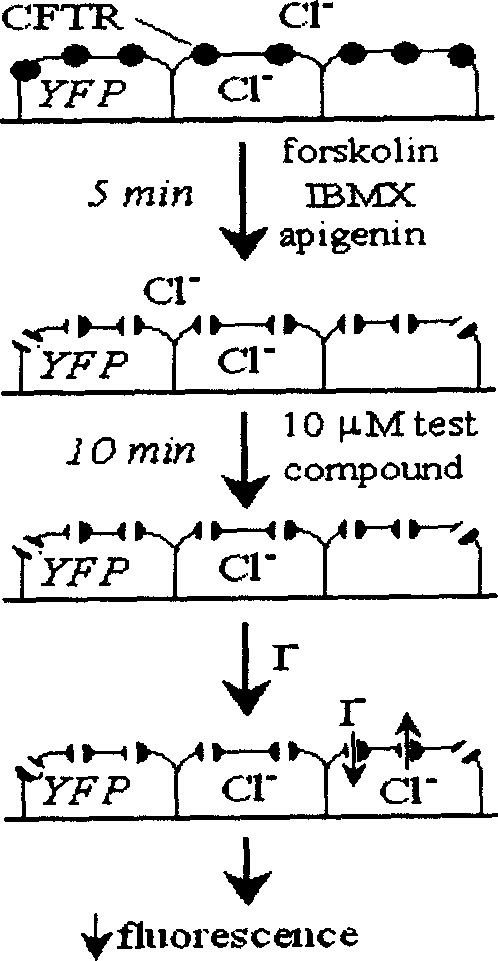
The present invention relates to the application of pyrimidone compounds in preparing medicine for treating secreted diarrhea and autosomal dominant inheritance polycystic kidney disease. Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) factor is one kind of chloridion channel protein activated with cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and during designing model, several CFTR activating ways are considered and applied in the screening process, so as to screen out pyrimidone compounds to prepare medicine for treating secreted diarrhea and autosomal dominant inheritance polycystic kidney disease. The present invention can prevent and treat swine diarrhea effectively and inhibit the liquid secretion of epidermis cell of autosomal dominant inheritance polycystic kidney cyst lining, without obvious toxicity.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
N-end monoclonal antibody MA7B1 of anti-human multicapsular protein-1
InactiveCN1526734AStrong specificityImprove stabilityImmunoglobulins against animals/humansMaterial analysisEscherichia coliFhit gene
The present invention relates to medicine molecular biology and immulogical detection technology, and is one kind of 1N-end monoclonal antibody MA7B1 of anti-human polycystic protein-1. According to cDNA sequence of human polycystic kidney disease-1 gene and the molecular structure of its encoded product, polycystic protein-1 (PC-1), the gene is cloned to cDNA encoding PC-1 and its prokaryotic expression carrier is constituted by means of molecular biology technology. N-end fusion protein of PC-1 is induced in colibacillus and anti-PC-1 N-end monoclonal antibody MA7B1 is prepared by means of hybrid tumor technology. Comprehensive performance test shows that the antibody has stable performance, high sensitivity and powerful specificity in immunohistochemistry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, immunoblotting and immunoprecipiation experiments, so that it may be used in preparing reagent for polycystic kidney disease mechanism research.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Methods for treating polycystic kidney disease and polycystic liver disease
ActiveUS20150105361A1Reduces and avoids symptom and causeGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemPhysiologyCyst
The present invention provides compounds of Formula (I) or (II), which are thought to be able to inhibit mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin) signaling pathway, induce UPR (unfolded protein response), and / or perturb mitochondrial function of a cyst cell (e.g., a cyst cell causing polycystic kidney disease (PKD, e.g., autosomal dominant PKD (ADPKD) or autosomal recessive PKD (ARPKD)) or polycystic liver disease (PLD, e.g., autosomal dominant PLD (ADPLD) or autosomal recessive PLD (ARPLD)). The invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions, kits, and methods involving the compounds described herein for use in treating PKD or PLD, inhibiting the growth of a cyst cell, and / or killing a cyst cell.
Owner:YALE UNIV +1
Compositions and methods for spinocerebellar ataxia
ActiveUS7585629B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEtiologyAutosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia
The autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxias (SCAs) represent a growing and heterogeneous clinical phenotype with ongoing discovery of causative etiologies. Methods: The authors collected DNA and clinically characterized a three-generation Filipino family segregating a dominant ataxia. Following elimination of several known SCA loci, a genome-wide linkage study was undertaken with additional fine mapping of 19q13. Results: Clinical characterization of affected family members revealed cerebellar signs including gait ataxia, limb ataxia / dysmetria, titubation, hypotonia, dysarthria, and nystagmus. Linkage was found in a ˜4 cM region of 19q13 bounded by markers D19S867 and D19S553, with a maximum LOD score of 3.89 at markers D19S904, D19S246, and D19S907. This region overlaps with, though markedly reduces the previously described SCA13 locus. Conclusion: An autosomal dominant cerebellar ataxia clinically distinguishable from SCA13 overlaps with the SCA13 locus on chromosome 19q13.3.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT
Reagent composition and detection method for detecting autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
PendingCN114480603ASolve puzzlesThe experimental method is simpleMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsGenomic DNA
The reagent composition for detecting the autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease comprises a primer group, a first reagent for extracting genomic DNA from a sample; the second reagent is used for carrying out long fragment PCR reaction by using the primer group; a third agent for processing the amplification product such that the amplification product can be used in a high-throughput sequencing technique; and the fourth reagent is used for performing high-throughput sequencing on the treated amplification product. Comprising the following steps: S1, amplifying a PKD1 gene by using a reagent composition according to any one of claims 1-7 through long-fragment PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction); s2, performing high-throughput sequencing on the amplified sequence obtained in the step (1); s3, comparing the sequencing result obtained in the step (2) with a PKD1 gene reference sequence, and determining a mutation site; s4, eliminating false gene locus interference through bioinformatics analysis, and determining a PKD1 true gene mutation locus; and S5, comparing the true gene mutation site determined in the step S4 with a known PKD1 gene mutation site, and determining a new mutation site on the PKD1 gene.
Owner:广州源古纪科技有限公司
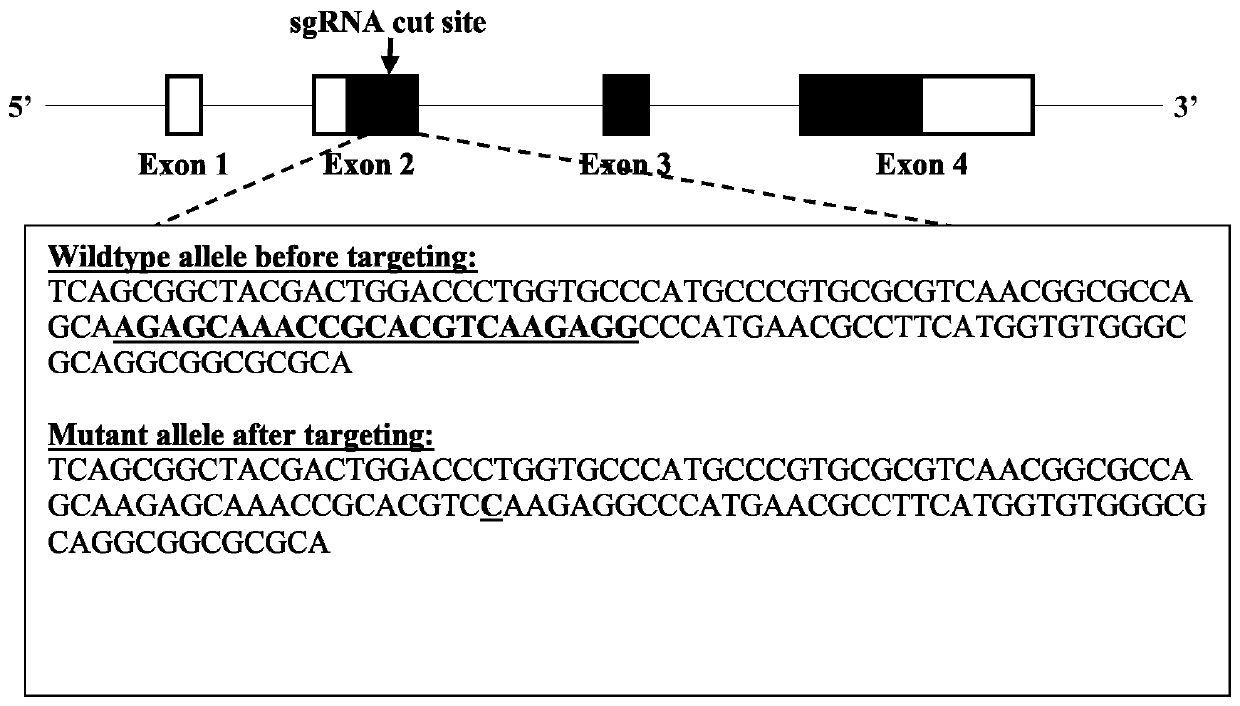
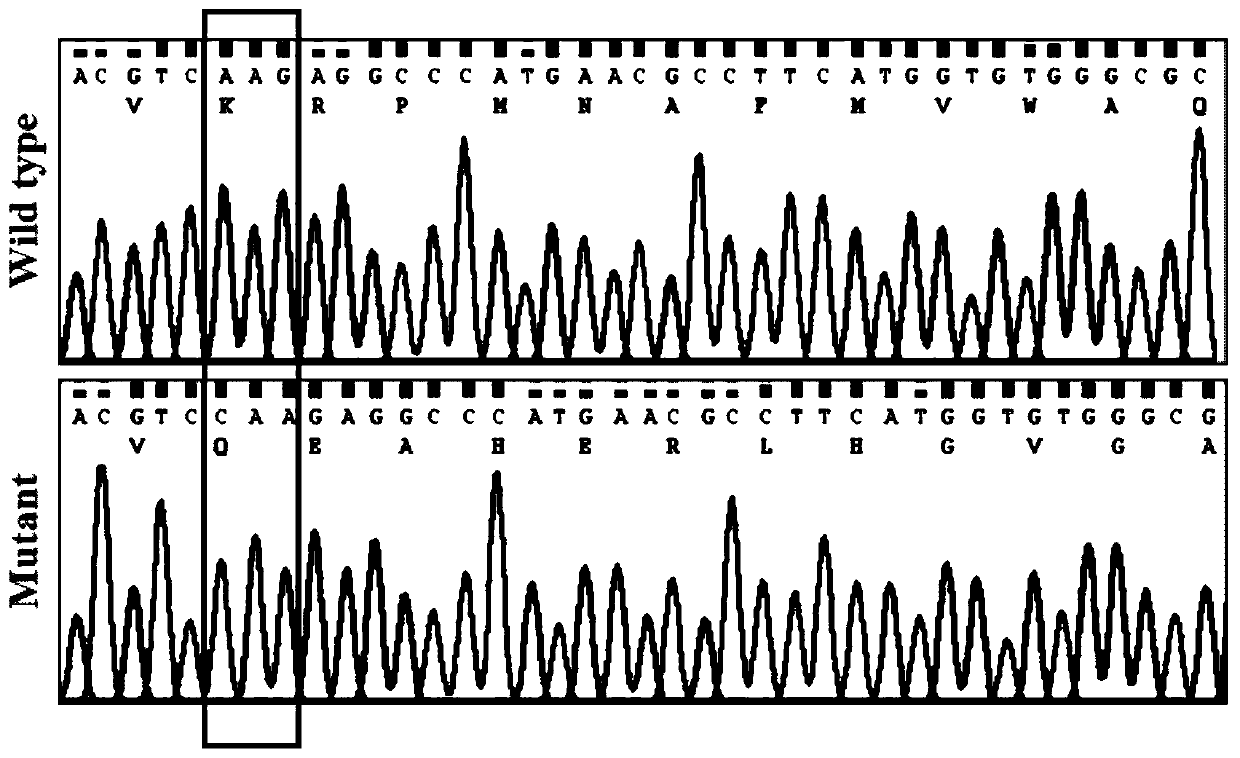
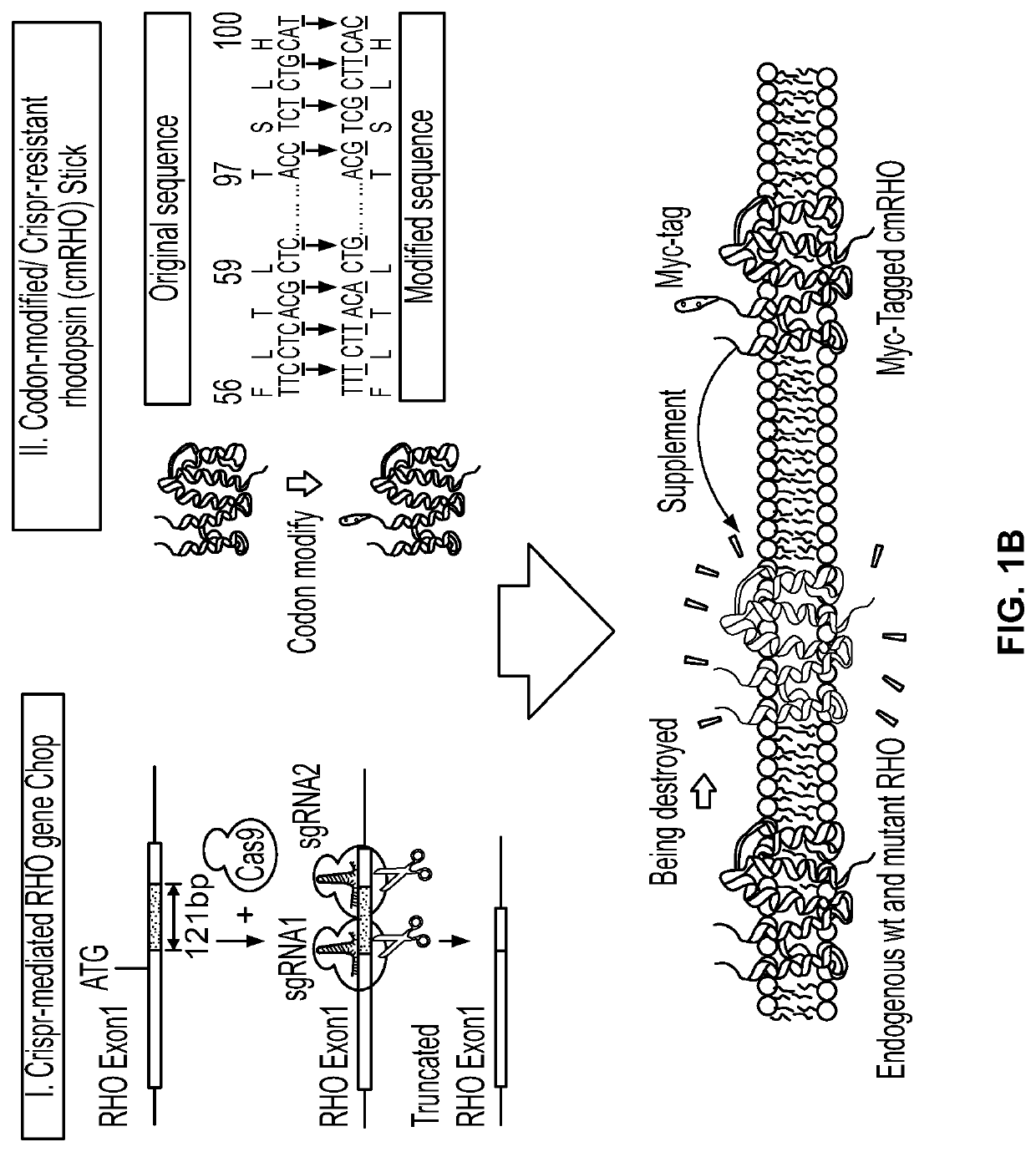
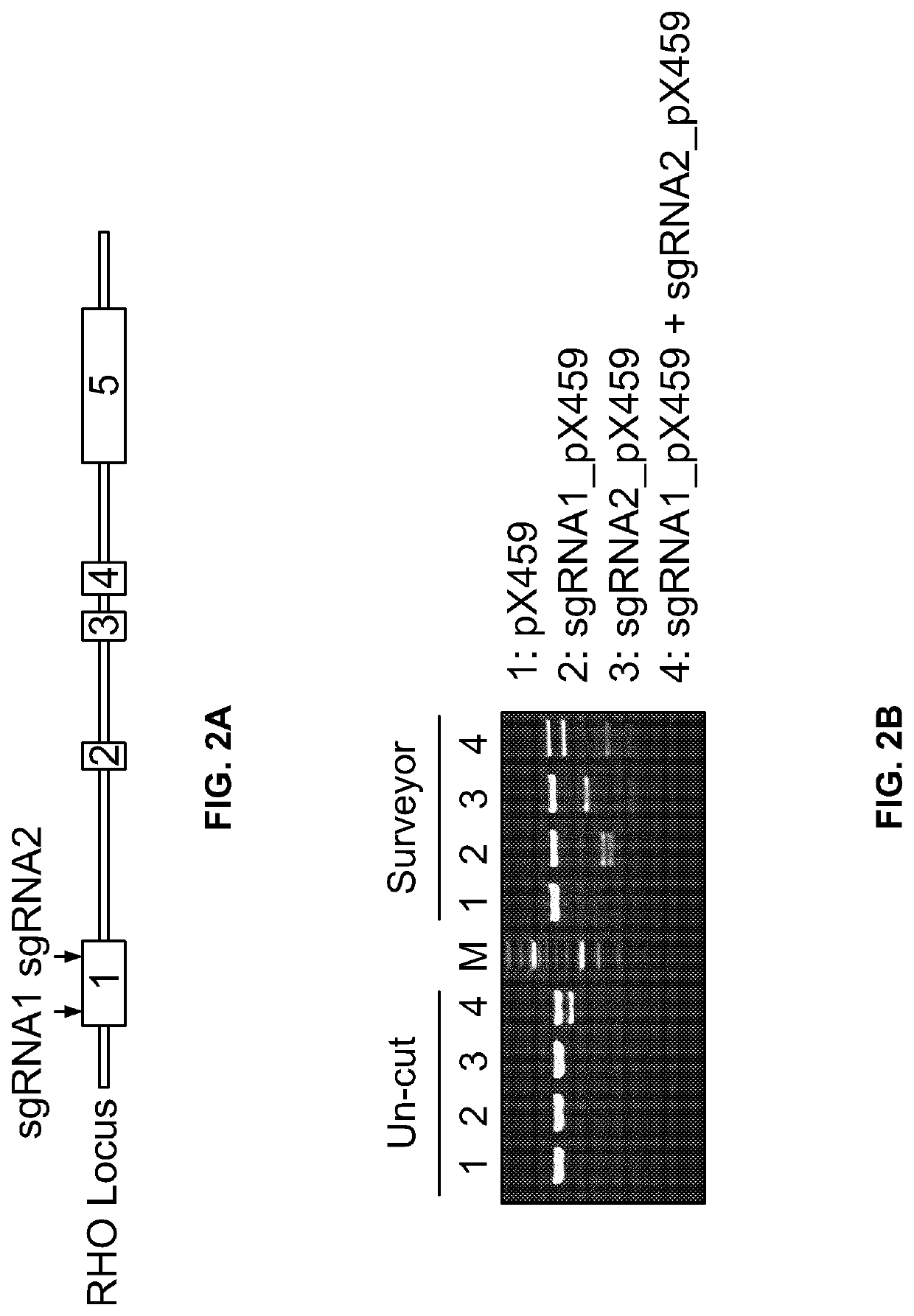
Gene Editing for Autosomal Dominant Diseases
The present disclosure provides methods for treating autosomal dominant diseases in a subject. In some aspects, the methods involve the use of a gene editing enzyme with a pair of unique guide RNA sequences that targets both mutant and wildtype forms of autosomal dominant disease-related gene for destruction in cells, and then supplying the cells with wildtype autosomal dominant disease-related gene cDNA which is codon modified to evade recognition by the guide RNAs. These methods are broadly applicable to any autosomal dominant disease.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
New uses of Shh signaling pathway inhibitor
InactiveCN106138050AReduce the degree of renal fibrosisReduce the degree of renal cystOrganic active ingredientsUrinary disorderCreatinine riseIsrapafant
The present invention discloses new uses of a Shh signaling pathway inhibitor. The new uses of the Shh signaling pathway inhibitor specifically comprises applications of the Shh signaling pathway inhibitor in preparation of autosomal domi-nant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) treatment product, wherein the Shh signaling pathway inhibitor is specifically Vismodegib. According to the present invention, a Vil-Cre:Pkd2f3 / f3 mouse as an ADPKD animal model, and the results show that with the Shh signaling pathway inhibitor Vismodegib, the renal cyst degree of the Vil-Cre:Pkd2f3 / f3 mouse can be reduced, the kidney weight ration of the Vil-Cre:Pkd2f3 / f3 mouse can be reduced, the contents of creatinine and urea nitrogen in the blood of the Vil-Cre:Pkd2f3 / f3 mouse can be reduced, and the renal fibrosis degree of the Vil-Cre:Pkd2f3 / f3 mouse can be reduced; and the important significance is provided for the analysis of the ADPKD pathogenesis and the research and development of the ADPKD treatment drug.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com