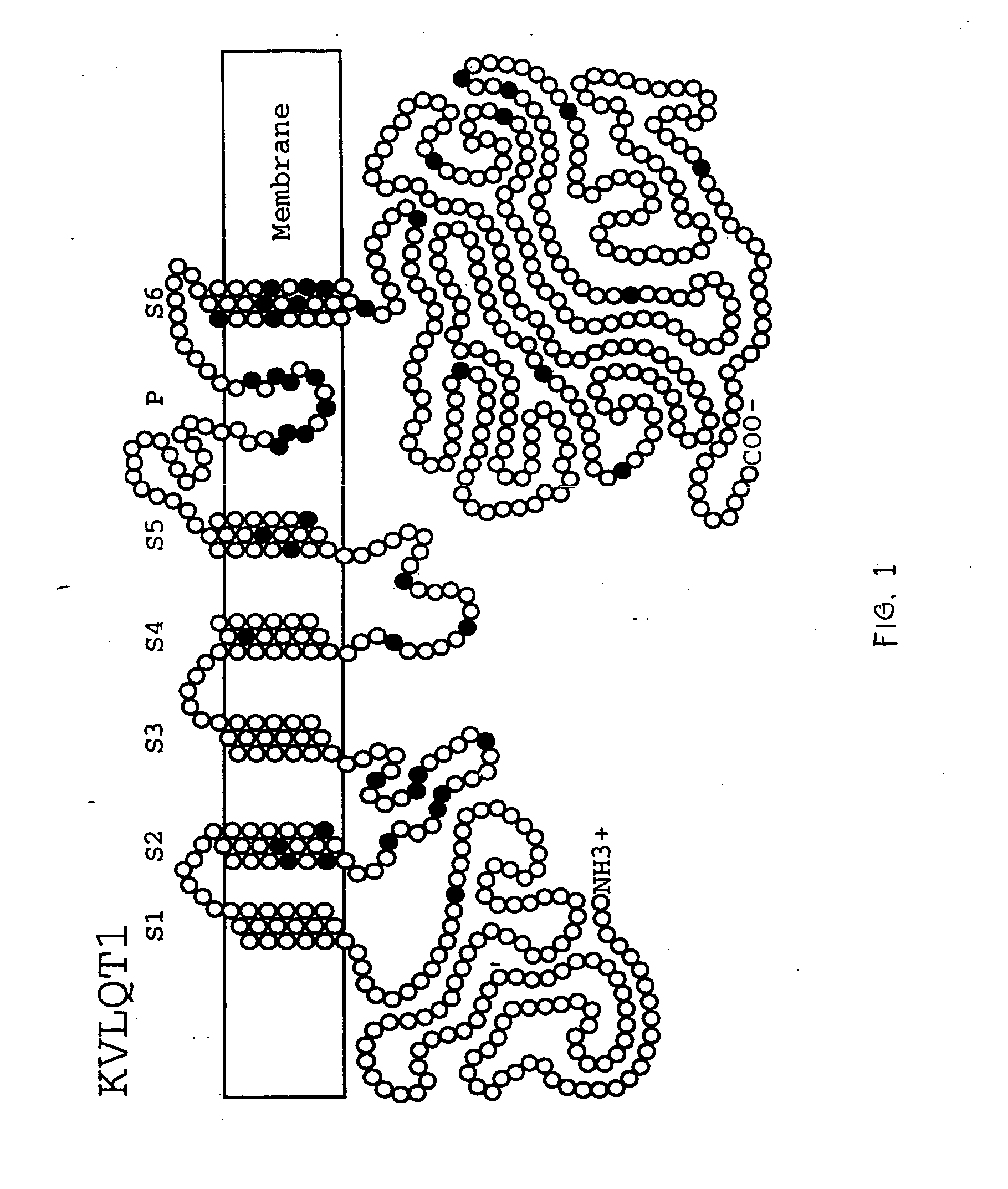
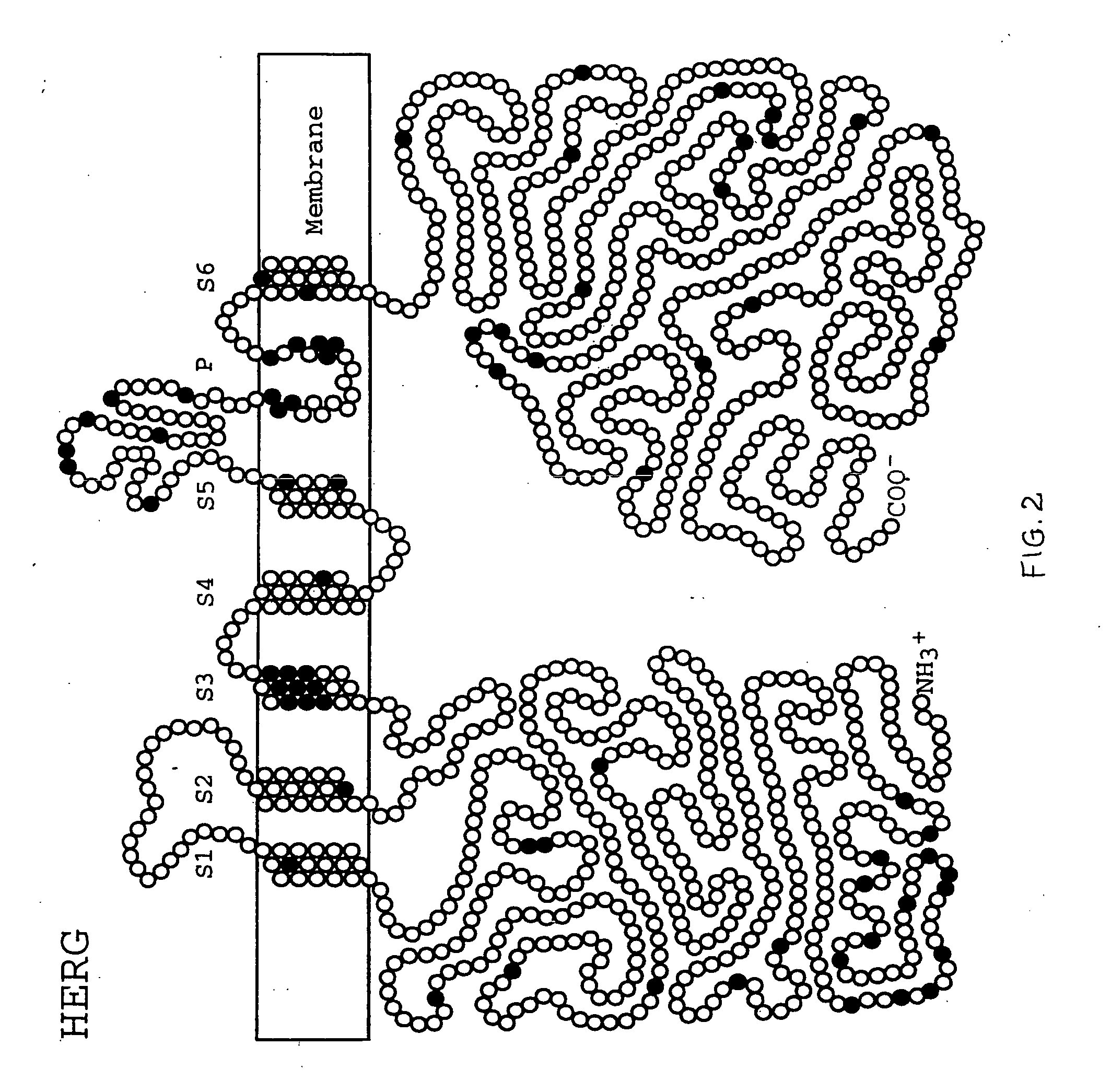
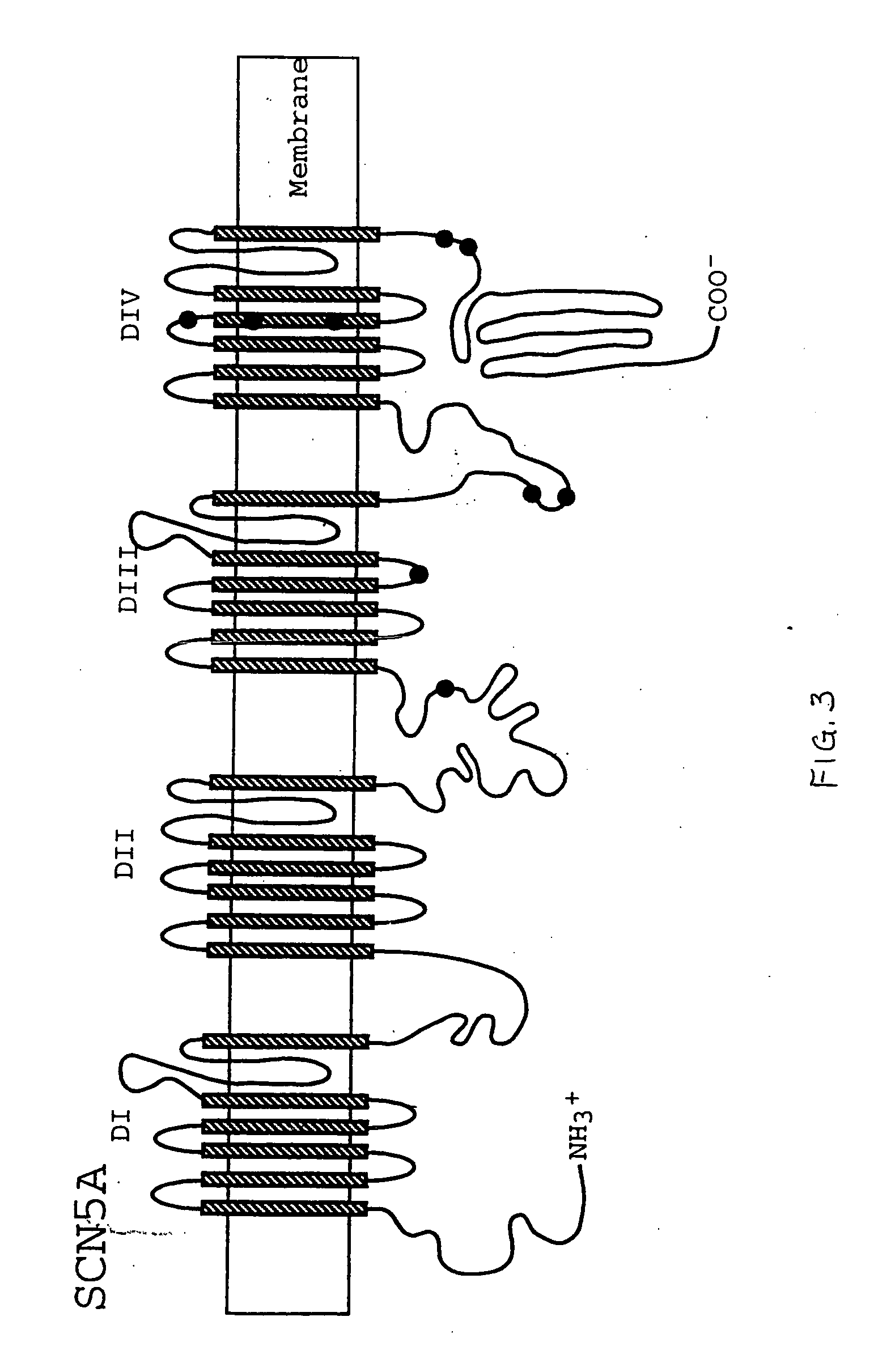
Alterations in the long QT syndrome genes KVLQT1 and SCN5A and methods for detecting same
a technology of kvlqt1 and scn5a, which is applied in the field of alterations in the long qt syndrome, can solve the problems of increasing the risk of arrhythmia, prolonging the cardiac action potential, and prolonging the qt interval
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Ascertainment and Phenotyping
[0061] Individuals were ascertained in clinics from North America and Europe. Individuals were evaluated for LQTS based on QTc (the QT interval corrected for heart rate) and for the presence of symptoms. In this study, we focused on the probands. Individuals show prolongation of the QT interval (QTc≧460 ms) and / or documented torsade de pointes, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest or aborted sudden death. Informed consent was obtained in accordance with local institutional review board guidelines. Phenotypic data were interpreted without knowledge of genotype. Sequence changes altering coding regions or predicted to affect splicing that were not detected in at least 400 control chromosomes were defined as mutations. No changes except known polymorphisms were detected ina ny of the genes in the control population. This does not exclude the possibility that some mutations are rare variants not associated with disease.
example 2
Mutational Analyses
[0062] To determine the spectrum of LQTS mutations, we used SSCP (Single Stand Conformation Polymorphism) and DNA sequence analyses to screen 262 unrelated individuals with LQTS. Seventeen primer pairs were used to screen KVLQT1 (Splawski et al., 1998), twenty-one primer pairs were used for HERG (Splawski et al., 1998) and three primer pairs were used for KCNE1 (Splawski et al., 1997a) and KCNE2 (Abbott et al., 1999). Thirty-three primer pairs (Wang Q. et al., 1996b) were used in SSCP analysis to screen all SCN5A exons in 50 individuals with suspected abnormalities in INa. Exons 23-28, in which mutations were previously identified, were screened in all 262 individuals.
[0063] Gender, age, QTc and presence of symptoms are summarized in Table 1. The average age at ascertainment was 29 with a corrected QT interval of 492 ms. Seventy-five percent had a history of symptoms and females predominated with an˜2:1 ratio. Although the numbers were small, corrected QT interv...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| electrophoretic mobility | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| nucleic acid amplification | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| acid | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com