Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
44results about How to "Uniform temperature profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
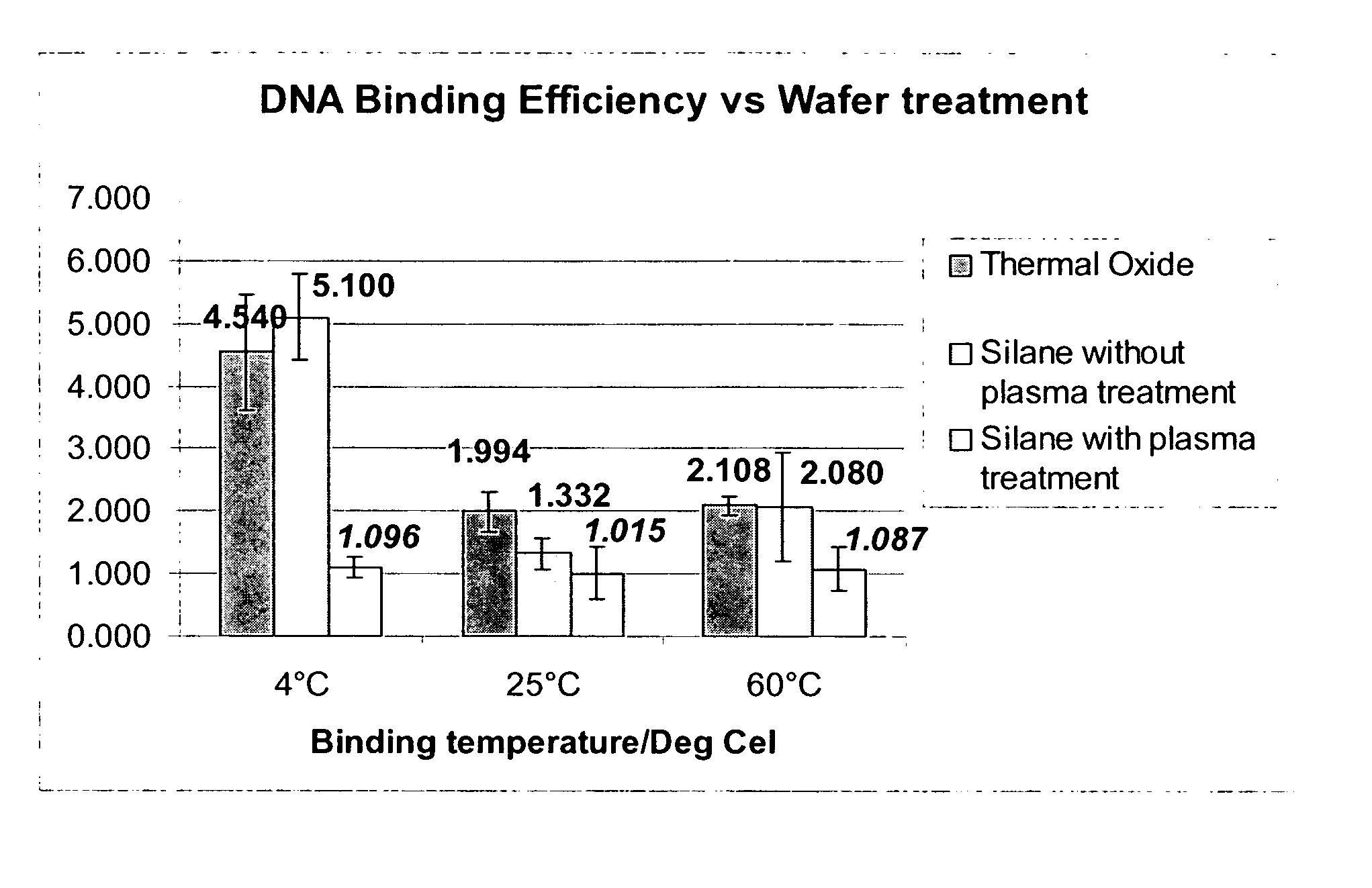
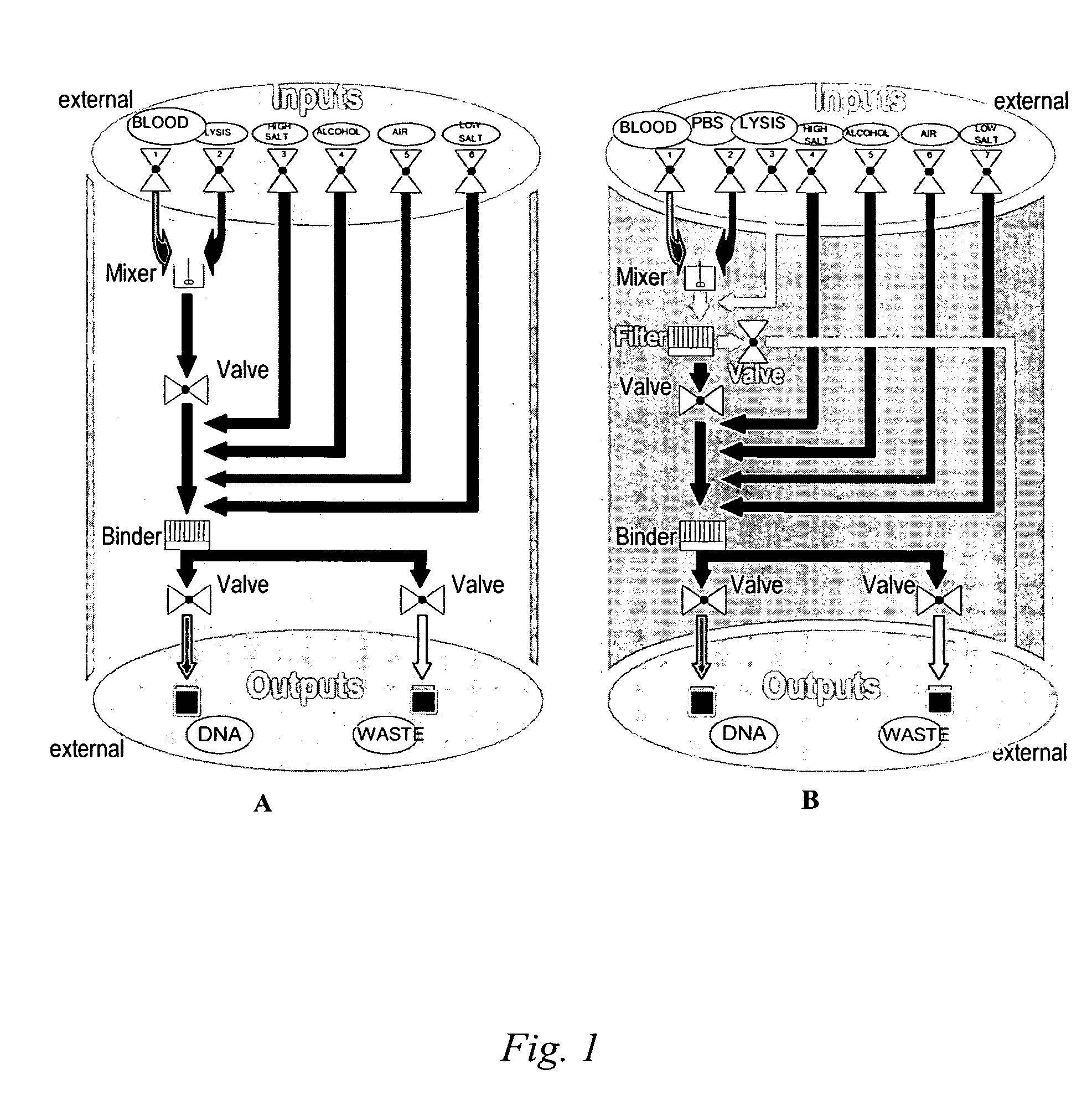
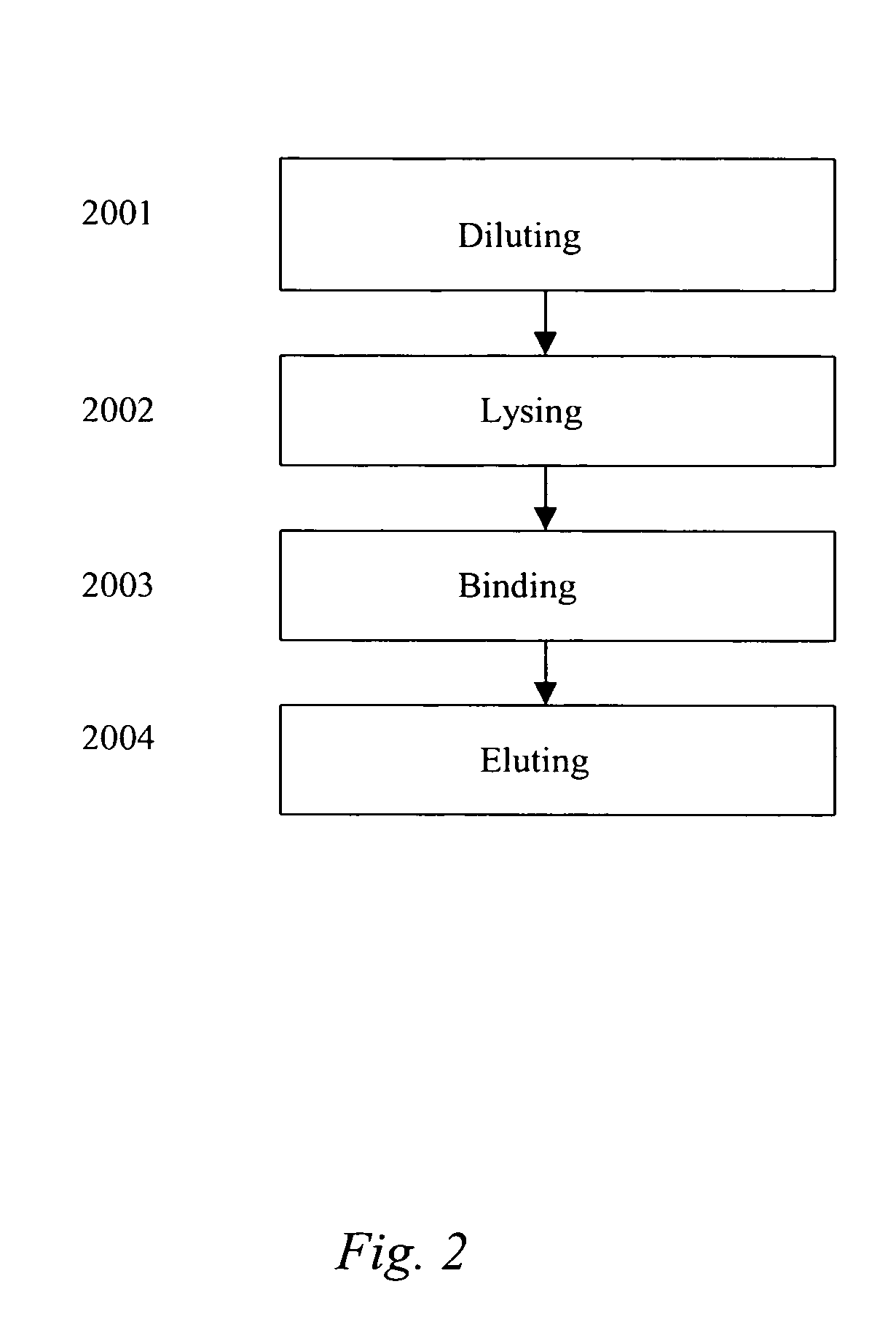
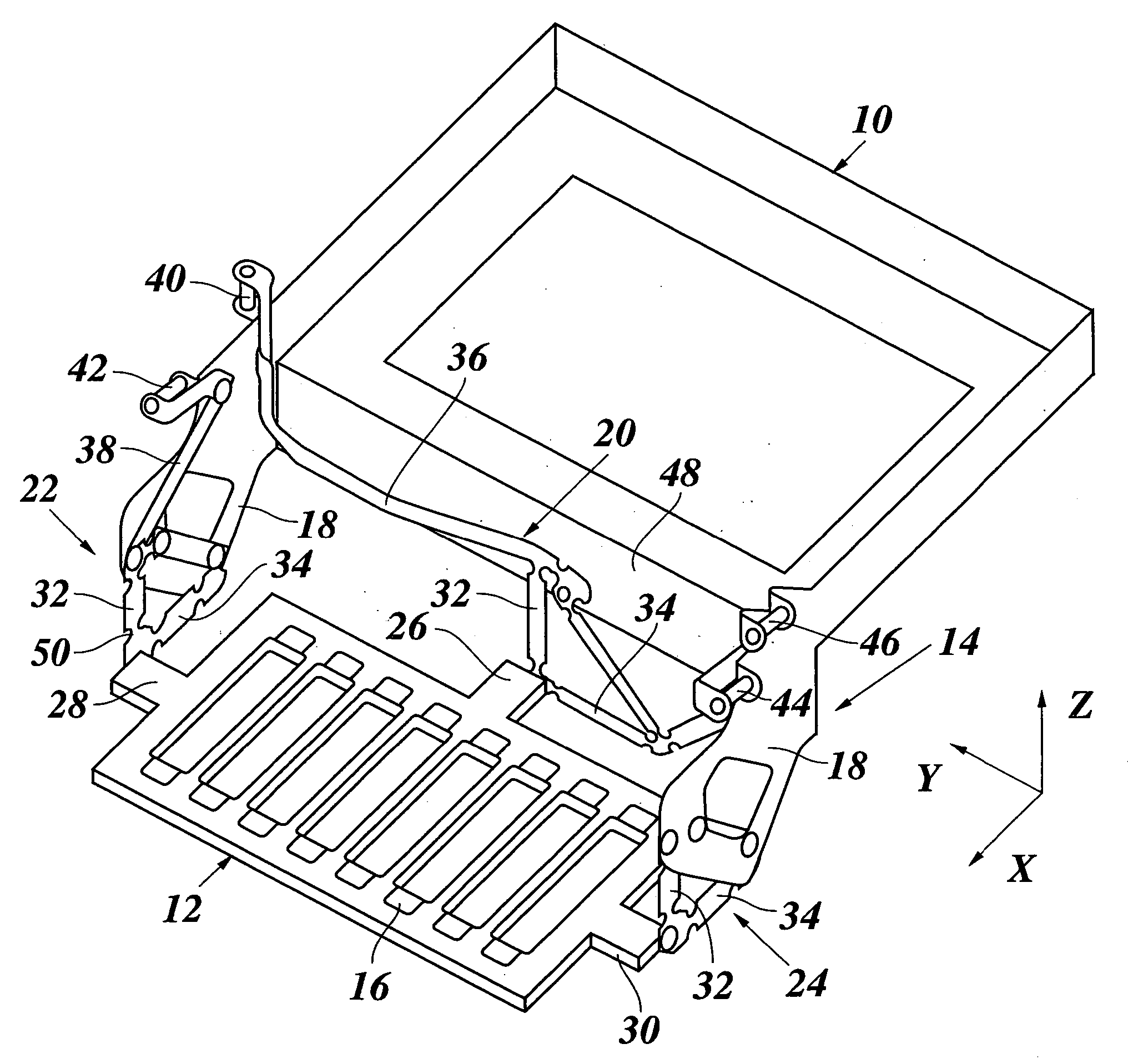
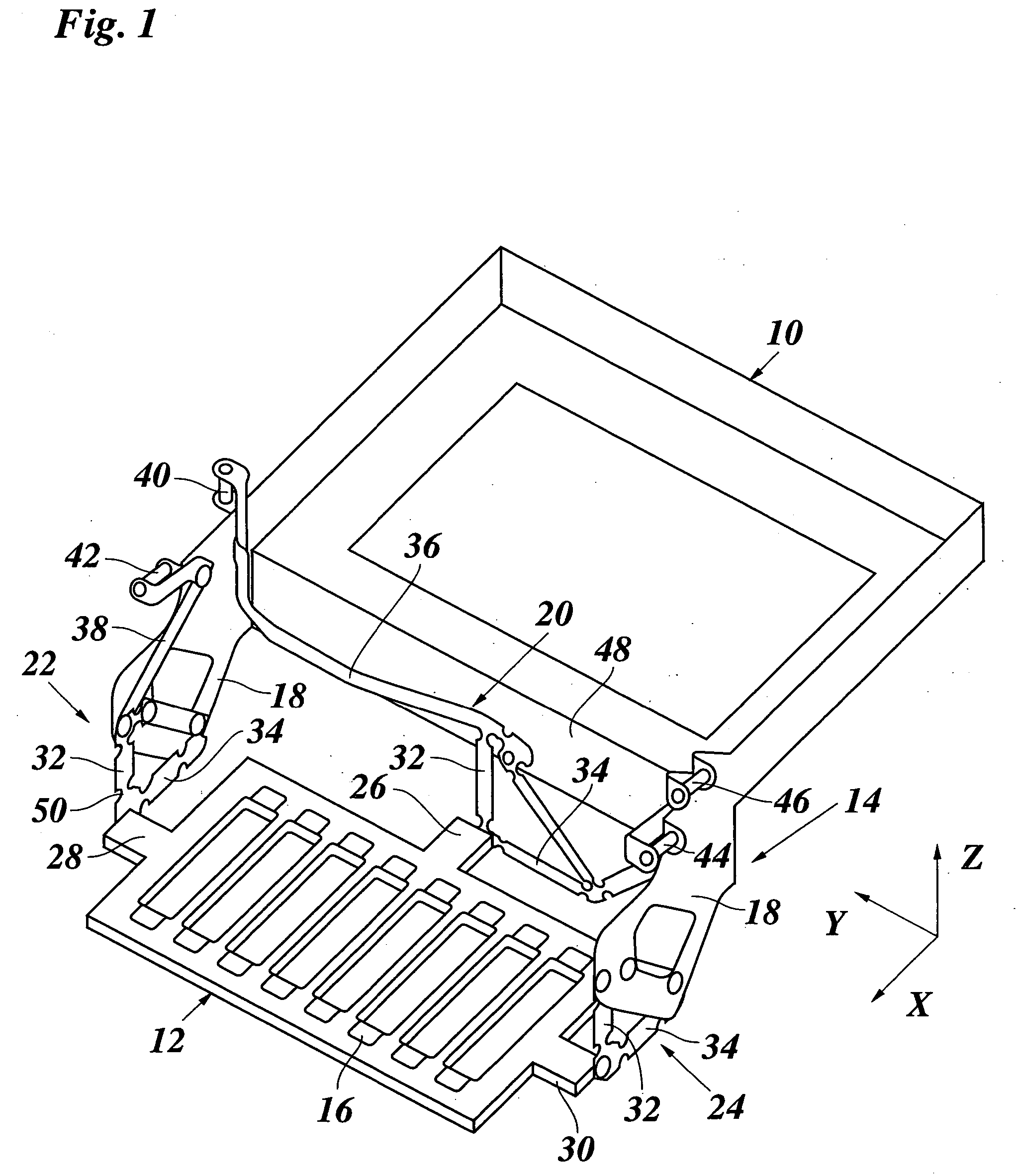
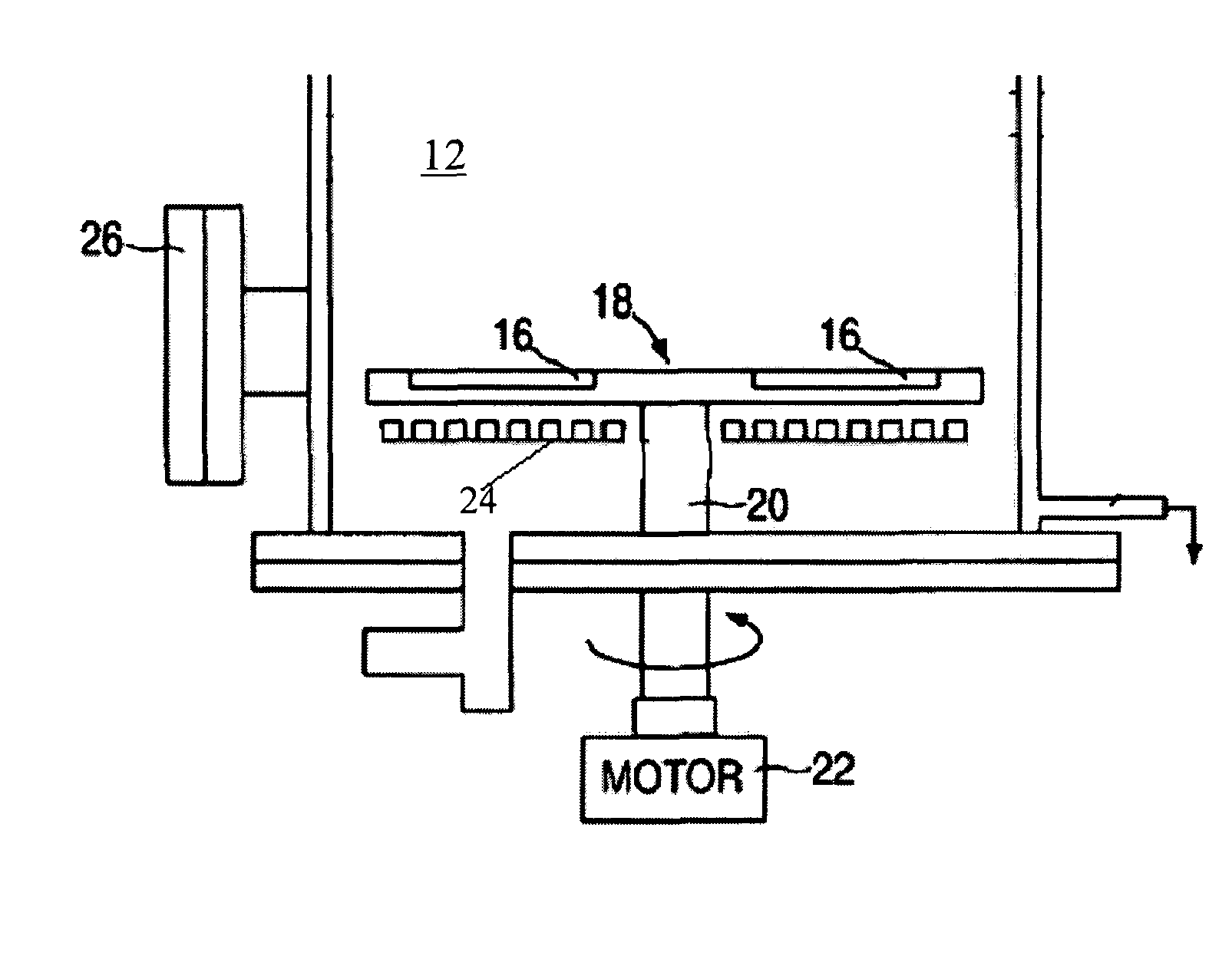
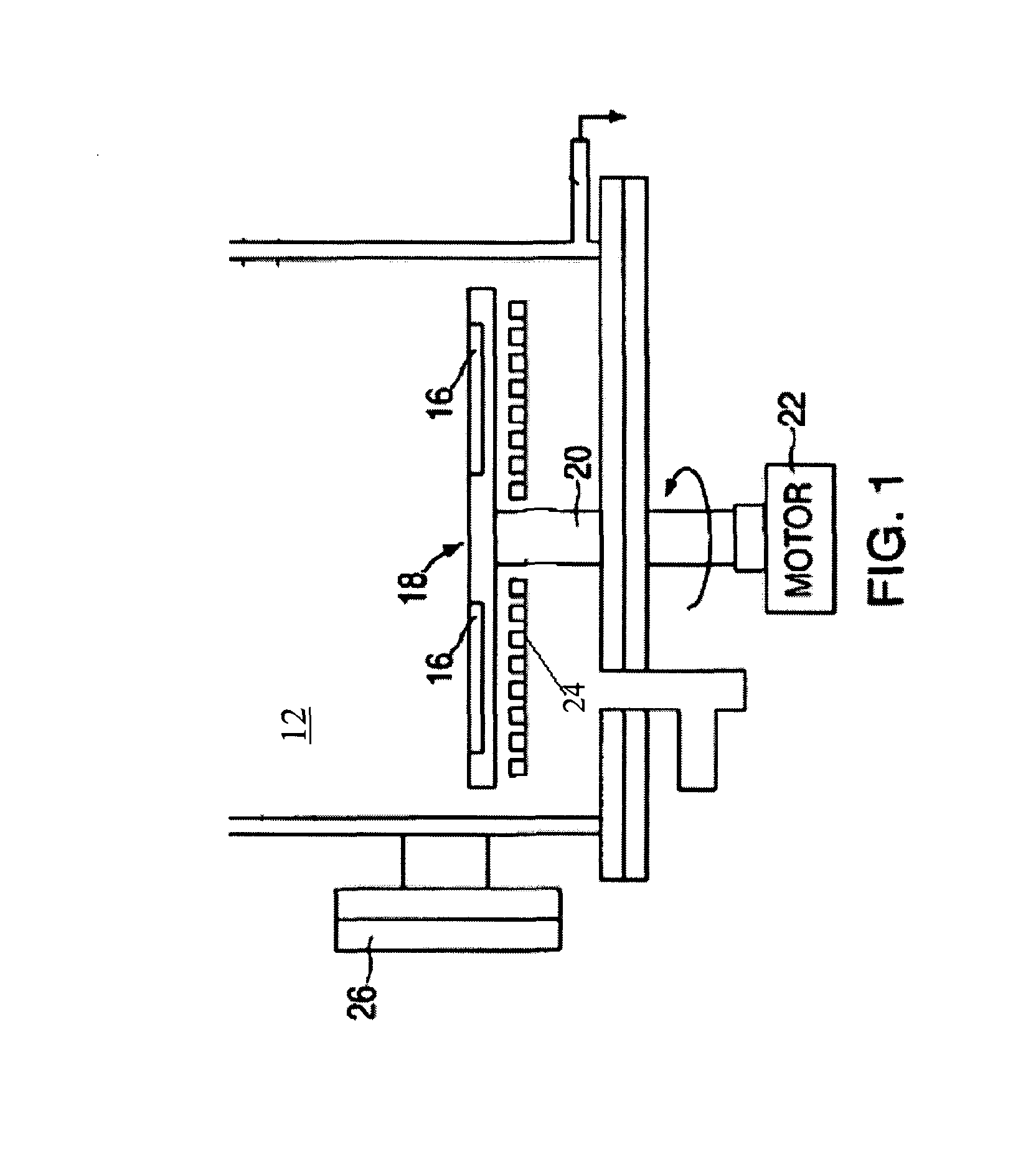
Nucleic acid purification chip
InactiveUS20050142565A1Reduced steady state power consumptionRapid changingBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsSingle chipCellular material
The present invention provides for a novel system of extracting and purifying nucleic acids (DNA, RNA, etc.) from cellular material like blood. Such a system of extraction and purification relies on novel monolithic microfluidic devices and methods of using these devices. Such devices comprise numerous components, monolithically-incorporated on an single chip, and further comprising novel nucleic acid binding materials. The present invention is also directed to method of preparing such novel nucleic binding materials.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Method for combustion of a fuel
InactiveUS7363756B2Increase speedAccelerated dilutionContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberFront velocity
In a method for the combustion of a fuel, a fuel or a premixed combustible mixture is introduced into a combustion space as a combustible fluid open jet. The velocity of the open jet is selected in such a way that it is impossible for a stable flame front to form, i.e. is in any event greater than the flame front velocity, and that, on account of a jet pump effect, flue gas is mixed into the combustible fluid jet from the combustion chamber in a jet-induced recirculation internally within the combustion chamber. The admixed flue gas dilutes and heats the combustible fluid. The heating causes the spontaneous ignition temperature to be exceeded, and a low-pollutant volumetric flame is formed in a highly dilute atmosphere.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Variable heat flux heat exchangers
InactiveUS20090120629A1Easy to adaptMinimal modificationChemical/physical/physico-chemical processesHeat transfer modificationHeat fluxHeat transmission
A system for heat exchange is provided in which process material flows through a heat exchanger comprising multiple heat transfer stages and the heating and or cooling power applied to each stage can be modified independently. The system comprises a unitary heat exchanger comprising a heat transfer surface comprising a plurality of elements or zones over which a process material can flow wherein each element or zone has independent means to set or control the level of heating or cooling within that zone.
Owner:ASHE MORRIS LTD
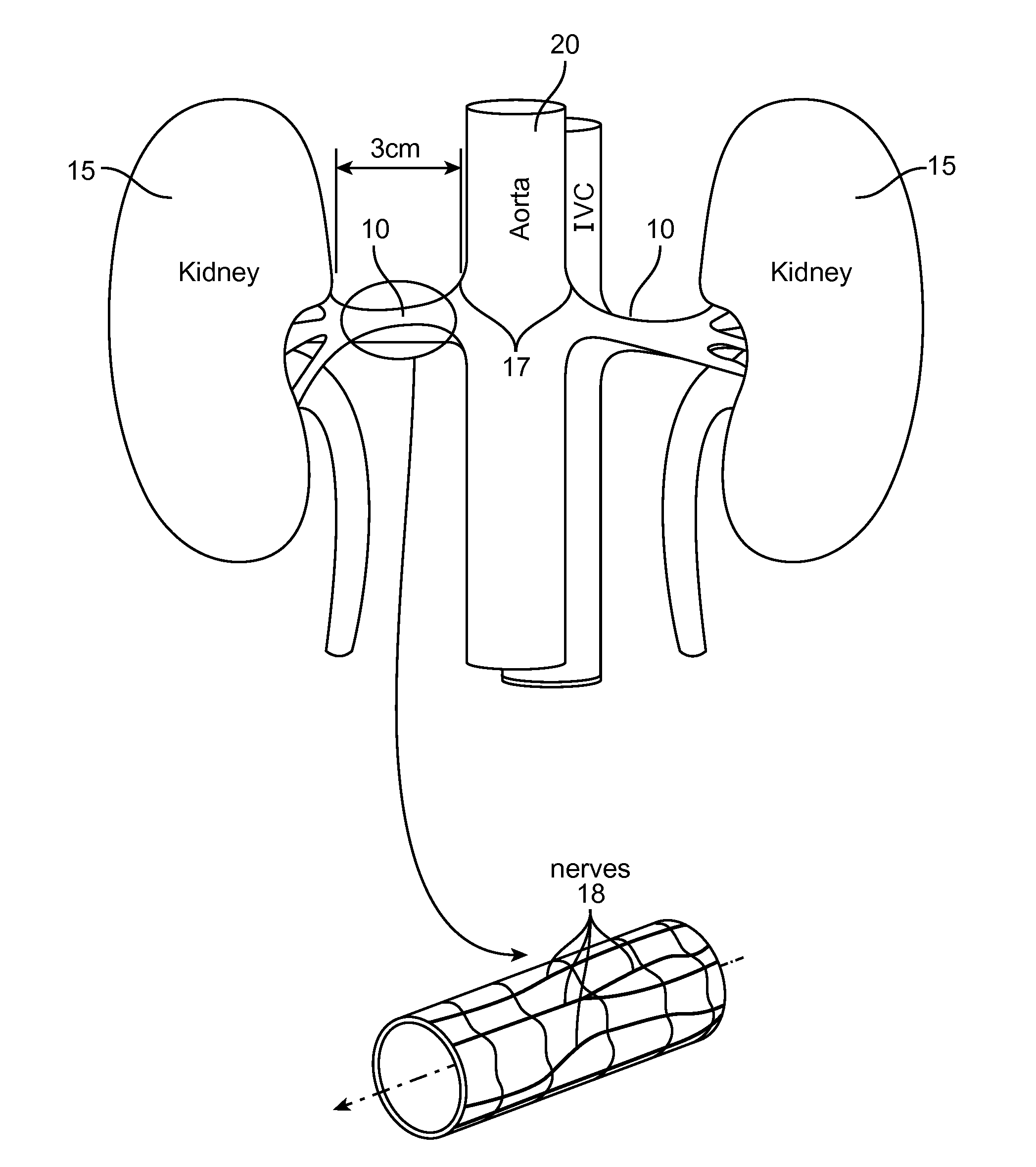
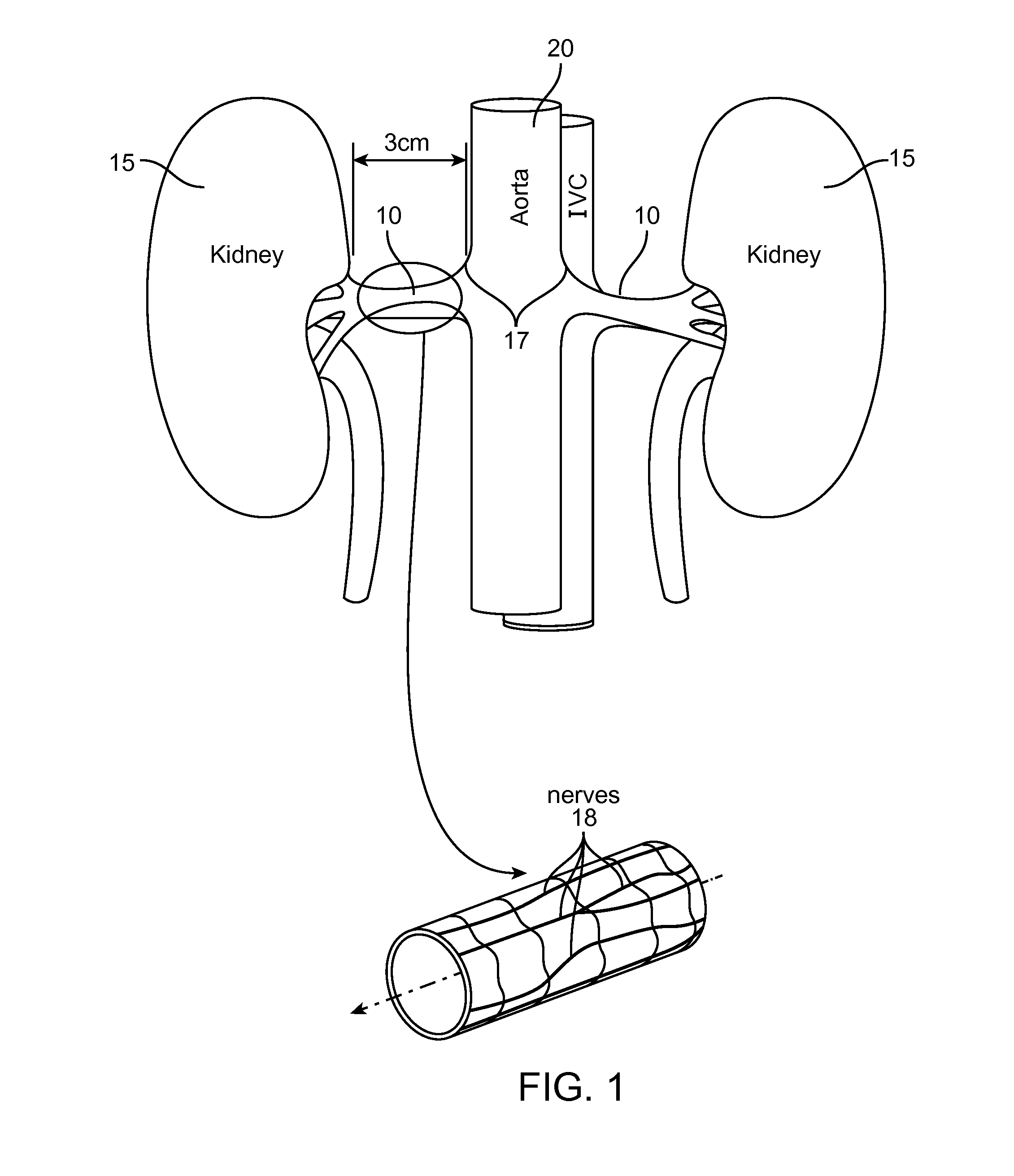
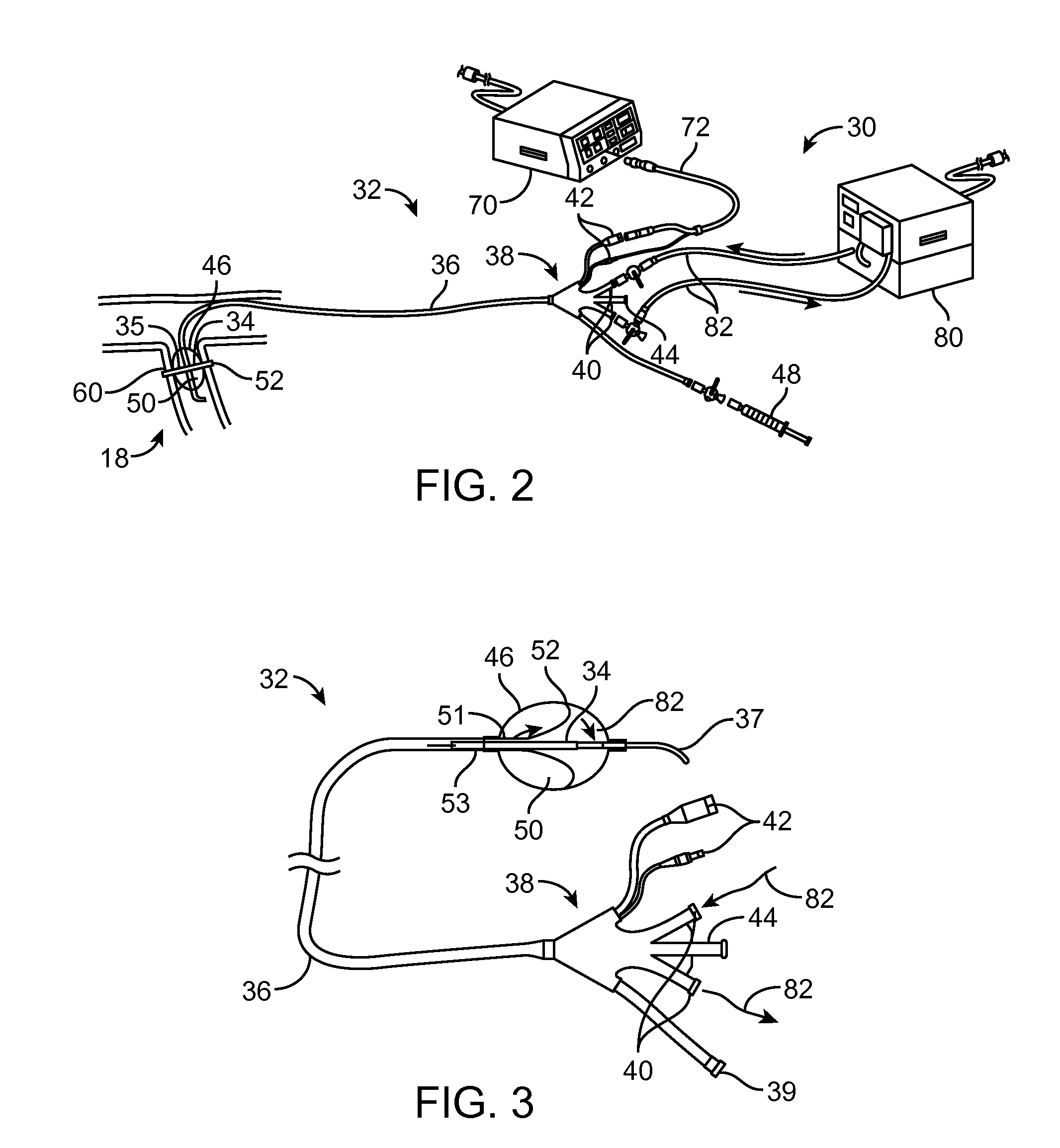
Method and apparatus employing ultrasound energy to remodulate vascular nerves
InactiveUS20110257562A1Minimize heat damageMinimize damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAcoustic energyVascular dilation
Methods and apparatus for treating hypertension and other vessel dilation conditions provide for delivering acoustic energy to a vascular nerve to remodel the tissue and nerves surrounding the vessel. In the case of treating hypertension, a catheter carrying an ultrasonic or other transducer is introduced to the renal vessel, and acoustic energy is delivered to the tissue containing nerves to remodel the tissue and remodulate the nerves.
Owner:SCHAER ALAN
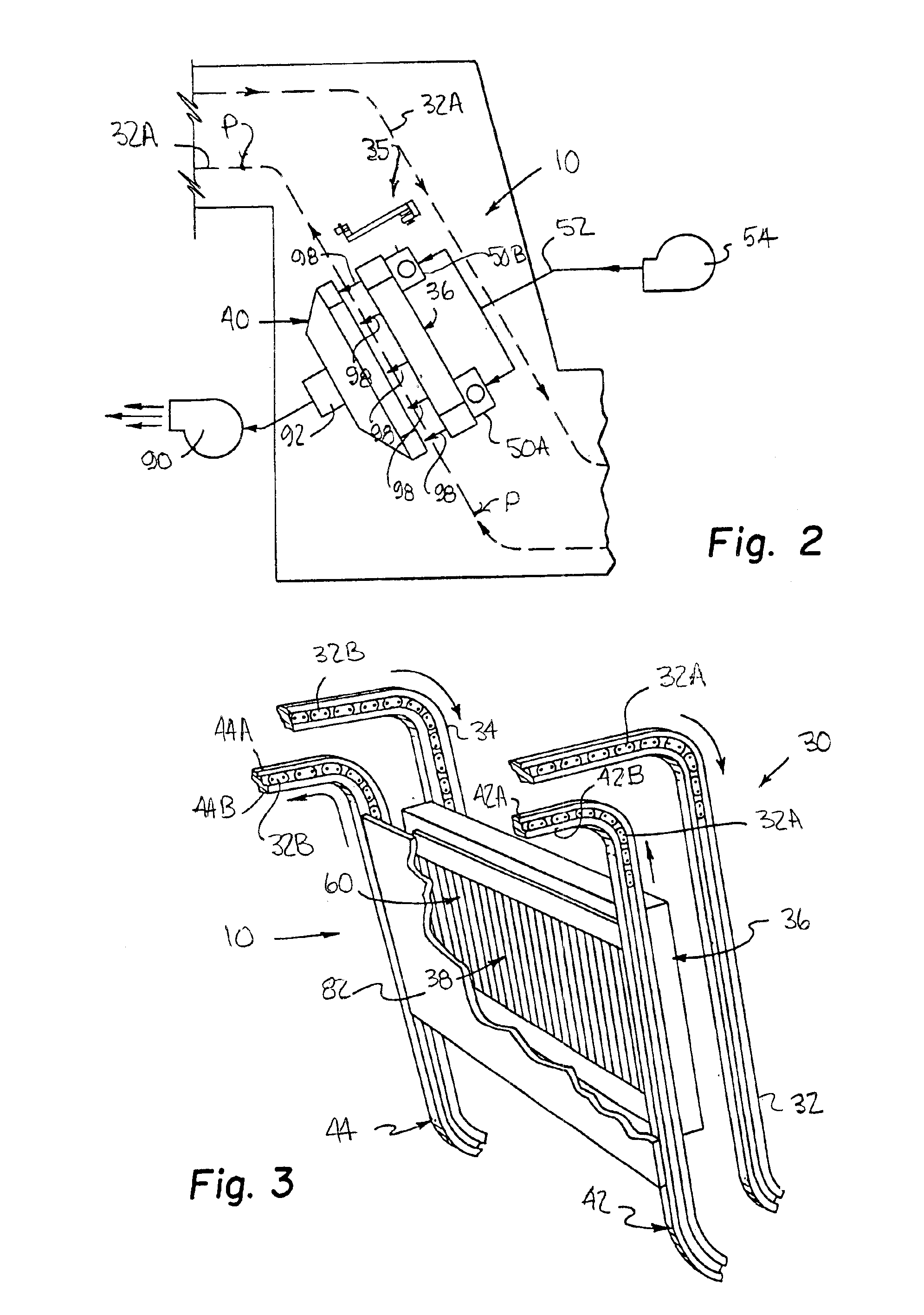
Power saving automatic zoned dryer apparatus and method
InactiveUS6877247B1Eliminates and greatly reduces needImprove paper qualityDrying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsAuto regulationEngineering
A computer controlled power saving automatic zoned dryer for a printing press has a dryer head facing the substrate travel path, having a multiplicity of IR lamps connected individually or in groups to form a plurality of heating zones running longitudinally and each extending laterally side by side across the substrate travel path. The radiant heat output of each heating zone is controlled separately by means of a control unit connected to a power supply. The control unit individually regulates output of the heating zones. Unneeded zones are turned off to reduce cost of power and conserve energy. A plurality of heat sensors spaced laterally across the substrate path measure the surface temperature of substrate heated areas corresponding to the heating zones being operated and maintain an automatic set point temperature. The temperature of each individual heated area can be regulated automatically by adjusting the output of its heating zone whereby printed substrates having a more even temperature profile are delivered. In an alternate manual mode any zone can be set independently to operate at any percentage of full available power from zero to 100%. Separate high velocity air scrubbers and additional air extraction are used to enhance the total drying effect of the zoned dryer assembly.
Owner:PRINTING RES
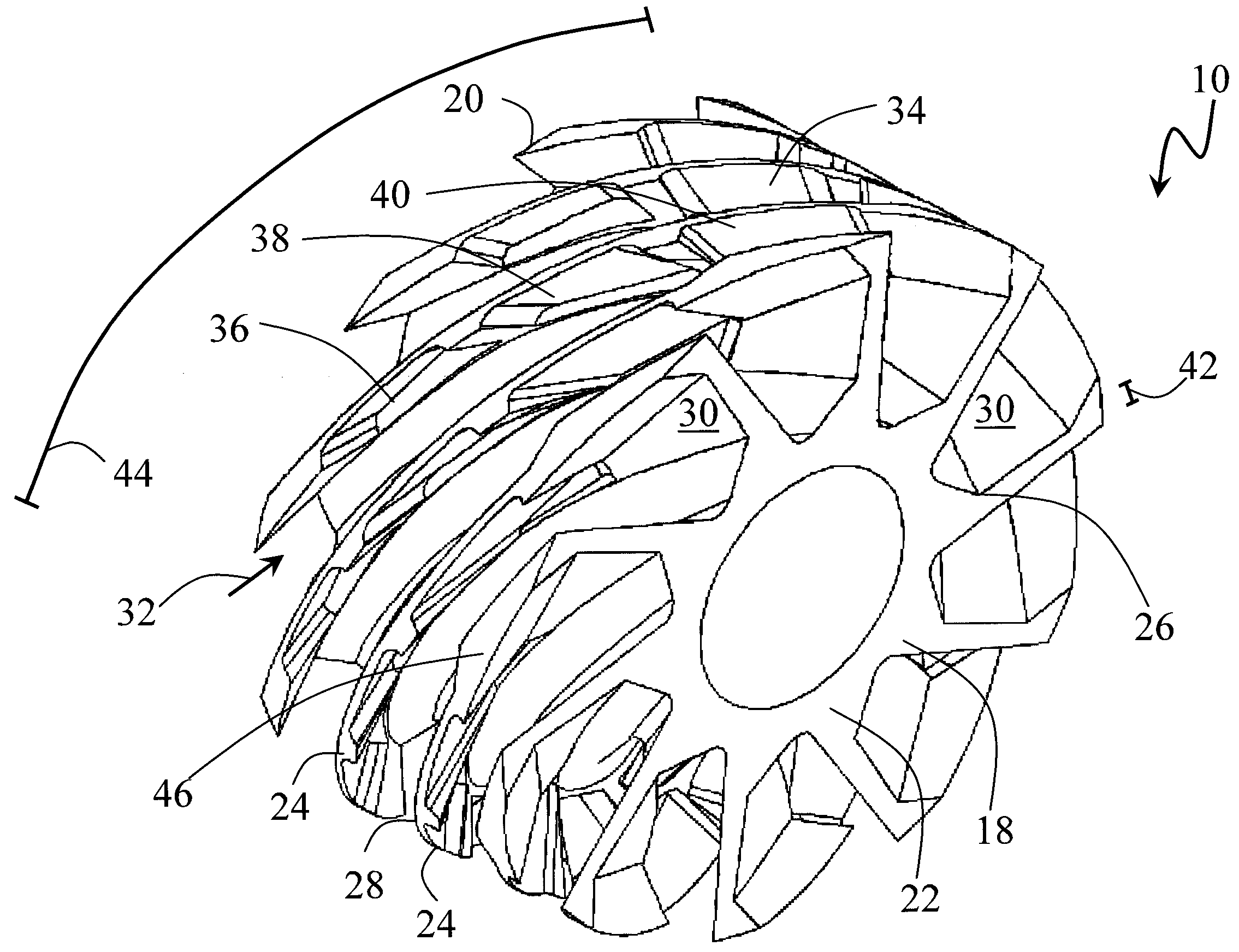
Apparatus and method for a gas turbine entrainment system
ActiveUS20090178412A1Reduce lossesFacilitate turbulenceContinuous combustion chamberEngine manufactureCombustion chamberCombustor
This invention relates to an apparatus for an entrainment system of a vortex burning combustion chamber or a vortex burning inter-turbine burner in a gas turbine. The entrainment system rapidly and thoroughly mixes hot combustion gases with non-combustion gases to reduce the gas temperature before entering a turbine. The entrainment system includes a plurality of helical vanes forming trenches and resulting in a highly helical flow path. The highly helical flow path provides an increased residence time for mixing of the combustion gases and non-combustion gases. Radial cavities in the helical vanes, canted vane angles and varying geometries further facilitate mixing while reducing losses. This invention also includes a method of mixing combustion and non-combustion gases in an entrainment system.
Owner:SPYTEK AEROSPACE CORP
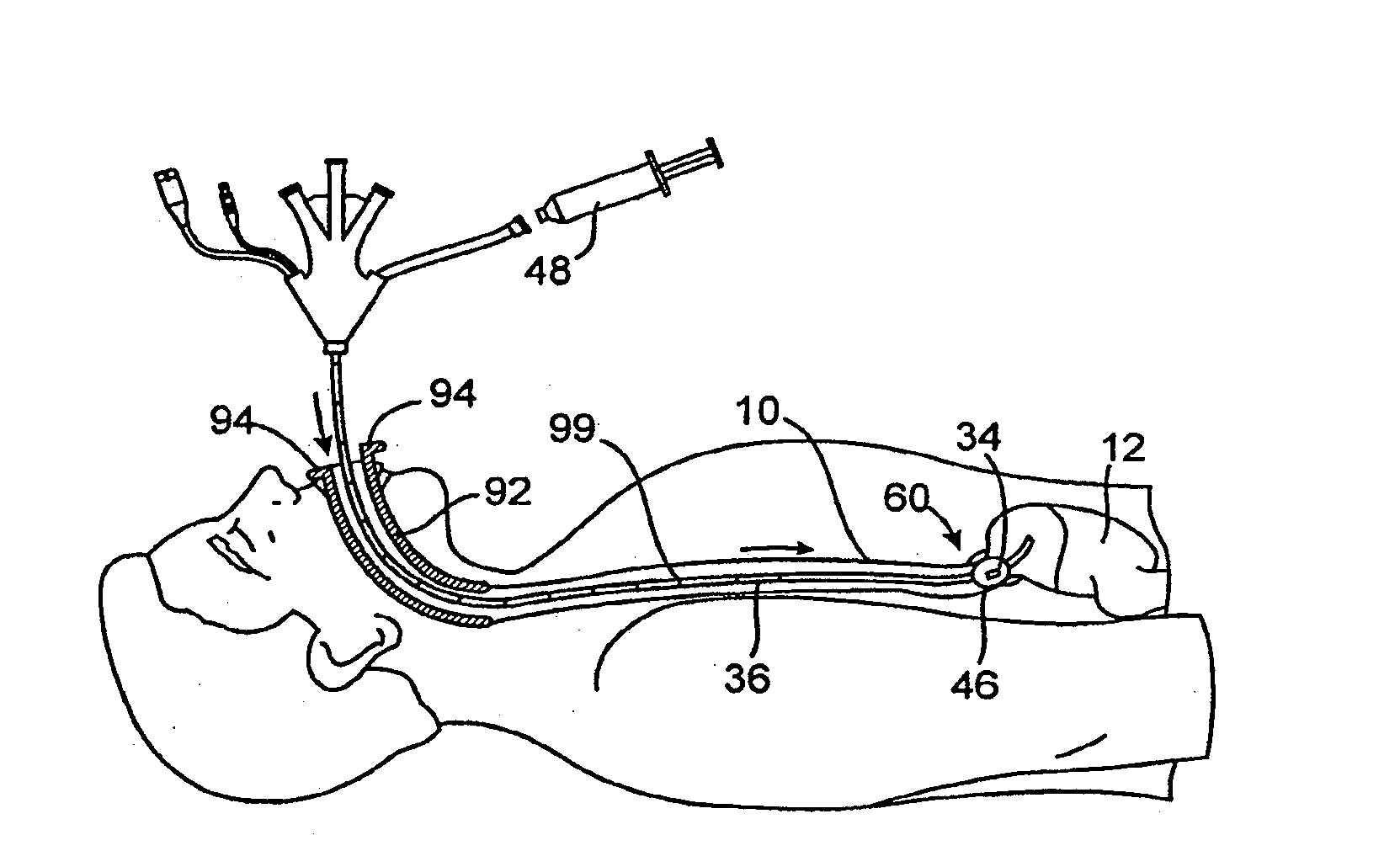
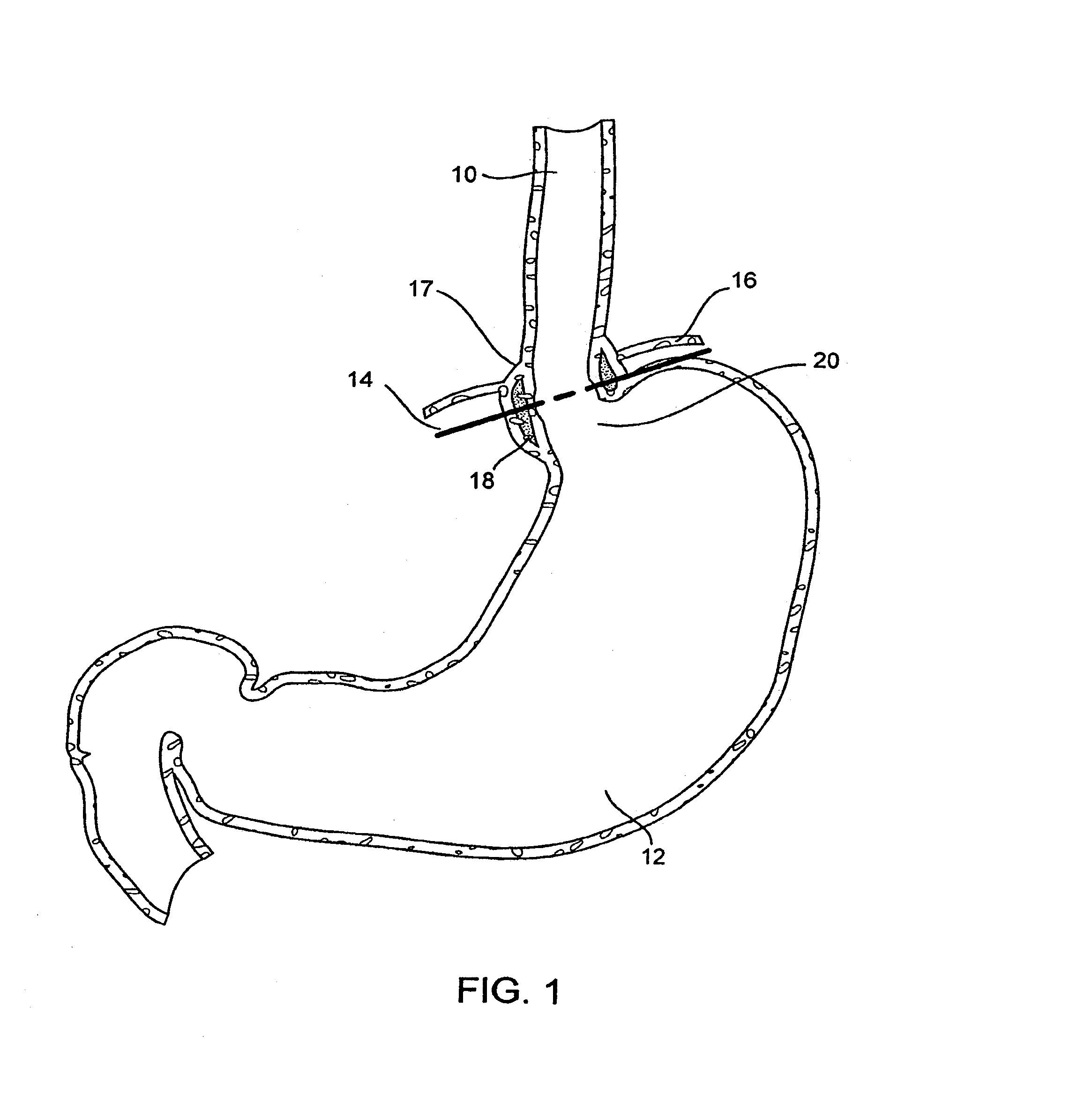
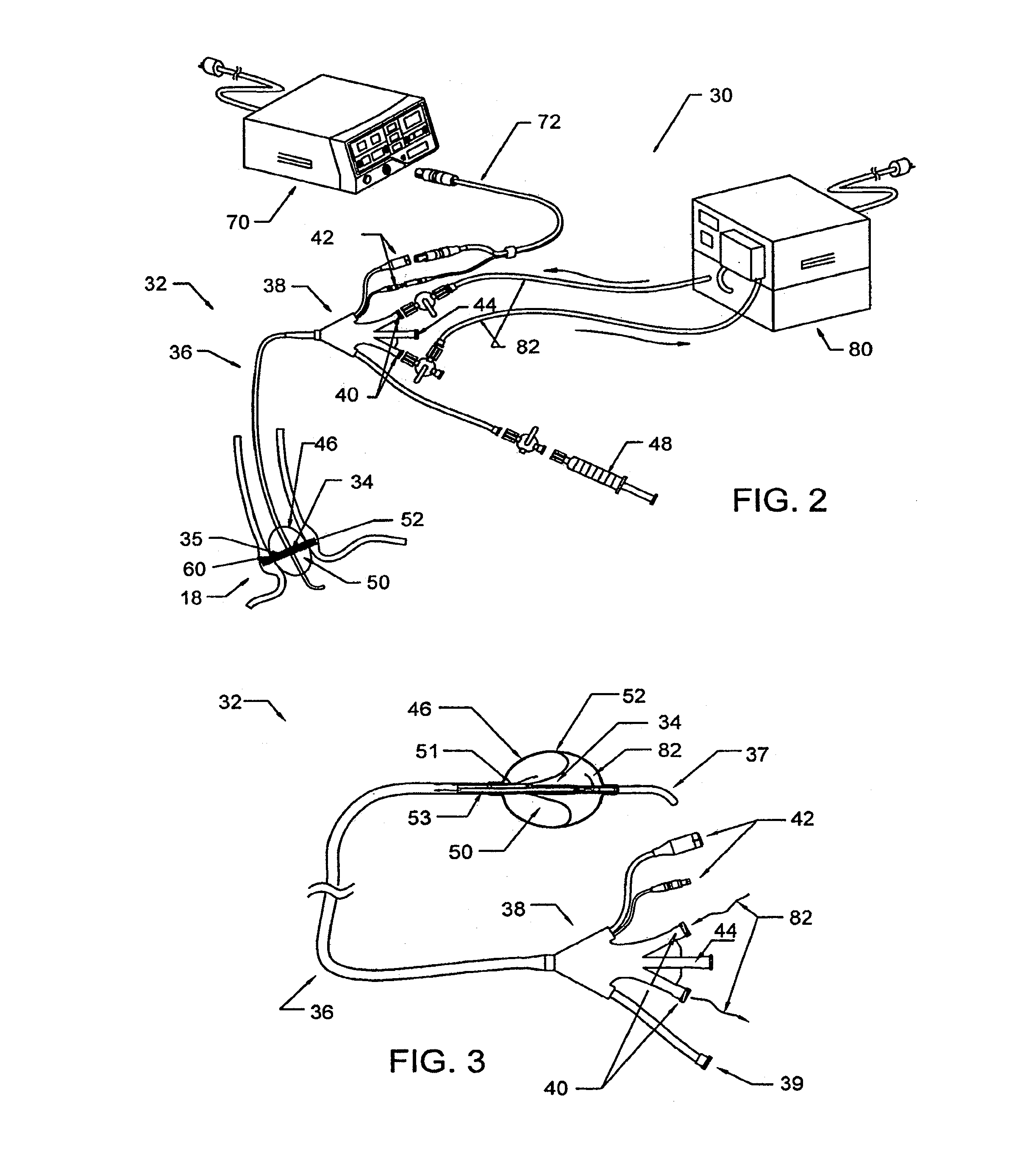
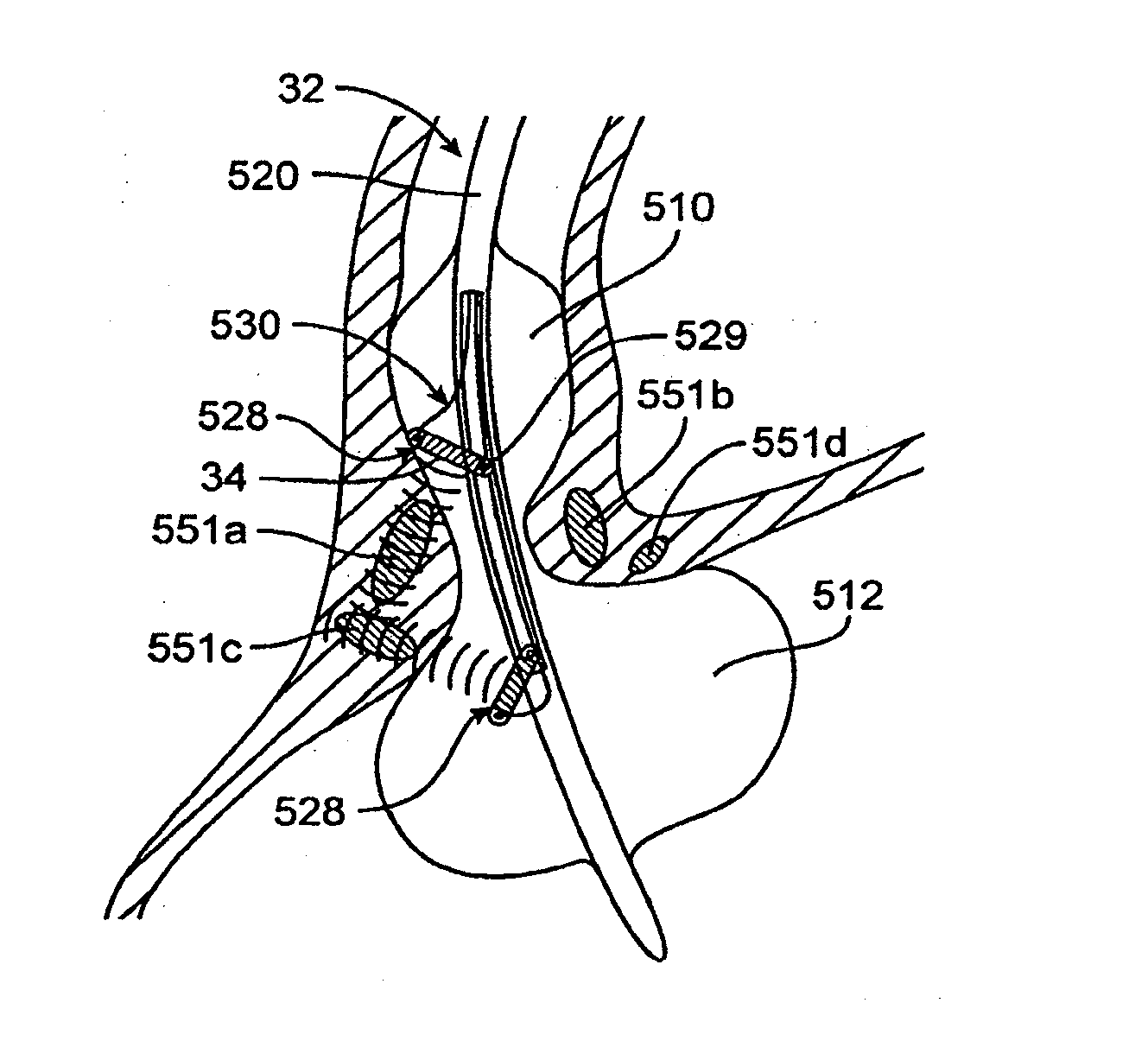
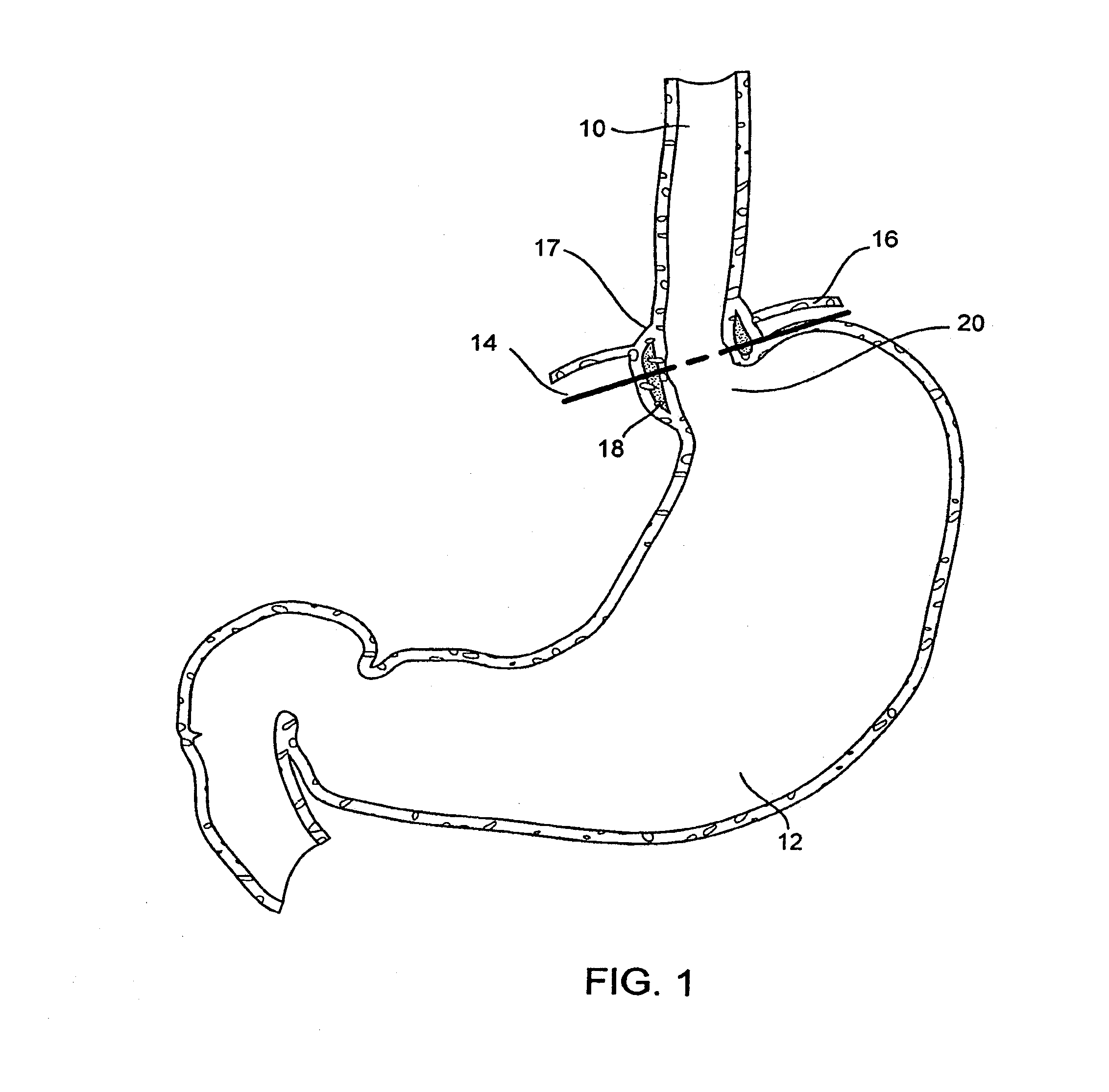
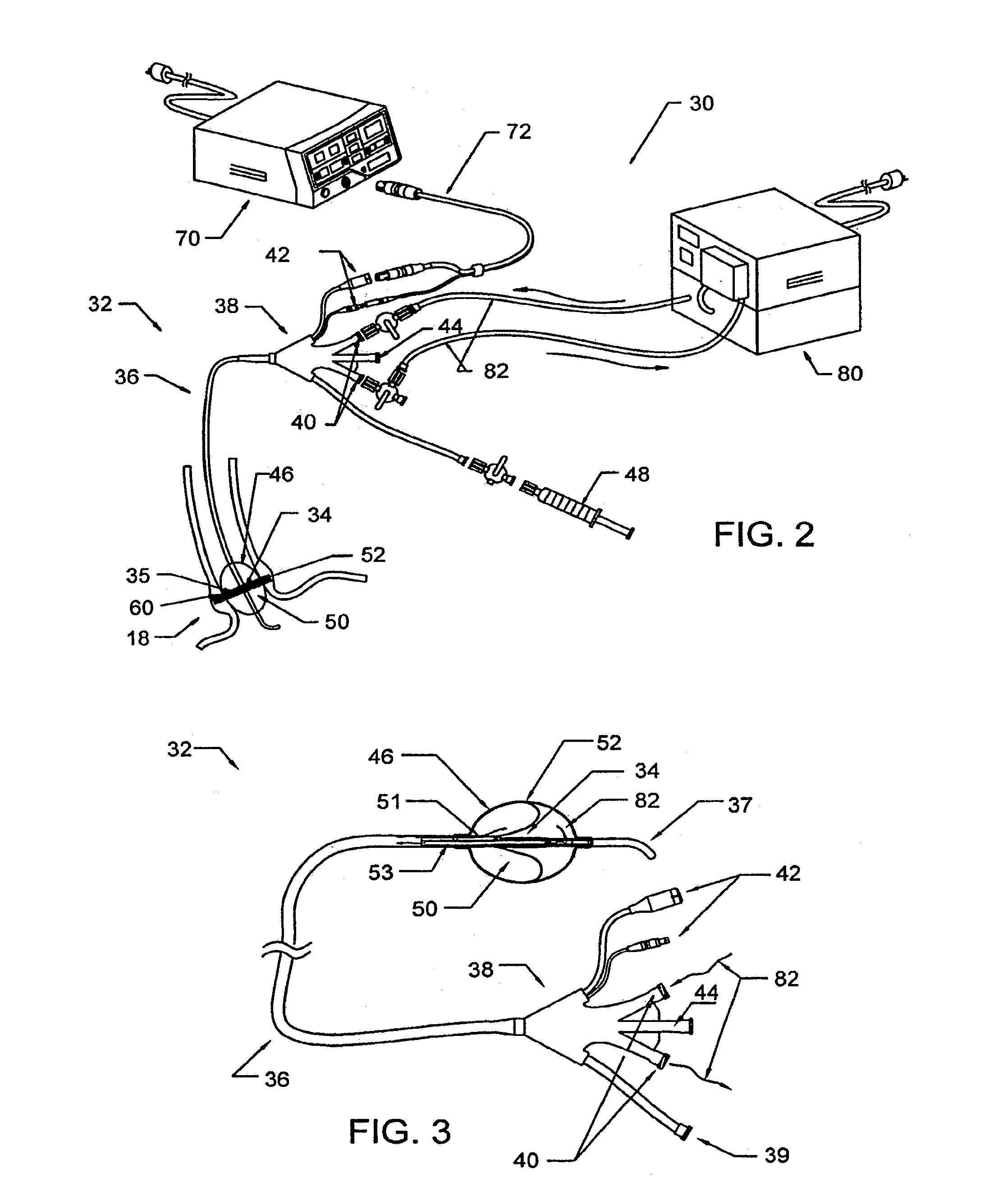
Method and apparatus employing ultrasound energy to treat body sphincters
InactiveUS20130072928A1Prevent and delay openingDecreased tissue complianceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAcoustic energySphincter
Methods and apparatus for treating gastroesophageal reflex and other luminal conditions provide for delivering acoustic energy to a body lumen to remodel tissue surrounding the body lumen. In the case of treating GERD, a catheter carrying an ultrasonic or other vibrational transducer is introduced to the lower esophageal sphincter, and acoustic energy is delivered to the sphincter in order to tighten or bulk the sphincter such that reflex is reduced.
Owner:RECOR MEDICAL INC
Intraluminal methods of ablating nerve tissue
InactiveUS20130131668A1Prevent and delay openingReduce complianceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyAcoustic energySphincter
Methods and apparatus for treating gastroesophageal reflex and other luminal conditions provide for delivering acoustic energy to a body lumen to remodel tissue surrounding the body lumen. In the case of treating GERD, a catheter carrying an ultrasonic or other vibrational transducer is introduced to the lower esophageal sphincter, and acoustic energy is delivered to the sphincter in order to tighten or bulk the sphincter such that reflex is reduced.
Owner:RECOR MEDICAL INC
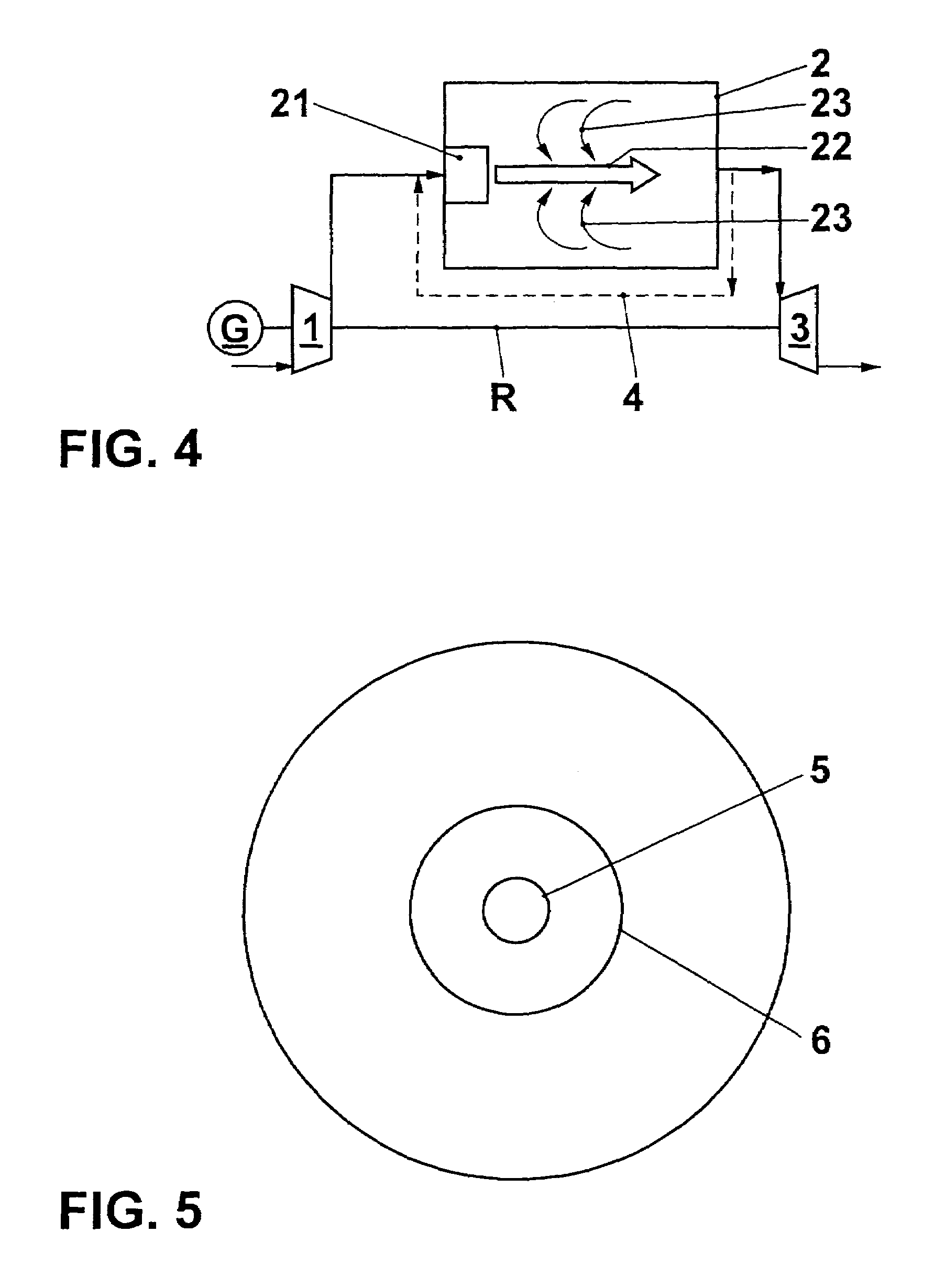
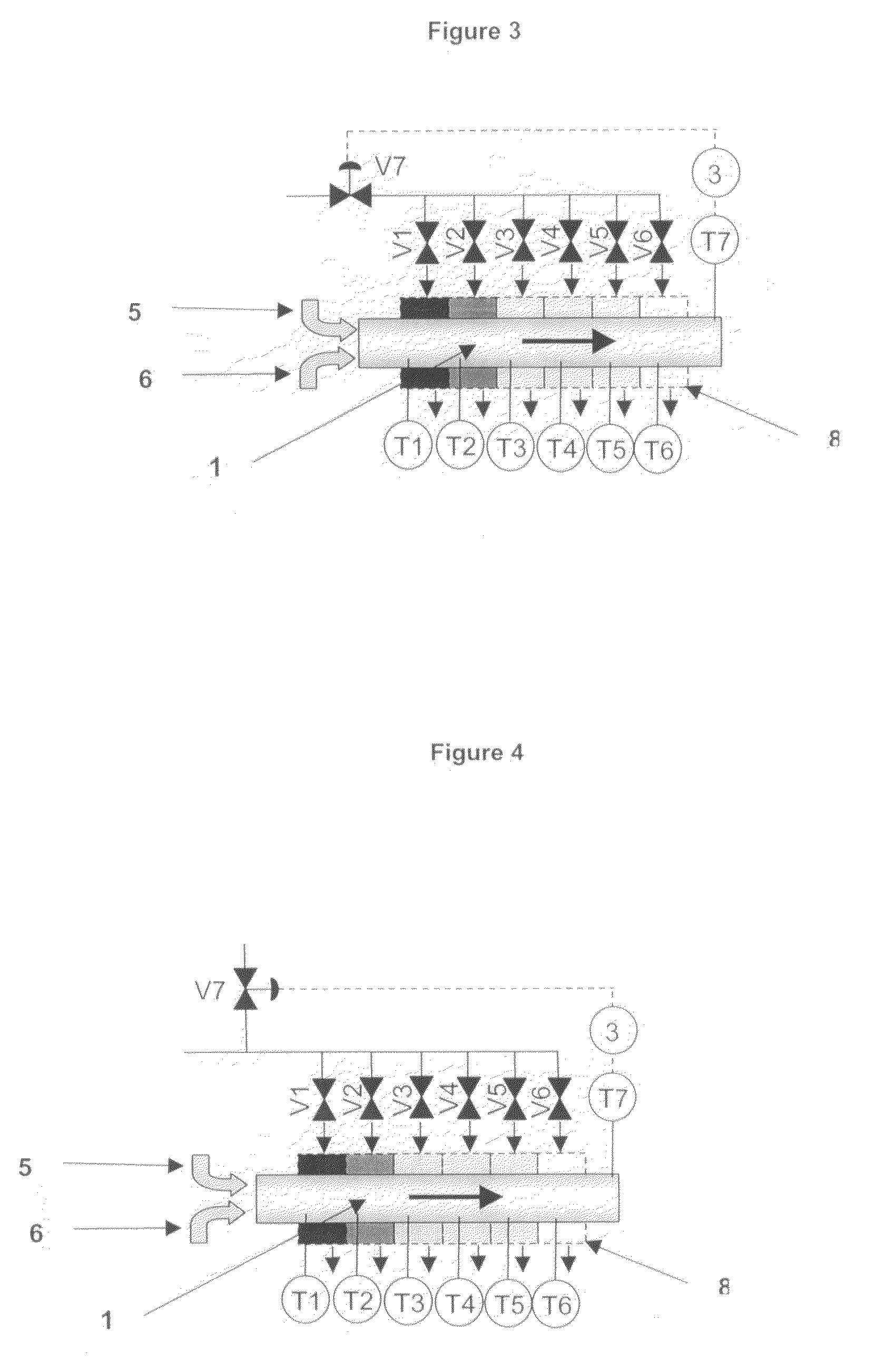
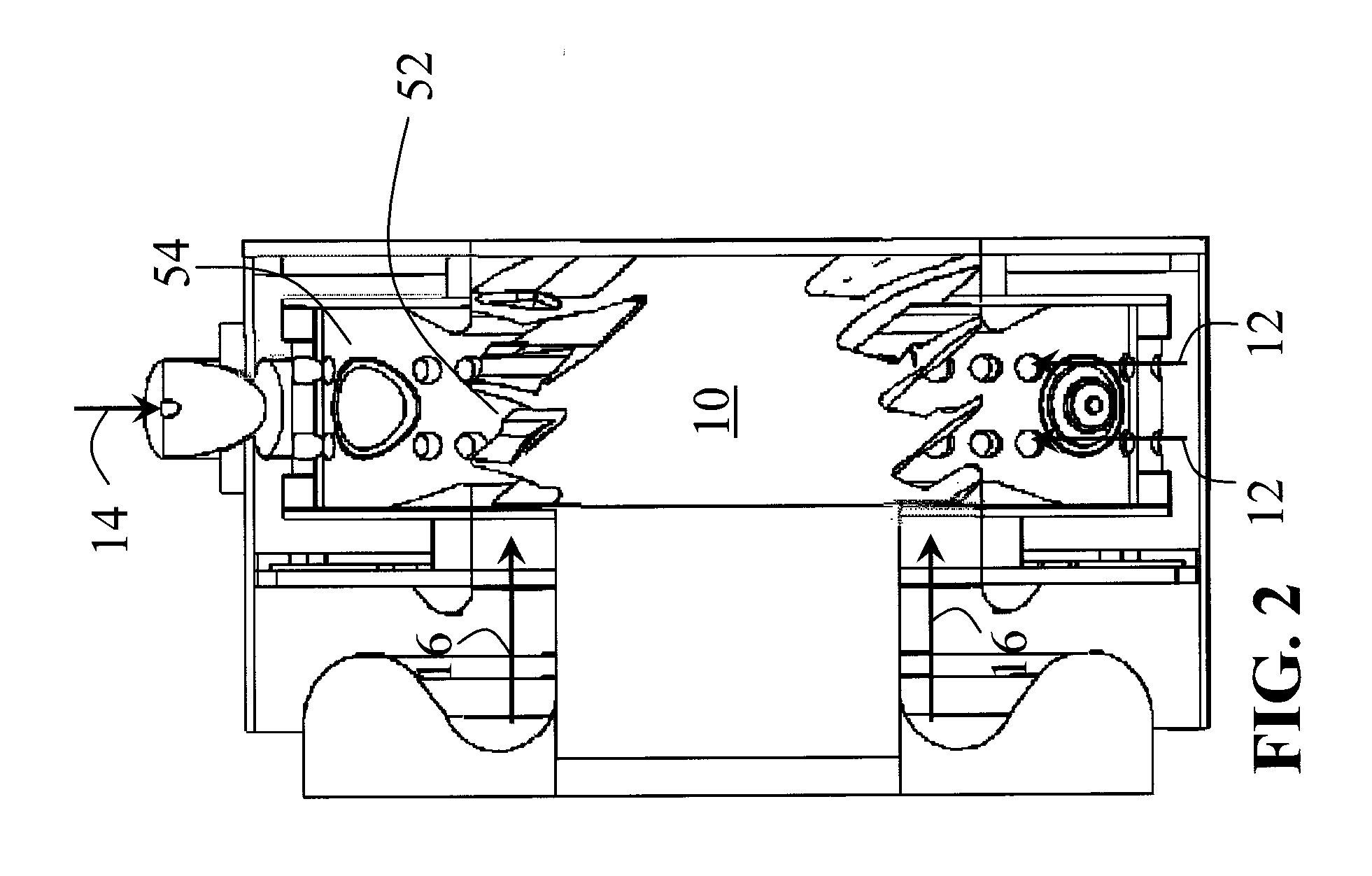
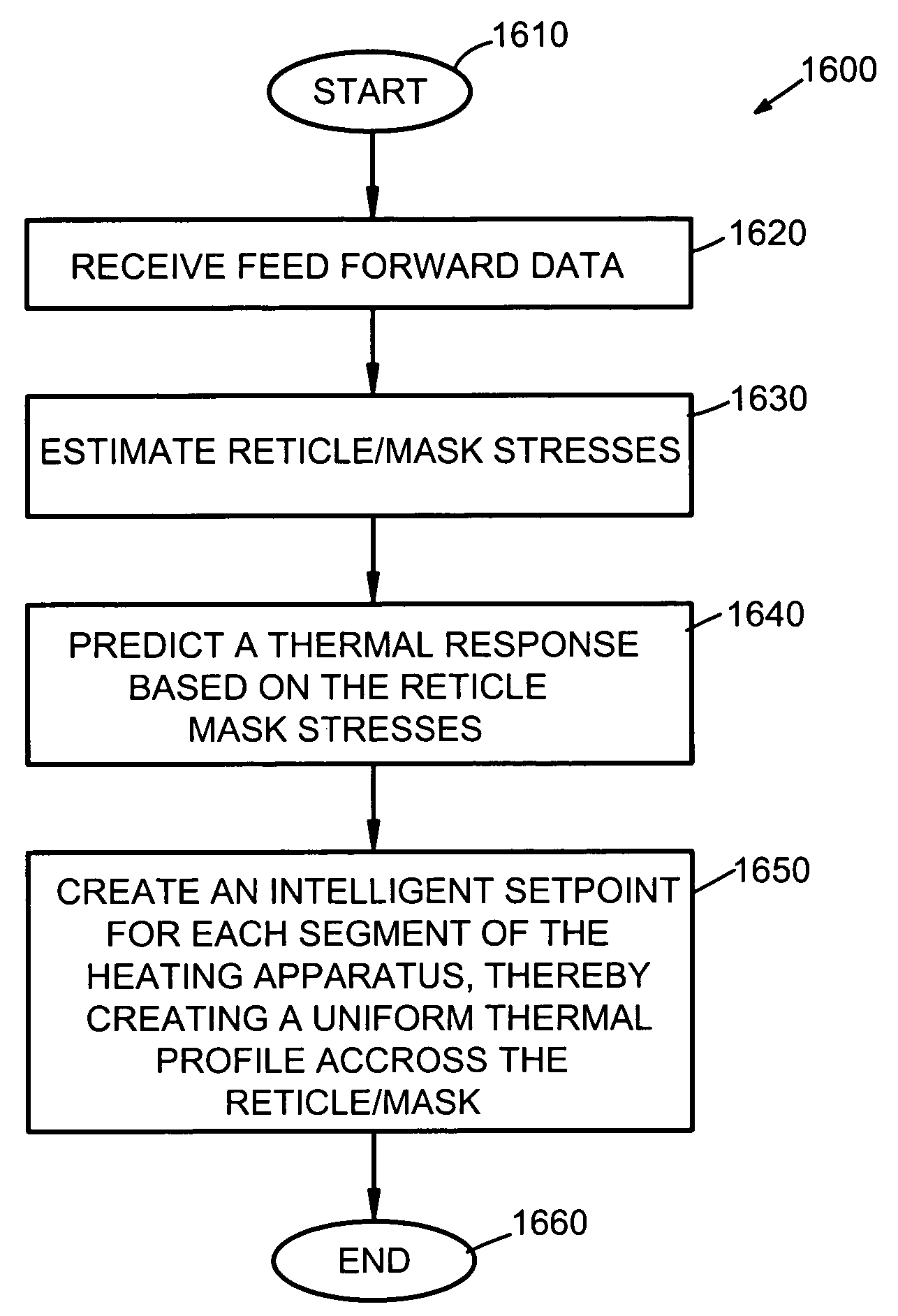
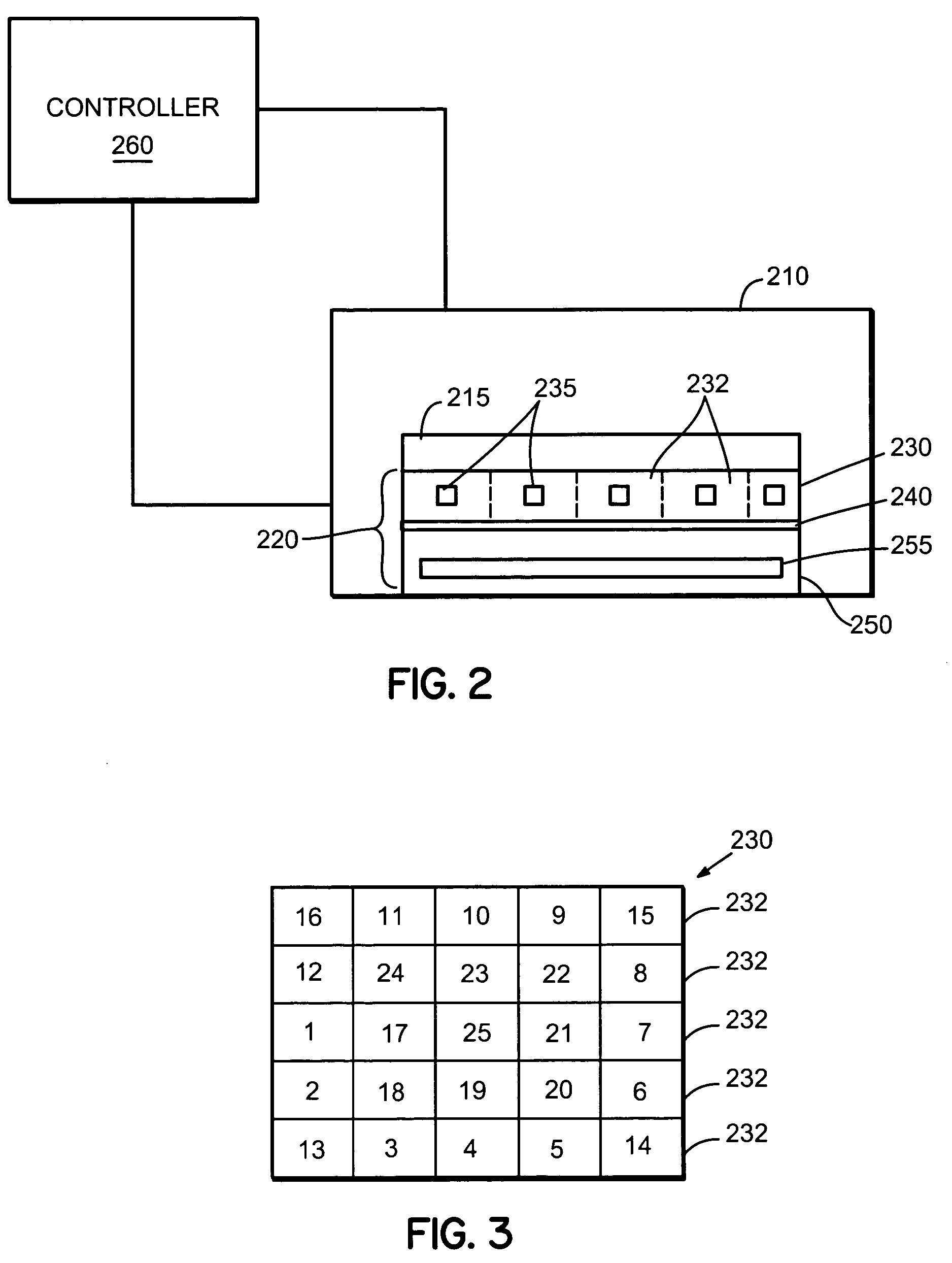
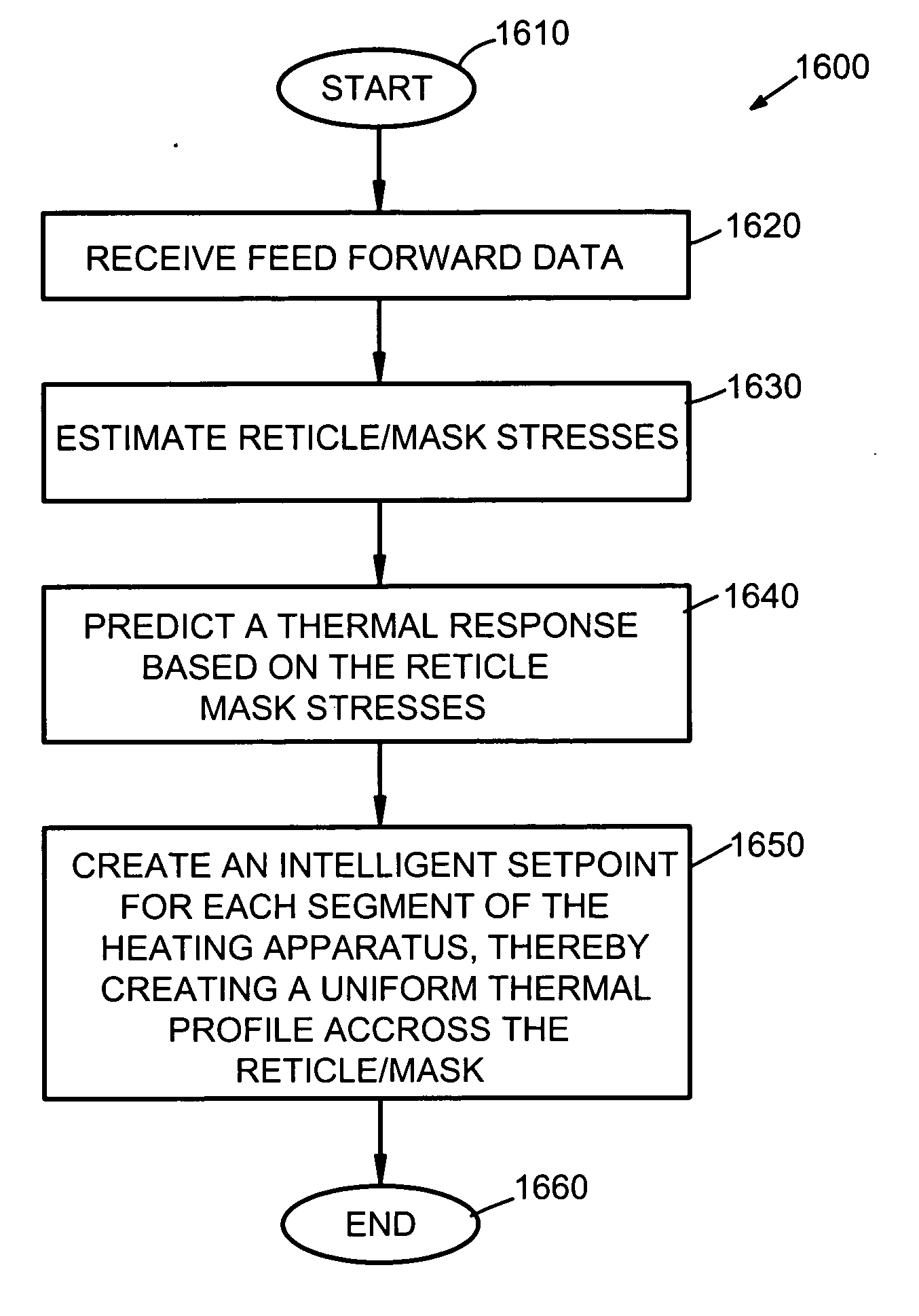
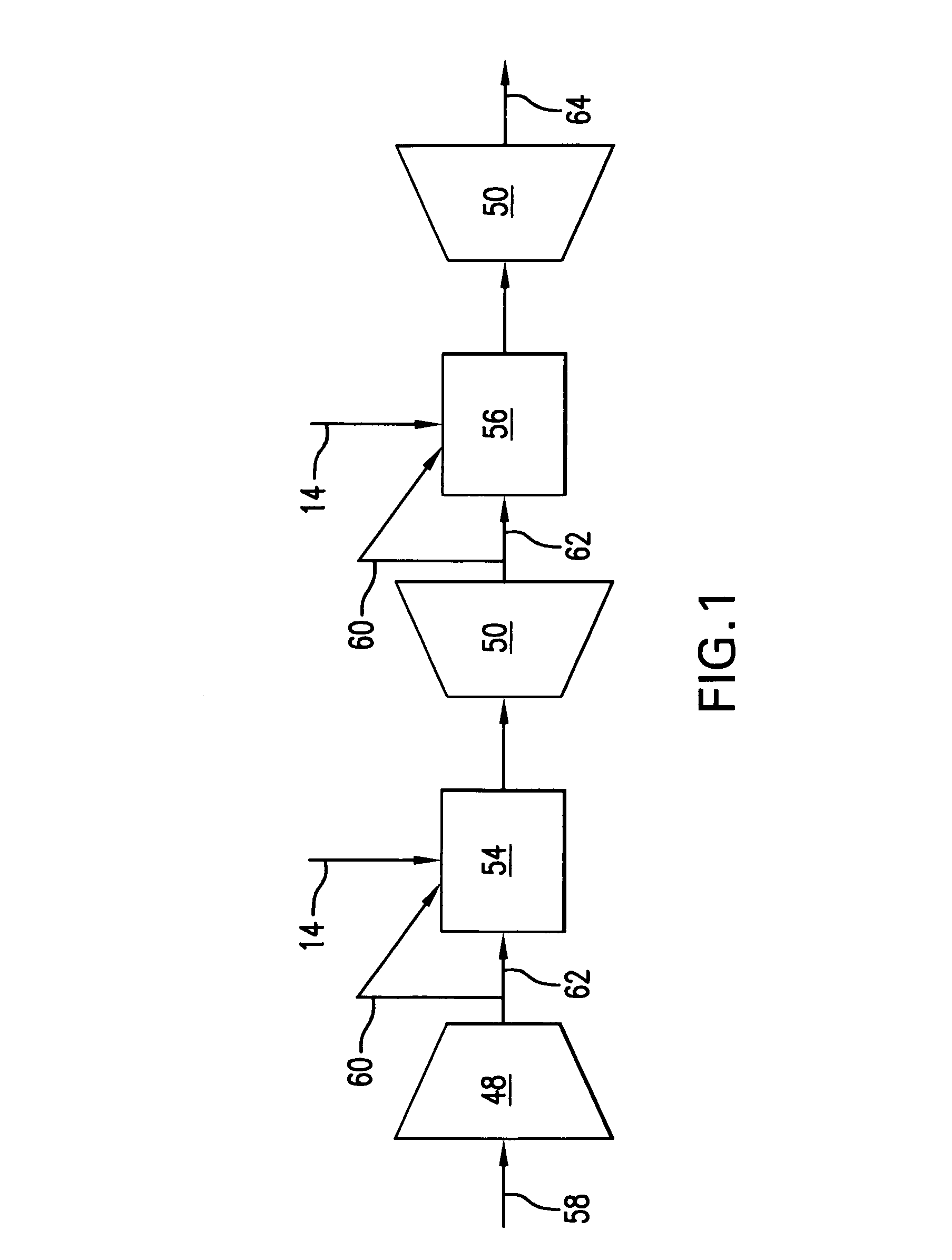
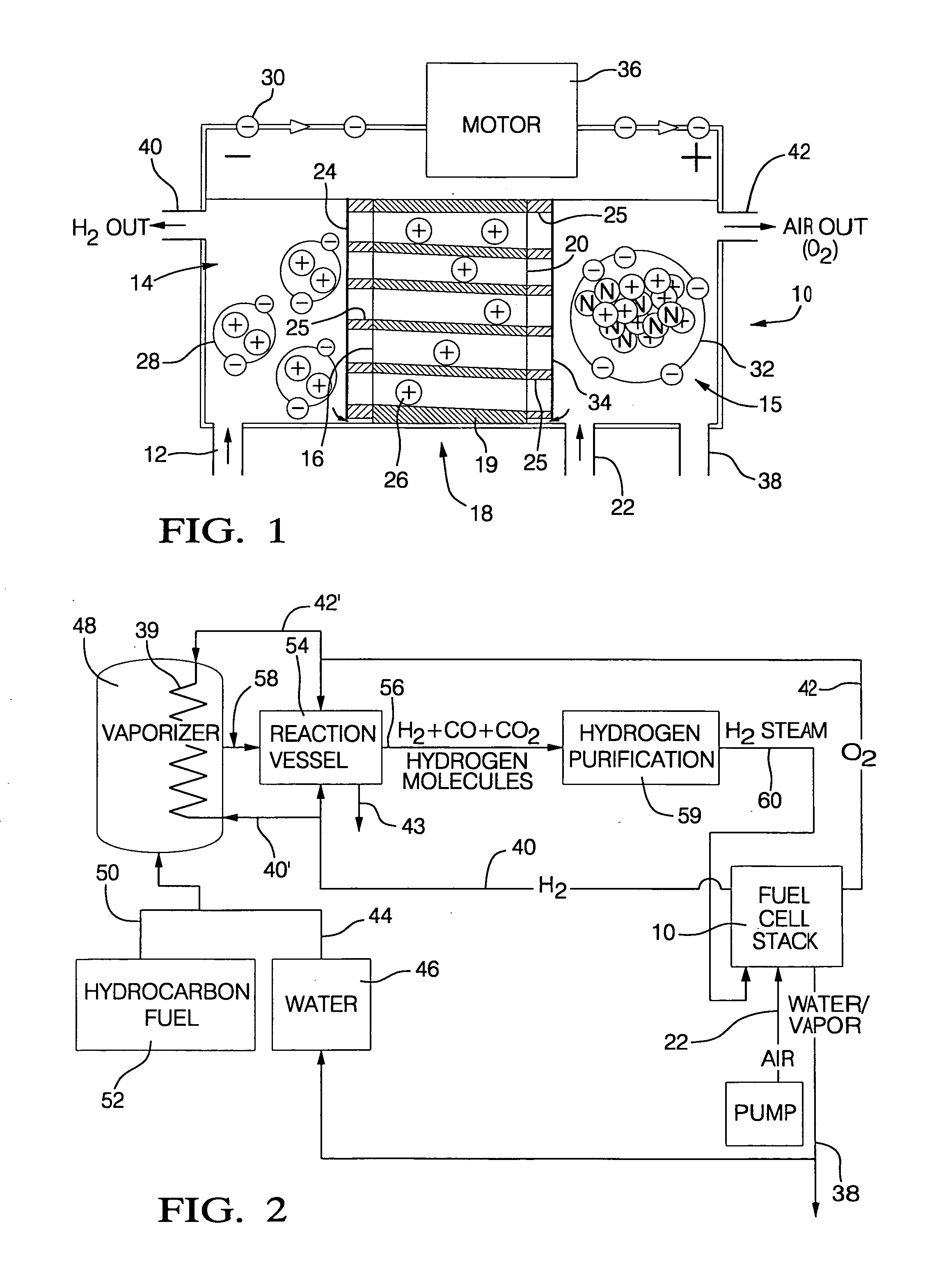
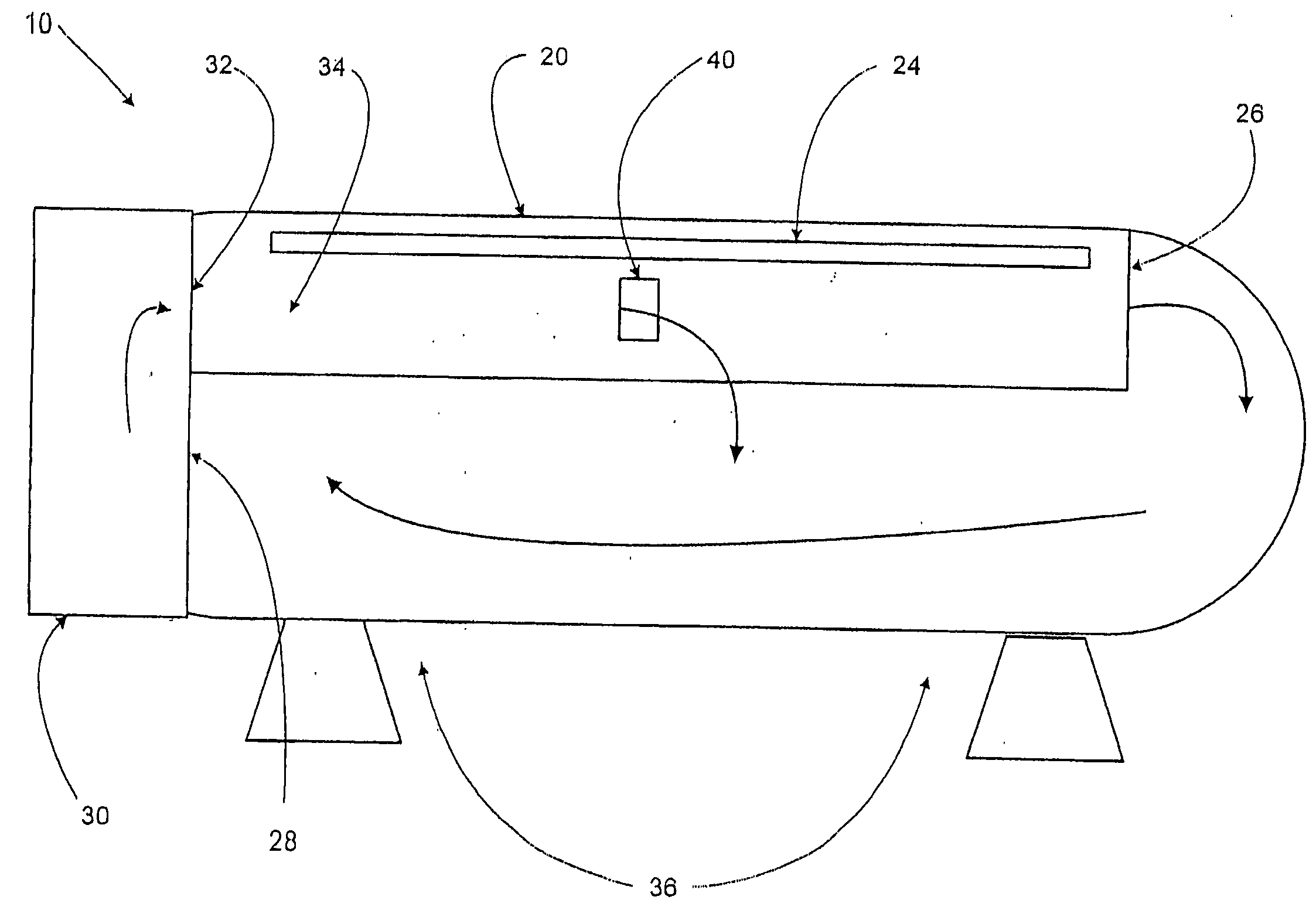
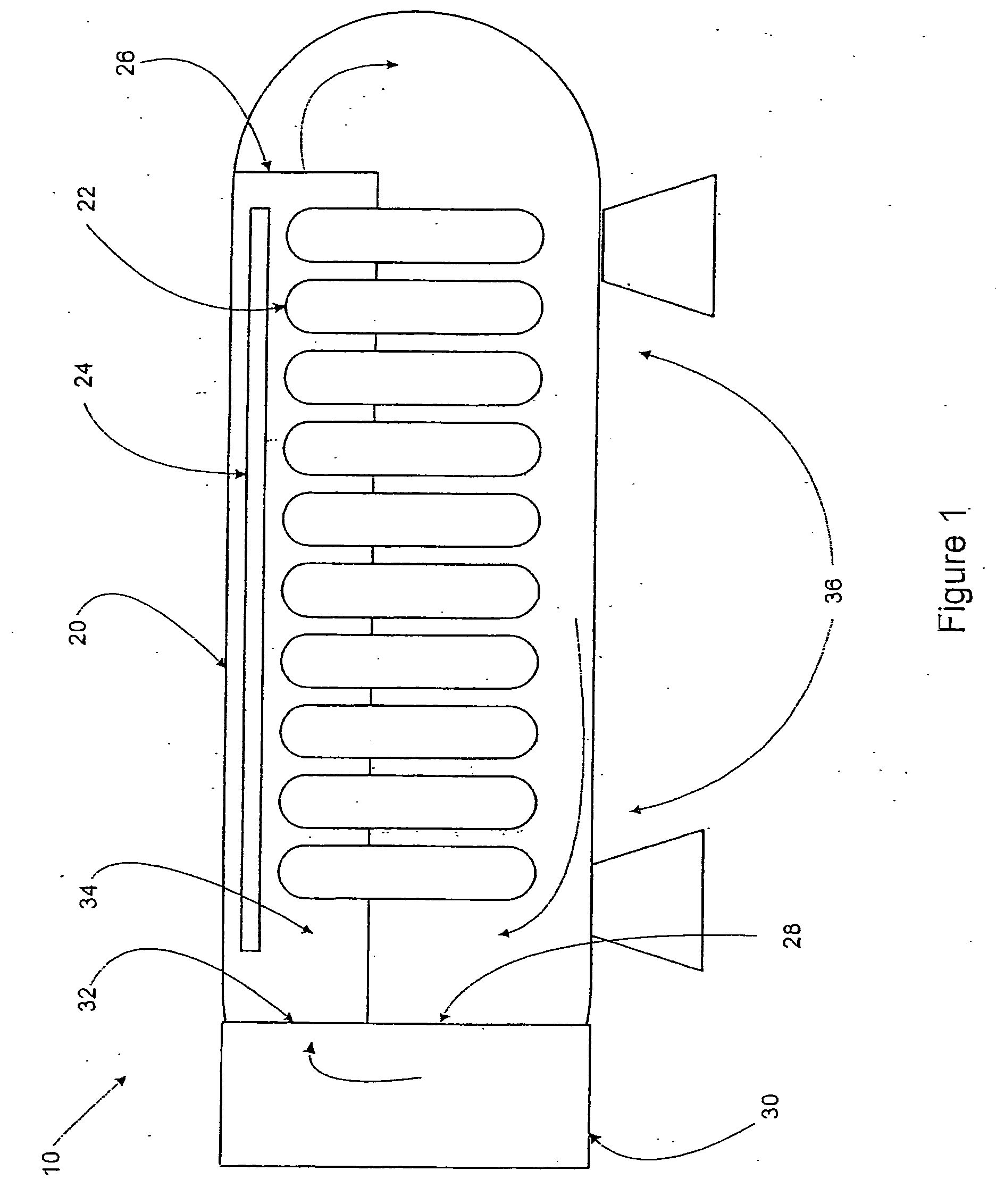
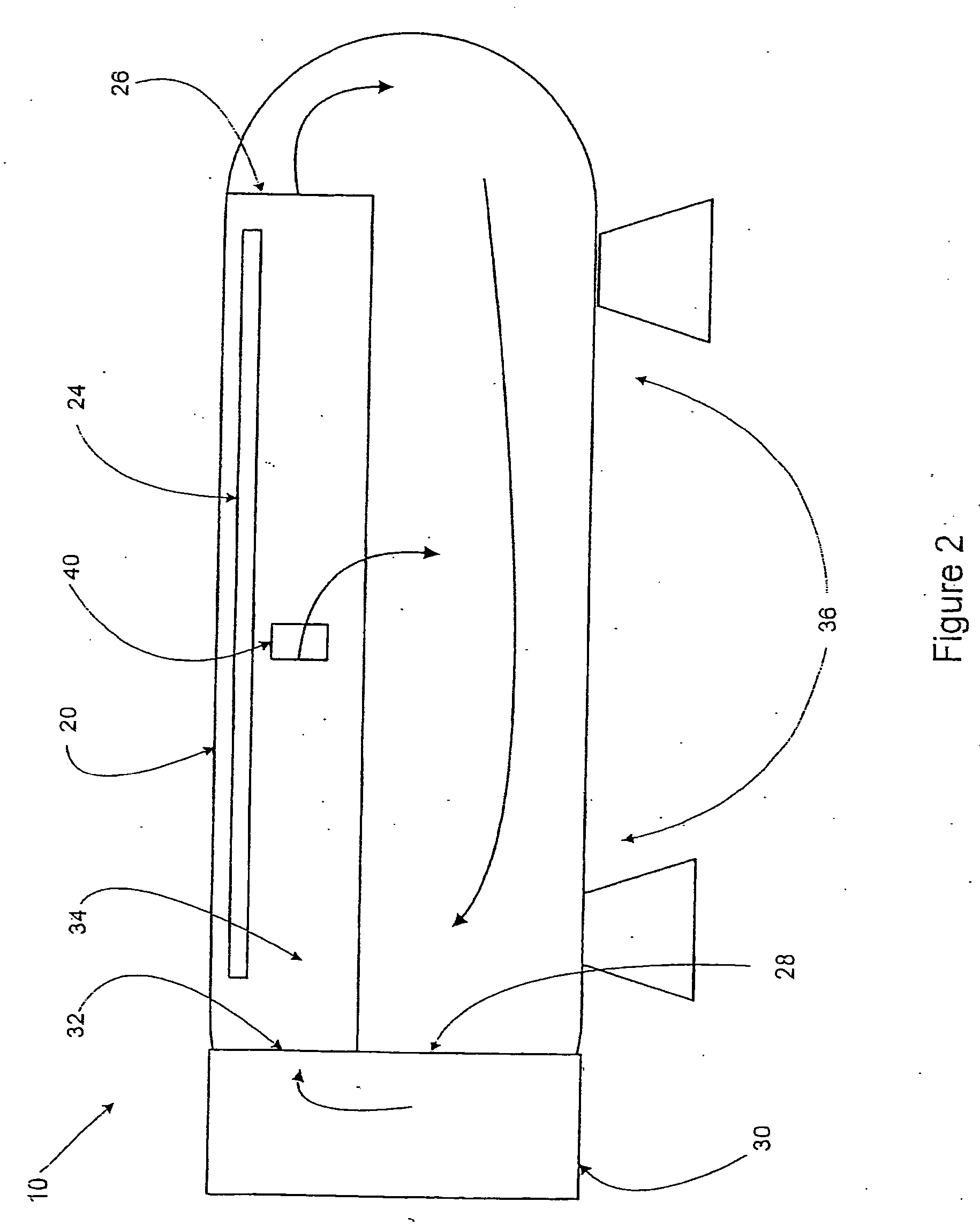
Adaptive real time control of a reticle/mask system
InactiveUS7025280B2Uniform temperature profileEasy to controlSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlDiffusionDynamic models
An adaptive real time thermal processing system is presented that includes a multivariable controller. Generally, the method includes creating a dynamic model of the thermal processing system; incorporating reticle / mask curvature in the dynamic model; coupling a diffusion-amplification model into the dynamic thermal model; creating a multivariable controller; parameterizing the nominal setpoints into a vector of intelligent setpoints; creating a process sensitivity matrix; creating intelligent setpoints using an efficient optimization method and process data; and establishing recipes that select appropriate models and setpoints during run-time.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Adaptive real time control of a reticle/mask system
InactiveUS20050167514A1Uniform temperature profileTemperature controlSpace heating and ventilationTemperatue controlDynamic modelsEngineering
An adaptive real time thermal processing system is presented that includes a multivariable controller. Generally, the method includes creating a dynamic model of the thermal processing system; incorporating reticle / mask curvature in the dynamic model; coupling a diffusion-amplification model into the dynamic thermal model; creating a multivariable controller; parameterizing the nominal setpoints into a vector of intelligent setpoints; creating a process sensitivity matrix; creating intelligent setpoints using an efficient optimization method and process data; and establishing recipes that select appropriate models and setpoints during run-time.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
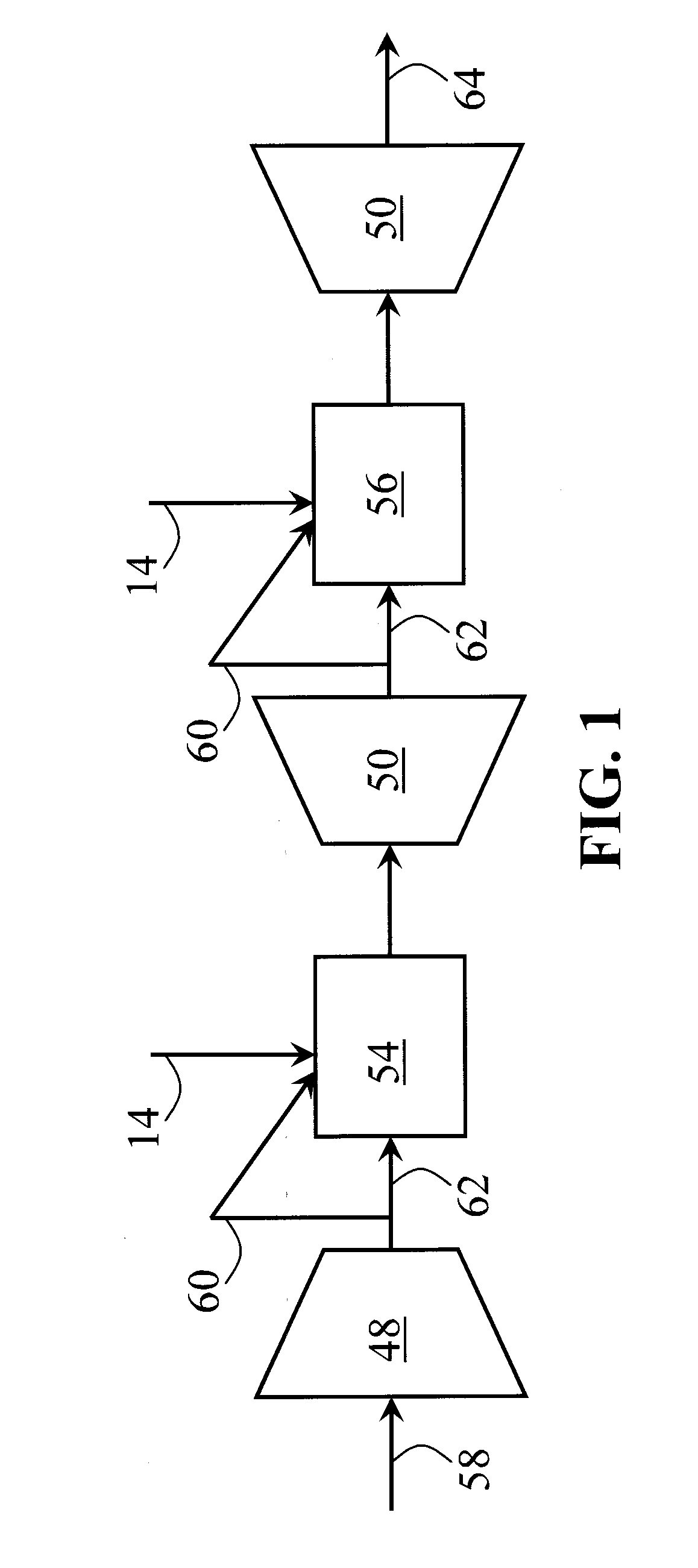
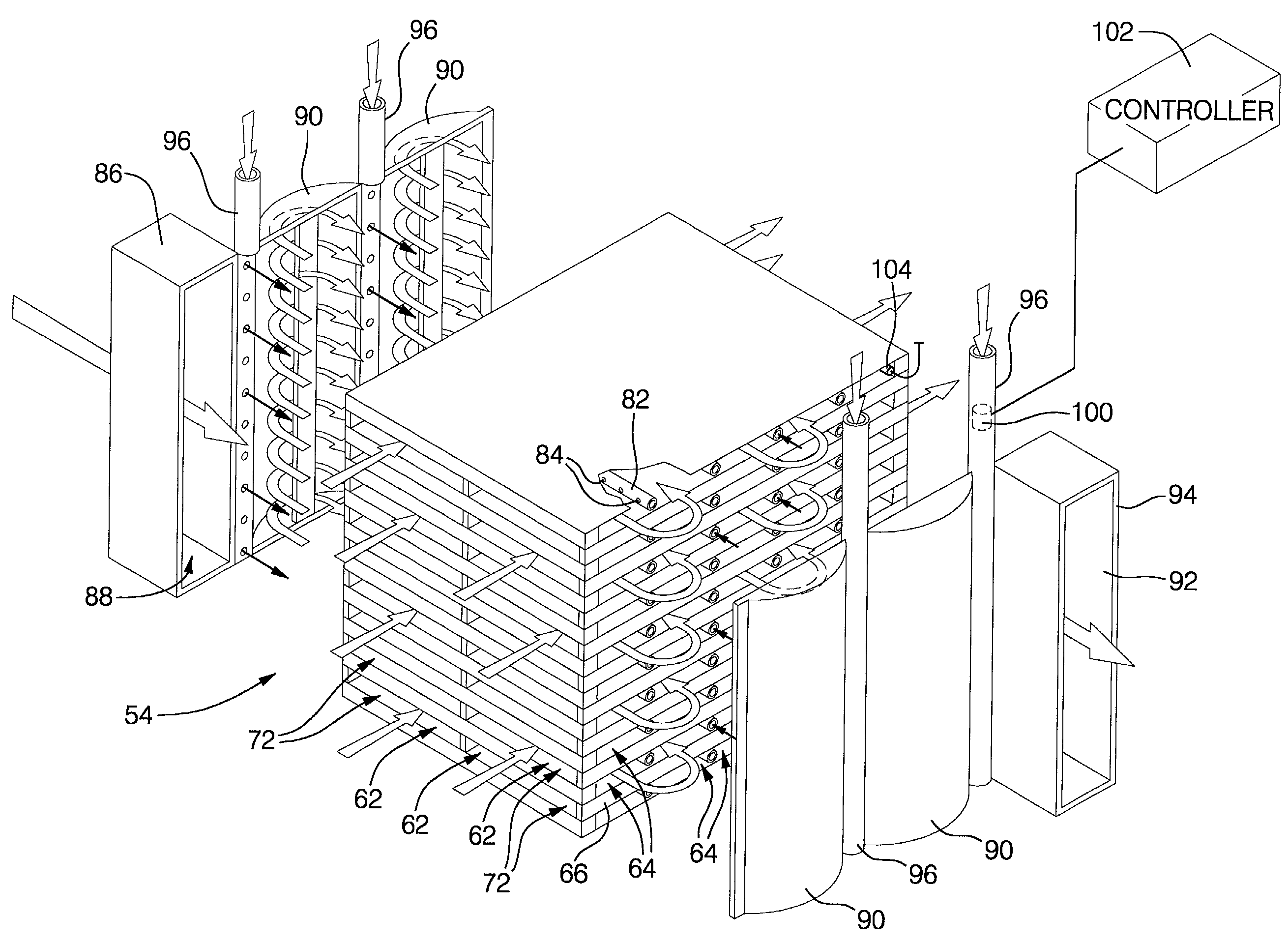
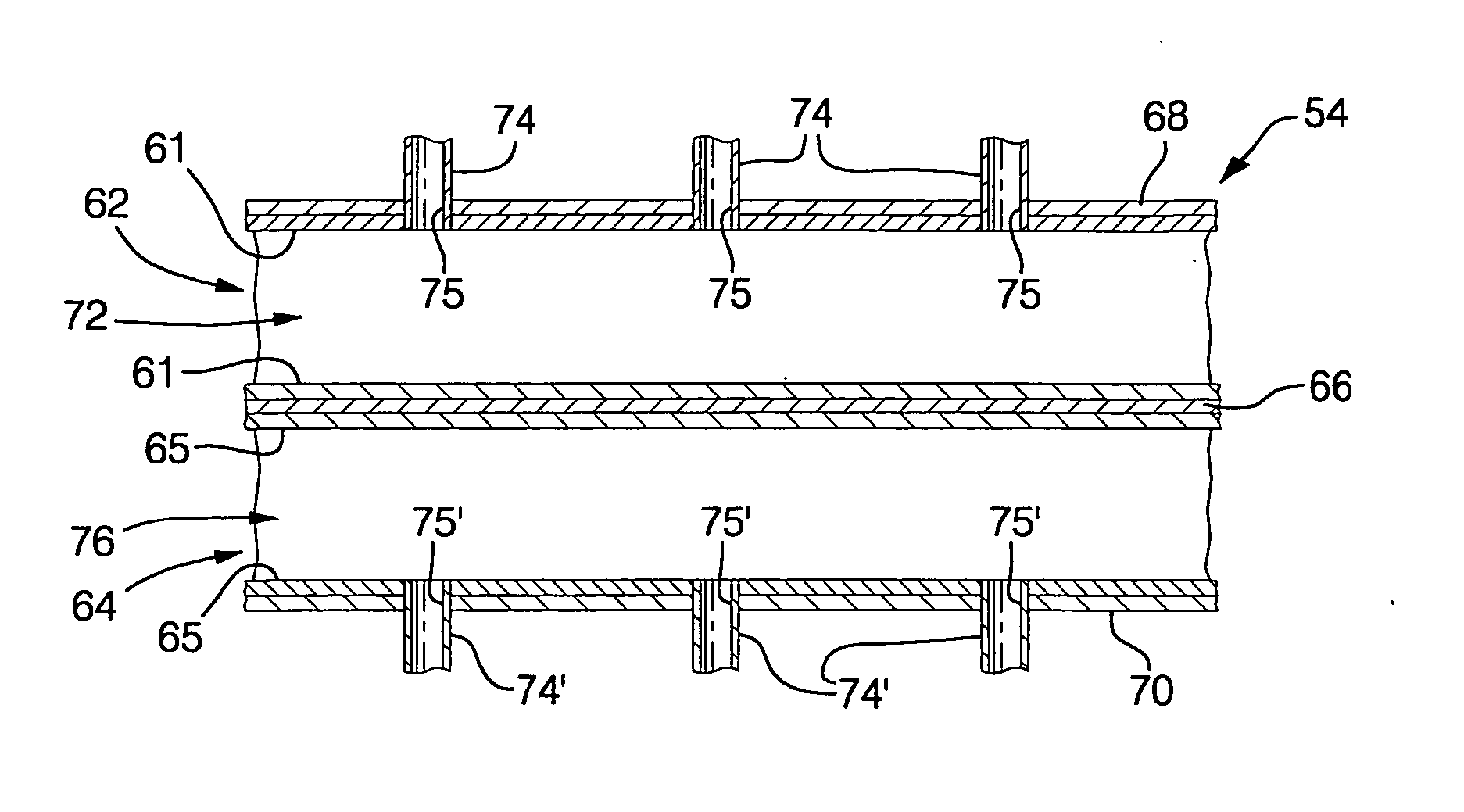
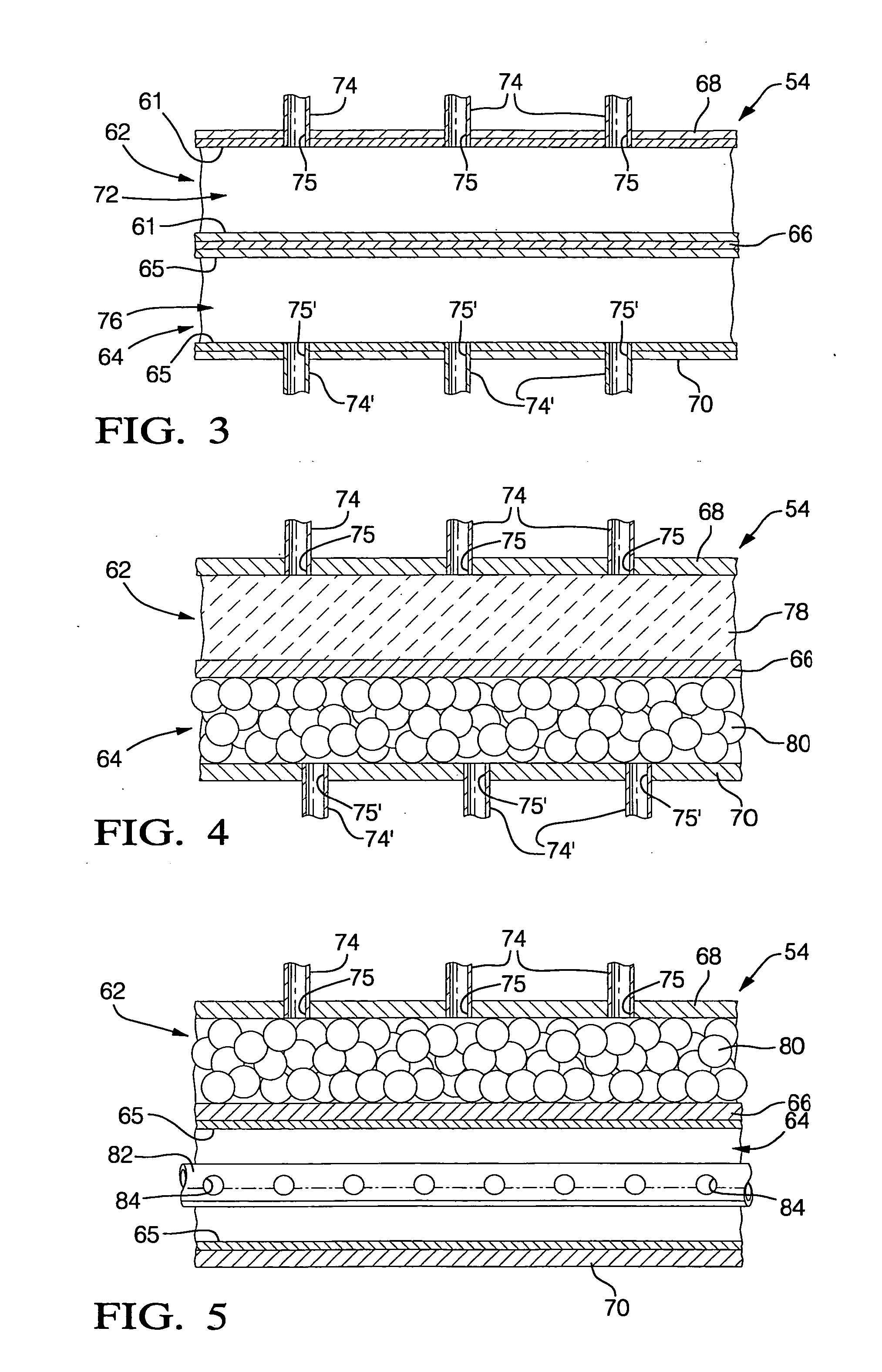
Multiple stage combustion process to maintain a controllable reformation temperature profile
InactiveUS20050048333A1Uniform exchangeGenerate uniformFuel cells groupingFuel cell auxillariesFuel cellsWorking fluid
A reaction vessel that integrates and balances an endothermic process with at least one exothermic process of the fuel cell system. Preferably the exothermic process is conducted in stages to provide more uniform and / or controllable heat generation and exchange, and to produce a uniform and / or controllable temperature profile in the endothermic reaction process. The invention allows for the elimination of the working fluid loop of prior art systems that had unsatisfactory response times at startup, and during transient conditions, and also added to the overall mass and volume of the fuel cell system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method and device for operating a multiple component technical system, particularly a combustion system for producing electrical energy
InactiveUS7181321B2Reduce operating costsSimple componentsLevel controlTemperatue controlCombustion systemReliability engineering
In a technical system a plurality of values associated respectively with a component are stored in at least one computer unit. The computer unit is enabled to trigger an evaluation of at least one other component with a value when a component begins or terminates operation, and the values of each component are added. The computer unit is also enabled to determine which components should be started or stopped based on the added values.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
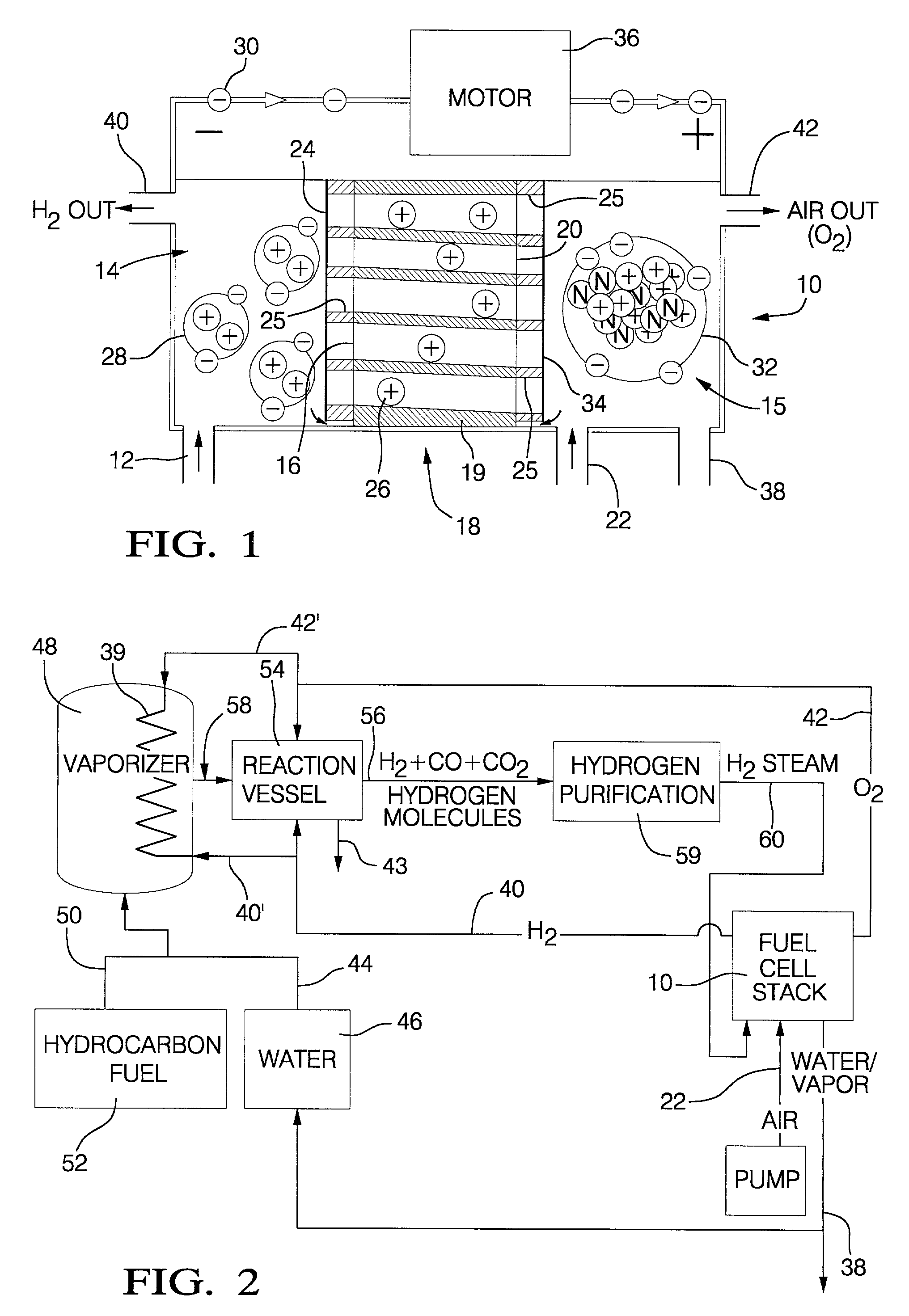
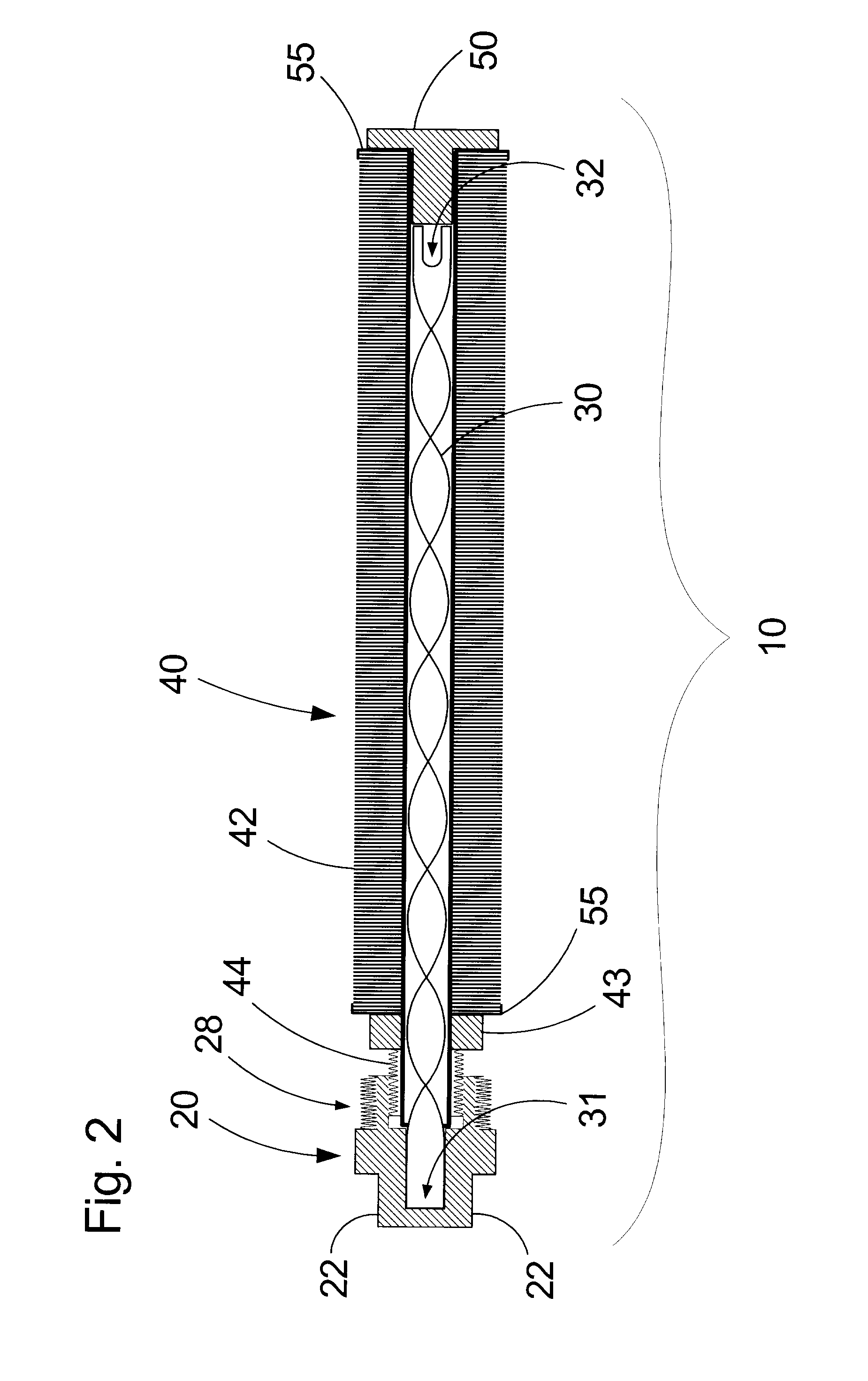
Fluid flow control for cool, efficient fuel cell operation
InactiveUS6572995B2Reduce the maximum temperatureImprove performanceFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsCoolant flow
A fuel cell stack (7) has a two-pass fuel flow field (11, 14) extending from a fuel inlet (8) around a fuel turnaround manifold (12) to a fuel outlet (15). The stack has two air flow fields (37, 40) extending from an air inlet (32) through an air turnaround manifold (38) to an air outlet (41), the air outlet (41) being adjacent to the fuel outlet (15). The stack includes a coolant flow field (23, 25, 27) which extends from a coolant inlet (21) to a coolant outlet (28), the coolant inlet being adjacent to both the fuel outlet and the air outlet. The fluid flow configuration provides lower temperature, a more even temperature profile, a higher coolant exit temperature, and permits operation with higher air utilization and lower coolant flow.
Owner:AUDI AG
Method for combustion of a fuel
InactiveUS20050282097A1Increase in flame volumeMinimize residence timeContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberFront velocity
In a method for the combustion of a fuel, a fuel or a premixed combustible mixture is introduced into a combustion space as a combustible fluid open jet. The velocity of the open jet is selected in such a way that it is impossible for a stable flame front to form, i.e. is in any event greater than the flame front velocity, and that, on account of a jet pump effect, flue gas is mixed into the combustible fluid jet from the combustion chamber in a jet-induced recirculation internally within the combustion chamber. The admixed flue gas dilutes and heats the combustible fluid. The heating causes the spontaneous ignition temperature to be exceeded, and a low-pollutant volumetric flame is formed in a highly dilute atmosphere.
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA SWITZERLAND AG
Apparatus and method for a gas turbine entrainment system
ActiveUS8015821B2Extended stayWell mixedContinuous combustion chamberEngine manufactureCombustion chamberCombustor
This invention relates to an apparatus for an entrainment system of a vortex burning combustion chamber or a vortex burning inter-turbine burner in a gas turbine. The entrainment system rapidly and thoroughly mixes hot combustion gases with non-combustion gases to reduce the gas temperature before entering a turbine. The entrainment system includes a plurality of helical vanes forming trenches and resulting in a highly helical flow path. The highly helical flow path provides an increased residence time for mixing of the combustion gases and non-combustion gases. Radial cavities in the helical vanes, canted vane angles and varying geometries further facilitate mixing while reducing losses. This invention also includes a method of mixing combustion and non-combustion gases in an entrainment system.
Owner:SPYTEK AEROSPACE CORP
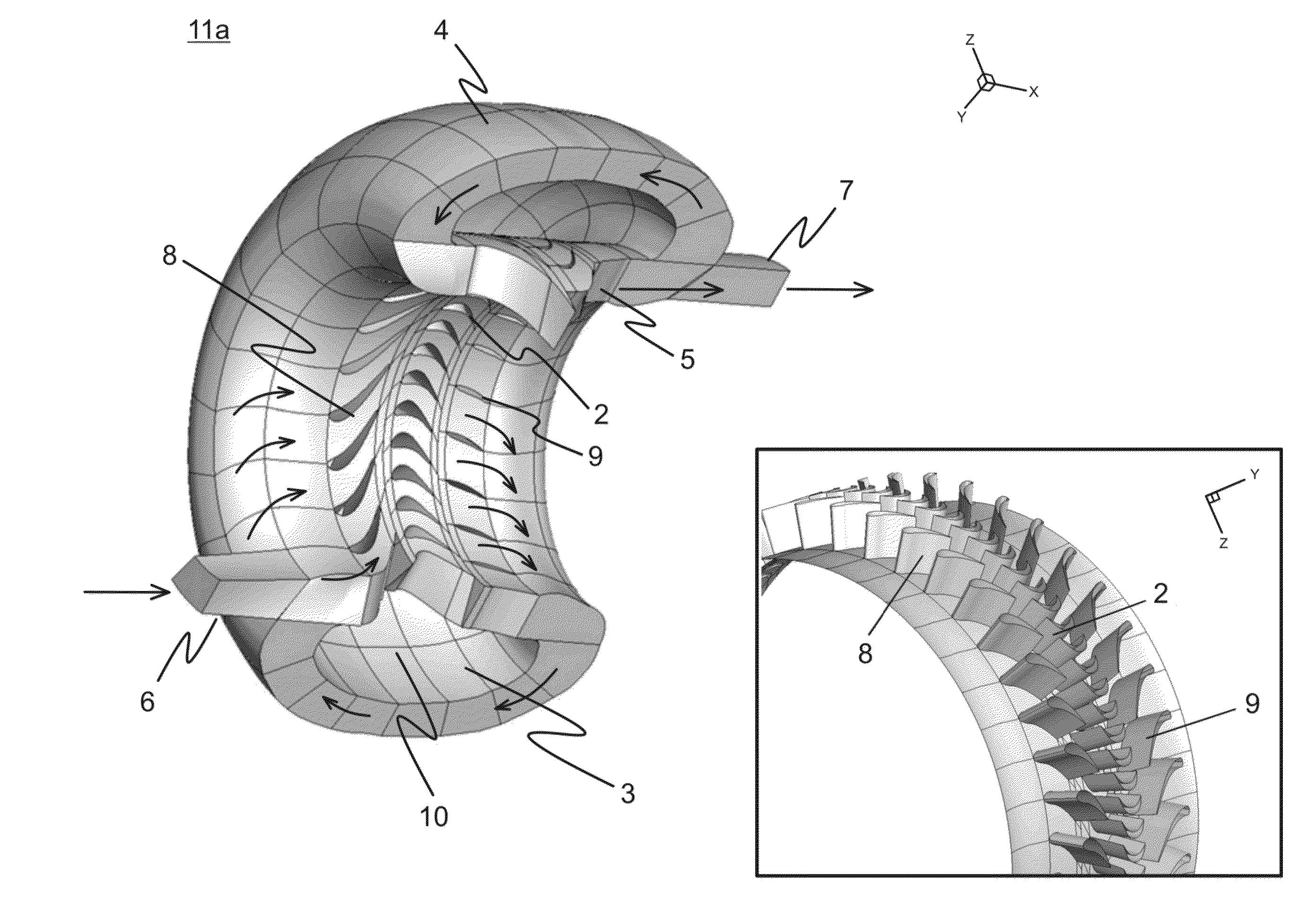
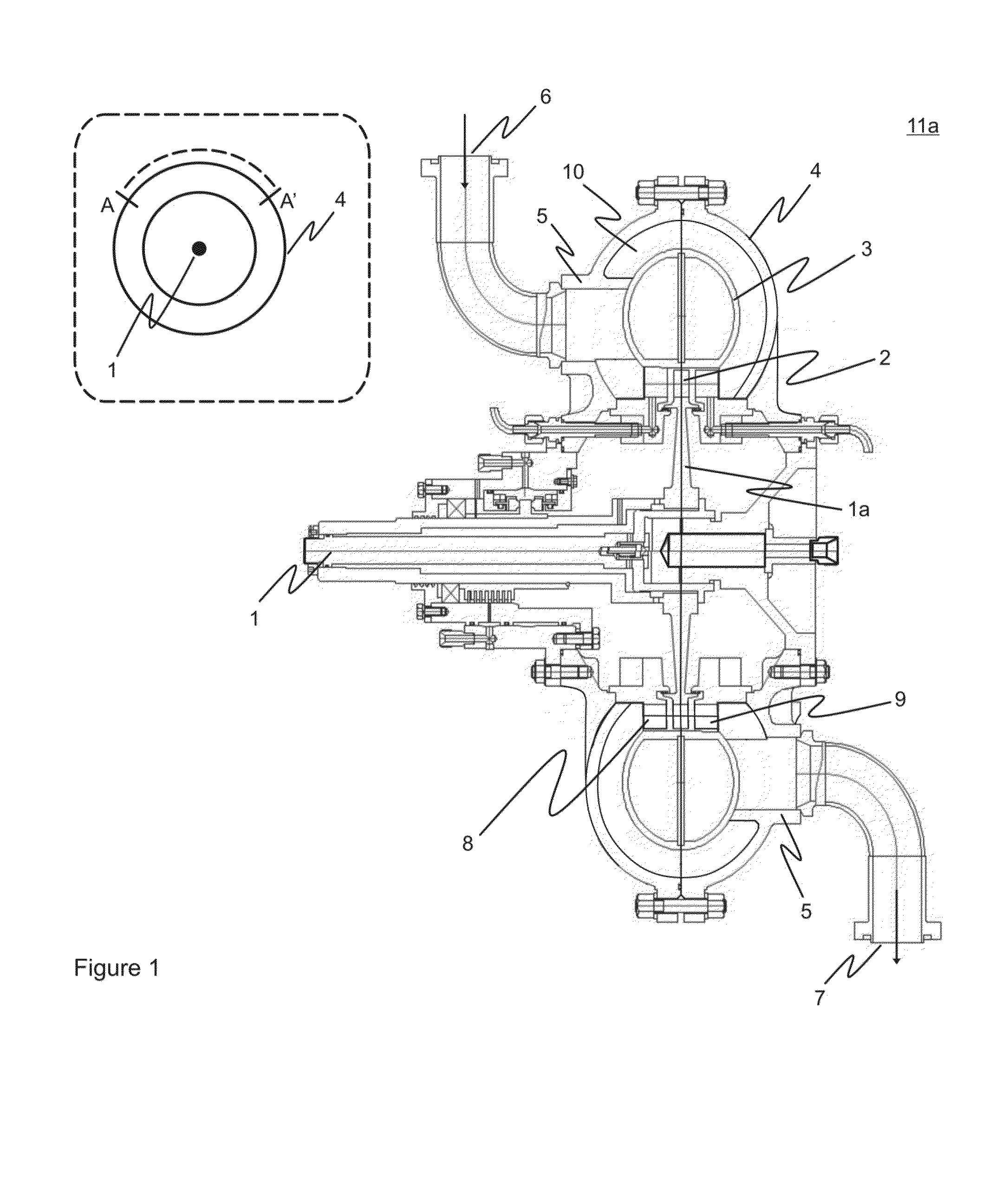
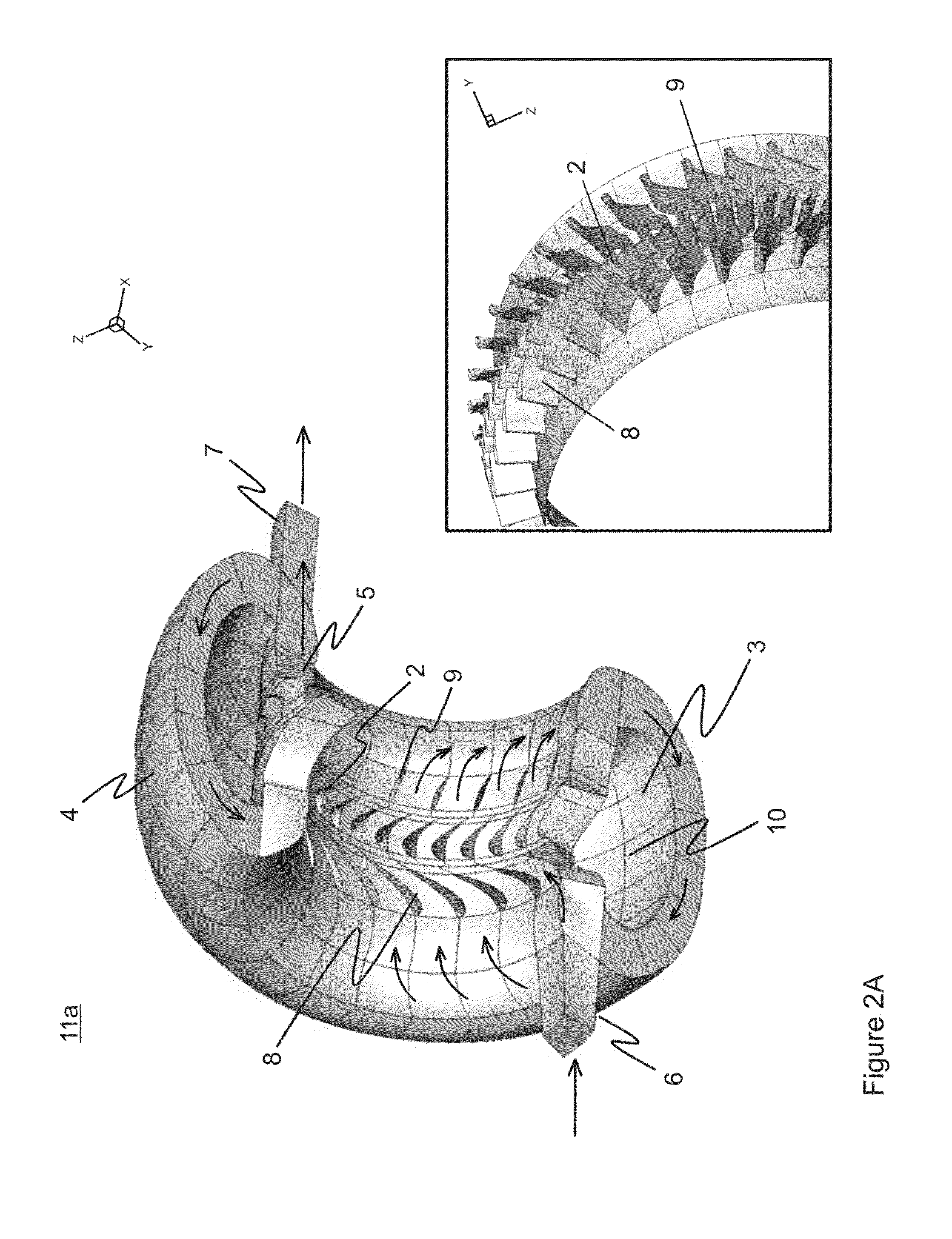
Process and rotary machine type reactor
ActiveUS20140243569A1Overcome limitationsReduce time of residenceThermal non-catalytic crackingUltra-high pressure processesShock waveProcess engineering
A rotary machine type shock wave reactor suitable for thermal cracking of hydrocarbon-containing materials includes a casing, a rotor whose periphery contains an axial-flow blade cascade, and a directing rim, provided with at least two stationary vane cascades, adjoining an axial-flow rotor cascade, wherein the casing substantially encloses the periphery of the rotor and the directing rim. The cascades are configured to direct feedstock containing process stream to repeatedly pass the cascades in a helical trajectory while propagating within the duct between the inlet and exit and to generate stationary shock-waves to heat the feedstock. The axial-flow rotor cascade is configured to provide kinetic energy and add velocity to feedstock containing process stream, and the stationary vanes located downstream the rotor cascade are configured to reduce the velocity of the stream and convert kinetic energy into heat. The reactor may also process carbohydrate- and glyceride-based feedstock, and gaseous biomass matter.
Owner:COOLBROOK
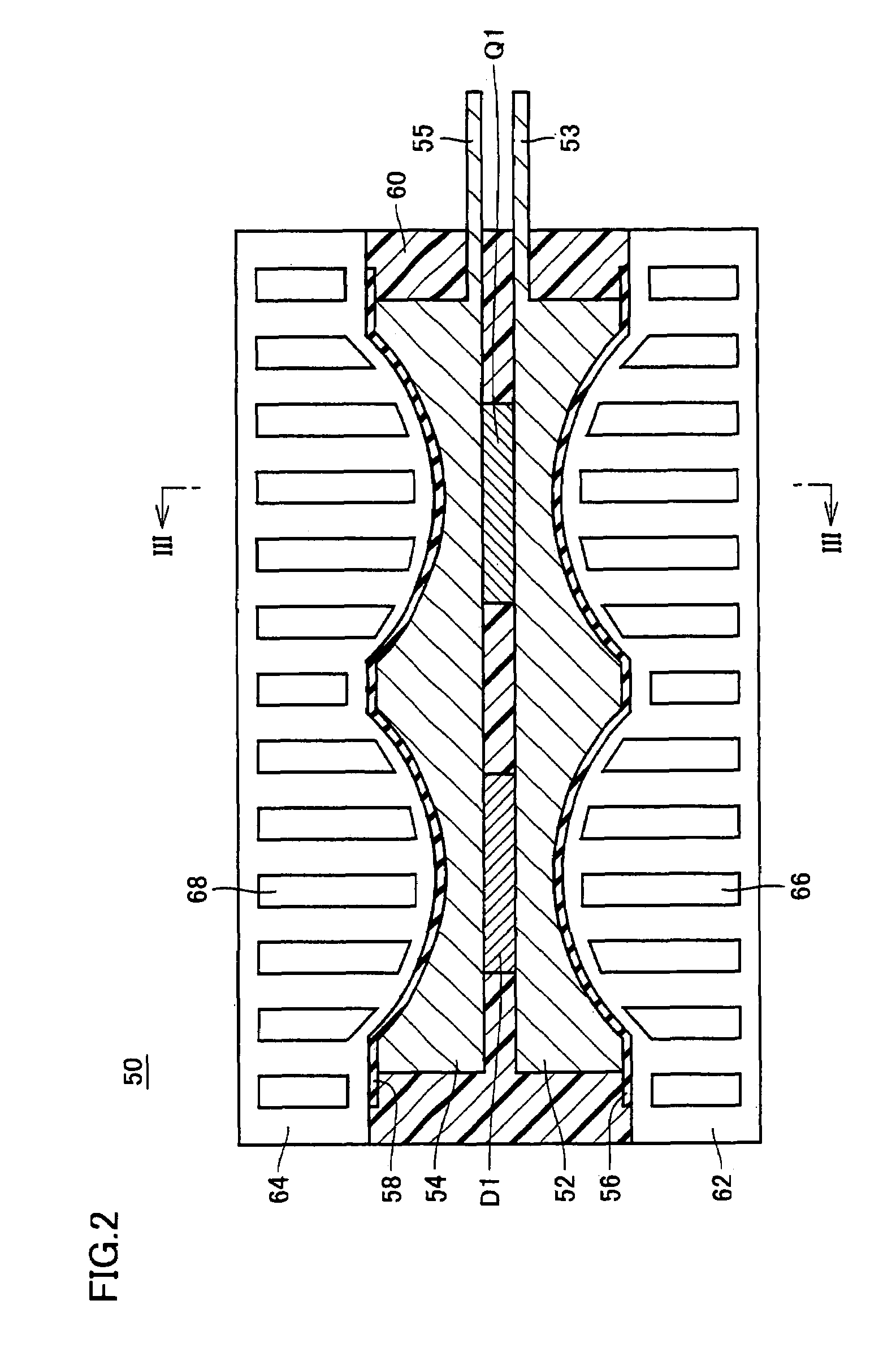
Semiconductor Module And Semiconductor Device
InactiveUS20080093730A1Small thicknessImprove cooling effectSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesDevice materialEngineering
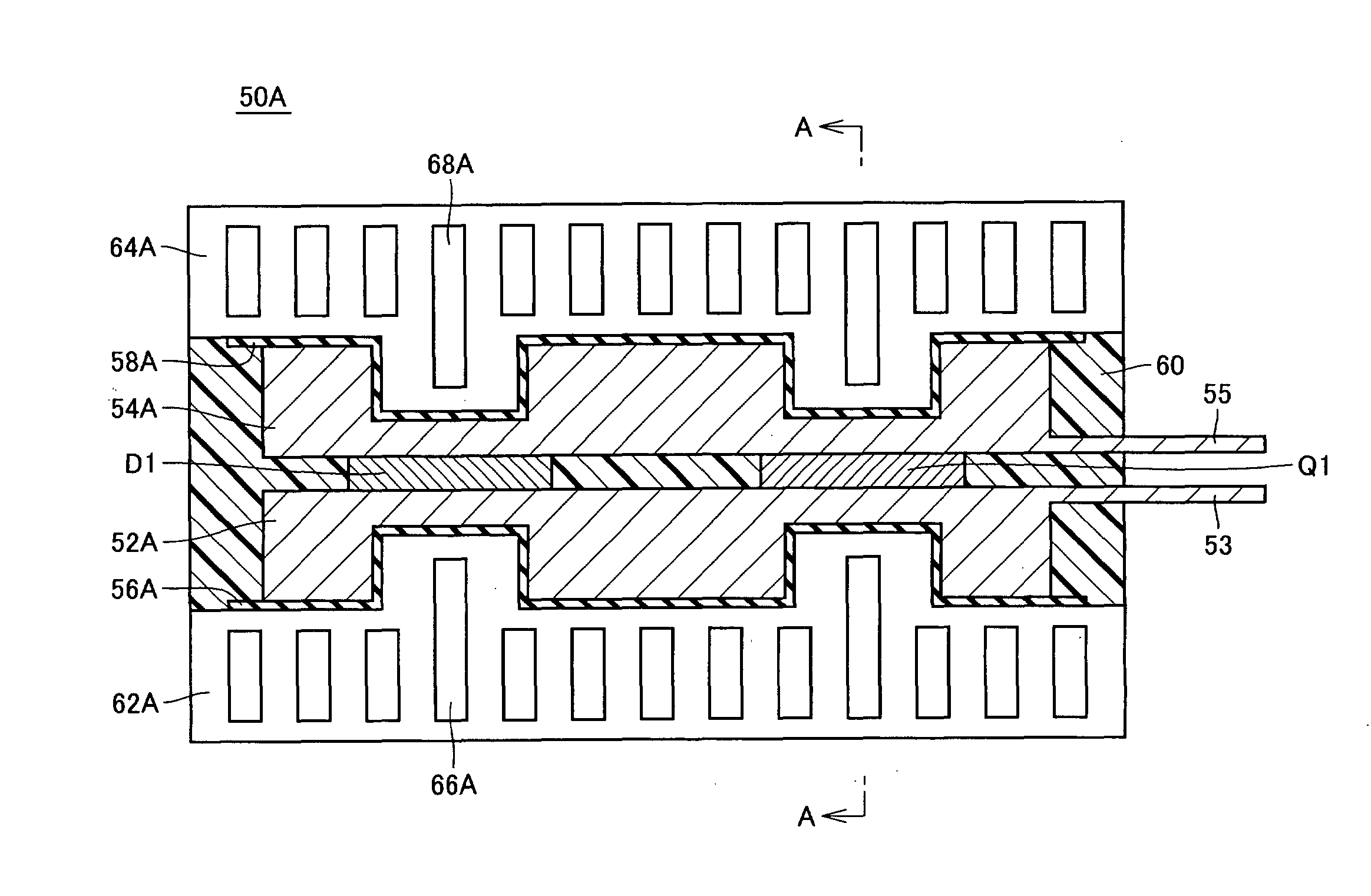
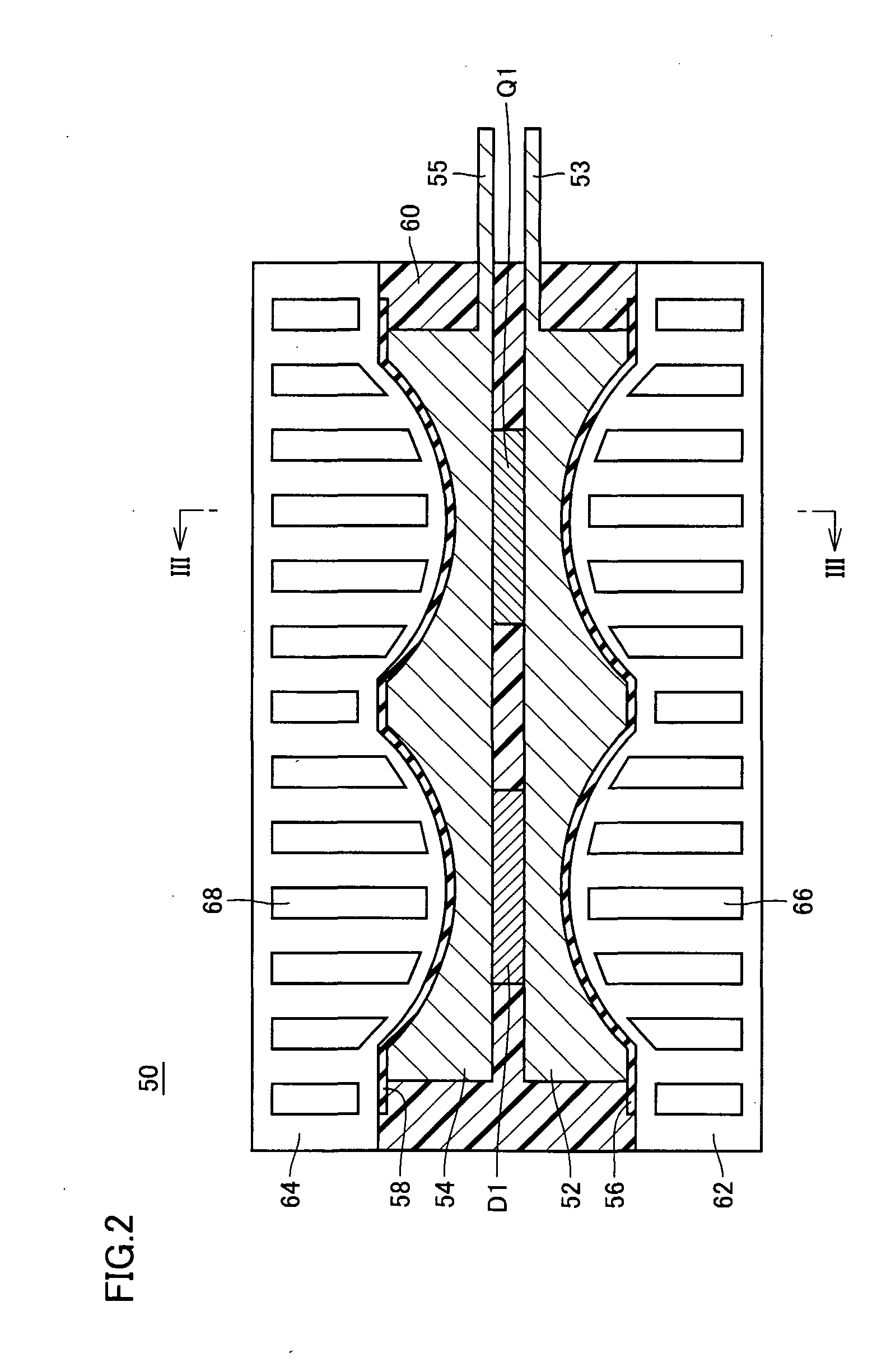
Electrode plates (52, 54) acting as a heat sink are arranged to sandwich a power transistor (Q1) and a diode (D1). Electrode plates (52, 54) at their surfaces opposite cooling elements (62, 64) at a portion opposite power transistor (Q1) and diode (D1) are formed to be smaller in thickness at a portion adjacent to power transistor (Q1) and diode (D1) substantially at the center than at a periphery. Cooling elements (62, 64) are disposed geometrically along electrode plates (52, 54) to sandwich electrode plates (52, 54)
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Fluid flow control for cool, efficient fuel cell operation
InactiveUS20030049506A1Improve air utilizationReduce the maximum temperatureFuel cell heat exchangeFuel cells groupingFuel cellsCoolant flow
A fuel cell stack (7) has a two-pass fuel flow field (11, 14) extending from a fuel inlet (8) around a fuel turnaround manifold (12) to a fuel outlet (15). The stack has two air flow fields (37, 40) extending from an air inlet (32) through an air turnaround manifold (38) to an air outlet (41), the air outlet (41) being adjacent to the fuel outlet (15). The stack includes a coolant flow field (23, 25, 27) which extends from a coolant inlet (21) to a coolant outlet (28), the coolant inlet being adjacent to both the fuel outlet and the air outlet. The fluid flow configuration provides lower temperature, a more even temperature profile, a higher coolant exit temperature, and permits operation with higher air utilization and lower coolant flow.
Owner:AUDI AG
Method and apparatus for preheating ventilation air for a building
InactiveUS20080060635A1Easy constructionSimpler and easy to installRoof covering using slabs/sheetsSolar heating energyShortest distanceShort distance
A solar air heating system for a building having a vertical, south-facing wall. The system has a perforated panel covering the wall. Vertical frame members fasten the panel to the wall to space the panel a short distance away from the wall and to form an air channel between the wall and panel. There is an air collecting space at the bottom of the channel, adjacent the wall. An air inlet in the wall connects the air collecting space to the interior of the building. A fan in the inlet draws outside air into the channel through the perforations in the panel, from the channel into the air collecting space, and from the air collecting space into the building through the air inlet.
Owner:MATRIX ENERGY
Fiberizing bushings and methods of using
InactiveUS7003986B2Increase the cross-sectional areaEliminate cold cornersGlass furnace apparatusRotary drum furnacesElectrical resistance and conductanceFiber
Electrical resistant bushings and methods for making fibers such as glass fibers by passing molten glass through these bushings to form fibers wherein the bushings have novel ears for attaching to electrical terminal clamps bringing electrical current to the bushing are disclosed. The novel ears have at least one generally V shaped notch at or near the unattached end of the ear to produce an improved temperature profile on the tip plate of the bushing. One preferred bushing of the invention has ears having 5 generally V shaped notches therein.
Owner:JOHNS MANVILLE INT INC
Printhead carriage
InactiveUS20060139400A1Easy constructionHigh adjustment accuracyInking apparatusPower drive mechanismsReciprocating motionEngineering
A printhead carriage including a body that is guided and driven for reciprocating movement in a printer, a mounting plate for a printhead assembly, and a suspension structure adjustably connecting the mounting plate to the body, the suspension structure having a framework of hinge plates having elastic hinges and at least one adjusting mechanism adapted to adjust the position of the mounting plate by elastically deflecting at least one of the hinges. An adjusting unit which provides for at least one degree of freedom of the mounting plate and includes two hinge plates that are connected to a common support point of the mounting plate and are oriented at right angles relative to one another, and the adjusting mechanism is adapted to push and / or pull one hinge plate in the longitudinal direction thereof, with the elastic deflection of at least one hinge of the other hinge plate.
Owner:OCE TECH
RF heater arrangement for substrate heating apparatus
InactiveUS7985295B1Minimizing levitationImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingChemical vapor deposition coatingLevitationSusceptor
An RF heating system for a substrate or substrates including a susceptor for supporting the substrate; one or more RF heating coils; and a platen disposed between the RF heating coil and the substrate. The platen is constructed of materials that become heated under RF energy, which will then radiate heat into the susceptor and the substrate. In this way the susceptor need not be constructed of materials that become heated under RF energy thus minimizing levitation. The platen provides a uniform temperature profile across the substrates, benefiting from a more diffused heat source. The RF heating system may also be utilized in CVD apparatus that deposits materials on a continuous tape or roll.
Owner:STRUCTURED MATERIALS
Multiple stage combustion process to maintain a controllable reformation temperature profile
InactiveUS7081312B1Uniform exchangeGenerate uniformHydrogen separation using solid contactCell electrodesWorking fluidFuel cells
A reaction vessel that integrates and balances an endothermic process with at least one exothermic process of the fuel cell system. Preferably the exothermic process is conducted in stages to provide more uniform and / or controllable heat generation and exchange, and to produce a uniform and / or controllable temperature profile in the endothermic reaction process. The invention allows for the elimination of the working fluid loop of prior art systems that had unsatisfactory response times at startup, and during transient conditions, and also added to the overall mass and volume of the fuel cell system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Heat dissipating fins opposite semiconductor elements
InactiveUS7687901B2Uniform temperature profileCooled more efficiently substantiallySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesTransistorHeat spreader
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Process and rotary machine type reactor
ActiveUS9234140B2Overcome limitationsShorten the timeThermal non-catalytic crackingUltra-high pressure processesShock waveProcess engineering
A rotary machine type shock wave reactor suitable for thermal cracking of hydrocarbon-containing materials includes a casing, a rotor whose periphery contains an axial-flow blade cascade, and a directing rim, provided with at least two stationary vane cascades, adjoining an axial-flow rotor cascade, wherein the casing substantially encloses the periphery of the rotor and the directing rim. The cascades are configured to direct feedstock containing process stream to repeatedly pass the cascades in a helical trajectory while propagating within the duct between the inlet and exit and to generate stationary shock-waves to heat the feedstock. The axial-flow rotor cascade is configured to provide kinetic energy and add velocity to feedstock containing process stream, and the stationary vanes located downstream the rotor cascade are configured to reduce the velocity of the stream and convert kinetic energy into heat. The reactor may also process carbohydrate-and glyceride-based feedstock, and gaseous biomass matter.
Owner:COOLBROOK
Turbulated immersion heat-exchange apparatus
InactiveUS20090218083A1Facilitates and enhances ease-of-flowUniform temperature profileInternal combustion piston enginesClosure meansCouplingTransmission channel
A submersible heat-exchanging apparatus comprises a cylindrical heat-exchange component configured with one end for sealingly engaging a terminal plug and the other end for sealingly engaging and communicating with a coupling manifold having opposed inflow and outflow ports. A flow-directing elongate insert is provided with one end configured to engage the coupling manifold interposed the inflow and outflow ports, and the other end provided with an aperture and configured for abutting the terminal plug. The flow-directing elongate insert is configured to slidingly contact and cooperate with the inner walls of the heat-conductive conduit thereby partitioning the heat-conductive conduit into two opposed fluid transmission channels wherein one channel communicates with the inlet port and the other channel communicates with the outlet port. The coupling manifold is configured to sealingly engage an aperature provided therefore in a fluid-containing receptacle whereby the heat-exchange component extends into the receptacle.
Owner:ARNOT ROGER
Multiple stage combustion process to maintain a controllable reformation temperature profile
InactiveUS20050048332A1Uniform exchangeUniform heat generationLaboratory glasswaresHydrogen/synthetic gas productionFuel cellsWorking fluid
A reaction vessel that integrates and balances an endothermic process with at least one exothermic process of the fuel cell system. Preferably the exothermic process is conducted in stages to provide more uniform and / or controllable heat generation and exchange, and to produce a uniform and / or controllable temperature profile in the endothermic reaction process. The invention allows for the elimination of the working fluid loop of prior art systems that had unsatisfactory response times at startup, and during transient conditions, and also added to the overall mass and volume of the fuel cell system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Printhead carriage
InactiveUS7419242B2Easy constructionStably holding the mounting plateInking apparatusPower drive mechanismsReciprocating motionDegrees of freedom
A printhead carriage including a body that is guided and driven for reciprocating movement in a printer, a mounting plate for a printhead assembly, and a suspension structure adjustably connecting the mounting plate to the body, the suspension structure having a framework of hinge plates having elastic hinges and at least one adjusting mechanism adapted to adjust the position of the mounting plate by elastically deflecting at least one of the hinges. An adjusting unit which provides for at least one degree of freedom of the mounting plate and includes two hinge plates that are connected to a common support point of the mounting plate and are oriented at right angles relative to one another, and the adjusting mechanism is adapted to push and / or pull one hinge plate in the longitudinal direction thereof, with the elastic deflection of at least one hinge of the other hinge plate.
Owner:OCE TECH
Heat converter for heating automobile
InactiveCN101738100AStrong BrazingPressure-resistant liquid-tightStationary conduit assembliesHeat exchanger casingsAir currentEngineering
The present invention relates to a heat converter (1) for heating an automobile. The heat converter has a plurality of flow passages, the first side of the flow passages is flowed through by a heat transport fluid, the second side is flowed and circulated by air, wherein, the heat transport fluid and the air current are intersect and form a converted circulation, and the heat transport fluid flows and turns back at least two times in an in opposite direction of the flowing of air. The present invention is characterized in that a flow passage is made of a set of sheets (2), wherein, each sheet (2) has two half-sheets (2a, 2b) and at least three flow paths that can be flowed through.
Owner:BEHR GMBH & CO KG
Autoclave for curing retreaded tires
InactiveUS20070079937A1Less-efficient heat transferImprove heat transfer performanceMuffle furnacesLaminationRetreadAutoclave
An improved autoclave for curing retread tires includes a chamber with circulating air flow having turbulence generating devices located in a middle length-wise portion of the chamber. The turbulence generating devices include apertures to guide air from a supply duct into the chamber, and / or wedge-shaped elements or fins mounted on the interior wall of the chamber to disrupt the air flow and cause turbulence.
Owner:MICHELIN RECH & TECH SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com