Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31results about How to "More dispersed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
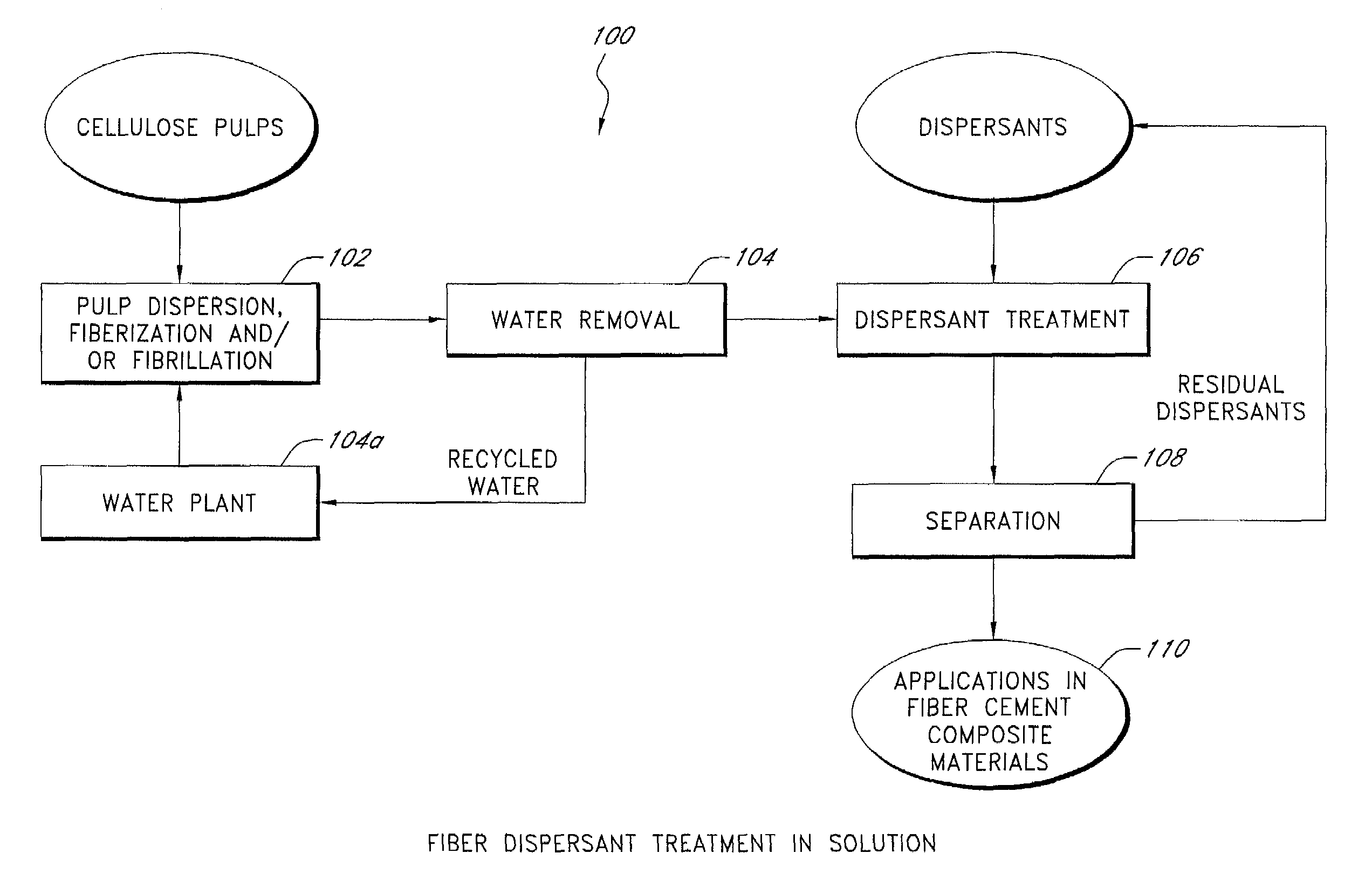
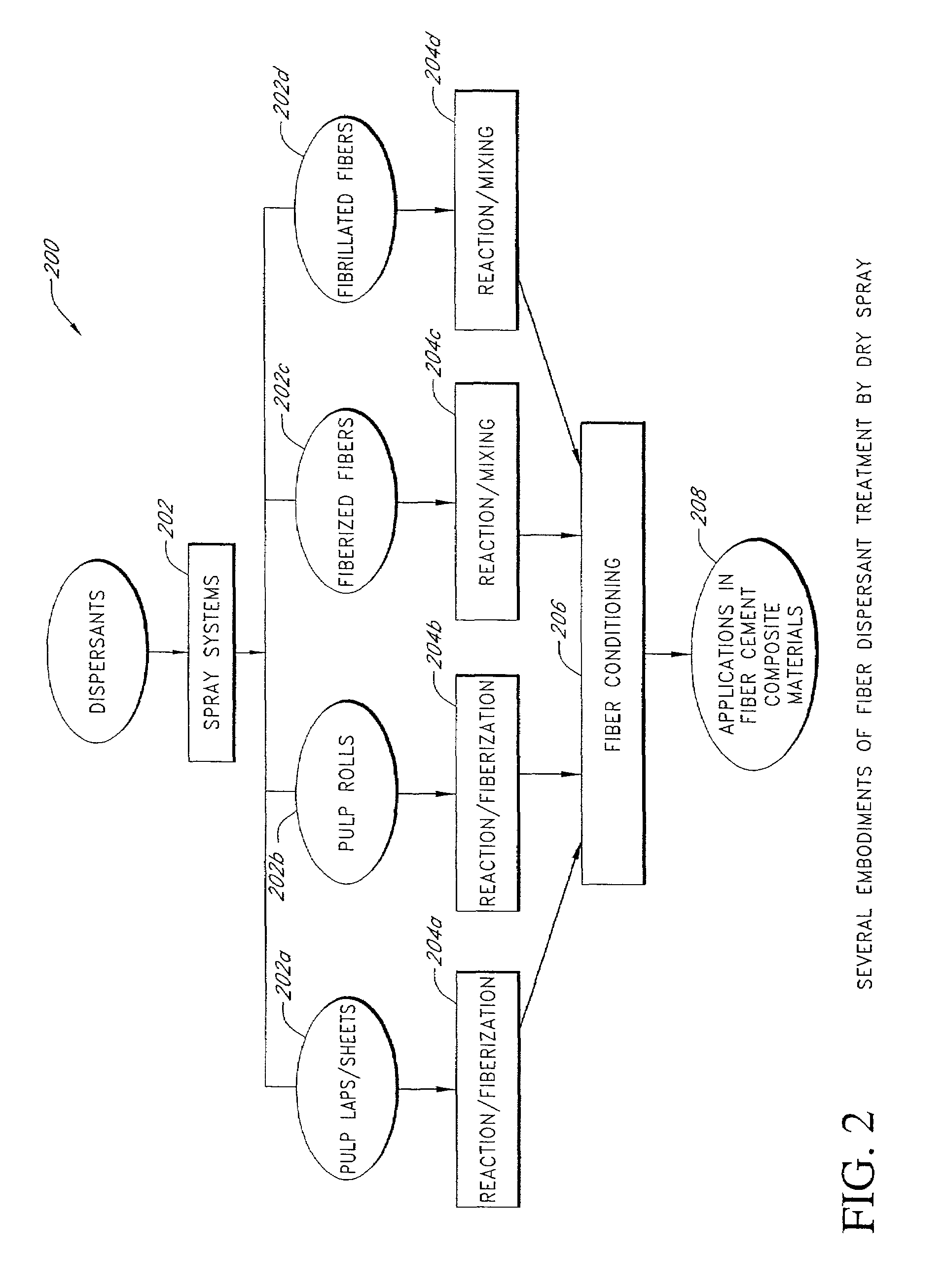
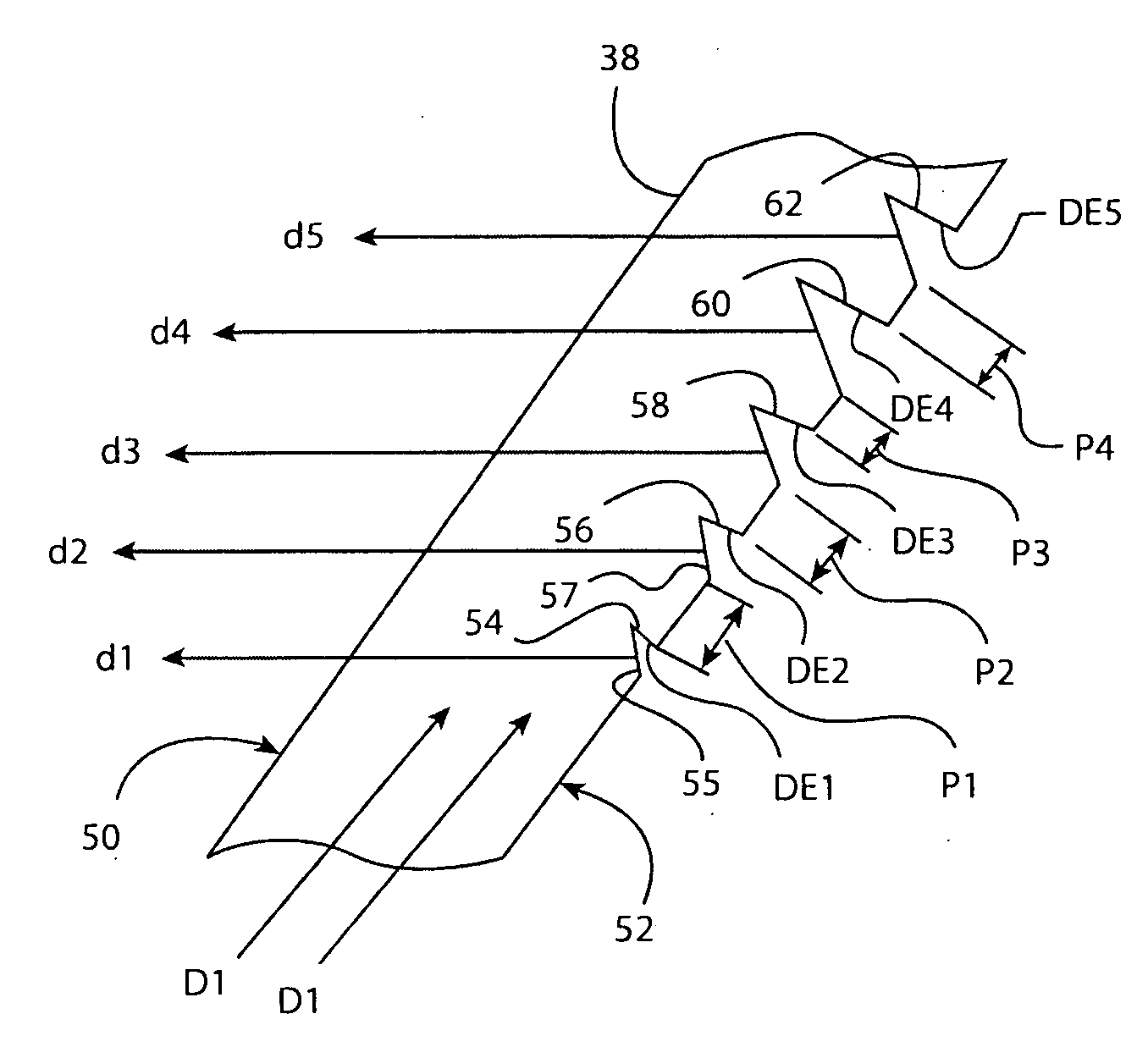
Fiber reinforced cement composite materials using chemically treated fibers with improved dispersibility
InactiveUS7344593B2Improve material propertyIncrease modulusPulp properties modificationSolid waste managementBuilding materialFibre reinforcement
A fiber-reinforced building material in one embodiment incorporates cellulose fibers that are chemically treated with a dispersant to impart improved dispersibility to the fibers. The fibers are treated with a dispersant which deactivates the hydroxyl sites of the fiber surfaces and in some cases, making the fiber surface more hydrophobic. The dispersant inhibits the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose fiber surface from bonding with hydroxyl groups of other fibers and from bonding with hydroxyl groups of the same fiber, thereby significantly reducing inter-fiber and intra-fiber hydrogen bonding. The treated fibers can be readily dispersed and uniformly distributed throughout a mixture without re-clustering or reclumping once the mechanical mixing action stops. The chemically treated fibers with improved dispersibility improve the fiber distribution and reinforcing efficiency, which in turn improves key physical and mechanical properties of the material such as the modulus of rupture, z-direction tensile strength, and toughness, and surface finishes. With improved fiber reinforcing efficiency, less dosage of fiber is needed to achieve the required physical and mechanical properties.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH
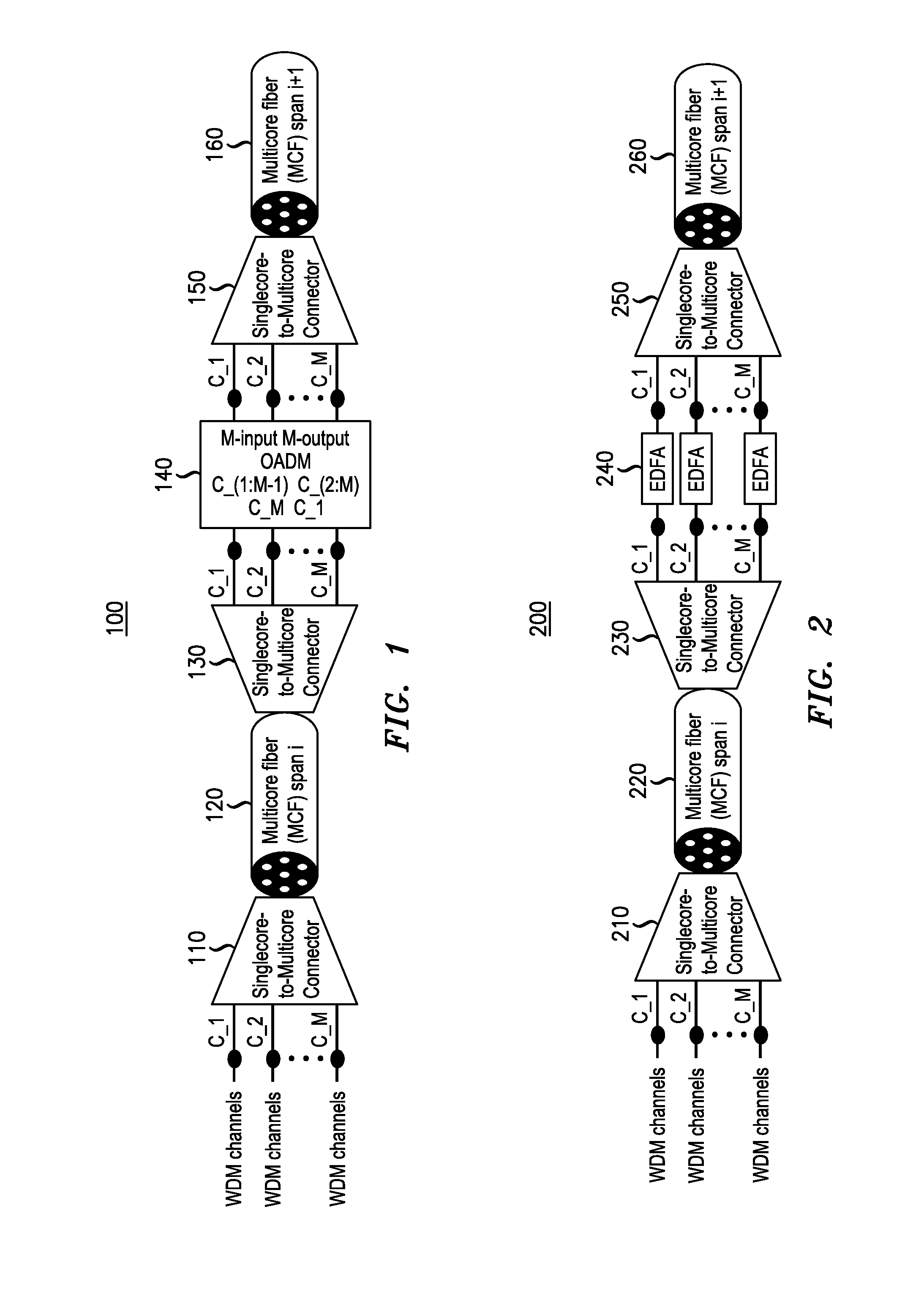
Method And Apparatus For Space-Division Multiplexing Systems
ActiveUS20130236175A1Reducing performance variationImprove system performanceMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFew mode fiberSignal on
A space division multiplexed (SDM) transmission system that includes at least two segments of transmission media in which a spatial assignment of the two segments is different is provided. For example, the SDM transmission may include a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and a second segment of transmission media having a second spatial assignment, wherein the first spatial assignment differs from the second spatial assignment. An example method obtains an optical signal on a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and forwards the optical signal on a second segment of transmission media with a different spatial assignment. The transmission media may be a multi-core fiber (MCF), a multi-mode fiber (MMF), a few-mode fiber (FMF), or a ribbon cable comprising nominally uncoupled single-mode fiber (SMF).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Flip chip type light-emitting element
ActiveUS20090039374A1Inhibit deteriorationIncrease interface areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContact electrodeLight transmission
In a flip chip type light-emitting element of the present invention, an n type contact electrode 14 is formed on an n layer 11 exposed in a comb-tooth shape, a light transmission electrode 15 made of an ITO is formed over the entire surface of an upper surface of a p layer 13 and twenty pad electrodes 16 are formed at prescribed intervals on the light transmission electrode 15. The plane form of the pad electrode 16 has four branches 16b protruding in the form of a cross from a circular central part 16a and the adjacent pad electrodes 16 connected to each other by the branches 16b.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Light guide for vehicle lamp assembly
InactiveUS20100202153A1Reduce brightnessMore dispersedPoint-like light sourceLighting support devicesLight guideEngineering
A light guide and various vehicular lamp assemblies using the same are presented herein. In one embodiment, the lamp assembly includes a light source, such as an LED module. A light coupler is operable to receive light from the light source, and distribute the light in a first direction. The light guide includes an elongated, curvilinear body with first and second longitudinal end faces, and opposing light-emitting and light-guiding surfaces extending between the two end faces on a respective side of the body. The first end face communicates with the light coupler to receive light therefrom. The light guide body transmits light generated by the light source along the longitudinal expanse thereof. The light-guiding surface includes an array of longitudinally-spaced optical grooves configured to refract light generated by the light source in a second direction. The depth of preselected optical grooves is varied along the length of the light guide.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Light guide plate with reflective light mixing
InactiveUS20070263409A1Discoloration of the LCD panel may be limited or eliminatedMore dispersedOptical light guidesReflectorsLighting systemDiffusion
A lighting system includes multiple lighting elements, a light guide, and a first selective wavelength reflective element for mixing light outside of the light guide. The lighting elements include a first lighting element having a first wavelength. The light guide receives light from the lighting elements. The first selective wavelength reflective element is positioned between the first lighting element and the light guide to partially transmit light of the first wavelength to the light guide, and to partially reflect light of the first wavelength. Partially reflecting light away from the light guide allows a fraction of the light to be mixed with another color of light prior to entering the light guide. By mixing multiple colors of light outside of the light guide in this manner, discoloration of the LCD panel may be limited or eliminated. Additionally, oversizing the diffusion panel may be limited or eliminated.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
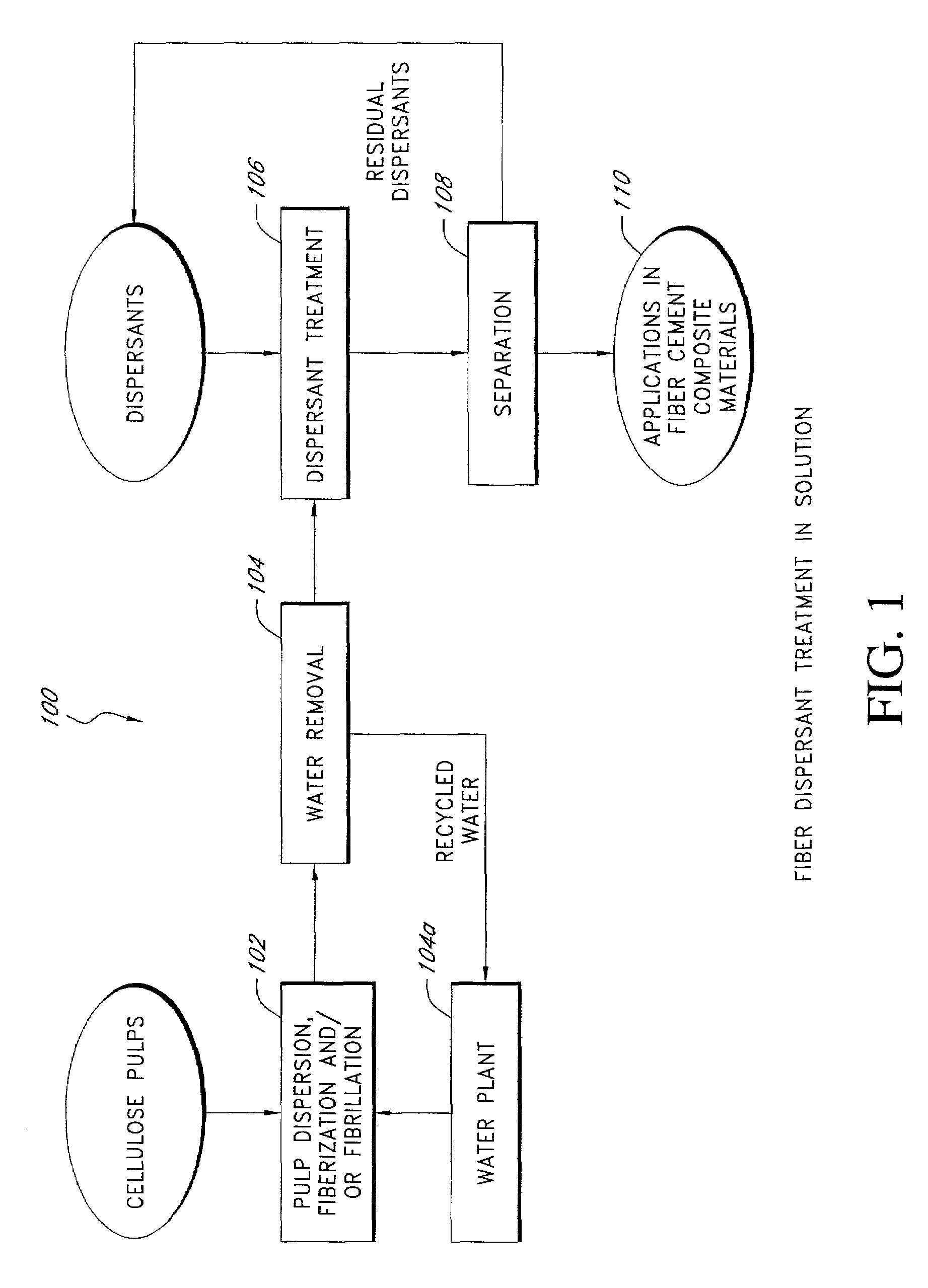
Fiber reinforced cement composite materials using chemically treated fibers with improved dispersibility
InactiveUS20080148999A1Good dispersionAvoid bondingPulp properties modificationSolid waste managementChemical treatmentSurface finish
A fiber-reinforced building material in one embodiment incorporates cellulose fibers that are chemically treated with a dispersant to impart improved dispersibility to the fibers. The fibers are treated with a dispersant which deactivates the hydroxyl sites of the fiber surfaces and in some cases, making the fiber surface more hydrophobic. The dispersant inhibits the hydroxyl groups on the cellulose fiber surface from bonding with hydroxyl groups of other fibers and from bonding with hydroxyl groups of the same fiber, thereby significantly reducing inter-fiber and intra-fiber hydrogen bonding. The treated fibers can be readily dispersed and uniformly distributed throughout a mixture without re-clustering or reclumping once the mechanical mixing action stops. The chemically treated fibers with improved dispersibility improve the fiber distribution and reinforcing efficiency, which in turn improves key physical and mechanical properties of the material such as the modulus of rupture, z-direction tensile strength, and toughness, and surface finishes. With improved fiber reinforcing efficiency, less dosage of fiber is needed to achieve the required physical and mechanical properties.
Owner:JAMES HARDIE TECH LTD
Slurry for thermal spraying
InactiveUS20170088928A1Low environmental loadFlat surfaceMolten spray coatingEmulsion paintsZeta potentialThermal spraying
To provide a slurry for thermal spraying capable of forming a favorable sprayed coating. The present invention provides a slurry for thermal spraying including spray particles including at least one material selected from the group consisting of ceramics, inorganic compounds, cermets, and metals and a dispersion medium. Here, the spray particles have an average particle size of 0.01 μm or more and 10 μm or less and are contained in the slurry for thermal spraying at a proportion of 10% by mass or more and 70% by mass or less. In the slurry for thermal spraying, the spray particles have a zeta potential of −200 mV or more and 200 mV or less.
Owner:FUJIMI INCORPORATED
Light guide for vehicle lamp assembly
InactiveUS8057081B2More dispersedReduce power consumptionLighting support devicesPoint-like light sourceLight guideEngineering
A light guide and various vehicular lamp assemblies using the same are presented herein. In one embodiment, the lamp assembly includes a light source, such as an LED module. A light coupler is operable to receive light from the light source, and distribute the light in a first direction. The light guide includes an elongated, curvilinear body with first and second longitudinal end faces, and opposing light-emitting and light-guiding surfaces extending between the two end faces on a respective side of the body. The first end face communicates with the light coupler to receive light therefrom. The light guide body transmits light generated by the light source along the longitudinal expanse thereof. The light-guiding surface includes an array of longitudinally-spaced optical grooves configured to refract light generated by the light source in a second direction. The depth of preselected optical grooves is varied along the length of the light guide.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Rubber composition and tire having tread thereof
InactiveUS6160047ALow bulk densityHigh volumeSpecial tyresTyre tread bands/patternsCarbon blackElastomer
A rubber composition as a blend comprised of an elastomer(s), and particulate reinforcement provided as an intimate blend of carbon black particles and fumed silica particles, together with a coupling agent. A tire having a component of such rubber composition such as, for example, a tread, is specifically contemplated.
Owner:THE GOODYEAR TIRE & RUBBER CO
Processes for dispersing an impact modifier in a macrocyclic polyester oligomer
The invention provides macrocyclic polyester oligomer compositions containing one or more impact modifiers, methods of dispersing an impact modifier in a macrocyclic polyester oligomer, and polymers and articles produced from a macrocyclic polyester oligomer composition containing one or more impact modifiers.
Owner:CYCLICS CORP
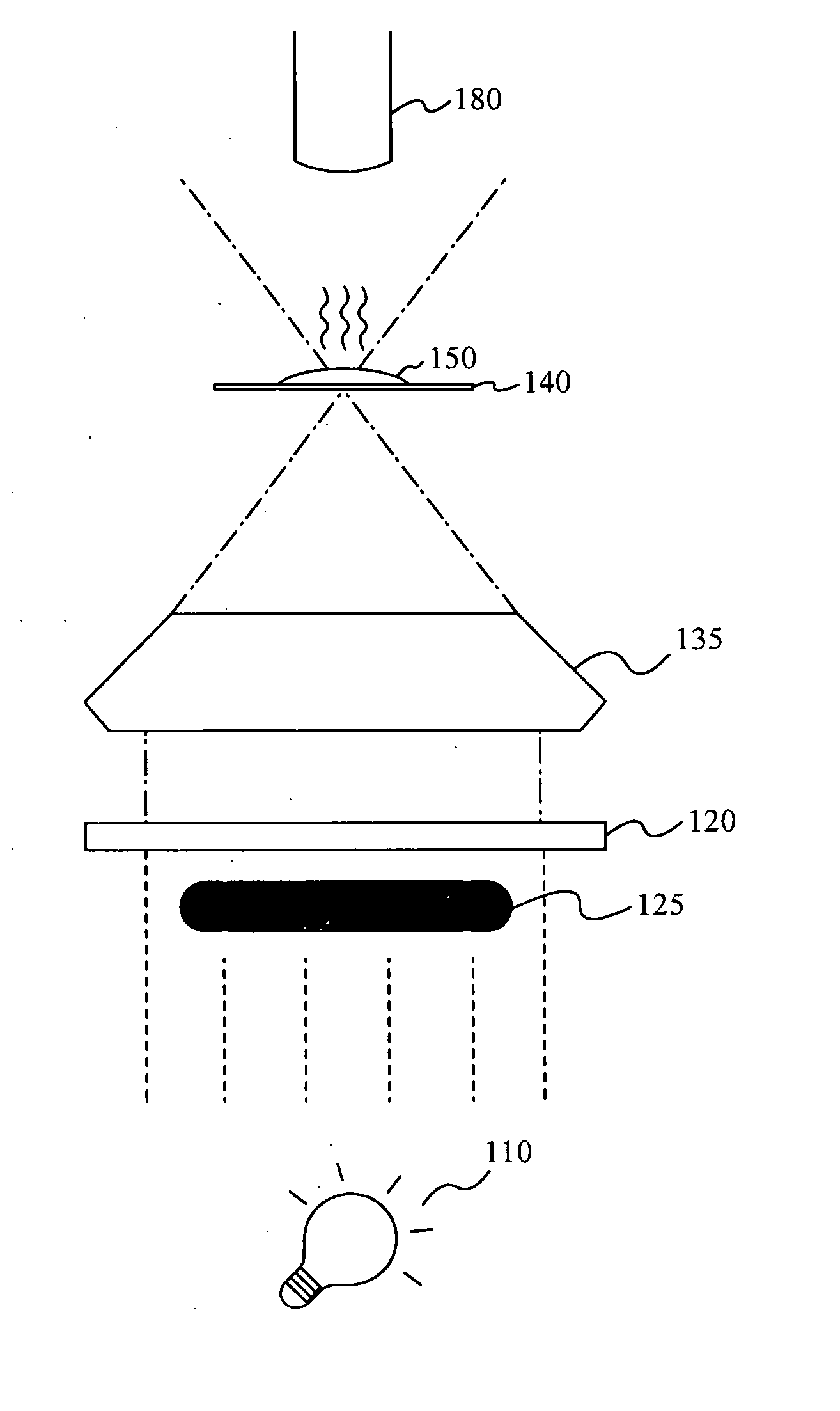
Simultaneous observation of darkfield images and fluorescence using filter and diaphragm
ActiveUS7688505B2More scattered lightMore dispersedMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesFluorescenceDiameter control
An annular diaphragm and filter used for the simultaneous observation of darkfield images and fluorescence. The diaphragm has a variable diameter controlled by a lever and a removable filter. The diaphragm is used to adjust the amount of unfiltered incident light which produces darkfield images when directed on a sample. The removable filter is used to filter light to a particular frequency for producing fluorescence images. An Acousto-Optical Tunable Filter, or other such tunable filter may be used with the diaphragm. A method of using the diaphragm and filter is also disclosed.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Simultaneous observation of darkfield images and fluorescence using filter and diaphragm
ActiveUS20070139764A1More scattered lightMore dispersedMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesFluorescenceAcousto-optics
An annular diaphragm and filter used for the simultaneous observation of darkfield images and fluorescence. The diaphragm has a variable diameter controlled by a lever and a removable filter. The diaphragm is used to adjust the amount of unfiltered incident light which produces darkfield images when directed on a sample. The removable filter is used to filter light to a particular frequency for producing fluorescence images. An Acousto-Optical Tunable Filter, or other such tunable filter may be used with the diaphragm. A method of using the diaphragm and filter is also disclosed.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Flip chip type light-emitting element
ActiveUS8148736B2Inhibit deteriorationIncrease interface areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesContact electrodeLight transmission
In a flip chip type light-emitting element of the present invention, an n type contact electrode 14 is formed on an n layer 11 exposed in a comb-tooth shape, a light transmission electrode 15 made of an ITO is formed over the entire surface of an upper surface of a p layer 13 and twenty pad electrodes 16 are formed at prescribed intervals on the light transmission electrode 15. The plane form of the pad electrode 16 has four branches 16b protruding in the form of a cross from a circular central part 16a and the adjacent pad electrodes 16 connected to each other by the branches 16b.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Catalytic layer structure for fuel cell
InactiveUS20110200916A1Reduce the amount requiredAvoid concentrationActive material electrodesFuel cellsHigh current densityIonomer
An object according to the present invention is to provide a catalyst layer for a fuel cell, which prevents the lowering of the performance due to the lack of oxygen in a high current density region and can provide a desired power, even when containing a small amount of catalyst particles. The catalyst layer for a fuel cell has a structure including: an electroconductive carrier made of a secondary particle which is formed by agglomerating a plurality of primary particles; catalyst particles which are dispersed on and carried by the electroconductive carrier; and an ionomer which covers the electroconductive carrier and the catalyst particles, wherein the catalyst particles have the particle quantity in a range of 0.05 mg / cm2 to 0.15 mg / cm2, the electroconductive carriers have the average secondary particle size in a range of 100 nm to 180 nm, and the ionomer has the film thickness in a range of 6 nm to 16 nm. Thereby, the catalyst layer for a fuel cell can reduce the amount of oxygen per one piece of the secondary particles to inhibit oxygen from concentrating on the surface of the ionomer, and shortens the diffusion distance of oxygen in the ionomer to alleviate a rate-controlled condition by the concentration diffusion process of oxygen in the catalyst layer.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Exhaust system of an internal combustion engine with mixer for a liquid reductant
InactiveUS20160177801A1More dispersedIncrease resistanceCombination devicesInternal combustion piston enginesWear resistantExhaust fumes
An exhaust system for an internal combustion engine includes an injection nozzle for injecting a liquid reductant into exhaust gas streaming through the exhaust system. A mixer is arranged in the exhaust-gas stream for swirling and dispersing the liquid reductant in the exhaust-gas stream. The mixer is provided with a heat-resistant, wear-resistant and corrosion-resistant non-stick coating which is made of a glass or ceramic material to promote rolling off of the reductant. A SCR catalyst is arranged downstream of the mixer for selective catalytic reduction of nitrogen oxides with the aid of the reductant or decomposition products of the reductant.
Owner:AUDI AG
Audio speaker cone appartus and method of manufacture
InactiveUS20060013433A1Superior tone and sonic propertyIncreased durabilityFibre diaphragmsTransducer detailsCompound (substance)Engineering
The invention provides for the construction of cones (12) of audio speaker (10) from at least some quantity of hemp fiber, alone or with other materials and / or binding chemicals. The hemp composition may range from approximately 2% to approximately 100% hemp fiber. The invention composition may be mixed, molded, pressed, and placed into a frame (14) in a traditional manner of speaker cone structure.
Owner:HARRISON JOHNG
Method and apparatus for space-division multiplexing systems
ActiveUS9344779B2Reduce variationMore dispersedMultiplex system selection arrangementsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFew mode fiberSignal on
A space division multiplexed (SDM) transmission system that includes at least two segments of transmission media in which a spatial assignment of the two segments is different is provided. For example, the SDM transmission may include a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and a second segment of transmission media having a second spatial assignment, wherein the first spatial assignment differs from the second spatial assignment. An example method obtains an optical signal on a first segment of transmission media having a first spatial assignment and forwards the optical signal on a second segment of transmission media with a different spatial assignment. The transmission media may be a multi-core fiber (MCF), a multi-mode fiber (MMF), a few-mode fiber (FMF), or a ribbon cable comprising nominally uncoupled single-mode fiber (SMF).
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Urea-terminated polyurethane dispersants
ActiveUS9410010B2Good dispersionHigh densityMeasurement apparatus componentsTransportation and packagingDisperse dyePolyurethane dispersion
The present invention relates to urea-terminated polyurethanes dispersants based on diols and polyether diols, aqueous dispersions of such polyurethanes, the manufacture of the urea terminated polyurethane dispersions and inks containing pigments and / or disperse dyes dispersed with these urea terminated polyurethane dispersants. The urea termination can have nonionic hydrophilic substituents.
Owner:DUPONT ELECTRONICS INC
Enzymatic oil recuperation process
ActiveUS20100240917A1High oil contentMore dispersedOrganic chemistryFermentationWater usePhospholipase
A process for the recuperation of acylglycerols or acylglycerols containing free fatty acids from gums, present as aqueous emulsions, said gums being obtained by subjecting triglyceride oil to one or more degumming processes, said recuperation process comprising the steps of: subjecting said gums to enzymatic hydrolysis catalysed by one or more enzymes with phospholipase activity; allowing said gums to separate into two or more phases, said two or more phases including at least an oily phase and an aqueous phase; and recuperating said oily phase comprising acylglycerols or acylglycerols containing free fatty acids; wherein said enzymatic hydrolysis is accelerated by adding at least part of the one or more enzymes with phospholipase activity to at least part of the water used in the recuperation and / or at least one degumming process; and / or at least part of said triglyceride oils treated in said degumming process; and / or by facilitating mixing at least part of said one or more enzymes with phospholipase activity into said gums by increasing the triglyceride oil content of said gums; and an oil obtained by this process.
Owner:DESMET BELGIUM
Probe card
InactiveUS7208964B2Increased complexityReduce coefficient of frictionSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementElectronic circuit testingProbe cardEngineering
It is an object of the present invention to provide an arch type probe capable of enduring a load caused by overdriving even if the probe is miniaturized, and a probe card using the same. An arch type probe 200 has a shape including a first quarter circle arc portion 210 which is supported at one end thereof by the base plate 100 and a second quarter circle arc portion 220 which is connected to the other end of the first quarter circle arc portion 210, extending toward the base plate and a little shorter than the first quarter circle arc portion 221. The top portion of the arch type probe 200 serves as a contact surface brought into contact with an electrode of a semiconductor water B.
Owner:NIHON DENSHIZAIRYO
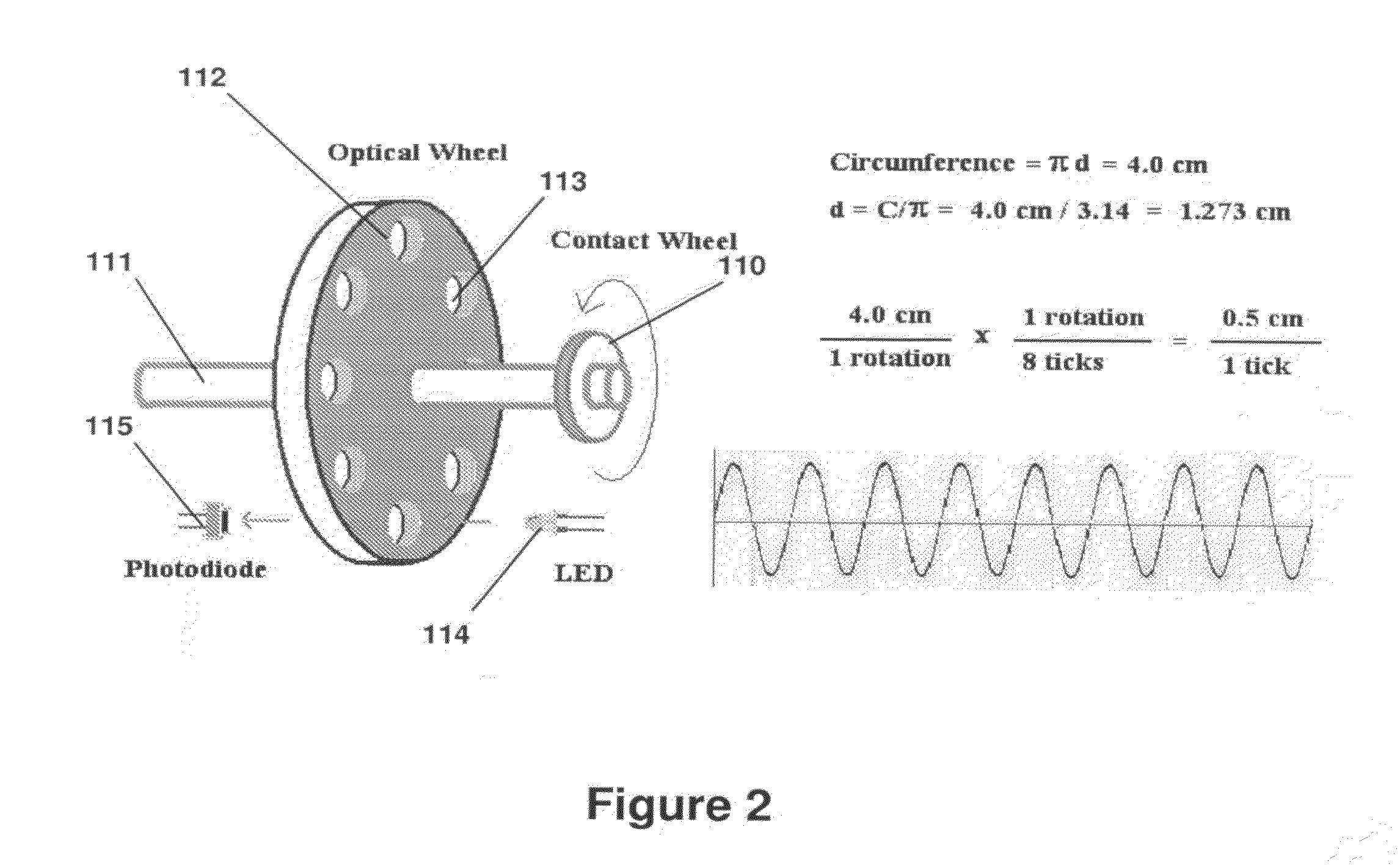
Digital distance measurer for nerve conduction studies
InactiveUS20120083684A1Inhibit excessive impulse dispersionIncrease efficiency and time and ease and accuracyPerson identificationSensorsEngineeringNerve conduction
Nerve conduction studies (NCS) are used to diagnose many types of disorders and are being employed more and more frequently. Current methods for distance measurement during a NCS are manual and often time consuming and vulnerable to considerable error. A device and system for electronically measuring distance during a NCS and automatically transferring the data is disclosed. In one embodiment, the device incorporates a contact wheel to travel across the surface of the subject's skin to measure the applicable distance.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Energy absorbing system and method
InactiveUS20020141818A1Easily instalEnsuring energy securityPasturing equipmentTraffic signalsEnergy absorbingCushion
Owner:MOORE JOSEPH W
Flat Ceiling Mounted Loudspeaker
A ceiling speaker mountable in a ceiling tile for mounting in a suspended ceiling of a room, includes a central woofer, and at least four surrounding pivoting tweeters that are independently adjustable so as to provide broad flat coverage throughout the room. A crossover network directs low frequency signals to the woofer and high frequency signals to the tweeters and an optional stereo separator circuit directs left and right signals to different pairs of the tweeters. A method for adjusting sound dispersion produced by the ceiling speaker is also disclosed.
Owner:KRAMER ELECTRONICS LTD
Semiconductor light-emitting structure
ActiveUS20120292657A1Effectively uniformityMore dispersedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesEngineeringElectrical conductor
A semiconductor light-emitting structure is provided, which includes a first doped type semiconductor layer, a light-emitting layer, a second doped type semiconductor layer, a first electrical transmission layer and at least one first conductor. The light-emitting layer is disposed on the first doped type semiconductor layer and the second doped type semiconductor layer is disposed on the light-emitting layer. The first electrical transmission layer is disposed on the first doped type semiconductor layer, in which a first interface is formed between the first electrical transmission layer and the first doped type semiconductor layer. The first conductor is disposed on the first doped type semiconductor layer. The first electrical transmission layer connects the first conductor. A second interface is formed between each of the first conductor and the first doped type semiconductor layer, and the resistance of the second interface is less than the resistance of the first interface.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Direct Metallization Process
InactiveUS20100034965A1Widen meansMinimizes and eliminates redepositionPrinted circuit aspectsLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingVacuum extractionOptoelectronics
An improved method of providing a carbon dispersion coating on surfaces of a substrate in a direct metallization process, wherein the substrate comprises conductive and non-conductive portions. The method comprises the steps of contacting the substrate with the carbon dispersion to coat the substrate with the carbon-containing dispersion and at least one of moving a non-absorbent roller over at least a portion of a substantially planar surface of the substrate to remove excess carbon dispersion from the substantially planar surface of the substrate and passing the substrate through a vacuum extraction chamber to extract excess carbon dispersion remaining on surfaces of the substrate. The method provides cleaner copper surfaces to minimize the microetch requirement and also prevents the carbon dispersion from undesirably redepositing on surfaces of the substrate.
Owner:MACDERMID ACUMEN INC
Side vertical mirror group and installation method thereof
A vertically-oriented lens assembly is disclosed which includes: a lens frame (1); an optical lens (2); two rigid supports (7) that are symmetric to each other with respect to a vertical central axis of the lens frame (1), both integral with the lens frame (1), and both in direct contact with the optical lens (2); an elastic support (4) disposed right under the optical lens (2) and brought into contact with the optical lens (2) by an adjusting screw (10); and a tightening screw (8) disposed on the top of the lens frame (1) for limiting radial displacement of the optical lens (2). A method for forming the vertically-oriented lens assembly is also disclosed, including: disposing the optical lens (2) on a rigid supporting member (5) of the lens frame (1) so that the optical lens (2) is vertically oriented; applying a force to the optical lens (2) via the tightening screw (8) to make the rigid supports (7) both abut the optical lens (2); adjusting a supporting force provided by the elastic support (4) to the optical lens (2) by the adjusting screw (10); attaching pre-tensioning spring leaf (6) and dispensing an adhesive through bores (3) to fixedly attach the optical lens (2) to the lens frame (1); and attaching an axial stop block (11), allowing high stability and a high surface precision and it can be used in engineering applications.
Owner:SHANGHAI MICRO ELECTRONICS EQUIP (GRP) CO LTD
Image forming apparatus
ActiveUS9075382B2Increase equipment costApparatus upsizing can be suppressedElectrographic process apparatusImage formationEngineering
Owner:SHARP KK
Automatic braking control device
ActiveUS9321438B2Improve accuracyImprove reliabilityBraking action transmissionAutomatic initiationsStart timeAutomatic braking
An automatic braking control device includes a temperature obtaining section for obtaining an index value of a temperature of brake fluid, a collision prediction time calculation section for calculating collision prediction time of a vehicle with an object, a collision determination section for determining whether the collision prediction time is less than or equal to a threshold, and a pressure control section for controlling a start timing of pressurization of the brake fluid when the collision prediction time is less than or equal to the threshold. The pressure control section sets the start timing to a first timing when the index value is a first temperature and to a second timing when the index value is a second temperature higher than the first temperature. Time from determination of the collision determination section to the first timing is shorter than time from the determination to the second timing.
Owner:HINO MOTORS LTD
Compact compound comprising silanized hydroxyl graphene with thermosetting polymer
PendingUS20220127464A1Improve toughnessImprove responsePigmenting treatmentMaterial nanotechnologyPolymer scienceThermosetting polymer
The present invention relates a compact compound and their preparation and more particularly to such compact compound prepared from hydroxyl graphene functionalized and combinations with thermosetting polymer with particular particles of specified size, shape and properties. The present invention relates generally to field of nanomaterials and preparation of nanomaterials as well as use of nanomaterials in architecture, engineering and interior design.
Owner:GRAPHENGLASS SL
Conductive composites
ActiveUS10930925B2Improve propertiesEnhance layeringCell electrodesSecondary cellsPolymer sciencePolymer chemistry
The invention relates to formulations comprising: (i) a first active material; (ii) a second active material; and (iii) a metal-coordination complex, wherein the first active material and the second active material have at least one surface property which is different, one from the other. Such formulations are more homogenous than those formed without the metal-coordination complex and can be used to form composite materials, such as those forming part of a conductive interface, having advantageous properties and providing for improvement in functionality of the conductive interface.
Owner:ANTEO ENERGY TECH PTY LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com