Turbulated immersion heat-exchange apparatus
a heat exchanger and immersion technology, applied in the field of heat exchangers, can solve the problems of accelerated wear and deterioration of the pump components, affecting the smooth and safe operation of the hydraulic control attachment, and preventing engine start-up, etc., to achieve rapid increase the temperature, facilitate the flow of pressurized fluid, and reduce the viscosity of cold-affected stored oils
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
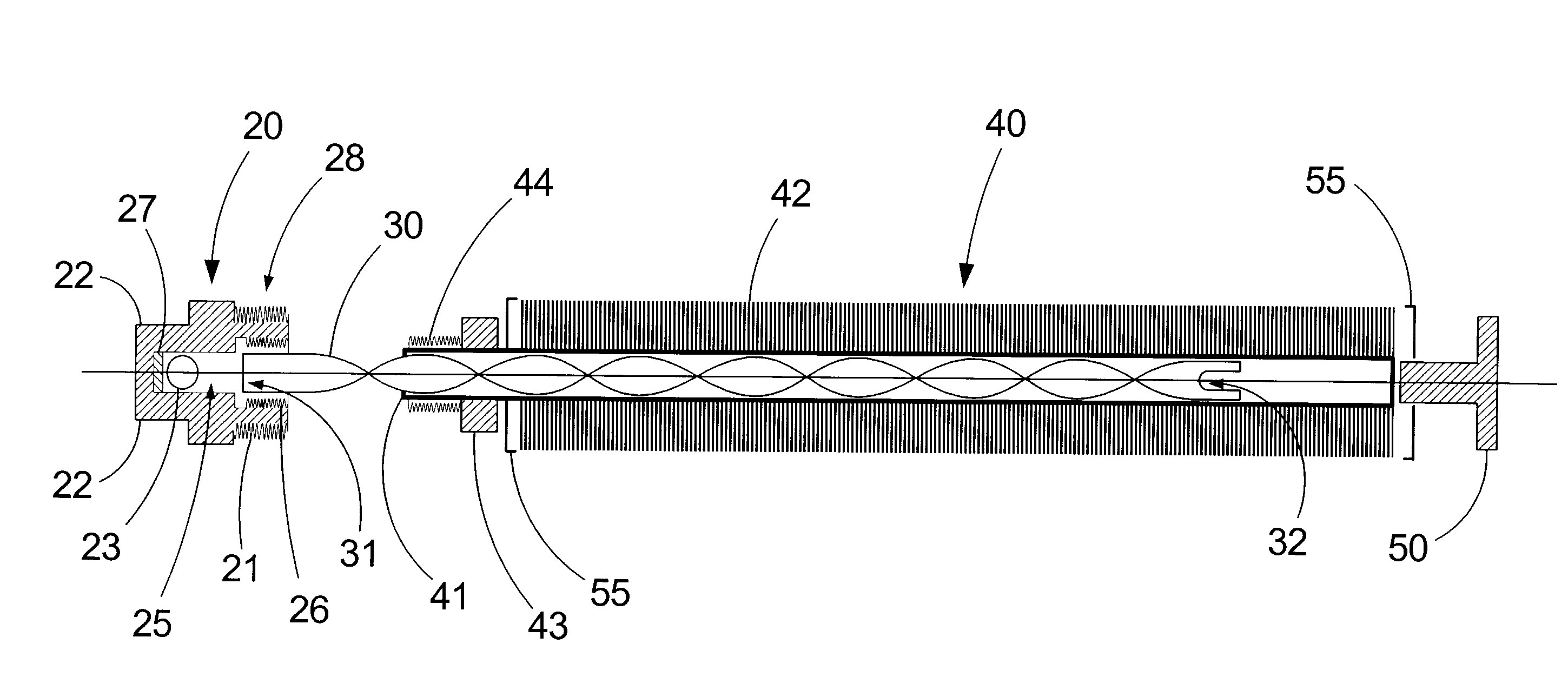
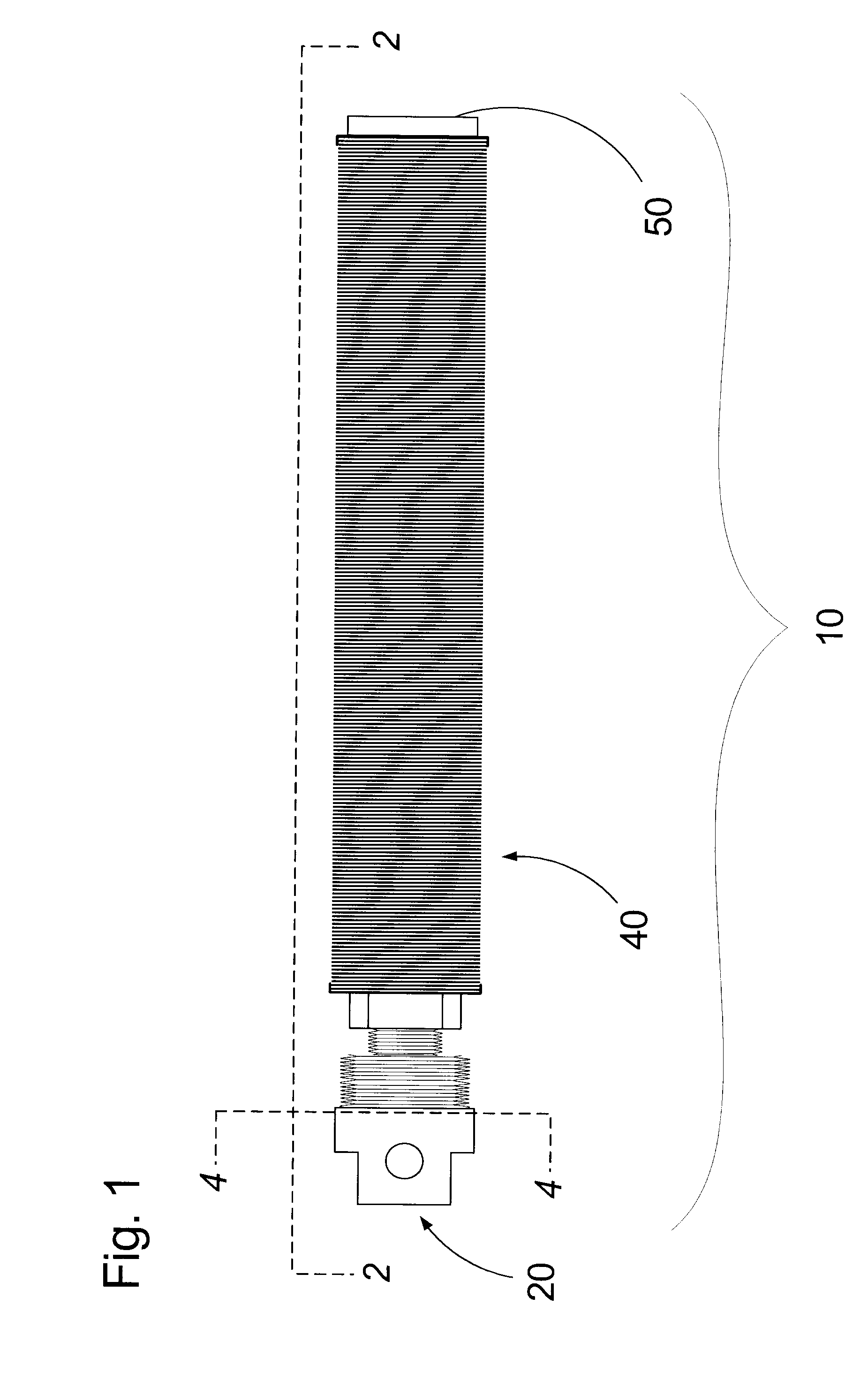
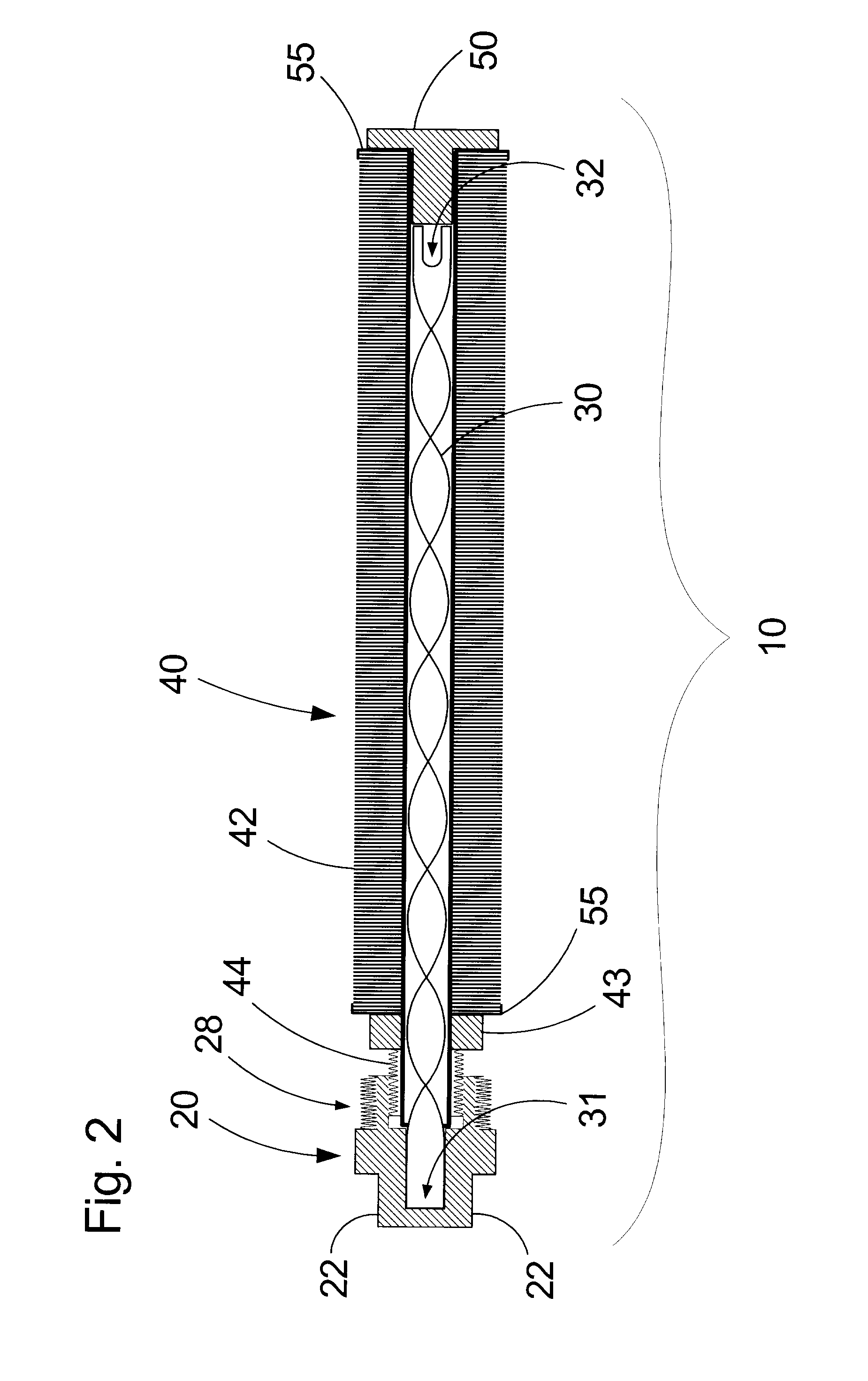
[0028]An exemplary embodiment of the turbulated submersible heat-exchange apparatus of the present invention is shown in the accompanying FIGS. 1-4, and is generally referred to by the numeral 10. The apparatus 10 comprises an elongate cylindrical heat-exchanging component 40 interconnected at one end with a coupling manifold 20 while the other end of component 40 is sealably engaged with a plug 50. A spiralled turbulator insert 30 extends through the heat-exchanging component 40 and abuts the manifold 20 and plug 50.
[0029]The coupling manifold 20 is provided with a collar 28 having an outward-facing male-threaded coupling portion 21 configured for threadably and sealably engaging a tank housing (not shown) and an inner-facing female-threaded coupling portion 26 for sealably interconnecting with the heat-exchanging component 40. A bore 25 extends through the collar 28 into the body of the coupling manifold 20 and communicates with a threaded inlet / outet port 23 and a threaded inlet / ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com