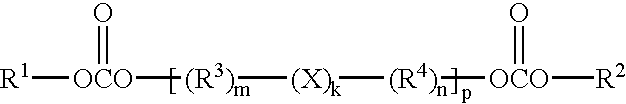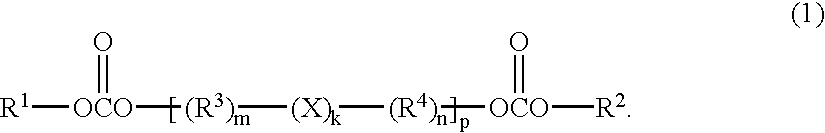Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2171results about "Electrolyte immobilisation/gelification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
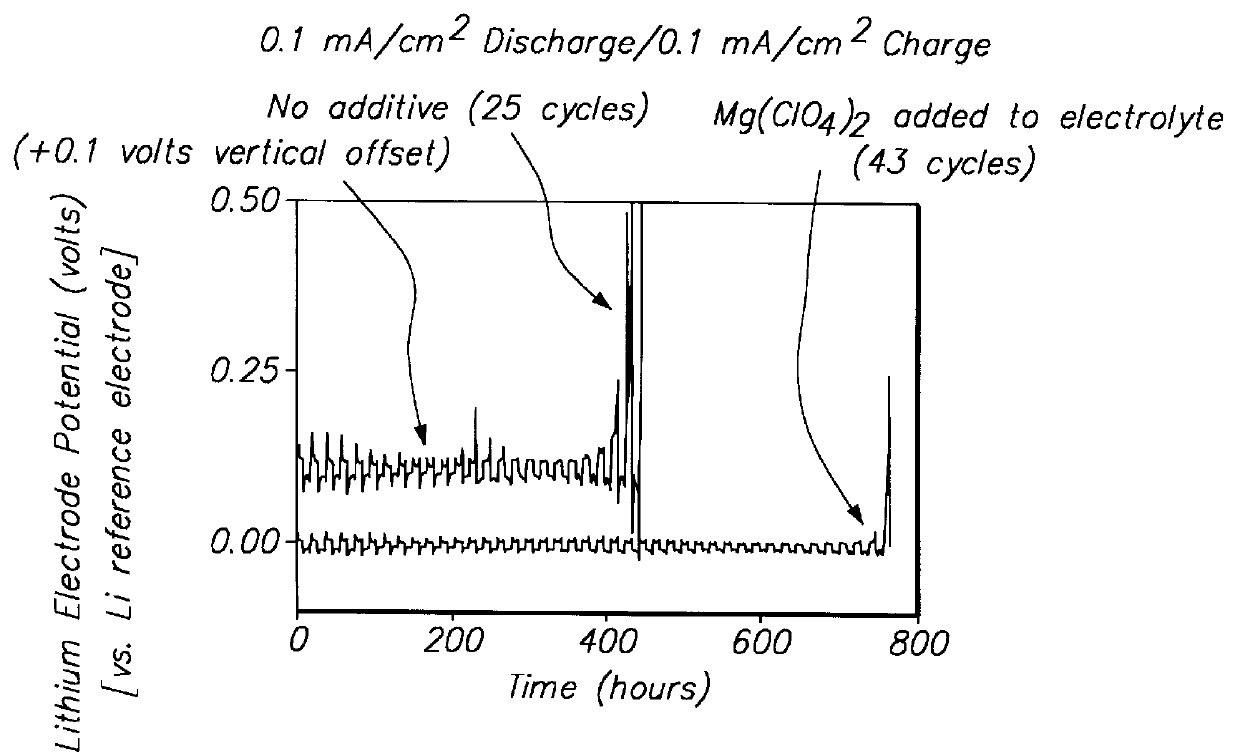
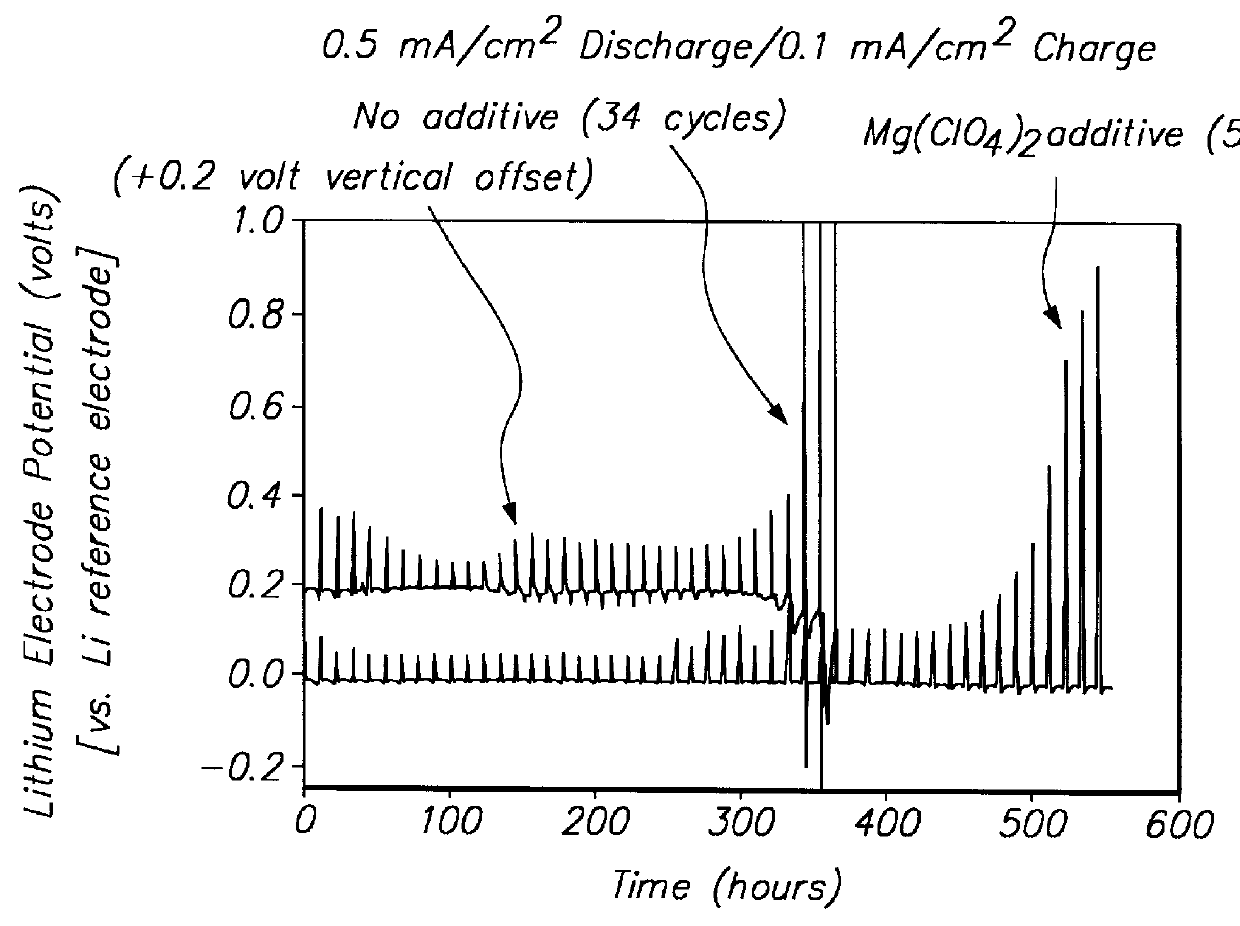
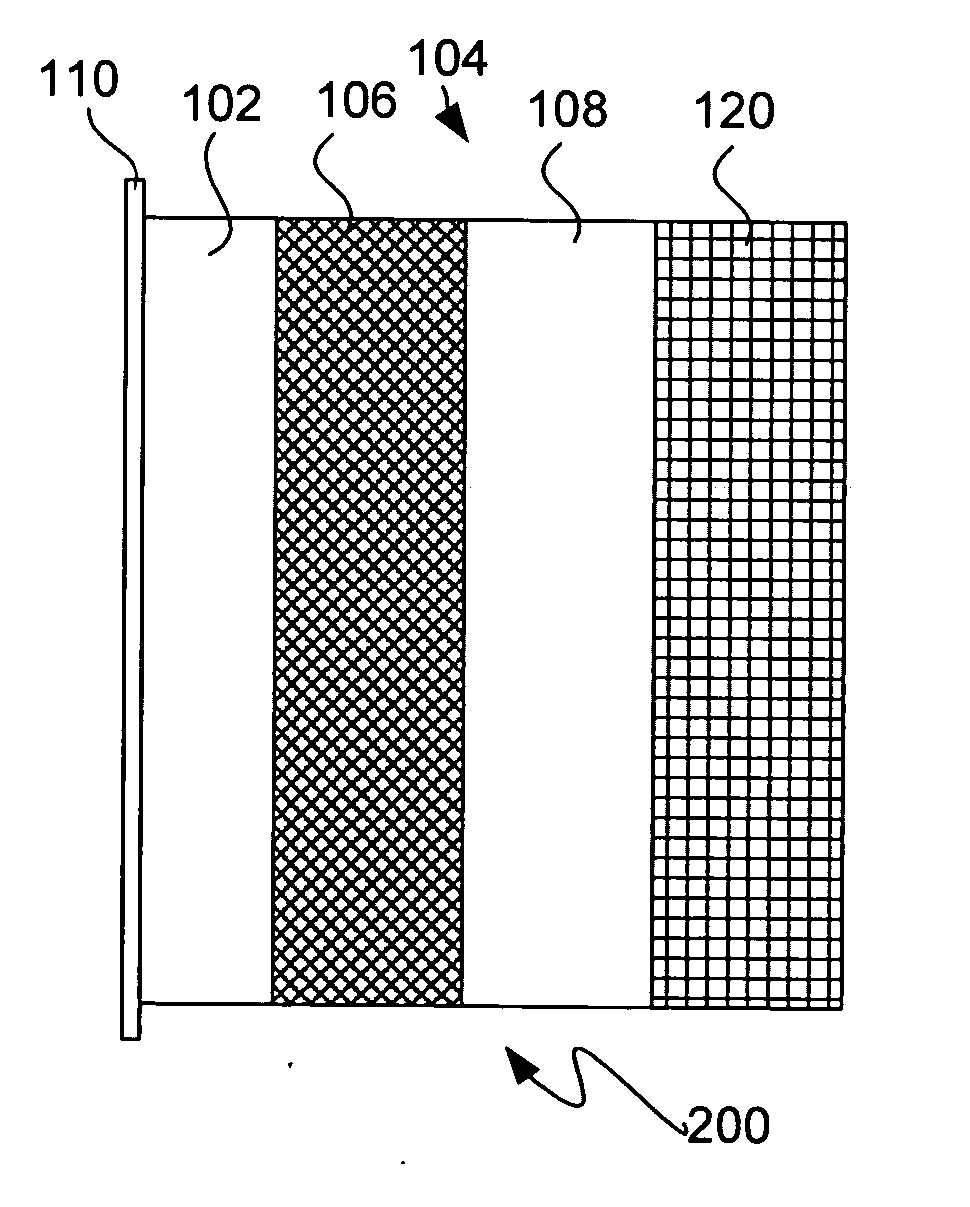
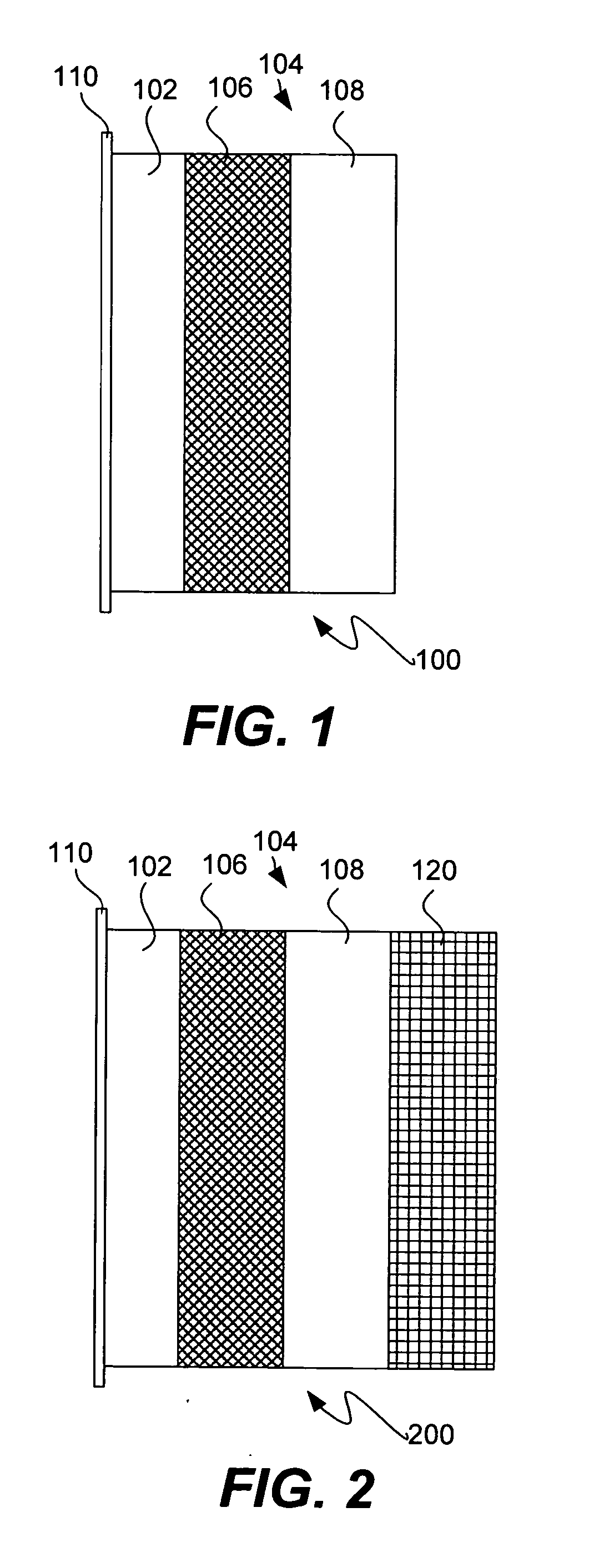
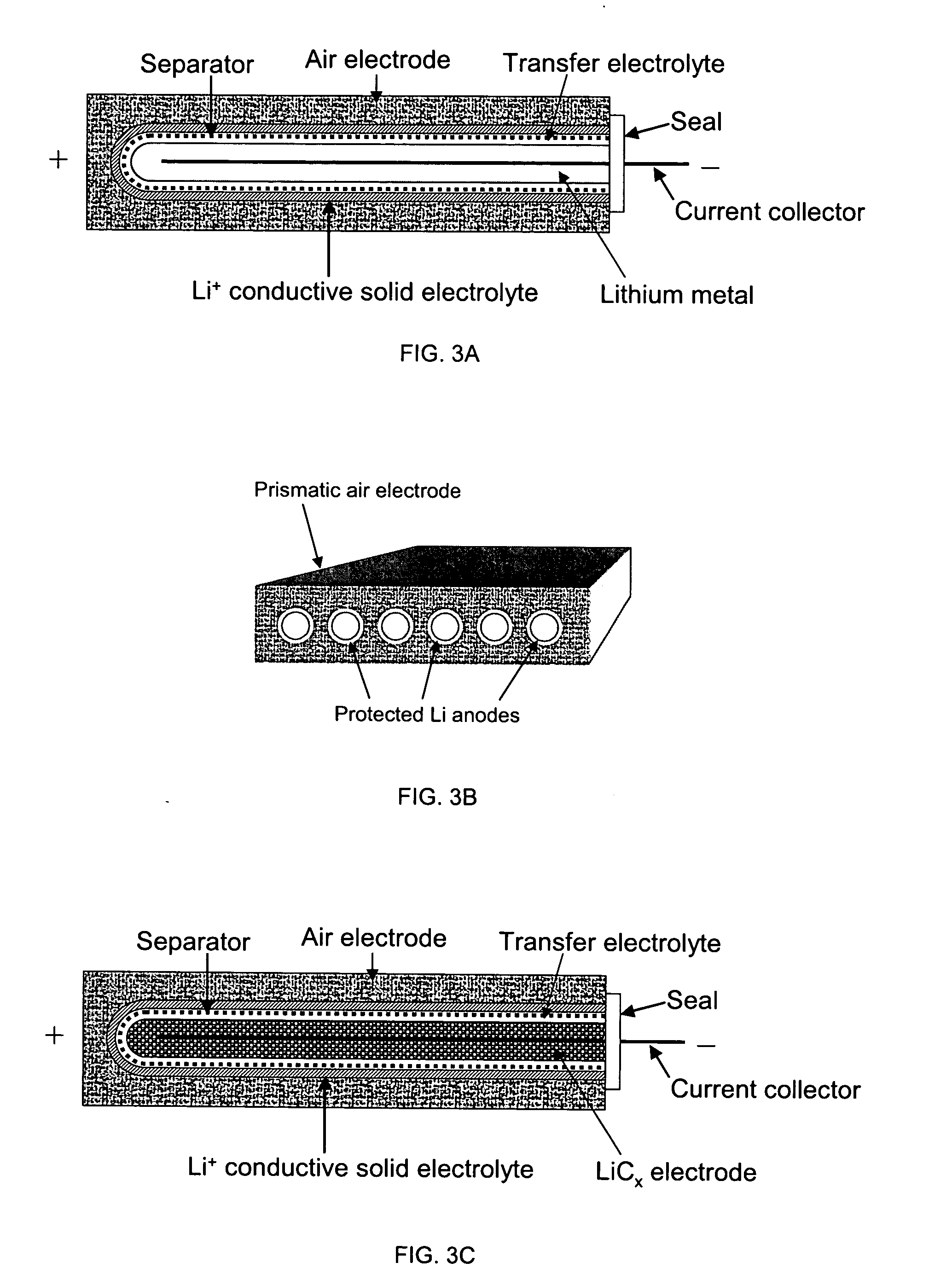
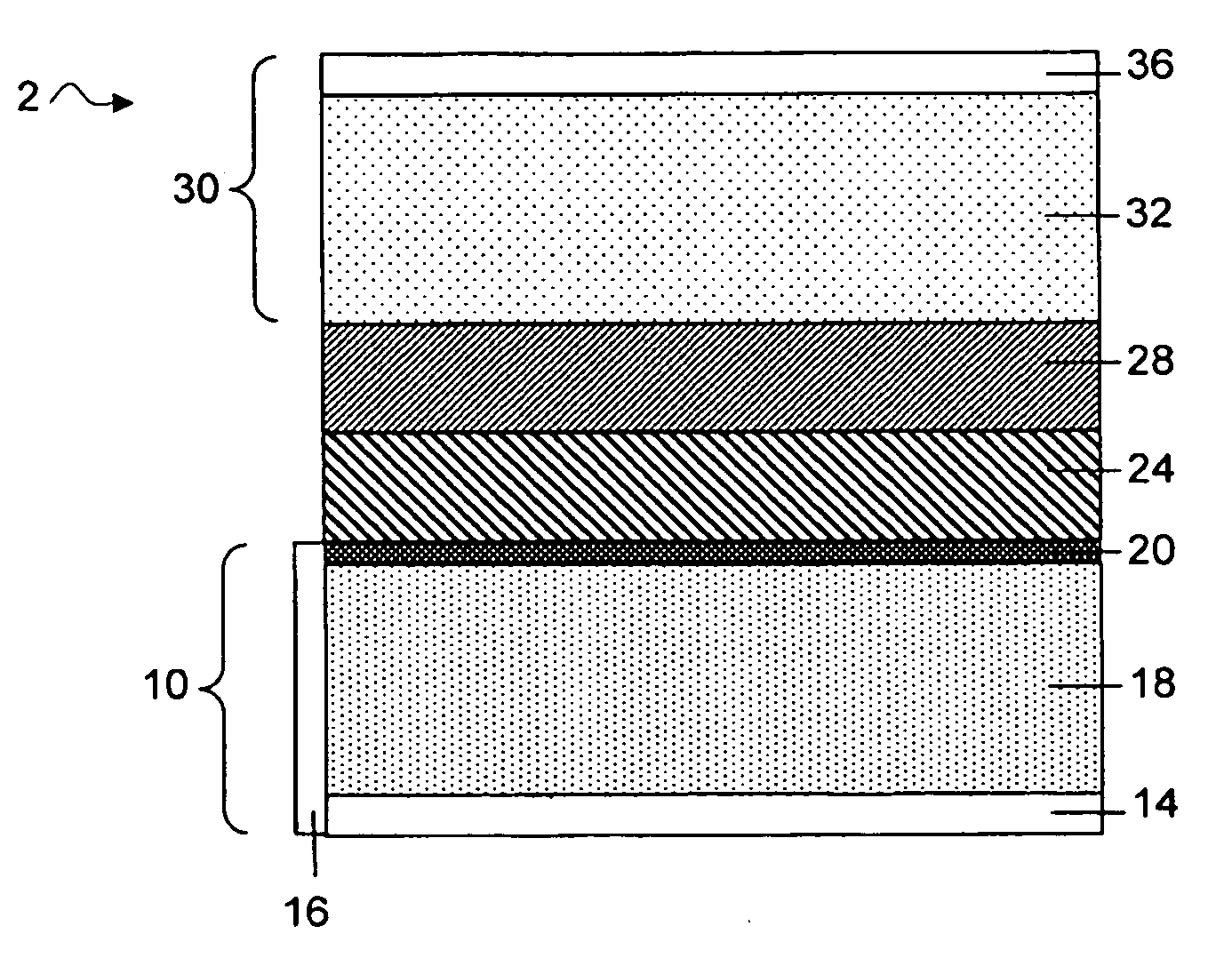
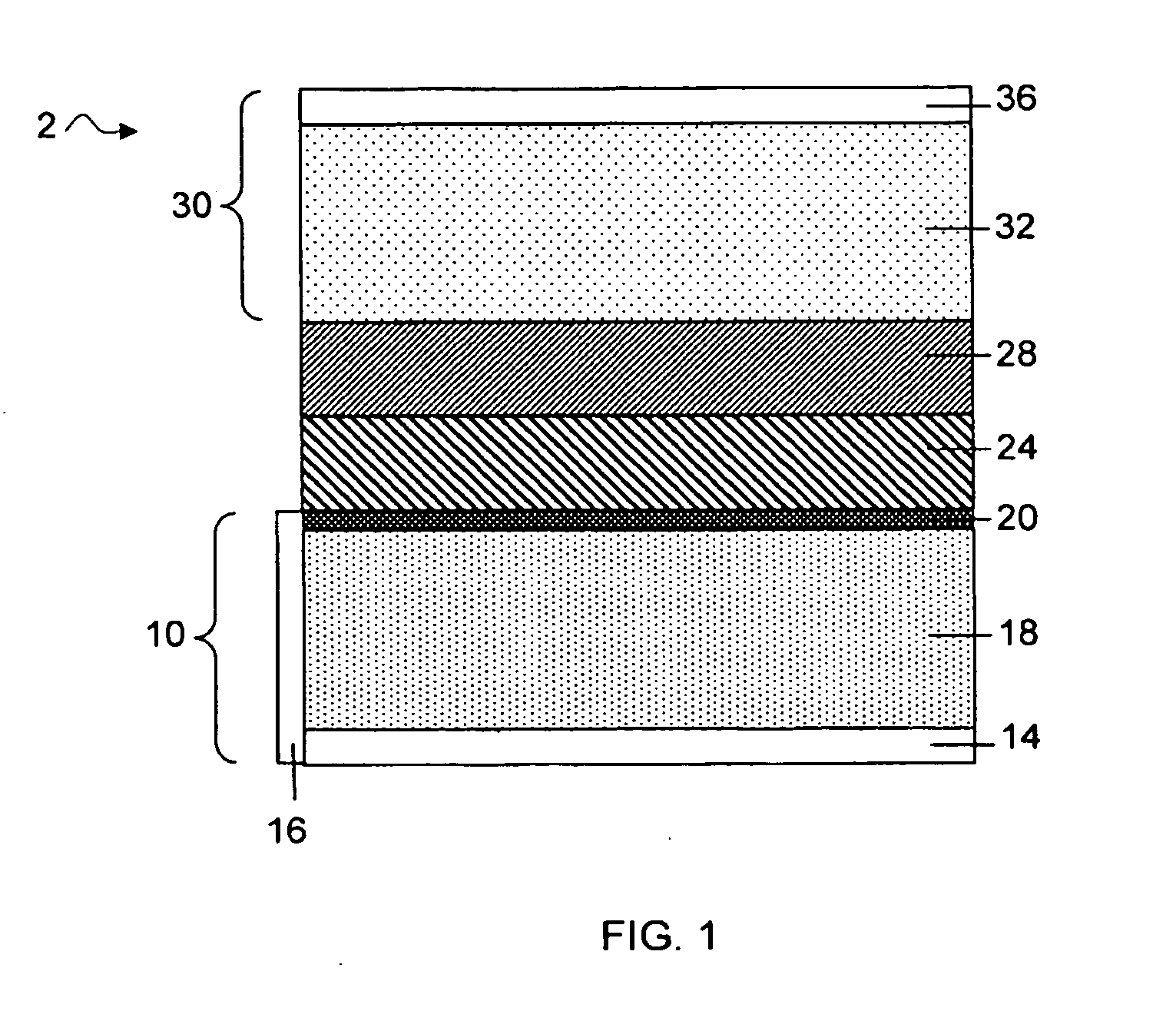
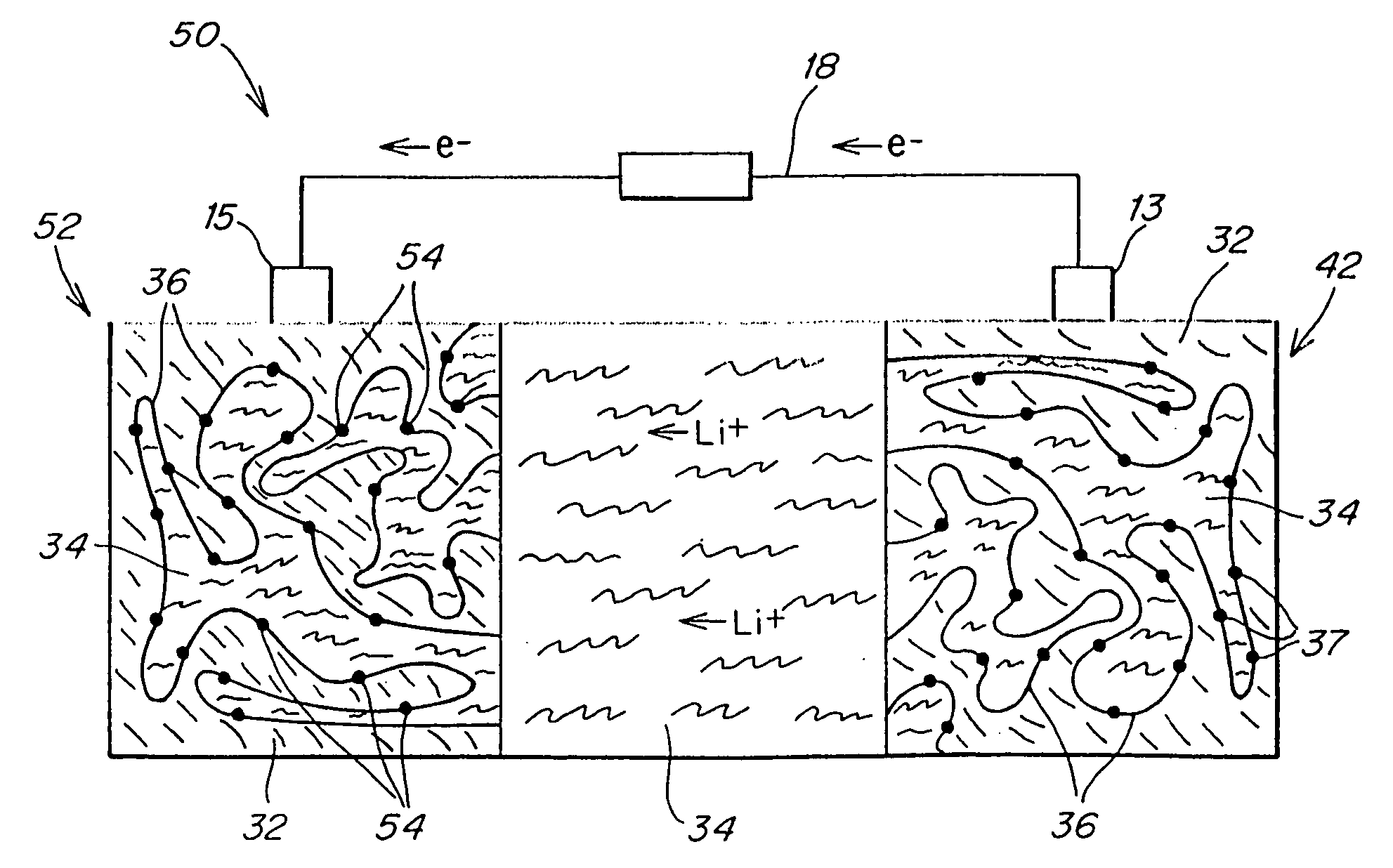
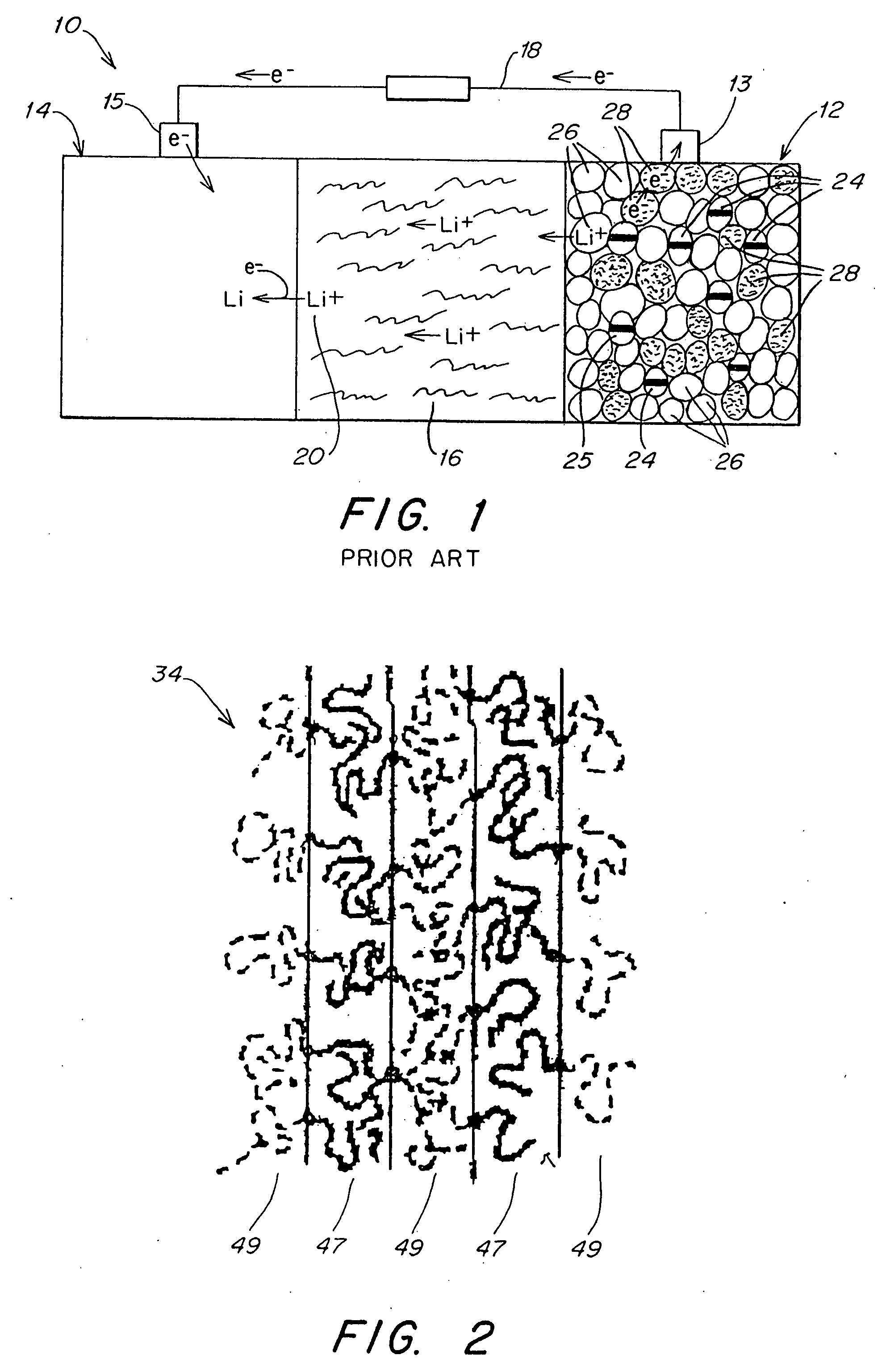
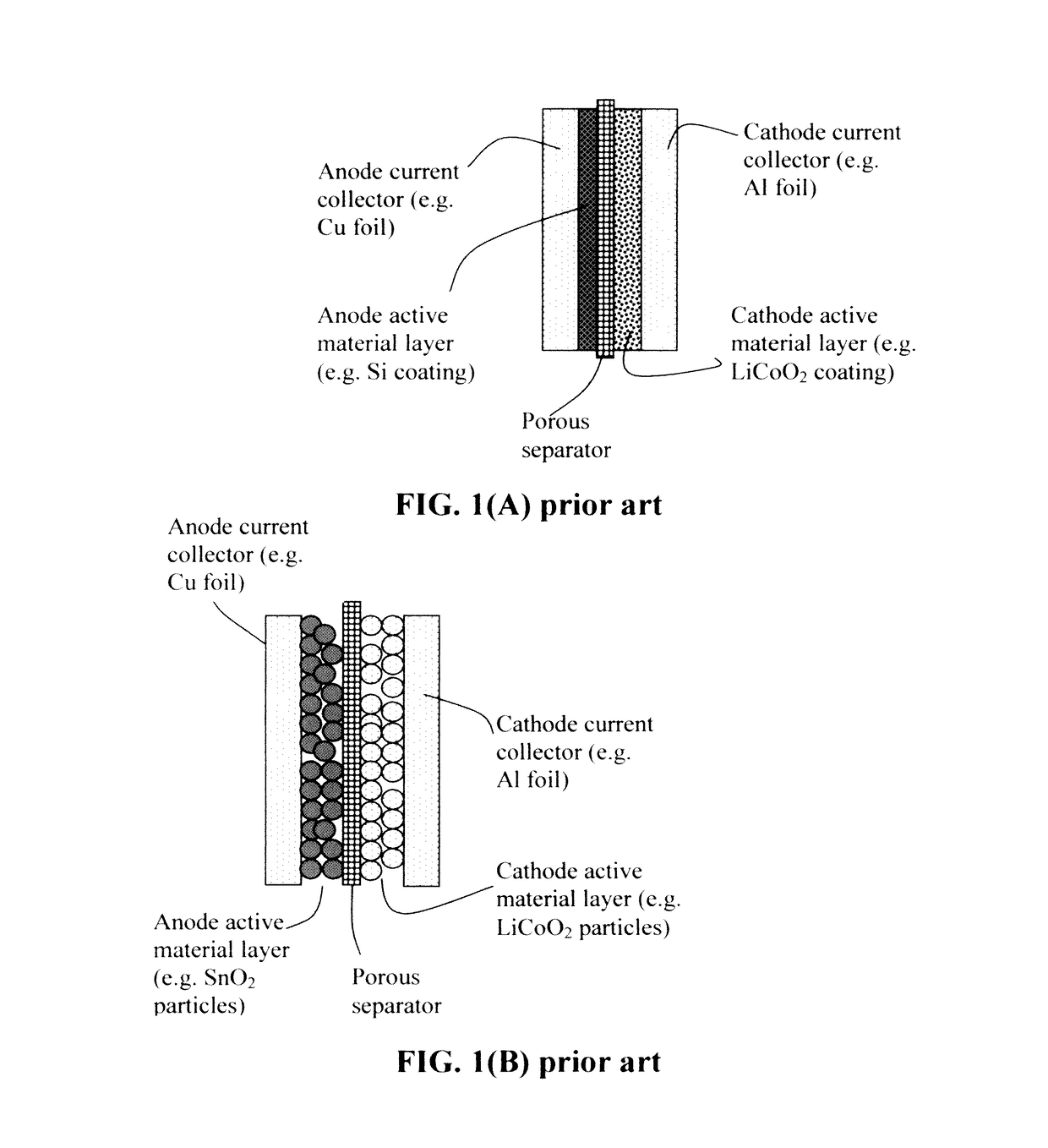
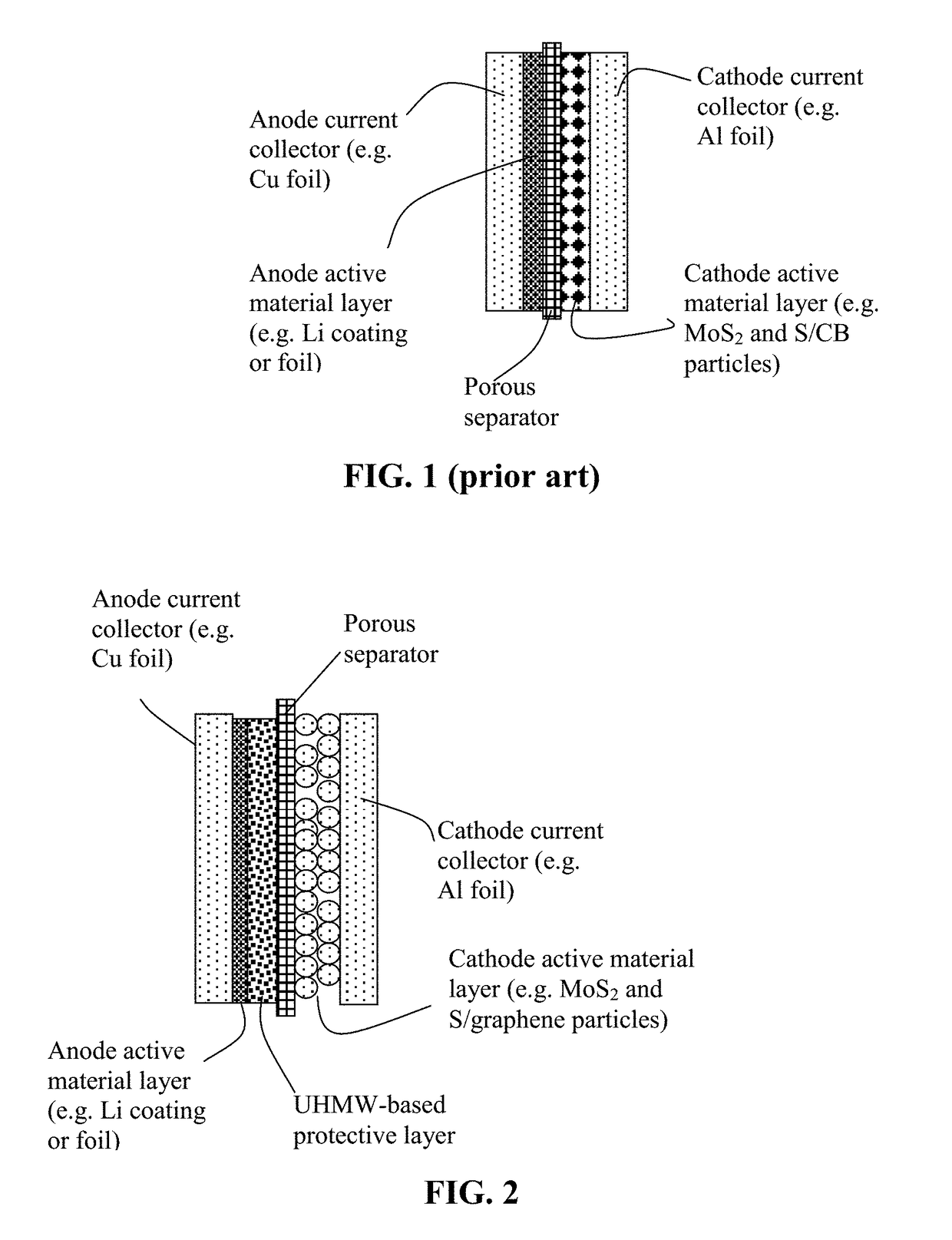
Protected active metal electrode and battery cell structures with non-aqueous interlayer architecture
ActiveUS7282295B2Avoid harmful reactionsFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsMetal electrodesBattery cell
Active metal and active metal intercalation electrode structures and battery cells having ionically conductive protective architecture including an active metal (e.g., lithium) conductive impervious layer separated from the electrode (anode) by a porous separator impregnated with a non-aqueous electrolyte (anolyte). This protective architecture prevents the active metal from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the impervious layer, which may include aqueous or non-aqueous liquid electrolytes (catholytes) and / or a variety electrochemically active materials, including liquid, solid and gaseous oxidizers. Safety additives and designs that facilitate manufacture are also provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Methods and reagents for enhancing the cycling efficiency of lithium polymer batteries
InactiveUS6017651AImprove efficiencyElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrochemical processing of electrodesLithium metalSulfur electrode
Batteries including a lithium electrode and a sulfur counter electrode that demonstrate improved cycling efficiencies are described. In one embodiment, an electrochemical cell having a lithium electrode and a sulfur electrode including at least one of elemental sulfur, lithium sulfide, and a lithium polysulfide is provided. The lithium electrode includes a surface coating that is effective to increase the cycling efficiency of said electrochemical cell. In a more particular embodiment, the lithium electrode is in an electrolyte solution, and, more particularly, an electrolyte solution including either elemental sulfur, a sulfide, or a polysulfide. In another embodiment, the coating is formed after the lithium electrode is contacted with the electrolyte. In a more particular embodiment, the coating is formed by a reaction between the lithium metal of the lithium electrode and a chemical species present in the electrolyte.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
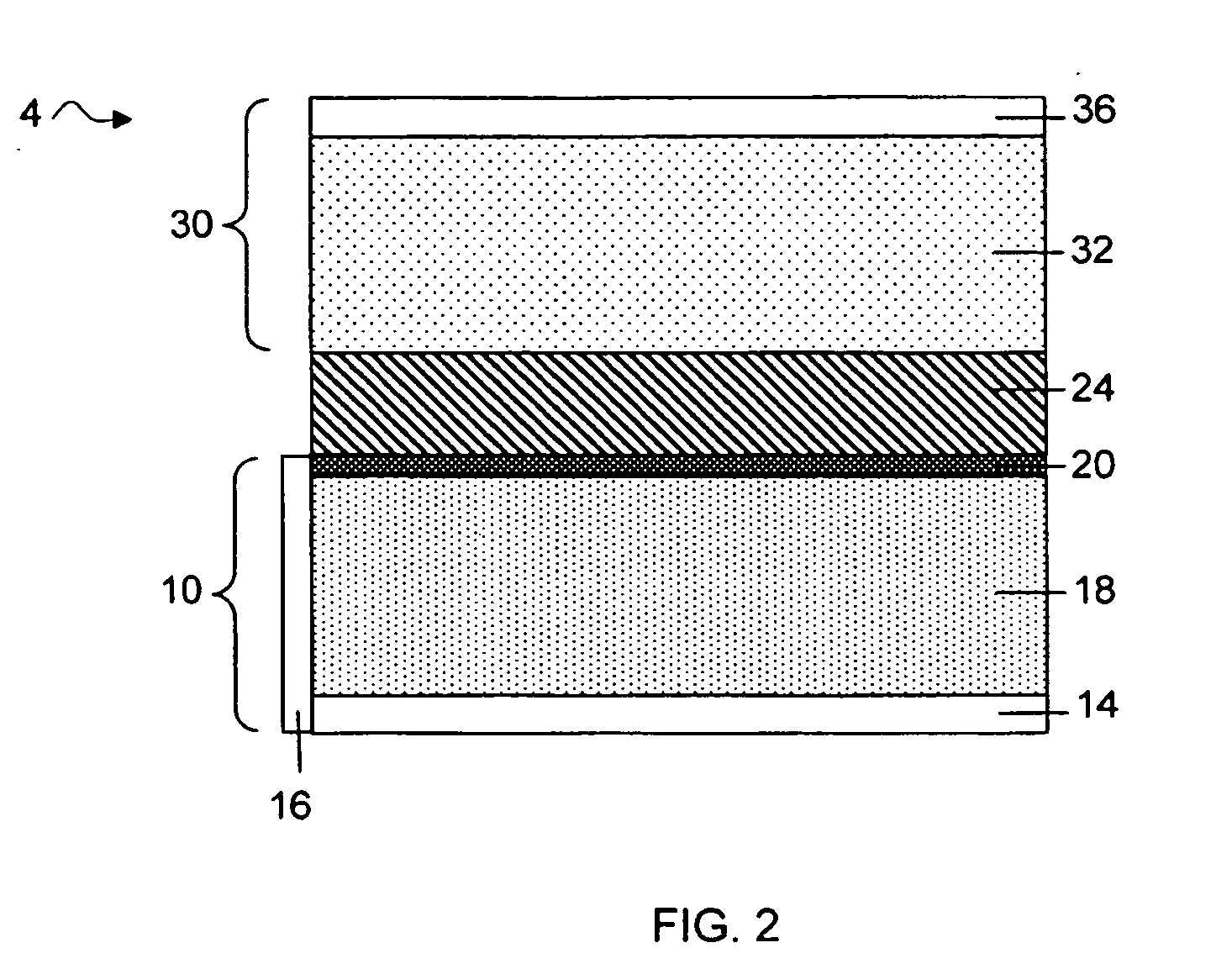
Protected active metal electrode and battery cell structures with non-aqueous interlayer architecture
ActiveUS20050175894A1Avoid harmful reactionsHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesMetal electrodesBattery cell
Active metal and active metal intercalation electrode structures and battery cells having ionically conductive protective architecture including an active metal (e.g., lithium) conductive impervious layer separated from the electrode (anode) by a porous separator impregnated with a non-aqueous electrolyte (anolyte). This protective architecture prevents the active metal from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the impervious layer, which may include aqueous or non-aqueous liquid electrolytes (catholytes) and / or a variety electrochemically active materials, including liquid, solid and gaseous oxidizers. Safety additives and designs that facilitate manufacture are also provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
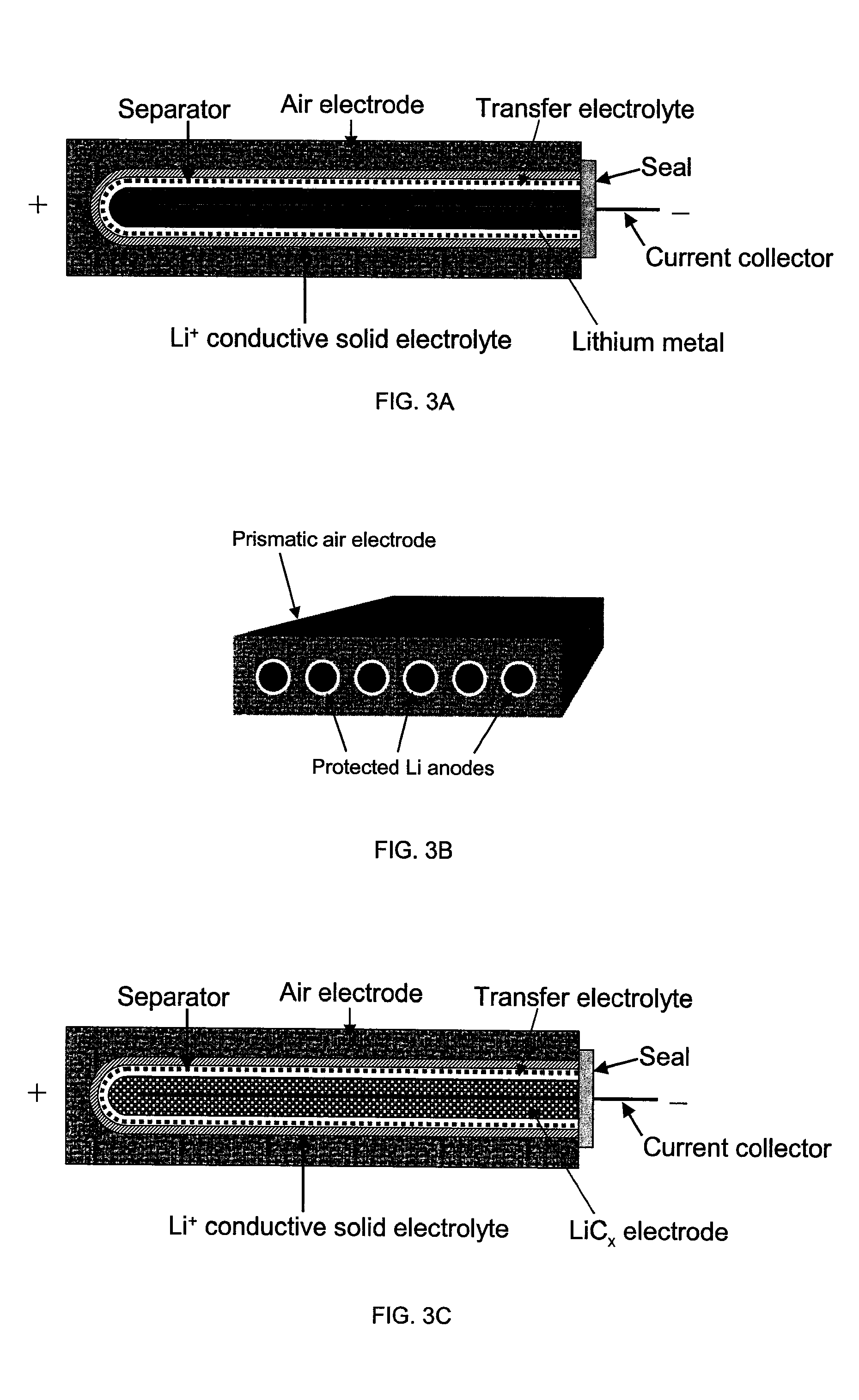
Li/air non-aqueous batteries
ActiveUS20070117007A1Improve battery performanceLarge capacityFuel and primary cellsFuel and secondary cellsLithiumOxygen
Non-aqueous alkali metal (e.g., Li) / oxygen battery cells constructed with a protected anode that minimizes anode degradation and maximizes cathode performance by enabling the use of cathode performance enhancing solvents in the catholyte have negligible self-discharge and high deliverable capacity. In particular, protected lithium-oxygen batteries with non-aqueous catholytes have this improved performance.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
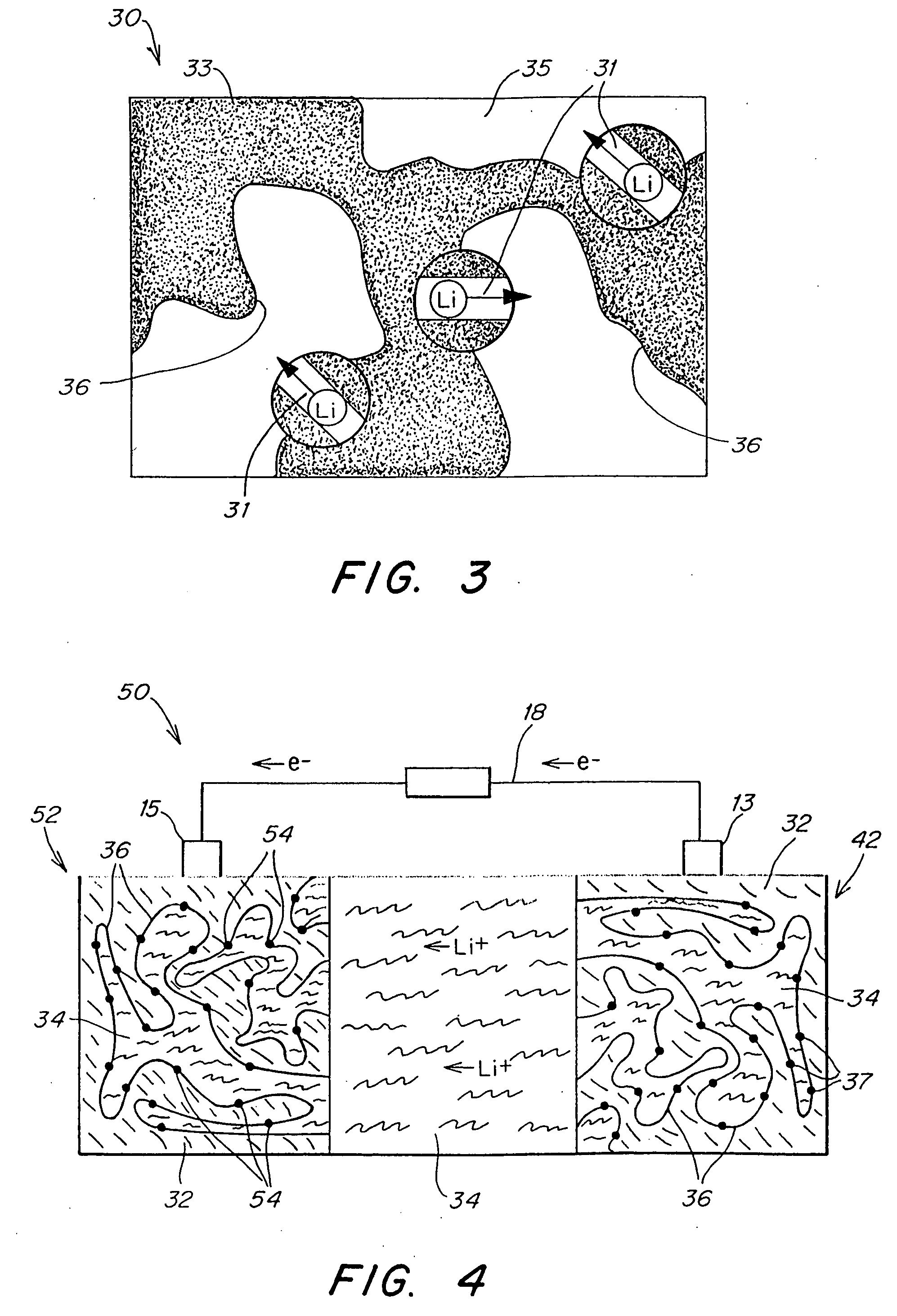
Separation of electrolytes
Methods and articles relating to separation of electrolyte compositions within lithium batteries are provided. The lithium batteries described herein may include an anode having lithium as the active anode species and a cathode having sulfur as the active cathode species. Suitable electrolytes for the lithium batteries can comprise a heterogeneous electrolyte including a first electrolyte solvent (e.g., dioxolane (DOL)) that partitions towards the anode and is favorable towards the anode (referred to herein as an “anode-side electrolyte solvent”) and a second electrolyte solvent (e.g., 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME)) that partitions towards the cathode and is favorable towards the cathode (and referred to herein as an “cathode-side electrolyte solvent”). By separating the electrolyte solvents during operation of the battery such that the anode-side electrolyte solvent is present disproportionately at the anode and the cathode-side electrolyte solvent is present disproportionately at the cathode, the battery can benefit from desirable characteristics of both electrolyte solvents (e.g., relatively low lithium reactivity of the anode-side electrolyte solvent and relatively high polysulfide solubility of the cathode-side electrolyte solvent).
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Thin-film batteries with soft and hard electrolyte layers and method
InactiveUS20070015060A1Improve environmental resistanceInhibition formationFinal product manufactureConductive materialLithium metalPolymer gel
A method and apparatus for making thin-film batteries having composite multi-layered electrolytes with soft electrolyte between hard electrolyte covering the negative and / or positive electrode, and the resulting batteries. In some embodiments, foil-core cathode sheets each having a cathode material (e.g., LiCoO2) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, and foil-core anode sheets having an anode material (e.g., lithium metal) covered by a hard electrolyte on both sides, are laminated using a soft (e.g., polymer gel) electrolyte sandwiched between alternating cathode and anode sheets. A hard glass-like electrolyte layer obtains a smooth hard positive-electrode lithium-metal layer upon charging, but when very thin, have randomly spaced pinholes / defects. When the hard layers are formed on both the positive and negative electrodes, one electrode's dendrite-short-causing defects on are not aligned with the other electrode's defects. The soft electrolyte layer both conducts ions across the gap between hard electrolyte layers and fills pinholes.
Owner:CYMBET CORP
Novel composite cathodes, electrochemical cells comprising novel composite cathodes, and processes for fabricating same
The present invention pertains to composite cathodes suitable for use in an electrochemical cell, said cathodes comprising: (a) an electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, wherein said electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, in its oxidized state, comprises a polysulfide moiety of the formula —Sm—, wherein m is an integer equal to or greater than 3; and, (b) an electroactive transition metal chalcogenide composition, which encapsulates said electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, and which retards the transport of anionic reduction products of said electroactive sulfur-containing cathode material, said electroactive transition metal chalcogenide composition comprising an electroactive transition metal chalcogenide having the formula MjYk(OR)l wherein: M is a transition metal; Y is the same or different at each occurrence and is oxygen, sulfur, or selenium; R is an organic group and is the same or different at each occurrence; j is an integer ranging from 1 to 12; k is a number ranging from 0 to 72; and l is a number ranging from 0 to 72; with the proviso that k and l cannot both be 0. The present invention also pertains to methods of making such composite cathodes, cells comprising such composite cathodes, and methods of making such cells.
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Organic/Inorganic Composite Separator Having Morphology Gradient, Manufacturing Method Thereof and Electrochemical Device Containing the Same
ActiveUS20080292968A1Improve featuresSolve Porosity InsufficiencyCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersFinal product manufacturePorous substrateSurface layer
Disclosed is an organic / inorganic composite separator including: a porous substrate having pores; and a porous active layer containing a mixture of inorganic particles and a binder polymer with which at least one surface of the porous substrate is coated. The organic / inorganic composite separator of the present invention may be useful to enhance peeling and scratch resistances and improve a lamination characteristic by introducing a porous active layer onto a porous substrate having pores, the porous active layer having heterogeneity of morphology toward a thickness direction in which a content ratio of the binder polymer / inorganic particles present in a surface layer is higher than that of the binder polymer / inorganic particles present inside the surface layer. Accordingly, the stability and performances of a battery can be improved together since the detachment of inorganic particles from the porous active layer may be reduced during the assembly process of the electrochemical device.
Owner:TORAY BATTERY SEPARATOR FILM +1
Methods and reagents for enhancing the cycling efficiency of lithium polymer batteries
InactiveUS6165644AImprove efficiencyElectrode rolling/calenderingElectrochemical processing of electrodesLithium metalSulfur electrode
Batteries including a lithium electrode and a sulfur counter electrode that demonstrate improved cycling efficiencies are described. In one embodiment, an electrochemical cell having a lithium electrode and a sulfur electrode including at least one of elemental sulfur, lithium sulfide, and a lithium polysulfide is provided. The lithium electrode includes a surface coating that is effective to increase the cycling efficiency of said electrochemical cell. In a more particular embodiment, the lithium electrode is in an electrolyte solution, and, more particularly, an electrolyte solution including either elemental sulfur, a sulfide, or a polysulfide. In another embodiment, the coating is formed after the lithium electrode is contacted with the electrolyte. In a more particular embodiment, the coating is formed by a reaction between the lithium metal of the lithium electrode and a chemical species present in the electrolyte.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Polymer electrolyte, intercalation compounds and electrodes for batteries
Solid battery components are provided. A block copolymeric electrolyte is non-crosslinked and non-glassy through the entire range of typical battery service temperatures, that is, through the entire range of at least from about 0° C. to about 70° C. The chains of which the copolymer is made each include at least one ionically-conductive block and at least one second block immiscible with the ionically-conductive block. The chains form an amorphous association and are arranged in an ordered nanostructure including a continuous matrix of amorphous ionically-conductive domains and amorphous second domains that are immiscible with the ionically-conductive domains. A compound is provided that has a formula of LixMyNzO2. M and N are each metal atoms or a main group elements, and x, y and z are each numbers from about 0 to about 1. y and z are chosen such that a formal charge on the MyNz portion of the compound is (4-x). In certain embodiments, these compounds are used in the cathodes of rechargeable batteries. The present invention also includes methods of predicting the potential utility of metal dichalgogenide compounds for use in lithium intercalation compounds. It also provides methods for processing lithium intercalation oxides with the structure and compositional homogeneity necessary to realize the increased formation energies of said compounds. An article is made of a dimensionally-stable, interpenetrating microstructure of a first phase including a first component and a second phase, immiscible with the first phase, including a second component. The first and second phases define interphase boundaries between them, and at least one particle is positioned between a first phase and a second phase at an interphase boundary. When the first and second phases are electronically-conductive and ionically-conductive polymers, respectively, and the particles are ion host particles, the arrangement is an electrode of a battery.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Lithium secondary battery and method for manufacturing thereof
InactiveUS20040072067A1Increase currentExtended discharge cycleFinal product manufactureElectrode carriers/collectorsLithiumElectrochemistry
A lithium secondary battery comprising an electrode in which an active material layer which includes an active material that electrochemically occludes and releases lithium is formed on a current collector, wherein cracks are formed in the active material layer by occlusion and release of lithium ions and thereafter a solid electrolyte is formed in the cracks in the active material layer.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
Protected lithium electrodes having a porous electrolyte interlayer and associated battery cells
ActiveUS20140170465A1Avoid harmful reactionsHybrid capacitor separatorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesBattery cellMetal
Active metal and active metal intercalation electrode structures and battery cells having ionically conductive protective architecture including an active metal (e.g., lithium) conductive impervious layer separated from the electrode (anode) by a porous separator impregnated with a non-aqueous electrolyte (anolyte). This protective architecture prevents the active metal from deleterious reaction with the environment on the other (cathode) side of the impervious layer, which may include aqueous or non-aqueous liquid electrolytes (catholytes) and / or a variety electrochemically active materials, including liquid, solid and gaseous oxidizers. Safety additives and designs that facilitate manufacture are also provided.
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
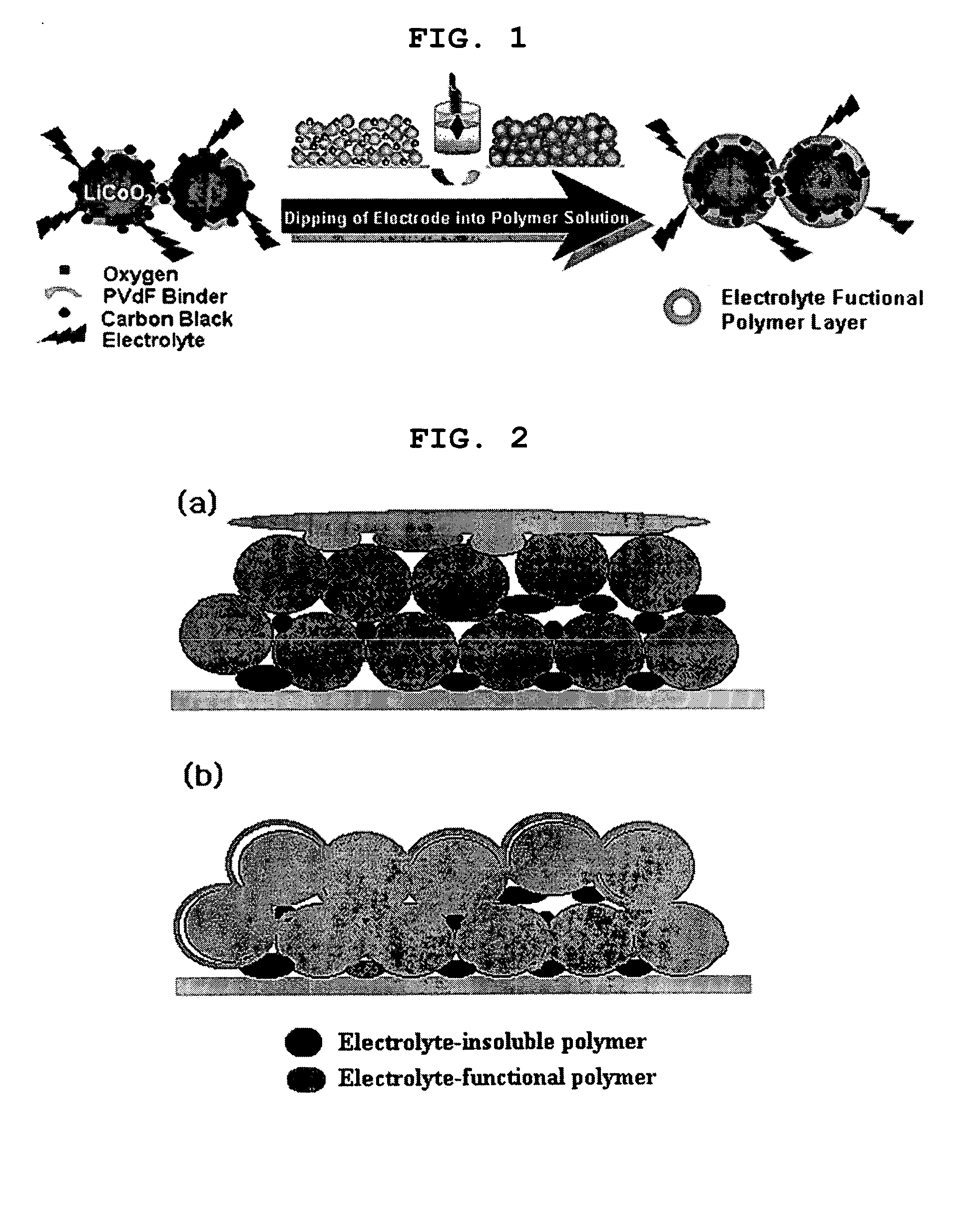
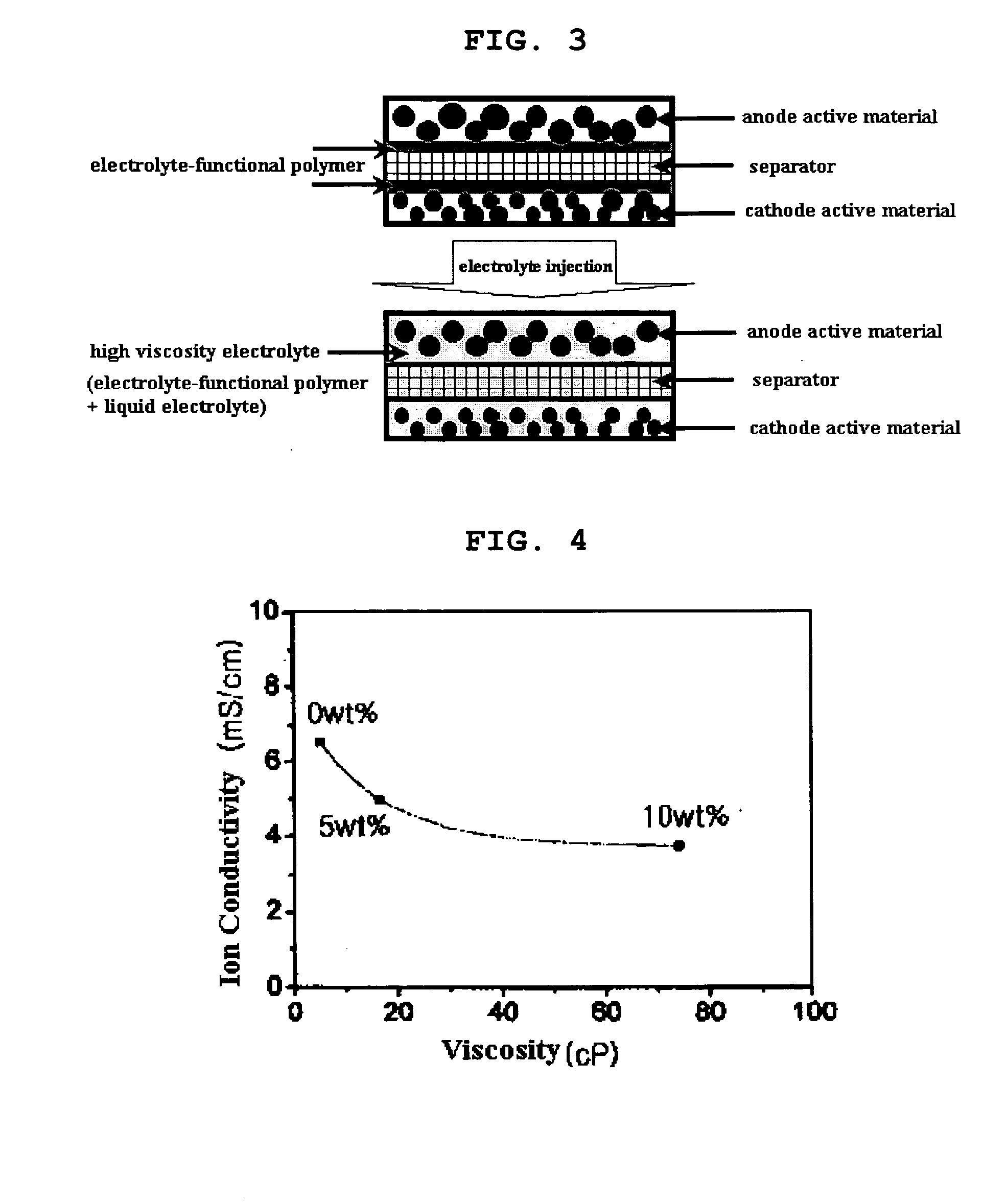
Functional polymer film-coated electrode and electrochemical device using the same
ActiveUS20050118508A1Lower performance requirementsImprove battery safetyGel electrodesElectrode carriers/collectorsSlurryPolymer thin films
The present invention provides an electrode in which an electrode active material particles as being interconnected are applied on current collector, wherein the interconnected surface of electrode active material particles is coated with a polymer, the polymer being present as an independent phase, while maintaining a pore structure formed among the interconnected electrode active material particles as well as an electrochemical device including the electrode. Also, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing an electrode coated with a polymer present on an interconnected surface of electrode active material as an independent phase, while maintaining a pore structure formed among the electrode active material particles, which comprises the steps of: (a) coating slurry for an electrode including an electrode active material on a current collector and drying it to form an electrode; and (b) dipping the electrode obtained from step (a) into a solution containing the polymer dissolved therein and a method for manufacturing an electrochemical device comprising the electrode obtained by the above method. The electrode coated with a polymer as an independent phase provides an electrochemical device with improved safety and prevents degradation of performance of an electrochemical device.
Owner:LG ENERGY SOLUTION LTD
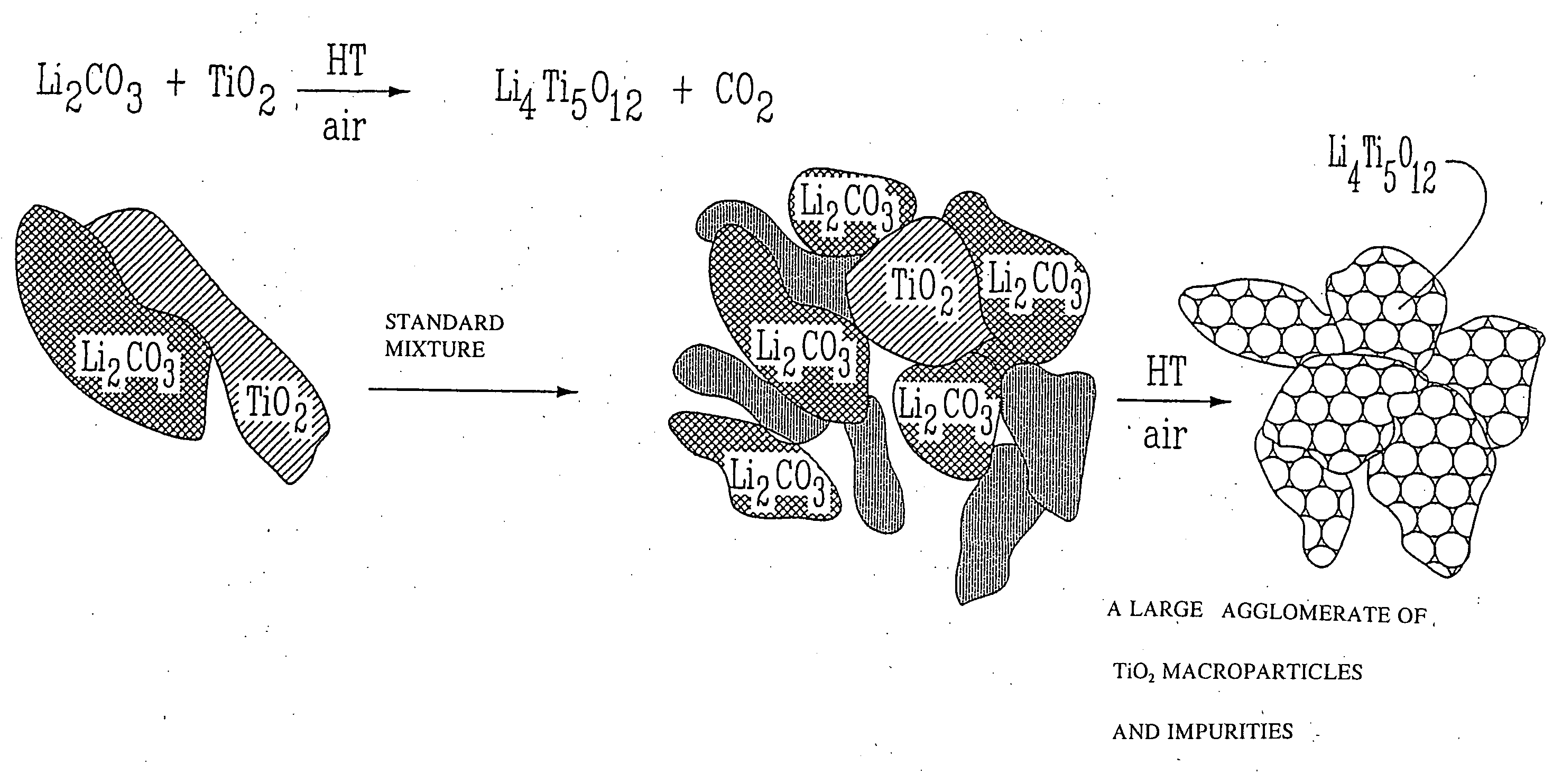
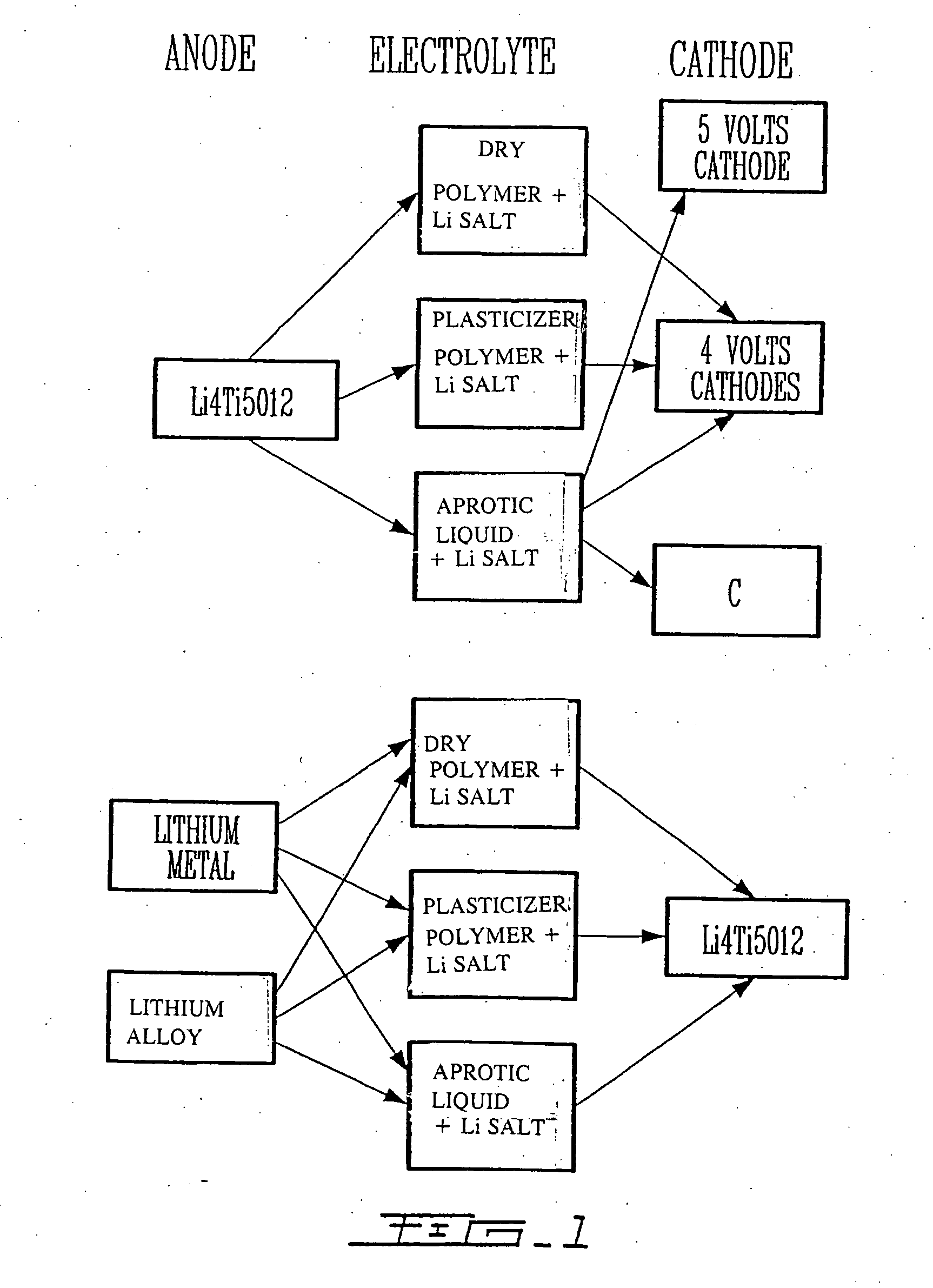
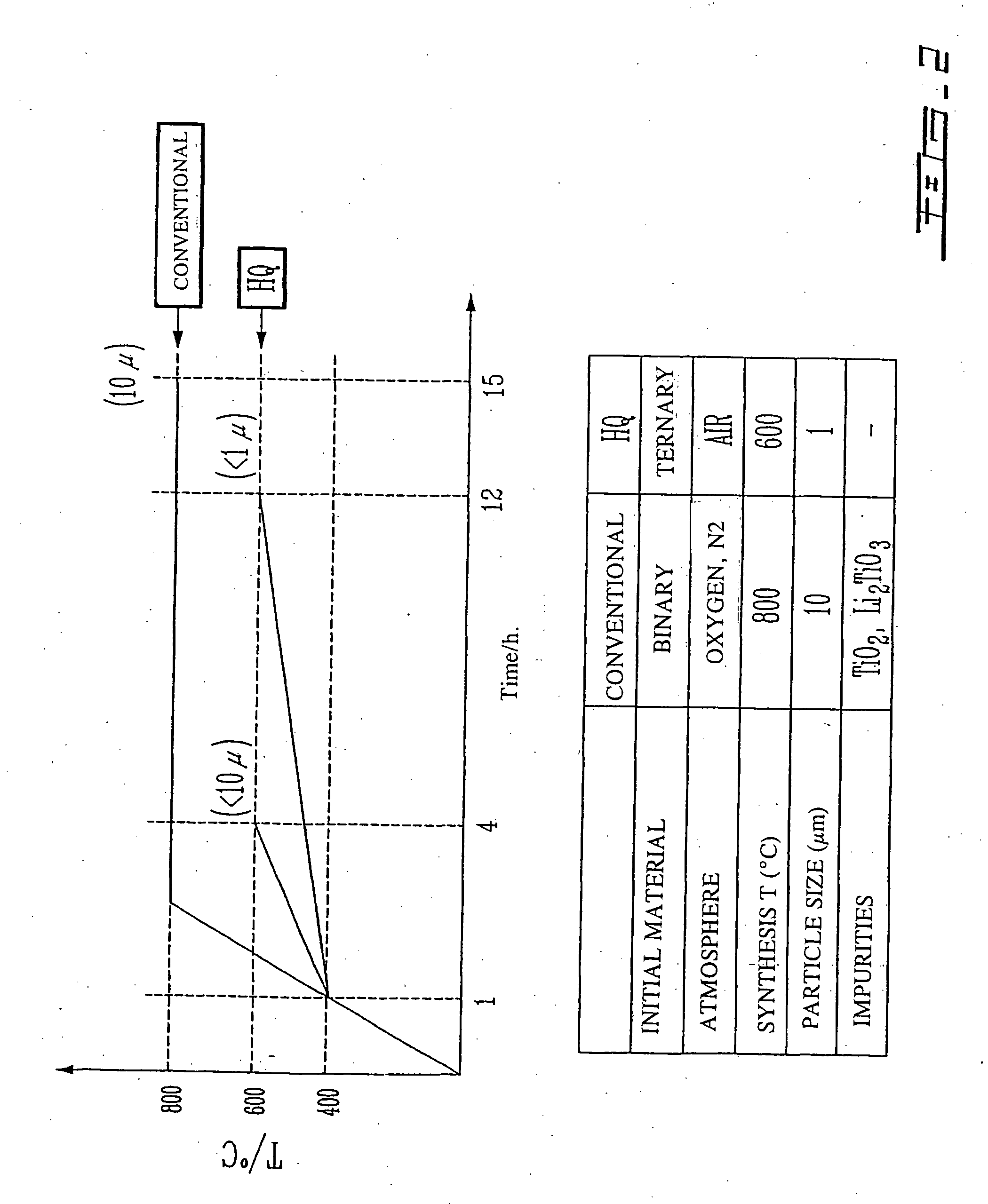
Li4Ti5O12, Li(4-alpha)Zalpha Ti5O12 or Li4ZbetaTi(5-beta)O12 particles, processes for obtaining same and use as electrochemical generators
Synthesis process for new particles of Li4Ti5O12, Li(4-alpha)ZalphaTi5O12 or Li4ZbetaTi(5-beta)O12, preferably having a spinel structure, wherein beta is greater than 0 and less than or equal to 0.5 (preferably having a spinel structure), alpha representing a number greater than zero and less than or equal to 0.33, Z representing a source of at least one metal, preferably chosen from the group made up of Mg, Nb, Al, Zr, Ni, Co. These particles coated with a layer of carbon notably exhibit electrochemical properties that are particularly interesting as components of anodes and / or cathodes in electrochemical generators.
Owner:HYDRO QUEBEC CORP
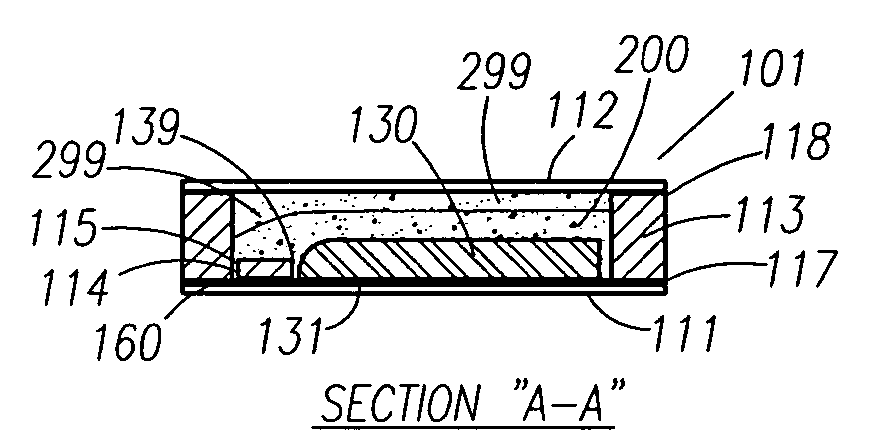
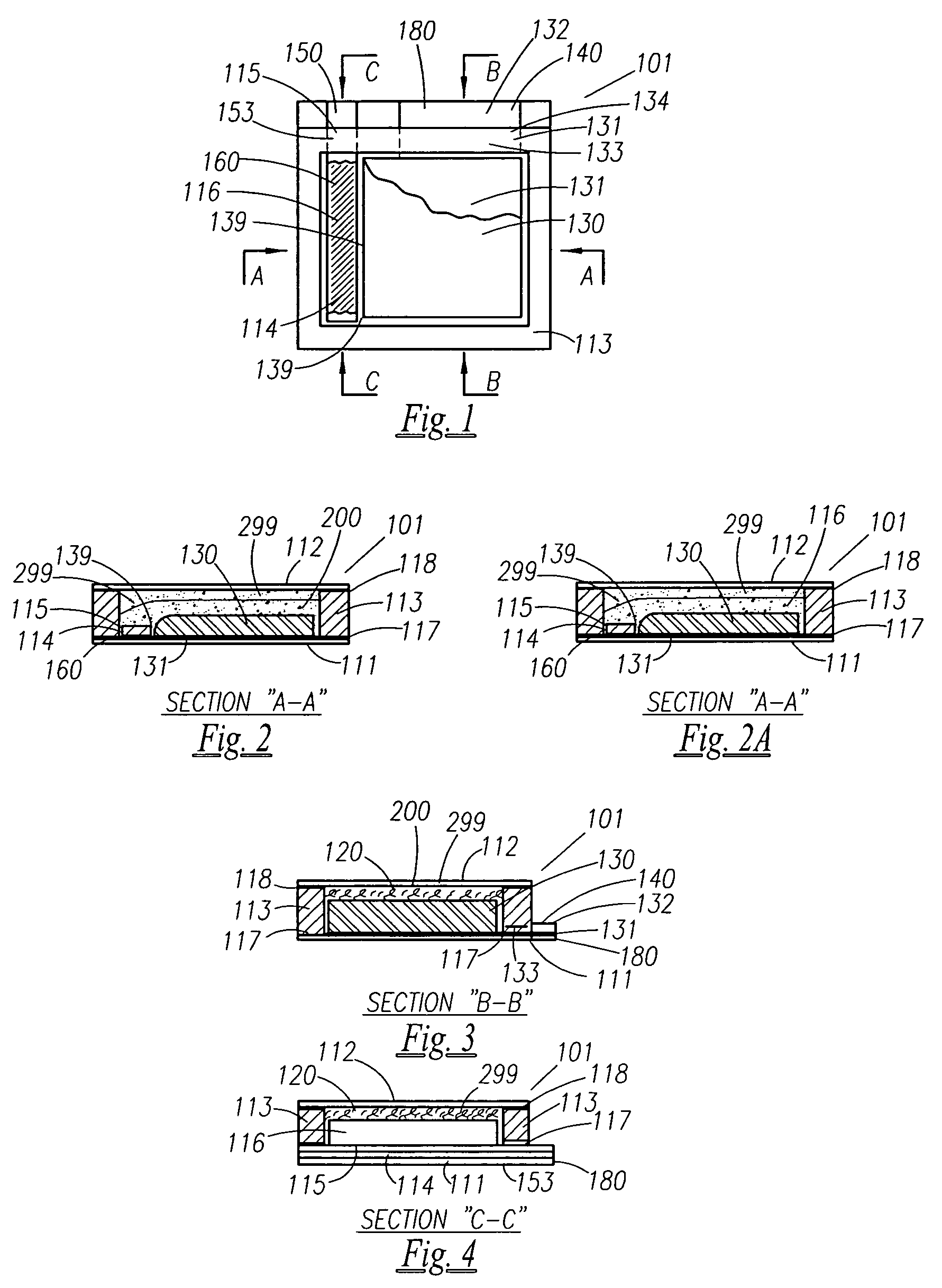
Thin printable electrochemical cell utilizing a "picture frame" and methods of making the same
A thin printed flexible electrochemical cell, and its method of manufacture, using a “picture frame” structure sealed, for example, with a high moisture and oxygen barrier polymer film and featuring, for example, a printed cathode deposited on an optional, highly conductive carbon printed cathode collector with a printed or a foil strip anode placed adjacent to the cathode. A viscous or gelled electrolyte is dispensed and / or printed in the cell, and a top laminate can then be sealed onto the picture frame. Such a construction could allow the entire cell to be made on a printing press, for example, as well as gives the opportunity to integrate the battery directly with an electronic application, for example.
Owner:BLUE SPARK INNOVATIONS LLC
Separation of electrolytes
Methods and articles relating to separation of electrolyte compositions within lithium batteries are provided. The lithium batteries described herein may include an anode having lithium as the active anode species and a cathode having sulfur as the active cathode species. Suitable electrolytes for the lithium batteries can comprise a heterogeneous electrolyte including a first electrolyte solvent (e.g., dioxolane (DOL)) that partitions towards the anode and is favorable towards the anode (referred to herein as an “anode-side electrolyte solvent”) and a second electrolyte solvent (e.g., 1,2-dimethoxyethane (DME)) that partitions towards the cathode and is favorable towards the cathode (and referred to herein as an “cathode-side electrolyte solvent”). By separating the electrolyte solvents during operation of the battery such that the anode-side electrolyte solvent is present disproportionately at the anode and the cathode-side electrolyte solvent is present disproportionately at the cathode, the battery can benefit from desirable characteristics of both electrolyte solvents (e.g., relatively low lithium reactivity of the anode-side electrolyte solvent and relatively high polysulfide solubility of the cathode-side electrolyte solvent).
Owner:SION POWER CORP
Positive electrode material for lithium ion battery with nonaqueous electrolyte, and battery using the same
ActiveUS20090029253A1Increase output powerAvoid crackingSmall-sized cells cases/jacketsLarge-sized cells cases/jacketsLithium-ion batteryComposite oxide
An object of the present invention is to provide a positive electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte lithium-ion battery which capable of discharging high output power and inhibiting cracking of secondary particle in the cyclic endurance at a high temperature. The above object can be attained by a positive electrode material for non-aqueous electrolyte lithium-ion battery of the present invention, characterized in that said material comprises secondary particles composed of primary particles of lithium nickel composite oxide containing the primary particles having different aspect ratios, and that at least a part of said primary particles having different aspect ratios are arranged so as to make the longitudinal direction (the long side direction) thereof oriented toward the center of the secondary particle.
Owner:ENVISION AESC JAPAN LTD +1
Process for manufacture of negative electrode material for a non-aqueous electrolyte secondary battery
InactiveUS20030175589A1Maintain good propertiesReduce battery sizeSolid electrolytesElectrode manufacturing processesAlloySolid solution
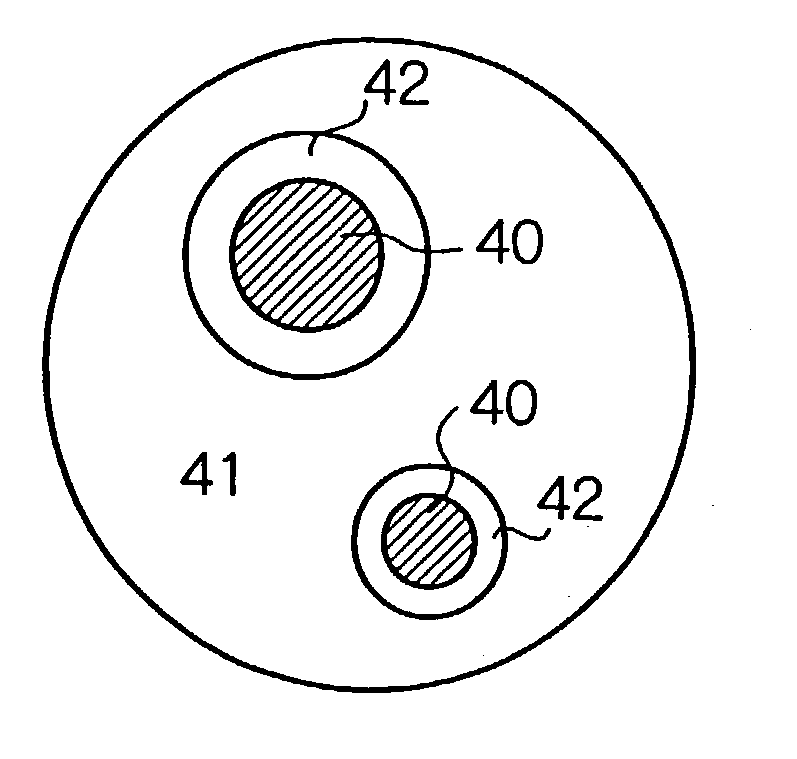
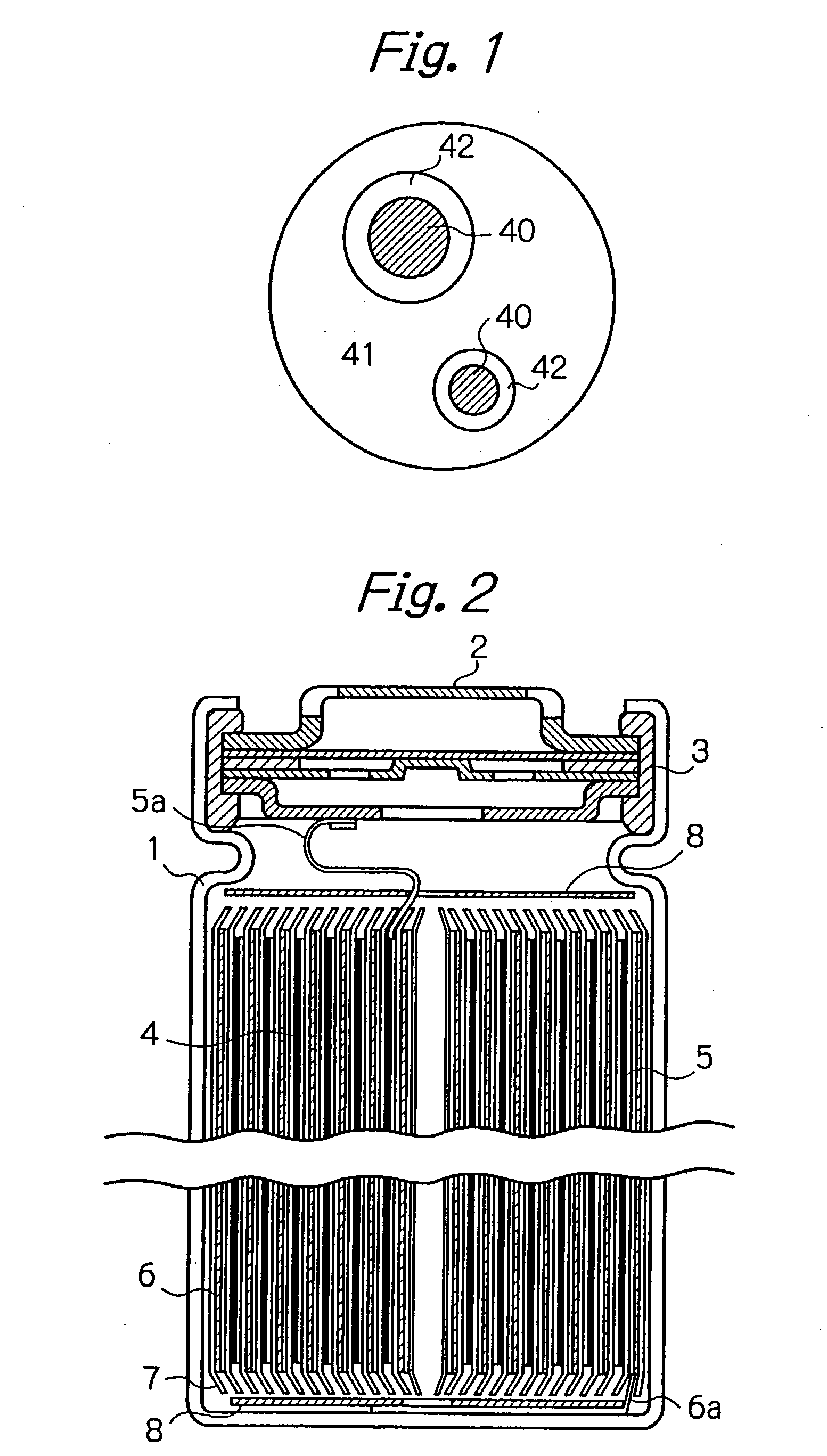
A negative electrode material for a nonaqueous electrolyte secondary battery having a high discharge capacity and a good cycle life is made from alloy particles having an average particle diameter of 0.1-50 mum and including Si phase grains 40 and a phase of a solid solution or an intermetallic compound of Si and other element selected from Group 2A elements, transition elements, Group 3B elements, and Group 4B elements from the long form periodic table (for example, an NiSi2 phase 42 and an [NiSi2+NiSi] phase 41) at least partially enveloping the Si phase grains. 5-99 wt % of this material is Si phase grains. The alloy particles can be manufactured by rapid solidification (such as atomization or roller quenching) of a melt including Si and the other element, or by adhering the other element to Si powder by electroless plating or mechanical alloying and then performing heat treatment. Even if rapid solidification is carried out, a negative electrode material having a good discharge capacity and cycle life is obtained without heat treatment.
Owner:CHUO DENKI KOGYO CO LTD
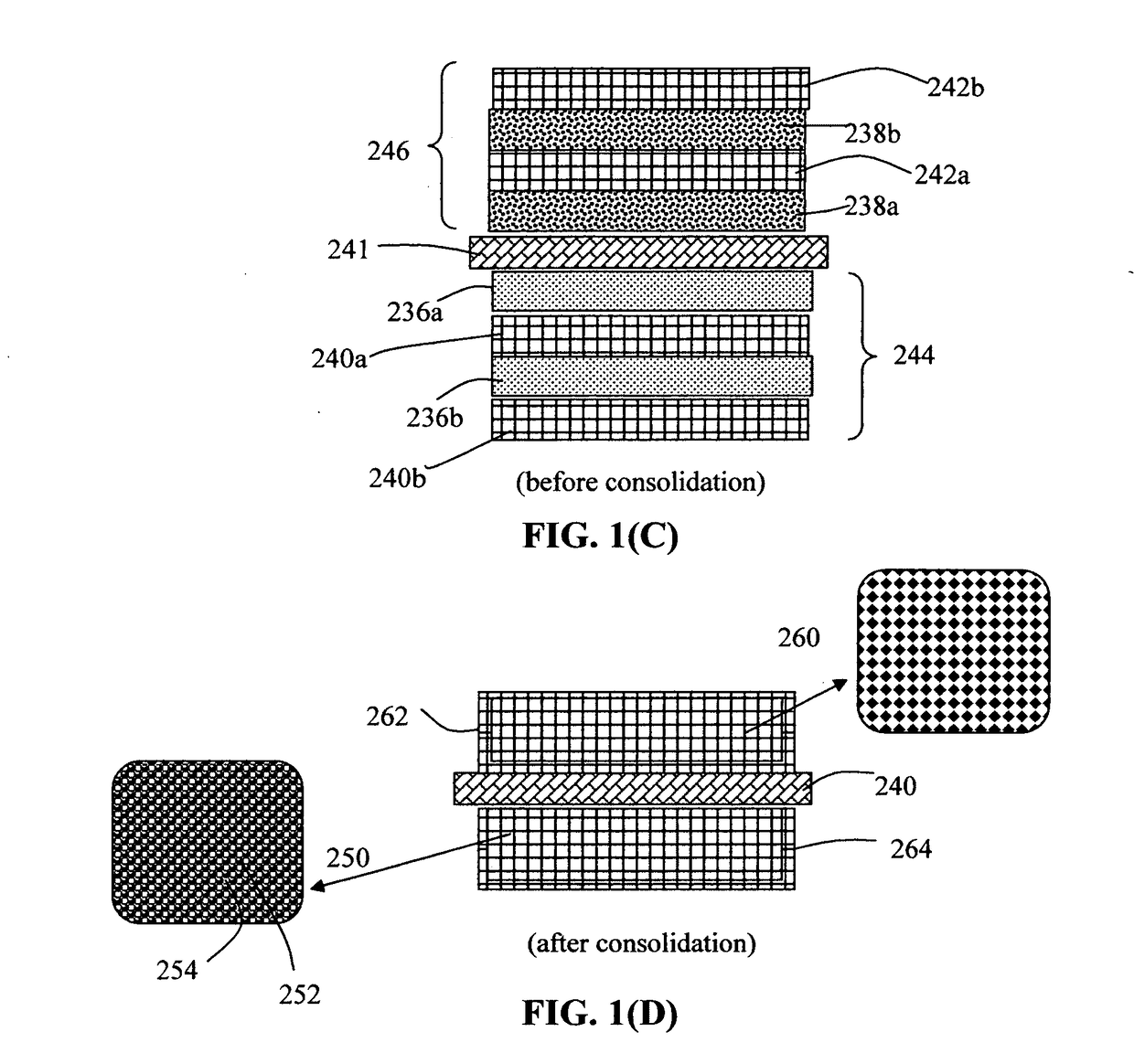
Process for producing lithium batteries having an ultra-high energy density
ActiveUS20170098856A1Increase energy densityImprove power densityFinal product manufactureNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsPorous layerHigh energy
A process for producing a lithium battery, comprising: (A) Preparing a plurality of conductive porous layers, wet anode layers, and wet cathode layers; (B) Stacking a desired number of porous layers and wet anode layers in an alternating manner to form an anode electrode having a thickness no less than 100 μm; (C) Placing a porous separator layer in contact with the anode electrode; (D) Stacking a desired number of porous layers wet cathode layers in an alternating manner to form a cathode electrode in contact with the porous separator, wherein the cathode electrode has a thickness no less than 100 μm; and (F) Assembling and sealing the anode electrode, separator, and cathode electrode in a housing to produce the lithium battery. The consolidated anode or cathode layer is preferably thicker than 300 more preferably thicker than 400 μm, and further more preferably greater than 500 μm.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
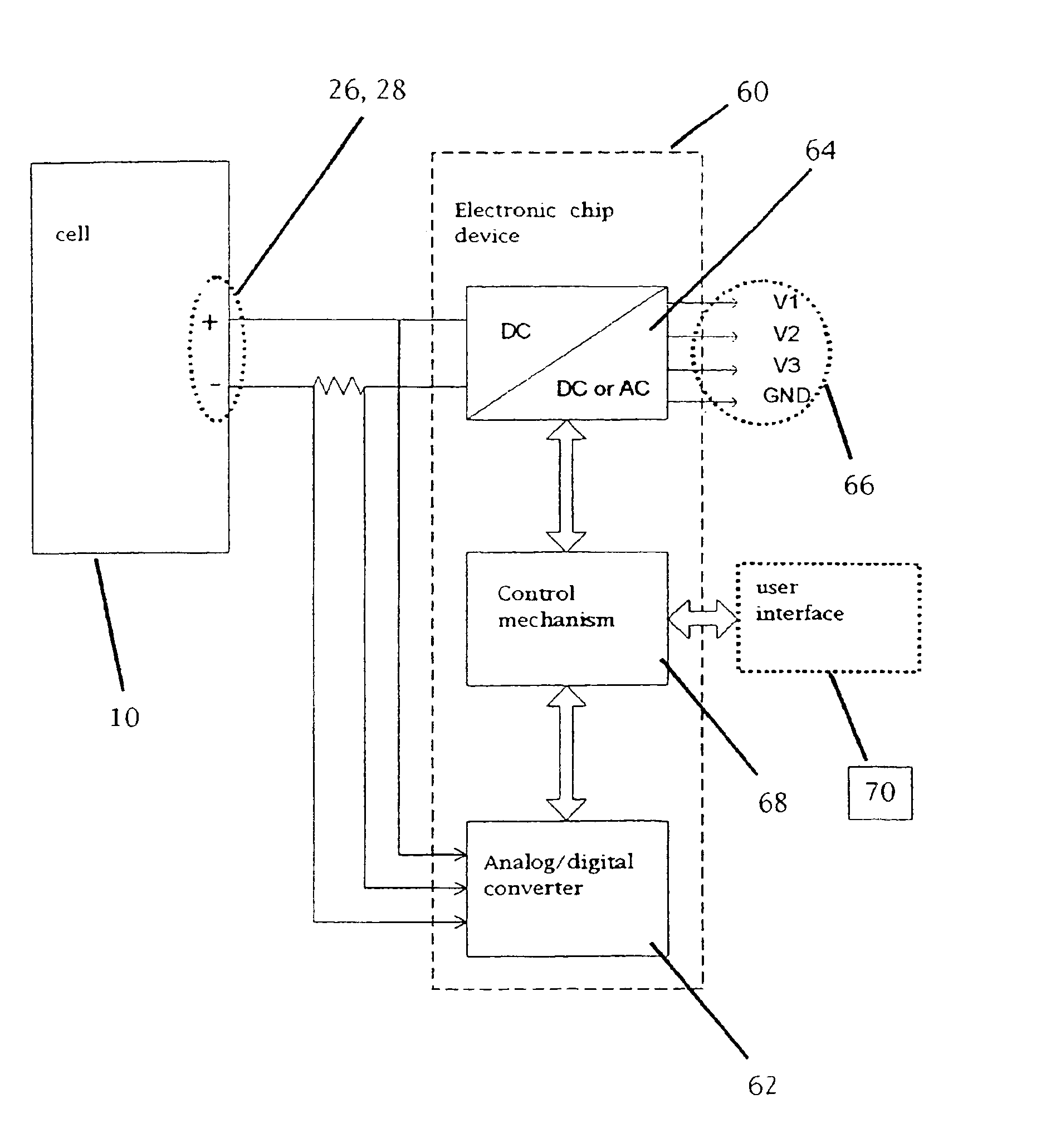
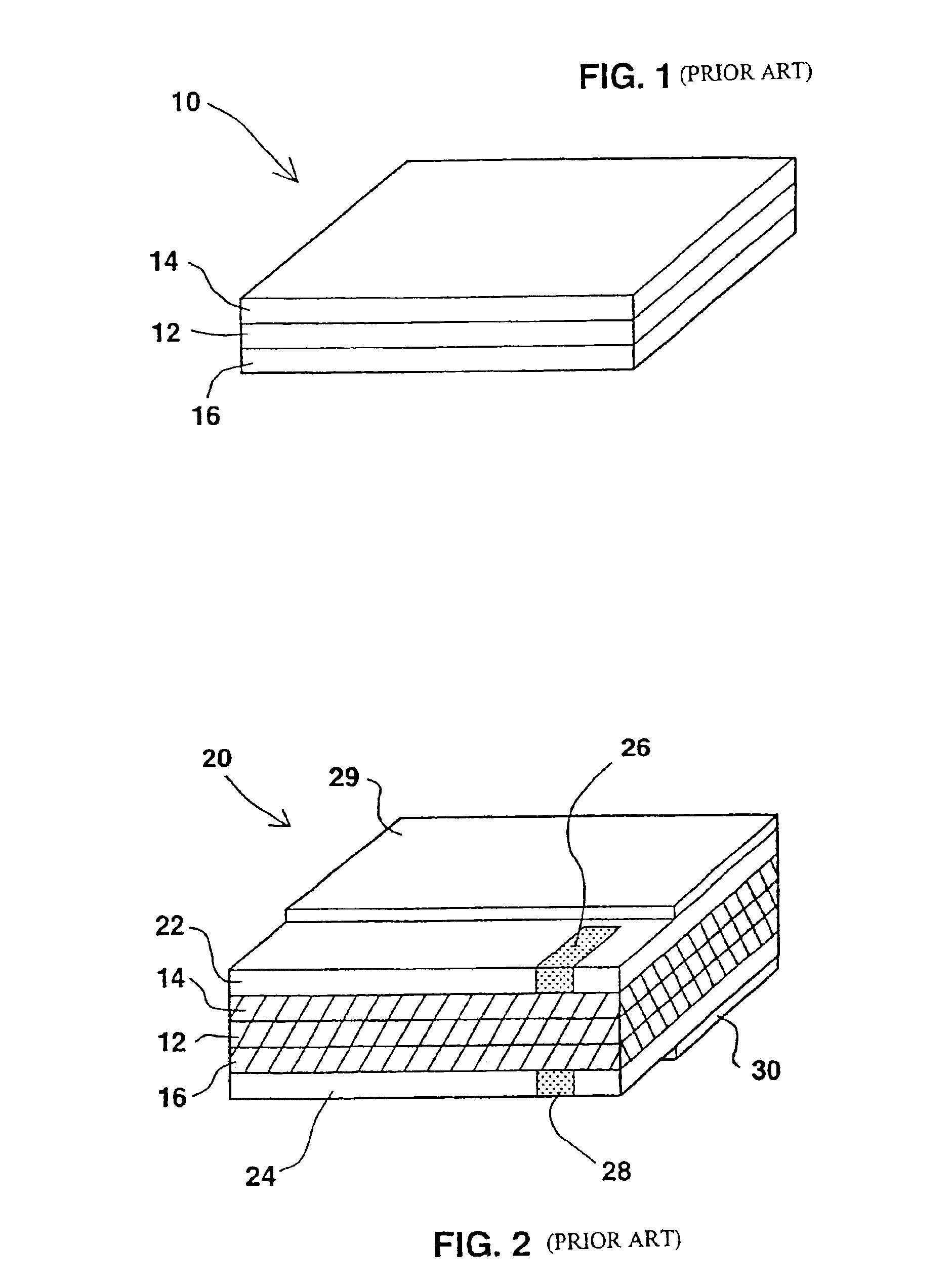
Functionally improved battery and method of making same
InactiveUS6855441B1Extended service lifePower outputBatteries circuit arrangementsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical batteryLiquid state
A functionally improved battery is disclosed. The battery includes a flexible thin layer open liquid state electrochemical cell (10) and an electronic chip device (60) integrally formed on or within the electrochemical cell (10). The cell (10) includes a first layer of insoluble negative pole (14), a second layer of insoluble positive pole (16) and a third layer of aqueous electrolyte (12). The third layer (12) is disposed between the first (14) and second (16) layers. The third layer (12) includes a diliquescent material for keeping the cell wet, an electroactive soluble material for ionic conductivity and a watersoluble polymer for viscosity. The viscosity adheres the first (14) and second (16) layer to the third layer (12). The chip (60) serves to improve the functionality of the battery.
Owner:POWER PAPER
Secondary cell electrode and fabrication method, and secondary cell, complex cell, and vehicle
InactiveUS20060251965A1Solid electrolyte cellsActive material electrodesElectrolyteMaterials science
In a nonaqueous electrolyte cell-oriented electrode (10), an electrode active material layer (12) formed on a collector (1) has a density gradient developed with a gradient of a varied concentration of a solid along a thickness from a surface of the electrode active material layer (12) toward the collector (1), and in a gel electrolyte cell-oriented electrode (30), an electrode active material layer (32) formed on a collector (1) has a density gradient developed with (a) gradient(s) of (a) varied concentration(s) of one or both of an electrolyte salt and a film forming material along a thickness from a surface of the electrode active material layer (32) toward the collector (1).
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
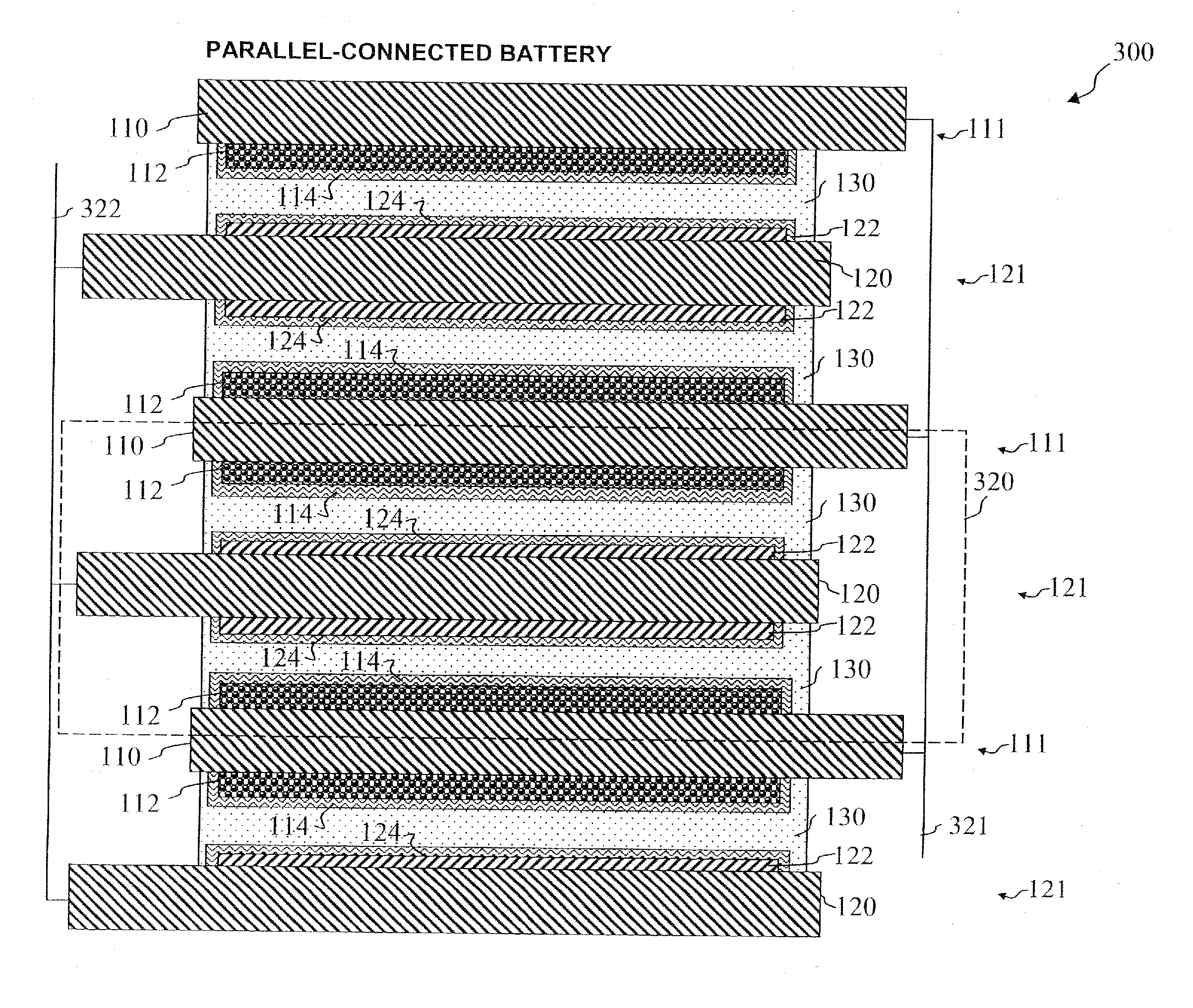
Polymer binder for electrochemical device comprising multiply stacked electrochemical cells
ActiveUS20060275661A1Increase in bulk energy densityHighly-integratedLarge-sized flat cells/batteriesFinal product manufactureMethacrylateMeth-
Disclosed is an electrochemical device, which comprises: (A) a binder comprising polymer particles obtained from the polymerization of: (a) 20-70 parts by weight of a (meth)acrylic acid ester monomer; (b) 20-60 parts by weight of a vinyl monomer; and (c) 0.01-30 parts by weight of an unsaturated carboxylic acid monomer, based on 100 parts by weight of a binder polymer; and (B) electrochemical cells stacked multiply by using the binder, wherein the binder allows electrode active material particles in an electrode to be fixed and interconnected among themselves and between the electrode active material and a collector, and the electrode and a separator that is in contact with the electrode are bonded to each other by way of hot fusion. The binder is also disclosed. The binder has excellent adhesion and thermal bonding characteristics, and thus is useful for an electrochemical device comprising multiply stacked electrochemical cells, and can improve the overall quality of a battery.
Owner:LG CHEM LTD
Polymer gel electrolyte, secondary cell, and electrical double-layer capacitor
InactiveUS20020102464A1Large capacityWide operating temperature rangeNon-metal conductorsHybrid capacitor electrolytesPolymer capacitorCapacitance
A polymer gel electrolyte includes an electrolyte solution composed of a plasticizer with at least two carbonate structures on the molecule and an electrolyte salt, in combination with a matrix polymer. Secondary batteries made with the polymer gel electrolyte can operate at a high capacitance and a high current, have a broad service temperature range and a high level of safety, and are thus particularly well-suited for use in such applications as lithium secondary cells and lithium ion secondary cells. Electrical double-layer capacitors made with the polymer gel electrolyte have a high output voltage, a large output current, a broad service temperature range and excellent safety.
Owner:NISSHINBO IND INC
Three dimensional Battery Architectures and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20110171518A1Electrode manufacturing processesFinal product manufactureConductive materialsThree dimensional electrode
A three-dimensional electrode structure for use in a battery comprising a porous three-dimensional substrate formed from a first electrically conductive material, an ion-conducting dielectric material disposed on the porous three dimensional substrate, and a second electrically conductive material disposed on the ion-conducting dielectric material, wherein the ion-conducting dielectric material separates the first electrically conductive material from the second electrically conductive material.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY +1
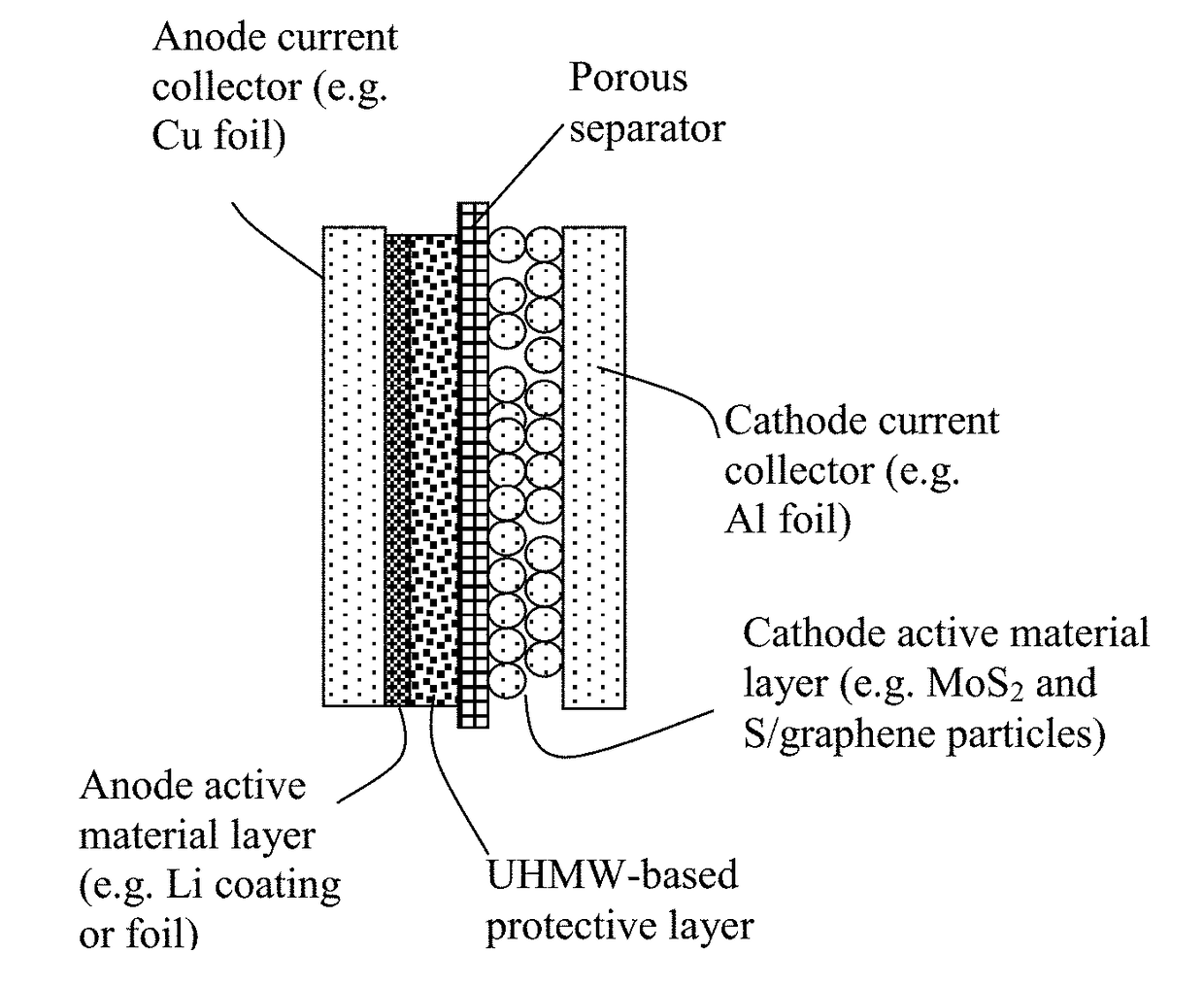
Lithium Metal Secondary Battery Containing an Anode-Protecting Polymer Layer and Manufacturing Method
ActiveUS20180294476A1Improve lithium ion conductivityReduce thicknessSolid electrolytesFuel and secondary cellsTensile strainLithium metal
Provided is lithium secondary battery comprising a cathode, an anode, and an electrolyte or separator-electrolyte assembly disposed between the cathode and the anode, wherein the anode comprises: (a) a foil or coating of lithium or lithium alloy as an anode active material; and (b) a thin layer of a high-elasticity polymer having a recoverable tensile strain no less than 5%, a lithium ion conductivity no less than 10−6 S / cm at room temperature, and a thickness from 1 nm to 10 μm, wherein the high-elasticity polymer contains an ultrahigh molecular weight polymer having a molecular weight from 0.5×106 to 9×106 g / mole and is disposed between the lithium or lithium alloy and the electrolyte or separator-electrolyte assembly.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
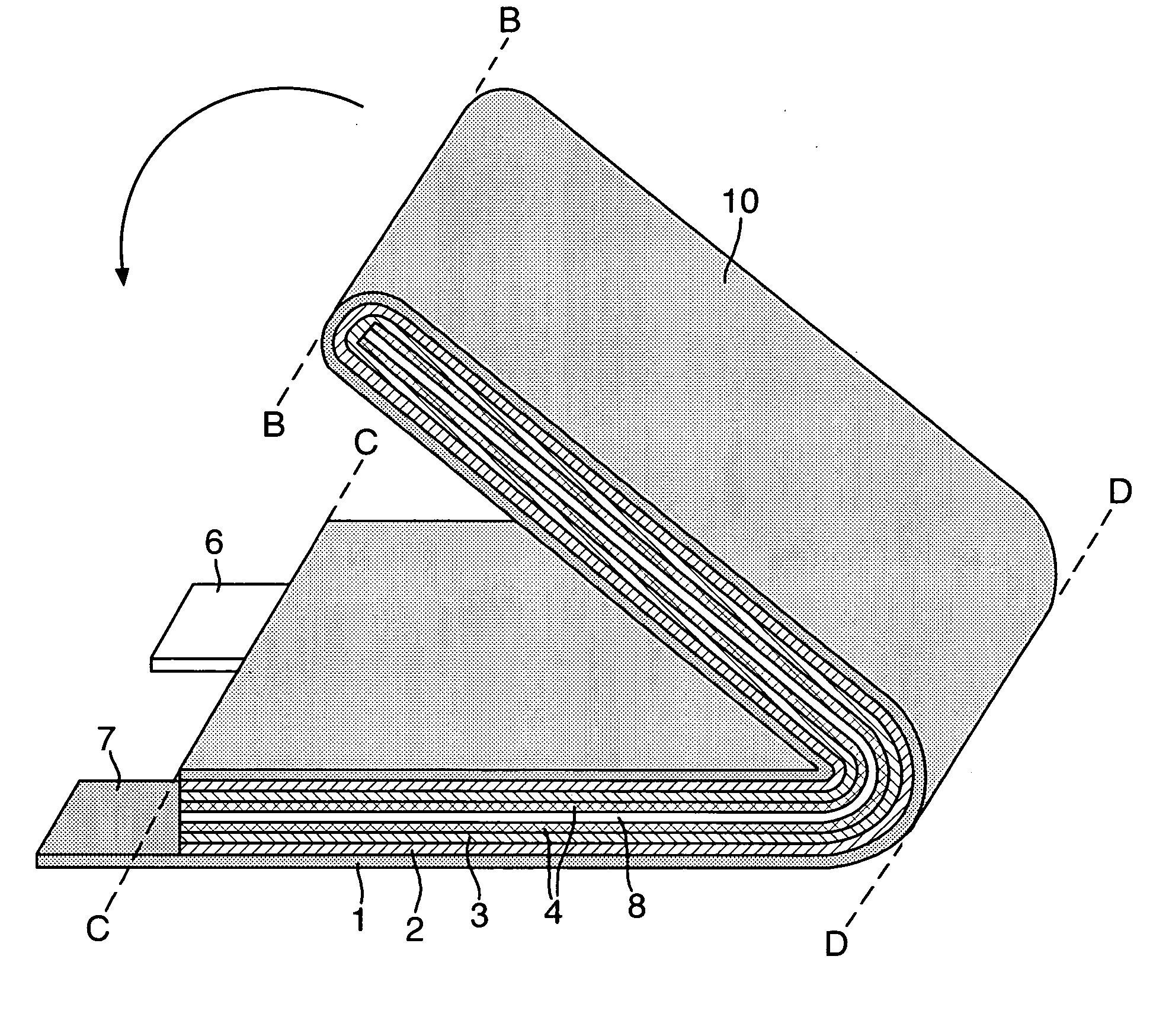
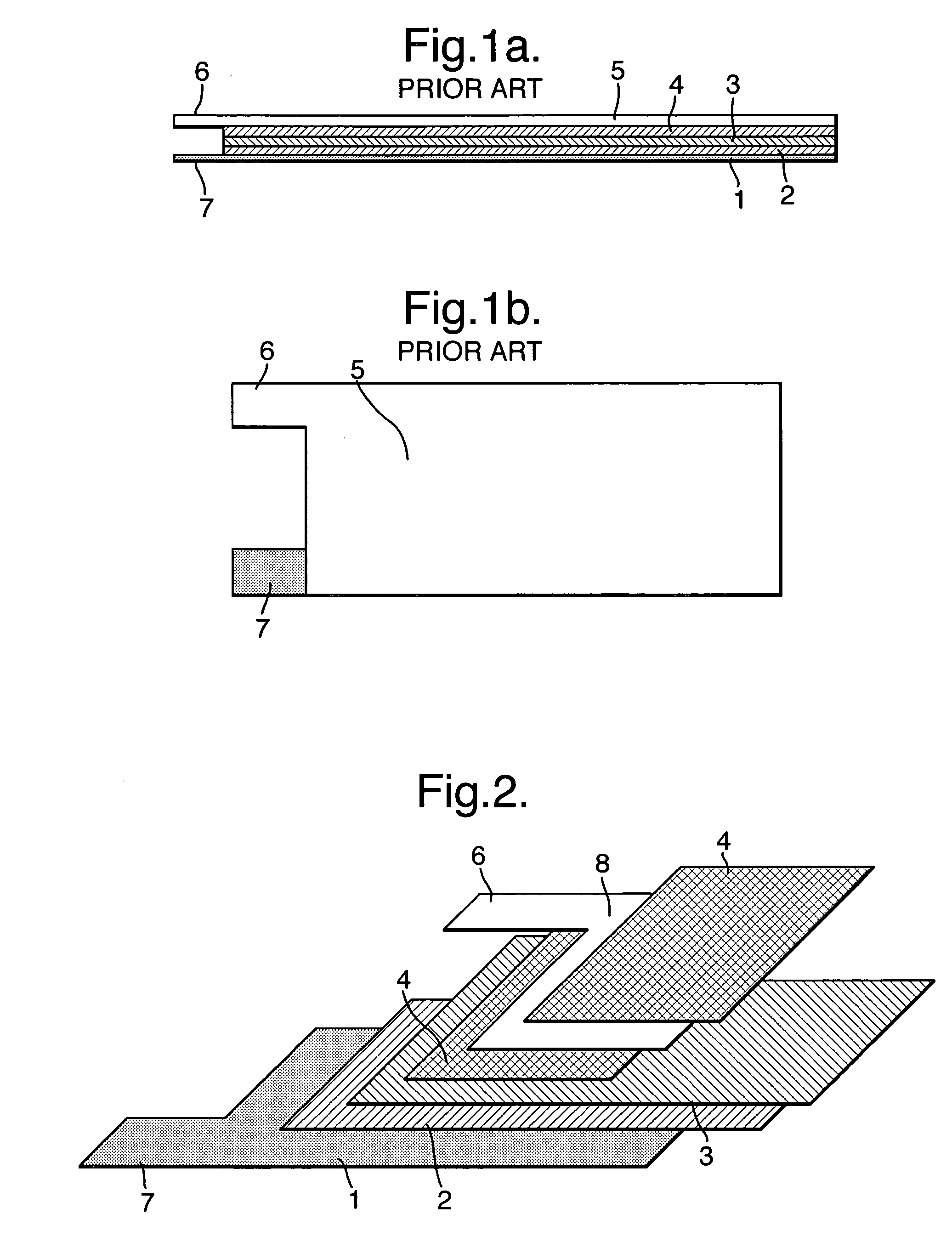
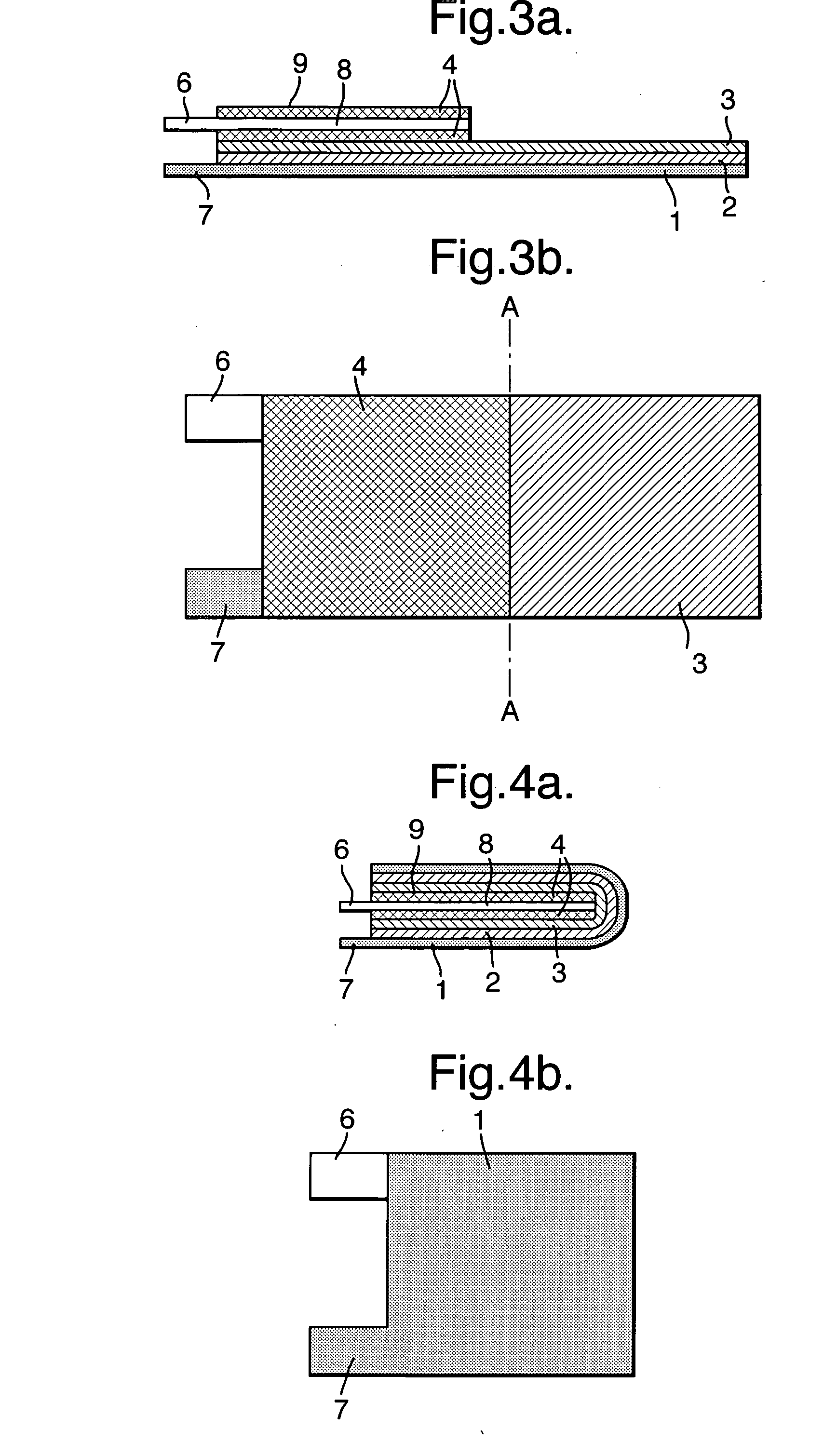
Electrode assembly
ActiveUS20050191545A1Increase energy densityReduce resistancePrimary cell maintainance/servicingFinal product manufactureEngineeringPrimary battery
An electrode assembly is formed by respectively overlaying a sheet cathode 1, a sheet separator 3 and a double-sided sheet anode 8 to form a stacked structure 10, and subjecting the stacked structure to multiple folds, wherein the initial fold comprises folding the cathode in half around the double-sided anode so as to surround the respective upper and lower active anode surfaces thereof. The multiple folds may comprise one or more subsequent parallel folds made with the fold line D-D extending perpendicular to the original length of the stacked structure such that its overall length is halved at each fold. A pouch battery comprising said electrode assembly has improved safety and performance characteristics. The pouch battery construction has especial application to lithium primary batteries.
Owner:QINETIQ LTD
Ambient temperature, rechargeable cells with metal salt-based electrodes and a system of cell component materials for use therein
InactiveUS6187479B1Improve battery performanceImprove performanceLead-acid accumulatorsNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsHalogenRechargeable cell
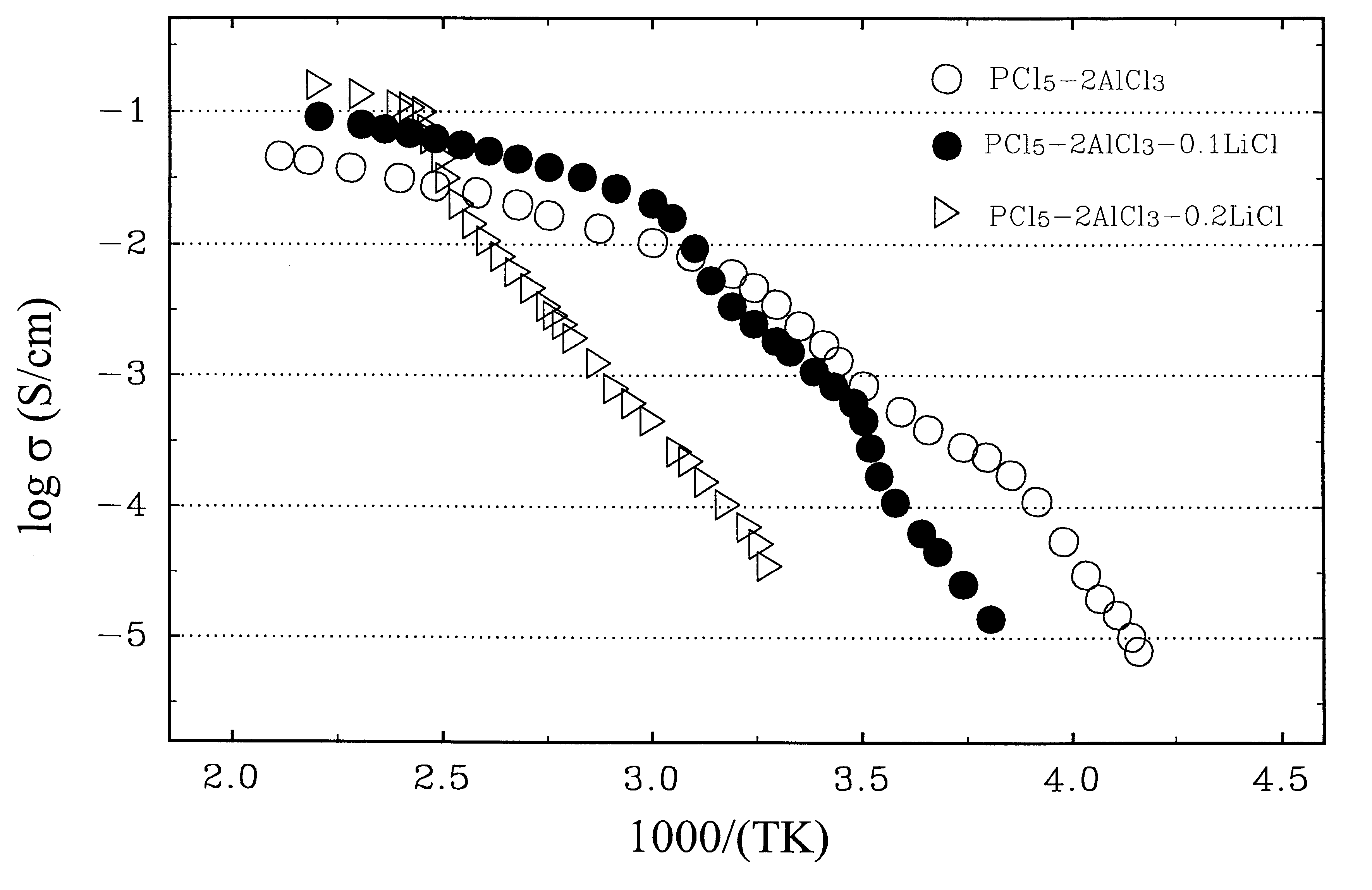
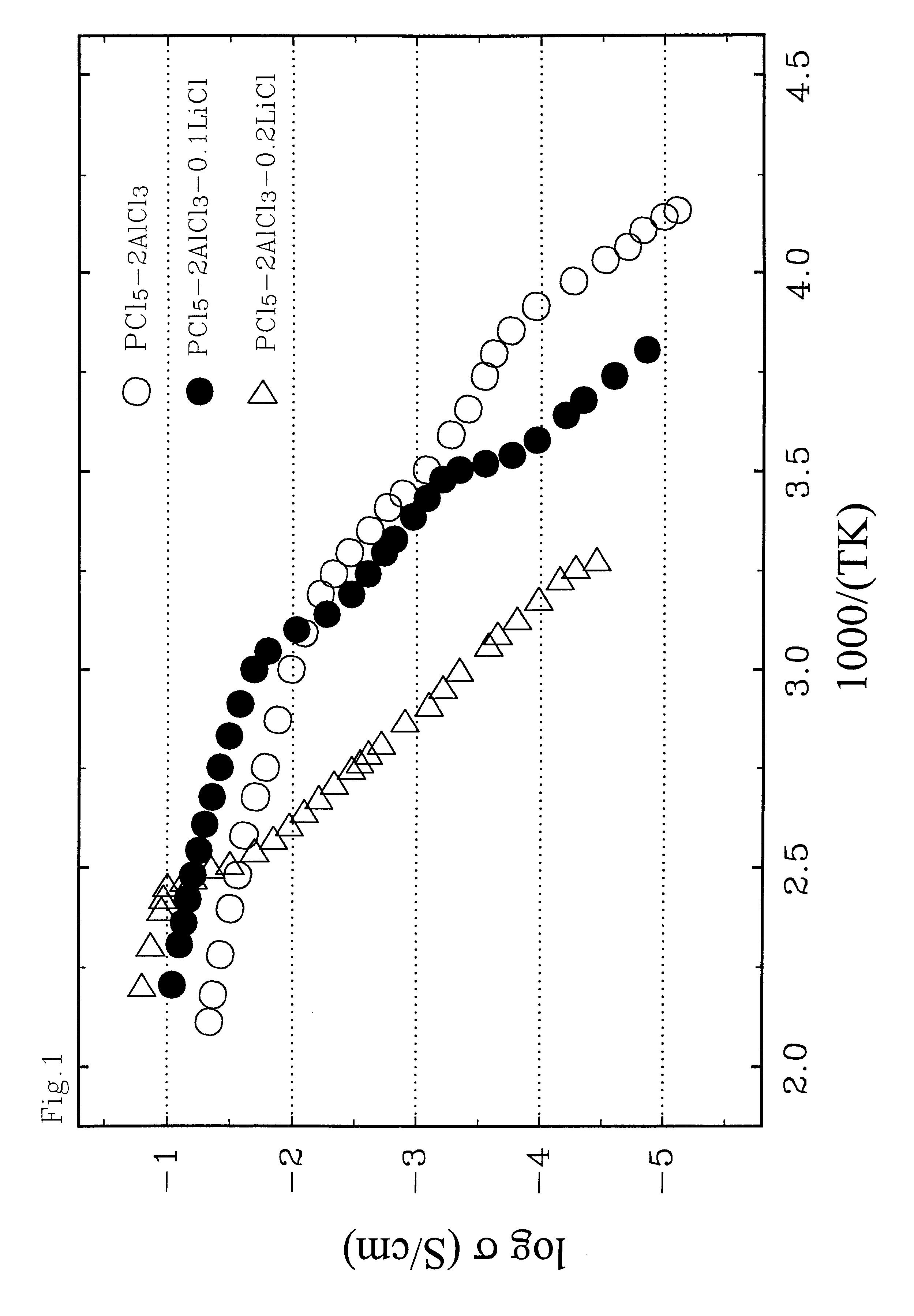
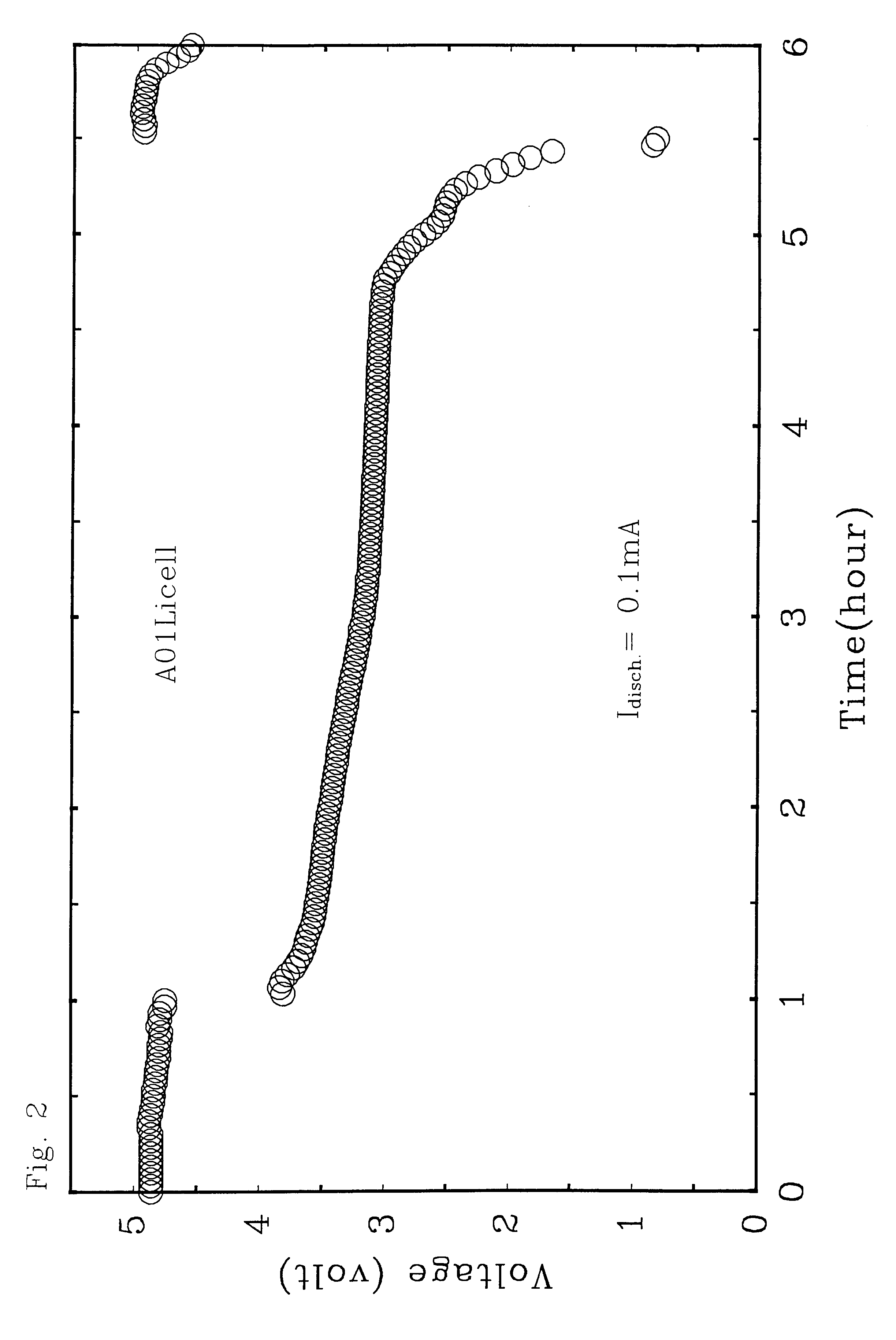
A rechargeable battery or cell is disclosed in which the electrode active material consists of at least one nonmetallic compound or salt of the electropositive species on which the cell is based, and the electrolyte or electrolyte solvent consists predominantly of a halogen-bearing or chalcogen-bearing covalent compound such as SOCl2 or SO2Cl2. Also disclosed are cell component materials which include electrodes that consist primarily of salts of the cell electropositive species and chemically compatible electrolytes. These latter electrolytes include several newly discovered ambient temperature molten salt systems based on the AlCl3-PCl5 binary and the AlCl3-PCl5-PCl3 ternaries.
Owner:LIU CHANGLE
Lithium secondary battery
ActiveUS20060246355A1Increasing internal ion-conductivitySafely preventing short circuitFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte cellsLithiumEngineering
A lithium secondary battery includes an electrode assembly having two electrodes and a separator interposed between the two electrodes, and a case for storing the electrode assembly, wherein the separator is formed by using a binder and a filler including a solid electrolyte having lithium ion conductivity. The lithium secondary battery has a separator and an electrolyte capable of increasing internal ion-conductivity. Also, a lithium secondary battery has a separator capable of safely preventing a short circuit between the electrodes in a possibly high temperature.
Owner:SAMSUNG SDI CO LTD
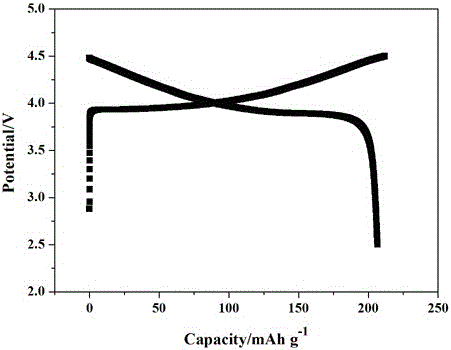
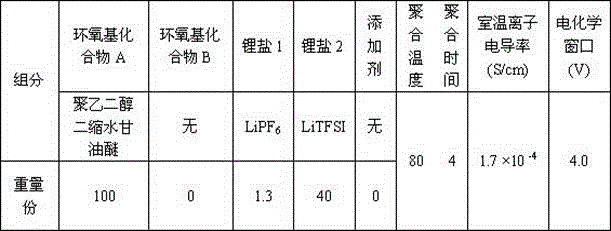
Preparation method of all-solid polymer electrolyte through in-situ ring opening polymerization of epoxy compound, and application of the all-solid polymer electrolyte in all-solid lithium battery
ActiveCN105914405AIncrease contactImprove interface compatibilityFinal product manufactureLi-accumulatorsEpoxySolid state electrolyte
The invention discloses a preparation method of an all-solid polymer electrolyte through in-situ ring opening polymerization of an epoxy compound, and an application of the all-solid polymer electrolyte in an all-solid battery. The preparation method is characterized in that a liquid-state epoxy compound, a lithium salt, a battery additive and the like are employed as precursors and are injected into between a positive pole sheet and a negative pole sheet of the battery, and under a heating condition, in-situ polymerization solidification is carried out to form the all-solid polymer electrolyte, and furthermore, the all-solid battery is produced. The ionic conductivity at room temperature of the all-solid polymer electrolyte can reach from 1*10<-5> S / cm to 9*10<-3> S / cm and electric potential window is 3.5-5 V. The all-solid polymer electrolyte is prepared through the in-situ copolymerization method, so that the all-solid polymer electrolyte has excellent contact with electrodes, thereby greatly improving interface compatibility of the solid-state battery, reducing interface wetting and modification steps of the solid-state battery, reducing production cost of the solid-state battery and improving performances of the solid-state battery. The invention also discloses an all-solid polymer lithium battery assembled from the all-solid polymer electrolyte.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-energy, rechargeable, electrochemical cells with non-aqueous electrolytes
InactiveUS6316141B1Non-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsElectrolysisHigh energy
A non-aqueous electrolyte for use in an electrochemical cell comprising: (a) at least one organic solvent; (b) at least one electrolytically active salt represented by the formula:in which: M' is selected from a group consisting of magnesium, calcium, aluminum, lithium and sodium; Z is selected from a group consisting of aluminum, boron, phosphorus, antimony and arsenic; R represents radical selected from the following groups: alkyl, alkenyl, aryl, phenyl, benzyl, and amido; X is a halogen (I, Br, Cl, F); m=1-3; and n=0-5 and q=6 in the case of Z=phosphorus, antimony and arsenic, and n=0-3 and q=4 in the case of Z=aluminum and boron. Rechargeable, high energy density electrochemical cells containing an intercalation cathode, a metal anode, and an electrolyte of the above-described type are also disclosed.
Owner:BAR ILAN UNIV
Popular searches
Organic electrolyte cells Non-aqueous electrolyte accumulator electrodes Aqueous electrolytes Aqueous electrolyte cells Cell component details Electrolyte accumulators manufacture Lead-acid accumulators construction Electrolyte immobilisation/gelification Printed batteries Secondary cells charging/discharging
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com