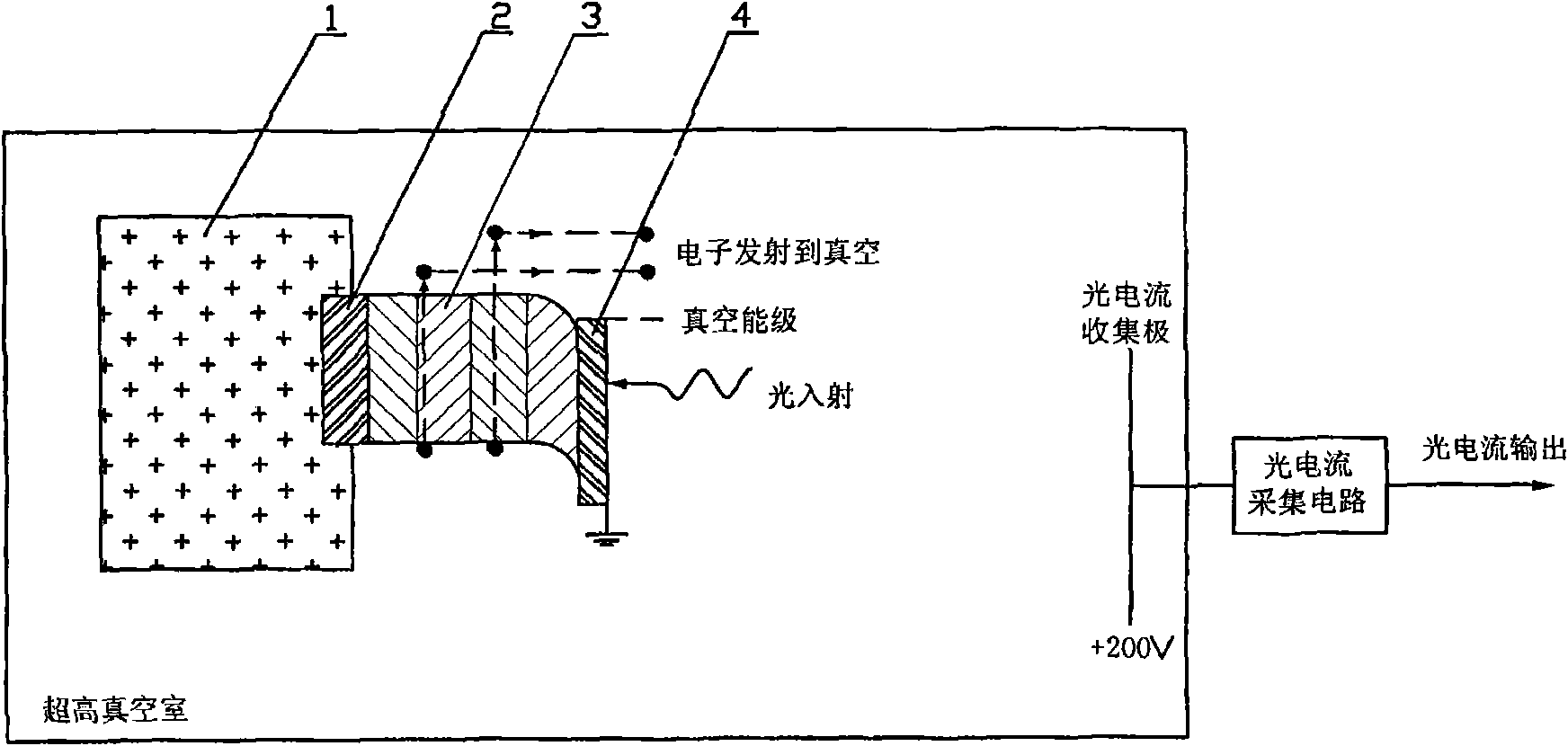
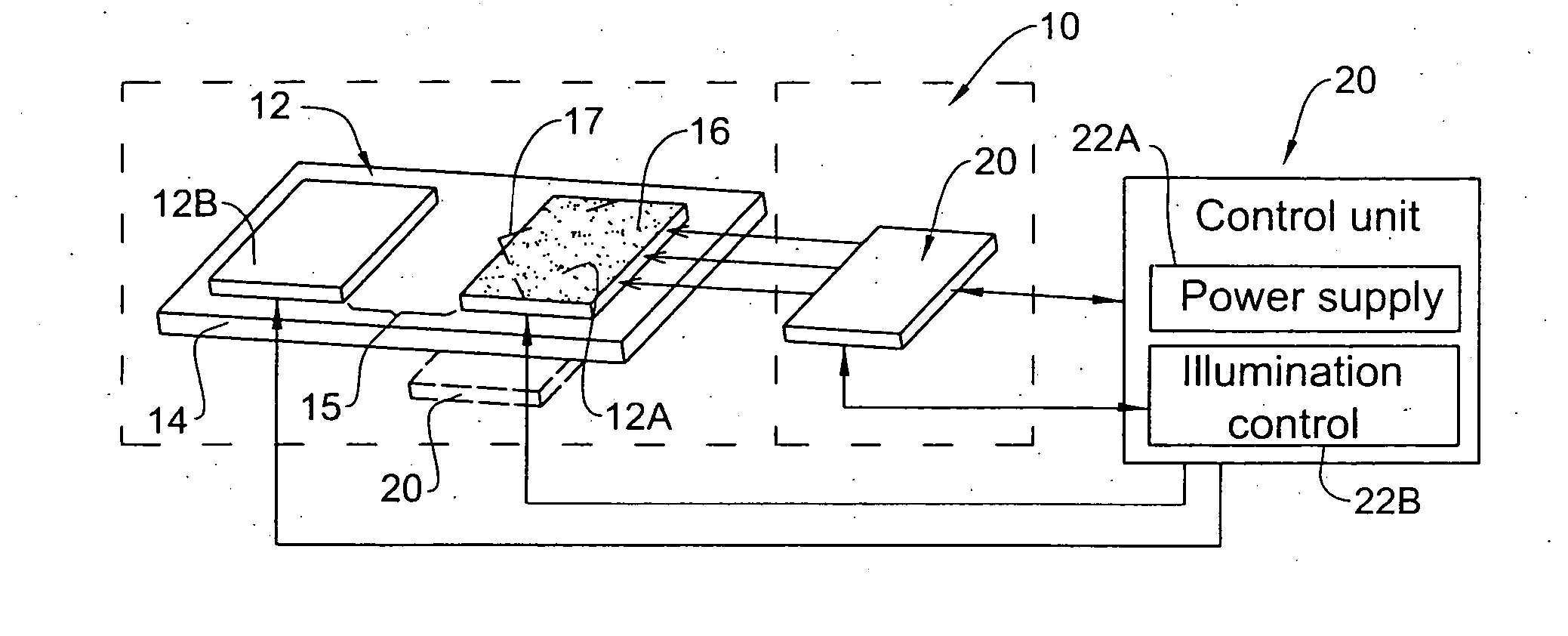
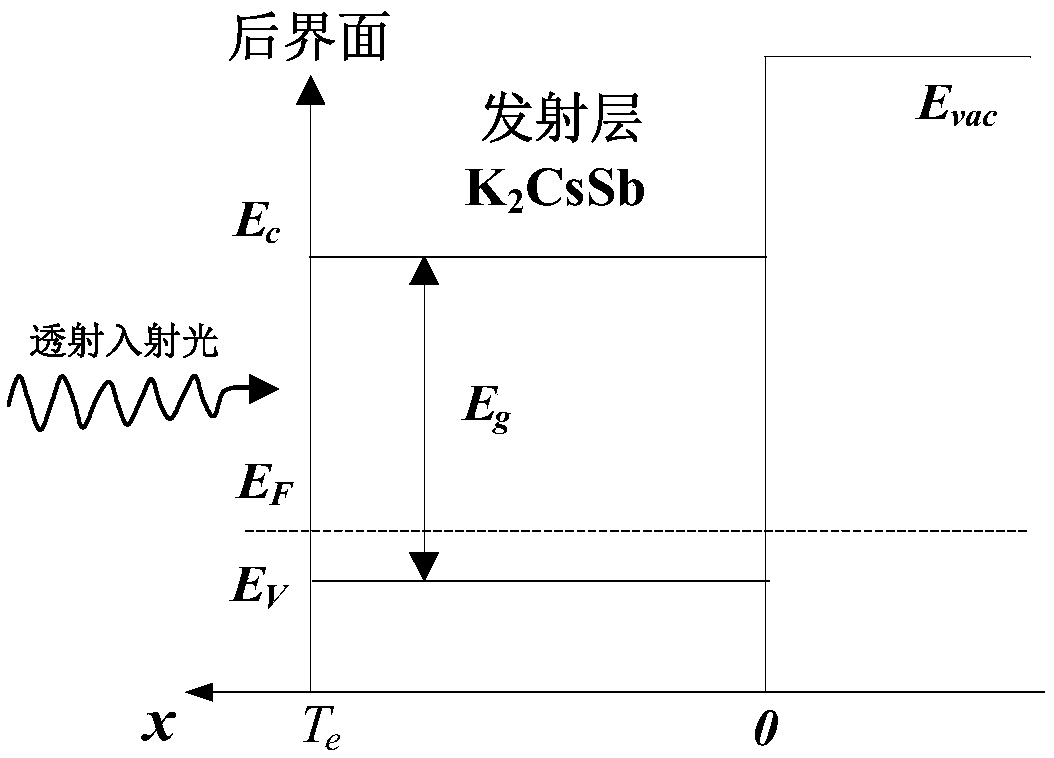
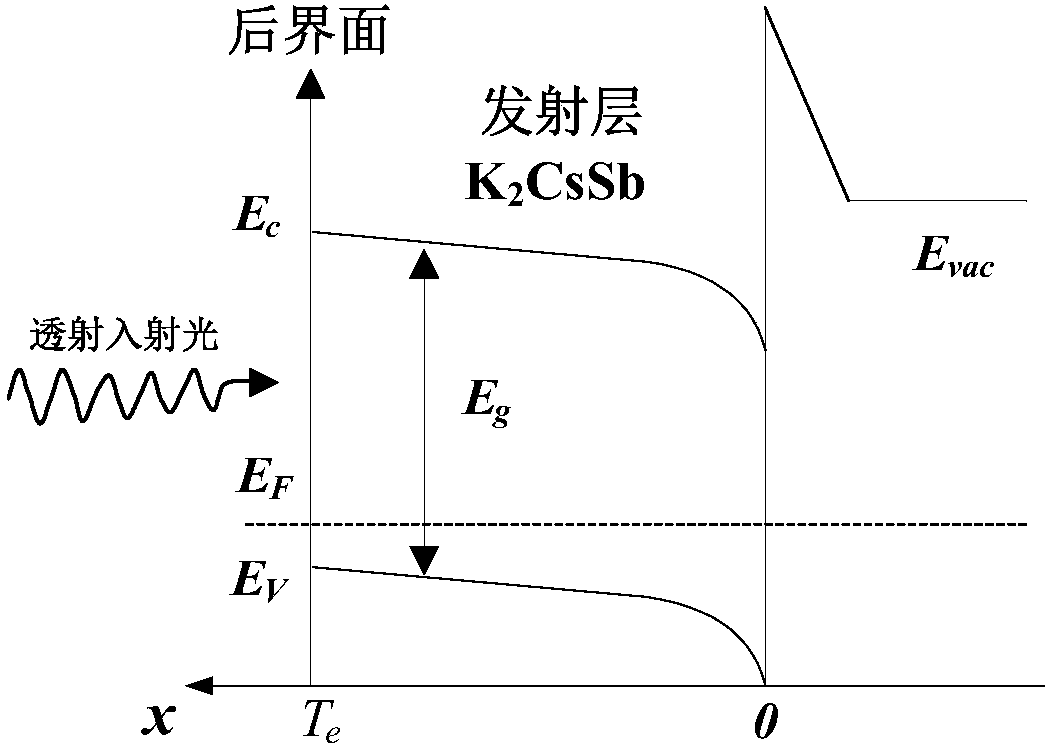
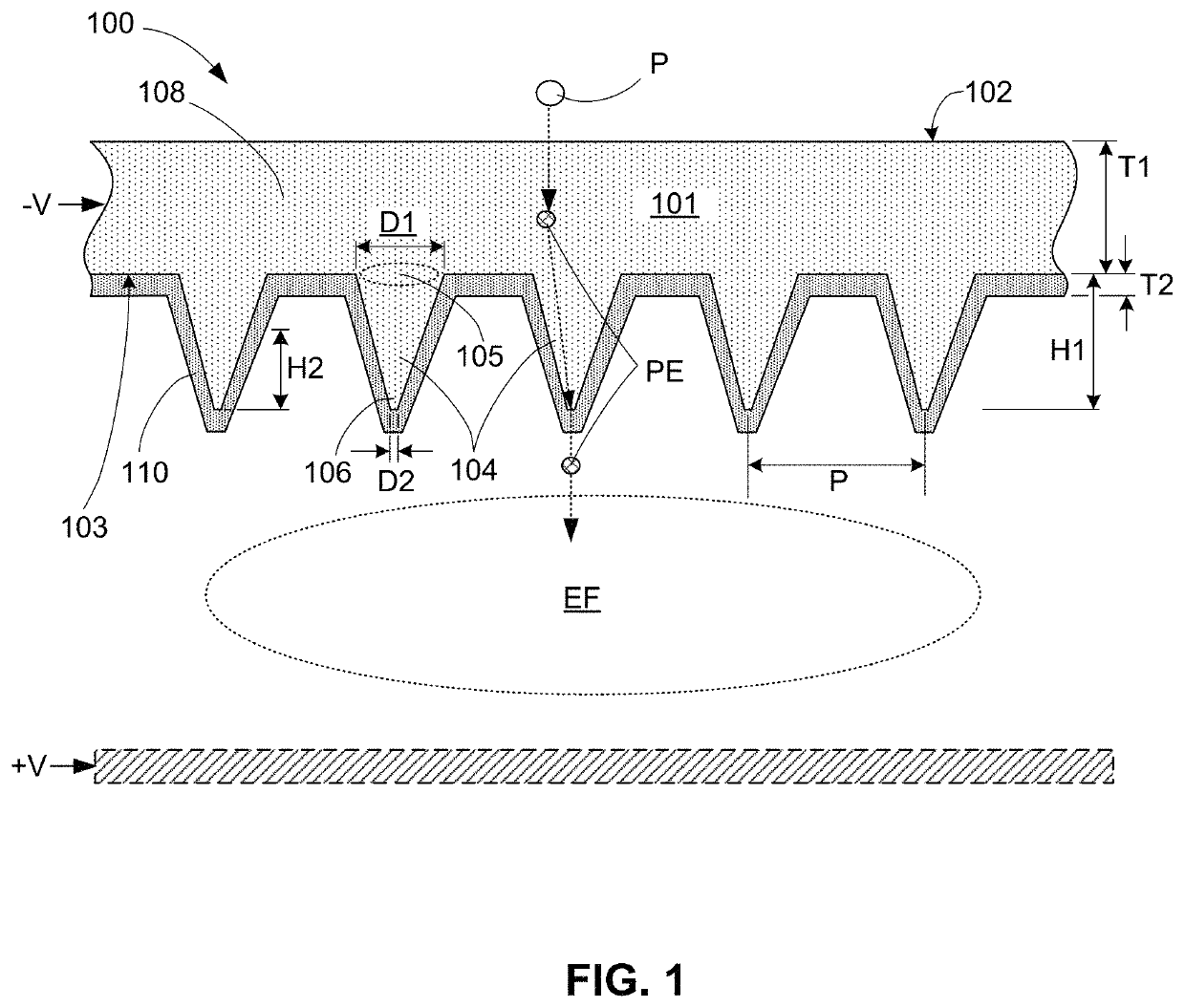
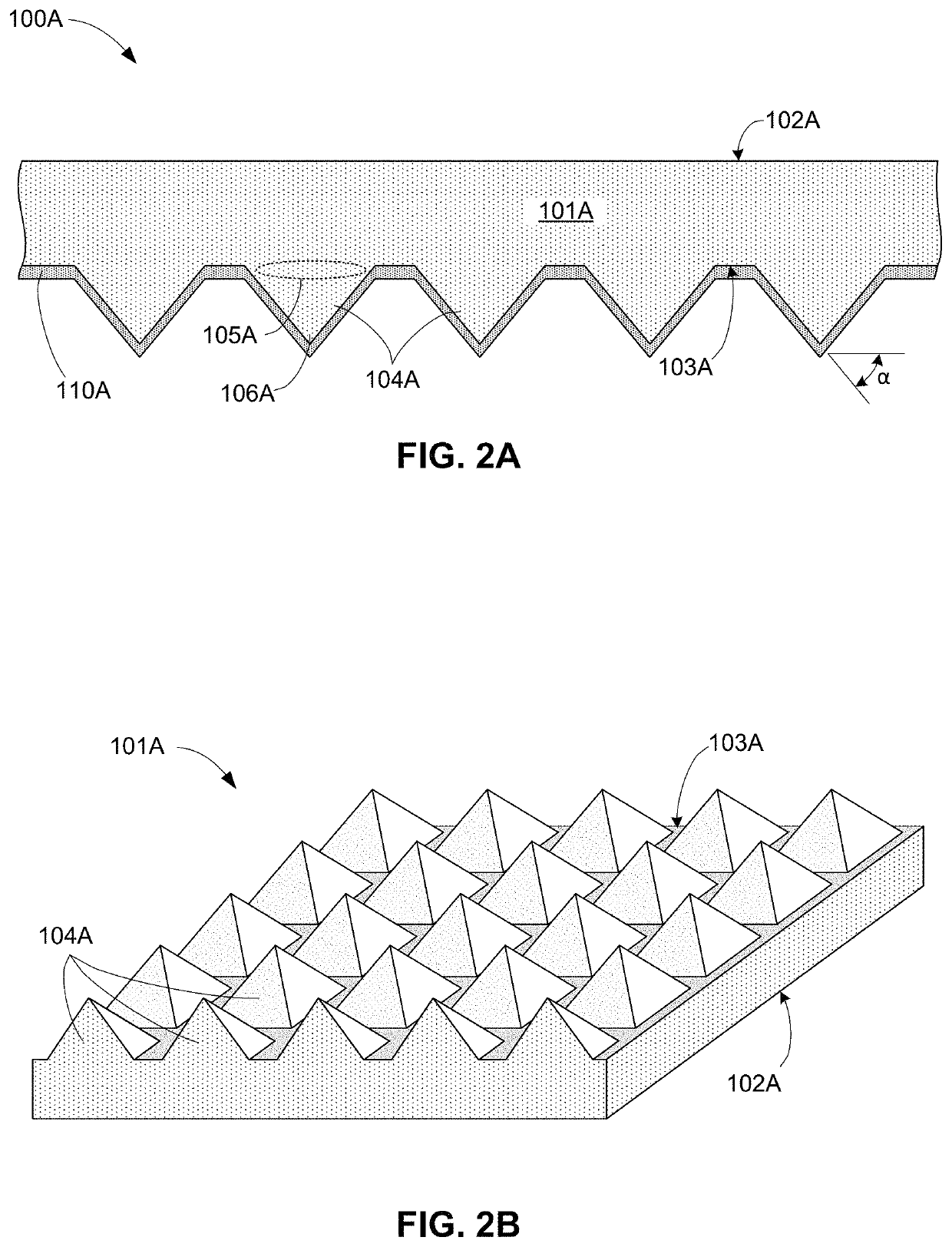
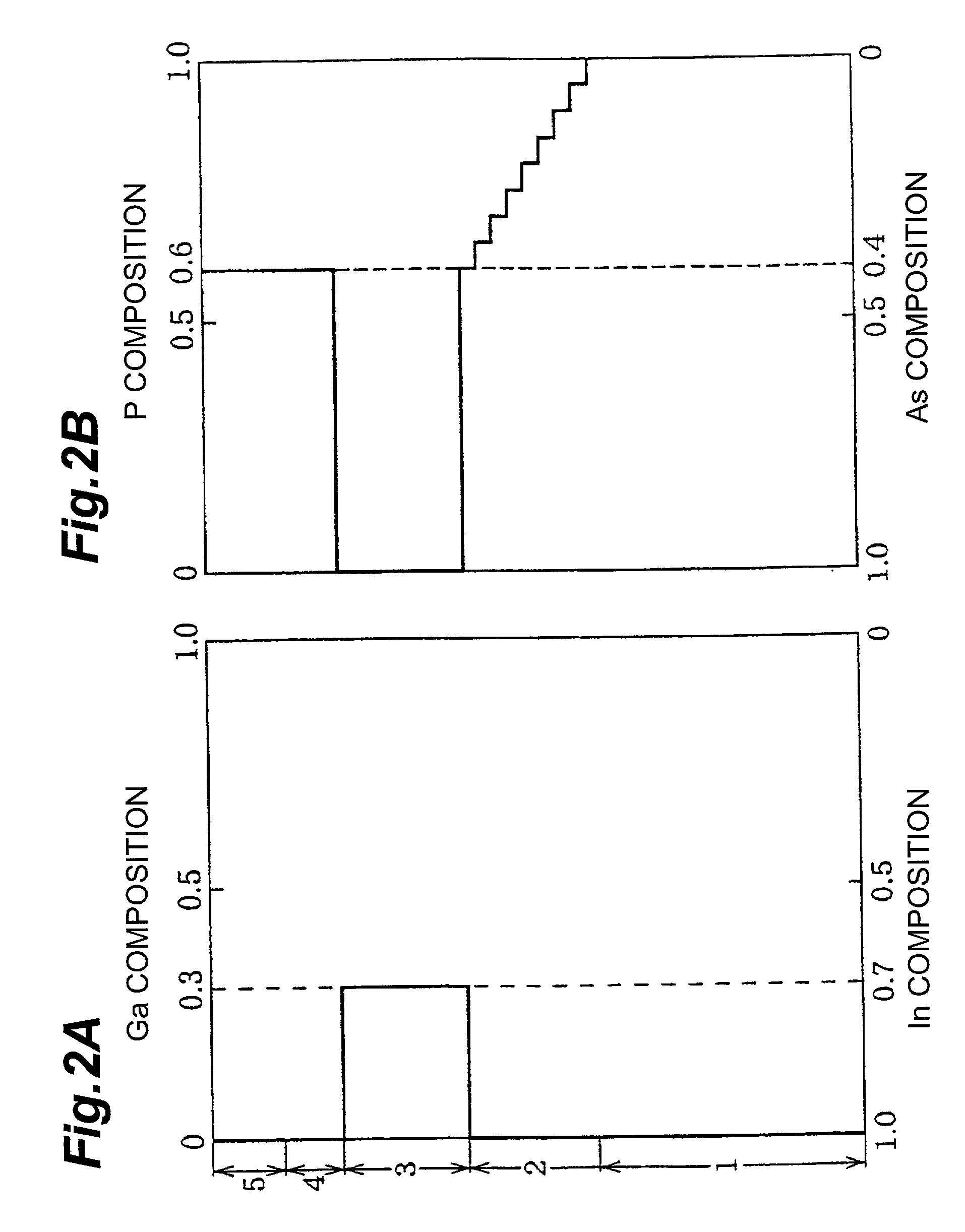
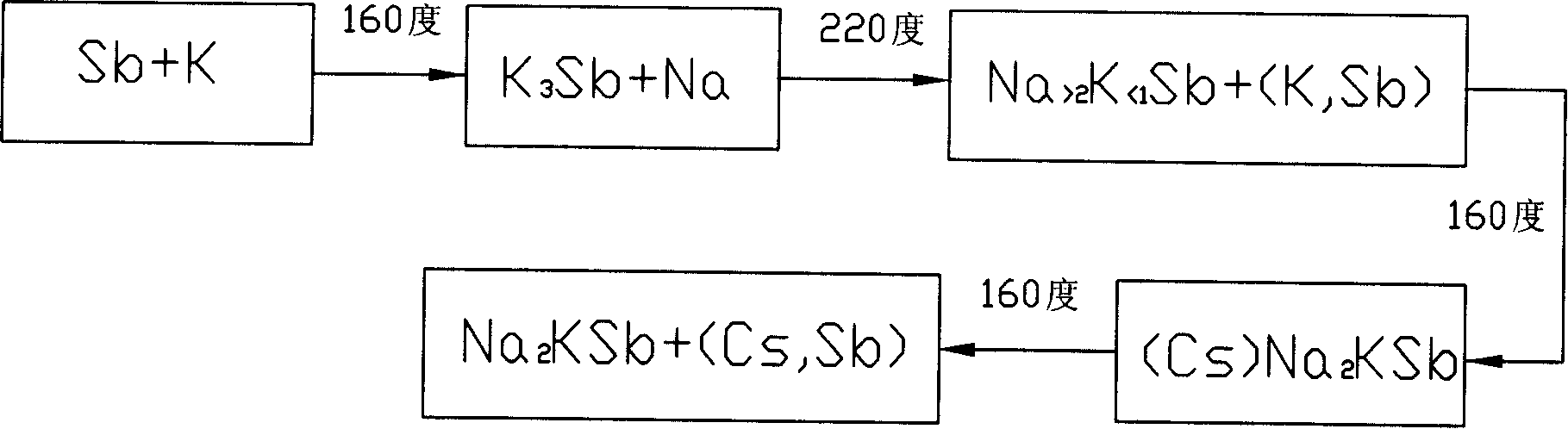
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
219results about "Photo-emissive cathodes" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High data rate smart sensor technology
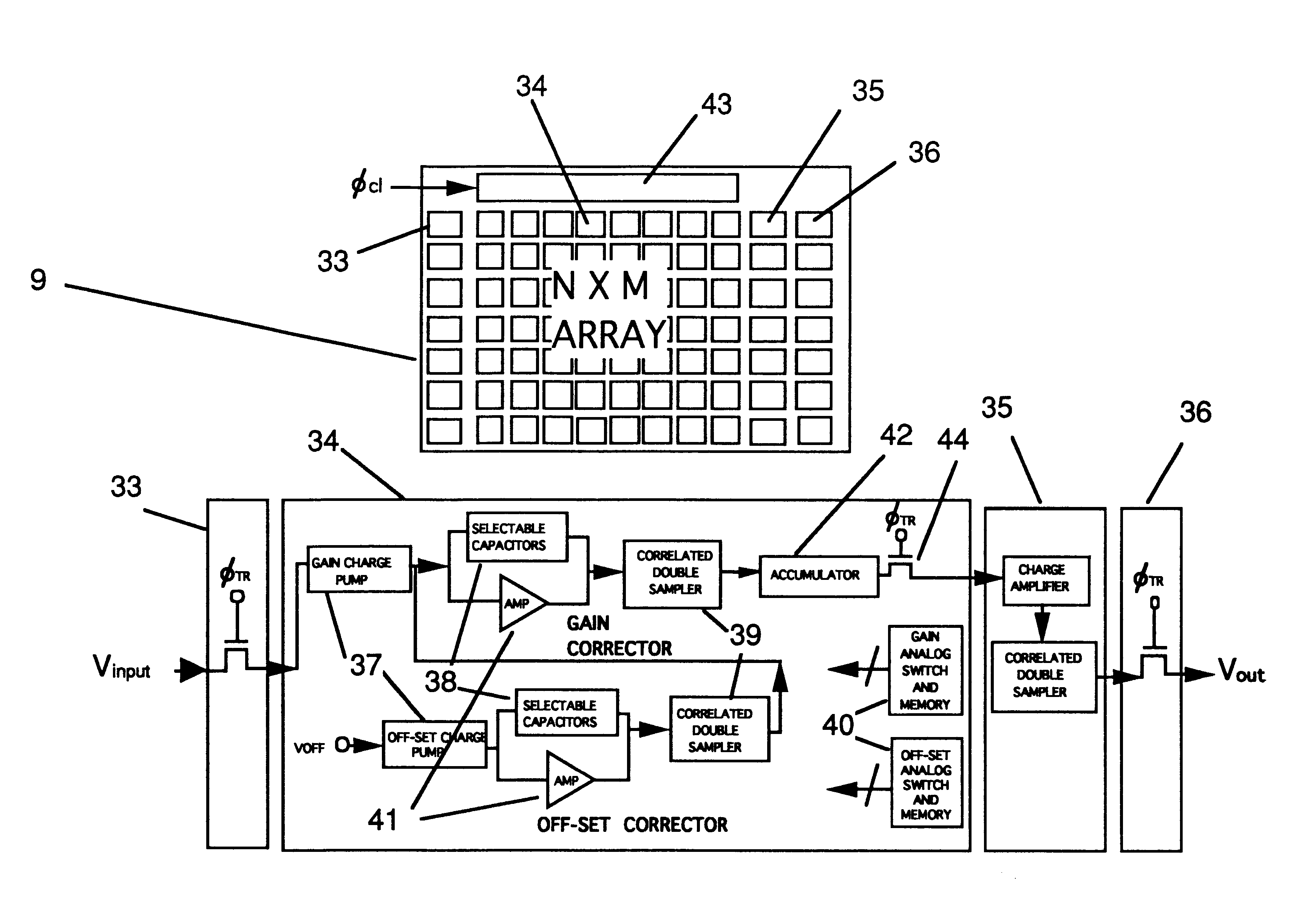
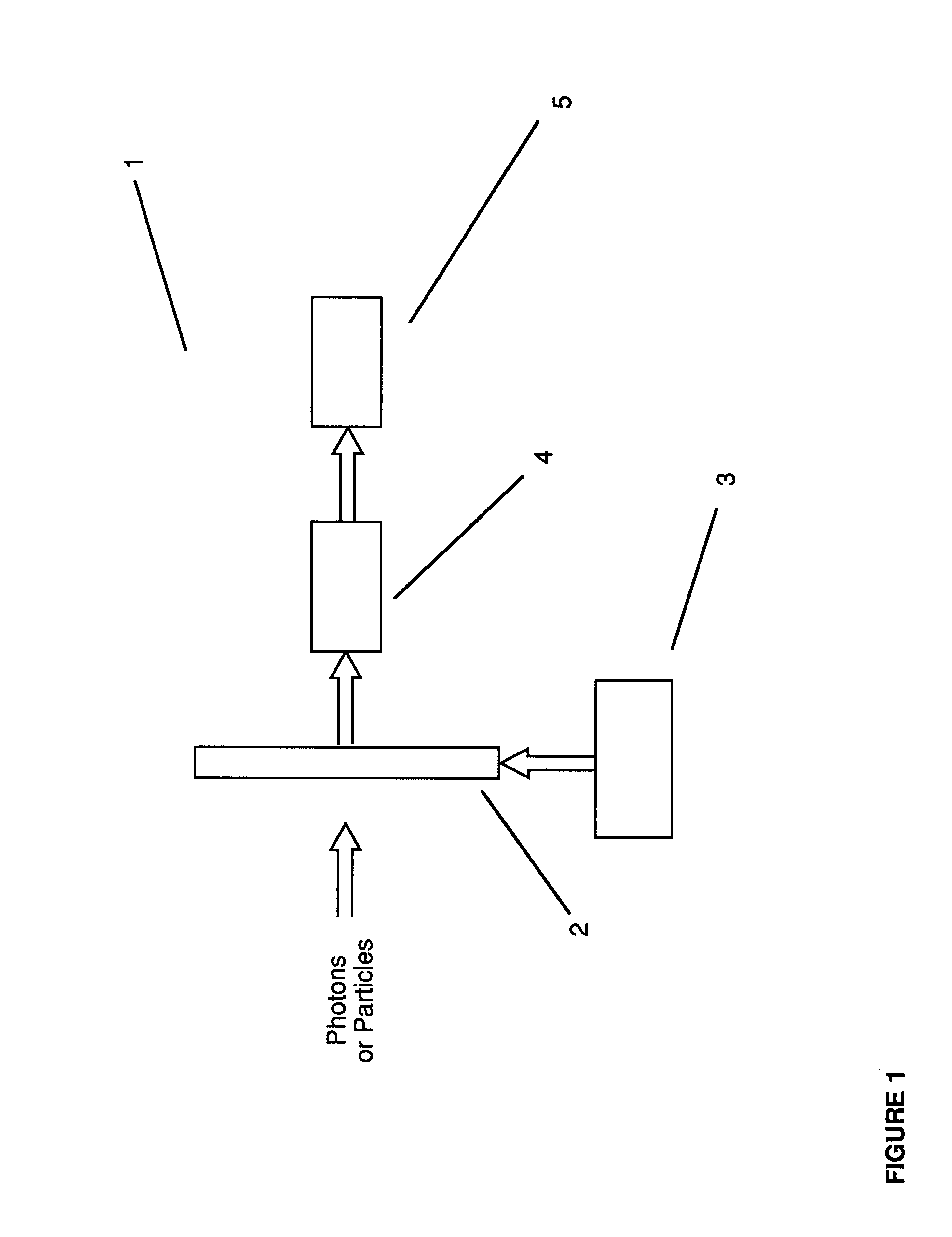
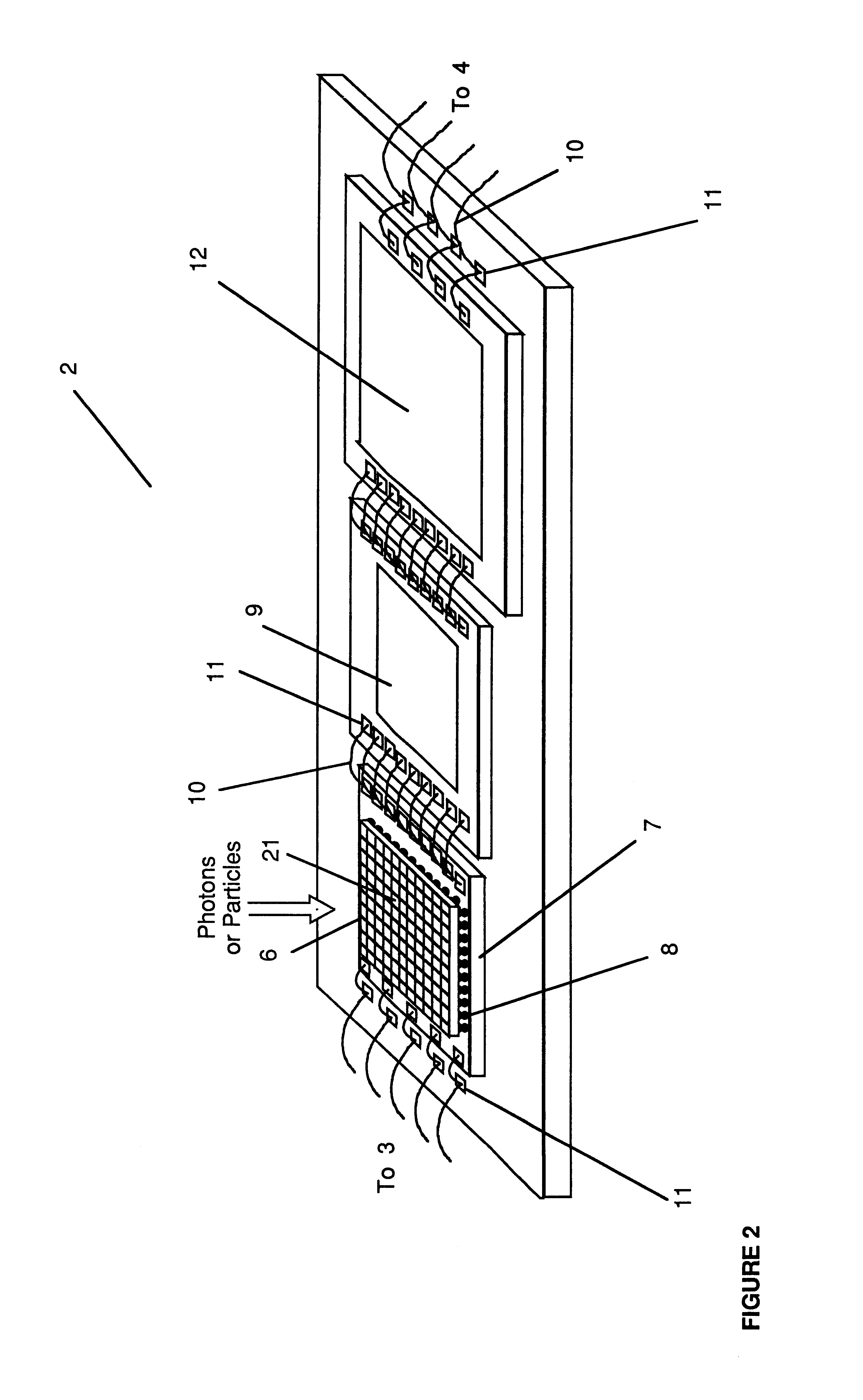
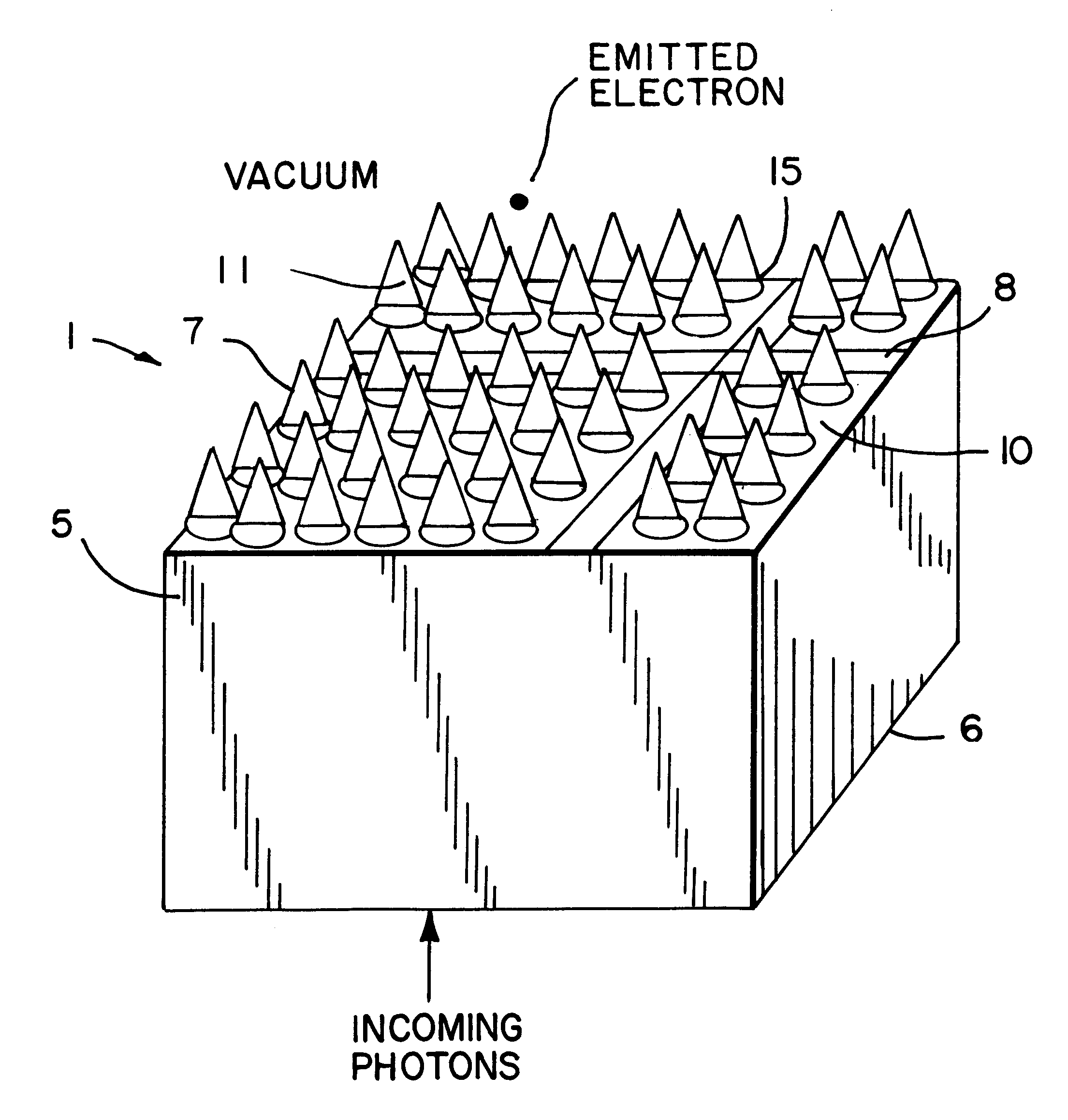
InactiveUS6362482B1Overcome problemsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesSolid-state devicesAnalog image processingSignal on
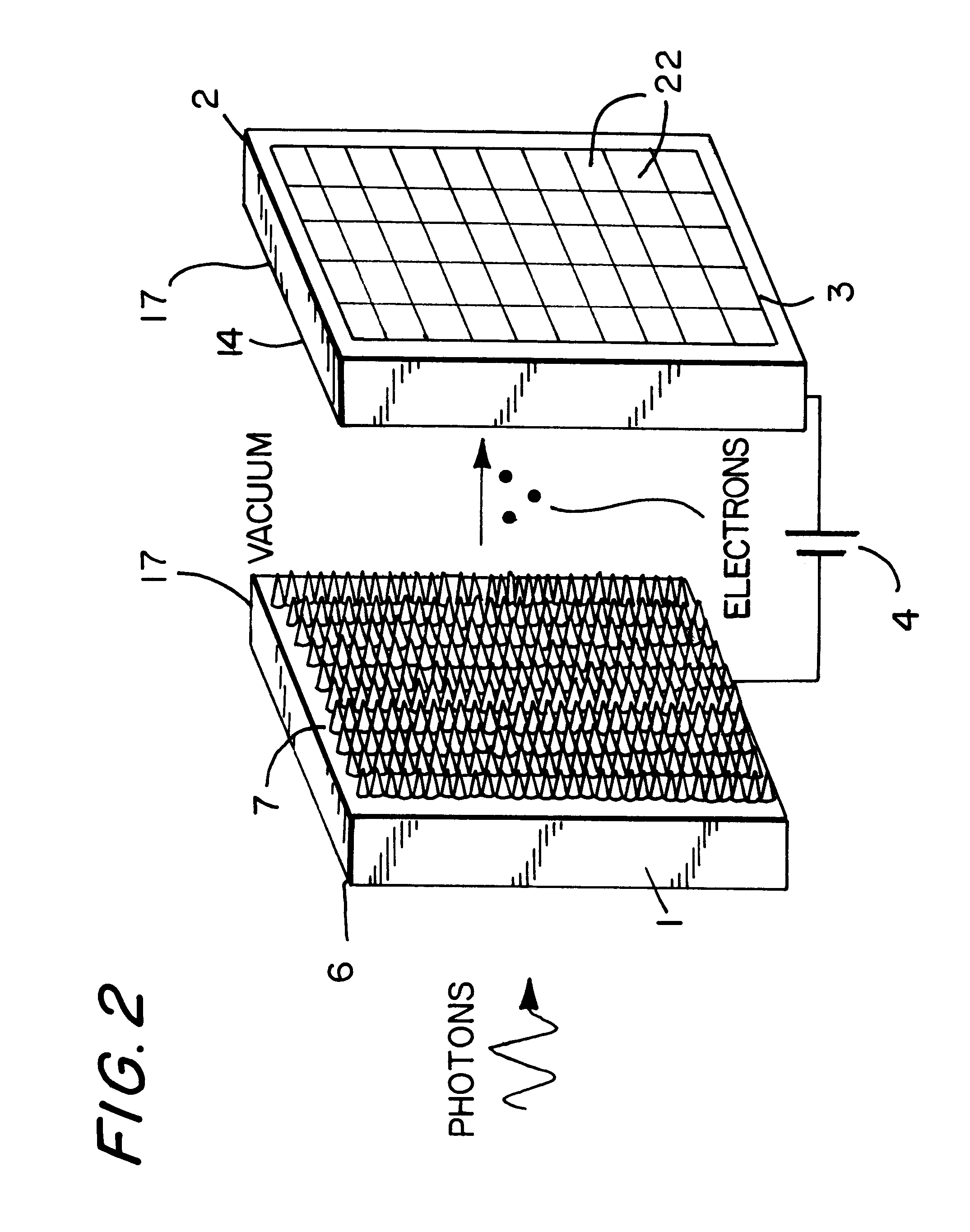
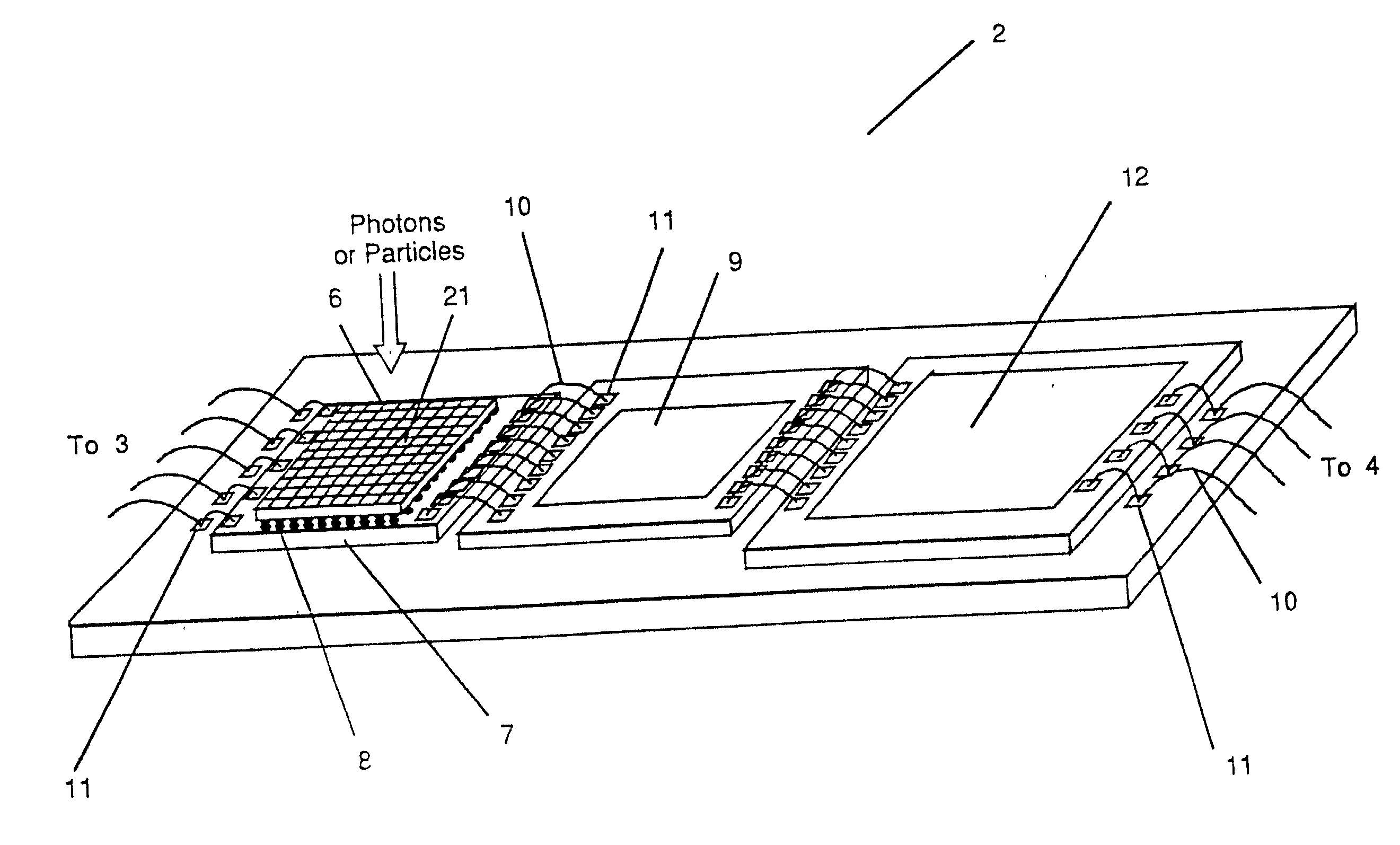
A device for the high-speed analysis of photon- or particle-generated image data or for the high-speed energy-discrimination analysis of photon- or particle-counting data. The device uses a sensor that collects the photons or particles on an array of solid state detectors, as electrical analog signals, and stores the analog-signal information on capacitors of readout arrays associated with the detector arrays. Integration of the photon or particle flux signals on the readout arrays proceeds for a given time frame and then image-related signals are transferred to an analog correction processor. The analog correction processor is comprised of one or more integrated circuit chips where each chip contains an array of correction processor unit cells. In these unit cells signals are corrected, in parallel, for gain and offset nonuniformities in the detection and processing chain. Corrections to all the signals are made in a time frame or less and the information is then transferred to an analog image processor. Particle-counting data is transferred directly from the readout array chips to the analog image processor. The analog image processor is comprised of one or more integrated circuit chips where each chip is made up of an array of image processor unit cells. Each unit cell contains circuitry for implementing an image processing or energy discrimination algorithm, and circuitry for outputting the signals and / or the position of only those unit cells for which the algorithm is satisfied. The analog image processor chip may also contain circuitry that counts the number of cells for which the algorithms have been satisfied. The analog image processor implements the algorithm and outputs the data in a time frame or less.
Owner:CONTINENTAL ADVANCED LIDAR SOLUTIONS US LLC
Semiconductor X-ray photocathodes devices
InactiveUS6201257B1Reduce noiseHigh x-ray energy discriminationDischarge tube luminescnet screensCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesPhotocathodePhotonic sensor
An energy dispersive x-ray and gamma-ray photon counter is described. The counter uses a photon sensor which incorporates a unique photocathode called Advanced Semiconductor Emitter Technology for X-rays (ASET-X) as its critical element for converting the detected photons to electrons which are emitted into a vacuum. The electrons are multiplied by accelerations and collisions creating a signal larger than the sensor noise and thus allowing the photon to be energy resolved very accurately, to within ionization statistics. Because the signal is already above the sensor noise it does not have to be noise filtered therefore allowing high-speed counting. The photon sensor can also be used as a device to visualize and image gamma-ray and x-ray sources.
Owner:ADVANCED SCI CONCEPTS
Photocathode
InactiveUS20070096648A1Bias voltage can be appliedReduce contact resistancePhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesSemiconductor materialsPhotocathode
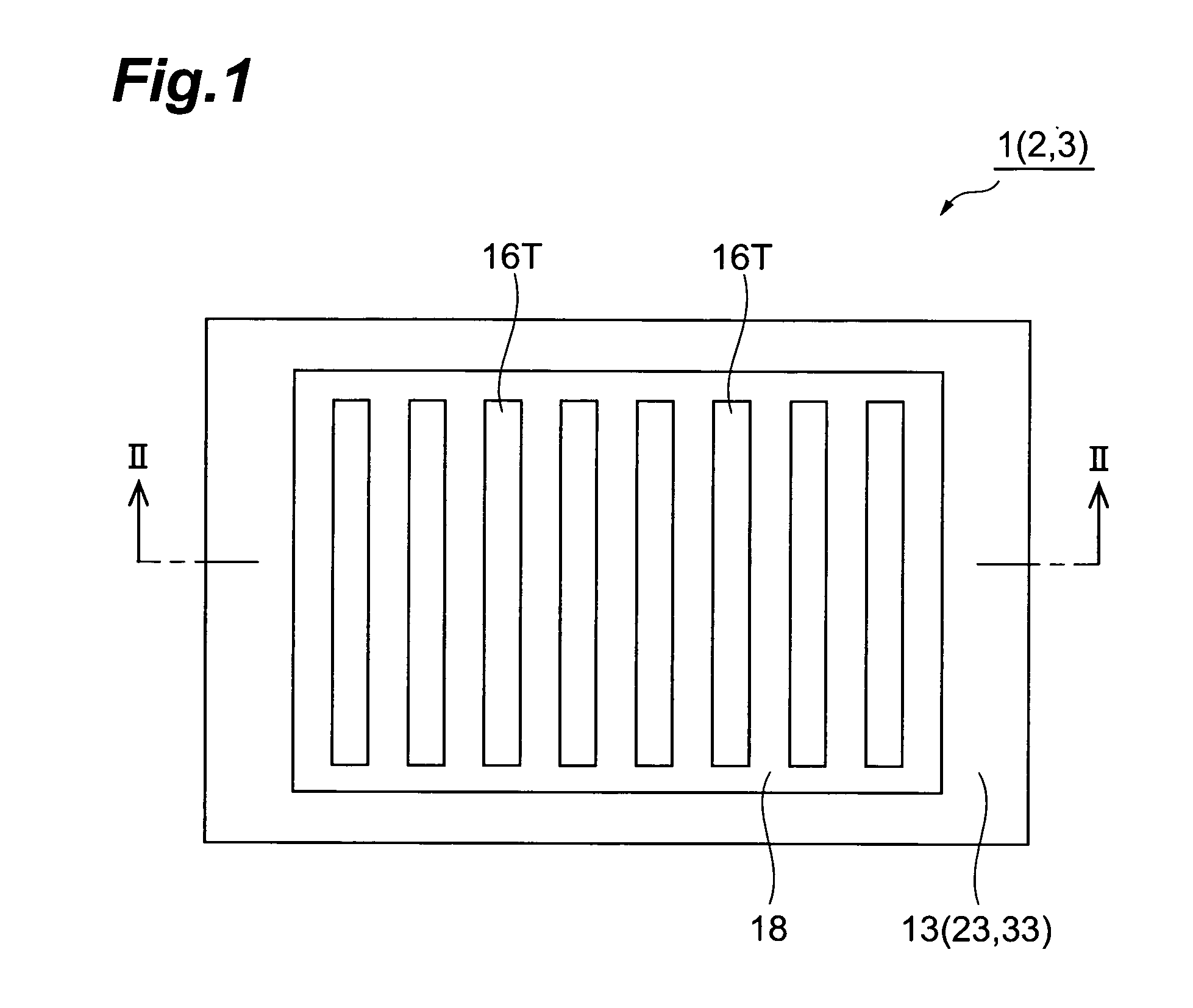
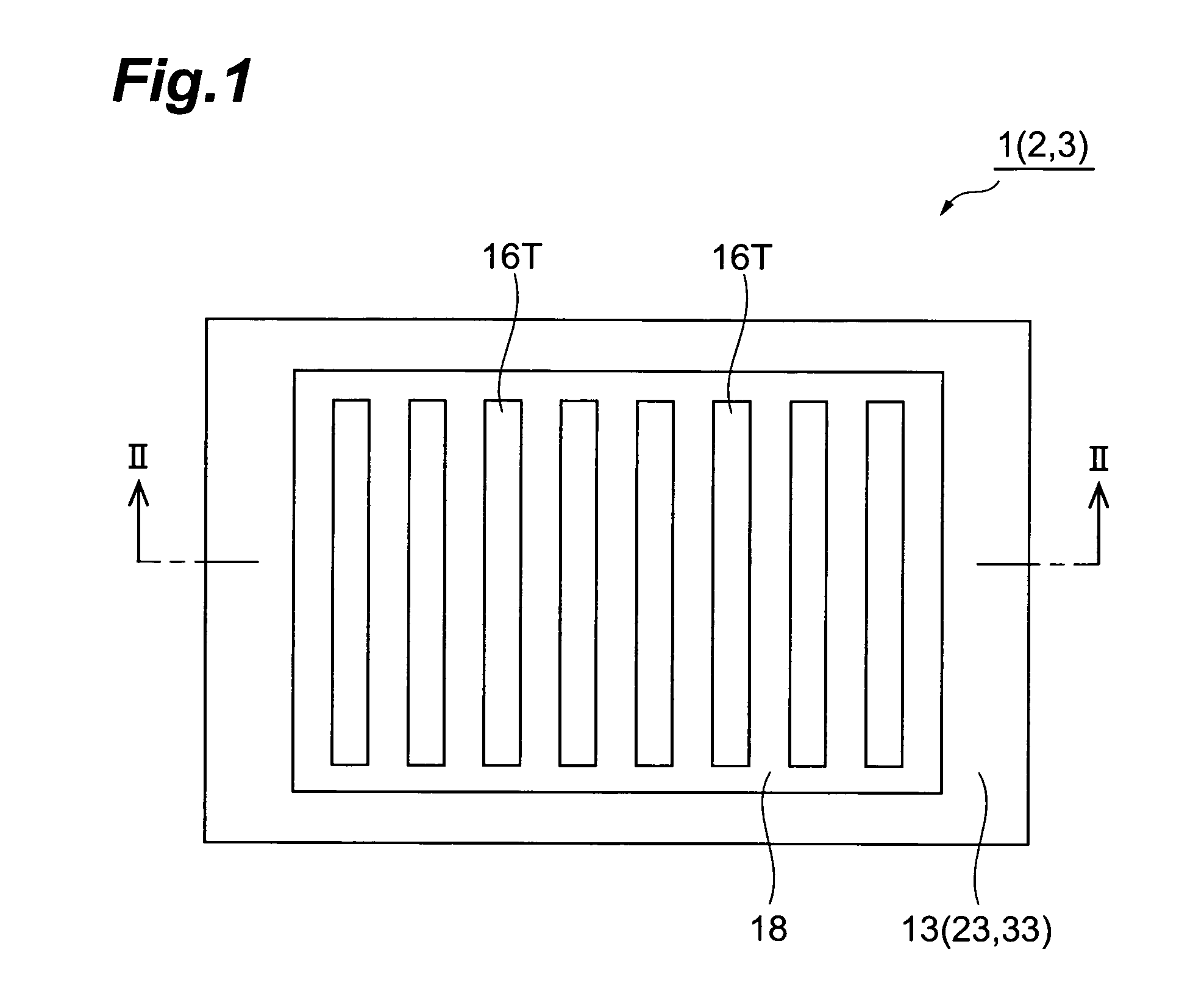
A semiconductor photocathode 1 includes: a transparent substrate 11; a first electrode 13, formed on the transparent substrate 11 and enabling passage of light that has been transmitted through the transparent substrate 11; a window layer 14, formed on the first electrode 13 and formed of a semiconductor material with a thickness of no less than 10 nm and no more than 200 nm; a light absorbing layer 15, formed on the window layer 14, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the window layer 14, is narrower in energy band gap than the window layer 14, and in which photoelectrons are excited in response to the incidence of light; an electron emission layer 16, formed on the light absorbing layer 15, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the light absorbing layer 15, and emitting the photoelectrons excited in the light absorbing layer 15 to the exterior from a surface; and a second electrode 18, formed on the electron emission layer.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Photocathode comprising a plurality of openings on an electron emission layer
InactiveUS7816866B2Bias voltage can be appliedReduce contact resistancePhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesSemiconductor materialsPhotocathode
A semiconductor photocathode 1 includes: a transparent substrate 11; a first electrode 13, formed on the transparent substrate 11 and enabling passage of light that has been transmitted through the transparent substrate 11; a window layer 14, formed on the first electrode 13 and formed of a semiconductor material with a thickness of no less than 10 nm and no more than 200 nm; a light absorbing layer 15, formed on the window layer 14, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the window layer 14, is narrower in energy band gap than the window layer 14, and in which photoelectrons are excited in response to the incidence of light; an electron emission layer 16, formed on the light absorbing layer 15, formed of a semiconductor material that is lattice matched to the light absorbing layer 15, and emitting the photoelectrons excited in the light absorbing layer 15 to the exterior from a surface; and a second electrode 18, formed on the electron emission layer.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
High data rate smart sensor
InactiveUS20030029989A1Overcome problemsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesSolid-state devicesAnalog image processingImaging data
Owner:CONTINENTAL AUTONOMOUS MOBILITY US LLC
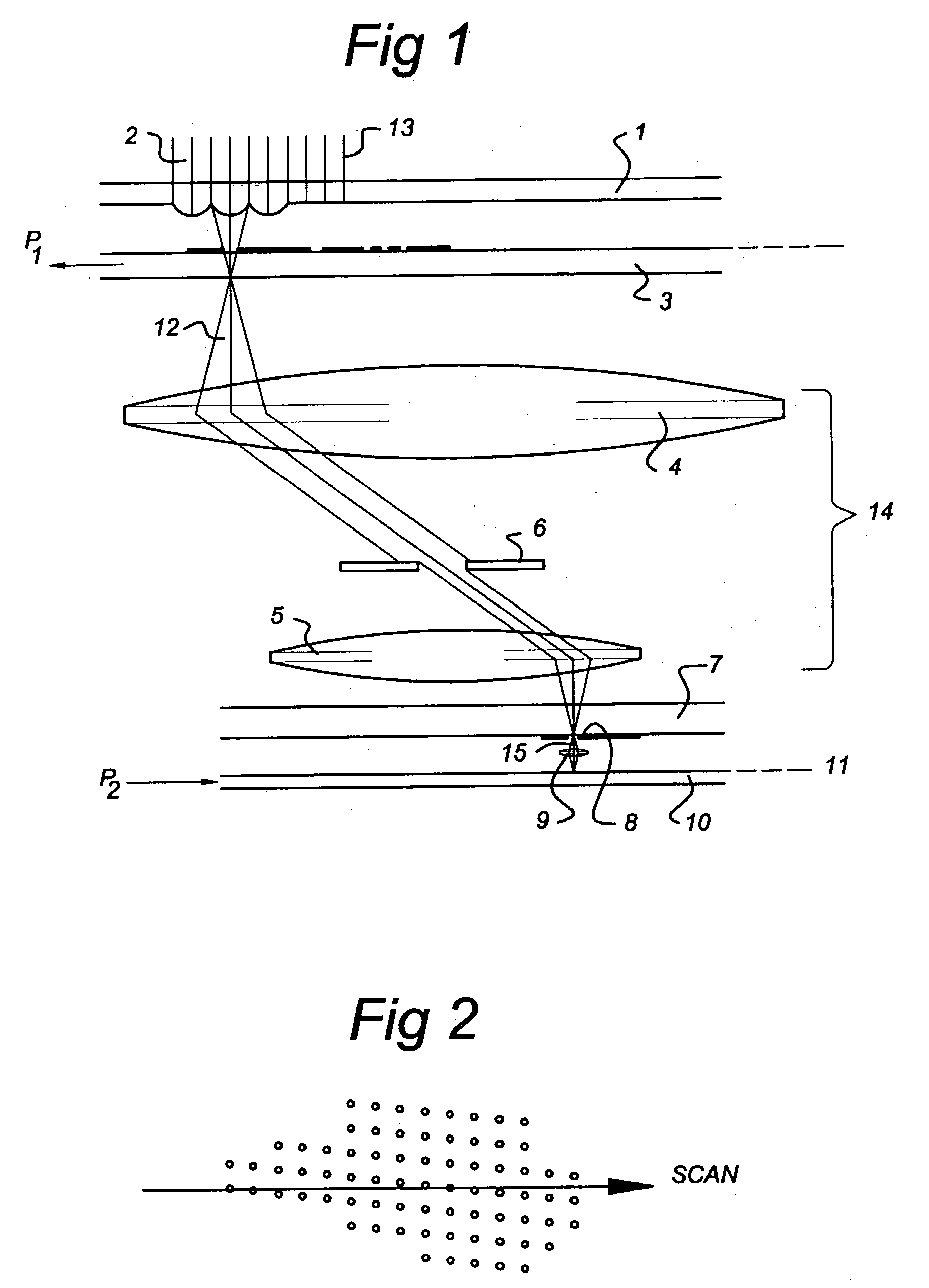
Field emission photo-cathode array for lithography system and lithography system provided with such an array
InactiveUS20030178583A1Increase productionEfficiency of electron generation in the converter layer will be increasedElectric discharge tubesNanoinformaticsElectron sourceLithographic artist
The present invention relates to the use of an electron source in a lithography system for producing a plurality of electron beams directed towards an object to be processed, said electron source comprising a plurality of field emitters, characterized in that said electron source comprises a semiconductor layer with a plurality of tips, said use including the steps of: producing a plurality of light spots on said electron source, producing one light spot on one field emitter; exciting electrons to a conduction band (Ec) by light from a light spot within said field emitter by a photo-electric effect; accelerating said electrons in said conduction band (Ec) towards said tips and tunnelling them outside tips in order to generate electrons for said plurality of electron beams, causing tips to generate electrons for said electron beam having a spot smaller than 100 nm on an object to be processed, each spot of light triggering an electron beam from one tip.
Owner:ASML NETHERLANDS BV
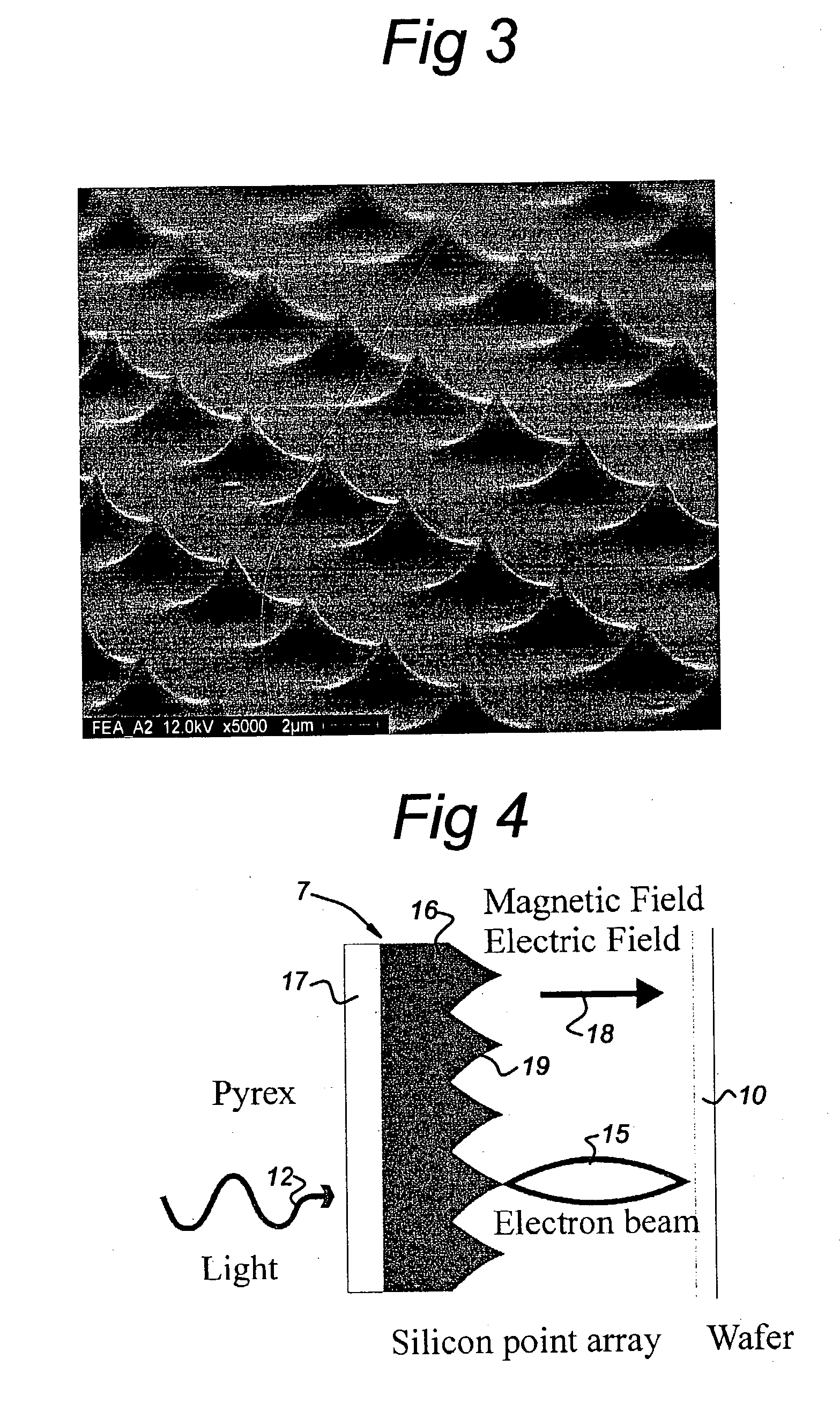
Photocathode including field emitter array on a silicon substrate with boron layer
ActiveUS20160343532A1Improve work functionReduce potential barrierSolid-state devicesImage pickup tubesPhotocathodeWhiskers
A photocathode utilizes an field emitter array (FEA) integrally formed on a silicon substrate to enhance photoelectron emissions, and a thin boron layer disposed directly on the output surface of the FEA to prevent oxidation. The field emitters are formed by protrusions having various shapes (e.g., pyramids or rounded whiskers) disposed in a two-dimensional periodic pattern, and may be configured to operate in a reverse bias mode. An optional gate layer is provided to control emission currents. An optional second boron layer is formed on the illuminated (top) surface, and an optional anti-reflective material layer is formed on the second boron layer. An optional external potential is generated between the opposing illuminated and output surfaces. An optional combination of n-type silicon field emitter and p-i-n photodiode film is formed by a special doping scheme and by applying an external potential. The photocathode forms part of sensor and inspection systems.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Semiconductor photocathode
InactiveUS6917058B2Decrease in time resolutionIncrease the electric field strengthSolid-state devicesPhoto-emissive cathodesInfraredPhotocathode
In the case of a thick light-absorbing layer 2, a phenomenon of a decrease in the time resolution occurs. However, when the thickness of the light-absorbing layer 2 is limited, a portion of low electron concentration in one electron group is cut out, and hence overlap regions of adjacent electron concentration distributions decrease. Therefore, by shortening the transit time necessary for the passage of electrons, regions of overlapping electron distributions due to diffusion can also be suppressed. Furthermore, the strength of an electric field within a light-absorbing layer can be increased by thinning the light-absorbing layer. Therefore, the time resolution of infrared rays can be remarkably improved by a synergistic action of these effects. If it is assumed that the time resolution is 40 ps (picoseconds), for example, when the thickness of a light-absorbing layer is 1.3 μm which is nearly equal to the wavelength of infrared, then a possible time resolution is 7.5 ps when this thickness is 0.19 μm.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Electron tube
InactiveUS20070176160A1Reduced crystal defectHigh sensitivityPhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotocathodeCrystallographic defect
A GaN-based semiconductor photocathode is applied to an electron tube. A GaN-based compound semiconductor layer is laterally grown on a substrate, and incorporated in the electron tube. The crystal defects of the compound semiconductor layer are reduced, whereby an electron tube which has inconceivably high sensitivity is realized.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
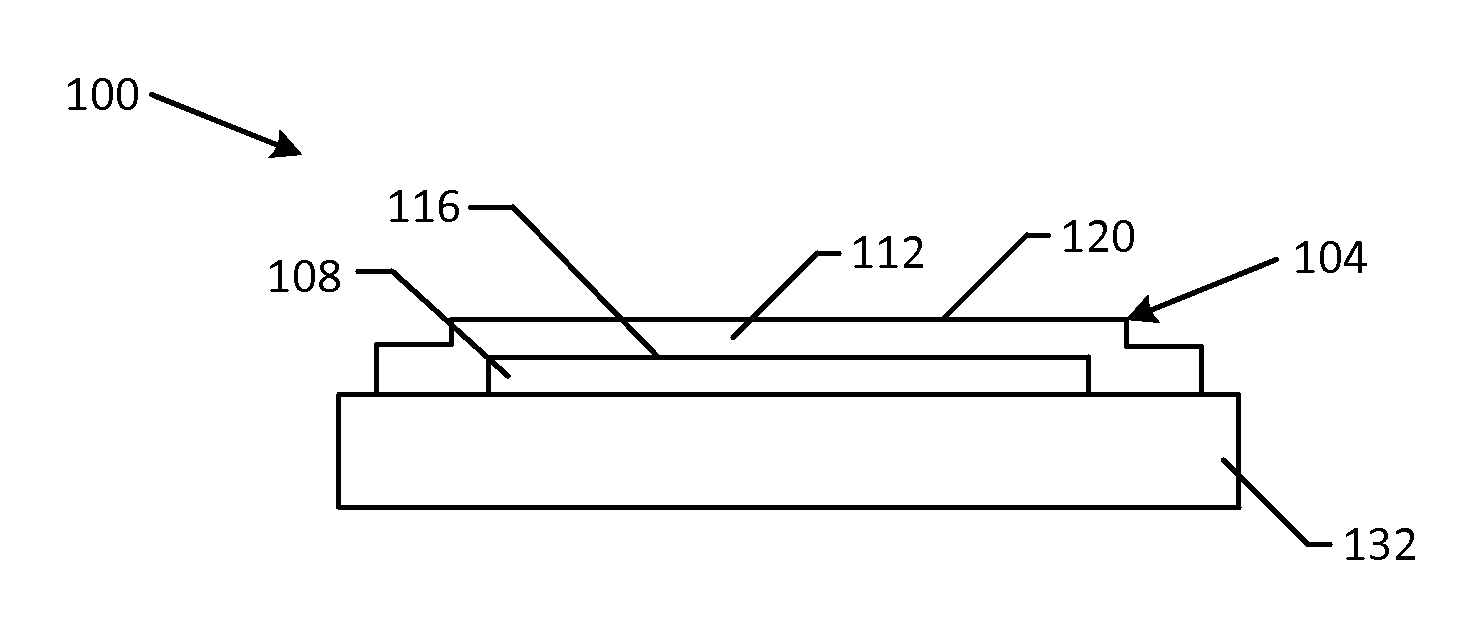
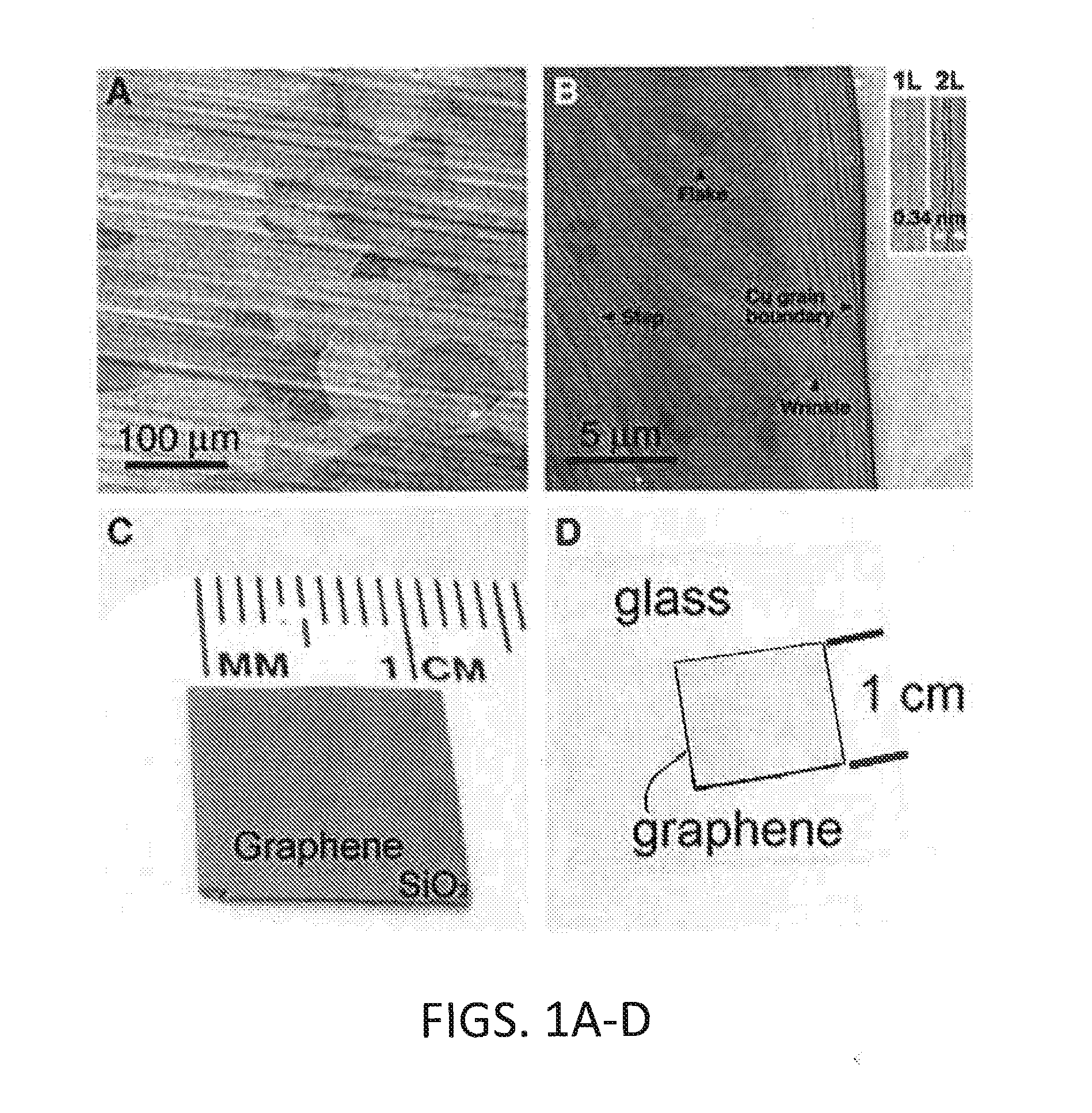
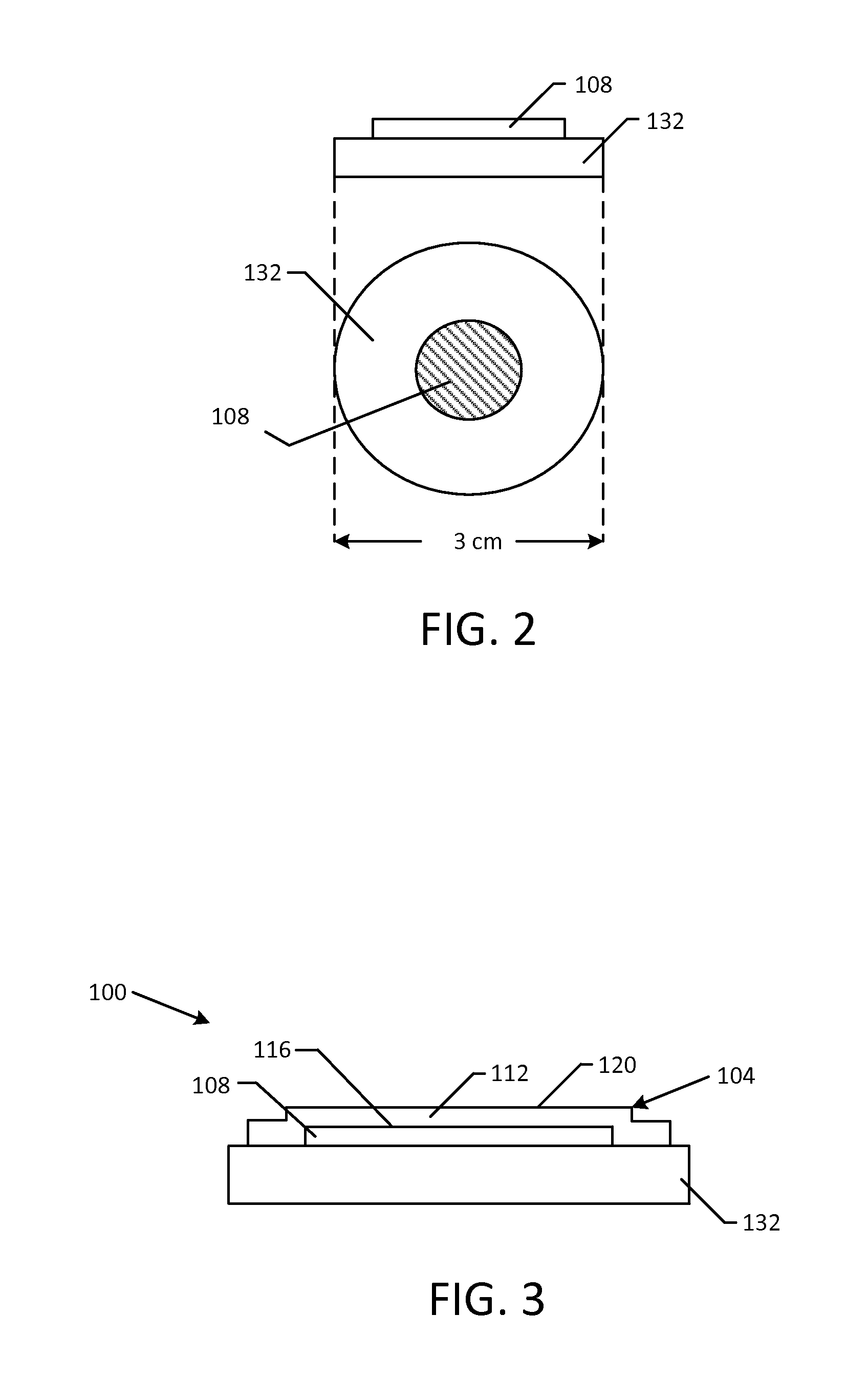
Graphene Shield Enhanced Photocathodes and Methods for Making the Same
InactiveUS20130293100A1Lower work functionLong life-timePhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesQuantum efficiencyElectron source
Disclosed are graphene shield enhanced photocathodes, such as high QE photocathodes. In certain embodiments, a monolayer graphene shield membrane ruggedizes a high quantum efficiency photoemission electron source by protecting a photosensitive film of the photocathode, extending operational lifetime and simplifying its integration in practical electron sources. In certain embodiments of the disclosed graphene shield enhanced photocathodes, the graphene serves as a transparent shield that does not inhibit photon or electron transmission but isolates the photosensitive film of the photocathode from reactive gas species, preventing contamination and yielding longer lifetime.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
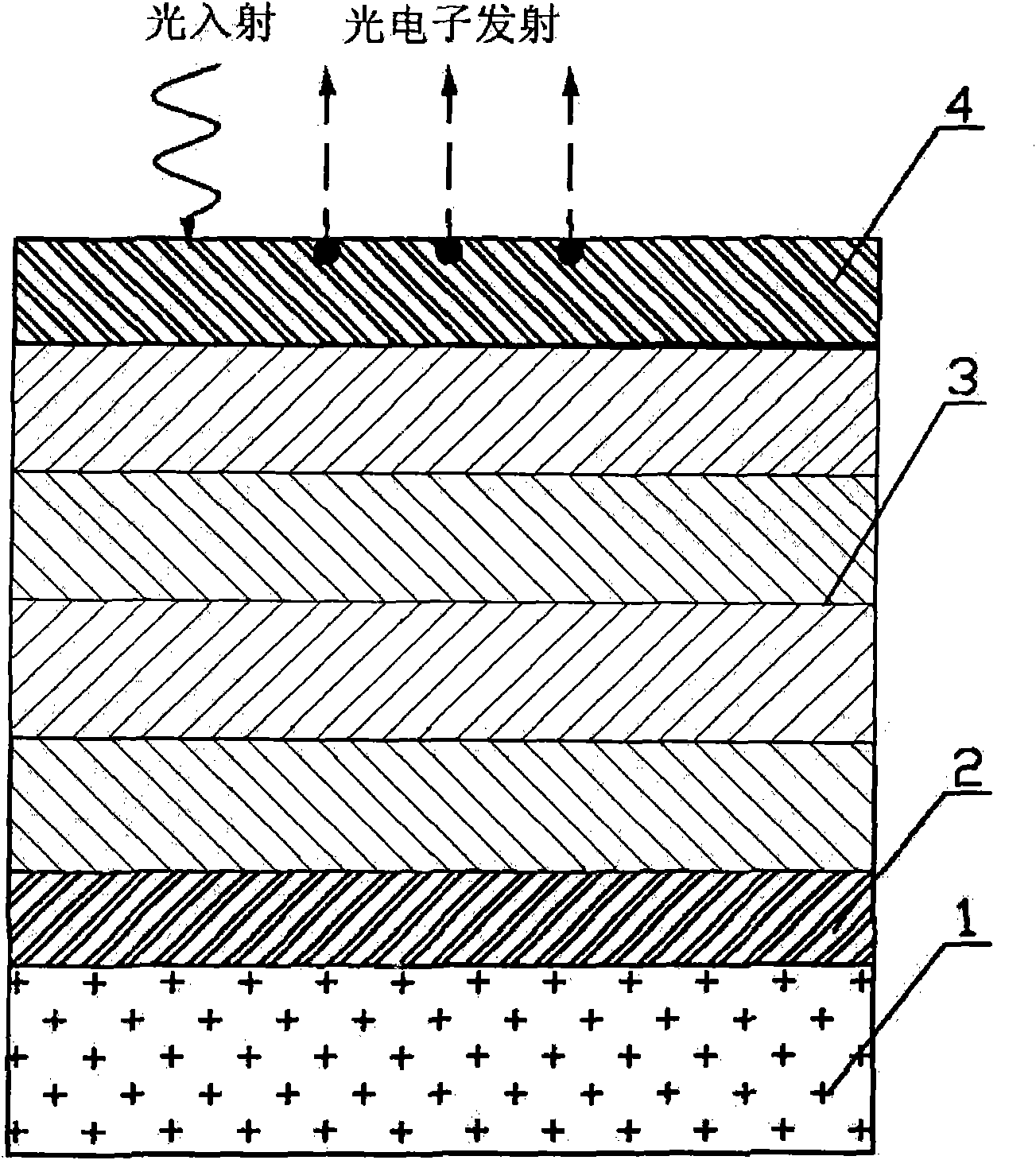
Multi-component gradient-doping GaN UV (Ultraviolet) light cathode material structure and manufacture method thereof
InactiveCN102064206AIncreased escape depthImprove quantum efficiencyFinal product manufacturePhoto-emissive cathodesQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
The invention provides a reflection-type GaN UV (Ultraviolet) light cathode material structure and a manufacture method thereof. The structure comprises a substrate, an involuntarily doping AlN buffer layer, a p-type GaxAI1-xN multi-component mix-crystal photoelectric emission layer and a Cs or Cs / O active layer, wherein the involuntarily doping AlN buffer layer grows on the substrate; the p-type GaxAI1-xN multi-component mix-crystal photoelectric emission layer epitaxially grows on the AlN buffer layer; and the Cs or Cs / O active layer is absorbed on the front surface of the p-type GaxAI1-xN multi-component mix-crystal photoelectric emission layer and has the thickness of an nm order of magnitude. By adopting the multi-component and gradient-doping photoelectric emission layer, the structure increases the escape depth of photonexcited electrons in the emission layer and improves the possibility for emitting the electrons in the emission layer into vacuum so as to improve the whole quantum efficiency of the GaN UV light cathode and acquire higher UV sensibility.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electron emission device
ActiveUS20050018467A1Improve performanceEasy to manufactureStatic indicating devicesImage/pattern display tubesOptoelectronicsElectron
An electrons' emission device is presented. The device comprises an electrodes' arrangement including at least one Cathode electrode and at least one Anode electrode, the Cathode and Anode electrodes being arranged in a spaced-apart relationship; the device being configured to expose said at least one Cathode electrode to exciting illumination to thereby cause electrons' emission from said Cathode electrode, the device being operable as a photoemission switching device.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Micro-channel plate type photomultiplier tube with high quantum efficiency and preparation method thereof, and dual-alkali photocathode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107622930AHigh cathode quantum efficiencyStrong consistencyMultiplier cathode arrangementsVacuum evaporation coatingQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
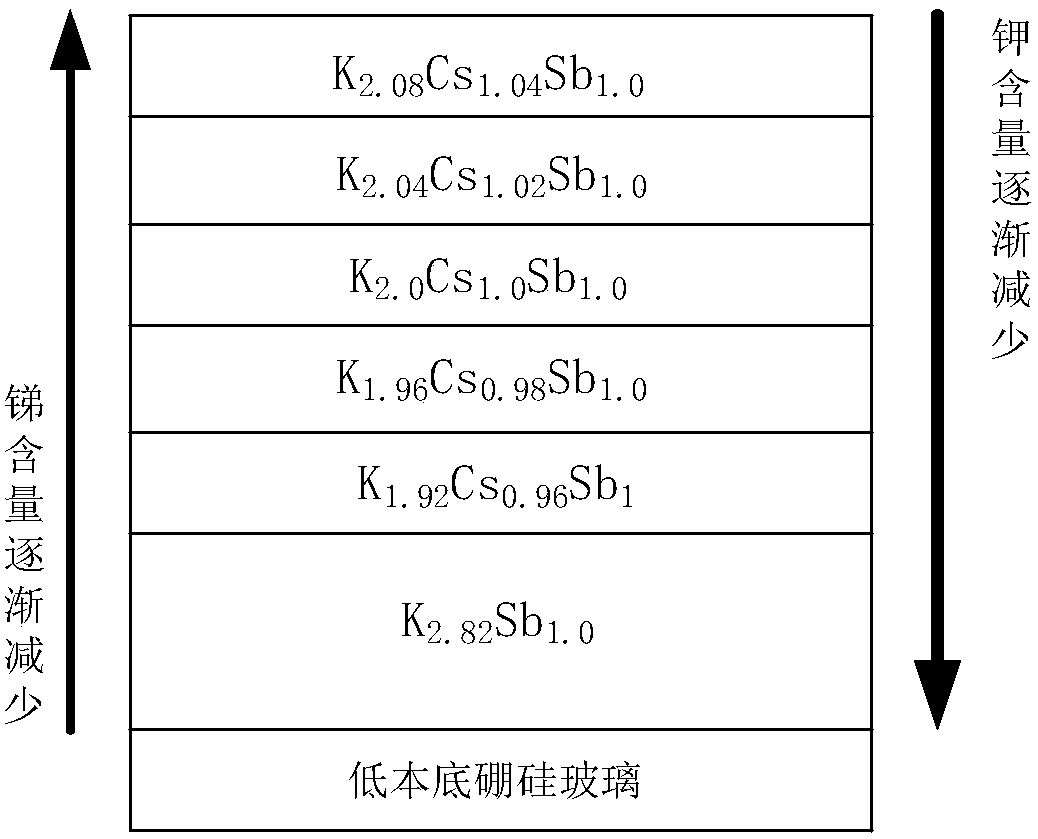
The invention discloses a micro-channel plate type photomultiplier tube with high quantum efficiency and a preparation method thereof, and a dual-alkali photocathode and a preparation method thereof.Obtained dual-alkali photocathodes are sequentially stacked on the substrate in a multi-layer alkali antimonide manner; and the components of the alkali antimonide change based on a rule that antimonyelements decrease gradually and alkali metal increases gradually in a direction from the substrate of the dual-alkali photocathode to the outer surface. Therefore, the obtained stable dual-alkali photocathode structure has high repeatability; and a self-built electric field is formed inside the dual-alkali photocathode, so that electrons are excited in vacuum and thus the obtained micro-channel plate type photomultiplier tube has the high quantum efficiency.
Owner:NORTH NIGHT VISION TECH +1
Photocathode
InactiveUS20010001226A1Multiplier cathode arrangementsCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesInfraredPhotocathode
A photocathode having a UV glass substrate and a laminate composed of a SiO2 layer, a GaAlN layer, a Group III-V nitride semiconductor layer and an AlN buffer layer provided on the UV glass substrate in succession. The UV glass substrate, which absorbs infrared rays, can be heat treated at a high speed by photoheating. Further, the UV glass substrate, which is transparent to ultraviolet rays, permits ultraviolet rays to be introduced into the Group III-V nitride semiconductor layer where photoelectric conversion occurs.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
NEA electron source for vertically emitting AlGaAs/GaAs nanowires
InactiveCN104752117ASuppress emissionHigh vertical emission efficiency at the topElectric discharge tubesPhoto-emissive cathodesElectron sourceBiological activation
The invention provides an NEA electron source for vertically emitting AlGaAs / GaAs nanowires. A p type GaAs is taken as a substrate layer, a variable-band gap AlGaAs emission layer of which the Al component is linearly and gradually reduced to zero from high to low, and a GaAs emission layer are orderly grown on the GaAs substrate layer, next, a variable-band gap AlGaAs / GaAs nanowire array emission layer is obtained by use of a reactive ion etching technique, and then Cs / O excitation is performed in an ultrahigh vacuum system so as to form a Cs-O activation layer on the variable-band gap AlGaAs / GaAs nanowire array emission layer; in addition, a built-in electric field is formed on the variable-band gap AlGaAs / GaAs nanowire array emission layer in the vertical direction, and the photoelectrons in the nanowires are controlled to directionally drift and be emitted by use of the built-in electric field, so that the photoelectric emission of the side surface can be effectively inhibited, and therefore, the application of the variable-band gap AlGaAs / GaAs material is expanded; the nanowire array structure is capable of improving the photoelectric emission efficiency.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
GaAs nanowire array photocathode and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN103594302AReduce reflectivityShorten the transportation distancePhoto-emissive cathodesNanotechnologyElectronic band structureEmission efficiency
The invention discloses a GaSa nanowire array photocathode and a manufacturing method of the GaSa nanowire array photocathode. The cathode is composed of a GaSa substrate layer, A GaSa nanowire array emission layer and a Cs / O activation layer. The method includes the steps that GaSa nanowire array material is manufactured on a GaSa substrate with a certain thickness by the adoption of a dry etching technology, the GaSa nanowire array photocathode is manufactured in an ultrahigh vacuum activation system, after the GaSa nanowire material is activated to be the photocathode, and a Cs-O layer is adsorbed around whole nanowires to generate negative electron affinity, so that an energy band structure is formed on the GaSa nanowires with the middle higher than the periphery. A nanowire array structure is beneficial to photon absorption, and the nanowire photocathode energy band structure is beneficial to photoelectronic emission, so that photon absorption and electron emission efficiency of the material is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Transmission type photoelectric cathode and electron tube
InactiveUS20050174052A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease brightnessMultiplier cathode arrangementsPhoto-emissive cathodesPhotocathodePlane of incidence
A transmission type photocathode of the present invention comprises a light absorption layer 1 formed of diamond or a material containing diamond as a main component, a supporting frame 21 for reinforcing the mechanical strength of the light absorption layer 1, a first electrode 31 provided at the plane of incidence of the light absorption layer 1, and a second electrode 32 provided at the plane of emission of the light absorption layer 1. A voltage is applied between the plane of incidence and plane of emission of the light absorption layer 1 to form an electric field in the light absorption layer 1. When light to be detected is made incident and photoelectrons occur in the light absorption layer 1, the photoelectrons are accelerated to the plane of emission by the electric field formed in the light absorption layer 1, and emitted to the outside of the transmission type photocathode.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
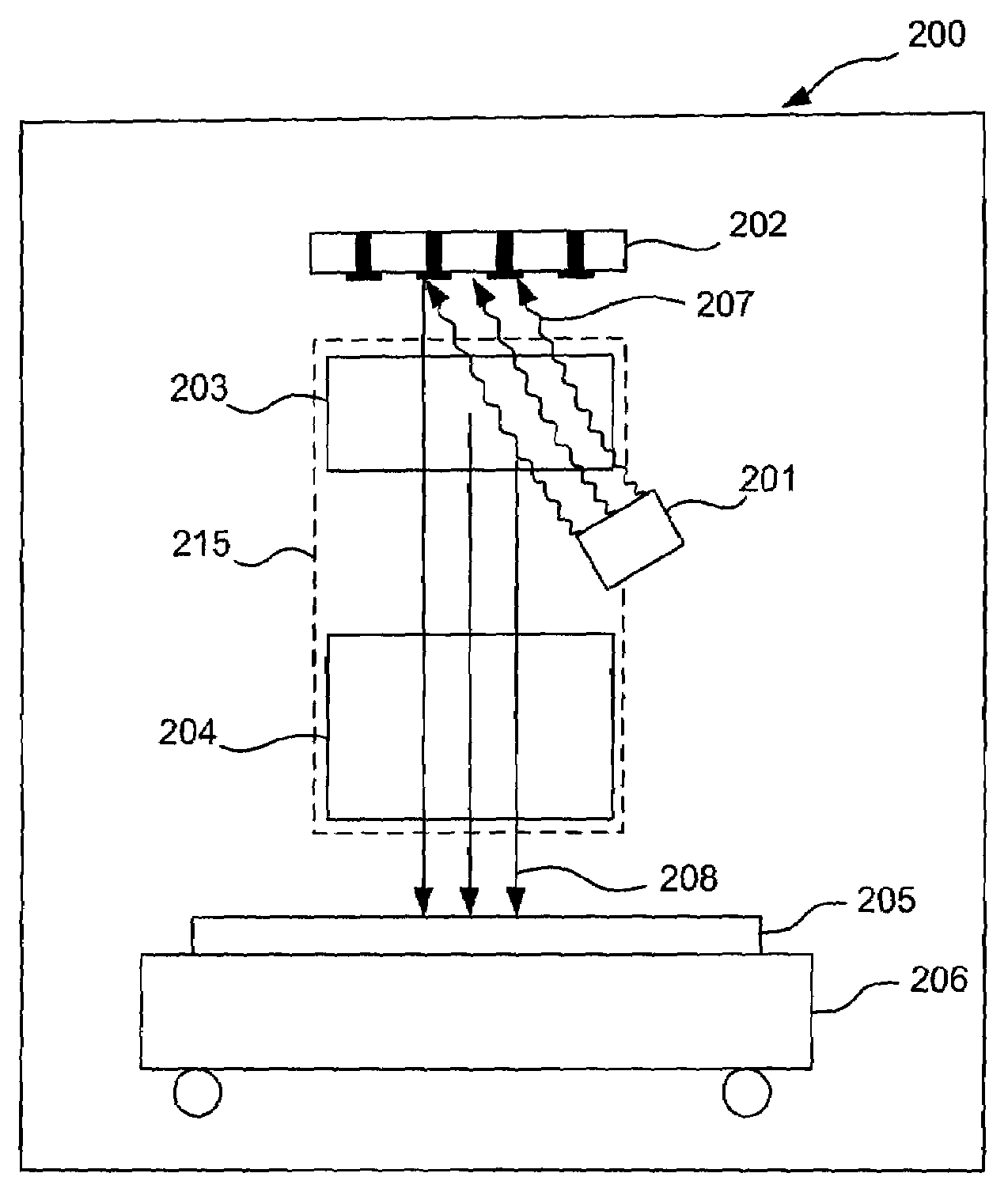
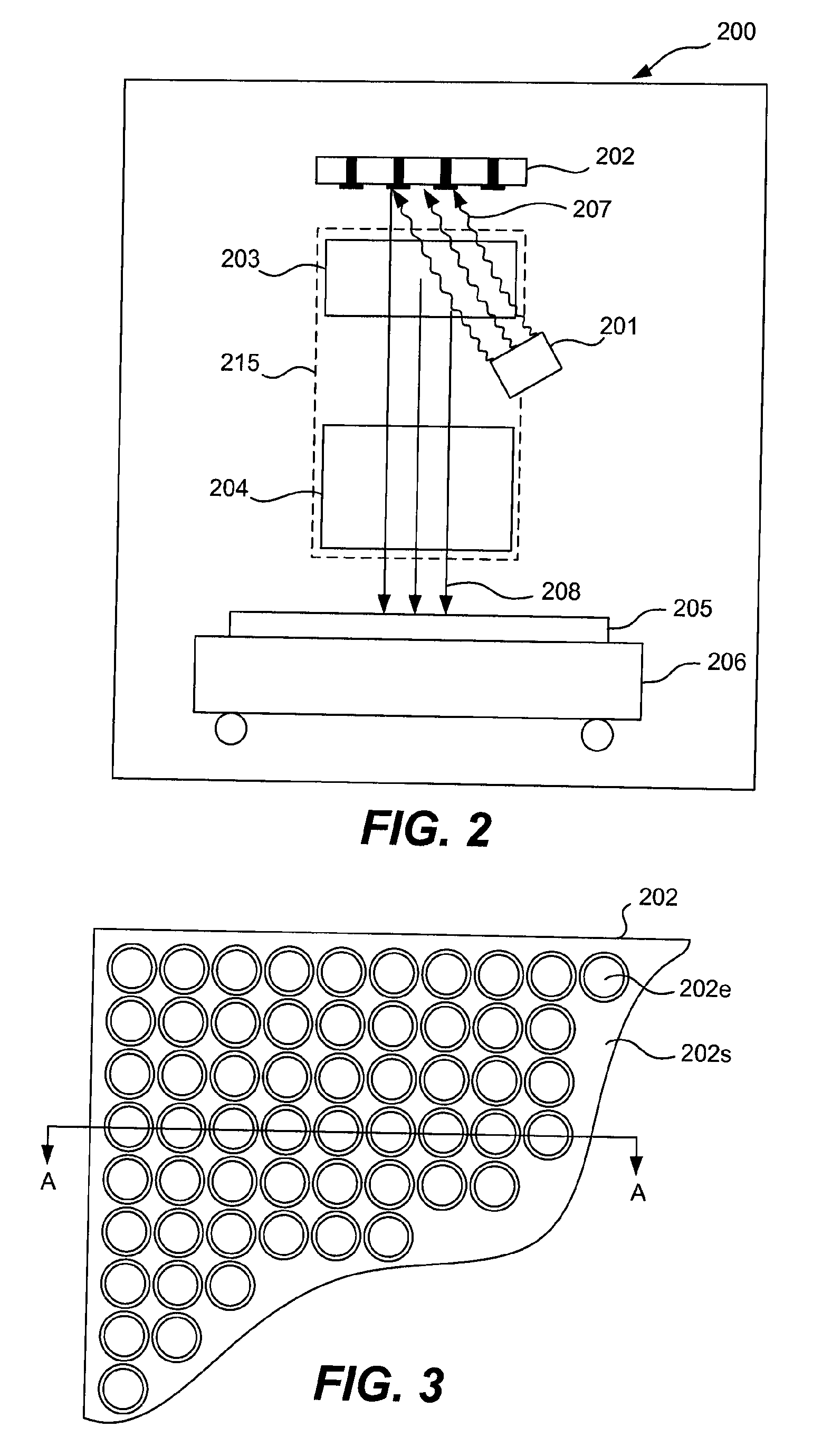
Electron beam lithography method and apparatus using a dynamically controlled photocathode
ActiveUS20080169436A1Thermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotocathodeBeam pattern
Embodiments of the invention include an electron beam lithography device using a dynamically controllable photocathode capable of producing a patterned electron beam. One such implementation includes a dynamic pattern generator configurable to produce an electron beam having a desired image pattern impressed thereon. Such an electron beam pattern being enabled by selectively activating programmable photoemissive elements of the pattern generator. The apparatus further including an illumination source arranged to direct a light beam onto the dynamic pattern generator to produce the electron beam having the desired pattern. The electron beam being directed through associated electron optics configured to receive the electron beam from the dynamic pattern generator and direct the electron beam onto a target substrate mounted on a stage.
Owner:KLA TENCOR TECH CORP
Reflective NEA GaN nanowire array photoelectric negative electrode and manufacturing method therefor
InactiveCN105428183AImprove quantum efficiencyReduce lossesMaterial nanotechnologyPhoto-emissive cathodesSic substratePhotocathode
The invention proposes a reflective NEA GaN nanowire array photoelectric negative electrode and a manufacturing method therefor. The reflective NEA GaN nanowire array photoelectric negative electrode is obtained by growing p-type GaN nanowires on the surface of an Si or SiC substrate and performing Cs / O activation on a grown nanowire array. The reflective NEA GaN nanowire array photoelectric negative electrode comprises a substrate layer and a nanowire array emission layer positioned on the surface of the substrate layer, wherein the nanowire array emission layer consists of a plurality of p-type GaN nanowires; Cs / O activation layers are adsorbed on the surfaces of the p-type GaN nanowires; and the substrate layer is Si or SiC. According to the reflective NEA GaN nanowire array photoelectric negative electrode, the photoelectron transmission distance can be reduced while the material emission rate is reduced; and photons are fully absorbed by controlling the diameters of the nanowires, so that the quantum efficiency of the GaN photoelectric negative electrode is improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
High-sensitivity antimony alkali photocathode and photomultiplier
InactiveCN103715033AHigh sensitivityImprove absorption ratePhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
Disclosed are a high-sensitivity antimony alkali photocathode and a photomultiplier. Compared with a traditional photocathode, the sensitivity of the photocathode is significantly improved. The high-sensitivity antimony alkali photocathode comprises a photocathode substrate, wherein a cathode anti-reflection layer is arranged on the photocathode substrate, and an antimony alkali photocathode emission layer is arranged on the cathode anti-reflection layer. The refractive index of the anti-reflection layer ranges from 2.3 to 2.6, and therefore loss of incident light can be greatly reduced; furthermore, electrons of which the advancing direction is opposite to the direction of the incident light can be reversed in a certain extent, and therefore the quantum efficiency of the photocathode can be improved.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Photocathode based on novel nanostructure and preparation method thereof
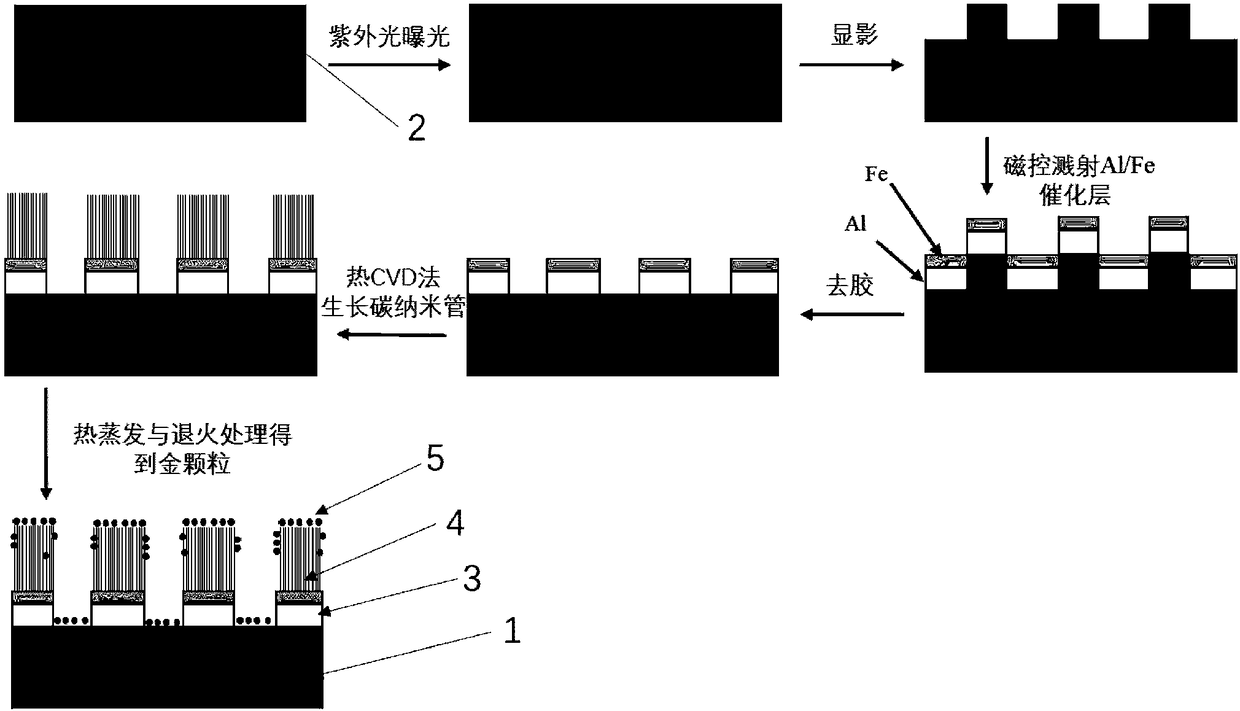
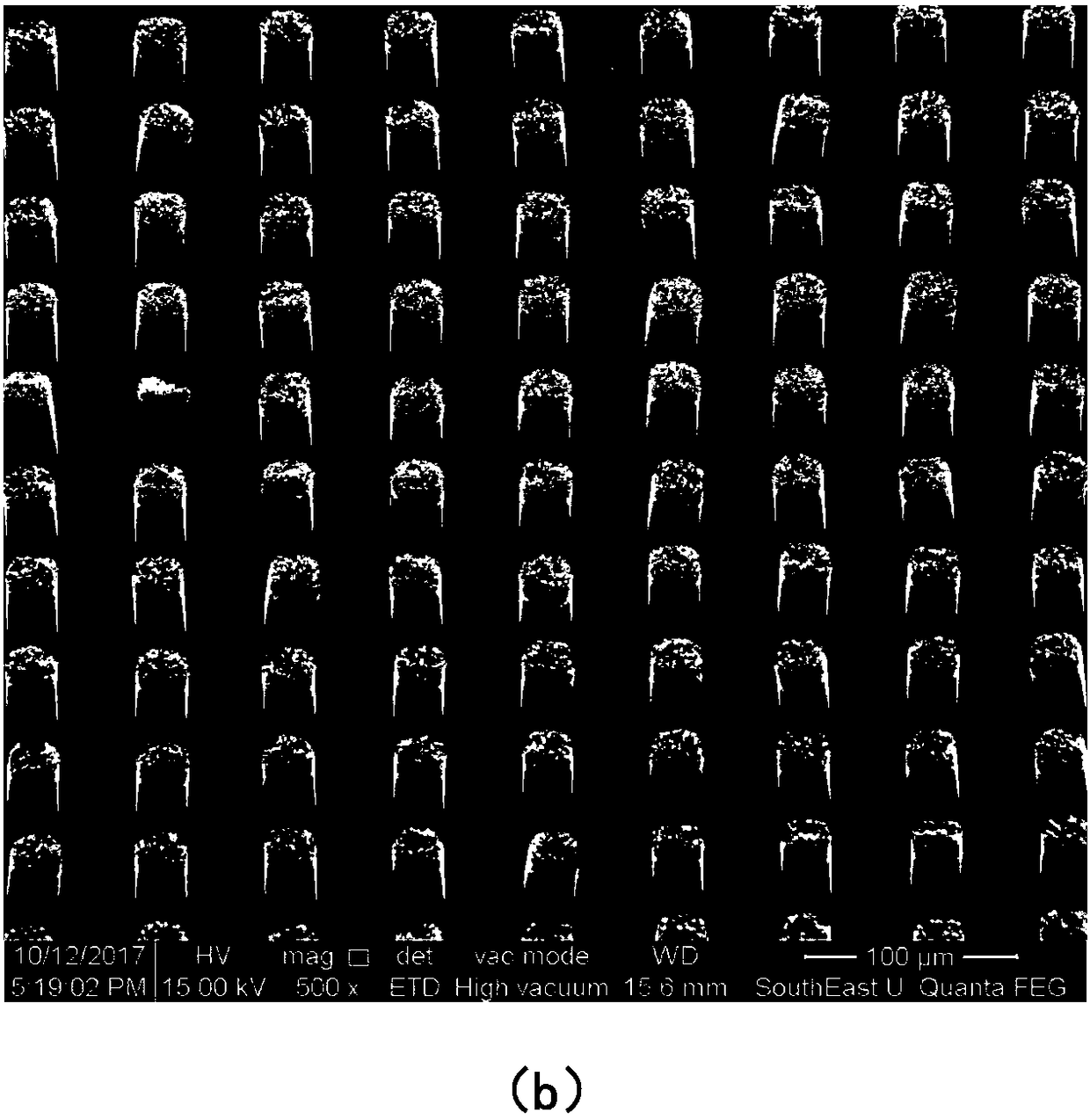
ActiveCN108231507AAvoid electrostatic shielding effectsTake advantage ofMaterial nanotechnologyPhoto-emissive cathodesPhotocathodeLight energy
The invention provides a novel nanostructure photocathode which comprises a patterned catalytic layer, a patterned vertical carbon nanotube formed on the catalytic layer and a metal nanoparticle witha plasmon effect modified on the vertical carbon nanotube. The invention further provides a preparation method of the novel nanostructure photocathode. The novel nanostructure photocathode and the preparation method provided by the invention have the benefits that an electrostatic shielding effect on the cathode surface can be effectively prevented through the patterning treatment of a cathode electron emission material, and a fringe effect is fully utilized, so that a cathode surface barrier is compressed, and a threshold of light energy required for electron emission is lowered; the carbon nanotube and the metal nanoparticle are combined, so that the excellent electrical performance and the environmental stability of the carbon nanotube are utilized, and meanwhile, a surface plasmon resonance effect of the metal nanoparticle is also utilized. Therefore, the enhancement of a light wave local electric field and the photon absorption enhancement can be realized.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Hybrid solar generator
A solar generator can include a photon-enhanced thermionic emission generator with a cathode to receive solar radiation. The photon-enhanced thermionic emission generator can include an anode that in conjunction with the cathode generates a first current and waste heat from the solar radiation. A thermoelectric generator can be thermally coupled to the anode and can convert the waste heat from the anode into a second current. A circuit can connect to the photon-enhanced thermionic emission generator and to the thermoelectric generator and can combine the first and the second currents into an output current.
Owner:GE AVIATION SYST LLC
Photoelectric cathode and process for preparing vacuum ultraviolet electric device using said cathode
InactiveCN1945776ALower requirementReduce energy consumptionPhoto-emissive cathodesCold cathode manufacturePhotocathodeCurrent technology
This invention discloses a photoelectric cathode composed of three compound layers, in which, the base layer is made of an ultraviolet transmitting base material, the mid layer is a transparent conduction layer film characterizing that the third layer is a photoelectric emission layer composed of a ZnO film or nanometer line arrays. A method for preparing vacuum UV-devices by said photoelectric cathodes includes the following steps: A, preparation of photoelectric cathodes, B, molding films of the ZnO photoelectric cathode and testing the performance, selecting cathodes meeting the requirement to exhaust and package, packaging the devices applying said photoelectric cathode, which fully utilizes the photoemission and field emission effect of ZnO to solve the shortcoming of the current technology.
Owner:SICHUAN TIANWEI ELECTRONICS
Semiconductor photocathode and method for manufacturing the same
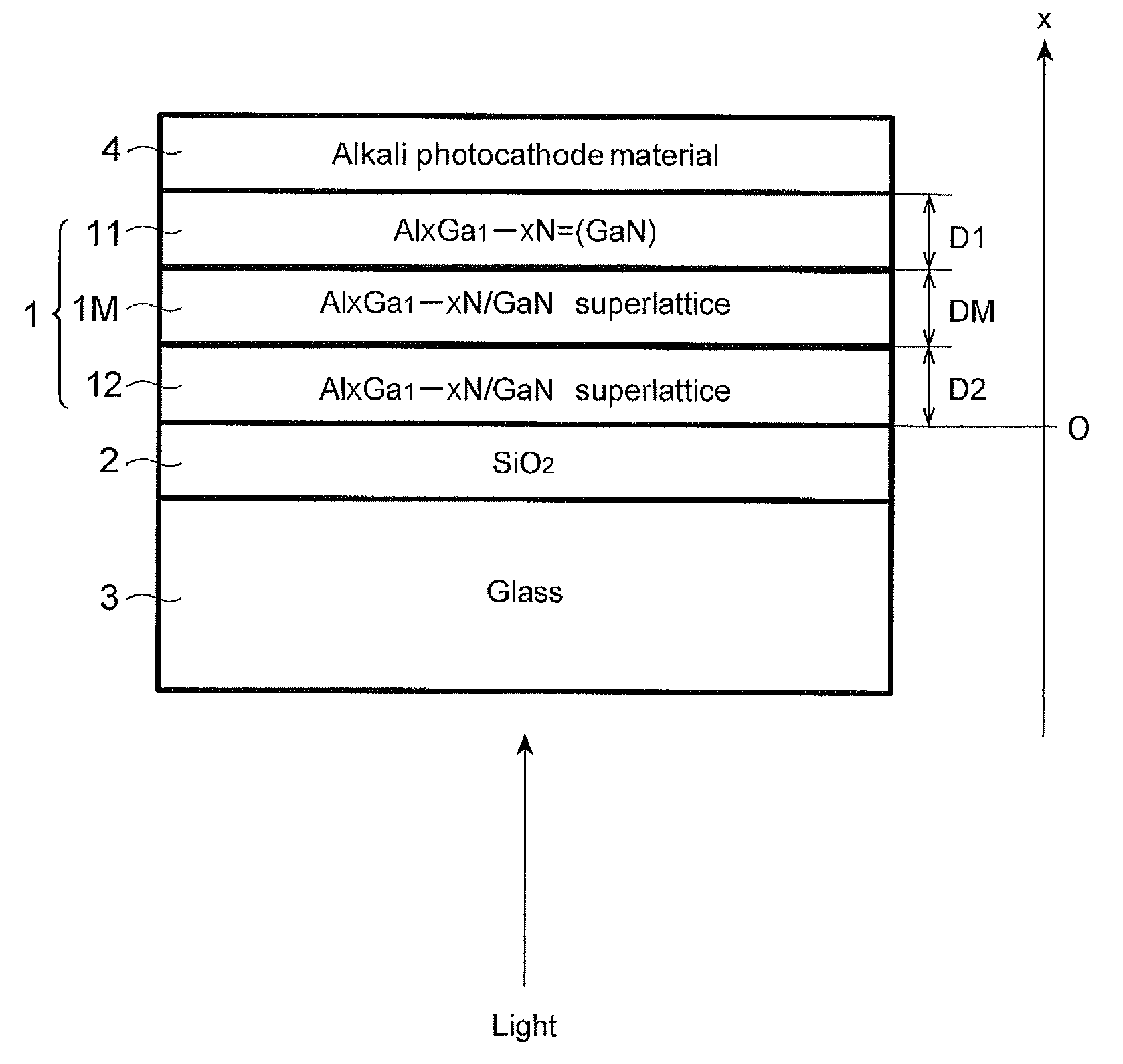
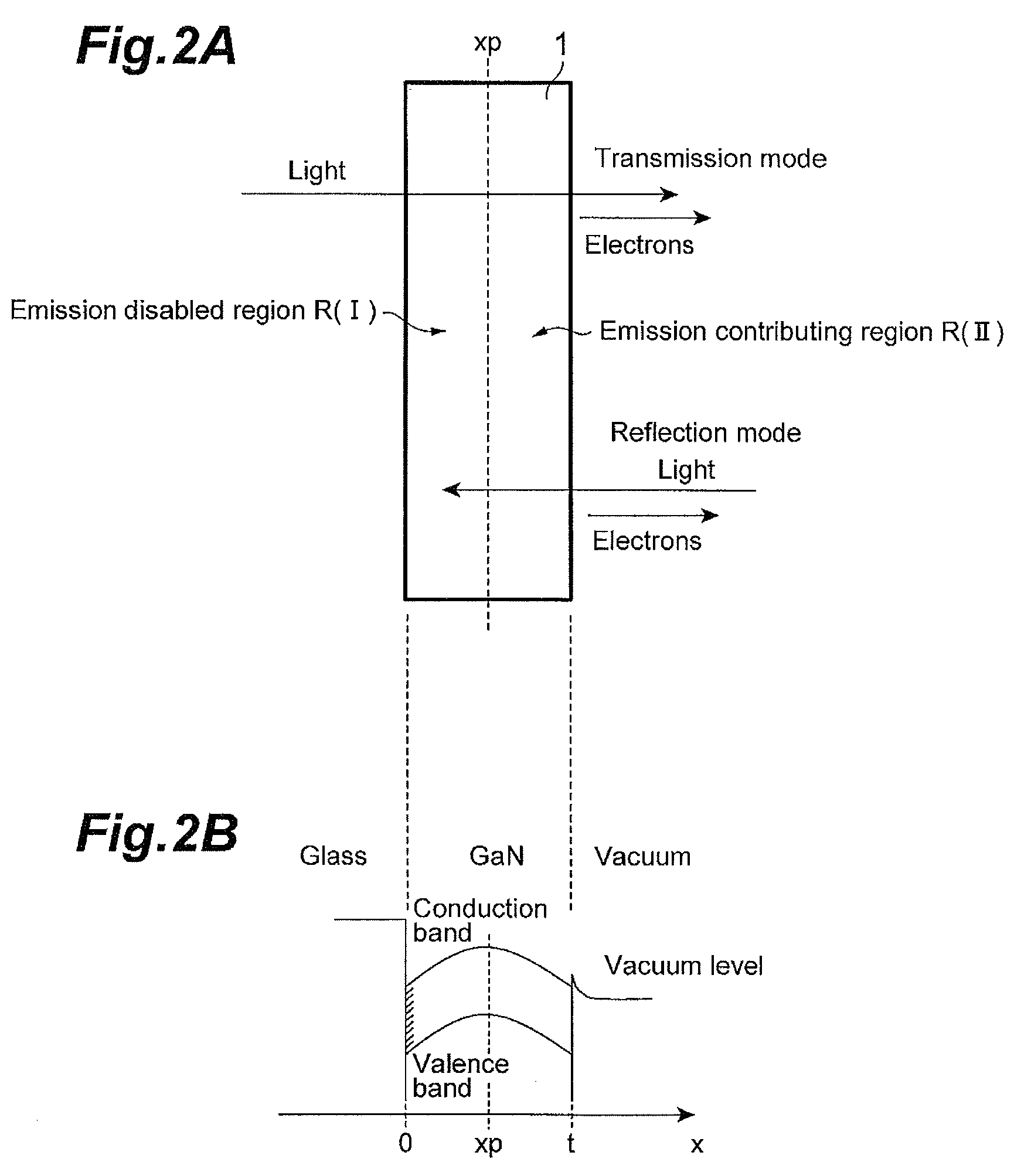
ActiveUS20130248815A1Improve quantum efficiencyEasy to produceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImage pickup tubesPhotocathodeSemiconductor
A semiconductor photocathode includes an AlXGa1-XN layer (0≦X<1) bonded to a glass substrate via an SiO2 layer and an alkali-metal-containing layer formed on the AlXGa1-XN layer. The AlXGa1-XN layer includes a first region, a second region, an intermediate region between the first and second regions. The second region has a semiconductor superlattice structure formed by laminating a barrier layer and a well layer alternately, the intermediate region has a semiconductor superlattice structure formed by laminating a barrier layer and a well layer alternately. When a pair of adjacent barrier and well layers is defined as a unit section, an average value of a composition ratio X of Al in a unit section decreases monotonously with distance from an interface position between the second region and the SiO2 layer at least in the intermediate region.
Owner:SANKEN ELECTRIC CO LTD +1
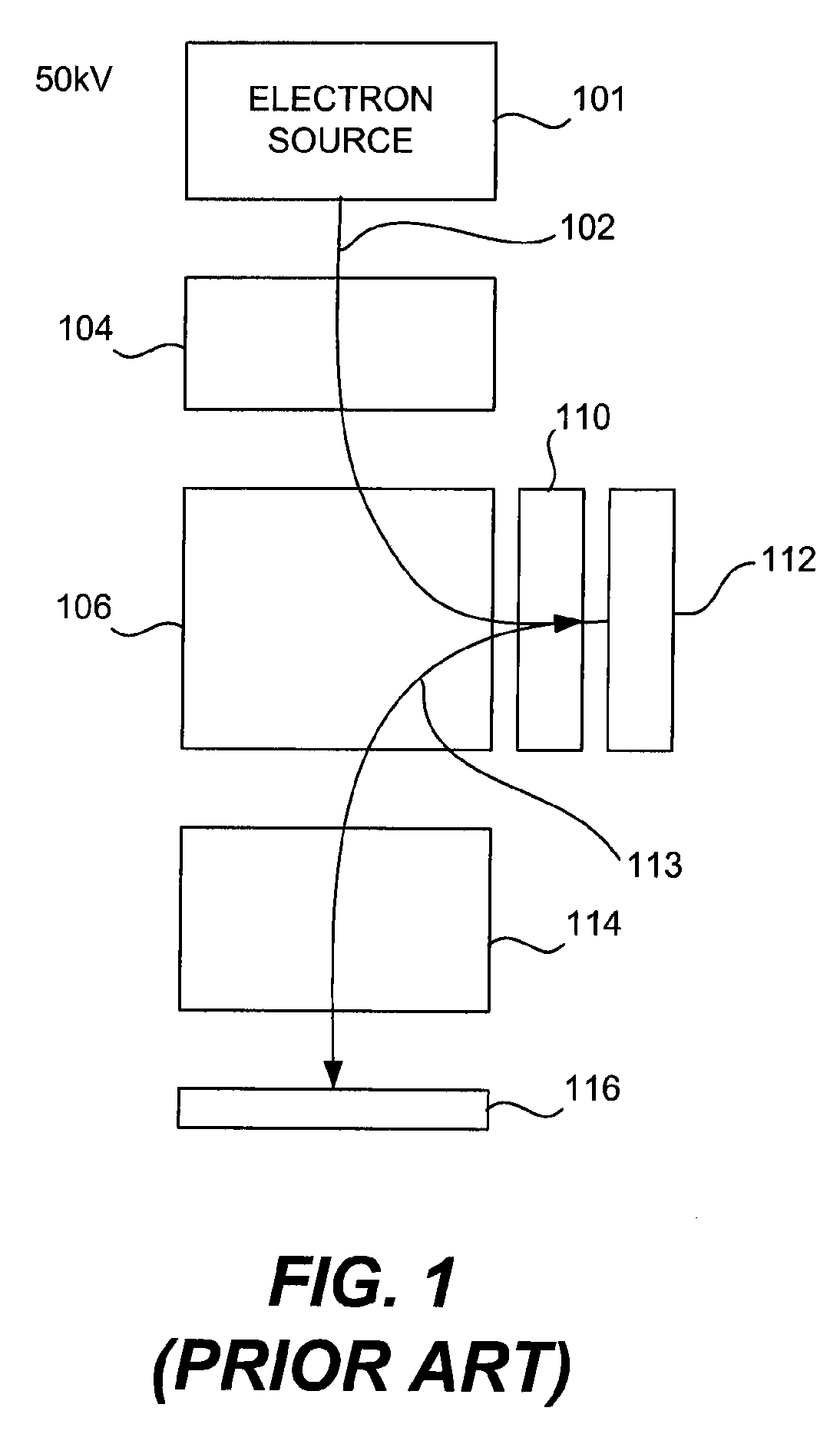
Polarized pulsed front-end beam source for electron microscope
InactiveUS20070228286A1Improve performanceThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron sourceBeam source
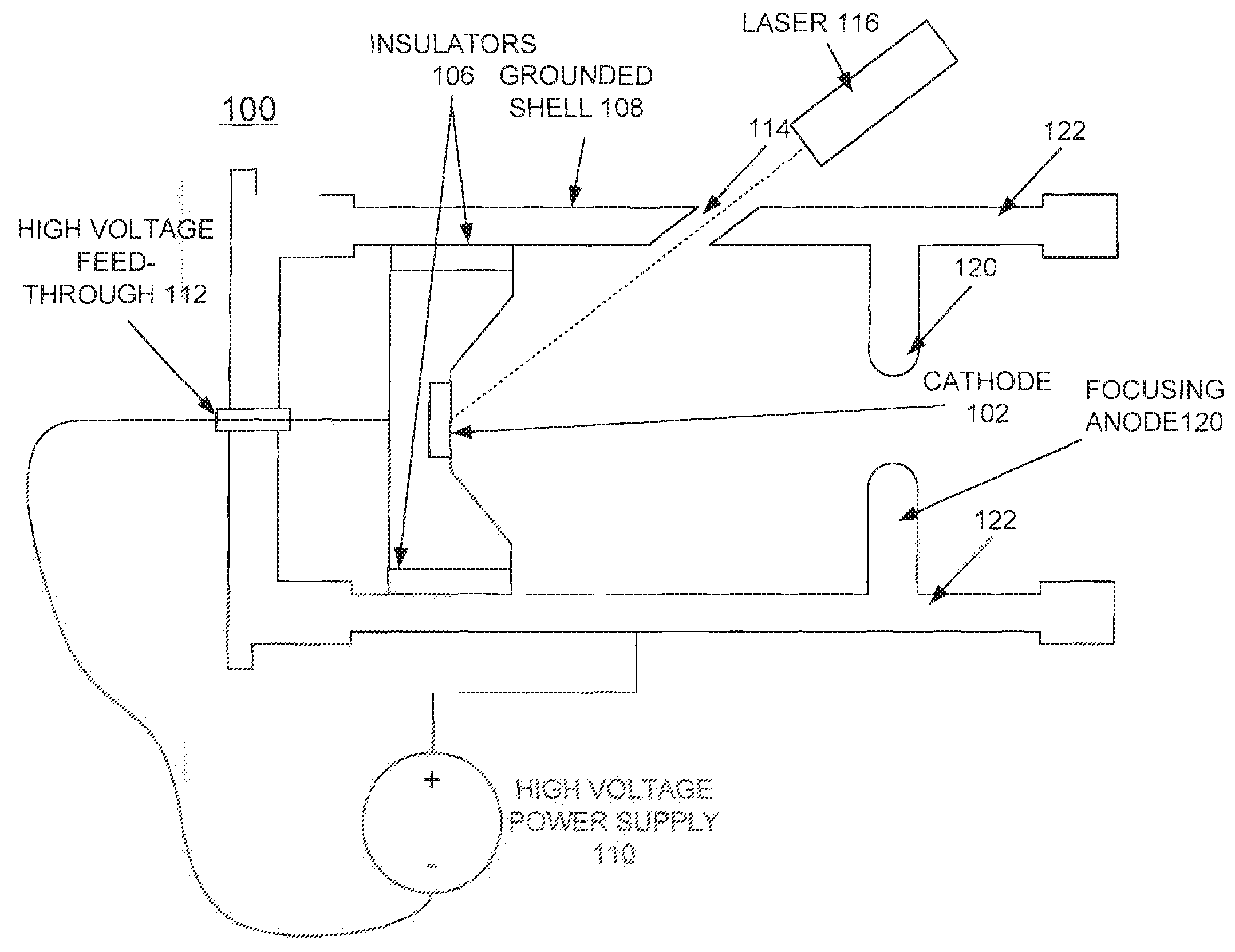
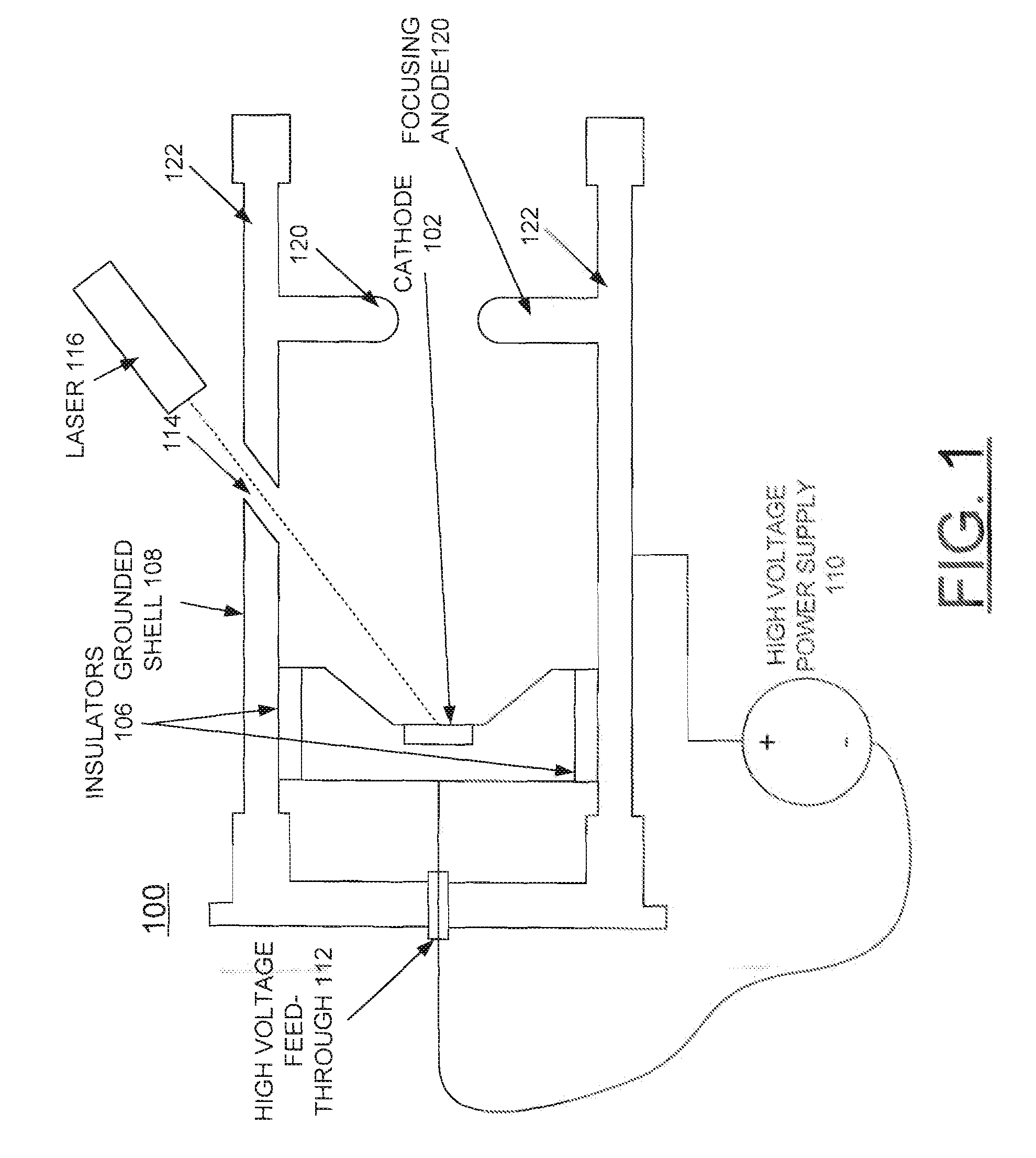
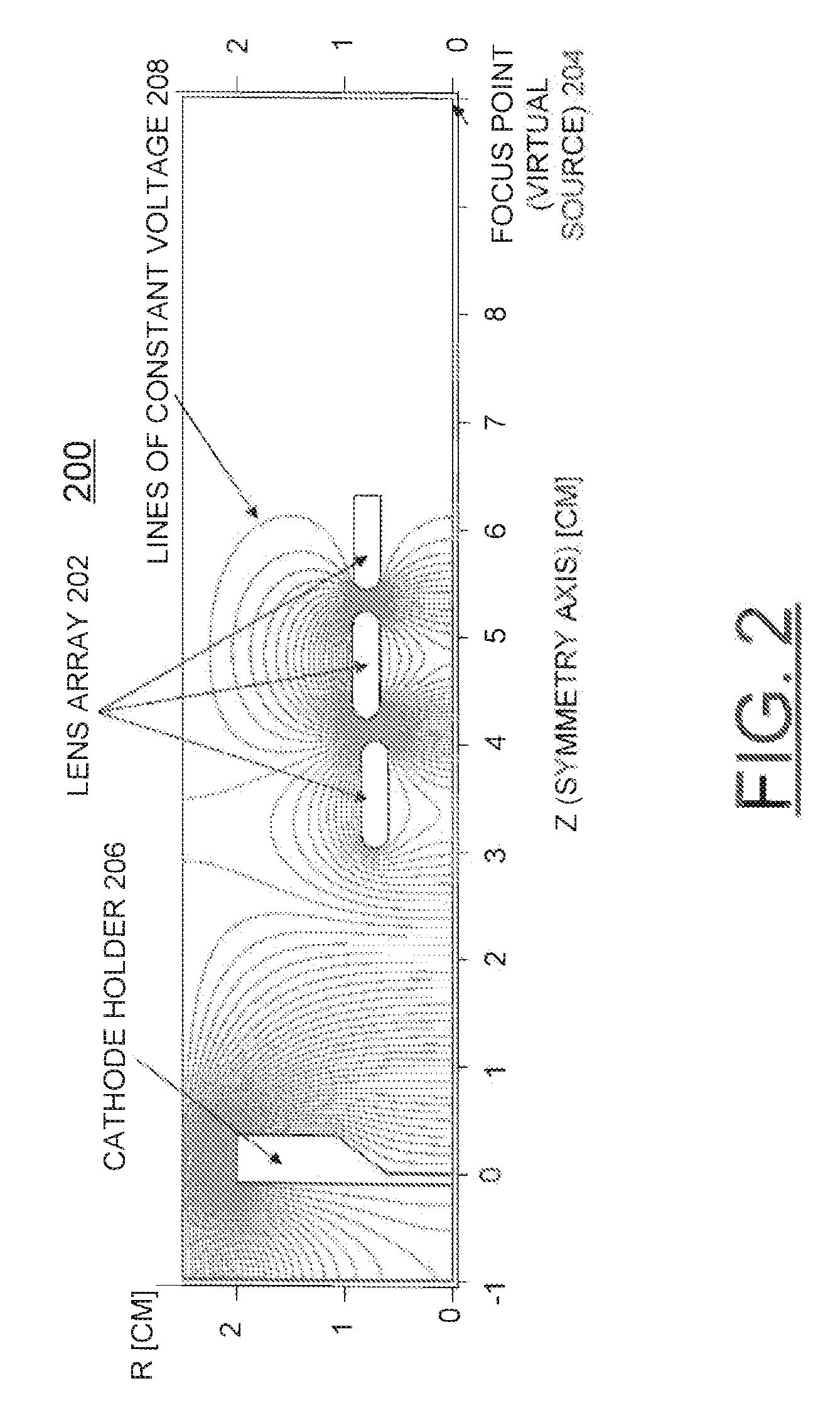
A method and an electron source are provided for generating polarized electrons for an electron microscope. The electron source includes a photoemissive cathode and a low-power drive laser. The geometry of the photoemissive cathode uses a generally planar emission surface, which is imaged to approximately 1 / 100 its initial size via electrostatic focusing elements. The virtual emitter, or image spot, then is used as an electron source by a conventional microscope column.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
Electronic switching device
ActiveUS7646149B2Improve performanceEasy to manufactureStatic indicating devicesImage/pattern display tubesElectronic switchOptoelectronics
An electrons' emission device is presented. The device comprises an electrodes' arrangement including at least one Cathode electrode and at least one Anode electrode, the Cathode and Anode electrodes being arranged in a spaced-apart relationship; the device being configured to expose said at least one Cathode electrode to exciting illumination to thereby cause electrons' emission from said Cathode electrode, the device being operable as a photoemission switching device.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Photocathode including field emitter array on a silicon substrate with boron layer
ActiveUS10748730B2Avoiding negative aspectImprove work functionSolid-state devicesImage pickup tubesPhotocathodeReverse bias
A photocathode utilizes an field emitter array (FEA) integrally formed on a silicon substrate to enhance photoelectron emissions, and a thin boron layer disposed directly on the output surface of the FEA to prevent oxidation. The field emitters are formed by protrusions having various shapes (e.g., pyramids or rounded whiskers) disposed in a two-dimensional periodic pattern, and may be configured to operate in a reverse bias mode. An optional gate layer is provided to control emission currents. An optional second boron layer is formed on the illuminated (top) surface, and an optional anti-reflective material layer is formed on the second boron layer. An optional external potential is generated between the opposing illuminated and output surfaces. An optional combination of n-type silicon field emitter and p-i-n photodiode film is formed by a special doping scheme and by applying an external potential. The photocathode forms part of sensor and inspection systems.
Owner:KLA CORP
Photocathode and electron tube
InactiveUS20020011787A1Lattice mismatching is alleviatedPhoto-emissive cathodesPhotoelectric discharge tubesPhotocathodeContact layer
This photocathode comprises: InP substrate 1; InAsx2P1-x2(0<x2<1) buffer layer 2; Inx1Ga1-x1As (1>x1>0.53) light-absorbing layer 3; InAsx3P1-x3 (0<x3<1) electron-emitting layer 4; InAsx3P1-x3 contact layer 5 formed on the electron-emitting layer 4; active layer 8 of an alkali metal or its oxide or fluoride formed on the exposed surface of electron-emitting layer 4; and electrodes 6 and 7.
Owner:HAMAMATSU PHOTONICS KK
Field-assisted multiple alkalis photo-cathode
The invention discloses a field-assistant multi-alkali IR photocathode. A metal grid is arranged behind a multi-alkali photocathode by a predetermined distance, and a voltage is applied by an external circuit to form a uniform electric field at the emergent face of photoelectrons. The multi-alkali photocathode is subjected to IR extension treatment, and comprises Na2KSb 80-90 percent, and K2CsSb 10-20 percent. By forming a uniform externally-applied electric field within a certain distance from the emergent surface of the photocathode, the inventive device can make the multi-alkali photocathode produce photoelectric response to near infrared waveband having a wavelength of at least 1,064 nm, and the photocathode has higher stability and the noise background than Ag-O-Cs cathode and higher photoelectric sensitivity and time characteristics than combined photocathode and has affinity for negative ions of III-V group. The IR photocathode has simple process and device and easy implementation, and can be made to product and fill the blank of existing vacuum IR photocathode in our country.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
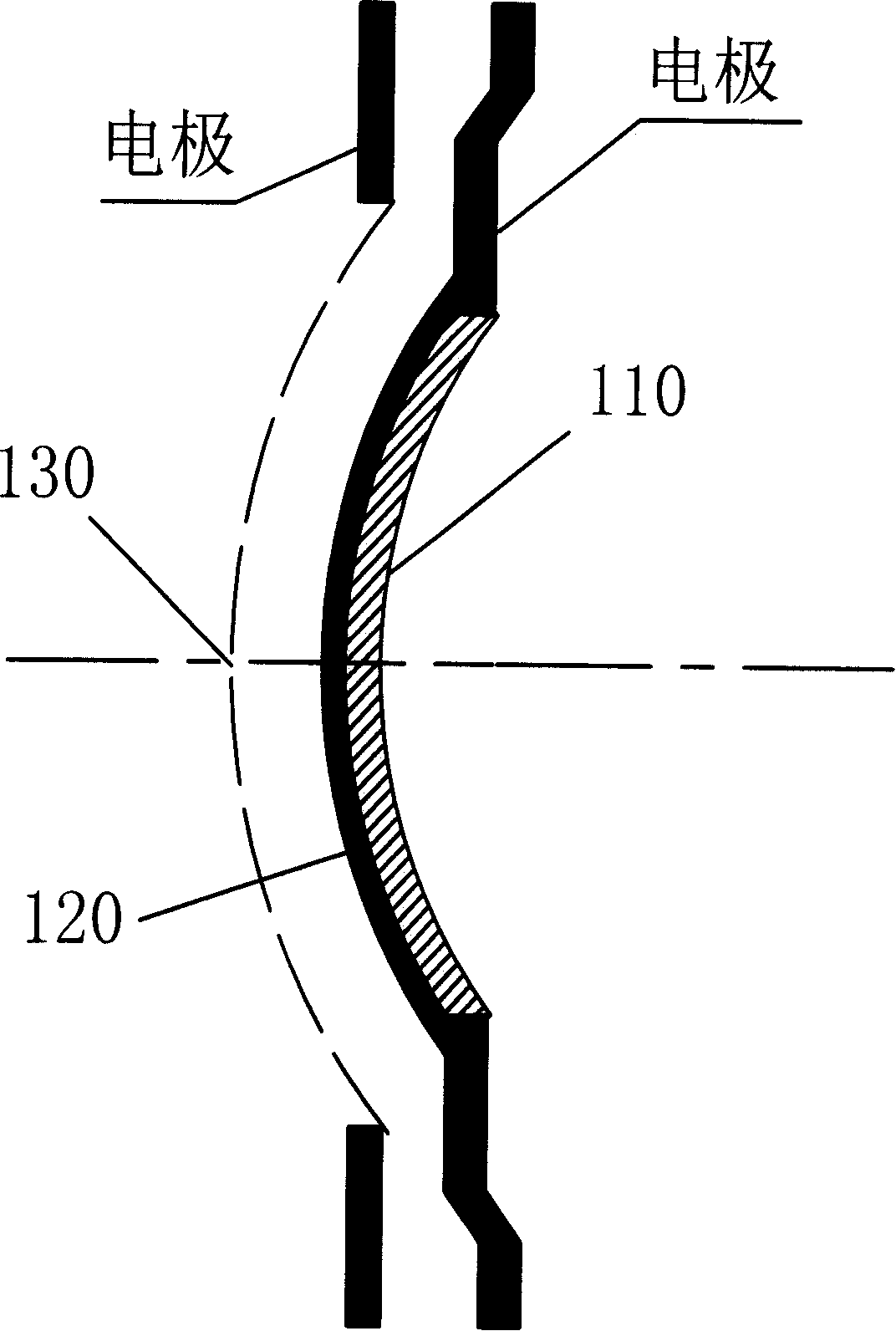
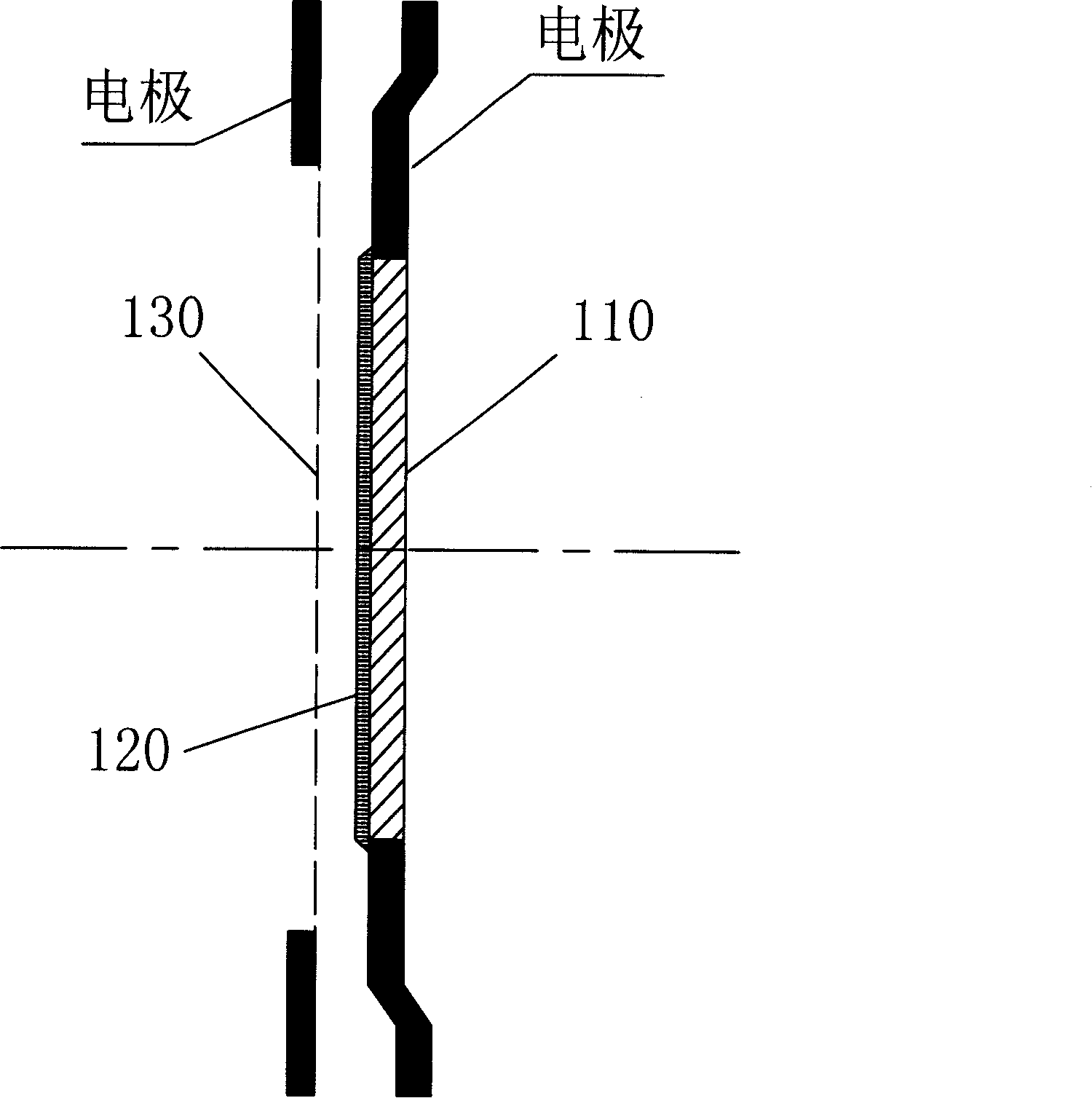
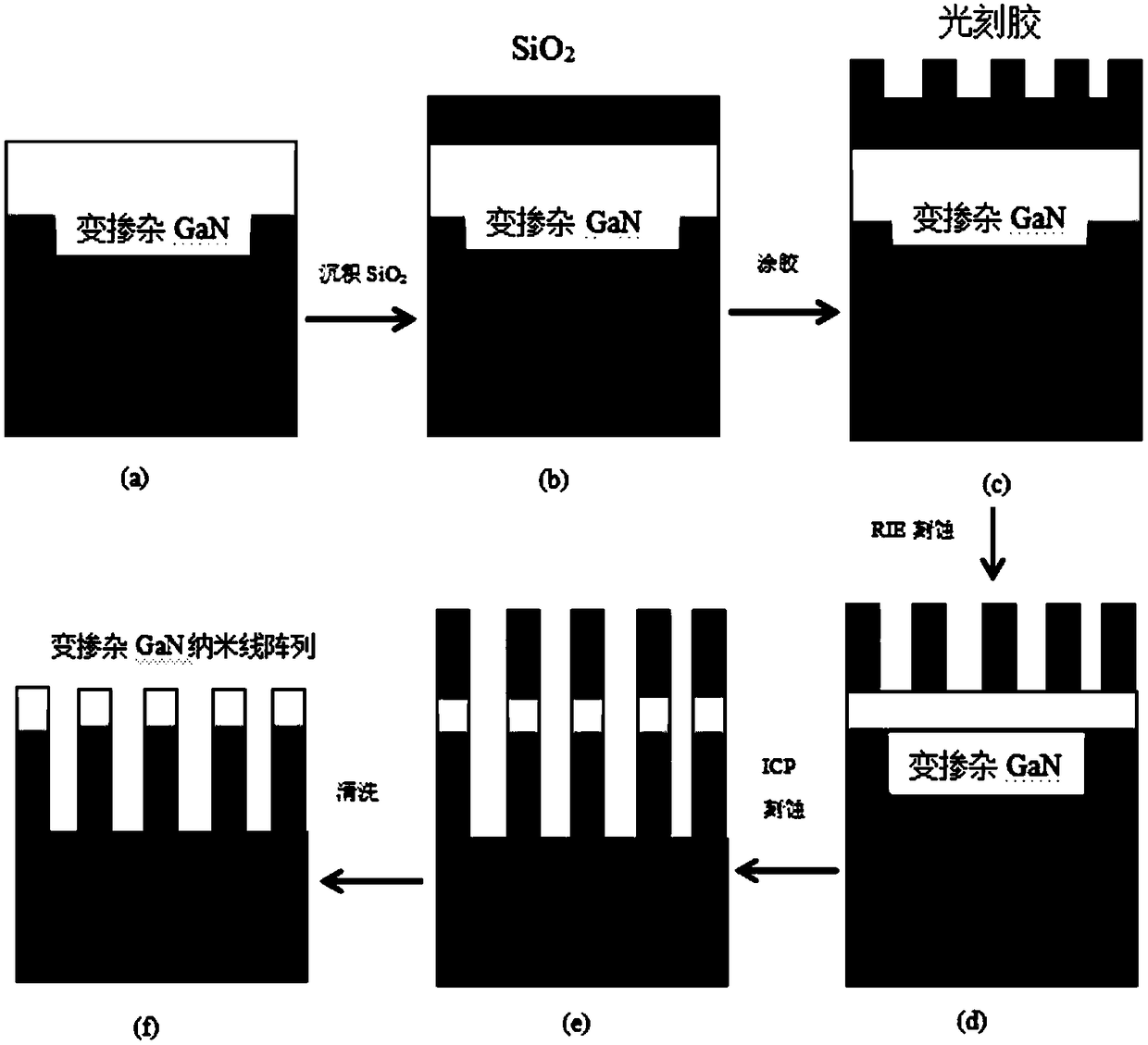
Variable doped GaN nanowire array photocathode and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108630510AImproving photoemission quantum efficiencyOvercoming conflicting thickness requirementsMaterial nanotechnologyPhoto-emissive cathodesQuantum efficiencyPhotocathode
The invention provides a variable doped GaN nanowire array photocathode, comprising a substrate, an AlN buffer layer grown on the substrate, a photoemissive layer grown on the AlN buffer layer, and aCs / O activation layer located on the photoemissive layer, wherein the photoemissive layer is a p-type GaN nanowire array composed of a plurality of equally spaced p-type doped GaN nanowires, and the doping concentration of the p-type doped GaN nanowires gradually decreases from the surface of the buffer layer to the outside. By adopting the variable doped structure having the doping concentrationdecreasing from the surface of the buffer layer to the outside, a built-in electric field for helping in transporting photoelectrons to the surface can be generated in the photocathode of the GaN nanowire array, so that the internal transport efficiency and surface escape probability of photoelectrons are improved, and the photoemissive quantum efficiency of the photocathode is ultimately improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com